A CORROSION MANAGEMENT AND APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING MAGAZINE FROM OUTOKUMPU 3-4/2013. The two phased optimization of duplex stainless steel
|
|
|
- Neil Stone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A CORROSION MANAGEMEN AND APPLICAIONS ENGINEERING MAGAZINE FROM OUOKUMPU 3-4/2013 he two phased optimization of duplex stainless steel
2 2 he two phased optimization of duplex stainless steel Presenter: Jan. Y. Jonsson, Alexander hulin,sukanya Hägg Outokumpu Stainless AB, Avesta Research Centre, Avesta, Sweden. Rachel Pettersson, Jernkontoret, Swedish Steel Producers Association, Stockholm, Sweden. Abstract Duplex stainless steels are well known for high strength in comparison to their austenitic counterparts. hey also have good cost efficiency providing required properties without the level of exposure to nickel price volatility seen for many austenitic grades. he development of these two phased grades is a continuous process and a natural focus is to optimize the composition to obtain the maximum possible benefit from the alloying elements. One proven way of doing this is to decrease the content of nickel while increasing the amount of other austenitizing elements such as nitrogen and manganese. Nitrogen has a strong beneficial influence on both strength and corrosion resistance. his alloying concept has been used successfully in the lean duplex grades, which have corrosion resistance on a par with standard austenitic grades. he most recent contribution based on this concept is the lean duplex grade LDX 24 with enhanced strength but a corrosion resistance which is still close to that of the standard duplex grade 05. When testing the corrosion resistance in the duplex grades it is important to consider whether there is an imbalance in the corrosion resistance of the individual phases. he development of the super duplex grade 27 was reported to be based on the concept that the grade exhibits optimal pitting corrosion resistance when annealed at a temperature where the localized corrosion resistance equivalent is equal in both phases. Such an optimization naturally also involves other concepts such as phase balance elemental partitioning and structural stability. his paper aims to take such considerations a step further, using an analysis which acknowledges the different performance of the austenite and ferrite phases in duplex grades and addresses the possibility that they do not need to have the equal PRE to give the alloy a maximum critical pitting temperature, CP. his concept has proven useful in duplex alloy development especially for molybdenum alloyed grades where the resistance against pitting corrosion is high. he paper exemplifies these considerations both by examining a number of different variants of the standard duplex grade 05 and by evaluation of a series of model alloys. he partitioning of alloying elements is determined by EDS/WDS analysis and correlated to predictions using the thermodynamic software hermo-calc. he location of pitting attack is evaluated in the different cases and the discussion focuses on the possible mechanisms behind the observed results. Introduction Duplex stainless steels are well known for high strength in comparison to their austenitic counterparts. hey also have good cost efficiency, providing required properties without the level of exposure to nickel price volatility seen for many austenitic grades. he development of these two phased grades is a continuous process and a natural focus is to optimize the composition to obtain the maximum possible benefit from the alloying elements. he term maximum possible benefit can be interpreted in many ways; one may consider that a low price is beneficial while another may think that e.g. higher impact toughness is more beneficial. hese different interpretations can be met by varying the chemical composition of the steel melts. he duplex grade 05 is a good example of this; Outokumpu Avesta Works has 4 different melt codes of the 05. One is the Outokumpu standard while the others fulfill three specific requirements; lower price, higher impact toughness or lower ferrite content. his paper focuses on the partitioning of the alloying elements and the effect that this has on the pitting resistance of each phase. he partitioning of alloying elements is determined by EDS analysis and correlated to predictions using the thermodynamic software hermo-calc. he duplex grades LDX 24 and EDX 24 M together with a set of experimental alloys are used to exemplify the alloying concept.
3 3 Materials and experimental procedure Materials he investigated materials are 05 as well as the leaner duplex steel grades; LDX 24 and EDX 24 M, the chemical composition of the grades are presented in able 1. All materials has been examined after a solution annealing in 10 C followed by 15s in air and a final water quench. he pitting resistance equivalent (PRE) is commonly used to estimate the corrosion resistance of stainless steel grades. here are different opinions on the exact formulation of the PRE formula, as discussed in a review paper (Pettersson & Flyg, 2004) and this work uses PRE(NMn) where the positive effect of nitrogen and a slight negative effect of manganese is taken into account. It can be noted that the overall effect associated with manganese alloying can nevertheless be positive, since this element increases the nitrogen solubility. he PRE(NMn) formula is given below able 1 and it contains a coefficient of for nitrogen and -1 for the manganese content. he most common PRE formula, PRE(N), uses a factor 16 or for nitrogen and it does not take into account any effect of manganese. his common formula is used in various situations where the general pitting resistance of a specific material needs to be evaluated, a customer specification can e.g. contain a requirement that sets a lower limit of PRE(N) that the material needs to fulfill. In addition to the commercially available alloys above, a set of small (0 g) experimental alloys were used to show how the optimization concept taken from the commercially available materials can be used on a real case. hese materials are shown in able 2. As for the commercial alloys, these materials were investigated after solution annealing at 10 C followed by 15 seconds in air prior to water quenching. Metallographic examination he microstructure was examined after a chemical etching in a modified Beraha II solution (ml HCl, 100ml H g K 2 SO 5 ). he ferrite contents were evaluated with light optical microscopy (LOM) using image analysis according to ASM E 12. he same etchant was also used for detecting pit initiation sites after corrosion testing. For comparison of the pitting resistance in each phase using the individual phase PRE the chemical composition of the austenite and the ferrite was analyzed with scanning electron microscope with energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS). Calibration was performed using actual plate material as reference sample. he N-content was analyzed using wavelength dispersive spectroscopy, WDS. In this case a set of stainless steel materials with known N-contents was used a reference material. Corrosion testing he CP-testing has been performed according to ASM G1 in a 1M NaCl solution for the commercial alloys 05, LDX 24 and EDX 24. A 1 cm 2 test area was used for the commercial steels and 10 cm 2 for the set of laboratory materials. Materials Plate thickness (mm) Chemical composition (wt.%) PRE(NMn) * 05 alloys Cr Ni Mo N Mn Alloy A Alloy B Alloy C Alloy D Alloy E LDX EDX 24 M able 1 Chemical composition in % by weight of the duplex stainless steel materials investigated. *Pitting resistance equivalent. PRE(NMn) = %Cr+3.3%Mo+%N-%Mn. Materials Chemical composition (wt.%) PRE(NMn) * Experimental alloys Cr Ni Mo N Mn Alloy I Alloy J Alloy K Alloy L able 2 Chemical composition in % by weight of the duplex laboratory materials. * Pitting resistance equivalent. PRE(NMn) = %Cr+3.3%Mo+%N-%Mn.
4 4 Results and Discussions he commercial duplex alloys he chemical analyses of the alloy and specifically of the austenite and the ferrite are shown in able 3 together with the corresponding PRE(NMn) and the CP results. It is noted that CP increases with the PRE(NMn) in all cases except for alloy E which has a lower CP in spite of the higher PRE(NMn). he majority of the nitrogen found in a duplex alloys is located in the austenite phase, which contains approximately 10 times the nitrogen in the ferrite phase. It is noted that the addition of nitrogen in duplex grades has many benefits, such as higher strength as for LDX 24, but the resistance towards pitting is not in general favored by this addition if the only other adjustment is a decrease in nickel content, in part exemplified by alloys A-C. An increase in nitrogen can improve the austenite PRE but primarily increases the austenite fraction and will have to be balanced with higher levels of ferrite stabilizers such as chromium and molybdenum. Lowering the nickel content will lower the PRE of the already weakest phase, the ferrite, even though nickel is not a factor in the PRE formula, because of its influence on phase balance and elemental partitioning. his is exemplified in Figure 1 below for an alloy space around 05. Looking at initiation sites of the corrosion samples it can be seen that in samples from alloy E the austenite phase is predominantly attacked and this the weaker phase, see Figure 2. he ferrite phase is seen to be the weaker phase in all other tested alloys. he results have further been illustrated in Figure 3 to Figure 6 which show the results from able 3 graphically. he figures show the CP as a function of the PRE(N) for the general composition, which is the commonly used procedure, as well as the PRE(NMn) in the individual phases; the austenite phase, the ferrite phase and the weakest phase, which in the case of Alloy E is the austenite but in all other steels is the ferrite. Materials Chemical composition (wt.%) PRE(NMn) CP ( C) 05 alloys Cr Ni Mo N Mn Alloy A BCC FCC Alloy B BCC FCC Alloy C BCC FCC Alloy D BCC FCC Alloy E BCC FCC LDX BCC FCC EDX 24 M BCC FCC able 3 Chemical composition % by weight in austenite and ferrite analysed by SEM-EDS with WDS-analysis for N.
5 5 Investergation: 05CPN100 (MLR) Contour Plot = 1100, Cr =.5, Mo = 3 PREFCC PREFCC N N Ni Ni PRE ot Ferrit N 0.19 N Ni Ni Figure 1 Example of influence of Ni and N on ferrite content and PRE(NMn). Figure 2 Micro photos of surface sections of polished and etched CP samples indicating pit initiation in the ferrite to the left for sample A and in the austenite to the right for sample E (see arrow).
6 Critical pitting temperature G1 ( C) R 2 = PRE(N) Critical pitting temperature G1 ( C) R 2 = PRE(N) Figure 3 CP vs. PRE(N) of the general chemical composition. PRE(N)=%Cr+3,3%Mo+16%N. Figure 4 CP vs. PRE(NMn) of the austenite phase Critical pitting temperature G1 ( C) R 2 = PRE(N) Critical pitting temperature G1 ( C) R 2 = PRE(N) Figure 5 CP vs. PRE(NMn) of the ferrite phase. Figure 6 CP vs. PRE(NMn) of the weaker phase. red dot represent Alloy E. In Figure 3 it is indicated quite strongly that the overall PRE(NMn) formula only moderately describes the resistance towards pitting corrosion for the examined materials. Figure 4 indicate no direct correlation between the CP and the PRE(NMn) in the austenite phase while Figure 5, on the contrary, shows quite a good correlation. However, Figure 6 clearly shows that the PRE(NMn) of the weaker phase correlates very well with the CP results from this investigation. he PRE(NMn) in each individual phase and the resulting CP are further graphically shown in Figure 7. his view shows quite well that the CP follows the PRE(NMn) of the ferrite phase except for Alloy E where the CP drops somewhat in spite of an increase in the PRE(NMn) in both phases. As indicated by the metallographic investigation, the austenite phase is the weaker phase in Alloy E and the PRE(NMn) of this phase correlate very well with the slightly lower CP. It is important to note that nickel and nitrogen contents are the predominant variables in the alloys. he nickel content governs the alloying distribution between phases and thus the PRE of each phase, the higher the nickel content, the higher fraction of chromium and molybdenum in the ferrite. his is quite clear when looking at the higher alloyed grades in Figure 7: all have quite similar PRE in the austenite phase while the ferrite phase PRE is gradually increasing, notably because of the increasing nickel content in the alloys, able 1. he CP also increases and correlates quite well with the PRE except for Alloy E as shown in Figure 5 and 6. PRE (NMn) EDX 24 (34.2 C) Ferrite phase Austenite phase CP LDX (42.3 C) Alloy A (52.9 C) Alloy B (53.3 C) Alloy C (56.4 C) Alloy D (58.8 C) Alloy E (57.1 C) Figure 7 PRE(NMn) in ferrite phase and austenite phase from EDS analysis and CP. he result indicate that a switch from ferrite to the austenite as the weak phase does not occur until the local corrosion resistance in the austenite is a certain degree lower than that of the ferrite. It is not seen as soon as the PRE of the austenite falls below that of the ferrite. he conclusion is therefore that the pitting resistance of the austenite is better than the PRE suggests, or conversely that the pitting resistance of the ferrite is lower than CP (NMn)
7 7 the PRE would indicate. he reasons for this are open to speculation but it is hardly surprising that such a simplified, generalized expression as PRE neglects to take into account the way in which alloying elements can contribute to the formation, maintenance and repair of the passive film on fcc and bcc substrates. For example, it is conceivable that the nitrogen in ferrite has no positive effect, or that molybdenum is more efficiently utilized in fcc. In this context it should, however, be borne in mind that AES studies (Olsson, 1996) have shown good lateral mobility of elements forming the passive film. A further consideration is the phase ratio: Alloy E has the lowest ferrite content of the 7 alloys tested. In purely statistical terms a higher percentage of austenite increases the risk for the weakest link to be found in the austenite if the two phases are equally resistant to pitting. If there is a protective function of the ferritic phase this should also be lower with less ferrite. Looking at the leaner duplex steels, they all have a weaker ferritic phase which follows which follows the general trend. See example in Figure 8. Concept of optimized alloying of a duplex steel With the previous results in mind one strategy to optimize the alloying content of a duplex grade is to aim to achieve the highest pitting resistance for a certain overall PRE. he results from the 05 variants indicate that the alloying content should be designed for the ferrite to only just be the weak phase, without any unnecessary over alloying of the austenite. It seems that if the PRE in the ferrite phase is 1.5 to 2.5 units higher than that of the austenite then the ferrite is still the weak phase but if the difference is larger the austenite becomes the weak phase, this will also result in a drop in pitting resistance. It should however be pointed out that this difference for 05-type grades, and the result may not be directly applicable to other alloy systems and duplex grades. Using hermo-calc, software for thermodynamic calculations, examination to optimize an alloying window can be performed. As an example optimizing Cr, Ni, Mo and N for ferrite content as well as a specific difference between the PRE value in the ferrite and the austenite have been done around the alloying range of 05. he results indicate that the window for optimization is quite narrow, see Figure 9. Comparing hermo-calc and SEM-EDSvalues a small difference can be seen but the overall trend is very similar. Laboratory melts he results have been used as a basis for preparation of a set of laboratory alloys with somewhat higher total PRE(NMn) than 05. he different PRE(NMn) values and the resulting pitting temperatures can be seen in Figure 10. he results indicate that pitting corrosion initiates in the austenite for alloy I and J and in the ferrite for alloy K and L, see Figure 11. he earlier interpretations of the 05 pit initiation sites are thus reinforced with these observations. A clearly lower PRE(NMn) in the austenite phase than in the ferrite phase make initiation take place in the austenite. By comparing the corrosion result with phase PRE(NMn) it can be concluded that an optimized alloy in this design window seems to need a PRE(NMn) difference between phases of between 2 and 6. Additional melts are needed to achieve a more precise definition of the optimization window, and the difference in corrosion resistance between alloy K and L merits further elucidation. Figure 8 Micro photos for surface sections of polished and etched CP tested samples indicating initiation in the ferrite (1) for EDX 24 M and (2) for LDX 24. PRE (Mn) Alloy I (49 C) Ferrite phase Austenite phase CP Alloy J (62 C) Alloy K (76 C) Alloy L (76 C) Figure 10 PRE(NMn) in ferrite phase and austenite phase from EDS analysis for four laboratory alloys. he results show quite clearly that the traditional PRE formula should generally only be used as a first approximation of pitting resistance. It can however without much change be used as a good tool for optimization in a local alloying window and for best use also by considering the resistance of each phase. CP ( C)
8 8 Investergation: 05CPN100 (MLR) Sweet Spot = Femite ( ) PREFCC (34 ). PREBCC (,5 ). DiffPRE (5 25) Sweet Spot Criteria met 3 Criteria met 2 Criterion met 1 Mo = N = N = N = Ni = 4,5 Ni = 5.25 Ni = 6 Figure 9 Example of optimization using hermo-calc where green areas represent alloys with difference in phase PRE(NMn) of max 2.5 (higher PRE in the ferrite phase) and austenite PRE(NMn) of min 34 and a ferrite PRE(NMn) of min.5. Figure 11 Micro photos for surface sections of polished and etched CP tested samples indicating initiations in the ferrite to the left for sample I and in the austenite to the right for sample K.
9 9 CONCLUSIONS o optimize an alloy towards pitting corrosion a better tool than using PRE-formula for the overall composition is to use a PRE-formula for each phase. A key in optimization of duplex steel towards pitting corrosion is to find the change from ferritic to austenitic pit initiation. REFERENCES Olsson, C.-O. A. (1996). Analysis by AES and XPS of the influence of nitrogen and molybdenum on the passivation of 05 austenot-ferritic stainless steels. Acciaio Inossidabile. Pettersson, R., & Flyg, J. (2004). Electrochemical evaluation of pitting and crevice corrosion resistance of stainless steels in NaCl and NaBr. Acom. his article was first published in the Proceedings of the Stainless Steel World Conference & Expo 2013, 12th - 14th November, 2013, Maastricht, he Netherlands KCI Publishing, 2013.
10 Working towards a world that lasts forever EN-GB, Art 58, 12, 13. Outokumpu works with its partners to create long lasting solutions for the tools of modern life and the world s most critical problems: clean energy, clean water and efficient infrastructure. Our goal is a world that lasts forever. Information given in this brochure may be subject to alterations without notice. Care has been taken to ensure that the contents of this publication are accurate but Outokumpu and its affiliated companies do not accept responsibility for errors or for information which is found to be misleading. Suggestions for or descriptions of the end use or application of products or methods of working are for information only and Outokumpu and its affiliated companies accept no liability in respect thereof. Before using products supplied or manufactured by the company the customer should satisfy himself of their suitability. research.stainless@outokumpu.com outokumpu.com
Corrosion Properties of Enhanced Duplex Steel UNS S32304
 A CORROSION MANAGEMENT AND APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING MAGAZINE FROM OUTOKUMPU Corrosion Properties of Enhanced Duplex Steel UNS S3234 2/215 2/215 2 Corrosion Properties of Enhanced Duplex Steel UNS S3234
A CORROSION MANAGEMENT AND APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING MAGAZINE FROM OUTOKUMPU Corrosion Properties of Enhanced Duplex Steel UNS S3234 2/215 2/215 2 Corrosion Properties of Enhanced Duplex Steel UNS S3234
Forta FDX 27 ASTM FDX 27 / UNS S82031
 Forta FDX 27 ASTM FDX 27 / UNS S82031 General characteristics Ferritic-austenitic stainless steels also referred to as duplex stainless steels, combine many of the beneficial properties of ferritic and
Forta FDX 27 ASTM FDX 27 / UNS S82031 General characteristics Ferritic-austenitic stainless steels also referred to as duplex stainless steels, combine many of the beneficial properties of ferritic and
Ultra 904L EN , ASTM UNS N08904
 Ultra 904L EN 1.4539, ASTM UNS N08904 General characteristics High Ni and Mo austenitic grade with very high resistance to corrosion. Commonly used in chemical and petrochemical industry for handling medium
Ultra 904L EN 1.4539, ASTM UNS N08904 General characteristics High Ni and Mo austenitic grade with very high resistance to corrosion. Commonly used in chemical and petrochemical industry for handling medium
Therma 314/4841 EN , ASTM TYPE 314
 Therma 314/4841 EN 1.4841, ASTM TYPE 314 General characteristics Austenitic heat resisting grade with excellent oxidation resistance. Commonly used for furnace equipment, super heater suspensions, enameling
Therma 314/4841 EN 1.4841, ASTM TYPE 314 General characteristics Austenitic heat resisting grade with excellent oxidation resistance. Commonly used for furnace equipment, super heater suspensions, enameling
Therma 4828 EN
 Therma 4828 EN 1.4828 General characteristics Austenitic grade with improved oxidation resistance. Commonly used for furnace equipment (esp. supporting parts), annealing and hardening boxes, air heaters.
Therma 4828 EN 1.4828 General characteristics Austenitic grade with improved oxidation resistance. Commonly used for furnace equipment (esp. supporting parts), annealing and hardening boxes, air heaters.
Therma 310S/4845 EN , ASTM TYPE 310S / UNS S31008
 Therma 310S/4845 EN 1.4845, ASTM TYPE 310S / UNS S31008 General characteristics Austenitic heat resisting 4845 grade with very good oxidation resistance. This grade 4845 belongs to austenitic chromium-
Therma 310S/4845 EN 1.4845, ASTM TYPE 310S / UNS S31008 General characteristics Austenitic heat resisting 4845 grade with very good oxidation resistance. This grade 4845 belongs to austenitic chromium-
Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers
 Materials Selection for Condensing Economizers Gary M. Carinci, Ph.D. Outokumpu Stainless Outokumpu Stainless Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers Temperature ph control Sulfur
Materials Selection for Condensing Economizers Gary M. Carinci, Ph.D. Outokumpu Stainless Outokumpu Stainless Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers Temperature ph control Sulfur
Forta LDX 2101 EN , ASTM UNS S32101
 Forta LDX 2101 EN 1.4162, ASTM UNS S32101 General characteristics Forta LDX 2101 is a lean-alloyed duplex product with good resistance to localized and uniform corrosion, as well as stress corrosion cracking,
Forta LDX 2101 EN 1.4162, ASTM UNS S32101 General characteristics Forta LDX 2101 is a lean-alloyed duplex product with good resistance to localized and uniform corrosion, as well as stress corrosion cracking,
Ultra 654 SMO EN , ASTM UNS S32654
 Ultra 654 SMO EN 1.4652, ASTM UNS S32654 General characteristics 7% Mo, very high N alloyed austenitic grade. The most corrosion resistant stainless steel in the world. High mechanical strength. Useful
Ultra 654 SMO EN 1.4652, ASTM UNS S32654 General characteristics 7% Mo, very high N alloyed austenitic grade. The most corrosion resistant stainless steel in the world. High mechanical strength. Useful
Forta SDX 100 EN , ASTM UNS S32760
 Forta SDX 100 EN 1.4501, ASTM UNS S32760 General characteristics Austenitic-ferritic stainless steel also referred to as duplex stainless steels, combine many of the beneficial properties of ferritic and
Forta SDX 100 EN 1.4501, ASTM UNS S32760 General characteristics Austenitic-ferritic stainless steel also referred to as duplex stainless steels, combine many of the beneficial properties of ferritic and
Ultra 6XN EN , ASTM UNS N08926
 Ultra 6XN EN 1.4529, ASTM UNS N08926 General characteristics 6% Mo, high Ni, and N alloyed austenitic grade with extremely high resistance to both uniform and localized corrosion. Commonly used in applications
Ultra 6XN EN 1.4529, ASTM UNS N08926 General characteristics 6% Mo, high Ni, and N alloyed austenitic grade with extremely high resistance to both uniform and localized corrosion. Commonly used in applications
Forta SDX 100 EN , ASTM UNS S32760
 Forta SDX 100 EN 1.4501, ASTM UNS S32760 General characteristics Austenitic-ferritic stainless steel also referred to as duplex stainless steels, combine many of the beneficial properties of ferritic and
Forta SDX 100 EN 1.4501, ASTM UNS S32760 General characteristics Austenitic-ferritic stainless steel also referred to as duplex stainless steels, combine many of the beneficial properties of ferritic and
Supra 316plus EN , ASTM UNS S31655
 Supra 316plus EN 1.4420, ASTM UNS S31655 General characteristics With its high chromium content, Supra 316 plus content delivers high strength, good formability, and excellent weldability, making it ideal
Supra 316plus EN 1.4420, ASTM UNS S31655 General characteristics With its high chromium content, Supra 316 plus content delivers high strength, good formability, and excellent weldability, making it ideal
Moda 410L/4003 EN , ASTM UNS S40977
 Moda 410L/4003 EN 1.4003, ASTM UNS S40977 General characteristics Moda 410L/4003 is a weldable ferritic stainless steel with elevated yield strength and resistance to abrasion. Its better corrosion resistance
Moda 410L/4003 EN 1.4003, ASTM UNS S40977 General characteristics Moda 410L/4003 is a weldable ferritic stainless steel with elevated yield strength and resistance to abrasion. Its better corrosion resistance
Moda 430/4016 EN , ASTM TYPE 430 / UNS S43000
 Moda 430/4016 EN 1.4016, ASTM TYPE 430 / UNS S43000 General characteristics Moda 430/4016 is a classic 16 chromium ferritic stainless steel. Good corrosion resistance in mildly corrosive environments combined
Moda 430/4016 EN 1.4016, ASTM TYPE 430 / UNS S43000 General characteristics Moda 430/4016 is a classic 16 chromium ferritic stainless steel. Good corrosion resistance in mildly corrosive environments combined
Forta SDX 2507 EN , ASTM UNS S32750
 Forta SDX 2507 EN 1.4410, ASTM UNS S32750 General characteristics Forta SDX 2507 is a super duplex product with higher corrosion resistance and mechanical strength than Forta DX 2205. Often used in extremely
Forta SDX 2507 EN 1.4410, ASTM UNS S32750 General characteristics Forta SDX 2507 is a super duplex product with higher corrosion resistance and mechanical strength than Forta DX 2205. Often used in extremely
Prodec 303/4305 EN , ASTM TYPE 303
 Prodec 303/4305 EN 1.4305, ASTM TYPE 303 General characteristics Prodec 303/4305 is for applications that use 303/1.4305. It gives you faster machining, longer tool life, better tolerances, superior machined
Prodec 303/4305 EN 1.4305, ASTM TYPE 303 General characteristics Prodec 303/4305 is for applications that use 303/1.4305. It gives you faster machining, longer tool life, better tolerances, superior machined
Chemical characteristics The chemical composition is shown in Table 1. Outokumpu EN ASTM
 for Bar Applications has a unique combination of characteristics (good corrosion properties, high strength and good machinability), which together with its relative price stability, makes it the material
for Bar Applications has a unique combination of characteristics (good corrosion properties, high strength and good machinability), which together with its relative price stability, makes it the material
Stainless steels for mildly corrosive environments
 Stainless steels for mildly corrosive environments Outokumpu Moda range outokumpu.com/moda We believe in a world that lasts forever Outokumpu is a global leader in the advanced materials business, creating
Stainless steels for mildly corrosive environments Outokumpu Moda range outokumpu.com/moda We believe in a world that lasts forever Outokumpu is a global leader in the advanced materials business, creating
Heat treatable for greater hardness and strength
 Heat treatable for greater hardness and strength Outokumpu Dura range datasheet General characteristics The Dura range contains 14 high hardness and precipitation hardening (PH) stainless steel products.
Heat treatable for greater hardness and strength Outokumpu Dura range datasheet General characteristics The Dura range contains 14 high hardness and precipitation hardening (PH) stainless steel products.
ATI ATI 2205 Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel. Technical Data Sheet
 Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogenenhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly improve
Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogenenhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly improve
FATIGUE OF DUPLEX STEELS IN CORROSIVE ENVIRONMENT
 5th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING ADDING INNOVATION CAPACITY OF LABOUR FORCE AND ENTREPRENEURS" 20 22 April 2006, Tallinn, Estonia FATIGUE OF DUPLEX STEELS IN CORROSIVE
5th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING ADDING INNOVATION CAPACITY OF LABOUR FORCE AND ENTREPRENEURS" 20 22 April 2006, Tallinn, Estonia FATIGUE OF DUPLEX STEELS IN CORROSIVE
Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes
 Cast materials Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes Our customer-focused R&D and continuous research on new material options enable us to develop equipment with a strong
Cast materials Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes Our customer-focused R&D and continuous research on new material options enable us to develop equipment with a strong
J2101 UNS S32101 EN
 J2101 UNS S32101 EN 1.4162 DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL General Characteristics: Lean Duplex Stainless steel 2101 (UNS S32101) possesses high strength coupled with corrosion resistance comparable to austenitic
J2101 UNS S32101 EN 1.4162 DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL General Characteristics: Lean Duplex Stainless steel 2101 (UNS S32101) possesses high strength coupled with corrosion resistance comparable to austenitic
STAINLESS STEEL SELECTION FOR FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION EQUIPMENT
 STAINLESS STEEL SELECTION FOR FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION EQUIPMENT Gary M. Carinci William A. Pratt Outokumpu Stainless 3209 McKnight East Drive Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15237 gcarinci@tmr-inc.com Abstract
STAINLESS STEEL SELECTION FOR FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION EQUIPMENT Gary M. Carinci William A. Pratt Outokumpu Stainless 3209 McKnight East Drive Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15237 gcarinci@tmr-inc.com Abstract
ATI 2205 ATI Technical Data Sheet. Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES. (UNS S31803 and S32205)
 ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
Chapter 7. Stainless Steels. /MS371/ Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys
 Chapter 7 Stainless Steels Stainless steels at least % Cr in iron is required (max 30% Cr) Cr: to make iron surface by forming a surface oxide film protecting the underlying metal from corrosion Ni: to
Chapter 7 Stainless Steels Stainless steels at least % Cr in iron is required (max 30% Cr) Cr: to make iron surface by forming a surface oxide film protecting the underlying metal from corrosion Ni: to
Outokumpu 2507 UNS S32750
 UNS S32750 North American Version Imperial Units Design Features Very high strength High resistance to pitting, crevice, and general corrosion Very high resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking
UNS S32750 North American Version Imperial Units Design Features Very high strength High resistance to pitting, crevice, and general corrosion Very high resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking
 http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper presented at International Conference on Residual Stresses, 3-7 July 2016, Sydney, Australia. Citation for the original published paper:
http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper presented at International Conference on Residual Stresses, 3-7 July 2016, Sydney, Australia. Citation for the original published paper:
SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3RE60 is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: High resistance to stress corrosion cracking (SCC)
SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3RE60 is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: High resistance to stress corrosion cracking (SCC)
Welding Consumables for Lean Duplex Stainless Steels
 Welding Consumables for Lean Duplex Stainless Steels Graham Holloway, Adam Marshall & Zhuyao Zhang Metrode Products Ltd, UK Presenter: Presenter - Graham Holloway Graham Holloway has been at Metrode Products
Welding Consumables for Lean Duplex Stainless Steels Graham Holloway, Adam Marshall & Zhuyao Zhang Metrode Products Ltd, UK Presenter: Presenter - Graham Holloway Graham Holloway has been at Metrode Products
Don t Repeat Mistakes! An SWRO Plant Case Study
 Don t Repeat Mistakes! An SWRO Plant Case Study Authors: Jan Olsson and Malin Snis Presenter: Malin Snis Abstract The paper describes a failure investigation of high-pressure piping made of 904L from a
Don t Repeat Mistakes! An SWRO Plant Case Study Authors: Jan Olsson and Malin Snis Presenter: Malin Snis Abstract The paper describes a failure investigation of high-pressure piping made of 904L from a
GUIDE TO STAINLESS STEELS AND DESALINATION
 GUIDE TO STAINLESS STEELS AND DESALINATION 1.0 DESALINATION: AN OVERVIEW. Water, water everywhere, nor any drop to drink. 71% of the Earth s surface is covered by water but of this 96.5% is found in seas
GUIDE TO STAINLESS STEELS AND DESALINATION 1.0 DESALINATION: AN OVERVIEW. Water, water everywhere, nor any drop to drink. 71% of the Earth s surface is covered by water but of this 96.5% is found in seas
GUIDE TO STAINLESS STEELS AND DESALINATION
 GUIDE TO STAINLESS STEELS AND DESALINATION 1.0 DESALINATION: AN OVERVIEW. Water, water everywhere, nor any drop to drink. 71% of the Earth s surface is covered by water but of this 96.5% is found in seas
GUIDE TO STAINLESS STEELS AND DESALINATION 1.0 DESALINATION: AN OVERVIEW. Water, water everywhere, nor any drop to drink. 71% of the Earth s surface is covered by water but of this 96.5% is found in seas
Sulzer Pumps. Cast Materials. The Heart of Your Process
 Sulzer Pumps Cast Materials The Heart of Your Process Sulzer Pumps Striving to Serve You Better Sulzer Pumps is a leading global supplier of reliable products and innovative pumping solutions for end users.
Sulzer Pumps Cast Materials The Heart of Your Process Sulzer Pumps Striving to Serve You Better Sulzer Pumps is a leading global supplier of reliable products and innovative pumping solutions for end users.
Macrographs & Micrographs
 OVERVIEW Keyhole gas tungsten arc welding is applicable to a wide range of materials. However, it is true to say its attractiveness is strongly correlated to the cost of the material being welded. This
OVERVIEW Keyhole gas tungsten arc welding is applicable to a wide range of materials. However, it is true to say its attractiveness is strongly correlated to the cost of the material being welded. This
family of stainless steels can be divided into five (5) categories:
 Welcome to the fifth issue of Tech Talk. This newsletter covers a range of topics on various welding products, applications, metallurgy, techniques, and economics. Previous issues are archived at www.unibraze.com.
Welcome to the fifth issue of Tech Talk. This newsletter covers a range of topics on various welding products, applications, metallurgy, techniques, and economics. Previous issues are archived at www.unibraze.com.
Microstructural Analysis of Selected Corroded Materials from Nigeria Oil and Gas Industry
 American Journal of Materials Science: 2011; 1(2): 108-112 DOI: 10.5923/j.materials.20110102.18 Microstructural Analysis of Selected Corroded Materials from Nigeria Oil and Gas Industry Ajide *, Makinde,
American Journal of Materials Science: 2011; 1(2): 108-112 DOI: 10.5923/j.materials.20110102.18 Microstructural Analysis of Selected Corroded Materials from Nigeria Oil and Gas Industry Ajide *, Makinde,
Influence of rapid cooling rates for HIP on mechanical and corrosion properties of UNS S32205
 Influence of rapid cooling rates for HIP on mechanical and corrosion properties of UNS S32205 Arnulf Hörtnagl 1, Paul Gümpel 1, Michael Hamentgen², Beat Hofer³ Institute for Materials System Technology
Influence of rapid cooling rates for HIP on mechanical and corrosion properties of UNS S32205 Arnulf Hörtnagl 1, Paul Gümpel 1, Michael Hamentgen², Beat Hofer³ Institute for Materials System Technology
STAINLESS STEELS. Experience has shown that, at least for stainless. for Corrosion Resistance
 STAINLESS STEELS for Corrosion Resistance Newly developed stainless steels provide increased corrosion resistance, improved mechanical properties, easier forming and fabrication, and/or improved economy.
STAINLESS STEELS for Corrosion Resistance Newly developed stainless steels provide increased corrosion resistance, improved mechanical properties, easier forming and fabrication, and/or improved economy.
The microstructural development of type 321 Austenitic Stainless Steel with long term ageing
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository The microstructural development of type 321 Austenitic Stainless Steel with long term ageing This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository The microstructural development of type 321 Austenitic Stainless Steel with long term ageing This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Low Nickel austenite a cost efficient alternative to 304/4301. Gabriele Brückner Head of product development EMEA Outokumpu May 27, 2015
 Low Nickel austenite a cost efficient alternative to 304/4301 Gabriele Brückner Head of product development EMEA Outokumpu May 27, 2015 Content 1. Market situation 2. Development of cost-effective CrNi
Low Nickel austenite a cost efficient alternative to 304/4301 Gabriele Brückner Head of product development EMEA Outokumpu May 27, 2015 Content 1. Market situation 2. Development of cost-effective CrNi
Duplex Stainless Steel
 Duplex Stainless Steel Steel grades Outokumpu EN ASTM LDX 211 1.4162 S3211 SAF 234 1.4362 S3234 25 1.4462 S325 S3183 SAF 257 1.441 S3275 Characteristic properties High strength Good to very good resistance
Duplex Stainless Steel Steel grades Outokumpu EN ASTM LDX 211 1.4162 S3211 SAF 234 1.4362 S3234 25 1.4462 S325 S3183 SAF 257 1.441 S3275 Characteristic properties High strength Good to very good resistance
Alloy Steels. Engineering Materials. Introduction : Msc. Shaymaa Mahmood
 Alloy Steels Introduction : Steels are, essentially, alloys of iron and carbon, containing up to 1.5 % of carbon. Steel is made by oxidizing away the impurities that are present in the iron produced in
Alloy Steels Introduction : Steels are, essentially, alloys of iron and carbon, containing up to 1.5 % of carbon. Steel is made by oxidizing away the impurities that are present in the iron produced in
Outokumpu Experience May 22-23, 2013 Old Billingsgate, London, UK
 Outokumpu Experience 2013 May 22-23, 2013 Old Billingsgate, London, UK Outokumpu New Duplex Alloys Peter Samuelsson SVP R&D & Technology Outokumpu HPSA Outokumpu Experience 2013 May 23, 2013 2 Market Introduction
Outokumpu Experience 2013 May 22-23, 2013 Old Billingsgate, London, UK Outokumpu New Duplex Alloys Peter Samuelsson SVP R&D & Technology Outokumpu HPSA Outokumpu Experience 2013 May 23, 2013 2 Market Introduction
Outokumpu Experience May 22-23, 2013 Old Billingsgate, London, UK
 Outokumpu Experience 2013 May 22-23, 2013 Old Billingsgate, London, UK Outokumpu New Duplex Alloys Peter Samuelsson SVP R&D & Technology Outokumpu HPSA Outokumpu Experience 2013 May 23, 2013 2 Market Introduction
Outokumpu Experience 2013 May 22-23, 2013 Old Billingsgate, London, UK Outokumpu New Duplex Alloys Peter Samuelsson SVP R&D & Technology Outokumpu HPSA Outokumpu Experience 2013 May 23, 2013 2 Market Introduction
INFLUENCE OF THE FILLER METAL IN WELDED POINTS OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEELS
 INFLUENCE OF THE FILLER METAL IN WELDED POINTS OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEELS Edmundo Roldan C., Eng CIATEQ A. C. Campus Querétaro. Querétaro, Qro Juan Hernandez A., PhD Eleazar Salinas R. PhD Eduardo Cerecedo
INFLUENCE OF THE FILLER METAL IN WELDED POINTS OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEELS Edmundo Roldan C., Eng CIATEQ A. C. Campus Querétaro. Querétaro, Qro Juan Hernandez A., PhD Eleazar Salinas R. PhD Eduardo Cerecedo
NITRONIC 19D LEAN DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL
 Chemical Processing Desalination/Water Treatment Oil Field Undersea Tubing AK STEEL NITRONIC 19D STAINLESS STEEL is a molybdenum-free, low nickel lean duplex stainless steel. The combination of strength,
Chemical Processing Desalination/Water Treatment Oil Field Undersea Tubing AK STEEL NITRONIC 19D STAINLESS STEEL is a molybdenum-free, low nickel lean duplex stainless steel. The combination of strength,
Grades : SS 304, 304L, 304H, 316, 316L, 316LN, 316Ti, 309, 310S, 317L, 321, 347,
 Unifit MetalloysInc (UMI) is one of the leading Manufacturer, Exporter and Supplier of High Quality Stainless Steel Pipes & Tubes, Flanges, Pipe Fittings, Round Bars, Sheets and Plates Etc.Stainless steel
Unifit MetalloysInc (UMI) is one of the leading Manufacturer, Exporter and Supplier of High Quality Stainless Steel Pipes & Tubes, Flanges, Pipe Fittings, Round Bars, Sheets and Plates Etc.Stainless steel
LASER SURFACE ALLOYING OF MIDDLE CARBON STEEL IN ORDER TO INCREASE ITS CAVITATION EROSION RESISTANCE. Marek Szkodo
 LASER SURFACE ALLOYING OF MIDDLE CARBON STEEL IN ORDER TO INCREASE ITS CAVITATION EROSION RESISTANCE Marek Szkodo Technical University of Gdansk, Department of Material Engineering, Gdańsk, ul. Narutowicza
LASER SURFACE ALLOYING OF MIDDLE CARBON STEEL IN ORDER TO INCREASE ITS CAVITATION EROSION RESISTANCE Marek Szkodo Technical University of Gdansk, Department of Material Engineering, Gdańsk, ul. Narutowicza
PRODUCT: WELDED PIPE SPECIFICATION: 355.6*9.52 MATERIAL: S32205 PRODUCT: SEAMLESS PIPE. SPECIFICATION: Φ33mm*1mm MATERIAL: S31803
 Special Piping Materials is renowned for the high volume of Duplex and Super Duplex products that it stocks. It supplies these materials to countless companies around the world who use its product s in
Special Piping Materials is renowned for the high volume of Duplex and Super Duplex products that it stocks. It supplies these materials to countless companies around the world who use its product s in
Phase Transformations in Metals Tuesday, December 24, 2013 Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE 1
 Ferrite - BCC Martensite - BCT Fe 3 C (cementite)- orthorhombic Austenite - FCC Chapter 10 Phase Transformations in Metals Tuesday, December 24, 2013 Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE 1 Why do we study
Ferrite - BCC Martensite - BCT Fe 3 C (cementite)- orthorhombic Austenite - FCC Chapter 10 Phase Transformations in Metals Tuesday, December 24, 2013 Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE 1 Why do we study
Duplex Stainless Steel
 Duplex Stainless Steel Steel grades Outokumpu EN ASTM LDX 211 1.4162 S3211 SAF 234 1.4362 S3234 1.4462 S3 S3183 SAF 257 1.441 S3275 Characteristic properties High strength Good to very good resistance
Duplex Stainless Steel Steel grades Outokumpu EN ASTM LDX 211 1.4162 S3211 SAF 234 1.4362 S3234 1.4462 S3 S3183 SAF 257 1.441 S3275 Characteristic properties High strength Good to very good resistance
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
NITRONIC 19D LEAN DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL. Excellent Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance. Improved Welding Characteristics
 NITRONIC 19D LEAN DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Excellent Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance High Strength Improved Welding Characteristics Resists Sigma Phase Formation
NITRONIC 19D LEAN DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Excellent Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance High Strength Improved Welding Characteristics Resists Sigma Phase Formation
Impact of heat treatment on microstructure of steel 30X padded with wire G18 8Mn
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Impact of heat treatment on microstructure of steel 30X padded with wire G18 8Mn To cite this article: Mirosaw omozik and Janusz Adamiec 2012 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Impact of heat treatment on microstructure of steel 30X padded with wire G18 8Mn To cite this article: Mirosaw omozik and Janusz Adamiec 2012 IOP
Stainless Steel Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Industry news. Recent findings on pitting and crevice corrosion: comparing SAF 2707 HD
 Recent findings on pitting and crevice corrosion: comparing SAF 2707 HD a cura di: Alessandra Spaghetti alessandra.spaghetti@sandvik.com - Sandvik Materials Technology INTRODUCTION Hyper-duplex is a grade
Recent findings on pitting and crevice corrosion: comparing SAF 2707 HD a cura di: Alessandra Spaghetti alessandra.spaghetti@sandvik.com - Sandvik Materials Technology INTRODUCTION Hyper-duplex is a grade
Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316
 Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316 Manish Kumar Verma Mechanical, Columbia Institute of Engineering & Technology, Raipur (India) ABSTRACT Austenitic Stainless steels
Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316 Manish Kumar Verma Mechanical, Columbia Institute of Engineering & Technology, Raipur (India) ABSTRACT Austenitic Stainless steels
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING
 DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
The Many Facets and Complexities of 316L and the Effect on Properties
 The Many Facets and Complexities of 316L and the Effect on Properties Ingrid Hauer Miller Höganäs AB, Höganäs, Sweden state and country Ingrid.hauer@hoganas.com, +46702066244 Abstract One of the most widely
The Many Facets and Complexities of 316L and the Effect on Properties Ingrid Hauer Miller Höganäs AB, Höganäs, Sweden state and country Ingrid.hauer@hoganas.com, +46702066244 Abstract One of the most widely
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS
 DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS corrosion resistant alloys ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS corrosion resistant alloys ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
PAGE 1/6 ZAPP PRECISION WIRE INCOLOY ALLOY 27-7MO (UNS S31277)
 ZAPP PRECISION WIRE INCOLOY ALLOY (UNS S31277) QUALITY SYSTEM CERTIFIED TO ISO 9001:2008 INCOLOY ALLOY (UNS S31277) WIRE FOR: _ Armoring applications on electromechanical cables _ Wirelines for down hole
ZAPP PRECISION WIRE INCOLOY ALLOY (UNS S31277) QUALITY SYSTEM CERTIFIED TO ISO 9001:2008 INCOLOY ALLOY (UNS S31277) WIRE FOR: _ Armoring applications on electromechanical cables _ Wirelines for down hole
Martensitic. stainless steels. Types 410, 420, 425 Mod, and 440A TECHNICAL DATA BLUE SHEET GENERAL PROPERTIES APPLICATIONS PRODUCT FORM
 TECHNICAL DATA BLUE SHEET Martensitic Stainless Steels s 410, 420, 425 Mod, and 440A GENERAL PROPERTIES Allegheny Ludlum s 410, 420, 425 Modified, and 440A (see composition on Page 2) are hardenable, straight-chromium
TECHNICAL DATA BLUE SHEET Martensitic Stainless Steels s 410, 420, 425 Mod, and 440A GENERAL PROPERTIES Allegheny Ludlum s 410, 420, 425 Modified, and 440A (see composition on Page 2) are hardenable, straight-chromium
Activating Your Ideas. Stainless steel for metallurgical processes
 Activating Your Ideas Stainless steel for metallurgical processes Inspired by the elements. On all continents. Metallurgical processes from ore milling to product recovery take place in tough conditions.
Activating Your Ideas Stainless steel for metallurgical processes Inspired by the elements. On all continents. Metallurgical processes from ore milling to product recovery take place in tough conditions.
Failure Analysis of Cracked Reducer Flange
 J Fail. Anal. and Preven. (2010) 10:480 485 DOI 10.1007/s11668-010-9389-9 Failure Analysis of Cracked Reducer Flange Khaled Habib Submitted: 18 May 2010/in revised form: 29 July 2010/Published online:
J Fail. Anal. and Preven. (2010) 10:480 485 DOI 10.1007/s11668-010-9389-9 Failure Analysis of Cracked Reducer Flange Khaled Habib Submitted: 18 May 2010/in revised form: 29 July 2010/Published online:
Overmatching Superalloy Consumable Inco-weld 686CPT Broadens its Applications to Include Welding Super Austenitic and Super Duplex Stainless Steels
 Overmatching Superalloy Consumable Inco-weld 686CPT Broadens its Applications to Include Welding Super Austenitic and Super Duplex Stainless Steels P0468 Authors: Ph.D C. Thornton, B.Sc C. Cooper Special
Overmatching Superalloy Consumable Inco-weld 686CPT Broadens its Applications to Include Welding Super Austenitic and Super Duplex Stainless Steels P0468 Authors: Ph.D C. Thornton, B.Sc C. Cooper Special
Crack Initiation and Crack Propagation of Pre-corroded Ni-16Cr Alloy in 4.5%NaCl Aqueous Solution
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 8 (August. 2013), V2 PP 11-15 Crack Initiation and Crack Propagation of Pre-corroded Ni-16Cr Alloy in 4.5%NaCl Aqueous
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 8 (August. 2013), V2 PP 11-15 Crack Initiation and Crack Propagation of Pre-corroded Ni-16Cr Alloy in 4.5%NaCl Aqueous
Back to Basics Stainless Steel. Tom Mackerras National Engineering Manager
 Back to Basics Stainless Steel Tom Mackerras National Engineering Manager Winery Engineers Conference 2018 26 July 2018 1 What is Stainless Steel? Group of steels which have a minimum of 10.5% Cr Creates
Back to Basics Stainless Steel Tom Mackerras National Engineering Manager Winery Engineers Conference 2018 26 July 2018 1 What is Stainless Steel? Group of steels which have a minimum of 10.5% Cr Creates
Research and Development of Cold Rolled Hot-dip Galvanized DP590 Steel with Low Cost
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Research and Development of Cold Rolled Hot-dip Galvanized DP590 Steel with Low Cost Yun
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Research and Development of Cold Rolled Hot-dip Galvanized DP590 Steel with Low Cost Yun
Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure, Hardness and Wear Behavior of Super Duplex Stainless Steel AISI 2507
 American Journal of Materials Science 215, 5(3C): 48-52 DOI: 1.5923/c.materials.212.1 Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure, Hardness and Wear Behavior of Super Duplex Stainless Steel AISI 27 Mahesh
American Journal of Materials Science 215, 5(3C): 48-52 DOI: 1.5923/c.materials.212.1 Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure, Hardness and Wear Behavior of Super Duplex Stainless Steel AISI 27 Mahesh
GLORIA STEEL LIMITED Web:www.gloriasteel.com Fax: (UNS S32205/S31803) EN duplex stainless steel
 2205 (UNS S32205/S31803) EN 1.4462 duplex stainless steel A 22Cr-3Mo Stainless Steel Alloy 2205 is a 22% Chromium, 3% Molybdenum, 5-6% Nickel, nitrogen alloyed duplex stainless steel with high general,
2205 (UNS S32205/S31803) EN 1.4462 duplex stainless steel A 22Cr-3Mo Stainless Steel Alloy 2205 is a 22% Chromium, 3% Molybdenum, 5-6% Nickel, nitrogen alloyed duplex stainless steel with high general,
PRODUCTION AND HEAT TREATMENT OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FORGINGS
 PRODUCTION AND HEAT TREATMENT OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FORGINGS Ing. Martin BALCAR, Ph.D. 1), Ing. Libor SOCHOR 1), Ing. Jaroslav NOVÁK 1), Ing. Ludvík MARTÍNEK, Ph.D. 1), Ing. Pavel FILA 1), Ing. Josef
PRODUCTION AND HEAT TREATMENT OF DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FORGINGS Ing. Martin BALCAR, Ph.D. 1), Ing. Libor SOCHOR 1), Ing. Jaroslav NOVÁK 1), Ing. Ludvík MARTÍNEK, Ph.D. 1), Ing. Pavel FILA 1), Ing. Josef
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Effect of Precipitation Hardening on Microstructural Characteristics of 15-5 Ph Steel
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 1 (November 2013), PP. 22-26 Effect of Precipitation Hardening on Microstructural
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 1 (November 2013), PP. 22-26 Effect of Precipitation Hardening on Microstructural
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Duplex and high-strength stainless steels
 Duplex and high-strength stainless steels Outokumpu Forta range outokumpu.com/forta We believe in a world that lasts forever The inside view Duplex and other high strength stainless steels that enable
Duplex and high-strength stainless steels Outokumpu Forta range outokumpu.com/forta We believe in a world that lasts forever The inside view Duplex and other high strength stainless steels that enable
SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sanicro 29 is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel (CRA) for OCTG downhole applications in particularly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized
SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sanicro 29 is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel (CRA) for OCTG downhole applications in particularly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized
Experimental and Numerical Investigation for Quench Annealed 316L Stainless Steel by Number of Quenching Media
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. V (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 96-103 www.iosrjournals.org Experimental and Numerical
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. V (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 96-103 www.iosrjournals.org Experimental and Numerical
HEAT TREATMENT OF REACTOR VESSEL STEEL AISI 321
 HEAT TREATMENT OF REACTOR VESSEL STEEL AISI 321 Pavel PODANÝ a, Petr MARTÍNEK a, Petr NACHÁZEL a, Martin BALCAR b a COMTES FHT a.s., Dobřany, Czech Republic, EU, comtes@comtesfht.cz b ŽDAS a.s., Žďár nad
HEAT TREATMENT OF REACTOR VESSEL STEEL AISI 321 Pavel PODANÝ a, Petr MARTÍNEK a, Petr NACHÁZEL a, Martin BALCAR b a COMTES FHT a.s., Dobřany, Czech Republic, EU, comtes@comtesfht.cz b ŽDAS a.s., Žďár nad
Analysis of Stainless Steel by Dual View Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectrometry
 Application Note - AN1505 Analysis of Stainless Steel by Dual View Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectrometry Introduction Page 1 Stainless steels are a corrosion resistant family of iron alloys that have
Application Note - AN1505 Analysis of Stainless Steel by Dual View Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectrometry Introduction Page 1 Stainless steels are a corrosion resistant family of iron alloys that have
Selection and use of stainless steels in water systems
 Selection and use of stainless steels in water systems PierreJean Cunat, EuroInox, Brussels 1. Background Stainless Steel is being used for water treatment and supply systems. It is used for numerous applications
Selection and use of stainless steels in water systems PierreJean Cunat, EuroInox, Brussels 1. Background Stainless Steel is being used for water treatment and supply systems. It is used for numerous applications
THE MICROSTRUCTURES AND HARDNESS ANALYSIS OF A NEW HYPOEUTECTOID STEELS WITH 0.3 % MO. Edyta ROŻNIATA
 THE MICROSTRUCTURES AND HARDNESS ANALYSIS OF A NEW HYPOEUTECTOID STEELS WITH 0.3 MO Edyta ROŻNIATA AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Metals Engineering and Industrial Computer Science
THE MICROSTRUCTURES AND HARDNESS ANALYSIS OF A NEW HYPOEUTECTOID STEELS WITH 0.3 MO Edyta ROŻNIATA AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Metals Engineering and Industrial Computer Science
Investigation of aging heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of 316L austenitic stainless steel weld metal
 Computational Methods and Experiments in Material Characterisation II 63 Investigation of aging heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of 316L austenitic stainless steel weld metal
Computational Methods and Experiments in Material Characterisation II 63 Investigation of aging heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of 316L austenitic stainless steel weld metal
Welding wire. Wire types and designations
 Features Consumables for welding stainless steels and nickel-based alloys Welding wire for optimum corrosion properties MIG/MAG (GMAW) TIG (GTAW) Submerged arc (SAW) Product range Avesta Welding supplies
Features Consumables for welding stainless steels and nickel-based alloys Welding wire for optimum corrosion properties MIG/MAG (GMAW) TIG (GTAW) Submerged arc (SAW) Product range Avesta Welding supplies
STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS
 STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS Alloys: 304 304L 310 316 316L 316LN 316Ti 316LVM 6Mo 21-6-9 22-13-5 904L Alloys 304 / 304L Alloys 304 / 304L (UNS S30400 / S30403) Alloys 304 (S30400) and 304L (S30403) stainless
STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS Alloys: 304 304L 310 316 316L 316LN 316Ti 316LVM 6Mo 21-6-9 22-13-5 904L Alloys 304 / 304L Alloys 304 / 304L (UNS S30400 / S30403) Alloys 304 (S30400) and 304L (S30403) stainless
ANALYSIS OF THE DAMAGE OF A PRESSURE VESSEL MATERIAL IN SIMULATION EXPERIMENTS FOR LWR ACCIDENT SCENARIOS
 ANALYSIS OF THE DAMAGE OF A PRESSURE VESSEL MATERIAL IN SIMULATION EXPERIMENTS FOR LWR ACCIDENT SCENARIOS 1. Introduction Gudrun Mueller and Hans-Georg Willschuetz Considering the hypothetical core melt
ANALYSIS OF THE DAMAGE OF A PRESSURE VESSEL MATERIAL IN SIMULATION EXPERIMENTS FOR LWR ACCIDENT SCENARIOS 1. Introduction Gudrun Mueller and Hans-Georg Willschuetz Considering the hypothetical core melt
Causes and Remediation of Corrosion Failure of Duplex Stainless Steel Equipment in a PVC Plant
 acom AVESTA SHEFFIELD CORROSION MANAGEMENT AND APPLICATION ENGINEERING 3-2000 Causes and Remediation of Corrosion Failure of Duplex Stainless Steel Equipment in a PVC Plant Dr. Michael Davies, CARIAD Consultants,
acom AVESTA SHEFFIELD CORROSION MANAGEMENT AND APPLICATION ENGINEERING 3-2000 Causes and Remediation of Corrosion Failure of Duplex Stainless Steel Equipment in a PVC Plant Dr. Michael Davies, CARIAD Consultants,
PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATIONS OF LOW-NICKEL STAINLESS STEELS FOR STRUCTURAL APPLICATIONS
 PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATIONS OF LOW-NICKEL STAINLESS STEELS FOR STRUCTURAL APPLICATIONS J. Kerr and R. Paton Mintek, Private Bag X3015, Randburg. 2125. South Africa. E-mail: jonathank@mintek.co.za ABSTRACT
PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATIONS OF LOW-NICKEL STAINLESS STEELS FOR STRUCTURAL APPLICATIONS J. Kerr and R. Paton Mintek, Private Bag X3015, Randburg. 2125. South Africa. E-mail: jonathank@mintek.co.za ABSTRACT
Protective Nitrided Layers on Ferrite-Austenite Chromium Steel
 ISSN 1392 1320 MATERIALS SCIENCE (MEDŽIAGOTYRA). Vol. 11, No. 3. 2005 Protective Nitrided Layers on Ferrite-Austenite Chromium Steel Jaroslaw BIELAWSKI, Jolanta BARANOWSKA, Kazimierz SZCZECIŃSKI Institute
ISSN 1392 1320 MATERIALS SCIENCE (MEDŽIAGOTYRA). Vol. 11, No. 3. 2005 Protective Nitrided Layers on Ferrite-Austenite Chromium Steel Jaroslaw BIELAWSKI, Jolanta BARANOWSKA, Kazimierz SZCZECIŃSKI Institute
Phase Transformations in Cast Superaustenitic Stainless Steels
 Materials Science and Engineering Publications Materials Science and Engineering 12-2009 Phase Transformations in Cast Superaustenitic Stainless Steels Nathaniel S.L. Phillips Iowa State University L.
Materials Science and Engineering Publications Materials Science and Engineering 12-2009 Phase Transformations in Cast Superaustenitic Stainless Steels Nathaniel S.L. Phillips Iowa State University L.
MATERIAL TESTING AND CORROSION EXPERIENCE IN CRUDE UPGRADER ATMOSPHERIC DISTILLATION UNIT
 MATERIAL TESTING AND CORROSION EXPERIENCE IN CRUDE UPGRADER ATMOSPHERIC DISTILLATION UNIT Tore Arnesen 1, María Specht 2, Henry Tovar 2, Erik Rodriguez 2 Statoil, Research Center, Norway 1 PDVSA Intevep,
MATERIAL TESTING AND CORROSION EXPERIENCE IN CRUDE UPGRADER ATMOSPHERIC DISTILLATION UNIT Tore Arnesen 1, María Specht 2, Henry Tovar 2, Erik Rodriguez 2 Statoil, Research Center, Norway 1 PDVSA Intevep,
Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets)
 Datasheet updated 2013 11 28 14:13:21 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets) Sandvik SAF 2205 is a duplex (austenitic ferritic) stainless steel characterized by: High resistance
Datasheet updated 2013 11 28 14:13:21 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets) Sandvik SAF 2205 is a duplex (austenitic ferritic) stainless steel characterized by: High resistance
ANALYSIS OF A CRACKED HEAT EXCHANGER TUBE
 Steel Image Inc., Failure Analysis and Metallography 7 Innovation Drive, Suite 155, Flamborough Ontario, Canada, L9H 7H9, (289) 895-8363 ANALYSIS OF A CRACKED HEAT EXCHANGER TUBE EXAMPLE REPORT OVERVIEW
Steel Image Inc., Failure Analysis and Metallography 7 Innovation Drive, Suite 155, Flamborough Ontario, Canada, L9H 7H9, (289) 895-8363 ANALYSIS OF A CRACKED HEAT EXCHANGER TUBE EXAMPLE REPORT OVERVIEW
WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS
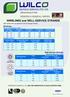 WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS High quality wire and strand for the oil and gas industry. Wirelines Minimum Breaking Loads Diameter in mm HT Carbon EHT Carbon ZERON 100VHX 0.092 2.34 1,950 1,980 1,350
WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS High quality wire and strand for the oil and gas industry. Wirelines Minimum Breaking Loads Diameter in mm HT Carbon EHT Carbon ZERON 100VHX 0.092 2.34 1,950 1,980 1,350
Seam Welded Air-Hardenable Corrosion Resistant Steel Tubing: Automotive Applications Overview
 KVA, Inc. / 124 S. Market Place, Suite 200 / Escondido, CA. 92029 U.S.A. (760) 489-5821 phone (760) 489-5823 fax 1-888-410-WELD www.kvastainless.com Seam Welded Air-Hardenable Corrosion Resistant Steel
KVA, Inc. / 124 S. Market Place, Suite 200 / Escondido, CA. 92029 U.S.A. (760) 489-5821 phone (760) 489-5823 fax 1-888-410-WELD www.kvastainless.com Seam Welded Air-Hardenable Corrosion Resistant Steel
CHROMESHIELD 22 STAINLESS STEEL
 CHROMESHIELD 22 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Appliances Food Service Equipment Architectural Welded Components Tubing Cookware Applications Potential CHROMESHIELD 22 Stainless Steel
CHROMESHIELD 22 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Appliances Food Service Equipment Architectural Welded Components Tubing Cookware Applications Potential CHROMESHIELD 22 Stainless Steel
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Hareness Circle Industrial Estate Aberdeen Scotland AB12 3LY Contact: Mrs D McAdam Tel: +44 (0)1224-890020 Fax: +44 (0)1224-890220 E-Mail:
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Hareness Circle Industrial Estate Aberdeen Scotland AB12 3LY Contact: Mrs D McAdam Tel: +44 (0)1224-890020 Fax: +44 (0)1224-890220 E-Mail:
We believe in a world that lasts forever. Contents. Meeting the material challenges of the oil & gas industry...4. Overview of product offering...
 Oil & Gas Contents Meeting the material challenges of the oil & gas industry...4 Overview of product offering...6 Exploration applications...9 Topside applications...10 Onshore applications...12 Cases...13
Oil & Gas Contents Meeting the material challenges of the oil & gas industry...4 Overview of product offering...6 Exploration applications...9 Topside applications...10 Onshore applications...12 Cases...13
Insititue of Paper Science and Technology Central Files CORROSION CONTROL ANNUAL RESEARCH REVIEW HANDOUT BOOK
 Insititue of Paper Science and Technology Central Files CORROSION CONTROL ANNUAL RESEARCH REVIEW HANDOUT BOOK J CORROSION CONTROL HANDOUT BOOK April 2, 1991 CONTENTS PROJECT 3309 FUNDAMENTALS OF CORROSION
Insititue of Paper Science and Technology Central Files CORROSION CONTROL ANNUAL RESEARCH REVIEW HANDOUT BOOK J CORROSION CONTROL HANDOUT BOOK April 2, 1991 CONTENTS PROJECT 3309 FUNDAMENTALS OF CORROSION
