UCRL Rev.l DISCLAIMER PREPRINT SELECTION OF BARRIER METALS FOR A WASTE PACKAGE IN TUFF. E. W. Russell R. D. McCright W. C.
|
|
|
- Arthur Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ~.- I I, UCRL Rev.l UCRL Rev. 1 DE PREPRINT j SELECTION OF BARRIER METALS FOR A WASTE PACKAGE IN TUFF E. W. Russell R. D. McCright W. C. O'Neal This paper was prepared for the 1983 annual meeting of the Materials Research Society, November 14-17, Boston, MA October This is a preprint of a paper intended for publication in a journal or proceedings. Since changes may be made before publication, this preprint is made available with the understanding that it will not be cited or reproduced without the permission of the author. 1' DISCLAIMER - This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the United States Government. Neither the United States Government nor any agency thereof, nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, - apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the United States Government or any agency thereof. The views and opinions of authors expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the United States Government or any agency thereof.
2 I Portions of this document may be illegible in electronic image products. mes are produced from the best available original d0cuiilent.,,
3 1 SELECTION OF BARRIER METALS FOR A WASTE PACKAGE IN TUFF* E. W. Russell, R. D. McCright, and W. C. O'Neal Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA ABSTRACT The Nevada Nuclear Waste Storage Investigations (NNWSI) project under the Civilian Radioactive Waste Management Program is planning a repository at Yucca Mountain at the Nevada Test Site for isolation of high-level nuclear waste. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is developing designs for an engineered barrier system.containing several barriers such as the waste form, a canister and/or an overpack, packing, and near field host rock. In this paper we address the selection of metal containment barriers. SUMMARY We have selected a few candidate metals for conceptual design of canisters and overpacks, and for use in corrosion tests under repository conditions. Important materials properties data,reflecting engineering design requirements for potential candidate materials were developed. The metals that were initially considered fall into the following categories: stainless steels--austenitic, ferritic, and duplex; high-nickel alloys, titanium alloys, zirconium alloys, copper-nickel alloys, low-carbon steels, and cast irons. These metals are all commercially available. Our procedure was to determine and evaluate the engineering properties considered to be important in meeting design requirements cost-effectively--corrosion resistance, tensile strength, weldability, etc. Four general categories were considered: e General and local corrosion resistance e Fabrication costs e Required mechanical properties 0 Weldability From this analysis we selected four metals for canister and overpack materials, and one for hole liners: 1. AISI 304L stainless steel. 2. AISI 321 stainless steel. 3. AISI 316L stainless steel. 4. Incoloy 825 nickel-base alloy. 5. AISI 1020 carbon steel (for horizontal borehole liners). The reference canister and overpack metal is AISI 304L stainless steel, but alternative metals will also be considered for two reasons: (1) to provide a replacement material until the reference material is confirmed by testing under site specific conditions; (2) to provide comparative data to support the choice of.ais1 304L stainless steel as the reference material during the regulatory review. *Work performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under contract number W-7405-ENG-48.
4 2 WASTE PACKAGE CONCEPTUAL DESIGNS We are designing waste packages to meet the Final Rule, NRC locfr Part 60 and derivative requirements [1,3]. To comply with these we have developed design requirements (Table I). The waste package designs considered in the evaluation and selection of metals for canisters, overpacks and liners are given below [2,33: 1.0 Reference designs emplaced in vertical boreholes with no liner and no packing. 1.1 Defense high-level waste (DEILW): emplacement of 61-cm diam 304L pour canister, 1-cm thick. 1.2 Commercial high-level waste (CHLW): emplacement of 32-cm diam 304L pour canister, 1-cm thick. 1.3 Spent fuel: emplacement of consolidated spent fuel rods in a 304L canister, 1-cm thick. These dimensions are assumed by LLNL at this time for conceptual design purposes only. 2.0 Alternative designs for vertical boreholes. 2.1 Alternative metals to 304L for canisters and overpacks. 2.2 Overpacks for DEILW and CHLW for those canisters which do not meet acceptance criteria-when received at the MJWSI repository. 2.3 Use of packing for spent fuel canisters if the engineered system does not meet the release rate requirement. 3.0 Horizontal emplacement of waste packages within steel borehole liners. TABLE I The LLNL design requirements derived from NRC 1OCFR60. Waste packages shall be hesigned to: Contain the waste for 300 to 1000 years. Maintain a release rate less than 1 part in 100,000 per year of radionuclide inventory present at the end of the containment period (300 years minimum). Be retrievable for 50 years after emplacement of the first waste package. Meet nuclear criticality standards, e.g., not exceed an effective multiplication factor (Keff) of Not exceed temperature limits of the waste forms, which are 773 K (5OOOC) for DHLW glass, 673 K (400OC) for CHLW glass, and 623 K (35OOC) for spent fuel (this is necessary to meet the 1 part in 100,000 per year requirement). Not leak radioactive material in excess of applicable federal and state standards after a drop test of two times waste package length onto an unyielding surface, at the minimum anticipated handling temperature. Not leak radioactive material in excess of applicable federal and state standards after sustaining a 1073 K (8OO0C), 30-min fire test. Not leak radioactive material in excess of applicable federal and state standards during or after transportation, handling, emplacement, retrieval and expected seismic loads. Further, these loads must not compromise long-term performance. Retain legible, externally labeled identification up to and including retrieval. Meet federal regulatory requirements for transportation of high level nuclear waste (DHLW and CHLW pour canisters). Meet requirements with considerations for cost-effectiveness, including direct package costs and related repository system costs through the operational period.
5 3 EMPLACEMENT ENVIRONMENT The NNWSI project has selected the Topopah Spring Member of the Paintbrush Tuff as the target horizon for a repository sited at Yucca Mountain. The repository will be located in a welded portion of the tuff unit and will lie approximately 350 to 400 meters below the surface level. The static water level is over 100 meters below the repository level. The waste canisters will not be submerged id water, but will be subjected to constant contact with water vapor and to intermittent contact with about 8 mm/yr o seeping liquid water 131. The pressure exerted on the canisters by the environment will be approximately 1 atmosphere with no hydrostatic pressure because there is not a continuum of water above or around the canisters. The gaseous environment to which the canister is exposed will be of air plus water vapor when the temperature is more than C. Wetted corrosion of the canister or overpack will begin after the temperature has dropped to less than 95-1OO0C. This is because liquid water cannot exist in the unsaturated zone (vadose zone) at temperatures higher than 95-1OO0C, the 1 atmosphere boiling point of water. Calculations of thermal history for canisters and overpacks show that for DHLW, the temperature drops below 100 C in about 60 years after emplacement and for CHLW, temperature will drop below 100 C approximately 180 years after waste emplacement. For spent fuel packages, the canister temperature will remain 100 C or greater for approximately 1000 years after emplacement. The unsaturated zone just above the water table and atmosphere of the repository will be mildly oxidizing, and there will be a decaying gamma flux starting at up to 1.1 x lo5 rem/hr for commercial high-level waste [21. NOMINATION OF CANDIDATE METALS A list of 17 candidate metals which potentially will meet our design requirements is given in Table 11. These metal alloys are of three types: (1) iron-base alloys with a ferritic structure; (2) iron-base to nickel-base alloys with an austenitic structure; and (3) copper, titanium, and zirconium-base alloys. The list of metals will be screened to yield the five top-contenders. 1. Iron-base alloys with a ferritic structure The ferritic metals considered for this group are low-carbon steels, that may have a high corrosion rate in the anticipated oxidizing environment of the repository. The redeeming properties of these steels are: lowest overall unit cost; acceptable strength at-room temperature and 800OC; and good weldability. We considered two low-carbon steels, AISI 1020 steel and ASTM A537B steel. Carbon steel is the reference metal for horizontal borehole liners, based on its low cost and projected survival during the retrieval period. Alloying carbon steels with chromium and molybdenum increases corrosion resistance under oxidizing conditions. The ferritic alloy steels under consideration are expected to be resistant to attack by pitting and crevice corrosion as well as to stress corrosion cracking. The shortcomings of this group are low fracture toughness values as well as poor weldability. The ferritic alloy steels considered are AISI 409 Ti stabilized stainless steel and 26 Cr - 1 Mo stainless steel. 2. Iron-base to nickel-base alloys with an austenitic structure The NNWSI reference canister and overpack metal, which also is the reference for the DHLW and CHLW pour-canisters, is AISI 304L Stainless
6 4 TABLE 11. Candidate metals for overpacks. Commercial material designation Chemical composition (wt%) 1. AISI 1020 cs C , Mn.3-.6, P.04 max, S.05 max (UNS G10200) 2. ASTM A537B cs C.24 max, Mn , P.035 max, S.04 max, Si.15-.5, Cr.25 max, Ni.25 max, Mo.08 max, Cu.35 max 3. AISI 409 ss C.08 max, Cr , Mn 1.0 max, Ni 0.50 max, (UNS S40900) P.04 max, S.045 max, Si 1.0 max, Ti 6XC min max Cr - 1 Mo ss C.06 max, Cr , Cu.2 max, Mn.4 max, (UNS '34626) Mo , N.04 max, Ni.05 max, P.04 max, S.02 max, Si.75 max, Ti , Other Ti 7X (c+n) min 5. AISI 304L ss C max, Cr , Mn 2.00 max, Ni (UNS S30403) , P max, S max, Si 1.00 max 6. AISI 321 SS C 0.08 max, Cr , Mn 2.00 max, Ni (UNS S32100) , P max, S max, Si 1.00 max, Ti 5X C min ' 10. AISI 316L ss (UNS ) AISI 317L ss (UNS S31703) Nitronic 33 ss (UNS S24000) JS 700 ss (UNS N08700) C max, Cr , Mn 2.00 max, Mo , Ni , P max, S max, Si 1.00 max C max, Cr , Mn 2.00 max, Mo , Ni , P max, S max, Si 1.00 max C 0.08 max, Cr , Mn , N , Ni , P max, S max, Si 1.00 max C.04 max, Ni , Cr , Mo , Nb 8X C min-.04 max, Si 1.0 max, Mn 2.0 max, P.04 max, S ;03 max, C$.5 max 11. Ferralium 255 ss C.04 max, Cr , Mo , Ni , (UNS ) Si 1.0 max, Mn 1.5 max, N.lo-. 25, Cu Incoloy 825 A1 0.2 max, C 0.05 max, Cr , Cu , (UNS N08825) Fe bal, Mn 1.0 max, Mo , Ni , S 0.03 max, Si 0.5 max, Ti Inconel 625 A max, C 0.10 max, Nb , Cr (UNS N06625) , Fe 5.0 max, Mn 0.50 max, Mo , Ni bal, P max, S max, Si 0.50 max, Ti 0.40 max 14. Ti Grade 2 C 0.10 max, H max, Fe 0.30 max, N 0.03 max, (UNS R50400) max, Ti Rem
7 5 15. Ti Grade 12 N.03 max, C.08 max, H.015 max, Fe.3 max, 0.25 max, Mo.2-.4, Ni.6-.9, Ti Rem 16. Zr 702 (UNS R60702) C 0.05 max, H max, Hf 4.5 max, N max, Other Zr + Hf 99.2 min, Fe + Cr 0.2 max 17. Cupronickel 70/30 Cu 67.0 min, Ni , +... (UNS ( ) steel. The engineering properties of 304L stainless steel rank very well with the exception of susceptibility to localized corrosion and to stress corrosion cracking. If intergranular stress corrosion cracking is excessive for 304L stainless steel in the Topopah Spring environment, other stabilized austenitic stainless steels, such as 321 stainless steel, or nickel-base alloys, such as Incoloy 825, are appropriate choices. If transgranular stress corrosion cracking is a problem for the austenitic stainless steels, an alloy with greater than 20% nickel content [4,5], such as Incoloy 825, is appropriate. If pitting and/or crevice corrosion attack is excessive in 304L stainless steel, then an alloy with increased molybdenum, e.g., AISI 316L and AISI 317L stainless steels, or Incoloy 825, will increase the resistance to these forms of corrosion. All of the 300 series stainless steels may be specified with the extra-low carbon (-02 max) modification to avoid sensitization in the high-temperature glass pouring process, and in the final top-cap weld on canisters and overpacks. 3. Copper, Titanium, and Zirconium-base alloys The titanium alloys are expected to be very resistant to conditions that may occur in a strong field of,gamma radiation. These alloys are also very resistant to localized forms of corrosion, but lose most of their mechanical strength at 8OOOC. When compared to the other metals, cupronickel 70/30 has competitive strength and weldability properties, but is vulnerable to corrosion by nitric acid and other oxidizing species in a radiolyzed air-water environment. Zirconium alloys have proven performance in aqueous, radiolyzed environments, but exhibit low mechanical strengths at 800 C as well as marginal fracture toughness values at -18OC, and are the most costly of the candidate metals considered. 1. Corrosion Data There is abundant evidence in the literature 161 ~. that when moist air is irradiated with ionizing radiation, nitric acid will form. In radiation corrosion experiments with moist air [7-lo], it has generally been found that metals known to be vulnerable to corrosion by nitric acid are also corroded in irradiated, moist air. For conditions in the tuff repository, the relative increases in corrosion rates would probably be significant for copper-based alloys. Makepeace [lo] reported a 6-month irradiation experiment which indicated that certain austenitic stainless steels and nickel-based alloys had very low corrosion rates in moist air irradiated with a gamma-ray flux of 5 to 6 megarads per hour at ambient temperature. Under the same conditions, copper samples showed higher corrosion rates. Although this experiment was carried out at a higher dose rate, a lower temperature, and for much shorter times than are of interest for the tuff repository, the results are indicative of the type of corrosion behavior to be expected under irradiation conditions. Presently no long-term underground corrosion data exist for our candidate metals in an environment exactly like that at Yucca
8 6 Mountain However, underground corrosion data for a few of the candidate metals were found for Chino silt loam for a 14-year test Table I11 lists the significant attributes of both environments and presents available data. The data indicate the following for the Chino silt loam environment: A Mo-containing austenitic stainless steel (i.e., type 316) performed better than an ordinary Ni-Cr austenitic stainless steel (i.e., type 304). Ferritic stainless steels (i.e., types 430 and 410) did not perform as well as 304 stainless steel. Performance was determined by general corrosion and pitting corrosion rates on coupons of these alloys buried in soil. Relationships between the corrosivity of soils and factors such as soil resistivity, ph, aeration, and the corrosion products formed, have been suggested in the literature [11,121. Although major differences are shown between the "Chino silt loam" environment and the Topopah Spring tuff of Yucca Mountain environment, there are also some similarities, and use of these data represent estimates for long-term underground conditlions until site-sp-ecific data for the repository environment become available. 2. Material and Fabrication Costs Rolled and welded pipe manufacturing pr.ocesses are representative of the kind of fabrication involved in manufacturing canisters and overpacks. Diameters of 0.3 m to 0.91 m represent the upper limit of canisters and overpack diameters that we contemplate in our designs, SO TABLE 111. Underground environments. Topopah Spring Chino silt loam 1113 tuff 121 (14-yr data) - Chemical concen- Si , Na-51.0, K-4.9, Na+K-76 5, Ca-124, trations of water extract (ppm) Ba-0.003, Ca-14.0, Mg-2.1, Fe-0.04, A1-0.03, F-2.2, Mg-22, HC03-13, C1-60.5, SO4-169 C1-7.5, N03-5.6, Li-0.05,' Sr-0.05, SO4-22.0, po4-o.12, ~c0~ Water 8 mm/yr (net) 386 m/yr (average rainfall furnished by the. Resistivity PH Redox Air-pore space % moisture Atmosphere Temperature Radiation field Areal thermal loading Corrosion products Pitting corrosion data AISI 304 s. stl. AISI 316 s. stl. AISI 430 s. stl. AISI 410 s. stl. Internal drainage high 'L neutral oxidizing 17% 14% air-water/film-steam C gamma 1.1 x lo5 rem/hr max 50 kw/acre scale TBD (to be determined) TBD TBD TBD TBD U.S. low 'L neutral oxidizing 16% 26% air-water/film 1 O C- 28OC background solar scale Weather Bureau) 1.1 mpy (28 vm/yr) 4 x 10-5 mpy (10-3 pm/yr) 4.4 mpy (112 pm/yr) 4.4 mpy (112 pm/yr) good
9 7 we used the cost of 0.91 m (36 in.) diameter by 12.7 mm (1/2 in.) wall welded pipe as a measure. These costs were obtained by.telephone contact with commercial fabricators. The costs of alternative fabrication processes such as extrusion and centrifugal casting were also considered, but were rejected due to high cost or failure to meet our minimum design requirements. 3. Mechanical Properties Mechanical -properties - of interest include fracture toughness at 255 K (-18OC), elongation, nil-ductility temperature, tensile strength, and yield strength at 1073 K (8OOOC). Fracture toughness is dictated by the requirement that the waste package survive a drop test from a height of two times the package length without leaking. During transportation and at Yucca Mountain, minimum handling temperatures are roughly 255 R (-18OC). The ductility (elongation) is also important to the drop test requirement. The fracture toughness of certain alloys exhibits significant variations with changes in temperature. The ultimate tensile strength is-a measure of the stress which will lead to fracture of the material. The margin between the yield strength and the ultimate strength is a measure of the degree to which stretching and bending rather than fracture takes place after the yield strength is exceeded. Actual designs will load the material to a stress below the yield strength including a factor of safety. The yield strength at 1073 K (800OC) is related to the requirement of surviving a 1073 K (8OO0C), 30-min fire test without leaking. 4. Weldability The waste package containment barrier will have-several welded joints. The final weld of the top-cap to the main overpack and canister bodies will be done remotely. Possible welding problems were identified by yes (1) or no (0) binary evaluation of the following characteristics: preheat requirements, special interpass temperature, postheat requirements, special welding atmosphere, low weld toughness, nonstandard welding process, nonstandard nondestructive evaluation process, special cleanliness during fit-up, and not economical relative to 304 stainless steel. The overall weldability also includes all dimensional and mechanical property requirements of the weld and heat-affected zone. RESULTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS Analysis of the data resulted in selection of five metals out of the seventeen candidates. Table IV scores and ranks the candidates. The following summarizes the metals chosen as top-ranked in satisfying all of the design requirements for canisters and overpacks. 1. AISI 304L Stainless Steel - a low carbon, general-purpose austenitic stainless steel. We will further specify a premium grade with a carbon content less than O.O2%.C if experimental results and analysis indicate that chromium carbide precipitation (sensitization) will occur during welding and glass pouring. This is designated the reference metal. 2. AISI 321 Stainless Steel - a general-purpose, austenitic stainless steel with a titanium addition for stabilization of the carbon, thus preventing the formation of chromium-carbides (sensitization) during welding and glass pouring, as well as over long periods of time, at low tempera tures ( O C) (a1 ter na t ive. 3. AISI 316L Stainless Steel - a low carbon, austenitic stainless steel with the addition of 2-3% molybdenum for more resistance to pitting corrosion than type 304L. We will further specify a premium grade with a
10 8 TABLE IV. Ranking summary for candidate metals. Material designation Corrosion Mechanical Weldor composition resistance properties ability Cost Score Rankb AISI 1020 steel Oa A537 steel st. steel Cr - 1 Mo steel 1 ' L st. steel 1 2 ~ st. steel L st. steel L st. steel Nitronic JS Ferralium Incoloy Inconel Ti Code Ti Code Zr Cu - Ni 70/ ao = some disadvantages; 1 = suitable; 2 = superior. bl = highest; 3 = lowest. carbon content less than 0.02% C if experimental results and analysis indicate that chromium carbide precipitation (sensitization) will occur during welding and glass pouring (alternative). 4. Incoloy a nickel-iron-chromium-molybdenum-copper austenitic alloy designed for extremely corrosive environments. This alloy is stabilized with titanium to resist intergranular corrosion and intergranular stress corrosion cracking. The nickel content makes it very resistant to transgranular stress corrosion cracking. The molybdenum and copper give this alloy resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. The high chromium content gives it resistance to various types of oxidizing environments (alternative). 5. AISI 1020 Steel - a low carbon, general-purpose steel for the reference metal, for horizontal borehole liners, appropriate for a 50-year retrieval period. CONCLUSION Our analysis indicates five metals that best satisfy the requirements for disposal of high-level waste at the NNWSI proposed repository at Yucca Mountain. Testing is in progress on these metals for further development of the waste package design for the unsaturated zone. The reference canister and overpack metal is AISI 304L stainless steel, and the primary alternative metals are AISI 321, AISI 316L, and Incoloy 825. For borehole liners, 1020 carbon steel has been chosen as the reference metal.
11 9 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors wish to express appreciation to Dr. Richard Van Konynenburg of LLNL for his thorough review of #is paper. REFERENCES 1. Federal Register, Vol. 48 No. 120, 10 CFR Part 60, "Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Wastes in Geologic Repositories Technical Criteria," Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Final Rule, June 21, J. R. Schornhorst et al., Conceptual Waste Package Designs for Disposal of Nuclear Waste in Tuff, Westinghouse AESD, Pittsburgh, PA, ONWI-439, April 1983, Battelle, Office of Nuclear Waste Isolation, Columbus, OH. 3. W. C. O'Neal, A. J. Rothman, D. W. Gregg, J. N. Hockman, M. A. Revelli, E. W. Russell, and 5. R. Schornhorst, Design of a Nuclear Waste Package for Emplacement in Tuff, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, UCRL-88192, February, F. L. LaQue and H.R. Copson, Corrosion Resistance of Metals and Alloys (Reinhold Publishing Corp., New York, 1963). 5. Case Histories in Failure Analysis, P. M. Unterweiser, Ed. (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1979). 6. S. C. Lind, C. J. Hochanadel, and J. A. Ghormley, Radiation Chemistry of Gases (Reinhold Publishing Corp., New York, 19611, Chapter W. Primak and L. H. Fuchs, "Transportation of Matter and Radioactivity by Ionized Air Corrosion," Physics Today 2, 15 (1954). 8. W. Primak and L. H. Fuchs, "Nitrogen Fixation in a Nuclear Reactor," Nucleonics 13, No. 3, 38 (1955). 9. A. V. Byalobzheskii, Radiation Corrosion, Izdatel' stvo "Nauka," Moskva 1967 (translated by Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem, 1970). 10. C. E. Makepeace, "Design and Analysis of Corrosion Experiments for Testing Materials Exposed to Gamma Radiation," J. of Testing and Evaluation 2, 202 (1974). 11. Melvin Romanoff, Underground Corrosion, National Bureau of standards Circular 579, Washington, D.C. (April 1957).
12 K. Nuttall and V.F. Urbanic, An Assessment of Materials for Nuclear Fuel Immobilization Containers, Whiteshell Nuclear Research Establishment, Pinawa, Manitoba, AECL-6440 (September 1981). 13. M. D. Merz, State-of-the-Art Report on Corrosion Data Pertaining to Metallic Barriers for Nuclear Waste Repositories, Pacific Northwest Laboratory, Richland, WA, PNL-4474 (October 1982) ;. :',. -...I '
13 DISCLAIMER This document was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the United States Govemment. Neither the United States Government nor the University of California nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefuliess of any information, apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference herein to any specific commercial products, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the United States Government or the University of California. The-views and opinions-of authors expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the United States Government thereof, and shall not be used for advertising or product endorsement purposes.
A.J. Rothman. M.A. Revelli
 I P DESIGN OF A NUCLEAR-WASTE PACKAGE FOR EMPLACEMENT IN TUFF W.C. O'Neal A.J. Rothman. D.W. Gregg J.N. Hockman M.A. Revelli E.W. Russell J.R. Schornhorst ANS/ASME Waste Management '83 Tucson, Arizona
I P DESIGN OF A NUCLEAR-WASTE PACKAGE FOR EMPLACEMENT IN TUFF W.C. O'Neal A.J. Rothman. D.W. Gregg J.N. Hockman M.A. Revelli E.W. Russell J.R. Schornhorst ANS/ASME Waste Management '83 Tucson, Arizona
Containment Barrier Metals for High-Level Waste Packages in a Tuff Repository
 DISCLAIMER UCRL-53449 Distribution Category UC-70 This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the United States Government. Neither the United States Government nor any agency
DISCLAIMER UCRL-53449 Distribution Category UC-70 This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the United States Government. Neither the United States Government nor any agency
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Stainless Steel Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes
 Cast materials Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes Our customer-focused R&D and continuous research on new material options enable us to develop equipment with a strong
Cast materials Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes Our customer-focused R&D and continuous research on new material options enable us to develop equipment with a strong
SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3RE60 is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: High resistance to stress corrosion cracking (SCC)
SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3RE60 is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: High resistance to stress corrosion cracking (SCC)
Effect of Areal Power Density and Relative Humidity on Corrosion Resistant Container Performance
 UCRL-JC-119119 PREPRNT Effect of Areal Power Density and Relative Humidity on Corrosion Resistant Container Performance JamesD. Gansemer Alan Lamont This paper was pre ared for submittal to the K American
UCRL-JC-119119 PREPRNT Effect of Areal Power Density and Relative Humidity on Corrosion Resistant Container Performance JamesD. Gansemer Alan Lamont This paper was pre ared for submittal to the K American
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Incoloy Alloy 800H/800HT (UNS N08810/088011)
 Incoloy 800H/800HT (UNS N08810/088011) Incoloy 800H/HT is an outstanding corrosion resistant alloy that is recommended for use in the high temperature industrial conditions. It has higher strength than
Incoloy 800H/800HT (UNS N08810/088011) Incoloy 800H/HT is an outstanding corrosion resistant alloy that is recommended for use in the high temperature industrial conditions. It has higher strength than
Nickel & Stainless Steel. Product Range
 Nickel & Stainless Steel Product Range General Index ITEM BRAND SIZE Inconel 600 Inconel 601 Inconel alloy Inconel 625 Inconel 718 Monel 400 Monel alloy Monel K500 Nickel 52 Nickel alloy Nickel 200 Nickel
Nickel & Stainless Steel Product Range General Index ITEM BRAND SIZE Inconel 600 Inconel 601 Inconel alloy Inconel 625 Inconel 718 Monel 400 Monel alloy Monel K500 Nickel 52 Nickel alloy Nickel 200 Nickel
ATI 2205 ATI Technical Data Sheet. Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES. (UNS S31803 and S32205)
 ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
441 STAINLESS STEEL. Good High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance. Applications Potential
 441 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Equiaxed Microstructure Good High-Temperature Strength Good High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance Applications Potential AK Steel 441 is used in
441 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Equiaxed Microstructure Good High-Temperature Strength Good High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance Applications Potential AK Steel 441 is used in
SANDVIK 3R12 FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3R12 FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R12 is an austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content used for medical and dental instruments.
SANDVIK 3R12 FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R12 is an austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content used for medical and dental instruments.
More Oxidation and Creep Resistance Upgrade for Type 409. Potential Substitute for 18 Cr-Cb & Type 439. Excellent Forming and Welding Characteristics
 11 Cr-Cb STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N More Oxidation and Creep Resistance Upgrade for Type 409 Potential Substitute for 18 Cr-Cb & Type 439 Excellent Forming and Welding Characteristics
11 Cr-Cb STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N More Oxidation and Creep Resistance Upgrade for Type 409 Potential Substitute for 18 Cr-Cb & Type 439 Excellent Forming and Welding Characteristics
Tensile Properties of Alloy 617 Bar Stock
 INL/EXT-13-29671 Tensile Properties of Alloy 617 Bar Stock J. K. Wright N. J. Lybeck R. N. Wright July 2013 The INL is a U.S. Department of Energy National Laboratory operated by Battelle Energy Alliance
INL/EXT-13-29671 Tensile Properties of Alloy 617 Bar Stock J. K. Wright N. J. Lybeck R. N. Wright July 2013 The INL is a U.S. Department of Energy National Laboratory operated by Battelle Energy Alliance
SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R65 is a molybdenum-alloyed austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content. STANDARDS ASTM: TP316L, TP316 UNS: S31603, S31600
SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R65 is a molybdenum-alloyed austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content. STANDARDS ASTM: TP316L, TP316 UNS: S31603, S31600
15 Cr-Cb ULTRA FORM STAINLESS STEEL
 15 Cr-Cb ULTRA FORM STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Good Elevated Temperature Strength Weldable Oxidation Resistance Resistant to Intergranular Corrosion Fine Uniform Formable Grain
15 Cr-Cb ULTRA FORM STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Good Elevated Temperature Strength Weldable Oxidation Resistance Resistant to Intergranular Corrosion Fine Uniform Formable Grain
PAGE 1/6 ZAPP PRECISION WIRE INCOLOY ALLOY 27-7MO (UNS S31277)
 ZAPP PRECISION WIRE INCOLOY ALLOY (UNS S31277) QUALITY SYSTEM CERTIFIED TO ISO 9001:2008 INCOLOY ALLOY (UNS S31277) WIRE FOR: _ Armoring applications on electromechanical cables _ Wirelines for down hole
ZAPP PRECISION WIRE INCOLOY ALLOY (UNS S31277) QUALITY SYSTEM CERTIFIED TO ISO 9001:2008 INCOLOY ALLOY (UNS S31277) WIRE FOR: _ Armoring applications on electromechanical cables _ Wirelines for down hole
SANDVIK 254 SMO TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 254 SMO TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 254 SMO is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel developed for use in seawater and other aggressive chloride-bearing media. The steel is characterized
SANDVIK 254 SMO TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 254 SMO is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel developed for use in seawater and other aggressive chloride-bearing media. The steel is characterized
Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steels Under Tuff Repository Environmental Conditions. R. Daniel McCright Haskell Weiss
 ^F-tMHS'7-^ C CvO UCRL--D0 875»E05 002247 Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steels Under Tuff Repository Environmental Conditions R. Daniel McCright Haskell Weiss Materials Research Society 1984 Annual Meeting
^F-tMHS'7-^ C CvO UCRL--D0 875»E05 002247 Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steels Under Tuff Repository Environmental Conditions R. Daniel McCright Haskell Weiss Materials Research Society 1984 Annual Meeting
North American Stainless
 North American Stainless Long Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet AISI 409Ni UNS S40976 INTRODUCTION 409Ni (409NiCb) is a low-chromium columbium-stabilized ferritic stainless steel with small additions
North American Stainless Long Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet AISI 409Ni UNS S40976 INTRODUCTION 409Ni (409NiCb) is a low-chromium columbium-stabilized ferritic stainless steel with small additions
SANDVIK SAF 2304 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK SAF 2304 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik SAF 2304 is a lean duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: Very good resistance to stress corrosion
SANDVIK SAF 2304 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik SAF 2304 is a lean duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: Very good resistance to stress corrosion
Hastelloy C-2000 (UNS N06200)
 Hastelloy C-2000 (UNS N06200) Hastelloy C-2000 is a versatile alloy that provides high resistance to variety of chemicals including sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and other strong acidic media. It offers
Hastelloy C-2000 (UNS N06200) Hastelloy C-2000 is a versatile alloy that provides high resistance to variety of chemicals including sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and other strong acidic media. It offers
CHROMESHIELD 22 STAINLESS STEEL
 CHROMESHIELD 22 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Appliances Food Service Equipment Architectural Welded Components Tubing Cookware Applications Potential CHROMESHIELD 22 Stainless Steel
CHROMESHIELD 22 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Appliances Food Service Equipment Architectural Welded Components Tubing Cookware Applications Potential CHROMESHIELD 22 Stainless Steel
Nickel Based Superalloy Hastelloy B-3 (UNS N10675)
 Nickel Based Superalloy Hastelloy B-3 (UNS N10675) Hastelloy B-3 is manufactured for providing excellent resistance to reducing acids at the different content %s and temperature limits. It shows better
Nickel Based Superalloy Hastelloy B-3 (UNS N10675) Hastelloy B-3 is manufactured for providing excellent resistance to reducing acids at the different content %s and temperature limits. It shows better
NITRONIC 19D LEAN DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL. Excellent Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance. Improved Welding Characteristics
 NITRONIC 19D LEAN DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Excellent Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance High Strength Improved Welding Characteristics Resists Sigma Phase Formation
NITRONIC 19D LEAN DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Excellent Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance High Strength Improved Welding Characteristics Resists Sigma Phase Formation
430 ULTRA FORM 430 STAINLESS STEEL
 43 ULTRA FORM 43 STAINLESS STEEL Appliances Food Equipment General Construction Interior Architectural Trim Restaurant Equipment AK STEEL 43 ULTRA FORM STAINLESS STEEL was developed as a more formable
43 ULTRA FORM 43 STAINLESS STEEL Appliances Food Equipment General Construction Interior Architectural Trim Restaurant Equipment AK STEEL 43 ULTRA FORM STAINLESS STEEL was developed as a more formable
RELIABLE PIPES & TUBES LTD.
 RELIABLE PIPES & TUBES LTD. OHSAS 18001:2007 CERTIFIED ISO 9001:2008 CERTIFIED ISO 14001:2004 CERTIFIED PED CERT NO 01 202 IND/Q-11-0033 GOVT. RECOGNIZED EXPORT HOUSE Manufacturer & Exporters of Monel,
RELIABLE PIPES & TUBES LTD. OHSAS 18001:2007 CERTIFIED ISO 9001:2008 CERTIFIED ISO 14001:2004 CERTIFIED PED CERT NO 01 202 IND/Q-11-0033 GOVT. RECOGNIZED EXPORT HOUSE Manufacturer & Exporters of Monel,
PRESSURFECT CNG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 PRESSURFECT CNG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Pressurfect CNG is a dual grade certified (ASTM 316/316L) austenitic chromium-nickel steel with minimum 2.5% molybdenum and a low carbon content used for
PRESSURFECT CNG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Pressurfect CNG is a dual grade certified (ASTM 316/316L) austenitic chromium-nickel steel with minimum 2.5% molybdenum and a low carbon content used for
Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets)
 Datasheet updated 2013 11 28 14:13:21 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets) Sandvik SAF 2205 is a duplex (austenitic ferritic) stainless steel characterized by: High resistance
Datasheet updated 2013 11 28 14:13:21 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets) Sandvik SAF 2205 is a duplex (austenitic ferritic) stainless steel characterized by: High resistance
Chemical characteristics The chemical composition is shown in Table 1. Outokumpu EN ASTM
 for Bar Applications has a unique combination of characteristics (good corrosion properties, high strength and good machinability), which together with its relative price stability, makes it the material
for Bar Applications has a unique combination of characteristics (good corrosion properties, high strength and good machinability), which together with its relative price stability, makes it the material
SEMASPEC Test Method for Metallurgical Analysis for Gas Distribution System Components
 SEMASPEC Test Method for Metallurgical Analysis for Gas Distribution System Components Technology Transfer 91060574B-STD and the logo are registered service marks of, Inc. 1996, Inc. SEMASPEC Test Method
SEMASPEC Test Method for Metallurgical Analysis for Gas Distribution System Components Technology Transfer 91060574B-STD and the logo are registered service marks of, Inc. 1996, Inc. SEMASPEC Test Method
Corrosion of Weldments
 Corrosion of Weldments Edited by J. R. Davis Davis & Associates ASM International Materials Park, OH 44073-0002 Copyright 2006 by ASM International All rights reserved No part of this book may be reproduced,
Corrosion of Weldments Edited by J. R. Davis Davis & Associates ASM International Materials Park, OH 44073-0002 Copyright 2006 by ASM International All rights reserved No part of this book may be reproduced,
2017 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting September 10 (Sun) ~ 14 (Thu), 2017 Ramada Plaza Jeju Jeju Island, Korea
 FRESH WATER QUENCHING OF ALLOYS OF NUCLEAR INTEREST INCLUDING FeCrAl FOR ACCIDENT TOLERANT FUEL CLADDING Michael Schuster 1, Cole Crawford 1, and Raul B. Rebak 1 1 GE Global Research: 1 Research Circle,
FRESH WATER QUENCHING OF ALLOYS OF NUCLEAR INTEREST INCLUDING FeCrAl FOR ACCIDENT TOLERANT FUEL CLADDING Michael Schuster 1, Cole Crawford 1, and Raul B. Rebak 1 1 GE Global Research: 1 Research Circle,
SANDVIK 3R60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3R60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R60 is an austenitic chromium-nickel steel with minimum 2.5% molybdenum and a low carbon content. Sandvik 3R60 is also available in a variant for
SANDVIK 3R60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R60 is an austenitic chromium-nickel steel with minimum 2.5% molybdenum and a low carbon content. Sandvik 3R60 is also available in a variant for
304/304L STAINLESS STEEL
 304/304L STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Architectural Moldings and Trim Textile Kitchen Equipment Paper Pharmaceutical and Chemical Industry Processing Equipment Applications Potential
304/304L STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Architectural Moldings and Trim Textile Kitchen Equipment Paper Pharmaceutical and Chemical Industry Processing Equipment Applications Potential
North American Stainless
 North American Stainless Long Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet AISI 430 UNS S43000 EN 1.4016 INTRODUCTION 430 SS is a plain chromium ferritic stainless steel. With 17% chromium, the steel has good
North American Stainless Long Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet AISI 430 UNS S43000 EN 1.4016 INTRODUCTION 430 SS is a plain chromium ferritic stainless steel. With 17% chromium, the steel has good
Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316
 Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316 Manish Kumar Verma Mechanical, Columbia Institute of Engineering & Technology, Raipur (India) ABSTRACT Austenitic Stainless steels
Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316 Manish Kumar Verma Mechanical, Columbia Institute of Engineering & Technology, Raipur (India) ABSTRACT Austenitic Stainless steels
Chapter 7. Stainless Steels. /MS371/ Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys
 Chapter 7 Stainless Steels Stainless steels at least % Cr in iron is required (max 30% Cr) Cr: to make iron surface by forming a surface oxide film protecting the underlying metal from corrosion Ni: to
Chapter 7 Stainless Steels Stainless steels at least % Cr in iron is required (max 30% Cr) Cr: to make iron surface by forming a surface oxide film protecting the underlying metal from corrosion Ni: to
Hastelloy G-30 (UNS N06030) Chemical Composition
 Hastelloy G-30 (UNS N06030) Hastelloy G-30 is commonly used for providing excellent resistance to chemical conditions. It offers resistance to nitric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric
Hastelloy G-30 (UNS N06030) Hastelloy G-30 is commonly used for providing excellent resistance to chemical conditions. It offers resistance to nitric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric
409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL
 409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Superior Corrosion Resistance to Mild and Low-Alloy Steels Cost Effective Alternative to Austenitic Stainless AK Steel 409 Ni Stainless Steel
409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Superior Corrosion Resistance to Mild and Low-Alloy Steels Cost Effective Alternative to Austenitic Stainless AK Steel 409 Ni Stainless Steel
AEROSPACE MATERIAL SPECIFICATION
 AEROSPACE MATERIAL SPECIFICATION AMS 5659L Issued SEP 1965 Revised JAN 2004 Superseding AMS 5659K Steel, Corrosion-Resistant, Bars, Wire, Forgings, Rings, and Extrusions 15Cr - 4.5Ni - 0.30CB (Nb) - 3.5Cu
AEROSPACE MATERIAL SPECIFICATION AMS 5659L Issued SEP 1965 Revised JAN 2004 Superseding AMS 5659K Steel, Corrosion-Resistant, Bars, Wire, Forgings, Rings, and Extrusions 15Cr - 4.5Ni - 0.30CB (Nb) - 3.5Cu
STANDARD FERRITIC STAINLESS STEELS
 T e c h n i c a l B r o c h u r e STANDARD FERRITIC STAINLESS STEELS Unity AISI UNS EN U-40910 409 S40910 1.4512 U-430 430 S43000 1.4016 U-430DDQ 430 S43000 1.4016 U-439 439 S43035 1.4510 - S43940 U-1.4509
T e c h n i c a l B r o c h u r e STANDARD FERRITIC STAINLESS STEELS Unity AISI UNS EN U-40910 409 S40910 1.4512 U-430 430 S43000 1.4016 U-430DDQ 430 S43000 1.4016 U-439 439 S43035 1.4510 - S43940 U-1.4509
Stainless Steel 310/310S (UNS S31000/ UNS S31008)
 Stainless Steel 310/310S (UNS S31000/ UNS S31008) Austenitic Stainless Steel 310/310S offers excellent resistance to oxidation up to 2000oF. It is a low grade steel that prevents embrittlement and sensitization.
Stainless Steel 310/310S (UNS S31000/ UNS S31008) Austenitic Stainless Steel 310/310S offers excellent resistance to oxidation up to 2000oF. It is a low grade steel that prevents embrittlement and sensitization.
Los Alamos. Development of Materials Related to the 60T and 100T Magnets. Ke Han, CMS John David Embury, CMS. NHMFL Tallahassee Annual Report
 Title: Author(s): Submitted to: Development of Materials Related to the 60T and 100T Magnets Ke Han, CMS John David Embury, CMS NHMFL Tallahassee Annual Report Los Alamos NATIONAL LABORATORY Los Alamos
Title: Author(s): Submitted to: Development of Materials Related to the 60T and 100T Magnets Ke Han, CMS John David Embury, CMS NHMFL Tallahassee Annual Report Los Alamos NATIONAL LABORATORY Los Alamos
STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS
 STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS Alloys: 304 304L 310 316 316L 316LN 316Ti 316LVM 6Mo 21-6-9 22-13-5 904L Alloys 304 / 304L Alloys 304 / 304L (UNS S30400 / S30403) Alloys 304 (S30400) and 304L (S30403) stainless
STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS Alloys: 304 304L 310 316 316L 316LN 316Ti 316LVM 6Mo 21-6-9 22-13-5 904L Alloys 304 / 304L Alloys 304 / 304L (UNS S30400 / S30403) Alloys 304 (S30400) and 304L (S30403) stainless
1. Scope :- 2. Referenced Documents :-
 Standard Specification for Forged or Rolled N06030, N06022, N06035, N06200, N06059, N06686, N08020, N08024, N 08026, N08367, N10276, N10665, N10675, N 10629, N08031, N06045, N06025, and R20033 Alloy Pipe
Standard Specification for Forged or Rolled N06030, N06022, N06035, N06200, N06059, N06686, N08020, N08024, N 08026, N08367, N10276, N10665, N10675, N 10629, N08031, N06045, N06025, and R20033 Alloy Pipe
ATI ATI 2205 Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel. Technical Data Sheet
 Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogenenhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly improve
Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogenenhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly improve
Subway Cars. Applications Potential
 301 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Aircraft Structural Parts Roof Drainage Cooking Utensils Automotive Trim Subway Cars Applications Potential Type 301 is an austenitic chromium-nickel
301 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Aircraft Structural Parts Roof Drainage Cooking Utensils Automotive Trim Subway Cars Applications Potential Type 301 is an austenitic chromium-nickel
Applications Potential
 P R O D U C T D A T A B U L L E T I N STAINLESS 301STEEL UNS S30100 High Strength and Good Ductility When Cold Worked Excellent Corrosion Resistance Readily Welded Readily Formed and Drawn Economical Oxidation
P R O D U C T D A T A B U L L E T I N STAINLESS 301STEEL UNS S30100 High Strength and Good Ductility When Cold Worked Excellent Corrosion Resistance Readily Welded Readily Formed and Drawn Economical Oxidation
NITRONIC 19D LEAN DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL
 Chemical Processing Desalination/Water Treatment Oil Field Undersea Tubing AK STEEL NITRONIC 19D STAINLESS STEEL is a molybdenum-free, low nickel lean duplex stainless steel. The combination of strength,
Chemical Processing Desalination/Water Treatment Oil Field Undersea Tubing AK STEEL NITRONIC 19D STAINLESS STEEL is a molybdenum-free, low nickel lean duplex stainless steel. The combination of strength,
Moda 430/4016 EN , ASTM TYPE 430 / UNS S43000
 Moda 430/4016 EN 1.4016, ASTM TYPE 430 / UNS S43000 General characteristics Moda 430/4016 is a classic 16 chromium ferritic stainless steel. Good corrosion resistance in mildly corrosive environments combined
Moda 430/4016 EN 1.4016, ASTM TYPE 430 / UNS S43000 General characteristics Moda 430/4016 is a classic 16 chromium ferritic stainless steel. Good corrosion resistance in mildly corrosive environments combined
409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL
 409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL Bus Frames Dryer Component Intermodal Containers Rail Cars Trailers AK STEEL 409 Ni is an ideal material for applications requiring weldability and toughness superior to standard
409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL Bus Frames Dryer Component Intermodal Containers Rail Cars Trailers AK STEEL 409 Ni is an ideal material for applications requiring weldability and toughness superior to standard
41003 STAINLESS STEEL
 41003 STAINLESS STEEL D ATA S H E E T Formable and Weldable in Heavy Sections Refined Grain Structure Leads to Good Toughness Ferritic as Annealed Low Cost AK Steel 41003 is an economical ferritic stainless
41003 STAINLESS STEEL D ATA S H E E T Formable and Weldable in Heavy Sections Refined Grain Structure Leads to Good Toughness Ferritic as Annealed Low Cost AK Steel 41003 is an economical ferritic stainless
301 STAINLESS STEEL. Aircraft Structural Parts. Automotive Trim. Cooking Utensils. Roof Drainage. Subway Cars
 301 STAINLESS STEEL Aircraft Structural Parts Automotive Trim Cooking Utensils Roof Drainage Subway Cars TYPE 301 is an austenitic, chromium-nickel stainless steel. This alloy is non-magnetic in the annealed
301 STAINLESS STEEL Aircraft Structural Parts Automotive Trim Cooking Utensils Roof Drainage Subway Cars TYPE 301 is an austenitic, chromium-nickel stainless steel. This alloy is non-magnetic in the annealed
Sodium Carbonate Salt Transport System
 . t UCRL-JC-121685 PREPRINT Sodium Carbonate Salt Transport System W. Brummond This paper was prepared for submittal to the California Polytechnic State University Senior Engineering Class, ME428 Industrial
. t UCRL-JC-121685 PREPRINT Sodium Carbonate Salt Transport System W. Brummond This paper was prepared for submittal to the California Polytechnic State University Senior Engineering Class, ME428 Industrial
ATI 825 ATI 825. Technical Data Sheet. Nickel-base Alloy INTRODUCTION PRODUCT FORMS SPECIFICATIONS & CERTIFICATES (UNS N08825)
 ATI 825 Nickel-base (UNS N08825) INTRODUCTION ATI 825 alloy (UNS N08825) is an austenitic nickel-iron-chromium-molybdenum-copper alloy containing high levels of chromium, nickel, molybdenum and copper
ATI 825 Nickel-base (UNS N08825) INTRODUCTION ATI 825 alloy (UNS N08825) is an austenitic nickel-iron-chromium-molybdenum-copper alloy containing high levels of chromium, nickel, molybdenum and copper
316/316L STAINLESS STEEL
 316/316L STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Valve and Pump Trim Digesters Chemical Equipment Evaporators Pharmaceutical and Photographic Equipment Applications Potential Type 316 Stainless
316/316L STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Valve and Pump Trim Digesters Chemical Equipment Evaporators Pharmaceutical and Photographic Equipment Applications Potential Type 316 Stainless
304/304L STAINLESS STEEL
 304/304L STAINLESS STEEL Architecural Moldings Kitchen Equipment Industrial Processing Equipment High strength, excellent corrosion resistance and excellent formability make Types 304 and 304L useful for
304/304L STAINLESS STEEL Architecural Moldings Kitchen Equipment Industrial Processing Equipment High strength, excellent corrosion resistance and excellent formability make Types 304 and 304L useful for
Nickel Based Superalloy Incoloy 800 (UNS N08800)
 Nickel Based Superalloy Incoloy 800 (UNS N08800) Nickel-Iron-Chromium alloy Incoloy 800 has fine strength and suitable resistance to oxidation and carburization at high temperatures. It offers elevated
Nickel Based Superalloy Incoloy 800 (UNS N08800) Nickel-Iron-Chromium alloy Incoloy 800 has fine strength and suitable resistance to oxidation and carburization at high temperatures. It offers elevated
Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service
 SA-268/SA-268M ASME BPVC.II.A-2015 Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers a number of
SA-268/SA-268M ASME BPVC.II.A-2015 Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers a number of
WHAT IS THE ACTUAL COST OF YOUR COMMERCIAL WATER HEATER? LOOKING BEYOND EFFICIENCY INCREASING ROI THROUGH WATER HEATER MATERIAL SELECTION
 Engineered Water Heating Solutions WHAT IS THE ACTUAL COST OF YOUR COMMERCIAL WATER HEATER? LOOKING BEYOND EFFICIENCY INCREASING ROI THROUGH WATER HEATER MATERIAL SELECTION Water Heater Efficiency Water
Engineered Water Heating Solutions WHAT IS THE ACTUAL COST OF YOUR COMMERCIAL WATER HEATER? LOOKING BEYOND EFFICIENCY INCREASING ROI THROUGH WATER HEATER MATERIAL SELECTION Water Heater Efficiency Water
Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers
 Materials Selection for Condensing Economizers Gary M. Carinci, Ph.D. Outokumpu Stainless Outokumpu Stainless Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers Temperature ph control Sulfur
Materials Selection for Condensing Economizers Gary M. Carinci, Ph.D. Outokumpu Stainless Outokumpu Stainless Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers Temperature ph control Sulfur
family of stainless steels can be divided into five (5) categories:
 Welcome to the fifth issue of Tech Talk. This newsletter covers a range of topics on various welding products, applications, metallurgy, techniques, and economics. Previous issues are archived at www.unibraze.com.
Welcome to the fifth issue of Tech Talk. This newsletter covers a range of topics on various welding products, applications, metallurgy, techniques, and economics. Previous issues are archived at www.unibraze.com.
Calculation of Heater-tube Thickness in Petroleum Refineries API STANDARD 530 SEVENTH EDITION, APRIL 2015
 Calculation of Heater-tube Thickness in Petroleum Refineries API STANDARD 530 SEVENTH EDITION, APRIL 2015 Special Notes API publications necessarily address problems of a general nature. With respect to
Calculation of Heater-tube Thickness in Petroleum Refineries API STANDARD 530 SEVENTH EDITION, APRIL 2015 Special Notes API publications necessarily address problems of a general nature. With respect to
SANICRO 30 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANICRO 30 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sanicro 30 is a low-carbon version of Alloy 800 austenitic nickel-iron-chromium alloy. The grade is used for steam generator tubing in nuclear stations (PWR)
SANICRO 30 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sanicro 30 is a low-carbon version of Alloy 800 austenitic nickel-iron-chromium alloy. The grade is used for steam generator tubing in nuclear stations (PWR)
SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX STRIP STEEL
 SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX STRIP STEEL DATASHEET Sandvik Springflex is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless spring steel with very good spring properties and excellent corrosion resistance. Sandvik Springflex
SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX STRIP STEEL DATASHEET Sandvik Springflex is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless spring steel with very good spring properties and excellent corrosion resistance. Sandvik Springflex
Relationship Between Design and Materials for Thermal Power Plants. S. C. Chetal
 Relationship Between Design and Materials for Thermal Power Plants S. C. Chetal Contents *Introduction to design codes *Operational life vs design basis life *Material selection basics *Materials for boiler
Relationship Between Design and Materials for Thermal Power Plants S. C. Chetal Contents *Introduction to design codes *Operational life vs design basis life *Material selection basics *Materials for boiler
NICKEL CHROMIUM ALLOYS
 NICKEL CHROMIUM AND NICKEL THORIA ALLOYS 1 NICKEL CHROMIUM ALLOYS Two distinct groups of nickel chromium alloys for high temperature uses are as follow. The first group, which includes cast alloys containing
NICKEL CHROMIUM AND NICKEL THORIA ALLOYS 1 NICKEL CHROMIUM ALLOYS Two distinct groups of nickel chromium alloys for high temperature uses are as follow. The first group, which includes cast alloys containing
AL 29-4C AL 29-4C. Technical Data Sheet. Stainless Steel: Superferritic INTRODUCTION (UNS S44735)
 AL 29-4C Stainless Steel: Superferritic (UNS S44735) INTRODUCTION AL 29-4C alloy, is a superferritic stainless steel developed by ATI in the early 1980s specifically for power plant surface condenser tubing.
AL 29-4C Stainless Steel: Superferritic (UNS S44735) INTRODUCTION AL 29-4C alloy, is a superferritic stainless steel developed by ATI in the early 1980s specifically for power plant surface condenser tubing.
Chemical Processing Equipment. Distillation Towers. Oil Refineries
 410S STAINLESS STEEL Chemical Processing Equipment Distillation Towers Oil Refineries Trays TYPE 410S is a low-carbon, non-hardening ferritic stainless steel. The ability to cool from elevated temperatures
410S STAINLESS STEEL Chemical Processing Equipment Distillation Towers Oil Refineries Trays TYPE 410S is a low-carbon, non-hardening ferritic stainless steel. The ability to cool from elevated temperatures
Supra 316plus EN , ASTM UNS S31655
 Supra 316plus EN 1.4420, ASTM UNS S31655 General characteristics With its high chromium content, Supra 316 plus content delivers high strength, good formability, and excellent weldability, making it ideal
Supra 316plus EN 1.4420, ASTM UNS S31655 General characteristics With its high chromium content, Supra 316 plus content delivers high strength, good formability, and excellent weldability, making it ideal
ATI 332Mo. ATI 332Mo. Technical Data Sheet. Stainless Steel: Austenitic GENERAL PROPERTIES COMPOSITION PHYSICAL PROPERTIES (UNS S35125)
 ATI 332Mo Stainless Steel: Austenitic (UNS S35125) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI s ATI 332Mo alloy is an austenitic stainless steel intended primarily as an economical material for automotive flexible connectors.
ATI 332Mo Stainless Steel: Austenitic (UNS S35125) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI s ATI 332Mo alloy is an austenitic stainless steel intended primarily as an economical material for automotive flexible connectors.
ATI 321 /ATI 347 /ATI 348
 ATI 321 /ATI 347 /ATI 348 Stainless Steel: Austenitic (UNS S32100, S34700, S34800) GENERAL INFORMATION ATI 321 (UNS S32100), ATI 347 (UNS S34700), and ATI 348 (UNS S34800) alloys are stabilized stainless
ATI 321 /ATI 347 /ATI 348 Stainless Steel: Austenitic (UNS S32100, S34700, S34800) GENERAL INFORMATION ATI 321 (UNS S32100), ATI 347 (UNS S34700), and ATI 348 (UNS S34800) alloys are stabilized stainless
Diffusion Coatings for Corrosion Resistant Components in Coal Gasification Systems
 Technical Progress Report January 2005 Diffusion Coatings for Corrosion Resistant Components in Coal Gasification Systems Quarterly Technical Progress Report 4 Covering the period April 1, 2004 through
Technical Progress Report January 2005 Diffusion Coatings for Corrosion Resistant Components in Coal Gasification Systems Quarterly Technical Progress Report 4 Covering the period April 1, 2004 through
STAINLESS STEELS. Experience has shown that, at least for stainless. for Corrosion Resistance
 STAINLESS STEELS for Corrosion Resistance Newly developed stainless steels provide increased corrosion resistance, improved mechanical properties, easier forming and fabrication, and/or improved economy.
STAINLESS STEELS for Corrosion Resistance Newly developed stainless steels provide increased corrosion resistance, improved mechanical properties, easier forming and fabrication, and/or improved economy.
Recent Trends in Establishing Seismic Design Rules and Standards to Meet Facility Performance Goals. Thomas A. Nelson
 UCRL-JC-125800 Preprint Recent Trends in Establishing Seismic Design Rules and Standards to Meet Facility Performance Goals Thomas A. Nelson This paper was prepared for submittal to American Society of
UCRL-JC-125800 Preprint Recent Trends in Establishing Seismic Design Rules and Standards to Meet Facility Performance Goals Thomas A. Nelson This paper was prepared for submittal to American Society of
Born from fire, made to endure NICKEL ALLOYS
 Born from fire, made to endure NICKEL ALLOYS Acroni is the largest slovenian steel manufacturer, which in order to produce steel recycles scrap in an electric arc furnace, casts it on continuous caster
Born from fire, made to endure NICKEL ALLOYS Acroni is the largest slovenian steel manufacturer, which in order to produce steel recycles scrap in an electric arc furnace, casts it on continuous caster
May 21-24,1995 A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF GRAIN SIZE ON THE BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF SILICON CARBIDE. Carl F. Cline
 w-9.5053 7-5 3 UCRL-JC-118421 PREPRINT A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF GRAIN SIZE ON THE BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF SILICON CARBIDE. Carl F. Cline This paper was prepared forthe 15th International Symposium on
w-9.5053 7-5 3 UCRL-JC-118421 PREPRINT A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF GRAIN SIZE ON THE BALLISTIC PERFORMANCE OF SILICON CARBIDE. Carl F. Cline This paper was prepared forthe 15th International Symposium on
P409L/409CB Stainless Steel
 P49L/49CB Stainless Steel Description P49L/49CB is a ferritic, weldable grade of stainless steel with key performance features, including high compressibility, enhanced green strength and good sinterability.
P49L/49CB Stainless Steel Description P49L/49CB is a ferritic, weldable grade of stainless steel with key performance features, including high compressibility, enhanced green strength and good sinterability.
Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service 1
 Designation: A 268/A 268M 0 An American National Standard Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service This standard is issued under
Designation: A 268/A 268M 0 An American National Standard Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service This standard is issued under
Summary of Personal Monitoring Data for Asbestos-Related Maintenance Work at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
 UCRL-JC- 122097 PREPRINT Summary of Personal Monitoring Data for Asbestos-Related Maintenance Work at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory S.M. Franaszek RJ. Kelly This paper was prepared for submittal
UCRL-JC- 122097 PREPRINT Summary of Personal Monitoring Data for Asbestos-Related Maintenance Work at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory S.M. Franaszek RJ. Kelly This paper was prepared for submittal
THERMAK 17 STAINLESS STEEL
 THERMAK 17 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N High Temperature Strength Superior Oxidation Resistance Excellent Thermal Fatigue Resistance Equiaxed Microstructure Applications Potential
THERMAK 17 STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N High Temperature Strength Superior Oxidation Resistance Excellent Thermal Fatigue Resistance Equiaxed Microstructure Applications Potential
Stainless Sheet 201, 301, 304, 304L, 309, 7 gauge - 28 gauge 316, 316L, 321, 409, 410, (.1793 to.0149 ) up to 72 wide 410S, 430, 439
 Providing a World of Metals to Canada Diversified is a stainless steel and aluminum service center providing sheet, plate, bar, strip, tubing and structural angle to the Canadian market since 1971. After
Providing a World of Metals to Canada Diversified is a stainless steel and aluminum service center providing sheet, plate, bar, strip, tubing and structural angle to the Canadian market since 1971. After
Structural Channels A-36:20-40 LG. Standard Beams
 Floor Plates #/Sq. Ft. 14 Ga. 3.75 12 Ga. 5.25 1/8 6.16 3/16 8.71 1/4 11.26 5/16 13.81 3/8 16.37 Plates #/Sq. Ft. 3/16 7.66 1/4 10.21 5/16 12.76 3/8 15.32 7/16 17.87 1/2 20.42 9/16 22.97 5/8 25.52 3/4
Floor Plates #/Sq. Ft. 14 Ga. 3.75 12 Ga. 5.25 1/8 6.16 3/16 8.71 1/4 11.26 5/16 13.81 3/8 16.37 Plates #/Sq. Ft. 3/16 7.66 1/4 10.21 5/16 12.76 3/8 15.32 7/16 17.87 1/2 20.42 9/16 22.97 5/8 25.52 3/4
THERMAK 17. High Temperature Strength. Superior Oxidation Resistance. Excellent Thermal Fatigue Resistance. Equiaxed Microstructure
 THERMAK 17 Stainless STEEL Product Data Bulletin Applications Potential High Temperature Strength Superior Oxidation Resistance Excellent Thermal Fatigue Resistance Equiaxed Microstructure THERMAK 17 Stainless
THERMAK 17 Stainless STEEL Product Data Bulletin Applications Potential High Temperature Strength Superior Oxidation Resistance Excellent Thermal Fatigue Resistance Equiaxed Microstructure THERMAK 17 Stainless
Problem Steels 1. Welding Consumables Problem Steels. Section 12 - Welding Consumables. 12 Problem Steels. Welding of Problem Steels 2
 Problem Steels 1 Afrox Product Reference Manual Problem Steels Section - Problem Steels 1 Welding of Problem Steels 2 Problem Steels Electrodes 3 Problem Steels MIG & TIG Wires 7 Problem Steels Flux Cored
Problem Steels 1 Afrox Product Reference Manual Problem Steels Section - Problem Steels 1 Welding of Problem Steels 2 Problem Steels Electrodes 3 Problem Steels MIG & TIG Wires 7 Problem Steels Flux Cored
C Cr Ni Mn Mo N < 2 > Thermal conductivity (W m - 1 K - 1 ) Resistivity
 Indu UR 316L UR 316L: A 2%Mo containing 18Cr - 1Ni austenitic stainless UR 316L is one of the basic grade of the stainless s range. The addition of molybdenum improves its resistance to pitting and crevice
Indu UR 316L UR 316L: A 2%Mo containing 18Cr - 1Ni austenitic stainless UR 316L is one of the basic grade of the stainless s range. The addition of molybdenum improves its resistance to pitting and crevice
AUTOMOTIVE EXHAUST SYSTEM MATERIALS COMPARATOR
 AUTOMOTIVE EXHAUST SYSTEM MATERIALS COMPARATOR AK Steel manufactures stainless steels for exhaust system components to meet lightweighting and durability requirements. Combined with industry experience
AUTOMOTIVE EXHAUST SYSTEM MATERIALS COMPARATOR AK Steel manufactures stainless steels for exhaust system components to meet lightweighting and durability requirements. Combined with industry experience
1. Introduction. 2. Objective of development and effects of alloying elements
 Recent boilers have been designed for higher temperatures and pressures than those in the past and require steels with high temperature strength that is greater than that of conventional 18-8 austenitic
Recent boilers have been designed for higher temperatures and pressures than those in the past and require steels with high temperature strength that is greater than that of conventional 18-8 austenitic
WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS
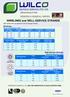 WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS High quality wire and strand for the oil and gas industry. Wirelines Minimum Breaking Loads Diameter in mm HT Carbon EHT Carbon ZERON 100VHX 0.092 2.34 1,950 1,980 1,350
WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS High quality wire and strand for the oil and gas industry. Wirelines Minimum Breaking Loads Diameter in mm HT Carbon EHT Carbon ZERON 100VHX 0.092 2.34 1,950 1,980 1,350
Sandvik 316 (Plate and sheet)
 Datasheet updated 2014 01 29 12:21:53 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik 316 (Plate and sheet) Sandvik 316 is a molybdenum alloyed austenitic chromium nickel steel. STANDARDS ASTM 316 UNS S31600
Datasheet updated 2014 01 29 12:21:53 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik 316 (Plate and sheet) Sandvik 316 is a molybdenum alloyed austenitic chromium nickel steel. STANDARDS ASTM 316 UNS S31600
Use the arrow keys to easily navigate through the course.
 STEEL Use the arrow keys to easily navigate through the course. Back Next 1 STEEL 2 A BRIEF HISTORY OF STEEL The history of steel is closely connected to the development of human culture and civilization.
STEEL Use the arrow keys to easily navigate through the course. Back Next 1 STEEL 2 A BRIEF HISTORY OF STEEL The history of steel is closely connected to the development of human culture and civilization.
Stability of Optical Elements in the NIF Target Area Building
 UCRL-JC-129682 PREPRINT Stability of Optical Elements in the NIF Target Area Building David J. Trummer Richard J. Foley Gene S. Shaw This paper was prepared for submittal to the 3rd Annual International
UCRL-JC-129682 PREPRINT Stability of Optical Elements in the NIF Target Area Building David J. Trummer Richard J. Foley Gene S. Shaw This paper was prepared for submittal to the 3rd Annual International
Stainless Steel & Stainless Steel Fasteners Chemical, Physical and Mechanical Properties
 Stainless Steel & Stainless Steel Fasteners Chemical, Physical and Mechanical Properties Stainless steel describes a family of steels highly resistant to tarnishing and rusting that contain at least two
Stainless Steel & Stainless Steel Fasteners Chemical, Physical and Mechanical Properties Stainless steel describes a family of steels highly resistant to tarnishing and rusting that contain at least two
AEROSPACE MATERIAL SPECIFICATION
 AEROSPACE MATERIAL SPECIFICATION AMS 5643Q Issued OCT 1951 Revised JAN 2003 Superseding AMS 5643P Steel, Corrosion-Resistant, Bars, Wire, Forgings, Tubing, and Rings 16Cr - 4.0Ni - 0.30Cb - 4.0Cu Solution
AEROSPACE MATERIAL SPECIFICATION AMS 5643Q Issued OCT 1951 Revised JAN 2003 Superseding AMS 5643P Steel, Corrosion-Resistant, Bars, Wire, Forgings, Tubing, and Rings 16Cr - 4.0Ni - 0.30Cb - 4.0Cu Solution
ATI Nb. ATI Nb. Technical Data Sheet. Stainless Steel: Austenitic GENERAL PROPERTIES SPECIFICATION COVERAGE CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 ATI 20-25+Nb Stainless Steel: Austenitic (UNS S35140) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 20-25+Nb alloy is an austenitic stainless steel intended primarily for elevated temperature service. This alloy fills a performance
ATI 20-25+Nb Stainless Steel: Austenitic (UNS S35140) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 20-25+Nb alloy is an austenitic stainless steel intended primarily for elevated temperature service. This alloy fills a performance
