Complexation Reaction Using Ammonium Based Chloride Compounds for Preparation of Eutectic Mixtures
|
|
|
- Brendan Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Complexation Reaction Using Ammonium Based Chloride Compounds for Preparation of Eutectic Mixtures Ahmad Adlie Shamsuri (Corresponding author) Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Institute of Bioscience Universiti Putra Malaysia, UPM Serdang Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia Dzulkefly Kuang Abdullah Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Institute of Bioscience Universiti Putra Malaysia, UPM Serdang Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia The research is financed by Universiti Putra Malaysia under Research University Grant Scheme ( RU) Abstract In this study, we are interested in the eutectic processing of chloride compounds and decided to focus on ammonium based compounds that can provide sufficient insight in the fundamental chemistry. 10 types of ammonium based chloride compounds namely ammonium chloride, methanaminium chloride, dimethylammonium chloride, trimethylammonium chloride, tetramethylammonium chloride, dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride, hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride, phenyltrimethylammonium chloride, benzyltrimethylammonium chloride and (vinylbenzyl)trimethylammonium chloride were used in this study. This research led to a hypothesis that the ammonium based chloride compounds could be reacted with urea through complexation reaction giving eutectic mixtures. However, functional groups have plays an important role to influence melting points of these eutectic mixtures. This is regarded to be a motivating finding that will be important for the most future research work involving complexation reaction for the production of eutectic mixtures. Keywords: Eutectic mixture, Ammonium based chloride compounds, Complexation reaction, Ionic liquids 1. Introduction Eutectic mixtures which are materials consisting of components that form a low melting point mixture, provide a unique substance for developing advanced materials and usually cheaper with less time-consuming than the development of new materials. It is composed of a mixture with a melting point much lower than each of the individual components. For example, changing metal such as tin and lead into metallic eutectic is a common way to make them low melting point material usually used in soldering (Kanchanomai, et al., 2002). ther eutectic mixture is sodium chloride and water; it has a eutectic point of C (Chen, et al., 2005) it is used to aid ice removal or to produce low temperatures ice. Eutectic mixtures are simple to prepare, the components of the eutectic can be easily mixed and converted without further purification. Most recently, eutectic mixtures were utilized to produce ionic liquids that might be used as green solvents (Hou, et al., 2008). Since little information using common ammonium based compounds as eutectic components is known concerning the chloride compounds (except for choline chloride) related to the preparation of eutectic mixture. Therefore, we have produced some eutectic mixtures using common ammonium based chloride compounds. Previous study has shown that complexation reaction was used to produce eutectic mixture by means of ammonium based chloride compounds such as choline chloride with urea as complexing agent (Abbott, et al., 2003), although low melting point of eutectic mixture was observed in that study, but we have found that the role of functional groups in ammonium based chloride compounds for producing eutectic mixtures through complexation reaction is still not fully discovered and identified. In this study, eutectic mixtures have been prepared via complexation reaction by Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education 161
2 means of ammonium based chloride compounds with different functional groups; its physical appearance and melting point were also studied. 2. Materials and methods 2.1 Materials Ammonium chloride, methanaminium chloride, dimethylammonium chloride, trimethylammonium chloride, tetramethylammonium chloride, dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride, hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride, phenyltrimethylammonium chloride, benzyltrimethylammonium chloride and (vinylbenzyl)trimethylammonium chloride were supplied by Sigma Aldrich. Urea was also obtained from Sigma Aldrich. All chemicals purity 98.0% and were recrystallized before use. 2.2 Preparation of eutectic mixture Preparation of eutectic mixture via complexation reaction was done according to (Abbott, et al., 2007). In this study, ammonium based chloride compounds were mixed in the flask with urea as 1:2 mole ratios, respectively. The flask was immersed in oil bath at 100 C and stirred for at least 1 hour. Then, the reaction mixture was dried for overnight at 100 C in a vacuum oven to obtain the final product and prior to the melting point measurements. 2.3 Melting point characterization Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis was conducted on a Mettler Toledo DSC822 e apparatus using the STAR analysis software under a constant stream of nitrogen at flow rate of 50 ml/min. The samples were tightly sealed in aluminium pans. The samples were first heated to 100 C to eliminate the thermal history. The analyses were carried out in a temperature range of 25 to 350ºC with a heating rate of 10ºC/min to obtain the melting point, T m which were determined from thermograms during the programmed reheating steps. 3. Results and discussion 3.1 Physical appearance Table 1 shows the physical appearances profile of eutectic mixtures at room temperature (25ºC). All prepared eutectic mixtures are solid at ambient temperature corresponding to physical properties of its individual components. Ammonium based chloride compounds are composed of nitrogen cations and chloride ions, so, they have tendency to form eutectic mixture with complexing agent (urea) assisted by elevated temperature (Abbott, et al., 2003). It can also be seen in Table 1 all eutectic mixtures are solid possibly due to high melting points. Nonetheless, DSC thermal analysis was carried out to determine the melting points accurately. 3.2 DSC characterization Table 2 shows the melting points of pristine eutectic components were supplied by Sigma Aldrich MSDS, which obviously high. DSC is a well known as technique which gives an exhaustive overview the relevant thermal analysis (Ford & Timmins, 1989). The calorimetric data was obtained by heating the eutectic mixtures; all melting points corresponding with the peaks of DSC traces were listed in Table 3. Each melting point of DSC traces means a crystalline melting point of the eutectic mixtures. From this result, it can be observed that the melting points of eutectic mixtures are different from its pristine eutectic components. In other words, melting points of eutectic mixtures are significantly lower than its individual components. Therefore, in this study all eutectic mixtures were indicating absolute eutectic behaviour due to the reduction in melting points. In Table 3 it seems that the complexation reaction has been taking place which chloride ions complexed with urea. The reasons why they have low melting points are basically the endothermic shifted to the lower temperature after complexing agent was given to the ammonium based chloride compounds. Mostly the chloride ions could be reacted with urea through complexation reaction assisted by high temperature condition. The complexation reaction of chloride ions with urea is actually driven by hydrogen bonding between them (Abbott, et al., 2003). Although hydrogen bonding is fully known as strong bond between the hydrogen atom with the organic constituents such as nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine (Brady, et al., 2000), essentially, hydrogen bonding also could be formed between the hydrogen atoms with the electronegative constituent such as chloride ions. In this case, the hydrogen atoms of complexing agent are attached to the chloride ions from ammonium based chloride compounds that relatively electronegative to form chloride ions complex. Since eutectic mixtures consist of nitrogen cations and complex anions so, when higher temperature was applied, these structures possible dissociated cations from anion relations owing to the larger size ratios thus, offered weak interactions, as a result increased degrees of freedom and amounts motion of nitrogen cations and complex anions. Apart from that, the reason we have chosen 1:2 mole ratio is when chloride compound or complexing agent are more or less than that composition the tendency to form 162 ISSN E-ISSN
3 complex anions are low (Abbott, et al., 2003). Formation of hydrogen bonding between eutectic components in the eutectic mixtures has been shown in Figure 1. In the pristine ammonium based chloride compounds phase, the interactions between cations and anions are generally stronger, which are normally held together by strong ionic bond. As a result, compounds in these structures tend to have higher melting points compared to the nitrogen cations and complex anions of the eutectic mixtures. The highest melting point is can be observed for eutectic mixture of ammonium chloride and urea which contained fully hydrogen atoms. Hence, nitrogen cations with the hydrogen atoms in the all side group causing the melting point slightly decreased to a value below its origin. Eutectic mixtures with ammonium based chloride compounds that consisted of methyl branches such as methanaminium chloride, dimethylammonium chloride, trimethylammonium chloride and tetramethylammonium chloride have significant results related to the melting point reduction compared with ammonium chloride. A completely unexpected observation can be seen for eutectic components of dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride and hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride give important results, due to their melting points far away from individual components eventhough they have longest alkyl chains contrasted to tetramethylammonium chloride. While, with phenyl and benzyl functional group as can be seen on eutectic mixture of phenyltrimethylammonium chloride and benzyltrimethylammonium chloride with urea, respectively were demonstrating higher melting point than (vinylbenzyl)trimethylammonium chloride. The melting points of these eutectic mixtures are dependent upon the interaction lattice energies of the ammonium based chloride compounds with complexing agent and the entropy changes arising from forming eutectics, therefore the reduction of melting point are measure of the entropy change (Abbott, et al., 2004). However, first it is important to relate the structure of the ammonium based chloride compounds to the melting points of the eutectic mixtures. The DSC results clearly show to relate to the differences of chemical structure between each eutectic mixture. In other words, the highest of the melting point may suggest the existence of inappropriate character of the functional groups in the nitrogen cations (Abbott, et al., 2001) in term of reducing the melting point. The appropriate functional groups of ammonium based chloride compounds will create the suitable eutectic components for preparation of low melting points eutectic mixtures. In addition, melting points of eutectic mixtures also decrease with the larger more asymmetric nitrogen cations (Buzzeo, et al., 2004), which the highest melting points are observed with the more symmetric nitrogen cations. This may be a reason for the highest melting points of eutectic components such as ammonium chloride and tetramethylammonium chloride also the lowest melting points of dimethylammonium chloride and hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride. n the other hand, in comparison with phenyl and benzyl functional group, the lower melting point is observed for (vinylbenzyl)trimethylammonium chloride, possibly due to the larger size of nitrogen cations providing greater asymmetry. Based on this study, the order of melting point reduction for varying functional groups for the ammonium based chloride compounds has been shown in Figure Conclusions This study was indicated that eutectic mixtures were successfully produced by using ammonium based chloride compounds and complexing agent specifically urea. Based on these results, it is clear that ammonium based chloride compounds can undergo reactions with the urea through complexation reaction. The most important and intriguing discovery from this research is the fact that the functional groups of ammonium based chloride compounds are necessarily have play an important role to influence the melting point. The order of melting point reduction for varying functional groups is hydrogen > alkyl > phenyl > benzyl > vinylbenzyl > fatty alkyl. Eutectic components should be having appropriate functional group that will not influence functionality of nitrogen cations so that can reduce melting points of eutectic mixtures to the lowest points. This information is regarded as the motivating finding that will be the most important for future studies involving complexation reaction therefore, could be useful for fundamental chemistry especially if wanted to generate low melting points of eutectic mixtures for developing advanced materials such as ionic liquids. References Abbott, A. P., Capper, G., Davies, D. L., Munro, H. L., Rasheed, R. K., & Tambyrajah, V. (2001). Preparation of novel, moisture-stable, Lewis-acidic ionic liquids containing quaternary ammonium salts with functional side chains. Chemical Communications, 19, Abbott, A. P., Capper, G., Davies, D. L., Rasheed, R. K., & Tambyrajah, V. (2003). Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chemical Communications, 1, Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education 163
4 Abbott, A.P., Boothby, D., Capper, G., Davies, D. L., & Rasheed, R. K. (2004). Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 126, Abbott, A. P., Capper, G., McKenzie, K. J., & Ryder, K. S. (2007). Electrodeposition of zinc-tin alloys from deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 599, Brady, J. E., Russel, J. W., & Holum, J. R. (2000). Chemistry: Matter and Its changes. New York, United States: John Wiley & Sons Inc. pp Buzzeo, M. C., Evans, R. G., & Compton, R. G. (2004). Non-haloaluminate room-temperature ionic liquids in electrochemistry a review. European Journal of Chemical Physics and Physical Chemistry, 5, Chen, N., Morikawa, J., & Hashimoto, T. (2005). Effect of cryoprotectans on eutectics of NaCl 2H 2 /ice and KCl/ice studied by temperature wave analysis and differential scanning calorimetry. Thermochimica Acta, 431, Ford, J. L., & Timmins, P. (1989). Pharmaceutical Thermal Analysis - Techniques and Applications. Chichester, England: Ellis Horwood. pp Hou, Y., Gu, Y., hang, S., Yang, F., Ding, H., & Shan, Y. (2008). Novel binary eutectic mixtures based on imidazole. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 143, Kanchanomai, C., Miyashita, Y., & Mutoh, Y. (2002). Strain-rate effects on low cycle fatigue mechanisms of a eutectic Sn Pb solder. International Journal of Fatigue, 24, Table 1. Physical appearances of eutectic mixtures at room temperature (25ºC) Eutectic mixture ammonium chloride + urea methanaminium chloride + urea dimethylammonium chloride + urea trimethylammonium chloride + urea tetramethylammonium chloride + urea dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride + urea hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride + urea phenyltrimethylammonium chloride + urea benzyltrimethylammonium chloride + urea (vinylbenzyl)trimethylammonium chloride + urea Appearance Table 2. Melting points of eutectic components as obtained from MSDS data Eutectic component Melting point, T m (ºC)* ammonium chloride 340 methanaminium chloride dimethylammonium chloride trimethylammonium chloride tetramethylammonium chloride >300 dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride 246 hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride phenyltrimethylammonium chloride benzyltrimethylammonium chloride 239 (vinylbenzyl)trimethylammonium chloride 240 urea * obtained from Sigma Aldrich 164 ISSN E-ISSN
5 Table 3. Melting points of eutectic mixtures as determined from DSC data Eutectic mixture Melting point, T m (ºC) ammonium chloride + urea methanaminium chloride + urea dimethylammonium chloride + urea trimethylammonium chloride + urea tetramethylammonium chloride + urea dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride + urea hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride + urea phenyltrimethylammonium chloride + urea benzyltrimethylammonium chloride + urea (vinylbenzyl)trimethylammonium chloride + urea M Cl - M + = ammonium based cation Figure 1. Formation of hydrogen bonding between eutectic components in the eutectic mixtures N + Cl - = hydrogen > alkyl > phenyl > benzyl > vinylbenzyl > fatty alkyl Figure 2. The order of melting point reduction for varying functional groups Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education 165
Dependence of Eutectic - Composition on Densities of Components of Binary Eutectic Mixtures of Solid Carboxylic Acids
 IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) ISSN: 2278-5736. Volume 3, Issue 1 (Nov. Dec. 2012), PP 18-22 Dependence of Eutectic - Composition on Densities of Components of Binary Eutectic Mixtures of
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) ISSN: 2278-5736. Volume 3, Issue 1 (Nov. Dec. 2012), PP 18-22 Dependence of Eutectic - Composition on Densities of Components of Binary Eutectic Mixtures of
Physical pharmacy. dr basam al zayady
 Physical pharmacy Lec 5 dr basam al zayady Liquefaction of Gases: When a gas is cooled, it loses some of its kinetic energy in the form of heat, and the velocity of the molecules decreases. If pressure
Physical pharmacy Lec 5 dr basam al zayady Liquefaction of Gases: When a gas is cooled, it loses some of its kinetic energy in the form of heat, and the velocity of the molecules decreases. If pressure
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION 1. SYNTHESIS OF THE MONOMERS 2-(Methylacryloyloxy)ethyl-trimethylammonium tetrafluoroborate ([MATMA][BF 4 ]) and p-vinylbenzyltrimethylammonium tetrafluoroborate ([VBTMA][BF 4 ])
SUPPORTING INFORMATION 1. SYNTHESIS OF THE MONOMERS 2-(Methylacryloyloxy)ethyl-trimethylammonium tetrafluoroborate ([MATMA][BF 4 ]) and p-vinylbenzyltrimethylammonium tetrafluoroborate ([VBTMA][BF 4 ])
Electricity and Chemistry
 Electricity and Chemistry Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the reactions involving the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice-versa. Electrochemical
Electricity and Chemistry Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the reactions involving the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice-versa. Electrochemical
Thermal Characteristics of Eutectic Mixture of Capric-Lauric Acids as Phase Change Material (PCM) in Gypsum Board
 Jurnal Teknologi Proses Media Publikasi Karya Ilmiah Teknik Kimia 6(1) Januari 2007: 31 38 ISSN 1412-7814 Thermal Characteristics of Eutectic Mixture of Capric-Lauric Acids as Phase Change Material (PCM)
Jurnal Teknologi Proses Media Publikasi Karya Ilmiah Teknik Kimia 6(1) Januari 2007: 31 38 ISSN 1412-7814 Thermal Characteristics of Eutectic Mixture of Capric-Lauric Acids as Phase Change Material (PCM)
I. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES PROPERTY METALS NON-METALS
 Elements can be classified as metals and non-metals on the basis of their properties. Example of some metals are : Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu) Examples of some non-metals are :
Elements can be classified as metals and non-metals on the basis of their properties. Example of some metals are : Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu) Examples of some non-metals are :
Suggest one reason why spoons are electroplated. ... Why is hydrogen produced at the negative electrode and not sodium?
 Q1.This question is about electrolysis. (a) Metal spoons can be coated with silver. This is called electroplating. Suggest one reason why spoons are electroplated. (b) When sodium chloride solution is
Q1.This question is about electrolysis. (a) Metal spoons can be coated with silver. This is called electroplating. Suggest one reason why spoons are electroplated. (b) When sodium chloride solution is
The forces between iodine molecules are stronger 1. (b) anything in range +30 to It contains ions which can move 1. (f) hydrogen iodine 1 [6]
![The forces between iodine molecules are stronger 1. (b) anything in range +30 to It contains ions which can move 1. (f) hydrogen iodine 1 [6] The forces between iodine molecules are stronger 1. (b) anything in range +30 to It contains ions which can move 1. (f) hydrogen iodine 1 [6]](/thumbs/89/100151757.jpg) M.(a) The forces between iodine molecules are stronger (b) anything in range +30 to +20 (c) Brown (d) 2 I + Cl 2 I 2 + 2 Cl (e) It contains ions which can move (f) hydrogen iodine [6] Page 2 M2.(a) giant
M.(a) The forces between iodine molecules are stronger (b) anything in range +30 to +20 (c) Brown (d) 2 I + Cl 2 I 2 + 2 Cl (e) It contains ions which can move (f) hydrogen iodine [6] Page 2 M2.(a) giant
I. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES. PROPERTY METALS NON-METALS 1.Lustre Metals have shining surface. They do not have shining surface.
 Elements can be classified as metals and non-metals on the basis of their properties. Example of some metals are : Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu) Examples of some non-metals are :
Elements can be classified as metals and non-metals on the basis of their properties. Example of some metals are : Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu) Examples of some non-metals are :
Experiment 3: Determination of an Empirical Formula
 Background Information The composition of a compound is defined by its chemical formula, which gives the number ratio of the different elements in the compound. For example, water has a fixed composition
Background Information The composition of a compound is defined by its chemical formula, which gives the number ratio of the different elements in the compound. For example, water has a fixed composition
ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2004
 ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2004 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2004 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
ELECTROPLATING IN NOVEL DEEP EUTECTIC SOLVENT ELECTROLYTES
 ELECTROPLATING IN NOVEL DEEP EUTECTIC SOLVENT ELECTROLYTES Supported by C. Andrew 1,2 *, M.O. Aremu 2 and O.A. Ushie 2 1 Chemistry Department, University of Leicester, Leicester, LE1 7RH, UK 2 Department
ELECTROPLATING IN NOVEL DEEP EUTECTIC SOLVENT ELECTROLYTES Supported by C. Andrew 1,2 *, M.O. Aremu 2 and O.A. Ushie 2 1 Chemistry Department, University of Leicester, Leicester, LE1 7RH, UK 2 Department
9.2.1 Similarities and trends in the properties of the Group II metals magnesium to barium and their compounds
 9.2 Group II Content 9.2.1 Similarities and trends in the properties of the Group II metals magnesium to barium and their compounds Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) (b) (c) (d) describe
9.2 Group II Content 9.2.1 Similarities and trends in the properties of the Group II metals magnesium to barium and their compounds Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) (b) (c) (d) describe
The Recrystallization of Benzoic Acid and Determination of its Melting Point
 Doreen Foy Organic Chemistry 1 Laboratory The Recrystallization of Benzoic Acid and Determination of its Melting Point Hannah Loch 10/01/2012 Abstract The goal of the experiment was to obtain pure benzoic
Doreen Foy Organic Chemistry 1 Laboratory The Recrystallization of Benzoic Acid and Determination of its Melting Point Hannah Loch 10/01/2012 Abstract The goal of the experiment was to obtain pure benzoic
Module: 9 Lecture: 39
 Module: 9 Lecture: 39 AMMONIUM CHLORIDE INTRODUCTION Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is white crystalline salt highly soluble in water. Solutions of ammonium chloride are mildly acidic. Sal ammoniac is a name
Module: 9 Lecture: 39 AMMONIUM CHLORIDE INTRODUCTION Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is white crystalline salt highly soluble in water. Solutions of ammonium chloride are mildly acidic. Sal ammoniac is a name
THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEMS STEARIC / LAURIC ACID MIXTURES AS PHASE CHANGE MATERIALS
 3.014 MATERIALS LABORATORY MODULE- β1 September 26 30, 2005 GEETHA P. BERERA THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEMS STEARIC / LAURIC ACID MIXTURES AS PHASE CHANGE MATERIALS OBJECTIVES: Prepare stearic acid and
3.014 MATERIALS LABORATORY MODULE- β1 September 26 30, 2005 GEETHA P. BERERA THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEMS STEARIC / LAURIC ACID MIXTURES AS PHASE CHANGE MATERIALS OBJECTIVES: Prepare stearic acid and
Conductometric Studies on Terbium Soaps
 Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2012, 30(1), 45-51 OI: 10.4152/pea.201201045 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Conductometric Studies on Terbium Soaps Kamal Kishore * and S.K Upadhyaya P.G.
Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2012, 30(1), 45-51 OI: 10.4152/pea.201201045 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Conductometric Studies on Terbium Soaps Kamal Kishore * and S.K Upadhyaya P.G.
ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2000
 ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2000 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2000 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
DRUG- POLYMER COMPATIBILITY STUDIES
 Chapter 3 DRUG- POLYMER COMPATIBILITY STUDIES 3.1. DRUG- POLYMER COMPATIBILITY STUDIES Drug polymer compatibility studies were carried out by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and fourier transmission
Chapter 3 DRUG- POLYMER COMPATIBILITY STUDIES 3.1. DRUG- POLYMER COMPATIBILITY STUDIES Drug polymer compatibility studies were carried out by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and fourier transmission
GraspIT AQA GCSE Chemical changes
 A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Conditioning-Free Electrolytes for Magnesium Batteries Using Sulfone-Ether Mixtures with Increased Thermal Stability Laura C. Merrill and Jennifer L. Schaefer*, University of Notre
Supporting Information Conditioning-Free Electrolytes for Magnesium Batteries Using Sulfone-Ether Mixtures with Increased Thermal Stability Laura C. Merrill and Jennifer L. Schaefer*, University of Notre
Revision checklist SC10 13
 SC10 Electrolytic Processes SC10a Electrolysis State the meaning of the term electrolyte. Outline what happens during electrolysis. Explain the movement of the ions during electrolysis. H Write half equations
SC10 Electrolytic Processes SC10a Electrolysis State the meaning of the term electrolyte. Outline what happens during electrolysis. Explain the movement of the ions during electrolysis. H Write half equations
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 26 Electronic Supplementary Information Condensed phase behaviour of ionic liquid benzene mixtures:
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 26 Electronic Supplementary Information Condensed phase behaviour of ionic liquid benzene mixtures:
Phase diagrams are diagrammatic representations of the phases present in a
 Chapter 4 What is a binary phase diagram? Phase diagrams are diagrammatic representations of the phases present in a system under specified equilibrium conditions, most often composition, temperature and
Chapter 4 What is a binary phase diagram? Phase diagrams are diagrammatic representations of the phases present in a system under specified equilibrium conditions, most often composition, temperature and
Effect of degassing electrolyte on polarisation curve shape with the aim to apply knowledge to electrochemical machining
 KES Transactions on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing I Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2014 : pp.566-573 : Paper sdm14-041 Effect of degassing electrolyte on polarisation curve shape with the
KES Transactions on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing I Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2014 : pp.566-573 : Paper sdm14-041 Effect of degassing electrolyte on polarisation curve shape with the
A SOLVENT-FREE COMPOSITE SOLID ELECTROLYTES OF Li 2 CO 3 Al 2 O 3 SYSTEM PREPARED VIA WATER BASED SOL GEL METHOD
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS A SOLVENT-FREE COMPOSITE SOLID ELECTROLYTES OF Li 2 CO 3 Al 2 O 3 SYSTEM PREPARED VIA WATER BASED SOL GEL METHOD M. Sulaiman 1, *, A.A. Rahman 1, N.S.
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS A SOLVENT-FREE COMPOSITE SOLID ELECTROLYTES OF Li 2 CO 3 Al 2 O 3 SYSTEM PREPARED VIA WATER BASED SOL GEL METHOD M. Sulaiman 1, *, A.A. Rahman 1, N.S.
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 18 - The Representative Elements: Groups 1A through 4A
 AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 18 - The Representative Elements: Groups 1A through 4A 18.1 A Survey of the Representative Elements A. Basic Trends 1. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations 2. Nonmetals
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 18 - The Representative Elements: Groups 1A through 4A 18.1 A Survey of the Representative Elements A. Basic Trends 1. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations 2. Nonmetals
G16 - THERMAL ANALYSIS
 001-1012PDG.pdf 1 1 G16 - THERMAL ANALYSIS 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thermal analysis is a group of techniques in which the variation of a physical property of a substance is measured as a function of temperature.
001-1012PDG.pdf 1 1 G16 - THERMAL ANALYSIS 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thermal analysis is a group of techniques in which the variation of a physical property of a substance is measured as a function of temperature.
INTERFLUX ELECTRONICS NV
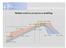 Reflow soldering temperature profiling Min : 30sec Max : 120sec Max : +4 C/sec Max : 250 C Min : 230 C Min: +0,5 C/sec Min : +1 C/sec Max : +3 C/sec Max : +1 C/sec Max : -6 C/sec Min : -2 C/sec Min : +1
Reflow soldering temperature profiling Min : 30sec Max : 120sec Max : +4 C/sec Max : 250 C Min : 230 C Min: +0,5 C/sec Min : +1 C/sec Max : +3 C/sec Max : +1 C/sec Max : -6 C/sec Min : -2 C/sec Min : +1
What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen?
 EXERCISE.1 Question 1: What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen? Solution 1: Book Name: Selina concise (a) Aqua fortis: Nitric acid is called aqua fortis. Aqua fortis means strong
EXERCISE.1 Question 1: What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen? Solution 1: Book Name: Selina concise (a) Aqua fortis: Nitric acid is called aqua fortis. Aqua fortis means strong
MR. D HR UV AS HE R I.C.S.E. BOA RD PAP ER ICSE
 MR D HR UV AS HE R ICSE BOA RD PAP ER 200 4 1 ICSE-2004 Section A (40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 (a) Choose the letters A,B,C or D to match the descriptions (i) to (iv)
MR D HR UV AS HE R ICSE BOA RD PAP ER 200 4 1 ICSE-2004 Section A (40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 (a) Choose the letters A,B,C or D to match the descriptions (i) to (iv)
Double Award Science: Chemistry
 New Specification Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 2015 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C1 Higher Tier ML [GSD22] WEDNESDAY 25 FEBRUARY 2015, MORNING
New Specification Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 2015 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C1 Higher Tier ML [GSD22] WEDNESDAY 25 FEBRUARY 2015, MORNING
ATOM STRUCTURE AND BONDING OF METALS
 ATOM STRUCTURE AND BONDING OF METALS The atom is composed of a small, central nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons. Shells, or energy levels of electrons surround this nucleus. These electrons
ATOM STRUCTURE AND BONDING OF METALS The atom is composed of a small, central nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons. Shells, or energy levels of electrons surround this nucleus. These electrons
XRD, DTA AND DENSITY STUDIES OF LITHIUM BORATE GLASSES CONTAINING COPPER A. A. Soliman
 , pp. 188 197 XRD, DTA AND DENSITY STUDIES OF LITHIUM BORATE GLASSES CONTAINING COPPER A. A. Soliman Physics Department, Faculty of Girls, Ain Shams University, Heliopolis, Egypt Received 4 November, 2008
, pp. 188 197 XRD, DTA AND DENSITY STUDIES OF LITHIUM BORATE GLASSES CONTAINING COPPER A. A. Soliman Physics Department, Faculty of Girls, Ain Shams University, Heliopolis, Egypt Received 4 November, 2008
THE EFFECT OF CRUCIBLE TYPE ON DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY (DSC) MEASUREMENTS
 THE EFFECT OF CRUCIBLE TYPE ON DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY (DSC) MEASUREMENTS Graham S Arthur and Craig Williams Syngenta, Huddersfield Manufacturing Centre, PO Box A38 Leeds Road, Huddersfield,
THE EFFECT OF CRUCIBLE TYPE ON DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY (DSC) MEASUREMENTS Graham S Arthur and Craig Williams Syngenta, Huddersfield Manufacturing Centre, PO Box A38 Leeds Road, Huddersfield,
AQA Chemistry A-level
 AQA Chemistry A-level Required Practical 10 Preparation of a pure organic solid, test of its purity, and preparation of a pure organic liquid Reflux Reflux: continuous boiling and condensing of a reaction
AQA Chemistry A-level Required Practical 10 Preparation of a pure organic solid, test of its purity, and preparation of a pure organic liquid Reflux Reflux: continuous boiling and condensing of a reaction
S1 Building Blocks Summary Notes
 S1 Building Blocks Summary Notes Atoms & Molecules 1 We are developing our understanding of atoms and molecules. Atoms are the simplest building blocks of every substance in the universe. There are just
S1 Building Blocks Summary Notes Atoms & Molecules 1 We are developing our understanding of atoms and molecules. Atoms are the simplest building blocks of every substance in the universe. There are just
A vapor (or gas) needs a completely enclosed container to have a definite volume; it will readily take on any shape imposed.
 Overview: Amorphous and crystalline solid states. States of matter. General description. A vapor (or gas) needs a completely enclosed container to have a definite volume; it will readily take on any shape
Overview: Amorphous and crystalline solid states. States of matter. General description. A vapor (or gas) needs a completely enclosed container to have a definite volume; it will readily take on any shape
New Sustainable Electrolytes for Metal Finishing and Electropolishing
 IMF New Sustainable Electrolytes for Metal Finishing and Electropolishing (aerospace investment castings) Karl S. Ryder Scionix Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, University of Leicester, Leicester,
IMF New Sustainable Electrolytes for Metal Finishing and Electropolishing (aerospace investment castings) Karl S. Ryder Scionix Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, University of Leicester, Leicester,
E24 PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Distillation, recrystallisation, melting and boiling point determination
 E24 PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Distillation, recrystallisation, melting and boiling point determination THE TASK To learn the main techniques of purifying organic compounds. THE SKILLS By the end
E24 PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Distillation, recrystallisation, melting and boiling point determination THE TASK To learn the main techniques of purifying organic compounds. THE SKILLS By the end
The table shows the students suggestions about the identity of P.
 1 Three students, X, Y and Z, were told that solid P reacts with dilute acids and also conducts electricity. The table shows the students suggestions about the identity of P. Which of the students are
1 Three students, X, Y and Z, were told that solid P reacts with dilute acids and also conducts electricity. The table shows the students suggestions about the identity of P. Which of the students are
Physical Aging and Fragility of Amorphous Sucrose by DSC
 Physical Aging and Fragility of Amorphous Sucrose by DSC R. Bruce Cassel, Ph.D. TA Instruments, 109 Lukens Drive, New Castle DE 19720, USA ABSTRACT A method for quantifying physical aging and fragility
Physical Aging and Fragility of Amorphous Sucrose by DSC R. Bruce Cassel, Ph.D. TA Instruments, 109 Lukens Drive, New Castle DE 19720, USA ABSTRACT A method for quantifying physical aging and fragility
Materials are all substances and include metals, ceramics and plastics as well as natural and new substances.
 National 4 Materials It is hard to imagine life without mobile gadgets such as iphones, ipads and MP3 players. Yet twenty years ago these handy gadgets such as the mobile phone where bigger and cost five
National 4 Materials It is hard to imagine life without mobile gadgets such as iphones, ipads and MP3 players. Yet twenty years ago these handy gadgets such as the mobile phone where bigger and cost five
Year 7 Homework Booklet. Name. Teacher. Elements, compounds and reactions
 Year 7 Homework Booklet Name Teacher Elements, compounds and reactions Task number Task Success criteria 1 Homework quiz- Finding elements and building the Periodic table Research and complete the questions
Year 7 Homework Booklet Name Teacher Elements, compounds and reactions Task number Task Success criteria 1 Homework quiz- Finding elements and building the Periodic table Research and complete the questions
Chapter 1. Crystal Structure
 Chapter 1. Crystal Structure Crystalline solids: The atoms, molecules or ions pack together in an ordered arrangement Amorphous solids: No ordered structure to the particles of the solid. No well defined
Chapter 1. Crystal Structure Crystalline solids: The atoms, molecules or ions pack together in an ordered arrangement Amorphous solids: No ordered structure to the particles of the solid. No well defined
Q1. From the following list of substances, choose the substances which meet the description given in parts (i) to (v) below :
 Questions:- Q1. From the following list of substances, choose the substances which meet the description given in parts (i) to (v) below : Ammonium chloride, ammonium nitrate, chlorine, dilute hydrochloric
Questions:- Q1. From the following list of substances, choose the substances which meet the description given in parts (i) to (v) below : Ammonium chloride, ammonium nitrate, chlorine, dilute hydrochloric
2A Chemistry - Classification of Substances
 CHEMISTRY The world is made up of a variety of substances. Some of these occur naturally in our environment, others are made through the combination of naturally occurring substances to form new materials.
CHEMISTRY The world is made up of a variety of substances. Some of these occur naturally in our environment, others are made through the combination of naturally occurring substances to form new materials.
Changes for Organic Chemistry 2521 Labs
 Changes for Organic Chemistry 2521 Labs Chapter 3 Crystallization Part 1 (Starts on page 56) Test the solubility of three compounds with three solvents. There are four compounds to choose from: 1. Resorcinol
Changes for Organic Chemistry 2521 Labs Chapter 3 Crystallization Part 1 (Starts on page 56) Test the solubility of three compounds with three solvents. There are four compounds to choose from: 1. Resorcinol
Chemistry. Student Number. Mark / 25. The Chemical Earth and Metals Modules Test General Instructions. Total Marks 25
 Student Number Mark / 25 Chemistry The Chemical Earth and Metals Modules Test 2002 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 40 minutes Write using black or blue pen Draw diagrams using
Student Number Mark / 25 Chemistry The Chemical Earth and Metals Modules Test 2002 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 40 minutes Write using black or blue pen Draw diagrams using
Physical Aging and Fragility of Amorphous Polyethylene Terephthalate
 Physical Aging and Fragility of Amorphous Polyethylene Terephthalate R. Bruce Cassel, Ph.D. TA Instruments, 109 Lukens Drive, New Castle, DE 19720, USA ABSTRACT Physical aging of amorphous polyethylene
Physical Aging and Fragility of Amorphous Polyethylene Terephthalate R. Bruce Cassel, Ph.D. TA Instruments, 109 Lukens Drive, New Castle, DE 19720, USA ABSTRACT Physical aging of amorphous polyethylene
CHEM 200/202. Professor Gregory P. Holland Office: GMCS-213C. All s are to be sent to:
 CHEM 200/202 Professor Gregory P. Holland Office: GMCS-213C All emails are to be sent to: chem200@mail.sdsu.edu My office hours will be held in GMCS-212 on Monday from 12:00 pm to 2:00 pm or by appointment.
CHEM 200/202 Professor Gregory P. Holland Office: GMCS-213C All emails are to be sent to: chem200@mail.sdsu.edu My office hours will be held in GMCS-212 on Monday from 12:00 pm to 2:00 pm or by appointment.
Effect of Die Bonding Condition for Die Attach Film Performance in 3D QFN Stacked Die.
 Effect of Die Bonding Condition for Die Attach Film Performance in 3D QFN Stacked Die. A. JALAR, M. F. ROSLE, M. A. A. HAMID. School of Applied Physics, Faculty of Science and Technology Universiti Kebangsaan
Effect of Die Bonding Condition for Die Attach Film Performance in 3D QFN Stacked Die. A. JALAR, M. F. ROSLE, M. A. A. HAMID. School of Applied Physics, Faculty of Science and Technology Universiti Kebangsaan
Chemical reactions and electrolysis
 Chemical reactions and electrolysis Higher Revision Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 95 minutes Marks: 95 marks Comments: Page of 29 (a) Magnesium metal is shaped to make magnesium ribbon. Explain why
Chemical reactions and electrolysis Higher Revision Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 95 minutes Marks: 95 marks Comments: Page of 29 (a) Magnesium metal is shaped to make magnesium ribbon. Explain why
Combining crystal structure and interaction topology for interpreting functional molecular solids: A study of theophylline cocrystals
 Combining crystal structure and interaction topology for interpreting functional molecular solids: A study of theophylline cocrystals Aditya B. Singaraju1, Kyle Nguyen1, Paula Gawedzki1, Fischer Herald1,
Combining crystal structure and interaction topology for interpreting functional molecular solids: A study of theophylline cocrystals Aditya B. Singaraju1, Kyle Nguyen1, Paula Gawedzki1, Fischer Herald1,
BORABU-MASABA DISTRICTS JOINT EVALUATION TEST 2012 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E)
 Name. School Candidate s Signature. Index No /. Date. 233/2 CHEMISTRY Paper 2 (Theory) JULY / AUGUST - 2012 Time: 2 Hours BORABU-MASABA DISTRICTS JOINT EVALUATION TEST 2012 Kenya Certificate of Secondary
Name. School Candidate s Signature. Index No /. Date. 233/2 CHEMISTRY Paper 2 (Theory) JULY / AUGUST - 2012 Time: 2 Hours BORABU-MASABA DISTRICTS JOINT EVALUATION TEST 2012 Kenya Certificate of Secondary
Supplementary Information.
 Supplementary Information. This file contains additional experimental and analytical information. The organic ionic plastic crystals were synthesised according to the literature procedures. 1-4 Chemicals:
Supplementary Information. This file contains additional experimental and analytical information. The organic ionic plastic crystals were synthesised according to the literature procedures. 1-4 Chemicals:
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2. (Two hours) You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
METALS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS
 METALS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS Metals are elements whose atoms ionize by electron loss, while non-metals are elements whose atoms ionize by electron gain. Metals are in groups 1, 2 and 3 of the periodic table.
METALS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS Metals are elements whose atoms ionize by electron loss, while non-metals are elements whose atoms ionize by electron gain. Metals are in groups 1, 2 and 3 of the periodic table.
Ultra purification of Ionic Liquids by Melt Crystallisation
 BIWIC 2006 p. 79 Ultra purification of Ionic Liquids by Melt Crystallisation Prof. Dr. A. König 1, Prof. Dr. P. Wasserscheid 2 1 Chair of Separation Science and Technology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg,
BIWIC 2006 p. 79 Ultra purification of Ionic Liquids by Melt Crystallisation Prof. Dr. A. König 1, Prof. Dr. P. Wasserscheid 2 1 Chair of Separation Science and Technology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg,
Experiment: Preparation of Adipic Acid by Oxidative Cleavage
 Experiment: Preparation of Adipic Acid by xidative Cleavage INTRDUCTIN The carbon-carbon double bond of an alkene is a site of relatively high electron density and therefore is susceptible to oxidation.
Experiment: Preparation of Adipic Acid by xidative Cleavage INTRDUCTIN The carbon-carbon double bond of an alkene is a site of relatively high electron density and therefore is susceptible to oxidation.
WJEC England GCSE Chemistry. Topic 11: Production, use and disposal of important chemicals and materials. Notes
 WJEC England GCSE Chemistry Topic 11: Production, use and disposal of important chemicals and materials Notes (Content in bold is for Higher Tier only) The Haber process Used to manufacture ammonia, which
WJEC England GCSE Chemistry Topic 11: Production, use and disposal of important chemicals and materials Notes (Content in bold is for Higher Tier only) The Haber process Used to manufacture ammonia, which
Laboratory Exercise #6 - Introduction to Oceanography
 Laboratory Exercise #6 - Introduction to Oceanography Page # - 1 A. Introduction Oceanography is obviously the study of the oceans. However, there are many different branches within the science of oceanography
Laboratory Exercise #6 - Introduction to Oceanography Page # - 1 A. Introduction Oceanography is obviously the study of the oceans. However, there are many different branches within the science of oceanography
Electrochemical cells use spontaneous redox reactions to convert chemical energy to electrical energy.
 ELECTROLYSIS: -the process of supplying electrical energy to a molten ionic compound or a solution containing ions so as to produce a chemical change (causing a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur).
ELECTROLYSIS: -the process of supplying electrical energy to a molten ionic compound or a solution containing ions so as to produce a chemical change (causing a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur).
High temperature oxidation of iron-iron oxide core-shell nanowires composed of iron nanoparticles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 High temperature oxidation of iron-iron oxide core-shell nanowires composed of
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 High temperature oxidation of iron-iron oxide core-shell nanowires composed of
Mechanical Properties of LDPE/Ethylene-1-butene Copolymer Films Crosslinked by Radiation
 J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 12, No. 6, (2006) 888-892 Mechanical Properties of LDPE/Ethylene-1-butene Copolymer Films Crosslinked by Radiation Young Chang Nho, Jeong Il Kim, and Phil Hyun Kang Radiation Application
J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 12, No. 6, (2006) 888-892 Mechanical Properties of LDPE/Ethylene-1-butene Copolymer Films Crosslinked by Radiation Young Chang Nho, Jeong Il Kim, and Phil Hyun Kang Radiation Application
MR. D HR UV AS HE R I.C.S.E. BOA RD PAP ER ICSE-2005
 MR D HR UV AS HE R ICSE BOA RD PAP ER 200 5 1 ICSE-2005 Section A (40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 (a) Write balanced equation s for the following reactions: - [5] (i) Potassium
MR D HR UV AS HE R ICSE BOA RD PAP ER 200 5 1 ICSE-2005 Section A (40 Marks) (Attempt all questions from this section) Question 1 (a) Write balanced equation s for the following reactions: - [5] (i) Potassium
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of anodizing concentration and electric potential on surface morphology and corrosion behavior of anodized magnesium in
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of anodizing concentration and electric potential on surface morphology and corrosion behavior of anodized magnesium in
MSE 352 Engineering Ceramics II
 Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi, Ghana MSE 352 Engineering Ceramics II Ing. Anthony Andrews (PhD) Department of Materials Engineering Faculty of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering
Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi, Ghana MSE 352 Engineering Ceramics II Ing. Anthony Andrews (PhD) Department of Materials Engineering Faculty of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering
DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes
 1 Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY Exam 14 PAPER 1 DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions - This paper consists of 50 compulsory objective questions - Answer the questions by writing the correct
1 Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY Exam 14 PAPER 1 DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions - This paper consists of 50 compulsory objective questions - Answer the questions by writing the correct
ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 1996
 ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 1996 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 1996 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
Thermoresponsive poly(ionic liquid) hydrogels
 Supporting information Thermoresponsive poly(ionic liquid) hydrogels Bartosz Ziółkowski and Dermot Diamond* a a CLARITY, The Centre for Sensor Web Technologies, National Centre for Sensor Research, School
Supporting information Thermoresponsive poly(ionic liquid) hydrogels Bartosz Ziółkowski and Dermot Diamond* a a CLARITY, The Centre for Sensor Web Technologies, National Centre for Sensor Research, School
Nanoconfinement Crystallization of Frustrated Alkyl Groups: Crossover of Mesophase to Crystalline Structure
 Nanoconfinement Crystallization of Frustrated Alkyl Groups: Crossover of Mesophase to Crystalline Structure Haifeng Shi,,,* Haixia Wang, John H. Xin, Xingxiang Zhang, and Dujin Wang, * State Key Laboratory
Nanoconfinement Crystallization of Frustrated Alkyl Groups: Crossover of Mesophase to Crystalline Structure Haifeng Shi,,,* Haixia Wang, John H. Xin, Xingxiang Zhang, and Dujin Wang, * State Key Laboratory
Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy
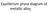 Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy Motivation New structure, concentration (mixing level) (at what temperature? for how long? ) Phase Diagrams - Introduction. Many materials systems can exist
Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy Motivation New structure, concentration (mixing level) (at what temperature? for how long? ) Phase Diagrams - Introduction. Many materials systems can exist
 Solid State-1 1) Ionic solids are characterised by 1) Good conductivity in solid state 2) High vapour pressure 3) Low melting point 4) Solubility in polar solvents 2) Three metals X, Y and Z are crystallised
Solid State-1 1) Ionic solids are characterised by 1) Good conductivity in solid state 2) High vapour pressure 3) Low melting point 4) Solubility in polar solvents 2) Three metals X, Y and Z are crystallised
SEAWATER 101. Seawater s Amazing Physical and Chemical Properties. Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor
 SEAWATER 101 Seawater s Amazing Physical and Chemical Properties Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor The Nature of Water Topics To Be Covered Elements of Water Chemical Bonding The Water
SEAWATER 101 Seawater s Amazing Physical and Chemical Properties Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor The Nature of Water Topics To Be Covered Elements of Water Chemical Bonding The Water
(06) WMP/Jun10/CHEM5
 Period 3 Elements 6 2 Sodium, aluminium and silicon are solid elements with a silver colour. These elements react with oxygen to form oxides with high melting points. Aluminium is a reactive metal, but
Period 3 Elements 6 2 Sodium, aluminium and silicon are solid elements with a silver colour. These elements react with oxygen to form oxides with high melting points. Aluminium is a reactive metal, but
7. Experimental. 7.1 Flame retardant treatment
 7. Experimental 7.1 Flame retardant treatment Unsized polyester fabric (150 g/m2) was obtained from Wesco Fabrics. The fabrics were woven from fibre produced by South African Nylon Spinners (SANS). The
7. Experimental 7.1 Flame retardant treatment Unsized polyester fabric (150 g/m2) was obtained from Wesco Fabrics. The fabrics were woven from fibre produced by South African Nylon Spinners (SANS). The
Chapter Overview. Water molecule. Atomic Structure. Hydrogen Bonding. Hydrogen Bonding. CHAPTER 5 Water and Seawater
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 5 Water and Seawater Water has many unique thermal and dissolving properties. Seawater is mostly water molecules but has dissolved substances. Ocean is layered by salinity and
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 5 Water and Seawater Water has many unique thermal and dissolving properties. Seawater is mostly water molecules but has dissolved substances. Ocean is layered by salinity and
Topic 9 National 4 Chemistry Summary Notes. Metals and Alloys. Materials
 Topic 9 National 4 Chemistry Summary Notes Metals and Alloys LI 1 Materials Materials are all substances and include: metals ceramics plastics natural substances novel substances. Materials can be used
Topic 9 National 4 Chemistry Summary Notes Metals and Alloys LI 1 Materials Materials are all substances and include: metals ceramics plastics natural substances novel substances. Materials can be used
MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM)
 MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady Department of Geology Smith College Northampton, MA 01063 jbrady@science.smith.edu INTRODUCTION When two cations have the same
MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady Department of Geology Smith College Northampton, MA 01063 jbrady@science.smith.edu INTRODUCTION When two cations have the same
TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III
 Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III Topic 2.3: Crystalline defects. Solid solutions. 1 PERFECT AND IMPERFECT CRYSTALS Perfect
Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III Topic 2.3: Crystalline defects. Solid solutions. 1 PERFECT AND IMPERFECT CRYSTALS Perfect
Trimethyl Gallium.-(1) Preparation. We prepared trimethyl gallium. capillary B. When it was desired to withdraw dimethyl zinc, the ampule
 292 CHEMISTRY: KRA US AND TOONDER PROC. N. A. S. TRIMETHYL GALLIUM, TRIMETHYL GALLIUM ETHERATE AND TRIMETHYL GALLIUM AMMINE BY CHARLrEs A. KRAUS AND FRANK E. TOONDER' CHEmcAL LABORATORY, BROWN UNIVERSITY
292 CHEMISTRY: KRA US AND TOONDER PROC. N. A. S. TRIMETHYL GALLIUM, TRIMETHYL GALLIUM ETHERATE AND TRIMETHYL GALLIUM AMMINE BY CHARLrEs A. KRAUS AND FRANK E. TOONDER' CHEmcAL LABORATORY, BROWN UNIVERSITY
MELTING POINT DEPRESSION OF IONIC SALTS INDUCED BY COMPRESSED CARBON DIOXIDE
 MELTIG POIT DEPRESSIO OF IOIC SALTS IDUCED BY COMPRESSED CARBO DIOXIDE M. Manic 1, A. Serbanovic 1, A.R. Sampaio de Sousa 1, Gonçalo B.S.M. Carrera 2, Z. Petrovski 1, Luís C. Branco 1, Carlos A.M. Afonso
MELTIG POIT DEPRESSIO OF IOIC SALTS IDUCED BY COMPRESSED CARBO DIOXIDE M. Manic 1, A. Serbanovic 1, A.R. Sampaio de Sousa 1, Gonçalo B.S.M. Carrera 2, Z. Petrovski 1, Luís C. Branco 1, Carlos A.M. Afonso
Explain whether this process is oxidation or reduction.
 1 Electroplating steel objects with silver involves a three-step process. step 1 A coating of copper is applied to the object. step 2 A coating of nickel is applied to the object. step 3 The coating of
1 Electroplating steel objects with silver involves a three-step process. step 1 A coating of copper is applied to the object. step 2 A coating of nickel is applied to the object. step 3 The coating of
G Trap Ion Exchange Selection Kit
 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name G Trap Ion Exchange Selection Kit CM, DEAE, Q and SP Agarose Fast Flow columns (Cat. # 786
G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name G Trap Ion Exchange Selection Kit CM, DEAE, Q and SP Agarose Fast Flow columns (Cat. # 786
There are many types of alloying systems which they are:
 Phase Equilibrium Diagrams:- Phase equilibrium diagram is a graphic relationship between temperature and weight ratios of elements and alloys contribute to the built of the diagram. Where Phase is a uniform
Phase Equilibrium Diagrams:- Phase equilibrium diagram is a graphic relationship between temperature and weight ratios of elements and alloys contribute to the built of the diagram. Where Phase is a uniform
LAB II CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND CRYSTAL GROWTH PART 1: CRYSTAL GROWTH. I. Introduction
 LAB II CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND CRYSTAL GROWTH This lab will be divided into two parts. In the first part, you will be growing crystals from a seed crystal in a very visual demonstration of heterogeneous
LAB II CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND CRYSTAL GROWTH This lab will be divided into two parts. In the first part, you will be growing crystals from a seed crystal in a very visual demonstration of heterogeneous
Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Some Oxazole and Thiazole Derivatives
 Human Journals Research Article February 15 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Sujit Kumar Mohanty et al. Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Some Oxazole and Thiazole Derivatives
Human Journals Research Article February 15 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Sujit Kumar Mohanty et al. Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Some Oxazole and Thiazole Derivatives
Thermodynamics of C60 Solutes in Three Non-Aqueous Solvents
 Thermodynamics of C60 Solutes in Three Non-Aqueous Solvents William Steinsmith, MD 11-19-13 Buckyball molecules (C60) forming solutes in any of three organic solvents have a eutectic-cusp triple-point
Thermodynamics of C60 Solutes in Three Non-Aqueous Solvents William Steinsmith, MD 11-19-13 Buckyball molecules (C60) forming solutes in any of three organic solvents have a eutectic-cusp triple-point
A NEW APPROACH TO THE PROBLEM OF CORROSION CONTROL IN MARINE ENVIRONMENT. By Boris A. Miksic. Published: November-December 1975 Marine Equipment News
 A NEW APPROACH TO THE PROBLEM OF CORROSION CONTROL IN MARINE ENVIRONMENT By Boris A. Miksic Published: November-December 1975 Marine Equipment News Boris A. Miksic is a senior research engineer with Northern
A NEW APPROACH TO THE PROBLEM OF CORROSION CONTROL IN MARINE ENVIRONMENT By Boris A. Miksic Published: November-December 1975 Marine Equipment News Boris A. Miksic is a senior research engineer with Northern
Metallic Materials-Phase Diagrams
 Engineering Alloys Metals and alloys have many useful engineering properties and so have wide spread application in engineering designs. Iron and its alloys (principally steel) account for about 90 percent
Engineering Alloys Metals and alloys have many useful engineering properties and so have wide spread application in engineering designs. Iron and its alloys (principally steel) account for about 90 percent
19. The preparation and purification of methyl-3-nitrobenzoate Student Sheet
 19. The preparation and purification of methyl-3-nitrobenzoate Student Sheet In this experiment you will learn or develop skills in preparative organic chemistry by making and purifying a sample of an
19. The preparation and purification of methyl-3-nitrobenzoate Student Sheet In this experiment you will learn or develop skills in preparative organic chemistry by making and purifying a sample of an
Sodium, Na. Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 7.3 to 7.5.
 Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 7.3 to 7.5 Forms of Carbon How do the group 13 elements differ? Boron is a metalloid (i.e.
Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 7.3 to 7.5 Forms of Carbon How do the group 13 elements differ? Boron is a metalloid (i.e.
Analysis of plating grain size effect on whisker
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 23 (2009) 2885~2890 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-009-0720-x Analysis of plating grain
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 23 (2009) 2885~2890 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-009-0720-x Analysis of plating grain
INVESTIGATION OF THE POLYMORPHISM OF SULFATHIAZOLE BY A COMBINED DSC-HSM APPROACH
 INVESTIGATION OF THE POLYMORPHISM OF SULFATHIAZOLE BY A COMBINED DSC-HSM APPROACH M. R. Abu Bakar, C. D. Rielly, Z. K. Nagy Department of Chemical Engineering, Loughborough University, Loughborough, Leics.,
INVESTIGATION OF THE POLYMORPHISM OF SULFATHIAZOLE BY A COMBINED DSC-HSM APPROACH M. R. Abu Bakar, C. D. Rielly, Z. K. Nagy Department of Chemical Engineering, Loughborough University, Loughborough, Leics.,
Q1.A student investigated the temperature change when zinc reacts with copper sulfate solution.
 Q1.A student investigated the temperature change when zinc reacts with copper sulfate solution. The student used a different concentration of copper sulfate solution for each experiment. The student used
Q1.A student investigated the temperature change when zinc reacts with copper sulfate solution. The student used a different concentration of copper sulfate solution for each experiment. The student used
Crystallization & Filtration
 Crystallization & Filtration Purification of Salicyclic Acid and Sodium Chloride Separation processes Liquid-liquid extraction Adsorption Filtration Solid-liquid extraction (leaching) Elution chromatography
Crystallization & Filtration Purification of Salicyclic Acid and Sodium Chloride Separation processes Liquid-liquid extraction Adsorption Filtration Solid-liquid extraction (leaching) Elution chromatography
Electrochemical properties of alkal. Citation Electrochimica Acta (2010), 55(3):
 KURENAI : Kyoto University Researc Title Electrochemical properties of alkal bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amides Author(s) Kubota, Keigo; Tamaki, Kenichiro; N Takuya; Hagiwara, Rika Citation Electrochimica
KURENAI : Kyoto University Researc Title Electrochemical properties of alkal bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amides Author(s) Kubota, Keigo; Tamaki, Kenichiro; N Takuya; Hagiwara, Rika Citation Electrochimica
mixtures of alkali bis(fluorosulfon Author(s) Kubota, Keigo; Nohira, Toshiyuki; H Citation Electrochimica Acta (2012), 66: 320
 New inorganic ionic liquids Titletemperatures and wide electrochemic possess mixtures of alkali bis(fluorosulfon Author(s) Kubota, Keigo; Nohira, Toshiyuki; H Citation Electrochimica Acta (2012), 66: 320
New inorganic ionic liquids Titletemperatures and wide electrochemic possess mixtures of alkali bis(fluorosulfon Author(s) Kubota, Keigo; Nohira, Toshiyuki; H Citation Electrochimica Acta (2012), 66: 320
Thermal Analysis. Dr. Lidia Tajber School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin
 Thermal Analysis Dr. Lidia Tajber School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin Characterisation for Pharma Active pharmaceutical ingredients (API, drugs) Organic molecules, peptides,
Thermal Analysis Dr. Lidia Tajber School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin Characterisation for Pharma Active pharmaceutical ingredients (API, drugs) Organic molecules, peptides,
