Oxygen reaction on titanium catalysed by gold, platinum and palladium*
|
|
|
- Maude Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY 14 (1984) Oxygen reaction on titanium catalysed by gold, platinum and palladium* R. ZEJNILOVIC, M. PJEg~I(~, M. gljuki~ Faculty of Metallurgy, University of Titograd, Titog-rad, Yugoslavia A. R. DESPI~ Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy, University of Beograd, Beograd, Yugoslavia Received 11 July 1983; revised 6 October 1983 Electrocatalytic properties of titanium surfaces coated with small amounts ( mg cm -2) of Au, Pt, Pd and their mixtures, with respect to both oxygen evolution and reduction in alkaline solution have been investigated. It was found that all the samples exhibited higher electrochemical activity than the corresponding compact metal surfaces. This could be ascribed to a larger specific surface area of the dispersed catalysis than that of the smooth metal surfaces. The best performance was obtained with dispersed palladium, the potential gap between oxygen evolution and reduction at 1 macm -2 being reduced to 0.66 V. 1. Introduction Titanium is known to be a very suitable electrode material for industrial electrochemical applications especially for anodic processes involving gas evolution. In attempts to carry out the reverse cathodic reduction processes, e.g. in fuel cells, other materials have been used such as carbon or other more expensive metals (nickel, silver) with significantly higher specific weight. Since carbon cannot be used for rechargeable batteries of the fuel cell or hybride type (e.g. metal-oxygen cells) a metal carrier becomes unavoidable. In spite of its obvious advantages, no attempt to use titanium as a base for gas diffusion rechargeable electrodes, has so far been published. Since porous titanium bodies can be obtained by sintering titanium powder without difficulty, it was considered worthwhile to investigate the possibility of finding materials which would make the titanium surface catalytically active for both the anodic and the cathodic process in the electrochemical reaction of oxygen in alkaline solutions. Much work has been reported in the field of electrocatalysis of the oxygen reaction not only with respect to types of catalysts but also to modes of preparation, the latter having a major effect on performance (e.g. [1]). However, in the work cited the emphasis has been on reducing polarization and increasing stability in either the cathodic or the anodic process. Little attempt has been made to investigate the problem of dual function of the electrode, i.e. to overcome or reduce the potential gap between cathodic and anodic polarization and investigate stability under such changing directions of current. In the present work the whole noble metal group of catalysts, chemically deposited on titanium, was scanned, but only results obtained with gold, platinum and palladium are reported here. Investigation has been undertaken of the behaviour of the metals alone or in mixtures deposited on compact titanium surfaces in small amounts ranging from to 0.6 mg cm -2. The structure of the deposits has been investigated by X-ray and electronic microscopy. Electrochemical investigations involved obtaining * Reported in part at the 3ist Meeting of ISE, Venice, September X/84 $ Chapman and Hall Ltd. 481
2 482 R. ZEJNILOVI(~, A. R. DESPI(~, M. PJE~(['I(~ AND M. SLJUKII2 (a) potential sweep voltammograms both for electrodes in the absence of any electrochemically active gas, and in the presence of oxygen in solution; (b) steady-state potentiostatic polarization curves for both oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution on titanium plated with gold, platinum, palladium and their mixtures. Since palladium exhibited the most promising properties, some additional electrochemical investigations have been performed with this metal. 2. Experimental details Compact commercial grade titanium was made in the form of flat cylinders (8 mm in diameter) for use in a rotating disc electrode assembly. For structural investigations the discs were mirror polished by the usual techniques prior to depositing the catalysts. The adherence to such surfaces was, however, rather poor so that catalysts could not withstand anodic polarization for more than a few hours. Therefore, for electrochemical investigations, the polished surface of the cyclinders was etched in a mixture of 10% HC1 and 10% H2C204"2H20, and then in 5% HNO3 for 30 min. This made the surface evenly dim. The noble metal catalysts were introduced to the titanium surfaces from corresponding acid aqueous solutions of their chlorides (of concentration 2-5 mg cm -a) spread by means of a micropipette in a volume sufficient to deposit a desired amount of metal. After evaporating water and acid, the samples were heated in a laboratory kiln open to the atmosphere at 500~ for 3 h. Mixed noble metal catalysts were made by mixing solutions in the desired proportion before spreading. X-ray analysis of the surface structure was made with a Phillips PW 1730 X-ray assembly with a vertical goniometer PW 1050 and a nonrotating sample holder. The Bragg method was applied using a copper tube at 35 kv (20 ma) with the radiation filtered through an AMR graphite monochromator. The identification was done using ASTM tables. Scanning electron microscopy of the sample surfaces was carried out with a JSM-35 JEOL instrument, with magnification ranging from 200 to Electrochemical properties were assessed by recording potential sweep voltammograms and steady-state polarization curves under hydrodynamic conditions provided by rotating the electrode. Potential sweep investigations were performed using Stonehart BC 1200 and PAR M 173 potentiostats with a universal programmer PAR M 175 and a Hewlett-Packard 7015 B X-Y recorder. The same equipment and a Hewlett-Packard 412 A voltameter was used for steady-state potentiostatic investigations. The electrochemical cell was fitted with a home-made rotating disc electrode assembly. A Hg/HgO reference electrode in the same solution was connected to the rotating disc via a Luggin capillary. The cell was closed and insulated from the atmosphere in the usual manner. The solution was 1 M in NaOH made up using triply distilled water. The potential sweep voltammogram for platinum was used as a criterion of purity. Gaseous nitrogen, purified through molecular sieves and over copper turnings, was bubbled through the cell for measurements made in the absence of oxygen. For those made in the presence of the latter, oxygen gas was also purified through molecular sieves. The temperature was maintained at 25~ 3. Results 3.1. X-ray The X-ray reflections obtained with different catalytic surfaces are summarized in Fig. 1. Besides the titanium base and its surface oxide, they revealed the presence of pure noble metal phases as well as some mixed phases (intermetallic compounds and solid solutions) of all the noble metals with titanium [2]. The alloy of gold with platinum and palladium also gave some weak reflection. There was some proportionality between the amount of all the deposited metals and the intensities of their reflections. No such proportionality was found for the AuTi3 phase however. The intensity of reflections from that phase was more or less constant, indicating that it is formed only at the roots of the noble metal grains.
3 OXYGEN REACTION ON Ti CATALYSED BY Au, Pt AND Pd 483 4~176 t J mgcm-2 3 T[ 05 o Au [] Pd ~ u Yi 3 --Ti2Pd Au *Ti Fig. 1. X-ray analysis of electrodes of titanium catalysed by noble metals. (I/11 = ratio of intensity of the given phase to that of titanium base.) 9 Au; o Au + Ti; e AuTi3; Pt; + Pt~Ti; ~ Pd;9 Ti2Pd;,7 Pd+ Ti Electron microscopy The granular structure of the deposit could be particularly well seen by scanning electron microscopy in the case of gold, as shown in Fig. 2. Tulip-form gold particles were of the order of 1-2/~m in diameter. The deposit of palladium was of a finer grain structure while in the mixed palladium-gold deposit, separate gold particles could be seen although of almost an order of magnitude smaller in size than in the case of pure gold Potential sweep voltammograms in the absence of oxygen The voltammograms obtained with titanium coated by the three pure noble metal catalysts are compared in Figs. 3-5 with those for the corresponding compact metals. It is seen that in the case of gold some inhibition of oxide formation arises. Conversely, in the case of platinum and palladium the metal dispersed on titanium exhibits considerably higher activities both in the oxidation and reduction of the noble metal as well as for hydrogen evolution. For palladium a new peak appears at V vs standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). In the anodic direction there are two peaks corresponding to oxidation of hydrogen at and V vs SHE (compared to a single peak at V for compact palladium) and an oxidation wave with E1/2 = 0.2 V. Voltammograms for titanium coated with mixed catalysts, obtained by mixing gold solution with those containing Pt and Pd are shown in Fig. 6. Combinations of gold with platinum and palladium are seen to give voltammograms in which those of pure metals seem to be superimposed upon each other. It is worth noting the potentials of the peaks for the reduction of the noble metal oxides as given in Table 1, since they determine whether the oxygen reduction should take place on oxide covered or bare metal surfaces Potential sweep voltammograms in the presence of oxygen The voltammograms for gold-plated titanium are shown in Fig. 7, compared to that for compact gold [3]. It is seen that the catalyst plated on the polished titanium surface exhibits smaller activity (reduction current at a given potential) than the compact metal. That plated on the etched surface, however, exhibits a larger activity. Characteristic are two reduction waves. The height of the second wave at a given rotation speed is the same as those obtained on platinum or palladium (cf. Figs. 8 and 9) while that of the first wave tends to be half that of the second wave. The half-wave potentials are listed in Table 2. There is little difference between those obtained with the cathodic and the anodic sweep. The catalyst at the etched titanium, however, exhibits a higher catalytic activity (more positive half-wave potential) than compact gold. The same applies to platinum [4] coated on etched titanium as seen in Fig. 8. The higher catalytic activity (cf. Table 2) coincides with increased pseudo-capacitance, higher oxide
4 484 R. ZEJNILOVI(~, A. R. DESPI(~, M. PJE~CI(~ AND M. ~LJUKI(~ Fig. 2. Scanning electron micrograph of titanium surface covered by gold particles: (a) 2000 (b) X. reduction peaks and an increased diffusion limiting current of almost 50%, reflecting the effect of surface roughening on the hydrodynamics of the rotating disc. There is not much difference in E1/2 between the cathodic and the anodic sweep although the large difference in the beginning of the limiting current plateau indicates that the reduction of the oxide in the cathodic sweep occurs only at potentials more negative than Ell2. The opposite case is found with palladium [5], as shown in Fig. 9. There, the E1/2 for oxygen reduction on the oxide covered surface (cathodic sweep) is significantly more negative (about 200 mv) than that on the reduced surface (anodic sweep). Reduction of the oxide on palladium is well expressed as the peak in the cathodic sweep. In the anodic sweep the dip in the oxygen reduction limiting current plateau is due to the reduction of hydrogen imbibed during hydrogen evolution at the cathodic limit of the sweep. On both platinum and palladium a single reduction wave is observed. It was considered interesting to discover to r',d\ 100mVls /~ 100r-~Vls Au/comp 0.25mA. F,,/ A~,/Ti, H \ / \j Fig. 3. Potential sweep voltammograms for compact gold and gold deposited on titanium in 1M NaOH in the absence of oxygen (sweep rate of 100 mv s-l). Fig. 4. Potential sweep voltammograms for compact platinum and platinum deposited on titanium in 1M NaOH in the absence of oxygen (sweep rate 100 mv s-l).
5 OXYGEN REACTION ON Ti CATALYSED BY Au, Pt AND Pd rn2?nj3V 5s '/f7 <'a,,/"f:"= U Table 1. Potentials of the reduction peaks of oxides Sample Ep {V vs SHE) Recorded Remarks at sweep rate (mvs -a) Au(Comp) Au(Ti) Pt(Comp) Pt (Ti) Pd(Comp) Pd(Ti) to increased, depending on anodic limit Fig. 5. Potential sweep voltammograms for compact palladium and palladium deposited on titanium in 1M NaOH in the absence of oxygen (sweep rate 1130 mv s-a). what extent the amounts of Pt and Pd on titanium can be reduced without significant loss of the catalytic activity. Hence, the contents of these metals were varied, from 0.6 mg cm -2 downwards. It was found that half-wave potentials did not change with contents of 0.07 and 0.05 mg cm -2 of Pt and Pd respectively. However, sharp changes in the negative direction occurred beyond these limits. Potential sweep voltammograms for mixed noble metal catalysts are shown in Fig. 10. Addition of platinum and palladium to gold i. N i" / x 100mVls.. /9 I ~,..... AI I /: ", Q25mA~ "... " J'iJ l." " \... ~'~ -"J... /.." ". ~,,... L... I... ~"...x~;.. /..... f ~ i "." ~" "'" I ""..... " [J, -.-" \\ '-.. I.-" Au/]5 I!",, '4.'. lj r:. :" I. i'- "" " "-" 0~ " Au 102Ft/q ~1 \ I Au i 02Pd/Ti I II Fig. 6. Potential sweep voltammogmms for compact gold and combination coatings of titanium with gold and platinum and gold and palladium, in 1M NaOH in the absence of oxygen (sweep rate 100 mv s-a). J is seen to eliminate the first wave. Hence, the diffusion limiting currents become similar to those for pure palladium and palladium catalyst. Other characteristics of the voltammograms for the latter two metals (cf. Figs. 10 and 11) also mask those of gold except for the reduction peak of the oxide of the latter which is seen clearly before the beginning of the oxygen reduction wave. The catalytic activities (cf. Table 2) of the mixed catalysts are higher than that of pure gold but lower than that on pure platinum and palladium. The effects of varying the metal-to-metal ratio in the case of Au-Pd mixtures are seen in Fig. 11. The effect of gold is seen in the fact that the surface is more active in the cathodic sweep than that with pure palladium. The height of the oxide reduction peak at the beginning of the diffusion limiting current plateau is proportional to the palladium content in the mixture. The catalytic effect in the anodic sweep seems to pass through a minimum with the Ev2 changing from + 30 through + 10 to + 60 mv vs SHE for palladium contents of 0.2, 0.4 and 0.6 g cm -2, respectively Steady-state polarization measurements As already indicated by the potential sweep voltammograms, transport of oxygen from the bulk of solution in the cathodic reduction process leads to a diffusion limited current density. The latter was, as has been proven by the fact that it followed closely the Levich dependence
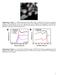
6 486 R. ZEJNILOVId, A. R. DESPI~, M. PJE~dIC AND M. ~LJUKIC 025mA o,, ~" ~,,,.~.--~/ E,~ ;;=.. L--~ ==:~ /97'-~ "~..;~-y-~ Au/com p '7/ff "j.,,j/. / / / ~ " Au/]] nonpotished I/ i~ / Fig. 7. Same as Fig. 3 but in the presence of oxygen in solution. on the square root of the speed of rotation of the disc electrode [6]. Hence, in making the steadystate polarization plots this effect has been corrected for, by using corrected current density values, lc~ i i c =.. i D (1) ld--l where id is the diffusion limiting current density, and i is the measured current density value. In such a way Fig. 12 was obtained for pure noble metal catalysts. It can be seen that gold exhibits the lowest catalytic activity of the three metals. At low current densities it gives linear Tafel functions with slopes of RT/F in both cathodic and anodic directions. In both directions there is appreciable curving at higher current densities which cannot be ascribed to difficulties in transport. The most active catalyst for both the anodic and cathodic process is palladium plated on titanium, giving linear Tafel functions in both directions with 120 and 40 mv decade -1 slopes, respectively. The cathodic Tafel line seems to start at the peroxide reduction potential, since the anodic lines also tend to a reversible potential other than that of 02 reduction at low current densities (dashed line). In general, metals plated on titanium gave larger current density values at a given potential than the compact metals alone. The polarization in the case of mixed Au-Pd catalysts was between those of pure gold and palladium. Table 3 lists loomv 5s 0251A~-* ~ loomv5s / Jli!,,, EH,if...~'f-,, Pd/cornp/" tl,;, II Pt/comp 4 ~ //! Pt/Ti Fig. 8. Same as Fig. 4 but in the presence of oxygen in solution. Fig. 9. Same as Fig. 5 but in the presence of oxygen in solution.
7 OXYGEN REACTION ON Ti CATALYSED BY Au, Pt AND Pd 487 Table 2. Half-wave potentials of oxygen reduction in 1M NaOH at different catalytic surfaces Ell 2 (m V vs SHE) Surface On oxidized On reduced surface surface Au-compact Au (0.6*) on Ti Pt-compact Pt (0.4) on Ti Pd-compact Pd (0.6) on Ti current densities at typical anodic and cathodic potentials as well as the potential gap at a common current density of 1 ma cm %V5s 025mA U! 0.2Au i 06Pd/Ti/ 0.4Au i 0.4Pd/Ti/ -,- 0.6Au i 0.2Pd/Ti/ 4. Discussion The noble metals are seen to plate upon titanium with some interaction with the substrate, or with each other when plated in a mixture. The interaction with titanium seems to provide a well conducting contact and satisfactory adhesion, especially when the titanium surface is roughened by etching. However, in most cases these interactions seem to play little role in the electrochemical behaviour t00rnvls...,.---" 9 -' ",4.." --~..~ / i t i H ~ - ~. ' ~..~.,,:..~... i i, L L L [ i. -~2''" i,,~!,q_ A0 02e/T /"/-: _.---%" / Y? /-" / ilf.....,...- fi!..... / if/ \: "F!j!j r I Fig. 10. Same as Fig. 6 but in the presence of oxygen in solution. Fig. 11. Potential sweep voltammograms of titanium covered by mixed noble metal catalysts of varying metalto-metal ratio in 1M NaOH in the presence of oxygen in solution (sweep rate 100 mv s-l). of the catalyst. This could be concluded by inspection of the potential sweep voltammograms. In the absence of oxygen in solution, with the exception of palladium, the voltammograms for the catalysts dispersed upon the titanium surface in qualitative aspects reproduce those of the corresponding compact metals. Neither new peaks nor significant shifts of peak potentials are found. In the case of palladium, interaction with the substrate seems to play a significant role. The changes in the voltammogram compared to the compact metal could hardly be accounted for by assuming a high degree of dispersion (increased surface roughness factor) of palladium. The fact that no new features are found with mixed metal catalysts compared to pure metals, indicates that their alloying plays no significant role. Similarly the slopes of the Tafel plots indicate that oxygen reduction and evolution on catalysts dispersed on titanium follow the same mechanism as on the corresponding compact metal surfaces. The activities of the dispersed catalysts, however, differ significantly from those
8 488 R. ZEJNILOVIC, A. R. DESPIC, M. PJE~CIC AND M. ~LJUKIC 80( 9,~'#;:f!~ r 60( 40( 2O( ~ / // // w ~ ".* ( -80~ 9 oi~ t,o " L. LD/(Lo-L)(mAcm-2 ) " lo, o Fig. 12. Steady-state polarization measurements of oxygen evolution and reduction on compact gold, platinum and pauadium as well as on those deposited on titanium, in I M NaOH. o Au; 9 Au(Ti); u Pt; 9 Pt(Ti); z~ Pd; 9 Pd(Ti). of the compact metal, in most cases being higher at the former. It is questionable if they are accounted for by merely an increase in surface roughness. Palladium is seen to be the best catalyst of the three metals investigated as far as the electrochemical properties are concerned. The problem of its stability was outside the scope of this work, but within hours of its investigation no indication of a fast degradation was found. Even though the investigated metals proved to be rather good catalysts for both reduction and evolution of oxygen, the potential gap could not be said to have been overcome. It is a likely consequence of the different mechanisms of the cathodic and anodic processes. The deviations of the anodic polarization curves at low current densities towards a potential more negative than the thermodynamic reversible potential of oxygen (denoted in Fig. 12) indicates that the open circuit potential is determined basically by the reaction of the peroxide present in the vicinity of the electrode. References [ 1 ] E. Yeager, in 'Proceedings of the Workshop on Electrocatalysis on Nonmetallic Surface', National Bureau of Standards Special Publication 455, 9-12 December, [2] Power Diffraction File, ICPDS, Pennsylvania, USA (1974). [3] R.W. ZuriUa, R. K. Sen and E. Yeager, J. Electrochem. Soc. 125 (1978) [4] A. Damjanovi6, M. A. Genshaw and J. O'M. Bockris, ibid. 114 (1967) 466. [5] A. Damjanovid and V. Brusi6, Electrochim. Acta 11 (1966) 791. [6] V.G. Levich, Acta Physicochim URSS 17 (1942) 257. Table 3. Current densities at constant potentials and potential gap at a constant current density for different catalysts Catalyst Jan (700 m V vs SHE] icath (---1 O0 m V SHE) AE(1 ma cm-2) (ma cm-:) (ma cm -2) (V) Au(comp) Au(Ti) Pt(comp) Pt(Ti) Pd(comp) Pd(Ti) Au Pd(Ti) Au Pd(Ti) Au Pd(Ti)
THE ELECTROLYTIC DEPOSITION OF CARBON FROM MOLTEN Li 2 CO 3
 THE ELECTROLYTIC DEPOSITION OF CARBON FROM MOLTEN LJ 2 COT THE ELECTROLYTIC DEPOSITION OF CARBON FROM MOLTEN Li 2 CO 3 ii I n>11111 III : MK0400059 A.T.Dimitrov!. - Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy,
THE ELECTROLYTIC DEPOSITION OF CARBON FROM MOLTEN LJ 2 COT THE ELECTROLYTIC DEPOSITION OF CARBON FROM MOLTEN Li 2 CO 3 ii I n>11111 III : MK0400059 A.T.Dimitrov!. - Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy,
sensors ISSN by MDPI
 Sensors 27, 7, 1-15 Full Paper sensors ISSN 1424-822 27 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.org/sensors Determination of Critical Conditions for the Formation of Electrodeposited Copper Structures Suitable for Electrodes
Sensors 27, 7, 1-15 Full Paper sensors ISSN 1424-822 27 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.org/sensors Determination of Critical Conditions for the Formation of Electrodeposited Copper Structures Suitable for Electrodes
Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction
 Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction Jing-Fang Huang,* a and Wen-Rhone Chang a Supporting information Experimental Section
Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction Jing-Fang Huang,* a and Wen-Rhone Chang a Supporting information Experimental Section
Potentiodynamic Scanning (PDS) of Stainless Steel Karen Louise de Sousa Pesse
 Potentiodynamic Scanning (PDS) of Stainless Steel 8-2-26 Supervision: Elien Wallaert Introduction In order to investigate the corrosion resistance of Stainless steel in a specific environment, the practical
Potentiodynamic Scanning (PDS) of Stainless Steel 8-2-26 Supervision: Elien Wallaert Introduction In order to investigate the corrosion resistance of Stainless steel in a specific environment, the practical
Supplementary Figure S1 TEM images. TEM images of mesoporous polymer nanospheres (MPNs-n) synthesized with different ethanol amount.
 Supplementary Figure S1 TEM images. TEM images of mesoporous polymer nanospheres (MPNs-n) synthesized with different ethanol amount. S1 Supplementary Figure S2 Photography. Photography illustration of
Supplementary Figure S1 TEM images. TEM images of mesoporous polymer nanospheres (MPNs-n) synthesized with different ethanol amount. S1 Supplementary Figure S2 Photography. Photography illustration of
Pulsed Electrodeposited Nickel Cerium for Hydrogen Production Studies 54
 Pulsed Electrodeposited Nickel Cerium for Hydrogen Production Studies 54 T. Sivaranjani 1, T.A. Revathy 1, K. Dhanapal 1, V. Narayanan 2, A. Stephen 1,a 1 Materials Science Centre, Department of Nuclear
Pulsed Electrodeposited Nickel Cerium for Hydrogen Production Studies 54 T. Sivaranjani 1, T.A. Revathy 1, K. Dhanapal 1, V. Narayanan 2, A. Stephen 1,a 1 Materials Science Centre, Department of Nuclear
PULSE ELECTRODEPOSITION OF Pt Co CATALYST ONTO GLASSY CARBON FOR OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION TO USE IN PEMFC
 PULSE ELECTRODEPOSITION OF Pt Co CATALYST ONTO GLASSY CARBON FOR OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION TO USE IN PEMFC Jittima Sriwannaboot a,b, Nisit Tantavichet a,b,* a) Center of Excellence on Petrochemical and
PULSE ELECTRODEPOSITION OF Pt Co CATALYST ONTO GLASSY CARBON FOR OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION TO USE IN PEMFC Jittima Sriwannaboot a,b, Nisit Tantavichet a,b,* a) Center of Excellence on Petrochemical and
Kinetic Characteristics of Different Materials used for Bolting Applications
 Kinetic Characteristics of Different Materials used for Bolting Applications Report Kinetic Characteristics of Different Materials used for Bolting Applications Overview One of the most common problems
Kinetic Characteristics of Different Materials used for Bolting Applications Report Kinetic Characteristics of Different Materials used for Bolting Applications Overview One of the most common problems
Corrosion Rate Measurement on C-Steel
 Measurements of corrosion rate on Carbon-steel using Electrochemical (potentiodynamic Polarization, EIS etc.) technique. Corrosion Rate Measurement on C-Steel Abdullah Al Ashraf 1. Introduction: The degradation
Measurements of corrosion rate on Carbon-steel using Electrochemical (potentiodynamic Polarization, EIS etc.) technique. Corrosion Rate Measurement on C-Steel Abdullah Al Ashraf 1. Introduction: The degradation
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Experimental Methods Pt ALD. The precursor used for ALD was trimethyl-methylcyclopentadienyl-platinum(iv) (MeCpPtMe 3 ) (Strem Chemicals, 99%), which has been widely reported for
Supporting Information Experimental Methods Pt ALD. The precursor used for ALD was trimethyl-methylcyclopentadienyl-platinum(iv) (MeCpPtMe 3 ) (Strem Chemicals, 99%), which has been widely reported for
CORROSION & ITS CONTROL -Content. Introduction Classification Galvanic series Factors affecting Protection methods Summary
 CORROSION & ITS CONTROL -Content Introduction Classification Galvanic series Factors affecting Protection methods Summary 3 Learning Objectives At the end of the chapter the learner will be able to; 1.
CORROSION & ITS CONTROL -Content Introduction Classification Galvanic series Factors affecting Protection methods Summary 3 Learning Objectives At the end of the chapter the learner will be able to; 1.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Title: Platinum Particles Supported On Titanium Nitride: An Efficient Electrode Material for the Oxidation of Methanol in Alkaline Media Authors: M. M. Ottakam Thotiyl, T. Ravikumar
Supporting Information Title: Platinum Particles Supported On Titanium Nitride: An Efficient Electrode Material for the Oxidation of Methanol in Alkaline Media Authors: M. M. Ottakam Thotiyl, T. Ravikumar
Chapter 3. Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Glucose on Copper Oxide Modified Copper Electrode
 Chapter 3 Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Glucose on Copper Oxide Modified Copper Electrode 3. Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Glucose on Copper Oxide Modified Copper Electrode In order to combat the drawbacks
Chapter 3 Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Glucose on Copper Oxide Modified Copper Electrode 3. Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Glucose on Copper Oxide Modified Copper Electrode In order to combat the drawbacks
ELECTROCHEMICAL REDUCTION OF TITANIUM DIOXIDE THIN FILM IN LiCl-KCl-CaCl 2 EUTECTIC MELT
 ELECTROCHEMICAL REDUCTION OF TITANIUM DIOXIDE THIN FILM IN LiCl-KCl-CaCl 2 EUTECTIC MELT Yasushi Katayama Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University 3-14-1, Hiyoshi,
ELECTROCHEMICAL REDUCTION OF TITANIUM DIOXIDE THIN FILM IN LiCl-KCl-CaCl 2 EUTECTIC MELT Yasushi Katayama Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University 3-14-1, Hiyoshi,
Electrochemical response of permanent magnets in different solutions
 Electrochemical response of permanent magnets in different solutions G. Gaona-Tiburcio, F. Almeraya-Calderón, J. G. Chacón-Nava, J. A. Matutes-Aquino, A. Martínez-Villafañe Abstract Materials for permanent
Electrochemical response of permanent magnets in different solutions G. Gaona-Tiburcio, F. Almeraya-Calderón, J. G. Chacón-Nava, J. A. Matutes-Aquino, A. Martínez-Villafañe Abstract Materials for permanent
Improving Electrocatalytic Activity of LaNiO 3 Films by Deposition on Foam Nickel Substrates
 Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2011, 29(5), 335-342 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201105335 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Improving Electrocatalytic Activity of LaNiO 3 Films by Deposition on Foam
Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2011, 29(5), 335-342 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201105335 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Improving Electrocatalytic Activity of LaNiO 3 Films by Deposition on Foam
Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 14, March 2007, pp. 161-165 Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy V S Muralidharan Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi 630 006, India Received
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 14, March 2007, pp. 161-165 Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy V S Muralidharan Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi 630 006, India Received
Supplementary Figure 1. SEM and TEM images of CoO/CNF before and after galvanostatic cycles. (a) SEM image of CNF. (b) SEM image of CoO NPs uniformly
 Supplementary Figure 1. SEM and TEM images of CoO/CNF before and after galvanostatic cycles. (a) SEM image of CNF. (b) SEM image of CoO NPs uniformly distributed on CNF. (c) SEM image of 2-cycle CoO/CNF.
Supplementary Figure 1. SEM and TEM images of CoO/CNF before and after galvanostatic cycles. (a) SEM image of CNF. (b) SEM image of CoO NPs uniformly distributed on CNF. (c) SEM image of 2-cycle CoO/CNF.
ELECTROLYTIC PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Ni}Fe}Mo ALLOYS: CATHODE MATERIALS FOR ALKALINE WATER ELECTROLYSIS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENERGY RESEARCH SHORT COMMUNICATION ELECTROLYTIC PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Ni}Fe}Mo ALLOYS: CATHODE MATERIALS FOR ALKALINE WATER ELECTROLYSIS L. RAMESH, B. S. SHESHADRI
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENERGY RESEARCH SHORT COMMUNICATION ELECTROLYTIC PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Ni}Fe}Mo ALLOYS: CATHODE MATERIALS FOR ALKALINE WATER ELECTROLYSIS L. RAMESH, B. S. SHESHADRI
Membraneless Hydrogen Peroxide Micro Semi-Fuel Cell for Portable Applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Membraneless Hydrogen Peroxide Micro Semi-Fuel Cell
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Membraneless Hydrogen Peroxide Micro Semi-Fuel Cell
N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Ruthenium @ N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Ruthenium @ N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
DEVELOPMENT OF ELECTROLESS PROCESS FOR DEPOSITION OF ZN SILICATE COATINGS
 REPORT OF THE FINAL PROJECT ENTITLED: DEVELOPMENT OF ELECTROLESS PROCESS FOR DEPOSITION OF ZN SILICATE COATINGS by Veeraraghavan S Basker Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Carolina
REPORT OF THE FINAL PROJECT ENTITLED: DEVELOPMENT OF ELECTROLESS PROCESS FOR DEPOSITION OF ZN SILICATE COATINGS by Veeraraghavan S Basker Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Carolina
Novel Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries
 Novel Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries John Bradley May 18th 2012 Project Supervisors: Prof. West & Chaou Tan Abstract The effect of carbon coating on two novel battery cathode materials LiMnP 2 O 7
Novel Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries John Bradley May 18th 2012 Project Supervisors: Prof. West & Chaou Tan Abstract The effect of carbon coating on two novel battery cathode materials LiMnP 2 O 7
A study of the influence of copper on the gold electrowinning process
 A study of the influence of copper on the gold electrowinning process by J. Steyn and R.F. Sandenbergh* Paper written on project work carried out in partial fulfilment of B.Eng (Metallurgical Engineering)
A study of the influence of copper on the gold electrowinning process by J. Steyn and R.F. Sandenbergh* Paper written on project work carried out in partial fulfilment of B.Eng (Metallurgical Engineering)
An Investigation on Metallic Bipolar Plate Corrosion in Simulated Anode and Cathode Environments of PEM Fuel Cells using Potential-pH Diagrams
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 1(2006)447-455 www.electrochemsci.org An Investigation on Metallic Bipolar Plate Corrosion in Simulated Anode and Cathode Environments of PEM Fuel Cells using Potential-pH Diagrams
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 1(2006)447-455 www.electrochemsci.org An Investigation on Metallic Bipolar Plate Corrosion in Simulated Anode and Cathode Environments of PEM Fuel Cells using Potential-pH Diagrams
Development of Corrosion Probe based on Solid State Reference Electrodes 1 Introduction
 Development of Corrosion Probe based on Solid State Reference Electrodes BYUNG GI PARK*, IN HYOUNG RHEE**, DAECHUL CHO** *FNC Technology Co. Ltd., SNU Research Park Innovation Center #421, San 4-1 Bongchun-dong,
Development of Corrosion Probe based on Solid State Reference Electrodes BYUNG GI PARK*, IN HYOUNG RHEE**, DAECHUL CHO** *FNC Technology Co. Ltd., SNU Research Park Innovation Center #421, San 4-1 Bongchun-dong,
Heng-Pan Yang, Sen Qin, Ying-Na Yue, Li Liu, Huan Wang* and Jia-Xing Lu**
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary information for Entrapment of a pyridine derivative within
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary information for Entrapment of a pyridine derivative within
Electronic Supporting Information
 Electronic Supporting Information Electrochemically-Triggered Motion of Catalytic Nanomotors Percy Calvo-Marzal, Kalayil Manian Manesh, Daniel Kagan, Shankar Balasubramanian, Maria Cardona, Gerd-Uwe Flechsig,
Electronic Supporting Information Electrochemically-Triggered Motion of Catalytic Nanomotors Percy Calvo-Marzal, Kalayil Manian Manesh, Daniel Kagan, Shankar Balasubramanian, Maria Cardona, Gerd-Uwe Flechsig,
Estimation of Corrosion Protection Condition on Buried Steel Pipeline under Cathodic Protection with IR-free Probe
 WP3-6 Estimation of Corrosion Protection Condition on Buried Steel Pipeline under Cathodic Protection with IR-free Probe Akinobu Nishikawa, Masahiro Sawai and Hidemasa Nonaka Osaka Gas Co., Ltd. JAPAN
WP3-6 Estimation of Corrosion Protection Condition on Buried Steel Pipeline under Cathodic Protection with IR-free Probe Akinobu Nishikawa, Masahiro Sawai and Hidemasa Nonaka Osaka Gas Co., Ltd. JAPAN
Solution. Yoshio Takasu*, Norihiro Yoshinaga and Wataru Sugimoto
 Oxygen Reduction Behavior of RuO 2 /Ti, IrO 2 /Ti and IrM (M: Ru, Mo, W, V) O x /Ti Binary Oxide Electrodes in a Sulfuric Acid Solution Yoshio Takasu*, Norihiro Yoshinaga and Wataru Sugimoto Department
Oxygen Reduction Behavior of RuO 2 /Ti, IrO 2 /Ti and IrM (M: Ru, Mo, W, V) O x /Ti Binary Oxide Electrodes in a Sulfuric Acid Solution Yoshio Takasu*, Norihiro Yoshinaga and Wataru Sugimoto Department
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information for Ta and Nb co-doped TiO 2, and Its Carbon-Hybrid
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information for Ta and Nb co-doped TiO 2, and Its Carbon-Hybrid
ELECTROCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CoCl 2 (PPh 3 ) 2
 CHAPTER 5 ELECTROCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CoCl 2 (PPh 3 ) 2 This chapter dwells on characterization of the synthesized CoCl 2 (PPh 3 ) 2 in a mixture of acetonitrile and pentanol (1:1), using both electrochemical
CHAPTER 5 ELECTROCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CoCl 2 (PPh 3 ) 2 This chapter dwells on characterization of the synthesized CoCl 2 (PPh 3 ) 2 in a mixture of acetonitrile and pentanol (1:1), using both electrochemical
Optimization of porous current collectors for PEM water electrolysers
 Optimization of porous current collectors for PEM water electrolysers S. Grigoriev a, I. Baranov a, P. Millet b, Z. Li c, V. Fateev a a Hydrogen Energy and Plasma Technology Institute of Russian Research
Optimization of porous current collectors for PEM water electrolysers S. Grigoriev a, I. Baranov a, P. Millet b, Z. Li c, V. Fateev a a Hydrogen Energy and Plasma Technology Institute of Russian Research
Supplementary Materials for
 www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/2/e1400215/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Near-infrared driven decomposition of metal precursors yields amorphous electrocatalytic films Danielle A. Salvatore,
www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/2/e1400215/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Near-infrared driven decomposition of metal precursors yields amorphous electrocatalytic films Danielle A. Salvatore,
POLARIZATION MEASUREMENTS ON IRON IN ALKALINE SOLUTIONS AT HIGH PRESSURES AND HIGH TEMPERATURES.
 POLARIZATION MEASUREMENTS ON IRON IN ALKALINE SOLUTIONS AT HIGH PRESSURES AND HIGH TEMPERATURES. W M. M. HUIJBREGTS, * G. YAN OSCH* A. SNEL * *NV KEMA, Arnhem, The Netherlands During the last few years
POLARIZATION MEASUREMENTS ON IRON IN ALKALINE SOLUTIONS AT HIGH PRESSURES AND HIGH TEMPERATURES. W M. M. HUIJBREGTS, * G. YAN OSCH* A. SNEL * *NV KEMA, Arnhem, The Netherlands During the last few years
Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells
 Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells Huanying Liu, a, b Xuefeng Zhu, a * Mojie Cheng, c You Cong, a Weishen Yang a * a State Key Laboratory of Catalysis,
Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells Huanying Liu, a, b Xuefeng Zhu, a * Mojie Cheng, c You Cong, a Weishen Yang a * a State Key Laboratory of Catalysis,
Novel Fuel Cell MEA Based on Pt-C Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering
 10.1149/08008.0225ecst The Electrochemical Society Novel Fuel Cell MEA Based on Pt-C Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering A. Ostroverkh a, V. Johanek a, M. Dubau a, P. Kus a, K. Veltruska a, M. Vaclavu a,
10.1149/08008.0225ecst The Electrochemical Society Novel Fuel Cell MEA Based on Pt-C Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering A. Ostroverkh a, V. Johanek a, M. Dubau a, P. Kus a, K. Veltruska a, M. Vaclavu a,
Investigation of anode materials for lithium-ion batteries
 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2006 Investigation of anode materials for lithium-ion batteries Ling Yuan University
University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2006 Investigation of anode materials for lithium-ion batteries Ling Yuan University
M.N.Singh, D.K.Basu, A.K.Bhattmishra and S. K.Narang CORROSION RESISTANT ELECRODEPOSITED ZINC COATING FROM ZINC DROSS
 ..:: CORCON 2UU2 ::.. SPEAKERS (Basic Corrosion) 04 TECHNICAL A SPEAKERS A ABOUT NA( M.N.Singh, D.K.Basu, A.K.Bhattmishra and S. K.Narang M. N. Singh, D. K. Basu, A. K. Bhattmishra and S. K. Narang National
..:: CORCON 2UU2 ::.. SPEAKERS (Basic Corrosion) 04 TECHNICAL A SPEAKERS A ABOUT NA( M.N.Singh, D.K.Basu, A.K.Bhattmishra and S. K.Narang M. N. Singh, D. K. Basu, A. K. Bhattmishra and S. K. Narang National
Non-Platinum metal oxide nano particles and nano clusters as oxygen reduction catalysts in fuel cells.
 Non-Platinum metal oxide nano particles and nano clusters as oxygen reduction catalysts in fuel cells. Louis Cindrella, Robert Jeyachandran To cite this version: Louis Cindrella, Robert Jeyachandran. Non-Platinum
Non-Platinum metal oxide nano particles and nano clusters as oxygen reduction catalysts in fuel cells. Louis Cindrella, Robert Jeyachandran To cite this version: Louis Cindrella, Robert Jeyachandran. Non-Platinum
Electrochemical cells use spontaneous redox reactions to convert chemical energy to electrical energy.
 ELECTROLYSIS: -the process of supplying electrical energy to a molten ionic compound or a solution containing ions so as to produce a chemical change (causing a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur).
ELECTROLYSIS: -the process of supplying electrical energy to a molten ionic compound or a solution containing ions so as to produce a chemical change (causing a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur).
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Effect of water electrolysis catalysts on carbon corrosion in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells Sang-Eun Jang, Hansung Kim* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Supporting Information Effect of water electrolysis catalysts on carbon corrosion in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells Sang-Eun Jang, Hansung Kim* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Chapter 7. Evaluation of Electrode Performance by. Electrochemical Impedance
 Chapter 7 Evaluation of Electrode Performance by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) 7.1 Introduction A significant fraction of internal resistance of a cell comes from the interfacial polarization
Chapter 7 Evaluation of Electrode Performance by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) 7.1 Introduction A significant fraction of internal resistance of a cell comes from the interfacial polarization
Platinum Nanostructures by Template Wetting Nanofabrication and Their Use in a Miniature Fuel Cell Membrane Electrode Assembly
 Platinum Nanostructures by Template Wetting Nanofabrication and Their Use in a Miniature Fuel Cell Membrane Electrode Assembly Eric Broaddus, Jared Fernandez, and Scott A. Gold Institute for Micromanufacturing,
Platinum Nanostructures by Template Wetting Nanofabrication and Their Use in a Miniature Fuel Cell Membrane Electrode Assembly Eric Broaddus, Jared Fernandez, and Scott A. Gold Institute for Micromanufacturing,
LASER SURFACE MELTING OF 17-4 PH PRECIPITATION-HARDENABLE STAINLESS STEEL Paper 1203
 LASER SURFACE MELTING OF 7- PH PRECIPITATION-HARDENABLE STAINLESS STEEL Paper 0 Zhichao Cheng, Chi Tat Kwok, Kin Ho Lo, Department of Electromechanical Engineering, University of Macau, Taipa, Macau Abstract
LASER SURFACE MELTING OF 7- PH PRECIPITATION-HARDENABLE STAINLESS STEEL Paper 0 Zhichao Cheng, Chi Tat Kwok, Kin Ho Lo, Department of Electromechanical Engineering, University of Macau, Taipa, Macau Abstract
Corrosion Resistant Evaluation of Oxygen Solid-Solution Strengthened Pure Titanium
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43(2) 381 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43(2) : 381-392 http://epg.science.cmu.ac.th/ejournal/ Contributed Paper Corrosion Resistant Evaluation of Oxygen Solid-Solution Strengthened
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43(2) 381 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43(2) : 381-392 http://epg.science.cmu.ac.th/ejournal/ Contributed Paper Corrosion Resistant Evaluation of Oxygen Solid-Solution Strengthened
Applied Surface Science
 Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 4192 4196 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Surface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Electrodeposited ruthenium oxide thin films
Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 4192 4196 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Surface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Electrodeposited ruthenium oxide thin films
Thermodynamics and Electrode Potential ME Dr. Zuhair M. Gasem
 Thermodynamics and Electrode Potential ME 472-062 Copyright Dr. Zuhair M. Gasem Corrosion Science and Engineering 2 Corrosion Science Engineering: corrosion forms, and controlling methods Chpater2 Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics and Electrode Potential ME 472-062 Copyright Dr. Zuhair M. Gasem Corrosion Science and Engineering 2 Corrosion Science Engineering: corrosion forms, and controlling methods Chpater2 Thermodynamics
Preparation of porous manganese hydroxide film and its application in supercapacitors
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 46A, May 2007, pp. 736-741 Preparation of porous manganese hydroxide film and its application in supercapacitors Zhen Fan, Jinhua Chen*, Feng Sun, Lei Yang, Yan Xu & Yafei
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 46A, May 2007, pp. 736-741 Preparation of porous manganese hydroxide film and its application in supercapacitors Zhen Fan, Jinhua Chen*, Feng Sun, Lei Yang, Yan Xu & Yafei
EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE
 EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE Noor Zaimah 1, Azieyanti Nurain 1 and Sakhawat Hussain 2 1 Department
EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE Noor Zaimah 1, Azieyanti Nurain 1 and Sakhawat Hussain 2 1 Department
The Seventh International Conference on Cold Fusion (ICCF-7). Vancouver, Canada, April (1998), ENECO, Inc., Salt Lake City, UT., p. 356.
 1 The Seventh International Conference on Cold Fusion. 1998 (ICCF-7). Vancouver, Canada, April 19-24 (1998), ENECO, Inc., Salt Lake City, UT., p. 356. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OPEN-CIRCUIT-VOLTAGE AND HEAT
1 The Seventh International Conference on Cold Fusion. 1998 (ICCF-7). Vancouver, Canada, April 19-24 (1998), ENECO, Inc., Salt Lake City, UT., p. 356. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OPEN-CIRCUIT-VOLTAGE AND HEAT
Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 2.
 Supplementary Figure 1. STEM annular dark field (ADF) image of NiO/Ni-CNT showing non-uniform coating of NiO nanoparticles on Ni cores (the red circles show individual NiO nanoparticles with different
Supplementary Figure 1. STEM annular dark field (ADF) image of NiO/Ni-CNT showing non-uniform coating of NiO nanoparticles on Ni cores (the red circles show individual NiO nanoparticles with different
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalysis via Electrodeposited Amorphous α Phase Nickel-Cobalt Hydroxide Nanodendrite Forests By Anirudh Balram, Hanfei Zhang, and Sunand
Supporting Information Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalysis via Electrodeposited Amorphous α Phase Nickel-Cobalt Hydroxide Nanodendrite Forests By Anirudh Balram, Hanfei Zhang, and Sunand
The Role of Surface Oxophilicity in Copper-catalyzed Water Dissociation
 Supporting Information The Role of Surface Oxophilicity in Copper-catalyzed Water Dissociation Wesley Luc, 1 Zhao Jiang, 2,3 Jingguang G. Chen,*,3 and Feng Jiao*,1 [1] Center for Catalytic Science and
Supporting Information The Role of Surface Oxophilicity in Copper-catalyzed Water Dissociation Wesley Luc, 1 Zhao Jiang, 2,3 Jingguang G. Chen,*,3 and Feng Jiao*,1 [1] Center for Catalytic Science and
Method Excitation signal applied Wave response based on method Linear Differential pulse Square wave Cyclic Developed current recorded
 Voltammetry Electrochemistry techniques based on current (i) measurement as function of voltage (E appl ) Working electrode (microelectrode) place where redox occurs surface area few mm 2 to limit current
Voltammetry Electrochemistry techniques based on current (i) measurement as function of voltage (E appl ) Working electrode (microelectrode) place where redox occurs surface area few mm 2 to limit current
HYDROGEN ABSORPTION INTO ALPHA TITANIUM ALLOYS
 16th International Corrosion Congress September 19-24, 25, Beijing, China HYDROGEN ABSORPTION INTO ALPHA TITANIUM ALLOYS Li Yan, J. J. Noël, Z. Qin, D. W. Shoesmith*, Department of Chemistry, University
16th International Corrosion Congress September 19-24, 25, Beijing, China HYDROGEN ABSORPTION INTO ALPHA TITANIUM ALLOYS Li Yan, J. J. Noël, Z. Qin, D. W. Shoesmith*, Department of Chemistry, University
De-ionized water. Nickel target. Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup.
 Graphite Electrode Graphite Electrode De-ionized water Nickel target Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup. Intensity ( a.u.) Ni(OH) 2 deposited on the graphite blank
Graphite Electrode Graphite Electrode De-ionized water Nickel target Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup. Intensity ( a.u.) Ni(OH) 2 deposited on the graphite blank
Report On Adsorption/Desorption Studies of CO on PEM Electrodes Using Cyclic Voltammetry. Sethuraman, Vijay Anand
 Report On Adsorption/Desorption Studies of CO on PEM Electrodes Using Cyclic Voltammetry Sethuraman, Vijay Anand I. AIM: The aim of this study is to calculate the adsorption and desorption rate constants
Report On Adsorption/Desorption Studies of CO on PEM Electrodes Using Cyclic Voltammetry Sethuraman, Vijay Anand I. AIM: The aim of this study is to calculate the adsorption and desorption rate constants
INFLUENCE OF SURFACE FINISH PARAMETERS ON CORROSION OF ZINC
 Qatar Univ. Sci. Bull. (1989), 9: 65-77 NFLUENCE OF SURFACE FNSH PARAMETERS ON CORROSON OF ZNC By M.Y. MOURAD* and A.Y. KANDEL** *Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science **Mechanical Engineering Department,
Qatar Univ. Sci. Bull. (1989), 9: 65-77 NFLUENCE OF SURFACE FNSH PARAMETERS ON CORROSON OF ZNC By M.Y. MOURAD* and A.Y. KANDEL** *Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science **Mechanical Engineering Department,
Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs Catalysts Prepared by Pulse Potential Plating Methods
 Solid State Phenomena Vols. 124-126 (2007) pp 1039-1042 Online: 2007-06-15 (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.124-126.1039 Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs
Solid State Phenomena Vols. 124-126 (2007) pp 1039-1042 Online: 2007-06-15 (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.124-126.1039 Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs
Comparison between the article and script of thesis
 Comparison between the article and script of thesis All nanomaterials and a part of results presented and discussed in this article titled Efficient multi-metallic anode catalysts in a PEM water electrolyzer
Comparison between the article and script of thesis All nanomaterials and a part of results presented and discussed in this article titled Efficient multi-metallic anode catalysts in a PEM water electrolyzer
Supporting Information for. Exploring a wider range of Mg-Ca-Zn metallic glass as biocompatible alloys using combinatorial sputtering
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for Exploring a wider range of Mg-Ca-Zn metallic glass as biocompatible
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for Exploring a wider range of Mg-Ca-Zn metallic glass as biocompatible
CORROSION PROPERTIES OF CERMET COATINGS SPRAYED BY HIGH-VELOCITY OXYGEN-FUEL. Dragos UŢU, Iosif HULKA, Viorel-Aurel ŞERBAN, Hannelore FILIPESCU
 Abstract CORROSION PROPERTIES OF CERMET COATINGS SPRAYED BY HIGH-VELOCITY OXYGEN-FUEL Dragos UŢU, Iosif HULKA, Viorel-Aurel ŞERBAN, Hannelore FILIPESCU Politehnica University of Timisoara, Romania, dragosutu@yahoo.com,
Abstract CORROSION PROPERTIES OF CERMET COATINGS SPRAYED BY HIGH-VELOCITY OXYGEN-FUEL Dragos UŢU, Iosif HULKA, Viorel-Aurel ŞERBAN, Hannelore FILIPESCU Politehnica University of Timisoara, Romania, dragosutu@yahoo.com,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Electrochemical reduction of CO 2 at Copper Nanofoams Sujat Sen a, Dan Liu a and G. Tayhas R. Palmore a, b, * a Department of Chemistry and b School of Engineering, Brown University,
Supporting Information Electrochemical reduction of CO 2 at Copper Nanofoams Sujat Sen a, Dan Liu a and G. Tayhas R. Palmore a, b, * a Department of Chemistry and b School of Engineering, Brown University,
Electricity and Chemistry
 Electricity and Chemistry Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the reactions involving the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice-versa. Electrochemical
Electricity and Chemistry Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the reactions involving the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice-versa. Electrochemical
ACCELERATED CORROSION TESTING OF GALVANIC COUPLES. James F. Dante, Josh Averett, Fritz Friedersdorf, and Christy Vestal
 ACCELERATED CORROSION TESTING OF GALVANIC COUPLES James F. Dante, Josh Averett, Fritz Friedersdorf, and Christy Vestal Luna Innovations 706 Forest St. Suite A Charlottesville, VA 22903 dantej@lunainnovations.com
ACCELERATED CORROSION TESTING OF GALVANIC COUPLES James F. Dante, Josh Averett, Fritz Friedersdorf, and Christy Vestal Luna Innovations 706 Forest St. Suite A Charlottesville, VA 22903 dantej@lunainnovations.com
Thermogravimetric Thin Aqueous Film Corrosion Studies of Alloy 22; Calcium Chloride Solutions at 150 C and Atmospheric Pressure
 Thermogravimetric Thin Aqueous Film Corrosion Studies of Alloy 22; Calcium Chloride Solutions at 150 C and Atmospheric Pressure Phillip Hailey and Greg Gdowski Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore,
Thermogravimetric Thin Aqueous Film Corrosion Studies of Alloy 22; Calcium Chloride Solutions at 150 C and Atmospheric Pressure Phillip Hailey and Greg Gdowski Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore,
Corrosion of Nickel-Chromium Alloy in the Molten Mixture LiF-NaF-KF
 Corrosion of Nickel-Chromium Alloy in the Molten Mixture LiF-NaF-KF Vladimír Danielik*, Pavel Fellner, Marta Ambrová, Oldřich Matal a Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Technology and Materials, Faculty
Corrosion of Nickel-Chromium Alloy in the Molten Mixture LiF-NaF-KF Vladimír Danielik*, Pavel Fellner, Marta Ambrová, Oldřich Matal a Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Technology and Materials, Faculty
Metal Plates: Challenges and Perspectives for PEM Fuel Cells and Electrolyzers
 Pivotal Technologies for the New Energy Economy Today! Metal Plates: Challenges and Perspectives for PEM Fuel Cells and Electrolyzers Gerald DeCuollo TreadStone Technologies, Inc. April 16, 2012 TreadStone
Pivotal Technologies for the New Energy Economy Today! Metal Plates: Challenges and Perspectives for PEM Fuel Cells and Electrolyzers Gerald DeCuollo TreadStone Technologies, Inc. April 16, 2012 TreadStone
Characterization of Oxide Film Formed on Ck45 Steel by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Method
 Journal of Mechanical Research and Application ISSN: 2251-7383, eissn: 2251-7391 Vol. 4, No. 2, 2012, 57-61 Characterization of Oxide Film Formed on Ck45 Steel by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Method JMRA
Journal of Mechanical Research and Application ISSN: 2251-7383, eissn: 2251-7391 Vol. 4, No. 2, 2012, 57-61 Characterization of Oxide Film Formed on Ck45 Steel by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Method JMRA
Studies of platinum electroplating baths Part IV: Deposits on copper from Q bath
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY 26 (1996) 873-880 Studies of platinum electroplating baths Part IV: Deposits on copper from Q bath W. J. BASIRUN, D. PLETCHER, A. SARABY-REINTJES Department of Chemistry,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY 26 (1996) 873-880 Studies of platinum electroplating baths Part IV: Deposits on copper from Q bath W. J. BASIRUN, D. PLETCHER, A. SARABY-REINTJES Department of Chemistry,
One-Pot Synthesis, Photoluminescence, and Electrocatalytic Properties of Subnanometer-Sized Copper Clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc.
 One-Pot Synthesis, Photoluminescence, and Electrocatalytic Properties of Subnanometer-Sized Copper Clusters W. Wei, Y. Lu, W. Chen, and S. Chen* State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun
One-Pot Synthesis, Photoluminescence, and Electrocatalytic Properties of Subnanometer-Sized Copper Clusters W. Wei, Y. Lu, W. Chen, and S. Chen* State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun
On-chip metal/polypyrrole quasi-reference electrodes for robust ISFET operation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 On-chip metal/polypyrrole quasi-reference electrodes for robust ISFET operation Carlos Duarte-Guevara
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 On-chip metal/polypyrrole quasi-reference electrodes for robust ISFET operation Carlos Duarte-Guevara
UNIT-I ELECTROCHEMISTRY PART-A
 UNIT-I ELECTROCHEMISTRY PART-A 1. What is electrochemistry? 2. What do you understand by electrode potential? 3. Define E.M.F of an electrochemical cell? 4. Define (a) Single electrode potential (b) Standard
UNIT-I ELECTROCHEMISTRY PART-A 1. What is electrochemistry? 2. What do you understand by electrode potential? 3. Define E.M.F of an electrochemical cell? 4. Define (a) Single electrode potential (b) Standard
ELECTROCHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF POLYPYRROLE (PPy) and PPy METAL COMPOSITES ON COPPER and INVESTIGATION OF THEIR ANTICORROSIVE PROPERTIES
 ELECTROCHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF POLYPYRROLE (PPy) and PPy METAL COMPOSITES ON COPPER and INVESTIGATION OF THEIR ANTICORROSIVE PROPERTIES Sibel Zor, Hatice Özkazanç Kocaeli University, Department of Chemistry,
ELECTROCHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF POLYPYRROLE (PPy) and PPy METAL COMPOSITES ON COPPER and INVESTIGATION OF THEIR ANTICORROSIVE PROPERTIES Sibel Zor, Hatice Özkazanç Kocaeli University, Department of Chemistry,
Fused-Salt Electrodeposition of Thin-Layer Silicon
 NREL/CP-450-22928 UC Category: 1250 Fused-Salt Electrodeposition of Thin-Layer Silicon J.T. Moore, T.H. Wang, M.J. Heben, K. Douglas, and T.F. Ciszek Presented at the 26th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists
NREL/CP-450-22928 UC Category: 1250 Fused-Salt Electrodeposition of Thin-Layer Silicon J.T. Moore, T.H. Wang, M.J. Heben, K. Douglas, and T.F. Ciszek Presented at the 26th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists
XXXX ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF COMPOUNDS OR NON- METALS; APPARATUS THEREFOR [2]
![XXXX ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF COMPOUNDS OR NON- METALS; APPARATUS THEREFOR [2] XXXX ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF COMPOUNDS OR NON- METALS; APPARATUS THEREFOR [2]](/thumbs/90/101393130.jpg) XXXX C25 ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR (electrodialysis, electro-osmosis, separation of liquids by electricity B01D; working of metal by the action of a high concentration
XXXX C25 ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR (electrodialysis, electro-osmosis, separation of liquids by electricity B01D; working of metal by the action of a high concentration
Supplementary Information. Reversible superconductor-insulator transition in LiTi 2 O 4 induced by
 Supplementary Information Reversible superconductor-insulator transition in LiTi 2 O 4 induced by Li-ion electrochemical reaction K. Yoshimatsu 1,*, M. Niwa 1, H. Mashiko 1, T. Oshima 1 & A. Ohtomo 1,2
Supplementary Information Reversible superconductor-insulator transition in LiTi 2 O 4 induced by Li-ion electrochemical reaction K. Yoshimatsu 1,*, M. Niwa 1, H. Mashiko 1, T. Oshima 1 & A. Ohtomo 1,2
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for 3D Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Aerogel-Supported Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Zhong-Shuai Wu, Shubin Yang, Yi Sun, Khaled
Supporting Information for 3D Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Aerogel-Supported Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Zhong-Shuai Wu, Shubin Yang, Yi Sun, Khaled
Electrodeposition of Electroactive Co B and Co B C Alloys for Water Splitting Process in 8 M NaOH Solutions
 Electrocatalysis (2018) 9:189 203 DOI 10.1007/s12678-017-0401-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Electrodeposition of Electroactive Co B and Co B C Alloys for Water Splitting Process in 8 M NaOH Solutions Dawid Kutyła
Electrocatalysis (2018) 9:189 203 DOI 10.1007/s12678-017-0401-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Electrodeposition of Electroactive Co B and Co B C Alloys for Water Splitting Process in 8 M NaOH Solutions Dawid Kutyła
SPORADIC OBSERVATION OF THE FLEISCHMANN- PONS HEAT EFFECT
 Kainthla, R.C., et al., Sporadic observation of the Fleischmann-Pons heat effect. Electrochim. Acta, 1989. 34: p. 1315. SPORADIC OBSERVATION OF THE FLEISCHMANN- PONS HEAT EFFECT R. C. Kainthla, O. Velev,
Kainthla, R.C., et al., Sporadic observation of the Fleischmann-Pons heat effect. Electrochim. Acta, 1989. 34: p. 1315. SPORADIC OBSERVATION OF THE FLEISCHMANN- PONS HEAT EFFECT R. C. Kainthla, O. Velev,
Corrosion and Protection of a Conductive Silver Paste
 Journal of the Electrochemical Society, Vol. 142, No. 8, 1995, pp. 2591-2594. ISSN: (Print 0013-4651) (Online 1945-7111) DOI: 10.1149/1.2050058 http://www.electrochem.org/ http://scitation.aip.org/jes
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, Vol. 142, No. 8, 1995, pp. 2591-2594. ISSN: (Print 0013-4651) (Online 1945-7111) DOI: 10.1149/1.2050058 http://www.electrochem.org/ http://scitation.aip.org/jes
Durability study of Pt 3 Ni 1 catalysts as cathode in PEM fuel cells
 Electrochemistry Communications 6 (2004) 795 799 www.elsevier.com/locate/elecom Durability study of Pt 3 Ni 1 catalysts as cathode in PEM fuel cells Hector R. Colon-Mercado, Hansung Kim, Branko N. Popov
Electrochemistry Communications 6 (2004) 795 799 www.elsevier.com/locate/elecom Durability study of Pt 3 Ni 1 catalysts as cathode in PEM fuel cells Hector R. Colon-Mercado, Hansung Kim, Branko N. Popov
SIGNIFICANCE OF HYDROGEN EVOLUTION IN CATHODIC PROTECTION OF STEEL IN SEAWATER
 SIGNIFICANCE OF HYDROGEN EVOLUTION IN CATHODIC PROTECTION OF STEEL IN SEAWATER Trine Okstad, Øyvind Rannestad, Roy Johnsen () and Kemal Nisancioglu Department of Materials Science and Engineering ( ()
SIGNIFICANCE OF HYDROGEN EVOLUTION IN CATHODIC PROTECTION OF STEEL IN SEAWATER Trine Okstad, Øyvind Rannestad, Roy Johnsen () and Kemal Nisancioglu Department of Materials Science and Engineering ( ()
Densification and grain growth of TiO 2 -doped ZnO
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 25, No. 4, 2007 Densification and grain growth of TiO 2 -doped ZnO K. YILDIZ *, N. KARAKU, N. TOPLAN, H. Ö. TOPLAN Sakarya University, Metallurgy and Materials Engineering,
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 25, No. 4, 2007 Densification and grain growth of TiO 2 -doped ZnO K. YILDIZ *, N. KARAKU, N. TOPLAN, H. Ö. TOPLAN Sakarya University, Metallurgy and Materials Engineering,
Development of Composite Bipolar Plates for PEMFC
 Development of Composite Bipolar Plates for PEMFC 1. Introduction Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is a very promising power source for residential and mobile applications with its favorable
Development of Composite Bipolar Plates for PEMFC 1. Introduction Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is a very promising power source for residential and mobile applications with its favorable
Hydrogen Permeation of Pipeline Steel under Sour Condensate Film Condition
 Hydrogen Permeation of Pipeline Steel under Sour Condensate Film Condition Zhaoyang Cui, Lei Zhang, Yanni Sun, Rufei Ma, Mingliang Liu and Minxu Lu Institute of Advanced Materials and Technology, University
Hydrogen Permeation of Pipeline Steel under Sour Condensate Film Condition Zhaoyang Cui, Lei Zhang, Yanni Sun, Rufei Ma, Mingliang Liu and Minxu Lu Institute of Advanced Materials and Technology, University
CLEANING AND PREVENTION OF INORGANIC DEPOSITS IN PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS USING PULSATING CURRENT
 ECI Symposium Series, Volume RP5: Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Heat Exchanger Fouling and Cleaning - Challenges and Opportunities, Editors Hans Müller-Steinhagen, M. Reza Malayeri, and
ECI Symposium Series, Volume RP5: Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Heat Exchanger Fouling and Cleaning - Challenges and Opportunities, Editors Hans Müller-Steinhagen, M. Reza Malayeri, and
Phase Formation in Gold-Tin Alloys Electroplated from a Non-cyanide Bath
 Phase Formation in Gold-Tin Alloys Electroplated from a Non-cyanide Bath Yahui Zhang and Douglas G. Ivey Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada
Phase Formation in Gold-Tin Alloys Electroplated from a Non-cyanide Bath Yahui Zhang and Douglas G. Ivey Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Sustainable Energy & Fuels. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information for Chemical Science, DOI: 10.1039/ ((please add manuscript
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Sustainable Energy & Fuels. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information for Chemical Science, DOI: 10.1039/ ((please add manuscript
Direct Electroless Silver Plating on Copper Metal from Succinimide Complex Bath Using Imidazole as the Reducing Agent
 Technical Paper Direct Electroless Silver Plating on Copper Metal from Succinimide Complex Bath Using Imidazole as Reducing Agent Hidemi NAWAFUNE*, Keiko SHIROGUCHI**, Shozo MIZUMOTO*, Yasuhito KOHASHI***
Technical Paper Direct Electroless Silver Plating on Copper Metal from Succinimide Complex Bath Using Imidazole as Reducing Agent Hidemi NAWAFUNE*, Keiko SHIROGUCHI**, Shozo MIZUMOTO*, Yasuhito KOHASHI***
Chapter 16 Corrosion and Degradation of Materials
 Chapter 16 Corrosion and Degradation of Materials Concept Check 16.1 Question: Would you expect iron to corrode in water of high purity? Why or why not? Answer: Iron would not corrode in water of high
Chapter 16 Corrosion and Degradation of Materials Concept Check 16.1 Question: Would you expect iron to corrode in water of high purity? Why or why not? Answer: Iron would not corrode in water of high
COMPARATIVE CORROSION BEHAVIOR OF PURE COPPER AND BRASS IN 3.5% NaCl SOLUTION
 COMPARATIVE CORROSION BEHAVIOR OF PURE COPPER AND BRASS IN 3.5% NaCl SOLUTION Lidia BENEA, Eliza DĂNĂILĂ Competences Center: Interfaces-Tribocorrosion-Electrochemical Systems (CC-ITES), Faculty of Engineering,
COMPARATIVE CORROSION BEHAVIOR OF PURE COPPER AND BRASS IN 3.5% NaCl SOLUTION Lidia BENEA, Eliza DĂNĂILĂ Competences Center: Interfaces-Tribocorrosion-Electrochemical Systems (CC-ITES), Faculty of Engineering,
Galvanic corrosion evaluation of 6061 aluminum coupled to CVD coated stainless steel Elizabeth Sikora and Barbara Shaw 6/9/2016
 SHAW AND ASSOCIATES CONSULTING Galvanic corrosion evaluation of 6061 aluminum coupled to CVD coated stainless steel Elizabeth Sikora and Barbara Shaw 6/9/2016 Evaluation of galvanic corrosion of aluminum
SHAW AND ASSOCIATES CONSULTING Galvanic corrosion evaluation of 6061 aluminum coupled to CVD coated stainless steel Elizabeth Sikora and Barbara Shaw 6/9/2016 Evaluation of galvanic corrosion of aluminum
FORMATION OF TiO 2 THIN FILM BY ION-BEAM-MIXING METHOD AND ITS APPLICATION AS THE CORROSION PROTECTING FILM
 ORAL REFERENCE:ICF100266OR FORMATION OF TiO 2 THIN FILM BY ION-BEAM-MIXING METHOD AND ITS APPLICATION AS THE CORROSION PROTECTING FILM Yuji KIMURA 1 and Hirotsugu SAITO 1 1 Dept. of Materials Science and
ORAL REFERENCE:ICF100266OR FORMATION OF TiO 2 THIN FILM BY ION-BEAM-MIXING METHOD AND ITS APPLICATION AS THE CORROSION PROTECTING FILM Yuji KIMURA 1 and Hirotsugu SAITO 1 1 Dept. of Materials Science and
Electrochemical screening of several alloys for use in a flue-gas desulphurisation prescrubber
 36 1989 ROI www.hbscc.nl - 1 - Electrochemical screening of several alloys for use in a flue-gas desulphurisation prescrubber L.M. Butter, E.J.A. Vogelaar, W.M.M. Huijbregts Kema Scientific & Technical
36 1989 ROI www.hbscc.nl - 1 - Electrochemical screening of several alloys for use in a flue-gas desulphurisation prescrubber L.M. Butter, E.J.A. Vogelaar, W.M.M. Huijbregts Kema Scientific & Technical
Electrochemical Behavior of Thin Film Analogs of Mg (Zn,Cu,Al) 2
 Journal of the Electrochemical Society, Vol. 148, No. 9, 2001, pp. B348-B356. ISSN: (Print 0013-4651) (Online 1945-7111) DOI: 10.1149/1.1386626 http://www.electrochem.org/ http://scitation.aip.org/jes
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, Vol. 148, No. 9, 2001, pp. B348-B356. ISSN: (Print 0013-4651) (Online 1945-7111) DOI: 10.1149/1.1386626 http://www.electrochem.org/ http://scitation.aip.org/jes
International Journal of Chemical Studies
 ISSN: 2321-4902 Volume 1 Issue 1 Online Available at www.chemijournal.com International Journal of Chemical Studies Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients and Layer Thickness for Oxidation the Ferrocene
ISSN: 2321-4902 Volume 1 Issue 1 Online Available at www.chemijournal.com International Journal of Chemical Studies Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients and Layer Thickness for Oxidation the Ferrocene
Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as. Negative Electrode Materials
 Supplementary Information: Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as Negative Electrode Materials X. P. Gao, S. M. Yao, T. Y. Yan, Z. Zhou Institute of New Energy Material Chemistry,
Supplementary Information: Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as Negative Electrode Materials X. P. Gao, S. M. Yao, T. Y. Yan, Z. Zhou Institute of New Energy Material Chemistry,
MICROWAVE SINTERING OF ELECTROLESS Ni PLATED B 4 C POWDERS. Ayhan EROL, Ahmet YONETKEN
 Afyon Kocatepe Üniversitesi Özel Sayı Afyon Kocatepe University FEN BİLİMLERİ DERGİSİ 223-228 JOURNAL OF SCIENCE MICROWAVE SINTERING OF ELECTROLESS Ni PLATED B 4 C POWDERS Ayhan EROL, Ahmet YONETKEN Afyon
Afyon Kocatepe Üniversitesi Özel Sayı Afyon Kocatepe University FEN BİLİMLERİ DERGİSİ 223-228 JOURNAL OF SCIENCE MICROWAVE SINTERING OF ELECTROLESS Ni PLATED B 4 C POWDERS Ayhan EROL, Ahmet YONETKEN Afyon
