Influence of ph and bath composition on properties of Ni Fe alloy films synthesized by electrodeposition
|
|
|
- Antonia Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 2, April 2012, pp c Indian Academy of Sciences. Influence of ph and bath composition on properties of Ni Fe alloy films synthesized by electrodeposition XINGHUA SU 1 and CHENGWEN QIANG 2, 1 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chang an University, Xi an , China 2 China and Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Science, Lanzhou , China MS received 1 April 2011; revised 14 May 2011 Abstract. Fe Ni films were electrodeposited on ITO glass substrates from the electrolytes with different molar ratio of Ni 2+ /Fe 2+ and different ph values (2 1, 2 9, 3 7and4 3) at 25 C. The properties of Fe Ni alloy films depend on both Ni 2+ and Fe 2+ concentrations in electrolyte and ph values. The content of Ni increases from 38% to 84% as the mole ratio of NiSO 4 /FeSO 4 increasing from 0 50/0 50 to 0 90/0 10 in electrolyte and slightly decreases from 65% to 42% as the ph values increase from 2 1 to4 3. The X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that the structures of the films strongly depend on the Ni content in the binary films. The magnetic performance of the films shows that the saturation magnetization (M s ) decreases from emu/cm 3 to emu/cm 3 with the ph value increasing from 2 1 to4 3and the saturation magnetization (M s ) and coercivity (H c ) move up from emu/cm 3 and Oe to emu/cm 3 and Oe with the increase of Ni 2+ concentration in the electrolyte, respectively. Keywords. Fe Ni film; electrodeposition; anomalous codeposition; magnetic property. 1. Introduction Magnetic films have attracted much attention due to their potential applications in small electric components, such as radio-frequency thin film inductors and computer read/write heads. Single ferromagnetic films of transition metals such as nickel, cobalt, iron and their alloys are typical magnetic materials applicable in soft-magnetic and anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) (Korenivski 2000; Siritaratiwat et al 2000; Valeri et al 2001; Jartych et al 2002; Chisholm et al 2007). These materials are important for applications as well as for fabrication. For example, films of Ni Fe binary alloy are used for recording, memory and storage devices (Romankiw et al 1970; Venkatasetty 1970). The most common film growth processes such as sputtering, molecular beam epitaxy require high or ultrahigh vacuum. It is also possible to prepare such ferromagnetic films by electroplating, which does not need any vacuum system. Moreover, it has more advantages like low cost and easy control by changing the electrodeposition parameters in the experiment. Quantities of metallic coatings were prepared by the electroplating method, such as Ni Co (Marikkannu et al 2007), Cu Sn (Lodhi et al 2007), Zn Co (Chen and Sun 2001) and Zn Ni (Beltowska-Lehman et al 2002), composite films of Ni SiC (Gyftou et al 2008) and Fe Cr P (Li et al 2008) were also prepared by the electro-plating method. In electrodeposition the growth mechanism, morphology and micro-structural properties of the film Author for correspondence (qiangchw08@lzu.edu.cn) depend on electrodeposition conditions such as electrolyte composition, electrolyte ph and deposition potential. Electrodeposition of Fe Ni alloy was classified as anomalous codeposition, because the less noble metal was deposited preferentially (Zech et al 1999). According to the earlier studies, the anomalous behaviour was caused by the preferential absorption of iron hydroxide on the cathode, which leads to higher deposition ratio of Fe than Ni (Krause et al 1997). However, this hypothesis could not explain experimental works. While, according to the new model, NiOH + and FeOH + formed from the hydrolysis of Ni 2+ and Fe 2+, are discharged at the cathode surface. The anomalous codeposition is attributed to the high concentrations of FeOH + near electrode (Sasaki and Talbot 2000). The most comprehensive model of the Fe Ni alloy electrodeposition was presented by Matlosz (1993), who proposed that reduction of each metal ion occurred through a two-step mechanism. The first step involved the adsorption of a monovalent intermediate and the next step was its reduction to the elemental state. Anomalous codeposition was carried out from the preferential surface coverage of the absorbed iron intermediate (Yin 1997; Sasaki and Talbot 2000). The difficulties introduced by anomalous codeposition inherent to the Fe Ni alloy, has necessitated empirically developed coating bath, which typically contain different organic additives (Lieder and Biallozor 1985; Yin and Lin 1996; Harris et al 1999). It is well known that the properties of Fe Ni films are seriously affected by their compositions and structures (Osaka 1999), thus a reliable control of the composition and structure is an important issue in designing the magnetic functionality of these materials. Since the magnetic properties of 183
2 184 Xinghua Su and Chengwen Qiang Fe Ni alloys are seriously affected by their compositions and structures (Passal 1966, 1967; Friemel 1966, 1967; Beltowska-Lenman and Riesenkampf 1980; Schwarzacher and Lashmore 1996; Osaka et al 1998; Osaka 1999), a reliable control of the composition and textural properties (e.g. crystalline structures, morphologies, roughness, etc) through plating is an important issue in designing the magnetic functionality of these materials. For example, the nanostructured permalloy (i.e. Ni 81 Fe 19 alloy) has been found to be a high-quality magnetic recording material (Chueng et al 1994a, b). Zhang and Ivey (2004) studied magnetic properties of Ni Fe Co alloys and demonstrated that the magnetic properties were sensitive to the composition and ph levels. Additionally, they have previously reported that Fe Co films with different morphology and Co content were successfully electrodeposited on ITO glasses from the electrolyte containing different Co 2+ and ph values. The result shows that the saturation magnetization of the Fe Co alloy films reaches a maximum value of emu/cm 3 and coercivity (H c ) reaches a minimum value of Oe of the Co: Fe=4:1. M S reaches a maximum value of emu/cm 3 and H C reaches a minimum value of Oe of the Co: Fe=4:1 at ph=2 9 (Qiang et al 2010). In this study, the structure and magnetic property of electrodeposited Fe Ni films were investigated as a function of the molar ratio of Ni 2+ /Fe 2+ and ph values in electrolyte. It was clearly observed that the surface morphology and magnetic property were changed significantly with the electrolyte ph and different molar ratios of Ni 2+ /Fe 2+ in electrolyte. 2. Experimental In this study, Ni Fe films were grown from an electrolyte containing Ni 2+ and Fe 2+ ions under potentiostatic conditions. Electrodeposition was performed in an electrochemical cell with three electrodes using a potentiostat. ITO glass with an area of 3 cm 2 was used as substrates. Before deposition, ITO glass was first cleaned with acetone for 30 min and then alcohol for 30 min, finally rinsed in distilled water. The reference electrode was a saturated calomel electrode (SCE). The anode was iron plate of dimension, 3 cm 2.Prior to deposition, the iron plate was first mechanically polished and then washed in dilute sulfuric acid and distilled water. Both electrodes were immersed in the same electrolyte. The compositions of the electrolytes with different molar ratiosofni 2+ /Fe 2+ were shown in table 1, together with major plating parameters. The total concentration of ferrous sulfate [FeSO 4 7H 2 O] and nickel sulfate [NiSO 4 6H 2 O] was kept at 0 20 M. All chemicals were of reagent grade and dissolved in distilled water. Electrolytes of the same composition but with different ph values were also prepared for comparison. The electrolyte composed of 0 12 M nickel sulfate [NiSO 4 6H 2 O], 0 08 M ferrous sulfate [FeSO 4 7H 2 O], 0 4 M boric acid [H 3 BO 3 ], 1 7 mm ascorbic acid [C 6 H 8 O 6 ] and 1 38 mm thiourea [CH 4 N 2 S] with different ph values of 2 1, 2 9, 3 7 and 4 5 adjusted by sodium hydroxide [NaOH] Table 1. Reagents Constitution and operating conditions of plating bath. Concentration FeSO 4 7H 2 O 0 10,0 08,0 06,0 04,0 02 M dm 3 NiSO 4 6H 2 O 0 10,0 12,0 14,0 16,0 18 M dm 3 H 3 BO M dm 3 Ascorbic acid 1 70 mm dm 3 Thiourea 1 38 mm dm 3 Temperature Room temperature ph values 2 9 Current density 0 5A dm 2 Plating duration 480 s Anode Iron plate Cathode ITO glass and sulphuric acid [H 2 SO 4 ]. Ni Fe films were deposited at a cathode potential of 1 5 V vs SCE. All the films were plated at a current density of 0 5A dm 2 at 25 C without stirring. The chemical composition of the films was analysed by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were performed on Rigaku D/Max-2400 X-ray diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation (40 kv, 60 ma). XRD data were recorded in a range from 25 to 90 with a step width of 0 02 and a counting time of 3 s per step. The morphology of the films was analysed on a Hitachi S-4800 field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM) operating at an acceleration voltage of 5 kv. The magnetic properties of the Fe 1 x Ni x films were measured by a Lake Shore 7304 vibrating sample magnetometer at room temperature. 3. Results and discussion 3.1 Effect of Ni % in electrolyte 3.1a ICP analysis: ICP AES measurement of the obtained films shows significant differences that exist between the actual compositions and the ratio of precursor electrolyte. The total concentration of ferrous sulfate [FeSO 4 7H 2 O] and nickel sulfate [NiSO 4 6H 2 O] was kept at 0 20 M. By changing the molar ratio of Ni 2+ /Fe 2+ in the reaction electrolyte from 0 50/0 50 to 0 90/0 10, the Ni content x in the films ranges from 38% to 84%. Meanwhile, the Fe content in the films decreases from 62% to 16%. As can be seen in figure 1, the Ni content is always lower than that in electrolytes demonstrating the existence of anomalous codeposition during the electrodeposition process. According to Matlosz s (1993) definition, the codeposition of iron-group metals (e.g. Fe, Co and Ni) is widely recognized as an anomalous electroplating type. The sequence of metal hydroxide ions with respect to increase in the adsorption ability is Ni(OH) + < Fe(OH) + (Yin and Lin 1996). The reaction mechanism is generally processed as following (Yin and Lin 1996; Harris et al 1999): 2H 2 O + 2e H 2 + 2OH, (1)
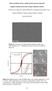
3 Ni-Fe alloy films synthesized by electrodeposition 185 Figure 1. Effect of molar ratio of NiSO 4 /FeSO 4 in electrolyte on film composition. and FeNi (211) of cubic structure. As shown in figure 2, the diffraction peaks of FeNi (110) shows stronger preferred orientation than that of FeNi (211) and FeNi (200) at any Ni content x. From the inset in figure 2, we can see that the diffraction peaks in the XRD patterns shift slightly towards low angles with increasing Ni content x, indicating increased lattice constant with increasing Ni content x. This can be attributed to the large atom radius of Ni (0 162 nm) as compared to the atom radium of Fe (0 110 nm). The incorporation of large atoms into the lattice of the film would expand the lattice and increase the lattice parameters (Kakatkar et al 1996; Tilak et al 1997). The average grain size for all the Fe Ni films estimated from the diffraction peak widths by Scherrer equation increases from 104 to 294 nm with the Co content x increasing from 0 38 to On the basis of above discussion, the structure of the deposited Fe Ni films strongly depends on both Ni 2+ and Fe 2+ concentrations in the electrolyte. 3.1c SEM analysis: Figure 3 displays the surface morphologies of Fe 1 x Ni x films with different Ni contents (x = 0 38, 0 55, 0 63, 0 69 and 0 84). Although the morphological investigation indicated that all the films have similar grainy structure, it is clearly found that the morphologies of the films are significantly influenced by both Ni 2+ and Fe 2+ concentrations in the plating bath. With increased Ni, the surface of the films becomes more rough and have larger grains. The effect is attributed to different compositions. From the morphologies, we can see that size of the films increase from 100 nm to 300 nm with Ni content x increasing from 0 38 to The average grain size determined by the SEM observations is in agreement with the average grain size estimated by XRD analysis, indicating that the granules in the Fe Ni films observed by SEM are grains and crystallites. Figure 2. XRD patterns of Fe 1 x Ni x films with Ni contents of x = 0 38, 0 55, 0 63, 0 69 and The inset shows the magnified (110) diffraction peaks of XRD patterns. M 2+ + OH MOH +, (2) MOH + (MOH) + ads, (3) (MOH) + ads + 2e M + OH, (4) where M indicates iron and nickel atoms. Although many attempts have been made to explain the anomalous codeposition of alloys, there is still no universally accepted theory. 3.1b XRD analysis: The XRD patterns of the prepared Fe 1 x Ni x films with different Ni contents, x, areshownin figure 2. The three diffraction peaks located at about 45 6, 64 9 and 82 3 are corresponding to FeNi (110), FeNi (200) 3.1d Magnetic property analysis: Figure 4 shows the dependence of saturation magnetization (M s ) and coercivity (H c ) of the films deposited from the electrolyte containing different mole ratios of Ni 2+ and Fe 2+. It can be seen that the saturation magnetization (M s ) moves up from emu/cm 3 to emu/cm 3 with the increase of Ni 2+ concentration in the electrolyte. The increase of the saturation magnetization (M s ) can be attributed to the increase of Ni content in the deposited films which is consistent with the previous ICP analysis. The coercivity (H c ) decreases with Ni content x increasing from 0 38 to 0 55, reaches a minimum value of Oe at x = 0 55, and then increases with further increasing of x. The coercivity (H c ) may be effected by two factors. First, the existence of defects in the films. Second, the increase of Ni content in the films. In this group of experiment, the effect of defect can be neglected compared with the sharp increase of Ni in the films resulting in an increase of coercivity (H c ).
4 186 Xinghua Su and Chengwen Qiang (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Figure 3. SEM images of Fe Ni films deposited at different Ni contents (a) Fe 0 62 Ni 0 38, (b)fe 0 45 Ni 0 55,(c) Fe 0 37 Ni 0 63,(d)Fe 0 31 Ni 0 69 and (e) Fe 0 16 Ni Figure 4. Dependence of saturation magnetization (M s ) and coercivity (H c ) of Fe Ni films on Ni content x. Figure 5. Dependence of Ni content in films on ph value.
5 Ni-Fe alloy films synthesized by electrodeposition Effects of ph values 3.2a ICP analysis: The effect of ph values on the composition of deposited films is shown in figure 5. It is found that the content of Ni in the deposited films falls from 65 to 42%, the content of Fe increases from 35 to 58% as the ph values vary from 2 1 to 4 3. The electrodeposition process is mainly dominated by anomalous codeposition. The electrodeposition process is mainly dominated by three factors: (i) the dissolution of the freshly deposited metal atoms on the substrate because of the acid condition in the electrolyte, (ii) the formation and absorption of metals hydroxides on the electrode surface and (iii) the anomalous electrodeposition of the metals. A lower ph value favours the dissolution of freshly deposited metals and depresses the formation and absorption of metal hydroxides, the process is predominated by the second factor except the anomalous electrodeposition resulting in a higher nickel content in the films due to the higher Ni 2+ in the electrolyte. Nevertheless, a higher ph value favours the formation and absorption of metals hydroxides and depresses the dissolution of the freshly deposited metals; the process is predominated by the anomalous deposition of the metals resulting in a lower nickel content because of the preferential absorption of iron hydroxides in the electrolyte (Yin and Lin 1996; Harris et al 1999). Figure 6. values. XRD patterns of Fe Ni films deposited at different ph 3.2b XRD analysis: Figure 6 shows the XRD patterns of Fe Ni films deposited at different ph values, the electrolyte containing 0 12 M NiSO 4 6H 2 O M FeSO 4 7H 2 O MH 3 BO mmc 6 H 8 O mm CH 4 N 2 S at room temperature. The diffraction peaks corresponding to Fe Ni alloys are found on all the curves, indicating the micro-crystalline structure of the films plated from the electrolytes of four ph values. As noticed in figure 6, no other diffraction peaks are found except the FeNi peaks located at about 45 6,64 9 and 82 3 corresponding to FeNi (110), (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 7. SEM images of Fe Ni films deposited at different ph values (a)ph = 2 10, (b)ph = 2 90, (c) ph= 3 70 and (d)ph= 4 50.
6 188 Xinghua Su and Chengwen Qiang increase in ph values. Coercivity (H c ) reaches a minimum value of Oe at ph = 2 9. On the basis of the above results, decrease of saturation magnetization (M s ) is caused by the increase of Fe which has lower saturation magnetization (M s ) than Ni in the films. The coercivity (H c ) is sensitive to the phase, defect, stress and thickness of the films (Li et al 2008). 4. Conclusions Figure 8. Dependence of saturation magnetization (M s ) and coercivity (H c ) of Fe Ni films on ph value. FeNi (200) and FeNi (211) of cubic structure. As shown in figure 6, the diffraction peaks of FeNi (110) shows stronger preferred orientation than that of FeNi (200) and FeNi (211) at any ph values. From the inset in figure 6, we can see that the diffraction peaks in the XRD patterns shift slightly towards high angles with increasing ph values, indicating decreasing lattice constant with increasing ph values. This can be attributed to the small atom radius of Fe (0 110 nm) as compared to the atom radium of Ni (0 162 nm). The incorporation of small atoms into the lattice of the film would shrink the lattice and decrease the lattice parameters (Kakatkar et al 1996; Tilak et al 1997). 3.2c SEM analysis: Figure 7 shows the surface morphology of the films deposited at different ph values from the electrolyte containing 0 12 M NiSO 4 6H 2 O M FeSO 4 7H 2 O M H 3 BO mm C 6 H 8 O mm CH 4 N 2 S at room temperature. The surface morphology is strongly influenced by the electrolyte ph. The films prepared at low ph values (2 10 and 2 90) show a relatively smooth surface and smaller grains compared to those prepared at high ph values (3 70 and 4 50). It is clearly indicated that with the ph values increasing, the surface of the films become more rough. This change may be explained by the hydrogen evolution, which is favoured at low ph values. Recent studies also showed that deposition parameters, for example ph, affect the microstructure of electrodeposited metal films (Alper et al 2008; Kockar et al 2010; Qiang et al 2010; Tian et al 2011). 3.2d Magnetic property analysis: Dependence of M S and H C of the Fe Ni films on the different ph values is shown in figure 8. It can be seen that the saturation magnetization (M s ) decreases from emu/cm 3 to emu/cm 3 with ph value increasing from 2 1 to 4 3. The coercivity (H c ) of the films slightly reduces from Oe of ph 2 1 to43 14 Oe of ph 2 9, and then increases with further Fe Ni films with different Ni content and morphology were successfully electrodeposited on ITO glass from the electrolytes containing both different Ni 2+ and Fe 2+ concentrations and different ph values without stirring. The content of nickel gradually increases from 38% to 84% as the mole ratio of NiSO 4 /FeSO 4 varying from 0 50/0 50 to 0 90/0 10 in electrolyte and the content of Ni slightly decreases from 65% to 42% as the ph values vary from 2 1 to4 3. The Fe 1 x Ni x films have the same structure with Ni content x increasing from 0 38 to The XRD and morphology investigation indicate that films have similar structure. However, the films grown in high ph values (3 7 and 4 5) have larger grains compared to those prepared at low ph values (2 1 and 2 9). The magnetic performance of the films shows that the saturation magnetization (M s ) moves up from emu/cm 3 to emu/cm 3 with the increase of Ni 2+ concentration in the electrolyte. The coercivity (H c ) decreases with the Ni content x increasing from 0 38 to 0 55, reaches a minimum value of Oe at x = 0 55, and then increases with further increase of Ni 2+ concentration in the electrolyte. The saturation magnetization (M s ) decreases from emu/cm 3 to emu/cm 3 with the ph value increasing from 2 1 to4 3. References Alper M, Kockar H, Safak M and Baykul M C 2008 J. Alloys. Compd Beltowska-Lenman E and Riesenkampf A 1980 Surf. Technol Beltowska-Lehman E, Ozga P, Swiatek Z and Lupi C 2002 Surf. Coat. Technol Chen Y and Sun I W 2001 Electrochim. Acta Chisholm C, Kuzmann E, EI-Sharif M, Doyle O, Stichleutner S, Solymos K, Homonnay Z and Vertes A 2007 Appl. Surf. Sci Chueng C, Djuanda F, Erb U and Palumbo G 1994 Mater. Sci. Eng. A85 39 Chueng C, Palumbo G and Erb U 1994 Scr. Metal. Mater Friemel F 1966 East German Patent Friemel F 1967 Chem. Abstr Gyftou P, Pavlatou E A and Spyrellis N 2008 Appl. Surf. Sci Harris T M, Wilson J L and Bleakley M 1999 J. Electrochem. Soc Jartych E, Jalochowiski M and Budzynski M 2002 Appl. Surf. Sci
7 Ni-Fe alloy films synthesized by electrodeposition 189 Kakatkar S V, Kakatkar S S, Patil R S, Sankpal A M, Suryawanshi S S, Bhosale D N and Sawant S R 1996 Phys. Status Solidi B Kockar Hakan, Alper Mursel, Sahin Turgut and Karaagac Oznur 2010 J. Magn. Magn. Mater Korenivski V 2000 J. Magn. Magn. Mater Krause T, Arulnayagam L and Pritzke M 1997 J. Electrochem. Soc Li B S, Lin A, Wu X, Zhang Y M and Gan F X 2008 J. Alloys. Compd Lieder M and Biallozor S 1985 Surf. Technol Lodhi Z F, Mol J M C, Hamer W J, Terryn H A and DeWit J H W 2007 Electrochim. Acta Marikkannu K R, Paruthimal Kalaignan G and Vasudevan T 2007 J. Alloys Compd Matlosz M 1993 J. Electrochem. Soc Osaka T 1999 Electrochem. Acta Osaka T, Takai M, Ohashi K, Saito M and Yamada K 1998 Nature Passal F 1966 US Patent Passal F 1967 Chem. Abstr Qiang C W, Xu J C, Xiao S T, Jiao Y J, Zhang Z Q, Liu Y, Tian L L and Zhou Z G 2010 Appl. Surf. Sci Romankiw L T, Croll I M and Hatzakis M 1970 IEEE Trans. Magn Sasaki K Y and Talbot J B 2000 J. Electrochem. Soc Schwarzacher W and Lashmore D S 1996 IEEE Trans. Hagn. MAG Siritaratiwat A, Hill E W, Stutt I, Fallon J M and Grundy P J 2000 Sensor Actuat. A: Phys Tian L L, Xu J C and Qiang C W 2011 Appl. Surf. Sci Tilak B V, Gendron A S and Mosoiu M A 1997 J. Electrochem. Soc Valeri S, Giovanardi C, Borghi A, di Bona A and Luches P 2001 Appl. Surf. Sci Venkatasetty H V 1970 J. Electrochem. Soc Yin K M 1997 J. Electrochem. Soc Yin K M and Lin B T 1996 Surf. Technol Zech Z, Podlaha E J and Landolt D 1999 J. Electrochem. Soc Zhang Y H and Ivey D L G 2004 Chem. Mater
Mechanical and magnetic properties of nanostructured CoNiP films
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2 journal of August 2006 physics pp. 341 349 Mechanical and magnetic properties of nanostructured CoNiP films R N EMERSON 1, C JOSEPH KENNADY 2, and S
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2 journal of August 2006 physics pp. 341 349 Mechanical and magnetic properties of nanostructured CoNiP films R N EMERSON 1, C JOSEPH KENNADY 2, and S
Galvanostatic charge discharge tests, 57 Fe and 119 Sn Mössbauer and XRD measurements on novel Sn-Ni-Fe electrodeposits
 Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-012-0693-5 Galvanostatic charge discharge tests, 57 Fe and 119 Sn Mössbauer and XRD measurements on novel Sn-Ni-Fe electrodeposits G. B. Lak E. Kuzmann M. El-Sharif
Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-012-0693-5 Galvanostatic charge discharge tests, 57 Fe and 119 Sn Mössbauer and XRD measurements on novel Sn-Ni-Fe electrodeposits G. B. Lak E. Kuzmann M. El-Sharif
A STUDY ON STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF ELECTROPLATED NANO CRYSTALLINE NICKEL BASED THIN FILMS
 ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in A STUDY ON STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF ELECTROPLATED NANO CRYSTALLINE NICKEL BASED THIN FILMS R.
ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in A STUDY ON STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF ELECTROPLATED NANO CRYSTALLINE NICKEL BASED THIN FILMS R.
Effects of Bath Temperature on Electrodeposited Permanent Magnetic Co-Pt-W(P) Films
 2214 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, Vol. 28, No. 12 Hongliang Ge et al. Effects of Bath Temperature on Electrodeposited Permanent Magnetic Co-Pt-W(P) Films Hongliang Ge, * Qiong Wu, Guoying Wei, Xinyan
2214 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, Vol. 28, No. 12 Hongliang Ge et al. Effects of Bath Temperature on Electrodeposited Permanent Magnetic Co-Pt-W(P) Films Hongliang Ge, * Qiong Wu, Guoying Wei, Xinyan
Investigation on the effect of Electro-co-deposition process parameter bath temperature on Nano Structured Ni-WC Composite coating properties
 International Journal of Materials Science ISSN 0973-4589 Volume 11, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9-15 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Investigation on the effect of Electro-co-deposition
International Journal of Materials Science ISSN 0973-4589 Volume 11, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9-15 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Investigation on the effect of Electro-co-deposition
GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE
 Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 8, September 29, p. 415 419 GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR, * MSS s College
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 8, September 29, p. 415 419 GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR, * MSS s College
Effects of organic additive saccharin on the magnetic properties of CoMnP thin films
 Material Science Research India Vol. 7(1), 159-166 (2010) Effects of organic additive saccharin on the magnetic properties of CoMnP thin films M.RM. KRISHNAPPA¹*, N. RAJASEKARAN², S. GANESAN 3 and R.N.
Material Science Research India Vol. 7(1), 159-166 (2010) Effects of organic additive saccharin on the magnetic properties of CoMnP thin films M.RM. KRISHNAPPA¹*, N. RAJASEKARAN², S. GANESAN 3 and R.N.
Potentiostatic Electrodeposition of Co-Ni-Fe Alloy Particles Thin Film in a Sulfate Medium
 Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2017, 35(1), 1-12 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201701001 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Potentiostatic Electrodeposition of Co-Ni-Fe Alloy Particles Thin Film in a Sulfate
Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2017, 35(1), 1-12 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201701001 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Potentiostatic Electrodeposition of Co-Ni-Fe Alloy Particles Thin Film in a Sulfate
The effect of pulsed electrodeposition parameters on the microstructure and magnetic properties of the CoNi nanowires
 JNS 1 (2012) 249-255 The effect of pulsed electrodeposition parameters on the microstructure and magnetic properties of the CoNi nanowires M. Almasi Kashi *, A. Ramazani, N. Akhshi, E. J. Khamse, Z. Fallah
JNS 1 (2012) 249-255 The effect of pulsed electrodeposition parameters on the microstructure and magnetic properties of the CoNi nanowires M. Almasi Kashi *, A. Ramazani, N. Akhshi, E. J. Khamse, Z. Fallah
A Study on the Electrodeposition of NiFe Alloy Thin Films Using Chronocoulometry and Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microgravimetry
 994 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2001, Vol. 22, No. 9 Noseung Myung A Study on the Electrodeposition of NiFe Alloy Thin Films Using Chronocoulometry and Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microgravimetry Noseung
994 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2001, Vol. 22, No. 9 Noseung Myung A Study on the Electrodeposition of NiFe Alloy Thin Films Using Chronocoulometry and Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microgravimetry Noseung
Bipolar performance of the electroplated iron nickel deposits for water electrolysis
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 8 (00) 588 596 Bipolar performance of the electroplated iron nickel deposits for water electrolysis Chi-Chang Hu, Yau-Ruen Wu Department of Chemical Engineering, National
Materials Chemistry and Physics 8 (00) 588 596 Bipolar performance of the electroplated iron nickel deposits for water electrolysis Chi-Chang Hu, Yau-Ruen Wu Department of Chemical Engineering, National
Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 14, March 2007, pp. 161-165 Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy V S Muralidharan Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi 630 006, India Received
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 14, March 2007, pp. 161-165 Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy V S Muralidharan Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi 630 006, India Received
De-ionized water. Nickel target. Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup.
 Graphite Electrode Graphite Electrode De-ionized water Nickel target Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup. Intensity ( a.u.) Ni(OH) 2 deposited on the graphite blank
Graphite Electrode Graphite Electrode De-ionized water Nickel target Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup. Intensity ( a.u.) Ni(OH) 2 deposited on the graphite blank
ELECTRODEPOSITED Ni-Fe-S FILMS WITH HIGH RESISTIVITY FOR MAGNETIC RECORDING DEVICES
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 6, No. 2, June 2004, p. 641-645 ELECTRODEPOSITED Ni-Fe-S FILMS WITH HIGH RESISTIVITY FOR MAGNETIC RECORDING DEVICES N. Suli anu, F. Brînz Department
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 6, No. 2, June 2004, p. 641-645 ELECTRODEPOSITED Ni-Fe-S FILMS WITH HIGH RESISTIVITY FOR MAGNETIC RECORDING DEVICES N. Suli anu, F. Brînz Department
Studies on Alloys and Composites that Undergo Anomalous Codeposition
 Studies on Alloys and Composites that Undergo Anomalous Codeposition Electrochemical of of South Columbia, SC908 09, 1998 Electrochemical Systems Studied FeNi alloys and FeNiSiO composites Electrodeposition
Studies on Alloys and Composites that Undergo Anomalous Codeposition Electrochemical of of South Columbia, SC908 09, 1998 Electrochemical Systems Studied FeNi alloys and FeNiSiO composites Electrodeposition
NASF SURFACE TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPERS 80 (7), 1-8 (April 2016) 10th Quarterly Report April - June 2015 AESF Research Project #R-117
 10th Quarterly Report April - June 2015 AESF Research Project #R-117 Electrodeposition of Ni-Fe-Mo-W Alloys by Prof. E.J. Podlaha-Murphy, * and A. Kola Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts, USA
10th Quarterly Report April - June 2015 AESF Research Project #R-117 Electrodeposition of Ni-Fe-Mo-W Alloys by Prof. E.J. Podlaha-Murphy, * and A. Kola Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts, USA
Mössbauer and XRD study of novel quaternary Sn-Fe-Co-Ni electroplated alloy
 Hyperfine Interact (2017) 238:97 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-017-1474-y Mössbauer and XRD study of novel quaternary Sn-Fe-Co-Ni electroplated alloy E. Kuzmann 1 L. Sziráki 1 S. Stichleutner 2 Z. Homonnay
Hyperfine Interact (2017) 238:97 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-017-1474-y Mössbauer and XRD study of novel quaternary Sn-Fe-Co-Ni electroplated alloy E. Kuzmann 1 L. Sziráki 1 S. Stichleutner 2 Z. Homonnay
Electrolytic deposition of Zn-Mn-Mo alloys from a citrate bath
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 17, September 2010, pp. 381-385 Electrolytic deposition of Zn-Mn-Mo alloys from a citrate bath Renu Rastogi* & Archana Pandey Department of Chemistry, Brahmanand
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 17, September 2010, pp. 381-385 Electrolytic deposition of Zn-Mn-Mo alloys from a citrate bath Renu Rastogi* & Archana Pandey Department of Chemistry, Brahmanand
Pulse electrodeposition and corrosion properties of Ni Si 3 N 4 nanocomposite coatings
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 3, May 2014, pp. 721 728. Indian Academy of Sciences. Pulse electrodeposition and corrosion properties of Ni Si 3 N 4 nanocomposite coatings S KASTURIBAI 1,2 and G PARUTHIMAL
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 3, May 2014, pp. 721 728. Indian Academy of Sciences. Pulse electrodeposition and corrosion properties of Ni Si 3 N 4 nanocomposite coatings S KASTURIBAI 1,2 and G PARUTHIMAL
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT FERROUS CONCENTRATION ON STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ELECTRODEPOSITED FeNiCo THIN FILMS
 EFFECT OF DIFFERENT FERROUS CONCENTRATION ON STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ELECTRODEPOSITED FeNiCo THIN FILMS K. Mohan Rangam Kadiresan 1,V. Senthil Kumar 2 1 Research Scholar, 2 Associate Professor,
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT FERROUS CONCENTRATION ON STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ELECTRODEPOSITED FeNiCo THIN FILMS K. Mohan Rangam Kadiresan 1,V. Senthil Kumar 2 1 Research Scholar, 2 Associate Professor,
ELECTRIDEPOSITION AND WEAR BEHAVIOR OF NANO-STRUCTURED Cr-WC COMPOSITE COATINGS FROM A TRIVALENT CHROMIUM BATH
 2nd International Conference on Ultrafine Grained & Nanostructured Materials (UFGNSM) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 5 (2012) 737 743 World Scientific Publishing Company
2nd International Conference on Ultrafine Grained & Nanostructured Materials (UFGNSM) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 5 (2012) 737 743 World Scientific Publishing Company
Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films
 Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films H. R. Kulkarni KJ College of Engineering and Management Research, Pune, India Abstract: ZnS thin films were prepared by pulsed electrodeposition
Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films H. R. Kulkarni KJ College of Engineering and Management Research, Pune, India Abstract: ZnS thin films were prepared by pulsed electrodeposition
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT COBALT CONCENTRATION ON PROPERTIES OF ELECTRODEPOSITED NiCoCr THIN FILMS
 ISSN: 974-1496 e-issn: 976-83 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in EFFECT OF DIFFERENT COBALT CONCENTRATION ON S. P. Meena 1,* and R. Ashokkumar 2 1,* Research Scholar,
ISSN: 974-1496 e-issn: 976-83 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in EFFECT OF DIFFERENT COBALT CONCENTRATION ON S. P. Meena 1,* and R. Ashokkumar 2 1,* Research Scholar,
The Deposition Characteristics of Accelerated Nonformaldehyde Electroless Copper Plating
 C558 Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 15 8 C558-C562 23 13-4651/23/15 8 /C558/5/$7. The Electrochemical Society, Inc. The Deposition Characteristics of Accelerated Nonformaldehyde Electroless Copper
C558 Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 15 8 C558-C562 23 13-4651/23/15 8 /C558/5/$7. The Electrochemical Society, Inc. The Deposition Characteristics of Accelerated Nonformaldehyde Electroless Copper
Electrosynthesis of iron, cobalt and zinc microcrystals and. magnetic enhancement of the oxygen reduction reaction
 M / [A m 2 kg -1 ] Electrosynthesis of iron, cobalt and zinc microcrystals and magnetic enhancement of the oxygen reduction reaction Lorena M. A. Monzon*, Karsten Rode, M. Venkatesan and J.M.D. Coey School
M / [A m 2 kg -1 ] Electrosynthesis of iron, cobalt and zinc microcrystals and magnetic enhancement of the oxygen reduction reaction Lorena M. A. Monzon*, Karsten Rode, M. Venkatesan and J.M.D. Coey School
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalysis via Electrodeposited Amorphous α Phase Nickel-Cobalt Hydroxide Nanodendrite Forests By Anirudh Balram, Hanfei Zhang, and Sunand
Supporting Information Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalysis via Electrodeposited Amorphous α Phase Nickel-Cobalt Hydroxide Nanodendrite Forests By Anirudh Balram, Hanfei Zhang, and Sunand
Department of Physics, Velalar College of Engineering and Technology, Erode , India.
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.6, No.1, pp 509-514, Jan-March 14 Effect of NaH 2 PO 2 on Electrodeposited Ferrous Tungsten Phosphorous Thin Film N.Thangaraj
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.6, No.1, pp 509-514, Jan-March 14 Effect of NaH 2 PO 2 on Electrodeposited Ferrous Tungsten Phosphorous Thin Film N.Thangaraj
Effect of lactic acid on nucleation morphology and surface roughness of electroless Ni P deposition in nanoscale
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 4, August 2012, pp. 561 566. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Effect of lactic acid on nucleation morphology and surface roughness of electroless Ni P deposition in nanoscale
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 4, August 2012, pp. 561 566. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Effect of lactic acid on nucleation morphology and surface roughness of electroless Ni P deposition in nanoscale
Structural and magnetic properties of electrodeposited Ni-Fe-W-S thin films
 OPTOELECTRONICS AND ADVANCED MATERIALS RAPID COMMUNICATIONS Vol. 6, No. 3-4, March - April 212, p. 383-388 Structural and magnetic properties of electrodeposited Ni-Fe-W-S thin films R. KANNAN *, S. GANESAN
OPTOELECTRONICS AND ADVANCED MATERIALS RAPID COMMUNICATIONS Vol. 6, No. 3-4, March - April 212, p. 383-388 Structural and magnetic properties of electrodeposited Ni-Fe-W-S thin films R. KANNAN *, S. GANESAN
Electrodeposition and Properties of ZnFeNi Alloys. Ismail Hakki Karahan
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 46, NO. 1 FEBRUARY 2008 Electrodeposition and Properties of ZnFeNi Alloys Ismail Hakki Karahan Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and Arts, Kilis 7 Aralik Universty,
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 46, NO. 1 FEBRUARY 2008 Electrodeposition and Properties of ZnFeNi Alloys Ismail Hakki Karahan Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and Arts, Kilis 7 Aralik Universty,
Optimized by Disorder Engineering on Iron doped Ni 3 S 2. nanosheets for Oxygen Evolution Reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Data Optimized by Disorder Engineering on Iron doped Ni 3 S 2 nanosheets for Oxygen
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Data Optimized by Disorder Engineering on Iron doped Ni 3 S 2 nanosheets for Oxygen
Novel concept of rechargeable battery using iron oxide nanorods. anode and nickel hydroxide cathode in aqueous electrolyte
 Supplementary Information for: Novel concept of rechargeable battery using iron oxide nanorods anode and nickel hydroxide cathode in aqueous electrolyte Zhaolin Liu *, Siok Wei Tay and Xu Li Institute
Supplementary Information for: Novel concept of rechargeable battery using iron oxide nanorods anode and nickel hydroxide cathode in aqueous electrolyte Zhaolin Liu *, Siok Wei Tay and Xu Li Institute
METAL FINISHING. (As per revised VTU syllabus: )
 METAL FINISHING (As per revised VTU syllabus: 2015-16) Definition: It is a process in which a specimen metal (article) is coated with another metal or a polymer in order to modify the surface properties
METAL FINISHING (As per revised VTU syllabus: 2015-16) Definition: It is a process in which a specimen metal (article) is coated with another metal or a polymer in order to modify the surface properties
Lahore College for Women University, Lahore-54000, Pakistan
 1 Structural Characterization and Optical Properties of cobalt oxide Thin Films *Zohra Nazir Kayani 1), Saliha Arshad 1), Saira Riaz 2), Rehana Zia 1) and Shahzad Naseem 2) 1) Lahore College for Women
1 Structural Characterization and Optical Properties of cobalt oxide Thin Films *Zohra Nazir Kayani 1), Saliha Arshad 1), Saira Riaz 2), Rehana Zia 1) and Shahzad Naseem 2) 1) Lahore College for Women
The effect of peptone on the structure of electrodeposited Sn-Fe binary alloys
 Hyperfine Interact (2016) 237:20 DOI 10.1007/s10751-016-1226-4 The effect of peptone on the structure of electrodeposited Sn-Fe binary alloys G. B. Lak 1 L. Sziráki 2 E. Kuzmann 2 S. Stichleutner 2,3 C.
Hyperfine Interact (2016) 237:20 DOI 10.1007/s10751-016-1226-4 The effect of peptone on the structure of electrodeposited Sn-Fe binary alloys G. B. Lak 1 L. Sziráki 2 E. Kuzmann 2 S. Stichleutner 2,3 C.
J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26(11),
 J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26(11), 1016-1020. Effects of Current Density on the Microstructure and the Corrosion Resistance of Alumina Coatings Embedded with SiC Nano-particles Produced by Micro-arc
J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26(11), 1016-1020. Effects of Current Density on the Microstructure and the Corrosion Resistance of Alumina Coatings Embedded with SiC Nano-particles Produced by Micro-arc
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Experimental All the chemicals were of analytical grade and used without
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Experimental All the chemicals were of analytical grade and used without
INFLUENCE OF PHOSPHOROUS AND UREA ON THE MAGNETIC AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED FEPTP FILMS
 , pp. 276-281 INFLUENCE OF PHOSPHOROUS AND UREA ON THE MAGNETIC AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED FEPTP FILMS T. M. Selvakumari a*, P. Muthukumar b, S. Ganesan c, and R. N. Emerson d a,b Department
, pp. 276-281 INFLUENCE OF PHOSPHOROUS AND UREA ON THE MAGNETIC AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED FEPTP FILMS T. M. Selvakumari a*, P. Muthukumar b, S. Ganesan c, and R. N. Emerson d a,b Department
Three-dimensional NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Film for Highefficiency
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Three-dimensional NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Film for Highefficiency Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Three-dimensional NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Film for Highefficiency Oxygen Evolution Reaction
3d metallic layers electrochemically deposited from nearly nonaqueous electrolyte *
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 26, No. 3, 2008 3d metallic layers electrochemically deposited from nearly nonaqueous electrolyte * W. OLSZEWSKI 1**, K. SZYMAŃSKI 1, M. BIERNACKA 1, R. SOBIECKI 2 1 Faculty
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 26, No. 3, 2008 3d metallic layers electrochemically deposited from nearly nonaqueous electrolyte * W. OLSZEWSKI 1**, K. SZYMAŃSKI 1, M. BIERNACKA 1, R. SOBIECKI 2 1 Faculty
Effect of bath temperature on the magnetic and mechanical properties of nanostructured FePtP hard magnetic films
 OPTOELECTRONICS AND ADVANCED MATERIALS RAPID COMMUNICATIONS Vol. 4, No. 7, July 2010, p. 976-981 Effect of bath temperature on the magnetic and mechanical properties of nanostructured FePtP hard magnetic
OPTOELECTRONICS AND ADVANCED MATERIALS RAPID COMMUNICATIONS Vol. 4, No. 7, July 2010, p. 976-981 Effect of bath temperature on the magnetic and mechanical properties of nanostructured FePtP hard magnetic
Performance Evaluation of Zinc Deposited Mild Steel in Chloride Medium.
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6 (2011) 3254-3263 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Performance Evaluation of Zinc Deposited Mild Steel in Chloride Medium. Popoola A.P.I
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6 (2011) 3254-3263 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Performance Evaluation of Zinc Deposited Mild Steel in Chloride Medium. Popoola A.P.I
Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as. Negative Electrode Materials
 Supplementary Information: Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as Negative Electrode Materials X. P. Gao, S. M. Yao, T. Y. Yan, Z. Zhou Institute of New Energy Material Chemistry,
Supplementary Information: Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as Negative Electrode Materials X. P. Gao, S. M. Yao, T. Y. Yan, Z. Zhou Institute of New Energy Material Chemistry,
Electrodeposition and characterisation of Ni-based anticorrosive coatings
 Electrodeposition and characterisation of Ni-based anticorrosive coatings Agnieszka Bigos 1. Introduction Hard chromium coatings, characterized by enhanced functional properties, are widely used in many
Electrodeposition and characterisation of Ni-based anticorrosive coatings Agnieszka Bigos 1. Introduction Hard chromium coatings, characterized by enhanced functional properties, are widely used in many
ELECTROFABRICATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED MULTILAYER COATINGS FOR BETTER CORROSION PROTECTION
 NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2013, 4 (3), P. 409 416 ELECTROFABRICATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED MULTILAYER COATINGS FOR BETTER CORROSION PROTECTION R. R. Vaishaka, A. C. Hegde* Electrochemistry
NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2013, 4 (3), P. 409 416 ELECTROFABRICATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED MULTILAYER COATINGS FOR BETTER CORROSION PROTECTION R. R. Vaishaka, A. C. Hegde* Electrochemistry
INFLUENCE OF TRI SODIUM CITRATE BATH CONCENTRATION ON THE ELECTRO DEPOSITION OF Ni-Fe-W-S THIN FILMS
 Journal of Ovonic Research Vol. 9, No. 2, March - April 2013, p. 45-54 INFLUENCE OF TRI SODIUM CITRATE BATH CONCENTRATION ON THE ELECTRO DEPOSITION OF Ni-Fe-W-S THIN FILMS R. KANNAN a*, R.KANAGARAJ b S.
Journal of Ovonic Research Vol. 9, No. 2, March - April 2013, p. 45-54 INFLUENCE OF TRI SODIUM CITRATE BATH CONCENTRATION ON THE ELECTRO DEPOSITION OF Ni-Fe-W-S THIN FILMS R. KANNAN a*, R.KANAGARAJ b S.
Electronic Supporting Information. Synthesis of single crystalline hexagonal nanobricks of
 Electronic Supporting Information Synthesis of single crystalline hexagonal nanobricks of LiNi 1/3 Co 1/3 Mn 1/3 O 2 with high percentage of exposed {010} active facets as high rate performance cathode
Electronic Supporting Information Synthesis of single crystalline hexagonal nanobricks of LiNi 1/3 Co 1/3 Mn 1/3 O 2 with high percentage of exposed {010} active facets as high rate performance cathode
Effect of bath types on sonoelectrodeposited Cu/Ni Multilayer at low temperature
 Archived in http://dspace.nitrkl.ac.in/dspace Silver Jubilee International Conference 10 th Conference of International Academy of Physical Sciences CONIAPS-X January 12-14 2008 Guru Ghasidas University,
Archived in http://dspace.nitrkl.ac.in/dspace Silver Jubilee International Conference 10 th Conference of International Academy of Physical Sciences CONIAPS-X January 12-14 2008 Guru Ghasidas University,
Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration
 International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 5 No. 5, May, 2016 Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration I. B. Obasi 1 and J. C. Osuwa 2
International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 5 No. 5, May, 2016 Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration I. B. Obasi 1 and J. C. Osuwa 2
Mechanical Properti es of ZnO:Mo Transparent Conducting Oxide Thin Film Prepared by Sputtering
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 51, NO. 3 June 2013 Mechanical Properti es of ZnO:Mo Transparent Conducting Oxide Thin Film Prepared by Sputtering Y. C. Lin, C. C. Chen, and W. Y. Lai Department of Mechatronics
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 51, NO. 3 June 2013 Mechanical Properti es of ZnO:Mo Transparent Conducting Oxide Thin Film Prepared by Sputtering Y. C. Lin, C. C. Chen, and W. Y. Lai Department of Mechatronics
Electrochemical Deposition and Characterization of Zinc-Cobalt
 Electrochemical Deposition and Characterization of Zinc-Cobalt Neha Deshmukh 1, R. K. Pathak 2 1, 2 Govt. Holkar Science College, Department of Chemistry, Indore - 451, India Abstract: Various protective
Electrochemical Deposition and Characterization of Zinc-Cobalt Neha Deshmukh 1, R. K. Pathak 2 1, 2 Govt. Holkar Science College, Department of Chemistry, Indore - 451, India Abstract: Various protective
Effects of Saccharin Addition on Surface Morphology and Microstructure of Electrodeposited Cu-In Alloy
 Effects of Saccharin Addition on Surface Morphology and Microstructure of Electrodeposited Cu-In Alloy Hsiang Chen a *, Yih-Min Yeh b, Ching-Pang Chen c Abstract In this research, material quality of electrodeposited
Effects of Saccharin Addition on Surface Morphology and Microstructure of Electrodeposited Cu-In Alloy Hsiang Chen a *, Yih-Min Yeh b, Ching-Pang Chen c Abstract In this research, material quality of electrodeposited
Anisotropic Magnetism and Magnetoresistance in Iron Nanowire Arrays
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 47, NO. 6 DECEMBER 2009 Anisotropic Magnetism and Magnetoresistance in Iron Nanowire Arrays M. N. Ou, 1,2 T. J. Yang, 2 and Y. Y. Chen 1 1 Institute of Physics, Academia
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 47, NO. 6 DECEMBER 2009 Anisotropic Magnetism and Magnetoresistance in Iron Nanowire Arrays M. N. Ou, 1,2 T. J. Yang, 2 and Y. Y. Chen 1 1 Institute of Physics, Academia
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT CURRENT DENSITY ON CHARACTERISTICS OF NiFeP NANO ALLOY THIN FILMS
 ISSN: 974-1496 e-issn: 976-83 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT CURRENT DENSITY ON CHARACTERISTICS OF C. Devi 1,2,* and R. Ashokkumar 3
ISSN: 974-1496 e-issn: 976-83 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT CURRENT DENSITY ON CHARACTERISTICS OF C. Devi 1,2,* and R. Ashokkumar 3
A Novel Electrodeposition Process for Plating Zn-Ni-Cd Alloys
 Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 150 2 C81-C88 2003 0013-4651/2003/150 2 /C81/8/$7.00 The Electrochemical Society, Inc. A Novel Electrodeposition Process for Plating Zn-Ni-Cd Alloys Hansung Kim,
Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 150 2 C81-C88 2003 0013-4651/2003/150 2 /C81/8/$7.00 The Electrochemical Society, Inc. A Novel Electrodeposition Process for Plating Zn-Ni-Cd Alloys Hansung Kim,
Size dependent optical characteristics of chemically deposited nanostructured ZnS thin films
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 30, No. 2, April 2007, pp. 147 151. Indian Academy of Sciences. Size dependent optical characteristics of chemically deposited nanostructured ZnS thin films A U UBALE*, V S SANGAWAR
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 30, No. 2, April 2007, pp. 147 151. Indian Academy of Sciences. Size dependent optical characteristics of chemically deposited nanostructured ZnS thin films A U UBALE*, V S SANGAWAR
Order-Disorder Transformation in Fe 50 Co 50 Particles Synthesized by Polyol Process
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 4 (21) pp. 77 to 711 #21 The Japan Institute of Metals Order-Disorder Transformation in Fe 5 Co 5 Particles Synthesized by Polyol Process G. B. Chon 1, K. Shinoda 1,
Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 4 (21) pp. 77 to 711 #21 The Japan Institute of Metals Order-Disorder Transformation in Fe 5 Co 5 Particles Synthesized by Polyol Process G. B. Chon 1, K. Shinoda 1,
CORROSION BEHAVIOUR OF COATED HOLLOW SPHERES IN ACETATE BUFFER WITH KCl
 Powder Metallurgy Progress, Vol.7 (2007), No 2 103 CORROSION BEHAVIOUR OF COATED HOLLOW SPHERES IN ACETATE BUFFER WITH KCl A. Fedorková, R. Oriňáková, M. Kupková, E. Dudrová, M. Kabátová Abstract The potentiodynamic
Powder Metallurgy Progress, Vol.7 (2007), No 2 103 CORROSION BEHAVIOUR OF COATED HOLLOW SPHERES IN ACETATE BUFFER WITH KCl A. Fedorková, R. Oriňáková, M. Kupková, E. Dudrová, M. Kabátová Abstract The potentiodynamic
Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs Catalysts Prepared by Pulse Potential Plating Methods
 Solid State Phenomena Vols. 124-126 (2007) pp 1039-1042 Online: 2007-06-15 (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.124-126.1039 Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs
Solid State Phenomena Vols. 124-126 (2007) pp 1039-1042 Online: 2007-06-15 (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.124-126.1039 Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs
EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE
 EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE Noor Zaimah 1, Azieyanti Nurain 1 and Sakhawat Hussain 2 1 Department
EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE Noor Zaimah 1, Azieyanti Nurain 1 and Sakhawat Hussain 2 1 Department
Integrated CoPtP Permanent Magnets for MEMS Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting Applications
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Integrated CoPtP Permanent Magnets for MEMS Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting Applications Related content - Electrodeposition of hard magnetic CoPtP
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Integrated CoPtP Permanent Magnets for MEMS Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting Applications Related content - Electrodeposition of hard magnetic CoPtP
Three-dimensional Nano-electrode. by Metal-Nanowire-Nonwoven Clothes
 Supporting Information for Three-dimensional Nano-electrode by Metal-Nanowire-Nonwoven Clothes Makoto Kawamori,* Takahiro Asai, Yoshimasa Shirai, Shunsuke Yagi, Masatsugu Oishi, Tetsu Ichitsubo, and Eiichiro
Supporting Information for Three-dimensional Nano-electrode by Metal-Nanowire-Nonwoven Clothes Makoto Kawamori,* Takahiro Asai, Yoshimasa Shirai, Shunsuke Yagi, Masatsugu Oishi, Tetsu Ichitsubo, and Eiichiro
Deposited by Sputtering of Sn and SnO 2
 Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society Vol. 49, No. 5, pp. 448~453, 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.4191/kcers.2012.49.5.448 Comparative Study of Nitrogen Incorporated SnO 2 Deposited by Sputtering of Sn and
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society Vol. 49, No. 5, pp. 448~453, 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.4191/kcers.2012.49.5.448 Comparative Study of Nitrogen Incorporated SnO 2 Deposited by Sputtering of Sn and
EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT ELECTROLYTE SYSTEMS ON THE FORMATION OF MICRO-ARC OXIDATION CERAMIC COATINGS OF 6061 ALUMINUM ALLOY
 16 Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. (01) 16-10 Y.J. Liu, EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT ELECTROLYTE SYSTEMS ON THE FORMATION OF MICRO-ARC OXIDATION CERAMIC COATINGS OF 6061 ALUMINUM ALLOY Y.J. Liu 1, J.Y. Xu1, W. Lin, C. Gao
16 Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. (01) 16-10 Y.J. Liu, EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT ELECTROLYTE SYSTEMS ON THE FORMATION OF MICRO-ARC OXIDATION CERAMIC COATINGS OF 6061 ALUMINUM ALLOY Y.J. Liu 1, J.Y. Xu1, W. Lin, C. Gao
Supplementary Figure 1 The lithium polysulfide distribution on the patterned electrode.
 Supplementary Figure 1.The lithium polysulfide distribution on the patterned electrode. SEM image of the ITO-carbon electrode after dipping into Li 2 S 8 solution and drying, which shows the random distribution
Supplementary Figure 1.The lithium polysulfide distribution on the patterned electrode. SEM image of the ITO-carbon electrode after dipping into Li 2 S 8 solution and drying, which shows the random distribution
General Introduction to Microstructure Technology p. 1 What is Microstructure Technology? p. 1 From Microstructure Technology to Microsystems
 General Introduction to Microstructure Technology p. 1 What is Microstructure Technology? p. 1 From Microstructure Technology to Microsystems Technology p. 9 The Parallels to Microelectronics p. 15 The
General Introduction to Microstructure Technology p. 1 What is Microstructure Technology? p. 1 From Microstructure Technology to Microsystems Technology p. 9 The Parallels to Microelectronics p. 15 The
Microstructure and tribological properties of electrodeposited Ni Co alloy deposits
 Applied Surface Science 242 (2005) 326 332 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Microstructure and tribological properties of electrodeposited Ni Co alloy deposits Liping Wang a,b, Yan Gao a,b, Qunji Xue a,
Applied Surface Science 242 (2005) 326 332 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Microstructure and tribological properties of electrodeposited Ni Co alloy deposits Liping Wang a,b, Yan Gao a,b, Qunji Xue a,
Zn Ni alloy A probable replacement to Cadmium coating R Mani Sravani, Meenu Srivastava Surface Engineering Division, CSIR NAL, Bangalore
 Zn Ni alloy A probable replacement to Cadmium coating R Mani Sravani, Meenu Srivastava Surface Engineering Division, CSIR NAL, Bangalore 560017. 1.0 Introduction Cadmium (Cd) is an important metal which,
Zn Ni alloy A probable replacement to Cadmium coating R Mani Sravani, Meenu Srivastava Surface Engineering Division, CSIR NAL, Bangalore 560017. 1.0 Introduction Cadmium (Cd) is an important metal which,
Characterisation of nickel deposits from nickel acetate bath
 Characterisation of nickel deposits from nickel acetate bath R. Srinivasan* and G. N. K. Ramesh Bapu The electrodeposition of nickel on mild steel was carried out using a nickel acetate bath. Cathodic
Characterisation of nickel deposits from nickel acetate bath R. Srinivasan* and G. N. K. Ramesh Bapu The electrodeposition of nickel on mild steel was carried out using a nickel acetate bath. Cathodic
Ceramic Processing Research
 Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 17, No. 11, pp. 1192~1196 (2016) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Degradation mechanism of the complementary electrochromic devices with WO 3 and
Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 17, No. 11, pp. 1192~1196 (2016) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Degradation mechanism of the complementary electrochromic devices with WO 3 and
More Thin Film X-ray Scattering and X-ray Reflectivity
 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory More Thin Film X-ray Scattering and X-ray Reflectivity Mike Toney, SSRL 1. Introduction (real space reciprocal space) 2. Polycrystalline film (no texture) RuPt
Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory More Thin Film X-ray Scattering and X-ray Reflectivity Mike Toney, SSRL 1. Introduction (real space reciprocal space) 2. Polycrystalline film (no texture) RuPt
Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates
 Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 90 (2006) 753 759 www.elsevier.com/locate/solmat Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates K.R. Murali a,, A. Austine
Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 90 (2006) 753 759 www.elsevier.com/locate/solmat Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates K.R. Murali a,, A. Austine
Design and Fabrication of Low Power Consumption Micro Fluxgate Sensor
 Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Design and Fabrication of Low Power Consumption Micro Fluxgate Sensor 1, 2 HUI LV, 1 SHIBIN LIU 1 School of Electronics
Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Design and Fabrication of Low Power Consumption Micro Fluxgate Sensor 1, 2 HUI LV, 1 SHIBIN LIU 1 School of Electronics
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai , PR China
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Synthetic antiferromagnet with Heusler alloy Co 2 FeAl ferromagnetic layers
 Synthetic antiferromagnet with Heusler alloy Co 2 FeAl ferromagnetic layers X. G. Xu, D. L. Zhang, X. Q. Li, J. Bao, Y. Jiang State Key Laboratory for Advanced Metals and Materials, School of Materials
Synthetic antiferromagnet with Heusler alloy Co 2 FeAl ferromagnetic layers X. G. Xu, D. L. Zhang, X. Q. Li, J. Bao, Y. Jiang State Key Laboratory for Advanced Metals and Materials, School of Materials
Effect of Anodizing Potential on the Surface Morphology and Corrosion Property of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 6 (21) pp. 119 to 1113 #21 The Japan Institute of Metals Effect of Anodizing Potential on the Surface Morphology and Corrosion Property of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy S. A.
Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 6 (21) pp. 119 to 1113 #21 The Japan Institute of Metals Effect of Anodizing Potential on the Surface Morphology and Corrosion Property of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy S. A.
6th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2016)
 6th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2016) Porous Co3O4 irregular Micro-cubes with lithium storage performances Ting Wanga, Hao Zhengb, Jinsong Chengc,
6th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2016) Porous Co3O4 irregular Micro-cubes with lithium storage performances Ting Wanga, Hao Zhengb, Jinsong Chengc,
Studies on the Influence of Potential and Electrochemical Conditions on Zinc-Nickel Alloys Electrodeposition
 ACTA CHEMICA IASI, 17, 219-228 (2009) Studies on the Influence of Potential and Electrochemical Conditions on Zinc-Nickel Alloys Electrodeposition Violeta Vasilache a and Traian Vasilache b a Faculty of
ACTA CHEMICA IASI, 17, 219-228 (2009) Studies on the Influence of Potential and Electrochemical Conditions on Zinc-Nickel Alloys Electrodeposition Violeta Vasilache a and Traian Vasilache b a Faculty of
Synthesis and Characterization of nanocrystalline Ni-Co-Zn ferrite by Sol-gel Auto-Combustion method.
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 12, December-212 1 Synthesis and Characterization of nanocrystalline Ni-Co- ferrite by Sol-gel Auto-Combustion method. R. B. Bhise
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 12, December-212 1 Synthesis and Characterization of nanocrystalline Ni-Co- ferrite by Sol-gel Auto-Combustion method. R. B. Bhise
Electrodeposition of Electroactive Co B and Co B C Alloys for Water Splitting Process in 8 M NaOH Solutions
 Electrocatalysis (2018) 9:189 203 DOI 10.1007/s12678-017-0401-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Electrodeposition of Electroactive Co B and Co B C Alloys for Water Splitting Process in 8 M NaOH Solutions Dawid Kutyła
Electrocatalysis (2018) 9:189 203 DOI 10.1007/s12678-017-0401-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Electrodeposition of Electroactive Co B and Co B C Alloys for Water Splitting Process in 8 M NaOH Solutions Dawid Kutyła
Supporting information
 Supporting information Cu 2 O-Cu Hybrid Foams as High-Performance Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Media Han Xu, Jin-Xian Feng, Ye-Xiang Tong, and Gao-Ren Li* MOE Laboratory of
Supporting information Cu 2 O-Cu Hybrid Foams as High-Performance Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Media Han Xu, Jin-Xian Feng, Ye-Xiang Tong, and Gao-Ren Li* MOE Laboratory of
Revue science des matériaux, Laboratoire LARHYSS ISSN
 Surface morphology, structural and electrical properties of electrodeposited Fe 85 Ni 15 /ITO films a LEPCM, Department of physics, University of Batna, Algeria. b Thin films and interfaces laboratory,
Surface morphology, structural and electrical properties of electrodeposited Fe 85 Ni 15 /ITO films a LEPCM, Department of physics, University of Batna, Algeria. b Thin films and interfaces laboratory,
Supporting Information. Hematite photoanode with gradient structure shows an unprecedentedly low onset
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Supporting Information Hematite photoanode with gradient structure shows an unprecedentedly
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Supporting Information Hematite photoanode with gradient structure shows an unprecedentedly
Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the
 Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the Current Materials Accomplishments till date As the structural
Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the Current Materials Accomplishments till date As the structural
LOW CARBON STEEL WITH NANOSTRUCTURED SURFACE LAYER INDUCED BY HIGH-ENERGY SHOT PEENING
 Scripta mater. 44 (2001) 1791 1795 www.elsevier.com/locate/scriptamat LOW CARBON STEEL WITH NANOSTRUCTURED SURFACE LAYER INDUCED BY HIGH-ENERGY SHOT PEENING G. Liu 1, S.C. Wang 1, X.F. Lou 1,J.Lu 2 and
Scripta mater. 44 (2001) 1791 1795 www.elsevier.com/locate/scriptamat LOW CARBON STEEL WITH NANOSTRUCTURED SURFACE LAYER INDUCED BY HIGH-ENERGY SHOT PEENING G. Liu 1, S.C. Wang 1, X.F. Lou 1,J.Lu 2 and
STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES AND COMPOSITION ANALYSIS OF Cu Ni Co ALLOY THIN FILM
 SOLID STATE PHYSICS STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES AND COMPOSITION ANALYSIS OF Cu Ni Co ALLOY THIN FILM V. CIUPINĂ 1, G. PRODAN 1, V. IONESCU 1, C. CASAPU 1, D. MANOLE 1, D. TUDORAN 1, E. VASILE 2, I. M. OANCEA
SOLID STATE PHYSICS STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES AND COMPOSITION ANALYSIS OF Cu Ni Co ALLOY THIN FILM V. CIUPINĂ 1, G. PRODAN 1, V. IONESCU 1, C. CASAPU 1, D. MANOLE 1, D. TUDORAN 1, E. VASILE 2, I. M. OANCEA
DC electrochemical deposition of CdSe nanorods array using porous anodic aluminum oxide template
 Materials Science and Engineering A303 (2001) 19 23 www.elsevier.com/locate/msea DC electrochemical deposition of CdSe nanorods array using porous anodic aluminum oxide template Cheng-min Shen, Xiao-gang
Materials Science and Engineering A303 (2001) 19 23 www.elsevier.com/locate/msea DC electrochemical deposition of CdSe nanorods array using porous anodic aluminum oxide template Cheng-min Shen, Xiao-gang
Formation of Cupric Oxide Films on Quartz Substrates by Annealing the Copper Films
 Journal of Applied Chemical Research, 9, 2, 73-79 (2015) Journal of Applied Chemical Research www.jacr.kiau.ac.ir Formation of Cupric Oxide Films on Quartz Substrates by Annealing the Copper Films Abstract
Journal of Applied Chemical Research, 9, 2, 73-79 (2015) Journal of Applied Chemical Research www.jacr.kiau.ac.ir Formation of Cupric Oxide Films on Quartz Substrates by Annealing the Copper Films Abstract
Papilla-like Magnetic Particles with Hierarchical Structure. for Oil Removal from Water
 Papilla-like Magnetic Particles with Hierarchical Structure for Oil Removal from Water By Li-Ping Xu, a Xiuwen Wu, a Jingxin Meng, b Jitao Peng, a Yongqiang Wen, a Xueji Zhang, a and Shutao Wang* b a Research
Papilla-like Magnetic Particles with Hierarchical Structure for Oil Removal from Water By Li-Ping Xu, a Xiuwen Wu, a Jingxin Meng, b Jitao Peng, a Yongqiang Wen, a Xueji Zhang, a and Shutao Wang* b a Research
Magnetic and Magneto-Transport Properties of Mn-Doped Germanium Films
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-5, Issue-12, pp-308-312 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Magnetic and Magneto-Transport Properties of
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-5, Issue-12, pp-308-312 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Magnetic and Magneto-Transport Properties of
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information In situ electrochemical activation of Ni-based colloids from NiCl 2 electrode
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information In situ electrochemical activation of Ni-based colloids from NiCl 2 electrode
High energy all-solid-state lithium batteries with
 Supporting Information High energy all-solid-state lithium batteries with ultralong cycle life Xiayin Yao, Deng Liu, Chunsheng Wang, Peng Long, Gang Peng, Yong-Sheng Hu, *, Hong Li, Liquan Chen, and Xiaoxiong
Supporting Information High energy all-solid-state lithium batteries with ultralong cycle life Xiayin Yao, Deng Liu, Chunsheng Wang, Peng Long, Gang Peng, Yong-Sheng Hu, *, Hong Li, Liquan Chen, and Xiaoxiong
Determination of Pyridinium-1-Propane-2- Hydroxide-3-Sulfonate and Saccharin in a Bright Nickel Electroplating Bath
 AESF Foundation Determination of Pyridinium-1-Propane-2- Hydroxide-3-Sulfonate and Saccharin in a Bright Nickel Electroplating Bath Ying Zheng, Canzhu Gao * and Rutao Liu School of Environmental Science
AESF Foundation Determination of Pyridinium-1-Propane-2- Hydroxide-3-Sulfonate and Saccharin in a Bright Nickel Electroplating Bath Ying Zheng, Canzhu Gao * and Rutao Liu School of Environmental Science
Structural and Magnetic Studies of Nickel- Boron alloy
 Structural and Magnetic Studies of Nickel- Boron alloy K. Dhanapal 1, T. A. Revathy 1, V Narayanan 2, and A Stephen 1,* 1 Material Science Centre, Dept. of Nuclear Physics, University of Madras, Guindy
Structural and Magnetic Studies of Nickel- Boron alloy K. Dhanapal 1, T. A. Revathy 1, V Narayanan 2, and A Stephen 1,* 1 Material Science Centre, Dept. of Nuclear Physics, University of Madras, Guindy
Electrodeposition of Magnetic Materials
 Electrodeposition of Magnetic Materials Neil Robertson HGST, a Western Digital Company San Jose Research Center San Jose, California Electrodeposition and the HDD Business HDD s are a very high volume
Electrodeposition of Magnetic Materials Neil Robertson HGST, a Western Digital Company San Jose Research Center San Jose, California Electrodeposition and the HDD Business HDD s are a very high volume
Bonding strength of Al/Mg/Al alloy tri-metallic laminates fabricated
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 34, No. 4, July 2011, pp. 805 810. Indian Academy of Sciences. Bonding strength of Al/Mg/Al alloy tri-metallic laminates fabricated by hot rolling X P ZHANG, *, M J TAN, T H YANG,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 34, No. 4, July 2011, pp. 805 810. Indian Academy of Sciences. Bonding strength of Al/Mg/Al alloy tri-metallic laminates fabricated by hot rolling X P ZHANG, *, M J TAN, T H YANG,
Grain Sizes and Surface Roughness in Platinum and Gold Thin Films. L.L. Melo, A. R. Vaz, M.C. Salvadori, M. Cattani
 Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials Vols. 20-21 (2004) pp. 623-628 online at http://www.scientific.net 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Grain Sizes and Surface Roughness in Platinum
Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials Vols. 20-21 (2004) pp. 623-628 online at http://www.scientific.net 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Grain Sizes and Surface Roughness in Platinum
Characterization of Oxide Film Formed on Ck45 Steel by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Method
 Journal of Mechanical Research and Application ISSN: 2251-7383, eissn: 2251-7391 Vol. 4, No. 2, 2012, 57-61 Characterization of Oxide Film Formed on Ck45 Steel by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Method JMRA
Journal of Mechanical Research and Application ISSN: 2251-7383, eissn: 2251-7391 Vol. 4, No. 2, 2012, 57-61 Characterization of Oxide Film Formed on Ck45 Steel by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Method JMRA
Fabrication and characterization of Ni SiC Cr nanocomposite coatings
 Appl Nanosci (2013) 3:357 362 DOI 10.1007/s13204-012-0136-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fabrication and characterization of Ni SiC Cr nanocomposite coatings Mehran Masoudi Mansor Hashim Halimah Mohamed Kamari Mohd
Appl Nanosci (2013) 3:357 362 DOI 10.1007/s13204-012-0136-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fabrication and characterization of Ni SiC Cr nanocomposite coatings Mehran Masoudi Mansor Hashim Halimah Mohamed Kamari Mohd
A Low-Cost High-Energy Potassium Cathode
 Supporting information A Low-Cost High-Energy Potassium Cathode Leigang Xue, Yutao Li, Hongcai Gao, Weidong Zhou, Xujie Lü, Watchareeya Kaveevivitchai, Arumugam Manthiram, and John B. Goodenough * Materials
Supporting information A Low-Cost High-Energy Potassium Cathode Leigang Xue, Yutao Li, Hongcai Gao, Weidong Zhou, Xujie Lü, Watchareeya Kaveevivitchai, Arumugam Manthiram, and John B. Goodenough * Materials
