Calculating growth rate of water hyacinth pollution wise (in relation to trophic state)
|
|
|
- Frederica Thompson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: (O) (P) Volume-7, Issue-7, July 7 Calculating growth rate of water hyacinth pollution wise (in relation to trophic state) Rinku Verma, Sivappa Abstract This study was carried out with respect to calculating growth rate of water hyacinth in relation to the trophic state of the water body. 5 water hyacinth plants about from each lake were taken. The concentrations of phosphorous, nitrogen, potassium and calcium were determined. Biochemical oxygen demand and dissolved oxygen were also determined. Various growth aspects like total number of leaves were counted, root and petiole length were recorded, leaf area was plotted to obtain surface area. Growth Index was calculated based on fresh weight of the plant was chosen to study the growth of water hyacinth with respect to pollution levels of the 5 lakes. Growth Index was calculated using the equation GI = (A / M) where M = Mean fresh weight of 53 water hyacinth plants collected from 5 lakes. A = Mean fresh weight of water hyacinth plants collected from a particular lake in a particular month. A correlation of GI to pollution status of lakes was made and a correlation of lake water constituents with growth parameters of water hyacinth was done: The fresh mean weight of water hyacinth plants collected over months period was distinctly higher for polluted Lakes when compared to less polluted lakes. Mean petiole length of plants collected from Yelahanka, Nagavara and Hebbal Lakes (polluted) were greater as compared to those collected from and Doddabommsandra Lakes (less polluted). TSI based on TP was 88.8 for Nagavara lake which was Hypereutrophic and eutrophic for lake where TP was GI of water hyacinth plants showed a correlation coefficient of +.6 to TP. This study concludes that higher the pollution level of the lake, higher would be the growth rate of water hyacinth. Polluted lakes had strong and sturdy petioles and more GI compared to less polluted lakes. TP versus GI, showed a good positive person s correlation coefficient. TP the limiting nutrient has significant impact on the pollution level. Index Terms Growth rate, Trophic state, water hyacinth, Growth Index, Fresh weight. I. INTRODUCTION Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus on growth rate of water hyacinth: Demonstration of the use of water hyacinth for nutrient removal and 8% reduction in ammonia nitrogen was observed when the aerated effluent passed through a water hyacinth pond with a retention time of ten days []. Plants growing in nutrient rich waters have been found to possess long petioles (up to cm) and roots, which are about 6 cm long []. Positive correlation between the concentration of phosphorous in the medium and the concentration within the Rinku Verma, Department of Farm Forestry & Environmental Science, College of Sericulture, Chintamani, Karnataka, University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore 5665 Karnataka Sivappa, Department of Farm Forestry & Environmental Science, College of Sericulture, Chintamani, Karnataka, University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore 5665 Karnataka plants was observed [3]. Maximum growth of water hyacinth occurred in water with a phosphorous concentration of ppm [4]. Also increased phosphorous content in nutrient rich waters promote healthy root growth [5]. Nitrogen concentration did not produce any profound effect on biomass production though nitrogen is essential to some extent for biomass production as well as plant multiplication conducted in some studies [6]. Nitrogen limitations in lakes may be attributable to high phosphate supply from the rivers and high losses of macrophyte nitrogen during floods [7]. Water hyacinth releases large quantities of juice, which have high nitrogen content, total solids and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) [8]. The disposal of this press liquor into water bodies would result in eutrophication. Nitrogen along with phosphorous has been considered the primary nutrients causing excessive growth of aquatic plants. According to Hutchinson nitrogen would limit the production of aquatic plants when the Nitrogen/Phosphorous (N/P) ratio is less than 8 (by weight) whereas phosphorous may limit plant production when the ratio is high [9]. Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorous (TN/TP) ratio > 3 were primarily phosphorus limited and lakes with TN/TP < were primarily nitrogen limited found in lakes []. Lakes with TN/TP ratios between and 3 were assumed to have a balanced nutrient status. Water hyacinth plant contains calcium to an extent of.66% of its dry weight. Potassium is the most abundant metallic element in water hyacinth constituting about 3% of the dry weight of the plant [ & ]. Highest biomass increase was obtained at 6 mg/l potassium concentration [6]. Potassium has no effect on multiplication of water hyacinth but it does increase the biomass of individual plants [3]. Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Dissolved Oxygen (DO) on growth rate of water hyacinth showed that there was a close relationship between hydrophytes growth and nutrient removal from the effluents. A comparatively more rapid drop in BOD, as well as a fair increase in DO and biomass was observed [4]. II. MATERIALS AND METHODS Collection of water hyacinth plants from the 5 lakes: 5 water hyacinth plants (i.e. plants from each lake) were brought to the laboratory each month, with each plant in a separate plastic bag from July 9 to June. Water hyacinth plants were not collected from Hebbal Lake in July 9 and from Nagavara Lake in May and June. Hebbal Lake was taken up for desilting from March ; so plants were not collected from March to June. A total of 53 plants were inspected showing maximum growth. Care was taken to collect well grown, healthy plants from different water hyacinth growing regions of the lake. In August 9 and November 9, 5 water samples were 85
2 Calculating growth rate of water hyacinth pollution wise (in relation to trophic state) collected from each lake and concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium and calcium were determined. BOD and DO were also determined, as indicated in the previous chapter. Measurement of growth parameters of water hyacinth: Various aspects of growth of water hyacinth plant were measured. Total number of leaves present in each plant was counted. Root length and petiole length were recorded. Every leaf in a water hyacinth plant was plotted on a graph paper and its surface area was calculated by counting the squares enclosed by the leaf surface. The surface area of each leaf in a plant was added to get the total surface area of leaves (cm ) of a water hyacinth plant. Fresh weight of each water hyacinth plant was also recorded. Mean fresh weight, mean number of leaves, mean root length, mean petiole length and mean surface area of leaves of water hyacinth plants was taken (in gm) from each of the 5 lakes (5lakes*plants = 5 plants). Hence Growth Index calculated based on fresh weight of the plant was chosen to study the growth of water hyacinth with respect to pollution levels of the 5 lakes. Calculation of Growth Index (GI): GI of plants collected in a particular month from a particular lake was computed by dividing the mean fresh weight of plants collected (in that month from that lake) by the mean fresh weight of all plants collected from 5 lakes during July 9 to June. GI is calculated by the following formula: GI = (A / M) (Equation No.) Let M = Mean fresh weight of 53 water hyacinth plants collected from 5 lakes from July 9 to Jun. A = Mean fresh weight of water hyacinth plants collected from a particular lake in a particular month. In other words, the mean fresh weight of 53 water hyacinth plants was considered as standard mean fresh weight. The mean fresh weight of sample plants collected from each of the five lakes once every month was compared to the standard mean fresh weight to get the GI of the water hyacinth plants collected. Correlation of GI to pollution status of lakes: The GI and water quality parameters have been correlated using the Pearson s Correlation coefficient. The strength of the linear association between two variables is quantified by the correlation coefficient. The correlation coefficient is often more useful than a graphical depiction in determining the strength of the association between two variables. III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Studies conducted were as follows: ) Study of growth parameters of water hyacinth plants. ) Study of growth rate (represented by GI) of water hyacinth in relation to pollution levels (represented by trophic state) of 5 lakes under study. Correlation of lake water constituents with growth parameters of water hyacinth: A water hyacinth plant just like any other plant has roots, petioles and leaves. In order to study the effect of lake nutrient concentration on growth of water hyacinth plants, it was important to study the growth parameters (like number of leaves, root length, etc.,) of water hyacinth plant with respect to the pollution levels. The fresh mean weight of water hyacinth plants collected over months period is distinctly higher for Yelahanka, Nagavara and Hebbal Lakes when compared to and Doddabommsandra Lakes (Table ). Mean number of leaves in a water hyacinth plant collected varied between.8 for Nagavara and Doddabommsandra Lake and.4 for Hebbal Lake. Table. Mean fresh weight and root length of water hyacinth plants collected from the 5 lakes ( plants from each lake) from July 9 to June. Growth Parameters Name of lakes/month mean fresh weight of plants (in gm) mean root length of plants (in cms) Yelaha nka 5.68 Nagav ara Names of Lakes Heb bal 8.7 Jak kur Doddabomms andra No significant difference in number of leaves was observed in plants collected from all the 5 lakes. From Table, the mean root length of monthly samples of water hyacinth was high in Yelahanka (4.5 cm) followed by Doddabommsandra (. cm), (.8 cm), Hebbal (7.9 cm) and Nagavara (6.5 cm) Lakes. In July, August, September 9, February, March, May and June, Yelahanka Lake had higher mean root length. Doddabommsandra Lake had higher mean root length in December 9 and January. In October, November 9 and April, water hyacinth plants from Lake had longer mean root length than other lakes. In case of lower concentration or no nutrients present in the lakes, the water hyacinth roots grow deeper in search of nutrients required for their growth. This leads to longer root lengths in less polluted lakes. While, in more polluted water bodies, the roots are shorter as nutrients are readily available. Petiole lengths were seen to be greater in polluted lakes. It was observed that the colour of the root varied from the young to matured water hyacinth plants; the young roots were purple and became darker as they matured. Mean petiole length of plants collected from Yelahanka, Nagavara and Hebbal Lakes were greater as compared to those collected from and Doddabommsandra Lakes. The petioles in water hyacinth plants collected from Yelahanka, Nagavara and Hebbal Lakes were strong and sturdy as compared to petioles seen in plants collected from and Doddabommsandra Lakes. Total leaf surface area was seen to be more in plants collected from Yelahanka, Nagavara and Hebbal Lakes when compared to plants collected from and Doddabommsandra Lakes. Mean leaf surface area was seen to be more in plants collected from Yelahanka, Nagavara and Hebbal Lakes when compared to plants collected from and Doddabommsandra Lakes. After analyzing various growth parameters of water hyacinth plants, fresh weight, petiole length and leaf surface area of water hyacinth were found to be the major distinguishing growth parameters. 86
3 TP concentration (in mg/l) Growth Index (in number) TP concentration (in mg/l) Growth Index (in number) Growth Index of water hyacinth International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: (O) (P) Volume-7, Issue-7, July Mean Growth Index of water hyacinth growning in 5 lakes from July 9 to June Yelahanka Nagavara Hebbal Name of lakes Doddabommsandra GI for months Figure. Mean GI of water hyacinth plants in the 5 lakes during July 9 to June. Study of growth of water hyacinth plants in relation to pollution level of the lakes: Comparison of GI of water hyacinth plants and nutrients in lake water: Discharge of sewage is the prime source of phosphorous in the water of all the 5 lakes taken up for study. The prime reason for the growth of water hyacinth weed in all these 5 lakes causing hyper-eutrophic condition is pollution. The discharge of untreated sewage results in high concentration of phosphorous and nitrogen in lake water and accumulation of phosphorous and nitrogen in lake sediment bed by sedimentation of organic solids. Besides, the dead water hyacinth plants and dead algae also contribute to the accumulation of organic nutrients in the lakebed. The accumulated nutrients in the lakebed get released back into the lake water due to temperature changes causing thermal inversion and mixing of lake water [5]. Water hyacinth collected from Yelahanka, Nagavara and Hebbal Lakes showed higher GI as compared to water hyacinth collected from and Doddabommsandra Lakes in August 9 and November 9 (Table & Figure ). It was observed that more the concentration of TP in the lake water, higher was the GI of water hyacinth. This was confirmed in the correlation chart of TP vs. GI of water hyacinth plants (in Figure ). Higher the nitrogen concentration in lake water, higher was the GI of water hyacinth plants. The extent of correlation between Total Nitrogen (TN) and the GI was also determined by a linear plot. Total Phosphorous (TP) and mean Growth Index of water hyacinth from the 5 lakes during August Name of lakes GI TP Total Phosphorous (TP) and mean Growth Index of water hyacinth from the 5 lakes during November Name of lakes Figure. Histogram showing TP concentration and monthly mean GI of water hyacinth collected from 5 lakes during August 9 and Nov 9. Comparison of Total leaf surface area of water hyacinth plant with TP in lake water: TSI based on TP and Total leaf surface area of water hyacinth plants for the month of August 9 and November 9 showed Yelahanka, Nagavara and Hebbal lakes had higher TP concentration and higher surface area of leaf of water hyacinth plant when compared to and Doddabommsandra Lakes. The number of leaves of water hyacinth plants, in more polluted and less polluted lakes did not vary much (Figure 3) indicating that the number of leaves of water hyacinth cannot be used to study the effect of pollution. Yelahanka, Nagavara water had higher TP concentration and higher surface area of leaf of water hyacinth plant when compared to and Doddabommsandra Lakes. Water hyacinth collected from Yelahanka and Doddabommsandra Lakes showed that mean number of leaf in more polluted (Yelahanka) Lake and less polluted (Doddabommsandra) Lake are not much differing. The water hyacinth plants collected from highly polluted Nagavara Lake, with high nutrient levels had longer petioles in comparison to plants collected from lesser polluted Lake with low nutrient levels. Water hyacinth plants collected from Lake had smaller petioles which were usually bulbous. Yelahanka was more polluted in comparison to. Comparison of growth of water hyacinth in more polluted lakes and less polluted lakes: Lake qualities indicated by trophic status. Mean petiole length in water hyacinth plant was more in polluted Yelahanka Lake when compared to less polluted Lake. GI TP 87
4 mean petiole length (in cm) mean number of leaves mean fresh weight (in gm) Calculating growth rate of water hyacinth pollution wise (in relation to trophic state) Table. Growth Index (GI) of water hyacinth plants collected from 5 lakes from July 9 June Name of lakes Jul- Aug- Monthly mean Growth Index (GI) of plants collected from July 9 to June Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan- Feb- Mar - Apr- May - Jun- Total Growth Index -GI No. of months Annual Mean Growth Index Y N * * 3..3 H * * * * * J D Total Mean number of leaves in water hyacinth collected from Nagavara and Lakes from July 9 to April Mean fresh weight of water hyacinth collected from Nagavara and Lakes from July 9 to April Naga var a. 5. Nagavara months: July 9 to April Figure 3. Time series chart showing mean number of leaves of water hyacinth plant in more polluted Nagavara Lake and less polluted Lake from July 9 to April. Mean petiole length of water hyacinth from Nagavara and Lakes from July 9 to April months: July 9 to April Nagavara months: July 9 to April Figure 4a. Time series chart showing mean petiole length of water hyacinth plant in more polluted Nagavara Lake and less polluted Lake. Figure 4b. Time series chart showing mean fresh weight of water hyacinth plant in more polluted Nagavara Lake and less polluted Lake (from July 9 to April ). The mean petiole length of a water hyacinth plant was more in more polluted Nagavara Lake when compared to less polluted Lake (Figure 4a). In all the months, Nagavara showed higher fresh weight except in the month of April (Figure 4b). Petiole length seems to be an indicator of pollution level in water hyacinth i.e. higher the pollution level longer is the petiole. Mean fresh weight of a water hyacinth plant collected from Yelahanka Lake (polluted lake) was more when compared to that from Doddabommsandra Lake (less polluted lake). Mean total surface area of all leaves of water hyacinth plants was higher in the more polluted Nagavara Lake than in the less polluted Lake. This indicates that, water hyacinth plants collected from polluted, Yelahanka Lake had more leaf surface area when compared to those collected from the less polluted Doddabommsandra Lake. Larger leaf surface area was prevalent in water hyacinth plants in more polluted water than in less polluted water. 88
5 DO concentration (in mg/l) Growth Index International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: (O) (P) Volume-7, Issue-7, July 7 Correlation of lake water constituents to various aspects of growth of water hyacinth: The growth of the individual plant in relation to the concentration of essential nutrients nitrogen and phosphorous were studied with respect to water hyacinth plants collected from each lake. The correlation of TP concentration in lake water with growth parameters showed that the rate of growth of water hyacinth plant had a linear positive relationship to the TP concentration in the water of 5 lakes. The values of TP concentration in the 5 lakes is plotted in the graph (Figures ) and the fresh weight of water hyacinth is given in Table. The Pearson s Correlation coefficient for TP versus GI was found to be +.6, indicating a good correlation, (the correlation coefficient is nearing to ) Figure 5.The growth rate of water hyacinth tends to increase as the pollution (TP concentration) level of the lake increases. The graphical plot for TP concentration in lake water vs. mean number of leaf shows the Pearson s Correlation coefficient obtained was only., showing that the pollution level of lake had no significant impact on the number of leaf of water hyacinth plants. The correlation coefficient was.was less than.5 indicating a poor correlation between the pollution level of lakes and number of leaves of water hyacinth. The Pearson s Correlation coefficient obtained for TP versus root length of water hyacinth was only -.7, indicating the pollution level of lake had no significant impact on the root length of water hyacinth plants. The correlation coefficient of.7 close to zero indicated no correlation between pollution level of lake water and root length of the water hyacinth plants. The graphical plot for TP concentration in lake water vs. mean petiole length of water hyacinth plants showed the Pearson s Correlation coefficient to be +.64 indicating the pollution level of lake had significant impact on the petiole length in water hyacinth plants. The correlation coefficient of +.64 was near to showing good correlation of pollution level of lake water and petiole length of the water hyacinth plants. The graphical plot for TP concentration in lake water vs. mean total leaf surface area of water hyacinth plants from 5 lakes showed the Pearson s Correlation coefficient to be +.56, showing the pollution level of lake had significant impact on the leaf surface area of water hyacinth. The correlation coefficient of +.56 was near to showing a good correlation between pollution level of lake water and mean leaf surface area of the water hyacinth plants. Correlation of water quality parameters to GI of water hyacinth plant: It is observed that the rate of growth of water hyacinth had a linear positive relationship to the TP concentration in the water of 5 lakes (Figure 5).The line of best fit for the graphical plot of phosphorous concentration in the lake water vs. overall GI of water hyacinth is shown in Figure 5. The line of best fit showed the correlation of GI to concentration of phosphorous in lake water having Pearson s Correlation coefficient of +.6 indicating a strong correlation. Lower the concentration of phosphorous in the lake water, lower was the GI of water hyacinth; and as the phosphorous concentration in the lake water increased the overall GI of water hyacinth also increased Effect of Total Phosphorous (TP) concentration on Growth Index of water hyacinth y =.63x Total Phosphorous (in mg/l) Effect of Growth Index of water hyacinth on dissolved oxygen (DO) y = -.897x Growth Index Figure 5. Graphical plot of Total Phosphorous (TP) concentration in lake water versus Growth Index of water hyacinth. Figure 6. Graphical plot of Growth Index of water hyacinth plants to DO level in lake water. Correlation of TN to mean GI of water hyacinth plants from 5 lakes: The Pearson s Correlation coefficient obtained was +.43, TP in lake water showed a correlation coefficient of +.6 to the GI indicating GI was strongly correlated to the TP when compared to TN. The limiting nutrient phosphorous, had significant impact on the pollution level of lake water and also to the growth of water hyacinth, indicating higher the pollution level of the lake, higher would be the growth of water hyacinth. Correlation of Ca concentration in lake water to GI showed a positive correlation of +.8 indicating a poor positive correlation between the calcium present in the lake water to the growth of water hyacinth plants. The correlation of potassium concentration in lake water to GI showed a positive correlation of +.37 indicating a poor positive correlation between the potassium present in the lake water and the growth of water hyacinth plants. The correlation of BOD concentration in lake water to GI indicated poor correlation coefficient of.37. The correlation of DO concentration in lake water to GI showed a correlation coefficient of -.46 (Figure 6). The profuse growth of water hyacinth plants shuts down wind induced natural aeration and penetration of sunlight into the lake water. This results in reduced algal growth, which eliminates the contribution of DO to the lake water. Anaerobic digestion of organic sludge deposits further contributes to the depletion of DO in the 89
6 Calculating growth rate of water hyacinth pollution wise (in relation to trophic state) water hyacinth covered areas. Thus explaining, the negative correlation of DO content in the water to the growth of water hyacinth plants on the lake water (Figure 6). The GI of water hyacinth plants and corresponding DO concentration in lake water had a correlation coefficient of -.46 (showing no correlation) and the line of best fit equation y = -.897x Table 3. Summary of Correlation coefficients. Parameters Pearson s Correlation coefficient Type of correlation TP vs. GI.6 Positive correlation TN vs. GI.43 Positive correlation Ca vs. GI.8 Low Positive correlation K vs. GI.37 Positive correlation BOD vs. GI.37 Positive correlation GI vs. DO -.46 Negative correlation Table 3 shows the Pearson s Correlation coefficient for the various parameters to the GI of water hyacinth. GI of water hyacinth plants exhibited strong positive correlation to TP concentration of lake water (Figure ). The studies made on various growth aspects of water hyacinth like mean petiole length, mean fresh weight of the plants, mean leaf surface area have shown that lakes which are highly polluted had given rise to higher growth rate of water hyacinth. The mean petiole length in Nagavara Lake was higher than that of Lake during the period July 9 to June. Mean fresh weight of water hyacinth grown in Nagavara Lake was higher than that in Lake during the period July 9 to June. Mean leaf surface area of water hyacinth grown in Nagavara Lake was higher than that in Lake during the period July 9 to June. TSI based on TP was 88.8 for Nagavara lake which was Hypereutrophic and eutrophic for Lake where TP was Hence Nagavara Lake was highly polluted as compared to Lake. Nitrogen concentration vs. mean GI of water hyacinth was plotted and a straight line linear plot satisfying the equation Y =.446X was obtained. The Pearson s Correlation coefficient obtained in this case was +.43 whereas, GI of water hyacinth plants showed a correlation coefficient of +.6 to TP. In other words, Growth of water hyacinth was strongly correlated to TP (correlation coefficient >.5) as compared to TN (correlation coefficient <.5). Hence TP which was the limiting nutrient had significant impact on the pollution level of lake water and the growth of water hyacinth. This indicates that higher the pollution level of the lake, higher would be the growth rate of water hyacinth. Calcium present in the lake water to the GI of water hyacinth plants in the lakes shows a positive correlation of +.8. This indicates a poor positive correlation between the calcium present in the lake water and the GI (or growth rate) of water hyacinth plants. The graphical plot of potassium present in the lake water to the GI of water hyacinth plants in the lakes showed a positive correlation of This indicates a poor positive correlation between the potassium present in the lake water and the GI of water hyacinth plants. Correlation plot of BOD to the growth of water hyacinth plants showed a positive correlation coefficient of.37. This indicates poor correlation between the BOD in the lake water and the GI of water hyacinth plants. DO showed a negative correlation to the GI of water hyacinth (correlation coefficient -.46). This indicates that more the area covered by water hyacinth, lesser would be the DO concentration in the lake water. As the phosphorous concentration in the lake water increased the overall GI of water hyacinth also increased. TP the limiting nutrient has significant impact on the pollution level then higher would be the growth rate of water hyacinth. TP versus GI, showed a good positive person s correlation coefficient. Pearson s Correlation coefficient of TP, TN, and the GI of water hyacinth indicated good correlation. Highly polluted lakes gave rise to higher growth rate of water hyacinth. Polluted lakes had strong and sturdy petioles and more GI compared to less polluted lakes. REFERENCES [] Sheffield CW. Hyacinth Control Journal. 967, 6: 7-3. [] Gopal B and Sharma, DP. Hindiasia, New Delhi, India. 98, 9 pp. [3] Haller WT and Sutton DL. Hyacinth Control Journal. 973, : [4] Hill MP. 8. In: Proceedings of the first IOBC Global Working Group Meeting for the Biological and Integrated Control of Water Hyacinth, November 6-9, Zimbabwe. 8, 8 pp. [5] Wakefield JW and Beck, WM, Hyacinth Control Journal.96, :. [6] Singh HD, Nag B, Sarma, AK, and Baruch, JN. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Water Hyacinth. G. Thyagarajan (Ed.). Hyderabad, India 984, pp 43-63, 5 pp. [7] Carigan R, Neiff JJ and Planas, D. Limnology and Oceanography. 4, 39: [8] Bagnall LO. In: Annual Meeting of American Society of Agriculture and Engineering. 973, 3 pp. [9] Hutchinson GF. A treatise on Limnology, Volume. 957, 5 pp. [] Smith VH. Science. 983, : [] Parra JV, and Hortenstine, CC. Hyacinth Control Journal. 974, : [] Wolverton BC and Mc Donald RC. Economic Botany. 98, 34: [3] Baruah JN and Singh HD. In: International Conference on Water Hyacinth, Regional Research Laboratory, Hyderabad, India [4] Pant AB, Kapil MK and Joshi P. Agricultural and Biological Research. 4, : -. [5] UNEP: Technical Publication Series. 9,. 375 pp. 9
Case Study. BiOWiSH Aqua has Positive Long-Term Effects. Biological Help for the Human Race
 Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua has Positive Long-Term Effects After Two Years, Sustains Improved Effluent Quality in South Korean Slaughterhouse Executive Summary BiOWiSH Aqua was implemented in a South Korean
Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua has Positive Long-Term Effects After Two Years, Sustains Improved Effluent Quality in South Korean Slaughterhouse Executive Summary BiOWiSH Aqua was implemented in a South Korean
ROTIFERS ABUNDANCE AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO WATER QUALITY IN THE PANDU LAKE, BODHAN, TELANGANA, INDIA
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 4, No 4, 215, 1188 1194 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) ROTIFERS ABUNDANCE AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO WATER QUALITY IN THE PANDU LAKE,
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 4, No 4, 215, 1188 1194 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) ROTIFERS ABUNDANCE AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO WATER QUALITY IN THE PANDU LAKE,
Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed
 Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed Linda Green URI Watershed Watch 1-87-95, lgreen@uri.edu WATER QUALITY IS A REFLECTION OF THE ACTIVITIES IN THE LANDS AND WATERS
Long-Term Volunteer Lake Monitoring in the Upper Woonasquatucket Watershed Linda Green URI Watershed Watch 1-87-95, lgreen@uri.edu WATER QUALITY IS A REFLECTION OF THE ACTIVITIES IN THE LANDS AND WATERS
Monitoring Update April 1, Northeast Aquatic Research George Knoecklein Hillary Kenyon Sabina Perkins
 Monitoring Update April 1, 215 Northeast Aquatic Research George Knoecklein Hillary Kenyon Sabina Perkins Lake Monitoring Approach for 214 Tonight's discussion will focus on in-lake aspects: Assessment
Monitoring Update April 1, 215 Northeast Aquatic Research George Knoecklein Hillary Kenyon Sabina Perkins Lake Monitoring Approach for 214 Tonight's discussion will focus on in-lake aspects: Assessment
CITY OF LONDON WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT 2013 ANNUAL REPORT ADELAIDE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT
 CITY OF LONDON WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT 2013 ANNUAL REPORT ADELAIDE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT FEBRUARY 2014 Adelaide Wastewater Treatment Plant 2013
CITY OF LONDON WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT 2013 ANNUAL REPORT ADELAIDE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT FEBRUARY 2014 Adelaide Wastewater Treatment Plant 2013
Wastewater Treatment through Root Zone Technology with Special Reference to Shahpura Lake of Bhopal (M. P.), India
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2014. 12, 3: 169-175 Wastewater Treatment through Root Zone Technology with Special Reference to Shahpura Lake of Bhopal (M. P.), India Kalpana
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2014. 12, 3: 169-175 Wastewater Treatment through Root Zone Technology with Special Reference to Shahpura Lake of Bhopal (M. P.), India Kalpana
Bolton Town Hall February 24, George Knoecklein Northeast Aquatic Research Mansfield, CT
 Bolton Town Hall February 24, 214 George Knoecklein Northeast Aquatic Research Mansfield, CT Working Hypothesis 1. Deep drawdowns of Middle Bolton Lake fueled high growth rates of naiad in Lower Bolton
Bolton Town Hall February 24, 214 George Knoecklein Northeast Aquatic Research Mansfield, CT Working Hypothesis 1. Deep drawdowns of Middle Bolton Lake fueled high growth rates of naiad in Lower Bolton
A Study of Eutrophication Phenomenon of a Lake of a Modern City of India
 A Study of Eutrophication Phenomenon of a Lake of a Modern City of India Shilpa (Student of Masters in Engineering in Environmental Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering, PEC University of Technology,
A Study of Eutrophication Phenomenon of a Lake of a Modern City of India Shilpa (Student of Masters in Engineering in Environmental Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering, PEC University of Technology,
Biodegradation Test of Chemical Substances
 Biodegradation Test of Chemical Substances I. Scope of application A standard method for the biodegradation test of chemical substances is described as follows. II. Terms The terms used in this test method
Biodegradation Test of Chemical Substances I. Scope of application A standard method for the biodegradation test of chemical substances is described as follows. II. Terms The terms used in this test method
EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS ON FISH GROWTH
 ISSN: 976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 22-138(Online) EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS ON FISH GROWTH SONIA BAJAJ 1 Department of Zoology, Shri ShankaracharyaMahavidyalaya, Bhilai, Chhattisgarh, India ABSTRACT Primary
ISSN: 976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 22-138(Online) EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS ON FISH GROWTH SONIA BAJAJ 1 Department of Zoology, Shri ShankaracharyaMahavidyalaya, Bhilai, Chhattisgarh, India ABSTRACT Primary
Effect of Turbidity on Dissolved Oxygen in the Lake Macatawa. Watershed
 Effect of Turbidity on Dissolved Oxygen in the Lake Macatawa Watershed Hope College GES 401 Research Project Group Members: Peter Van Heest, Rachel Burkhart, Wyatt Curry Advisor: Dr. G. Peaslee Introduction
Effect of Turbidity on Dissolved Oxygen in the Lake Macatawa Watershed Hope College GES 401 Research Project Group Members: Peter Van Heest, Rachel Burkhart, Wyatt Curry Advisor: Dr. G. Peaslee Introduction
NUTRIENT REDUCTION THROUGH THE USE OF ADVANCED BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENT RECOVERY. Rick Johnson Vice President, Market Development
 NUTRIENT REDUCTION THROUGH THE USE OF ADVANCED BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENT RECOVERY Rick Johnson Vice President, Market Development 1 Agenda What is the trend Technology description Results Economics "Vision without
NUTRIENT REDUCTION THROUGH THE USE OF ADVANCED BIOLOGICAL NUTRIENT RECOVERY Rick Johnson Vice President, Market Development 1 Agenda What is the trend Technology description Results Economics "Vision without
Nuisance Algae and the Huron River: Recent Changes and Future Trends
 Nuisance Algae and the Huron River: Recent Changes and Future Trends Prof. John T. Lehman 5 October 20 Overview of this Talk Review nuisance conditions Nutrient budgets along the river Differences between
Nuisance Algae and the Huron River: Recent Changes and Future Trends Prof. John T. Lehman 5 October 20 Overview of this Talk Review nuisance conditions Nutrient budgets along the river Differences between
Causes and Possible Corrections for Nuisance Algae Conditions in Huron River Lakes: Summary Findings from 2003, 2004, and Prof John T.
 Causes and Possible Corrections for Nuisance Algae Conditions in Huron River Lakes: Summary Findings from 23, 24, and 25 Prof John T. Lehman Middle Huron Partners 8 November 25 Welcome Summary of public
Causes and Possible Corrections for Nuisance Algae Conditions in Huron River Lakes: Summary Findings from 23, 24, and 25 Prof John T. Lehman Middle Huron Partners 8 November 25 Welcome Summary of public
EGANVILLE SEWAGE SYSTEM 2013 PERFORMANCE REPORT
 EGANVILLE SEWAGE SYSTEM 2013 PERFORMANCE REPORT Township of Bonnechere Valley Water and Sewage Department January 2014 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Introduction... 4 Report Availability...
EGANVILLE SEWAGE SYSTEM 2013 PERFORMANCE REPORT Township of Bonnechere Valley Water and Sewage Department January 2014 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Introduction... 4 Report Availability...
PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1386
 STUDIES ON HEAVY METAL CONCENTRATION AND EUTROPHICATION THROUGH POLLUTED LAKES AND MITIGATION THROUGH BIOREMEDIATION A CASE STUDY ON BYRAMANGALA LAKE, RAMANAGRAM DISTRICT, KARNATAKA PROJECT REFERENCE NO.
STUDIES ON HEAVY METAL CONCENTRATION AND EUTROPHICATION THROUGH POLLUTED LAKES AND MITIGATION THROUGH BIOREMEDIATION A CASE STUDY ON BYRAMANGALA LAKE, RAMANAGRAM DISTRICT, KARNATAKA PROJECT REFERENCE NO.
Watershed and Water Quality Modeling to Support TMDL Determinations Lake Oologah
 Watershed and Water Quality Modeling to Support TMDL Determinations Lake Oologah 26 th Annual Conference Oklahoma Clean Lakes and Watersheds Association (OCLWA) April 5-6, 2017 Stillwater, Oklahoma Lake
Watershed and Water Quality Modeling to Support TMDL Determinations Lake Oologah 26 th Annual Conference Oklahoma Clean Lakes and Watersheds Association (OCLWA) April 5-6, 2017 Stillwater, Oklahoma Lake
Performance Evaluation of the Moores Creek Advanced Water Resource Recovery Facility
 Performance Evaluation of the Moores Creek Advanced Water Resource Recovery Facility Richard W. Gullick, Ph.D. Director of Operations Timothy Castillo Wastewater Manager Presented to the Albemarle County
Performance Evaluation of the Moores Creek Advanced Water Resource Recovery Facility Richard W. Gullick, Ph.D. Director of Operations Timothy Castillo Wastewater Manager Presented to the Albemarle County
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF HOUSEHOLD WASTEWATER TREATMENT BY DUCKWEED BATCH REACTOR
 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF HOUSEHOLD WASTEWATER TREATMENT BY DUCKWEED BATCH REACTOR Udaya Simha L 1, Achyuth K. N 2 1 Professor, PG Studies in Environmental Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering,
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF HOUSEHOLD WASTEWATER TREATMENT BY DUCKWEED BATCH REACTOR Udaya Simha L 1, Achyuth K. N 2 1 Professor, PG Studies in Environmental Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering,
2017 Annual Performance Report
 2017 Annual Performance Report Thornbury Wastewater Treatment Plant and Associated Collection System Prepared by: Wastewater Operations Staff Reporting Period: January 1 December 31, 2017 1 P age Executive
2017 Annual Performance Report Thornbury Wastewater Treatment Plant and Associated Collection System Prepared by: Wastewater Operations Staff Reporting Period: January 1 December 31, 2017 1 P age Executive
Case Study. Biological Help for the Human Race. BiOWiSH Aqua Improves Nutrient Removal in a Wastewater Treatment Plant - Oberon, Australia
 Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua BiOWiSH Aqua Improves Nutrient Removal in a Wastewater Treatment Plant - Oberon, Australia BiOWiSH Aqua Executive Summary A bioaugmentation program using BiOWiSH Aqua was implemented
Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua BiOWiSH Aqua Improves Nutrient Removal in a Wastewater Treatment Plant - Oberon, Australia BiOWiSH Aqua Executive Summary A bioaugmentation program using BiOWiSH Aqua was implemented
Figure 1. Platte River Sub-Watersheds and Monitoring Locations.
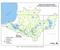 Figure 1. Platte River Sub-Watersheds and Monitoring Locations. 10 2 1 9 7 BL Pond 8 Hatchery 6 3 5 4 1 Platte River at Fewins Rd 6 B. Creek to Hatchery Spring 2 Platte River at Stone Bridge 7 Platte River
Figure 1. Platte River Sub-Watersheds and Monitoring Locations. 10 2 1 9 7 BL Pond 8 Hatchery 6 3 5 4 1 Platte River at Fewins Rd 6 B. Creek to Hatchery Spring 2 Platte River at Stone Bridge 7 Platte River
Effluent Treatment Alternatives
 Effluent Treatment Alternatives Harry Daniels Professor and Extension Specialist Department of Biology North Carolina State University Ohla Sydorovych Postdoctoral Research Associate Department of Agricultural
Effluent Treatment Alternatives Harry Daniels Professor and Extension Specialist Department of Biology North Carolina State University Ohla Sydorovych Postdoctoral Research Associate Department of Agricultural
Water Resources Director: Chris Graybeal
 Water Resources Director: Chris Graybeal Our Mission To promote and protect the environment, preserve natural resources, and ensure the health and safety of our customers. Granite Falls Wastewater Treatment
Water Resources Director: Chris Graybeal Our Mission To promote and protect the environment, preserve natural resources, and ensure the health and safety of our customers. Granite Falls Wastewater Treatment
Water Quality Analysis of Lakewood Lakes
 Water Quality Analysis of Lakewood Lakes December 2016 Prepared by WEST Consultants, Inc. Bellevue, Washington With support from HDR, Inc., Olympia, Washington TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... V
Water Quality Analysis of Lakewood Lakes December 2016 Prepared by WEST Consultants, Inc. Bellevue, Washington With support from HDR, Inc., Olympia, Washington TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... V
Progress of Water Environmental Governance/Management and Future Challenges in Sri Lanka
 AYUBOWAN Progress of Water Environmental Governance/Management and Future Challenges in Sri Lanka By Dr. R M S K Ratnayake Director Central Environmental Authority Sri Lanka Democratic Socialist Republic
AYUBOWAN Progress of Water Environmental Governance/Management and Future Challenges in Sri Lanka By Dr. R M S K Ratnayake Director Central Environmental Authority Sri Lanka Democratic Socialist Republic
Result data last updated. 10 July Map of Norske Skog Albury Paper Mills Environmental Protection Licence compliance monitoring sites
 A full copy of our license can be found on the EPA website under the following address http://www.epa.nsw.gov.au/prpoeoapp/viewpoeolicence.aspx?docid=32757&sysuid=1&licid=1272 Result data last updated
A full copy of our license can be found on the EPA website under the following address http://www.epa.nsw.gov.au/prpoeoapp/viewpoeolicence.aspx?docid=32757&sysuid=1&licid=1272 Result data last updated
Impacts to Aquatic Habitats from Land-Use or Is It Polluted?
 Impacts to Aquatic Habitats from Land-Use or Is It Polluted? Water Pollution is: The addition of excessive carbon to a system The addition of large amounts of materials to water that causes adverse changes
Impacts to Aquatic Habitats from Land-Use or Is It Polluted? Water Pollution is: The addition of excessive carbon to a system The addition of large amounts of materials to water that causes adverse changes
STUDIES ON REMOVAL OF TOXIC HEAVY METALS FROM WATER BY Eichhornia crassipes
 Indian J.Sci.Res.3(2) : 99-103, 2012 STUDIES ON REMOVAL OF TOXIC HEAVY METALS FROM WATER BY Eichhornia crassipes a1 SUJATA GAHERWAR AND PRAGYA KULKARNI b a Department of Botany, Shri Shankaracharya Mahavidyalaya,
Indian J.Sci.Res.3(2) : 99-103, 2012 STUDIES ON REMOVAL OF TOXIC HEAVY METALS FROM WATER BY Eichhornia crassipes a1 SUJATA GAHERWAR AND PRAGYA KULKARNI b a Department of Botany, Shri Shankaracharya Mahavidyalaya,
Nygaard s Algal Index in Determination of Trophic State of lake Ecosystem
 Nygaard s Algal Index in Determination of Trophic State of lake Ecosystem M.K. Mahesh1 and S. P. Hosmani2 1.Professor and Head, Department of Botany, Yuvaraja s College, Mysore 2.Professor and Head, Department
Nygaard s Algal Index in Determination of Trophic State of lake Ecosystem M.K. Mahesh1 and S. P. Hosmani2 1.Professor and Head, Department of Botany, Yuvaraja s College, Mysore 2.Professor and Head, Department
Electric Forward Market Report
 Mar-01 Mar-02 Jun-02 Sep-02 Dec-02 Mar-03 Jun-03 Sep-03 Dec-03 Mar-04 Jun-04 Sep-04 Dec-04 Mar-05 May-05 Aug-05 Nov-05 Feb-06 Jun-06 Sep-06 Dec-06 Mar-07 Jun-07 Sep-07 Dec-07 Apr-08 Jun-08 Sep-08 Dec-08
Mar-01 Mar-02 Jun-02 Sep-02 Dec-02 Mar-03 Jun-03 Sep-03 Dec-03 Mar-04 Jun-04 Sep-04 Dec-04 Mar-05 May-05 Aug-05 Nov-05 Feb-06 Jun-06 Sep-06 Dec-06 Mar-07 Jun-07 Sep-07 Dec-07 Apr-08 Jun-08 Sep-08 Dec-08
Lagoons Operation and Management in New Brunswick
 Lagoons Operation and Management in New Brunswick Lagoons Provide secondary treatment to domestic wastewater by the action of bacteria stabilizing the organic matter in the wastewater. Benefits of lagoons:
Lagoons Operation and Management in New Brunswick Lagoons Provide secondary treatment to domestic wastewater by the action of bacteria stabilizing the organic matter in the wastewater. Benefits of lagoons:
Woking. q business confidence report
 Woking q1 business confidence report Woking q1 report headlines saw a new record in company registrations in Woking when compared to any previous. was a record quarter for company registrations in Woking
Woking q1 business confidence report Woking q1 report headlines saw a new record in company registrations in Woking when compared to any previous. was a record quarter for company registrations in Woking
NALMS 2003 Protecting Our Lakes' Legacy
 NALMS 2003 Protecting Our Lakes' Legacy Performance of Nitrex for Nitrogen Removal and Phosphex and PhosRID for Phosphorus Removal From Wastewater November 6, 2003 Pio Lombardo, P.E. Lombardo Associates,
NALMS 2003 Protecting Our Lakes' Legacy Performance of Nitrex for Nitrogen Removal and Phosphex and PhosRID for Phosphorus Removal From Wastewater November 6, 2003 Pio Lombardo, P.E. Lombardo Associates,
JEDDAH INDUSTRIAL CITY
 JEDDAH INDUSTRIAL CITY WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT A Presentation by : Engr. Mowafaq Al-Sugeir Managing Director ICDOC SAWEA 2007 WORKSHOP, AL-KHOBER 4 December 2007 Built & Being Operated by : on Build-Operate-Transfer
JEDDAH INDUSTRIAL CITY WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT A Presentation by : Engr. Mowafaq Al-Sugeir Managing Director ICDOC SAWEA 2007 WORKSHOP, AL-KHOBER 4 December 2007 Built & Being Operated by : on Build-Operate-Transfer
Water Quality Study In the Streams of Flint Creek and Flint River Watersheds For TMDL Development
 Water Quality Study In the Streams of Flint Creek and Flint River Watersheds For TMDL Development Idris Abdi Doctoral Dissertation Presentation Major Advisor: Dr. Teferi Tsegaye April 18, 2005 Alabama
Water Quality Study In the Streams of Flint Creek and Flint River Watersheds For TMDL Development Idris Abdi Doctoral Dissertation Presentation Major Advisor: Dr. Teferi Tsegaye April 18, 2005 Alabama
Lake Washington. Water Quality Assessment Report. Copyright 2012 PLM Lake & Land Management Corp.
 Lake Washington 2012 Water Quality Assessment Report Copyright 2012 PLM Lake & Land Management Corp. Water Quality Report On May 22nd, June 18th, July 30th, August 29th, and September 27 th, 2012, PLM
Lake Washington 2012 Water Quality Assessment Report Copyright 2012 PLM Lake & Land Management Corp. Water Quality Report On May 22nd, June 18th, July 30th, August 29th, and September 27 th, 2012, PLM
Pulp and Paper Mill Southeastern United States
 Comprehensive Aerated Stabilization Basin Evaluation Pulp and Paper Mill Southeastern United States Conducted by: Michael H. Foster Beth Guidotti Todd Talley Christopher Agosta Environmental Business Specialists,
Comprehensive Aerated Stabilization Basin Evaluation Pulp and Paper Mill Southeastern United States Conducted by: Michael H. Foster Beth Guidotti Todd Talley Christopher Agosta Environmental Business Specialists,
Relationships between Residence Time and Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Nutrient-Rich River System
 Relationships between Residence Time and Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Nutrient-Rich River System Michael F. Coveney, John C. Hendrickson, Erich R. Marzolf, Rolland S. Fulton, Jian J. Di, Clifford P. Neubauer,
Relationships between Residence Time and Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Nutrient-Rich River System Michael F. Coveney, John C. Hendrickson, Erich R. Marzolf, Rolland S. Fulton, Jian J. Di, Clifford P. Neubauer,
Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua Lake Remediation BiOWiSH Aqua Ranisagar Chaupati Lake, India Executive Summary Objective Background Available Sizes
 Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua Lake Remediation Ranisagar Chaupati Lake, India Executive Summary Findings BiOWiSH Aqua achieved rapid bioremediation to significantly improve the water quality of Ranisagar Chaupati
Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua Lake Remediation Ranisagar Chaupati Lake, India Executive Summary Findings BiOWiSH Aqua achieved rapid bioremediation to significantly improve the water quality of Ranisagar Chaupati
Comparison of the Physico-Chemical Parameters of Two Lakes at Lodra and Nardipur under Biotic Stress
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2012 1 Comparison of the Physico-Chemical Parameters of Two Lakes at Lodra and Nardipur under Biotic Stress 1
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2012 1 Comparison of the Physico-Chemical Parameters of Two Lakes at Lodra and Nardipur under Biotic Stress 1
2016 Summit Lake Water Quality Report Prepared by Thurston County Environmental Health Division
 ! 216 Summit Lake Water Quality Report Prepared by Thurston County Environmental Health Division PART OF TOTTEN INLET WATERSHED LENGTH OF LAKE: 2.2 miles SHORELINE LENGTH: 5.6 miles LAKE SIZE: 53 acres
! 216 Summit Lake Water Quality Report Prepared by Thurston County Environmental Health Division PART OF TOTTEN INLET WATERSHED LENGTH OF LAKE: 2.2 miles SHORELINE LENGTH: 5.6 miles LAKE SIZE: 53 acres
This document can be made available in other accessible formats as soon as practicable and upon request. Staff Report. Infrastructure & Public Works
 This document can be made available in other accessible formats as soon as practicable and upon request Staff Report Infrastructure & Public Works Report To: Committee of the Whole Meeting Date: March
This document can be made available in other accessible formats as soon as practicable and upon request Staff Report Infrastructure & Public Works Report To: Committee of the Whole Meeting Date: March
Tarrant Regional Water District Water Quality Trend Analysis Final Report Executive Summary. July 2011
 Tarrant Regional Water District Water Quality Trend Analysis 1989-2009 Final Report Executive Summary July 2011 Prepared for Tarrant Regional Water District 201 North Shore Drive Fort Worth, TX 76135 Phone:
Tarrant Regional Water District Water Quality Trend Analysis 1989-2009 Final Report Executive Summary July 2011 Prepared for Tarrant Regional Water District 201 North Shore Drive Fort Worth, TX 76135 Phone:
University of Arkansas, Fayetteville. Marc Nelson. L. Wade Cash. Keith Trost. Jennifer Purtle
 University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Technical Reports Arkansas Water Resources Center 6-1-2005 Water Quality Sampling, Analysis and Annual Load Determinations for Nutrients and Sediment
University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Technical Reports Arkansas Water Resources Center 6-1-2005 Water Quality Sampling, Analysis and Annual Load Determinations for Nutrients and Sediment
Total Maximum Daily Load Development for Unnamed Tributary to Pitts Creek. Public Meeting March 26, Why Are We Here
 Total Maximum Daily Load Development for Unnamed Tributary to Pitts Creek Public Meeting March, Why Are We Here. Learn about water quality of the stream. Discuss the Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) development.
Total Maximum Daily Load Development for Unnamed Tributary to Pitts Creek Public Meeting March, Why Are We Here. Learn about water quality of the stream. Discuss the Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) development.
RE: Annual Report 2016 Wardsville Wastewater Treatment Plant and Collection System
 14 th, 217 Tom Clubb 3232 White Oak Road, 3 rd Floor London ON N6E 1L8 Attention: Mr. Clubb RE: Annual Report 216 Wardsville Wastewater Treatment Plant and Collection System The Ontario Clean Water Agency
14 th, 217 Tom Clubb 3232 White Oak Road, 3 rd Floor London ON N6E 1L8 Attention: Mr. Clubb RE: Annual Report 216 Wardsville Wastewater Treatment Plant and Collection System The Ontario Clean Water Agency
2007 Inland and Purdy Reservoirs Report. Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring Program
 2007 Inland and Purdy Reservoirs Report Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring Program Field Operations Division Environmental Indicators Section Aquatic Assessment Unit June 2012 Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring
2007 Inland and Purdy Reservoirs Report Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring Program Field Operations Division Environmental Indicators Section Aquatic Assessment Unit June 2012 Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring
Eutrophication. How can aquatic ecosystems change over time?
 Why? Eutrophication How can aquatic ecosystems change over time? If you could travel back in time millions of years, the land masses on Earth would not look like they do today. Huge areas were covered
Why? Eutrophication How can aquatic ecosystems change over time? If you could travel back in time millions of years, the land masses on Earth would not look like they do today. Huge areas were covered
EUTROPHICATION. Student Lab Workbook
 EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
Stonecrest Estates Sewage Treatment Plant 2017 Annual Report
 2017 Stonecrest Estates Sewage Treatment Plant 2017 Annual Report The Corporation of the City of Quinte West 0 Contents Table of Figures... 1 Executive Summary... 3 Summary and Interpretation of Monitoring
2017 Stonecrest Estates Sewage Treatment Plant 2017 Annual Report The Corporation of the City of Quinte West 0 Contents Table of Figures... 1 Executive Summary... 3 Summary and Interpretation of Monitoring
CASE STUDY: CLEAN-FLO inversion oxygenation reverses eutrophication - improves raw drinking
 CASE STUDY: CLEAN-FLO inversion oxygenation reverses eutrophication - improves raw drinking water The Challenge Toa Vaca dam was built in 1972 to create a 247 acre raw drinking water reservoir in Puerto
CASE STUDY: CLEAN-FLO inversion oxygenation reverses eutrophication - improves raw drinking water The Challenge Toa Vaca dam was built in 1972 to create a 247 acre raw drinking water reservoir in Puerto
WASTEWATER TREATMENT
 WASTEWATER TREATMENT Every community produces both liquid and solid wastes. The liquid portion-wastewater-is essentially the water supply of the community after it has been fouled by a variety of uses.
WASTEWATER TREATMENT Every community produces both liquid and solid wastes. The liquid portion-wastewater-is essentially the water supply of the community after it has been fouled by a variety of uses.
Inside of forest (for example) Research Flow
 Study on Relationship between Watershed Hydrology and Lake Water Environment by the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Shimane University Hiroaki SOMURA Watershed degradation + Global warming Background
Study on Relationship between Watershed Hydrology and Lake Water Environment by the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Shimane University Hiroaki SOMURA Watershed degradation + Global warming Background
WATER QUALITY ENGINEERING
 WATER QUALITY ENGINEERING Zerihun Alemayehu (AAiT-CED) Water Quality Management The control of pollution from human activities so that the water is not degraded to the point that it is no longer suitable
WATER QUALITY ENGINEERING Zerihun Alemayehu (AAiT-CED) Water Quality Management The control of pollution from human activities so that the water is not degraded to the point that it is no longer suitable
Appendix 5. Fox River Study Group Interim Monitoring Evaluation
 Appendix 5. Fox River Study Group Interim Monitoring Evaluation Introduction Submitted to Fox River Study Group 6 March 3 The purpose of this report is to review data collected by the Fox River Study Group
Appendix 5. Fox River Study Group Interim Monitoring Evaluation Introduction Submitted to Fox River Study Group 6 March 3 The purpose of this report is to review data collected by the Fox River Study Group
Effectiveness of Aeration Units in Improving Water Quality of Lower Lake, Bhopal, India
 Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 2, No. 1, 26, 87-95 Effectiveness of Aeration Units in Improving Water Quality of Lower Lake, Bhopal, India Neelam Verma 1 and Savita Dixit 2 1. Govternment Geetanjali Girls P.G.
Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 2, No. 1, 26, 87-95 Effectiveness of Aeration Units in Improving Water Quality of Lower Lake, Bhopal, India Neelam Verma 1 and Savita Dixit 2 1. Govternment Geetanjali Girls P.G.
Primary Productivity of Phytoplankton in Kotwal Reservoir and their Potential Ecological Significance
 Research Journal of Chemical Sciences ISSN 2231-606X Primary Productivity of Phytoplankton in Kotwal Reservoir and their Potential Ecological Significance Abstract Dandolia H.S. 1, Kadam C.P. 1, Shrotriy
Research Journal of Chemical Sciences ISSN 2231-606X Primary Productivity of Phytoplankton in Kotwal Reservoir and their Potential Ecological Significance Abstract Dandolia H.S. 1, Kadam C.P. 1, Shrotriy
Understanding and Acting: Community
 Understanding and Acting: Community Catchment t Management age e at Loweswater Lisa Norton, Claire Waterton, Judith Tsouvalis, Stephen Maberly, Linda May, Alex Elliott, Nigel Watson, John Rockliffe, Leslie
Understanding and Acting: Community Catchment t Management age e at Loweswater Lisa Norton, Claire Waterton, Judith Tsouvalis, Stephen Maberly, Linda May, Alex Elliott, Nigel Watson, John Rockliffe, Leslie
VARIATIONS IN DISSOLVED OXYGEN AND BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND IN TWO FRESHWATER LAKES OF BODHAN, ANDHRA PRADESH, INDIA
 Nature Environment and Pollution Technology Technoscience Publications Vol. 6 No.4 pp. 623-628 2007 VARIATIONS IN DISSOLVED OXYGEN AND BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND IN TWO FRESHWATER LAKES OF BODHAN, ANDHRA
Nature Environment and Pollution Technology Technoscience Publications Vol. 6 No.4 pp. 623-628 2007 VARIATIONS IN DISSOLVED OXYGEN AND BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND IN TWO FRESHWATER LAKES OF BODHAN, ANDHRA
Streamside Management. How the area around your pond effects the water.
 Streamside Management Zones and Water Quality How the area around your pond effects the water. Stream(pond)side Management Zone A streamside management zone (SMZ) is a strip of land immediately adjacent
Streamside Management Zones and Water Quality How the area around your pond effects the water. Stream(pond)side Management Zone A streamside management zone (SMZ) is a strip of land immediately adjacent
TREATMENT OF SUGAR PROCESS WASTE WATER AND BIOGAS PRODUCTION USING ALGAL BIOMASS
 TREATMENT OF SUGAR PROCESS WASTE WATER AND BIOGAS PRODUCTION USING ALGAL BIOMASS COLLEGE : BASAVESHWAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), BAGALKOT DEPARTMENT : ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
TREATMENT OF SUGAR PROCESS WASTE WATER AND BIOGAS PRODUCTION USING ALGAL BIOMASS COLLEGE : BASAVESHWAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), BAGALKOT DEPARTMENT : ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
Efficient Design Configurations for Biological Nutrient Removal
 Efficient Design Configurations for Biological Nutrient Removal A Case Study: Upper Blackstone Water Pollution Abatement District Jane E. Madden, P.E., BCEE August 30, 2017 UBWPAD Wastewater Treatment
Efficient Design Configurations for Biological Nutrient Removal A Case Study: Upper Blackstone Water Pollution Abatement District Jane E. Madden, P.E., BCEE August 30, 2017 UBWPAD Wastewater Treatment
CITY OF LONDON ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS GREENWAY POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE 2013 ANNUAL REPORT
 CITY OF LONDON ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS GREENWAY POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE 2013 ANNUAL REPORT FEBRUARY 2014 SUMMARY This annual report is in response
CITY OF LONDON ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS GREENWAY POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE 2013 ANNUAL REPORT FEBRUARY 2014 SUMMARY This annual report is in response
Little Cypress Bayou Special Study - Subwatershed 1.10
 - Subwatershed 1.1 Sabine River Authority of Texas August 31, 21 Prepared in Cooperation with the Texas Natural Resource Conservation Commission Under the Authorization of the Texas Clean Rivers Act Table
- Subwatershed 1.1 Sabine River Authority of Texas August 31, 21 Prepared in Cooperation with the Texas Natural Resource Conservation Commission Under the Authorization of the Texas Clean Rivers Act Table
Cooperative Monitoring Program nutrient monitoring results
 Cooperative Monitoring Program nutrient monitoring results Nutrient Water Quality Symposium, Santa Maria Central Coast Water Quality Preservation, Inc. Executive Director: Kirk Schmidt (831-750-5449, kschmidt@ccwqp.org)
Cooperative Monitoring Program nutrient monitoring results Nutrient Water Quality Symposium, Santa Maria Central Coast Water Quality Preservation, Inc. Executive Director: Kirk Schmidt (831-750-5449, kschmidt@ccwqp.org)
Technical Memorandum. 201 N. Civic Drive, #115 Walnut Creek, CA Tel: Fax:
 201 N. Civic Drive, #115 Walnut Creek, CA 94596-3867 Tel: 925.937.9010 Fax: 925.937.9026 Technical Memorandum Prepared for: City of Sunnyvale, Sunnyvale, CA Project Title: Sunnyvale Strategic Infrastructure
201 N. Civic Drive, #115 Walnut Creek, CA 94596-3867 Tel: 925.937.9010 Fax: 925.937.9026 Technical Memorandum Prepared for: City of Sunnyvale, Sunnyvale, CA Project Title: Sunnyvale Strategic Infrastructure
Shawn P. McElmurry, Ph.D., P.E. Wayne State University Rem Confesor Jr.,PhD. NCWQR, Heidelberg University
 Shawn P. McElmurry, Ph.D., P.E. Wayne State University Rem Confesor Jr.,PhD. NCWQR, Heidelberg University Great Lake Great Challenges Forum 2013 Oakland University March 14, 2013 Review over 240 primary
Shawn P. McElmurry, Ph.D., P.E. Wayne State University Rem Confesor Jr.,PhD. NCWQR, Heidelberg University Great Lake Great Challenges Forum 2013 Oakland University March 14, 2013 Review over 240 primary
DO is one of the most important constituents of natural water systems; as fish and other aquatic animal species require oxygen.
 MODELLING WATER QUALITY oxygen_sag.pdf Simple River Model DO is one of the most important constituents of natural water systems; as fish and other aquatic animal species require oxygen. Stream must have
MODELLING WATER QUALITY oxygen_sag.pdf Simple River Model DO is one of the most important constituents of natural water systems; as fish and other aquatic animal species require oxygen. Stream must have
l ake Biology terc.ucdavis.edu
 l ake Biology Algae growth (primary productivity) Yearly since 1959 Primary productivity (PPr) is a measure of the rate at which algae produce biomass through photosynthesis. At Lake Tahoe, it has been
l ake Biology Algae growth (primary productivity) Yearly since 1959 Primary productivity (PPr) is a measure of the rate at which algae produce biomass through photosynthesis. At Lake Tahoe, it has been
Environmental Science 101 Water. Fall Learning Objectives: Reading Assignment:
 Environmental Science 101 Water Fall 2012 1 Lecture Outline: 16. SURFACE WATER OLLUTION A. Two Kinds of Aquatic lants B. Upsetting the Balance by Nutrient Enrichment C. Idaho Examples D. Sources of Nutrients
Environmental Science 101 Water Fall 2012 1 Lecture Outline: 16. SURFACE WATER OLLUTION A. Two Kinds of Aquatic lants B. Upsetting the Balance by Nutrient Enrichment C. Idaho Examples D. Sources of Nutrients
Water Quality Management for Coastal Aquaculture
 SUB Hamburg A/534446 Water Quality Management for Coastal Aquaculture By Sukumar Bandyopadhyay Former Professor and Emeritus Fellow Indian institute of Technology Kharagpur 2008 DAYA PUBLISHING HOUSE Delhi
SUB Hamburg A/534446 Water Quality Management for Coastal Aquaculture By Sukumar Bandyopadhyay Former Professor and Emeritus Fellow Indian institute of Technology Kharagpur 2008 DAYA PUBLISHING HOUSE Delhi
Why Water Quality? FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE March 26, 2013
 Nutrients Nutrients Microbes Rulers of the World Microbes and Redox Potential Dissolved Oxygen Nitrogen Cycle From Waste to Gas Phosphorus Cycle or Recycle Algae The Miracle of Life Stormwater - Loadings
Nutrients Nutrients Microbes Rulers of the World Microbes and Redox Potential Dissolved Oxygen Nitrogen Cycle From Waste to Gas Phosphorus Cycle or Recycle Algae The Miracle of Life Stormwater - Loadings
Best Practice in Sewage and Effluent Treatment Technologies
 Best Practice in Sewage and Effluent Treatment Technologies Contents 1 Wastewater - Introduction 1 1.1 Earth s ecological system 1 1.1.1 Water effect on ecology 2 1.1.2 Wastewater generation 3 1.2 Wastewater
Best Practice in Sewage and Effluent Treatment Technologies Contents 1 Wastewater - Introduction 1 1.1 Earth s ecological system 1 1.1.1 Water effect on ecology 2 1.1.2 Wastewater generation 3 1.2 Wastewater
Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong
 Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong Prof. Paul J. Harrison Atmospheric, Marine & Coastal Environment Program Institute for the Environment HK University of Science & Technology Outline Background
Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong Prof. Paul J. Harrison Atmospheric, Marine & Coastal Environment Program Institute for the Environment HK University of Science & Technology Outline Background
GENERATION, CHARACTERISTICS AND TREATMENT OF MUNICIPAL WASTEWATER IN MADURAI CITY
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 6, Issue 9, Sep 2015, pp. 58-70, Article ID: IJCIET_06_09_006 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtypeijciet&vtype=6&itype=9
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 6, Issue 9, Sep 2015, pp. 58-70, Article ID: IJCIET_06_09_006 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtypeijciet&vtype=6&itype=9
Acidity and Alkalinity:
 Evaluation of Pollution Sources to Lake Glenville Quarterly Report December 2018 Kimberlee K Hall, PhD Environmental Health Program, Western Carolina University Summary Chemical and microbial analysis
Evaluation of Pollution Sources to Lake Glenville Quarterly Report December 2018 Kimberlee K Hall, PhD Environmental Health Program, Western Carolina University Summary Chemical and microbial analysis
Technical Memorandum BCWA
 Technical Memorandum BCWA Date: February 8, 2017 To: Bear Creek Watershed Association From: Russell N. Clayshulte, Manager Re: BCWA TM 2016.04 BCR 2016 Summary Table 1 BCR Summary Statistics... 1 Table
Technical Memorandum BCWA Date: February 8, 2017 To: Bear Creek Watershed Association From: Russell N. Clayshulte, Manager Re: BCWA TM 2016.04 BCR 2016 Summary Table 1 BCR Summary Statistics... 1 Table
INTRODUCTION ALake with high levels of nutrients and algae is said to be eutrophic. Eutrophication of lakes and reservoirs has become one of the most
 STATUS OF LAKES BEFORE AND AFTER RESTORATION A CASE STUDY ON ULSOOR, SANKEY, HEBBAL & MADIVAL LAKES OF BANGALORE, KARNATAKA. PATTUSAMY.V AND Dr. NANDINI.N INTRODUCTION ALake with high levels of nutrients
STATUS OF LAKES BEFORE AND AFTER RESTORATION A CASE STUDY ON ULSOOR, SANKEY, HEBBAL & MADIVAL LAKES OF BANGALORE, KARNATAKA. PATTUSAMY.V AND Dr. NANDINI.N INTRODUCTION ALake with high levels of nutrients
ArchaeaSolutions, Inc. Improved Wastewater Processing Driven by Arkea
 ArchaeaSolutions, Inc. Improved Wastewater Processing Driven by Arkea Background ArchaeaSolutions, Inc. is a high-science company focused on the use of Archaea organisms to assist natural cycle processes.
ArchaeaSolutions, Inc. Improved Wastewater Processing Driven by Arkea Background ArchaeaSolutions, Inc. is a high-science company focused on the use of Archaea organisms to assist natural cycle processes.
Kansas Case Study Kanopolis Reservoir and Salina, KS
 Kansas Case Study Kanopolis Reservoir and Salina, KS Western State Water Council Water Quantity/Quality Workshop October 6, 2015 Mike Tate, P.E. Kansas Department of Health and Environment Kanopolis Reservoir
Kansas Case Study Kanopolis Reservoir and Salina, KS Western State Water Council Water Quantity/Quality Workshop October 6, 2015 Mike Tate, P.E. Kansas Department of Health and Environment Kanopolis Reservoir
Nutrient Cycling and Water Quality on California Rangelands
 Nutrient Cycling and Water Quality on California Rangelands Randy Dahlgren Department of Land, Air and Water Resources University of California - Davis Core Research Team Barbara Allen-Diaz Rob Atwill
Nutrient Cycling and Water Quality on California Rangelands Randy Dahlgren Department of Land, Air and Water Resources University of California - Davis Core Research Team Barbara Allen-Diaz Rob Atwill
Rainbow Creek TMDL Monitoring Program Report for October 2016 through September 2017
 Rainbow Creek TMDL Monitoring Program Report for October 2016 through September 2017 Introduction The Rainbow Creek monitoring program has been developed to provide water quality data in support of the
Rainbow Creek TMDL Monitoring Program Report for October 2016 through September 2017 Introduction The Rainbow Creek monitoring program has been developed to provide water quality data in support of the
Nathan Whalen, Water Resources Specialist, Portland Water District February, 2010
 Characterization of Sebago Lake Lower Bay Trophic State Since 1976 A Statistical Calibration of Pre-1990 Secchi Transparency, Total Phosphorous and Chlorophyll a to Post- 1990 Secchi Transparency, Total
Characterization of Sebago Lake Lower Bay Trophic State Since 1976 A Statistical Calibration of Pre-1990 Secchi Transparency, Total Phosphorous and Chlorophyll a to Post- 1990 Secchi Transparency, Total
Lake Pepin Photo by Guy Schmickle
 Options for Meeting Water Quality Standards Lake Pepin Technical Conference September 23, 28 Lake Pepin Photo by Guy Schmickle Overview Role of modeling in the TMDL Main features of UMR-LP Model Reductions
Options for Meeting Water Quality Standards Lake Pepin Technical Conference September 23, 28 Lake Pepin Photo by Guy Schmickle Overview Role of modeling in the TMDL Main features of UMR-LP Model Reductions
2006 Aliceville Reservoir Report. Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring Program
 2006 Aliceville Reservoir Report Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring Program Field Operations Division Environmental Indicators Section Aquatic Assessment Unit May 2011 Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring Program
2006 Aliceville Reservoir Report Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring Program Field Operations Division Environmental Indicators Section Aquatic Assessment Unit May 2011 Rivers and Reservoirs Monitoring Program
Feel free to contact me should you require any additional information regarding the report. I can be reached at
 February 28, 217 Tom Clubb 3232 White Oak Road, 3 rd Floor London ON N6E 1L8 Attention: Mr. Clubb RE: Annual Report 216 Glencoe Wastewater Treatment Plant The Ontario Clean Water Agency is the Operating
February 28, 217 Tom Clubb 3232 White Oak Road, 3 rd Floor London ON N6E 1L8 Attention: Mr. Clubb RE: Annual Report 216 Glencoe Wastewater Treatment Plant The Ontario Clean Water Agency is the Operating
Management of Water Quality Issues in Urban Stormwater Ponds
 Management of Water Quality Issues in Urban Stormwater Ponds Ryan Xu and Ricky Kwan Storm Consulting October 2018 Bringing engineering to life Presentation Outline 1.0 Background 2.0 Project Description
Management of Water Quality Issues in Urban Stormwater Ponds Ryan Xu and Ricky Kwan Storm Consulting October 2018 Bringing engineering to life Presentation Outline 1.0 Background 2.0 Project Description
Do You Know. Your Co$ts? Tom Stow Operations & Maintenance Division Manager Clean Water Services
 Do You Know Your Co$ts? Tom Stow Operations & Maintenance Division Manager Clean Water Services Would you like to take the stress out of budget prep? Have you calculated the annual dose for each chemical
Do You Know Your Co$ts? Tom Stow Operations & Maintenance Division Manager Clean Water Services Would you like to take the stress out of budget prep? Have you calculated the annual dose for each chemical
Water Monitoring - Teralba Quarry EPA Point No.4 - Adit Overflow
 No. Dates Water Monitoring - Teralba Quarry - 2018 - EPA Point No.4 - Adit Overflow EPA No 4-148 ABCDE EPA No 4-149 ABCDE EPA No 4-150 ABCDE January 2018. Febrary 2018. March 2018. EPA No 4-151 AB April
No. Dates Water Monitoring - Teralba Quarry - 2018 - EPA Point No.4 - Adit Overflow EPA No 4-148 ABCDE EPA No 4-149 ABCDE EPA No 4-150 ABCDE January 2018. Febrary 2018. March 2018. EPA No 4-151 AB April
Constructed Wetlands
 Constructed Wetlands Constructed Wetlands Artificial wastewater treatment systems consisting of shallow ponds or channels which have been planted with aquatic plants to treat wastewater. Rely upon natural
Constructed Wetlands Constructed Wetlands Artificial wastewater treatment systems consisting of shallow ponds or channels which have been planted with aquatic plants to treat wastewater. Rely upon natural
AGENDA CHANNEL ISLANDS HARBOR TASK FORCE SPECIAL MEETING
 A. Roll Call B. Pledge of Allegiance C. New Business AGENDA CHANNEL ISLANDS HARBOR TASK FORCE SPECIAL MEETING Monday, October 22, 2018, 6:00pm Performing Arts Center, Ventura Room 800 Hobson Way, Oxnard,
A. Roll Call B. Pledge of Allegiance C. New Business AGENDA CHANNEL ISLANDS HARBOR TASK FORCE SPECIAL MEETING Monday, October 22, 2018, 6:00pm Performing Arts Center, Ventura Room 800 Hobson Way, Oxnard,
Watershed - Lake Model to Support TMDL Determinations for Lake Thunderbird
 Watershed - Lake Model to Support TMDL Determinations for Lake Thunderbird 18 th Annual EPA Region 6 Stormwater Conference Workshop 5: TMDLs and You October 3, 2016 Oklahoma City, OK Lake Thunderbird Watershed-Lake
Watershed - Lake Model to Support TMDL Determinations for Lake Thunderbird 18 th Annual EPA Region 6 Stormwater Conference Workshop 5: TMDLs and You October 3, 2016 Oklahoma City, OK Lake Thunderbird Watershed-Lake
Mandeville Wetland Assimilation Monitoring Report
 Mandeville Wetland Assimilation Monitoring Report July-September 218 By: Robert R. Lane, PhD For: David degeneres Rachael G. Hunter, PhD Director of Public Works John W. Day, PhD City of Mandeville Comite
Mandeville Wetland Assimilation Monitoring Report July-September 218 By: Robert R. Lane, PhD For: David degeneres Rachael G. Hunter, PhD Director of Public Works John W. Day, PhD City of Mandeville Comite
Understanding and Managing the Range of Phosphorus Forms Contributing to Eutrophication
 Understanding and Managing the Range of Phosphorus Forms Contributing to Eutrophication Marc Stutter, Benoit Demars The Macaulay Land Use Research Institute, Aberdeen, UK Session 3: Monitoring and evaluation
Understanding and Managing the Range of Phosphorus Forms Contributing to Eutrophication Marc Stutter, Benoit Demars The Macaulay Land Use Research Institute, Aberdeen, UK Session 3: Monitoring and evaluation
The Myakka River. Presented to the Myakka River Management Coordinating Council January 9, 2009
 The Myakka River Presented to the Myakka River Management Coordinating Council January 9, 2009 Kathryn L. Meaux Environmental Specialist III Sarasota County Integrated Water Resources Historical Monitoring
The Myakka River Presented to the Myakka River Management Coordinating Council January 9, 2009 Kathryn L. Meaux Environmental Specialist III Sarasota County Integrated Water Resources Historical Monitoring
IMPACT OF INCREASING OXYGEN IN STORMWATER PONDS. Astha Vashisht, WCI Environmental Solutions Inc.*
 IMPACT OF INCREASING OXYGEN IN STORMWATER PONDS Astha Vashisht, WCI Environmental Solutions Inc.* *WCI Environmental Solutions Inc., 1680 Woodward Drive, Suite 203, Ottawa, Ontario, K2C 3R7, avashisht@wcienvironmental.ca
IMPACT OF INCREASING OXYGEN IN STORMWATER PONDS Astha Vashisht, WCI Environmental Solutions Inc.* *WCI Environmental Solutions Inc., 1680 Woodward Drive, Suite 203, Ottawa, Ontario, K2C 3R7, avashisht@wcienvironmental.ca
Future climate scenarios for phosphorus and nitrogen dynamics in the Gulf of Riga
 Future climate scenarios for phosphorus and nitrogen dynamics in the Gulf of Riga Bärbel Müller Karulis, Latvian Institute of Aquatic Ecology Juris Aigars, Latvian Institute of Aquatic Ecology In colaboration
Future climate scenarios for phosphorus and nitrogen dynamics in the Gulf of Riga Bärbel Müller Karulis, Latvian Institute of Aquatic Ecology Juris Aigars, Latvian Institute of Aquatic Ecology In colaboration
Modeling the production of multiple ecosystems services from agricultural and forest landscape in Rhode Island
 Modeling the production of multiple ecosystems services from agricultural and forest landscape in Rhode Island Tingting Liu a, Nathaniel H. Merrill a, Arthur J. Gold b, Dorothy Q. Kellogg b and Emi Uchida
Modeling the production of multiple ecosystems services from agricultural and forest landscape in Rhode Island Tingting Liu a, Nathaniel H. Merrill a, Arthur J. Gold b, Dorothy Q. Kellogg b and Emi Uchida
Loweswater Care Programme
 Loweswater Care Programme 2012-2015 DEFRA Catchment Restoration Fund Project Improving Water Quality in Loweswater Vikki Salas, West Cumbria Rivers Trust Previous Loweswater projects: University College
Loweswater Care Programme 2012-2015 DEFRA Catchment Restoration Fund Project Improving Water Quality in Loweswater Vikki Salas, West Cumbria Rivers Trust Previous Loweswater projects: University College
