Effect of Leaching and Gypsum Content on Properties of Gypseous Soil
|
|
|
- Janel Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 9, September Effect of Leaching and Gypsum Content on Properties of Gypseous Soil Fauziah Ahmad, Md Azlin Md Said, Lamyaa Najah School of Civil Engineering, Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia Abstract- Gypseous soil is one of problematic soils to be used as foundation of road, building and other structures. It is considerably strong and has good properties when it is dry. The problem appears when constructing heavy buildings or hydraulic structures on these soils after wetted by water from rainfall or from the raising of water table level from any source and leaching the salts from the soil. The primary objective of this paper is to presents the current state of the gypseous soil subject to leaching. A review is provided aiming to discuss the effect of gypsum content and leaching on gypseous soil. T Index Terms- Gypseous soil, Gypsum content, Leaching I. INTRODUCTION he gypseous soil is a soil which has enough gypsum content to change or affect its engineering properties. Gypseous soils are usually stiff in their dry state due to the cementing action provided by gypsum, but great loss of strength and pronounced increase in compressibility occur when gypsum is dissolved by partial or full saturation. This problem becomes more severe when the water flows through such soils causing loss of mass due to the leaching of gypsum. Leaching is the process of removal of salts and soluble materials from soil by flowing water. Soils which contain soluble materials exhibit continuous variations in their engineering properties upon leaching. These changes create serious problems to the structure constructed on or within these soils Leaching Leaching is the process by which liquids percolate whether naturally or artificially through a porous material resulting in the dissolving and washing of soluble constituents out of the percolated material, Al-Zgry (1993). In practice of soil mechanics, Leaching can be defined as a process, which removes materials in solution (e.g. salts) and cementation agent from a section in the soil profile Brenner et.al. (1981) Distribution of Gypseous Soils (Alphen and Romero, 1971), estimates these soils would cover roughly km 2. According to the United Nations, Food and Agriculture Organization, (FAO, 1990) increase the extent of gypseous soils to ( ) million km 2, with major areas in the Middle East and the southern parts of the former USSR. Gypseous soils can be found mainly in Russia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Oman, China, Algeria and Egypt. In these countries the gypseous soils cover about 10% to 36% of the total area of each country. More recent figures (Al-Banna, 2004) reported that gypseous soils cover about km 2 of the world; this estimation depends on the UNISCO maps, Figure (1) 1.1. Definitions Gypseous soil Gypseous soils are soils that contain gypsum. Gypsum is a mineral salt represented by Hydrated Calcium Sulphate (CaSO4.2H2O) formed from 20.9% combined with water H2O, 46.6%, Sulphur Trioxide (SO3) and 32.5% Calcium Oxide (CaO). It has low specific gravity 2.32, which generated large influence on the physical and mechanical properties of soil containing large amount of these materials, Nashat (1990).
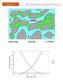
2 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 9, September Figure (1): Distribution of gypseous soils in the world (after FAO, 1990) In Iraq, Ismael (1994) estimated that about 31.7% of the area of Iraq is covered with gypseous soil with gypsum percentage ranging between (10-70%). In the upper parts of the AL-Jazirah area where the gypsum content varies from (3-10) %, the annual rainfall exceeds 350mm in this area. While the lower parts of it, where the annual rainfall is less than 250mm contain higher percent of gypsum and may exceed 50%. Thus, these soils are concentrated in Anna, Baiji, Faluja, Heet, Karkuk, Mosul, Najif, Nassiriya, Ramadi, Samarah, and Tikrit as shown in Figure (2). Figure (2): Distribution of gypseous soils in Iraq at depths ( ) mm, (after Al-Kaabi, 2007).
3 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 9, September II. EFFECT OF GYPSUM CONTENT AND LEACHING ON THE PROPERTIES OF GYPSEOUS SOIL Laboratory models Many researchers investigated the effect of gypsum content and leaching on the properties of gypseous soil by conducted series of laboratory tests using manual or modified equipment. Table below content brief description for this study: Author Seleam (1988) Nashat (1990) Description of work studied the effect of gypsum contents and leaching on properties of (undisturbed) sandy gypseous soil with gypsum content between (26 %), (60%) and (80 %), she reported that the gypseous soil exhibited a very high shear strength due to the cementation action the internal fraction (ø), and the shear parameters decreased during the leaching due to the reduction the cementation. Also, it was concluded that the total volume change and compression index (Cc) decrease with increasing the gypsum content, as results of increasing the cementing action of gypsum. The compression index increases during the leaching of soil due to the reduction in the cementing action of gypsum. Examined the behavior of gypseous soils in Iraq by conducting a laboratory testing program on samples taken from Baiji, Tellafer and Al-Dour in Iraq. The leaching process was conducted under various hydraulic gradients and different stress levels. The hydraulic conductivity fluctuated with time with a general decreasing trend. This fluctuation was attributed to the voids enlargement as a result of gypsum removal and blocking of some flow paths resulted from leaching collapse. It has been shown that the hydraulic conductivity tends to increase with the increase of hydraulic gradient and decreases with the applied stress level. The strain-time behavior revealed that the continuous dissolution of gypsum caused correspondingly a continuous settlement. The strain-logarithm of the effective vertical stress relations approached straight lines for the leached soils. It was pointed out that under low stresses (less than 100 kpa), the leaching strain was Al-Busoda (1999) Al- (2001) Qaissy proportional with the hydraulic gradient whereas, this behavior reversed when the stress level increased. It was found that leaching is responsible for approximately half or more of the expected settlement. From the results of consolidated undrained conventional triaxial compression tests, it was reported that the leaching process softened the soil and increased its plasticity studied the effect of leaching on the geotechnical properties of a gypseous soil taken from Tikrit at Saladdin governorate in Iraq. Two types of tests were utilized namely; the triaxial-permeability leaching test and the oedometer-permeability leaching test. The permeability exhibited slow rate of reduction before reaching a constant value. It was inversely proportional to the applied stress. No fluctuation with time was observed. Higher and more accurate values of the permeability coefficient were obtained from the triaxialpermeability leaching tests. The leaching strain increased linearly with the increase of percentage of dissolved gypsum and that the void ratio remains almost constant during leaching under high stresses. It has been reported that the soil compressibility increases due to leaching. The coefficient of volume compressibility (m v ) and the compression index (c c ) were reduced whereas the swell index (c s )was unaffected. A reduction in shear strength was noticed due to leaching. This reduction was attributed to the cohesion intercept due to the loss of cementing material. It was suggested that the collapse associated with leaching process tends to keep the overall particles contact area constant. So, an approximately constant friction angle was recorded. A theoretical prediction was suggested to estimate leaching strain from the given values of leaching stress and soil permeability. conducted an extensive program of laboratory tests on Al-Tharthar soil (with 79% gypsum content). A series of permeability-leaching tests was carried out under different values of over-consolidation ratio, stress level
4 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 9, September and soaking period. It was concluded that the void ratio remains almost constant for normally consolidated specimens, whereas it increases with time in a proportional manner to the over-consolidation ratio and soaking period for over-consolidated specimens. The time required to achieve a certain degree of leaching was inversely proportional to the over-consolidation ratio and soaking period. Higher values of soil permeability were recorded for overconsolidation samples compared to that of normally consolidated ones. Numerical and Analytical Investigations Numerical methods have proved successful in approximating the effects of many factors, which render the stress-deformation behavior highly complex and nonlinear. The numerical methods show promise of incorporating a number of other factors. These factors, which are influenced in deformation behavior of soils and rocks, are physical structure, porosity, density, stress history, loading characteristics, existence and movement of fluids in the pores, time-dependent or viscous effects in the solid skeleton and the pore fluids, and geologic features. Moreover, the initial success of the finite element method has indicated that some of these factors have a more significant effect than had been expected (Mansor, 2005). Author Al-Mufty, (1997) Description of work Utilized partial differential equation for governing the mass-transport to assess the variation of gypsum content of the soil during dissolution by ground water flow. The bounding surface plasticity model was applied with some modifications to formulate the constitutive stress-strain relationship. Solving the problem by finite element method showed that the collapse amount depends on the initial water content and initial void ratio before wetting, and the shear strength parameters were affected by the leaching percentage and by the amount of gypsum in the soil. Al-Jubair, (2002) Studied the stress deformation of gypseous soils using the boundary surface plasticity model. The finite element method was used to solve equilibrium and continuity equations in coupled analysis. Then, he solved the continuity equation for steady state in order to calculate the pore water pressure needed in solving the partial differential equation of masstransport that used for describing the phenomenon of gypsum dissolution and Al-Obaidi, (2007) Karkush (2008) Namiq and Nashat (2011) its transport by flowing water. The adopted approach showed a good agreement between the results of the presented model and the experimental results, which were carried out on overconsolidated gypseous samples, obtained from other authors. A continuous increase in settlement was observed when the leaching process continued. presented a theoretical work to study the behavior of gypsouse soils. The computer algorithm solves the three equations equilibrium, flow and advectiondispersion equations. She used some of the results obtained from the experimental work as input data in the developed computer algorithm. The results as compared with experimental works showed that there is a work relationship between dissolution of gypsum and time of leaching which affects displacement, pore water pressure and dissolved gypsum or concentration. developed a numerical model simulating the behavior of gypseous soils of different gypsum content and exposed to surcharge and water head at the same time. The numerical model solves three partial differential equations equilibrium equations, continuity equations and masstransport equations at the specified time. The obtained results from the numerical model, which are the variation of dissolved gypsum and leaching strain, show more reliable results in agreement with those obtained experimentally using large scale Row cell. examined the influence of leaching on volume change of gypseous soil by a laboratory testing program (One dimensional compression) were conducted in Rowe cells on relatively undisturbed soil samples from a site in northern Iraq. He found that conventional consolidation tests and interpretation procedures are not applicable to the gypseous soil investigation and derivation of a phenomenological expression that characterizes stress-strain time relations during leaching of the gypseous soil. III. CONCLUSIONS Some of the major conclusions include: 1. The leaching of gypsum causes serious damages to structures that are constructed on gypseous soils.
5 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 9, September The flow of water through the soil increased initially with time due to the enlargement of voids and then decreased due to the collapsing of soil structure until it reached a steady state condition. 3. The strength parameters reduced due to leaching. The solubility of salts was proportional to the applied consolidation pressure. 4. The leaching strain increased linearly with the increase of percentage of dissolved gypsum. 5. The soil compressibility increases during the leaching due to the reduction in the cementing action of gypsum. The coefficient of volume compressibility (m v ) and the compression index (c c ) reduced. 6. The total volume change decrease with increasing the gypsum cntent REFERENCES [1] Al-Banna, L.A.A., (2004), "Effect of Soaking and Leaching on the Dissolution of Al-Dour Gypseous Soil", M.Sc. Thesis, Building and Construction Department, University of Technology, Baghdad, Iraq. [2] Al-Busoda, B. S. (1999), "Studies on the Behavior of Gypseous Soil and Its Treatment during Loading", M.Sc. Thesis, Civil Eng. Dept. University of Baghdad. [3] Al- Qaissy, F. F. (1989), "Effect of Gypsum Content and Its Migration on Compressibility and Shear Strength of the soil ", M.Sc. Thesis, Building and Construction Department, University of Technology, Baghdad. [4] Alphen, J.G. and Romero, F.D.R. (1971): "Gypsiferous Soils: Notes on their Characteristics and Management", International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement, Bulletin 12, Wageningen, Netherlands. [5] Al-Zgry, E.A., (1993): "The effect of leaching on lime stabilized gypseous soil". M.Sc. Thesis, Dep.of Civil Engineering, University of Mousl. [6] Al-Obaidi, A.L.M. (2007), "Gypseferous Soil Behavior by Finite Element Method", Ph.D. Thesis, Civil Eng. Dept., University of Baghdad. [7] Brenner,R.,Nutalaya,P.;Chilingraian,G. and Robertston, J. (1981): "Engineering Geology of Soft Clay" in "Soft Clay Engineering", Edited by Brand and Brenner, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company. Cited by El- Rawi,1995 [8] FAO Report (1990): "Managements of Gypsiferous Soils". Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Bulletin No.62, Rome. [9] Ismael, H.N. (1994), "The Use of Gypseous Soils", Symposium on the Gypseous Soils and its Effect on Structures, N.C.C.L, Baghdad. [10] Karkush, M. O., Al-Shakarchi,Y. J. and Al-Jorany, A. N. (2008), "Theoretical modeling and experimental investigation of the leaching behavior of salty soils, ICCBT E - (11) - pp [11] Namiq, L.I. and Nashat, I.H. (2001): "Influence of leaching on volume change of a gypseous soil". Geo-Frontiers 2011, ASCE, pp [12] Nashat, I.H. (1990): "Engineering Characteristics of Some Gypseous Soils in Iraq". Ph.D. Thesis, Civil Engineering Department, University of Baghdad. [13] Seleam, S. N., (1988), "Geotechnical characteristics of Gypseous Sandy Soil Including the Effect of Contamination with Some Oil Products", M.Sc. Thesis, University of Technology, Baghdad. [14] AL-Kaabi, F., 2007; Distribution of the Gypsiferous Soil in Iraq, Iraq Geological Survey, report No AUTHORS First Author Fauziah Ahmad, School of Civil Engineering, Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia Second Author Md Azlin Md Said, School of Civil Engineering, Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia Third Author Lamyaa Najah, School of Civil Engineering, Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
CHARACTERISTICS OF GYPSEOUS SOILS TREATED WITH CALCIUM CHLORIDE SOLUTION
 Number 3 Volume Septemper13 26 Journal of Engineering Dr. Saad Farhan Al-Abdullah Highway Nabeel Shaker Mahmood Al-Dulaimi Engineering Dept., Al-Mustansiria University ABSTRACT Gypseous Soils are distributed
Number 3 Volume Septemper13 26 Journal of Engineering Dr. Saad Farhan Al-Abdullah Highway Nabeel Shaker Mahmood Al-Dulaimi Engineering Dept., Al-Mustansiria University ABSTRACT Gypseous Soils are distributed
EFFECT OF SOAKING ON THE COMPACTION CHARACTERISTICS OF AL-NAJAF SAND SOIL
 Kufa Journal of Engineering Vol. 9, No., April 018, PP. 1-1 Received 11 April 017, accepted 19 June 017 EFFECT OF SOAKING ON THE COMPACTION CHARACTERISTICS OF AL-NAJAF SAND SOIL Mohammed S. Mahmood 1 1
Kufa Journal of Engineering Vol. 9, No., April 018, PP. 1-1 Received 11 April 017, accepted 19 June 017 EFFECT OF SOAKING ON THE COMPACTION CHARACTERISTICS OF AL-NAJAF SAND SOIL Mohammed S. Mahmood 1 1
Influence of the Use of Additives on the Properties of Compacted Gypseous Soils
 Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume 7, No. 4, 13 Influence of the Use of Additives on the Properties of Compacted Gypseous Soils M.Sc., Dept. of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, University
Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume 7, No. 4, 13 Influence of the Use of Additives on the Properties of Compacted Gypseous Soils M.Sc., Dept. of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, University
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON BEARING CAPACITY OF SKIRTED FOUNDATIONS ON DRY GYPSEOUS SOIL
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 10, October 2018, pp. 1910 1922, Article ID: IJCIET_09_10_190 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=10
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 10, October 2018, pp. 1910 1922, Article ID: IJCIET_09_10_190 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=10
Code No: RR Set No. 1
 Code No: RR320101 Set No. 1 III B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2008 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING (Civil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal
Code No: RR320101 Set No. 1 III B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2008 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING (Civil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal
EFFECT OF SAND ADDITIVES ON THE ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF FINE GRAINED SOILS
 EFFECT OF SAND ADDITIVES ON THE ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF FINE GRAINED SOILS Orabi S. Al Rawi 1, Mohammed N. Assaf 1 and Nidal M. Hussein 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Isra University, Amman, Jordan
EFFECT OF SAND ADDITIVES ON THE ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF FINE GRAINED SOILS Orabi S. Al Rawi 1, Mohammed N. Assaf 1 and Nidal M. Hussein 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Isra University, Amman, Jordan
Effect of Soil Reinforcement on Shear Strength and Settlement of Cohesive- Frictional Soil
 Int. J. of GEOMATE, Sept., Int. J. 212, of GEOMATE, Vol. 3, No. Sept., 1 (Sl. 212, No. 5), Vol. pp. 3, 38-313 No. 1 (Sl. No. 5), pp. 38-313 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., ISSN:2186-2982(P), 2186-299(O),
Int. J. of GEOMATE, Sept., Int. J. 212, of GEOMATE, Vol. 3, No. Sept., 1 (Sl. 212, No. 5), Vol. pp. 3, 38-313 No. 1 (Sl. No. 5), pp. 38-313 Geotec., Const. Mat. & Env., ISSN:2186-2982(P), 2186-299(O),
USE OF ELECTRICAL TECHNIQUES FOR ACCELERATING
 USE OF ELECTRICAL TECHNIQUES FOR ACCELERATING THE CONSOLIDATION OF CLAYEY SOILS Nogueira Santos, João Alves joao.n.santos@ist.utl.pt IST, Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal ABSTRACT The aim of this
USE OF ELECTRICAL TECHNIQUES FOR ACCELERATING THE CONSOLIDATION OF CLAYEY SOILS Nogueira Santos, João Alves joao.n.santos@ist.utl.pt IST, Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal ABSTRACT The aim of this
Ch 6 Foundation Engineering
 Ch. 6 - Strength and Stiffness of Clay Page 1 Ch 6 Foundation Engineering Reading Assignment Ch. 6 Lecture Notes Sections 6.1-6.3, 6.5 (Salgado) Other Materials Homework Assignment 6 Problems 6-11, 6-12
Ch. 6 - Strength and Stiffness of Clay Page 1 Ch 6 Foundation Engineering Reading Assignment Ch. 6 Lecture Notes Sections 6.1-6.3, 6.5 (Salgado) Other Materials Homework Assignment 6 Problems 6-11, 6-12
ENHANCING THE ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF COHESIVE SOILS USING PORTLAND CEMENT
 ENHANCING THE ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF COHESIVE SOILS USING PORTLAND CEMENT Orabi S. Al Rawi and Mohammed N. Assaf Department of Civil Engineering, Isra University, Amman, Jordan E-Mail: orabi.alrawi@iu.edu.jo
ENHANCING THE ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF COHESIVE SOILS USING PORTLAND CEMENT Orabi S. Al Rawi and Mohammed N. Assaf Department of Civil Engineering, Isra University, Amman, Jordan E-Mail: orabi.alrawi@iu.edu.jo
2012 Soil Mechanics I and Exercises Final Examination
 2012 Soil Mechanics I and Exercises Final Examination 2013/1/22 (Tue) 13:00-15:00 Kyotsu 155 Kyotsu 1 Kyotsu 3 W2 Lecture room Attention: There are four questions and four answer sheets. Write down your
2012 Soil Mechanics I and Exercises Final Examination 2013/1/22 (Tue) 13:00-15:00 Kyotsu 155 Kyotsu 1 Kyotsu 3 W2 Lecture room Attention: There are four questions and four answer sheets. Write down your
Brooks/Cole Thomson LearningiM. Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering. Braja M. Das. California State University, Sacramento
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering Braja M. Das California State University, Sacramento Brooks/Cole Thomson LearningiM Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States CHAPTER
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering Braja M. Das California State University, Sacramento Brooks/Cole Thomson LearningiM Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States CHAPTER
Beyond Engineering & Testing, LLC.
 in Round Rock, Texas, USA has demonstrated proficiency for the testing of construction materials and has conformed to the requirements established in AASHTO R 18 and the AASHTO Accreditation policies established
in Round Rock, Texas, USA has demonstrated proficiency for the testing of construction materials and has conformed to the requirements established in AASHTO R 18 and the AASHTO Accreditation policies established
PARAMETRIC STUDY OF SHALLOW FOUNDATION BEARING CAPACITY IN CLAYEY SOIL
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 10, October 2018, pp. 1223 1230, Article ID: IJCIET_09_10_121 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=10
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 10, October 2018, pp. 1223 1230, Article ID: IJCIET_09_10_121 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=10
PE Exam Review - Geotechnical
 PE Exam Review - Geotechnical Resources and Visual Aids Item Page I. Glossary... 11 II. Parameters... 9 III. Equations....11 IV. Tables, Charts & Diagrams... 14 1. Module 1 - Soil Classification... 14
PE Exam Review - Geotechnical Resources and Visual Aids Item Page I. Glossary... 11 II. Parameters... 9 III. Equations....11 IV. Tables, Charts & Diagrams... 14 1. Module 1 - Soil Classification... 14
Inclusion Effect on Heterogeneity of Excess Pore Water Pressure Distribution in Composite Clay
 Inclusion Effect on Heterogeneity of Excess Pore Water Pressure Distribution in Composite Clay J. Jalili Payame Noor University, Iran M. K. Jafari & A. Shafiee International Institute of Earthquake Engineering
Inclusion Effect on Heterogeneity of Excess Pore Water Pressure Distribution in Composite Clay J. Jalili Payame Noor University, Iran M. K. Jafari & A. Shafiee International Institute of Earthquake Engineering
Heating Pulse Tests under Constant Volume on Natural Boom Clay. Experimental Results and Numerical Simulations
 Heating Pulse Tests under Constant Volume on Natural Boom Clay. Experimental Results and Numerical Simulations Analice Lima 1, Enrique Romero 1, Jean Vaunat 1, Antonio Gens 1 & Xiangling Li 2 1 Universitat
Heating Pulse Tests under Constant Volume on Natural Boom Clay. Experimental Results and Numerical Simulations Analice Lima 1, Enrique Romero 1, Jean Vaunat 1, Antonio Gens 1 & Xiangling Li 2 1 Universitat
Importance of tailings properties for closure
 Proceedings of Mine Closure Solutions, 2014 April 26 30, 2014, Ouro Preto, Minas Gerais, Brazil Published by InfoMine, 2014 InfoMine, ISBN: 978-0-9917905-4-8 Importance of tailings properties for closure
Proceedings of Mine Closure Solutions, 2014 April 26 30, 2014, Ouro Preto, Minas Gerais, Brazil Published by InfoMine, 2014 InfoMine, ISBN: 978-0-9917905-4-8 Importance of tailings properties for closure
SOIL IMPROVEMENT USING WASTE TIRE CHIPS
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 8, August 2018, pp. 1338 1345, Article ID: IJCIET_09_08_135 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=8
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 8, August 2018, pp. 1338 1345, Article ID: IJCIET_09_08_135 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=8
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Soil Mechanics Lab ECIV 3151 Final Exam 2016/2017
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Soil Mechanics Lab ECIV 3151 Final Exam 2016/2017 Instructors: Dr. Jehad T. Hamad Engr. Yasser M. Almadhoun Examination Date:
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Soil Mechanics Lab ECIV 3151 Final Exam 2016/2017 Instructors: Dr. Jehad T. Hamad Engr. Yasser M. Almadhoun Examination Date:
COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool. Faculty of Civil Engineering UiTM, Malaysia
 COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool Faculty of Civil Engineering, Malaysia Name : COURSE CONTENTS Use of Plaxis Getting Started Exercise 1: Elastic analysis of drained footing
COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool Faculty of Civil Engineering, Malaysia Name : COURSE CONTENTS Use of Plaxis Getting Started Exercise 1: Elastic analysis of drained footing
Monitoring a Drilled Shaft Retaining Wall in Expansive Clay: Long-Term Performance in Response to Moisture Fluctuations
 1348 Brown, A.C., Dellinger, G., Helwa, A., El-Mohtar, C., Zornberg, J.G., and Gilbert, R.B. (2015). Monitoring a Drilled Shaft Retaining Wall in Expansive Clay: Long-Term Performance in Response to Moisture
1348 Brown, A.C., Dellinger, G., Helwa, A., El-Mohtar, C., Zornberg, J.G., and Gilbert, R.B. (2015). Monitoring a Drilled Shaft Retaining Wall in Expansive Clay: Long-Term Performance in Response to Moisture
Back-Analysis of Weathering Destructuration of a Lumpy Clay Fill
 Back-Analysis of Weathering Destructuration of a Lumpy Clay Fill J Najser Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Science, Czech Republic (jannajser@centrum.cz) D Mašín Charles University in Prague, Faculty
Back-Analysis of Weathering Destructuration of a Lumpy Clay Fill J Najser Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Science, Czech Republic (jannajser@centrum.cz) D Mašín Charles University in Prague, Faculty
Capability Statement
 Capability Statement Trilab is Australasia's leading independent supplier of specialised soil and rock mechanics testing, to the Asia-Pacific mining, civil construction and infrastructure industries. Two
Capability Statement Trilab is Australasia's leading independent supplier of specialised soil and rock mechanics testing, to the Asia-Pacific mining, civil construction and infrastructure industries. Two
Chapter 11 Compressibility of Soil
 Page 11 1 Chapter 11 Compressibility of Soil 1. The compression of soil layers as a result of foundation or other loadings is caused by (a) deformation of soil particles. (b) relocation of soil particles.
Page 11 1 Chapter 11 Compressibility of Soil 1. The compression of soil layers as a result of foundation or other loadings is caused by (a) deformation of soil particles. (b) relocation of soil particles.
Geotechnical Performance of ATA -Treated Fluid Fine Tailings
 Geotechnical Performance of ATA -Treated Fluid Fine Tailings T. Moore, Thurber Engineering Ltd., Canada C. Zhang, Thurber Engineering Ltd., Canada M. Pinheiro, Thurber Engineering Ltd., Canada Outline
Geotechnical Performance of ATA -Treated Fluid Fine Tailings T. Moore, Thurber Engineering Ltd., Canada C. Zhang, Thurber Engineering Ltd., Canada M. Pinheiro, Thurber Engineering Ltd., Canada Outline
CEX6230 GEOTECHNICS Dear Student:
 CEX6230 GEOTECHNICS 31.05.2010 Dear Student: Geotechnics (CEX6230) discusses design and construction aspects of Geotechnical Engineering. Even though this course requires a pass in CEX4230, I find that
CEX6230 GEOTECHNICS 31.05.2010 Dear Student: Geotechnics (CEX6230) discusses design and construction aspects of Geotechnical Engineering. Even though this course requires a pass in CEX4230, I find that
Use and Measurement of Fully Softened Shear Strength in Engineering Practice
 VIRGINIA TECH The Charles E. Via Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering GEO Omaha 2019, 36th Annual Geotechnical Conference Use and Measurement of Fully Softened Shear Strength in Engineering
VIRGINIA TECH The Charles E. Via Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering GEO Omaha 2019, 36th Annual Geotechnical Conference Use and Measurement of Fully Softened Shear Strength in Engineering
Influence of unloading soil modulus on horizontal deformation of diaphragm wall
 Influence of unloading soil modulus on horizontal deformation of diaphragm wall Hoang Viet NGUYEN 1 and Thi Dieu Chinh LUU 2 1 Lecturer, Soil Mechanics and Foundation Department, National University of
Influence of unloading soil modulus on horizontal deformation of diaphragm wall Hoang Viet NGUYEN 1 and Thi Dieu Chinh LUU 2 1 Lecturer, Soil Mechanics and Foundation Department, National University of
Feasibility of Lime Stabilized Expansive Soil as a Subbase Material for Flexible Pavements
 Feasibility of Lime Stabilized Expansive Soil as a Subbase Material for Flexible Pavements S. Patel 1, L. M. Reddy 2 And P. M. Chaudhary 3 Abstract A large portion of India roughly equal to 0.8 million
Feasibility of Lime Stabilized Expansive Soil as a Subbase Material for Flexible Pavements S. Patel 1, L. M. Reddy 2 And P. M. Chaudhary 3 Abstract A large portion of India roughly equal to 0.8 million
Effect of stabilizers on the shear strength of residual soil
 Effect of stabilizers on the shear strength of residual soil Lamyaa Najah Snodi 1,*, Yahya Atemimi 2 and Fauziah binti Ahmad 3 1 Civil Engineering Department, College of Engineering, Tikrit University,
Effect of stabilizers on the shear strength of residual soil Lamyaa Najah Snodi 1,*, Yahya Atemimi 2 and Fauziah binti Ahmad 3 1 Civil Engineering Department, College of Engineering, Tikrit University,
EARTHQUAKE EFFECT ON SINGLE PILE BEHAVIOR WITH VARIOUS FACTOR OF SAFETY AND DEPTH TO DIAMETER RATIO IN LIQUEFIABLE SAND
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 4, April 218, pp. 1253 1262, Article ID: IJCIET_9_4_14 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=4
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 4, April 218, pp. 1253 1262, Article ID: IJCIET_9_4_14 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=4
IRAQI GYPSEOUS SOIL STABILIZED BY ORDINARY AND ENCASED STONE COLUMNS
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 6, November-December 216, pp. 179 192, Article ID: IJCIET_7_6_2 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=6
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 6, November-December 216, pp. 179 192, Article ID: IJCIET_7_6_2 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=6
A Study of Loading Time Effect in Oedometer Test
 A Study of Loading Time Effect in Oedometer Test *Sanchari Halder 1, Ji-Seung Park 2 and Myoung-Soo Won 3 1), 2), 3) Department of Civil Engineering, Kunsan National University, Gunsan, South Korea 1)
A Study of Loading Time Effect in Oedometer Test *Sanchari Halder 1, Ji-Seung Park 2 and Myoung-Soo Won 3 1), 2), 3) Department of Civil Engineering, Kunsan National University, Gunsan, South Korea 1)
Void structure of Auckland residual soil using X-ray CT scanning
 Proc. 18 th NZGS Geotechnical Symposium on Soil-Structure Interaction. Ed. CY Chin, Auckland Naotaka Kikkawa, Michael Pender, Rolando Orense and Peter Liu Faculty of Engineering, University of Auckland,
Proc. 18 th NZGS Geotechnical Symposium on Soil-Structure Interaction. Ed. CY Chin, Auckland Naotaka Kikkawa, Michael Pender, Rolando Orense and Peter Liu Faculty of Engineering, University of Auckland,
Investigation on creep behavior of geo-materials with suction control technique
 Investigation on creep behavior of geo-materials with suction control technique Tomoyoshi NISHIMURA Department of Civil Engineering, Ashikaga Institute of Technology, Tochigi, Japan Abstract. The compacted
Investigation on creep behavior of geo-materials with suction control technique Tomoyoshi NISHIMURA Department of Civil Engineering, Ashikaga Institute of Technology, Tochigi, Japan Abstract. The compacted
TABLE OF CONTENTS. List of figures... xvii
 TABLE OF CONTENTS List of figures... xvii CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 Background of the Research Project... 1 1.2 Scope and Objectives of the Research Programme... 2 1.3 Layout of the Thesis and Overview
TABLE OF CONTENTS List of figures... xvii CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 Background of the Research Project... 1 1.2 Scope and Objectives of the Research Programme... 2 1.3 Layout of the Thesis and Overview
STUDY OF RADIAL PORE WATER PRESSURE DISSIPATION DURING CONSOLIDATION USING PLUS & BAND SHAPE SAND DRAIN
 IGC 9, Guntur, INDIA Study of Radial Pore Water Pressure Dissipation during Consolidation Using Plus & Band Shape Sand Drain STUDY OF RADIAL PORE WATER PRESSURE DISSIPATION DURING CONSOLIDATION USING PLUS
IGC 9, Guntur, INDIA Study of Radial Pore Water Pressure Dissipation during Consolidation Using Plus & Band Shape Sand Drain STUDY OF RADIAL PORE WATER PRESSURE DISSIPATION DURING CONSOLIDATION USING PLUS
SEEPAGE ANALYSIS UNDERNEATH DIYALA WEIR FOUNDATION
 Thirteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 13 009, Hurghada, Egypt SEEPAGE ANALYSIS UNDERNEATH DIYALA WEIR FOUNDATION Saleh I. Khassaf 1, Aqeel Sh. Al-Adili, and Rafid S. Rasheed 3 1 Asst.
Thirteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 13 009, Hurghada, Egypt SEEPAGE ANALYSIS UNDERNEATH DIYALA WEIR FOUNDATION Saleh I. Khassaf 1, Aqeel Sh. Al-Adili, and Rafid S. Rasheed 3 1 Asst.
AVOIDING EXCESSIVE DISPLACEMENTS: A NEW DESIGN APPROACH FOR RETAINING WALLS
 International Conference on Structural and Foundation Failures August 2-4, 4, Singapore AVOIDING EXCESSIVE DISPLACEMENTS: A NEW DESIGN APPROACH FOR RETAINING WALLS A. S. Osman and M.D. Bolton Department
International Conference on Structural and Foundation Failures August 2-4, 4, Singapore AVOIDING EXCESSIVE DISPLACEMENTS: A NEW DESIGN APPROACH FOR RETAINING WALLS A. S. Osman and M.D. Bolton Department
Secondary Consolidation and the effect of Surcharge Load
 Secondary Consolidation and the effect of Surcharge Load Thuvaragasingam Bagavasingam University of Moratuwa Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract This paper analyses the behavior of soft clays during consolidation
Secondary Consolidation and the effect of Surcharge Load Thuvaragasingam Bagavasingam University of Moratuwa Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract This paper analyses the behavior of soft clays during consolidation
DISPERSIVE SOILS. Dispersive soils are those in which the clay content has a high percentage of sodium.
 DISPERSIVE SOILS Dispersive soils are those in which the clay content has a high percentage of sodium. This clay fraction readily breaks down to form a suspension in water. 1 Some types of clay minerals
DISPERSIVE SOILS Dispersive soils are those in which the clay content has a high percentage of sodium. This clay fraction readily breaks down to form a suspension in water. 1 Some types of clay minerals
Undrained monotonic behaviour of pumice sand
 Orense, R.P. (213) Proc. 19 th NZGS Geotechnical Symposium. Ed. CY Chin, Queenstown R P Orense Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Auckland r.orense@auckland.ac.nz (Corresponding
Orense, R.P. (213) Proc. 19 th NZGS Geotechnical Symposium. Ed. CY Chin, Queenstown R P Orense Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Auckland r.orense@auckland.ac.nz (Corresponding
Soil Stabilization using Rice Husk
 Soil Stabilization using Rice Husk Prof. Mahadeva M 1, Dr. D L Venkatesh Babu 1, Sharmila H C 3 1 Assistant Professo, Department of civil Engineering, Shri Pillappa College of Engineering 2 Professor and
Soil Stabilization using Rice Husk Prof. Mahadeva M 1, Dr. D L Venkatesh Babu 1, Sharmila H C 3 1 Assistant Professo, Department of civil Engineering, Shri Pillappa College of Engineering 2 Professor and
LNAPL migration through soil cement barrier with and without flow condition
 As. J. Energy Env. 2009, 10(03), 185-193 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Research Article LNAPL migration through soil cement barrier
As. J. Energy Env. 2009, 10(03), 185-193 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Research Article LNAPL migration through soil cement barrier
Probabilistic Cost Optimisation of Soil Improvement Strategies
 Probabilistic Cost Optimisation of Soil Improvement Strategies G.B. de Vries 1 ; P.H.A.J.M. van Gelder 2 ; J.K. Vrijling 2 1 Van Oord ACZ, Jan Blankenweg 2, 4200 AL Gorinchem, The Netherlands (E-mail:
Probabilistic Cost Optimisation of Soil Improvement Strategies G.B. de Vries 1 ; P.H.A.J.M. van Gelder 2 ; J.K. Vrijling 2 1 Van Oord ACZ, Jan Blankenweg 2, 4200 AL Gorinchem, The Netherlands (E-mail:
Lecture 5. Soil Water Characteristic Curves (SWCC)
 Lecture 5 Soil Water Characteristic Curves (SWCC) Surface Tension, Review Physical Model for Capillary The capillary model provides a mathematical relationship between the radius of curvature of the air-water
Lecture 5 Soil Water Characteristic Curves (SWCC) Surface Tension, Review Physical Model for Capillary The capillary model provides a mathematical relationship between the radius of curvature of the air-water
Study on Coefficient of Permeability of Copper slag when admixed with Lime and Cement
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 7, Issue 6 (Jul. - Aug. 2013), PP 19-25 Study on Coefficient of Permeability of Copper slag when
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 7, Issue 6 (Jul. - Aug. 2013), PP 19-25 Study on Coefficient of Permeability of Copper slag when
Unloading-Reloading Lines as a Function of Preconsolidation Pressure 1
 Digest 2007, December 2007 1141-1151 Unloading-Reloading Lines as a Function of Preconsolidation Pressure 1 Özer ÇİNİCİOĞLU * ABSTRACT This paper presents the improvement of the extended power function
Digest 2007, December 2007 1141-1151 Unloading-Reloading Lines as a Function of Preconsolidation Pressure 1 Özer ÇİNİCİOĞLU * ABSTRACT This paper presents the improvement of the extended power function
Basic behaviour study of cement treated Singapore marine clay
 ABSTRACT Basic behaviour study of cement treated Singapore marine clay Mohanadas H. C. Department of Civil Engineering, National University of Singapore Block E1A #7-3, 1 Engineering Drive 2, Singapore
ABSTRACT Basic behaviour study of cement treated Singapore marine clay Mohanadas H. C. Department of Civil Engineering, National University of Singapore Block E1A #7-3, 1 Engineering Drive 2, Singapore
Permanent Link:
 Citation: Amiralian, S and Chegenizadeh, A and Nikraz, Hamid. 2012. Laboratory Investigation on the Effect of Lime on Compressibility of Soil, in A. Chang and T. Yingthawornsuk (ed), International Conference
Citation: Amiralian, S and Chegenizadeh, A and Nikraz, Hamid. 2012. Laboratory Investigation on the Effect of Lime on Compressibility of Soil, in A. Chang and T. Yingthawornsuk (ed), International Conference
SEEPAGE FLOW-STABILITY ANALYSIS OF THE RIVERBANK OF SAIGON RIVER DUE TO RIVER WATER LEVEL FLUCTUATION
 Geotech., Const. Mat. and Env., ISSN:2186-2982(P), 2186-2990(O), Japan SEEPAGE FLOW-STABILITY ANALYSIS OF THE RIVERBANK OF SAIGON RIVER DUE TO RIVER WATER LEVEL FLUCTUATION A. Oya 1, H.H. Bui 2, N. Hiraoka
Geotech., Const. Mat. and Env., ISSN:2186-2982(P), 2186-2990(O), Japan SEEPAGE FLOW-STABILITY ANALYSIS OF THE RIVERBANK OF SAIGON RIVER DUE TO RIVER WATER LEVEL FLUCTUATION A. Oya 1, H.H. Bui 2, N. Hiraoka
EFFECT OF CHROME TANNING EFFLUENT ON COHESIVE SOILS
 EFFECT OF CHROME TANNING EFFLUENT ON COHESIVE SOILS S. Sathish 1, K. Thamaraiselvan 2, P.A. Theenesh 3, C. Venkatesh 4, T.R. Banu Chander 5 1,2,3,4UG Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Valliammai
EFFECT OF CHROME TANNING EFFLUENT ON COHESIVE SOILS S. Sathish 1, K. Thamaraiselvan 2, P.A. Theenesh 3, C. Venkatesh 4, T.R. Banu Chander 5 1,2,3,4UG Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Valliammai
Seepage-Stress Coupled Analysis on Shield Tunnel Face Stability in Layered Soil
 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics, Robotics and Automation (ICMRA 2015) Seepage-Stress Coupled Analysis on Shield Tunnel Face Stability in Layered Soil Yongli Fan 1, a, Zemin Ren 2,b, Kun Liu
3rd International Conference on Mechatronics, Robotics and Automation (ICMRA 2015) Seepage-Stress Coupled Analysis on Shield Tunnel Face Stability in Layered Soil Yongli Fan 1, a, Zemin Ren 2,b, Kun Liu
Soil Mechanics FLUID FLW IN SOIL ONE DIMENSIONAL FLOW. Tikrit University. College of Engineering Civil engineering Department
 Tikrit University FLUID FLW IN SOIL ONE DIMENSIONAL FLOW College of Engineering Civil engineering Department Soil Mechanics 3 rd Class Lecture notes Up Copyrights 2016 Soil is a three phase medium --------
Tikrit University FLUID FLW IN SOIL ONE DIMENSIONAL FLOW College of Engineering Civil engineering Department Soil Mechanics 3 rd Class Lecture notes Up Copyrights 2016 Soil is a three phase medium --------
POTENTIAL FOR CARBON CAPTURE AND SEQUESTRATION (CCS) IN FLORIDA
 POTENTIAL FOR CARBON CAPTURE AND SEQUESTRATION (CCS) IN FLORIDA JEFFREY CUNNINGHAM YOGI GOSWAMI MARK STEWART MAYA TROTZ 28 SEPTEMBER 2011 Project Team Principal Investigator (PI): Mark Stewart (USF, Department
POTENTIAL FOR CARBON CAPTURE AND SEQUESTRATION (CCS) IN FLORIDA JEFFREY CUNNINGHAM YOGI GOSWAMI MARK STEWART MAYA TROTZ 28 SEPTEMBER 2011 Project Team Principal Investigator (PI): Mark Stewart (USF, Department
SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES GROUNDWATER. Instructor. Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ
 SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES GROUNDWATER Instructor Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus SEES 503 Sustainable Water
SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES GROUNDWATER Instructor Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus SEES 503 Sustainable Water
Conclusions. Chapter Summary and concluding remarks Three-phase FE model within thermoporoelasticity
 Chapter 7 Conclusions 7.1 Summary and concluding remarks 7.1.1 Three-phase FE model within thermoporoelasticity A three-phase FE model for freezing soils consisting of solid grains, pore water and pore
Chapter 7 Conclusions 7.1 Summary and concluding remarks 7.1.1 Three-phase FE model within thermoporoelasticity A three-phase FE model for freezing soils consisting of solid grains, pore water and pore
Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site
 Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site Liwen CAO *, Dongmei WU, Yong WANG, Ke HAN, Xue QU and Pan HUO School of Resource and Earth Science, China University of Mining and Technology,
Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site Liwen CAO *, Dongmei WU, Yong WANG, Ke HAN, Xue QU and Pan HUO School of Resource and Earth Science, China University of Mining and Technology,
Module 3. DYNAMIC SOIL PROPERTIES (Lectures 10 to 16)
 Module 3 DYNAMIC SOIL PROPERTIES (Lectures 10 to 16) Lecture 16 Topics 3.9 DAMPING RATIO 3.10 CYCLIC NONLINEAR MODELS 3.11 ADVANCED CONSTITUTIVE MODELS 3.12 STRENGTH OF CYCLICALLY LOADED SOILS 3.12.1 Definitions
Module 3 DYNAMIC SOIL PROPERTIES (Lectures 10 to 16) Lecture 16 Topics 3.9 DAMPING RATIO 3.10 CYCLIC NONLINEAR MODELS 3.11 ADVANCED CONSTITUTIVE MODELS 3.12 STRENGTH OF CYCLICALLY LOADED SOILS 3.12.1 Definitions
Design of deep excavations with FEM - Influence of constitutive model and comparison of EC7 design approaches
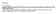 Reference: H.F. Schweiger Design of deep excavations with FEM - Influence of constitutive model and comparison of EC7 design approaches Proc. of the 21 Earth Retention Conference (Finno,R.J., Hashash,
Reference: H.F. Schweiger Design of deep excavations with FEM - Influence of constitutive model and comparison of EC7 design approaches Proc. of the 21 Earth Retention Conference (Finno,R.J., Hashash,
THE ENERGY ABSORPTION OF ALUMINIUM HONEYCOMB UNDER QUASI-STATIC LOADING
 4 th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, December 26-28, 2001, Dhaka, Bangladesh/pp. I 35-40 THE ENERGY ABSORPTION OF ALUMINIUM HONEYCOMB UNDER QUASI-STATIC LOADING Dr. Md Radzai Said*
4 th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, December 26-28, 2001, Dhaka, Bangladesh/pp. I 35-40 THE ENERGY ABSORPTION OF ALUMINIUM HONEYCOMB UNDER QUASI-STATIC LOADING Dr. Md Radzai Said*
SWELLING BEHAVIOUR OF ENGINEERED CLAY SOILS
 SWELLING BEHAVIOUR OF ENGINEERED CLAY SOILS Agus Setyo Muntohar 1 & Roslan Hashim 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Muhammadiyah University of Yogyakarta Jl. HOS. Cokroaminoto 17 Yogyakarta, Indonesia
SWELLING BEHAVIOUR OF ENGINEERED CLAY SOILS Agus Setyo Muntohar 1 & Roslan Hashim 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Muhammadiyah University of Yogyakarta Jl. HOS. Cokroaminoto 17 Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Numerical Modeling of Slab-On-Grade Foundations
 Numerical Modeling of Slab-On-Grade Foundations M. D. Fredlund 1, J. R. Stianson 2, D. G. Fredlund 3, H. Vu 4, and R. C. Thode 5 1 SoilVision Systems Ltd., 2109 McKinnon Ave S., Saskatoon, SK S7J 1N3;
Numerical Modeling of Slab-On-Grade Foundations M. D. Fredlund 1, J. R. Stianson 2, D. G. Fredlund 3, H. Vu 4, and R. C. Thode 5 1 SoilVision Systems Ltd., 2109 McKinnon Ave S., Saskatoon, SK S7J 1N3;
Compressibility of Soil. Chapter 11
 Compressibility of Soil Chapter 11 TOPICS INTRODUCTION ELASTIC SETTLEMENT Stress distribution in soil masses CONSOLIDATION SETTLEMENT Fundamentals of consolidation Calculation of 1-D Consolidation Settlement
Compressibility of Soil Chapter 11 TOPICS INTRODUCTION ELASTIC SETTLEMENT Stress distribution in soil masses CONSOLIDATION SETTLEMENT Fundamentals of consolidation Calculation of 1-D Consolidation Settlement
Time-Dependent Strength Behavior of Soil-Bentonite Slurry Wall Backfill
 Time-Dependent Strength Behavior of Soil-Bentonite Slurry Wall Backfill Jeffrey Evans 1, and Christopher Ryan 2 1 Bucknell University, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Lewisburg, PA 17837
Time-Dependent Strength Behavior of Soil-Bentonite Slurry Wall Backfill Jeffrey Evans 1, and Christopher Ryan 2 1 Bucknell University, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Lewisburg, PA 17837
Numerical Simulation of Liquefaction Deformation of Sand Layer around Bucket Foundations under Dynamic Loadings
 The Open Ocean Engineering Journal, 2010, 3, 75-81 75 Open Access Numerical Simulation of Liquefaction Deformation of Sand Layer around Bucket Foundations under Dynamic Loadings Chi Li 1,*, Xiaobing Lu
The Open Ocean Engineering Journal, 2010, 3, 75-81 75 Open Access Numerical Simulation of Liquefaction Deformation of Sand Layer around Bucket Foundations under Dynamic Loadings Chi Li 1,*, Xiaobing Lu
AGING EFFECT ON RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LIQUEFACTION STRENGTH AND CONE RESISTANCE OF SAND CONTAINING NON-PLASTIC FINES
 4th Japan-Taiwan Joint Worlshop on Geotechnical Hazards from Large Earthquakes and Heavy Rainfalls 25-28, October, 2010, Sendai, Japan AGING EFFECT ON RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LIQUEFACTION STRENGTH AND CONE
4th Japan-Taiwan Joint Worlshop on Geotechnical Hazards from Large Earthquakes and Heavy Rainfalls 25-28, October, 2010, Sendai, Japan AGING EFFECT ON RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LIQUEFACTION STRENGTH AND CONE
LABORATORY STUDY OF FINE GRAINED SOIL IMPROVEMENT USING LIME MORTAR STONE COLUMNS
 International Symposium on Geotechnical Engineering, Ground Improvement and Geosynthetics for Human Security and Environmental Preservation, Bangkok, Thailand LABORATORY STUDY OF FINE GRAINED SOIL IMPROVEMENT
International Symposium on Geotechnical Engineering, Ground Improvement and Geosynthetics for Human Security and Environmental Preservation, Bangkok, Thailand LABORATORY STUDY OF FINE GRAINED SOIL IMPROVEMENT
A Laboratory Evaluation of Stabilization of Salty Clay Soil by Using Chloride Compounds
 A Laboratory Evaluation of Stabilization of Salty Clay Soil by Using Chloride Compounds Jitesh Kumar Jain 1, Pradeep Kumar Jain 2, Amit Mittal 3, Hitesh Nagar 4 1,2,3,4 Assistant Professor, Department
A Laboratory Evaluation of Stabilization of Salty Clay Soil by Using Chloride Compounds Jitesh Kumar Jain 1, Pradeep Kumar Jain 2, Amit Mittal 3, Hitesh Nagar 4 1,2,3,4 Assistant Professor, Department
Unsaturated Seepage Modeling Made Easy
 Seepage Modeling Made Easy Murray D. Fredlund Department of Civil Engineering University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Sask., Canada Introduction Fresh out of university, one of the first challenges I was
Seepage Modeling Made Easy Murray D. Fredlund Department of Civil Engineering University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Sask., Canada Introduction Fresh out of university, one of the first challenges I was
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Thermal Effect on Lateral Earth Pressure of Cement Treated Clay Layer
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 7(13) November 213, Pages: 114-123 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Thermal Effect on
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 7(13) November 213, Pages: 114-123 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Thermal Effect on
Foundation Engineering CE Introduction. Prof. H. Alawaji. Room No. 2A- 47/1, Tel
 Foundation Engineering CE 483 1. Introduction Prof. H. Alawaji Email: alawaji@ksu.edu.sa Room No. 2A- 47/1, Tel. 01-46- Contents Introduction Course General Information Prior Knowledge required for the
Foundation Engineering CE 483 1. Introduction Prof. H. Alawaji Email: alawaji@ksu.edu.sa Room No. 2A- 47/1, Tel. 01-46- Contents Introduction Course General Information Prior Knowledge required for the
Research Areas: Subsurface Flow & Transport (modified after Springer; YZ s expertise/interest marked by X )
 Research Areas: Subsurface Flow & Transport (modified after Springer; YZ s expertise/interest marked by X ) Classification Description A Fundamental of Transport in Porous Media A1 Phenomenological theory
Research Areas: Subsurface Flow & Transport (modified after Springer; YZ s expertise/interest marked by X ) Classification Description A Fundamental of Transport in Porous Media A1 Phenomenological theory
Finite Element Analysis of Flexible Anchored Sheet Pile Walls: Effect of Mode of Construction and Dewatering Naveen Kumar 1, Arindam Dey 2*
 Golden Jubilee Conference of the IGS Bangalore Chapter, Geo-Innovations, 30-31 October 2014 Finite Element Analysis of Flexible Anchored Sheet Pile Walls: Effect of Mode of Construction and Dewatering
Golden Jubilee Conference of the IGS Bangalore Chapter, Geo-Innovations, 30-31 October 2014 Finite Element Analysis of Flexible Anchored Sheet Pile Walls: Effect of Mode of Construction and Dewatering
CIV E Geotechnical Engineering I Consolidation
 Purpose Determine the magnitude and time rate of settlement for a compressible cohesive soil. Required reading Das 2006 Sections 10.4 to 10.16 (pages 312 to 358). Theory Bringing soil samples into the
Purpose Determine the magnitude and time rate of settlement for a compressible cohesive soil. Required reading Das 2006 Sections 10.4 to 10.16 (pages 312 to 358). Theory Bringing soil samples into the
Collapsible Behavior of Pond ash Jyotirmayee Mallick 1, Deepika P. Palai 2
 Collapsible Behavior of Pond ash Jyotirmayee Mallick 1, Deepika P. Palai 2 1Civil Engineering Dept., N.I.T. Rourkela, Odisha-769008 India. Email: jyotir105@gmail.com 2Civil Engineering Dept., CAPGS, BPUT,
Collapsible Behavior of Pond ash Jyotirmayee Mallick 1, Deepika P. Palai 2 1Civil Engineering Dept., N.I.T. Rourkela, Odisha-769008 India. Email: jyotir105@gmail.com 2Civil Engineering Dept., CAPGS, BPUT,
Material properties of Tailings from Swedish mines
 Material properties of Tailings from Swedish mines I. Jantzer Luleå University of Technology, Sweden, Isabel.Jantzer@ltu.se A. Bjelkevik Sweco AB, Sweden, Annika.Bjelkevik@sweco.se K. Pousette Luleå University
Material properties of Tailings from Swedish mines I. Jantzer Luleå University of Technology, Sweden, Isabel.Jantzer@ltu.se A. Bjelkevik Sweco AB, Sweden, Annika.Bjelkevik@sweco.se K. Pousette Luleå University
Evaluation conduct of deep foundations using 3D finite element approach
 American Journal of Civil Engineering 2013; 1(3): 129-134 Published online ecember 20, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce) doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.20130103.17 Evaluation conduct of deep foundations
American Journal of Civil Engineering 2013; 1(3): 129-134 Published online ecember 20, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce) doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.20130103.17 Evaluation conduct of deep foundations
Performance of axially loaded single pile embedded in cohesive soil with cavities
 Performance of axially loaded single pile embedded in cohesive soil with cavities Al Jazaairry, AA and Toma Sabbagh, TM Title Authors Type URL Performance of axially loaded single pile embedded in cohesive
Performance of axially loaded single pile embedded in cohesive soil with cavities Al Jazaairry, AA and Toma Sabbagh, TM Title Authors Type URL Performance of axially loaded single pile embedded in cohesive
BEHAVIOUR OF GEOTEXTILE REINFORCED STONE COLUMNS MANITA DAS, A.K.DEY ABSTRACT
 BEHAVIOUR OF GEOTEXTILE REINFORCED STONE COLUMNS MANITA DAS, A.K.DEY ABSTRACT Stone columns are being used to improve the bearing capacity and reduce the settlement of a weak or soft soil. The improvement
BEHAVIOUR OF GEOTEXTILE REINFORCED STONE COLUMNS MANITA DAS, A.K.DEY ABSTRACT Stone columns are being used to improve the bearing capacity and reduce the settlement of a weak or soft soil. The improvement
Geotechnical Measurements & Explorations Prof.NiharRanjanPatra Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Geotechnical Measurements & Explorations Prof.NiharRanjanPatra Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture No. # 01 Consolidation and Consolidation Settlement (Refer
Geotechnical Measurements & Explorations Prof.NiharRanjanPatra Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture No. # 01 Consolidation and Consolidation Settlement (Refer
STUDY ON STABILIZATION OF ORGANIC SOIL WITH FLY ASH
 Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) STUDY ON STABILIZATION
Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) STUDY ON STABILIZATION
The Effect of Groundwater Seepage on Stability of Tunnel by Using Strength Reduction Method Considering Fluid Solid Coupling
 International Journal of Transportation Engineering and Technology 2018; 4(4): 75-82 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijtet doi: 10.11648/j.ijtet.20180404.12 ISSN: 2575-1743 (Print); ISSN: 2575-1751
International Journal of Transportation Engineering and Technology 2018; 4(4): 75-82 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijtet doi: 10.11648/j.ijtet.20180404.12 ISSN: 2575-1743 (Print); ISSN: 2575-1751
GeoTesting Express, Inc.
 in Acton, Massachusetts, USA has demonstrated proficiency for the testing of construction materials and has conformed to the requirements established in AASHTO R 18 and the AASHTO Accreditation policies
in Acton, Massachusetts, USA has demonstrated proficiency for the testing of construction materials and has conformed to the requirements established in AASHTO R 18 and the AASHTO Accreditation policies
Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) in Florida
 Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) in Florida J E F F R E Y C U N N I N G H A M Y O G I G O S W A M I M A R K S T E W A R T M A Y A T R O T Z 2 9 S E P T E M B E R 2 0 1 0 Project Team Principal Investigator
Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) in Florida J E F F R E Y C U N N I N G H A M Y O G I G O S W A M I M A R K S T E W A R T M A Y A T R O T Z 2 9 S E P T E M B E R 2 0 1 0 Project Team Principal Investigator
Improvement of Unconfined Compressive Strength of Natural Organic Soil
 ISSN 2224-579 (Paper) ISSN 2225-514 (Online) Vol.9, No.1, 217 Improvement of Unconfined Compressive Strength of Natural Organic Soil Adel H. Majeed 1, Abbas A. O. Al Zayadi 2, *Jasim M. Abdul Abbas 3 1.
ISSN 2224-579 (Paper) ISSN 2225-514 (Online) Vol.9, No.1, 217 Improvement of Unconfined Compressive Strength of Natural Organic Soil Adel H. Majeed 1, Abbas A. O. Al Zayadi 2, *Jasim M. Abdul Abbas 3 1.
Probabilistic Analysis of Shallow Foundation Settlement considering Soil Parameters Uncertainty Effects
 Open Journal of Geology, 2017, 7, 731-743 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg ISSN Online: 2161-7589 ISSN Print: 2161-7570 Probabilistic Analysis of Shallow Foundation Settlement considering Soil Parameters
Open Journal of Geology, 2017, 7, 731-743 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg ISSN Online: 2161-7589 ISSN Print: 2161-7570 Probabilistic Analysis of Shallow Foundation Settlement considering Soil Parameters
Geotechnics, Inc. East Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA
 in East Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA has demonstrated proficiency for the testing of construction materials and has conformed to the requirements established in AASHTO R 18 and the AASHTO Accreditation
in East Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA has demonstrated proficiency for the testing of construction materials and has conformed to the requirements established in AASHTO R 18 and the AASHTO Accreditation
STRENGTH AND DEFORMATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CEMENT TREATED SOFT BANGLADESH CLAYS
 STRENGTH AND DEFORMATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CEMENT TREATED SOFT BANGLADESH CLAYS (Date received:5.4.2011/date approved: 11.8.2011) Md. Mokhlesur Rahman 1, Abu Taher Md. Zillur Rabbi 2 and Abu Siddique
STRENGTH AND DEFORMATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CEMENT TREATED SOFT BANGLADESH CLAYS (Date received:5.4.2011/date approved: 11.8.2011) Md. Mokhlesur Rahman 1, Abu Taher Md. Zillur Rabbi 2 and Abu Siddique
Improvement Of Sandy Soil Properties By Using Bentonite
 Improvement Of Sandy Soil Properties By Using Bentonite Assistant Lecturer. Tawfiq Aamir Jawad / Department of Structures and Water Resources/ E-mail. Tawfeeq76@yahoo.com Assistant Lecturer. Asaad Mohammed
Improvement Of Sandy Soil Properties By Using Bentonite Assistant Lecturer. Tawfiq Aamir Jawad / Department of Structures and Water Resources/ E-mail. Tawfeeq76@yahoo.com Assistant Lecturer. Asaad Mohammed
Liquefaction Strength compared with Cone Resistance in Triaxial Specimen considering Aging Affect of Sand containing Non-Plastic Fines
 Liquefaction Strength compared with Cone Resistance in Triaxial Specimen considering Aging Affect of Sand containing Non-Plastic Fines Takaji.Kokusho 1), Fumiki.Ito 2) and Yota.Nagao 3) 1) Professor, Faculty
Liquefaction Strength compared with Cone Resistance in Triaxial Specimen considering Aging Affect of Sand containing Non-Plastic Fines Takaji.Kokusho 1), Fumiki.Ito 2) and Yota.Nagao 3) 1) Professor, Faculty
Three-dimensional computer simulation of soil nailing support in deep foundation pit
 Three-dimensional computer simulation of soil nailing support in deep foundation pit Abstract Chang Zhi Zhu 1,2*, Quan Chen Gao 1 1 School of Mechanics & Civil Engineering, China University of Mining &
Three-dimensional computer simulation of soil nailing support in deep foundation pit Abstract Chang Zhi Zhu 1,2*, Quan Chen Gao 1 1 School of Mechanics & Civil Engineering, China University of Mining &
Construction of a 12m High Embankment in Hydraulic Sand Fill
 Construction of a m High Embankment in Hydraulic Sand Fill W. H. Ting Consulting Engineer, Malaysia tingwh@pop.jaring.my D. E. L. Ong Ph.D Research Scholar, National University of Singapore, Singapore
Construction of a m High Embankment in Hydraulic Sand Fill W. H. Ting Consulting Engineer, Malaysia tingwh@pop.jaring.my D. E. L. Ong Ph.D Research Scholar, National University of Singapore, Singapore
Chapter 2. Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties
 Chapter 2 Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties Table of Contents Pages 1. Introduction... 3 2. Rock and Minerals... 3 3. Porosity... 4 3.1. Porosity Classification... 6 3.2. Range of porosity values for
Chapter 2 Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties Table of Contents Pages 1. Introduction... 3 2. Rock and Minerals... 3 3. Porosity... 4 3.1. Porosity Classification... 6 3.2. Range of porosity values for
Open Access Experimental Study on Road Properties of High Liquid Limit Soil in Yunfu Highway
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 46 The Open Construction and Building Technology Journal, 2015, 9, 46-51 Open Access Experimental Study on Road Properties of High Liquid Limit Soil
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 46 The Open Construction and Building Technology Journal, 2015, 9, 46-51 Open Access Experimental Study on Road Properties of High Liquid Limit Soil
Strength Behaviour of Cohesive Soils Reinforced with Fibers
 International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 4 (2014), pp. 353-360 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Strength Behaviour of Cohesive
International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 4 (2014), pp. 353-360 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Strength Behaviour of Cohesive
Engineering Properties of Soft Organic Soil Underlying Dredge Fill Areas of Dhaka, Bangladesh
 Engineering Properties of Soft Organic Soil Underlying Dredge Fill Areas of Dhaka, Bangladesh Md. Anisuzzaman, and Arifuzzaman Abstract Over the past 45 years, Dhaka city has experienced a rapid growth
Engineering Properties of Soft Organic Soil Underlying Dredge Fill Areas of Dhaka, Bangladesh Md. Anisuzzaman, and Arifuzzaman Abstract Over the past 45 years, Dhaka city has experienced a rapid growth
NUMERICAL MODELING FOR UNDRAINED SHEAR STRENGTH OF CLAYS SUBJECTED TO DIFFERENT PLASTICITY INDEXES
 Journal of GeoEngineering, Vol. 8, Ho No. and 3, Hsieh: pp. 91-1, Numerical December Modeling 213 for Undrained Shear Strength of Clays Subjected to Different Plasticity Indexes 91 NUMERICAL MODELING FOR
Journal of GeoEngineering, Vol. 8, Ho No. and 3, Hsieh: pp. 91-1, Numerical December Modeling 213 for Undrained Shear Strength of Clays Subjected to Different Plasticity Indexes 91 NUMERICAL MODELING FOR
SOIL MECHANICS CIVIL ENGINEERING VIRTUAL LABORATORY
 SOIL MECHANICS CIVIL ENGINEERING VIRTUAL LABORATORY EXPERIMENT: 10 TRIAXIAL TEST AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To find the shear of the soil by Undrained Triaxial Test. APPARATUS REQUIRED: a) Special: i. A constant
SOIL MECHANICS CIVIL ENGINEERING VIRTUAL LABORATORY EXPERIMENT: 10 TRIAXIAL TEST AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To find the shear of the soil by Undrained Triaxial Test. APPARATUS REQUIRED: a) Special: i. A constant
