MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING
|
|
|
- Marybeth Farmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING
2 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION Itis a computational technique that converts themaster schedule for end products into a detailed schedule for the raw materials and componentsused in the end products. The detailed schedule identifies the quantities of each raw material and component item. It also indicates when each item must be ordered and deliveredto meet the master schedule for final products.
3 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION MRP is often thought of as a method of inventory control. Even though it is an effective tool for minimizing unnecessaryinventoryinvestment, MRP is also useful in production scheduling and purchasing of materials.
4 MATERIAL REOUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION The distinction between independent demand and dependent demand is important in MRP.
5 MATERIAL REOUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION lndependent demand means that demand for a product is unrelated to demand forother items. Final products and spare parts are examples of items whose demand is independent.independent demand patterns must usually be forecasted.
6 MATERIAL REOUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION Dependent demandmeans that demand for the item is directly related to the demand for some other item, usuallya final product. The dependency usually derives from the fact that the item is a component of the other product. Not only component parts but also raw materials and subassemblies are examples of items subject to dependent demand.
7 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION Whereas demand for the firm's end products must often be forecasted, the raw materialsand component parts should not be forecasted. Once the delivery schedule for end products isestablished, the requirements for components and raw materials can be directly calculated.
8 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION For example. even though demand for automobiles in a given month can onlybe forecasted. once the quantity is established and production is scheduled, we know thatfive tires will be needed to deliver the car (don't forget the spare).
9 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION MRP is the appropriatetechnique for determining quantities of dependent demand items. These items constitutethe inventory of manufacturing: raw materials, work-in-process (WIP), componentparts, and sub-assemblies.that is why MRP is such a powerful technique in the planning andcontrol of manufacturing inventories. For independent demand items, inventory control isoften accomplished using Older point systems.
10 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION The concept of MRP is relatively straightforward. Its implementation is complicatedby the sheer magnitude of the data to be processed, The master schedule provides theoverall production plan for the final products in terms of month-by-month deliveries. Eachproduct may contain hundreds of individual components. These components are producedfrom raw materials, some of which arc common among the components.
11 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION For-example, severalcomponents may be made out of the same gauge sheet steel. The components are assembledinto simple subassemblies. and these subassemblies are put together into morecomplex subassemblies, and so on, until the final products are assembled. Each step in themanufacturingand assembly sequence takes time. All of these factors must be incorporatedinto the MRP calculations. Although each calculation is uncomplicated, thethe magnitude of the data isso large that the' application of MRP is practically impossible except bycomputer processing.
12 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Inputs to the MRP System There are just three primary inputs to any MRP system: 1. The master production schedule (MPS) 2. Thebill of material (BOM) 3. Inventory status data
13 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Inputs to the MRP System The MPS drives the requirements, the BOMdefines the product assembly structure, and inventory status data tells the system what will be available to meet requirements in each period. Each plays a critical role in the logic of the system, anddata accuracy in each is a prerequisite for effective MRP use.
14 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Master Production Schedule Since the fundamental assumption of dependent demand systems is that demand for all components is dependent on demand for the end item, it should come as no surprise that the end-item production schedule drives the system. This production schedule for end items is called the master production schedule, or MPS, and is the first of three inputs to the MRP system. The MPS drives the calculations that determine the materials required for production, so it can be considered the heart of the MRP system.
15 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Master Production Schedule The MPS is a simple concept, albeit one that is critical to the function of MRP. Productionrequirements for each end item are grouped into time buckets, or time periods. Time buckets can beanywhere from a day to a quarter or longer, but the most widely used time interval is one week.
16 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Master Production Schedule The MPS, then, is simply comprised of scheduled production requirements for each product, byperiod, for the entire planning horizon. Two major considerations go into the generation of the MPSthat are critical to the proper functioning of the MRP system in which it is used. First, the requirementsmust be accurate. Although seemingly obvious, inaccurate requirements flow down to thecomponent levels in the MRP system and therefore affect each and every component in the product.
17 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Master Production Schedule Inaccuracies therefore can (and do) cause both inventory shortages and excess on a broad scale, along with their associated costs and production delays. Second, the requirements must be feasible. Even accurate demand forecasts are of limited value if the plant capacity is inadequate to meet their associated levels and timing of production. For this reason, most modern MRP systems are capacity constrained, meaning they contain a capacity requirements planning (CRP) module that adjusts the MPS to a feasible level before the final material plan is executed
18 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Bill of Material If the MPS is the heart of the MRP system, the BOM is the skeleton that holds itall together. At its most basic level, the BOM is a database containing all parts. More importantly, itdefines the sequential material and assembly relationships required to produce an end item. It thereforelinks each part to its next-higher assembly, which is then linked to its nexthigher assembly, andso on all the way up to the end item. This system of linking is called pegging, and is critical to thebasic logic of MRP. Using the simple bicycle example, the spokes, rim, hub, tire tube, and tire areall pegged to the wheel assembly, which is then pegged to the bicycle assembly.
19 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Bill of Material Consider a realistic case with multiple products, each containing hundreds of parts. Many of the parts may be used on several different products and are therefore referred to as common parts. Further complicating the situation is the case where a particular part is used in different subassemblies of the same product (i.e., it has multiple parents). Clearly, a
20 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Inventory Status Data The third major input to MRP is inventory status data. These data ensure the currency of the requirements calculations, since they tell the system the quantities that are on-handor expected to arrive for each item in each time bucket. The inventory status data is critical to MRP logic. Net requirements are calculated by subtracting the current inventory available from the totalor gross requirements. These calculations are performed over time, thus giving an accurate picture of future requirements.
21 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING Inventory Status Data In addition to the on-hand and expected quantities, inventory status data generally include someindicative data elements for each item. These elements include general descriptive fields like partnumber, name, and description. They also contain stocking data needed in the calculation of material requirements, such as lead time, safety stock level, and lot size.
22 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING In very basic terms, MRP schedules the required quantities of parts to arrive at the correct times.
23 MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION
24 MATERIAL REOUIREMENTS PLANNING INTRODUCTION
25 MATERIAL REOUIREMENTS PLANNING advantages & disadvantages The MRP program generates a variety of outputs that can be used in pjanningand managing plant operations. The outputs include: (I) planned order releases. which provide theauthoritv to place orders thai have heen planned by the MRP systcm:(2) report of plannedorder future part (k (1) rescheduling notices, indicating changes in due datesfor open orders: (4) cancelation notices, indicating that certain open orders have been canceledbecause of changes in the MPS; (.:1) reports on inventory status; (6) performance reportsof various types. indicating costs.item usage, actual versus planned lead times.and so on: (7) exception reports. showing deviations from the schedule, orders that are overdue,scrap, and so on: and (R) inventory forecasts. indicating projected inventory levels in future periods
26 MATERIAL REOUIREMENTS PLANNING advantages & disadvantages Of the production output listed, the planned order releases are the most important because they drive the production system. Planned order releases are of two kinds, purchase orders and work orders. Purchase orders provide the authority to purchase raw materials or parts from outside vendors, with quantities and delivery dates specified. Work orders generate the authority to produce parts or assemble subassemblies or products in the company's own factory. Again quantities to be completed and completion dates are specified.
27 MATERIAL REOUIREMENTS PLANNING advantages & disadvantages Many benefits are claimed for a well-designed MRP system. Benefits reported by users include the following: (1) production in inventory, (2) quicker response to changes in demand than is possible with a manual requirements planning system. (3) reduced setup and product changeover costs, (4) better machine utilization (5) improved capacity to respond to changes in the master Schedule (6) as an aid in developing the master schedule.
28 MATERIAL REOUIREMENTS PLANNING advantages & disadvantages Notwithstanding these claimed benefits, the success rate in implementing MRP systems throughout industry has been less than perfect. Reasons why some MRP systems have not been successful include: (I) The application was not appropriate, usually because the product structure did not fit the data requirements of MRP (2) The MRP computations were based on inaccurate data (3) The MPS was not coupled with a capacity planning system. therefore the MRP program generated an unrealistic schedule of work orders that overloaded the factory.
29
30
31 Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
32 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Material Requirements Planning (MRP) obtains future requirements for finished products from a master production schedule and uses this and other information to generate the requirements for all the sub-assemblies, the components and the raw materials that will be making up the finished product. Although MRP is a generic methodology, it is almost always implemented via computer software called MRP systems.
33 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) MRP is specifically concerned with the manufacture of multicomponent assemblies and relies on the fact that the demands for all subassemblies, components and raw materials are known and are dependent upon the demand for the finished products. The sub-assemblies, components, and raw materials are said to have "dependent demands." There are also some items, which have "independent demands," that is, the demand for them does not depend on the demand for any other item.
34 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The MRP system requires three types of information: 1. The master production schedule for the finished products, 2. The bill of material which contains details as to the kind of raw materials, components and sub-assemblies that go to make up the finished products, 3. Information concerning the status of all materials held in the inventory.
35 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Having performed its calculations, MRP then produces reports, the majority of which are concerned with what and when to manufacture or order (fig 1.).
36 Material Requirements Planning General MRP System Outline (Fig. 1)
37 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Bills of material (BOM) play a key role in MRP. They are sets of files which contain the "recipe" for each finished product. Each "recipe" consists of information regarding which materials, components and subassemblies go together to make up a finished product, held on what is often known as a product structure file. Furthermore, all the standard information about each item, such as part number, description, unit of measure, lead time for manufacturing or procurement etc., is held on what is often known as a part master file.
38 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) For each finished product a bill of material is originally created from the design and production engineering information. This information will initially be in the form of drawings (Fig. 2) and assembly charts (Fig. 3), which, together with information on the relevant lead times, form the basis of the inputs to the BOM (Fig. 4).
39 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The information on the BOM needs to be accurate, since inaccuracies can lead to incorrect items or incorrect quantities of items being ordered. However, the problem of file accuracy is complicated by the fact that in many operating environments there are continual changes to the BOM in the form of product modifications. These modifications may originate from many sources, for example, safety legislation, production process changes and improvements for marketing purposes.
40 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The form of drawings(fig. 2)
41 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The assembly chart(fig. 3)
42 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Form the basis of the inputs to the BOM(Fig. 4)
43 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Figure 4 is a bill of materials for the 60 cm spirit level (Fig. 2). It is called an indented bill because the dependence of parts and components is indicated by indenting items in the list. All the numbers preceding the materials indicate the quantity of that item required for one unit of the item on which it is dependent. For example, each horizontal tube assembly (Part #A3567) requires 15 ml of fluid (Part #R2110).
44 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The inventory status filekeeps a record of all transactions and balances of all stock throughout the organization. The transactions are mainly receipts and issues, starting with the "on order" condition and eventually finishing with the issue of the completed product out of the factory.
45 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Other transactions may record occurrences, such as inspection rejects or stock adjustments as a result of physical stock checks. Many organizations use the concept of the "stock condition" to describe the stage to which the material has reached, for example: 500 kg of aluminium part #R7208 has been inspected and is in the raw material store ready for issue into work in progress.
46 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The MRP system carries out calculations on a level by level basis which converts the master schedule of finished products into suggested orders for all the subassemblies, components and raw materials. These calculations or "requirements generation runs" are likely to be carried out on the computer every one or two weeks so that the situation is kept constantly up to date.
47 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) At each level of assembly breakdown, the MRP system undertakes three steps in its calculations before continuing to the next lower level. These steps are as follows:
48 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) 1. It generates gross requirementsfor the item by "exploding" the "planned start" quantities of the next higher level assembly, by reference to the bill of material structure file. For example, a "planned start" of 200 spirit levels (Part No. A 1234) in week 15 would be exploded to give gross requirements of 1,200 screws (Part No. F1006) in week 15. (Refer to Figure 3 for an assembly chart).
49 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) 2. The gross requirements are amended by the amount of inventory of that item that is expected to be available in each week i.e. on hand plus scheduled receipts. This information is obtained from the inventory status file and the amended requirements are called the net requiremerits, e.g. in week 15 a total of 800 screws are expected to be available, so the gross requirement of 1,200 is amended to give a net requirement of 400 screws in week 15.
50 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) 3. The net requirements are then offset by the relevant lead time for initiating the manufacture or purchase of the item, e.g. if the lead time for the screws (Part No. F1006) is four weeks, the net requirement of 400 screws in week 15 are offset as follows:
51 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) To summarize, in its simplest form, the MRP system would calculate the requirement of screws for each period of the planning horizon as in Figure 5.
52 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Bill of Materials for 60 cm Spirit Level (fig 5)
53 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) This calculation assumes that the only use of the screw (Part No. F1006) is in the assembly of the 60 cm spirit level. If this were not the case and if its usage were common to other products assembled by the organization, for example 40 cm and 80 cm spirit levels, then the gross requirements for the screw would have been the aggregated requirements generated from the planned starts of all the assemblies using that screw.
54 Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
55 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Safety stocksare held in any manufacturing system to cater for uncertainty. In an MRP system the major cause of uncertainty, that of the future usage of the item, has been mainly eliminated since items should be produced to meet a plan -the master schedule. However, safety stocks are still needed because of uncertainties in supply both in terms of the variation of actual lead times and the variation of quantities supplied, caused by inspection rejects and material shortages. There will also be changes of demand, caused by short-term emergency changes to the master schedule and unexpected demands for items, such as spares.
56 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Statistical techniques of establishing safety stocks have been developed for application to MRP; these fall into three main categories: Fixed quantity safety stock, Safety times, Percentage increases in requirements.
57 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Fixed quantity safety stocksare introduced by triggering a net requirement, whenever the projected stock on hand reaches a safety stock level, as opposed to zero. Figure 6 shows examples of MRP calculations with and without a fixed quantity safety stock.
58 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) MRP Calculation Example (fig 6)
59 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The calculation of the size of the fixed quantity stock should be related to the cause of the unexpected usage during the lead time. For example, if the unplanned demand is primarily due to unforecasted spares demand for the item, then a historical analysis of this variation may lead towards the setting of a satisfactory safety stock level.
60 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) However, since in most cases, variations in usage and supply could be the result of many factors and since there are not any "scientific" methods of setting safety stocks in MRP systems, "rule of thumb" approximations have been applied. For example, it may be satisfactory to initially set the safety stock level at one week's average requirement or one week's "maximum" requirement. However, it is essential that the usage of the safety stock be monitored and the level then be adjusted accordingly, i.e. too frequent use of the safety stock would suggest the need for a higher safety level whereas; infrequent use would suggest a lower one.
61 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The safety timeapproach for setting safety margins is essentially "planning to make items available earlier than they are required." The introduction of safety time is straightforward in that the net requirements are offset by the lead time plus, the safety time to produce planned starts. Figure 7 shows examples of MRP calculations with and without a safety time.
62 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The Effect of Safety Time (Fig 7)
63 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The choice of the length of the safety time could, perhaps, be related to the variability of the manufacturing or procurement lead time of the item being considered. However, since other factors may influence the use of the safety stock generated by the use of safety time, an arbitrary setting of the safety time and subsequent adjustment, based on the monitoring of the usage of the safety stock, is necessary.
64 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) The setting of safety margins by the percentage increases in requirements method is particularly suitable for dealing with the variations in supply, caused by scrap or process yield losses and are often implemented as "scrap factors" or "shrinkage factors." This type of safety margin is introduced by increasing the net requirements by a factor to produce planned starts. An example is shown in figure 8.
65 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Effect of a Scrap Factor (fig 8)
66 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) MRP is an effective ordering method for dependent demand situations, where the placement of an order or the start of a production batch for a part, is determined by the timing and usage of the part in a subsequent stage of production.
67 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Since MRP decisions for a production stage (what to manufacture, how many, and when) are coordinated with other decisions for the stages, it is natural to extend MRP to include capacity planning, shop floor control, and purchasing. In this case the term MRP denotes Manufacturing Resource Planning as opposed to Material Requirements Planning.
68 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Although this extended MRP, referred to as closed loop MRP or MRP II, ties the financial and marketing functions to the operations function (Fig. 9), including additional features, such as costing and simulation possibilities, the basic mechanism of the MRP and MRP II systems, the time-phased material or resource preparation process, remains the same. MRP II therefore, provides a vehicle for coordinating the efforts of manufacturing, finance, marketing, engineering, and personnel departments toward a common business plan.
69 Material Requirements Planning Manufacturing Resource Planning (fig 9)
70
71
Chapter 18. Materials Requirements Planning
 1 Chapter 18 Materials Requirements Planning Material Requirements Planning 2 Materials requirements planning (MRP) is a means for determining the number of parts, components, and materials needed to produce
1 Chapter 18 Materials Requirements Planning Material Requirements Planning 2 Materials requirements planning (MRP) is a means for determining the number of parts, components, and materials needed to produce
PLANNING FOR PRODUCTION
 PLANNING FOR PRODUCTION Forecasting Forecasting is the first major activity in the planning, involving careful study of past data and present scenario to estimate the occurence, timing or magnitude of
PLANNING FOR PRODUCTION Forecasting Forecasting is the first major activity in the planning, involving careful study of past data and present scenario to estimate the occurence, timing or magnitude of
Material Resources Planning
 Operations and Supply Planning PGDM 2018-20 Material Resources Planning Vinay Kumar Kalakbandi Assistant Professor Operations Management 170 Introduction Computerised information system Aids in planning
Operations and Supply Planning PGDM 2018-20 Material Resources Planning Vinay Kumar Kalakbandi Assistant Professor Operations Management 170 Introduction Computerised information system Aids in planning
Resources Planning. Introduction
 Operations Management - II PGDM 2017-19 Resources Planning Vinay Kumar Kalakbandi Assistant Professor Operations Management Survey No. 38, Cherlaguda Village, Shamshabad Mandal, RR District, Hyderabad-
Operations Management - II PGDM 2017-19 Resources Planning Vinay Kumar Kalakbandi Assistant Professor Operations Management Survey No. 38, Cherlaguda Village, Shamshabad Mandal, RR District, Hyderabad-
PRODUCTION SCHEDULING PART-A
 PRODUCTION SCHEDULING PART-A 1. List out any five priority sequencing rules. (Nov-2017) First come, first served (FCFS) Last come, first served (LCFS) Earliest due date (EDD) Shortest processing time (SPT)
PRODUCTION SCHEDULING PART-A 1. List out any five priority sequencing rules. (Nov-2017) First come, first served (FCFS) Last come, first served (LCFS) Earliest due date (EDD) Shortest processing time (SPT)
 PRODUCTION PLANNING ANDCONTROL AND COMPUTER AIDED PRODUCTION PLANNING Production is a process whereby raw material is converted into semi-finished products and thereby adds to the value of utility of products,
PRODUCTION PLANNING ANDCONTROL AND COMPUTER AIDED PRODUCTION PLANNING Production is a process whereby raw material is converted into semi-finished products and thereby adds to the value of utility of products,
History IE 376 PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS. Course Notes Lecture #2.A Material Requirements Planning
 IE PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS Course Notes Lecture #.A Material Requirements Planning IE Bilkent University Manufacturing Planning and Control System Routing file Resource planning Bills of material
IE PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS Course Notes Lecture #.A Material Requirements Planning IE Bilkent University Manufacturing Planning and Control System Routing file Resource planning Bills of material
Oman College of Management and Technology
 Oman College of Management and Technology Course 803303 PIS Chapter 7 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) CS/MIS Department What is MRP? (Material Requirements Planning) Is a basic tool for performing
Oman College of Management and Technology Course 803303 PIS Chapter 7 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) CS/MIS Department What is MRP? (Material Requirements Planning) Is a basic tool for performing
There are three options available for coping with variations in demand:
 Module 3E10 Operations management for Engineers - Crib 1 (a) Define the theoretical capacity of a manufacturing line. Explain why the actual capacity of a manufacturing line is often different from its
Module 3E10 Operations management for Engineers - Crib 1 (a) Define the theoretical capacity of a manufacturing line. Explain why the actual capacity of a manufacturing line is often different from its
Chapter 6 RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS. Prepared by Mark A. Jacobs, PhD
 Chapter 6 RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS Prepared by Mark A. Jacobs, PhD LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Describe the hierarchical operations planning process in terms of materials planning (APP,
Chapter 6 RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS Prepared by Mark A. Jacobs, PhD LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Describe the hierarchical operations planning process in terms of materials planning (APP,
A typical manufacturing plant
 CHAPTER6: PRODUCTION PLANNING & CONTROL Production planning is concerned with the determination of production, inventory, and work force levels to meet fluctuating demand A typical manufacturing plant
CHAPTER6: PRODUCTION PLANNING & CONTROL Production planning is concerned with the determination of production, inventory, and work force levels to meet fluctuating demand A typical manufacturing plant
9. What are the activities within the scope of production planning? 1. Aggregate production planning
 UNIT-II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING 1. Define Process Planning Process planning involves determining the sequence of processing and assembly steps that must be accomplished
UNIT-II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING 1. Define Process Planning Process planning involves determining the sequence of processing and assembly steps that must be accomplished
Production Management and Scheduling
 Production Management and Scheduling Meet Your Due Dates Your production process can be simple or complex, time consuming or quick, but one thing remains constant the drive to meet your customer s delivery
Production Management and Scheduling Meet Your Due Dates Your production process can be simple or complex, time consuming or quick, but one thing remains constant the drive to meet your customer s delivery
IV/IV B.Tech (Mech. Engg.) 7th sem, Regular Exam, Nov Sub: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT [14ME705/A] Scheme of valuation cum Solution set
![IV/IV B.Tech (Mech. Engg.) 7th sem, Regular Exam, Nov Sub: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT [14ME705/A] Scheme of valuation cum Solution set IV/IV B.Tech (Mech. Engg.) 7th sem, Regular Exam, Nov Sub: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT [14ME705/A] Scheme of valuation cum Solution set](/thumbs/88/114995879.jpg) IV/IV B.Tech (Mech. Engg.) 7th sem, Regular Exam, Nov 2017 Sub: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT [14ME705/A] Scheme of valuation cum Solution set 1 1 x 12 = 12 M a) Forecasts are estimates of occurrence, timing or
IV/IV B.Tech (Mech. Engg.) 7th sem, Regular Exam, Nov 2017 Sub: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT [14ME705/A] Scheme of valuation cum Solution set 1 1 x 12 = 12 M a) Forecasts are estimates of occurrence, timing or
UNIT II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING
 UNIT II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING 2 Process Planning Product design for each product has been developed in the design department. To convert the product design into
UNIT II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING 2 Process Planning Product design for each product has been developed in the design department. To convert the product design into
Net Requirements Plan. The logic of net requirements. MRP Planning Sheet. Gross Requirements Schedule
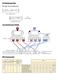 Net Requirements Plan The logic of net requirements Gross Requirements Schedule MRP Planning Sheet Safety Stock BOMs, inventory records, purchase and production quantities may not be perfect Consideration
Net Requirements Plan The logic of net requirements Gross Requirements Schedule MRP Planning Sheet Safety Stock BOMs, inventory records, purchase and production quantities may not be perfect Consideration
Manajemen Persediaan. MRP Lot For Lot. Modul ke: Fakultas FEB. Program Studi Manajemen
 Modul ke: 10 Manajemen Persediaan MRP Lot For Lot Fakultas FEB Program Studi Manajemen Learning Objectives Describe the conditions under which MRP is most appropriate. Describe the inputs, outputs, and
Modul ke: 10 Manajemen Persediaan MRP Lot For Lot Fakultas FEB Program Studi Manajemen Learning Objectives Describe the conditions under which MRP is most appropriate. Describe the inputs, outputs, and
GBI - Introductory Course 6/11/2015
 SAP University Alliances Version 2.11 Authors Bret Wagner Stefan Weidner Production Planning and Execution (PP) Product 6.0 EhP4 Global Bike Inc. Level Beginner Focus Cross-functional integration Production
SAP University Alliances Version 2.11 Authors Bret Wagner Stefan Weidner Production Planning and Execution (PP) Product 6.0 EhP4 Global Bike Inc. Level Beginner Focus Cross-functional integration Production
Materials Requirements Planning
 Materials Requirements Planning Independent and Dependent Demand Independent Demand A Dependent Demand B(4) C(2) D(2) E(1) D(3) F(2) Independent demand is uncertain. Dependent demand is certain. Dependent
Materials Requirements Planning Independent and Dependent Demand Independent Demand A Dependent Demand B(4) C(2) D(2) E(1) D(3) F(2) Independent demand is uncertain. Dependent demand is certain. Dependent
7/14/2010. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
 15 Resource Planning PowerPoint Slides by Jeff Heyl For Operations Management, 9e by Krajewski/Ritzman/Malhotra 21 Pearson Education 15 1 Resource Planning At the heart of any organization Starts t with
15 Resource Planning PowerPoint Slides by Jeff Heyl For Operations Management, 9e by Krajewski/Ritzman/Malhotra 21 Pearson Education 15 1 Resource Planning At the heart of any organization Starts t with
2 Production Planning
 1 2 Production Planning "The wise man must be wise before, not after, the event." (Epicharmus, approx. 550 BC 460 BC) In this chapter I will present the basic planning approaches used in the SAP system.
1 2 Production Planning "The wise man must be wise before, not after, the event." (Epicharmus, approx. 550 BC 460 BC) In this chapter I will present the basic planning approaches used in the SAP system.
Subbu Ramakrishnan. Manufacturing Finance with SAP. ERP Financials. Bonn Boston
 Subbu Ramakrishnan Manufacturing Finance with SAP ERP Financials Bonn Boston Contents at a Glance 1 Overview of Manufacturing Scenarios Supported by SAP... 25 2 Overview of Finance Activities in a Make-to-Stock
Subbu Ramakrishnan Manufacturing Finance with SAP ERP Financials Bonn Boston Contents at a Glance 1 Overview of Manufacturing Scenarios Supported by SAP... 25 2 Overview of Finance Activities in a Make-to-Stock
Priority for MRP. Run MRP based on actual orders, forecasts or static requirements. Run MRP simulations until you re satisfied with the plans
 WHY CHOOSE PRIORITY? WORLD S MOST CONFIGURABLE ERP tailor fields, screens, menus, reports, stationery drag and drop workflows business rules, automated data entry, automated repetitive tasks Priority for
WHY CHOOSE PRIORITY? WORLD S MOST CONFIGURABLE ERP tailor fields, screens, menus, reports, stationery drag and drop workflows business rules, automated data entry, automated repetitive tasks Priority for
Enterprise Resource Planning
 Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning What Is ERP? Software designed for organizing and managing business processes Modules share information across all business functions Can share customer sales
Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning What Is ERP? Software designed for organizing and managing business processes Modules share information across all business functions Can share customer sales
Materials and Resource Requirements Planning
 CHAPTER FIFTEEN Materials and Resource Requirements Planning McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Where We Are Now Relationships Sustainability Globalization
CHAPTER FIFTEEN Materials and Resource Requirements Planning McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Where We Are Now Relationships Sustainability Globalization
Note 8: Materials Requirements Planning
 Note 8: Materials Requirements Planning In materials requirements planning (MRP), orders for component parts are timed to coincide with the production schedule of the products in which they are used. We
Note 8: Materials Requirements Planning In materials requirements planning (MRP), orders for component parts are timed to coincide with the production schedule of the products in which they are used. We
THE MRP CHALLENGE IN THE 21 ST CENTURY. All material and content copyright 2016 Demand Driven Institute. All rights reserved.
 THE MRP CHALLENGE IN THE 21 ST CENTURY The MRP Revolution Joe Orlicky Features: Time Phased Planning Level by level BOM explosion Dependent demand planning Benefits: Component synchronization Reduction
THE MRP CHALLENGE IN THE 21 ST CENTURY The MRP Revolution Joe Orlicky Features: Time Phased Planning Level by level BOM explosion Dependent demand planning Benefits: Component synchronization Reduction
Managing Items. Explanation on beas extended view of Item Master Data
 Managing Items Explanation on beas extended view of Item Master Data Boyum Solutions IT A/S beas Tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. PROCESS... 3 2.1. Header... 4 2.2. General Tab... 4 2.3.
Managing Items Explanation on beas extended view of Item Master Data Boyum Solutions IT A/S beas Tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. PROCESS... 3 2.1. Header... 4 2.2. General Tab... 4 2.3.
Breakdown. Learn the implications of the breakdown field in Item Master Data
 Breakdown Learn the implications of the breakdown field in Item Master Data Boyum Solution IT A/S beas tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. Process... 2 2.1. Mode of procurement in beas...
Breakdown Learn the implications of the breakdown field in Item Master Data Boyum Solution IT A/S beas tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. Process... 2 2.1. Mode of procurement in beas...
Notes for Production and Operations Management- I
 Notes for Production and Operations Management- I Factors affecting Process Design Decisions Nature of product/service demand Degree of vertical integration Production Flexibility Degree of automation
Notes for Production and Operations Management- I Factors affecting Process Design Decisions Nature of product/service demand Degree of vertical integration Production Flexibility Degree of automation
University of Puerto Rico Mayagüez Campus Industrial Engineering Department
 University of Puerto Rico Mayagüez Campus Industrial Engineering Department Research Study Titled: Teaching Industrial Engineering to Generation Y Students through Computer Games National Science Foundation
University of Puerto Rico Mayagüez Campus Industrial Engineering Department Research Study Titled: Teaching Industrial Engineering to Generation Y Students through Computer Games National Science Foundation
CAD/CAM CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION. Dr. Ibrahim Naimi
 CAD/CAM CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Production System Facilities The facilities in the production system are the factory, production machines and tooling, material handling equipment,
CAD/CAM CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Production System Facilities The facilities in the production system are the factory, production machines and tooling, material handling equipment,
7/8/2017 CAD/CAM. Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi. Chapter one. Introduction
 CAD/CAM Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter one Introduction 1 2 3 Production System Facilities The facilities in the production system are the factory, production machines and tooling, material handling equipment,
CAD/CAM Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter one Introduction 1 2 3 Production System Facilities The facilities in the production system are the factory, production machines and tooling, material handling equipment,
MATERIAL AND CAPACITY REQUIREMENTS PLANNING (MRP AND CRP) Part -1. Dr. Mahmoud Abbas Mahmoud Al-Naimi Assistant Professor
 MATERIAL AND CAPACITY REQUIREMENTS PLANNING (MRP AND CRP) Part -1 Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University of Technology
MATERIAL AND CAPACITY REQUIREMENTS PLANNING (MRP AND CRP) Part -1 Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University of Technology
LOT SIZING IN MRP. Week Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected available balance Net Requirements
 LOT SIZING IN MRP The net data is subjected lot sizing Lot sizes developed can satisfy the net for one or more weeks The basic trade-off involves the elimination of one or more setups at the expense of
LOT SIZING IN MRP The net data is subjected lot sizing Lot sizes developed can satisfy the net for one or more weeks The basic trade-off involves the elimination of one or more setups at the expense of
MATERIAL REQUIREMENT PLANNING
 2 MATERIAL REQUIREMENT PLANNING MGT2405, University of Toronto, Denny Hong-Mo Yeh Material requirement planning is not only a technique for planning material requirements. It is also a logic that relates
2 MATERIAL REQUIREMENT PLANNING MGT2405, University of Toronto, Denny Hong-Mo Yeh Material requirement planning is not only a technique for planning material requirements. It is also a logic that relates
Hybrid Manufacturing Methods
 Hybrid Manufacturing Methods The following manufacturing execution and costing methods are supported in SyteLine. These methods can be combined in a single environment so that the optimal method is used
Hybrid Manufacturing Methods The following manufacturing execution and costing methods are supported in SyteLine. These methods can be combined in a single environment so that the optimal method is used
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP 14. Outline
 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP 14 1 Outline Global Company Profile: Wheeled Coach Dependent Demand Dependent Inventory Model Requirements MRP Structure MRP Management 2 1 Outline - Continued
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP 14 1 Outline Global Company Profile: Wheeled Coach Dependent Demand Dependent Inventory Model Requirements MRP Structure MRP Management 2 1 Outline - Continued
QMRP Base System. Highlights:
 The QMRP Base System consists of the menu and security systems, inventory control, product structure processing, product costing, and manufacturing order processing. Additional functionality is provided
The QMRP Base System consists of the menu and security systems, inventory control, product structure processing, product costing, and manufacturing order processing. Additional functionality is provided
Material Requirements Planning (MRP), chap 15
 Material Requirements Planning (MRP), chap 15 Chapter 15: Learning Outcomes When you complete this chapter you should be able to: 1. Develop a product structure 2. Build a gross requirements plan 3. Build
Material Requirements Planning (MRP), chap 15 Chapter 15: Learning Outcomes When you complete this chapter you should be able to: 1. Develop a product structure 2. Build a gross requirements plan 3. Build
Virtual Pull Systems. Don Guild, Synchronous Management INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION Have you implemented kanban yet? Have you been unable to roll it out or just abandoned it? Most companies who begin kanban implementation struggle to finish the job. In too many cases, the
INTRODUCTION Have you implemented kanban yet? Have you been unable to roll it out or just abandoned it? Most companies who begin kanban implementation struggle to finish the job. In too many cases, the
PRODUCTION EXECUTION
 PRODUCTION EXECUTION Table of contents Course Map Module 1: Production Planning Overview Module 2: Master Data Module 3: Production Execution Process Module 4: Process Manufacturing Module 5: Summary What
PRODUCTION EXECUTION Table of contents Course Map Module 1: Production Planning Overview Module 2: Master Data Module 3: Production Execution Process Module 4: Process Manufacturing Module 5: Summary What
Manufacturing Functionlity in Microsoft Dynamics GP. Gain complete control over your inventory, production and orders.
 Manufacturing Functionlity in Microsoft Dynamics GP Gain complete control over your inventory, production and orders. Control your Inventory Costing and Inventory Control Are you confident and in control
Manufacturing Functionlity in Microsoft Dynamics GP Gain complete control over your inventory, production and orders. Control your Inventory Costing and Inventory Control Are you confident and in control
Part IV Methods for Dependent Demand
 Part IV Methods for Dependent Demand Chapter 9 Material Requirements Planning 1 Aims of the Chapter After reading this chapter you should be able to do the following: Understand the limitations of independent
Part IV Methods for Dependent Demand Chapter 9 Material Requirements Planning 1 Aims of the Chapter After reading this chapter you should be able to do the following: Understand the limitations of independent
MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE (MPS)
 MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE (MPS) Anticipated build schedule for manufacturing end products (or product options) A statement of production, not a statement of market demand MPS takes into account capacity
MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE (MPS) Anticipated build schedule for manufacturing end products (or product options) A statement of production, not a statement of market demand MPS takes into account capacity
Engineer to Order In Microsoft Dynamics NAV
 Microsoft Dynamics NAV is a robust ERP system which is designed to handle a broad spectrum of manufacturing requirements. It includes several unique features which support engineering-to-order (ETO) manufacturing
Microsoft Dynamics NAV is a robust ERP system which is designed to handle a broad spectrum of manufacturing requirements. It includes several unique features which support engineering-to-order (ETO) manufacturing
Chapter 12. Enterprise Resource Planning
 Chapter 12 Enterprise Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Organizes and manages a company s business processes by sharing information across functional areas Connects with supply-chain
Chapter 12 Enterprise Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Organizes and manages a company s business processes by sharing information across functional areas Connects with supply-chain
The Priority Enterprise Management System
 The Priority Enterprise Management System Production Control Contents Introduction...2 Work Orders...2 Issues to the Plant Floor...3 Issues Plan...3 Issues to Floor Stock...3 Issues to Kits...4 Manual
The Priority Enterprise Management System Production Control Contents Introduction...2 Work Orders...2 Issues to the Plant Floor...3 Issues Plan...3 Issues to Floor Stock...3 Issues to Kits...4 Manual
Create a Standard Cost Estimate. Hint: The marking allowance is done by the instructor.
 Unit 9 Exercise 41 479 Create a Standard Cost Estimate Business Example Now that you have changed the BOM and the routing you need to calculate the cost for your finished product T-F1## again. You run
Unit 9 Exercise 41 479 Create a Standard Cost Estimate Business Example Now that you have changed the BOM and the routing you need to calculate the cost for your finished product T-F1## again. You run
Operational Logistics Management (OLM612S)
 Ester Kalipi (M.LSCM.; B. Hons Logistics; B-tech. BA.; Dip. BA.; Cert. BA.) Operational Logistics Management (OLM612S) Unit 2: Logistics Planning 21 February 2018 Table of contents Unit Objectives The
Ester Kalipi (M.LSCM.; B. Hons Logistics; B-tech. BA.; Dip. BA.; Cert. BA.) Operational Logistics Management (OLM612S) Unit 2: Logistics Planning 21 February 2018 Table of contents Unit Objectives The
PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL
 5 PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL CHAPTER OUTLINE 5.1 Introduction and Meaning 5.2 Need for Production Planning and Control 5.3 Objectives of PP & C 5.4 Phases of PP & C 5.5 Functions of PP & C 5.6 Operations
5 PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL CHAPTER OUTLINE 5.1 Introduction and Meaning 5.2 Need for Production Planning and Control 5.3 Objectives of PP & C 5.4 Phases of PP & C 5.5 Functions of PP & C 5.6 Operations
Time to Shipment MRP Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Benefits and Features 4 2 MRP Overview 6 3 MRP Phases 10 4 Phase 1 - Plan Times to Shipment 12 5 Phase 2 - Plan Supply Pipelines 25 6 Phase 3 - Generate Jobs and POs 34 7
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Benefits and Features 4 2 MRP Overview 6 3 MRP Phases 10 4 Phase 1 - Plan Times to Shipment 12 5 Phase 2 - Plan Supply Pipelines 25 6 Phase 3 - Generate Jobs and POs 34 7
UNIT 9 PULL VS. PUSH SYSTEM
 UNIT 9 PULL VS. PUSH SYSTEM Structure 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Manufacturing Resources Planning 9.2.1 MRP Revisited 9.2.2 MRP to MRP II 9.2.3 Is MRP II the Ultimate Manufacturing Planning and Control System?
UNIT 9 PULL VS. PUSH SYSTEM Structure 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Manufacturing Resources Planning 9.2.1 MRP Revisited 9.2.2 MRP to MRP II 9.2.3 Is MRP II the Ultimate Manufacturing Planning and Control System?
AVANTUS TRAINING PTE LTD
 Manufacturing II in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2009 Course 80261A: 3 Days; Instructor-Led About this Course This three-day course explores the advanced manufacturing functionality of Microsoft Dynamics NAV
Manufacturing II in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2009 Course 80261A: 3 Days; Instructor-Led About this Course This three-day course explores the advanced manufacturing functionality of Microsoft Dynamics NAV
Sage 200 Manufacturing Datasheet
 Sage 200 Datasheet Sage 200 is a powerful manufacturing solution that enables you to manage your entire supply chain in detail, end to end, giving you the information needed to manage and control your
Sage 200 Datasheet Sage 200 is a powerful manufacturing solution that enables you to manage your entire supply chain in detail, end to end, giving you the information needed to manage and control your
Supply Planning in Microsoft
 Supply Planning in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 Technical White Paper Supply Planning in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013... 4 Central Concepts of the Planning System... 5 Planning Parameters... 5 Planning Starting
Supply Planning in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 Technical White Paper Supply Planning in Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013... 4 Central Concepts of the Planning System... 5 Planning Parameters... 5 Planning Starting
MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING AND ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS: AN OVERVIEW
 MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING AND ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS: AN OVERVIEW Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University
MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING AND ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS: AN OVERVIEW Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University
Test-king.C_TSCM42_65.80 Questions
 Test-king.C_TSCM42_65.80 Questions Number: C_TSCM42_65 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 4.9 http://www.gratisexam.com/ C_TSCM42_65 SAP Certified Application Associate - Production -
Test-king.C_TSCM42_65.80 Questions Number: C_TSCM42_65 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 4.9 http://www.gratisexam.com/ C_TSCM42_65 SAP Certified Application Associate - Production -
Industrial Engineering Prof. Inderdeep Singh Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Industrial Engineering Prof. Inderdeep Singh Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 04 Lecture - 04 Sales Forecasting I A very warm welcome
Industrial Engineering Prof. Inderdeep Singh Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 04 Lecture - 04 Sales Forecasting I A very warm welcome
AUTOSIMPLY. Manufacturing Order. Features. About AutoSimply
 AUTOSIMPLY Manufacturing Order About AutoSimply Autosimply is a Sage Developer Partner since 2004. Founded by a group of ACCPAC consultants with over 10 years project experience, we know and understand
AUTOSIMPLY Manufacturing Order About AutoSimply Autosimply is a Sage Developer Partner since 2004. Founded by a group of ACCPAC consultants with over 10 years project experience, we know and understand
How much money can you add to the bottom line with good inventory management?
 Inventory Management Key Concepts: Inventory are those stocks or items used to support production (raw materials and work-in-process items), supporting activities (maintenance, repair, and operating supplies),
Inventory Management Key Concepts: Inventory are those stocks or items used to support production (raw materials and work-in-process items), supporting activities (maintenance, repair, and operating supplies),
Connecting S&OP to the Shop Floor: Here s How!
 Connecting S&OP to the Shop Floor: Here s How! J. E. Boyer Company, Inc. John E. Boyer, President Copyright 2004 by J. E. Boyer Company, Inc. No portion of this article may be reproduced in whole or in
Connecting S&OP to the Shop Floor: Here s How! J. E. Boyer Company, Inc. John E. Boyer, President Copyright 2004 by J. E. Boyer Company, Inc. No portion of this article may be reproduced in whole or in
Outline. Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations
 JIT and Lean Operations Outline Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations Eliminate Waste Remove Variability Improve
JIT and Lean Operations Outline Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations Eliminate Waste Remove Variability Improve
Manufacturing Resource Planning
 Outline Manufacturing Resource Planning MRP The Strategic Importance of Short- Term Scheduling Scheduling Issues Forward and Backward Scheduling Scheduling Criteria Outline Continued Scheduling Process-Focused
Outline Manufacturing Resource Planning MRP The Strategic Importance of Short- Term Scheduling Scheduling Issues Forward and Backward Scheduling Scheduling Criteria Outline Continued Scheduling Process-Focused
What can Visual Planner do for you Rick Worley TriMin Systems April 2016
 What can Visual Planner do for you Rick Worley TriMin Systems April 2016 Infor Planning Tools MRP Traditional Materials Planning in Batch Mode Requires support from CRP Visual Planner Advanced Material
What can Visual Planner do for you Rick Worley TriMin Systems April 2016 Infor Planning Tools MRP Traditional Materials Planning in Batch Mode Requires support from CRP Visual Planner Advanced Material
Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems
 Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems Lecture Outline 5 Part 4 Instructor: Trevor Nadeau Examples: Functional Area Info Systems 2 Functional Area Information Systems 3 Computers in Manufacturing
Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems Lecture Outline 5 Part 4 Instructor: Trevor Nadeau Examples: Functional Area Info Systems 2 Functional Area Information Systems 3 Computers in Manufacturing
i -Global System Production Management Module User Manual
 i -Global System Production Management Module User Manual 1 i-global System Copyright 2004, i-global Solutions Limited. All rights reserved. Production Management Module User Manual -- Version: 1.03 This
i -Global System Production Management Module User Manual 1 i-global System Copyright 2004, i-global Solutions Limited. All rights reserved. Production Management Module User Manual -- Version: 1.03 This
TU-E2020 ADVANCED OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT. Master Production Scheduling Material Requirements Planning
 TU-E2020 ADVANCED OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Master Production Scheduling Material Requirements Planning Schedule for classes 26.10 Introduction to the Course / TS 27.10 Different models of Planning for Production
TU-E2020 ADVANCED OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Master Production Scheduling Material Requirements Planning Schedule for classes 26.10 Introduction to the Course / TS 27.10 Different models of Planning for Production
Chapter 6 Resource Planning Systems
 Chapter 6 Resource Planning Systems TRUE/FALSE 1. The resource and operations planning done by operations managers is intended to balance capacity and output. 2. MRP is the production planning system intended
Chapter 6 Resource Planning Systems TRUE/FALSE 1. The resource and operations planning done by operations managers is intended to balance capacity and output. 2. MRP is the production planning system intended
02/10/2016. Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems. Examples: Functional Area Info Systems. Functional Area Information Systems
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems Lecture Outline 5, Part 4 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Examples:
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems Lecture Outline 5, Part 4 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Examples:
DOWNLOAD PDF BENEFITS OF MATERIAL REQUIREMENT PLANNING
 Chapter 1 : Material requirements planning - Wikipedia Some of the benefits of material requirements planning (MRP) software include elimination of excess inventory, cost savings, and simplified production
Chapter 1 : Material requirements planning - Wikipedia Some of the benefits of material requirements planning (MRP) software include elimination of excess inventory, cost savings, and simplified production
Operation Process Charting: How It s Made Here. APICS Fraser Valley November 2016 Presented by: Richard Ranftl (BCIT)
 Operation Process Charting: How It s Made Here APICS Fraser Valley November 2016 Presented by: Richard Ranftl (BCIT) Manufacturing Systems What do we need to have in place to make the system functional?
Operation Process Charting: How It s Made Here APICS Fraser Valley November 2016 Presented by: Richard Ranftl (BCIT) Manufacturing Systems What do we need to have in place to make the system functional?
Inventory Management 101 Basic Principles SmartOps Corporation. All rights reserved Copyright 2005 TeknOkret Services. All Rights Reserved.
 Inventory Management 101 Basic Principles 1 Agenda Basic Concepts Simple Inventory Models Batch Size 2 Supply Chain Building Blocks SKU: Stocking keeping unit Stocking Point: Inventory storage Item A Loc
Inventory Management 101 Basic Principles 1 Agenda Basic Concepts Simple Inventory Models Batch Size 2 Supply Chain Building Blocks SKU: Stocking keeping unit Stocking Point: Inventory storage Item A Loc
MRP Configuration - Adobe Interactive Forms (Japanese) - SCN Wiki
 Page 1 of 19 Getting Started Newsletters Store Welcome, Guest Login Register Search the Community Products Services & Support About SCN Downloads Industries Training & Education Partnership Developer Center
Page 1 of 19 Getting Started Newsletters Store Welcome, Guest Login Register Search the Community Products Services & Support About SCN Downloads Industries Training & Education Partnership Developer Center
INTEGRATED. Reservations, Tracking, and Action Messages. Microsoft Dynamics NAV 5.0. Technical White Paper
 INTEGRATED Microsoft Dynamics NAV 5.0 Reservations, Tracking, and Action Messages Technical White Paper This paper provides a conceptual and technical overview of the reservations, tracking an actions
INTEGRATED Microsoft Dynamics NAV 5.0 Reservations, Tracking, and Action Messages Technical White Paper This paper provides a conceptual and technical overview of the reservations, tracking an actions
Financial Transfer Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need the Financial Transfer 6 3 Total Control Workflow 10 4 Financial Transfer Overview 12 5 Multiple Operating Entities Setup 15 6 General Ledger
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need the Financial Transfer 6 3 Total Control Workflow 10 4 Financial Transfer Overview 12 5 Multiple Operating Entities Setup 15 6 General Ledger
Cover-Time Planning, An alternative to Material Requirements Planning; with customer order production abilities and restricted Work-In-Process *
 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Systems Management IESM 2007 May 30 - June 2, 2007 BEIJING - CHINA Cover-Time Planning, An alternative to Material Requirements Planning; with customer
International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Systems Management IESM 2007 May 30 - June 2, 2007 BEIJING - CHINA Cover-Time Planning, An alternative to Material Requirements Planning; with customer
Exact Globe Next Manufacturing. User Guide
 Exact Globe Next Manufacturing User Guide Exact Globe Next Manufacturing Despite the continued efforts of Exact to ensure that the information in this document is as complete and up-to-date as possible,
Exact Globe Next Manufacturing User Guide Exact Globe Next Manufacturing Despite the continued efforts of Exact to ensure that the information in this document is as complete and up-to-date as possible,
CP-81 The best waze to get to destination MRP! Paul Whiteman Lexell Blue Susan Pucciano Lexell Blue
 CP-81 The best waze to get to destination MRP! Paul Whiteman Lexell Blue Susan Pucciano Lexell Blue Agenda Introductions Manufacturing Maturity and MRP Roadmap System Configuration and Master Data Setup
CP-81 The best waze to get to destination MRP! Paul Whiteman Lexell Blue Susan Pucciano Lexell Blue Agenda Introductions Manufacturing Maturity and MRP Roadmap System Configuration and Master Data Setup
CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business
 Basics of Supply Chain Management Jayanta Kumar Bandyopadhyay CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business Contents
Basics of Supply Chain Management Jayanta Kumar Bandyopadhyay CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business Contents
What is MRP (I, II, III) 1. MRP-I
 What is MRP (I, II, III) 1. MRP-I Introduction: Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a software based production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Although
What is MRP (I, II, III) 1. MRP-I Introduction: Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a software based production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Although
A Diagnostic Approach to Scheduling
 Harish C Bahl * Neelam Bahl California State University, Chico, CA, U.S.A. Several algorithms and methodologies have been proposed for a variety of environments. In this paper, we suggest a diagnostic
Harish C Bahl * Neelam Bahl California State University, Chico, CA, U.S.A. Several algorithms and methodologies have been proposed for a variety of environments. In this paper, we suggest a diagnostic
WEBTECH ERP WEBTECH SYSTEM
 WEBTECH SYSTEM Plot No 11, 2nd Floor, Shri Nagar, IT Park Road, Near Gayatri Nagar, Parsodi, Nagpur 440025 (INDIA) Telephone: +91 0712-6605019 Mobile: 09096038065 Email: info@webtechsystem.in www.webtechsystem.in
WEBTECH SYSTEM Plot No 11, 2nd Floor, Shri Nagar, IT Park Road, Near Gayatri Nagar, Parsodi, Nagpur 440025 (INDIA) Telephone: +91 0712-6605019 Mobile: 09096038065 Email: info@webtechsystem.in www.webtechsystem.in
IT 470a Six Sigma Chapter X
 Chapter X Lean Enterprise IT 470a Six Sigma Chapter X Definitions Raw Materials component items purchased and received from suppliers WIP work in process, items that are in production on the factory floor
Chapter X Lean Enterprise IT 470a Six Sigma Chapter X Definitions Raw Materials component items purchased and received from suppliers WIP work in process, items that are in production on the factory floor
SAP Certified Application Associate - Production - Planning & Manufacturing with SAP ERP 6.0 EHP6
 1 SAP - C_TSCM42_66 SAP Certified Application Associate - Production - Planning & Manufacturing with SAP ERP 6.0 EHP6 QUESTION: 1 You want to use the function "Read PP master data" in the production order.
1 SAP - C_TSCM42_66 SAP Certified Application Associate - Production - Planning & Manufacturing with SAP ERP 6.0 EHP6 QUESTION: 1 You want to use the function "Read PP master data" in the production order.
Collaborative Process Engineering Framework for Ground Vehicle Systems Manufacturing #193
 2011 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND INTEGRATION (SE) MINI-SYMPOSIUM AUGUST 9-11 DEARBORN, MICHIGAN Collaborative Process Engineering Framework
2011 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND INTEGRATION (SE) MINI-SYMPOSIUM AUGUST 9-11 DEARBORN, MICHIGAN Collaborative Process Engineering Framework
Successfully completing this course helps the reader prepare for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Manufacturing certification exam.
 MICROSOFT DYNAMICS NAV COURSE OUTLINE 1) MICROSOFT DYNAMICS NAV MANUFACTURING Module 1: Manufacturing Course Overview This module provides an overview of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Manufacturing course.
MICROSOFT DYNAMICS NAV COURSE OUTLINE 1) MICROSOFT DYNAMICS NAV MANUFACTURING Module 1: Manufacturing Course Overview This module provides an overview of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Manufacturing course.
Inventory Control Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need Inventory Control 6 3 Total Control Workflow 8 4 Inventory Control Elements 10 5 Locations 12 6 Lot/Serial Control 16 7 PO Receipts 18 8 Job
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need Inventory Control 6 3 Total Control Workflow 8 4 Inventory Control Elements 10 5 Locations 12 6 Lot/Serial Control 16 7 PO Receipts 18 8 Job
Purchasing Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Purchasing Overview 4 2 Item Sources 6 3 P Item MRP Settings 8 4 Purchasing Long Lead Days Items 18 5 Replacing Blanket POs with Generated POs 20 6 PO Generation 1 PO Generation
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Purchasing Overview 4 2 Item Sources 6 3 P Item MRP Settings 8 4 Purchasing Long Lead Days Items 18 5 Replacing Blanket POs with Generated POs 20 6 PO Generation 1 PO Generation
Manufacturing Efficiency Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 5 2 What Is Manufacturing Efficiency? 7 3 The Seven Essential Processes 8 4 Essential #1 - Plan a Strategic Inventory 1 Strategic Inventory - Overview 10 11
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 5 2 What Is Manufacturing Efficiency? 7 3 The Seven Essential Processes 8 4 Essential #1 - Plan a Strategic Inventory 1 Strategic Inventory - Overview 10 11
Introductory Exercise: The Trucks Case
 Prelude 7 ERP Introductory Exercise: The Trucks Case G. Baglin and Ch. van Delft HEC Paris Introductory Exercise: The Trucks Case - 2 - Objective of this exercise Assumptions and notations This exercise
Prelude 7 ERP Introductory Exercise: The Trucks Case G. Baglin and Ch. van Delft HEC Paris Introductory Exercise: The Trucks Case - 2 - Objective of this exercise Assumptions and notations This exercise
Requirements Planning Implementation Guide Release 9.2
 [1]JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Applications Requirements Planning Implementation Guide Release 9.2 E63942-04 April 2018 Describes how to set up and use JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Requirements Planning to create
[1]JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Applications Requirements Planning Implementation Guide Release 9.2 E63942-04 April 2018 Describes how to set up and use JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Requirements Planning to create
PRODUCTION ACTIVITY CONTROL (PAC)
 PRODUCTION ACTIVITY CONTROL (PAC) Concerns execution of material plans Contains shop floor control (SFC), and vendor scheduling and follow-up SFC encompasses detailed scheduling and control of individual
PRODUCTION ACTIVITY CONTROL (PAC) Concerns execution of material plans Contains shop floor control (SFC), and vendor scheduling and follow-up SFC encompasses detailed scheduling and control of individual
KEY ISSUES in Advanced Operations Management. Timo Seppälä
 KEY ISSUES in Advanced Operations Management Timo Seppälä Production as a value creation process Operations system forms the transformation process between the inputs and the outputs of a manufacturing
KEY ISSUES in Advanced Operations Management Timo Seppälä Production as a value creation process Operations system forms the transformation process between the inputs and the outputs of a manufacturing
Factory Modeling. The Priority Enterprise Management System. Contents
 The Priority Enterprise Management System Factory Modeling Contents Introduction...2 Parts...3 Bills of Materials and Revisions...3 Engineering Change Orders (ECO)...4 Part Routings...4 s...5 Work Cells...5
The Priority Enterprise Management System Factory Modeling Contents Introduction...2 Parts...3 Bills of Materials and Revisions...3 Engineering Change Orders (ECO)...4 Part Routings...4 s...5 Work Cells...5
Planning. Dr. Richard Jerz rjerz.com
 Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Introduction to Production Planning
 Introduction to Production Planning Production Planning: what does it deal with? 2 The Production Manager question is: WHAT ( which product ), WHEN ( considered some time horizon ), HOW ( with which materials
Introduction to Production Planning Production Planning: what does it deal with? 2 The Production Manager question is: WHAT ( which product ), WHEN ( considered some time horizon ), HOW ( with which materials
One Software to manage your entire bakery business.
 One Software to manage your entire bakery business. Why choose ibake ERP : ibake ERP is an enterprise-class ERP solution for bakeries that manages POS, front office, manufacturing, warehouse, inventory
One Software to manage your entire bakery business. Why choose ibake ERP : ibake ERP is an enterprise-class ERP solution for bakeries that manages POS, front office, manufacturing, warehouse, inventory
Custom Manufacturing Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need Custom Manufacturing 5 3 Total Control Workflow 8 4 Custom Manufacturing Sequence of Events 10 5 Advance Setup - Standard Processes 12 6 Advance
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need Custom Manufacturing 5 3 Total Control Workflow 8 4 Custom Manufacturing Sequence of Events 10 5 Advance Setup - Standard Processes 12 6 Advance
Planning. Planning Horizon. Stages of Planning. Dr. Richard Jerz
 Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
