Evolution and Ecology
|
|
|
- Judith Pope
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evolution and Ecology REVIEW QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following cannot be an example of evolution? a. As a consequence of legislation promoting cleaner air, the frequency of black peppered moths in Europe has decreased in the last half century. b. After repeated exposure to high temperatures, an individual turtle can tolerate heat more successfully. c. As a consequence of climate change, robins in the northeastern United States sing earlier in the spring than they did two decades ago. d. Due to a genetic bottleneck, the frequency of one allele has increased in a population of the fruit fly Drosophila subobscura. 2. Tall people generally have tall parents, and short people tend to have short parents. Based on this observation, we can infer that height is a. evolving in the human population. b. due to a single gene. c. a heritable trait. d. not a genetically-based trait. 3. Grasshoppers and crickets share many similar characteristics such as general body form, elongated hind wings (which they use for jumping), and particular wing structures. The simplest hypothesis that would explain the similarities between these insects is that they resulted from a. shared ancestry. b. gene flow. c. genetic drift. d. mutation. 4. Which process is the least likely to be the direct cause of appreciable change in allele frequencies over short periods of time? a. Mutation b. Genetic drift in small populations c. Gene flow d. Directional selection 5. Which of the following can produce new combinations of alleles in a population? a. Directional selection b. Stabilizing selection c. Genetic drift d. Recombination 6. After large seeds became more common, the average beak size of the medium ground finch increased in size over the course of a few years. This change was most likely a case of a. disruptive selection. b. directional selection. c. stabilizing selection. d. genetic drift. pg. 1
2 Human Impacts on Evolution 1. Trophy hunting in bighorn sheep has had an inadvertent evolutionary consequence: the sheep have become and their horns have become. a. larger; larger b. larger; smaller c. smaller; larger d. smaller; smaller The graphs below show the changes associated with the overall size of bighorn sheep (top), and the size of their horns (bottom) during the period between 1975 and According to the graphs, the sheep in 2005 on average weighed approximately than sheep weighed in a. 10 kg less b. 20 kg less c. 10 kg more d. 20 kg more 3. According to the graphs, the sheep in 2005 had horns that were approximately than average horn lengths found in sheep in a. 20 cm shorter b. 26 cm shorter c. 30 cm shorter d. 38 cm longer pg. 2
3 NATURAL SELECTION Refer to the diagram below showing four cases of selection on egg number in a population of flour beetles. The solid blue line represents the frequency of the original population, and the dashed red lines represent the frequency distributions after eight generations. 1. Which of the following most likely represents a case of disruptive selection? a. Graph A b. Graph B c. Graph C d. Graph D 2. Which of the following most likely represents a case of stabilizing selection? a. Graph A b. Graph B c. Graph C d. Graph D 3. Graph B most likely represents a case of a. stabilizing selection. b. directional selection. c. disruptive selection. d. increased mutation. pg. 3
4 4. In which case did the variance within the population for egg laying increase the most? a. A b. B c. C d. D 5. In which process do some individuals have heritable phenotypic traits that give them an advantage in either survival or reproduction? a. Directional selection b. Disruptive selection c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 6. Which process changes allele frequencies by chance alone? a. Disruptive selection b. Stabilizing selection c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 7. Which statement about genetic drift is false? a. It affects allele frequencies the most when populations are small. b. It can cause slightly deleterious alleles to be fixed in populations. c. It tends to decrease genetic variation within populations. d. It tends to decrease genetic differences among different populations. 8. What factor is important in minimizing the impacts of genetic drift? a. Mutation rate b. Population size c. Generation time of the organism d. None of the above; the effects of genetic drift are constant across all populations. 9. Which pair of evolutionary processes can introduce new alleles into a population? a. Mutation and recombination b. Genetic drift and recombination c. Disruptive selection and gene flow d. Gene flow and mutation 10. Suppose that several flies of a population that previously fed on blueberries start to feed on honeysuckle. Due to genetic differences that accumulate as the flies adapt to feeding on honeysuckle, these honeysuckle flies eventually breed earlier than the ancestral flies. This change most likely represents an early stage of speciation brought about by a. a geographical barrier. b. an ecological barrier (specifically temporal isolation). c. genetic drift. d. adaptive radiations. 11. As a habitat becomes fragmented, the population sizes of a species in the habitat should, effects of genetic drift should, and genetic variation within populations of this species should. a. increase; increase; increase b. increase; increase; decrease c. decrease; increase; decrease d. decrease; decrease; increase pg. 4
5 1. 4. Refer the figure below. You are studying a remote island before and after a volcanic eruption. Data at time 1 was collected one month before the eruption, and data at time 2 was collected one month after the eruption. All of the species on the island are endemic. The island is 100 km across. Species A and B (the two snail species) generally only move a distance of 2 m a day. Species C (the bird) often covers 20 km a day in search of food. After the eruption, the lava flow hardens, and the island is divided by a 20-km strip of bare rock with few if any resources these animals need to survive. Figure 1 1. Would you expect to see a change in patterns of gene flow in species B and C? Why or why not? 2. Deaths of individuals due to the volcanic eruption could change the frequency of alleles in these very small island populations. However, you do not have data on the allele frequencies before and after the eruption for any of these species. Based on your understanding of genetic change, do you expect that these three species would be affected by genetic drift? Why or why not? 3. Based on your knowledge of gene flow, genetic drift, and speciation, what do you predict will happen over the long term to these species? Do you predict that the current species will remain the same species, or do you think they might split? How would you be able to determine whether a species had split into two new species? 4. What is the most likely explanation for what happened to species A as a result of the volcanic eruption? pg. 5
6 Figure 2 Textbook Reference: Concept 6.4 Long-term patterns of evolution are shaped by large-scale processes such as speciation, mass extinction, and adaptive radiation Bloom s Category: 5. Evaluating 1. Which species is the oldest? What evidence do you have to support this? 2. Which two species are most closely related? What evidence do you have to support this? 3. Species D is no longer living. When could it have become extinct? 4. When did an adaptive radiation take place? 5. Suppose that species B, C, E, and F all share characteristics that are very different from those of species D, but there are currently no living species that fill the gap between the B/C/E/F group and species D. Now suppose you could team up with a paleontologist to look for fossils to better understand how B/C/E/F became so different from species D. What age of rocks would you look for to target your search? pg. 6
5/2/ Genes and Variation. How Common Is Genetic Variation? Variation and Gene Pools
 16-1 Genes 16-1 and Variation Genes and Variation 1 of 24 How Common Is Genetic Variation? How Common Is Genetic Variation? Many genes have at least two forms, or alleles. All organisms have genetic variation
16-1 Genes 16-1 and Variation Genes and Variation 1 of 24 How Common Is Genetic Variation? How Common Is Genetic Variation? Many genes have at least two forms, or alleles. All organisms have genetic variation
Summary Genes and Variation Evolution as Genetic Change. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Summary Evolution of Populations 16 1 Genes and Variation Darwin s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. Beginning with variation, we now know that traits are controlled by
Chapter 16 Summary Evolution of Populations 16 1 Genes and Variation Darwin s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. Beginning with variation, we now know that traits are controlled by
Lesson Overview. What would happen when genetics answered questions about how heredity works?
 17.1 Darwin developed his theory of evolution without knowing how heritable traits passed from one generation to the next or where heritable variation came from. What would happen when genetics answered
17.1 Darwin developed his theory of evolution without knowing how heritable traits passed from one generation to the next or where heritable variation came from. What would happen when genetics answered
The Theory of Evolution
 The Theory of Evolution Mechanisms of Evolution Notes Pt. 4 Population Genetics & Evolution IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER: Populations, not individuals, evolve. Population = a group of individuals of the same
The Theory of Evolution Mechanisms of Evolution Notes Pt. 4 Population Genetics & Evolution IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER: Populations, not individuals, evolve. Population = a group of individuals of the same
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population. KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool.
 11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. 11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population! Genetic variation in a population increases the chance that some individuals
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. 11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population! Genetic variation in a population increases the chance that some individuals
Pre-AP Biology Evolution Review
 Pre-AP Biology Evolution Review Variation in Beak Size in Medium Ground Finch If you wanted to look for a change in phenotype beak size over time in a population of finch (which would be evidence of natural
Pre-AP Biology Evolution Review Variation in Beak Size in Medium Ground Finch If you wanted to look for a change in phenotype beak size over time in a population of finch (which would be evidence of natural
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population. KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool.
 11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. 11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population Genetic variation in a population increases the chance that some individuals
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. 11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population Genetic variation in a population increases the chance that some individuals
Section KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool.
 Section 11.1 KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. Genetic variation in a population increases the chance that some individuals will survive. Why it s beneficial: Genetic variation leads
Section 11.1 KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. Genetic variation in a population increases the chance that some individuals will survive. Why it s beneficial: Genetic variation leads
UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 11: The Evolution of Populations
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
All the, including all the different alleles, that are present in a
 Evolution as Genetic Change: chapter 16 Date name A group of individuals of the same species that interbreed. All the, including all the different alleles, that are present in a Relative Allele frequency
Evolution as Genetic Change: chapter 16 Date name A group of individuals of the same species that interbreed. All the, including all the different alleles, that are present in a Relative Allele frequency
REVIEW 5: EVOLUTION UNIT. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Period Date REVIEW 5: EVOLUTION UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Darwin s Principle of Natural Selection a. Variation individuals within a population possess
Period Date REVIEW 5: EVOLUTION UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Darwin s Principle of Natural Selection a. Variation individuals within a population possess
Study Guide A. Answer Key. The Evolution of Populations
 The Evolution of Populations Answer Key SECTION 1. GENETIC VARIATION WITHIN POPULATIONS 1. b 2. d 3. gene pool 4. combinations of alleles 5. allele frequencies 6. ratio or percentage 7. mutation 8. recombination
The Evolution of Populations Answer Key SECTION 1. GENETIC VARIATION WITHIN POPULATIONS 1. b 2. d 3. gene pool 4. combinations of alleles 5. allele frequencies 6. ratio or percentage 7. mutation 8. recombination
11.1. A population shares a common gene pool. The Evolution of Populations CHAPTER 11. Fill in the concept map below.
 SECTION 11.1 GENETIC VARIATION WITHIN POPULATIONS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. VOCABULARY gene pool allele frequency MAIN IDEA: Genetic variation in a population increases
SECTION 11.1 GENETIC VARIATION WITHIN POPULATIONS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. VOCABULARY gene pool allele frequency MAIN IDEA: Genetic variation in a population increases
3. A student performed a gel electrophoresis experiment. The results are represented in the diagram below.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the statement below and on your knowledge of biology. Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the statement below and on your knowledge of biology. Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount
Evolution. Population Genetics. Targets: Alleles and Genes 3/30/2014
 Targets: Alleles and Genes Evolution Population Genetics 1. I can explain how genetic variation in a species increases chances for survival 2. I can write an example of how lethal alleles are stored in
Targets: Alleles and Genes Evolution Population Genetics 1. I can explain how genetic variation in a species increases chances for survival 2. I can write an example of how lethal alleles are stored in
5 FINGERS OF EVOLUTION
 MICROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Microevolution refers to changes in allele frequencies in a population over time. NATURAL SELECTION
MICROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Microevolution refers to changes in allele frequencies in a population over time. NATURAL SELECTION
Evolution in a Genetic Context
 Evolution in a Genetic Context What is evolution? Evolution is the process of change over time. In terms of genetics and evolution, our knowledge of DNA and phenotypic expression allow us to understand
Evolution in a Genetic Context What is evolution? Evolution is the process of change over time. In terms of genetics and evolution, our knowledge of DNA and phenotypic expression allow us to understand
CHAPTER 12 MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION
 CHAPTER 12 MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION 12.1 Genetic Variation DNA biological code for inheritable traits GENES units of DNA molecule in a chromosome LOCI location of specific gene on DNA molecules DIPLOID
CHAPTER 12 MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION 12.1 Genetic Variation DNA biological code for inheritable traits GENES units of DNA molecule in a chromosome LOCI location of specific gene on DNA molecules DIPLOID
Population- group of individuals of the SAME species that live in the same area Species- a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce
 Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: Population- group of individuals of the SAME species that live in the same area Species- a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce FERTILE offspring Allele-
Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: Population- group of individuals of the SAME species that live in the same area Species- a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce FERTILE offspring Allele-
The Evolution of Populations
 Microevolution The Evolution of Populations C H A P T E R 2 3 Change in allele frequencies over generations Three mechanisms cause allele frequency change: Natural selection (leads to adaptation) Genetic
Microevolution The Evolution of Populations C H A P T E R 2 3 Change in allele frequencies over generations Three mechanisms cause allele frequency change: Natural selection (leads to adaptation) Genetic
Chapter 3: Evolutionary genetics of natural populations
 Chapter 3: Evolutionary genetics of natural populations What is Evolution? Change in the frequency of an allele within a population Evolution acts on DIVERSITY to cause adaptive change Ex. Light vs. Dark
Chapter 3: Evolutionary genetics of natural populations What is Evolution? Change in the frequency of an allele within a population Evolution acts on DIVERSITY to cause adaptive change Ex. Light vs. Dark
CH. 22/23 WARM-UP. 1. List 5 different pieces of evidence for evolution.
 CH. 22/23 WARM-UP 1. List 5 different pieces of evidence for evolution. 2. (Review) What are the 3 ways that sexual reproduction produces genetic diversity? 3. What is 1 thing you are grateful for today?
CH. 22/23 WARM-UP 1. List 5 different pieces of evidence for evolution. 2. (Review) What are the 3 ways that sexual reproduction produces genetic diversity? 3. What is 1 thing you are grateful for today?
EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS Genes and Variation
 Section Outline Section 16-1 EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS Genes and Variation When Darwin developed his theory of evolution, he didn t know how HEREDITY worked. http://www.answers.com/topic/gregor-mendel Mendel
Section Outline Section 16-1 EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS Genes and Variation When Darwin developed his theory of evolution, he didn t know how HEREDITY worked. http://www.answers.com/topic/gregor-mendel Mendel
How Populations Evolve. Chapter 15
 How Populations Evolve Chapter 15 Populations Evolve Biological evolution does not change individuals It changes a population Traits in a population vary among individuals Evolution is change in frequency
How Populations Evolve Chapter 15 Populations Evolve Biological evolution does not change individuals It changes a population Traits in a population vary among individuals Evolution is change in frequency
BIOLOGY 3201 UNIT 4 EVOLUTION CH MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION
 BIOLOGY 3201 UNIT 4 EVOLUTION CH. 20 - MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION POPULATION GENETICS AND HARDY WEINBERG PRINCIPLE Population genetics: this is a study of the genes in a population and how they may or may
BIOLOGY 3201 UNIT 4 EVOLUTION CH. 20 - MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION POPULATION GENETICS AND HARDY WEINBERG PRINCIPLE Population genetics: this is a study of the genes in a population and how they may or may
We can use a Punnett Square to determine how the gametes will recombine in the next, or F2 generation.
 AP Lab 7: The Mendelian Genetics of Corn Objectives: In this laboratory investigation, you will: Use corn to study genetic crosses, recognize contrasting phenotypes, collect data from F 2 ears of corn,
AP Lab 7: The Mendelian Genetics of Corn Objectives: In this laboratory investigation, you will: Use corn to study genetic crosses, recognize contrasting phenotypes, collect data from F 2 ears of corn,
Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations This chapter begins with the idea that we focused on as we closed the last chapter: Individuals do not evolve! Populations evolve.
AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations This chapter begins with the idea that we focused on as we closed the last chapter: Individuals do not evolve! Populations evolve.
What is a mutation? What causes mutations?
 What is a mutation? What causes mutations? Mutations A mutation is a change in the structure or amount of an organism s genetic material. When a change in genotype produces a change in phenotype, the individual
What is a mutation? What causes mutations? Mutations A mutation is a change in the structure or amount of an organism s genetic material. When a change in genotype produces a change in phenotype, the individual
Population Genetics. Chapter 16
 Population Genetics Chapter 16 Populations and Gene Pools Evolution is the change of genetic composition of populations over time. Microevolution is change within species which can occur over dozens of
Population Genetics Chapter 16 Populations and Gene Pools Evolution is the change of genetic composition of populations over time. Microevolution is change within species which can occur over dozens of
Genetic variation and change the short version
 Part 1: Biodiversity and variation Genetic variation and change the short version Define biodiversity and describe its advantages. Why is variation important to a species? What is DNA? A chromosome? A
Part 1: Biodiversity and variation Genetic variation and change the short version Define biodiversity and describe its advantages. Why is variation important to a species? What is DNA? A chromosome? A
Introduction Chapter 23 - EVOLUTION of
 Introduction Chapter 23 - EVOLUTION of POPULATIONS The blue-footed booby has adaptations that make it suited to its environment. These include webbed feet, streamlined shape that minimizes friction when
Introduction Chapter 23 - EVOLUTION of POPULATIONS The blue-footed booby has adaptations that make it suited to its environment. These include webbed feet, streamlined shape that minimizes friction when
17.1 What Is It That Evolves? Microevolution. Microevolution. Ch. 17 Microevolution. Genes. Population
 Ch. 17 Microevolution 17.1 What Is It That Evolves? Microevolution Population Defined as all the members of a single species living in a defined geographical area at a given time A sexually reproducing
Ch. 17 Microevolution 17.1 What Is It That Evolves? Microevolution Population Defined as all the members of a single species living in a defined geographical area at a given time A sexually reproducing
The Evolution of Populations
 The Evolution of Populations Population genetics Population: a localized group of individuals belonging to the same species Species: a group of populations whose individuals have the potential to interbreed
The Evolution of Populations Population genetics Population: a localized group of individuals belonging to the same species Species: a group of populations whose individuals have the potential to interbreed
Zoology Evolution and Gene Frequencies
 Zoology Evolution and Gene Frequencies I. any change in the frequency of alleles (and resulting phenotypes) in a population. A. Individuals show genetic variation, but express the genes they have inherited.
Zoology Evolution and Gene Frequencies I. any change in the frequency of alleles (and resulting phenotypes) in a population. A. Individuals show genetic variation, but express the genes they have inherited.
-Is change in the allele frequencies of a population over generations -This is evolution on its smallest scale
 Remember: -Evolution is a change in species over time -Heritable variations exist within a population -These variations can result in differential reproductive success -Over generations this can result
Remember: -Evolution is a change in species over time -Heritable variations exist within a population -These variations can result in differential reproductive success -Over generations this can result
Evolution of Populations (Ch. 17)
 Evolution of Populations (Ch. 17) Doonesbury - Sunday February 8, 2004 Beak depth of Beak depth Where does Variation come from? Mutation Wet year random changes to DNA errors in gamete production Dry year
Evolution of Populations (Ch. 17) Doonesbury - Sunday February 8, 2004 Beak depth of Beak depth Where does Variation come from? Mutation Wet year random changes to DNA errors in gamete production Dry year
Hardy-Weinberg Principle 4/5/09. Chapter 20. Godfrey H. Hardy: English mathematician Wilhelm Weinberg: German physician
 Chapter 20 1 Godfrey H. Hardy: English mathematician Wilhelm Weinberg: German physician Concluded that: The original proportions of the genotypes in a population will remain constant from generation to
Chapter 20 1 Godfrey H. Hardy: English mathematician Wilhelm Weinberg: German physician Concluded that: The original proportions of the genotypes in a population will remain constant from generation to
16.2 Evolution as Genetic Change
 16.2 Evolution as Genetic Change 1 of 40 16-2 Evolution as Genetic Change 16-2 Evolution as Genetic Change If an individual dies without reproducing, it does not contribute to the gene pool. If an individual
16.2 Evolution as Genetic Change 1 of 40 16-2 Evolution as Genetic Change 16-2 Evolution as Genetic Change If an individual dies without reproducing, it does not contribute to the gene pool. If an individual
Genes and Variation. Section 16-1 pgs
 Genes and Variation Section 16-1 pgs 393-396 Genes and Variation As Darwin developed his theory of evolution, he worked under a serious handicap. He didn t know how heredity worked! Although Mendel s work
Genes and Variation Section 16-1 pgs 393-396 Genes and Variation As Darwin developed his theory of evolution, he worked under a serious handicap. He didn t know how heredity worked! Although Mendel s work
Quiz will begin at 10:00 am. Please Sign In
 Quiz will begin at 10:00 am Please Sign In You have 15 minutes to complete the quiz Put all your belongings away, including phones Put your name and date on the top of the page Circle your answer clearly
Quiz will begin at 10:00 am Please Sign In You have 15 minutes to complete the quiz Put all your belongings away, including phones Put your name and date on the top of the page Circle your answer clearly
Chapter 8: Evolution Lesson 8.3: Microevolution and the Genetics of Populations
 Chapter 8: Evolution Lesson 8.3: Microevolution and the Genetics of Populations Microevolution refers to varieties within a given type. Change happens within a group, but the descendant is clearly of the
Chapter 8: Evolution Lesson 8.3: Microevolution and the Genetics of Populations Microevolution refers to varieties within a given type. Change happens within a group, but the descendant is clearly of the
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.21 POPULATION GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HARDY-WEINBERG Hardy-Weinberg is a formula used to measure the frequencies of and genotypes in a population Allelic frequencies are the frequency of alleles in a population
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HARDY-WEINBERG Hardy-Weinberg is a formula used to measure the frequencies of and genotypes in a population Allelic frequencies are the frequency of alleles in a population
AP Biology Laboratory 8 Population Genetics Virtual Student Guide
 AP Biology Laboratory 8 Population Genetics Virtual Student Guide http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/index.html Introduction The Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic equilibrium provides a
AP Biology Laboratory 8 Population Genetics Virtual Student Guide http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/index.html Introduction The Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic equilibrium provides a
The Modern Synthesis. Causes of microevolution. The Modern Synthesis. Microevolution. Genetic Drift. Genetic drift example
 The Modern Synthesis Populations are the units of evolution Natural selection plays an important role in evolution, but is not the only factor Speciation is at the boundary between microevolution and macroevolution
The Modern Synthesis Populations are the units of evolution Natural selection plays an important role in evolution, but is not the only factor Speciation is at the boundary between microevolution and macroevolution
LABORATORY 8. POPULATION GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
 STUDENT GUIDE LABORATORY 8. POPULATION GENETICS AND EVOLUTION Objectives In this activity, you will learn about the Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic equilibrium study the relationship between evolution and
STUDENT GUIDE LABORATORY 8. POPULATION GENETICS AND EVOLUTION Objectives In this activity, you will learn about the Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic equilibrium study the relationship between evolution and
LAB. POPULATION GENETICS. 1. Explain what is meant by a population being in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
 Period Date LAB. POPULATION GENETICS PRE-LAB 1. Explain what is meant by a population being in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. 2. List and briefly explain the 5 conditions that need to be met to maintain a
Period Date LAB. POPULATION GENETICS PRE-LAB 1. Explain what is meant by a population being in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. 2. List and briefly explain the 5 conditions that need to be met to maintain a
Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. Explain disruptive selection using an example. What effects speciation most?
 Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. disruptive selection using an Disruptive selection is when the average physical characteristic of a population is not beneficial. Example:
Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. disruptive selection using an Disruptive selection is when the average physical characteristic of a population is not beneficial. Example:
THE EVOLUTION OF DARWIN S THEORY PT 1. Chapter 16-17
 THE EVOLUTION OF DARWIN S THEORY PT 1 Chapter 16-17 From Darwin to Today Darwin provided compelling evidence that species and populations change. What he didn t know (and neither did anyone else at the
THE EVOLUTION OF DARWIN S THEORY PT 1 Chapter 16-17 From Darwin to Today Darwin provided compelling evidence that species and populations change. What he didn t know (and neither did anyone else at the
Science / Accelerated 6 Year At A Glance. Accelerated 6 Science Year-at-a-Glance ARKANSAS STATE SCIENCE STANDARDS
 Science / Accelerated 6 Year At A Glance Accelerated 6 Science Year-at-a-Glance ARKANSAS STATE SCIENCE STANDARDS Unit 1 History of Earth Unit 2 Natural Selection Unit 3 Life Science: Growth, Development,
Science / Accelerated 6 Year At A Glance Accelerated 6 Science Year-at-a-Glance ARKANSAS STATE SCIENCE STANDARDS Unit 1 History of Earth Unit 2 Natural Selection Unit 3 Life Science: Growth, Development,
Genetic drift and Mutations. February 4 th 2015
 Genetic drift and Mutations February 4 th 2015 Review Broccoli of today are descended from Brassica oleracea. Only the plants with the widest stalks were selected for. What type of evolutionary change
Genetic drift and Mutations February 4 th 2015 Review Broccoli of today are descended from Brassica oleracea. Only the plants with the widest stalks were selected for. What type of evolutionary change
The Modern Synthesis. Terms and Concepts. Evolutionary Processes. I. Introduction: Where do we go from here? What do these things have in common?
 Evolutionary Processes I. Introduction - The modern synthesis Reading: Chap. 25 II. No evolution: Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium A. Population genetics B. Assumptions of H-W III. Causes of microevolution (forces
Evolutionary Processes I. Introduction - The modern synthesis Reading: Chap. 25 II. No evolution: Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium A. Population genetics B. Assumptions of H-W III. Causes of microevolution (forces
Michelle Wang Department of Biology, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario Biology 206 (2008)
 An investigation of the fitness and strength of selection on the white-eye mutation of Drosophila melanogaster in two population sizes under light and dark treatments over three generations Image Source:
An investigation of the fitness and strength of selection on the white-eye mutation of Drosophila melanogaster in two population sizes under light and dark treatments over three generations Image Source:
Population Genetics Modern Synthesis Theory The Hardy-Weinberg Theorem Assumptions of the H-W Theorem
 Population Genetics A Population is: a group of same species organisms living in an area An allele is: one of a number of alternative forms of the same gene that may occur at a given site on a chromosome.
Population Genetics A Population is: a group of same species organisms living in an area An allele is: one of a number of alternative forms of the same gene that may occur at a given site on a chromosome.
Mutation and sexual reproduction produce the genetic variation that makes evolution possible. [2]
![Mutation and sexual reproduction produce the genetic variation that makes evolution possible. [2] Mutation and sexual reproduction produce the genetic variation that makes evolution possible. [2]](/thumbs/94/121106508.jpg) GUIDED READING - Ch. 23 POPULATION EVOLUTION NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
GUIDED READING - Ch. 23 POPULATION EVOLUTION NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
Chapter 25 Population Genetics
 Chapter 25 Population Genetics Population Genetics -- the discipline within evolutionary biology that studies changes in allele frequencies. Population -- a group of individuals from the same species that
Chapter 25 Population Genetics Population Genetics -- the discipline within evolutionary biology that studies changes in allele frequencies. Population -- a group of individuals from the same species that
University of York Department of Biology B. Sc Stage 2 Degree Examinations
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: University of York Department of Biology B. Sc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2016-17 Evolutionary and Population Genetics Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: University of York Department of Biology B. Sc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2016-17 Evolutionary and Population Genetics Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
Exercise 8C: Selection
 STUDENT GUIDE Exercise 8C: Selection 4. Look back at the five conditions that must be met for allele frequencies to remain constant. Which, if any, of these conditions might not have been met in this simulation?
STUDENT GUIDE Exercise 8C: Selection 4. Look back at the five conditions that must be met for allele frequencies to remain constant. Which, if any, of these conditions might not have been met in this simulation?
wheat yield (tonnes ha 1 ) year Key: total yield contribution to yield made by selective breeding Fig. 4.1
 1 Wheat is an important food crop in many European countries. Developments in farming allowed the yield of wheat produced by farms in the UK to increase rapidly in the second half of the 20th century.
1 Wheat is an important food crop in many European countries. Developments in farming allowed the yield of wheat produced by farms in the UK to increase rapidly in the second half of the 20th century.
Genetics and Evolution. Mary Susan Mardon
 Genetics and Evolution Mary Susan Mardon Nucleotides Building blocks of DNA and RNA. Each nucleotide contains: phosphate group. deoxyribose (DNA), ribose (RNA) nitrogen base. * adenine * cytosine * thymine
Genetics and Evolution Mary Susan Mardon Nucleotides Building blocks of DNA and RNA. Each nucleotide contains: phosphate group. deoxyribose (DNA), ribose (RNA) nitrogen base. * adenine * cytosine * thymine
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Genetics
 thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Genetics 1 Some important terms Using the example of tall (T) and short (t) pea plants, explain the meaning of the following terms: Gene Allele Phenotype Genotype Homozygous
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology Unit 5 Genetics 1 Some important terms Using the example of tall (T) and short (t) pea plants, explain the meaning of the following terms: Gene Allele Phenotype Genotype Homozygous
larger voles lose less heat / are better insulated or more energy stored
 Page of Mark schemes any five from: genetic variation exists in a population or variation caused by mutation / change in gene / in DNA larger voles have smaller or have more fat they accept as larger voles
Page of Mark schemes any five from: genetic variation exists in a population or variation caused by mutation / change in gene / in DNA larger voles have smaller or have more fat they accept as larger voles
Variation Chapter 9 10/6/2014. Some terms. Variation in phenotype can be due to genes AND environment: Is variation genetic, environmental, or both?
 Frequency 10/6/2014 Variation Chapter 9 Some terms Genotype Allele form of a gene, distinguished by effect on phenotype Haplotype form of a gene, distinguished by DNA sequence Gene copy number of copies
Frequency 10/6/2014 Variation Chapter 9 Some terms Genotype Allele form of a gene, distinguished by effect on phenotype Haplotype form of a gene, distinguished by DNA sequence Gene copy number of copies
(02) Answer all questions in the spaces provided. The diagram shows part of a pre-mrna molecule. Part X. Name the two substances that make up part X.
 2 Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 The diagram shows part of a pre-mrna molecule. A U C C G U Part X 1 (a) (i) Name the two substances that make up part X.... and... 1 (a) (ii) Give the sequence
2 Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 The diagram shows part of a pre-mrna molecule. A U C C G U Part X 1 (a) (i) Name the two substances that make up part X.... and... 1 (a) (ii) Give the sequence
The Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation Allele and phenotype frequencies in rock pocket mouse populations
 The Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation Allele and phenotype frequencies in rock pocket mouse populations Name: Per. Introduction The tiny rock pocket mouse weighs just 15 grams, about
The Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation Allele and phenotype frequencies in rock pocket mouse populations Name: Per. Introduction The tiny rock pocket mouse weighs just 15 grams, about
Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations. 1. Populations & Gene Pools. Populations & Gene Pools 12/2/ Populations and Gene Pools
 Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations 1. Populations and Gene Pools 2. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium 3. A Closer Look at Natural Selection 1. Populations & Gene Pools Chapter Reading pp. 481-484, 488-491
Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations 1. Populations and Gene Pools 2. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium 3. A Closer Look at Natural Selection 1. Populations & Gene Pools Chapter Reading pp. 481-484, 488-491
The Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
 ALLELE AND PHENOTYPE FREQUENCIES IN ROCK POCKET MOUSE POPULATIONS INTRODUCTION The tiny rock pocket mouse weighs just 15 grams, about as much as a handful of paper clips. A typical rock pocket mouse is
ALLELE AND PHENOTYPE FREQUENCIES IN ROCK POCKET MOUSE POPULATIONS INTRODUCTION The tiny rock pocket mouse weighs just 15 grams, about as much as a handful of paper clips. A typical rock pocket mouse is
Genetic Variation. Genetic Variation within Populations. Population Genetics. Darwin s Observations
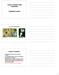 Genetic Variation within Populations Population Genetics Darwin s Observations Genetic Variation Underlying phenotypic variation is genetic variation. The potential for genetic variation in individuals
Genetic Variation within Populations Population Genetics Darwin s Observations Genetic Variation Underlying phenotypic variation is genetic variation. The potential for genetic variation in individuals
The Evolution of Populations
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 23 The Evolution of Populations
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 23 The Evolution of Populations
Evolution of Populations
 Chapter 23. Evolution of Populations 1 Populations evolve Natural selection acts on individuals differential survival survival of the fittest differential reproductive success bear more offspring Populations
Chapter 23. Evolution of Populations 1 Populations evolve Natural selection acts on individuals differential survival survival of the fittest differential reproductive success bear more offspring Populations
Evolution is a process of change through time. A change in species over time.
 Theory of Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution is a process of change through time. A change in species over time. Theories of evolution provide an explanation for the differences and similarities in
Theory of Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution is a process of change through time. A change in species over time. Theories of evolution provide an explanation for the differences and similarities in
MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION CHAPTER 20
 MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION CHAPTER 20 Objectives State the Hardy-Weinburg theorem Write the Hardy-Weinburg equation and be able to use it to calculate allele and genotype frequencies List the conditions
MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION CHAPTER 20 Objectives State the Hardy-Weinburg theorem Write the Hardy-Weinburg equation and be able to use it to calculate allele and genotype frequencies List the conditions
Evolutionary Genetics
 Evolutionary Genetics LV 25600-01 Lecture with exercises 6KP Genetic Drift 1 HS2018 A Primer of Ecological Genetics Chapter 3 - Genetic Drift - Page 52-55!2 Population tn Population tn+1 In each generation,
Evolutionary Genetics LV 25600-01 Lecture with exercises 6KP Genetic Drift 1 HS2018 A Primer of Ecological Genetics Chapter 3 - Genetic Drift - Page 52-55!2 Population tn Population tn+1 In each generation,
mrna for protein translation
 Biology 1B Evolution Lecture 5 (March 5, 2010), Genetic Drift and Migration Mutation What is mutation? Changes in the coding sequence Changes in gene regulation, or how the genes are expressed as amino
Biology 1B Evolution Lecture 5 (March 5, 2010), Genetic Drift and Migration Mutation What is mutation? Changes in the coding sequence Changes in gene regulation, or how the genes are expressed as amino
In the mid-20th century the structure of DNA was discovered. What is a section of DNA which codes for one specific protein called?
 Q1.Our understanding of genetics and inheritance has improved due to the work of many scientists. (a) Draw one line from each scientist to the description of their significant work. Scientist Description
Q1.Our understanding of genetics and inheritance has improved due to the work of many scientists. (a) Draw one line from each scientist to the description of their significant work. Scientist Description
Week 7 - Natural Selection and Genetic Variation for Allozymes
 Week 7 - Natural Selection and Genetic Variation for Allozymes Introduction In today's laboratory exercise, we will explore the potential for natural selection to cause evolutionary change, and we will
Week 7 - Natural Selection and Genetic Variation for Allozymes Introduction In today's laboratory exercise, we will explore the potential for natural selection to cause evolutionary change, and we will
Biology Evolution: Natural Selection II
 a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Biology Evolution: Natural Selection II Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching
a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Biology Evolution: Natural Selection II Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching
Block: Science 10 Biology Biology Review Package. 1. What is the full name for DNA? Label the following diagram on the right. Deoxyriboucleic Acid
 Review Package 1. What is the full name for DNA? Label the following diagram on the right. Deoxyriboucleic Acid 2. What is the function of DNA? DNA provides the genetic code for organisms. It makes you
Review Package 1. What is the full name for DNA? Label the following diagram on the right. Deoxyriboucleic Acid 2. What is the function of DNA? DNA provides the genetic code for organisms. It makes you
EXERCISE 1. Testing Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. 1a. Fill in Table 1. Calculate the initial genotype and allele frequencies.
 Biology 152/153 Hardy-Weinberg Mating Game EXERCISE 1 Testing Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Hypothesis: The Hardy-Weinberg Theorem says that allele frequencies will not change over generations under the following
Biology 152/153 Hardy-Weinberg Mating Game EXERCISE 1 Testing Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Hypothesis: The Hardy-Weinberg Theorem says that allele frequencies will not change over generations under the following
Natural Selection in Drosophila melanogaster
 Natural Selection in Drosophila melanogaster Selena Healey Matthew Reise, Madison Hayes, Amber Cuenin April 14, 2016 Abstract Studying whether or not a population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is an
Natural Selection in Drosophila melanogaster Selena Healey Matthew Reise, Madison Hayes, Amber Cuenin April 14, 2016 Abstract Studying whether or not a population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is an
Tree Perspectives. Teacher Directions
 Tree Perspectives Teacher Directions 1. Students use their science knowledge and observations to write a special type of poem called a haiku. Haikus have tricky rules: They are usually about nature, they
Tree Perspectives Teacher Directions 1. Students use their science knowledge and observations to write a special type of poem called a haiku. Haikus have tricky rules: They are usually about nature, they
Genetics 1 Star Test
 Name: ate: 1. The accompanying data table summarizes the results of an investigation in which seeds from the same plant were grown under different conditions of temperature and relative humidity. 2. The
Name: ate: 1. The accompanying data table summarizes the results of an investigation in which seeds from the same plant were grown under different conditions of temperature and relative humidity. 2. The
MICROEVOLUTION. On the Origin of Species WHAT IS A SPECIES? WHAT IS A POPULATION? Genetic variation: how do new forms arise?
 MICROEVOLUTION On the Origin of Species WHAT IS A SPECIES? Individuals in one or more populations Potential to interbreed Produce fertile offspring WHAT IS A POPULATION? Group of interacting individuals
MICROEVOLUTION On the Origin of Species WHAT IS A SPECIES? Individuals in one or more populations Potential to interbreed Produce fertile offspring WHAT IS A POPULATION? Group of interacting individuals
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype?
 FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
Heredity and DNA Assignment 1
 Heredity and DNA Assignment 1 Name 1. Which sequence best represents the relationship between DNA and the traits of an organism? A B C D 2. In some people, the lack of a particular causes a disease. Scientists
Heredity and DNA Assignment 1 Name 1. Which sequence best represents the relationship between DNA and the traits of an organism? A B C D 2. In some people, the lack of a particular causes a disease. Scientists
3. Flee & Dog: Fleas feed upon the blood of a dog or other animals. The fleas can cause itching and can pass disease.
 Interpreting Ecological Relationships: predation, parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, & competition Directions: For each of the following identify the correct ecological relationship. (Note: Each term
Interpreting Ecological Relationships: predation, parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, & competition Directions: For each of the following identify the correct ecological relationship. (Note: Each term
Fruit Fly Exercise 7 Level 2
 Name Fruit Fly Exercise 7 Level 2 Goal In this exercise, you will use StarGenetics, a software tool that simulates mating experiments, to analyze the nature and mode of inheritance of specific genetic
Name Fruit Fly Exercise 7 Level 2 Goal In this exercise, you will use StarGenetics, a software tool that simulates mating experiments, to analyze the nature and mode of inheritance of specific genetic
Quantitative Genetics
 Quantitative Genetics Polygenic traits Quantitative Genetics 1. Controlled by several to many genes 2. Continuous variation more variation not as easily characterized into classes; individuals fall into
Quantitative Genetics Polygenic traits Quantitative Genetics 1. Controlled by several to many genes 2. Continuous variation more variation not as easily characterized into classes; individuals fall into
B7 Quick Revision Questions
 B7 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 What type of variation is due to differences that arise during development? Answer 1... of 50 Environmental
B7 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 What type of variation is due to differences that arise during development? Answer 1... of 50 Environmental
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype?
 FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
Lesson: Measuring Microevolution
 Lesson: Measuring Microevolution Recall that a GENE is a unit of inheritance. Different forms of the same gene are called LLELES (uh-leelz ) lleles arise from an original gene via the process of MUTTION.
Lesson: Measuring Microevolution Recall that a GENE is a unit of inheritance. Different forms of the same gene are called LLELES (uh-leelz ) lleles arise from an original gene via the process of MUTTION.
Genetic Equilibrium: Human Diversity Student Version
 Genetic Equilibrium: Human Diversity Student Version Key Concepts: A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live and breed in the same area. Alleles are alternate forms of genes. In
Genetic Equilibrium: Human Diversity Student Version Key Concepts: A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live and breed in the same area. Alleles are alternate forms of genes. In
Page # Effect of high adult mortality on amount of early reproduction: Effect of high adult mortality on larval development time:
 FROM Wednesday - end of lecture on comparative life histories: A laboratory evolution experiment - effects of different rates of adult mortality on life history traits in Drosophila (fruit flies) Question:
FROM Wednesday - end of lecture on comparative life histories: A laboratory evolution experiment - effects of different rates of adult mortality on life history traits in Drosophila (fruit flies) Question:
Practice CH 15. Short Answer. Self-Quiz Questions
 Practice CH 15 Short Answer Self-Quiz Questions 1. A man with hemophilia (a recessive, sex-linked condition. has a daughter of normal phenotype) She marries a man who is normal for the trait. What is the
Practice CH 15 Short Answer Self-Quiz Questions 1. A man with hemophilia (a recessive, sex-linked condition. has a daughter of normal phenotype) She marries a man who is normal for the trait. What is the
The diagram shows two patterns of cell division. Cell division type A is used in gamete formation. Cell division type B is used in normal growth.
 The diagram shows two patterns of cell division. Cell division type A is used in gamete formation. Cell division type B is used in normal growth. Name the two types of cell division, A and B, shown in
The diagram shows two patterns of cell division. Cell division type A is used in gamete formation. Cell division type B is used in normal growth. Name the two types of cell division, A and B, shown in
LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER I ANSWER BOOKLET
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2014 LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER I EXAMINATION NUMBER ANSWER BOOKLET QUESTION 1 1.1 Select the term in Column B which best matches the description in Column A.
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2014 LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER I EXAMINATION NUMBER ANSWER BOOKLET QUESTION 1 1.1 Select the term in Column B which best matches the description in Column A.
Introduction. Let s try this again. Do you change during your lifetime? Do you evolve??
 Introduction Let s try this again Do you change during your lifetime? Do you evolve?? What questions couldn t Darwin answer? What if he could have called Mendel as a lifeline? Population genetics was born
Introduction Let s try this again Do you change during your lifetime? Do you evolve?? What questions couldn t Darwin answer? What if he could have called Mendel as a lifeline? Population genetics was born
Science 20. Unit D: Changes in Living Systems. Assignment Booklet D2
 Science 20 Unit D: Changes in Living Systems Assignment Booklet D2 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 2 Assignment Total Possible Marks 55 Your Mark Science 20 Unit D: Changes in
Science 20 Unit D: Changes in Living Systems Assignment Booklet D2 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 2 Assignment Total Possible Marks 55 Your Mark Science 20 Unit D: Changes in
Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide Instructions: 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. 3.
Name: Period: Date: Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide Instructions: 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. 3.
LAB ACTIVITY ONE POPULATION GENETICS AND EVOLUTION 2017
 OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. learn about the Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic equilibrium, and 2. study the relationship between evolution and changes in allele frequency by using your class to represent
OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. learn about the Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic equilibrium, and 2. study the relationship between evolution and changes in allele frequency by using your class to represent
7-1. Read this exercise before you come to the laboratory. Review the lecture notes from October 15 (Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium)
 7-1 Biology 1001 Lab 7: POPULATION GENETICS PREPARTION Read this exercise before you come to the laboratory. Review the lecture notes from October 15 (Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium) OBECTIVES At the end of
7-1 Biology 1001 Lab 7: POPULATION GENETICS PREPARTION Read this exercise before you come to the laboratory. Review the lecture notes from October 15 (Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium) OBECTIVES At the end of
