FAO Regional Conference for the Near East
|
|
|
- Bertha Little
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 s February 2014 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Organisation des Nations Unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture Продовольственная и cельскохозяйственная организация Объединенных Наций FAO Regional Conference for the Near East NERC/14/4 Rev.2 Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura E Thirty-second Session Rome, Italy, February 2014 State of Food and Agriculture in the Near East and North Africa Region EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The number of chronically undernourished people in the Region in reached 79.4 million, representing 11.2% of the population which was higher than in the period. In addition, an estimated 31.0% of children under five are stunted. On the other side of the malnutrition spectrum, nearly one quarter of the population in the region is obese. In addition to the long standing structural constraints, conflicts and/or civil insecurity were the driving factors of food insecurity in the region in In response to the recommendation of the 31 st Session of NERC, this document outlines a set of key actions at national, regional and international levels as essential elements of a regional food security strategy for the Near East and North Africa. Major observations on efforts to address food security and nutrition challenges across the region include: lack of appropriate coordination of the multisectoral aspects of food security and nutrition, and the weak focus on building long-term resilience in order to cope with the vulnerabilities to which countries in the region are exposed. The proposed set of actions will need to be implemented in a coordinated manner for building effective and resilient food security and nutrition institutions, markets and production systems. This document can be accessed using the Quick Response Code on this page; a FAO initiative to minimize its environmental impact and promote greener communications. Other documents can be consulted at
2 2 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 Table of Contents Pages I Introduction. 3 II Undernourishment and Malnutrition in the Region 3 III Underlying Food Security Challenges 5 A Demographic trends... 5 B Increasing food import dependency... 5 C High incidence of natural and man-made disasters. 6 D Policy and institutional framework.. 7 IV Elements for a Regional Strategy.. 8 A Selected measures at the national level. 8 B Selected policy options at the regional level. 10 C Selected policy options at the international level.. 11 V Guidance Sought... 12
3 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 3 I. INTRODUCTION 1. Countries in the Near East and North Africa (NENA) Region are facing enormous challenges in their efforts to achieve their goals of eradicating hunger and malnutrition while sustainably managing their natural resources. In addition to the structural challenges of high population growth, growing urbanisation, limited and fragile natural resource base, high exposure to climate change and low productivity, the Region is particularly vulnerable to increases and volatility in international food prices. This is compounded by the increasing incidence of natural and human-made disasters, including frequent incidence of droughts, trans-boundary animal diseases and conflicts. 2. Section II reviews progress in hunger reduction, and current levels and prevalence of undernourishment in the Region. In light of these trends and the food security challenges identified in Section III, Section IV highlights key actions at national, regional and international levels that are essential ingredients of a regional food security strategy, in response to the recommendation of the 31 st Session of NERC 1. II. UNDERNOURISHMENT AND MALNUTRITION IN THE REGION 3. Food security in the region is characterized by wide variations as some of its members are classified among the world's most undernourished countries while others are among the most affluent. Available regional data show that the number of the chronically undernourished in NENA in remains high, at about 79.4 million people, which represents 11.2 % of its population (Table 1). This is slightly above the number of the undernourished in The regional averages may actually be higher, as several countries in the Region remain under protracted conflict, with limited update data. 4. A significant achievement in the Region has been the progress in meeting MDG1 target of halving the proportion of undernourishment by seven countries: Algeria, Azerbaijan, Djibouti, Jordan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic and Turkmenistan. Ten other countries are expected to meet the MDG target by 2015 or have the prevalence below 5%, while 3 countries have shown no progress or deterioration in the MDG target. 5. The simultaneous occurrence of under- and over-nutrition among different population groups in the NENA Region, the so called double burden of malnutrition, has been instilling at different paces in almost all of the countries, and in some cases deteriorating in recent years. Chronic under-nutrition as measured by stunting among children under 5 is estimated at around 31.0%. Among the 36 countries with the highest burden of stunting in the world, six (Afghanistan, Egypt, Iraq, Turkey, Sudan, Yemen) are in NENA. On the other end of the spectrum, nearly one-quarter of the population is considered obese, putting NENA among the regions with the highest prevalence of obesity (Table 1). This is double the world average and nearly three times that of developing countries as a whole. Micro-nutrient deficiencies are also common in both affluent and less affluent countries, with anaemia and its associated implications for health, school enrolment and productivity, being a significant public health concern in the region. 1 Section II reviews the food insecurity situation in the 30 member countries of NERC, based on available information, while sections III and IV focus on the 19 countries that are operationally supported by the FAO Regional Office for the Near East and North Africa: Algeria, Bahrain, Egypt, the Islamic Rep. of Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Yemen.
4 4 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 Table 1. Prevalence of undernourishment and malnutrition in the NENA Region Country Number of people undernourished (millions) Prevalence of undernourishment (%) Prevalence of stunting among children (%) Prevalence of obesity among adults (%) Various years 2008 Afghanistan na Algeria 1.4 ns 5.5 < Azerbaijan 1.7 ns 23.8 < Bahrain na na na na Cyprus na 23.4 Djibouti Egypt 1.3 ns 2.3 < Iran 1.8 ns 3.3 < Iraq Jordan 0.2 ns 6.1 < Kuwait 0.8 ns 39.3 < Kyrgyz Rep Lebanon 0.1 ns 3.5 < Libya 0 ns 0.9 < Malta 0 ns 1.2 <5 na 26.6 Mauritania Morocco Oman 0 na 0 na Pakistan Qatar na na na na Saudi Arabia 0.5 ns 3.1 < Somalia 4.7 na 71.9 na Sudan na na na na Syria Tajikistan Tunisia 0.1 ns 0.9 < Turkey 0.3 ns 0.6 < Turkmenistan 0.3 ns 9.2 < United Arab Emirates 0 ns 1.1 <5 na 33.7 Yemen NENA Palestine Developing Countries Developed Countries < 5 < World Notes: <5 less than 5%; ns - not statistically significant; na - not available Source: Compiled from FAO various sources; WHO global database on Child Growth and Malnutrition
5 NERC/14/4 Rev Conflict and/or civil insecurity remained the single most important driving factor of food insecurity in the region in For instance in Yemen, Afghanistan, Somalia, Sudan, Iraq, Pakistan, West Bank and Gaza Strip (WBGS), most of Syria and Syria crisis-affected countries, the increase in the number of food insecure was mainly due to the on-going conflicts. Several recent assessments and studies by FAO, WFP and IFPRI in some of the countries experiencing conflict and civil insecurity confirm the existence of large number of people who are highly food insecure. Within Syria, for instance, it is now estimated that 6.3 million people are highly vulnerable and in critical need of sustained food and agricultural assistance. Similarly, the countries affected by the Syrian crises continue to receive influx of refugees in the border communities. The total number of registered Syrian refugees reached more than 2.1 million as of November These refugees are mostly residing in Lebanon, Jordan, Turkey Iraq, and Egypt. III. UNDERLYING FOOD SECURITY CHALLENGES 7. The Region has wealthy but food-deficient countries, as well as poor countries with relatively high potential for food production, making the food security challenges of the Region somewhat unique. Despite this disparity, countries in the Region face some major common challenges. A. Demographic trends 8. The NENA Region 2 is characterized by high population annual growth rate (2%) compared with the world average (1.2%) 3. Nearly one-third of the population is under 15 years of age. In addition 70% of the population of the region will be living in cities by A rapidly increasing urban population, which has distinctly different food consumption habits and a greater dependence on the market than the rural population, is a particular challenge for the food system. Living in cities alters lifestyles and physical activity: people consume a higher share of animal-source products and processed foods, with a higher risk of overweight and obesity than rural dwellers. On the other hand, urbanization has also been associated with a number of positive socio-economic trends such as reduction in child mortality rates and better access to education. B. Increasing food import dependency 9. As a consequence of the high population growth rates, increasing urbanization and growth in incomes, slow growth in domestic production, demand for food in the region over the past decades has surpassed domestic production. With the exception of fruit and vegetables, all other major food commodity groups have experienced a widening gap between aggregate consumption and domestic production. As a result, the region has become increasingly dependent on the world market to meet its basic food needs. In , the region imported 47% of its needs of cereals, 72% of vegetable oils and 60% of sugar. Cereals, the main import item in the region, account for about 40% of the region s total food imports. 10. The aggregate dependency on food imports masks a wide variation between commodities and countries. Some countries have achieved impressive gains in meeting a greater share of their food needs from domestic sources while others have been less successful in doing so. 11. For the 19 NENA countries, projections to 2022, carried out in the context of the OECD/FAO medium-term food outlook, point to an increasing dependence on the world market for most of its basic foodstuffs (Table 2). For the wealthy countries, this development reflects an increasing capacity to import and improve diets while, for others, it presents a growing burden to import basic foodstuffs and hence leads to deteriorating diets. 2 From this section onwards NENA Region refers to the 19 countries defined in footnote 1. 3 Average of
6 6 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 Table 2. Projections of food imports of the NENA Region to 2022 Imports Annual Self sufficiency Share in World Share in World Share in World Volume (1000 MT) Growth Ratio (%) Imports (%) Consumption (%) Production (%) Rate (%) Wheat Coarse Grains Rice Butter Cheese Skim Milk Powder Whole Milk Powder Beef & Veal Poultry Meat Sheep Meat Oilseeds Vegetable Oils Sugar Source: Compiled from OECD/FAO annual projections database. 12. The burden of food imports. The average share of food imports in total merchandise imports stood at 10% for the Region, i.e. twice the world average. However, the average share of food imports in total merchandise exports for the region is not substantially different from the world average (6.5% vs. 4.8%), but this is largely due to the oil-rich countries of the region. About nine countries spend over 20% of their merchandise export earnings on food imports, while four spend over 100%. It is clear that the vulnerability of countries due to their reliance on the world food market depends on how much they import in relation to their needs and on their ability to afford such imports. Countries with a relatively high self-sufficiency ratio (SSR) and a positive overall trade balance in total merchandise trade (net overall exporters) would be in better position to meet their food import needs (Figure 1), while countries with low SSR and a negative overall trade balance would be the most vulnerable. 13. Low productivity and high food losses. For a region that is so dependent on the world market for meeting its food needs, two factors aggravating this situation stand out: low productivity of basic food commodities and the high losses along the food supply chain. At 1.8 MT/ha in , cereal yields of the region are only 56% of the world average, and a mere 25% of those attained in Western Europe (Figure 2). There is scope for increasing production and productivity in most of the countries in the Region, particularly in Least Developed countries (Sudan, Yemen and Mauritania). An estimated 20% of food supplies suitable for human consumption are being lost, which indicates there could potentially be substantial gains from reducing food losses and waste in the Region as detailed in document NERC/14/6. C. High incidence of natural and man-made disasters 14. Countries in the Region are facing a wide range of natural and human-made shocks, including frequent incidences of droughts, high exposure to climate change, transboundary animal and plant pests and diseases, e.g. locusts or highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI), conflicts and socioeconomic difficulties/instability (e.g. Arab spring or Syria crisis), or in case of protracted crises (Sudan, WBGS, Yemen) a combination of natural and human-induced factors. The region exhibits the highest number and intensity of conflicts in the world.
7 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 7 D. Policy and institutional framework 15. Efforts have been exerted by all countries in the region to address the above-mentioned food security and nutrition challenges with various degrees of success and failure. Observations, based on past review and analysis, show that major shortcomings in these efforts are the lack of appropriate coordination of the multi-sectoral aspects of food security and nutrition, and a weak focus on building long-term resilience to tap on existing opportunities and cope with the vulnerabilities to which these countries are exposed. Figure 1. Self-sufficiency ratio (SSR) against total merchandise trade balance Morocco Egypt Sudan Iran (IR) Syria Cereal SSR (%) 50 Tunisia 40 Iraq 30 Mauritania Algeria Yemen Saudi Arabia 20 Lebanon 10 Libya Jordan Bahrain Kuwait UAE 0 Oman Qatar Total merchandize net exports/gdp (%) Source: Based on FAOSTAT and World Bank data Figure 2. Comparisons of trends in cereal yields W. Europe World NENA Source: Based on FAOSTAT data.
8 8 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 IV. ELEMENTS FOR A REGIONAL STRATEGY 16. This section attempts to respond to the request of the 31 st Session of NERC for formulating a regional food security strategy. Considering the diversity of country situations, the paper does not propose a strategy in itself, but rather identifies key policy options from which countries can draw selectively, based on their environmental, economic and social context, to address their food security challenges. These options have been grouped by nature of actions: at national, regional and international levels A. Selected measures at the national level 17. Food security issues are a continuous preoccupation of the countries of the region and a multitude of measures and policy initiatives have been considered and implemented. From the many studies, reports and consultations conducted by FAO and other organizations, three strategic areas for action at the national level are considered critical for improved food security and nutrition in the region: enhancing domestic food supply and improving rural livelihoods by addressing lagging productivity growth through increased investment in research and development; reducing exposure to market volatility and other shocks by improving supply chain efficiency; strengthening safety nets and promoting nutrition education. 18. Below are key actions proposed under each of the three strategic areas. These actions need to be implemented in a coordinated manner for building effective and resilient food security and nutrition institutions, markets and production systems. Enhancing domestic food supply and improving rural livelihoods 19. Increasing food productivity especially by smallholders. 4 In countries with relatively abundant agricultural resources, low agriculture productivity is linked to both limited investment in research and development, which stands at less than 1% of GDP, and to slow adoption by farmers of existing effective technologies which, in turn, points to serious deficiencies in extensions policies and institutions. As a result of the food-price spikes in , there has been a renewed interest to allocate more public investment for increasing the productivity of the food system. Key elements of a comprehensive approach to increasing agriculture productivity in the region will include: i) reform of extension policies to promote public private partnership in extension services and upscale farmer field schools; ii) strengthening of farmers associations and cooperative; iii) increasing over a sustained period of expenditure in R&D; and iv) promotion of regional collaboration. 20. Providing targeted support to farmers. The countries of the Region differ considerably as regards their capacity to support their farmers. Some have ample resources to afford a high degree of support and they have done so in recent years, although not always with full regard to economic and environmental feasibility. Others have limited possibilities for providing subsidies to their farmers. In all cases, consideration could be given to targeted market-smart input subsidies to increase productivity. 21. Investing in rural livelihoods and employment generation for youth and women. Recent political upheavals in several countries in the Region have been underpinned by, inter alia, unemployment, especially of the urban youth. The agriculture sector has an important role to play as a provider of gainful employment, considering that the sector is of pivotal importance in the economies of several countries in the Region. Related policies should include, inter alia, public investment in essential rural infrastructure such as organized and well-functioning local product markets, improving the quality and relevance of educational and vocational training for the types of skills demanded by the market; facilitating access to credit and financial services, especially for youth and youth groups; providing support services to rural SMEs to harness the potential of food processing, retail and other aspects of the rural non-farm sector; supporting high-value agriculture and non-farm rural sector while enhancing rural-urban linkages 4 In Countries with significant Agriculture base
9 NERC/14/4 Rev Managing water resources in a sustainable manner. Availability of fresh water is the binding factor for agriculture production in the NENA Region. Document NERC/14/5 articulates the various actions for better management of water resources in the Region. 23. Reducing food losses and waste. Document NERC/14/7 summarises the necessary measures for reducing food losses and waste in the region. Key among these measures are: strengthening databases on losses and waste; investing in infrastructure; promoting innovation and technologies; streamlining institutions and regulations dealing with food losses and waste; raising awareness about ways of reducing losses at all levels; and building technical capacity. Reducing exposure to market volatility and other shocks 24. Managing risks and role of food security reserves. For a region with high dependency on food imports, the associated price and availability risks are major concerns. While there is very little that can be done by the importing countries unilaterally to reduce the incidence of these risks, they can employ various risk management tools to ensure some certainty on the availability of supplies as well as to reduce exposure to world price volatility. Hedging instruments such as future contracts or option contracts which transfer the price risk to someone else but at some cost. While some countries have the full knowledge capacity to take advantage of these instruments, others may need adequate technical assistance from specialized agencies. Food security stocks appear to be a more attractive option for countries in the region, in terms of both price and availability, because stockholding is fully under government control and can be used flexibly. However, stocks tie up capital, supplies are prone to physical deterioration and losses, and thus expensive to maintain. Hence, determining the size of food security stocks based on assessed contingencies and establishing clear rules of accumulation and release are critical parameters. 25. Retaining flexibility in border protection. Despite the variability in world agricultural prices and the sharp increases in recent years that are projected to continue for some time, past experience indicates the real possibility for much lower and even depressed prices at some time in the future. Resorting to border protection has been the main instrument against depressed world prices in developing countries, mainly because of lack of budgetary resources to support farmers. Countries of the Region should preserve some flexibility, in the form of bound tariffs above applied levels, in order to defend against external price volatilities. 26. Rationalizing land acquisitions. As part of the quest to minimize the risks emanating from the world market, several countries of the region (in particular GCC countries) have been investing in landabundant countries by buying or leasing land to ensure a secure access to food produced on such land. There are potentially mutual benefits from such transactions, as long as certain principles are adhered to, as regards, inter alia, tenure rights, compensation, employment creation, distribution of harvests and other benefits. As regards the investing countries themselves, land acquisitions may also pose a number of risks, including political disruptions in the host country. Strengthening safety nets and promoting diet diversification and nutrition education 27. Promoting diet diversification and nutrition education. Increasing availability of and access to food is not enough, on its own, to address the double burden of malnutrition in the Region. Government policies need to consciously make the food supply more diversified and adapted to the nutritional challenges of the population, whether through the promotion of more diversified cropping patterns. In addition, nutrition-sensitive producer and/or consumer subsidy schemes, or trade policies conducive to better nutrition, are paramount. On the other hand, increasing consumers knowledge of what constitutes good nutrition can help consumers make healthier dietary choices and follow healthier lifestyles 5. Nutrition education in schools, especially through garden-based learning, is particularly 5 The FAO and WHO have been promoting nutrition education and related guidelines since the International Conference on Nutrition in 1992.
10 10 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 interesting in addressing problems of malnutrition and behaviour. Similarly integrating nutrition education and awareness raising into programs that aim to improve household food security and livelihoods, especially when targeting women, has been shown to improve the nutritional outcomes of the more vulnerable, especially children. 28. Improving efficiency and effectiveness of social safety nets (SSNs). In the face of scarce resources, refocusing nutrition-enhancing interventions on vulnerable groups would require shifting resources from universal subsidies to targeted programmes, together with consolidation of numerous fragmented interventions of the latter into fewer comprehensive targeted packages. An overriding objective in reforming SSNs, especially those that address food and nutrition needs, should be enhancing their impact. This calls for more than simply feeding people today. It requires supporting social inclusion and better nutrition outcomes by prioritizing interventions that promote investment in human capital with an ultimate goal of breaking the poverty trap. Social safety net programmes should be fiscally sustainable, cost effective, flexible and responsive to changing needs, especially in periods of crisis. 29. Most countries of the region have at least one cash-transfer program that could be adapted and scaled-up to become a significant safety net. In this respect, conditional cash transfers are an attractive option that could foster human capital development and help break the cycle of poverty. Nonconditional cash transfer should be favoured in crisis situations and for highly vulnerable populations. 30. Considering incentives and disincentive measures to reduce malnutrition. Food-based SSNs have generally promoted the consumption of energy-rich staple foods. However, much less common have been incentives to encourage the consumption of a more diverse food basket (including desirable food items such as fruit and vegetables), or disincentive measures to discourage the consumption of energy-dense and nutrient-poor foods. In their efforts to address malnutrition, especially overweight and obesity, countries of the region could look at the option of introducing such measures. Reviewing the content of the food subsidy basket to make it more nutrient-rich and less energy dense is one option. Taxing energy-dense and nutrient-poor foods and using the revenues to subsidize nutrient-rich foods and to finance health and social security expenditures could be another option. 31. Relieving demographic pressures: Policy options for making durable improvements in food security over the longer term must combine measures that address both the supply and the demand for food. Countries with high fertility rates have ample scope for establishing and/or strengthening existing family planning services, including publicly supported nationwide information, education and communication programmes on family planning. The need for such programmes is much greater in rural areas where family planning services and access to information are generally limited. B. Selected policy options at the regional level 32. As the countries of the region share many common threats and challenges in their efforts to improve food security, regional cooperation and joint action in response to some of these challenges would render national efforts much more effective. 33. Strengthening regional cooperation. As members of the WTO (plus those in the process of accession) most countries of the region have transitioned to a rules-based trading system with lower tariff barriers. However, much remains to be done at the regional level, especially in i) reducing nontariff barriers and divergence in regulatory frameworks, ii) harmonizing domestic policies and procedures, iii) trade facilitation, iv) improving transportation facilities, and v) undertaking related regional infrastructural projects. Greater integration in the trade area could also facilitate better collaboration between countries of the region in promoting policies in international fora on issues of crucial regional importance, especially on food security. One obvious opportunity is in the multilateral negotiations under the WTO because by taking a unanimous common position, the Region would be much more effective in promoting issues of importance to food security and nutrition. 34. Considering regional food security stocks. Beyond what was explained in Paragraph 30, food reserves at the regional or sub-regional level could also be considered. Regional food security stocks are based on the concept of pooling resources into a common reserve, to be drawn upon based on preagreed rules. The establishment of such regional reserves would entail the earmarking of a certain
11 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 11 percentage of each country s national stocks into the regional food reserve. The obvious benefits of pooling resources at a regional level would include establishing economies of scale, greater price stability, enhanced regional cooperation and integration, facilitated movement of supplies across borders, enhanced regional market information and monitoring of available food supplies. 35. Improving market information, coordination and knowledge exchange. Recent episodes of price volatility revealed the need for strengthening market information systems on basic foodstuffs at regional level. This would reduce uncertainties and panic behaviour by consumers and others in the supply chain, especially during periods of crises, and allow governments to better gauge the volume of imports, thus avoiding fiscal and food security adversities. Putting a trade surveillance system in place. For the region to be prepared to face threats of import surges in periods of depressed world prices and for timely scheduling of cereal imports in situations of increasing prices, an effective trade surveillance system at the regional level could provide timely market information and give an early warning of impending problems. Such a regional system could be a complement to the already constituted Agricultural Market Information System (AMIS) 6. Promoting multi-stakeholder dialogue and knowledge exchange. Given the diversity in country food security experiences, there is scope for governments and other stakeholders to exchange related knowledge and good practices. Further to the NERC-31 recommendation, a regional coordination mechanism linked to CFS has been established by FAO and other UN agencies. It needs to be appropriated by countries and institutionalized. 36. Cooperating in conflict resolution. The Region suffers from serious and protracted conflict situations impacting negatively on all aspects of human welfare including food security. As conflicts extend beyond national borders, regional cooperation in conflict resolution is imperative. C. Selected policy options at the international level 37. The international community has a role to play in supporting the region s efforts to improve food security sustainably. Actions by the international community should aim basically at reducing the incidence of volatility in the world market and alleviating its adverse effects when it is unavoidable. These include, inter alia, promoting improvements in the international policy environment, especially in the trade area, and providing technical support and material assistance to improve resilience. 38. Strengthening food assistance programmes. Food aid has been a valuable resource for helping food deficit countries meet their food needs. However, food aid s role as a general assistance to countries in bridging their import gap has become rather limited as volumes have dwindled. Yet, food aid remains a critical resource in periods of natural and human-made disasters. Considering the growing incidence of emergency situations in the Region, broadening the food aid donor base beyond the traditional contributors would allow the system to better respond to increasing needs. Some countries of the Region that have the means to do so (especially in the form of cash resources) could become much more involved in food assistance initiatives and in supporting established international institutional arrangements, such as the Food Assistance Convention (FAC) and the UN World Food Programme (WFP). 39. Implementing the Marrakesh Decision. 7 The Marrakesh Decision, an integral part of the Uruguay Round Agreement, recognizes that certain vulnerable countries that depend on the world market for a substantial part of their basic food needs may face additional difficulties in financing basic foodstuffs as a result of anticipated higher prices from the implementation of the Agreement on Agriculture. Existing IMF facilities have proven to be of limited value in connection with the Marrakesh Decision. 40. The soaring world food prices of highlighted the continued need for a functional multilateral instrument to help affected countries finance imports of basic foodstuffs. This could take 6 Saudi Arabia participates as a member of the G20 group and Egypt as a major food trading country. 7 Decision on Measures Concerning the Possible Negative Effects of the Reform Programme on Least-Developed and Net Food-Importing Developing Countries.
12 12 NERC/14/4 Rev.2 the form of credit guarantees to meet the cost of excess food import bills. In the spirit of the Marrakesh Decision, such an instrument would reassure net food importing countries that the world market is an affordable source of food supplies. NENA countries should continue to support related initiatives at the WTO. 41. Strengthening WTO disciplines on export restrictions. Many of the countries that faced domestic supply imbalances during the and periods of high food prices practised export prohibitions and restrictions. This included several major exporters. The potential effects of export restrictions on importing countries, especially net food-importing countries, can be serious, in terms of both aggravating the increase in world prices and limiting physical availability of food supplies. While WTO rules and disciplines applicable to importation are binding, the same is not applicable to export prohibitions and restrictions. Countries in the region should continue to support measures aimed at removing food export restrictions or taxes for food purchased for non-commercial humanitarian purposes, such as purchases by the WFP. 42. Rationalizing biofuel mandates and related policies. The diversion of large quantities of foodstuffs into biofuel production has contributed to world price volatility in recent years. This phenomenon has been largely driven by large and often highly distorting subsidies as well as policy directives and inflexible biofuel mandates of some large food producing countries. Going a step further, flexible mandates could make diversion to biofuels conditional on the price of food, so that mandated annual targets can be reduced or eliminated if food prices rise beyond some trigger level. Such novel approaches by the international community should receive the support of the countries of the region, as they offer promising ways of stabilizing world food prices. V. GUIDANCE SOUGHT 43. The FAO regional initiative on building resilience for improved food security and nutrition in NENA, as outlined in document NERC/14/2, attempts to contribute to the adoption of a coherent framework for food security and nutrition at country and regional levels along the lines of the policy elements identified in this document. 44. The Regional Conference is invited to: note the persistence of high levels of undernourishment and malnutrition in the Region, and the fact that conflicts and civil insecurity are major factors aggravating the situation; take note of the proposed elements for a regional strategy for food security and nutrition and encourage countries to step up efforts for improved and coherent policy frameworks for food security and nutrition at the national and regional levels; welcome the launch by FAO of the regional initiative on FSN and call on countries to support the initiative, including through provision of extra-budgetary funding; call on countries to agree on an appropriate institutional framework to host the regional coordination mechanism on food security and nutrition proposed by the 31 st NERC.
Status and Progress of CPFs in the NENA Region February 2016 FAO RNE Regional Professional Staff Meeting
 Status and Progress of CPFs in the NENA Region Status of CPFs (as of January 2016) 2 PLANNED: Libya & Syrian Arab Republic 6 EXPIRING IN THE NEXT BIENNIUM: Algeria, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Mauritania, Morocco
Status and Progress of CPFs in the NENA Region Status of CPFs (as of January 2016) 2 PLANNED: Libya & Syrian Arab Republic 6 EXPIRING IN THE NEXT BIENNIUM: Algeria, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Mauritania, Morocco
CFS contribution to the 2018 High Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development global review
 CFS contribution to the 2018 High Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development global review Transformation towards sustainable and resilient societies In depth-review of SDGs 6, 7, 11, 12, 15, 17
CFS contribution to the 2018 High Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development global review Transformation towards sustainable and resilient societies In depth-review of SDGs 6, 7, 11, 12, 15, 17
Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development and Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development
 Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development and Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development Joint Technical Meeting Arab Coordination Group Institutions and The OECD Development Assistance Committee Vienna,
Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development and Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development Joint Technical Meeting Arab Coordination Group Institutions and The OECD Development Assistance Committee Vienna,
YEMEN PLAN OF ACTION. Towards Resilient and Sustainable Livelihoods for Agriculture and Food and Nutrition Security SUMMARY
 YEMEN PLAN OF ACTION Towards Resilient and Sustainable Livelihoods for Agriculture and Food and Nutrition Security 2014 2018 SUMMARY INTRODUCTION Yemen, one of the least developed countries in the world,
YEMEN PLAN OF ACTION Towards Resilient and Sustainable Livelihoods for Agriculture and Food and Nutrition Security 2014 2018 SUMMARY INTRODUCTION Yemen, one of the least developed countries in the world,
Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa
 Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa Shawki Barghouti Director General International Center for Biosaline Agriculture 1 water scarcity
Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa Shawki Barghouti Director General International Center for Biosaline Agriculture 1 water scarcity
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations in Lebanon
 Projects Brief Lebanon 2015 Projects Brief Lebanon 2015 Contribute to the promotion of rural development and poverty alleviation, through supporting to the agricultural production systems to overcome agricultural
Projects Brief Lebanon 2015 Projects Brief Lebanon 2015 Contribute to the promotion of rural development and poverty alleviation, through supporting to the agricultural production systems to overcome agricultural
AGRO-INDUSTRY IN THE OIC MEMBER COUNTRIES: AN OVERVIEW OF POTENTIALS
 ORGANISATION OF THE ISLAMIC CONFERENCE STATISTICAL, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING CENTRE FOR ISLAMIC COUNTRIES OIC OUTLOOK March 2010 AGRO-INDUSTRY IN THE OIC MEMBER COUNTRIES: AN OVERVIEW
ORGANISATION OF THE ISLAMIC CONFERENCE STATISTICAL, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING CENTRE FOR ISLAMIC COUNTRIES OIC OUTLOOK March 2010 AGRO-INDUSTRY IN THE OIC MEMBER COUNTRIES: AN OVERVIEW
Food Security, Nutrition and Price Stability
 Food Security, Nutrition and Price Stability EGM on Post-2015 UN Development Agenda New York, 27-29 Feb 2012 Mark Smulders Senior Economist Agricultural Economic Development Division Economic and Social
Food Security, Nutrition and Price Stability EGM on Post-2015 UN Development Agenda New York, 27-29 Feb 2012 Mark Smulders Senior Economist Agricultural Economic Development Division Economic and Social
FAO REGIONAL CONFERENCE FOR THE NEAR EAST
 April 2016 NERC/16/6 E FAO REGIONAL CONFERENCE FOR THE NEAR EAST Thirty-third Session Rome, Italy, 9-13 May 2016 Small-scale Farmers and Women Empowerment in the Near East and North Africa Region EXECUTIVE
April 2016 NERC/16/6 E FAO REGIONAL CONFERENCE FOR THE NEAR EAST Thirty-third Session Rome, Italy, 9-13 May 2016 Small-scale Farmers and Women Empowerment in the Near East and North Africa Region EXECUTIVE
Reducing Rural Poverty: Social Protection, Access and Decent Employment
 Reducing Rural Poverty: Social Protection, Access and Decent Employment Natalia Winder Rossi Deputy Director (a.i) Social Policies and Rural Institutions Division Social Protection Team Leader, FAO New
Reducing Rural Poverty: Social Protection, Access and Decent Employment Natalia Winder Rossi Deputy Director (a.i) Social Policies and Rural Institutions Division Social Protection Team Leader, FAO New
FRENCH FOOD AID IN 2012
 FRENCH FOOD AID IN 2012 Welcome French food aid is the responsibility of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The Ministry addresses this issue as part of French development aid policy and its strategy for
FRENCH FOOD AID IN 2012 Welcome French food aid is the responsibility of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The Ministry addresses this issue as part of French development aid policy and its strategy for
G20 Initiative for Rural Youth Employment Supporting the Next Generation in Rural Development, Agriculture and Food Security in developing countries
 G20 Initiative for Rural Youth Employment Supporting the Next Generation in Rural Development, Agriculture and Food Security in developing countries 1. We acknowledge that rural youth employment in developing
G20 Initiative for Rural Youth Employment Supporting the Next Generation in Rural Development, Agriculture and Food Security in developing countries 1. We acknowledge that rural youth employment in developing
THIRTIETH FAO REGIONAL CONFERENCE
 December 2010 NERC/10/INF/4 E THIRTIETH FAO REGIONAL CONFERENCE FOR THE NEAR EAST Khartoum, the Republic of the Sudan, 4-8 December 2010 Statement by the Director-General of FAO Mr. President, Mr. Independent
December 2010 NERC/10/INF/4 E THIRTIETH FAO REGIONAL CONFERENCE FOR THE NEAR EAST Khartoum, the Republic of the Sudan, 4-8 December 2010 Statement by the Director-General of FAO Mr. President, Mr. Independent
CL 158/3 Web Annex 2: Output indicators and targets
 October 2017 CL 158/3-WA2 E CL 158/3 Web Annex 2: Output indicators and targets 2018-19 This document can be accessed using the Quick Response Code on this page; an FAO initiative to minimize its environmental
October 2017 CL 158/3-WA2 E CL 158/3 Web Annex 2: Output indicators and targets 2018-19 This document can be accessed using the Quick Response Code on this page; an FAO initiative to minimize its environmental
Chronic Hunger Falling, But One in Nine People Still Affected
 Chronic Hunger Falling, But One in Nine People Still Affected Gaelle Gourmelon December 1, 2014 A lthough the proportion of people experiencing chronic hunger is decreasing globally, one in nine individuals
Chronic Hunger Falling, But One in Nine People Still Affected Gaelle Gourmelon December 1, 2014 A lthough the proportion of people experiencing chronic hunger is decreasing globally, one in nine individuals
AGENDA FOR FOOD SECURITY AND RESILIENCE
 AGENDA FOR FOOD SECURITY AND RESILIENCE Twenty-six international development agencies encourage Canada to demonstrate global leadership by re-investing in food security for vulnerable people in developing
AGENDA FOR FOOD SECURITY AND RESILIENCE Twenty-six international development agencies encourage Canada to demonstrate global leadership by re-investing in food security for vulnerable people in developing
UNITED NATIONS DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME (UNDP) Contribution to the 2015 United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) Integration Segment
 UNITED NATIONS DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME (UNDP) Contribution to the 2015 United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) Integration Segment ACHIEVING SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT THROUGH EMPLOYMENT CREATION
UNITED NATIONS DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME (UNDP) Contribution to the 2015 United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) Integration Segment ACHIEVING SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT THROUGH EMPLOYMENT CREATION
AGRICULTURE & RURAL DEVELOPMENT IN MENA
 S E C T O R B R I E F AGRICULTURE & RURAL DEVELOPMENT IN MENA West Bank & Gaza Integrated Community Development Project The Project goals are to improve the quality, and availability of basic social, and
S E C T O R B R I E F AGRICULTURE & RURAL DEVELOPMENT IN MENA West Bank & Gaza Integrated Community Development Project The Project goals are to improve the quality, and availability of basic social, and
100% 80% 60% 40% 20% Spain Finland China Chile Tunisia. Mali. Egypt. Benin
 Diets Food consumption is now more centred on a narrow base of staple grains and on increased consumption of meat and dairy products. Starchy staples such as roots and tubers are relatively less important
Diets Food consumption is now more centred on a narrow base of staple grains and on increased consumption of meat and dairy products. Starchy staples such as roots and tubers are relatively less important
foodfirst: The Future of Farming and Food Security in Africa
 foodfirst: The Future of Farming and Food Security in Africa Mr Graziano da Silva, Director-General FAO It is an honor to be here today at the foodfirst Conference: The Future of Farming and Food Security
foodfirst: The Future of Farming and Food Security in Africa Mr Graziano da Silva, Director-General FAO It is an honor to be here today at the foodfirst Conference: The Future of Farming and Food Security
Strengthening the resilience of livelihood in protracted crises in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, The Niger and Somalia
 Strengthening the resilience of livelihood in protracted crises in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, The Niger and Somalia Why is the RBA Resilience Initiative Innovative? The government of Canada
Strengthening the resilience of livelihood in protracted crises in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, The Niger and Somalia Why is the RBA Resilience Initiative Innovative? The government of Canada
CARICOM Regional Food and Nutrition Security Explained
 Promoting CARICOM Food and Nutrition Security CARICOM Regional Food and Nutrition Security Explained VI working Group Meeting (GT2025) of the Hunger Free Latin America and the Caribbean Initiative International
Promoting CARICOM Food and Nutrition Security CARICOM Regional Food and Nutrition Security Explained VI working Group Meeting (GT2025) of the Hunger Free Latin America and the Caribbean Initiative International
Council of the European Union Brussels, 19 September 2014 (OR. en)
 Council of the European Union Brussels, 19 September 2014 (OR. en) 13364/14 AGRI 588 NOTE From: To: Subject: Presidency Delegations Informal meeting of the Agriculture Ministers in Milan "How can EU agriculture
Council of the European Union Brussels, 19 September 2014 (OR. en) 13364/14 AGRI 588 NOTE From: To: Subject: Presidency Delegations Informal meeting of the Agriculture Ministers in Milan "How can EU agriculture
MINISTÈRE DES AFFAIRES ÉTRANGÈRES ET EUROPÉENNES 20 December /5 6th World Water Forum Ministerial Process Draft document
 MINISTÈRE DES AFFAIRES ÉTRANGÈRES ET EUROPÉENNES 20 December 2011 1/5 6th World Water Forum Ministerial Process Draft document 1. We the Ministers and Heads of Delegations assembled in Marseille, France,
MINISTÈRE DES AFFAIRES ÉTRANGÈRES ET EUROPÉENNES 20 December 2011 1/5 6th World Water Forum Ministerial Process Draft document 1. We the Ministers and Heads of Delegations assembled in Marseille, France,
Global Forum for Food and Agriculture Communiqué 2018
 20 January 2018 the English Version is authentic Global Forum for Food and Agriculture Communiqué 2018 "Shaping the Future of Livestock sustainably, responsibly, efficiently" Preamble We, the agriculture
20 January 2018 the English Version is authentic Global Forum for Food and Agriculture Communiqué 2018 "Shaping the Future of Livestock sustainably, responsibly, efficiently" Preamble We, the agriculture
Global Pulse Production and Consumption Trends: The Potential of Pulses to Achieve Feed the Future Food and Nutritional Security Goals
 Global Pulse Production and Consumption Trends: The Potential of Pulses to Achieve Feed the Future Food and Nutritional Security Goals Mywish Maredia Department of Agricultural, Food and Resource Economics,
Global Pulse Production and Consumption Trends: The Potential of Pulses to Achieve Feed the Future Food and Nutritional Security Goals Mywish Maredia Department of Agricultural, Food and Resource Economics,
Swift and coordinated action is needed to halve hunger and extreme poverty everywhere by 2015
 PREPARATORY MEETING FOR 2005 ECOSOC HIGH-LEVEL SEGMENT 16-17 March 2005 Achieving the internationally agreed development goals, including those contained in the Millennium Declaration, as well as implementing
PREPARATORY MEETING FOR 2005 ECOSOC HIGH-LEVEL SEGMENT 16-17 March 2005 Achieving the internationally agreed development goals, including those contained in the Millennium Declaration, as well as implementing
Grain Production and Food Security in Arab Countries
 Agricultural Economics, 2 (1988) 39-56 Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam- Printed in The Netherlands 39 Grain Production and Food Security in Arab Countries Mieczystaw Adamowicz Department of
Agricultural Economics, 2 (1988) 39-56 Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam- Printed in The Netherlands 39 Grain Production and Food Security in Arab Countries Mieczystaw Adamowicz Department of
Middle-East and North Africa Middle East and North Africa Transport Solutions in Fragile Settings
 Middle-East and North Africa Middle East and North Africa Transport Solutions in Fragile Settings Nicolas Peltier-Thiberge February 2016 Outline 1. Introduction: the World Bank MNA Strategy 2. Operationalizing
Middle-East and North Africa Middle East and North Africa Transport Solutions in Fragile Settings Nicolas Peltier-Thiberge February 2016 Outline 1. Introduction: the World Bank MNA Strategy 2. Operationalizing
From MDGs to SDGs: Addressing Zero Hunger Challenge in LDCs
 From MDGs to SDGs: Addressing Zero Hunger Challenge in LDCs Dr. Xuan LI Senior Policy Officer Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations Third session of the Committee on Macroeconomic
From MDGs to SDGs: Addressing Zero Hunger Challenge in LDCs Dr. Xuan LI Senior Policy Officer Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations Third session of the Committee on Macroeconomic
Resource Mobilization - Roles and Responsibilities
 Resource Mobilization - Roles and Responsibilities Annex I This document sets out the roles and responsibilities for resource mobilization and their link to the Project Cycle. Policy and Principles 1 Resource
Resource Mobilization - Roles and Responsibilities Annex I This document sets out the roles and responsibilities for resource mobilization and their link to the Project Cycle. Policy and Principles 1 Resource
Food Security Information for Action. Food Security Concepts and Frameworks. Lesson 1. What is Food Security? Learner s Notes
 Food Security Information for Action Food Security Concepts and Frameworks Lesson 1 What is Food Security? Learner s Notes This course is funded by the European Union and developed by the Food and Agriculture
Food Security Information for Action Food Security Concepts and Frameworks Lesson 1 What is Food Security? Learner s Notes This course is funded by the European Union and developed by the Food and Agriculture
FOOD COMMODITY MARKETS: GLOBAL TRENDS AND EMERGING ISSUES
 MULTI-YEAR EXPERT MEETING ON COMMODITIES AND DEVELOPMENT 9-10 April 2014 FOOD COMMODITY MARKETS: GLOBAL TRENDS AND EMERGING ISSUES by Mr. Boubaker Ben-Belhassen UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
MULTI-YEAR EXPERT MEETING ON COMMODITIES AND DEVELOPMENT 9-10 April 2014 FOOD COMMODITY MARKETS: GLOBAL TRENDS AND EMERGING ISSUES by Mr. Boubaker Ben-Belhassen UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
Food Security and its Measurement in Egypt
 Food Security and its Measurement in Egypt Racha Ramadan Assistant professor at Faculty of Economics and Political Science-Cairo University (Egypt) By 2050, around 9 billion people will need to be fed.
Food Security and its Measurement in Egypt Racha Ramadan Assistant professor at Faculty of Economics and Political Science-Cairo University (Egypt) By 2050, around 9 billion people will need to be fed.
Photographs courtesy of: FAO/Sia Kambou.
 chad The Appeal for Chad was launched globally on the 14th December 2012 as part of the Consolidated Appeals Process (CAP). For a complete overview of FAO s component of the 2013 CAP, please go to www.fao.org/emergencies.
chad The Appeal for Chad was launched globally on the 14th December 2012 as part of the Consolidated Appeals Process (CAP). For a complete overview of FAO s component of the 2013 CAP, please go to www.fao.org/emergencies.
SOFI 2017: Questions & Answers
 SOFI 2017: Questions & Answers HUNGER AND FOOD SECURITY 1. What are the main reasons for the recent increase in hunger? The recent increase in the prevalence of undernourishment can be attributed to a
SOFI 2017: Questions & Answers HUNGER AND FOOD SECURITY 1. What are the main reasons for the recent increase in hunger? The recent increase in the prevalence of undernourishment can be attributed to a
Spotlight 6: Food and nutrition security
 Spotlight 6: Food and nutrition security Improved nutrition is an essential element of inclusive rural transformation Food and nutrition security reliable access to food in sufficient quantity and quality
Spotlight 6: Food and nutrition security Improved nutrition is an essential element of inclusive rural transformation Food and nutrition security reliable access to food in sufficient quantity and quality
3 rd REGIONAL MULTI-STAKEHOLDER WORKSHOP ON FOOD SECURITY AND NUTRITION
 3 rd REGIONAL MULTI-STAKEHOLDER WORKSHOP ON FOOD SECURITY AND NUTRITION 4-6 November 2013, Tunis, Tunisia Regional Office for the Near East and North Africa, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United
3 rd REGIONAL MULTI-STAKEHOLDER WORKSHOP ON FOOD SECURITY AND NUTRITION 4-6 November 2013, Tunis, Tunisia Regional Office for the Near East and North Africa, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United
EU agricultural policy in a global context
 Reflections on the CAP from a long-run perspective Brussels, 26 February 2009 AgFoodTrade New Issues in Agricultural, Food & Bioenergy Trade EU agricultural policy in a global context Giovanni Anania Department
Reflections on the CAP from a long-run perspective Brussels, 26 February 2009 AgFoodTrade New Issues in Agricultural, Food & Bioenergy Trade EU agricultural policy in a global context Giovanni Anania Department
CHALLENGES AND PROSPECTS FOR IMPROVING THE AGRICULTURAL STATISTICAL CAPACITY IN THE COMCEC REGION
 CHALLENGES AND PROSPECTS FOR IMPROVING THE AGRICULTURAL STATISTICAL CAPACITY IN THE COMCEC REGION April 3, 2014 ANKARA ASSESSMENT OF AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS IN THE COMCEC REGION Index of Agricultural Statistics
CHALLENGES AND PROSPECTS FOR IMPROVING THE AGRICULTURAL STATISTICAL CAPACITY IN THE COMCEC REGION April 3, 2014 ANKARA ASSESSMENT OF AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS IN THE COMCEC REGION Index of Agricultural Statistics
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) Regional Office for West Asia (ROWA)
 Green Industries, Sustainable Un nited Nat tions Env vironme ent Progr ramme Consumption and Production and dg Green Economy By: Fareed I. Bushehri The Role of Green Industries in Promoting Socio-Economic
Green Industries, Sustainable Un nited Nat tions Env vironme ent Progr ramme Consumption and Production and dg Green Economy By: Fareed I. Bushehri The Role of Green Industries in Promoting Socio-Economic
Empowering women and youth in agriculture and food systems
 G7 International Forum for Empowering Women and Youth in the Agriculture and Food Systems Tokyo, 12 December 2016 Empowering women and youth in agriculture and food systems Clara Mi Young Park Gender Rural
G7 International Forum for Empowering Women and Youth in the Agriculture and Food Systems Tokyo, 12 December 2016 Empowering women and youth in agriculture and food systems Clara Mi Young Park Gender Rural
Support for the implementation and development of the CountrySTAT Framework in the Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO) countries
 FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS TECHNICAL COOPERATION PROGRAMME Countries: Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, Republic of Azerbaijan, Islamic Republic of Iran, Republic of Kazakhstan,
FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS TECHNICAL COOPERATION PROGRAMME Countries: Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, Republic of Azerbaijan, Islamic Republic of Iran, Republic of Kazakhstan,
Progress in reducing hunger after the World Food Summit
 Progress in reducing hunger after the World Food Summit Arne Oshaug The World Food Summit (WFS) was held in November 1996. The WFS, as spelled out in its final document, clearly indicated what was needed
Progress in reducing hunger after the World Food Summit Arne Oshaug The World Food Summit (WFS) was held in November 1996. The WFS, as spelled out in its final document, clearly indicated what was needed
The Mountain Partnership and the NENA Region. Amman 2014
 The Mountain Partnership and the NENA Region Amman 2014 In this presentation: The Mountain Agenda since 1992 What is the Mountain Partnership Why mountains are important in the NENA Region What is the
The Mountain Partnership and the NENA Region Amman 2014 In this presentation: The Mountain Agenda since 1992 What is the Mountain Partnership Why mountains are important in the NENA Region What is the
Agriculture is the main source of livelihood for more than two-thirds of the population.
 Agriculture is the main source of livelihood for more than two-thirds of the population. Background YEMEN Yemen has suffered from internal conflicts and clashes for several years, resulting in severe disruptions
Agriculture is the main source of livelihood for more than two-thirds of the population. Background YEMEN Yemen has suffered from internal conflicts and clashes for several years, resulting in severe disruptions
Agriculture in A changing world. Dr. Agnes M. Kalibata Minister of State in charge of Agriculture (Rwanda)
 Agriculture in A changing world Dr. Agnes M. Kalibata Minister of State in charge of Agriculture (Rwanda) Characteristics of Agriculture in Africa Largest contributor to GDP (32%) Main source of income
Agriculture in A changing world Dr. Agnes M. Kalibata Minister of State in charge of Agriculture (Rwanda) Characteristics of Agriculture in Africa Largest contributor to GDP (32%) Main source of income
Rising Food Prices in East Asia: Challenges and Policy Options
 Rising Food Prices in East Asia: Challenges and Policy Options Luc Christiaensen,, World Bank, presentation at the Managing Vulnerability in East Asia workshop, Bangkok, June 25-26, 26, 2008 Outline Where
Rising Food Prices in East Asia: Challenges and Policy Options Luc Christiaensen,, World Bank, presentation at the Managing Vulnerability in East Asia workshop, Bangkok, June 25-26, 26, 2008 Outline Where
CLIMATE CHANGE AND THE ENVIRONMENT INTEGRATION IN NORTH AFRICA: ISSUES AND OPTIONS. Climate Change & Human Security: African Perspectives
 CLIMATE CHANGE AND THE ENVIRONMENT INTEGRATION IN NORTH AFRICA: ISSUES AND OPTIONS Climate Change & Human Security: African Perspectives Prepared for conference Climate Change and Human Security in the
CLIMATE CHANGE AND THE ENVIRONMENT INTEGRATION IN NORTH AFRICA: ISSUES AND OPTIONS Climate Change & Human Security: African Perspectives Prepared for conference Climate Change and Human Security in the
Putting food on the table for socially disadvantaged Australians: Food security as a social determinant
 Putting food on the table for socially disadvantaged Australians: Food security as a social determinant Martin Laverty Founding Chair, SDoHA Federation CEO, Royal Flying Doctor Service What I ll cover
Putting food on the table for socially disadvantaged Australians: Food security as a social determinant Martin Laverty Founding Chair, SDoHA Federation CEO, Royal Flying Doctor Service What I ll cover
PRIMA Info and networking event 8 November 2017
 PRIMA Info and networking event 8 November 2017 Angelo Riccaboni Professor of Business Administration University of Siena, Italy Chair Fundación PRIMA, Barcelona SDSN Overall SDG Index: Top 8/157 Countries:
PRIMA Info and networking event 8 November 2017 Angelo Riccaboni Professor of Business Administration University of Siena, Italy Chair Fundación PRIMA, Barcelona SDSN Overall SDG Index: Top 8/157 Countries:
CIRCLES June 18, Richard Berkland VALMONT IRRIGATION Valleyirrigation.com
 CIRCLES June 18, 2014 Richard Berkland VALMONT IRRIGATION Valleyirrigation.com 1 Pivot development in Western U.S. 2 Hectares Irrigated by Method - USA Source: 1998, 2003, 2008 Farm and Ranch Irrigation
CIRCLES June 18, 2014 Richard Berkland VALMONT IRRIGATION Valleyirrigation.com 1 Pivot development in Western U.S. 2 Hectares Irrigated by Method - USA Source: 1998, 2003, 2008 Farm and Ranch Irrigation
Country Profile: Food Security Indicators
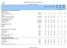 Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment - - - - na na na Number of undernourished millions ns ns ns ns na
Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment - - - - na na na Number of undernourished millions ns ns ns ns na
Supporting smallholder market participation through Zambia s Home Grown School Feeding programme
 Supporting smallholder market participation through Zambia s Home Grown School Feeding programme Presented at the Pro-Poor Agricultural development: Agricultural Interventions and the Complementary role
Supporting smallholder market participation through Zambia s Home Grown School Feeding programme Presented at the Pro-Poor Agricultural development: Agricultural Interventions and the Complementary role
Linking Agriculture and Nutrition: What are the Opportunities?
 Agriculture and Nutrition Working Together to Improve Nutritional Outcomes: The Global Landscape Marie Ruel, IFPRI Linking Agriculture and Nutrition: What are the Opportunities? Marie Ruel, IFPRI CHANGE
Agriculture and Nutrition Working Together to Improve Nutritional Outcomes: The Global Landscape Marie Ruel, IFPRI Linking Agriculture and Nutrition: What are the Opportunities? Marie Ruel, IFPRI CHANGE
HIGH-LEVEL TASK FORCE ON THE GLOBAL FOOD CRISIS COMPREHENSIVE FRAMEWORK FOR ACTION JULY 2008
 HIGH-LEVEL TASK FORCE ON THE GLOBAL FOOD CRISIS COMPREHENSIVE FRAMEWORK FOR ACTION JULY 2008 1 FOREWORD On 29 April 2008, the Chief Executives Board (CEB) of the United Nations decided to establish a High-Level
HIGH-LEVEL TASK FORCE ON THE GLOBAL FOOD CRISIS COMPREHENSIVE FRAMEWORK FOR ACTION JULY 2008 1 FOREWORD On 29 April 2008, the Chief Executives Board (CEB) of the United Nations decided to establish a High-Level
REGIONAL TRAINING COURSE. Child Poverty and Disparity Measurement and Analysis March Cairo, Egypt
 REGIONAL TRAINING COURSE Child Poverty and Disparity Measurement and Analysis 9-14 March 2013 Cairo, Egypt Background The Middle East and North Africa (MENA) is a complex and diverse region that is experiencing
REGIONAL TRAINING COURSE Child Poverty and Disparity Measurement and Analysis 9-14 March 2013 Cairo, Egypt Background The Middle East and North Africa (MENA) is a complex and diverse region that is experiencing
Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture in the Arab Region
 2015 Regional Coordination Mechanism (RCM) Issues Brief for the Arab Sustainable Development Report Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture in the Arab Region Author: Mohamed Aw-Dahir (Mohamed.awdahir@fao.org),
2015 Regional Coordination Mechanism (RCM) Issues Brief for the Arab Sustainable Development Report Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture in the Arab Region Author: Mohamed Aw-Dahir (Mohamed.awdahir@fao.org),
How Trade Liberalization Can Benefit the Environment (or The Fallacy of Food Miles )
 How Trade Liberalization Can Benefit the Environment (or The Fallacy of Food Miles ) Robert L. Thompson Gardner Endowed Chair in Agricultural Policy University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 12 May 2008
How Trade Liberalization Can Benefit the Environment (or The Fallacy of Food Miles ) Robert L. Thompson Gardner Endowed Chair in Agricultural Policy University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 12 May 2008
Malawi Agriculture and Food Security
 Malawi Agriculture and Food Security By Timothy Gondwe 1 and Mizeck Chagunda 2 1 Lilongwe University of Agriculture and Natural Resources (LUANAR) 2 SRUC (Scotland s Rural College) Presented at the Scotland
Malawi Agriculture and Food Security By Timothy Gondwe 1 and Mizeck Chagunda 2 1 Lilongwe University of Agriculture and Natural Resources (LUANAR) 2 SRUC (Scotland s Rural College) Presented at the Scotland
Regional Conference for Europe
 March 2014 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Organisation des Nations Unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture Продовольственная и cельскохозяйственная организация Объединенных
March 2014 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Organisation des Nations Unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture Продовольственная и cельскохозяйственная организация Объединенных
The Role of AU/NEPAD in Social Protection
 The Role of AU/NEPAD in Social Protection Study Tour - Social Protection in Brazil Brasilia, Brazil 26 August 2008 Boitshepo Bibi Giyose Food and Nutrition Security Advisor AU/NEPAD NEPAD - what is it?
The Role of AU/NEPAD in Social Protection Study Tour - Social Protection in Brazil Brasilia, Brazil 26 August 2008 Boitshepo Bibi Giyose Food and Nutrition Security Advisor AU/NEPAD NEPAD - what is it?
Gender and Financing for Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation in the Philippines
 Gender and Financing for Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation in the Philippines A Pro-poor and Gendersensitive Perspective By: Athena Peralta Objectives of the Case Study The study aims to critically
Gender and Financing for Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation in the Philippines A Pro-poor and Gendersensitive Perspective By: Athena Peralta Objectives of the Case Study The study aims to critically
November Food and. Agricultura. Organization of the United Nations COUNCIL. Hundred and Forty-fifth Session. Rome, 3-7 December 2012
 November 2012 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Organisation des Nations Unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture Продовольственная и cельскохозяйственная организация Объединенных
November 2012 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Organisation des Nations Unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture Продовольственная и cельскохозяйственная организация Объединенных
Making Climate Finance Work in Agriculture
 Making Climate Finance Work in Agriculture This note has been prepared by members of the Investment Action Group as background to the Climate Finance session of the Annual Forum of the Global Alliance
Making Climate Finance Work in Agriculture This note has been prepared by members of the Investment Action Group as background to the Climate Finance session of the Annual Forum of the Global Alliance
The fate of agriculture in MENA countries
 Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics University of California, Davis Rosenberg International Forum on Water Policy Aqaba, Jordan March 24-25, 2013 Water scarcity and agriculture in MENA Water
Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics University of California, Davis Rosenberg International Forum on Water Policy Aqaba, Jordan March 24-25, 2013 Water scarcity and agriculture in MENA Water
The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is the first common policy adopted by the
 Evaluation of Agricultural Policy Reforms in the European Union OECD 2011 Executive Summary The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is the first common policy adopted by the European Community under the Treaty
Evaluation of Agricultural Policy Reforms in the European Union OECD 2011 Executive Summary The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is the first common policy adopted by the European Community under the Treaty
Water Resources Data APPENDIX 1. Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region. Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region
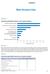 APPENDIX 1 Water Resources Data FIGURE A1.1 Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region Australia and New Zealand Latin America and the Caribbean North America Europe and Central Asia Sub-Saharan
APPENDIX 1 Water Resources Data FIGURE A1.1 Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region Australia and New Zealand Latin America and the Caribbean North America Europe and Central Asia Sub-Saharan
April 2016 PC 119/4. Hundred and Nineteenth Session. Rome, May Strategy for FAO s work on Climate Change - roadmap
 April 2016 PC 119/4 E PROGRAMME COMMITTEE Hundred and Nineteenth Session Rome, 16-20 May 2016 Strategy for FAO s work on Climate Change - roadmap Queries on the substantive content of this document may
April 2016 PC 119/4 E PROGRAMME COMMITTEE Hundred and Nineteenth Session Rome, 16-20 May 2016 Strategy for FAO s work on Climate Change - roadmap Queries on the substantive content of this document may
Strategic objective No. 2: Create greater opportunities for women and men to secure decent employment and income
 EMPLOYMENT Strategic objective No. 2: Create greater opportunities for women and men to secure decent employment and income 66. Closing the employment gap is at the heart of the decent work agenda. Unemployment
EMPLOYMENT Strategic objective No. 2: Create greater opportunities for women and men to secure decent employment and income 66. Closing the employment gap is at the heart of the decent work agenda. Unemployment
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Livelihood Support Options
 The Role of Technology in Enhancing Livelihood Support Options Kennedy Onyango Director - Community Initiatives and Social Support Organization (CISSO) cisso@africamail.com BACKGROUND OF THE PAPER: Achieving
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Livelihood Support Options Kennedy Onyango Director - Community Initiatives and Social Support Organization (CISSO) cisso@africamail.com BACKGROUND OF THE PAPER: Achieving
Managing Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) in SPECA Countries: Completing the Transition
 Managing Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) in SPECA Countries: Completing the Transition Kees van der Meer, UNIDO and STDF consultant Presented at UNSPECA Aid for Trade Ministerial Meeting SPS
Managing Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) in SPECA Countries: Completing the Transition Kees van der Meer, UNIDO and STDF consultant Presented at UNSPECA Aid for Trade Ministerial Meeting SPS
Mainstreaming nutrition in agriculture investment plans Lessons learnt, challenges and opportunities
 Mainstreaming nutrition in agriculture investment plans Lessons learnt, challenges and opportunities Charlotte Dufour Nutrition Division Food & Agriculture Organization (FAO) Structure of the presentation
Mainstreaming nutrition in agriculture investment plans Lessons learnt, challenges and opportunities Charlotte Dufour Nutrition Division Food & Agriculture Organization (FAO) Structure of the presentation
New approaches to the measurement of the state of food insecurity
 FAO-OEA/CIE-IICA WORKING GROUP ON AGRICULTURAL AND LIVESTOCK STATISTICS FOR LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN Twenty-sixth Session New approaches to the measurement of the state of food insecurity FAO Statistics
FAO-OEA/CIE-IICA WORKING GROUP ON AGRICULTURAL AND LIVESTOCK STATISTICS FOR LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN Twenty-sixth Session New approaches to the measurement of the state of food insecurity FAO Statistics
E-Government Readiness Index
 E-GOVERNMENT READINESS IN THE MEMBER COUNTRIES INTRODUCTION Today we are living in an era of speed caused by the technological progress of mankind which has a deep impact on each and every process in both
E-GOVERNMENT READINESS IN THE MEMBER COUNTRIES INTRODUCTION Today we are living in an era of speed caused by the technological progress of mankind which has a deep impact on each and every process in both
REGIONAL GENDER EQUALITY STRATEGY
 REGIONAL GENDER EQUALITY STRATEGY For the Near East and North Africa 2017-2020 REGIONAL GENDER EQUALITY STRATEGY For the Near East and North Africa 2017-2020 FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED
REGIONAL GENDER EQUALITY STRATEGY For the Near East and North Africa 2017-2020 REGIONAL GENDER EQUALITY STRATEGY For the Near East and North Africa 2017-2020 FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED
Budget Increases to Protracted Relief and Recovery Operations Madagascar
 Executive Board Second Regular Session Rome, 14 18 November 2016 Distribution: General Date: 2 November 2016 Original: English Agenda Item 8 WFP/EB.2/2016/8-C/5 Projects for Executive Board Approval For
Executive Board Second Regular Session Rome, 14 18 November 2016 Distribution: General Date: 2 November 2016 Original: English Agenda Item 8 WFP/EB.2/2016/8-C/5 Projects for Executive Board Approval For
COHERENCE BETWEEN KENYA S PRSP, ERS AND ACHIEVEMENT OF MDGs. Nicholas N. Waiyaki
 COHERENCE BETWEEN KENYA S PRSP, ERS AND ACHIEVEMENT OF MDGs Nicholas N. Waiyaki Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper (PRSP) PRSP was launched by Govt in 2001 Developed as a short-term term strategy for meeting
COHERENCE BETWEEN KENYA S PRSP, ERS AND ACHIEVEMENT OF MDGs Nicholas N. Waiyaki Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper (PRSP) PRSP was launched by Govt in 2001 Developed as a short-term term strategy for meeting
Agriculture in China - Successes, Challenges, and Prospects. Prof. Zhihao Zheng College of Economics & Management China Agricultural University
 Agriculture in China - Successes, Challenges, and Prospects Prof. Zhihao Zheng College of Economics & Management China Agricultural University I. Success 1. For the past three decades (1978-2010), China
Agriculture in China - Successes, Challenges, and Prospects Prof. Zhihao Zheng College of Economics & Management China Agricultural University I. Success 1. For the past three decades (1978-2010), China
Production and consumption of wheat in Uzbekistan: issues and possible solutions
 Production and consumption of wheat in Uzbekistan: issues and possible solutions Bakhrom Mirkasimov and Ziyodullo Parpiev (Westminster International University in Tashkent) OUTLINE Production of wheat
Production and consumption of wheat in Uzbekistan: issues and possible solutions Bakhrom Mirkasimov and Ziyodullo Parpiev (Westminster International University in Tashkent) OUTLINE Production of wheat
THE MAKIG OF SOCIAL PROTECTION IN ETHIOPIA
 THE MAKIG OF SOCIAL PROTECTION IN ETHIOPIA Aseffa Abreha May 2013 Introduction Social protection is conceived in several ways and generally interchangeably used with social security, social safety net,
THE MAKIG OF SOCIAL PROTECTION IN ETHIOPIA Aseffa Abreha May 2013 Introduction Social protection is conceived in several ways and generally interchangeably used with social security, social safety net,
Chapter 2. OVERVIEW OF THE OECD INDICATORS OF AGRICULTURAL SUPPORT
 Chapter 2. OVERVIEW OF THE OECD INDICATORS OF AGRICULTURAL SUPPORT 7. This chapter begins with a brief summary of why the OECD indicators of agricultural support ( the indicators ) have been developed.
Chapter 2. OVERVIEW OF THE OECD INDICATORS OF AGRICULTURAL SUPPORT 7. This chapter begins with a brief summary of why the OECD indicators of agricultural support ( the indicators ) have been developed.
Theme 2: Competing Claims on Natural Resources
 Theme 2: Competing Claims on Natural Resources Problem description Natural resources lie at the heart of social, political and economic life in most developing countries. Agriculture, natural resources
Theme 2: Competing Claims on Natural Resources Problem description Natural resources lie at the heart of social, political and economic life in most developing countries. Agriculture, natural resources
ENHANCING FOOD MARKET TRANSPARENCY AND POLICY COORDINATION
 ENHANCING FOOD MARKET TRANSPARENCY AND POLICY COORDINATION Updated programme document with extended duration until 31 December 2019 PROJECT DOCUMENT Country(ies): Project Title (Long): Project Title (short):
ENHANCING FOOD MARKET TRANSPARENCY AND POLICY COORDINATION Updated programme document with extended duration until 31 December 2019 PROJECT DOCUMENT Country(ies): Project Title (Long): Project Title (short):
Food Prices: What information and regulations to avoid extreme events
 Food Prices: What information and regulations to avoid extreme events Maximo Torero m.torero@cigar.org International Food Policy Research Institute Website: Conference blog: foodsecure.eu foodsecureblog.wordpress.com
Food Prices: What information and regulations to avoid extreme events Maximo Torero m.torero@cigar.org International Food Policy Research Institute Website: Conference blog: foodsecure.eu foodsecureblog.wordpress.com
production, particularly among women, can be highlighted and must be addressed.
 Gender-Aware Programs and Women s Roles in Agricultural Value Chains in Liberia Ministry of Gender and Development, Government of Liberia PREM Gender and Development Group, World Bank The success and sustainability
Gender-Aware Programs and Women s Roles in Agricultural Value Chains in Liberia Ministry of Gender and Development, Government of Liberia PREM Gender and Development Group, World Bank The success and sustainability
India Perspectives. Post-2015 Development Agenda. Food Security
 India Perspectives Post-2015 Development Agenda Food Security SPEAKERS AND CONTRIBUTORS Mark Rosegrant Director, Environment and Production Technology Division, International Food Policy Research Institute
India Perspectives Post-2015 Development Agenda Food Security SPEAKERS AND CONTRIBUTORS Mark Rosegrant Director, Environment and Production Technology Division, International Food Policy Research Institute
Brasilia Declaration and Action Agenda. adopted at the. International Conference on South-South and Triangular Cooperation
 Brasilia Declaration and Action Agenda adopted at the International Conference on South-South and Triangular Cooperation Leveraging Innovations from the Global South to Support Rural Transformation in
Brasilia Declaration and Action Agenda adopted at the International Conference on South-South and Triangular Cooperation Leveraging Innovations from the Global South to Support Rural Transformation in
Agriculture and natural resources
 Agriculture and natural resources Current status Characteristics of agriculture in the Arab region Agriculture contributes significantly to regional GDP and exports and to per capita incomes. Region-wide,
Agriculture and natural resources Current status Characteristics of agriculture in the Arab region Agriculture contributes significantly to regional GDP and exports and to per capita incomes. Region-wide,
Country Profile: Food Security Indicators
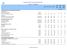 Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment - - - - na na na Number of undernourished millions ns ns ns ns na
Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment - - - - na na na Number of undernourished millions ns ns ns ns na
The Relevance Of Livelihoods Approaches To Food Insecurity Measurement
 The Relevance Of Livelihoods Approaches To Food Insecurity Measurement Karim Hussein, ODI Introduction A core aim of this paper is to situate the discussion of food security and livelihoods approaches
The Relevance Of Livelihoods Approaches To Food Insecurity Measurement Karim Hussein, ODI Introduction A core aim of this paper is to situate the discussion of food security and livelihoods approaches
The Sahel Beyond the Headlines: Population, Climate and Resources. Roger-Mark De Souza Director of Population, Environmental Security and Resilience
 The Sahel Beyond the Headlines: Population, Climate and Resources Roger-Mark De Souza Director of Population, Environmental Security and Resilience The Sahel and Resilience What is Resilience? Resilience
The Sahel Beyond the Headlines: Population, Climate and Resources Roger-Mark De Souza Director of Population, Environmental Security and Resilience The Sahel and Resilience What is Resilience? Resilience
Climate Change in the MENA Region: Effects on Water and Agriculture
 Climate Change in the MENA Region: Effects on Water and Agriculture Dr Shawki Barghouti International Center for Biosaline Agriculture Presented at: Addressing Climate Change in the Middle East and North
Climate Change in the MENA Region: Effects on Water and Agriculture Dr Shawki Barghouti International Center for Biosaline Agriculture Presented at: Addressing Climate Change in the Middle East and North
Sustainability Criteria for Water Resource Systems
 Sustainability Criteria for Water Resource Systems David Watkins Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering October 15, 2004 Acknowledgments Task Committee on Sustainability Criteria, Water Resources
Sustainability Criteria for Water Resource Systems David Watkins Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering October 15, 2004 Acknowledgments Task Committee on Sustainability Criteria, Water Resources
FAO FOOD LOSS REDUCTION STRATEGY
 FOOD LOSS REDUCTION STRATEGY FAO FOOD LOSS REDUCTION STRATEGY IMPORTANCE OF FOOD LOSSES AND FOOD WASTE dairy products fish and seafood meat fruits and vegetables oilseeds and pulses roots and tubers cereals
FOOD LOSS REDUCTION STRATEGY FAO FOOD LOSS REDUCTION STRATEGY IMPORTANCE OF FOOD LOSSES AND FOOD WASTE dairy products fish and seafood meat fruits and vegetables oilseeds and pulses roots and tubers cereals
NERC/12/REP REPORT. Thirty-first FAO Regional Conference for the Near East. Rome Italy May 2012
 NERC/12/REP REPORT Rome Italy 14 18 May 2012 Thirty-first FAO Regional Conference for the Near East FAO Member Nations in the Near East Region Afghanistan Kuwait Saudi Arabia Algeria Kyrgyzstan Somalia
NERC/12/REP REPORT Rome Italy 14 18 May 2012 Thirty-first FAO Regional Conference for the Near East FAO Member Nations in the Near East Region Afghanistan Kuwait Saudi Arabia Algeria Kyrgyzstan Somalia
Presentation by Hon. John Kiyonga Munyes, EGH, MP Minister for Labour Government of the Republic of Kenya
 NATIONAL VOLUNTARY PRESENTATION TO THE ECOSOC 2012 ANNUAL MINISTERIAL REVIEW Promoting productive capacity, employment and decent work to eradicate poverty in the context of inclusive, sustainable and
NATIONAL VOLUNTARY PRESENTATION TO THE ECOSOC 2012 ANNUAL MINISTERIAL REVIEW Promoting productive capacity, employment and decent work to eradicate poverty in the context of inclusive, sustainable and
