Supplemental Figures Normal SNL (L4)
|
|
|
- Barry Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
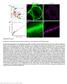
1 Supplemental Figures Normal Gly PKγ PKγ T SNL (L5) Gly PKγ PKγ T SNL (L4) Gly PKγ PKγ T Figure S1. The relative positions of the recorded neuronal pairs in L4 and L5 slices., audal;, dorsal;, rostral;, ventral. Gly: glycinergic cell; PKγ: PKγ positive cell; T: transient central cell.
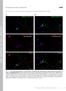
2 ed (Biocytin) ed (Biocytin) PKγ cell Gly cell Green (PKγ) Green (PKγ) IPSP PKγ 2.5 m Gly 50 m Figure S2. An example of monosynaptic inhibitory connection between Gly and PKγ+ neurons sampled from naïve rats. (A) 30 μm thick optical stack image of morphology and location of the recorded neuronal pair. Arrows indicate the presynaptic PKγ+ cell, arrowhead indicates putative axon. (B) 1 μm thick optical stacks of the recorded PKγ+ cell. Scale bar, 100 μm. () Bottom trace recorded from the presynaptic Gly neuron shows action potentials (s) initiated by three successive depolarizing pulses. Top trace recorded from the postsynaptic PKγ+ neuron shows evoked unitary IPSPs which display short-term potentiation.
3 ed (Biocytin) ed (Biocytin) T cell PKγ cell Green (PKγ) Green (PKγ) 1 m EPSP T PKγ 50 m Figure S3. An example of a monosynaptic excitatory connection between PKγ+ and transient central (T) neurons sampled from naïve rats. (A) 30 μm thick optical stack image of morphology and location of the recorded neuronal pair. Arrows indicate the presynaptic PKγ+ positive cell, arrowhead indicates putative axon. (B) 1 μm thick optical stacks of the recorded PKγ+ cell. Scale bar, 100 μm. () Bottom trace recorded from the presynaptic PKγ+ neuron shows s initiated by three successive depolarizing pulses. Top trace recorded from the postsynaptic T neuron shows evoked unitary EPSPs which display short-term depression.
4 PKγ cell ed (Biocytin) ed (Biocytin) Green (PKγ) Green (PKγ) Gly cell IPSP PKγ 2.5 m Gly 50 m Figure S4. An example of a monosynaptic inhibitory connection between Gly and PKγ+ neurons sampled from SNL rats. (A) 30 μm thick optical stack image of morphology and location of the recorded neuronal pair. Arrows indicate the presynaptic PKγ+ positive cell. (B) 1 μm thick optical stacks of the recorded PKγ+ cell. Scale bar, 100 μm. () Bottom trace recorded from the presynaptic Gly neuron shows s initiated by three successive depolarizing pulses. Top trace recorded from the postsynaptic PKγ+ neuron shows evoked unitary IPSPs which display short-term depression.
5 ed (Biocytin) ed (Biocytin) T cell PKγ cell Green (PKγ) Green (PKγ) 1 m EPSP T PKγ 50 m Figure S5. An example of a monosynaptic excitatory connection between PKγ+ and transient central (T) neurons sampled from SNL rats. (A) 30 μm thick optical stack image of morphology and location of the recorded neuronal pair. Arrows indicate the presynaptic PKγ+ positive cell, arrowhead indicates putative axon. (B) 1 μm thick optical stacks of the recorded PKγ+ cell. Scale bar, 100 μm. () Bottom trace recorded from the presynaptic PKγ+ neuron shows s initiated by three successive depolarizing pulses. Top trace recorded from the postsynaptic T neuron shows evoked unitary EPSPs displaying short-term potentiation.
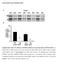
6 A Extracellular recording Suction electrode L5 orsal oot B ompound s stimuli ( ) 12 Aβ ( ) Aδ ( ) Time (ms) ompound s 0-1 stimuli ( ) Aβ Aδ (1.3 ) (2-10 ) Time (ms) Figure S6. orsal root compound recordings to determine the response thresholds for the activation of Aβ, Aδ and fibers. (A) Schematic of the experimental setup for recording compound s from the L5 dorsal root () under our recording conditions. A suction electrode was placed at one end to stimulate dorsal root and another at the opposite end to record extracellular compound s. (B-) epresentative compound s recorded from the at different stimulus intensities. The stimulus intensities for activation of Aβ, Aδ and fibers were determined at the range of , and 2-10, respectively.
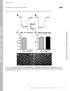
7 Supplementary Table 1. omparison of electrophysiological features between naïve and SNL rats Normal (L5) SNL (L4) SNL (L5) ell type Gly PKγ T Gly PKγ T Gly PKγ T MPs (-m) 50.7± ±2.7 (34) 61.3± ± ±2.7 (12) 60.5± ±2.7 (9) 60.5± ±4.4 (7) pattern tonic transient transient tonic transient transient tonic transient transient frequency (Hz) 8.5± ±5.3* (34) 4.2± ± ±5.2* (12) 4.6± ±3.7 (9) 21.6±6.7* 5.1±3.1 (7) Gly: glycinergic cell; PKγ: PKγ positive cell; T: transient central cell; MPs: resting membrane potentials; pattern: action potential discharge patterns to prolonged (1000 ms) depolarizing pulses; frequency: action potential discharge frequency to prolonged (1000 ms) depolarizing pulses; Tonic pattern: at moderately superthreshold depolarizations, Gly cells uniformly discharged tonically (repetitively at relatively regular intervals); Transient pattern: T and PKγ neurons were equally consistent in exhibiting a burst of impulses followed by silence during maintained depolarization, but the latter with higher frequency (*P < 0.01, compared with T cells). esults were reported as mean ± SEM (n). 1
Transient and selective suppression of neural activity with infrared light
 Supplementary Material Transient and selective suppression of neural activity with infrared light Authors: Austin R. Duke 1, Michael W. Jenkins 2, Hui Lu 3, Jeffrey M. McManus 3, Hillel J. Chiel 3,2,4,
Supplementary Material Transient and selective suppression of neural activity with infrared light Authors: Austin R. Duke 1, Michael W. Jenkins 2, Hui Lu 3, Jeffrey M. McManus 3, Hillel J. Chiel 3,2,4,
Ascorbic acid: a useful reductant to avoid oxidation of catecholamines in electrophysiological experiments in vitro?
 Neuroscience Letters, 116 (1990) 287 292 287 Elsevier Scientific Publishers Ireland Ltd. NSL 07080 Ascorbic acid: a useful reductant to avoid oxidation of catecholamines in electrophysiological experiments
Neuroscience Letters, 116 (1990) 287 292 287 Elsevier Scientific Publishers Ireland Ltd. NSL 07080 Ascorbic acid: a useful reductant to avoid oxidation of catecholamines in electrophysiological experiments
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
(A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure 1 Figure S1. Expression of the non-alpha nachr subunit ACR-2. (A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1 animal. Wide-field
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure 1 Figure S1. Expression of the non-alpha nachr subunit ACR-2. (A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1 animal. Wide-field
100 pa. 1 mv. 3 Tetanus
 Aβ -4 inhibition of LTP is prevented by manipulation of a signalling pathway involving caspase- 3, Akt and GSK-3 Jihoon Jo, Daniel J. Whitcomb, Kimberly Moore Olsen, Talitha L. Kerrigan, Joyce Shih-Ching
Aβ -4 inhibition of LTP is prevented by manipulation of a signalling pathway involving caspase- 3, Akt and GSK-3 Jihoon Jo, Daniel J. Whitcomb, Kimberly Moore Olsen, Talitha L. Kerrigan, Joyce Shih-Ching
Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins (a) BiFC signal development observed when cells were transfected with stomatin VC/-VN, STOML1-VC/- VN, STOML2-VC/-VN,
Supplementary Figure 1 Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins (a) BiFC signal development observed when cells were transfected with stomatin VC/-VN, STOML1-VC/- VN, STOML2-VC/-VN,
A Toolbox for Spatiotemporal Analysis of Voltage-Sensitive Dye Imaging Data in Brain Slices
 A Toolbox for Spatiotemporal Analysis of Voltage-Sensitive Dye Imaging Data in Brain Slices The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
A Toolbox for Spatiotemporal Analysis of Voltage-Sensitive Dye Imaging Data in Brain Slices The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Cellular adhesion and neuronal excitability on functionalised diamond surfaces
 Cellular adhesion and neuronal excitability on functionalised diamond surfaces P. Ariano 1,2, P. Baldelli 1,3, E. Carbone1,3, A. Gilardino1,2, A. Lo Giudice1,4, D. Lovisolo1,2, C. Manfredotti1,4, M. Novara1,3,
Cellular adhesion and neuronal excitability on functionalised diamond surfaces P. Ariano 1,2, P. Baldelli 1,3, E. Carbone1,3, A. Gilardino1,2, A. Lo Giudice1,4, D. Lovisolo1,2, C. Manfredotti1,4, M. Novara1,3,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Comprehensive opto-mechanical design of the dual-axis microscope.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comprehensive opto-mechanical design of the dual-axis microscope. (a) The complete microscope is shown to scale. The laser beam is depicted in light red. (b) A close-up view of the
Supplementary Figure 1 Comprehensive opto-mechanical design of the dual-axis microscope. (a) The complete microscope is shown to scale. The laser beam is depicted in light red. (b) A close-up view of the
Activation of raphe nuclei triggers rapid and distinct effects on parallel olfactory bulb output channels
 Activation of raphe nuclei triggers rapid and distinct effects on parallel olfactory bulb output channels Vikrant Kapoor, Allison C Provost, Prateek Agarwal, & Venkatesh N Murthy, 6 Nature America, Inc.
Activation of raphe nuclei triggers rapid and distinct effects on parallel olfactory bulb output channels Vikrant Kapoor, Allison C Provost, Prateek Agarwal, & Venkatesh N Murthy, 6 Nature America, Inc.
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/325/5941/756/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Synaptic Integration in Tuft Dendrites of Layer 5 Pyramidal Neurons: A New Unifying Principle Matthew E. Larkum,* Thomas
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/325/5941/756/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Synaptic Integration in Tuft Dendrites of Layer 5 Pyramidal Neurons: A New Unifying Principle Matthew E. Larkum,* Thomas
In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary
 Supplementary Methods In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary somatosensory cortex (S1), forepaw
Supplementary Methods In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary somatosensory cortex (S1), forepaw
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. VEH NI Supplementary Figure 1. Cannula tip placement in mice infused with vehicle (VEH) or anisomycin (NI). Cannula tip placement in mice infused with VEH (open circles) or NI (solid
Supplementary Figure 1. VEH NI Supplementary Figure 1. Cannula tip placement in mice infused with vehicle (VEH) or anisomycin (NI). Cannula tip placement in mice infused with VEH (open circles) or NI (solid
Panx2 expression modulates neuronal differentiation SUPPLEMENTAL DATA. Figure Legends
 Panx2 expression modulates neuronal differentiation SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure Legends Suppl. Fig. S1. Antigenic determinants of the Panx2 antibodies employed in this study. (A) Schematic of mouse Panx2
Panx2 expression modulates neuronal differentiation SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure Legends Suppl. Fig. S1. Antigenic determinants of the Panx2 antibodies employed in this study. (A) Schematic of mouse Panx2
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Fig. S1. FlicR0.1 response to electric field stimulation in HeLa cells and membrane potential step in HEK293 cells (A) Image of HeLa cells expressing FlicR0.1. Scale bar 10 μm. (B)
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Fig. S1. FlicR0.1 response to electric field stimulation in HeLa cells and membrane potential step in HEK293 cells (A) Image of HeLa cells expressing FlicR0.1. Scale bar 10 μm. (B)
Cell type specific genetic and optogenetic tools reveal hippocampal CA2 circuits
 Cell type specific genetic and optogenetic tools reveal hippocampal circuits Keigo Kohara 1,6, Michele Pignatelli 1,6, Alexander J Rivest 1,6, Hae-Yoon Jung 1, Takashi Kitamura 1, Junghyup Suh 1, Dominic
Cell type specific genetic and optogenetic tools reveal hippocampal circuits Keigo Kohara 1,6, Michele Pignatelli 1,6, Alexander J Rivest 1,6, Hae-Yoon Jung 1, Takashi Kitamura 1, Junghyup Suh 1, Dominic
Supporting Online Material for
 Correction: 21 May 2009 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1168878/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Phasic Firing in Dopaminergic Neurons Is Sufficient for Behavioral Conditioning Hsing-Chen Tsai, Feng
Correction: 21 May 2009 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1168878/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Phasic Firing in Dopaminergic Neurons Is Sufficient for Behavioral Conditioning Hsing-Chen Tsai, Feng
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1. Neuropods contact nerves but not blood vessels. We used a vessel painting technique with the lipophilic dye DiI to determine the relationship of enteroendocrine cells
Supplementary Information Figure S1. Neuropods contact nerves but not blood vessels. We used a vessel painting technique with the lipophilic dye DiI to determine the relationship of enteroendocrine cells
Supplementary Figure 1. Pathologically phosphorylated Tau is localized to the presynaptic terminals of Alzheimer s disease (AD) patient brains.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Pathologically phosphorylated Tau is localized to the presynaptic terminals of Alzheimer s disease (AD) patient brains. Ultrathin (70 nm) sections of healthy control or AD patient
Supplementary Figure 1. Pathologically phosphorylated Tau is localized to the presynaptic terminals of Alzheimer s disease (AD) patient brains. Ultrathin (70 nm) sections of healthy control or AD patient
Spontaneous network activity visualized by ultrasensitive Ca 2+ indicators, yellow Cameleon-Nano
 nature methods Spontaneous network activity visualized by ultrasensitive Ca 2+ indicators, yellow Cameleon-Nano Kazuki Horikawa, Yoshiyuki Yamada, Tomoki Matsuda, Kentarou Kobayashi, Mitsuhiro Hashimoto,
nature methods Spontaneous network activity visualized by ultrasensitive Ca 2+ indicators, yellow Cameleon-Nano Kazuki Horikawa, Yoshiyuki Yamada, Tomoki Matsuda, Kentarou Kobayashi, Mitsuhiro Hashimoto,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1008382107 SI Methods Tissue Fixation. Adult rats, mice, and Oprd1 exon 1-deleted mice (Jackson Lab) were anesthetized and perfused with 20 ml of warm saline,
Supporting Information Wang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1008382107 SI Methods Tissue Fixation. Adult rats, mice, and Oprd1 exon 1-deleted mice (Jackson Lab) were anesthetized and perfused with 20 ml of warm saline,
Supplementary Figure 1. Serial deletion mutants of BLITz.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
A role for Piezo 2 inexchange protein activated by camp1-dependent mechanical allodynia
 Supplementary Information A role for Piezo 2 inexchange protein activated by camp1-dependent mechanical allodynia Niels Eijkelkamp, John E. Linley, Jesus M. Torres, Lucy Bee, Anthony H. Dickenson, Martine
Supplementary Information A role for Piezo 2 inexchange protein activated by camp1-dependent mechanical allodynia Niels Eijkelkamp, John E. Linley, Jesus M. Torres, Lucy Bee, Anthony H. Dickenson, Martine
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Selective control of inhibitory synapse development by Slitrk3-PTPδ trans-synaptic interaction Hideto Takahashi 1, Kei-ichi Katayama 2, Kazuhiro Sohya 3,4, Hiroyuki Miyamoto 4,5,
Supplementary Information Selective control of inhibitory synapse development by Slitrk3-PTPδ trans-synaptic interaction Hideto Takahashi 1, Kei-ichi Katayama 2, Kazuhiro Sohya 3,4, Hiroyuki Miyamoto 4,5,
Supplemental Information. Characterization of Proprioceptive System. Dynamics in Behaving Drosophila Larvae. Using High-Speed Volumetric Microscopy
 urrent Biology, Volume 29 Supplemental Information haracterization of roprioceptive System Dynamics in Behaving Drosophila Larvae Using High-Speed Volumetric Microscopy Rebecca D. Vaadia, Wenze Li, Venkatakaushik
urrent Biology, Volume 29 Supplemental Information haracterization of roprioceptive System Dynamics in Behaving Drosophila Larvae Using High-Speed Volumetric Microscopy Rebecca D. Vaadia, Wenze Li, Venkatakaushik
Supplemental Information. Pacemaker and Plateau Potentials. Shape Output of a Developing. Locomotor Network. Current Biology, Volume 22
 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Pacemaker and Plateau Potentials Shape Output of a Developing Locomotor Network Huaxia Tong and Jonathan Robert McDearmid SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Pacemaker and Plateau Potentials Shape Output of a Developing Locomotor Network Huaxia Tong and Jonathan Robert McDearmid SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Hoopfer et al., Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure S1. Quantification of ORN axon degeneration
 Hoopfer et al., Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure S1. Quantification of ORN axon degeneration (A) Mean GFP intensity of commissural ORN axons 1 day after antennae removal. 1 day after cutting, wt ORNs
Hoopfer et al., Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure S1. Quantification of ORN axon degeneration (A) Mean GFP intensity of commissural ORN axons 1 day after antennae removal. 1 day after cutting, wt ORNs
Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray
 Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray Method in Brain Research 1. Non-Invasive (Human) o Imaging Computerized (Axial) Tomography (X-rays). Static pictures and high spatial resolution. Horizontal plane only.
Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray Method in Brain Research 1. Non-Invasive (Human) o Imaging Computerized (Axial) Tomography (X-rays). Static pictures and high spatial resolution. Horizontal plane only.
Changes in neuronal excitability serve as a mechanism of long-term memory for operant conditioning
 Changes in neuronal excitability serve as a mechanism of long-term memory for operant conditioning Riccardo Mozzachiodi., Fred. D. Lorenzetti, Douglas. A. Baxter and John. H. Byrne Supplementary Fig. 1
Changes in neuronal excitability serve as a mechanism of long-term memory for operant conditioning Riccardo Mozzachiodi., Fred. D. Lorenzetti, Douglas. A. Baxter and John. H. Byrne Supplementary Fig. 1
Mutants with the Ube3a null mutation (designated as AS mice) and mutants carrying the
 Material and Methods Breeding of mutants. Mutants with the Ube3a null mutation (designated as AS mice) and mutants carrying the targeted αcamkii-t305v/t306a mutation which prevents phosphorylation at these
Material and Methods Breeding of mutants. Mutants with the Ube3a null mutation (designated as AS mice) and mutants carrying the targeted αcamkii-t305v/t306a mutation which prevents phosphorylation at these
To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression
 Supplemental figures Supplemental Figure. 1. Silencing expression of Celsr3 by shrna. To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression plasmids for the shrna
Supplemental figures Supplemental Figure. 1. Silencing expression of Celsr3 by shrna. To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression plasmids for the shrna
Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein. complexes during long term depression
 Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
THE ELECTRO-DYNAMICS OF THE DENDRITIC SPACE IN PURKINJE CELLS OF THE CEREBELLUM
 Archives Italiennes de Biologie, 145: 211-233, 2007. THE ELECTRO-DYNAMICS OF THE DENDRITIC SPACE IN PURKINJE CELLS OF THE CEREBELLUM I.B. KULAGINA *, S.M. KOROGOD *, G. HORCHOLLE-BOSSAVIT, C. BATINI AND
Archives Italiennes de Biologie, 145: 211-233, 2007. THE ELECTRO-DYNAMICS OF THE DENDRITIC SPACE IN PURKINJE CELLS OF THE CEREBELLUM I.B. KULAGINA *, S.M. KOROGOD *, G. HORCHOLLE-BOSSAVIT, C. BATINI AND
Figures and figure supplements
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Figures and figure supplements Dendritic mitochondria reach stable positions during circuit development Michelle C Faits et al Faits et al. elife 2015;5:e11583. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.11583
RESEARCH ARTICLE Figures and figure supplements Dendritic mitochondria reach stable positions during circuit development Michelle C Faits et al Faits et al. elife 2015;5:e11583. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.11583
Solid-State Electronics
 Solid-State Electronics 52 (2008) 1364 1373 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Solid-State Electronics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sse Joining microelectronics and microionics: Nerve
Solid-State Electronics 52 (2008) 1364 1373 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Solid-State Electronics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sse Joining microelectronics and microionics: Nerve
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/2/e1601966/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Ultraflexible nanoelectronic probes form reliable, glial scar free neural integration Lan Luan, Xiaoling Wei, Zhengtuo
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/2/e1601966/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Ultraflexible nanoelectronic probes form reliable, glial scar free neural integration Lan Luan, Xiaoling Wei, Zhengtuo
STRATEGY FOR FITTING NEURONAL MODELS TO DUAL PATCH DATA UNDER MULTIPLE STIMULATION PROTOCOLS
 STRATEGY FOR FITTING NEURONAL MODELS TO DUAL PATCH DATA UNDER MULTIPLE STIMULATION PROTOCOLS GongyuY.Shen 1,2, Shuming Ye 1, Wei R.Chen 2, Jens Midtgaard 3, Gordon.M.Shepherd 2, Michael L.Hines 2 1 Zhejiang
STRATEGY FOR FITTING NEURONAL MODELS TO DUAL PATCH DATA UNDER MULTIPLE STIMULATION PROTOCOLS GongyuY.Shen 1,2, Shuming Ye 1, Wei R.Chen 2, Jens Midtgaard 3, Gordon.M.Shepherd 2, Michael L.Hines 2 1 Zhejiang
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Simultaneously recording from four neurons using PatchStar & MicroStar manipulators
 SciMethods: Applications Simultaneously recording from four neurons using PatchStar & MicroStar manipulators Christian Wilms 1, Therese Abrahamsson 2, Per Jesper Sjöström 2 1: Scientifica Ltd. Uckfield,
SciMethods: Applications Simultaneously recording from four neurons using PatchStar & MicroStar manipulators Christian Wilms 1, Therese Abrahamsson 2, Per Jesper Sjöström 2 1: Scientifica Ltd. Uckfield,
Controlling life with photons A new tool based on conjugated polymers
 Controlling life with photons A new tool based on conjugated polymers Maria Rosa Antognazza Center for Nanoscience and Technology @PoliMi The Italian Institute of Technology Controlling life with photons:
Controlling life with photons A new tool based on conjugated polymers Maria Rosa Antognazza Center for Nanoscience and Technology @PoliMi The Italian Institute of Technology Controlling life with photons:
Reliability, discriminability and stochastic synchronization of olfactory neurons
 Sensors and Actuators B xxx (2006) xxx xxx Reliability, discriminability and stochastic synchronization of olfactory neurons Roberto F. Galán a,b,, G. Bard Ermentrout b,c, Nathaniel N. Urban a,b a Carnegie
Sensors and Actuators B xxx (2006) xxx xxx Reliability, discriminability and stochastic synchronization of olfactory neurons Roberto F. Galán a,b,, G. Bard Ermentrout b,c, Nathaniel N. Urban a,b a Carnegie
Long-term dynamics of CA1 hippocampal place codes
 Long-term dynamics of CA1 hippocampal place codes Yaniv Ziv, Laurie D. Burns, Eric D. Cocker, Elizabeth O. Hamel, Kunal K. Ghosh, Lacey J. Kitch, Abbas El Gamal, and Mark J. Schnitzer Supplementary Fig.
Long-term dynamics of CA1 hippocampal place codes Yaniv Ziv, Laurie D. Burns, Eric D. Cocker, Elizabeth O. Hamel, Kunal K. Ghosh, Lacey J. Kitch, Abbas El Gamal, and Mark J. Schnitzer Supplementary Fig.
Detection of Action Potentials In Vitro by Changes in Refractive Index
 Detection of Action Potentials In Vitro by Changes in Refractive Index David Kleinfeld 1 and Arthur LaPorta 2 1 - Department of Physics, University of California, La Jolla, CA 92093-0319. 2- Laboratory
Detection of Action Potentials In Vitro by Changes in Refractive Index David Kleinfeld 1 and Arthur LaPorta 2 1 - Department of Physics, University of California, La Jolla, CA 92093-0319. 2- Laboratory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11685 Supplementary Figure 1. Scoring method for the behavioral assay as in an earlier study 1. 0: no response; 1: pause (hesitate); 2: recoil (anterior withdraw) with or without a turn;
doi:10.1038/nature11685 Supplementary Figure 1. Scoring method for the behavioral assay as in an earlier study 1. 0: no response; 1: pause (hesitate); 2: recoil (anterior withdraw) with or without a turn;
Left Habenula Mediates Light-Preference Behavior in Zebrafish via an Asymmetrical Visual Pathway
 Article Left Habenula Mediates Light-Preference Behavior in Zebrafish via an Asymmetrical Visual Pathway Highlights d Left dorsal habenula (L-dHb) mediates light-preference behavior in zebrafish d d d
Article Left Habenula Mediates Light-Preference Behavior in Zebrafish via an Asymmetrical Visual Pathway Highlights d Left dorsal habenula (L-dHb) mediates light-preference behavior in zebrafish d d d
In Vivo Light-Induced Activation of Neural Circuitry in Transgenic Mice Expressing Channelrhodopsin-2
 Neurotechnique In Vivo Light-Induced Activation of Neural Circuitry in Transgenic Mice Expressing Channelrhodopsin-2 Benjamin R. Arenkiel, 1,2 Joao Peca, 2,3 Ian G. Davison, 1,2 Catia Feliciano, 2,4 Karl
Neurotechnique In Vivo Light-Induced Activation of Neural Circuitry in Transgenic Mice Expressing Channelrhodopsin-2 Benjamin R. Arenkiel, 1,2 Joao Peca, 2,3 Ian G. Davison, 1,2 Catia Feliciano, 2,4 Karl
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Nanoscale localization precision and relative quantification of CB 1 receptors by 3D-STORM imaging (a) Schematic representation of the experimental paradigm for combined confocal/storm
Supplementary Figure 1 Nanoscale localization precision and relative quantification of CB 1 receptors by 3D-STORM imaging (a) Schematic representation of the experimental paradigm for combined confocal/storm
Improving Neuron Stimulation Efficency by Altering Electrode Geometry
 Improving Neuron Stimulation Efficency by Altering Electrode Geometry A. Ghazavi 1, D. Westwick 1, C. Luk 2, N. I. Syed 2 and C. Dalton 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
Improving Neuron Stimulation Efficency by Altering Electrode Geometry A. Ghazavi 1, D. Westwick 1, C. Luk 2, N. I. Syed 2 and C. Dalton 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
Hirudo Medicinalis Local Bending: Myomodulin Effects on the P to AP Synapse
 Hirudo Medicinalis Local Bending: Myomodulin Effects on the P to AP Synapse Masha Day and Eviatar Yemini PHYS 173/BGGN 266 Department of Physics, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093
Hirudo Medicinalis Local Bending: Myomodulin Effects on the P to AP Synapse Masha Day and Eviatar Yemini PHYS 173/BGGN 266 Department of Physics, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 Presynaptic nhibition: Primary Afferent Depolarization in Crayfish Neurons Author(s): Donald Kennedy, Ronald L. Calabrese, Jeffrey J. Wine Source: Science, New Series, Vol. 186, No. 4162 (Nov. 1, 1974),
Presynaptic nhibition: Primary Afferent Depolarization in Crayfish Neurons Author(s): Donald Kennedy, Ronald L. Calabrese, Jeffrey J. Wine Source: Science, New Series, Vol. 186, No. 4162 (Nov. 1, 1974),
Magneto: remote control over neuronal activity and behaviour. Yvette Zarb Division of Neurosurgery
 Magneto: remote control over neuronal activity and behaviour Yvette Zarb Division of Neurosurgery Gene expression Studying the actions specific cells and gene products is essential in understanding their
Magneto: remote control over neuronal activity and behaviour Yvette Zarb Division of Neurosurgery Gene expression Studying the actions specific cells and gene products is essential in understanding their
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Kanaani et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912101/dc1 Figure S1. The K2 rabbit polyclonal antibody is specific for GAD67,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Kanaani et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912101/dc1 Figure S1. The K2 rabbit polyclonal antibody is specific for GAD67,
Changes in Paired-Pulse Facilitation Suggest Presynaptic Involvement in Long-Term Potentiation
 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 1994, 14(g): 53255337 Changes in Paired-Pulse Facilitation Suggest Presynaptic Involvement in Long-Term Potentiation Paul E. Schulz, -* Erik P. Cook,* and Daniel
The Journal of Neuroscience, September 1994, 14(g): 53255337 Changes in Paired-Pulse Facilitation Suggest Presynaptic Involvement in Long-Term Potentiation Paul E. Schulz, -* Erik P. Cook,* and Daniel
Effects of neuroactive agents on axonal growth and pathfinding of. retinal ganglion cells generated from human stem cells
 Effects of neuroactive agents on axonal growth and pathfinding of retinal ganglion cells generated from human stem cells Tadashi Yokoi 1, M.D., Ph.D.; Taku Tanaka 1, Ph.D.; Emiko Matsuzaka 1, Ph.D.; Fuminobu
Effects of neuroactive agents on axonal growth and pathfinding of retinal ganglion cells generated from human stem cells Tadashi Yokoi 1, M.D., Ph.D.; Taku Tanaka 1, Ph.D.; Emiko Matsuzaka 1, Ph.D.; Fuminobu
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure S1. Efficacy of STIM1 knockdown by electroporation of STIM1 sirnas. (a) Western blot of FDB muscles from 4 mice treated with either STIM1-specific sirna (KD)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure S1. Efficacy of STIM1 knockdown by electroporation of STIM1 sirnas. (a) Western blot of FDB muscles from 4 mice treated with either STIM1-specific sirna (KD)
Automated whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology of neurons in vivo
 Nature Methods Automated whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology of neurons in vivo Suhasa B Kodandaramaiah, Giovanni Talei Franzesi, Brian Y Chow, Edward S Boyden & Craig R Forest Supplementary File
Nature Methods Automated whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology of neurons in vivo Suhasa B Kodandaramaiah, Giovanni Talei Franzesi, Brian Y Chow, Edward S Boyden & Craig R Forest Supplementary File
A new planar multielectrode array for extracellular recording: application to hippocampal acute slice
 Journal of Neuroscience Methods 93 (1999) 61 67 www.elsevier.com/locate/jneumeth A new planar multielectrode array for extracellular recording: application to hippocampal acute slice Hiroaki Oka *, Ken
Journal of Neuroscience Methods 93 (1999) 61 67 www.elsevier.com/locate/jneumeth A new planar multielectrode array for extracellular recording: application to hippocampal acute slice Hiroaki Oka *, Ken
TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON SIMULATED HUMAN NODAL ACTION POTENTIALS AND THEIR DEFINING CURRENT KINETICS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON SIMULATED HUMAN NODAL ACTION POTENTIALS AND THEIR DEFINING CURRENT KINETICS Mariya Daskalova 1, Stefan Krustev 2, Diana Stephanova 1 1 Institute of Biophysics and
ORIGINAL ARTICLES TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON SIMULATED HUMAN NODAL ACTION POTENTIALS AND THEIR DEFINING CURRENT KINETICS Mariya Daskalova 1, Stefan Krustev 2, Diana Stephanova 1 1 Institute of Biophysics and
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1. Generation of a synaptobrevin2-mrfp knock-in mouse. (a) Targeting strategy of Syb2-mRFP knock-in mouse leaving the synaptobrevin2 gene locus intact except
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1. Generation of a synaptobrevin2-mrfp knock-in mouse. (a) Targeting strategy of Syb2-mRFP knock-in mouse leaving the synaptobrevin2 gene locus intact except
Reliability and Heterogeneity of Calcium Signaling at Single Presynaptic Boutons of Cerebellar Granule Cells
 7888 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 25, 2007 27(30):7888 7898 Cellular/Molecular Reliability and Heterogeneity of Calcium Signaling at Single Presynaptic Boutons of Cerebellar Granule Cells Stephan
7888 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 25, 2007 27(30):7888 7898 Cellular/Molecular Reliability and Heterogeneity of Calcium Signaling at Single Presynaptic Boutons of Cerebellar Granule Cells Stephan
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Type of file: MOV Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Type of file: MOV Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for
DDendritic spines of central neurons can undergo large,
 Release of calcium from stores alters the morphology of dendritic spines in cultured hippocampal neurons E. Korkotian and M. Segal* Department of Neurobiology, The Weizmann Institute, Rehovot 76100, Israel
Release of calcium from stores alters the morphology of dendritic spines in cultured hippocampal neurons E. Korkotian and M. Segal* Department of Neurobiology, The Weizmann Institute, Rehovot 76100, Israel
Acoustically targeted chemogenetics for the non-invasive control of neural circuits
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0258-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Acoustically targeted chemogenetics for the non-invasive control of neural
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0258-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Acoustically targeted chemogenetics for the non-invasive control of neural
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels
 Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Properties of the H + -activated channel. a. Examples of ion currents at 70 mv caused by a rapid change from ph 7.4 to 6.0. b. ph response curves showing current change normalized
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Properties of the H + -activated channel. a. Examples of ion currents at 70 mv caused by a rapid change from ph 7.4 to 6.0. b. ph response curves showing current change normalized
The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience
 J Physiol 594.4 (2016) pp 915 936 915 The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience Contribution of postsynaptic T-type calcium channels to parallel fibre-purkinje cell synaptic responses Romain Ly 1,GuyBouvier
J Physiol 594.4 (2016) pp 915 936 915 The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience Contribution of postsynaptic T-type calcium channels to parallel fibre-purkinje cell synaptic responses Romain Ly 1,GuyBouvier
Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking
 Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking Chi Wai Lee, Jianzhong Han, James R. Bamburg, Liang Han, Rachel Lynn, and James Q. Zheng Supplementary Figures
Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking Chi Wai Lee, Jianzhong Han, James R. Bamburg, Liang Han, Rachel Lynn, and James Q. Zheng Supplementary Figures
Supplementary Information attached to:
 Supplementary Information attached to: "Involvement of TrkB- and p75 NTR -signaling pathways in two contrasting forms of long-lasting synaptic plasticity" by Sakuragi, S., Tominaga-Yoshino, K. & Ogura,
Supplementary Information attached to: "Involvement of TrkB- and p75 NTR -signaling pathways in two contrasting forms of long-lasting synaptic plasticity" by Sakuragi, S., Tominaga-Yoshino, K. & Ogura,
Measurement of ion channel functions under in vitro conditions. Dr. Norbert Nagy Research Associate Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy
 Measurement of ion channel functions under in vitro conditions Dr. Norbert Nagy Research Associate Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy Topics: -Electrophysiological techniques for basic research
Measurement of ion channel functions under in vitro conditions Dr. Norbert Nagy Research Associate Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy Topics: -Electrophysiological techniques for basic research
Supplementary Figure 2. Cell configuration and definition of the parameters for the equations.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Linear sweep voltammograms of EDOT (10 mm) and BQ (10 mm) measured independently in 0.1 M Bu 4 NClO 4 /MeCN using ITO working electrode (10 mm 10 mm) at a scan rate of 100 mv/s.
Supplementary Figure 1. Linear sweep voltammograms of EDOT (10 mm) and BQ (10 mm) measured independently in 0.1 M Bu 4 NClO 4 /MeCN using ITO working electrode (10 mm 10 mm) at a scan rate of 100 mv/s.
Polymer Composite with Carbon Nanofibers. Aligned during Thermal Drawing as a. Microelectrode for Chronic Neural Interfaces
 Polymer Composite with Carbon Nanofibers Aligned during Thermal Drawing as a Microelectrode for Chronic Neural Interfaces Yuanyuan Guo 1,2*, Shan Jiang 2, Benjamin J.B. Grena 3, Ian F. Kimbrough 4, Emily
Polymer Composite with Carbon Nanofibers Aligned during Thermal Drawing as a Microelectrode for Chronic Neural Interfaces Yuanyuan Guo 1,2*, Shan Jiang 2, Benjamin J.B. Grena 3, Ian F. Kimbrough 4, Emily
The Journal of Neuroscience, 2002, Vol. 22 RC203 1of6
 The Journal of Neuroscience, 2002, Vol. 22 RC203 1of6 Spatiotemporal Pattern of Motoneuron Activation in the Rostral Lumbar and the Sacral Segments during Locomotor-Like Activity in the Neonatal Mouse
The Journal of Neuroscience, 2002, Vol. 22 RC203 1of6 Spatiotemporal Pattern of Motoneuron Activation in the Rostral Lumbar and the Sacral Segments during Locomotor-Like Activity in the Neonatal Mouse
Biology. Subject 1 (Questions are in bold)
 Biology Subject 1 (Questions are in bold) Studying Cellular Neurophysiology often comes down to measuring ion flows. Why ionic flows through membranes are a key issue in neuronal function? In the following
Biology Subject 1 (Questions are in bold) Studying Cellular Neurophysiology often comes down to measuring ion flows. Why ionic flows through membranes are a key issue in neuronal function? In the following
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Haberman et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201108088/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Loss of neurotransmitter release in Drosophila photoreceptors
Supplemental material Haberman et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201108088/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Loss of neurotransmitter release in Drosophila photoreceptors
Branch-Specific Ca 2 Influx from Na -Dependent Dendritic Spikes in Olfactory Granule Cells
 30 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 4, 2006 26(1):30 40 Cellular/Molecular Branch-Specific Ca 2 Influx from Na -Dependent Dendritic Spikes in Olfactory Granule Cells Tibor Zelles, 2 Jamie D. Boyd,
30 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 4, 2006 26(1):30 40 Cellular/Molecular Branch-Specific Ca 2 Influx from Na -Dependent Dendritic Spikes in Olfactory Granule Cells Tibor Zelles, 2 Jamie D. Boyd,
A 256-by-256 CMOS Microelectrode Array for Extracellular Neural Stimulation of Acute Brain Slices. Columbia University, New York, NY
 A 256-by-256 CMOS Microelectrode Array for Extracellular Neural Stimulation of Acute Brain Slices Na Lei 1, K L Shepard 1, Brendon O Watson 2, Jason N MacLean 2, Rafael Yuste 2 1 Department of Electrical
A 256-by-256 CMOS Microelectrode Array for Extracellular Neural Stimulation of Acute Brain Slices Na Lei 1, K L Shepard 1, Brendon O Watson 2, Jason N MacLean 2, Rafael Yuste 2 1 Department of Electrical
Rapid differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional motor neurons by
 Supplementary Information Rapid differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional motor neurons by mrnas encoding transcription factors Sravan Kumar Goparaju, Kazuhisa Kohda, Keiji Ibata,
Supplementary Information Rapid differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional motor neurons by mrnas encoding transcription factors Sravan Kumar Goparaju, Kazuhisa Kohda, Keiji Ibata,
Defining rhythmic locomotor burst patterns using a continuous wavelet transform
 Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: Neurons and Networks in the Spinal Cord Defining rhythmic locomotor burst patterns using a continuous wavelet transform
Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: Neurons and Networks in the Spinal Cord Defining rhythmic locomotor burst patterns using a continuous wavelet transform
Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram showing software and hardware used for head fixation and water delivery, as well as picam-based imaging.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram showing software and hardware used for head fixation and water delivery, as well as picam-based imaging. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Layout of training cage for self-head-fixation.
Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram showing software and hardware used for head fixation and water delivery, as well as picam-based imaging. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Layout of training cage for self-head-fixation.
Attenuated Ca 2+ release in a mouse model of limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2A
 DiFranco et al. Skeletal Muscle (2016) 6:11 DOI 10.1186/s13395-016-0081-y RESEARCH Attenuated Ca 2+ release in a mouse model of limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2A Marino DiFranco 2,3*, Irina Kramerova 1,3,
DiFranco et al. Skeletal Muscle (2016) 6:11 DOI 10.1186/s13395-016-0081-y RESEARCH Attenuated Ca 2+ release in a mouse model of limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2A Marino DiFranco 2,3*, Irina Kramerova 1,3,
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels Improve Contrast Sensitivity of a Retinal Ganglion Cell
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 31, 2005 25(35):8097 8103 8097 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels Improve Contrast Sensitivity of a Retinal Ganglion Cell Narender K. Dhingra,
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 31, 2005 25(35):8097 8103 8097 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels Improve Contrast Sensitivity of a Retinal Ganglion Cell Narender K. Dhingra,
Synapsin Controls Both Reserve and Releasable Synaptic Vesicle Pools during Neuronal Activity and Short-Term Plasticity in Aplysia
 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 15, 2001, 21(12):4195 4206 Synapsin Controls Both Reserve and Releasable Synaptic Vesicle Pools during Neuronal Activity and Short-Term Plasticity in Aplysia Yann Humeau,
The Journal of Neuroscience, June 15, 2001, 21(12):4195 4206 Synapsin Controls Both Reserve and Releasable Synaptic Vesicle Pools during Neuronal Activity and Short-Term Plasticity in Aplysia Yann Humeau,
Supplemental Information. Pioneer Factor NeuroD1 Rearranges. Transcriptional and Epigenetic Profiles. to Execute Microglia-Neuron Conversion
 Neuron, Volume 101 Supplemental Information Pioneer Factor NeuroD1 Rearranges Transcriptional and Epigenetic Profiles to Execute Microglia-Neuron Conversion Taito Matsuda, Takashi Irie, Shutaro Katsurabayashi,
Neuron, Volume 101 Supplemental Information Pioneer Factor NeuroD1 Rearranges Transcriptional and Epigenetic Profiles to Execute Microglia-Neuron Conversion Taito Matsuda, Takashi Irie, Shutaro Katsurabayashi,
Distinctive Quantal Properties of Neurotransmission at Excitatory and Inhibitory Autapses Revealed Using Variance Mean Analysis
 The Journal of Neuroscience, December 10, 2008 28(50):13563 13573 13563 Cellular/Molecular Distinctive Quantal Properties of Neurotransmission at Excitatory and Inhibitory Autapses Revealed Using Variance
The Journal of Neuroscience, December 10, 2008 28(50):13563 13573 13563 Cellular/Molecular Distinctive Quantal Properties of Neurotransmission at Excitatory and Inhibitory Autapses Revealed Using Variance
Asymmetric endocytosis and remodeling of β1-integrin adhesions during growth cone chemorepulsion by MAG
 Asymmetric endocytosis and remodeling of β1-integrin adhesions during growth cone chemorepulsion by MAG Jacob H. Hines, Mohammad Abu-Rub and John R. Henley Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of FM 5-95
Asymmetric endocytosis and remodeling of β1-integrin adhesions during growth cone chemorepulsion by MAG Jacob H. Hines, Mohammad Abu-Rub and John R. Henley Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of FM 5-95
Spying on Cells: Cellular and Subcellular Analysis using Novel Polymeric Micro- and Nanostructures. Xin Zhang Associate Professor.
 Spying on Cells: Cellular and Subcellular Analysis using Novel Polymeric Micro- and Nanostructures Xin Zhang Associate Professor Boston University US-Korea Nano Forum April 2008 Road Map of Nanobio-sensors
Spying on Cells: Cellular and Subcellular Analysis using Novel Polymeric Micro- and Nanostructures Xin Zhang Associate Professor Boston University US-Korea Nano Forum April 2008 Road Map of Nanobio-sensors
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/327/5969/1145/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Cortical Plasticity Induced by Inhibitory Neuron Transplantation Derek G. Southwell, Robert C. Froemke, Arturo Alvarez-Buylla,*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/327/5969/1145/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Cortical Plasticity Induced by Inhibitory Neuron Transplantation Derek G. Southwell, Robert C. Froemke, Arturo Alvarez-Buylla,*
Two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging of primed SNARE complexes in presynaptic terminals and b cells
 Received 5 Jul 215 Accepted 3 Aug 215 Published 6 Oct 215 DOI: 1.138/ncomms9531 OPEN Two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging of primed SNARE complexes in presynaptic terminals and b cells Noriko Takahashi
Received 5 Jul 215 Accepted 3 Aug 215 Published 6 Oct 215 DOI: 1.138/ncomms9531 OPEN Two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging of primed SNARE complexes in presynaptic terminals and b cells Noriko Takahashi
Supplementary Figure S1. Plexiglas barrier prevented diffusion of TTX from mucosal to myenteric chamber. (a) Experimental setup: TTX was added to
 Supplementary Figure S1. Plexiglas barrier prevented diffusion of TTX from mucosal to myenteric chamber. (a) Experimental setup: TTX was added to either chamber. (b) Epithelial stimulation evokes action
Supplementary Figure S1. Plexiglas barrier prevented diffusion of TTX from mucosal to myenteric chamber. (a) Experimental setup: TTX was added to either chamber. (b) Epithelial stimulation evokes action
Neural coding in a single sensory neuron controlling opposite seeking behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans
 Neural coding in a single sensory neuron controlling opposite seeking behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans Atsushi Kuhara, Noriyuki Ohnishi, Tomoyasu Shimowada & Ikue Mori Supplementary Information Supplementary
Neural coding in a single sensory neuron controlling opposite seeking behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans Atsushi Kuhara, Noriyuki Ohnishi, Tomoyasu Shimowada & Ikue Mori Supplementary Information Supplementary
Engineering a functional neuro-muscular junction model in a chip
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Engineering a functional neuro-muscular junction model in a chip Ziqiu Tong, Oscar Seira, Cristina
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Engineering a functional neuro-muscular junction model in a chip Ziqiu Tong, Oscar Seira, Cristina
Pado, a fluorescent protein with proton channel activity can optically monitor membrane potential,
 Pado, a fluorescent protein with proton channel activity can optically monitor membrane potential, intracellular ph, and map gap junctions. Bok Eum Kang and Bradley J. Baker Supplemental figure 1. S1.
Pado, a fluorescent protein with proton channel activity can optically monitor membrane potential, intracellular ph, and map gap junctions. Bok Eum Kang and Bradley J. Baker Supplemental figure 1. S1.
Directing Astroglia from the Cerebral Cortex into Subtype Specific Functional Neurons
 Directing Astroglia from the Cerebral Cortex into Subtype Specific Functional Neurons Christophe Heinrich 1,2, Robert Blum 1., Sergio Gascón 1,2., Giacomo Masserdotti 1., Pratibha Tripathi 2, Rodrigo Sánchez
Directing Astroglia from the Cerebral Cortex into Subtype Specific Functional Neurons Christophe Heinrich 1,2, Robert Blum 1., Sergio Gascón 1,2., Giacomo Masserdotti 1., Pratibha Tripathi 2, Rodrigo Sánchez
CHO Na V 1.4 Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH CHO Na V 1.4 Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH CHO Na V 1.4 Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. B'SYS Na V 1.4 CELL LINE...2 1.1 THE VOLTAGE GATED SODIUM CHANNELS NA V 1.4...2
B SYS GmbH CHO Na V 1.4 Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH CHO Na V 1.4 Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. B'SYS Na V 1.4 CELL LINE...2 1.1 THE VOLTAGE GATED SODIUM CHANNELS NA V 1.4...2
Study of the characteristic of droplet transfer in laser-mig hybrid welding based on the phase matching control of laser pulse and arc waveform
 ICCM2015, 14-17 th July, Auckland, NZ Study of the characteristic of droplet transfer in laser-mig hybrid welding based on the phase matching control of laser pulse and arc waveform *G. Song¹, J.Wang¹,
ICCM2015, 14-17 th July, Auckland, NZ Study of the characteristic of droplet transfer in laser-mig hybrid welding based on the phase matching control of laser pulse and arc waveform *G. Song¹, J.Wang¹,
Alzheimer s Disease. Joachim Herz. STARS January 11, 2010
 Alzheimer s Disease Joachim Herz STARS January 11, 2010 1 The Hallmarks of Alzheimer Disease Amyloid Plaques Neurofibrillary Tangles From: Medical Library of Utah 1906 First description of Alzheimer s
Alzheimer s Disease Joachim Herz STARS January 11, 2010 1 The Hallmarks of Alzheimer Disease Amyloid Plaques Neurofibrillary Tangles From: Medical Library of Utah 1906 First description of Alzheimer s
Glial Cells Maintain Synaptic Structure and Function and Promote Development of the Neuromuscular Junction In Vivo
 Neuron, Vol. 40, 563 580, October 30, 2003, Copyright 2003 by Cell Press Glial Cells Maintain Synaptic Structure and Function and Promote Development of the Neuromuscular Junction In Vivo Linga V. Reddy,
Neuron, Vol. 40, 563 580, October 30, 2003, Copyright 2003 by Cell Press Glial Cells Maintain Synaptic Structure and Function and Promote Development of the Neuromuscular Junction In Vivo Linga V. Reddy,
Supplementary Information. spasticity after spinal cord injury
 Supplementary Information Down-regulation of the potassium-chloride cotransporter KCC2 contributes to spasticity after spinal cord injury Pascale Boulenguez, Sylvie Liabeuf, Rémi Bos, Hélène Bras, Céline
Supplementary Information Down-regulation of the potassium-chloride cotransporter KCC2 contributes to spasticity after spinal cord injury Pascale Boulenguez, Sylvie Liabeuf, Rémi Bos, Hélène Bras, Céline
1.7 on Nanion's SyncroPatch 384PE. The electrophysiology team at Nanion Technologies GmbH, Munich, Germany. Cells were kindly provided by Anaxon.
 Channel: h 1.7 Cells: CHO Tools: SyncroPatch 384PE Characterization of h 1.7 on Nanion's SyncroPatch 384PE The electrophysiology team at, Munich, Germany. Cells were kindly provided by Anaxon. Summary
Channel: h 1.7 Cells: CHO Tools: SyncroPatch 384PE Characterization of h 1.7 on Nanion's SyncroPatch 384PE The electrophysiology team at, Munich, Germany. Cells were kindly provided by Anaxon. Summary
Department of Physiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut 06510
 0270.6474/83/0311-2251$02.00/O The Journal of Neuroscience Copyright 0 Society for Neuroscience Vol. 3, No. 11, pp. 2251-2262 Printed in U.S.A. November 1983 OPTICAL MONITORING OF ACTIVITY FROM MANY AREAS
0270.6474/83/0311-2251$02.00/O The Journal of Neuroscience Copyright 0 Society for Neuroscience Vol. 3, No. 11, pp. 2251-2262 Printed in U.S.A. November 1983 OPTICAL MONITORING OF ACTIVITY FROM MANY AREAS
