Short Technical Reports
|
|
|
- Lorraine Lambert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Efficient Long-PCR Site- Specific Mutagenesis of a High GC Template BioTechniques 21: (September 1996) ABSTRACT A long PCR method was developed for the efficient site-specific mutagenesis of herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) DNA fragments with high GC content. In this protocol, a PCR product was partially extended first using a cloned DNA fragment. The final mutagenized fragment was produced after a second extension using another PCR product and final amplification using external primers. The sequential use of two extension reactions increased the predicted frequency of the engineered mutation in the final product to 100%. This method was used to generate a mutated glycoprotein K (gk) gene specified by HSV-1. A recombinant virus that carried the mutated gk gene caused extensive cell fusion of infected cells. INTRODUCTION One of the principal ways for polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-assisted mutagenesis is the overlap extension method, which requires that two different PCR DNA fragments overlap at the site to be mutagenized. This overlap is provided by a pair of mutagenic primers that produce the desired mutation (6,7). A variation of this two-step PCR theme is the megaprimer method, which utilizes one entire PCR fragment as a megaprimer and a distant primer (9). We have developed a long-pcr sitedirected mutagenesis method that results in nearly 100% mutagenesis of the final DNA products. This method utilizes long-pcr enzymes and conditions to efficiently amplify DNA fragments with above 50% GC content. We demonstrate this method by generating a new restriction endonuclease site and a missense mutation in the glycoprotein K (gk) gene specified by herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). A recombinant virus that carried the mutated gk gene caused extensive cell fusion of infected cells. MATERIALS AND METHODS Equipment and Reagents for PCR All experiments were performed using the GeneAmp PCR System 9600 (Perkin-Elmer, Norwalk, CT, USA). All PCR reagents were provided as part of the XL PCR Kit (Part No. N ; Perkin-Elmer). Hot-Start PCR was performed with AmpliWax PCR Gem 50 (Part No. N ; Perkin-Elmer).
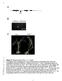
2 Restriction Enzymes, Bacterial Strains and Plasmid Vectors Restriction enzymes were obtained from New England Biolabs (Beverly, MA, USA). Plasmid vector puc19 and its host E. coli DH5αwere obtained from Bethesda Research Laboratories (Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Viruses and Cells HSV-1(KOS) was originally obtained from Dr. P.A. Schaffer, Dana- Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA. Virus stocks were made and titered as described previously (1). Transfections were carried out on rabbit skin cells using the calcium phosphate technique (3,5). Primers for Long PCR and Mutagenesis Primers P1 (5 -GTT CAT AAC CCA CGA TCG CAG TTG-3 ), P2 (5 - ΑΤΑ CGC TGG CTG GGT TGG TCT TGG T-3 ),mutagenic primer-mp3 (5 - TGG GGC GTA CTA CGT AAA TAC ATC-3 ), mutagenic primer-mp4 (5 - CGA TGT ATT TAC GTA GTA CGC CCC ACC-3 ), P5 (5 -GTT CGC GGT ACC CTG CAG CAA AG-3 ) and P6 (5 -ACG GCC AAT TGG GAC CCA TGG GCG G-3 ) were synthesized in our laboratory on an Applied Biosystems DNA Synthesizer Model 394 (Perkin-Elmer/Applied Biosystems Division [PE/ABI], Foster City, CA, USA) using phosphoramidite chemistry. The approximate location of primers P1, P2, MP3, MP4 and the gk gene on the viral genomic map is shown in Figure 1. The PCR fragment produced by the P1 and P2 primer pair was predicted to be 3340-bp-long with an average GC content of 64.3%. The DNA fragment amplified by P1/MP3 had a GC content of 66.1%, and the MP4/P2 PCR product had a GC content of 61.0%. Primers P5 and P6 bracket the point mutation and were used for detection of the engineered mutation in mutant viruses (Figure 1). Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the mutagenesis procedure. (A) The HSV-1 genome showing the location of all the primers and the UL53 (gk) gene. The location of the engineered mutation is denoted (^). (B and C) The P1/MP3 PCR product (B) and the MP4/P2 PCR product (C). (D) The cloned DNA gk fragment used for the first extension reaction. (E) The first extension reaction (---) of the P1/MP3 PCR product using the cloned gk DNA fragment. (F) The extension of the PCR product from step E using the PCR DNA fragment represented in step C. (G) The final PCR product using primers P1 and P2. This DNA fragment contains the desired mutation (^). Figure 2. Agarose gel electrophoresis of the different dsdna fragments amplified by PCR. Lane 1: λ phage DNA digested with HindIII (marker); lane 2: cloned gk 1020-bp DNA fragment; lane 3: P1/MP bp PCR product; lane 4: MP4/P bp PCR product; lane 5: P1/P bp PCR product; lane 6: Molecular mass marker (1-kbp ladder). 474 BioTechniques Vol. 21, No. 3 (1996)
3 Extension of the P1/MP3 PCR Product Using the Cloned gk DNA Fragment The PCR-derived DNA fragment (500 ng) was mixed with the cloned DNA fragment (125 ng), denatured and re-annealed. The total volume of DNA mixture was brought up to 55.6 µl, and the extension reaction mixture (100 µl) consisted of 55.6 µl DNA solution, 4.4 µl Mg(OAc) 2, 30.0 µl 3.3 XL buffer, 8.0 µl of 2.5 mm stock dntps, 2.0 µl rtth Pol. XL. The thermal profile was 3 min at 95 C; 1 min at 94 C and 15 min at 72 C repeated 7 times. Final Overlap-Extension The P1/MP3 PCR extended product (50 ng) was gel-purified using the Prep- A-Gene purification method as detailed by the manufacturer (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and was used for the next overlap-extension with the MP4/P2 PCR product (50 ng). The extension reaction mixture (100 µl) was as described above.the thermal profile was 3 min at 95 C; 1 min at 94 C and 15 min at 72 C repeated 3 times. Final PCR Conditions The primer pair P1/P2 was used to amplify the 3340-bp DNA fragment. One microliter undiluted and 1 µl from a 1:10 dilution of the final overlap-extension reaction were used in the final PCR. PCR parameters were 3 min at 95 C; 30 min at 94 C and 8 min at 68 C repeated 30 times and final extension for 15 min at 72 C. Hot-start conditions were applied according to the manufacturer (PE/ABI), and the composition of lower and upper reaction mixtures were as follows: lower reaction mixture (40 µl total) was: 12.4 µl water, 12.0 µl 3.3 XL Buffer, 8.0 µl of 2.5 mm stock dntps, 1.6 µl of 20 µm stock Primer P1, 1.6 µl of 20 µμ stock Primer P2, 4.4 µl of 25 mm stock Mg(OAc) 2 ; upper reaction mixture (60 µl) was: 38 µl water, 18 µl 3.3 XL Buffer, 1 µl of 7 µg/ml stock viral DNA, 2 µl of 2 U/mL stock rtth DNA Pol. XL. Preparation of Viral DNA and Marker-Transfer Experiments Viral DNAs were prepared as described (10). For marker-transfer studies, Vero cells were co-transfected with DNA fragments produced by PCR and intact wild-type HSV-1(KOS) viral DNA (1,2). For PCR analysis, viral DNA mini-preparations were prepared from plaque-purified virus stocks as described previously (1). Viral DNAs from each of the viral plaques were subjected to PCR analysis using internal gk primers P5 and P6, and the subsequent PCR products were digested with restriction endonuclease SnaBI. RESULTS Long-PCR of the HSV-1 gk Gene Region The gk gene is approximately 63% GC-rich; however, it contains short segments ( bp) with over 80% GC content (11). We were able to efficiently Figure 3. Agarose gel electrophoresis of dsdna fragments after the first extension. Lane 1: P1/MP bp PCR product; lane 2: λ phage DNA digested with HindIII (marker); lane 3: P1/MP3 PCR product after extension with the cloned gk DNA fragment; lane 4: cloned gk DNA fragment before extension (1020 bp); lane 5: P1/P bp PCR product. Figure 4. Agarose gel electrophoresis of mutagenized fragments restricted with SnaBI. Lane 1: λ phage DNA digested with HindIII (marker); lanes 2 and 3: P1/P2 mutagenized PCR products from fully and partially extended DNA species shown in Figure 3, lane 3; lane 4: P1/P2 unmutagenized PCR products; lanes 5 7: DNA fragments shown on lanes 2 4, respectively, digested with SnaBI; lane 8: molecular mass marker (1-kbp DNA ladder). Figure 5. Agarose gel electrophoresis of viral PCR products restricted with SnaBI. P5/P6 PCR product from a putative mutagenized syncytial mutant virus (lane 1), laboratory virus strain KOS (lane 3) and laboratory syncytial strain MP (lane 5). These three PCR DNA fragments were digested with SnaBI (lanes 2, 4 and 6, respectively). λ phage DNA digested with HindIII (lane 7). 476 BioTechniques Vol. 21, No. 3 (1996)
4 amplify up to 7 kbp of DNA sequence spanning the gk gene with an average GC content of over 67%. PCR of a 7- kbp DNA fragment produced approximately 0.3 µg per 100 µl reaction in comparison with over 2 µg for templates of up to 4.5 kbp (data not shown). PCR Mutagenesis We designed a pair of mutagenesis primers, MP3 and MP4, that created a new restriction endonuclease site (SnaBI and an Ala to Val change at position 40 of the gk primary sequence. Herpes simplex viruses that have Val at position 40 are known to cause extensive cell fusion of infected cells in tissue culture (4,8). The mutagenesis procedure is outlined in Figure 1 and is composed of three main steps. In step 1, the cloned gk gene is used to extend the P1:MP3 PCR product. Fifty percent of the extension reaction products are predicted to contain the engineered mutation. Similarly, in step 2, a second extension is predicted to raise the frequency of the mutation to 100%. The relevant PCR products are shown in Figure 2. P1/P2 produced a 3340-bp DNA fragment, primer pair P1/MP3 produced a 2257-bp DNA fragment and primer pair MP4/P2 produced a 1108-bp DNA fragment. A 1020-bp HindIII/HindIII DNA fragment containing the entire gk gene sequence was excised from plasmid vector puc19 and gel-purified. The primers that carried the desired mutations were MP3 and MP4 (Figure 1). The cloned gk DNA fragment (Figure 1D) was used to extend the 2257-bp DNA fragment generated by primer pair P1/MP3 (Figure 1B). The results of this experiment are shown in Figure 3. The P1/MP3 PCR-extended product produced two slower migrating DNA species. The largest DNA fragment was tentatively identified as representing the fully extended 3146-bp product. The second DNA species was assumed to represent a partially extended product. Each of these two DNA species was gel-purified and used separately for the next overlap extension with the MP4/P2 PCR product (Figure 1F). Final amplification was performed with primer pair P1/P2 (Figure 1G). PCRamplified DNA fragments of full length were produced by both the putative fully extended DNA species (Figure 4, lane 2) and by the partially extended DNA species (Figure 4, lane 3). Final PCR products were tested for the presence of a new SnaBI restriction endonuclease site by digestion with SnaBI. The unmutagenized P1/P2 PCR product (Figure 4, lane 4) contains a single SnaBI site, which upon digestion, produces two DNA fragments (Figure 4, lane 7). As expected, mutagenized PCR products (Figure 4, lanes 2 and 3) contained an additional SnaBI site producing three DNA fragments of the expected apparent molecular mass (Figure 4, lanes 5 and 6). A small amount of either unmutagenized or partially cleaved PCR product was also detected, as evidenced by the DNA species (Figure 4, lanes 5 and 6) that co-migrated with a similar DNA fragment visible in the unmutagenized sample (Figure 4, lane 7). Marker Transfer of the Syn1 Mutation (Ala to Val Change) and the SnaBI Restriction Site into the KOS Genome Full-length mutagenized DNA fragments were purified from agarose gels and were co-transfected with intact HSV-1(KOS) viral DNA into rabbit skin cells. Individual viral plaques were collected, virus was plaque-purified three times under agarose overlay and viral DNA stocks were prepared as described previously (1,2). Viral DNAs were subjected to PCR using primers P5 and P6, which were designed to bracket the site of the mutation (Figure 1A). P5 is located 377 bases 5 to the engineered SnaBI site, and P6 is located 1030 bases 3 to the SnaBI site. Therefore, digestion by SnaBI of the P5/P6 product is expected to produce two DNA species of approximately 377 and 1030 bp. PCR fragments obtained from purified viral DNAs were restricted with SnaBI. Viral isolate SJ101, which caused extensive cell fusion, contained the engineered SnaBI restriction site as seen by the predicted restriction profile (Figure 5, lane 2). Control viral strains HSV-1(KOS) (Figure 5, lane 1) and HSV-1(MP) (Figure 5, lane 6) did not contain this SnaBI restriction site. Vol. 21, No. 3 (1996) BioTechniques 477
5 DISCUSSION Mis-incorporation of nucleotides by the error-prone Taq DNA polymerase can prematurely terminate DNA synthesis during PCR amplification and result in lower PCR yields and inability to amplify relatively long DNA fragments of greater than 2 kbp. To increase the amplification efficiency of HSV-1 DNA fragments with an average GC content of 67%, and to overcome the possibility of generating random mutations within the amplified DNA sequence, we exclusively used the Long PCR Kit manufactured by Perkin-Elmer. This PCR kit utilizes a mixture of rtth DNA Polymerase, XL and Vent DNA Polymerases, which is known to correct mis-incorporated nucleotides and long-pcr conditions that result in efficient amplification of DNA templates. A major advantage of the site-directed mutagenesis method presented here over the splice overlap and megaprimer methods is that the sequential use of two extension steps and use of the cloned gk DNA fragment increases the predicted frequency of the engineered mutation in the final product to nearly 100%. This is because DNA polymerases can extend only in the 5 to 3 direction (Figure 1). The overlap of the cloned DNA gk fragment with the first PCR product is only 106 bases, yet it results in an efficient extension of approximately 3000 bases. It is possible that much longer primers of approximately nucleotides may render a single-step overlap-extension protocol feasible. However, long primers require substantial purification, and they are expensive to synthesize. The visualization and gel purification of the initially extended PCR using the cloned gk gene provide an intermediate quality-control checkpoint, which, in our opinion, outweighs the additional labor associated with this purification. We have found that this is an efficient and reproducible method to mutagenize long DNA fragments of herpes simplex viruses with above 50% GC content. REFERENCES 1.Baghian, A., L. Huang, S. Newman, S. Jayachendra and K.G. Kousoulas Truncation of the carboxy-terminal 28 amino acids of glycoprotein B specified by herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant amb causes extensive cell fusion. J. Virol. 67: Cavalcoli, J.D., A. Baghian, F.L. Homa and K.G. Kousoulas Resolution of genotypic and phenotypic properties of herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature sensitive mutant (KOS) tsz47: evidence for allelic complementation in the UL28 gene. Virology 197: Chen, C. and H. Okayama High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: DebRoy, C Nucleotide sequence of the herpes simplex virus type-2 syn gene that causes cell fusion. Gene 88: Graham, F.L. and A.J. van der Eb A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology 52:
6 6.Ho, S.N., H.D. Hunt, R.M. Horton, J.K. Pullen and L.R. Pease Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77: Horton, R.M., S.N. Ho, J.K. Pullen, H.D. Hunt, Z. Cai and L.R. Pease Gene splicing by overlap extension. Methods Enzymol. 217: Pogue-Geile, K.L., G.T. Lee, S.K. Shapira and P.G. Spear Fine mapping of mutations in the fusion-inducing MP strain of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology 136: Sarkar, G. and S.S. Sommer The megaprimer method of site-directed mutagenesis. BioTechniques 8: Walboomers, J.M. and J. Ter Schagget A new method for the isolation of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA. Virology 74: Zhang, X. and K.G. Kousoulas Direct sequencing of PCR-amplified high GC DNA. BioTechniques 14: This publication is identified as #120 of the VMP Gene Probes and Expression Systems Laboratory GeneLab. This work was supported by Public Health Service Grant No. A to K.G.K. G.R. was supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute through an undergraduate science enhancement grant to Louisiana State University. V.C. is a senior postdoctoral fellow and visiting scientist from the Institute of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Kiev, Ukraine. Address correspondence to Konstantin G. Kousoulas, Department of Veterinary Microbiology & Parasitology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA , USA. Internet: vtgusk@lsuvax.sncc.lsu.edu Received 30 June 1995; accepted 18 March Vladimir Chouljenko, Sukhanya Jayachandra, Galina Rybachuk and Konstantin G. Kousoulas School of Veterinary Medicine Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA, USA Quantitative Multiple Competitive PCR of HIV-1 DNA in a Single Reaction Tube BioTechniques 21: (September 1996) ABSTRACT A quantitative multiple competitive PCR (QMC-PCR) for determination of DNA copy numbers is described. Four competitive DNA templates for the env region of HIV-1 were constructed with sizes longer (187 and 163 bp) or shorter (122 and 105 bp) than the 142 bp of the wild-type PCR product. Varying amounts of each of these competitors are introduced together with the sample into a single reaction tube. Since competitors and wild-type fragments share the same primer recognition sequence (SK68/SK69), amplification occurs according to the rate of the introduced copy numbers. The PCR products are run on an agarose gel, and the copy number of the sample is determined by analyzing the bands with a video densitometer and calculating the equivalence point in a linear regression plot. INTRODUCTION Over the past years, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology has been widely used for highly sensitive molecular diagnosis of infectious agents, including human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). For quantitation of specific nucleic acid templates, competitive PCR seems to be the most promising approach. This method overcomes the variabilities of PCR by co-amplification of internal competitive standard DNA and specific template in the same reaction tube and thus allows more accurate quantitation. Although a great variety of competitive PCR protocols are in use (1 3,5,8), they all involve mixing varying amounts of competitor, usually different in size from the wild-type product, with a constant amount of the sample to be determined. This requires at least four to five different PCRs to obtain an accurate determination of copy number in a regression plot. Recently this meth- Vol. 21, No. 3 (1996)
Cat. # Product Size DS130 DynaExpress TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1
 Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base. excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps
 Supporting information Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps Jan Riedl, Aaron M. Fleming, and Cynthia J. Burrows*
Supporting information Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps Jan Riedl, Aaron M. Fleming, and Cynthia J. Burrows*
PCR analysis was performed to show the presence and the integrity of the var1csa and var-
 Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis. Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010
 Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures)
 Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau What is Biotechnology? From Merriam-Webster: the manipulation of living organisms or their components to produce useful usually commercial
7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau What is Biotechnology? From Merriam-Webster: the manipulation of living organisms or their components to produce useful usually commercial
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR
 Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification
 Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis
 3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
Disease and selection in the human genome 3
 Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Legends for supplementary figures 1-3
 High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit
 1. Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit For fast and sensitive one-step RT-PCR www.tiangen.com/en RT121221 Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit Kit Contents Cat. no. KR113 Contents Hotmaster Taq Polymerase (2.5 U/μl) Quant
1. Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit For fast and sensitive one-step RT-PCR www.tiangen.com/en RT121221 Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit Kit Contents Cat. no. KR113 Contents Hotmaster Taq Polymerase (2.5 U/μl) Quant
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Data Sheet Quick PCR Cloning Kit
 Data Sheet Quick PCR Cloning Kit 6044 Cornerstone Ct. West, Ste. E DESCRIPTION: The Quick PCR Cloning Kit is a simple and highly efficient method to insert any gene or DNA fragment into a vector, without
Data Sheet Quick PCR Cloning Kit 6044 Cornerstone Ct. West, Ste. E DESCRIPTION: The Quick PCR Cloning Kit is a simple and highly efficient method to insert any gene or DNA fragment into a vector, without
Expression of Recombinant Proteins
 Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Hes6. PPARα. PPARγ HNF4 CD36
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
Supplementary. Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids. complementary to positions from 77 of the SRα '- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C
 Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual
 MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor AtADF4 mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB
 Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Materials Protein synthesis kit. This kit consists of 24 amino acids, 24 transfer RNAs, four messenger RNAs and one ribosome (see below).
 Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Y-chromosomal haplogroup typing Using SBE reaction
 Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Amplification Products for PCR and RT-PCR
 Selection guide Polymerase Hot start Comment UptiTherm DNA pol. no Most economic. Lower error rate than Taq polymerase Available in several formats, master mix including or not dntp, Mg 2+..., in gel format
Selection guide Polymerase Hot start Comment UptiTherm DNA pol. no Most economic. Lower error rate than Taq polymerase Available in several formats, master mix including or not dntp, Mg 2+..., in gel format
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines
 Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
MOLECULAR CLONING OF THE PHILIPPINE ISOLATE OF BANANA BUNCHY TOP VIRUS (BBTV)
 Trans. Natl. Acad.Sci. Tech. Philippines 21: 287-291 (1999). ISSN 0 J J 5-8848 MOLECULAR CLONING OF THE PHILIPPINE ISOLATE OF BANANA BUNCHY TOP VIRUS (BBTV) VERMANDO M. AQUINO I, HUI WANG2, EVELYN MAE
Trans. Natl. Acad.Sci. Tech. Philippines 21: 287-291 (1999). ISSN 0 J J 5-8848 MOLECULAR CLONING OF THE PHILIPPINE ISOLATE OF BANANA BUNCHY TOP VIRUS (BBTV) VERMANDO M. AQUINO I, HUI WANG2, EVELYN MAE
Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template.
 Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template. Fengtao Luo 1, Xiaolan Du 1, Tujun Weng 1, Xuan Wen 1, Junlan Huang 1, Lin Chen 1 Running title: Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis
Efficient Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis directly from Genomic Template. Fengtao Luo 1, Xiaolan Du 1, Tujun Weng 1, Xuan Wen 1, Junlan Huang 1, Lin Chen 1 Running title: Multi-site-directed Mutagenesis
MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3
 Cat. # R076A For Research Use MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. General PCR Reaction Mix... 3 V. Primer Design...
Cat. # R076A For Research Use MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. General PCR Reaction Mix... 3 V. Primer Design...
PrimeSTAR Max DNA Polymerase
 Cat. # R045A For Research Use PrimeSTAR Max DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Components...3 Storage...3 General Composition of PCR Reaction Mixture...3 V.
Cat. # R045A For Research Use PrimeSTAR Max DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Components...3 Storage...3 General Composition of PCR Reaction Mixture...3 V.
A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique Xiaoli Zhu,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique Xiaoli Zhu,
FAQs: PCR Polymerases from Takara Bio
 FAQs: PCR Polymerases from Takara Bio Contents: PCR Basics Q1 Q2 Q3 What parameters do I need to consider when designing primers? What is the optimum amount of template to use? Which conditions are particularly
FAQs: PCR Polymerases from Takara Bio Contents: PCR Basics Q1 Q2 Q3 What parameters do I need to consider when designing primers? What is the optimum amount of template to use? Which conditions are particularly
P HENIX. PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide Tools For Life Science Discovery RESEARCH PRODUCTS
 PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide PHENIX offers a broad line of premium quality PCR Enzymes. This PCR Enzyme Guide will help simplify your polymerase selection process. Each DNA Polymerase has different characteristics
PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide PHENIX offers a broad line of premium quality PCR Enzymes. This PCR Enzyme Guide will help simplify your polymerase selection process. Each DNA Polymerase has different characteristics
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Amplified segment of DNA can be purified from bacteria in sufficient quantity and quality for :
 Transformation Insertion of DNA of interest Amplification Amplified segment of DNA can be purified from bacteria in sufficient quantity and quality for : DNA Sequence. Understand relatedness of genes and
Transformation Insertion of DNA of interest Amplification Amplified segment of DNA can be purified from bacteria in sufficient quantity and quality for : DNA Sequence. Understand relatedness of genes and
MCB421 FALL2005 EXAM#3 ANSWERS Page 1 of 12. ANSWER: Both transposon types form small duplications of adjacent host DNA sequences.
 Page 1 of 12 (10pts) 1. There are two mechanisms for transposition used by bacterial transposable elements: replicative (Tn3) and non-replicative (Tn5 and Tn10). Compare and contrast the two mechanisms
Page 1 of 12 (10pts) 1. There are two mechanisms for transposition used by bacterial transposable elements: replicative (Tn3) and non-replicative (Tn5 and Tn10). Compare and contrast the two mechanisms
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques
 Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Glycoprotein B Specified by Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 1993, p. 2396-2401 0022-538X/93/042396-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 67, No. 4 Truncation of the Carboxy-Terminal 28 Amino Acids of Glycoprotein
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 1993, p. 2396-2401 0022-538X/93/042396-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 67, No. 4 Truncation of the Carboxy-Terminal 28 Amino Acids of Glycoprotein
Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering
 Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering Harris Wang, Ph.D. Department of Systems Biology Department of Pathology & Cell Biology http://wanglab.c2b2.columbia.edu Rise of Genomics An Expanding Toolbox Esvelt
Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering Harris Wang, Ph.D. Department of Systems Biology Department of Pathology & Cell Biology http://wanglab.c2b2.columbia.edu Rise of Genomics An Expanding Toolbox Esvelt
MUTAGENESIS OF THE PROMOTER OF THE OIL PALM HOMOGENTISATE GERANYLGERANYL TRANSFERASE GENE (HGGT) BY PCR-DRIVEN OVERLAP EXTENSION
 ICBAA2017-30 MUTAGENESIS OF THE PROMOTER OF THE OIL PALM HOMOGENTISATE GERANYLGERANYL TRANSFERASE GENE (HGGT) BY PCR-DRIVEN OVERLAP EXTENSION Mohd Shahrul Nizwanshah Karim and Siti Nor Akmar Abdullah Laboratory
ICBAA2017-30 MUTAGENESIS OF THE PROMOTER OF THE OIL PALM HOMOGENTISATE GERANYLGERANYL TRANSFERASE GENE (HGGT) BY PCR-DRIVEN OVERLAP EXTENSION Mohd Shahrul Nizwanshah Karim and Siti Nor Akmar Abdullah Laboratory
User Manual. Catalog No.: DWSK-V101 (10 rxns), DWSK-V102 (25 rxns) For Research Use Only
 DNA Walking SpeedUp TM Kit SpeedUp Sequencing SpeedUp BAC Clone Sequencing SpeedUp Genome Walking SpeedUp Transgene Location Detection SpeedUp Deletion/ Insertion/ Isoform Detection User Manual Version
DNA Walking SpeedUp TM Kit SpeedUp Sequencing SpeedUp BAC Clone Sequencing SpeedUp Genome Walking SpeedUp Transgene Location Detection SpeedUp Deletion/ Insertion/ Isoform Detection User Manual Version
PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System
 PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0178 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 3 IV Shipping and Storage. 3 V Simplified Procedures. 3 VI Detailed
PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0178 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 3 IV Shipping and Storage. 3 V Simplified Procedures. 3 VI Detailed
Regulation of enzyme synthesis
 Regulation of enzyme synthesis The lac operon is an example of an inducible operon - it is normally off, but when a molecule called an inducer is present, the operon turns on. The trp operon is an example
Regulation of enzyme synthesis The lac operon is an example of an inducible operon - it is normally off, but when a molecule called an inducer is present, the operon turns on. The trp operon is an example
QUICK-Clone TM User Manual. cdna
 QUICK-Clone TM User Manual cdna PT1150-1 (PR752268) Published 25 May 2007 Table of Contents I. Introduction 3 II. Applications Discussion 4 A. Primer Design 4 B. Setting up the PCR Reaction 4 C. Example
QUICK-Clone TM User Manual cdna PT1150-1 (PR752268) Published 25 May 2007 Table of Contents I. Introduction 3 II. Applications Discussion 4 A. Primer Design 4 B. Setting up the PCR Reaction 4 C. Example
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Platinum II Taq Hot-Start DNA Polymerase for high-throughput PCR
 WHITE PAPER Platinum II Taq Hot-Start DNA Polymerase Platinum II Taq Hot-Start DNA Polymerase for high-throughput PCR Abstract The advances in thermal cycler technology permit a substantial increase in
WHITE PAPER Platinum II Taq Hot-Start DNA Polymerase Platinum II Taq Hot-Start DNA Polymerase for high-throughput PCR Abstract The advances in thermal cycler technology permit a substantial increase in
Executive Summary. clinical supply services
 clinical supply services case study Development and NDA-level validation of quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qpcr) procedure for detection and quantification of residual E.coli genomic DNA Executive
clinical supply services case study Development and NDA-level validation of quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qpcr) procedure for detection and quantification of residual E.coli genomic DNA Executive
Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR
 Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual
 Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual Cat. Nos. 632638, 632639, 632635, 632636, 632637 (040618) 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA U.S. Technical Support:
Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual Cat. Nos. 632638, 632639, 632635, 632636, 632637 (040618) 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA U.S. Technical Support:
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean SYHT0H2 by Real-time PCR. Validated Method
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology and Genomics Unit Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean SYHT0H2 by Real-time PCR
EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology and Genomics Unit Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean SYHT0H2 by Real-time PCR
Recombinant DNA recombinant DNA DNA cloning gene cloning
 DNA Technology Recombinant DNA In recombinant DNA, DNA from two different sources, often two species, are combined into the same DNA molecule. DNA cloning permits production of multiple copies of a specific
DNA Technology Recombinant DNA In recombinant DNA, DNA from two different sources, often two species, are combined into the same DNA molecule. DNA cloning permits production of multiple copies of a specific
Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Table of Contents. I. Description...2. Components...2. Storage...2. Features...2. V. General Composition of PCR Reaction Mixture...
 Table of Contents I. Description...2 II. Components...2 III. Storage...2 IV. Features...2 V. General Composition of PCR Reaction Mixture...5 VI. PCR Conditions...5 VII. Optimization of Parameters...6 VIII.
Table of Contents I. Description...2 II. Components...2 III. Storage...2 IV. Features...2 V. General Composition of PCR Reaction Mixture...5 VI. PCR Conditions...5 VII. Optimization of Parameters...6 VIII.
Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design
 Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a powerful technique used for the amplification of a specific segment of a nucleic acid
Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a powerful technique used for the amplification of a specific segment of a nucleic acid
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
Supplementary Information. Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins
 Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual
 Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual Cat. No. 631444 (120114) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA
Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual Cat. No. 631444 (120114) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA
California Institute of Technology. Directed evolution. Dr. F.H. Arnold s lab
 Directed evolution. Dr. F.H. Arnold s lab May 4, 1999 Mutagenic PCR -[Mn] The amount of Mn used in the reaction should be titrated to produce the desired mutagenic rate. Libraries that have close to 30%
Directed evolution. Dr. F.H. Arnold s lab May 4, 1999 Mutagenic PCR -[Mn] The amount of Mn used in the reaction should be titrated to produce the desired mutagenic rate. Libraries that have close to 30%
Fast and efficient site-directed mutagenesis with Platinum SuperFi DNA Polymerase
 APPLICATION NOTE Platinum Superi Polymerase ast and efficient site-directed mutagenesis with Platinum Superi Polymerase Introduction Site-directed mutagenesis is one of the most essential techniques to
APPLICATION NOTE Platinum Superi Polymerase ast and efficient site-directed mutagenesis with Platinum Superi Polymerase Introduction Site-directed mutagenesis is one of the most essential techniques to
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.20 - BIOTECHNOLOGY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), , DOI: /bi00034a013
 Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
GENOTYPING BY PCR PROTOCOL FORM MUTANT MOUSE REGIONAL RESOURCE CENTER North America, International
 Please provide the following information required for genetic analysis of your mutant mice. Please fill in form electronically by tabbing through the text fields. The first 2 pages are protected with gray
Please provide the following information required for genetic analysis of your mutant mice. Please fill in form electronically by tabbing through the text fields. The first 2 pages are protected with gray
SuperiorScript III cdna Synthesis Kit Instruction Manual
 SuperiorScript III cdna Synthesis Kit Instruction Manual Cat.# EZ405S, EZ405M SuperiorScript III cdna Synthesis Kit Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Kit... 4 III. Procedure... 5 IV. Control Experiment
SuperiorScript III cdna Synthesis Kit Instruction Manual Cat.# EZ405S, EZ405M SuperiorScript III cdna Synthesis Kit Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Kit... 4 III. Procedure... 5 IV. Control Experiment
Puro. Knockout Detection (KOD) Kit
 Puro Knockout Detection (KOD) Kit Cat. No. CC-03 18 Oct. 2016 Contents I. Kit Contents and Storage II. Product Overview III. Methods Experimental Outline Genomic DNA Preparation Obtain Hybrid DNA Digest
Puro Knockout Detection (KOD) Kit Cat. No. CC-03 18 Oct. 2016 Contents I. Kit Contents and Storage II. Product Overview III. Methods Experimental Outline Genomic DNA Preparation Obtain Hybrid DNA Digest
BSCI410-Liu/Spring 06 Exam #1 Feb. 23, 06
 Your Name: Your UID# 1. (20 points) Match following mutations with corresponding mutagens (X-RAY, Ds transposon excision, UV, EMS, Proflavin) a) Thymidine dimmers b) Breakage of DNA backbone c) Frameshift
Your Name: Your UID# 1. (20 points) Match following mutations with corresponding mutagens (X-RAY, Ds transposon excision, UV, EMS, Proflavin) a) Thymidine dimmers b) Breakage of DNA backbone c) Frameshift
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
AP Biology: Unit 5: Development. Forensic DNA Fingerprinting: Using Restriction Enzymes Bio-Rad DNA Fingerprinting Kit
 Forensic DNA Fingerprinting: Using Restriction Enzymes Bio-Rad DNA Fingerprinting Kit Background: Scientists working in forensic labs are often asked to perform DNA profiling or fingerprinting to analyze
Forensic DNA Fingerprinting: Using Restriction Enzymes Bio-Rad DNA Fingerprinting Kit Background: Scientists working in forensic labs are often asked to perform DNA profiling or fingerprinting to analyze
RPA-AB RPA-C Supplemental Figure S1: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification.
 RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/direct_detection_of_genotype.html 1 Like most other model organism Arabidopsis thaliana has a sequenced genome? What do we mean by sequenced genome? What sort of info
http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/direct_detection_of_genotype.html 1 Like most other model organism Arabidopsis thaliana has a sequenced genome? What do we mean by sequenced genome? What sort of info
Polymerase Chain Reaction
 Polymerase Chain Reaction Problem Suppose you have a patient with an infection or a heritable disease. You want to know which infection or disease it is and.. you want to know it fast and... from as little
Polymerase Chain Reaction Problem Suppose you have a patient with an infection or a heritable disease. You want to know which infection or disease it is and.. you want to know it fast and... from as little
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
NZYGene Synthesis kit
 Kit components Component Concentration Amount NZYGene Synthesis kit Catalogue number: MB33901, 10 reactions GS DNA Polymerase 1U/ μl 30 μl Reaction Buffer for GS DNA Polymerase 10 150 μl dntp mix 2 mm
Kit components Component Concentration Amount NZYGene Synthesis kit Catalogue number: MB33901, 10 reactions GS DNA Polymerase 1U/ μl 30 μl Reaction Buffer for GS DNA Polymerase 10 150 μl dntp mix 2 mm
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system
 Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells
 Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases
 nature methods Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases Daniel G Gibson, Lei Young, Ray-Yuan Chuang, J Craig Venter, Clyde A Hutchison III & Hamilton O Smith Supplementary figures
nature methods Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases Daniel G Gibson, Lei Young, Ray-Yuan Chuang, J Craig Venter, Clyde A Hutchison III & Hamilton O Smith Supplementary figures
4. Analysing genes II Isolate mutants*
 .. 4. Analysing s II Isolate mutants* Using the mutant to isolate the classify mutants by complementation analysis wild type study phenotype of mutants mutant 1 - use mutant to isolate sequence put individual
.. 4. Analysing s II Isolate mutants* Using the mutant to isolate the classify mutants by complementation analysis wild type study phenotype of mutants mutant 1 - use mutant to isolate sequence put individual
Lecture 18. PCR Technology. Growing PCR Industry
 Lecture 18 PCR Technology Growing PCR Industry Basic PCR, Cloning of PCR product, RT-PCR, RACE, Quantitative PCR, Multiplex PCR, Hot start PCR, Touchdown PCR,PCR sequencing.. How PCR started The DNA duplex
Lecture 18 PCR Technology Growing PCR Industry Basic PCR, Cloning of PCR product, RT-PCR, RACE, Quantitative PCR, Multiplex PCR, Hot start PCR, Touchdown PCR,PCR sequencing.. How PCR started The DNA duplex
SpeedSTAR HS DNA Polymerase
 Cat. # RR070A For Research Use SpeedSTAR HS DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. Supplied buffers... 3 V. General reaction mixture...
Cat. # RR070A For Research Use SpeedSTAR HS DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. Supplied buffers... 3 V. General reaction mixture...
HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit
 HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM031 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 3.5 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM031 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 3.5 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
XXII DNA cloning and sequencing. Outline
 XXII DNA cloning and sequencing 1) Deriving DNA for cloning Outline 2) Vectors; forming recombinant DNA; cloning DNA; and screening for clones containing recombinant DNA [replica plating and autoradiography;
XXII DNA cloning and sequencing 1) Deriving DNA for cloning Outline 2) Vectors; forming recombinant DNA; cloning DNA; and screening for clones containing recombinant DNA [replica plating and autoradiography;
Manipulation of Purified DNA
 Manipulation of Purified DNA To produce the recombinant DNA molecule, the vector, as well as the DNA to be cloned, must be cut at specific points and then joined together in a controlled manner by DNA
Manipulation of Purified DNA To produce the recombinant DNA molecule, the vector, as well as the DNA to be cloned, must be cut at specific points and then joined together in a controlled manner by DNA
Supporting Online Information
 Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Some types of Mutagenesis
 Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Diagnosis Sanger. Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms. Volume 1: Help! No Data! GENEWIZ Technical Support
 Diagnosis Sanger Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms GENEWIZ Technical Support DNAseq@genewiz.com Troubleshooting This troubleshooting guide is based on common issues seen from samples within
Diagnosis Sanger Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms GENEWIZ Technical Support DNAseq@genewiz.com Troubleshooting This troubleshooting guide is based on common issues seen from samples within
The Biotechnology Toolbox
 Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Overexpression Normal expression Overexpression Normal expression. 26 (21.1%) N (%) P-value a N (%)
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
Cat. # RR430S RR430A. For Research Use. SYBR Fast qpcr Mix. Product Manual. v201610da
 For Research Use SYBR Fast qpcr Mix Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 4 III. Components... 5 IV. Storage... 5 V. Features... 6 VI. Precautions... 6 VII. Protocol...
For Research Use SYBR Fast qpcr Mix Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 4 III. Components... 5 IV. Storage... 5 V. Features... 6 VI. Precautions... 6 VII. Protocol...
winter savings one place High Quality Costs Less Look inside to find great deals on Thermo Scientific products for all your molecular biology needs
 A quarterly publication containing special offers for significant savings on a variety of molecular biology products CDA winter savings High Quality Costs Less RNAi PCR / qpcr Look inside to find great
A quarterly publication containing special offers for significant savings on a variety of molecular biology products CDA winter savings High Quality Costs Less RNAi PCR / qpcr Look inside to find great
Supplementary Figure 1A A404 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid
 Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
E-Supporting Information-1 (ESI-1) Ionic liquids promote PCR amplification of DNA
 E-Supporting Information-1 (ESI-1) Ionic liquids promote PCR amplification of DNA Yugang Shi, ab Yen-Liang Liu, a Peng-Yeh Lai, c Ming-Chung Tseng, a Min-Jen Tseng, c Yudong Li, b and Yen-Ho Chu* a a Department
E-Supporting Information-1 (ESI-1) Ionic liquids promote PCR amplification of DNA Yugang Shi, ab Yen-Liang Liu, a Peng-Yeh Lai, c Ming-Chung Tseng, a Min-Jen Tseng, c Yudong Li, b and Yen-Ho Chu* a a Department
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of maize MON by Real-time PCR. Validated Method
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Health, Consumers & Reference Materials Food & Feed Compliance Unit Event-specific Method for the Quantification of maize MON 87403 by Real-time PCR Validated
EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Health, Consumers & Reference Materials Food & Feed Compliance Unit Event-specific Method for the Quantification of maize MON 87403 by Real-time PCR Validated
