Station 1: Fossil Records
|
|
|
- Grant Bell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Station 1: Fossil Records 1. First, write the scientific definition of the following key terms in your NB, under the heading Fossil Records, write definitions in your own words but be sure not to leave out important parts. Fossil Sedimentary rock Natural selection Next, examine the diagram (left) to answer the questions below in complete sentences. 2. Explain what this diagram is communicating. 3. Is this diagram showing direct evidence or an inference based on reasoning? Explain. This diagram shows insects and a lizard trapped in fossilized tree sap (amber) from millions of years ago and how they look today. 4. Explain how organisms could not change over time and natural selection still be true and happening?
2 Which layers are oldest? Can you put them in order from youngest to oldest?
3 Station 7: Descent with modification Examine the diagrams and descriptions in the table about horse evolution on the back and use that information to answer the questions in complete sentences in your NB 1. Define: Descent with modification 2. Hyracotherium lived in a dense forest area dominated by a rich undergrowth of ferns. Discuss why the small body size might be an advantage in this type of environment? 3. A change in vegetation from dense forest to grasslands occurred due to climate changes and this selected for changes in the shape of the horse s leg and body size. Explain how these changes in vegetation could lead to the evolution of the horse. 4. The teeth of the browsers* (such as Mesohippus) were covered with a thick layer of enamel (hard outer-coating of teeth). The teeth of the modern-day horses, by comparison, have less enamel and appear to be much wider and flatter. Provide scientific reasoning to explain these changes seen in horse teeth over time. *Browsers vs. Grazers: Browsers strip off and eat leaves, bark, and green stems from plants, while grazers clip vegetation like grasses at or near ground level. Deer, such as white-tailed deer in the Rocky Mountains, are browsers. The disadvantage of browsing is that height may make vegetation inaccessible (hence the long neck of the browsing giraffe), and often-times browsers eat parts of the vegetation that are low in nutrients, chemically defended (bitter/poisonous), or both. Grazers, such as sheep and cattle, can feed on the much more nutrient-rich grasses. Examine the images of modern horse variations at left. 5. All of these variations have come about in the last 4,000 to 6,000 years as humans domesticated horses for work, travel, and show. Explain how all of these variations can happen in such a relatively short period of time when previous changes took millions of years.
4 Hyracotherium 37 million years ago Mesohippus 24 million years ago Merychippus 5 million years ago Pliohippus 1.6 million years ago Equus modern-day horse EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION STATIONS Time frame Diagram Description of horse This horse lives in the grassy plains area It eats grasses and is classified as a grazer It is approximately 1.6 m (5.2 ft.) tall It has a single visible digit This horse lived in areas with shrubs and on the grassy plains It ate grasses and is classified as a grazer It was approximately 1.0 m (3.2 ft.) tall It had a single visible digit This horse lived in areas with shrubs and on the grassy plains It ate leafy vegetation and grasses and is classified as a grazer It was approximately 1.0 m (3.2 ft.) tall It has three visible digits This horse lived in thinly wooded areas. It ate leafy vegetation and is classified as a browser It was approximately the size of a small dog, about 0.6m (2 ft.) tall It had four visible digits This horse lived in thickly wooded areas It ate leafy vegetation and is classified as a browser It was approximately the size of a small dog, about 0.4 m (1.3 ft.) tall It had four visible digits
5 Station 2: Vestigial structures Examine the diagrams and visuals below with your group. Based on your observations and discussion, answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. Write a definition of a vestigial structure. 2. Name 3 vestigial organs that humans have and hypothesize what their purpose probably was. 3. Explain why snake legs are vestigial. 4. Explain the scientific reasoning of how a vestigial organ is evidence of evolution. Snakes evolved from four legged animals similar to lizards. Most species of snakes have lost all traces of limbs but snakes in the boa and python family have a tiny pair of hind legs. Unlike whales, the python's (or boa's) vestigial legs can actually be seen as a pair of "spurs" that stick out where the body ends and the tail begins. (Admittedly, it is difficult for an untrained person to tell where that is!) The vermiform appendix had digestive functions in the ancestral human species, probably helping the cellulose in grass breakdown in the intestine, as they were herbivours. The appendix has become vestigial in human beings because they have become very small in size and don t contribute in cellulose fermentation. However, several appendix problems occur in people and the removal of this part in the body will do no harm and is relatively common. Whales still have bones (not seen from outside) that are remnants from hind legs.
6 Station 3: Comparative Anatomy & Homologous Structures Analyze the diagram above then answer the following questions in complete sentences after discussing with your group. 1. Describe how the limbs of these seven organisms are similar and how are they different. 2. Explain why they are so similar in structure and yet can be used differently by the organism? How did this happen? 3. What does this help explain about how related or not these species are to each other? 4. Explain how these structures are evidence of evolution. This picture of bones is from a seal fin I found on the beach. My own piece of evidence collected from a backpacking trip to the Lost Coast in Northern California, summer 2013 (Me and a member of the Pinniped family (seals) both gesturing for world peace).
7 Station 4: Comparative Embryology Examine the diagrams of four different vertebrate organisms at the early embryo stage. Discuss differences with your group and then answer the questions in complete sentences. 1. Try to determine which embryo will develop into which organism- reptile, human, bird, fish. 2. Which ones out of the four do you think are most closely related, and why? 3. After reading the passage below, construct an explanation for which animal is more closely related to humans- chickens or fish? (put answer in CER format, complete sentences) Claim: Evidence: Reasoning:
8 Station 5: Genetic Evidence Gene sequence & protein sequences comparisons DNA is the code for making proteins, the closer the DNA, the closer the amino acid sequence, and thus the closer the final proteins are. Analyze the following data with your group: Amino Acid Sequences Baboon ASN THR THR GLY ASP GLU VAL ASP ASP SER PRO GLY GLY ASN ASN Chimp SER THR ALA GLY ASP GLU VAL GLU ASP THR PRO GLY GLY ALA ASN Lemur ALA THR SER GLY GLU LYS VAL GLU ASP SER PRO GLY SER HIS ASN Gorilla SER THR ALA GLY ASP GLU VAL GLU ASP THR PRO GLY GLY ALA ASN Human SER THR ALA GLY ASP GLU VAL GLU ASP THR PRO GLY GLY ALA ASN 1. For each primate in the table above, count the number of amino acids that are different from the human sequence. Record these numbers in a data table on your handout, draw one like the one shown below. 2. Calculate the percentage of differences of each primate compared to humans by dividing the number of amino acid differences by 15 and then multiplying by 100. Record these numbers in the data table you drew as well. Primate Baboon Chimpanzee Gorilla Lemur # of Amino Acids Different from Humans Percent Difference 3. Use this data to create a graph to better communicate your findings. Remember which graph type is good for comparing categories? Include title, label each axis with x and y AND the label (category/unit), make a key, include an appropriate scale. 4. Are your results surprising? Why or why not?
9 Chromosome comparisons: Another line of genetic evidence 5. Summarize the argument: what evidence exists that humans and great apes shared a common ancestor?
10 Station Six: Biogeography 1. Define Biogeography 2. Define a species 3. How did these three members of the camel family become different species? Claim: Evidence: Reasoning:
11 Biogeography Cont. Endemism is the ecological state of a species being unique to a defined geographic location, such as an island, nation, country or other defined zone, or habitat type; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. Madagascar an island off the coast of Africa has some of the world's most interesting animals. About 75 percent of the species found in Madagascar are endemic, found nowhere else on the planet. 1.) What kind of selection would be responsible for giving rise to so many different species on this one island? Would it be a different kind of selection for just the endemic species? What is doing the selecting?
12 Station 8: Evolution of a Scientific Theory Building Ideas to Explain How Evolution Happens 1.) Science is a communal effort- which scientists laid the foundation for Darwin s theory of natural selection? What ideas did they contribute that were crucial for Darwin to build on? (see back side) 2.) What do we know now about DNA and genetics that further disproves LaMarck s theory? 2.) Are humans subject to natural selection? Does our human population have all 4 required factors?
13
Evolution 1: Evidence of Evolution LabCh. 16
 Evidence of Evolution- Pre-AP Name: Per: COOK Background: Much evidence has been found to indicate that living things have evolved or changed gradually during their natural history. The study of fossils
Evidence of Evolution- Pre-AP Name: Per: COOK Background: Much evidence has been found to indicate that living things have evolved or changed gradually during their natural history. The study of fossils
Evolution is a process of change through time. A change in species over time.
 Theory of Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution is a process of change through time. A change in species over time. Theories of evolution provide an explanation for the differences and similarities in
Theory of Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution is a process of change through time. A change in species over time. Theories of evolution provide an explanation for the differences and similarities in
Station 1 DNA Evidence
 Station 1 DNA Evidence Cytochrome-c is a protein found in the mitochondria that is used in cellular respiration. This protein consists of a chain of 104 amino acids. The chart below shows the amino acid
Station 1 DNA Evidence Cytochrome-c is a protein found in the mitochondria that is used in cellular respiration. This protein consists of a chain of 104 amino acids. The chart below shows the amino acid
Name: TOC#. Data and Observations: Figure 1: Amino Acid Positions in the Hemoglobin of Some Vertebrates
 Name: TOC#. Comparing Primates Background: In The Descent of Man, the English naturalist Charles Darwin formulated the hypothesis that human beings and other primates have a common ancestor. A hypothesis
Name: TOC#. Comparing Primates Background: In The Descent of Man, the English naturalist Charles Darwin formulated the hypothesis that human beings and other primates have a common ancestor. A hypothesis
Name Date of Data Collection. Class Period Lab Days/Period Teacher
 Comparing Primates (adapted from Comparing Primates Lab, page 431-438, Biology Lab Manual, by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall Publishers, copyright 2000, ISBN 0-13-436796-0) Background: One of the most
Comparing Primates (adapted from Comparing Primates Lab, page 431-438, Biology Lab Manual, by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall Publishers, copyright 2000, ISBN 0-13-436796-0) Background: One of the most
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships. How do similarities in amino acid sequences of various species provide evidence for evolution?
 Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships Name: How do similarities in amino acid sequences of various species provide evidence for evolution? An important technique used in determining evolutionary
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships Name: How do similarities in amino acid sequences of various species provide evidence for evolution? An important technique used in determining evolutionary
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships
 Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships Pre-Lab Discussion Homologous structures -- those structures believed to have a common origin but not necessarily a common function -- provide some of
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships Pre-Lab Discussion Homologous structures -- those structures believed to have a common origin but not necessarily a common function -- provide some of
THE EVOLUTION OF DARWIN S THEORY PT 1. Chapter 16-17
 THE EVOLUTION OF DARWIN S THEORY PT 1 Chapter 16-17 From Darwin to Today Darwin provided compelling evidence that species and populations change. What he didn t know (and neither did anyone else at the
THE EVOLUTION OF DARWIN S THEORY PT 1 Chapter 16-17 From Darwin to Today Darwin provided compelling evidence that species and populations change. What he didn t know (and neither did anyone else at the
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships
 Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships One technique used to determine evolutionary relationships is to study the biochemical similarity of organisms. Though molds, aardvarks, and humans appear
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships One technique used to determine evolutionary relationships is to study the biochemical similarity of organisms. Though molds, aardvarks, and humans appear
YEAR 10 SCIENCE BIOLOGY UNIT TEST MAY 2014
 YEAR 10 SCIENCE BIOLOGY UNIT TEST MAY 2014 NAME: TEACHER: Section A: 10 Multiple Choice Questions /10 Marks Circle the best alternative on the answer sheet provided. Answer all questions. Section B: 8
YEAR 10 SCIENCE BIOLOGY UNIT TEST MAY 2014 NAME: TEACHER: Section A: 10 Multiple Choice Questions /10 Marks Circle the best alternative on the answer sheet provided. Answer all questions. Section B: 8
Investigating Common Descent: Formulating Explanations and Model
 Name Investigating Common Descent: Formulating Explanations and Model Background: Common Descent This activity has extensive historical roots. Few question the idea that Charles Darwin's Origin of Species
Name Investigating Common Descent: Formulating Explanations and Model Background: Common Descent This activity has extensive historical roots. Few question the idea that Charles Darwin's Origin of Species
Outline. Pseudogenes. Pseudo-genes. The genetic code (DNA version) What is a gene? What is a gene? Dead genes Vitamin C Urate oxidase. Alan R.
 Pseudogenes Alan R. Rogers January 15, 2016 Dead genes Vitamin C Urate oxidase ψmyh16 GBA Globins 1 / 35 2 / 35 Pseudo-genes Genes are DNA sequences that code for protein. Some genes are broken and cannot
Pseudogenes Alan R. Rogers January 15, 2016 Dead genes Vitamin C Urate oxidase ψmyh16 GBA Globins 1 / 35 2 / 35 Pseudo-genes Genes are DNA sequences that code for protein. Some genes are broken and cannot
Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA F Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/SCIENCE A A161/01 Modules B1 B2 B3 (Foundation Tier) *5955356589* Candidates answer on the Question
Oxford Cambridge and RSA F Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/SCIENCE A A161/01 Modules B1 B2 B3 (Foundation Tier) *5955356589* Candidates answer on the Question
Question #2 An animal that eats berries, insects and seeds would be placed in which classification? A) carnivore
 Name: lass: ate: Question #1 Which is the correct order of this food chain? ) plants, crickets, snakes, frogs ) snakes, frogs, crickets, plants ) snakes, crickets, frogs, plants ) plants, crickets, frogs,
Name: lass: ate: Question #1 Which is the correct order of this food chain? ) plants, crickets, snakes, frogs ) snakes, frogs, crickets, plants ) snakes, crickets, frogs, plants ) plants, crickets, frogs,
Biology. Semester 2 Exam Review. Name: Block: Replication Transcription Translation Genetic Engineering. Mutation Codon Anticodon DNA Fingerprint
 Biology Semester 2 Exam Review Name: Block: Unit 1: DNA Define the following terms on a separate sheet of paper: Replication Transcription Translation Genetic Engineering Mutation Codon Anticodon DNA Fingerprint
Biology Semester 2 Exam Review Name: Block: Unit 1: DNA Define the following terms on a separate sheet of paper: Replication Transcription Translation Genetic Engineering Mutation Codon Anticodon DNA Fingerprint
Adaptations and Food Webs
 Fourth Grade Science Assessments page 1 of 10 Adaptations and Food Webs (Life Science) Academic Standard: TLW explain how variations in physical characteristics can give organisms an advantage and how
Fourth Grade Science Assessments page 1 of 10 Adaptations and Food Webs (Life Science) Academic Standard: TLW explain how variations in physical characteristics can give organisms an advantage and how
Evolution and Ecology
 Evolution and Ecology REVIEW QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following cannot be an example of evolution? a. As a consequence of legislation promoting cleaner air, the frequency of black peppered
Evolution and Ecology REVIEW QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following cannot be an example of evolution? a. As a consequence of legislation promoting cleaner air, the frequency of black peppered
Suggest three factors that could have caused the population change between C and D( 3 marks)
 CHAPTER 2 ECOLOGY PAST KCSE QUESTIONS ON THE TOPIC 1. State how excessive use of pesticides may affect soil fertility 2. The graph below represents a population growth of a certain herbivore in a grassland
CHAPTER 2 ECOLOGY PAST KCSE QUESTIONS ON THE TOPIC 1. State how excessive use of pesticides may affect soil fertility 2. The graph below represents a population growth of a certain herbivore in a grassland
In the mid-20th century the structure of DNA was discovered. What is a section of DNA which codes for one specific protein called?
 Q1.Our understanding of genetics and inheritance has improved due to the work of many scientists. (a) Draw one line from each scientist to the description of their significant work. Scientist Description
Q1.Our understanding of genetics and inheritance has improved due to the work of many scientists. (a) Draw one line from each scientist to the description of their significant work. Scientist Description
Chapter 13. How Populations Evolve. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 13 How Populations Evolve PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane
Chapter 13 How Populations Evolve PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane
The photograph shows an aardvark. Aardvarks feed on insects that they dig from the soil. Aardvarks hunt for these insects at night.
 The photograph shows an aardvark. By Beige Alert [CC BY 2.0], via Flickr Aardvarks feed on insects that they dig from the soil. Aardvarks hunt for these insects at night. How does each of these adaptations
The photograph shows an aardvark. By Beige Alert [CC BY 2.0], via Flickr Aardvarks feed on insects that they dig from the soil. Aardvarks hunt for these insects at night. How does each of these adaptations
Name Date REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
 Name Date REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM 1. List the appropriate steps in planning/carrying out an experiment on the effect of heat on the function of a certain enzyme: Observe, define problem, form question, research
Name Date REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM 1. List the appropriate steps in planning/carrying out an experiment on the effect of heat on the function of a certain enzyme: Observe, define problem, form question, research
Genome 261, Spring 2007 ****** MIDTERM KEY ******
 (16 pts) Multiple True/False CIRCLE ALL ANSWERS THAT ARE TRUE!!!! 1. A gene is a sequence of deoxyribonucleotides. can be transcribed into RNA. typically codes for a protein. can have a slightly different
(16 pts) Multiple True/False CIRCLE ALL ANSWERS THAT ARE TRUE!!!! 1. A gene is a sequence of deoxyribonucleotides. can be transcribed into RNA. typically codes for a protein. can have a slightly different
Science 20. Unit D: Changes in Living Systems. Assignment Booklet D2
 Science 20 Unit D: Changes in Living Systems Assignment Booklet D2 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 2 Assignment Total Possible Marks 55 Your Mark Science 20 Unit D: Changes in
Science 20 Unit D: Changes in Living Systems Assignment Booklet D2 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 2 Assignment Total Possible Marks 55 Your Mark Science 20 Unit D: Changes in
Biology EOC Questions
 Biology EOC Questions 1 Coyotes eat proteins in food. The proteins break down due to enzymes produced in the stomach of the coyote. The production of these enzymes then causes more enzymes to be released
Biology EOC Questions 1 Coyotes eat proteins in food. The proteins break down due to enzymes produced in the stomach of the coyote. The production of these enzymes then causes more enzymes to be released
DATA. mrna CODON CHART
 Alien Encounters! Background: In the year 2050, an incredible archeological discovery was made in the middle of a remote area of South America. It was an area where a large meteor had struck Earth. A pile
Alien Encounters! Background: In the year 2050, an incredible archeological discovery was made in the middle of a remote area of South America. It was an area where a large meteor had struck Earth. A pile
Name: Date: Living Environment Period:
 Name: Living Environment Date: Period: Heredity & DNA 1. Arrange the following structures from largest to smallest. a chromosome a nucleus a gene 2. The diagram below represents a portion of a molecule
Name: Living Environment Date: Period: Heredity & DNA 1. Arrange the following structures from largest to smallest. a chromosome a nucleus a gene 2. The diagram below represents a portion of a molecule
REVIEW 5: EVOLUTION UNIT. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Period Date REVIEW 5: EVOLUTION UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Darwin s Principle of Natural Selection a. Variation individuals within a population possess
Period Date REVIEW 5: EVOLUTION UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Darwin s Principle of Natural Selection a. Variation individuals within a population possess
Changes in Biodiversity
 Changes in Biodiversity Hundreds of years ago, before North America was split up according to states and countries, native populations lived in the many varied areas of the continent. There were jungles,
Changes in Biodiversity Hundreds of years ago, before North America was split up according to states and countries, native populations lived in the many varied areas of the continent. There were jungles,
The diagram shows two patterns of cell division. Cell division type A is used in gamete formation. Cell division type B is used in normal growth.
 The diagram shows two patterns of cell division. Cell division type A is used in gamete formation. Cell division type B is used in normal growth. Name the two types of cell division, A and B, shown in
The diagram shows two patterns of cell division. Cell division type A is used in gamete formation. Cell division type B is used in normal growth. Name the two types of cell division, A and B, shown in
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Gene Mutations WS Summary: Students will learn about frame shift mutations and base substitution mutations. Goals & Objectives: Students will be able to demonstrate how mutations
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Gene Mutations WS Summary: Students will learn about frame shift mutations and base substitution mutations. Goals & Objectives: Students will be able to demonstrate how mutations
Harvesting Wheat Edible Schoolyard Pittsburgh. Fall September
 Harvesting Wheat Edible Schoolyard Pittsburgh Fall September MATERIALS World map showing the development of farming through the dispersal of the rice, maize, and wheat Hunter- gatherer vs. farmer game
Harvesting Wheat Edible Schoolyard Pittsburgh Fall September MATERIALS World map showing the development of farming through the dispersal of the rice, maize, and wheat Hunter- gatherer vs. farmer game
Biodiversity and the Distribution of Life Homework 1
 Unit 3 Homework Biodiversity and the Distribution of Life Homework. Marsh marigold is a waterside plant which grows beside burns. The abundance of marsh marigolds was estimated in five sampling areas beside
Unit 3 Homework Biodiversity and the Distribution of Life Homework. Marsh marigold is a waterside plant which grows beside burns. The abundance of marsh marigolds was estimated in five sampling areas beside
Pre-AP Biology Evolution Review
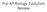 Pre-AP Biology Evolution Review Variation in Beak Size in Medium Ground Finch If you wanted to look for a change in phenotype beak size over time in a population of finch (which would be evidence of natural
Pre-AP Biology Evolution Review Variation in Beak Size in Medium Ground Finch If you wanted to look for a change in phenotype beak size over time in a population of finch (which would be evidence of natural
City parks: wildlife islands in a sea of cement Featured scientists: Remington Moll and Grant Woodard from Michigan State University
 City parks: wildlife islands in a sea of cement Featured scientists: Remington Moll and Grant Woodard from Michigan State University Research Background For most of our existence, humans have lived in
City parks: wildlife islands in a sea of cement Featured scientists: Remington Moll and Grant Woodard from Michigan State University Research Background For most of our existence, humans have lived in
3. A student performed a gel electrophoresis experiment. The results are represented in the diagram below.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the statement below and on your knowledge of biology. Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the statement below and on your knowledge of biology. Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount
There was a different theory at the same time as Darwin s theory.
 Q1.Charles Darwin proposed the theory of natural selection. Many people at the time did not accept his theory. (a) There was a different theory at the same time as Darwin s theory. The different theory
Q1.Charles Darwin proposed the theory of natural selection. Many people at the time did not accept his theory. (a) There was a different theory at the same time as Darwin s theory. The different theory
(a) The area of forest lost each year in Madagascar increased between 2009 and 2012.
 Q1.The graph below shows the area of forest lost in Madagascar from 2009 to 2012. (a) The area of forest lost each year in Madagascar increased between 2009 and 2012. Determine the total area of forest
Q1.The graph below shows the area of forest lost in Madagascar from 2009 to 2012. (a) The area of forest lost each year in Madagascar increased between 2009 and 2012. Determine the total area of forest
SCIENCE Assessment. Updates for Biology End-of-Course (EOC) Exam
 SCIENCE Assessment Updates for 2014 Biology End-of-Course (EOC) Exam Updates for 2014, Biology EOC Page 1 Student Sample Pages Student Name: Updates for 2014, Biology EOC Page 5 Directions: Answer questions
SCIENCE Assessment Updates for 2014 Biology End-of-Course (EOC) Exam Updates for 2014, Biology EOC Page 1 Student Sample Pages Student Name: Updates for 2014, Biology EOC Page 5 Directions: Answer questions
The Pieces Inside of You that Make You Who You Are. Genes and DNA
 The Pieces Inside of You that Make You Who You Are Genes and DNA Who are you? This question can be answered many ways Personality traits Kindness Vegetarian or Carnivore Athlete ***Traits you can control
The Pieces Inside of You that Make You Who You Are Genes and DNA Who are you? This question can be answered many ways Personality traits Kindness Vegetarian or Carnivore Athlete ***Traits you can control
Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Name: Date: Block: Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. Directions: Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Ecology Biotic factors Nonliving Environments Atmosphere Humans
Name: Date: Block: Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. Directions: Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Ecology Biotic factors Nonliving Environments Atmosphere Humans
Problem Set Unit The base ratios in the DNA and RNA for an onion (Allium cepa) are given below.
 Problem Set Unit 3 Name 1. Which molecule is found in both DNA and RNA? A. Ribose B. Uracil C. Phosphate D. Amino acid 2. Which molecules form the nucleotide marked in the diagram? A. phosphate, deoxyribose
Problem Set Unit 3 Name 1. Which molecule is found in both DNA and RNA? A. Ribose B. Uracil C. Phosphate D. Amino acid 2. Which molecules form the nucleotide marked in the diagram? A. phosphate, deoxyribose
1 Everything Is Connected
 CHAPTER 18 1 Everything Is Connected SECTION Interactions of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What do organisms in an ecosystem depend
CHAPTER 18 1 Everything Is Connected SECTION Interactions of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What do organisms in an ecosystem depend
Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide Instructions: 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. 3.
Name: Period: Date: Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide Instructions: 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. 3.
GCSE (9 1) Biology B (Twenty First Century Science) J257/04 Depth in biology (Higher Tier) Sample Question Paper SPECIMEN
 GCSE (9 1) Biology B (Twenty First Century Science) J257/04 Depth in biology (Higher Tier) Sample Question Paper H Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical
GCSE (9 1) Biology B (Twenty First Century Science) J257/04 Depth in biology (Higher Tier) Sample Question Paper H Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical
Modeling the Genetic Engineering of Trees
 Lab 17 Modeling the Genetic Engineering of Trees PROBLEM Can a plant be genetically engineered to take up more carbon dioxide? BACKGROUND Enabling trees to use carbon dioxide more efficiently may be a
Lab 17 Modeling the Genetic Engineering of Trees PROBLEM Can a plant be genetically engineered to take up more carbon dioxide? BACKGROUND Enabling trees to use carbon dioxide more efficiently may be a
1. All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food. a. Interaction b. Chain c. Network d. Web
 Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
PE PLE A WORLD OF DIFFERENCE: MADAGASCAR UNIT 8 PEOPLE AND WILDLIFE CONCEPT GRADE LEVEL. Part 1: SUBJECTS OBJECTIVES SKILLS.
 UNIT 8 PEOPLE AND WILDLIFE A WORLD OF DIFFERENCE: MADAGASCAR METHOD In small group simulations, students compare the biodiversity of a temperate forest to that of a tropical rainforest and explore the
UNIT 8 PEOPLE AND WILDLIFE A WORLD OF DIFFERENCE: MADAGASCAR METHOD In small group simulations, students compare the biodiversity of a temperate forest to that of a tropical rainforest and explore the
Science and Technology/Engineering
 MASSACHUSETTS COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT SYSTEM PRACTICE TEST Science and Technology/Engineering Grade 5 Student Name School Name District Name Grade 5 Science and Technology/Engineering PRACTICE TEST This
MASSACHUSETTS COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT SYSTEM PRACTICE TEST Science and Technology/Engineering Grade 5 Student Name School Name District Name Grade 5 Science and Technology/Engineering PRACTICE TEST This
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
 Biodiversity and Ecosystems 1.1 Importance of Biodiversity 1.2 Parts of an Ecosystem 1.3 Stable Ecosystems (quick recap on food webs/chains here) 1.4 Sampling Ecosystems 1.5 Biological Keys 1.Biodiversity
Biodiversity and Ecosystems 1.1 Importance of Biodiversity 1.2 Parts of an Ecosystem 1.3 Stable Ecosystems (quick recap on food webs/chains here) 1.4 Sampling Ecosystems 1.5 Biological Keys 1.Biodiversity
Using DNA sequence, distinguish species in the same genus from one another.
 Species Identification: Penguins 7. It s Not All Black and White! Name: Objective Using DNA sequence, distinguish species in the same genus from one another. Background In this activity, we will observe
Species Identification: Penguins 7. It s Not All Black and White! Name: Objective Using DNA sequence, distinguish species in the same genus from one another. Background In this activity, we will observe
Gozo College Boys Secondary Victoria - Gozo, Malta Ninu Cremona
 Gozo College Boys Secondary Victoria - Gozo, Malta Ninu Cremona Half Yearly Examination 2010 2011 Form 1 J.L. Integrated Science Time: 1½ Hours Name: Class: Instructions to Candidates Answer all fifteen
Gozo College Boys Secondary Victoria - Gozo, Malta Ninu Cremona Half Yearly Examination 2010 2011 Form 1 J.L. Integrated Science Time: 1½ Hours Name: Class: Instructions to Candidates Answer all fifteen
The Theory of Evolution
 The Theory of Evolution Mechanisms of Evolution Notes Pt. 4 Population Genetics & Evolution IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER: Populations, not individuals, evolve. Population = a group of individuals of the same
The Theory of Evolution Mechanisms of Evolution Notes Pt. 4 Population Genetics & Evolution IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER: Populations, not individuals, evolve. Population = a group of individuals of the same
DNA.notebook March 08, DNA Overview
 DNA Overview Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, must be able to do 2 things: 1) give instructions for building and maintaining cells. 2) be copied each time a cell divides. DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
DNA Overview Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, must be able to do 2 things: 1) give instructions for building and maintaining cells. 2) be copied each time a cell divides. DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
Food Chains and Webs. ecosystem: a community of living and nonliving things in their natural environment
 Think about the last meal you ate. Where did the food come from? Maybe it came from the grocery store or a restaurant. Maybe it even came from your backyard. Now think of a lion living on the plains in
Think about the last meal you ate. Where did the food come from? Maybe it came from the grocery store or a restaurant. Maybe it even came from your backyard. Now think of a lion living on the plains in
03-511/711 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall
 03-511/711 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 2011 1 Problem Set 0 Due Tuesday, September 6th This homework is intended to be a self-administered placement quiz, to help you (and me) determine
03-511/711 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 2011 1 Problem Set 0 Due Tuesday, September 6th This homework is intended to be a self-administered placement quiz, to help you (and me) determine
4.9AB Producers, Consumers, and Food Webs
 4.9AB Producers, Consumers, and Food Webs Key Concept 1: Producers need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make (produce) their own food. Consumers depend on plants or other organisms for food. Questions:
4.9AB Producers, Consumers, and Food Webs Key Concept 1: Producers need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make (produce) their own food. Consumers depend on plants or other organisms for food. Questions:
Additional Case Study: Amino Acids and Evolution
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Amino Acids and Evolution Objectives To use biochemical data to determine evolutionary relationships. To test the hypothesis that living things that are morphologically
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Amino Acids and Evolution Objectives To use biochemical data to determine evolutionary relationships. To test the hypothesis that living things that are morphologically
7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers,
 7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers, you are going to learn about how these organisms interact within an ecosystem. Picture a seal swimming in the
7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers, you are going to learn about how these organisms interact within an ecosystem. Picture a seal swimming in the
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P2 FEBRUARY/MARCH 2009 MARKS: 150 TIME: 2½ hours This question paper consists of 14 pages. Life Sciences/P2 2 DoE/Feb. March 2009 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P2 FEBRUARY/MARCH 2009 MARKS: 150 TIME: 2½ hours This question paper consists of 14 pages. Life Sciences/P2 2 DoE/Feb. March 2009 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Changes in Biodiversity
 Changes in Biodiversity Changes in Biodiversity Hundreds of years ago, before North America was split up according to states and countries, native populations lived in the many varied areas of the continent.
Changes in Biodiversity Changes in Biodiversity Hundreds of years ago, before North America was split up according to states and countries, native populations lived in the many varied areas of the continent.
HEMOGLOBIN: PHYSIOLOGICAL EXPRESSION AND EVOLUTION OF GENE CLUSTER
 HEMOGLOBIN: PHYSIOLOGICAL EXPRESSION AND EVOLUTION OF GENE CLUSTER I. Physiological Expression: HOW DO WE GET OXYGEN TO OUR BODY TISSUES? Oxygen has a low solubility in blood. During the course of animal
HEMOGLOBIN: PHYSIOLOGICAL EXPRESSION AND EVOLUTION OF GENE CLUSTER I. Physiological Expression: HOW DO WE GET OXYGEN TO OUR BODY TISSUES? Oxygen has a low solubility in blood. During the course of animal
Higher Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Topic 1.1 The Structure and Organisation of DNA
 Higher Unit : DNA and the Genome Topic. The Structure and Organisation of DNA. Which of the following diagrams shows the correct structure of DNA? 2. A section of double stranded DNA was found to have
Higher Unit : DNA and the Genome Topic. The Structure and Organisation of DNA. Which of the following diagrams shows the correct structure of DNA? 2. A section of double stranded DNA was found to have
Lesson Title: Habitat for Stream Insects: What Kind of Substrate is the Best Habitat for Aquatic Insects?
 Lesson Title: Habitat for Stream Insects: What Kind of Substrate is the Best Habitat for Aquatic Insects? NSF GK-12 Fellow: Tommy Detmer (Boulder, CO) Grade Level: 5th Type of Lesson: STEM Objectives:
Lesson Title: Habitat for Stream Insects: What Kind of Substrate is the Best Habitat for Aquatic Insects? NSF GK-12 Fellow: Tommy Detmer (Boulder, CO) Grade Level: 5th Type of Lesson: STEM Objectives:
Lesson Title: Habitat for Stream Insects: What Kind of Substrate is the Best Habitat for Aquatic Insects?
 Lesson Title: Habitat for Stream Insects: What Kind of Substrate is the Best Habitat for Aquatic Insects? NSF GK-12 Fellow: Tommy Detmer (Boulder, CO) Grade Level: Middle School Type of Lesson: Life Science
Lesson Title: Habitat for Stream Insects: What Kind of Substrate is the Best Habitat for Aquatic Insects? NSF GK-12 Fellow: Tommy Detmer (Boulder, CO) Grade Level: Middle School Type of Lesson: Life Science
Fishy Amino Acid Codon. UUU Phe UCU Ser UAU Tyr UGU Cys. UUC Phe UCC Ser UAC Tyr UGC Cys. UUA Leu UCA Ser UAA Stop UGA Stop
 Fishy Code Slips Fish 1 GGTTATAGAGGTACTACC Fish 2 GGCTTCAGAGGTACTACC Fish 3 CATAGCAGAGGTACTACC Fish 4 GGTTATTCTGTCTTATTG Fish 5 GGCTTCTCTGTCTTATTG Fish 6 CATAGCGCTGCAACTACC Fishy Amino Acid Codon UUU Phe
Fishy Code Slips Fish 1 GGTTATAGAGGTACTACC Fish 2 GGCTTCAGAGGTACTACC Fish 3 CATAGCAGAGGTACTACC Fish 4 GGTTATTCTGTCTTATTG Fish 5 GGCTTCTCTGTCTTATTG Fish 6 CATAGCGCTGCAACTACC Fishy Amino Acid Codon UUU Phe
GCSE (9 1) Combined Science (Biology) A (Gateway Science) J250/02 Paper 2, B4 B6 and CS7 (PAGs B1 B5)
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA GCSE (9 1) Combined Science (Biology) A (Gateway Science) Paper 2, B4 B6 and CS7 (PAGs B1 B5) (Foundation Tier) F Year 11 Test Time allowed: 1 hour 10 minutes You must have: a
Oxford Cambridge and RSA GCSE (9 1) Combined Science (Biology) A (Gateway Science) Paper 2, B4 B6 and CS7 (PAGs B1 B5) (Foundation Tier) F Year 11 Test Time allowed: 1 hour 10 minutes You must have: a
Summary Genes and Variation Evolution as Genetic Change. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Summary Evolution of Populations 16 1 Genes and Variation Darwin s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. Beginning with variation, we now know that traits are controlled by
Chapter 16 Summary Evolution of Populations 16 1 Genes and Variation Darwin s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. Beginning with variation, we now know that traits are controlled by
Common Assessment Cycle 2 Study Guide. 1. A producer gets energy from and converts it into food.
 Common Assessment Cycle 2 Study Guide Name: 1. A producer gets energy from and converts it into food. dead organic matter the Sun primary consumers secondary consumers 2. The picture below shows an owl
Common Assessment Cycle 2 Study Guide Name: 1. A producer gets energy from and converts it into food. dead organic matter the Sun primary consumers secondary consumers 2. The picture below shows an owl
Ecological Principles and Processes. Self-evaluations. Name. Ecological Principles & Processes workbook - self-evaluations.doc 1
 Ecological Principles and Processes Self-evaluations Name Ecological Principles & Processes workbook - self-evaluations.doc 1 Chapter 1. Introduction At the end of this chapter you should be able to: Understand
Ecological Principles and Processes Self-evaluations Name Ecological Principles & Processes workbook - self-evaluations.doc 1 Chapter 1. Introduction At the end of this chapter you should be able to: Understand
AT HOME: Individual Assignment (30 points) due at beginning of class on Friday, April 4 th. Questions on Bristlecone Pine and Data Collection Table
 In today s class, we introduce the Bristlecone pine project: AT HOME: Individual Assignment (30 points) due at beginning of class on Friday, April 4 th Questions on Bristlecone Pine and Data Collection
In today s class, we introduce the Bristlecone pine project: AT HOME: Individual Assignment (30 points) due at beginning of class on Friday, April 4 th Questions on Bristlecone Pine and Data Collection
Daily Agenda. Warm Up: Review. Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice. Redos
 Daily Agenda Warm Up: Review Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice Redos 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place? 3. Replicate this strand of DNA into complimentary
Daily Agenda Warm Up: Review Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice Redos 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place? 3. Replicate this strand of DNA into complimentary
Ecosystems. 6.L.2.2 Explain how plants respond to external stimuli (including dormancy and forms of tropism) to enhance survival in an environment.
 Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *16 111671 7 4* TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE 0608/03 Paper 3 May/June 2010
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *16 111671 7 4* TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE 0608/03 Paper 3 May/June 2010
Exam III: Friday April 28th
 Exam III: Friday April 28th Covers: Human Population Growth to Human Ecology and Conservation Key from 2005: Question 39 answer is D (10,000) not C Review Session: Wed April 26 5 PM in Biosciences East
Exam III: Friday April 28th Covers: Human Population Growth to Human Ecology and Conservation Key from 2005: Question 39 answer is D (10,000) not C Review Session: Wed April 26 5 PM in Biosciences East
Identify what is meant by the terms biotic and abiotic, and name examples of each.
 NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY - LIFE ON EARTH SUMMARY Biodiversity and the distribution of life Identify what is meant by the terms biotic and abiotic, and name examples of each. Identify the impact that biotic and
NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY - LIFE ON EARTH SUMMARY Biodiversity and the distribution of life Identify what is meant by the terms biotic and abiotic, and name examples of each. Identify the impact that biotic and
Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide Instructions: 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. 3.
Name: Period: Date: Module 20: Population Genetics, Student Learning Guide Instructions: 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. 3.
Genes and Variation. Section 16-1 pgs
 Genes and Variation Section 16-1 pgs 393-396 Genes and Variation As Darwin developed his theory of evolution, he worked under a serious handicap. He didn t know how heredity worked! Although Mendel s work
Genes and Variation Section 16-1 pgs 393-396 Genes and Variation As Darwin developed his theory of evolution, he worked under a serious handicap. He didn t know how heredity worked! Although Mendel s work
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i
 From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i How do the genes in our DNA influence our characteristics? A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i How do the genes in our DNA influence our characteristics? A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins
7.014 Solution Set 4
 7.014 Solution Set 4 Question 1 Shown below is a fragment of the sequence of a hypothetical bacterial gene. This gene encodes production of HWDWN, protein essential for metabolizing sugar yummose. The
7.014 Solution Set 4 Question 1 Shown below is a fragment of the sequence of a hypothetical bacterial gene. This gene encodes production of HWDWN, protein essential for metabolizing sugar yummose. The
Neandertal toe contains human DNA Analyses show humans and Neandertals mixed and mated far earlier than previously thought
 ANCIENT TIMES FOSSILS, GENETICS, HUMAN EVOLUTION Neandertal toe contains human DNA Analyses show humans and Neandertals mixed and mated far earlier than previously thought BY TINA HESMAN SAEY MAR 2, 2016
ANCIENT TIMES FOSSILS, GENETICS, HUMAN EVOLUTION Neandertal toe contains human DNA Analyses show humans and Neandertals mixed and mated far earlier than previously thought BY TINA HESMAN SAEY MAR 2, 2016
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number UNIT 2: VARIATION, HOMEOSTASIS AND MICRO-ORGANISMS FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE BIOLOGY Sample Assessment Materials 75 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE BIOLOGY UNIT 2: VARIATION, HOMEOSTASIS AND MICRO-ORGANISMS FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS (1
GCSE BIOLOGY Sample Assessment Materials 75 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE BIOLOGY UNIT 2: VARIATION, HOMEOSTASIS AND MICRO-ORGANISMS FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS (1
Science Curriculum. Saint Gerard Majella. Updated August 2016
 Science Curriculum Saint Gerard Majella Updated August 2016 GRADE: K 1. Identify non living things and the habitats and needs of living things. 2. Identify how plants and animals grow and change in their
Science Curriculum Saint Gerard Majella Updated August 2016 GRADE: K 1. Identify non living things and the habitats and needs of living things. 2. Identify how plants and animals grow and change in their
larger voles lose less heat / are better insulated or more energy stored
 Page of Mark schemes any five from: genetic variation exists in a population or variation caused by mutation / change in gene / in DNA larger voles have smaller or have more fat they accept as larger voles
Page of Mark schemes any five from: genetic variation exists in a population or variation caused by mutation / change in gene / in DNA larger voles have smaller or have more fat they accept as larger voles
8 th Grade Science 4th Quarter Final Study Guide ANSWER KEY
 Name: Period: Test Date: 8 th Grade Science 4th Quarter Final Study Guide ANSWER KEY Unit 1: Experimental Design 1. What is a hypothesis? A hypothesis is a possible explanation of a solution to a scientific
Name: Period: Test Date: 8 th Grade Science 4th Quarter Final Study Guide ANSWER KEY Unit 1: Experimental Design 1. What is a hypothesis? A hypothesis is a possible explanation of a solution to a scientific
Evolution of Populations
 Chapter 23. Evolution of Populations 1 Populations evolve Natural selection acts on individuals differential survival survival of the fittest differential reproductive success bear more offspring Populations
Chapter 23. Evolution of Populations 1 Populations evolve Natural selection acts on individuals differential survival survival of the fittest differential reproductive success bear more offspring Populations
1.3 Energy in Ecosystems Energy from the Sun greenhouse gases
 1.3 Energy in Ecosystems Energy from the Sun The Sun is the major source of energy for out planet. It causes evaporation of water from the oceans and lakes. Sunlight also provides the energy used by green
1.3 Energy in Ecosystems Energy from the Sun The Sun is the major source of energy for out planet. It causes evaporation of water from the oceans and lakes. Sunlight also provides the energy used by green
Using Playing Cards To Simulate a Molecular Clock
 O N L I N E I N Q U I RY & I N V E S T I G AT I O N Using Playing Cards To Simulate a Molecular Clock Changes in DNA base-pair order may serve as an indicator of the time elapsed since divergence from
O N L I N E I N Q U I RY & I N V E S T I G AT I O N Using Playing Cards To Simulate a Molecular Clock Changes in DNA base-pair order may serve as an indicator of the time elapsed since divergence from
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i
 How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
Biology COE Task Version September Salmonberry Plants
 Salmonberry Plants Salmonberry plants can be found all along the Pacific coast. Salmonberry plants are a food source for many animals in Pacific coast ecosystems including hummingbirds, deer, and bear.
Salmonberry Plants Salmonberry plants can be found all along the Pacific coast. Salmonberry plants are a food source for many animals in Pacific coast ecosystems including hummingbirds, deer, and bear.
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation
 Name: Hour: From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation Introduction: In this activity you will learn how the genes in our DNA influence our characteristics. For example, how can a gene cause albinism
Name: Hour: From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation Introduction: In this activity you will learn how the genes in our DNA influence our characteristics. For example, how can a gene cause albinism
Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA H Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/SCIENCE A A161/02 Modules B1 B2 B3 (Higher Tier) *5955871405* Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Oxford Cambridge and RSA H Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/SCIENCE A A161/02 Modules B1 B2 B3 (Higher Tier) *5955871405* Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA H Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/SCIENCE A A161/02 Modules B1 B2 B3 (Higher Tier) *5955871405* Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Oxford Cambridge and RSA H Tuesday 17 May 2016 Afternoon GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/SCIENCE A A161/02 Modules B1 B2 B3 (Higher Tier) *5955871405* Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Appendix 14B: TIMSS 2015 Fourth Grade Science Item Descriptions Developed During the TIMSS 2015 Benchmarking
 Appendix 14B: TIMSS 2015 Fourth Grade Science Item Descriptions Developed During the TIMSS 2015 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) S02_01 S03_01 S05_05 S07_01 S08_03 S10_01 S14_02
Appendix 14B: TIMSS 2015 Fourth Grade Science Item Descriptions Developed During the TIMSS 2015 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) S02_01 S03_01 S05_05 S07_01 S08_03 S10_01 S14_02
Activities for Exhibit Exploration
 This worksheet will help guide you as you investigate our exhibits. If you have a camera, some questions can be answered by taking a picture. Otherwise, you may write your answers into the space provided.
This worksheet will help guide you as you investigate our exhibits. If you have a camera, some questions can be answered by taking a picture. Otherwise, you may write your answers into the space provided.
7.014 Quiz II Handout
 7.014 Quiz II Handout Quiz II: Wednesday, March 17 12:05-12:55 54-100 **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Friday, March 12 7:00-9:00 pm room 54-100 Open Tutoring Session: Tuesday,
7.014 Quiz II Handout Quiz II: Wednesday, March 17 12:05-12:55 54-100 **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Friday, March 12 7:00-9:00 pm room 54-100 Open Tutoring Session: Tuesday,
Charles Darwin. Charles Darwin. Charles Darwin. Darwin s Observations. Darwin s Observations 1/4/2018. Microevolution: Unique Gene Pools
 Charles Darwin Microevolution: Unique Gene Pools Charles Darwin (1809-1882) is credited with proposing that the mechanism for the process of evolution is natural selection. Darwin spent five years on a
Charles Darwin Microevolution: Unique Gene Pools Charles Darwin (1809-1882) is credited with proposing that the mechanism for the process of evolution is natural selection. Darwin spent five years on a
Lab # Relationships and Biodiversity
 Name: Period: Date: Lab # Relationships and Biodiversity Introduction: Botana curus is a valuable plant because it produces Curol, a compound used for treating certain kinds of cancer. Curol cannot be
Name: Period: Date: Lab # Relationships and Biodiversity Introduction: Botana curus is a valuable plant because it produces Curol, a compound used for treating certain kinds of cancer. Curol cannot be
A consumer that eats secondary consumers is a tertiary, or third level, consumer. Snakes and hawks are often the tertiary consumers in a food chain.
 Your muscles use energy to help you move, and your nervous system uses energy to help you understand the world around you. But how does your body obtain and use this energy? Animals, including humans,
Your muscles use energy to help you move, and your nervous system uses energy to help you understand the world around you. But how does your body obtain and use this energy? Animals, including humans,
Team name Ecology Science Olympiad Exam Middle School Level (Division B)
 Team name Ecology Science Olympiad Exam Middle School Level (Division B) You have 50 minutes to complete this test. You may use a non-programmable calculator on this exam. The number of points available
Team name Ecology Science Olympiad Exam Middle School Level (Division B) You have 50 minutes to complete this test. You may use a non-programmable calculator on this exam. The number of points available
