De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 1er partie
|
|
|
- Erick Eaton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 1er partie Christophe Dubois INSERM UMR-S-1076, Faculté de Pharmacie, Marseille, France
2 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Injury creation Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation Red : Platelets Green : P-selectin Computer control
3 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Injury creation Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation Red : Platelets Green : P-selectin Computer control
4 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Injury creation Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation Red : Platelets Green : P-selectin Computer control
5 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Injury creation Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation Red : Platelets Green : P-selectin Computer control
6 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Injury creation Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation Red : Platelets Green : P-selectin Computer control
7 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Injury creation Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation Red : Platelets Green : P-selectin Computer control
8 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Injury creation Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation Red : Platelets Green : P-selectin Computer control
9 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Computer control Injury creation Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation
10 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Computer control Injury creation Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation
11 The Equipment Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Filter array Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Computer control Injury creation Brightfield Imaging TTL syncronisation
12 The Equipment Red : Platelets Green : Fibrin Realtime Fluorescence Imaging Xenon Lamp (DG4) Fast Low Resolution Camera Image Intensifier Ablation Laser (Nitrogen) Galvinometric positioning control Injury creation Filter array Halogen Lamp Uniblitz Shutter Brightfield Imaging Piezoelectric focusing collar TTL syncronisation Slidebook (3I) and Deconvolution module Computer control
13 The model of laser-induced injury
14 The model of laser-induced injury Advantages : - No major traumatism induced (by the surgery) for the mouse, - The skin is thin enough to obtain high resolution brightfield images, independently of the weight of the mouse - Both arteries and veins are present
15 The model of laser-induced injury Advantages : - No major traumatism induced (by the surgery) for the mouse, - The skin is thin enough to obtain high resolution brightfield images, independently of the weight of the mouse - Both arteries and veins are present - The size, the power and the localization of the injury are controlled
16 The model of laser-induced injury Advantages : - No major traumatism induced (by the surgery) for the mouse, - The skin is thin enough to obtain high resolution brightfield images, independently of the weight of the mouse - Both arteries and veins are present - The size, the power and the localization of the injury are controlled thrombi per mouse / 2 h of experiment
17 The model of laser-induced injury Advantages : - No major traumatism induced (by the surgery) for the mouse, - The skin is thin enough to obtain high resolution brightfield images, independently of the weight of the mouse - Both arteries and veins are present - The size, the power and the localization of the injury are controlled thrombi per mouse / 2 h of experiment BUT :
18 The model of laser-induced injury Advantages : - No major traumatism induced (by the surgery) for the mouse, - The skin is thin enough to obtain high resolution brightfield images, independently of the weight of the mouse - Both arteries and veins are present - The size, the power and the localization of the injury are controlled thrombi per mouse / 2 h of experiment BUT : When shooting using the laser pulse, it s impossible to predict that one are localized in the right plane (necessary to induce an injury).the same effect may be induced by 1, 5 or 50 laser pulses.
19 The model of laser-induced injury Advantages : - No major traumatism induced (by the surgery) for the mouse, - The skin is thin enough to obtain high resolution brightfield images, independently of the weight of the mouse - Both arteries and veins are present - The size, the power and the localization of the injury are controlled thrombi per mouse / 2 h of experiment BUT : When shooting using the laser pulse, it s impossible to predict that one are localized in the right plane (necessary to induce an injury).the same effect may be induced by 1, 5 or 50 laser pulses. The B&Bs model :
20 The model of laser-induced injury Advantages : - No major traumatism induced (by the surgery) for the mouse, - The skin is thin enough to obtain high resolution brightfield images, independently of the weight of the mouse - Both arteries and veins are present - The size, the power and the localization of the injury are controlled thrombi per mouse / 2 h of experiment BUT : When shooting using the laser pulse, it s impossible to predict that one are localized in the right plane (necessary to induce an injury).the same effect may be induced by 1, 5 or 50 laser pulses. The B&Bs model : The number of pulses must be as minimal as possible to induce a thrombus (thrombi are not occlusive)
21 Kinetics of platelet accumulation after a laser-induced injury F platelets (Integrated Fluorescent Intensity (arbitrary units)) Median of 33 thrombi in 3 mice Elapsed time (sec)
22 1- an interaction between Collagen and platelets is required for thrombus formation
23 Accumulation of platelets in vivo after a FeCl3-induced injury -Injury induced by 10% FeCl3 for 5 min on the mesentery muscle. -Infusion of antibody directed against αiib labeled with Alexa-660. WT FcRγ -/-
24 Accumulation of platelets in vivo after a FeCl3-induced injury -Injury induced by 10% FeCl3 for 5 min on the mesentery muscle. -Infusion of antibody directed against αiib labeled with Alexa-660. WT FcRγ -/-
25 Accumulation of platelets in vivo after a FeCl3-induced injury -Injury induced by 10% FeCl3 for 5 min on the mesentery muscle. -Infusion of antibody directed against αiib labeled with Alexa-660. WT FcRγ -/-
26 Platelet accumulation in GPVI depleted mice after a laser-induced injury (n = 40, 3 mice) (n = 35, 3 mice) GPVI is not involved in platelet accumulation after a laserinduced injury
27 Collagen exposure to the blood circulation after a laser or a FeCl3-induced injury - Infusion of an antibody directed against αiib + an antibody directed against Collagen type I.
28 Collagen exposure to the blood circulation after a laser or a FeCl3-induced injury - Infusion of an antibody directed against αiib + an antibody directed against Collagen type I. FeCl3 WT Collagen Platelets Collagen FcRγ Platelets
29 Collagen exposure to the blood circulation after a laser or a FeCl3-induced injury - Infusion of an antibody directed against αiib + an antibody directed against Collagen type I. FeCl3 WT Collagen Platelets Collagen FcRγ Laser Platelets Platelets Platelets
30 Conclusions - GPVI is involved in vivo in the adhesion of platelets when collagen is exposed to the blood circulation.
31 Conclusions - GPVI is involved in vivo in the adhesion of platelets when collagen is exposed to the blood circulation. - After a laser-induced injury, GPVI-collagen interaction is not involved in thrombus formation.
32 Conclusions - GPVI is involved in vivo in the adhesion of platelets when collagen is exposed to the blood circulation. - After a laser-induced injury, GPVI-collagen interaction is not involved in thrombus formation. - The study of a thrombus formation in vivo using either a laser or a chemical injury is complementary and necessary to understand the different pathways involved in the thrombosis process.
33 Role of the coagulation cascade in the formation of a thrombus WT mouse FVIII -/- mouse
34 Role of the coagulation cascade in the formation of a thrombus WT mouse FVIII -/- mouse The activation of the coagulation cascade plays a key role in the thrombus induced by the dye laser
35 Kinetics of thrombus formation in WT mice and PAR4 -/- mice WT PAR4 Null Real-time video Real-time video
36 Kinetics of thrombus formation in WT mice and PAR4 -/- mice
37 1- an interaction between Collagen and platelets is required for thrombus formation Following a laser-induced injury thrombin but not collagen is playing a key role in thrombus formation 13
38 2- In vitro, addition of thrombin to plasma (washed platelets) induces a stable aggregation of platelets and immediate secretion of granule contents
39
40 Expression of P-selectin by platelets in vivo Platelets in red P-selectin in green
41 Before injury WT 20 s 100 s 150 s
42 Before injury WT 20 s 100 s 150 s Platelets do not seem to express P-selectin during the first 20 sec
43 2- In vitro, addition of thrombin to plasma (washed platelets) induces a stable aggregation of platelets and immediate secretion of granule contents In our model, most of the «platelet aggregate» induced by thrombin is reversible and platelets do not immediatly express P-selectin 18
44 3- In vitro, addition of thrombin to washed platelets induces a prolonged calcium mobilization (via a sequential activation of PAR1 and PAR4)
45 Importance of the Calcium Mobilization on platelet Activation Thrombin ADP Thromboxane A2 PAR, P2Y1, TxA2R G 12/13 Gq Shape Change Secretion PLC Ca 2+ αiibβ3 activation Aggregation
46 Infusion of 250 x10 6 (20%) platelets loaded with 3 µm Fura 2AM. Fura 2-loaded Platelets were followed by excitation at 380 nm (Fura 2 AM) and Calcium mobilization was followed by excitation at 340 nm (Fura 2-AM bound to calcium). 21
47 small thrombus mean size thrombus mean size thrombus Occlusive thrombus
48 small thrombus mean size thrombus mean size thrombus Occlusive thrombus
49 Real time Images of Calcium Mobilization in Platelets Pre-injury 15 sec 30 sec 45 sec 90 sec 150 sec
50 Real time Images of Calcium Mobilization in Platelets Pre-injury 15 sec 30 sec 45 sec 90 sec 150 sec - Calcium signal was observed in the fura-2 loaded platelets - All the platelets participating in the growing thrombus do not mobilize calcium
51 How long does a platelet remain in a growing thrombus? Duration of platelet residence in a growing thrombus (sec) sec Platelets that mobilize calcium 11 sec Platelets that do not mobilize calcium 9 sec BAPTA-AM treated Platelets A platelet that mobilizes calcium remains in the thrombus longer than a platelet that does not mobilize calcium 24
52 200 n = 17 (events), 14 thrombi Duration of platelet adhesion (sec) y = x ; R 2 = Duration of Calcium Mobilization (sec)
53
54 10 8 F platelets rd region 2 nd region 1 st region Elapsed time (sec) st region F calcium / F platelets nd region 3 rd region Elapsed time (sec)
55 Characteristics of Calcium Mobilization In Vivo : - By infusing Fura-2 loaded platelets we were able to follow platelet accumulation and calcium mobilization in vivo. - Platelets bind to a growing thrombus without mobilizing calcium. - Platelets that mobilize calcium after incorporation into a thrombus stay longer in the thrombus than platelets that do not mobilize calcium. - There is a direct correlation between the time that a platelet spends in a growing thrombus and the duration of the calcium spike. - Only one calcium peak was detected in our model. 28
56 Involvement of Thrombin in platelet activation WT FcRγ -/- WT + Hirudin PAR4 -/- Dubois C. et al. JCI, 2007
57 Calcium Mobilization and Thrombus formation in PAR4 null mice Platelets Calcium F platelets (arbitrary units) PAR4 WT F calcium (arbitrary units) PAR4 WT Elapsed time (sec) PAR4 null mice generate significantly smaller thrombi than wildtype mice following laser injury. Elapsed time (sec) Calcium mobilization in platelets from PAR4 null mice can be detected but is much reduced compared to wildtype. Dubois C. et al. JCI, 2007
58 Involvement of Thrombin on platelet activation Dubois C. et al. JCI, 2007
59 Involvement of Thrombin on platelet activation 0.1 F calcium / F platelets (arbitrary units) WT vwf-/- FcRγ-/- WT + Lepirudin PAR4 -/- Dubois C. et al. JCI, 2007
60
61 4- In vitro, ADP is a secondary agonist playing a (limited) role in platelet aggregation induced by thrombin, mainly via P2Y12
62 Accumulation of platelets in vivo after gavage of mice by Clopidogrel (30 mg/kg by gavage) Control Clopidogrel Clopidogrel Mezouar S. et al., in preparation
63 Mezouar S. et al., in preparation
64 Effect of Ticagrelor on Thrombus formation : WT mouse ticagrelor 150ng/g ticagrelor 30ng/g Platelets in green ticagrelor 15 ng/g Mezouar S. et al., in preparation
65 Effect of Ticagrelor on Thrombus formation : N= 30, 4 mice for each condition Mezouar S. et al., in preparation
66
67 4- In vitro, ADP is a secondary agonist playing a (limited) role in platelet aggregation induced by thrombin, mainly via P2Y12
68 4- In vitro, ADP is a secondary agonist playing a (limited) role in platelet aggregation induced by thrombin, mainly via P2Y12 In our model ADP seems to play a key role in thrombus formation
69 In vitro Evidences That a pulse of a Dye Laser Activates the Endothelium HUVEC cells labeled with Fluo-3 Courtesy of Dr Ben Atkinson, 3I
70 In vitro Evidences That a pulse of a Dye Laser Activates the Endothelium HUVEC cells labeled with Fluo-3 Courtesy of Dr Ben Atkinson, 3I
71 In vitro Evidences That a pulse of a Dye Laser Activates the Endothelium HUVEC cells labeled with Fluo-3 Targeting of single cells within a confluent culture of endothelial cells initiated calcium elevation in the targeted cell and was followed by a wave of calcium elevation in surrounding cells. Courtesy of Dr Ben Atkinson, 3I
72 In vitro Evidences That a pulse of a Dye Laser Activates the Endothelium HUVEC cells labeled with Fluo-3 Targeting of single cells within a confluent culture of endothelial cells initiated calcium elevation in the targeted cell and was followed by a wave of calcium elevation in surrounding cells. Courtesy of Dr Ben Atkinson, 3I
73 In Vivo Evidences That a pulse of a Dye Laser Activates the Endothelium Uptake of Fluo-4AM by the endothelium Courtesy of Dr B. Atkinson, 3I
74 In Vivo Evidences That a pulse of a Dye Laser Activates the Endothelium Uptake of Fluo-4AM by the endothelium Courtesy of Dr B. Atkinson, 3I
75 In Vivo Evidences That a pulse of a Dye Laser Activates the Endothelium Uptake of Fluo-4AM by the endothelium The observed calcium elevation was rapid (within 30 s) and preceded detection of platelets in the developing thrombus. These results demonstrate that the endothelium activates rapidly prior to thrombus formation in the laser induced thrombosis model. (Atkinson et al., Blood, 2010) Courtesy of Dr B. Atkinson, 3I
76 In Vivo Evidences That a pulse of a Dye Laser Activates the Endothelium Uptake of Fluo-4AM by the endothelium The observed calcium elevation was rapid (within 30 s) and preceded detection of platelets in the developing thrombus. These results demonstrate that the endothelium activates rapidly prior to thrombus formation in the laser induced thrombosis model. (Atkinson et al., Blood, 2010) Courtesy of Dr B. Atkinson, 3I
77
78
79
80 41
81 5- In vitro, negatively charged phospholipids exposed at the surface of activated platelets served as a matrix for the activation of the coagulation cascade 41
82 Involvement of Thrombin on platelet activation
83 Involvement of Thrombin on platelet activation 0.1 F calcium / F platelets (arbitrary units) WT vwf-/- FcRγ-/- WT + Lepirudin PAR4 -/-
84 Platelet and fibrin accumulation in wild-type and PAR4 KO thrombi Wild-type PAR4 KO 150 ng/g mouse of anti-cd41 Fab-Alexa ng/g mouse of anti-fibrin-alexa x real time, recording over 5 minutes Platelets: Red Fibrin: Green Platelets + Fibrin: Yellow
85 Maximum fibrin generation WT PAR4 KO Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test: z=0.18. No significant difference.
86
87 5- In vitro, negatively charged phospholipids exposed at the surface of activated platelets served as a matrix for the activation of the coagulation cascade
88 5- In vitro, negatively charged phospholipids exposed at the surface of activated platelets served as a matrix for the activation of the coagulation cascade In our model, other activated membrane surfaces (independent of the accumulated platelets) are sufficient for fibrin generation.
89 46
90 In this model, how thrombin is generated? 46
91 J Exp Med Jun 2;197(11): Accumulation of tissue factor into developing thrombi in vivo is dependent upon microparticle P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 and platelet P-selectin. Falati S, Liu Q, Gross P, Merrill-Skoloff G, Chou J, Vandendries E, Celi A, Croce K, Furie BC, Furie B. Center for Hemostasis and Thrombosis Research, Research East 319, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, 330 Brookline Avenue, Boston, MA 02215, USA. Abstract Using a laser-induced endothelial injury model, we examined thrombus formation in the microcirculation of wild-type and genetically altered mice by real-time in vivo microscopy to analyze this complex physiologic process in a system that includes the vessel wall, the presence of flowing blood, and the absence of anticoagulants. We observe P-selectin expression, tissue factor accumulation, and fibrin generation after platelet localization in the developing thrombus in arterioles of wild-type mice. However, mice lacking P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) or P-selectin, or wild-type mice infused with blocking P-selectin antibodies, developed platelet thrombi containing minimal tissue factor and fibrin. To explore the delivery of tissue factor into a developing thrombus, we identified monocytederived microparticles in human platelet-poor plasma that express tissue factor, PSGL-1, and CD14. Fluorescently labeled mouse microparticles infused into a recipient mouse localized within the developing thrombus, indicating that one pathway for the initiation of blood coagulation in vivo involves the accumulation of tissue factor- and PSGL-1-containing microparticles in the platelet thrombus expressing P-selectin. These monocyte-derived microparticles bind to activated platelets in an interaction mediated by platelet P- selectin and microparticle PSGL-1. We propose that PSGL-1 plays a role in blood coagulation in addition to its known role in leukocyte trafficking. However : - Exogenous MPs : not a direct proof of concept 47 - P-selectin -/- and PSGL1-/- mice have a normal thrombus formation
92 1- Via Monocyte-derived MPs expressing TF J Exp Med Jun 2;197(11): Accumulation of tissue factor into developing thrombi in vivo is dependent upon microparticle P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 and platelet P-selectin. Falati S, Liu Q, Gross P, Merrill-Skoloff G, Chou J, Vandendries E, Celi A, Croce K, Furie BC, Furie B. Center for Hemostasis and Thrombosis Research, Research East 319, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, 330 Brookline Avenue, Boston, MA 02215, USA. Abstract Using a laser-induced endothelial injury model, we examined thrombus formation in the microcirculation of wild-type and genetically altered mice by real-time in vivo microscopy to analyze this complex physiologic process in a system that includes the vessel wall, the presence of flowing blood, and the absence of anticoagulants. We observe P-selectin expression, tissue factor accumulation, and fibrin generation after platelet localization in the developing thrombus in arterioles of wild-type mice. However, mice lacking P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) or P-selectin, or wild-type mice infused with blocking P-selectin antibodies, developed platelet thrombi containing minimal tissue factor and fibrin. To explore the delivery of tissue factor into a developing thrombus, we identified monocytederived microparticles in human platelet-poor plasma that express tissue factor, PSGL-1, and CD14. Fluorescently labeled mouse microparticles infused into a recipient mouse localized within the developing thrombus, indicating that one pathway for the initiation of blood coagulation in vivo involves the accumulation of tissue factor- and PSGL-1-containing microparticles in the platelet thrombus expressing P-selectin. These monocyte-derived microparticles bind to activated platelets in an interaction mediated by platelet P- selectin and microparticle PSGL-1. We propose that PSGL-1 plays a role in blood coagulation in addition to its known role in leukocyte trafficking. However : - Exogenous MPs : not a direct proof of concept 47 - P-selectin -/- and PSGL1-/- mice have a normal thrombus formation
93 2- Via PDI : involved TF generation after a laser-induced injury However : - PDI is not specific of TF and inhibition of PDI may involve much 48 more signaling pathways affecting indirectly thrombus generation
94 49
95 From Bizzozero G. (1882), Virchows Arch. Pathol. Physiol. 49
Isolation of mouse monocytes: Mouse monocytes were isolated using a modified
 Supplemental Material Extended Methods Isolation of mouse monocytes: Mouse monocytes were isolated using a modified method described (1). Citrated mouse whole blood was mixed with equal volume of PBS,
Supplemental Material Extended Methods Isolation of mouse monocytes: Mouse monocytes were isolated using a modified method described (1). Citrated mouse whole blood was mixed with equal volume of PBS,
Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets
 Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets Article Accepted Version Figures and Legends Moraes, L. A., Unsworth, A. J., Vaiyapuri, S., Ali, M. S., Sasikumar, P., Sage, T., Flora,
Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets Article Accepted Version Figures and Legends Moraes, L. A., Unsworth, A. J., Vaiyapuri, S., Ali, M. S., Sasikumar, P., Sage, T., Flora,
Supplement Figure 1. Characterization of the moab. (A) A series of moabs that are anti-hαiib-specific were tested for their ability to bind to
 Supplement Figure 1. Characterization of the 312.8 moab. (A) A series of moabs that are anti-hαiib-specific were tested for their ability to bind to platelets. The black line represents the 312.8 moab
Supplement Figure 1. Characterization of the 312.8 moab. (A) A series of moabs that are anti-hαiib-specific were tested for their ability to bind to platelets. The black line represents the 312.8 moab
(B) Comparable expression of major integrin subunits and glycoproteins on the surface of resting WT and Lnk -/- platelets.
 Supplemental Figure S1. Characteristics of Lnk -/- platelets. (A) Electron micrographs of resting platelets showing the normal intracellular structure of Lnk -/ platelets. Samples were fixed with 4% PFA
Supplemental Figure S1. Characteristics of Lnk -/- platelets. (A) Electron micrographs of resting platelets showing the normal intracellular structure of Lnk -/ platelets. Samples were fixed with 4% PFA
Hemostasis and Thrombosis
 Hemostasis Hemostasis and Thrombosis Normal hemostasis is a consequence of tightly regulated processes that maintain blood in a fluid state in normal vessels, yet also permit the rapid formation of a hemostatic
Hemostasis Hemostasis and Thrombosis Normal hemostasis is a consequence of tightly regulated processes that maintain blood in a fluid state in normal vessels, yet also permit the rapid formation of a hemostatic
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES/TABLES:
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES/TABLES: Journal: Nature Biotechnology Article Title: Correction of the coagulation defect in hemophilia using a factor Xa variant with novel engineered protease function. Authors:
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES/TABLES: Journal: Nature Biotechnology Article Title: Correction of the coagulation defect in hemophilia using a factor Xa variant with novel engineered protease function. Authors:
Center for Hemostasis and Thrombosis Research, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
 Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 1: 60 68 REVIEW Thrombus formation: direct real-time observation and digital analysis of thrombus assembly in a living mouse by confocal and widefield intravital
Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 1: 60 68 REVIEW Thrombus formation: direct real-time observation and digital analysis of thrombus assembly in a living mouse by confocal and widefield intravital
Leukocyte-versus microparticle-mediated tissue factor transfer during arteriolar thrombus development
 Leukocyte-versus microparticle-mediated tissue factor transfer during arteriolar thrombus development Peter L. Gross, 1 Barbara C. Furie, Glenn Merrill-Skoloff, Janet Chou, 2 and Bruce Furie 3 Center for
Leukocyte-versus microparticle-mediated tissue factor transfer during arteriolar thrombus development Peter L. Gross, 1 Barbara C. Furie, Glenn Merrill-Skoloff, Janet Chou, 2 and Bruce Furie 3 Center for
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly -
 BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY PART 2 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 231 11 TH JULY 2011 Dr Karen Hayes Royal Devon & Exeter Correspondence to: kmhayes@hotmail.co.uk QUESTIONS Before continuing, try to answer the
BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY PART 2 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 231 11 TH JULY 2011 Dr Karen Hayes Royal Devon & Exeter Correspondence to: kmhayes@hotmail.co.uk QUESTIONS Before continuing, try to answer the
Plasma fibronectin supports hemostasis and regulates thrombosis
 The Journal of Clinical Investigation Plasma fibronectin supports hemostasis and regulates thrombosis Yiming Wang, 1,2,3 Adili Reheman, 2 Christopher M. Spring, 2 Jalil Kalantari, 2,4 Alexandra H. Marshall,
The Journal of Clinical Investigation Plasma fibronectin supports hemostasis and regulates thrombosis Yiming Wang, 1,2,3 Adili Reheman, 2 Christopher M. Spring, 2 Jalil Kalantari, 2,4 Alexandra H. Marshall,
KILLING THROMBUS WITH
 KILLING THROMBUS WITH D. Dash Department of Biochemistry Institute of Medical Sciences Banaras Hindu University Thrombus has two components: (1) Protein Component composed of Insoluble Fibrin Clot (2)
KILLING THROMBUS WITH D. Dash Department of Biochemistry Institute of Medical Sciences Banaras Hindu University Thrombus has two components: (1) Protein Component composed of Insoluble Fibrin Clot (2)
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
POST-ISTH: Novità dal meeting di Toronto 2015 Piastrine: fisiopatologia. Erica De Candia Università Cattolica -Roma
 POST-ISTH: Novità dal meeting di Toronto 2015 Piastrine: fisiopatologia Erica De Candia Università Cattolica -Roma Novità ISTH 2015: Piastrine: Fisiopatologia i) Alternative platelet function throughout
POST-ISTH: Novità dal meeting di Toronto 2015 Piastrine: fisiopatologia Erica De Candia Università Cattolica -Roma Novità ISTH 2015: Piastrine: Fisiopatologia i) Alternative platelet function throughout
Person responsible (Chair): Martine Jandrot-Perrus, Hans Deckmyn
 NAME OF PROJECT: Measurement of platelet activation markers: usefulness, current practices, future. Subcommittee: Platelet physiology Person responsible (Chair): Martine Jandrot-Perrus, Hans Deckmyn Design:
NAME OF PROJECT: Measurement of platelet activation markers: usefulness, current practices, future. Subcommittee: Platelet physiology Person responsible (Chair): Martine Jandrot-Perrus, Hans Deckmyn Design:
General Principles of. Hemostasis. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 General Principles of Hemostasis Kristine Krafts, M.D. Hemostasis is a balancing act! pro-ting plugs up holes in blood vessels anti-ting keeps ting under control Pro-Clotting Pro-Clotting vessels platelets
General Principles of Hemostasis Kristine Krafts, M.D. Hemostasis is a balancing act! pro-ting plugs up holes in blood vessels anti-ting keeps ting under control Pro-Clotting Pro-Clotting vessels platelets
These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides.
 These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides. If you would like the 1 slide per page handouts, please ask
These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides. If you would like the 1 slide per page handouts, please ask
Hemostasis. by Mohie-Aldien Elsayed
 Hemostasis by Mohie-Aldien Elsayed Hemostasis Hemostasis is defined as the process that maintains the flowing blood in a fluid state and confined to the circulatory system Coagulation prevents excess blood
Hemostasis by Mohie-Aldien Elsayed Hemostasis Hemostasis is defined as the process that maintains the flowing blood in a fluid state and confined to the circulatory system Coagulation prevents excess blood
Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy
 Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy Associate Professor Department of Physiology Objectives At the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Recognize the different clotting factors 2. Understand
Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy Associate Professor Department of Physiology Objectives At the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Recognize the different clotting factors 2. Understand
Dr. Vivien Chen [FINAL REPORT: KANEMATSU Final report for Vivien Chen: Kanematsu Memorial Award Outcomes:
 Final report for Vivien Chen: Kanematsu Memorial Award 2011 Outcomes: Thank you awarding me the 2011 Kanematsu Memorial Award. The grant has been instrumental in setting up this project and helping establish
Final report for Vivien Chen: Kanematsu Memorial Award 2011 Outcomes: Thank you awarding me the 2011 Kanematsu Memorial Award. The grant has been instrumental in setting up this project and helping establish
Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis Jessica Kay Hansen University of Iowa Copyright 2014 Jessica Kay
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis Jessica Kay Hansen University of Iowa Copyright 2014 Jessica Kay
Membrane microvesicles: a circulating source for fibrinolysis, new antithrombotic
 Membrane microvesicles: a circulating source for fibrinolysis, new antithrombotic messengers 1 Laurent Plawinski, 2,3 Eduardo Anglés-Cano 1 CNRS UMR 5248 Imagerie Moléculaire et Nanobiotechnologie, Université
Membrane microvesicles: a circulating source for fibrinolysis, new antithrombotic messengers 1 Laurent Plawinski, 2,3 Eduardo Anglés-Cano 1 CNRS UMR 5248 Imagerie Moléculaire et Nanobiotechnologie, Université
Platelet Adhesion and Aggregation Assays
 PPLICTION NOTE Platelet dhesion and ggregation ssays Microfluidic assays enable multi-parametric investigation of platelet behavior under flow. Relevant Research reas: Vascular Biology, Thrombosis and
PPLICTION NOTE Platelet dhesion and ggregation ssays Microfluidic assays enable multi-parametric investigation of platelet behavior under flow. Relevant Research reas: Vascular Biology, Thrombosis and
Adv Pathophysiology Unit 4 Page 1 of 10. Learning Objectives for this file:
 Adv Pathophysiology Unit 4 Page 1 of 10 Learning Objectives for this file: Topics include structure & function of: 1. Coagulation process platelets, clotting factors 2. Coagulation cascade formation of
Adv Pathophysiology Unit 4 Page 1 of 10 Learning Objectives for this file: Topics include structure & function of: 1. Coagulation process platelets, clotting factors 2. Coagulation cascade formation of
Session 1 Topics. Vascular Phase of Hemostasis. Coagulation Pathway. Action of Unfractionated Heparin. Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy
 ~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 1 of 4 Session 1 Topics Review of coagulation and the vascular phase of hemostasis Unfractionated heparin Low molecular
~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 1 of 4 Session 1 Topics Review of coagulation and the vascular phase of hemostasis Unfractionated heparin Low molecular
Platelet deposition (%) Fibronectin
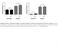 Platelet deposition (%) Platelet deposition (%) 60 p = 0.347 60 p = 1.000 40 p = 0.881 40 20 20 p = 0.114 0 Up Down Up Down 0 Up Down Up Down Fibrinogen Collagen I Fibronectin Collagen I Supplementary
Platelet deposition (%) Platelet deposition (%) 60 p = 0.347 60 p = 1.000 40 p = 0.881 40 20 20 p = 0.114 0 Up Down Up Down 0 Up Down Up Down Fibrinogen Collagen I Fibronectin Collagen I Supplementary
Chapter 19b Blood, cont d
 Chapter 19b Blood, cont d White Blood Cells WBCs account for less than 1% of blood volume. There are two major histological categories of WBCs the granulocytes and the agranulocytes. GRANULOCYTES are Basophils,
Chapter 19b Blood, cont d White Blood Cells WBCs account for less than 1% of blood volume. There are two major histological categories of WBCs the granulocytes and the agranulocytes. GRANULOCYTES are Basophils,
ISCT Paris April 25. Ex vivo platelet production Dominique Baruch INSERM UMR-S1140, Paris
 ISCT Paris April 25 Ex vivo platelet production Dominique Baruch INSERM UMR-S1140, Paris Platelet functions: to stop bleeding and beyond Adhesion Aggregation Clot retraction Secretion Procoagulant activity
ISCT Paris April 25 Ex vivo platelet production Dominique Baruch INSERM UMR-S1140, Paris Platelet functions: to stop bleeding and beyond Adhesion Aggregation Clot retraction Secretion Procoagulant activity
Lnk regulates integrin αiibβ3 outside-in signaling in mouse platelets, leading to stabilization of thrombus development in vivo
 Research article Lnk regulates integrin αiibβ3 outside-in signaling in mouse platelets, leading to stabilization of thrombus development in vivo Hitoshi Takizawa, 1 Satoshi Nishimura, 2,3,4 Naoya Takayama,
Research article Lnk regulates integrin αiibβ3 outside-in signaling in mouse platelets, leading to stabilization of thrombus development in vivo Hitoshi Takizawa, 1 Satoshi Nishimura, 2,3,4 Naoya Takayama,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1
 SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE 1 C D E F G * Supplementary Fig. 1: Platelets from Pik3c2b mice exhibit normal function. () Expression of platelet-specific glycoproteins on the surface of platelets in whole blood
SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE 1 C D E F G * Supplementary Fig. 1: Platelets from Pik3c2b mice exhibit normal function. () Expression of platelet-specific glycoproteins on the surface of platelets in whole blood
-- Laki J. Rousou, MS, MD et. al. -- Boston, Massachusetts. -- Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87:62 70.
 -- Laki J. Rousou, MS, MD et. al -- Boston, Massachusetts. -- Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87:62 70. Presented by: Int. 黃柏翔 Date: 2009 /02 / 25 Patient outcome after CABG surgery greatly influenced by patency
-- Laki J. Rousou, MS, MD et. al -- Boston, Massachusetts. -- Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87:62 70. Presented by: Int. 黃柏翔 Date: 2009 /02 / 25 Patient outcome after CABG surgery greatly influenced by patency
What Can We Learn from Animal Models of Coagulopathy and Bleeding (about plasma transfusion)?
 Test What Can We Learn from Animal Models of Coagulopathy and Bleeding (about plasma transfusion)? William Sheffield Associate Director, Research CBS Centre for Innovation, and Professor, Pathology and
Test What Can We Learn from Animal Models of Coagulopathy and Bleeding (about plasma transfusion)? William Sheffield Associate Director, Research CBS Centre for Innovation, and Professor, Pathology and
A systems approach to hemostasis: 3. Thrombus consolidation regulates intrathrombus solute transport and local thrombin activity
 Regular Article THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS A systems approach to hemostasis: 3. Thrombus consolidation regulates intrathrombus solute transport and local thrombin activity Timothy J. Stalker, 1 John D.
Regular Article THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS A systems approach to hemostasis: 3. Thrombus consolidation regulates intrathrombus solute transport and local thrombin activity Timothy J. Stalker, 1 John D.
Supplementary Figure 1. Microchannel controls & in vivo flow deceleration model.
 Mean flow velocity ( m.s ) a c Platelet velocity ( m.s ) [1 m from channel ottom] 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Localized crush injury & thromus growth acceleration Shear gradient geometry Straight channel (1,8 s
Mean flow velocity ( m.s ) a c Platelet velocity ( m.s ) [1 m from channel ottom] 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Localized crush injury & thromus growth acceleration Shear gradient geometry Straight channel (1,8 s
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Montfoort, M. L. (2014). Factor XI
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Montfoort, M. L. (2014). Factor XI
Platelets in mammals are anucleated cells that originate. Reviews. Adhesion Mechanisms in Platelet Function
 Reviews This Review is part of a thematic series on Mechanisms, Models, and In Vivo Imaging of Thrombus Formation, which includes the following articles: Activation of Platelet Function Through G Protein
Reviews This Review is part of a thematic series on Mechanisms, Models, and In Vivo Imaging of Thrombus Formation, which includes the following articles: Activation of Platelet Function Through G Protein
Connie H. Y. Wong, Craig N Jenne, Björn Petri, Navina L. Chrobok and Paul Kubes
 Nucleation of platelets with bloodborne pathogens on Kupffer cell precedes other innate immunity and contributes to bacterial clearance Connie H. Y. Wong, Craig N Jenne, Björn Petri, Navina L. Chrobok
Nucleation of platelets with bloodborne pathogens on Kupffer cell precedes other innate immunity and contributes to bacterial clearance Connie H. Y. Wong, Craig N Jenne, Björn Petri, Navina L. Chrobok
Ch 13: Blood. What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection:
 Ch 13: Blood What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection: SLOs Describe the composition of plasma and list the major functions of plasma proteins. Map hematopoiesis, starting from a pluripotent
Ch 13: Blood What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection: SLOs Describe the composition of plasma and list the major functions of plasma proteins. Map hematopoiesis, starting from a pluripotent
Supplementary Information. Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells
 Supplementary Information Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells Damian Medici 1, Eileen M. Shore 2,3,4, Vitali Y. Lounev 2,4, Frederick S. Kaplan 2,4,5, Raghu Kalluri
Supplementary Information Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells Damian Medici 1, Eileen M. Shore 2,3,4, Vitali Y. Lounev 2,4, Frederick S. Kaplan 2,4,5, Raghu Kalluri
Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders
 CAA 2015 Annual Conference Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders Bob Miller, A October 8, 2015 VWF has two jobs Loosely bound to protect FVIII and tether to site of injury All other coagulation factors also
CAA 2015 Annual Conference Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders Bob Miller, A October 8, 2015 VWF has two jobs Loosely bound to protect FVIII and tether to site of injury All other coagulation factors also
Local vasoconstriction. is due to local spasm of the smooth muscle (symp. reflex) can be maintained by platelet vasoconstrictors
 Hemostasis Hemostasis ( hemo =blood; sta= remain ) is the stoppage of bleeding, which is vitally important when blood vessels are damaged. Following an injury to blood vessels several actions may help
Hemostasis Hemostasis ( hemo =blood; sta= remain ) is the stoppage of bleeding, which is vitally important when blood vessels are damaged. Following an injury to blood vessels several actions may help
Platelet Activation by Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Haemostasis and Thrombosis
 1358 Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2009, 15, 1358-1372 Platelet Activation by Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Haemostasis and Thrombosis Steve P. Watson * Centre for Cardiovascular Sciences, Institute
1358 Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2009, 15, 1358-1372 Platelet Activation by Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Haemostasis and Thrombosis Steve P. Watson * Centre for Cardiovascular Sciences, Institute
Profibrinolytic diabody targeting PAI-1 and TAFI for treatment of acute thrombotic disorders
 ProFiDIΛ Profibrinolytic diabody targeting PAI-1 and TAFI for treatment of acute thrombotic disorders THROMBOLYSIS WITH IMPROVED SAFETY A valorisation project of Unmet Medical Need = Safe Thrombolysis
ProFiDIΛ Profibrinolytic diabody targeting PAI-1 and TAFI for treatment of acute thrombotic disorders THROMBOLYSIS WITH IMPROVED SAFETY A valorisation project of Unmet Medical Need = Safe Thrombolysis
BLOOD COAGULATION. 1. The initial phase of the process is vascular constriction. This limits the flow of blood to the area of injury.
 BLOOD COAGULATION The ability of the body to control the flow of blood following vascular injury is paramount to continued survival. The process of blood clotting and then the subsequent dissolution of
BLOOD COAGULATION The ability of the body to control the flow of blood following vascular injury is paramount to continued survival. The process of blood clotting and then the subsequent dissolution of
Endothelium conference
 Endothelium conference Epithelium FUNCTIONS: COVER ORGANS, LINE VISCERA AND BLOOD VESSELS, SECRETORY CELLS OF GLANDS DISTINGUISHING FEATURES AND DISTRIBUTION: ALWAYS SIT ON A BASEMENT MEMBRANE, BUT COME
Endothelium conference Epithelium FUNCTIONS: COVER ORGANS, LINE VISCERA AND BLOOD VESSELS, SECRETORY CELLS OF GLANDS DISTINGUISHING FEATURES AND DISTRIBUTION: ALWAYS SIT ON A BASEMENT MEMBRANE, BUT COME
Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time. Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO
 Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO Hemostasis A series of reactions that function to stop bleeding, maintaining
Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO Hemostasis A series of reactions that function to stop bleeding, maintaining
Microparticles and a P-selectin-mediated pathway of blood coagulation
 Disease Markers 20 (2004) 347 352 347 IOS Press Microparticles and a P-selectin-mediated pathway of blood coagulation Alessandro Celi a,c, Roberto Lorenzet b, Barbara C. Furie c and Bruce Furie c, a Laboratorio
Disease Markers 20 (2004) 347 352 347 IOS Press Microparticles and a P-selectin-mediated pathway of blood coagulation Alessandro Celi a,c, Roberto Lorenzet b, Barbara C. Furie c and Bruce Furie c, a Laboratorio
Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis Jun Xu 1, Xiaomei Zhang 2, Rosana Pelayo 3, Marc Monestier 4, Concetta T. Ammollo 1, Fabrizio Semeraro 1, Fletcher
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis Jun Xu 1, Xiaomei Zhang 2, Rosana Pelayo 3, Marc Monestier 4, Concetta T. Ammollo 1, Fabrizio Semeraro 1, Fletcher
Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human
 Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
C-type natriuretic peptide signalling and cardiovascular disease Adrian Hobbs
 C-type natriuretic peptide signalling and cardiovascular disease Adrian Hobbs Professor of Cardiovascular Pharmacology William Harvey Research Institute Barts & The London School of Medicine & Dentistry
C-type natriuretic peptide signalling and cardiovascular disease Adrian Hobbs Professor of Cardiovascular Pharmacology William Harvey Research Institute Barts & The London School of Medicine & Dentistry
Linking in silico and in vitro experiments to identify and evaluate a biomarker for enoxaparin activity
 Linking in silico and in vitro experiments to identify and evaluate a biomarker for enoxaparin activity Abhishek Gulati What is enoxaparin? Low molecular weight heparin anticoagulant Used to minimise the
Linking in silico and in vitro experiments to identify and evaluate a biomarker for enoxaparin activity Abhishek Gulati What is enoxaparin? Low molecular weight heparin anticoagulant Used to minimise the
Supporting Information. Engineering PD-1-Presenting Platelets for Cancer Immunotherapy
 Supporting Information Engineering PD-1-Presenting Platelets for Cancer Immunotherapy Xudong Zhang,,, #, Jinqiang Wang,, #, Zhaowei Chen, Quanyin Hu, Chao Wang, Junjie Yan, Gianpietro Dotti, Peng Huang,
Supporting Information Engineering PD-1-Presenting Platelets for Cancer Immunotherapy Xudong Zhang,,, #, Jinqiang Wang,, #, Zhaowei Chen, Quanyin Hu, Chao Wang, Junjie Yan, Gianpietro Dotti, Peng Huang,
engineering microvasculature-on-chip models as research-enabling systems for hemostasis and thrombosis
 engineering microvasculature-on-chip models as research-enabling systems for hemostasis and thrombosis Wilbur A. Lam, MD, PhD Associate Professor Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering
engineering microvasculature-on-chip models as research-enabling systems for hemostasis and thrombosis Wilbur A. Lam, MD, PhD Associate Professor Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering
Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor?
 Review article Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor? Bernhard Nieswandt and Steve P. Watson At sites of vascular injury, platelets come into contact with subendothelial collagen,
Review article Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor? Bernhard Nieswandt and Steve P. Watson At sites of vascular injury, platelets come into contact with subendothelial collagen,
In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit
 In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1323 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1323 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Coagulation in perspective: Blood management. Objectives
 Coagulation in perspective: Blood management Julie Wegner, PhD jawrbl@gmail.com Objectives To gain a basic understanding of the following: 1. Coagulation components and processes Why patients bleed. 2.
Coagulation in perspective: Blood management Julie Wegner, PhD jawrbl@gmail.com Objectives To gain a basic understanding of the following: 1. Coagulation components and processes Why patients bleed. 2.
Bivalirudin (Angiomax ) vs. Heparin during Peripheral Vascular Interventions: Which is Better and How to Decide?
 Bivalirudin (Angiomax ) vs. Heparin during Peripheral Vascular Interventions: Which is Better and How to Decide? Vinod Nair MD FACC FSCAI Cardiovascular Ins6tute of the South, Houma Financial Disclosure:
Bivalirudin (Angiomax ) vs. Heparin during Peripheral Vascular Interventions: Which is Better and How to Decide? Vinod Nair MD FACC FSCAI Cardiovascular Ins6tute of the South, Houma Financial Disclosure:
2013 Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Bleeding Disorders Second edition David Green MD PhD Professor of Medicine Emeritus Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chicago, Illinois, USA Christopher A Ludlam
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Bleeding Disorders Second edition David Green MD PhD Professor of Medicine Emeritus Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chicago, Illinois, USA Christopher A Ludlam
Pharmacology Lecture 5. Anticoagulants
 Pharmacology Lecture 5 Anticoagulants General overview Anti-thrombotic Drugs Antiplatlets Anticoagulants Fibrinolytics Anticoagulants Indirect Thrombin Inhibitors Anti-thrombotic effect is exerted by interaction
Pharmacology Lecture 5 Anticoagulants General overview Anti-thrombotic Drugs Antiplatlets Anticoagulants Fibrinolytics Anticoagulants Indirect Thrombin Inhibitors Anti-thrombotic effect is exerted by interaction
ADP, 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), EDTA and ethidium bromide were from Sigma.
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Expanded Materials and Methods Materials ADP, 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), EDTA and ethidium bromide were from Sigma. PAR-4 TRAP (AYPGKF) was custom synthesised by AnaSpec, USA. The
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Expanded Materials and Methods Materials ADP, 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), EDTA and ethidium bromide were from Sigma. PAR-4 TRAP (AYPGKF) was custom synthesised by AnaSpec, USA. The
Molecular Mechanism of Platelet Activation 제주대학교병원내과 주승재
 Molecular Mechanism of Platelet Activation 제주대학교병원내과 주승재 Platelet Adhesion, Activation and Aggregation Normal platelets in flowing blood Platelets adhering to damaged endothelium and undergoing activation
Molecular Mechanism of Platelet Activation 제주대학교병원내과 주승재 Platelet Adhesion, Activation and Aggregation Normal platelets in flowing blood Platelets adhering to damaged endothelium and undergoing activation
PLEASE DO NOT REMOVE THIS PAGE
 Thank you for downloading this document from the RMIT ResearchR Repository Citation: Alshahrani, M, Yang, E, Yip, C, Ghanem, S, Abdallah, S, deangelis, A, O'Malley, C, Moheimani, F, Najjar, S and Jackson,
Thank you for downloading this document from the RMIT ResearchR Repository Citation: Alshahrani, M, Yang, E, Yip, C, Ghanem, S, Abdallah, S, deangelis, A, O'Malley, C, Moheimani, F, Najjar, S and Jackson,
Hematology Emergencies: Problems with Platelets
 Hematology Emergencies: Problems with Platelets Christian Cable, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Texas A&M HSC College of Medicine Scott & White Healthcare Fundamentals
Hematology Emergencies: Problems with Platelets Christian Cable, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Texas A&M HSC College of Medicine Scott & White Healthcare Fundamentals
The Coagulation Workup In The Office Setting
 CAA Conference alm Springs 2012 The Coagulation Workup In The Office Setting CAA Conference alm Springs, October 2012 Robert Miller, A-C Henoch-Schoenlein urpura 1 CAA Conference alm Springs 2012 2 CAA
CAA Conference alm Springs 2012 The Coagulation Workup In The Office Setting CAA Conference alm Springs, October 2012 Robert Miller, A-C Henoch-Schoenlein urpura 1 CAA Conference alm Springs 2012 2 CAA
OERMATAN SULFATE: A NEW CONCEPT IN ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY
 OERMATAN SULFATE: A NEW CONCEPT IN ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY by JOANNE VAN RYN-McKENNA, B.Sc., M.Sc. A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the
OERMATAN SULFATE: A NEW CONCEPT IN ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY by JOANNE VAN RYN-McKENNA, B.Sc., M.Sc. A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the
Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy
 Jean-Francois Pittet, M.D. Depts of Anesthesia and Surgery Cardiovascular Research Institute University of California San Francisco Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy Plan 1. Description of the coagulation system
Jean-Francois Pittet, M.D. Depts of Anesthesia and Surgery Cardiovascular Research Institute University of California San Francisco Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy Plan 1. Description of the coagulation system
Regulation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and their Bone Marrow Niches by the Coagulation System*.
 Regulation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and their Bone Marrow Niches by the Coagulation System*. * Via PAR-1 & CXCR4 upregulation, SDF-1 secretion and EPCR shedding. By Tsvee Lapidot, Ph.D. Weizmann Institute
Regulation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and their Bone Marrow Niches by the Coagulation System*. * Via PAR-1 & CXCR4 upregulation, SDF-1 secretion and EPCR shedding. By Tsvee Lapidot, Ph.D. Weizmann Institute
Hypercoagulation. CP Conference 11/14/2006
 Hypercoagulation CP Conference 11/14/2006 Overview Hypercoagulation: poorly understood phenomena No definite cause is identified in > 40% of cases Three major factors in thrombus formation (Rudolf Virchow,
Hypercoagulation CP Conference 11/14/2006 Overview Hypercoagulation: poorly understood phenomena No definite cause is identified in > 40% of cases Three major factors in thrombus formation (Rudolf Virchow,
von Willebrand factor: a hemostatic protein
 von Willebrand factor: a hemostatic protein!"#$%&'()*+',,-.'/01*+23'45'6*78+95' Cécile Denis INSERM U770 Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France University of Ferrara October 19th, 2012! Presentation schedule! Basic
von Willebrand factor: a hemostatic protein!"#$%&'()*+',,-.'/01*+23'45'6*78+95' Cécile Denis INSERM U770 Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France University of Ferrara October 19th, 2012! Presentation schedule! Basic
A humanized GPVI mouse model to assess the antithrombotic. efficacy of anti-gpvi agents
 JPET Fast This article Forward. has not Published been copyedited on and January formatted. 11, The final 2012 version as DOI:10.1124/jpet.111.189050 may differ from this version. A humanized GPVI mouse
JPET Fast This article Forward. has not Published been copyedited on and January formatted. 11, The final 2012 version as DOI:10.1124/jpet.111.189050 may differ from this version. A humanized GPVI mouse
Caplacizumab. Wholly-owned anti-vwf Nanobody
 1 Caplacizumab Wholly-owned anti-vwf Nanobody First-in-class bivalent Nanobody with Orphan Drug Status and patent protection up to 2035 Developed for the treatment of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic
1 Caplacizumab Wholly-owned anti-vwf Nanobody First-in-class bivalent Nanobody with Orphan Drug Status and patent protection up to 2035 Developed for the treatment of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
Title: Interactions Between Stably Rolling Leukocytes In Vivo
 Brief Report: submitted to Physical Review E Title: Interactions Between Stably Rolling Leukocytes In Vivo Authors: Michael R. King, Aimee D. Ruscio, Michael B. Kim Department of Biomedical Engineering
Brief Report: submitted to Physical Review E Title: Interactions Between Stably Rolling Leukocytes In Vivo Authors: Michael R. King, Aimee D. Ruscio, Michael B. Kim Department of Biomedical Engineering
If not heparin for bypass then what? Dr Tony Moriarty Consultant Cardiac Anaesthetist Birmingham United Kingdom
 If not heparin for bypass then what? Dr Tony Moriarty Consultant Cardiac Anaesthetist Birmingham United Kingdom Heparin Discovered 1916, commercial available 1935 Heparin Is there an alternative, not really
If not heparin for bypass then what? Dr Tony Moriarty Consultant Cardiac Anaesthetist Birmingham United Kingdom Heparin Discovered 1916, commercial available 1935 Heparin Is there an alternative, not really
Using TEG in the ED, OR, and ICU. Don H. Van Boerum, MD, FACS
 Using TEG in the ED, OR, and ICU Don H. Van Boerum, MD, FACS Trauma Surgeon, Director of Surgical Critical Care, Co-Director of Shock Trauma ICU, Intermountain Medical Center, Intermountain Healthcare
Using TEG in the ED, OR, and ICU Don H. Van Boerum, MD, FACS Trauma Surgeon, Director of Surgical Critical Care, Co-Director of Shock Trauma ICU, Intermountain Medical Center, Intermountain Healthcare
Supplementary Figure 1 Caspase-8 deficient platelets respond normally to agonists and ABT-737 (A) Surface expression of GPIX, GPIb, GPVI and CD41
 Supplementary Figure 1 Caspase-8 deficient platelets respond normally to agonists and ABT-737 (A) Surface expression of GPIX, GPIb, GPVI and CD41 were assessed on purified platelets from Casp8 fl/fl and
Supplementary Figure 1 Caspase-8 deficient platelets respond normally to agonists and ABT-737 (A) Surface expression of GPIX, GPIb, GPVI and CD41 were assessed on purified platelets from Casp8 fl/fl and
A Microfluidic Approach For Investigating The Role Of Blood Flow In Thrombosis
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 2018 A Microfluidic Approach For Investigating The Role Of Blood Flow In Thrombosis Bradley Andrew Herbig University of
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 2018 A Microfluidic Approach For Investigating The Role Of Blood Flow In Thrombosis Bradley Andrew Herbig University of
Special Coagulation - APC Resistance. DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: Technical Support:
 Special Coagulation - APC Resistance DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: 1.800.526.5224 Technical Support:1.800.447.3846 www.diapharma.com 1 Review of Hemostasis Overview Pathways of coagulation, anticoagulation,
Special Coagulation - APC Resistance DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: 1.800.526.5224 Technical Support:1.800.447.3846 www.diapharma.com 1 Review of Hemostasis Overview Pathways of coagulation, anticoagulation,
Gap junctions are key mediators of intercellular communication,
 Gap Junctions and Connexin Hemichannels Underpin Hemostasis and Thrombosis Sakthivel Vaiyapuri, PhD; Chris I. Jones, PhD; Parvathy Sasikumar, MSc; Leonardo A. Moraes, PhD; Stephanie J. Munger, BS; Joy
Gap Junctions and Connexin Hemichannels Underpin Hemostasis and Thrombosis Sakthivel Vaiyapuri, PhD; Chris I. Jones, PhD; Parvathy Sasikumar, MSc; Leonardo A. Moraes, PhD; Stephanie J. Munger, BS; Joy
The Power in You. TM
 RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) The Power in You. TM Biologics Concentrated on Healing RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) The RegenKit THT is designed to be used
RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) The Power in You. TM Biologics Concentrated on Healing RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (A-PRP) The RegenKit THT is designed to be used
WFH 2014 World Congress Medical Free Paper 8 ALN AT3: An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia
 WFH 214 World Congress Medical Free Paper 8 ALN AT3: An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia May 15, 214 Akin Akinc, PhD Antithrombin and ALN-AT3 Program
WFH 214 World Congress Medical Free Paper 8 ALN AT3: An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia May 15, 214 Akin Akinc, PhD Antithrombin and ALN-AT3 Program
Reagents. N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fmlf), human thrombin, antihuman
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Materials and Methods Reagents. N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fmlf), human thrombin, antihuman talin1, and other chemicals were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). AntiphosphoAkt-Ser473
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Materials and Methods Reagents. N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fmlf), human thrombin, antihuman talin1, and other chemicals were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). AntiphosphoAkt-Ser473
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA
 Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0523 TITLE: Complement Activation Alters Platelet Function PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George Tsokos, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA
Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0523 TITLE: Complement Activation Alters Platelet Function PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George Tsokos, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA
Our detailed aims were:
 1 Fortsatt utveckling och validering av screeningtester för evaluering av industriellt och miljö producerade partiklars toxicitet (diarienr 150144 - Bo Nilsson) Aim The original aim of the study was to
1 Fortsatt utveckling och validering av screeningtester för evaluering av industriellt och miljö producerade partiklars toxicitet (diarienr 150144 - Bo Nilsson) Aim The original aim of the study was to
OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS
 OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD, FRCP(C) Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional Laboratory Medicine Program Professor, Pathology and Molecular
OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD, FRCP(C) Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional Laboratory Medicine Program Professor, Pathology and Molecular
Mouse Factor XII Total ELISA Kit
 Mouse Factor XII Total ELISA Kit Catalog No: IMFXIIKT-TOT Lot No: SAMPLE INTENDED USE This mouse coagulation Factor XII antigen assay is intended for the quantitative determination of total Factor XII
Mouse Factor XII Total ELISA Kit Catalog No: IMFXIIKT-TOT Lot No: SAMPLE INTENDED USE This mouse coagulation Factor XII antigen assay is intended for the quantitative determination of total Factor XII
BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer. Nil Emre, PhD BD Biosciences R&D Manager, Stem Cells and Cell Function
 BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer Nil Emre, PhD BD Biosciences R&D Manager, Stem Cells and Cell Function The BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer System An affordable, full-featured, easy-to-use flow cytometer Two lasers
BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer Nil Emre, PhD BD Biosciences R&D Manager, Stem Cells and Cell Function The BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer System An affordable, full-featured, easy-to-use flow cytometer Two lasers
Dr. Susan Louw Haematopathologist NHLS / WITS / SASTH
 Dr. Susan Louw Haematopathologist NHLS / WITS / SASTH Since 1948 Initially a research tool Utility in management of bleeding and thrombosis Guide clotting factor replacement, platelet / blood transfusions
Dr. Susan Louw Haematopathologist NHLS / WITS / SASTH Since 1948 Initially a research tool Utility in management of bleeding and thrombosis Guide clotting factor replacement, platelet / blood transfusions
OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH CONTRACT NO C-0118 CONTRACT N C-0149
 OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH CONTRACT NO0014-88-C-0118 CONTRACT N00014-94-C-0149 CO TECHNICAL REPORT 95-04 $ ) IN VIVO TRACKING OF PLATELETS: CIRCULATING DEGRANULATED PLATELETS RAPIDLY LOSE SURFACE P- SELECTIN
OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH CONTRACT NO0014-88-C-0118 CONTRACT N00014-94-C-0149 CO TECHNICAL REPORT 95-04 $ ) IN VIVO TRACKING OF PLATELETS: CIRCULATING DEGRANULATED PLATELETS RAPIDLY LOSE SURFACE P- SELECTIN
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Can Biomarkers Help to Guide Duration of Therapy After VTE? New Chest Guidelines 2016
 Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Can Biomarkers Help to Guide Duration of Therapy After VTE? Marlene Grenon, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco UCSF Vascular Surgery Symposium
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Can Biomarkers Help to Guide Duration of Therapy After VTE? Marlene Grenon, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco UCSF Vascular Surgery Symposium
Gap junctions are key mediators of intercellular communication,
 Gap Junctions and Connexin Hemichannels Underpin Hemostasis and Thrombosis Sakthivel Vaiyapuri, PhD; Chris I. Jones, PhD; Parvathy Sasikumar, MSc; Leonardo A. Moraes, PhD; Stephanie J. Munger, BS; Joy
Gap Junctions and Connexin Hemichannels Underpin Hemostasis and Thrombosis Sakthivel Vaiyapuri, PhD; Chris I. Jones, PhD; Parvathy Sasikumar, MSc; Leonardo A. Moraes, PhD; Stephanie J. Munger, BS; Joy
Gap junctions are key mediators of intercellular communication,
 Gap Junctions and Connexin Hemichannels Underpin Hemostasis and Thrombosis Sakthivel Vaiyapuri, PhD; Chris I. Jones, PhD; Parvathy Sasikumar, MSc; Leonardo A. Moraes, PhD; Stephanie J. Munger, BS; Joy
Gap Junctions and Connexin Hemichannels Underpin Hemostasis and Thrombosis Sakthivel Vaiyapuri, PhD; Chris I. Jones, PhD; Parvathy Sasikumar, MSc; Leonardo A. Moraes, PhD; Stephanie J. Munger, BS; Joy
Lina Al-Lawama. Rama Al-Ashqar. Malik Al-Zohlof
 2 Lina Al-Lawama Rama Al-Ashqar Malik Al-Zohlof Anticoagulant drugs Recap Last lecture we were talking about antiplatelet drugs, we mentioned 5 drugs : Aspirin which is used alone with patents that have
2 Lina Al-Lawama Rama Al-Ashqar Malik Al-Zohlof Anticoagulant drugs Recap Last lecture we were talking about antiplatelet drugs, we mentioned 5 drugs : Aspirin which is used alone with patents that have
Novel Anti-coagulant Agents. David G Hovord BA MB BChir FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor University of Michigan
 Novel Anti-coagulant Agents David G Hovord BA MB BChir FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor University of Michigan Objectives Provide an overview of the normal coagulation, including perioperative testing
Novel Anti-coagulant Agents David G Hovord BA MB BChir FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor University of Michigan Objectives Provide an overview of the normal coagulation, including perioperative testing
Test di funzione piastrinica
 PIASTRINE 2015 V CORSO NAZIONALE DI AGGIORNAMENTO Milano, 11-12 novembre Università degli Studi di Milano Test di funzione piastrinica Silvia Riondino IRCCS San Raffaele, Roma Università di Roma Tor Vergata
PIASTRINE 2015 V CORSO NAZIONALE DI AGGIORNAMENTO Milano, 11-12 novembre Università degli Studi di Milano Test di funzione piastrinica Silvia Riondino IRCCS San Raffaele, Roma Università di Roma Tor Vergata
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin
 Supplementary Information 1 Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin and ribosomal protein L19 (RPL19) mrna in cleft and bud epithelial cells of embryonic salivary
Supplementary Information 1 Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin and ribosomal protein L19 (RPL19) mrna in cleft and bud epithelial cells of embryonic salivary
Study of methods for platelet function testing in the perspective of lab-on-chip applications van Zijp, H.M.
 Study of methods for platelet function testing in the perspective of lab-on-chip applications van Zijp, H.M. DOI: 10.6100/IR741658 Published: 01/01/2013 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as
Study of methods for platelet function testing in the perspective of lab-on-chip applications van Zijp, H.M. DOI: 10.6100/IR741658 Published: 01/01/2013 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as
Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture.
 Liao et al., KLF4 regulates macrophage polarization Revision of Manuscript 45444-RG- Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture. Thioglycollate
Liao et al., KLF4 regulates macrophage polarization Revision of Manuscript 45444-RG- Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture. Thioglycollate
mediated by endothelial P-selectin
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 92, pp. 7450-7454, August 1995 Cell Biology Platelets roll on stimulated endothelium in vivo: An interaction mediated by endothelial P-selectin PAUL S. FRENETTE*t, ROBERT
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 92, pp. 7450-7454, August 1995 Cell Biology Platelets roll on stimulated endothelium in vivo: An interaction mediated by endothelial P-selectin PAUL S. FRENETTE*t, ROBERT
Studies seeking to understand the basis of thrombosis or to
 In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging of Large-Vessel Thrombosis in Mice Brian C. Cooley Objective Experimental studies of large-vessel thrombosis have been adapted for applications in mice, but they proffer limited
In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging of Large-Vessel Thrombosis in Mice Brian C. Cooley Objective Experimental studies of large-vessel thrombosis have been adapted for applications in mice, but they proffer limited
Characterization of antithrombin-specific RNA aptamers for use in anticoagulant therapy
 Characterization of antithrombin-specific RNA aptamers for use in anticoagulant therapy Yolanda M. Fortenberry, Ph.D. Hematology 2014 Conference Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine What are aptamers?
Characterization of antithrombin-specific RNA aptamers for use in anticoagulant therapy Yolanda M. Fortenberry, Ph.D. Hematology 2014 Conference Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine What are aptamers?
