Chapter 30. Replication. Meselson Stahl Experiment. BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2 Conceptual Mechanism of.
|
|
|
- Antony Simpson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 30 DNA Replication and Repair 2 Conceptual Mechanism of Replication Strand separation, with copying of each strand by Watson-Crick base pairing Fig 30.2 Three models for replication Conservative Semiconservative Dispersive See Fig Meselson Stahl Experiment DNA labeled with 15 NH 4 + Culture diluted with excess 14 NH 4 + DNA isolated and analyzed by ultracentrifugation (See Fig 30.4) Original DNA bands at g/ml First generation bands at g/ml Second generation bands at g/ml These density labeling experiments are most consistent with the semiconservative mechanism of replication. Subsequent analysis of the single strands of the hybrid after the first generation ruled out the dispersive mechanism. Chapter 30, page 1
2 4 Problems with Semiconservative Model Strands run in opposite directions Twisted strands must come apart Error rate must be very low (< 1 per bases copied) 5 Chemical Components of Replication Template DNA strand determining order of new bases Primer Strand grows at 3 end Deoxynucleotide triphosphates monomer unit is activated, adding to free 3 - OH of the primer See Fig 30.8 The alternative would be for the terminal end of the primer to carry the triphosphate group, with linkage made to OH of the monomer unit. 6 Some Features of Replication Bidirectional Two replication forks which move in opposite direction. Fig 30.5 Semidiscontinuous Leading strand copied continuously Lagging strand made in segments (Okasaki fragments) which must be joined. Fig 30.6 Chapter 30, page 2
3 7 Enzymology: DNA Polymerase Three different polymerases in E. coli Pol I, Pol II, and Pol III (order of discovery) See Table 30.1 Pol I monomer of 103 kd 400 molecules/cell; turnover 600/min Pol II monomer of 90 kd? Molecules/cell; turnover 30/min Pol III complex ( core contains 3 subunits) 40 molecules/cell; turnover 1200/min Pol III, the third disovered, does the bulk of new DNA synthesis. Pol I has a role in normal replication, but is also involved in DNA repair. Pol II is probably involved only in repair. 8 DNA Polymerase I First discovered Arthur Kornberg, 1957 Catalyzes incorporation of radioactive nucleotides into polymeric form Requires primer, template, and all dntp s Two additional enzymatic activities 3-5 exonuclease 5-3 exonuclease 9 Klenow Fragment of Pol I Contains the 5-3 polymerase and 3-5 exonuclease activity Fig diagram shows protein-dna interaction and two enzymatic sites Fig 30.9 shows model of fragment 3-5 Exonuclease has proofreading function Polymerase is slowed if there is a mismatch Mismatch corrected by exonuclease See Fig Klenow fragment is separated from the 5-3 exonuclease component by proteolytic action (subtilisin or trypsin) Chapter 30, page 3
4 Exonuclease Activity of Pol I Removes polymer in front of polymerase Allows nick translation of DNA with single strand cut See Fig Functions in lagging strand synthesis to remove RNA primers 11 DNA Polymerase III The "real" polymerase in E. coli At least 10 different subunits "Core" enzyme has three subunits - α, ε, and θ Alpha subunit is polymerase Epsilon subunit is 3'-exonuclease Theta function is unknown The beta subunit dimer forms a ring around DNA Fig Enormous processivity - 5 million bases! 12 Features of Replication Mostly in E. coli, but many features are general Replication is bidirectional The double helix must be unwound - by helicases Supercoiling must be compensated - by DNA gyrase Replication is semidiscontinuous Leading strand is formed continuously Lagging strand is formed from Okazaki fragments Chapter 30, page 4
5 13 More Features of Replication DNA Pol III uses an RNA primer A special primase forms the required primer DNA Pol I excises the primer DNA ligase seals the "nicks" between Okazaki fragments (See Figure for mechanism) See Figure for a view of replication fork 14 Mechanism of Replication Initiation Occurs at oric site (See Fig s and 30.17) Recognized by DnaA; requires ATP DnaB (a helicase) binds, delivered by DnaC and DnaT Strands separate and SSB binds Primase (an RNA polymerase) binds, forming the primosome SSB stands for single strand binding protein. A helicase unwinds DNA 15 Mechanism of Replication Elongation DNA Pol III complex binds at replication fork (Fig 30.17) DnaB serves as helicase to unwind strands SSB binds to keep strands separated Chapter 30, page 5
6 16 Mechanism of Replication Elongation, con t. Pol III forms an asymmetric dimer Lagging strand template forms a loop Okasaki fragments made on the lagging strand See Fig Gyrase, a topoisomerase II needed to introduce negative supercoiling ahead of replication fork Topoisomerase I needed behind replication site to relax supercoiling 17 Mechanism of Replication Termination Occurs at the Ter locus Replication forks meet here Ter sequence impedes replication fork progression Requires the Tus protein, a contrahelicase Daughter strands often concatenated and require topoisomerase II to separate. 18 Eukaryotic Replication Human cell has 6 billion base pairs to copy DNA is linear, not circular DNA is complexed with histones to form a nucleosome Cell cycle more complex (See Fig 30.19) G 1 phase growth and metabolic activity S phase DNA replication and growth G 2 phase preparation for division M phase mitosis and cell division Chapter 30, page 6
7 19 Eukaryotic Replication, con t Many replication origins replicators Every kbp Involves several protein complexes See Fig 30.20, but don t worry about details Involves 5 polymerases: (See Table 30.4) α--contains no 3 exonuclease β--similar to α, involved in repair γ--for replication of mitochondrial DNA δ--homologous to pol III, interacts with PCNA ε--major role, but unclear what (lagging strand?) PCNA is proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Forms a ring structure similar to β 2 clamp in E. coli that makes the reaction highly processive. (See Fig 30.21) 20 Eukaryotic Replication, con t Replication fork, leading strand and lagging strand synthesis, similar to prokaryotes but more complex. (See Fig 30.22) Regulatory proteins probably controlled by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation For example, the T antigen of SV40 virus Therefore complex second messenger signaling pathways are involved in the control 21 Eukaryotic Replication, con t Linear DNA has ends Lagging strand synthesis cannot occur at the 3 end of the lagging strand, leaving a dangling 3 single strand end Every round of replication leads to a shorter piece of DNA Problem is overcome by repeating units at ends of DNA called telomeres Chapter 30, page 7
8 22 Telomeres and Telomerase Telomerase adds repeated oligomers at the 3 end. Vertebrate telomers have TTAGGG consensus sequence An RNA dependent DNA polymerase A ribonucleoprotein containing 9-30 base RNA that serves as template DNA Polymerase can then copy the extended 3 end (See Fig and Page 382) 23 Telomeres and Telomerase, con t. Most somatic cells lack telomerase Germ line cells contain 1000 to 1700 copies Every cell division leads to some loss (~ 50 bp?) Therefore there are a limited number of cell divisions before a cell dies Cancer cells have regained telomerase and are therefore immortalized Telomerase research is important on two fronts. One is to find ways to turn off telomerase activity in cancer cells. Another is to find a way to turn on telomerase activity in somatic cells with the possibility of increasing normal life span. 24 Reverse Transcriptase Found in some RNA viruses, especially tumor viruses and AIDS virus Primer is a trna molecule captured by the virus RNA is the template to make a complementary DNA (cdna) to form a DNA-RNA hybrid Chapter 30, page 8
9 25 Reverse Transcriptase AZT is 3 -azido-2,3 - dideoxythymidine Three enzyme activities RNA-directed DNA polymerase Rnase H activity, degrades the RNA in the DNA-RNA hybrids DNA-directed DNA polymerase makes DNA duplex AZT inhibits HIV reverse transcriptase (See Fig 30.24) The DNA duplex can be the template for more viral particles, or can be integrated into the host genome by recombination and remain dormant. 26 DNA Repair DNA must be faithfully preserved with fewer than 1 in 10 9 to 1 in mistakes Even with proof reading normal error rate is much greater than this Errors can also occur chemically Deamination Loss of purine base Alkylation DNA can also be damaged more severely UV irradiation, X-ray, etc leading to thymine dimers, strand breakage, etc. 27 DNA Repair, con t. An elaborate set of repair systems is designed to overcome these various problems. Two principle mechanisms: Mismatch repair Reversing chemical damage Chapter 30, page 9
10 28 Mismatch Repair Recognize and remove mismatched bases Must distinguish the correct base from the incorrect base in the mismatch In E. coli, methylation of DNA helps keep track of old strand. Methylation occurs shortly after replication, but there is a short period when the old strand is methylated, and the new one is not. Methylation occurs at the Adenine of a GATC palindromic site. Recall the way methylation also plays a role in the restriction phenomenon, helping bacteria to distinguish their own DNA from foreign DNA. 29 Mismatch Repair One protein (Mut S) binds to mismatch site Another (Mut L) binds to MutS Another (Mut H) finds hemimethylated site Mut L bridges connection between Mut S and Mut H New strand is removed and replaced (maybe by Pol I?) Sometimes called long patch repair because long stretch of DNA is removed 30 Reversing Chemical Damage Pyrimidine dimers can be corrected by a photolyase using energy of visible light to break the dimer bonds Base Excision (See Fig 30.27) Glycosylase removes base, creates AP site An endonuclease breaks the backbone, and an exonuclease removes several bases Gap is filled by Pol I and DNA ligase Photolyase is also called photoreactivating enzyme. An AP site is an apurinic or apyrimidinic site where the sugar-phosphate backbone is intact. Chapter 30, page 10
11 31 Reversing Chemical Damage, con t. Nucleotide excision Removes larger sections of damaged DNA. An alternative way to correct thymine dimers. SOS Response Activation of a number of proteins in E. coli in response to UV damage. These include the recombination proteins involved in recombination (RecA, etc) Error prone repair occurs Recombination is enhanced to recapture stretches of DNA from other daughter strand when extensive damage is done. Chapter 30, page 11
The flow of Genetic information
 The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Welcome to Class 18! Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives. Replication is semiconservative! Replication: DNA DNA! Introductory Biochemistry!
 Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question? Traits are inherited on chromosomes, but what in the chromosomes is the genetic material? Two possibilities: Protein DNA Qualifications Protein:
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question? Traits are inherited on chromosomes, but what in the chromosomes is the genetic material? Two possibilities: Protein DNA Qualifications Protein:
DNA REPLICATION. Third Stage. Lec. 12 DNA Replication. Lecture No.: 12. A. Watson & Crick (1952) C. Cairns (1963) autoradiographic experiment
 Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 11 DNA Replication
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
DNA replication. - proteins for initiation of replication; - proteins for polymerization of nucleotides.
 DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
Requirements for the Genetic Material
 Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
Replication. Obaidur Rahman
 Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
DNA Replication semiconservative replication conservative replication dispersive replication DNA polymerase
 DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
Genetic Information: DNA replication
 Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Molecular Biology (2)
 Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
DNA replication. DNA replication. replication model. replication fork. chapter 6
 DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. January 25, 2006
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication
 3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
The replication forks Summarising what we know:
 When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two. Fig. 10-CO, p.240
 Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two Fig. 10-CO, p.240 Learning Objectives 1. What Is the Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell? 2. What Are the General Considerations in the Replication of DNA?
Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two Fig. 10-CO, p.240 Learning Objectives 1. What Is the Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell? 2. What Are the General Considerations in the Replication of DNA?
DNA metabolism. DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination
 DNA metabolism DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology Central Dogma or Flow of genetic information
DNA metabolism DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology Central Dogma or Flow of genetic information
DNA replication. DNA replication. replication model. replication fork. chapter 6
 DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.8 DNA REPLICATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 28, 2004
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 28, 2004 Conceptual model for proofreading based on kinetic considerations Fig. 24.44 stalling transient melting exonuclease site occupancy Following
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 28, 2004 Conceptual model for proofreading based on kinetic considerations Fig. 24.44 stalling transient melting exonuclease site occupancy Following
DNA REPLICATION. Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari»
 DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
Enzymes used in DNA Replication
 Enzymes used in DNA Replication This document holds the enzymes used in DNA replication, their pictorial representation and functioning. DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is the chief enzyme of DNA replication.
Enzymes used in DNA Replication This document holds the enzymes used in DNA replication, their pictorial representation and functioning. DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is the chief enzyme of DNA replication.
Chapter Twelve: DNA Replication and Recombination
 This is a document I found online that is based off of the fourth version of your book. Not everything will apply to the upcoming exam so you ll have to pick out what you thing is important and applicable.
This is a document I found online that is based off of the fourth version of your book. Not everything will apply to the upcoming exam so you ll have to pick out what you thing is important and applicable.
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions Life s Operating Instructions CONCEPTS: 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 16.2 Many proteins work together in DNA
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions Life s Operating Instructions CONCEPTS: 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 16.2 Many proteins work together in DNA
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material. The Nature of Genetic Material. Chemical Nature of Nucleic Acids. Chromosomes - DNA and protein
 Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule.
 1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule. 2. True or False? Dideoxy sequencing is a chain initiation method of DNA sequencing. 3. True
1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule. 2. True or False? Dideoxy sequencing is a chain initiation method of DNA sequencing. 3. True
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE
 STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 24, 2005
 DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
DNA Replication * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45475 1 DNA Replication * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m45475 1 DNA Replication * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
The Size and Packaging of Genomes
 DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
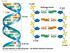 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 26, 2005
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION
 DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION THE CENTRAL DOGMA DNA Replication Transcription Translation STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF DNA DNA is present in the nucleus as CHROMATIN. The basic unit of chromatin is NUCLEOSOME
DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION THE CENTRAL DOGMA DNA Replication Transcription Translation STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF DNA DNA is present in the nucleus as CHROMATIN. The basic unit of chromatin is NUCLEOSOME
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
The Genetic Material. The Genetic Material. The Genetic Material. DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: Chapter 14 Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain is virulent - R strain is nonvirulent
DNA: Chapter 14 Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain is virulent - R strain is nonvirulent
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
Fidelity of DNA polymerase
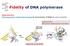 Fidelity of DNA polymerase Shape selectivity: DNA polymerase's conformational change for determination of fidelity for each nucleotide Induced fit: Structure determines function Matched nucleotide Fidelity
Fidelity of DNA polymerase Shape selectivity: DNA polymerase's conformational change for determination of fidelity for each nucleotide Induced fit: Structure determines function Matched nucleotide Fidelity
4) separates the DNA strands during replication a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. 5) covalently connects segments of DNA a. A b. B c. C d. D e.
 1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
Chromosomes. Nucleosome. Chromosome. DNA double helix. Coils. Supercoils. Histones
 Chromosomes Chromosome Nucleosome DNA double helix Coils Supercoils Histones Evidence That DNA Can Transform Bacteria Frederick Griffith s experiment 1928 Griffith called the phenomenon transformation
Chromosomes Chromosome Nucleosome DNA double helix Coils Supercoils Histones Evidence That DNA Can Transform Bacteria Frederick Griffith s experiment 1928 Griffith called the phenomenon transformation
DNA Metabolism. I. DNA Replication. A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding
 DNA Metabolism I. DNA Replication A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding B. DNA replication follows a set of fundamental rules 1. Semiconservative
DNA Metabolism I. DNA Replication A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding B. DNA replication follows a set of fundamental rules 1. Semiconservative
ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI REPLICATION - ENZYMES.
 ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI.9500244679 REPLICATION - ENZYMES DNA HELICASE Sparation of two strands- DNA helicase enzyme functions Unwinds DNA. DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen
ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI.9500244679 REPLICATION - ENZYMES DNA HELICASE Sparation of two strands- DNA helicase enzyme functions Unwinds DNA. DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen
DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul. Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47204 1 DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m47204 1 DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Hershey & Chase Avery, MacLeod, & McCarty DNA: The Genetic Material
 DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity
 All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis
 Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
BS GENOMES. DNA replication and repair
 BS2009 - GENOMES DNA replication and repair REPLICATION GENERAL PRINCIPLES START Must be ready Must know where to start FINISH Must all finish Must ensure that each piece of DNA is replicated only once
BS2009 - GENOMES DNA replication and repair REPLICATION GENERAL PRINCIPLES START Must be ready Must know where to start FINISH Must all finish Must ensure that each piece of DNA is replicated only once
DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
DNA Structure. DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 DNA Structure DNA is a nucleic acid. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, each composed of: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group (PO 4 ) a nitrogenous
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 DNA Structure DNA is a nucleic acid. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, each composed of: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group (PO 4 ) a nitrogenous
DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA
 DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
Chapter 12. DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 12 DNA Replication and Recombination I. DNA replication Three possible modes of replication A. Conservative entire original molecule maintained B. Semiconservative one strand is template for new
Chapter 12 DNA Replication and Recombination I. DNA replication Three possible modes of replication A. Conservative entire original molecule maintained B. Semiconservative one strand is template for new
DNA. Discovery of the DNA double helix
 DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA Replication. Packet #17 Chapter #16
 DNA Replication Packet #17 Chapter #16 1 HISTORICAL FACTS ABOUT DNA 2 Historical DNA Discoveries 1928 Frederick Griffith finds a substance in heat-killed bacteria that transforms living bacteria 1944 Oswald
DNA Replication Packet #17 Chapter #16 1 HISTORICAL FACTS ABOUT DNA 2 Historical DNA Discoveries 1928 Frederick Griffith finds a substance in heat-killed bacteria that transforms living bacteria 1944 Oswald
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription The metabolic processes described earlier (glycolysis, cellular respiration, photophosphorylation,
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription The metabolic processes described earlier (glycolysis, cellular respiration, photophosphorylation,
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 16 Objectives Describe the contributions of the following people: Griffith; Avery, McCary, and MacLeod; Hershey and Chase; Chargaff; Watson and Crick; Franklin;
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 16 Objectives Describe the contributions of the following people: Griffith; Avery, McCary, and MacLeod; Hershey and Chase; Chargaff; Watson and Crick; Franklin;
Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
DNA Replication and Repair
 DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of. Chapter 16. Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme
 Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme The Amazing Race What is the genetic material? DNA or protein? 1928 Griffith transformation of pneumonia
Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme The Amazing Race What is the genetic material? DNA or protein? 1928 Griffith transformation of pneumonia
Biochemistry. DNA Polymerase. Structure and Function of Biomolecules II. Principal Investigator
 Paper : 03 Module: 14 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry,
Paper : 03 Module: 14 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry,
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material hapter 14 1 Frederick Griffith 1928 Studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia 2 strains of Streptococcus S strain is virulent R strain is nonvirulent
DNA: The Genetic Material hapter 14 1 Frederick Griffith 1928 Studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia 2 strains of Streptococcus S strain is virulent R strain is nonvirulent
Tala Saleh. Tamer Barakat ... Anas Abu. Humaidan
 7 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat... Anas Abu. Humaidan Some Information in this lecture may not be mentioned by the Dr. as thoroughly as this sheet. But they cannot be overlooked for a better understanding,
7 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat... Anas Abu. Humaidan Some Information in this lecture may not be mentioned by the Dr. as thoroughly as this sheet. But they cannot be overlooked for a better understanding,
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA Replication. Rasime Kalkan,PhD.
 DNA Replication Rasime Kalkan,PhD. DNA Replication The process of copying one DNA molecule into two identical molecules is called DNA replication. DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied
DNA Replication Rasime Kalkan,PhD. DNA Replication The process of copying one DNA molecule into two identical molecules is called DNA replication. DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied
Overview: Life s Operating Instructions Concept 16.1: DNA is the genetic material The Search for the Genetic Material: Scientific Inquiry
 Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA, the substance of inheritance,
Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA, the substance of inheritance,
Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis is the key to expression of biological information - Structural Protein: bones, cartilage - Contractile Proteins: myosin, actin - Enzymes - Transport
Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis is the key to expression of biological information - Structural Protein: bones, cartilage - Contractile Proteins: myosin, actin - Enzymes - Transport
Genetic material must be able to:
 Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES
 MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES NAME: SID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 28 II 32 III 32 IV 30 V 28 150 PLEASE WRITE your NAME or SID number on each page. This exam must be written
MCB 110 Spring 2017 Exam 1 SIX PAGES NAME: SID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 28 II 32 III 32 IV 30 V 28 150 PLEASE WRITE your NAME or SID number on each page. This exam must be written
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork
 DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
CSIR UGC NET, GATE (ENGINEERING), GATE (Science), IIT-JAM, UGC NET, TIFR, IISc, NIMCET, JEST etc. JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY
 JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY REPLICATION TYPE OF DNA REPLICATION REPLICATION IN PROKARYOTES REPLICATION IN EUKARYOTES For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams 1-C-8, Sheela Chowdhary Road,
JNU CEEB SAMPLE THEORY REPLICATION TYPE OF DNA REPLICATION REPLICATION IN PROKARYOTES REPLICATION IN EUKARYOTES For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams 1-C-8, Sheela Chowdhary Road,
DNA and Replication 1
 DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March :24 pm
 Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
 Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity What is DNA? Answer: Molecule that carries the blueprint of life General Features: DNA is packages in chromosomes (DNA + Proteins) Gene = Functional segment of
Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity What is DNA? Answer: Molecule that carries the blueprint of life General Features: DNA is packages in chromosomes (DNA + Proteins) Gene = Functional segment of
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication
 3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
LECTURE 26. a) A light-independent repair mechanism that involves three steps:
 LECTURE 26 DNA REPAIR A. The capability for repair of damaged DNA is found in one form or another in all organisms. Prokaryotes (e.g., E. coli) have five repair systems, whereas higher organisms (e.g.,
LECTURE 26 DNA REPAIR A. The capability for repair of damaged DNA is found in one form or another in all organisms. Prokaryotes (e.g., E. coli) have five repair systems, whereas higher organisms (e.g.,
Double helix structure of DNA
 Replication Double helix structure of It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material. Watson & Crick
Replication Double helix structure of It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material. Watson & Crick
Chapter 9. Topics - Genetics - Flow of Genetics - Regulation - Mutation - Recombination
 Chapter 9 Topics - Genetics - Flow of Genetics - Regulation - Mutation - Recombination 1 Genetics Genome Chromosome Gene Protein Genotype Phenotype 2 Terms and concepts gene Fundamental unit of heredity
Chapter 9 Topics - Genetics - Flow of Genetics - Regulation - Mutation - Recombination 1 Genetics Genome Chromosome Gene Protein Genotype Phenotype 2 Terms and concepts gene Fundamental unit of heredity
STRUCTURE OF RNA. Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units. A ribonucleotide unit has: 5-Carbon ribose sugar.
 STRUCTURE OF RNA & REPLICATION BY:HIMANSHU LATAWA BIOLOGY LECTURER G.G.S.S.SIRHIND MANDI anshu223@gmail.com 9815543311 STRUCTURE OF RNA Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units.
STRUCTURE OF RNA & REPLICATION BY:HIMANSHU LATAWA BIOLOGY LECTURER G.G.S.S.SIRHIND MANDI anshu223@gmail.com 9815543311 STRUCTURE OF RNA Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units.
Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11
 Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11 Tutorial Week #9 DNA Replication Before the tutorial: Read ECB Chapter 6 p195-207, and review your lecture notes Read this tutorial and create a table of definitions and functions
Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11 Tutorial Week #9 DNA Replication Before the tutorial: Read ECB Chapter 6 p195-207, and review your lecture notes Read this tutorial and create a table of definitions and functions
Friday, April 17 th. Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation. AP Biology
 Friday, April 17 th Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation Today I will 1. Review the component parts of a DNA molecule. 2. Describe the process of transformation. 3. Explain what is meant by
Friday, April 17 th Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation Today I will 1. Review the component parts of a DNA molecule. 2. Describe the process of transformation. 3. Explain what is meant by
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information
 Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
Replication of DNA and Chromosomes
 Chapter 9. Replication of DNA and Chromosomes 1. Semiconservative Replication 2. DNA Polymerases and DNA Synthesis In Vitro 3. The Complex Replication Apparatus 4. Unique Aspects of Eukaryotic Chromosome
Chapter 9. Replication of DNA and Chromosomes 1. Semiconservative Replication 2. DNA Polymerases and DNA Synthesis In Vitro 3. The Complex Replication Apparatus 4. Unique Aspects of Eukaryotic Chromosome
copyright cmassengale 2
 1 copyright cmassengale 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino acids in long
1 copyright cmassengale 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino acids in long
AP Biology Chapter 16 Notes:
 AP Biology Chapter 16 Notes: I. Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance a. Overview: i. April 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick great the double helix model of DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid ii. DNA
AP Biology Chapter 16 Notes: I. Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance a. Overview: i. April 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick great the double helix model of DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid ii. DNA
DNA Replication. Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow!
 DNA Replication Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow! Must be fast! six billion base pairs in a single human cell
DNA Replication Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow! Must be fast! six billion base pairs in a single human cell
Proposed Models of DNA Replication. Conservative Model. Semi-Conservative Model. Dispersive model
 5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
