Gene expression during induced differentiation of sheep bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts
|
|
|
- Lynette Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gene expression during induced differentiation of sheep bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts Y. Hu, X.-X. Tang and H.-Y. He Department of Prosthodontics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang, China Corresponding author: H.-Y. He Genet. Mol. Res. 12 (4): (2013) Received October 5, 2012 Accepted September 20, 2013 Published December 11, 2013 DOI ABSTRACT. The aim of this study was to observe the dynamic expression of osteopontin, type I collagen, and osteocalcin genes during the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) into osteoblasts and confirm whether BMSCs can differentiate and mature into osteoblasts. A healthy, 2-month-old Altay tailed sheep was obtained, and 10 ml bone marrow was extracted from the posterior superior iliac spine of the sheep via puncture. Sheep BMSCs were extracted using a whole bone marrow culture method and cultured for osteogenic induction. Total RNA from the BMSCs was extracted, and the gene expression levels of osteopontin, type I collagen, and osteocalcin at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th passages of uninduced and induced BMSCs were detected using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. The surface antigen CD44 was also detected in the BMSCs. After induction by culturing in osteoinductive medium, BMSCs in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th passages displayed stagespecific expression of osteopontin, type I collagen, and osteocalcin genes. The positive expression rate of BMSC-specific antigen CD44 in the 4th passage of osteogenic-induced BMSCs was 99.8%. In vitro-cultured
2 Y. Hu et al sheep BMSCs in osteogenic culture medium gradually differentiated into osteoblasts, which stage-specifically expressed osteoblast-specific genes such as osteopontin, type I collagen, and osteocalcin at the 4th passage after induction. At this passage, these cells had osteoblast functions. Key words: Osteoblasts; Gene expression; Induced differentiation; Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; Sodium β-glycerophosphate INTRODUCTION Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) are multipotent stromal cells derived from the mesoderm. They are mainly present in the connective tissues and organ interstitium and are most abundant in bone marrow tissues but can also be isolated from fetal cord blood (Erices et al., 2000). Under certain induction conditions, BMSCs can differentiate into mesodermal cells such as osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes, and stromal cells. BMSCs also have low immunogenicity characteristics and immunomodulatory functions that can reduce the immune rejection that occurs after transplantation. Because they are easy to obtain and have strong osteogenic differentiation capabilities, BMSCs are often used as seeder cells for bone tissue engineering and as vector cells for gene therapy (Studeny et al., 2002; Potapova et al., 2004). Currently, the dynamic gene expression patterns that occur during the differentiation of BMSCs into osteoblasts remain unclear. Studies have shown that osteogenic-induced BMSCs express non-osteoblast-specific genes such as osteocalcin, osteopontin, and type I collagen. However, few studies have pursued the spatial and temporal sequences of osteocalcin, osteopontin, and type I collagen expression at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th passages of BMSCs after osteogenic induction. This study used a whole bone marrow adherence culture method to isolate and culture sheep BMSCs. Then, osteogenic induction on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th passages of cells was performed to observe the cell morphology changes of BMSCs during their differentiation into osteoblasts and to detect the expression of non-osteoblast-specific genes such as osteocalcin, osteopontin, and type I collagen. The positive rate of a BMSC antigen, CD44, was measured. The growth curve was measured using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The culture conditions, proliferation activity, expression of osteoblast-specific genes, and functional status of sheep BMSCs during differentiation into osteoblasts were also explored. MATERIAL AND METHODS Experimental animal The experimental animal was a healthy, male, 2-month-old Altay tailed sheep with a body weight of 6 kg. The experimental animal use permit No. was A , and the animal was provided by the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University. Isolation and primary culture of sheep BMSCs The Altay tailed sheep was anesthetized via intramuscular injection of 0.9 ml 10%
3 Gene expression and BMSCs 6529 chloral hydrate (v/v) and 0.6 ml diazepam. The limbs were immobilized, the surgical area was shaved, and routine disinfection and draping were performed. A bone marrow cavity puncture was performed at the posterior superior iliac spine. Ten millimeters of bone marrow was collected and placed separately in A and B centrifuge tubes containing 200 U/mL heparin. After through mixing, the 5 ml bone marrow in each tube was filtered through 200-mesh filters, diluted with 10-mL Dulbecco s modified Eagle medium/f12 (10% fetal bovine serum, v/v), and inoculated into 25-cm 2 culture flasks. After 3 days, half of the culture medium was replaced. All of the medium was replaced after 7 days, and then the medium was replaced every 3 days. The cells were passaged at a 1:3 ratio when they were 80-90% confluent. The vitality and growth of the cells were observed every day using an inverted fluorescence microscope. Flow cytometric identification Cells from the 2 groups at the 4th passage after induction were collected and they were digested using 2.5 g/l trypsin. After centrifugation, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) 3 times, and the cell concentration was adjusted to 1 x 10 6 cells/ ml. Fluorescence-labeled CD44 antibodies were added to each tube and incubated for 20 min in darkness. The unbound antibodies were washed off using PBS, and cell surface antigens were detected using a flow cytometer. Immunoglobulin G1 was added into the culture of the 4th passage of non-induced culture cells as a negative control. Differentiation of induced cultured BMSCs into osteoblasts The second passage of BMSCs (inoculation concentration, 1 x 10 6 cells/l) was cultured in mineralization osteoinductive culture medium (10% v/v fetal bovine serum, Dulbecco s modified Eagle medium/f12, 1 x 10-8 mm dexamethasone, 0.01 mm sodium β-glycerophosphate, 0.05 g/l vitamin C, 100 U/L penicillin, and 100 U/L streptomycin). The medium was changed every 3 days, and the cells were passaged when they became 80-90% confluent. Detection of BMSC growth curve Cells from the 2 groups at the 3rd, 5th, and 7th passages were inoculated onto 96-well plates at 5 x 10 4 cell/ml, 200 μl/well, and 5 wells per group. After inoculation, 20 μl MTT solution (MTT was dissolved in PBS at a concentration of 5 g/l, filter-sterilized, and stored at 4 C in darkness) was added to the wells every 24 h and incubated at 37 C for 4 h. After the culture medium was discarded, 150 μl dimethyl sulfoxide was added and vortexed for 10 min to dissolve the crystals fully. Optical density (OD) values were measured at 490 nm. An average OD value of 5 wells in each group was used to represent the growth condition of the 2 groups of cells. The growth curve of the cells was plotted using time as the horizontal axis and the OD value as the longitudinal axis. Total RNA extraction and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Total RNA was extracted with TRIzol(Beijing, Bioteck, China). The primers were designed using the Primer 5.0 software and synthesized by Shanghai ShengGong Company
4 Y. Hu et al (China). The primer sequences are shown in Table 1. The 50-µL sample of the PCR system included 25 µl of Premix Ex Taq (Beijing, Bioteck, China), 2 µl template complementary DNA, 1.0 µl forward and reverse primers (20 µm), and double-distilled water. Table 1. Primers used in this study. Gene Primers Products OPN Sense: 5ꞌ-AGGGACAGAACTCGGCCGTG-3ꞌ 259 bp Anti-sense: 5ꞌ-CCAGTGTATTGTGTTTGGCCCTC-3ꞌ OC Sense: 5ꞌ-CCCCATGCTCGCCCTGCTGG-3ꞌ 394 bp Anti-sense: 5ꞌ-TCTGGAGTTTATTCTAGAGCAGCG-3ꞌ Collagen-Ι Sense: 5ꞌ-ACCTACCACTGCAAGAACAGCG-3ꞌ 290 bp Anti-sense: 5ꞌ-AAGCAGACAGAGCCGATGTCG-3ꞌ RESULTS Observation of growth and morphology of sheep BMSCs Cells obtained with the whole bone marrow culture method displayed a scattered distribution at the bottom of the culture flasks, and they were mixed with bone marrow hematopoietic cells. A majority of the suspension cells could be removed after half of the medium was replaced the 3rd day after induction; the suspension cells were essentially all removed when the medium was changed after day 7. In the culture flask, some cells were adnately scattered, and the morphology of the cells showed spindles, triangles, and polygons. After 8 days, the number of adherent cells significantly increased, the number of cell divisions increased, and many swirl-shaped cell colonies were visible. The distribution of the cells was uneven, and many cells had 2 or 3 protrusions (Figure 1A). The morphology of the induced BMSCs changed from long spindles into squares and polygons, and the cell volume increased (Figure 1B). A B Figure 1. A. Non-induced culture BMSCs (100 X); B. induced apoptosis in cultured BMSCs (200 X). Growth curve of sheep BMSCs The MTT detection results of induced BMSCs showed that the induced cells at the
5 Gene expression and BMSCs 6531 third passage proliferated slowly the first 72 h after inoculation. After 96 h, the cells started to proliferate rapidly and entered the exponential growth phase. The proliferation of cells significantly decreased after 216 h, and the cells entered the plateau phase. Compared with that of the uninduced BMSCs, the proliferation of the induced BMSCs decreased (Figure 2). Figure 2. BMSCs growth curve of uninduced and induced group. Detection of sheep BMSC surface antigens Flow cytometric results showed that the CD44-positive rates of induced and uninduced cells at the 4th passage were 99.8 and 95.4%, respectively (Figure 3A, B), whereas the positive rate in the negative control cells was 0.6% (Figure 3C). A B C Figure 3. A. CD44-positive rate of 4th generation induced apoptosis cells; B. CD44-positive rate of 4th generation uninduced apoptosis cells; C. CD44-positive rate of control. Detection of genes in BMSCs during in vitro osteogenic differentiation During the process of osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs, the expression of mes-
6 Y. Hu et al senger RNAs (mrnas) for osteopontin, osteocalcin, and type I collagen occurred in a specific order. The induced BMSCs at the 1st passage expressed type I collagen. The induced BMSCs at the 2nd passage expressed type I collagen and osteopontin, and the induced BMSCs at the 3rd and 4th passages expressed type I collagen, osteocalcin, and osteopontin. The uninduced BMSCs at the 1st passage in the control group expressed type I collagen and osteopontin, whereas uninduced cells at the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th passages expressed only type I collagen. The PCR product of the osteopontin gene was approximately 259 bp, and the agarose gel electrophoresis results showed that the size of the target fragment was consistent with the marker. The gene fragment of osteocalcin was approximately 394 bp and consistent with the marker. The gene fragment of type I collagen was approximately 290 bp and consistent with the marker. The sequencing results showed that osteopontin, osteocalcin, and type I collagen had individual nucleotide mutations but contained no frameshift mutations. The electropherogram results are shown in Figure 4A-C. Figure 4. A. Electrophoresis of osteopontin gene. Lane β = β-actin; lanes 1 and 2 = OPN gene; lane 3 = negative control. B. Electrophoresis of osteocalcin gene. Lane β = β-actin; lanes 1 and 2: OC gene; lane 3 = negative control. C. Electrophoresis of type I collagen gene. Lane β = β-actin; lanes 1 and 2 = type I collagen gene gene; lane 3 = negative control. DISCUSSION BMSCs are believed to have multiple antigen markers and exhibit non-uniqueness; thus, a specific antigen marker for BMSCs remains to be found (Pittenger et al., 1999; Zhu et al., 2004; Delorme et al., 2006; Stolzing and Scutt, 2006; Sun et al., 2010). BMSCs and hematopoietic stem cells coexist in the bone marrow. BMSCs express no hematopoietic stem cell surface antigens such as hematopoietic stem cell marker antigen CD34 or white blood cell marker antigen CD45, but they do express adhesion molecules, growth factor receptors, and integrin family members,
7 Gene expression and BMSCs 6533 such as CD29, CD44, CD90, CD105, and CD166, of which CD44 is considered an important antigen marker of BMSCs. In this study, flow cytometry was used to screen for BMSC-specific antigen CD44. The results showed that the CD44-positive rate was 99.8% in induced cells at the 4th passage, 95.4% in uninduced cells at the 4th passage, and 0.7% in cells of the negative control group. With a gradual increase in the number of medium changes and passages, the confounding hematopoietic lineage cells were gradually removed, and the cultured BMSCs in the experimental groups continued to proliferate; thus, the CD44-positive rate increased. This result shows that the purity of the isolated and cultured BMSCs in this experiment was high, confirming that the cells were derived from differentiated BMSCs after induction. BMSCs can undergo osteoinduction in vitro; their differentiation and maturation into osteoblasts have 3 major stages: cell proliferation, matrix maturation, and mineralization. The differentiation process includes directional differentiation of multipotent stromal cells into preosteoblasts, immature osteoblasts, and mature osteoblasts (Cotter et al., 2008). The osteoblast cells predominantly express extracellular matrix proteins such as alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin, osteopontin, and type I collagen during the cell proliferation, matrix maturation, and mineralization phases. Observation of the mrna expression levels of these marker genes helps to some extent to distinguish the stages of differentiation and maturation of BMSCs into osteoblasts. Current studies have shown that type I collagen, osteopontin, and alkaline phosphatase are secreted during the early stage of osteogenic differentiation, whereas osteocalcin, a marker of a mature osteoblast differentiation, is a necessary factor for bone calcification and mineralization. After 1 week of culture, the expression levels of these genes usually increase (Balcerzak et al., 2003; Janssens et al., 2005; Osyczka and Leboy, 2005). This study showed that days 3-6 in sheep BMSC osteogenic induction culture constituted the cell proliferation phase, days 6-14 composed the matrix maturation phase, and days made up the mineralization phase. Therefore, the results revealed the expression mechanism of some nonspecific genes during the process of the induced differentiation of BMSCs into osteoblasts. The results also have important implications for the identification of the differentiation of BMSCs into osteoblasts, for the maturation status of BMSCs as they differentiate, and for the assessment of osteogenic functions. This study showed that the 1st passage of cultured, uninduced BMSCs expressed type I collagen and osteopontin, but cells at the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th passages expressed only type I collagen. The induced BMSC culture at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th passages did not express osteopontin, possibly because BMSCs at the 1st passage retained a small portion of hematopoietic stem cells, confounding cells, and some growth factors (Tang et al., 2005). With an increase in the number of medium changes, this small portion was removed; thus, the cultured BMSCs no longer expressed osteopontin. This study also showed that during osteogenic induction culture, induced BMSCs expressed type I collagen at the 1st passage, type I collagen and osteopontin at the 2nd passage, and type I collagen, osteocalcin, and osteopontin at the 3rd and 4th passages. During the process of induced differentiation of BMSCs into osteoblasts, with prolonged induction time, the 1st passage of BMSCs in the cell proliferation phase expressed type I collagen, the 2nd passage of BMSCs in the matrix maturation phase started to express osteopontin, and the 3rd and 4th passages of BMSCs in the mineralization phase expressed osteocalcin. These results indicated that BMSCs successfully differentiated and matured into osteoblasts, which was consistent with results reported by Balcerzak et al. (2003). The stage-specific expression of collagen, osteopontin, and osteocalcin mrnas showed
8 Y. Hu et al that BMSCs were differentiated into proliferation, matrix maturation, and mineralization phases. These results revealed the mechanism of expression of some genes during the osteogenicinduced differentiation of BMSCs. The induced BMSCs had certain osteogenic functions and potential, and they are expected to be used as ideal seed cells for bone tissue engineering. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Research supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (# ), the Autonomous Region Natural Science Genome Project (# A073), and the Xinjiang Medical Graduate Innovation Fund (#MC2010-8). REFERENCES Balcerzak M, Hamade E, Zhang L, Pikula S, et al. (2003). The roles of annexins and alkaline phosphatase in mineralization process. Acta Biochim. Pol. 50: Cotter EJ, Ip HS, Powderly WG and Doran PP (2008). Mechanism of HIV protein induced modulation of mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 9: 33. Delorme B, Chateauvieux S and Charbord P (2006). The concept of mesenchymal stem cells. Regen. Med. 1: Erices A, Conget P and Minguell JJ (2000). Mesenchymal progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Br. J. Haematol. 109: Janssens K, ten DP, Janssens S and Van HW (2005). Transforming growth factor-beta1 to the bone. Endocr. Rev. 26: Osyczka AM and Leboy PS (2005). Bone morphogenetic protein regulation of early osteoblast genes in human marrow stromal cells is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling. Endocrinology 146: Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, et al. (1999). Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284: Potapova I, Plotnikov A, Lu Z, Danilo P, Jr., et al. (2004). Human mesenchymal stem cells as a gene delivery system to create cardiac pacemakers. Circ. Res. 94: Stolzing A and Scutt A (2006). Age-related impairment of mesenchymal progenitor cell function. Aging. Cell 5: Studeny M, Marini FC, Champlin RE, Zompetta C, et al. (2002). Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells as vehicles for interferon-beta delivery into tumors. Cancer Res. 62: Sun K, Wang GB and Zu Y (2010). Different age children bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from autologous serum in vitro culture and into bone differentiation. Chin. Tissue Eng. Res. Clin. Rehabil. 14: Tang XX, He HY, Xu HF, Hu Y, et al. (2011). Effects of two separation methods on biological characteristics of sheep bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 15: Zhu H, Xu JZ and Zhou Q (2004). Different ages of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation study. Chin. J. Orthop. Surg. 12:
Effects of KAATSU Training on proliferation and differentiation of goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
 Chinese Journal of Laboratory Diagnosis Issued on 25 Aug 2016 Vol. 20, No. 8 P.1240 Effects of KAATSU Training on proliferation and differentiation of goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells YANG Yu-hui,
Chinese Journal of Laboratory Diagnosis Issued on 25 Aug 2016 Vol. 20, No. 8 P.1240 Effects of KAATSU Training on proliferation and differentiation of goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells YANG Yu-hui,
Application Note. Introduction. Kerry Thompson, Jeff Partridge, Paula Flaherty, Susan Qian, and Deepa Saxena
 Page 1 BD PureCoat ECM Mimetic Cultureware Fibronectin Peptide: Novel Synthetic, Animalfree Surface for Culture of Human Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Kerry Thompson, Jeff Partridge, Paula
Page 1 BD PureCoat ECM Mimetic Cultureware Fibronectin Peptide: Novel Synthetic, Animalfree Surface for Culture of Human Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Kerry Thompson, Jeff Partridge, Paula
Human Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Care Manual
 Human Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0101.001 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Bone Marrow Derived MSC (HBMMSC-F) Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier.
Human Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0101.001 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Bone Marrow Derived MSC (HBMMSC-F) Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier.
Cultrex Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products
 ITM-2011/06/07 Cultrex Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products Background: Mesenc ymal Stem Cells (MSC), also known as marrow stromal cells, are a self - renewing population of multipotent
ITM-2011/06/07 Cultrex Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products Background: Mesenc ymal Stem Cells (MSC), also known as marrow stromal cells, are a self - renewing population of multipotent
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
SuperTCRExpress TM Human TCR Vβ Repertoire CDR3 Diversity Determination (Spectratyping) and Quantitative Analysis Kit
 SuperTCRExpress TM Human TCR Vβ Repertoire CDR3 Diversity Determination (Spectratyping) and Quantitative Analysis Kit Cat. No. H0521 Size: 2 sets (22 Vβ families/each, with enzymes) H0522 Size: 4 sets
SuperTCRExpress TM Human TCR Vβ Repertoire CDR3 Diversity Determination (Spectratyping) and Quantitative Analysis Kit Cat. No. H0521 Size: 2 sets (22 Vβ families/each, with enzymes) H0522 Size: 4 sets
At the conclusion of this lesson you should be able to:
 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this lesson you should be able to: Understand the key terms and definitions regarding stem cells Differentiate between the adult and embryonic stem cells Differentiate
Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this lesson you should be able to: Understand the key terms and definitions regarding stem cells Differentiate between the adult and embryonic stem cells Differentiate
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
PCCS Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation Final Assignment. Igneris Rosado-Erazo. Panama College of Cell Science
 Running Head: Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation PCCS Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation Final Assignment Igneris Rosado-Erazo Panama College of Cell Science In partial fulfillment of
Running Head: Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation PCCS Growth Media, Cell Tagging, Cell Separation Final Assignment Igneris Rosado-Erazo Panama College of Cell Science In partial fulfillment of
DETERMINATION OF THE Rh FACTOR BY PCR
 DETERMINATION OF THE Rh FACTOR BY PCR Ref.: PCR2 1. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE The aim of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) by studying
DETERMINATION OF THE Rh FACTOR BY PCR Ref.: PCR2 1. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE The aim of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) by studying
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Mesenchymal Stem Cells Instruction Manual Product Size Catalog Number from Bone Marrow (hmsc-bm) from Umbilical Cord Matrix (hmsc-uc) from Adipose Tissue (hmsc-at) 500,000 cryopreserved cells 500,000 proliferating
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Instruction Manual Product Size Catalog Number from Bone Marrow (hmsc-bm) from Umbilical Cord Matrix (hmsc-uc) from Adipose Tissue (hmsc-at) 500,000 cryopreserved cells 500,000 proliferating
Marilyn G. Rimando, Hao-Hsiang Wu, Yu-An Liu, Chien-Wei Lee, Shu-Wen Kuo, Yin-
 Supplementary Information Glucocorticoid receptor and Histone Deacetylase 6 mediate the differential effect of dexamethasone during osteogenesis of Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) Marilyn G. Rimando,
Supplementary Information Glucocorticoid receptor and Histone Deacetylase 6 mediate the differential effect of dexamethasone during osteogenesis of Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) Marilyn G. Rimando,
Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Corning HYPER Technology Cell Culture Vessels
 Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Corning HYPER Technology Cell Culture Vessels SnAPPshots A brief technical report from the Corning Development Group Ana Maria P. Pardo and Mark E. Rothenberg,
Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Corning HYPER Technology Cell Culture Vessels SnAPPshots A brief technical report from the Corning Development Group Ana Maria P. Pardo and Mark E. Rothenberg,
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells
 Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
User Manual. OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cat. No. HUXUB-01001
 User Manual OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat. No. HUXUB-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product
User Manual OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat. No. HUXUB-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product
All quality control test results are reported on a lot specific Certificate of Analysis which is available at or upon request.
 PRIME-XV MSC Expansion XSFM Catalog # Product Size 91149 PRIME-XV MSC Expansion XSFM 250 ml and 1 L liquid Intended Use This product is for research use or further manufacturing use only. This product
PRIME-XV MSC Expansion XSFM Catalog # Product Size 91149 PRIME-XV MSC Expansion XSFM 250 ml and 1 L liquid Intended Use This product is for research use or further manufacturing use only. This product
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
 Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cells Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat# 5000-001-01 Primary Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Rat Bone Marrow
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cells Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat# 5000-001-01 Primary Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Rat Bone Marrow
User Manual. OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cat. No. HUXUB-01001
 User Manual OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat. No. HUXUB-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product
User Manual OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat. No. HUXUB-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product
User Manual. OriCell TM Rabbit Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Cat. No. RBXMX-01001
 User Manual OriCell TM Rabbit Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Cat. No. RBXMX-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product Application
User Manual OriCell TM Rabbit Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Cat. No. RBXMX-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product Application
All quality control test results are reported on a lot specific Certificate of Analysis which is available at or upon request.
 PRIME-XV MSC Expansion XSFM PRIME-XV MSC Expansion XSFM is a serum-free and xeno-free complete medium optimized for the maintenance and expansion of purified human MSCs. This product does not contain antibiotics.
PRIME-XV MSC Expansion XSFM PRIME-XV MSC Expansion XSFM is a serum-free and xeno-free complete medium optimized for the maintenance and expansion of purified human MSCs. This product does not contain antibiotics.
Alt-R CRISPR-Cpf1 System:
 user guide Alt-R CRISPR-Cpf1 System: Delivery of ribonucleoprotein complexes in HEK-293 cells using the Amaxa Nucleofector System See what more we can do for you at www.idtdna.com. For Research Use Only
user guide Alt-R CRISPR-Cpf1 System: Delivery of ribonucleoprotein complexes in HEK-293 cells using the Amaxa Nucleofector System See what more we can do for you at www.idtdna.com. For Research Use Only
Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization
 Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization Application Note Background Osteoblasts (HOB) are specialized fibroblasts that secrete and mineralize the bone matrix. They develop from mesenchymal precursors.
Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization Application Note Background Osteoblasts (HOB) are specialized fibroblasts that secrete and mineralize the bone matrix. They develop from mesenchymal precursors.
Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Of Cord Lining Membrane Stem Cells. Phan T.H., Masilamani J. and Ng Y.H.
 Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Of Cord Lining Membrane Stem Cells Phan T.H., Masilamani J. and Ng Y.H. Department of Bioengineering, National University of Singapore 21 Lower Kent Ridge Road, Singapore
Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Of Cord Lining Membrane Stem Cells Phan T.H., Masilamani J. and Ng Y.H. Department of Bioengineering, National University of Singapore 21 Lower Kent Ridge Road, Singapore
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis. Mitesh Shrestha
 Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Liquid. This product is shipped with dry ice. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
 PRIME-XV MSC Expansion SFM PRIME-XV MSC Expansion SFM is a serum-free complete medium optimized for the maintenance and expansion of purified human MSCs. This product does not contain antibiotics. Catalog
PRIME-XV MSC Expansion SFM PRIME-XV MSC Expansion SFM is a serum-free complete medium optimized for the maintenance and expansion of purified human MSCs. This product does not contain antibiotics. Catalog
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit. Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit
 Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Cat# 5000-001-K Primary Mesenchymal Stem Cells isolated
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Cat# 5000-001-K Primary Mesenchymal Stem Cells isolated
Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells
 Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells ABOUT US Irvine Scientific, a member of JX Holdings group, is a worldwide leader in the design, manufacture and distribution of medical devices, including Cell Therapy, Industrial
Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells ABOUT US Irvine Scientific, a member of JX Holdings group, is a worldwide leader in the design, manufacture and distribution of medical devices, including Cell Therapy, Industrial
Preparation of Mouse Bone Marrow Stromal Cells
 Preparation of Mouse Bone Marrow Stromal Cells A single-step stem cell purification method using adhesion to cell culture plastic was employed as described in the Reference. Briefly, neonatal and adult
Preparation of Mouse Bone Marrow Stromal Cells A single-step stem cell purification method using adhesion to cell culture plastic was employed as described in the Reference. Briefly, neonatal and adult
NPTEL Biotechnology Tissue Engineering. Stem cells
 Stem cells S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc
Stem cells S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc
Assuring Multipotency of human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hmsc)
 Assuring Multipotency of human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hmsc) Introduction Over the past decade, stem cell research has provided new avenues for deeper investigation into tissue repair and aging processes,
Assuring Multipotency of human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hmsc) Introduction Over the past decade, stem cell research has provided new avenues for deeper investigation into tissue repair and aging processes,
Stem Cel s Key Words:
 Stem Cells Key Words: Embryonic stem cells, Adult stem cells, ips cells, self-renewal, differentiation, pluripotent, multipotent, Inner cell mass, Nuclear transfer (Therapeutic cloning), Feeder cells,
Stem Cells Key Words: Embryonic stem cells, Adult stem cells, ips cells, self-renewal, differentiation, pluripotent, multipotent, Inner cell mass, Nuclear transfer (Therapeutic cloning), Feeder cells,
User Manual. OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cat. No. HUXUC-01001
 User Manual OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat. No. HUXUC-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product Applications
User Manual OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat. No. HUXUC-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product Applications
User Manual. OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cat. No. HUXUC-01001
 User Manual OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat. No. HUXUC-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product Applications
User Manual OriCell TM Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cat. No. HUXUC-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity 3 Product Applications
Modeling Cardiomyocyte Differentiation:
 icell Cardiac Progenitor Cells Prototype Application Protocol Wnt- and Activin/TGFβ-inhibitor Induction with Flow Cytometry Analysis Introduction The ability of cardiac progenitor cells to proliferate
icell Cardiac Progenitor Cells Prototype Application Protocol Wnt- and Activin/TGFβ-inhibitor Induction with Flow Cytometry Analysis Introduction The ability of cardiac progenitor cells to proliferate
User Manual. OriCell TM Dog Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal. Stem Cells (ADSCs) Cat. No. CAXMD-01001
 User Manual OriCell TM Dog Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ADSCs) Cat. No. CAXMD-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction... 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity. 3 Product
User Manual OriCell TM Dog Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ADSCs) Cat. No. CAXMD-01001 Table of Contents Contents and Storage 3 Product Introduction... 3 Cell Characteristics and Identity. 3 Product
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
BD IMag. Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM. Technical Data Sheet. Product Information
 Technical Data Sheet Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM Product Information Material Number: Size: Storage Buffer: 557812 5 ml Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Description
Technical Data Sheet Streptavidin Particles Plus - DM Product Information Material Number: Size: Storage Buffer: 557812 5 ml Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Description
ab Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis
 ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
ab Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis
 ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
Stem cells and tissue engineering
 Stem cells and tissue engineering S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative
Stem cells and tissue engineering S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative
jetcrispr RNP transfection reagent PROTOCOL
 jetcrispr RNP transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetcrispr is a RiboNucleoProtein (RNP) transfection reagent designed to perform CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in mammalian cells. This reagent has been
jetcrispr RNP transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION jetcrispr is a RiboNucleoProtein (RNP) transfection reagent designed to perform CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in mammalian cells. This reagent has been
5.4 PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT STEM CELL (PDLSC) ISOLATION. Having validated that the isolated PDL stromal cells possessed the major phenotypic
 5.4 PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT STEM CELL (PDLSC) ISOLATION Having validated that the isolated PDL stromal cells possessed the major phenotypic characteristics of their tissue of origin, we next focused on identifying
5.4 PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT STEM CELL (PDLSC) ISOLATION Having validated that the isolated PDL stromal cells possessed the major phenotypic characteristics of their tissue of origin, we next focused on identifying
AN EXAMINATION OF THE EFFECTS OF SIMVASTATIN ON INNATE IMMUNE RESPONSES TO S. AUREUS A RESEARCH PAPER BY TRACI STANKIEWICZ
 AN EXAMINATION OF THE EFFECTS OF SIMVASTATIN ON INNATE IMMUNE RESPONSES TO S. AUREUS A RESEARCH PAPER BY TRACI STANKIEWICZ SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIRMENTS SET
AN EXAMINATION OF THE EFFECTS OF SIMVASTATIN ON INNATE IMMUNE RESPONSES TO S. AUREUS A RESEARCH PAPER BY TRACI STANKIEWICZ SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIRMENTS SET
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by
 PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion
 Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Kit Components (Included) Cat # # of vials Product Name Quantity Storage Human Renal Cortical Epithelial Cells (HRCEpiC)
 3D Renal Tubule Formation Kit 3D-RTF Cat # 3D-4110 Product Description The human kidney is frequently exposed to drugs and toxic compounds, which can result in nephrotoxicity. A drug s uptake and clearance
3D Renal Tubule Formation Kit 3D-RTF Cat # 3D-4110 Product Description The human kidney is frequently exposed to drugs and toxic compounds, which can result in nephrotoxicity. A drug s uptake and clearance
North American Ginseng & Auricularia sp. mushroom aq. extract have beneficial effect on cyclophosphamide induced immunosuppression in mice
 North American Ginseng & Auricularia sp. mushroom aq. extract have beneficial effect on cyclophosphamide induced immunosuppression in mice Kyakulaga A. Hassan, Ed Lui OGIRC Journal club, October 2012 Department
North American Ginseng & Auricularia sp. mushroom aq. extract have beneficial effect on cyclophosphamide induced immunosuppression in mice Kyakulaga A. Hassan, Ed Lui OGIRC Journal club, October 2012 Department
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by
 PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
3T3-L1 Differentiation Protocol
 3T3-L1 Differentiation Protocol Written by Eisuke Kato on 2013/10/09 MATERIALS Dulbecco's Modified Eagles Medium (D-MEM) (High Glucose) with L-Glutamine and Phenol Red High glucose (Wako Chem 044-29765,
3T3-L1 Differentiation Protocol Written by Eisuke Kato on 2013/10/09 MATERIALS Dulbecco's Modified Eagles Medium (D-MEM) (High Glucose) with L-Glutamine and Phenol Red High glucose (Wako Chem 044-29765,
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit. Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit
 Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Cat# 5000-001-K Primary Mesenchymal Stem Cells isolated
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Cat# 5000-001-K Primary Mesenchymal Stem Cells isolated
Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit
 1. Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit For fast and sensitive one-step RT-PCR www.tiangen.com/en RT121221 Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit Kit Contents Cat. no. KR113 Contents Hotmaster Taq Polymerase (2.5 U/μl) Quant
1. Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit For fast and sensitive one-step RT-PCR www.tiangen.com/en RT121221 Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit Kit Contents Cat. no. KR113 Contents Hotmaster Taq Polymerase (2.5 U/μl) Quant
Fundamental properties of Stem Cells
 Stem cells Learning Goals: Define what a stem cell is and describe its general properties, using hematopoietic stem cells as an example. Describe to a non-scientist the current progress of human stem cell
Stem cells Learning Goals: Define what a stem cell is and describe its general properties, using hematopoietic stem cells as an example. Describe to a non-scientist the current progress of human stem cell
Human Gla-Osteocalcin High Sensitive EIA Kit
 Cat. # MK128 For Research Use Human Gla-Osteocalcin High Sensitive EIA Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 3 III. Components... 4 IV. Materials Required but not Provided...
Cat. # MK128 For Research Use Human Gla-Osteocalcin High Sensitive EIA Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 3 III. Components... 4 IV. Materials Required but not Provided...
Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit
 Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit Catalog Number SC010 Reagents for the identification of mouse bone marrow-derived stem cells (BMSC)/mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) by in vitro functional
Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit Catalog Number SC010 Reagents for the identification of mouse bone marrow-derived stem cells (BMSC)/mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) by in vitro functional
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT RosetteSep Human Progenitor Cell Basic Pre-Enrichment Cocktail
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Positive Selection Catalog #7897 EasySep Human Cord Blood CD Positive Selection For processing 000 ml of cord blood Description Isolate highly purified
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Positive Selection Catalog #7897 EasySep Human Cord Blood CD Positive Selection For processing 000 ml of cord blood Description Isolate highly purified
Technical Review. Real time PCR
 Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual
 Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual Cat. Nos. 632638, 632639, 632635, 632636, 632637 (040618) 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA U.S. Technical Support:
Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual Cat. Nos. 632638, 632639, 632635, 632636, 632637 (040618) 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA U.S. Technical Support:
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit
 Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Catalog Number KA1301 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Catalog Number KA1301 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General
HANDLING INSTRUCTIONS
 HANDLING INSTRUCTIONS CellGenix Human Umbilical Cord-derived Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (huc-msc) Order No.: 19401-005, 19401-010 For preclinical ex vivo use. Not intended for therapeutic use.
HANDLING INSTRUCTIONS CellGenix Human Umbilical Cord-derived Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (huc-msc) Order No.: 19401-005, 19401-010 For preclinical ex vivo use. Not intended for therapeutic use.
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX
 Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
Adipose Stem Cells as a Feeder Layer Reduce Apoptosis and p53 Gene Expression of Human Expanded Hematopoietic Stem Cells Derived from Cord Blood
 Adipose Stem Cells as a Feeder Layer Reduce Apoptosis and p53 Gene Expression of Human Expanded Hematopoietic Stem Cells Derived from Cord Blood Tahereh Foroutan 1 *, Aysan Farhadi 1, Bahram- Mohammad
Adipose Stem Cells as a Feeder Layer Reduce Apoptosis and p53 Gene Expression of Human Expanded Hematopoietic Stem Cells Derived from Cord Blood Tahereh Foroutan 1 *, Aysan Farhadi 1, Bahram- Mohammad
Genomic Sequencing. Genomic Sequencing. Maj Gen (R) Suhaib Ahmed, HI (M)
 Maj Gen (R) Suhaib Ahmed, HI (M) The process of determining the sequence of an unknown DNA is called sequencing. There are many approaches for DNA sequencing. In the last couple of decades automated Sanger
Maj Gen (R) Suhaib Ahmed, HI (M) The process of determining the sequence of an unknown DNA is called sequencing. There are many approaches for DNA sequencing. In the last couple of decades automated Sanger
Tissue Engineering. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for. Tissue Engineering
 Tissue Engineering Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering Reference: Culture of Cells for Tissue Engineering (Culture of Specialized Cells), Chapter 2 Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Date: 03.20.2012 Institute
Tissue Engineering Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering Reference: Culture of Cells for Tissue Engineering (Culture of Specialized Cells), Chapter 2 Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Date: 03.20.2012 Institute
In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay. Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung *
 In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung * Clinical Oncology Department, The Univerisity of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR *For
In vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Tube-formation Assay Josephine MY Ko and Maria Li Lung * Clinical Oncology Department, The Univerisity of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR *For
Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit
 Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Cat # 5000-001-K Primary Mesenchymal Stem Cells isolated and purified from Rat Bone Marrow
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Starter Kit Cat # 5000-001-K Primary Mesenchymal Stem Cells isolated and purified from Rat Bone Marrow
A Supersandwich Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (SFISH) Strategy. for Highly Sensitive and Selective mrna Imaging in Tumor Cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) A Supersandwich Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (SFISH)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) A Supersandwich Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (SFISH)
Osteogenic Differentiation and Analysis of MSC
 Osteogenic Differentiation and Analysis of MSC Application Note Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) are fibroblastoid multipotent adult stem cells with a high capacity for self-renewal. So far, these
Osteogenic Differentiation and Analysis of MSC Application Note Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) are fibroblastoid multipotent adult stem cells with a high capacity for self-renewal. So far, these
Supplementary Information Temperature-responsive Gene Silencing by a Smart Polymer
 Supplementary Information Temperature-responsive Gene Silencing by a Smart Polymer Mingming Wang, Yiyun Cheng * Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology, School of Life Sciences, East China Normal
Supplementary Information Temperature-responsive Gene Silencing by a Smart Polymer Mingming Wang, Yiyun Cheng * Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology, School of Life Sciences, East China Normal
Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Corning HYPER Technology Cell Culture Vessels
 Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Corning HYPER Technology Cell Culture Vessels SnAPPshots A brief technical report from the Corning Development Group Introduction Ana Maria P. Pardo and
Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Corning HYPER Technology Cell Culture Vessels SnAPPshots A brief technical report from the Corning Development Group Introduction Ana Maria P. Pardo and
Supplemental Information. Materials and methods.
 Supplemental Information Materials and methods. Cell culture. hmscs were isolated from bone marrow of 3 male donors, undergoing orthopedic surgery (mean age 69.7). Cells were cultured in high glucose DMEM
Supplemental Information Materials and methods. Cell culture. hmscs were isolated from bone marrow of 3 male donors, undergoing orthopedic surgery (mean age 69.7). Cells were cultured in high glucose DMEM
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT RosetteSep Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Complete Kit for Human Whole Blood CD+ Cells Catalog #1086 For processing 120 ml whole blood Description Isolate highly purified CD cells from human whole
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Complete Kit for Human Whole Blood CD+ Cells Catalog #1086 For processing 120 ml whole blood Description Isolate highly purified CD cells from human whole
TACS MTT Assays. Cell Proliferation and Viability Assays. Catalog Number: TA tests. Catalog Number: TA tests
 TACS MTT Assays Cell Proliferation and Viability Assays Catalog Number: TA5355-2500 tests Catalog Number: TA5412-5000 tests This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product. FOR
TACS MTT Assays Cell Proliferation and Viability Assays Catalog Number: TA5355-2500 tests Catalog Number: TA5412-5000 tests This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product. FOR
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Positive Selection Catalog #7896 EasySep Human Cord Blood CD Positive For processing 000 ml of cord blood Description Isolate highly purified CD+ cells
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Positive Selection Catalog #7896 EasySep Human Cord Blood CD Positive For processing 000 ml of cord blood Description Isolate highly purified CD+ cells
T ECHNICAL MANUAL. Culture of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using MesenCult -XF Medium
 T ECHNICAL MANUAL Culture of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using MesenCult -XF Medium i Table of Contents 1.0 Materials... 1 1.1 MesenCult -XF Medium and Required Products... 1 1.2 Additional Required
T ECHNICAL MANUAL Culture of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using MesenCult -XF Medium i Table of Contents 1.0 Materials... 1 1.1 MesenCult -XF Medium and Required Products... 1 1.2 Additional Required
g: relative centrifugal force R: radius of the rotor S: speed of the centrifuge in revolutions per minute
 Propagation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells The density of the colonies is the primary consideration in determining when the cells should be passaged. Cells grow densely should be passaged, even though the cells
Propagation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells The density of the colonies is the primary consideration in determining when the cells should be passaged. Cells grow densely should be passaged, even though the cells
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Transfection of neural stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent in StemPro medium
 TRANSFECTION PROTOCOL Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent Transfection of neural stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent in StemPro medium NSC media, passaging reagents, and complexation
TRANSFECTION PROTOCOL Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent Transfection of neural stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent in StemPro medium NSC media, passaging reagents, and complexation
STEMdiff Mesenchymal Progenitor Kit
 Defined culture kit for derivation and expansion of mesenchymal progenitor cells Catalog #05240 1 Kit Product Description STEMdiff Mesenchymal Progenitor Kit is a defined culture kit consisting of animal
Defined culture kit for derivation and expansion of mesenchymal progenitor cells Catalog #05240 1 Kit Product Description STEMdiff Mesenchymal Progenitor Kit is a defined culture kit consisting of animal
Human IFN-γ. Pre-Coated ELISA Kit
 Human IFN-γ (Interferon Gamma) Pre-Coated ELISA Kit Catalog No: 90-2067 1 96 well Format (96 tests) Detection Range: 15.6 1000 pg/ml Sensitivity: < 9.4 pg/ml This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro
Human IFN-γ (Interferon Gamma) Pre-Coated ELISA Kit Catalog No: 90-2067 1 96 well Format (96 tests) Detection Range: 15.6 1000 pg/ml Sensitivity: < 9.4 pg/ml This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro
Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ashley B. Allen, Hazel Y. Stevens, Robert E. Guldberg. Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA. Disclosures:
Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ashley B. Allen, Hazel Y. Stevens, Robert E. Guldberg. Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA. Disclosures:
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-5005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-5005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
Transfection of pluripotent stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem reagent in mtesr1 Medium on Geltrex matrix
 TRANSFECTION PROTOCOL Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent Transfection of pluripotent stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem reagent in mtesr1 Medium on Geltrex matrix PSC growth medium, passaging reagents,
TRANSFECTION PROTOCOL Lipofectamine Stem Transfection Reagent Transfection of pluripotent stem cells with Lipofectamine Stem reagent in mtesr1 Medium on Geltrex matrix PSC growth medium, passaging reagents,
Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative received
Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Pittsburgh Tissue Engineering Initiative received
User Manual. OriCell TM Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation Medium. Cat. No. GUXMX-90021
 User Manual OriCell TM Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation Cat. No. GUXMX-90021 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: OriCell TM Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation consists of optimized Mesenchymal
User Manual OriCell TM Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation Cat. No. GUXMX-90021 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: OriCell TM Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation consists of optimized Mesenchymal
Blotting Techniques (Southern blot, Northern blot, Western blot, and Eastern blot)
 Blotting Techniques (Southern blot, Northern blot, Western blot, and Eastern blot) Masheal Aljumaah SEP 2018 Learning Objectives: What is blotting? Blotting Techniques Types. Applications for each technique.
Blotting Techniques (Southern blot, Northern blot, Western blot, and Eastern blot) Masheal Aljumaah SEP 2018 Learning Objectives: What is blotting? Blotting Techniques Types. Applications for each technique.
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr)
 For Research Use Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 4 III. Components... 5 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 5 V. Storage... 5 VI.
For Research Use Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 4 III. Components... 5 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 5 V. Storage... 5 VI.
About ATCC. Established partner to global researchers and scientists
 Discovering ATCC Primary Immunology Cells - Model Systems to Study the Immune and Cardiovascular Systems James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC July 14, 2016 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
Discovering ATCC Primary Immunology Cells - Model Systems to Study the Immune and Cardiovascular Systems James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC July 14, 2016 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
StemXVivo. Mesoderm Kit. Catalog Number SC030B. Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm.
 StemXVivo Mesoderm Kit Catalog Number SC030B Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product.
StemXVivo Mesoderm Kit Catalog Number SC030B Reagents for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product.
FLT3-ITD REAL TIME PCR DETECTION KIT
 FLT3-ITD REAL TIME PCR DETECTION KIT ONKOTEST R3030-20 Keep the kit at -15 C to -25 C Rev. 1.4 Product Information FLT3 (fms-related tyrosine kinase 3) gene frequently mutated in acute myeloid leukemia
FLT3-ITD REAL TIME PCR DETECTION KIT ONKOTEST R3030-20 Keep the kit at -15 C to -25 C Rev. 1.4 Product Information FLT3 (fms-related tyrosine kinase 3) gene frequently mutated in acute myeloid leukemia
Edexcel (B) Biology A-level
 Edexcel (B) Biology A-level Topic 7: Modern Genetics Notes Using Gene Sequencing Genome = all of an organism s DNA, including mitochondrial/chloroplast DNA. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to amplify
Edexcel (B) Biology A-level Topic 7: Modern Genetics Notes Using Gene Sequencing Genome = all of an organism s DNA, including mitochondrial/chloroplast DNA. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to amplify
GSI Bovine TGF-β3 ELISA Kit-2 Plates DataSheet
 Transforming growth factor, beta 3 (TGF-β3) belongs to a large family of cytokines called the Transforming growth factor beta super family (1, 2), which includes the TGF-β family, bone morphogenetic proteins
Transforming growth factor, beta 3 (TGF-β3) belongs to a large family of cytokines called the Transforming growth factor beta super family (1, 2), which includes the TGF-β family, bone morphogenetic proteins
User Manual. OriCell TM C57BL/6 Mouse Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells With GFP (ADSCs/GFP) Cat. No. MUBMD-01
 User Manual OriCell TM C57BL/6 Mouse Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells With GFP (ADSCs/GFP) Cat. No. MUBMD-01 Table of Contents Contents and Storage. 3 Product Introduction. 3 Cell Characteristics
User Manual OriCell TM C57BL/6 Mouse Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells With GFP (ADSCs/GFP) Cat. No. MUBMD-01 Table of Contents Contents and Storage. 3 Product Introduction. 3 Cell Characteristics
Rapid Method for the Purification of Total RNA from Formalin- Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue Samples
 Application Note 17 RNA Sample Preparation Rapid Method for the Purification of Total RNA from Formalin- Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue Samples M. Melmogy 1, V. Misic 1, B. Lam, PhD 1, C. Dobbin,
Application Note 17 RNA Sample Preparation Rapid Method for the Purification of Total RNA from Formalin- Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue Samples M. Melmogy 1, V. Misic 1, B. Lam, PhD 1, C. Dobbin,
High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No
 for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No. 1 796 88 Principle Cells are lysed during a short incubation with Proteinase K in the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), which immediately
for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No. 1 796 88 Principle Cells are lysed during a short incubation with Proteinase K in the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), which immediately
Supplementary Figure 1. Antigens generated for mab development (a) K9M1P1-mIgG and hgh-k9m1p1 antigen (~37 kda) expression verified by western blot
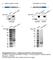 Supplementary Figure 1. Antigens generated for mab development (a) K9M1P1-mIgG and hgh-k9m1p1 antigen (~37 kda) expression verified by western blot (vector: ~25 kda). (b) Silver staining was used to assess
Supplementary Figure 1. Antigens generated for mab development (a) K9M1P1-mIgG and hgh-k9m1p1 antigen (~37 kda) expression verified by western blot (vector: ~25 kda). (b) Silver staining was used to assess
Modeling Cardiac Hypertrophy: Endothelin-1 Induction with qrt-pcr Analysis
 icell Cardiomyocytes Application Protocol Modeling Cardiac Hypertrophy: Endothelin-1 Induction with qrt-pcr Analysis Introduction Cardiac hypertrophy is characterized by several different cellular changes,
icell Cardiomyocytes Application Protocol Modeling Cardiac Hypertrophy: Endothelin-1 Induction with qrt-pcr Analysis Introduction Cardiac hypertrophy is characterized by several different cellular changes,
Introduction. Kit components. 50 Preps GF-PC-050. Product Catalog No. 200 Preps GF-PC Preps GF-PC Preps SAMPLE
 Introduction The GF-1 PCR Clean Up Kit is a system designed for rapid clean up of DNA bands ranging from 100bp to 20kb. The GF-1 PCR Clean Up Kit contains special buffers to provide the correct salt concentration
Introduction The GF-1 PCR Clean Up Kit is a system designed for rapid clean up of DNA bands ranging from 100bp to 20kb. The GF-1 PCR Clean Up Kit contains special buffers to provide the correct salt concentration
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1302 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1302 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
