Comparative Study of Pre Engineered and Conventional Steel Building
|
|
|
- Clifford Moody
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comparative Study of Pre Engineered and Conventional Steel Building M.K.S.S.Krishna Chaitanya 1 and M.K.M.V.Ratnam 2 1 Assistant Professor, CE Dept., Anil Neerukonda Institute of Technology &Sciences, Vishakapatnam, 2 Assistant Professor, HOD of CE Dept., D.N.R.College of Engineering &Technology, Bhimavaram, Abstract Pre Engineered Steel Buildings (PEB) fulfils the requirements of industrial steel structures along with reduced time and cost as compared to Conventional Steel Buildings (CSB). This methodology is versatile not only due to its quality predesigning and prefabrication, but also due to its light weight and economical construction. The present work presents the comparative study and design of conventional steel frames and Pre Engineered Buildings (PEB). In this work, an industrial building of length 60 m, with roofing system as conventional steel truss and pre engineered steel truss of span 20 m, at 6 m along the length and 6 m, 8 m & 6m bay width at end frames has been considered. Slope of roof truss is taken as 5.71 o. The eave height of these structures has been taken as 10 m. These structures have been analyzed and designed by using STAAD Pro V8i to compare the PEB and conventional steel truss. Design is based on IS: Steel with yield stress 250 MPa is considered. Loads considered in analysis are dead load, live load, wind load and seismic loads along with the various combinations as specified in IS: Dead load is taken based on IS: 875 (Part 1) Live load is taken based on IS: 875(Part-2) Wind load is taken based on IS: 875 (Part 3) It is assumed that the structure is located in Visakhapatnam city. Analysis results observed for base reactions and weight of the steel are compared for these three structures. Index Terms Conventional steel Buildings, Pre Engineered Steel Buildings,Seismic forces, Staad Pro V8i 1. INTRODUCTION India is the second fastest growing economy in the world and a lot of it is attributed to its construction industry which figures just next to agriculture in its economic contribution to the nation. In its steadfast development, the construction industry has discovered, invented and developed a number of technologies, systems and products; one of them being the concept of Pre-engineered Buildings (PEB). As opposed to being on-site fabricated, PEBs are delivered as a complete finished product to the site from a single supplier with a basic structural steel framework with attached factory finished cladding and roofing components. The structure is erected on the site by bolting the various building components together as per specifications. PEBs are developed using potential design software. The onset of technological advancement enabling 3D modelling and detailing of the proposed structure and coordination has revolutionized conventional building construction. PEBs have hit the construction market in a major way owing to the many benefits they possess. They exemplify the rising global construction, technology and while they oppose the practice of conventional building construction they simultaneously have taken it to a higher level too. Worldwide, they are a much used concept with studies revealing that 60% of the non-residential low-rise buildings in USA are pre-engineered; for India the concept has been gaining momentum and the scope of growth is guaranteed looking at India's huge infrastructural requirements. Studies already validate that India has the fastest growing market in the PEB construction segment. The scope of using PEBs ranges from showrooms, low height commercial complexes, industrial building and workshops, stadia, schools, bridges, fuel stations to aircraft hangars, exhibition centers, railway stations and metro applications. While we are still to see PEBs being used in residences in India, one can see their optimal use in warehouses, industrial sheds sports facilities etc. The Delhi Airport and the metro projects of Delhi, Bangalore and Mumbai are also examples of PEB applications. 358
2 Applications Pre-Engineered Building concept have wide applications including warehouses, factories, offices, workshops, gas stations, showrooms, vehicle parking sheds, aircraft hangars, metro stations, schools, recreational buildings, indoor stadium roofs, outdoor stadium canopies, railway platform shelters, bridges, auditoriums, etc. PEB structures can also be designed as re-locatable structures. a) Industrial: Factories, Workshops, Warehouses, Cold stores, Car parking sheds, Slaughter houses, Bulk product storage, harbors. b) Commercial: Showrooms, Distribution centers, Supermarkets, Fast food restaurants, Offices, Labor camps, Service stations, Shopping centers. c) Institutional: Schools, Exhibition halls, Hospitals, Theaters/auditoriums, Sports halls. d) Recreational:Gymnasiums, swimming pool enclosures, Indoor tennis courts. e) Aviation& Military: Aircraft hangars, Administration buildings, Residential barracks,support facilities. f) Agriculture: Poultry buildings, Dairy farms, Greenhouses, Grain storage, Animal confinement. Scope of present study This study mainly focuses on to compare the structural steel weight of Conventional Steel Building and Pre-engineered Steel Building using IS These structures are assumed to be located in Visakhapatnam. These buildings are analyzed and designed by using STAAD Pro V8i Software. In this study compare the how axial forces and moments are varies from type II structure to type III structure. Objectives of study Objectives identified for the present study have listed as follows. 1. To compare the steel take-off of the conventional steel building and Pre engineered building. 2. To compare the member end forces of Pre engineered building and Conventional steel building. 3. To compare the joint displacements of Pre engineered building and Conventional steel building. 2. METHODOLOGY In the present study two types of steel buildings designated as Type I and Type II are considered for the analysis, design and computing structural steel weight. Type I is Conventional Steel Building of length 60 m and span 20 m. Bay lengths are maintained at an interval of 6 m along length and 6 m, 8 m and 6m along span only for end frames. The height of the truss is taken as a minimum pitch that is th of span. So slope of roof is taken as 5.71 and covered with GI sheet. The spacing of purlins is maintained as 1.5 m. The eave height of the building has been taken as 10 m in which 3 m from ground level is used for brick work and remaining 7 m is used for cladding. Type II is Pre Engineered Steel Building of length 60 m and span 20 m. Bay lengths are maintained at an interval of 6 m along length and 6 m, 8 m and 6m along span only for end frames. The height of the truss is taken as a minimum pitch that is th of span. So slope of roof is taken as 5.71 and covered with GI sheet. The spacing of purlins is maintained as 1.5 m. The eave height of the building has been taken as 10 m in which 3 m from ground level is used for brick work and remaining 7 m is used as cladding. These two structures have been analyzed and designed by using STAAD Pro V8i to compare the structural steel weight for both PEB and conventional steel building. Analysis:- CSB frame of the structure considered in the study is as shown in Figure1 359
3 Figure1: Elevation of conventional steel truss with slope 5.71 Pre-Engineered Buildings The typical PEB frame of the structure considered for the present study is shown in Figure 2. Figure2: Elevation of PEB with slope 5.71 Table 1 Structure Parameters Type of building Type of structure Location Industrial building Single story industrial structure Visakhapatnam Area of building 1200 m 2 Eave height Span width Number of bays Single bay length 10 m 20 m 10 No s 6 m Total length 60 m Support condition Fixed (Main columns) Pinned (End wall columns) Roof slope 5.71 Loadings considered in the parametric study Primary loads acting on the structure have been considered as dead load, Live load, earthquake load and wind load. The load calculation for the structure can be carried out in accordance with IS: (Part-1, 2, and 3) and IS: For this structure wind load is critical than earthquake load. Hence, load combinations of dead load, live load, earthquake load and wind load are incorporated for design. Dead load Dead load on the roof trusses in single storey industrial buildings consists of dead load of 360
4 claddings and dead load of purlins, self weight of the trusses in addition to the weight of bracings etc. Further, additional special dead loads such as truss supported hoist dead loads, special ducting and ventilator weight etc. As the clear span length (column free span length) increases, the self weight of the moment resisting gable frame increases drastically. In such cases roof trusses are more economical. The dead load distributed over the roof is found to be in kn/m excluding the self weight. This load is applied as uniformly distributed load over the purlins while designing the structure by PEB and CSB concept. Live load The live load on roof trusses consist of the gravitational load due to erection and servicing as well as dust load etc. and the intensity is taken as per IS: (Part-2). Additional special live loads such as snow loads in very cold climates, crane live loads in trusses supporting monorails may have to be considered. The load assumed to be produced by the intended use or occupancy of a building including the weight of movable partitions, distributed, concentrated loads, load due to impact and vibration, and dust load but excluding wind, seismic, snow and other loads due to temperature changes, creep, shrinkage, differential settlement, etc. According to IS : 875 (Part 2) 1987, for roof with no access provided, the live load can be taken as 0.75 kn/m 2 with a reduction of 0.02 kn/m 2 for every one degree above 10 degrees of roof slope. Total uniform live load acting on the purlin of the CSB and PEB structures are found to be in kn/m. Earthquake Load Since earthquake load on a building depends on the mass of the building, earthquake loads usually do not govern the design of light industrial steel buildings. Wind loads usually govern. However, in the case of industrial buildings with a large mass located at the roof, the earthquake load may govern the design. These loads are calculated as per IS: Wind load Wind load on the roof trusses, unless the roof slope is too high, would be usually uplift force perpendicular to the roof, due to suction effect of the wind blowing over the roof. Hence the wind load on roof truss usually acts opposite to the gravity load, and its magnitude can be larger than gravity loads. The horizontal and vertical bracings used primarily to resist wind and other lateral loads in trusses. These bracings minimize the differential deflection between the different frames due to lateral loads in industrial buildings. They also provide lateral support to columns in small and tall buildings, thus increasing the buckling strength. Wind load is calculated as per IS: 875 (Part 3) The basic wind speed for the location of the building is found to be 50 m/s from the code. The wind load over the roof can be provided as uniformly distributed load acting outward over the purlins of PEB, and as uniformly distributed load acting outward over the CSB purlins. For side walls, the wind load is applied as uniformly distributed loads acting inward or outward to the walls according to the wind case. Basic wind Speed (V b) Basic wind speed is based on peak gust velocity averaged over a short time interval of about 3 seconds and corresponds to mean heights above ground level in an open terrain (Category 2). Basic wind speeds have been worked out for a 50 year return period. Design Wind Speed (V z) The basic wind speed (V b) for any site shall be modified to include the following effects to get design wind velocity at any height (V z) for the chosen structure. a) Risk level b) Terrain roughness, height and size of structure c) Local topography It can be mathematically expressed as follows. V z = V b k 1 k 2 k 3 where V z = design wind speed at any height z in m/s V b = basic wind speed in m/s k 1 = probability factor (risk coefficient) k 2 = terrain, height and structure size factor and 361
5 k 3 = topography factor. Design wind pressure (P z) The design wind pressure at any height above mean ground level shell be obtained by the following relationship between wind pressure and wind velocity. P z = 0.6 V z 2 Wind pressures and forces on buildings/structures General - The wind shall be calculated for: a) The building as a whole, b) Individual structural elements as roofs and walls, and c) Individual cladding units including glazing and their fixings. Pressure coefficients The pressure coefficients are always given for a particular surface or part of the surface of a building. The wind load acting normal to a surface is obtained by multiplying the area of that surface or its appropriate portion by the pressure coefficient (C p) and the design wind pressure at the height of the surface from the ground. Average values of pressure coefficients are given for critical wind directions in one or more quadrants. In order to determine the maximum wind load on the building, the total load should be calculated for each of the critical directions shown from all quadrants. Where considerable variation of pressure occurs over a surface, it has been subdivided and mean pressure coefficients given for each of its several parts. In addition, areas of high local suction (negative pressure concentration) frequently occurring near the edges of walls and roofs are separately shown. Coefficients for the local effects should only be used for calculation of forces on these local areas affecting roof sheeting, glass panels, and individual cladding units including their fixtures. They should not be used for calculating force on entire structural elements such as roof, walls or structure as a whole. Wind load on individual members When calculating the wind load on individual structural elements such as roofs and walls, and individual cladding units and their fittings, it is essential to take account of the pressure difference between opposite faces of such elements or units. For clad structures, it is, therefore, necessary to know the internal pressure as well as the external pressure. Then the wind load, F, acting in a direction normal to the individual structural element or cladding unit is: F = (C pe C pi) A P zwhere C pe = external pressure coefficient, C pi = internal pressure- coefficient, A = surface area of structural or cladding unit, and P z = Design wind pressure External pressure coefficients (C pe) Walls: Pitched roofs of rectangular clad buildings: The average external pressure coefficients and pressure concentration coefficients for pitched roofs of rectangular clad building shall be as given in Table 3.5. Where no pressure concentration coefficients are given, the average coefficients shall apply. Internal Pressure Coefficients (C pi) Internal air pressure in a building depends upon the degree of permeability of cladding to the flow of air. The internal air pressure may be positive or negative depending on the direction of flow of air in relation to openings in the buildings. In the case of buildings where the claddings permit the flow of air with openings not more than about 5 percent of the wall area but where there are no large openings, it is necessary to consider the possibility of the internal pressure being positive or negative. Two design conditions shall be examined, one with an internal pressure coefficient of +0.5 and another with an internal pressure coefficient of The internal pressure coefficients algebraically added to the external pressure coefficient and the analysis which indicates greater distress of the member shall be adopted. In most situations a simple inspection of the sign of external pressure will at once indicate the proper sign of the internal pressure coefficient to be taken for design. 362
6 Buildings with medium and large openings Buildings with medium and large openings may also exhibit either positive or negative internal pressure depending upon the direction of wind. Buildings with medium openings between about 5 to 20 percent of wall area shall be examined for an internal pressure coefficient of +0.5 and later with an internal pressure coefficient of -0.5 and the analysis which produces greater distress of the members shall be adopted. Buildings with large openings, that is, openings larger than 20 percent of the wall area shall be examined once with an internal pressure coefficient of +0.7 and again with an internal pressure coefficient of -0.7,and the analysis which produces greater distress on the members shall be adopted. In this work the building is assumed with medium openings between about 5 to 20 percent of wall area shall be examined for an internal pressure coefficient of +0.5 and later with an internal pressure coefficient of LOAD CALCULATIONS Span of the truss = 20 m Length of the building = 60 m Bay width = 6 m each Spacing of purlins = 1.5 m Height of the eaves = 10 m Height of the building at ridge = 11 m Dead load: (as per IS 875 (Part-1) 1987) Weight of the G.I sheeting = kn/m 2 (class 1 G.I sheeting, thickness 1.60 mm) Weight of fixings = kn/m 2 Weight of services = 0.1 kn/m 2 Total weight is = kn/m 2 Total weight on purlins = = kn/m 2. Live load: (as per IS 875 (Part-2) 1987) Live load on purlins = kn/m 2 Therefore live load on purlins at spacing = =1.130 kn/m 2. Earthquake load: (as per IS: 1893 (Part-1)-2002) Dead load = kn/m 2 Live load = kn/m 2 (25 of reduction as per is 1893 (Part-1)-2002) Total load = N/m 2 Bay width of the building is 5 m Therefore earthquake load on rafter = = kn/m. Wind load: (As per IS 875:Part-III) Location: Visakhapatnam. Risk coefficient factor (k 1) = 1 Terrain and height facto (k 2) = Topography factor (k 3) = 1 Design wind speed V z =V b k 1 k 2 k 3 Where V b = basic wind speed = 50 m/s Design wind speed V z = = m/s Design wind pressure P z 2 = 0.6 V z P z = P z = 1316 N/m 2 Table2: wind load left (C pi = -0.5) 363
7 Coefficients (C pe) (C pe -C pi ) Wind load (F) kn/m Table3: wind load right (C pi = -0.5) Coefficients (C pe ) (C pe-c pi) Wind load (F) kn/m Table4: wind load left (C pi = +0.5) Coefficients (C pe ) (C pe-c pi) Wind load (F) kn/m Table5: wind load right (C pi = +0.5) Coefficients (C pe ) (C pe -C pi ) Wind load (F) kn/m Table6: wind load parallel (C pi = -0.5) Coefficients (C pe) (C pe-c pi) Wind load (F) kn/m Table7: wind load parallel (C pi = +0.5) Coefficients (C pe) (C pe - C pi) Wind load (F) kn/m RESULTS AND DISSCUSSIONS Weight of steel (steel take-off) The weights of conventional steel building and PEB are calculated after the design. For conventional steel building the weight of the section is given in Table 8. For PEB with slope 5.71, the weight of sections is given in Table 9. Weight of the steel for the conventional steel building In order to calculate the steel weight of conventional steel building the following member properties are used (Table 8). Hot rolled I sections are assigned for columns. For the top chord, bottom chord and bracings Indian standard double angles are used. For purlins, girts and eave strut ISMC (Indian Standard Medium Channels) are used. Now using the above parameters the lengths and weights are calculated accordingly. Table 8: Steel take-off for conventional steel building 364
8 Profile Length (m) Weight (t) Tapered Member no: Tapered Member no: ST ISMC ST 250CS80 x ST 290ZS75 x ST 300ZS75 x ST ISMB ST ISA75x75x Prismatic Steel Total Weight of the steel for the PEB In order to calculate steel weight of PEB the following member properties are used (Table 9). For columns and rafters tapered I sections are assigned. For the purlins cold formed Z sections are used. For the girts cold formed C sections are used. For bracings Indian standard double angle sections are used. Now using the above parameters the lengths and weights are calculated accordingly. Table 9: Steel take-off for the PEB Profile Length(m) Weight (t) Tapered MembNo: Tapered MembNo: Tapered MembNo: Tapered MembNo: Tapered MembNo: Tapered MembNo: Tapered MembNo: ST 250CS80x ST 250ZS75X ST 260ZSx75x ST 300ZSx75x Total Comparison of member forces and joint displacements for CSB vs PEB Comparison of member forces and joint displacements at ridge and haunch portions with critical load and at same location was as mentioned below From the comparison it is observed that 1. At ridge and haunch of the building Maximum bending moment for PEB is more than CSB by 6.19 % and % this is due to the entire force will concentrated in PEB where as in CSB it is distributed. 2. At ridge of the building axial force for CSB is more than PEB by 2.2 %, at haunch of the building PEB is more than CSB by 27% this is due to the entire force has to transfer at haunch like beam action in PEB where as in CSB it is like a truss arrangement. 3. At ridge and haunch of the building shear force for PEB is more than CSB by 16.5 % and % this is due to the entire force will concentrated in PEB where as in CSB it is distributed. 4. At ridge the vertical displacement for PEB is 33mm where as for CSB it is 28mm. Both the displacements are within the allowable limit. 5. At haunch the horizontal displacement for PEB and CSB is 8mm.Both the displacements are within the allowable limit 5. CONCLUSIONS 365
9 After analysing, the following are the conclusions of Pre-Engineered steel Building when compared with Conventional Steel Buildings 1. The total steel take-off for PEB is 16% of the conventional steel building. 2. It is observed than maximum moment will be high for PEB than CSB 3. It is observed than maximum shear force will be high for PEB than CSB 4. For PEB the axial force at haunch is higher than CSB 5. For CSB the axial force at ridge is higher than PEB 6. REFERENCES [1] Bhavikatti S.S, Design of steel structures by limit state method as per IS , I.K.International publishing house Pvt.Ltd., NewDelhi, (2010). [2] Darshana P.Zoad, Evaluation of Pre- Engineering Structure Design by IS-800 as against Pre- Engineering Structure Design by AISC, International Journal of Engineering Research and technology (IJERT), Volume-1, issue 5, July 2012 [3] Duggal S.K, Limit State Design of steel Structural Tata McGraw Hill education [4] Subramanian N, Design of steel structures, Oxford higher education, Chennai (2008). [5] Subramanian. N, Pre- Engineered buildings selection of framing system, roofing and wall materials The Master builder, July,2008, pp [6] Zamil steel, Technical Manual January [7] IS 800, General construct in steel code of practice Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, (2007). [8] IS 875 (part 1) Code of practice for design loads (other than earthquake) for building and structures, dead loads, New Delhi,1987. [9] IS 875 (part 2) Code of practice for design loads (other than earthquake) for building and structures, Imposed loads, New Delhi, [10] IS 875 (part 3) Code of practice for design loads (other than earthquake) for building and structures, wind loads, New Delhi,1987. [11] IS Code of practice for Seismic loads [12] IS Code of Practice for Use of Cold-Formed Light Weight Gauge 366
Economizing Steel building using Pre-Engineered Steel Sections
 Economizing Steel building using Pre-Engineered Steel Sections Neha Kolate1, Shilpa Kewate2 1 P.G. student, Civil Engineering Department, Saraswati College of Engineering, Maharashtra, India, kolate.neha@gmail.com
Economizing Steel building using Pre-Engineered Steel Sections Neha Kolate1, Shilpa Kewate2 1 P.G. student, Civil Engineering Department, Saraswati College of Engineering, Maharashtra, India, kolate.neha@gmail.com
Optimization of Pre Engineered Buildings
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Optimization of Pre Engineered Buildings B K Raghu Prasad 1, Sunil kumar 2, Amaranth K 3 1 Professor (Retired), Civil Engineering Dept., IISC, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 2
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Optimization of Pre Engineered Buildings B K Raghu Prasad 1, Sunil kumar 2, Amaranth K 3 1 Professor (Retired), Civil Engineering Dept., IISC, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 2
A REVIEW ON VARIOUS TYPES OF INDUSTRIAL BUILDING
 A REVIEW ON VARIOUS TYPES OF INDUSTRIAL BUILDING Swapnil D. Bokade 1, Laxmikant Vairagade 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Nagpur University, Nagpur, India Swapnilbokade99@gmail.com 2 Department of
A REVIEW ON VARIOUS TYPES OF INDUSTRIAL BUILDING Swapnil D. Bokade 1, Laxmikant Vairagade 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Nagpur University, Nagpur, India Swapnilbokade99@gmail.com 2 Department of
A Comparative study on the Performance of PEB with CSB considering various parameters
 A Comparative study on the Performance of PEB with CSB considering various parameters Darshan Kalantri 1, Sujay Deshpande 2, Pavan Gudi 3 1 Post-Graduate Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, KLS Gogte
A Comparative study on the Performance of PEB with CSB considering various parameters Darshan Kalantri 1, Sujay Deshpande 2, Pavan Gudi 3 1 Post-Graduate Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, KLS Gogte
Review Paper on Comparison of Conventional Steel Building & Pre-Engineering Building
 Review Paper on Comparison of Conventional Steel Building & Pre-Engineering Building Sagar Wankhade 1, Prof. Dr. P. S. Pajgade 2 Department of Civil Engineering 1, 2, 3, 4 1, 2, 3, 4, Affiliation name
Review Paper on Comparison of Conventional Steel Building & Pre-Engineering Building Sagar Wankhade 1, Prof. Dr. P. S. Pajgade 2 Department of Civil Engineering 1, 2, 3, 4 1, 2, 3, 4, Affiliation name
Comparison between Design and Analysis of Various Configuration of Industrial Sheds
 Comparison between Design and Analysis of Various Configuration of Industrial Sheds Vrushali Bahadure 1, Prof. R.V.R.K.Prasad 2 1 Student, 2 Associate Professor 1 Department of Civil Engineering, KDK College
Comparison between Design and Analysis of Various Configuration of Industrial Sheds Vrushali Bahadure 1, Prof. R.V.R.K.Prasad 2 1 Student, 2 Associate Professor 1 Department of Civil Engineering, KDK College
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PRE-ENGINEERED BUILDING AND CONVENTIONAL STEEL STRUCTURES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PRE-ENGINEERED BUILDING AND CONVENTIONAL STEEL STRUCTURES Sudhir Singh Bhadoria 1, Yash Pathak 2 1Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, UIT-RGPV, Bhopal 2PG Student, Department
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PRE-ENGINEERED BUILDING AND CONVENTIONAL STEEL STRUCTURES Sudhir Singh Bhadoria 1, Yash Pathak 2 1Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, UIT-RGPV, Bhopal 2PG Student, Department
Evaluation Of Pre-Engineering Structure Design By IS-800 As Against Pre-Engineering Structure Design By AISC
 Ms. Darshana P. Zoad Department of Civil Engineering Karmaveer Dadasaheb Kannamwar College of Engineering, Nagpur 440 009 Evaluation Of Pre-Engineering Structure Design By IS-800 As Against Pre-Engineering
Ms. Darshana P. Zoad Department of Civil Engineering Karmaveer Dadasaheb Kannamwar College of Engineering, Nagpur 440 009 Evaluation Of Pre-Engineering Structure Design By IS-800 As Against Pre-Engineering
Comparative Study of Seismic Analysis and Design of Pre-Engineering Building with Conventional Industrial Building on different bay spacing
 Comparative Study of Seismic Analysis and Design of Pre-Engineering Building with Conventional Industrial Building on different bay spacing Muthu Meena M 1, Mr.Kammalakannan P 2 P.G. Student, Department
Comparative Study of Seismic Analysis and Design of Pre-Engineering Building with Conventional Industrial Building on different bay spacing Muthu Meena M 1, Mr.Kammalakannan P 2 P.G. Student, Department
A Comparative Study between RCC and Steel Design for Industrial and Commercial Structures
 A Comparative Study between RCC and Steel Design for Industrial and Commercial Structures M. SATYANARAYANA REDDY M.Tech Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Godavari Institute of Engineering & Technology,
A Comparative Study between RCC and Steel Design for Industrial and Commercial Structures M. SATYANARAYANA REDDY M.Tech Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Godavari Institute of Engineering & Technology,
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 11, November -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Structural
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 11, November -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Structural
COMPANY PROFILE. under effective guidance of highly experienced and integrated top management.
 COMPANY PROFILE Ganges group is a multi faced professionally managed organization, dealing in different fields of manufacturing. The group has interest & strong presence in di ersified field like solar
COMPANY PROFILE Ganges group is a multi faced professionally managed organization, dealing in different fields of manufacturing. The group has interest & strong presence in di ersified field like solar
The Design and Engineering of Fabric Membrane Clad Buildings
 The Design and Engineering of Fabric Membrane Clad Buildings Wayne Rendely PE 132 Columbia Street, Huntington Station, New York, 11746-1220 TEL (631) 351-1843 WayneRendelyPE.com ABSTRACT This paper reviews
The Design and Engineering of Fabric Membrane Clad Buildings Wayne Rendely PE 132 Columbia Street, Huntington Station, New York, 11746-1220 TEL (631) 351-1843 WayneRendelyPE.com ABSTRACT This paper reviews
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF HIGH-RISE BUILDING (G+30) USING STAAD.PRO
 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF HIGH-RISE BUILDING (G+30) USING STAAD.PRO BORUGADDA RAJU 1*, Mr. R.RATTAIAH 2* 1. II.M.Tech, Dept of CIVIL, AM Reddy Memorial College of Engineering & Technology, Petlurivaripalem.
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF HIGH-RISE BUILDING (G+30) USING STAAD.PRO BORUGADDA RAJU 1*, Mr. R.RATTAIAH 2* 1. II.M.Tech, Dept of CIVIL, AM Reddy Memorial College of Engineering & Technology, Petlurivaripalem.
Task Infracon Pvt. Ltd. Think Better; Plan Better ; Build Better
 Task Infracon Pvt. Ltd. Pre-Engineering Building-Aplication Warehouse Industrial Cold Storage Showroom Pharmaceutical Power Plant FMCG Automobile Agriculture Dairy Farm Multi-Storey Building Heavy Engineering
Task Infracon Pvt. Ltd. Pre-Engineering Building-Aplication Warehouse Industrial Cold Storage Showroom Pharmaceutical Power Plant FMCG Automobile Agriculture Dairy Farm Multi-Storey Building Heavy Engineering
2 Loads 2.1 BACKGROUND 2.2 DEAD LOADS
 Loads 15 2 Loads 2.1 BACKGROUND The loads to be considered in the design of portal frame buildings are dead, live, wind, seismic and occasionally snow loads, and combinations of these. Live loads generally
Loads 15 2 Loads 2.1 BACKGROUND The loads to be considered in the design of portal frame buildings are dead, live, wind, seismic and occasionally snow loads, and combinations of these. Live loads generally
Planning Analysis and Design of Industrial Building Using STAAD PRO
 Volume 119 No. 17 2018, 131-137 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ Planning Analysis and Design of Industrial Building Using STAAD PRO K. PRABIN
Volume 119 No. 17 2018, 131-137 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ Planning Analysis and Design of Industrial Building Using STAAD PRO K. PRABIN
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
 2.6 Portal frames Portal frames are the most commonly used structural forms for single-storey industrial structures. They are constructed mainly using hot-rolled sections, supporting the roofing and side
2.6 Portal frames Portal frames are the most commonly used structural forms for single-storey industrial structures. They are constructed mainly using hot-rolled sections, supporting the roofing and side
Mustafa & Kamal Ashraf Trading Co. PRE ENGINEERED BUILDING & STRUCTURAL STEEL MANUFACTURING TOTAL SOLUTION IN DESIGN, FABRICATION & INSTALLATION
 Mustafa & Kamal Ashraf Trading Co. PRE ENGINEERED BUILDING & STRUCTURAL STEEL MANUFACTURING TOTAL SOLUTION IN DESIGN, FABRICATION & INSTALLATION ISO 9001 Project: Logistic Extension Client: Khimji Ramdas
Mustafa & Kamal Ashraf Trading Co. PRE ENGINEERED BUILDING & STRUCTURAL STEEL MANUFACTURING TOTAL SOLUTION IN DESIGN, FABRICATION & INSTALLATION ISO 9001 Project: Logistic Extension Client: Khimji Ramdas
TRUSSES. (d) Bracings in Single Storey Buildings. Fig. 1 Types of Trusses
 27 TRUSSES 1.0 INTRODUCTION Trusses are triangular frame works in which the members are subjected to essentially axial forces due to externally applied load. They may be plane trusses [Fig. 1(a)], wherein
27 TRUSSES 1.0 INTRODUCTION Trusses are triangular frame works in which the members are subjected to essentially axial forces due to externally applied load. They may be plane trusses [Fig. 1(a)], wherein
Retrofitting of Truss under Increased Permeability Conditions
 ISSN (Print): 2347-671 Vol. 6, Issue 8, August 217 Retrofitting of Truss under Increased Permeability Conditions P Surekha 1, D.Pradeep 2, P. Veerabhadra Rao 3 PG Student, Department of Civil Engineering,
ISSN (Print): 2347-671 Vol. 6, Issue 8, August 217 Retrofitting of Truss under Increased Permeability Conditions P Surekha 1, D.Pradeep 2, P. Veerabhadra Rao 3 PG Student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Analysis and Design of an Earthquake Resistant Structure using STADD. Pro
 Analysis and Design of an Earthquake Resistant Structure using STADD. Pro Akshay R. Kohli 1, Prof. N. G. Gore 2 1B.E. Undergraduate, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering. 1,2 MGM s College
Analysis and Design of an Earthquake Resistant Structure using STADD. Pro Akshay R. Kohli 1, Prof. N. G. Gore 2 1B.E. Undergraduate, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering. 1,2 MGM s College
Analysis of Double Howe Steel Truss & Cantilever Truss Using Ansys Software
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 2017), PP 09-14 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of Double Howe Steel
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 2017), PP 09-14 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of Double Howe Steel
ISSN: [Phatanagre* et al., 6(2): February, 2017] Impact Factor: Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, AVCOE, Sangamner, India.
![ISSN: [Phatanagre* et al., 6(2): February, 2017] Impact Factor: Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, AVCOE, Sangamner, India. ISSN: [Phatanagre* et al., 6(2): February, 2017] Impact Factor: Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, AVCOE, Sangamner, India.](/thumbs/87/95889366.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY A REVIEW PAPER ON ALTERNATE DESIGN OF ROOFING SYSYTEM Phatangare Roshani Rambhau *1, Dr.Wakchaure M.R. *2 *1 PG Student, Department
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY A REVIEW PAPER ON ALTERNATE DESIGN OF ROOFING SYSYTEM Phatangare Roshani Rambhau *1, Dr.Wakchaure M.R. *2 *1 PG Student, Department
Comparison of Design Procedures for Pre Engineering Buildings (PEB): A Case Study
 Comparison of Design Procedures for Pre Engineering Buildings (PEB): A Case Study G. Sai Kiran, A. Kailasa Rao, R. Pradeep Kumar Abstract In recent years, the introduction of Pre Engineered Building (PEB)
Comparison of Design Procedures for Pre Engineering Buildings (PEB): A Case Study G. Sai Kiran, A. Kailasa Rao, R. Pradeep Kumar Abstract In recent years, the introduction of Pre Engineered Building (PEB)
8 Crane Runway Beams
 Design Procedure for Gantry Cranes 297 8 Crane Runway Beams 8.1 GENERAL Overhead travelling cranes or gantry cranes as shown in Figure 8.1 are generally used in workshops and warehouses where lifting capacity
Design Procedure for Gantry Cranes 297 8 Crane Runway Beams 8.1 GENERAL Overhead travelling cranes or gantry cranes as shown in Figure 8.1 are generally used in workshops and warehouses where lifting capacity
Full Paper Proc. of Int. Conf. on Advances in Civil Engineering 2012
 Behaviour of R.C.C. Tall Buildings Having Different Shapes Subjected to Wind Load Prof. Sarita Singla 1, Taranjeet Kaur 2, Megha Kalra 3 and Sanket Sharma 4 1 Email:ssaritasingla@yahoo.com 2 Baddi University/Civil
Behaviour of R.C.C. Tall Buildings Having Different Shapes Subjected to Wind Load Prof. Sarita Singla 1, Taranjeet Kaur 2, Megha Kalra 3 and Sanket Sharma 4 1 Email:ssaritasingla@yahoo.com 2 Baddi University/Civil
A Comparative Study of PEB Frames TCCS & TCMS1
 A Comparative Study of PEB Frames TCCS & TCMS1 Ajay Gopal Mishra 1, Mohd. Ahtasham 2, Dr. J.M Banday 3 Design Head, Department of Design and Drafting, Apex Buildsys, Noida, India 1 Post Graduate Structural
A Comparative Study of PEB Frames TCCS & TCMS1 Ajay Gopal Mishra 1, Mohd. Ahtasham 2, Dr. J.M Banday 3 Design Head, Department of Design and Drafting, Apex Buildsys, Noida, India 1 Post Graduate Structural
ABS Pre-Fab Building S ystem
 INTRODUCTION Accumech Building System P. Ltd. provides best quality profiled Roofing, Ceiling and Pre-engineered Building System. The demand in the market and due to our services and goodwill in the market,
INTRODUCTION Accumech Building System P. Ltd. provides best quality profiled Roofing, Ceiling and Pre-engineered Building System. The demand in the market and due to our services and goodwill in the market,
Lintels and Beams Engineering basis
 Lintels and Beams Engineering basis The calculator is intended for the design of lintels and beams in timber framed buildings generally within the scope of NZS 3604: 2011 Timber- framed buildings. However
Lintels and Beams Engineering basis The calculator is intended for the design of lintels and beams in timber framed buildings generally within the scope of NZS 3604: 2011 Timber- framed buildings. However
DESIGN OF PRE-ENGINEERED STEEL BUILDING FOR AIR CRAFT HANGAR USING STAAD PRO
 DESIGN OF PRE-ENGINEERED STEEL BUILDING FOR AIR CRAFT HANGAR USING STAAD PRO Shanagonda Akhila 1, Kolla Aswani Chandh 2 Department of Civil Engineering Vignan s Institute of Technology and Aeronautical
DESIGN OF PRE-ENGINEERED STEEL BUILDING FOR AIR CRAFT HANGAR USING STAAD PRO Shanagonda Akhila 1, Kolla Aswani Chandh 2 Department of Civil Engineering Vignan s Institute of Technology and Aeronautical
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May-2016 1059 Effective Study of Bracing Systems for Irregular Tall Steel Structures Narasimha Murthy K 1, Darshan SK 2, Karthik
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May-2016 1059 Effective Study of Bracing Systems for Irregular Tall Steel Structures Narasimha Murthy K 1, Darshan SK 2, Karthik
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON ANALYSIS OF STEEL TRUSS STRUCTURE AND RIGID FRAME BY USING STAAD PRO
 COMPARATIVE STUDY ON ANALYSIS OF STEEL TRUSS STRUCTURE AND RIGID FRAME BY USING STAAD PRO Dr. RAMAKRISHNA HEGDE 1, YOGESH G 2, SURAJ CHAVHAN 3 1HOD of Dept. of Civil Engineering, Srinivas School of Engineering,
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON ANALYSIS OF STEEL TRUSS STRUCTURE AND RIGID FRAME BY USING STAAD PRO Dr. RAMAKRISHNA HEGDE 1, YOGESH G 2, SURAJ CHAVHAN 3 1HOD of Dept. of Civil Engineering, Srinivas School of Engineering,
VP University WEBINAR Loads and Codes
 VP University WEBINAR Loads and Codes Building Codes 2 Builder Responsibilities VPC Loading Screens Load & Code Data Supplied by the Builder Verify with Engineer of Record Pursue most accurate data Assures
VP University WEBINAR Loads and Codes Building Codes 2 Builder Responsibilities VPC Loading Screens Load & Code Data Supplied by the Builder Verify with Engineer of Record Pursue most accurate data Assures
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF PRE ENGINEER FRAME WITH IS800:2007
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF PRE ENGINEER FRAME WITH IS800:2007 K SRINIJA 14C71D2011, M.Tech (Civil - Structural Engineering), Ellenki College of Engineering & Technology ABSTRACT Steel is the material of choice
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF PRE ENGINEER FRAME WITH IS800:2007 K SRINIJA 14C71D2011, M.Tech (Civil - Structural Engineering), Ellenki College of Engineering & Technology ABSTRACT Steel is the material of choice
RESPONSE OF STRUCTURAL STEEL FRAME BY USING SEMI-RIGID CONNECTIONS
 RESPONSE OF STRUCTURAL STEEL FRAME BY USING SEMI-RIGID CONNECTIONS Sanjaykumar N. Sonune 1, Dr. Nagesh L. Shelke 2, Prof. Shoeb Kalyani 3 1 ME Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Dr. D.Y. Patil School
RESPONSE OF STRUCTURAL STEEL FRAME BY USING SEMI-RIGID CONNECTIONS Sanjaykumar N. Sonune 1, Dr. Nagesh L. Shelke 2, Prof. Shoeb Kalyani 3 1 ME Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Dr. D.Y. Patil School
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION. Frame Types Available PRIMARY FRAMING. Gable Symmetrical
 : A ridged (double slope) building in which the ridge is in the center of the building. Gable: The triangular portion of the endwall from the level of the eave to the ridge of the roof. Gauge: Finish:
: A ridged (double slope) building in which the ridge is in the center of the building. Gable: The triangular portion of the endwall from the level of the eave to the ridge of the roof. Gauge: Finish:
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 6, June ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 6, June-26 36 DIAGRID STRUCTURAL SYSTEM FOR R.C.FRAMED MULTIED BUILDINGS Harshita Tripathi, Dr. Sarita Singla Abstract- One of
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 6, June-26 36 DIAGRID STRUCTURAL SYSTEM FOR R.C.FRAMED MULTIED BUILDINGS Harshita Tripathi, Dr. Sarita Singla Abstract- One of
HEAVY STEEL CONSTRUCTION
 HEAVY STEEL CONSTRUCTION PRE-ENGINEERED PRE ENGINEERED STEEL BUILDINGS Prismatic Constructions Work Shops, Storage Buildings etc. Figure 1 Figure 2 Prismatic steel constructions can be manufactured as
HEAVY STEEL CONSTRUCTION PRE-ENGINEERED PRE ENGINEERED STEEL BUILDINGS Prismatic Constructions Work Shops, Storage Buildings etc. Figure 1 Figure 2 Prismatic steel constructions can be manufactured as
STEEL STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS
 STEEL STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS Steel elements are of two basic types: Structural steel shapes are formed into their final shapes by hot-rolling. This method produces such common elements as wide flange sections,
STEEL STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS Steel elements are of two basic types: Structural steel shapes are formed into their final shapes by hot-rolling. This method produces such common elements as wide flange sections,
SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF A COMMERCIAL BUILDINGS (G+5) KORITALA SINDHUJA 1*, Mr. R.RATTAIAH 2*
 SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF A COMMERCIAL BUILDINGS (G+5) KORITALA SINDHUJA 1*, Mr. R.RATTAIAH 2* 1. II.M.Tech, Dept of CIVIL, AM Reddy Memorial College of Engineering & Technology, Petlurivaripalem.
SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF A COMMERCIAL BUILDINGS (G+5) KORITALA SINDHUJA 1*, Mr. R.RATTAIAH 2* 1. II.M.Tech, Dept of CIVIL, AM Reddy Memorial College of Engineering & Technology, Petlurivaripalem.
SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF A APARTMENT BUILDINGS (G+10) KAKARAPARTHY SIVA KARTHIK 1*, Mr. A.SRINIVASU 2*
 SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF A APARTMENT BUILDINGS (G+10) KAKARAPARTHY SIVA KARTHIK 1*, Mr. A.SRINIVASU 2* 1. II.M.Tech, Dept of CIVIL, AM Reddy Memorial College of Engineering & Technology, Petlurivaripalem.
SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF A APARTMENT BUILDINGS (G+10) KAKARAPARTHY SIVA KARTHIK 1*, Mr. A.SRINIVASU 2* 1. II.M.Tech, Dept of CIVIL, AM Reddy Memorial College of Engineering & Technology, Petlurivaripalem.
Wind Analysis of High Rise Building with Different Bracing Systems Amol S. Rajas, Dr.N.L.Shelke
 Wind Analysis of High Rise Building with Different Bracing Systems Amol S. Rajas, Dr.N.L.Shelke P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, D. Y. Patil School of Engineering& Technology, Lohegaon, Pune,
Wind Analysis of High Rise Building with Different Bracing Systems Amol S. Rajas, Dr.N.L.Shelke P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, D. Y. Patil School of Engineering& Technology, Lohegaon, Pune,
Lintels and Beams: Engineering Basis
 Lintels and Beams: Engineering Basis The calculator is intended for the design of lintels and beams in timber- framed buildings generally within the scope of NZS 3604. However, the range of applications,
Lintels and Beams: Engineering Basis The calculator is intended for the design of lintels and beams in timber- framed buildings generally within the scope of NZS 3604. However, the range of applications,
Comparative Study of R.C.C and Steel Concrete Composite Structures
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Comparative Study of R.C.C and Steel Concrete Composite Structures Shweta A. Wagh*, Dr. U. P. Waghe** *(Post Graduate Student in Structural Engineering, Y.C.C.E, Nagpur 441
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Comparative Study of R.C.C and Steel Concrete Composite Structures Shweta A. Wagh*, Dr. U. P. Waghe** *(Post Graduate Student in Structural Engineering, Y.C.C.E, Nagpur 441
Analysis Of Long Span Roof Truss
 Analysis Of Long Span Roof Truss Nalladurai V * Shankar P * * * P.G Student, Structural Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering, ** Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Nandha Engineering
Analysis Of Long Span Roof Truss Nalladurai V * Shankar P * * * P.G Student, Structural Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering, ** Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Nandha Engineering
S. Gandhi *1, Syed Rizwan 2
 2017 IJSRSET Volume 3 Issue 3 Print ISSN: 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Analysis and Design of Tall Building (G+21) Using ETABS S. Gandhi *1, Syed Rizwan
2017 IJSRSET Volume 3 Issue 3 Print ISSN: 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Analysis and Design of Tall Building (G+21) Using ETABS S. Gandhi *1, Syed Rizwan
BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDING FRAMES WITH STEEL PLATE SHEAR WALLS
 ASIAN JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING (BUILDING AND HOUSING) VOL. 11, NO. 1 (2010) PAGES 95-102 BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDING FRAMES WITH STEEL PLATE SHEAR WALLS R.S. Londhe * and A.P. Chavan Department of Applied
ASIAN JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING (BUILDING AND HOUSING) VOL. 11, NO. 1 (2010) PAGES 95-102 BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDING FRAMES WITH STEEL PLATE SHEAR WALLS R.S. Londhe * and A.P. Chavan Department of Applied
STEEL BUILDINGS IN EUROPE. Single-Storey Steel Buildings Part 2: Concept Design
 STEEL BUILDINGS IN EUROPE Single-Storey Steel Buildings Part 2: Concept Design 2.4 Airbus Industrie hanger, Toulouse, France The Airbus production hall in Toulouse covers 200000
STEEL BUILDINGS IN EUROPE Single-Storey Steel Buildings Part 2: Concept Design 2.4 Airbus Industrie hanger, Toulouse, France The Airbus production hall in Toulouse covers 200000
Pre-Engineered Construction Analysis and Design of Portal Frame
 Pre-Engineered Construction Analysis and Design of Portal Frame Ms. Neha Patel* 1,PG Scholar, Mrs. Shraddha Sharma* 2, Asso. Prof. Civil Engg. Dept. B.I.T. Bhilai (C.G.) Abstract Technological improvement
Pre-Engineered Construction Analysis and Design of Portal Frame Ms. Neha Patel* 1,PG Scholar, Mrs. Shraddha Sharma* 2, Asso. Prof. Civil Engg. Dept. B.I.T. Bhilai (C.G.) Abstract Technological improvement
COLD ROLLED STEEL. Pre-Engineered Buildings
 COLD ROLLED STEEL Pre-Engineered Buildings B U I L D I N G S Y S T E M S US ABOUT US Sharing a relentless commitment to efficiency and value, TSSC, a key member of the reputed Harwal Group, has been acknowledged
COLD ROLLED STEEL Pre-Engineered Buildings B U I L D I N G S Y S T E M S US ABOUT US Sharing a relentless commitment to efficiency and value, TSSC, a key member of the reputed Harwal Group, has been acknowledged
Pre-schematic Considerations. Who. What. Where
 Who What Where Who, What & Where Who are the users? Church School Manufacturers Researchers Who, What & Where What is the purpose? Fellowship Teaching Manufacturing Production Who, What & Where Location,
Who What Where Who, What & Where Who are the users? Church School Manufacturers Researchers Who, What & Where What is the purpose? Fellowship Teaching Manufacturing Production Who, What & Where Location,
7 Footings & Slabs 7.1 GENERAL
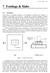 Footings & Slabs 269 7 Footings & Slabs 7.1 GENERAL Portal frames are commonly designed on the assumption of pinned bases, although it is sometimes an advantage to fix the bases. A pinned base is designed
Footings & Slabs 269 7 Footings & Slabs 7.1 GENERAL Portal frames are commonly designed on the assumption of pinned bases, although it is sometimes an advantage to fix the bases. A pinned base is designed
CVEN 483. Structural System Overview
 CVEN 483 Structural System Overview Dr. J. Bracci Fall 2001 Semester Presentation Overview 1. Building system primary function 2. Types of load 3. Building materials 4. Structural members 5. Structural
CVEN 483 Structural System Overview Dr. J. Bracci Fall 2001 Semester Presentation Overview 1. Building system primary function 2. Types of load 3. Building materials 4. Structural members 5. Structural
Behaviour of Symmetrical RCC and Steel Framed Structures Under Seismic and Wind Loading
 International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) Volume III, Issue VIII, August 16 ISSN 31 75 Behaviour of and Steel Framed Structures Under Seismic and Wind ing Avani Mandlik 1, S K
International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) Volume III, Issue VIII, August 16 ISSN 31 75 Behaviour of and Steel Framed Structures Under Seismic and Wind ing Avani Mandlik 1, S K
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction In the past it was common practice to teach structural analysis and stress analysis, or theory of structures and strength of materials as they were frequently known, as two separate
CHAPTER 1 Introduction In the past it was common practice to teach structural analysis and stress analysis, or theory of structures and strength of materials as they were frequently known, as two separate
Effect of 3-D Modeling on Design of Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. III (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 08-13 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of 3-D Modeling on
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. III (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 08-13 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of 3-D Modeling on
Analysis and Design of Multi-Storey Building Subjected to Lateral Forces
 Analysis and Design of MultiStorey Building Subjected to Lateral Forces Pratik Dadsena 1, Nishant Rajoria 2, Bhaskar Dadsena 3 Student, Department of Civil Engineering, S.E.T., Sharda University, Greater
Analysis and Design of MultiStorey Building Subjected to Lateral Forces Pratik Dadsena 1, Nishant Rajoria 2, Bhaskar Dadsena 3 Student, Department of Civil Engineering, S.E.T., Sharda University, Greater
SECTION PLATE CONNECTED WOOD TRUSSES
 SECTION 06173 PLATE CONNECTED WOOD TRUSSES PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Shop fabricated wood trusses for roof and floor framing. 2. Bridging, bracing, and anchorage. B. Related Sections:
SECTION 06173 PLATE CONNECTED WOOD TRUSSES PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Shop fabricated wood trusses for roof and floor framing. 2. Bridging, bracing, and anchorage. B. Related Sections:
Seismic Analysis And Design of a Commercial Buildings (G+5)
 Seismic Analysis And Design of a Commercial Buildings (G+5) Koritala Sindhua, PG student, Department of Civil Engineering, AM Reddy Engineering College,Narasaraopeta,Guntur Dist, Ap, JNTUK ABSTRACT The
Seismic Analysis And Design of a Commercial Buildings (G+5) Koritala Sindhua, PG student, Department of Civil Engineering, AM Reddy Engineering College,Narasaraopeta,Guntur Dist, Ap, JNTUK ABSTRACT The
General Structural Concerns
 1/28 General Structural Concerns Functionality / Stiffness deformations Stability equilibrium Strength material behaviour 2/28 Stability Loads act on structure tend to destabilise structure also tend to
1/28 General Structural Concerns Functionality / Stiffness deformations Stability equilibrium Strength material behaviour 2/28 Stability Loads act on structure tend to destabilise structure also tend to
Approaching towards innnovation. An ISO 9001:2015 Certified company
 Approaching towards innnovation An ISO 9001:2015 Certified company OVER VIEW Trident Steel Building Solutions is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer of Pre engineered steel buildings and structural
Approaching towards innnovation An ISO 9001:2015 Certified company OVER VIEW Trident Steel Building Solutions is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer of Pre engineered steel buildings and structural
OCTAGONAL SHAPE REDUCES AIRPLANE HANGAR COSTS
 OCTAGONAL SHAPE REDUCES AIRPLANE HANGAR COSTS While a square hangar would have been simpler to design, an octagonal building substantially reduced life cycle costs By Charles Sacre, P.E. THE PROGRAM FOR
OCTAGONAL SHAPE REDUCES AIRPLANE HANGAR COSTS While a square hangar would have been simpler to design, an octagonal building substantially reduced life cycle costs By Charles Sacre, P.E. THE PROGRAM FOR
Relative Investigation of Multi-storey Structure into PEB and RCC
 Relative Investigation of Multi-storey Structure into PEB and RCC Jyoti Aher Assistant Prof.: Department of Civil Engineering, S.S.Jondhale College of Engineering and technology, Asangaon, Shahapur ---------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------
Relative Investigation of Multi-storey Structure into PEB and RCC Jyoti Aher Assistant Prof.: Department of Civil Engineering, S.S.Jondhale College of Engineering and technology, Asangaon, Shahapur ---------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------
Analysis of Various Steel Bracing Systems using Steel Sections for High Rise Structures
 Analysis of Various Steel Bracing Systems using Steel Sections for High Rise Structures Y. U. Kulkarni 1 P. G. Chandak 1 M. K. Devtale 1 S.S. Sayyed 1 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,
Analysis of Various Steel Bracing Systems using Steel Sections for High Rise Structures Y. U. Kulkarni 1 P. G. Chandak 1 M. K. Devtale 1 S.S. Sayyed 1 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,
TECHNICAL REPORT 1. Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions. Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital. Hershey, Pennsylvania
 TECHNICAL REPORT 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital Matthew V Vandersall The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering
TECHNICAL REPORT 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital Matthew V Vandersall The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering
SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A MID RISE RCC BUILDING WITH SOFT STOREY AT GROUND FLOOR
 SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A MID RISE RCC BUILDING WITH SOFT STOREY AT GROUND FLOOR 1 DHARMESH VIJAYWARGIYA, 2 Dr. ABHAY SHARMA, 3 Dr. VIVEK GARG 1 Post Graduate Student, Civil Engineering Department, MANIT,
SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A MID RISE RCC BUILDING WITH SOFT STOREY AT GROUND FLOOR 1 DHARMESH VIJAYWARGIYA, 2 Dr. ABHAY SHARMA, 3 Dr. VIVEK GARG 1 Post Graduate Student, Civil Engineering Department, MANIT,
Wind Analysis and Design of G+11 Storied Building Using STAAD-Pro
 Wind Analysis and Design of G+11 Storied Building Using STAAD-Pro 1 Vikrant Trivedi, 2 Sumit Pahwa ------------------------------------------------------------------------***-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Wind Analysis and Design of G+11 Storied Building Using STAAD-Pro 1 Vikrant Trivedi, 2 Sumit Pahwa ------------------------------------------------------------------------***-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Comparative Study on Analysis and Cost of R.C.C. and Steel-Composite Structure
 Comparative Study on Analysis and Cost of R.C.C. and Steel-Composite Structure Renavikar Aniket V. 1, Suryawanshi Yogesh 2 1 Dept. of Civil Engineering ICOER Wagholi Pune 2 Professor, Department of Civil
Comparative Study on Analysis and Cost of R.C.C. and Steel-Composite Structure Renavikar Aniket V. 1, Suryawanshi Yogesh 2 1 Dept. of Civil Engineering ICOER Wagholi Pune 2 Professor, Department of Civil
International Journal of Engineering and Techniques - Volume 4 Issue 2, Mar Apr 2018
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Seismic Analysis of Steel Frames Subjected to Braced Connections Matha Prasad Adari* *Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering. NSRIT Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, INDIA. 1.INTRODUCTION
RESEARCH ARTICLE Seismic Analysis of Steel Frames Subjected to Braced Connections Matha Prasad Adari* *Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering. NSRIT Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, INDIA. 1.INTRODUCTION
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE Seismic Analysis of Irregular Multistoried Structure with Shear Wall J. V. Sunil Ganesh M.Tech IV Semester (CADS), Department of Civil Engineering S.D.M.
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE Seismic Analysis of Irregular Multistoried Structure with Shear Wall J. V. Sunil Ganesh M.Tech IV Semester (CADS), Department of Civil Engineering S.D.M.
WIND LOADS ON BUILDINGS MWFRS (ENVELOPE PROCEDURE)
 Chapter C28 WIND LOADS ON BUILDINGS MWFRS (ENVELOPE PROCEDURE) The Envelope Procedure is the former low-rise buildings provision in Method 2 of ASCE 7-05 for MWFRS. The simplified method in this chapter
Chapter C28 WIND LOADS ON BUILDINGS MWFRS (ENVELOPE PROCEDURE) The Envelope Procedure is the former low-rise buildings provision in Method 2 of ASCE 7-05 for MWFRS. The simplified method in this chapter
Development of a Cold Formed Steel Housing System
 Development of a Cold Formed Steel Housing System Shabari Indhuja.A 1, Narendra Prasad.D 2 P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Periyar Maniammai University, Vallam, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India
Development of a Cold Formed Steel Housing System Shabari Indhuja.A 1, Narendra Prasad.D 2 P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Periyar Maniammai University, Vallam, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India
Seismic Behaviour of Multistorey Steel Structure With Different Type of Bracing System
 Seismic Behaviour of Multistorey Steel Structure With Different Type of Bracing System Dibyaranjan Sahoo 1, Prof. Dr. P.K Parhi 2 1, 2 Civil Engineering Department 1, 2 College Of Engineering & Technology,
Seismic Behaviour of Multistorey Steel Structure With Different Type of Bracing System Dibyaranjan Sahoo 1, Prof. Dr. P.K Parhi 2 1, 2 Civil Engineering Department 1, 2 College Of Engineering & Technology,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 5, May ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 5, May-2014 22 COMPARITIVE STUDY OF EFFECT OF FLOATING COLUMNS ON THE COST ANALYSIS OF A STRUCTURE DESIGNED ON STADD PRO V8i.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 5, May-2014 22 COMPARITIVE STUDY OF EFFECT OF FLOATING COLUMNS ON THE COST ANALYSIS OF A STRUCTURE DESIGNED ON STADD PRO V8i.
The development of generic span tables for cold formed steel studs in residential and low-rise construction
 Australasian Structural Engineering Conference (ASEC), 26 27 June 2008, Melbourne Australia Paper No. 103 The development of generic span tables for cold formed steel studs in residential and low-rise
Australasian Structural Engineering Conference (ASEC), 26 27 June 2008, Melbourne Australia Paper No. 103 The development of generic span tables for cold formed steel studs in residential and low-rise
GENERAL FRAME INFORMATION
 GENERAL FRAME INFORMATION TAPERED BEAM, CLEAR SPAN, GABLE 1. Tapered Beam frames are an excellent solution for small buildings under 70 feet in width. 2. Straight columns provide maximum floor space and
GENERAL FRAME INFORMATION TAPERED BEAM, CLEAR SPAN, GABLE 1. Tapered Beam frames are an excellent solution for small buildings under 70 feet in width. 2. Straight columns provide maximum floor space and
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 05, 2016 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 05, 2016 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Seismic analysis of RC Building Frame with Different Bracing Systems Mohammed Ali Khan
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 05, 2016 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Seismic analysis of RC Building Frame with Different Bracing Systems Mohammed Ali Khan
PORTAL FRAMES 1.0 INTRODUCTION
 36 PORTAL FRAMES 1.0 INTRODUCTION The basic structural form of portal frames was developed during the Second World War, driven by the need to achieve the low - cost building envelope. Now they are the
36 PORTAL FRAMES 1.0 INTRODUCTION The basic structural form of portal frames was developed during the Second World War, driven by the need to achieve the low - cost building envelope. Now they are the
SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF SIX STOREYED RC FRAMED BUILDING WITH BRACING SYSTEMS
 SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF SIX STOREYED RC FRAMED BUILDING WITH BRACING SYSTEMS ABSTRACT Megha Kalra Assistant Professor, The North Cap University, Gurgaon(India) Multistoreyed buildings are most affected by
SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF SIX STOREYED RC FRAMED BUILDING WITH BRACING SYSTEMS ABSTRACT Megha Kalra Assistant Professor, The North Cap University, Gurgaon(India) Multistoreyed buildings are most affected by
SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF SIX STOREYED RC FRAMED BUILDING WITH BRACING SYSTEMS
 SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF SIX STOREYED RC FRAMED BUILDING WITH BRACING SYSTEMS ABSTRACT Megha Kalra Assistant Professor, The North Cap University, Gurgaon(India) Multistoreyed buildings are most affected by
SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF SIX STOREYED RC FRAMED BUILDING WITH BRACING SYSTEMS ABSTRACT Megha Kalra Assistant Professor, The North Cap University, Gurgaon(India) Multistoreyed buildings are most affected by
On Cold-Formed Steel Construction. Light Gauge Steel Engineers Association Washington, D.C Toll Free (866)
 TECHNICAL NOTE On Cold-Formed Steel Construction $5.00 Light Gauge Steel Engineers Association Washington, D.C. 20005 Toll Free (866) 465-4732 www.lgsea.com DESIGN OF BY-PASS SLIP CONNECTORS IN COLD-FORMED
TECHNICAL NOTE On Cold-Formed Steel Construction $5.00 Light Gauge Steel Engineers Association Washington, D.C. 20005 Toll Free (866) 465-4732 www.lgsea.com DESIGN OF BY-PASS SLIP CONNECTORS IN COLD-FORMED
STUDIES ON LOCATION OF SHEAR WALL IN BUILDINGS FOR STRUCTURAL STABILITY
 IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eissn: 2319-1163 pissn: 2321-738 STUDIES ON LOCATION OF SHEAR WALL IN BUILDINGS FOR STRUCTURAL STABILITY Sanjeebanee Behera 1, P.K
IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eissn: 2319-1163 pissn: 2321-738 STUDIES ON LOCATION OF SHEAR WALL IN BUILDINGS FOR STRUCTURAL STABILITY Sanjeebanee Behera 1, P.K
Seismic Analysis of RC Framed Building for Different Position of Shear wall
 ISSN(Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 Seismic Analysis of RC Framed Building for Different Position of Shear wall Anil Baral 1, Dr. SK.Yajdani 2 P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering,
ISSN(Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 Seismic Analysis of RC Framed Building for Different Position of Shear wall Anil Baral 1, Dr. SK.Yajdani 2 P.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering,
Dr. K. R. C. Reddy 1, Sandip A. Tupat 2 1,2
 The effect of zone factors on wind and earthquake loads of highrise structures Dr. K. R. C. Reddy 1, Sandip A. Tupat 1, Department of Civil Engineering, Kavikulguru Institute of Technology and Science.
The effect of zone factors on wind and earthquake loads of highrise structures Dr. K. R. C. Reddy 1, Sandip A. Tupat 1, Department of Civil Engineering, Kavikulguru Institute of Technology and Science.
Renovation of Buildings using Steel Technologies (ROBUST)
 Renovation of Buildings using Steel Technologies (ROBUST) RFCS Project RFSR-CT-2007-0043 WP 4.2 Renovation of roofs using open trusses in light steel C sections Date: 2009 Author: Mark Lawson SCI, Silwood
Renovation of Buildings using Steel Technologies (ROBUST) RFCS Project RFSR-CT-2007-0043 WP 4.2 Renovation of roofs using open trusses in light steel C sections Date: 2009 Author: Mark Lawson SCI, Silwood
Design of Long Span Exhibition Hall of Steel Structure
 Design of Long Span Exhibition Hall of Steel Structure Amit A. Gudadhe 1 Asst. Professor, Datta Meghe Institute of Engineering, Technology & Research, Salod (H), Wardha, Maharashtra, India ABSTRACT The
Design of Long Span Exhibition Hall of Steel Structure Amit A. Gudadhe 1 Asst. Professor, Datta Meghe Institute of Engineering, Technology & Research, Salod (H), Wardha, Maharashtra, India ABSTRACT The
GUIDELINES FOR SOLAR WATER HEATERS INSTALLATION
 REPUBLIC OF RWANDA RWANDA UTILITIES REGULATORY AGENCY GUIDELINES FOR SOLAR WATER HEATERS INSTALLATION November, 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS PURPOSE OF THIS DOCUMENT... 3 1. CITATION... 3 2. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS...
REPUBLIC OF RWANDA RWANDA UTILITIES REGULATORY AGENCY GUIDELINES FOR SOLAR WATER HEATERS INSTALLATION November, 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS PURPOSE OF THIS DOCUMENT... 3 1. CITATION... 3 2. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS...
International Journal of Research in Advent Technology Available Online at:
 DESIGN & OPTIMIZATION OF STEEL STRUCTURE FOR SOLAR ELECTRICAL PANEL Mr. Vijay B. Sarode 1, Prof. Prashant.N. Ulhe 2 1 2 Mechanical Engg Department 1 2 North Maharashtra University 1 Email- vijaysarode1975@gmail.com
DESIGN & OPTIMIZATION OF STEEL STRUCTURE FOR SOLAR ELECTRICAL PANEL Mr. Vijay B. Sarode 1, Prof. Prashant.N. Ulhe 2 1 2 Mechanical Engg Department 1 2 North Maharashtra University 1 Email- vijaysarode1975@gmail.com
A REVIEW ON DYNAMIC WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDING PROVIDED WITH STEEL BRACING AS PER PROPOSED DRAFT FOR INDIAN WIND CODE AND EFFECT OF SOFT STOREY
 International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: - Volume: Issue: Oct - www.irjet.net p-issn: - A REVIEW ON DYNAMIC WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDING PROVIDED WITH STEEL BRACING
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: - Volume: Issue: Oct - www.irjet.net p-issn: - A REVIEW ON DYNAMIC WIND ANALYSIS OF TALL BUILDING PROVIDED WITH STEEL BRACING
EFFECT OF COLUMN LOCATION ON PLAN OF MULTI- STORY BUILDING ON SHEAR LAG PHENOMENON
 The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India EFFECT OF COLUMN LOCATION ON PLAN OF MULTI- STORY BUILDING ON SHEAR LAG PHENOMENON G.J.Singh 1, S.Mandal 2 and
The Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, December 10 14, 2013, Chennai, India EFFECT OF COLUMN LOCATION ON PLAN OF MULTI- STORY BUILDING ON SHEAR LAG PHENOMENON G.J.Singh 1, S.Mandal 2 and
Intelligent Design of Industrial Steel Buildings A BIM Approach
 Intelligent Design of Industrial Steel Buildings A BIM Approach J.P. Rammant CEO of Nemetschek Scia BIM or Building Information Modelling is the evolutionary process of representing one central model within
Intelligent Design of Industrial Steel Buildings A BIM Approach J.P. Rammant CEO of Nemetschek Scia BIM or Building Information Modelling is the evolutionary process of representing one central model within
Optimization of 2-D Steel Truss by Grid Search Method
 Optimization of 2-D Steel Truss by Grid Search Method Chetan R. Kakadiya M.E. Structural Engineering, BVM College of Engineering, Vallabh Vidyanagar. Atul N. Desai Associate Professor [M. Tech.], Structural
Optimization of 2-D Steel Truss by Grid Search Method Chetan R. Kakadiya M.E. Structural Engineering, BVM College of Engineering, Vallabh Vidyanagar. Atul N. Desai Associate Professor [M. Tech.], Structural
became possible. By the late 1950s, rigid frames with 100-ft spans were made. Figure 1: Conventional Steel Frame
 Analysis and Comparative Study of Conventional Steel Structure with PEB Structure T D Mythili P.G. Student, M.Tech Structural Engineering, Prist University, Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India Abstract: Cost
Analysis and Comparative Study of Conventional Steel Structure with PEB Structure T D Mythili P.G. Student, M.Tech Structural Engineering, Prist University, Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India Abstract: Cost
Design Requirements of Buildings and Good Construction Practices in Seismic Zone
 Design Requirements of Buildings and Good Construction Practices in Seismic Zone CII Safety Symposium & Exposition 2015: 11th September 2015: Kolkata Stages of Structural Design Concept Finalisation of
Design Requirements of Buildings and Good Construction Practices in Seismic Zone CII Safety Symposium & Exposition 2015: 11th September 2015: Kolkata Stages of Structural Design Concept Finalisation of
Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Structural analysis
 9210-111 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Structural analysis Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler, drawing
9210-111 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Structural analysis Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler, drawing
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE6603: DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART-A 1. List the various types of connections used for connecting
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE6603: DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES QUESTION BANK UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART-A 1. List the various types of connections used for connecting
WOOD I-JOIST AWARENESS GUIDE
 WOOD I-JOIST AWARENESS GUIDE American Wood Council Flange Web Flange American Forest & Paper Association WOOD I-JOIST AWARENESS GUIDE The American Wood Council is part of the wood products group of the
WOOD I-JOIST AWARENESS GUIDE American Wood Council Flange Web Flange American Forest & Paper Association WOOD I-JOIST AWARENESS GUIDE The American Wood Council is part of the wood products group of the
WIND CODE EVALUATION. COLOMBIA Evaluation conducted by Guillermo Santana
 WIND CODE EVALUATION COLOMBIA Evaluation conducted by Guillermo Santana NAME OF DOCUMENT: Normas Colombianas de Diseño y Construcción Sismo Resistente (Colombian Standards for Seismic Resistant Design
WIND CODE EVALUATION COLOMBIA Evaluation conducted by Guillermo Santana NAME OF DOCUMENT: Normas Colombianas de Diseño y Construcción Sismo Resistente (Colombian Standards for Seismic Resistant Design
Studying a multistory building with different types of bracing
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 161 218 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Ahmed Falah
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 161 218 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Ahmed Falah
