Surface Subsidence Analysis Due to Longwall Underground Coal Mining Method in PT. Gerbang Daya Mandiri, Tenggarong, East Kalimantan
|
|
|
- Griselda Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
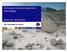
1 Kyushu University Global COE Program Journal of Novel Carbon Resource Sciences, Vol. 7, pp , Feb Surface Subsidence Analysis Due to Longwall Underground Coal Mining Method in PT. Gerbang Daya Mandiri, Tenggarong, East Kalimantan Tri Karian, Timbul M. P. Habeahan, Budi Sulistianto, Suseno Kramadibrata Institut Teknologi Bandung, Bandung 40132, Indonesia (Received November 16, 2012; accepted January 7, 2013) PT Gerbang Daya Mandiri will apply longwall underground coal mining method on its mine site, which is located in Kutai Region. Hence, surface subsidence would potentially occur at the surface area and consequently subsidence analysis including the likelihoods of subsidence profile, maximum value of subsidence and area of surface subsidence is needed. The analysis reveals that the maximum value that is calculated using empirical formulae of the UK National Coal Board differs to that of numerical analysis using distinct element method and the later also suggests that the coverage area of surface subsidence would be m Introduction The mine site of PT Gerbang Daya Mandiri (GDM) is located in Kutai Kertanegara, East Kalimantan, Indonesia (Fig. 1). GDM coal consists of several seams which are part of Kutai Basin Coal with average dip of 3 o -13 o and coal seam thickness varies from 0.1 to 9.8 meters. Despite open pit coal mine of GDM has been operating since October 2009, longwall underground coal mine method however should now be applied to keep the mine in operation and this is due to environmental constraints. It has been well accepted that the application of longwall underground coal mine may expect surface subsidence. Since most of the surface area is made use of farm land, rice field and settlement it is therefore important to carry out a comprehensive research of subsidence analysis. The research embraces prediction of maximum value of subsidence, subsidence profile and the area of surface subsidence from which potential remedial action could be prepared in early stage. In order to gain a complete picture of the subsidence analysis, the research is carried out in panel AF4 & AF5 and panel NB F3 & NB F4 on A seam and BC upper seam respectively (Fig. 2). AF4 AF5 L E G E N D Mine Design Seam A Mine Design Seam BC-Upper NB F3 NB F4 Concession Boundary Pipeline Fig. 2 Mine design of AF4, AF5, NB F4, and NB F4 1). Fig. 1 Location of GDM Coal Mine 1). 2. dimension and site investigation The geometry of panels AF4, AF5, NB F3 and NB F4 is given in Table 1. The lithology of the mining area at GDM is dominated by sandstone and claystone as can be seen in the bore-log of NED 02 borehole (Fig. 3). Highwall side of former open pit mine which shows interburden between seam 1, seam A and seam B is shown in Fig
2 Journal of Novel Carbon Resource Sciences, Vol.7, Feb Laboratory tests on rock samples obtained from the NED-02 borehole were conducted to determine the physical and mechanical properties and they are available in Table 2. Whereas the mechanical properties of the material of the bedding planes such as cohesion and internal friction of angle are given in Table 3. The subsidence analysis applies both numerical and empirical methods and uses the data of Tables 2 and 3 as well as data provided by the GDM Geotechnical Department. Seam A BC upper Depth low up 2 1 Table 1 geometry 1) Tilt Length Surface Sandstone Coal Seam Depth Width Height Fig. 3 Bore-log of NED 02 Borehole. A BC D E F Length Length 2.8 Depth A F A F NB F NB F Fig. 4 Interburden of Seam 1, A, and B from exposed highwall of open pit area. Table 2 Rock physical and mechanical properties 1) Material OB 1 Sandstone OB 1 IB 1-A IB A-BC Sandstone IB A-BC γ (gr/cm 3 ) Table 3 Contact plane characteristics 1,2) Contact Plane E (GPa) Cohesion (MPa) Internal Friction Angle Sandstone- Coal Sandstone Sandstone-Sandstone v C (MPa) ϕ ( ) B (GPa) Coal-Coal G (GPa) Coal E: modulus of elasticity; v: Poisson ratio; γ: density; c: cohesion; ϕ: internal friction angle; G: shear modulus; B: bulk modulus; σt: tensile strength. 3. Empirical analysis The maximum value of surface subsidence caused by extraction of an underground longwall panel can be predicted empirically using graphical method developed by the U.K. National Coal Board. By using this method the maximum surface subsidence (S) can be predicted from surface subsidence factor (F) times the thickness of coal seam, where the factor is obtained from the relationship between the factor to width and depth of the opening graph. Predicted surface subsidence (s) at various points above the longwall panel can be determined using the graph of the U.K. National Coal Board. The data used in this method consists of; h (depth of the panel center point), w (width of opening panel) and d (distance of various points along subsidence profile to the panel center point)
3 Surface Subsidence Analysis Due to Longwall Underground Coal Mining Method in PT. Gerbang Daya Mandiri, Tenggarong, East Kalimantan A correlation table between w/h and d/h is used then the values of s at various points are then calculated from the s/s ratio times S (maximum surface subsidence). Based on the dimension data of each panel the values F and w/h for each panel are obtained and presented in Table 4. Table 4 Values of surface subsidence factor and w/h of panel Surface Subsidence Factor (F) w/h onto the model is equivalent to the horizontal in-situ stress (σh) and is defined as 2/3 of σv for 300 m depth 3). The load works towards the x and z directions with g of 10 m/s 2. Seam A outcrop N Z E Seam BC outcrop AF AF NB F NB F Numerical analysis The numerical modeling is run based on 3-D Distinct Element Method using 3DEC Ver. 2.0 software. The first step is to model the geometry that is defined in three dimensions (see Fig. 5) and this is based on the GDM mine design as mentioned earlier. The model geometry is constructed by combining mine design, topographic maps, scanline data, mining situation maps, and the rock stratification. Different colors in Fig. 5 represent each rock strata found in borehole NED 02. The model of panel geometry is referred to the panels AF4 & AF5 and panels NB F3 & NB F4 of seam A and seam BC upper respectively (Figs. 6 and 7). After the model geometry has been defined, the second step is to model the material and discontinuities characteristics in the numerical analysis which consist of : 1. Building up discrete elements. The elements close to the panel are smaller mesh size than that of element further from the panel and that of close to the panel must have a mesh size smaller than that of panel dimension. 2. The material characteristics comply with the Mohr- Coulomb failure criterion. 3. The material properties of rock body include modulus of elasticity (E), Poisson ratio (v), density (γ), cohesion (c), internal friction angle (ϕ), shear modulus (G), bulk modulus (B) and tensile strength (σt). 4. The joint characteristics are represented by normal stiffness (Kn), shear stiffness (Ks), cohesion (C), tensile strength (σt) and internal friction angle (θ). The third step is to determine the load and boundary conditions. The boundary conditions for the model are defined as follows; displacements in the western and eastern of the model as well as in northern and southern of the model are only permitted in the y and z directions as well as in the x and y directions. At the lower limit of the model the displacement is only permitted in the direction of x-direction and z-direction. The load applied Fig. 5 Overall geometry model for numerical analysis. AF5 AF4 Fig. 6 Geometry model of panel AF4 and AF5 on Seam A. NB F3 NB F4 Fig. 7 Geometry model of panel NB F3 and NB F4 on Seam BC upper. 5. Result and discussion Table 5 indicates the values of the maximum surface subsidence for every single panel extraction based on calculation of the numerical and empirical methods. The subsidence profiles associated with the data given in Table 5 is exhibited in Figs. 8 to 11. The profiles are made by taking cross section perpendicular to each panel extraction direction and through each center of the panel
4 Journal of Novel Carbon Resource Sciences, Vol.7, Feb Table 5 Extracted Maximum value of surface subsidence due to single panel extraction Maximum Surface Subsidence Empirical Method Numerical Modeling Difference m % A F % A F % NB F % NB F % Fig. 8 Surface subsidence profile due to panel AF4 The difference values of the maximum surface subsidence calculated by both methods are attributed to the following conditions: the empirical method assumes that the entire material above the coal panel being isotropic, homogeneous and continuous. In addition, the panel geometry is considered flat and the calculation is merely based on depth, width and height of a panel only. On the other hand, the numerical method obviously allows the calculation using an-isotropic, non-homogeneous, non-continuous media and complex geometry conditions. Moreover, the basic physical and mechanical properties used in the both methods remain relatively the same. It is however important to note that the use of empirical method is always site specific as any empirical methods is derived from a certain site that possesses particular geological and geomechanical properties. Consequently, the use of any empirical method for other site might possibly yield unexpected recommendation in which cautious treatment should be exercised. Apparently, similar results are also experienced by Adamek et al. (1987) and Munson & Eichfield (1980). Thus, this research has then put special emphasis on subsidence analysis based on the numerical modeling. Another advantage of applying the numerical method is that the subsided area can be calculated and the individual areas for each panel are given in Table 6. Fig. 9 Surface subsidence profile due to panel AF5 Table 6 Area of subsidence due to single panel extraction based on numerical analysis Extracted Area of Subsidence ( 10 6 m 2 ) AF4 0.6 AF5 0.8 NB F3 0.9 NB F4 0.9 Fig. 10 Surface subsidence profile due to panel NB F3 Having done the predicted subsided area for each panel, the angle of draw can also be obtained as shown in Figs. 12 to 15. It can be noted that there will be two values of the angle of draw once the seam has an inclination or is tilting 4), i.e. lower and upper angle of draws. Table 7 provides the values of panel tilt, lower angle of draw and upper angle of draw. Table 7 Lower limit and upper limit angle of each extracted panel Fig. 11 Surface subsidence profile due to panel NB F4 Extracted Tilt Lower limit angle Upper limit angle AF AF NB F NB F
5 Surface Subsidence Analysis Due to Longwall Underground Coal Mining Method in PT. Gerbang Daya Mandiri, Tenggarong, East Kalimantan Fig. 12 Regional influences of panel AF4. Fig. 13 Regional influences of panel AF5. Fig. 14 Regional influences of panel NB F3. brings about 6 departure of the center the maximum surface subsidence off each panel center. Similarly happens to panels NB F3 and NB F4 which have the same panel inclination of 8.7 causes the centers of the maximum surface subsidence move away of 4 and 5 respectively (Figs. 14 and 15). In order to determine the surface subsidence due to extraction of all panels a principle in the numerical modeling so called superposition will be applied, in which individual values of the maximum surface subsidence of each panel are added up. By applying this principle, the maximum surface subsidence due to all panel extraction is obtained i.e., 2.5 meters. Yet, it would be interesting to find out how the values of the maximum surface subsidence calculated based on option-1: individual values of the maximum surface subsidence of each panel are added up (as mentioned above) and option-2: value of the maximum surface subsidence if entire panels are considered as one big panel The results of the exercise of these two options are given in Table 8 and Figs. 16, 17 and 18. It can be seen that the maximum surface subsidence of the option-2 is about 88% of that option-1, but the difference of the subsided areas (option-1 = m 2 and Option-2 = m 2 ) is only about 1% and insignificant. Having gone through all exercises it then be said that applying the superposition principle for a single panel extraction can be confirmed by that of entire panel 5. Conclusions Both methods of numerical and empirical can be used to predict surface subsidence due to an underground longwall coal mining From the foregoing analysis it can be noted that despite the fact many empirical method is usually derived from a specific site, this method suggests greater maximum surface subsidence, more practical, faster than that of the numerical one. Due to its site specific, this method is accordingly deemed inappropriate for application of this research. The superposition principle based on single panel extraction method and entire panel extraction method can be used in generating and calculating the subsidence profile as well as maximum surface subsidence respectively. The two methods apparently provide insignificantly different results. Fig. 15 Regional influences of panel NB F4. Numerical method suggests that panel inclination influences the center of the maximum surface subsidence 4). Regarding this matter, Figs. 12 and 13 show evidences of inclination of 8.7 of panels AF4 and AF5 Table 8 Extracted AF4, AF5, NB F3, NB F4 Comparison of maximum surface subsidence from numerical modeling result Maximum Surface Subsidence Single Extraction with Superposition Principle Entire Extraction
6 Journal of Novel Carbon Resource Sciences, Vol.7, Feb Elevation x-coordinate Single Extraction with Superposition Principle Entire Extraction Fig. 16 Comparison of surface subsidence profile from numerical modeling result. Fig. 17 Surface subsidence area due to the entire panel Fig. 18 Surface subsidence area due to the single panel extraction using superposition principle. Acknowledgements: The authors would like to acknowledge PT Gerbang Daya Mandiri (GDM) management for the possibility and opportunity to conduct this study, Dr. Bukin Daulay, Msc., Head of Research and Development for Mineral and Coal Technology (TekMira) for opportunity given to use 3DEC Software for numerical analysis, and also members of Mine Planning Laboratory, also Rock Mechanic and Mining Equipment Laboratory ITB for all support and discussion during conducting this research. References 1) PT LAPI ITB, Report submitted to PT Gerbang Daya Mandiri (2012). 2) W. Keilich, Coal Operator s Conference, 313, New South Wales (2006). 3) P. R. Shorey, International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 31(1), 23 (1994). 4) S. S. Peng, Coal Mine Ground Control, 1st ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York (1978). 5) B. N. Whittaker and D. J. Reddish, Subsidence: Occurence, Prediction, and Control, 1st ed., Elsevier Science Pub. Co., New York (1989). 6) Itasca, 3DEC User s Guide, version 2.0, Itasca Consulting Group Inc., Minnesota (1999). 7) V. Adamek And P. W. Jeran, Predictions of Surface Deformation over Longwall s in the Northern Appalachian Coalfield, Report of Investigations 9142 U.S. Bureau of Mines (1987). 8) D. E. Munson and W. F. Eichfield, Evaluation of European Empirical Methods for Subsidence in U.S. Coalfields, Springfield, Albuquerque (1980)
A Study of Angle of Draw in Mining Subsidence Using Numerical Modeling Techniques
 A Study of Angle of Draw in Mining Subsidence Using Numerical Modeling Techniques G. Ren*, J. Li School of Civil, Environmental and Chemical Engineering, RMIT University, GPO Box 2476V, Melbourne 3001,
A Study of Angle of Draw in Mining Subsidence Using Numerical Modeling Techniques G. Ren*, J. Li School of Civil, Environmental and Chemical Engineering, RMIT University, GPO Box 2476V, Melbourne 3001,
Prediction of Surface Subsidence Due to Inclined Very Shallow Coal Seam Mining Using FDM
 University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 29 Prediction of Surface Subsidence Due to Inclined Very Shallow Coal Seam Mining Using
University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 29 Prediction of Surface Subsidence Due to Inclined Very Shallow Coal Seam Mining Using
SDPS for Windows: An Integrated Approach to Ground Deformation Prediction
 SDPS for Windows: An Integrated Approach to Ground Deformation Prediction D. Newman, Appalachian Mining and Engineering, Inc./Geolab Z. Agioutantis Department of Mineral Resources Engineering, Technical
SDPS for Windows: An Integrated Approach to Ground Deformation Prediction D. Newman, Appalachian Mining and Engineering, Inc./Geolab Z. Agioutantis Department of Mineral Resources Engineering, Technical
Estimation of Lateral Earth Pressure on Cantilever Sheet Pile using Flat Dilatometer Test (DMT) Data: Numerical Study
 Estimation of Lateral Earth Pressure on Cantilever Sheet Pile using Flat Dilatometer Test (DMT) Data: Numerical Study Kousik Deb Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India. E-mail: kousik@civil.iitkgp.ernet.in
Estimation of Lateral Earth Pressure on Cantilever Sheet Pile using Flat Dilatometer Test (DMT) Data: Numerical Study Kousik Deb Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India. E-mail: kousik@civil.iitkgp.ernet.in
Effect of Constitutive Behaviour of Strata on the Prediction of Subsidence Above Single-seam and Multi-seam Supercritical Longwall Panels
 Effect of Constitutive Behaviour of Strata on the Prediction of Subsidence Above Single-seam and Multi-seam Supercritical Longwall Panels A M Suchowerska, CGMM 1, University of Newcastle J P Carter, CGMM,
Effect of Constitutive Behaviour of Strata on the Prediction of Subsidence Above Single-seam and Multi-seam Supercritical Longwall Panels A M Suchowerska, CGMM 1, University of Newcastle J P Carter, CGMM,
Case Studies in the Application of Influence Functions to Visualising Surface Subsidence
 University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 23 Case Studies in the Application of Influence Functions to Visualising Surface Subsidence
University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 23 Case Studies in the Application of Influence Functions to Visualising Surface Subsidence
Relationship between twin tunnels distance and surface subsidence in soft ground of Tabriz Metro - Iran
 University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2012 Relationship between twin tunnels distance and surface subsidence in soft ground
University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2012 Relationship between twin tunnels distance and surface subsidence in soft ground
BEARING CAPACITY IMPROVEMENT USING MICROPILES A CASE STUDY
 BEARING CAPACITY IMPROVEMENT USING MICROPILES A CASE STUDY G.L. Sivakumar Babu 1, B. R.Srinivasa Murthy 2, D.S. N. Murthy 3, M.S. Nataraj 4 ABSTRACT Micropiles have been used effectively in many applications
BEARING CAPACITY IMPROVEMENT USING MICROPILES A CASE STUDY G.L. Sivakumar Babu 1, B. R.Srinivasa Murthy 2, D.S. N. Murthy 3, M.S. Nataraj 4 ABSTRACT Micropiles have been used effectively in many applications
Static Response of Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls with Modular Block Facing
 Static Response of Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls with Modular Block Facing Morteza Sabet 1, Amir M. Halabian 2, Kazem Barkhordari 3 1 Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Yazd University
Static Response of Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls with Modular Block Facing Morteza Sabet 1, Amir M. Halabian 2, Kazem Barkhordari 3 1 Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Yazd University
A Risk Analysis Subsidence Approach for the Design of Coal Refuse Impoundments Overlying Mine Workings
 A Risk Analysis Subsidence Approach for the Design of Coal Refuse Impoundments Overlying Mine Workings M. Karmis Department of Mining and Minerals Engineering, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
A Risk Analysis Subsidence Approach for the Design of Coal Refuse Impoundments Overlying Mine Workings M. Karmis Department of Mining and Minerals Engineering, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Three-dimensional computer simulation of soil nailing support in deep foundation pit
 Three-dimensional computer simulation of soil nailing support in deep foundation pit Abstract Chang Zhi Zhu 1,2*, Quan Chen Gao 1 1 School of Mechanics & Civil Engineering, China University of Mining &
Three-dimensional computer simulation of soil nailing support in deep foundation pit Abstract Chang Zhi Zhu 1,2*, Quan Chen Gao 1 1 School of Mechanics & Civil Engineering, China University of Mining &
How to model Mohr-Coulomb interaction between elements in Abaqus
 How to model Mohr-Coulomb interaction between elements in Abaqus Problem description We want to model the interaction between two masonry walls and a timber beam. The elements are connected by special
How to model Mohr-Coulomb interaction between elements in Abaqus Problem description We want to model the interaction between two masonry walls and a timber beam. The elements are connected by special
2012 Soil Mechanics I and Exercises Final Examination
 2012 Soil Mechanics I and Exercises Final Examination 2013/1/22 (Tue) 13:00-15:00 Kyotsu 155 Kyotsu 1 Kyotsu 3 W2 Lecture room Attention: There are four questions and four answer sheets. Write down your
2012 Soil Mechanics I and Exercises Final Examination 2013/1/22 (Tue) 13:00-15:00 Kyotsu 155 Kyotsu 1 Kyotsu 3 W2 Lecture room Attention: There are four questions and four answer sheets. Write down your
Comparison of geotechnic softwares - Geo FEM, Plaxis, Z-Soil
 Comparison of geotechnic softwares - Geo FEM, Plaxis, Z-Soil Comparison du logiciel géotechnique Geo FEM, Plaxis, Z-Soil J. Pruška CTU in Prague FCE Department of Geotechnics, Prague, Czech Republic, Pruska@fsv.cvut.cz
Comparison of geotechnic softwares - Geo FEM, Plaxis, Z-Soil Comparison du logiciel géotechnique Geo FEM, Plaxis, Z-Soil J. Pruška CTU in Prague FCE Department of Geotechnics, Prague, Czech Republic, Pruska@fsv.cvut.cz
Insights into the mechanics of multi-seam subsidence from Ashton underground mine
 University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2017 Insights into the mechanics of multi-seam subsidence from Ashton underground mine
University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2017 Insights into the mechanics of multi-seam subsidence from Ashton underground mine
Subsidence Prediction Using SDPS
 Subsidence Prediction Using SDPS Prof. Zach Agioutantis University of Kentucky Lexington, KY September 11, 2015 Presentation Outline Basic concepts on subsidence / ground deformation prediction The SDPS
Subsidence Prediction Using SDPS Prof. Zach Agioutantis University of Kentucky Lexington, KY September 11, 2015 Presentation Outline Basic concepts on subsidence / ground deformation prediction The SDPS
Passage under Lövstavägen at Bypass Stockholm From Design to Realization
 Passage under Lövstavägen at Bypass Stockholm From Design to Realization Roslin Mattias 1, Borio Luca 2 and Tomas Hellström 3 1 Swedish Transport Administration, Solna Strandväg 98, 171 54 Solna, mattias.roslin@trafikverket.se
Passage under Lövstavägen at Bypass Stockholm From Design to Realization Roslin Mattias 1, Borio Luca 2 and Tomas Hellström 3 1 Swedish Transport Administration, Solna Strandväg 98, 171 54 Solna, mattias.roslin@trafikverket.se
Numerical Analysis of Pipe Roof Reinforcement in Soft Ground Tunnelling
 Numerical Analysis of Pipe Roof Reinforcement in Soft Ground Tunnelling W.L.Tan and P.G. Ranjith School of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798 Phone: 65-67905267,
Numerical Analysis of Pipe Roof Reinforcement in Soft Ground Tunnelling W.L.Tan and P.G. Ranjith School of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798 Phone: 65-67905267,
International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced Engineering (IJIRAE) ISSN: Issue 10, Volume 5 (October 2018)
 COMPARISON BETWEEN THIN SPRAY-ON LINERS AND SHOTCRETE AS SURFACE SUPPORT MECHANISMS IN TUNNELS Samuel Jjuuko * Department of Civil Engineering, University of Cape Town, South Africa sjjuuko1@gmail.com
COMPARISON BETWEEN THIN SPRAY-ON LINERS AND SHOTCRETE AS SURFACE SUPPORT MECHANISMS IN TUNNELS Samuel Jjuuko * Department of Civil Engineering, University of Cape Town, South Africa sjjuuko1@gmail.com
SETTLEMENTS DUE TO TUNNEL CONSTRUCTION
 5 SETTLEMENTS DUE TO TUNNEL CONSTRUCTION In this tutorial the construction of a shield tunnel in medium soft soil and the influence on a pile foundation is considered. A shield tunnel is constructed by
5 SETTLEMENTS DUE TO TUNNEL CONSTRUCTION In this tutorial the construction of a shield tunnel in medium soft soil and the influence on a pile foundation is considered. A shield tunnel is constructed by
Application of Highwall Mining System to Recover Residual Coal in End-walls
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 6 ( 2013 ) 311 318 International Symposium on Earth Science and Technology, CINEST 2012 Application of Highwall Mining System
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 6 ( 2013 ) 311 318 International Symposium on Earth Science and Technology, CINEST 2012 Application of Highwall Mining System
VOL. 11, NO. 16, AUGUST 2016 ISSN ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences
 COMPARISON OF STABILITY PERFORMANCE BETWEEN CONCRETE PILE AND CLOSED END STEEL PIPE OF SHORT PILED RAFT FOUNDATION SYSTEM FOR REDUCING SETTLEMENT ON PEAT Sajiharjo Marto Suro, Agus Sulaeman and Ismail
COMPARISON OF STABILITY PERFORMANCE BETWEEN CONCRETE PILE AND CLOSED END STEEL PIPE OF SHORT PILED RAFT FOUNDATION SYSTEM FOR REDUCING SETTLEMENT ON PEAT Sajiharjo Marto Suro, Agus Sulaeman and Ismail
Behaviour of Strip Footing on Geogrid Reinforced Slope subjected to Eccentric Load
 ISSN (Print): 2347-671 (An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization) Behaviour of Strip Footing on Geogrid Reinforced Slope subjected to Eccentric Load Dhiraj D. Patil 1, Sunil S. Pusadkar 2, Sanjay W. Thakare
ISSN (Print): 2347-671 (An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization) Behaviour of Strip Footing on Geogrid Reinforced Slope subjected to Eccentric Load Dhiraj D. Patil 1, Sunil S. Pusadkar 2, Sanjay W. Thakare
IDENTIFICATION OF FAILURE SURFACES IN DRAGLINE DUMPS OF OPENCAST COAL MINES
 IDENTIFICATION OF FAILURE SURFACES IN DRAGLINE DUMPS OF OPENCAST COAL MINES S. Sharma, S. Sengupta and I. Roy Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi,
IDENTIFICATION OF FAILURE SURFACES IN DRAGLINE DUMPS OF OPENCAST COAL MINES S. Sharma, S. Sengupta and I. Roy Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi,
3D EFFECTS OF DIFFERENTIAL SETTLEMENTS ON A SPECIAL MOMENT RESISTING FRAME DUE TO EARTHQUAKE
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 808 3D EFFECTS OF DIFFERENTIAL SETTLEMENTS ON A SPECIAL MOMENT RESISTING FRAME DUE TO EARTHQUAKE Behrouz
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 808 3D EFFECTS OF DIFFERENTIAL SETTLEMENTS ON A SPECIAL MOMENT RESISTING FRAME DUE TO EARTHQUAKE Behrouz
Numerical Analysis of a Novel Piling Framed Retaining Wall System
 The 12 th International Conference of International Association for Computer Methods and Advances in Geomechanics (IACMAG) 1-6 October, 2008 Goa, India Numerical Analysis of a Novel Piling Framed Retaining
The 12 th International Conference of International Association for Computer Methods and Advances in Geomechanics (IACMAG) 1-6 October, 2008 Goa, India Numerical Analysis of a Novel Piling Framed Retaining
Simulating Intact Rock Behaviour Using Bonded Particle and Bonded Block Models
 Simulating Intact Rock Behaviour Using Bonded Particle and Bonded Block Models Alexandr Turichshev John Hadjigeorgiou Seventh International Conference & Exhibition on Mass Mining MassMin 2016 / Sydney,
Simulating Intact Rock Behaviour Using Bonded Particle and Bonded Block Models Alexandr Turichshev John Hadjigeorgiou Seventh International Conference & Exhibition on Mass Mining MassMin 2016 / Sydney,
Roadway roof support design in critical areas at Anglo American Metallurgical Coal's underground operations
 University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2010 Roadway roof support design in critical areas at Anglo American Metallurgical Coal's
University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2010 Roadway roof support design in critical areas at Anglo American Metallurgical Coal's
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering STUDY OF BOREHOLE STABILITY OF MARCELLUS SHALE WELLS IN LONGWALL MINING AREAS Thesis in Energy and Mineral
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering STUDY OF BOREHOLE STABILITY OF MARCELLUS SHALE WELLS IN LONGWALL MINING AREAS Thesis in Energy and Mineral
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(10): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(10):391-398 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The anchor craning beam support technology of the
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(10):391-398 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The anchor craning beam support technology of the
.Jan NEMCIK *, Ernest BAAFI and Ian PORTER
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 10, No. 2 (170), 207 213, 2013 DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2013.0021 STABILISING ROCK SURFACES WITH A GLASS REINFORCED POLYMER SKIN.Jan NEMCIK *, Ernest BAAFI and Ian PORTER School of
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 10, No. 2 (170), 207 213, 2013 DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2013.0021 STABILISING ROCK SURFACES WITH A GLASS REINFORCED POLYMER SKIN.Jan NEMCIK *, Ernest BAAFI and Ian PORTER School of
SOIL PRESSURE IN EMBANKMENT STABILIZATIONS
 SOIL PRESSURE IN EMBANKMENT STABILIZATIONS Analysis of the 3D shadowing effect of piles Dipl.-Ing. M. Filus Fides DV-Partner GmbH ABSTRACT: Pile checks required by the codes alone are usually not sufficient
SOIL PRESSURE IN EMBANKMENT STABILIZATIONS Analysis of the 3D shadowing effect of piles Dipl.-Ing. M. Filus Fides DV-Partner GmbH ABSTRACT: Pile checks required by the codes alone are usually not sufficient
M.C. Christianson Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA
 UDEC Simulation of Triaxial Testing of Lithophysal Tuff UDEC Simulation of Triaxial Testing of Lithophysal Tuff M.C. Christianson Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA 7 M.P. Board
UDEC Simulation of Triaxial Testing of Lithophysal Tuff UDEC Simulation of Triaxial Testing of Lithophysal Tuff M.C. Christianson Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA 7 M.P. Board
Evaluation of negative skin friction on sheet pile walls at the Rio Grande dry dock, Brazil
 Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground Viggiani (ed) 2012 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-415-68367-8 Evaluation of negative skin friction on sheet pile walls at the
Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground Viggiani (ed) 2012 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-415-68367-8 Evaluation of negative skin friction on sheet pile walls at the
Chapter 7. Finite Elements Model and Results
 Chapter 7 Finite Elements Model and Results 7.1 Introduction In this chapter, a three dimensional model was presented. The analytical model was developed by using the finite elements method to simulate
Chapter 7 Finite Elements Model and Results 7.1 Introduction In this chapter, a three dimensional model was presented. The analytical model was developed by using the finite elements method to simulate
EFFECT OF DEEP EXCAVATION SUPPORTED BY CONCRETE SOLIDER PILE WITH STEEL SHEET PILE LAGGING WALL ON ADJACENT EXISTING BUILDINGS
 EFFECT OF DEEP EXCAVATION SUPPORTED BY CONCRETE SOLIDER PILE WITH STEEL SHEET PILE LAGGING WALL ON ADJACENT EXISTING BUILDINGS Mostafa Abdou 1 *, Ahamed Rushedy Towfeek 2, Waleed Hassan 3 1 prof. Dr.,
EFFECT OF DEEP EXCAVATION SUPPORTED BY CONCRETE SOLIDER PILE WITH STEEL SHEET PILE LAGGING WALL ON ADJACENT EXISTING BUILDINGS Mostafa Abdou 1 *, Ahamed Rushedy Towfeek 2, Waleed Hassan 3 1 prof. Dr.,
3. MINING SYSTEM AND RESOURCE RECOVERY
 3. MINING SYSTEM AND RESOURCE RECOVERY (SMP Guideline Section 6.1) 3.1. MINING METHOD Longwalls 705 to 710 will be extracted using a longwall retreating system of mining, an established method of coal
3. MINING SYSTEM AND RESOURCE RECOVERY (SMP Guideline Section 6.1) 3.1. MINING METHOD Longwalls 705 to 710 will be extracted using a longwall retreating system of mining, an established method of coal
Empirical Correlations of Longwall Subsidence Data for the Illinois Coal Basin
 Missouri University of Science and Technology Scholars' Mine International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering (2008) - Sixth International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical
Missouri University of Science and Technology Scholars' Mine International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering (2008) - Sixth International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical
Analysis of skin friction in prebored and precast piles
 Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication The 6th Japan-Korea Geotechnical Workshop Analysis of skin friction in prebored and precast piles Sangseom Jeong i), Gyoungja Jung ii), Dohyun Kim iii)
Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication The 6th Japan-Korea Geotechnical Workshop Analysis of skin friction in prebored and precast piles Sangseom Jeong i), Gyoungja Jung ii), Dohyun Kim iii)
CROWN PILLAR ON VENTILATION DRIFT AT DEEP MILL LEVEL ZONE (DMLZ) PT FREEPORT INDONESIA
 CROWN PILLAR ON VENTILATION DRIFT AT DEEP MILL LEVEL ZONE (DMLZ) PT FREEPORT INDONESIA Rian Nugroho, PT Freeport Indonesia, DMLZ Engineering, Papua, Indonesia Andrew Parhusip, PT Freeport Indonesia, DMLZ
CROWN PILLAR ON VENTILATION DRIFT AT DEEP MILL LEVEL ZONE (DMLZ) PT FREEPORT INDONESIA Rian Nugroho, PT Freeport Indonesia, DMLZ Engineering, Papua, Indonesia Andrew Parhusip, PT Freeport Indonesia, DMLZ
Spur Hill Underground Coking Coal Project. Groundwater Assessment for Gateway Application. Tuesday 16 June 2015
 Spur Hill Underground Coking Coal Project Groundwater Assessment for Gateway Application Tuesday 16 June 2015 HydroSimulations 2 Track record in groundwater assessment and modelling for water resources,
Spur Hill Underground Coking Coal Project Groundwater Assessment for Gateway Application Tuesday 16 June 2015 HydroSimulations 2 Track record in groundwater assessment and modelling for water resources,
Design Illustrations on the Use of Soil Nails to Upgrade Loose Fill Slopes
 Design Illustrations on the Use of Soil Nails to Upgrade Loose Fill Slopes Geotechnical Engineering Office and The Hong Kong Institution of Engineers (Geotechnical Division) November 2013 2 Disclaimer
Design Illustrations on the Use of Soil Nails to Upgrade Loose Fill Slopes Geotechnical Engineering Office and The Hong Kong Institution of Engineers (Geotechnical Division) November 2013 2 Disclaimer
Chapter 14 Lateral Earth Pressure
 Page 14 1 Chapter 14 Lateral Earth Pressure 1. Which of the following is not a retaining structure? (a) Retaining wall (b) Basement wall (c) Raft (d) Bulkhead 2. When a retaining structure does not move
Page 14 1 Chapter 14 Lateral Earth Pressure 1. Which of the following is not a retaining structure? (a) Retaining wall (b) Basement wall (c) Raft (d) Bulkhead 2. When a retaining structure does not move
Sheeting Wall Analysis by the Method of Dependent Pressures
 Sheeting Wall Analysis by the Method of Dependent Pressures Veronika Vaneckova FINE Ltd., Prague, Czech Republic. E-mail: veronika.vaneckova@fine.cz. Jiri Laurin FINE Ltd., Prague, Czech Republic. E-mail:
Sheeting Wall Analysis by the Method of Dependent Pressures Veronika Vaneckova FINE Ltd., Prague, Czech Republic. E-mail: veronika.vaneckova@fine.cz. Jiri Laurin FINE Ltd., Prague, Czech Republic. E-mail:
Performance of Reinforced Earth Retaining Wall with Fly Ash under Static and Dynamic Loading
 Performance of Reinforced Earth Retaining Wall with Fly Ash under Static and Dynamic Loading 1 Umesh Kumar N, 2 Padmashree M. Kalliamni 1 Geotechnical Engineer, 2 Assistant professor, 1 Civil Engineering
Performance of Reinforced Earth Retaining Wall with Fly Ash under Static and Dynamic Loading 1 Umesh Kumar N, 2 Padmashree M. Kalliamni 1 Geotechnical Engineer, 2 Assistant professor, 1 Civil Engineering
GEOTECHNICAL DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHODOLOGY OF A DEEP BASEMENT CUT NEXT TO SENSITIVE BUILDINGS
 GEOTECHNICAL DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHODOLOGY OF A DEEP BASEMENT CUT NEXT TO SENSITIVE BUILDINGS James Livingston 1 Ching Dai 2 1 Geotechnical engineer at Coffey Services (NZ) 2 Chartered Senior Principal
GEOTECHNICAL DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION METHODOLOGY OF A DEEP BASEMENT CUT NEXT TO SENSITIVE BUILDINGS James Livingston 1 Ching Dai 2 1 Geotechnical engineer at Coffey Services (NZ) 2 Chartered Senior Principal
Two-dimensional finite element analysis of influence of plasticity on the seismic soil micropiles structure interaction
 Technical Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences Available online at www.tjeas.com 2013 TJEAS Journal-2013-3-13/1301-1305 ISSN 2051-0853 2013 TJEAS Two-dimensional finite element analysis of influence
Technical Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences Available online at www.tjeas.com 2013 TJEAS Journal-2013-3-13/1301-1305 ISSN 2051-0853 2013 TJEAS Two-dimensional finite element analysis of influence
Study on Capping Options For Overburden Encapsulation to Prevent Acid Mine Drainage in Lati Coal Mine, Kalimantan, Indonesia
 Golden CO; USA Reliable Mine Water Technology IMWA 13 Study on Capping Options For Overburden Encapsulation to Prevent Acid Mine Drainage in Lati Coal Mine, Kalimantan, Indonesia Rudy Sayoga Gautama¹,
Golden CO; USA Reliable Mine Water Technology IMWA 13 Study on Capping Options For Overburden Encapsulation to Prevent Acid Mine Drainage in Lati Coal Mine, Kalimantan, Indonesia Rudy Sayoga Gautama¹,
Introduction to Longwall Mining and Subsidence
 Introduction to Longwall Mining and Subsidence Prepared by Mine Subsidence Engineering Consultants Level 1 / 228 Victoria Avenue Chatswood NSW 2067 PO Box 3047 Willoughby North NSW 2068 Tel. (02) 9413
Introduction to Longwall Mining and Subsidence Prepared by Mine Subsidence Engineering Consultants Level 1 / 228 Victoria Avenue Chatswood NSW 2067 PO Box 3047 Willoughby North NSW 2068 Tel. (02) 9413
Strip Footing - Ultimate Bearing Capacity
 Strip Footing - Ultimate Bearing Capacity analys: nonlin phase physic. constr: suppor tying. elemen: ct12e pstrai. load: deform weight. materi: consta crack cutoff elasti full harden isotro mohrco multil
Strip Footing - Ultimate Bearing Capacity analys: nonlin phase physic. constr: suppor tying. elemen: ct12e pstrai. load: deform weight. materi: consta crack cutoff elasti full harden isotro mohrco multil
Modelling ground subsidence at an underground coal gasification site
 Modelling ground subsidence at an underground coal gasification site Thushan Chandrasiri Ekneligoda University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg South Africa Underground coal gasification (UCG) offers
Modelling ground subsidence at an underground coal gasification site Thushan Chandrasiri Ekneligoda University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg South Africa Underground coal gasification (UCG) offers
Numerical Analysis of the Bearing Capacity of Strip Footing on Reinforced Soil Slope
 Numerical Analysis of the Bearing Capacity of Strip Footing on Reinforced Soil Slope Mohammadreza Hamzehpour Ahmadi 1, Adel Asakereh 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of Hormozgan, Pardis-E-Qeshm
Numerical Analysis of the Bearing Capacity of Strip Footing on Reinforced Soil Slope Mohammadreza Hamzehpour Ahmadi 1, Adel Asakereh 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of Hormozgan, Pardis-E-Qeshm
Ore Reserve Estimation of Saprolite Nickel Using Inverse Distance Method in PIT Block 3A Banggai Area Central Sulawesi
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Ore Reserve Estimation of Saprolite Nickel Using Inverse Distance Method in PIT Block 3A Banggai Area Central Sulawesi To cite this article: Muhammad
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Ore Reserve Estimation of Saprolite Nickel Using Inverse Distance Method in PIT Block 3A Banggai Area Central Sulawesi To cite this article: Muhammad
Comparison of the results of load test done on stone columns and rammed aggregate piers using numerical modeling
 Comparison of the results of load test done on stone columns and rammed aggregate piers using numerical modeling Ece Kurt Civil Eng., M.Sc.& Geoph. Eng., Istanbul, Turkey Berrak Teymur Asst. Prof. Dr.,
Comparison of the results of load test done on stone columns and rammed aggregate piers using numerical modeling Ece Kurt Civil Eng., M.Sc.& Geoph. Eng., Istanbul, Turkey Berrak Teymur Asst. Prof. Dr.,
Study on the settlement and the load-bearing capacity of Long An soft ground reinforced by the stone columns
 Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication International Mini Symposium CHUBU (IMS-CHUBU) Study on the settlement and the load-bearing capacity of Long An soft ground reinforced by the stone columns
Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication International Mini Symposium CHUBU (IMS-CHUBU) Study on the settlement and the load-bearing capacity of Long An soft ground reinforced by the stone columns
The design of soil nailed structures to AS4678
 The design of soil nailed structures to AS4678 Chris Bridges Technical Principal - Geotechnics chris.bridges@smec.com 7 December 2016 1 Presentation Layout Introduction Soil Nailing in AS4678 Design Process
The design of soil nailed structures to AS4678 Chris Bridges Technical Principal - Geotechnics chris.bridges@smec.com 7 December 2016 1 Presentation Layout Introduction Soil Nailing in AS4678 Design Process
Static Response of Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls with Nonuniform Reinforcement
 The International Journal of Geomechanics Volume 1, Number 4, 477 506 (2001) Static Response of Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls with Nonuniform Reinforcement K. Hatami, R.J. Bathurst, and P. Di Pietro
The International Journal of Geomechanics Volume 1, Number 4, 477 506 (2001) Static Response of Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls with Nonuniform Reinforcement K. Hatami, R.J. Bathurst, and P. Di Pietro
GROUND IMPROVEMENT USING DYNAMIC REPLACEMENT FOR NCIG CET3 COAL STOCKYARD
 FOR NCIG CET3 COAL STOCKYARD Charles CH Chua 1, Ming Lai 2, Graeme Hoffmann 2 and Brett Hawkins 1 1 Connell Hatch, Australia, 2 Keller Ground Engineering Pty Ltd ABSTRACT This paper presents an overview
FOR NCIG CET3 COAL STOCKYARD Charles CH Chua 1, Ming Lai 2, Graeme Hoffmann 2 and Brett Hawkins 1 1 Connell Hatch, Australia, 2 Keller Ground Engineering Pty Ltd ABSTRACT This paper presents an overview
MINING VOIDS AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON THE GROUND SURFACE
 MINING VOIDS AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON THE GROUND SURFACE Prof. EUGEN COZMA, Min.Eng.Ph.D., Prof. ILIE ONICA, Min.Eng.Ph.D., Ass.Prof. TUDOR GOLDAN, Min.Eng.Ph.D., Ass. BOGDAN COZMA, Mech.Eng., University
MINING VOIDS AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON THE GROUND SURFACE Prof. EUGEN COZMA, Min.Eng.Ph.D., Prof. ILIE ONICA, Min.Eng.Ph.D., Ass.Prof. TUDOR GOLDAN, Min.Eng.Ph.D., Ass. BOGDAN COZMA, Mech.Eng., University
Seismic bearing capacity factors for strip footings
 Seismic bearing capacity factors for strip footings Amir H.Shafiee 1, M.Jahanandish 2 1- Former MSc Student of Soil Mech. & Found. Eng., Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran 2- Associate Professor, Civil Eng.
Seismic bearing capacity factors for strip footings Amir H.Shafiee 1, M.Jahanandish 2 1- Former MSc Student of Soil Mech. & Found. Eng., Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran 2- Associate Professor, Civil Eng.
Evaluation of Pseudo Static coefficient for Soil nailed walls on the basis of Seismic behavior levels
 Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502. Evaluation of Pseudo Static coefficient for Soil nailed walls on the basis of Seismic behavior levels Abstract Majid yazdandoust 1*, Ali komak panah
Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502. Evaluation of Pseudo Static coefficient for Soil nailed walls on the basis of Seismic behavior levels Abstract Majid yazdandoust 1*, Ali komak panah
NPTEL Course. GROUND IMPROVEMENT Factors affecting the behaviour and performance of reinforced soil
 Lecture 27 NPTEL Course GROUND IMPROVEMENT Factors affecting the behaviour and performance of reinforced soil Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
Lecture 27 NPTEL Course GROUND IMPROVEMENT Factors affecting the behaviour and performance of reinforced soil Prof. G L Sivakumar Babu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
Question Paper Code : 11410
 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 11410 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY 2011 Fourth Semester Mechanical Engineering ME 2254 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (Common to Automobile Engineering and Production
Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 11410 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY 2011 Fourth Semester Mechanical Engineering ME 2254 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (Common to Automobile Engineering and Production
THE BEHAVIOR OF TWO MASONRY INFILLED FRAMES: A NUMERICAL STUDY
 THE BEHAVIOR OF TWO MASONRY INFILLED FRAMES: A NUMERICAL STUDY Giselle M. Fonseca *, Roberto M. Silva *, and Paulo B. Lourenço # * University Federal of Minas Gerais, School of Engineering Department of
THE BEHAVIOR OF TWO MASONRY INFILLED FRAMES: A NUMERICAL STUDY Giselle M. Fonseca *, Roberto M. Silva *, and Paulo B. Lourenço # * University Federal of Minas Gerais, School of Engineering Department of
Tunnel Excavation Works in Taksim-Kabataş Funicular System Project
 Tunnel Excavation Works in Taksim-Kabataş Funicular System Project E. Aykar & B. Arıoğlu Construction Industry Inc., Head Office, Çamlıca, Đstanbul, Turkey N. Erdirik & A.Yüksel & T. Özbayır Construction
Tunnel Excavation Works in Taksim-Kabataş Funicular System Project E. Aykar & B. Arıoğlu Construction Industry Inc., Head Office, Çamlıca, Đstanbul, Turkey N. Erdirik & A.Yüksel & T. Özbayır Construction
Numerical Analysis of the Durability of Retaining Wall with Anchor
 Numerical Analysis of the Durability of Retaining Wall with Anchor Qingyu Meng 1, 2, Chao Li 1, 2, Hongbo Zhang 1, 2, Xin Li 1, 2 1. School of Civil Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, 250061, China
Numerical Analysis of the Durability of Retaining Wall with Anchor Qingyu Meng 1, 2, Chao Li 1, 2, Hongbo Zhang 1, 2, Xin Li 1, 2 1. School of Civil Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, 250061, China
Example Application 11. Multistage Tunnel Excavation and Support
 Example Application 11 Multistage Tunnel Excavation and Support 1 Multi-Stage Tunnel Construction 2 Multistage Tunnel Conditions Rock Mass Properties Mohr-Coulomb Model unit weight 27,000 N/m 3 bulk modulus
Example Application 11 Multistage Tunnel Excavation and Support 1 Multi-Stage Tunnel Construction 2 Multistage Tunnel Conditions Rock Mass Properties Mohr-Coulomb Model unit weight 27,000 N/m 3 bulk modulus
NUMERICAL STUDY OF INVESTMENT BEHAVIOR CONTAINMENT WALLS (CASE STUDY STRUCTURAL GUARDIAN SYSTEMS PROJECT OF HABIB HOTEL OF MASHHAD)
 NUMERICAL STUDY OF INVESTMENT BEHAVIOR CONTAINMENT WALLS (CASE STUDY STRUCTURAL GUARDIAN SYSTEMS PROJECT OF HABIB HOTEL OF MASHHAD) Ali Eslam panahi 1, Soheil Ghareh 2 1 MSc in Civil Engineering - Geotechnical
NUMERICAL STUDY OF INVESTMENT BEHAVIOR CONTAINMENT WALLS (CASE STUDY STRUCTURAL GUARDIAN SYSTEMS PROJECT OF HABIB HOTEL OF MASHHAD) Ali Eslam panahi 1, Soheil Ghareh 2 1 MSc in Civil Engineering - Geotechnical
COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool. Faculty of Civil Engineering UiTM, Malaysia
 COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool Faculty of Civil Engineering, Malaysia Name : COURSE CONTENTS Use of Plaxis Getting Started Exercise 1: Elastic analysis of drained footing
COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool Faculty of Civil Engineering, Malaysia Name : COURSE CONTENTS Use of Plaxis Getting Started Exercise 1: Elastic analysis of drained footing
BEHAVIOUR OF SQUARE FOOTING RESTING ON TWO LAYERED CLAY DEPOSITS. Dr. Sunil S. Pusadkar 1, Sheetal M. Baral 2 ABSTRACT
 50 th IGC 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE 17 th 19 th DECEMBER 2015, Pune, Maharashtra, India Venue: College of Engineering (Estd. 1854), Pune, India BEHAVIOUR OF SQUARE FOOTING RESTING ON TWO LAYERED
50 th IGC 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE 17 th 19 th DECEMBER 2015, Pune, Maharashtra, India Venue: College of Engineering (Estd. 1854), Pune, India BEHAVIOUR OF SQUARE FOOTING RESTING ON TWO LAYERED
Modelling of Sheared Behaviour Bolts Across Joints
 University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2004 Modelling of Sheared Behaviour Bolts Across Joints H. Jalalifar University of Wollongong
University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2004 Modelling of Sheared Behaviour Bolts Across Joints H. Jalalifar University of Wollongong
Parametric Study on Geogrid-Reinforced Track Substructure
 IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 6, No. 2 / June 2013, pp. 59-63 ISSN 1976-9067(Print) ISSN 2288-3010(Online) Parametric Study on Geogrid-Reinforced Track Substructure Jeongho Oh Abstract The
IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 6, No. 2 / June 2013, pp. 59-63 ISSN 1976-9067(Print) ISSN 2288-3010(Online) Parametric Study on Geogrid-Reinforced Track Substructure Jeongho Oh Abstract The
Numerical Analysis of Lining Hinge in Tunnels
 International Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations vol. 4, issue 39, April 2015 ISSN: 2251-8843 Numerical Analysis of Lining Hinge in Tunnels Vahid Hosseinitoudeshki Department of Civil Engineering,
International Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations vol. 4, issue 39, April 2015 ISSN: 2251-8843 Numerical Analysis of Lining Hinge in Tunnels Vahid Hosseinitoudeshki Department of Civil Engineering,
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF GEOSYNTHETIC REINFORCED SOIL ABOVE A TUNNEL
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF GEOSYNTHETIC REINFORCED SOIL ABOVE A TUNNEL S.E. Ghoreishi Tayyebi 1, M.R. Babatabar 1 & A. Tahmasebi poor 2,* 1 Islamic Azad University, Ayatollah Amoli Branch, Departments of Civil
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF GEOSYNTHETIC REINFORCED SOIL ABOVE A TUNNEL S.E. Ghoreishi Tayyebi 1, M.R. Babatabar 1 & A. Tahmasebi poor 2,* 1 Islamic Azad University, Ayatollah Amoli Branch, Departments of Civil
Coal and Your Community
 Activity 4 oal and Your ommunity Activity 4 oal and Your ommunity Goals In this activity you will: Investigate the production and consumption of coal in the United States. Investigate how coal sources
Activity 4 oal and Your ommunity Activity 4 oal and Your ommunity Goals In this activity you will: Investigate the production and consumption of coal in the United States. Investigate how coal sources
Combination of undrained and drained analysis to design the temporary supports of a large diameter tunnel
 16 TH Australasian Tunnelling Conference 2017 30 October 1 November 2017 Combination of undrained and drained analysis to design the temporary supports of a large diameter tunnel R. Mahinroosta CSU Engineering,
16 TH Australasian Tunnelling Conference 2017 30 October 1 November 2017 Combination of undrained and drained analysis to design the temporary supports of a large diameter tunnel R. Mahinroosta CSU Engineering,
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING 2 MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS CE FOUNDATION ENGINEERING UNIT 1
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING 2 MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS CE6502 - FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Subject Code: CE6502 UNIT 1 1. What are the informations obtained
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING 2 MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS CE6502 - FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Subject Code: CE6502 UNIT 1 1. What are the informations obtained
Behavior of pile due to combined loading with lateral soil movement
 DOI 1.1186/s473-16-21-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Behavior of pile due to combined loading with lateral soil movement B. Jegatheeswaran 1* and K. Muthukkumaran 2 *Correspondence: jegatheesb@gmail.com
DOI 1.1186/s473-16-21-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Behavior of pile due to combined loading with lateral soil movement B. Jegatheeswaran 1* and K. Muthukkumaran 2 *Correspondence: jegatheesb@gmail.com
Mechanistic-Empirical Design of Chip- sealed Roads in SA. Christchurch workshop presentation 21/22 November 2002
 Mechanistic-Empirical Design of Chip- sealed Roads in SA Christchurch workshop presentation 21/22 November 2002 Structure of presentation Pavement materials Current SAMDM Variability and accuracy Distress
Mechanistic-Empirical Design of Chip- sealed Roads in SA Christchurch workshop presentation 21/22 November 2002 Structure of presentation Pavement materials Current SAMDM Variability and accuracy Distress
NUMERICAL STUDY OF OFFSHORE SKIRTED FOUNDATIONS SUBJECTED TO COMBINED LOADING
 NUMERICAL STUDY OF OFFSHORE SKIRTED FOUNDATIONS SUBJECTED TO COMBINED LOADING S.K. NAIK 1, S.M. DASAKA 2, and V.B. CHAUHAN 3 1 Former Post Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute
NUMERICAL STUDY OF OFFSHORE SKIRTED FOUNDATIONS SUBJECTED TO COMBINED LOADING S.K. NAIK 1, S.M. DASAKA 2, and V.B. CHAUHAN 3 1 Former Post Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute
Seismic Amplification of Double-Sided Geosynthetic-Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Seismic Amplification of Double-Sided Geosynthetic-Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls W. A.
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Seismic Amplification of Double-Sided Geosynthetic-Reinforced Soil Retaining Walls W. A.
Effect of Cavities on the Behaviour of Strip Footing Subjected to Inclined Load
 Effect of Cavities on the Behaviour of Strip Footing Subjected to Inclined Load Ali A. Al-Jazaairry, Tahsin T. Sabbagh Abstract One of the important concerns within the field of geotechnical engineering
Effect of Cavities on the Behaviour of Strip Footing Subjected to Inclined Load Ali A. Al-Jazaairry, Tahsin T. Sabbagh Abstract One of the important concerns within the field of geotechnical engineering
Numerical Simulation of Liquefaction Deformation of Sand Layer around Bucket Foundations under Dynamic Loadings
 The Open Ocean Engineering Journal, 2010, 3, 75-81 75 Open Access Numerical Simulation of Liquefaction Deformation of Sand Layer around Bucket Foundations under Dynamic Loadings Chi Li 1,*, Xiaobing Lu
The Open Ocean Engineering Journal, 2010, 3, 75-81 75 Open Access Numerical Simulation of Liquefaction Deformation of Sand Layer around Bucket Foundations under Dynamic Loadings Chi Li 1,*, Xiaobing Lu
Numerical Simulation of Soil Nailing Wall in Deep Foundation Pit
 2017 2 nd International Conference on Architectural Engineering and New Materials (ICAENM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-436-3 Numerical Simulation of Soil Nailing Wall in Deep Foundation Pit Xiao Jie Geng ABSTRACT
2017 2 nd International Conference on Architectural Engineering and New Materials (ICAENM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-436-3 Numerical Simulation of Soil Nailing Wall in Deep Foundation Pit Xiao Jie Geng ABSTRACT
Some geomechanical aspects of well integrity
 4th Meeting of the Well Bore Integrity Network, 18-19 March 2008 Some geomechanical aspects of well integrity Bogdan Orlic, Tjirk Benedictus Acknowledgements CASTOR project (EU-sponsored, 30 partners)
4th Meeting of the Well Bore Integrity Network, 18-19 March 2008 Some geomechanical aspects of well integrity Bogdan Orlic, Tjirk Benedictus Acknowledgements CASTOR project (EU-sponsored, 30 partners)
Evaluation of Geosynthetic Forces in GRSRW under Dynamic Condition
 Evaluation of Geosynthetic Forces in GRSRW under Dynamic Condition Kooshyar Passbakhsh, Maryam Yazdi Abstract Geosynthetics have proved to be suitable for reinforced soil retaining walls. Based on the
Evaluation of Geosynthetic Forces in GRSRW under Dynamic Condition Kooshyar Passbakhsh, Maryam Yazdi Abstract Geosynthetics have proved to be suitable for reinforced soil retaining walls. Based on the
EFFECTS ON UNDERGROUND TUNNEL WITH OR WITHOUT BUILDING AT TOP IN
 EFFECTS ON UNDERGROUND TUNNEL WITH OR WITHOUT BUILDING AT TOP IN DIFFERENT GROUND STRATA Sumit Ghangus Assistant Professor, Structural Engineering, (ASAP), Amity University Haryana, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
EFFECTS ON UNDERGROUND TUNNEL WITH OR WITHOUT BUILDING AT TOP IN DIFFERENT GROUND STRATA Sumit Ghangus Assistant Professor, Structural Engineering, (ASAP), Amity University Haryana, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
THE IMPACT OF EARTHQUAKES ON THE TUNNEL FROM HANOI METRO SYSTEM WHEN THE TUNNEL HAS A HORSESHOE SHAPE CROSS-SECTION
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 79 86, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_010 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=2
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 79 86, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_010 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=2
Mechanical and Environmental Properties of Plastics-included Landfills with Elastic Behavior
 December 21, 2016 3K133011 Mechanical and Environmental Properties of Plastics-included Landfills with Elastic Behavior (Resilient) Atsushi YAMAWAKI 1 Japan Industrial Waste Management Foundation Period
December 21, 2016 3K133011 Mechanical and Environmental Properties of Plastics-included Landfills with Elastic Behavior (Resilient) Atsushi YAMAWAKI 1 Japan Industrial Waste Management Foundation Period
Arctic Pipeline with Thaw Settlement Analysis by Finite Element Method
 Proceedings of the Twenty-sixth (2016) International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference Rhodes, Greece, June 26-July 1, 2016 Copyright 2016 by the International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers
Proceedings of the Twenty-sixth (2016) International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference Rhodes, Greece, June 26-July 1, 2016 Copyright 2016 by the International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers
Roof support and roadway serviceability assessment using beam-column principles
 University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2017 Roof support and roadway serviceability assessment using beam-column principles
University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2017 Roof support and roadway serviceability assessment using beam-column principles
Seismic Design of a Slope Stabilization Work Using Piles and Tendons
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Seismic Design of a Slope Stabilization Work Using Piles and Tendons H. Sanchez Lizarraga
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Seismic Design of a Slope Stabilization Work Using Piles and Tendons H. Sanchez Lizarraga
Modelling of Piled Raft Foundation on Soft Clay
 Modelling of Piled Raft Foundation on Soft Clay Mohamed A.Baqi Mahmoud 1 and Hussien Elarabi 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Khartoum 2 Building and Road Research
Modelling of Piled Raft Foundation on Soft Clay Mohamed A.Baqi Mahmoud 1 and Hussien Elarabi 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Khartoum 2 Building and Road Research
The Application of Flac3d Numerical Simulation Software to Determine the Reasonable Width of the Section Coal Pillar
 2012 International Conference on Education Technology and Computer (ICETC2012) IPCSIT vol.43 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore The Application of Flac3d Numerical Simulation Software to Determine the
2012 International Conference on Education Technology and Computer (ICETC2012) IPCSIT vol.43 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore The Application of Flac3d Numerical Simulation Software to Determine the
Geotechnical laboratory ( )
 VŠB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF OSTRAVA Faculty of Civil Engineering Department of Geotechnics and Underground Engineering Geotechnical laboratory (224-0268) Study support for combined form of bachelor study
VŠB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF OSTRAVA Faculty of Civil Engineering Department of Geotechnics and Underground Engineering Geotechnical laboratory (224-0268) Study support for combined form of bachelor study
Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York
 promoting access to White Rose research papers Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/ White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/42880/
promoting access to White Rose research papers Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/ White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/42880/
Interpretation of Danish Chalk Parameters Applicable to Foundation Design
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May Interpretation of Danish Chalk Parameters Applicable to Foundation Design L. Kellezi
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May Interpretation of Danish Chalk Parameters Applicable to Foundation Design L. Kellezi
Effects of Wall Embedded Length Ratio and Wall Thickness Ratio on Undrained Stability of Cantilever Piled Walls
 Engineering and Physical Sciences Effects of Wall Embedded Length Ratio and Wall Thickness Ratio on Undrained Stability of Cantilever Piled Walls Boonchai UKRITCHON *, Kant TEERAVONG and Suraparb KEAWSAWASVONG
Engineering and Physical Sciences Effects of Wall Embedded Length Ratio and Wall Thickness Ratio on Undrained Stability of Cantilever Piled Walls Boonchai UKRITCHON *, Kant TEERAVONG and Suraparb KEAWSAWASVONG
Shallow Cover Tunnel Under Heritage Listed Brick Buildings: Brisbane Boggo Road Busway Tunnel
 Shallow Cover Tunnel Under Heritage Listed Brick Buildings: Brisbane Boggo Road Busway Tunnel by Ted Nye, Tunnel Designer Manager, Sinclair Knight Merz and Max Kitson, Senior Geotechnical Engineer, Sinclair
Shallow Cover Tunnel Under Heritage Listed Brick Buildings: Brisbane Boggo Road Busway Tunnel by Ted Nye, Tunnel Designer Manager, Sinclair Knight Merz and Max Kitson, Senior Geotechnical Engineer, Sinclair
Figure 1 Swing Span Supported by Center Pivot Pier and Two Rest Piers
 Abstract SEISMIC RETROFIT OF UNREINFORCED STONE MASONRY BRIDGE PIERS AND DISCRETE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Jaw-Nan (Joe) Wang 1 ; Michael J. Abrahams 2 The seismic behavior of unreinforced stone masonry structures
Abstract SEISMIC RETROFIT OF UNREINFORCED STONE MASONRY BRIDGE PIERS AND DISCRETE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Jaw-Nan (Joe) Wang 1 ; Michael J. Abrahams 2 The seismic behavior of unreinforced stone masonry structures
