MARKET SQUARE PLAZA 17 NORTH SECOND STREET HARRISBURG, PENNSYLVANIA
|
|
|
- Ashley Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 17 NORTH SECOND STREET HARRISBURG, PENNSYLVANIA NICOLE L. RENNO SENIOR THESIS FINAL REPORT PENN STATE UNIVERSITY ARCHITECTURAL ENGINEERING STRUCTURAL OPTION APRIL 5, 2005
2
3 TABLE OF CONTENTS I. TABLE OF CONTENTS...1 II. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY...2 III. PROJECT BACKGROUND...3 IV. STRUCTURAL REDESIGN A. Load Calculations...8 B. Floor System Economization...13 C. Lateral Frame Update...19 D. Connection Optimization...23 V. BUILDING ENCLOSURE STUDY...26 VI. CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT EVALUATION...31 VII. CONCLUSIONS...34 VIII. REFERENCES...35 IX. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS...37 X. APPENDIX... A.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1
4 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Market Square Plaza Market Square Plaza is an 18 story, multi-use parking/office building currently under construction in downtown Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. At approximately 240 tall, Market Square Plaza will be the second tallest building in the city. The building is approximately 105 by 160 and will provide about 270,000 square feet of space. Structural System Redesign Floor System Economization In order to economize the gravity framing system, the structure was reconfigured, eliminating one beam per bay. The most economical design was then determined, considering the beam sizes, number of studs, and levels of camber. Lateral Frame Update In the latest building codes, lateral loads for buildings in the area of Market Square Plaza have been significantly increased. Therefore, the lateral system was designed to resist the higher loads. Additionally, the North-South frames were reconfigured to eliminate the costly moment connections. Connection Optimization In addition to the elimination of the moment connections, the bracing connections were reconfigured to eliminate costly field welds. Building Envelope Study Carbon fiber reinforced precast concrete panels were selected to replace the building s traditional precast panels. Carbon fiber reinforced panels possess many of the properties that make precast panels a favorable system while improving on many of precast panels disadvantages. Construction Management Evaluation Finally, the structural changes were evaluated according to schedule and budget. While updating the lateral system adds to the cost of the building, the floor framing redesign saves approximately an equal amount. Both system redesigns also improve upon the building s construction schedule. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 2
5 PROJECT BACKGROUND
6 BUILDING DESCRIPTION Market Square Plaza is a multi-function retail, ballroom, garage, and office building which was recently constructed in downtown Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. At 18 stories and 240 tall, Market Square Plaza is the second tallest building in the city. The building is approximately 105 by 160 and will provide about 270,000 square feet of space. The first floor of Market Square Plaza will include both retail space and lobby space. The second floor houses a ballroom which will be accessed through a connection to the next door hotel. A unique structural feature of the building is a massive truss which spans the ballroom and transfers column loads from the sixteen stories above. Floors three through ten contain parking for 252 cars. The parking garage is accessed from the adjacent parking garage and therefore contains no ramps. Finally, floors eleven to eighteen house office space which will be leased to individual tenants. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM Floor System A typical floor framing plan can be seen in Figure 1. Although some differences between floors do exist, the same basic framing layout prevails through floors two through eighteen. MARKET SQUARE PLAZA: PROJECT BACKGROUND 3
7 132 1" " TYPICAL EXTERIOR & INTERIOR BAYS MEMBERS CONTRIBUTING TO MAIN LATERAL RESISTING SYSTEMS " Figure 1: Typical Floor Framing Plan Partially composite steel beams with composite decking and one-way slabs compose the floor systems in Market Square Plaza. All beams and girders are simply supported with the exception of those which are part of the lateral force resisting moment frames. Bay sizes range from 30-6 to 34-6 in the North- South direction and 26 to 36-6 in the East-West direction The main disparity between the typical office floor system and parking floor system is the slab. A 5-1/4 light-weight concrete slab with composite metal deck is used for the office levels, and a 7 normal-weight concrete slab over 3 metal deck is used for the parking levels. Concrete strengths for the office slabs and parking slabs are 3,000 psi and 5,000 psi, respectively. MARKET SQUARE PLAZA: PROJECT BACKGROUND 4
8 Lateral System North-South Direction In the North-South direction, the lateral forces are primarily resisted by two combination moment/braced frames. Lateral forces are transferred to the frames by rigid diaphragms at each story level. Because the two frames are nearly identical, they will each resist approximately half of the direct lateral load in this direction. Additionally, as can be seen in the floor framing plan, eccentricity of the frames will produce torsional forces. The configuration of the frames in this direction can be seen in Figure 2. TYPICAL FRAME NORTH SOUTH RESISTANCE Figure 2 East-West Direction Two nearly identical braced frames resist lateral forces in the East-West direction. Figure 3 shows a typical braced frame in this direction. As in the North-South direction, rigid diaphragms transfer lateral loads to the frames in this direction. Again, eccentricities will result in torsion on the lateral force resisting elements. TYPICAL BRACED FRAME EAST WEST RESISTANCE Figure 3 MARKET SQUARE PLAZA: PROJECT BACKGROUND 5
9 Foundation Due to poor soil conditions at the site of Market Square Plaza, drilled piers transfer loads from the building to the ground. The drilled piers range in diameter from 3 to 5 and transfer loads to rock approximately 20 below grade. Additionally, a system of grade beams aids in resisting uplift forces on the piers. The ground level is supported by a 5 slab-on-grade. Roof A TPO membrane over built-up insulation supported by 3 metal deck composes the main roof and elevator mechanical room roof. Additionally, a curved standing seam metal roof adorns the South-West corner of the building. Enclosure The main building enclosure is composed of 7 thick precast concrete panels. Some of the large panels had to be cast with recessed areas in order to lighten them so that they could be lifted into place with a crane. Finally, an aluminum and glass curtain wall system was utilized on the first two levels of the southwest quadrant. ORIGINAL DESIGN CODES & STANDARDS The following design codes and standards were used in the original design of Market Square Plaza: The BOCA National Building Code 1996, Building Officials and Code Administrators International, Inc. Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures (ASCE 7-95), American Society of Civil Engineers. Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete, ACI , American Concrete Institute. MARKET SQUARE PLAZA: PROJECT BACKGROUND 6
10 REDESIGN CODES & STANDARDS Because new codes are continuously being incorporated into the design field, this analysis was performed according to the most current design codes and standards. The following codes are applicable to the redesign performed for this thesis project: International Building Code 2003 Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures (ASCE 7-02), American Society of Civil Engineers. Manual of Steel Construction Load and Resistance Factor Design, Third Edition, 2001, American Institute of Steel Construction. Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete, ACI , American Concrete Institute. MARKET SQUARE PLAZA: PROJECT BACKGROUND 7
11 STRUCTURAL REDESIGN: LOAD CALCULATIONS
12 DESIGN CODES & STANDARDS According to the 2003 International Building Code loads should be calculated according to ASCE Therefore, the gravity and lateral loads presented in this report were calculated according to this standard. GRAVITY LOADS Dead Loads Ground Floor 5 slab on grade 65 psf Superimposed Ceiling/Floor Finishes 15 psf MEP/Lighting 5 psf 85 psf Second Floor 5-1/4 light-weight concrete slab on deck 42 psf Superimposed Ceiling/Floor Finishes MEP/Lighting 15 psf 5 psf 62 psf Parking Floors 7 normal-weight concrete slab on deck 69 psf Superimposed MEP/Lighting 5 psf 74 psf Office Floors 5-1/4 light-weight concrete slab 42 psf Superimposed Ceiling/Floor Finishes MEP/Lighting 15 psf 5 psf 62 psf STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LOADS CALCULATIONS 8
13 Elevator Mechanical Room 12 normal-weight concrete slab 130 psf Superimposed Ceiling/Floor Finishes MEP/Lighting Roof Roof system MEP/Lighting 15 psf 5 psf 150 psf 25 psf 5 psf 30 psf Exterior Wall Dead Loads 7 Carbon Fiber Precast Panels 45 psf Glass Curtain Wall 15 psf Live Loads First Floor Retail Ballroom Parking Areas Office Office Corridors (above 1 st floor) Partitions High Density Storage Super High Density Storage Stairs Roof 100 psf 100 psf 40 psf 80 psf 80 psf 20 psf 150 psf 250 psf 100 psf 20 psf Roof Snow Load (Refer to Appendix A.1 for calculations) Snow load 21 psf Rain On Snow Surcharge 5 psf Lower Roof Drift Surcharge 25 psf (reduces to 0 at w=6 ) STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LOADS CALCULATIONS 9
14 LATERAL LOADS Seismic and wind loads have been calculated for the structure in the North-South and East-West direction. Hand calculations and spreadsheets used in determining the loads can be seen in A.1 to A.6. Wind Loads Wind pressures were calculated for the main lateral force resisting systems in each direction. The resultant wind pressures are represented in Figure 4. Figure 5 shows the story forces, which were determined using the tributary area of each story WIND PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION (PSF) EAST WEST DIRECTION WIND PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION (PSF) NORTH SOUTH DIRECTION Figure 4: Design Wind Pressures STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LOADS CALCULATIONS 10
15 EMR ROOF EMR FLOOR ROOF EMR ROOF EMR FLOOR ROOF TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR 9TH FLOOR 8TH FLOOR 7TH FLOOR 6TH FLOOR 5TH FLOOR 4TH FLOOR 3RD FLOOR TH FLOOR 9TH FLOOR 8TH FLOOR 7TH FLOOR 6TH FLOOR 5TH FLOOR 4TH FLOOR 3RD FLOOR ND FLOOR ND FLOOR WIND STORY FORCES (K) EAST WEST DIRECTION GROUND FLOOR Figure 5: Wind Story Forces WIND STORY FORCES (K) NORTH SOUTH DIRECTION GROUND FLOOR STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LOADS CALCULATIONS 11
16 Seismic Loads Seismic loads were calculated according to the equivalent lateral force procedure. Although the lateral force resisting systems differ in each direction, the response modification factor is the same for both systems. Therefore, the seismic lateral story forces are the same in each direction, as can be seen in Figure EMR ROOF EMR FLOOR ROOF EMR ROOF EMR FLOOR ROOF TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR TH FLOOR 9TH FLOOR 8TH FLOOR 7TH FLOOR 6TH FLOOR 5TH FLOOR 4TH FLOOR 3RD FLOOR TH FLOOR 9TH FLOOR 8TH FLOOR 7TH FLOOR 6TH FLOOR 5TH FLOOR 4TH FLOOR 3RD FLOOR 1.1 2ND FLOOR 1.1 2ND FLOOR V=312.7 k GROUND FLOOR V=312.7 k GROUND FLOOR SEISMIC STORY FORCES (K) EAST WEST DIRECTION Figure 6: Seismic Story Forces SEISMIC STORY FORCES (K) NORTH SOUTH DIRECTION STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LOADS CALCULATIONS 12
17 STRUCTURAL REDESIGN: FLOOR SYSTEM ECONOMIZATION
18 EXISTING GRAVITY SYSTEM DESIGN Market Square Plaza s gravity resisting system is composed of partially composite steel beams. In the parking levels, floors three through ten, slabs consist of 4 normal-weight concrete over 3 metal decking. Additionally, the parking level beams are cambered in order to counteract deflections due to construction loads. In the office levels, floors two and eleven through eighteen, a 3 ¼ lightweight slab over 2 composite metal decking resists loads. Typical exterior and interior bays of the parking and office levels can be seen below in Figures 7 and 8, respectively. The typical bays relative to the entire floor plan can be seen previously in Figure " W24x62 [36] 36 6" W21x44 [17] C= 3 4" W21x44 [17] C= 3 4" W21x44 [17] C= 3 4" W21x44 [17] C= 3 4" W21x44 [17] C= 3 4" [X] X IS THE NUMBER OF 3 4" DIAMETER HEADED SHEAR STUDS EVENLY SPACED ALONG BEAM C = CAMBER (INCHES) 7" NORMAL WEIGHT CONCRETE (F c=5000 PSF) #4 18" MID DEPTH RUNNING PERPENDICULAR TO BEAMS #4 24" MID DEPTH RUNNING PARALLEL TO BEAMS W24x76 [32] C= 3 4" 26 W16x26 [14] C= 3 4" W16x26 [14] C= 3 4" W16x26 [14] C= 3 4" W16x26 [14] C= 3 4" W16x26 [14] C= 3 4" W24x68 [26] C= 3 4" Figure 7: Typical Parking Bays STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: FLOOR SYSTEM ECONOMIZATION 13
19 30 6" W24x62 [36] 36 6" W21x44 [17] W21x44 [17] W21x44 [17] W21x44 [17] W21x44 [17] [X] X IS THE NUMBER OF 3 4" DIAMETER HEADED SHEAR STUDS EVENLY SPACED ALONG BEAM 3 1 4" LIGHTWEIGHT CONCRETE (F c=3000 PSF) 2" COMPOSITE METAL DECK (20 GAGE) 6X6 W2.0xW2.0 WWF W24x76 [32] 26 W16x26 [10] W16x26 [10] W16x26 [10] W16x26 [10] W16x26 [10] W24x62 [57] Figure 8: Typical Office Bays During the analysis of the existing framing system, it was found that by using LRFD procedures some members sizes could be decreased and the number of shear studs could be reduced from the original ASD structure. Therefore, the floor framing was redesigned according to LRFD requirements. Additionally, economizations were made in the basic framing geometry. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: FLOOR SYSTEM ECONOMIZATION 14
20 REDESIGN CRITERIA The following criteria was developed to be used as guidelines in the redesign and economization of the gravity system. Changes were made to improve the economy and constructability of the system, while preserving the original design goals. In the redesign of the floor framing systems the original slab configurations remained the same in order to provide adequate fire ratings and reinforcement protection. Secondly, the new floor system must meet vibration requirements suitable to the use of the structure. Members were designed to resist all of the construction loads while maintaining a deflection of L/360 or 1. This eliminates the need for shoring which is costly, time consuming, and site congesting. Additionally, beam cambering was considered to counteract deflections where most economical. Deflection criteria remained the same as used in the original design. Service live load deflections were limited to L/360 while total service live plus dead load deflections were limited to L/240. Bay configurations were chosen based on economy. Both the direction of framing members and the number of beams per bay was considered. Also, the level of composite action was determined based on the most economical configuration. As in the original design, live load reductions were used where applicable. The depth of the redesigned members must not inflict on the plenum space required by other systems, such as mechanical ductwork. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: FLOOR SYSTEM ECONOMIZATION 15
21 METHODS, TOOLS, & RESOURCES Loads Loads were calculated according to the most recent design code, IBC This resulted in few gravity load changes from the original design. Parking level loads were reduced from 50 psf to 40 psf, while changes in drift loads increased roof snow loads. Also, lower exterior wall loads resulted from the replacement of the traditional precast wall panels with carbon fiber reinforced wall panels. Refer to the section titled Structural System Redesign: Load Calculations for more detailed load information. Bay Configurations AISC s Parametric Bay Study Tool was used in order to determine the most economical number of beams per bay, as well as the most economical levels of camber. Using this tool, it was determined that by eliminating one beam per bay, a steel material savings could be generated. Reducing the number of beams per bay will also reduce labor costs and time associated with erection. Design Procedure After completing a preliminary analysis using AISC s Parametric Bay Study Tool to determine the most economical framing layout, a complete redesign of the gravity system was completed using RAM Structural System. Results of the computer analysis were then verified using hand calculations. GRAVITY SYSTEM REDESIGN A results summary of the gravity system redesign are shown in Figures 9 & 10. Figure 9 shows two typical parking level bays while Figure 10 presents two typical office level bays. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: FLOOR SYSTEM ECONOMIZATION 16
22 30 6" W18x40 [14] C=1" 36 6" W18x35 [12] C=1 1 2" W16x31 [12] C=2" W16x31 [12] C=2" W18x35 [12] C=1 1 2" [X] X IS THE NUMBER OF 3 4" DIAMETER HEADED SHEAR STUDS EVENLY SPACED ALONG BEAM C = CAMBER (INCHES) 7" NORMAL WEIGHT CONCRETE (F c=5000 PSF) OVER 3" METAL DECK W21x48 [16] C=1" 26 W14x22 [9] C=1" W14x22 [9] C=1" W14x22 [9] C=1" W14x22 [9] C=1" W21x44 [16] C=1" Figure 9: Typical Redesigned Parking Bays 30 6" W18x35 [29] C= 3 4" 36 6" W16x31 [40] C=1 1 4" W16x26 [46] C=1 1 2" W16x26 [46] C=1 1 2" W16x31 [40] C=1 1 4" [X] X IS THE NUMBER OF 3 4" DIAMETER HEADED SHEAR STUDS EVENLY SPACED ALONG BEAM 3 1 4" LIGHTWEIGHT CONCRETE (F c=3000 PSF) OVER 2" COMPOSITE METAL DECK W21x44 [39] C= 3 4" 26 W16x26 [16] W16x26 [16] W16x26 [16] W16x26 [16] W18x40 [43] C= 3 4" Figure 10: Typical Redesigned Office Bays STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: FLOOR SYSTEM ECONOMIZATION 17
23 CONCLUSIONS: GRAVITY SYSTEM REDESIGN Redesigning the gravity system of Market Square Plaza resulted in a significant cost savings. By eliminating one beam per bay, thus reducing the weight of steel and the number of members which must be erected, a total material and labor savings of $60,400 is generated. Additionally, eliminating the number of members which need to be erected also saves critical time on the schedule. For an in-depth study of the cost and time savings produced by the gravity system redesign, refer to the section titled Construction Management Evaluation. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: FLOOR SYSTEM ECONOMIZATION 18
24 STRUCTURAL REDESIGN: LATERAL FRAME UPDATE
25 EXISTING DESIGN ANALYSIS Market Square Plaza was originally designed using the 1996 BOCA National Building Code which references the 1996 edition of ASCE s Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures for use in determining lateral loads. However, in the 2002 publication of Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures significant changes have occurred to lateral loads as determined for this structure. First, the site of Market Square Plaza has been considerably increased from a 70 mile per hour wind zone to a 90 mile per hour wind zone. Further adding to the wind load increase, the Site Exposure Category A has been eliminated from the code. Therefore, when analyzed according to the most recent codes, Market Square Plaza s Site Exposure Category must be increased to a more severe Site Exposure Category B from Category A, as determined in the original design. Seismic loads have also been significantly increased in the most recent design codes. However, the lateral design of Market Square Plaza is governed primarily by wind loads. Therefore, the focus of this analysis is predominantly based on the effects of the increased wind loads. DESIGN CRITERIA The following criteria were considered in the redesign of the lateral system: The building s drift at each story was limited to H/400, a common industry standard and the drift limit of the original design. The HSS brace members were redesigned as W-shapes because W-shapes are less expensive and can easily accommodate bolted connections. Member depths are restricted in order to comply with the building s original architectural considerations. Deflection criteria remained the same as used in the original design. Service live load deflections were limited to L/360 while total service live plus dead load deflections were limited to L/240. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LATERAL FRAME UPDATE 19
26 METHODS, TOOLS, & RESOURCES Loads Lateral loads were determined for the redesign according to the 2002 Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, as referenced by the 2003 IBC. See Structural System Redesign: Load Calculations for details. Frame Configurations North-South Frame Configuration 1 An effort was made to eliminate the costly moment connections in the North-South frames. Due to architectural considerations, the bracing configuration of the center bay remained unchanged. Also, additional bracing was not considered because the members would infringe upon the open office spaces vital to the function of the building. The resulting frame configuration is shown in Figure 11. Figure 11: Typical Frame North-South Frame Configuration 2 The second frame configuration utilizes the same configuration as in the original design. While this frame contains moment connections, it does reduce the system s torsional sensitivity. This typical frame can be seen in Figure 12. Figure 12: Typical Frame STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LATERAL FRAME UPDATE 20
27 East-West Frame Configuration Finally, the configuration of the East-West frames remained unchanged from the original design. The braced frame efficiently resists lateral loads without interfering with architectural considerations. This typical frame can be seen in Figure 13. Design Procedure Each frame was first designed to satisfy strength requirements using RAM Frame. Next, member sizes were increased in order to satisfy drift requirements. The computer design was then verified using approximate hand calculations. LATERAL SYSTEM REDESIGN Figure 13: Typical Frame North-South Frame Configuration 1 Under the increased wind loads given in ASCE 7-02, very large members were needed to control the drift of the building in the North-South direction. In fact, the weight of steel for this design is approximately four times that of the original design. Resulting story drifts and corresponding drift limits can be seen in Appendix A.4. While the extremely large increase in steel poses a high cost for updating the lateral system to resist larger wind loads, some of this cost is offset by the elimination of moment connections. While connections account for a very small percentage of the weight of a steel structure, they account for a large portion of the cost. North-South Frame Configuration 2 The redesign of the existing lateral frame configuration to resist the higher loads referenced by current building codes results in a very large increase in the amount of steel needed for the lateral system. The quantity of steel needed for this configuration is very comparable to the quantity needed for Configuration 1. Additionally, Configuration 2 does not eliminate the moment connections, as does Configuration 1. Consequently, Configuration 2 will be much more uneconomical, and will therefore be eliminated as an alternate lateral system. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LATERAL FRAME UPDATE 21
28 East-West Frame Configuration The original bracing configuration was used in the redesign of the East-West frames. The most significant changes come from replacing the HSS brace members to W-shapes. Member sizes were designed to meet strength requirements and then increased in order to limit drifting to H/400 under the larger design loads. The resulting story drifts and corresponding drift limits can be seen in Appendix A.5. CONCLUSIONS: LATERAL SYSTEM REDESIGN The lateral system redesign of Market Square Plaza demonstrates the impact of recent code changes involving lateral loads. The changes given in ASCE 7-02 are most severe for this building. Not only has the design wind speed been increased from 70 mph to 90 mph, but the building must also be placed in a more severe Site Exposure Category. The redesign of the lateral system results in a staggering material cost increase of nearly $120,000. However, due to the elimination of moment connections and the redesign of bracing connections, much of this material cost will be offset. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: LATERAL FRAME UPDATE 22
29 STRUCTURAL REDESIGN: CONNECTION OPTIMIZATION
30 EXISTING CONNECTION DESIGN Moment Connections In the original design of Market Square Plaza, 72 moment connections exist in each of the North-South lateral resisting frames for a total of 144 moment connections. While moment frames are efficient at resisting lateral loads in terms of weight of steel required, moment connections come at a high price. Therefore, in the redesign of Market Square Plaza s lateral system, the moment connections were removed. While the resulting braced frame resulted in a large increase in the amount of steel, a considerable amount of this cost can be regained by eliminating the moment connections. M Backing Bar Stiffener Plates W27x84 Typ. Figure 14: Existing Moment Connection A typical moment connection is shown above in Figure 14. A beveled groove weld is used to connect the girder flanges to the column. Additionally, full depth stiffener plates prevent column side failures such as web yielding, web crippling, local flange bending, and web buckling. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: CONNECTION OPTIMIZATION 23
31 Bracing Connections A typical existing bracing connection can be seen below in Figure 15. Double angles along with bolts and welds attach the gusset plates to the beams and column as shown. A slot is cut in the HSS member to accommodate the gusset plate. Then, fillet welds are installed on each side to affix the member to the gusset plate. Typ Double Angles Connection Plate HSS Figure 15: Existing Bracing Connection Each frame in the East-West direction contains 78 bracing connections, while each of the North-South frames contain 72, for a total of 300 bracing connections in the entire lateral system. With such a large number of connections, changes which produce small savings per connection can produce a significant reduction in cost. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: CONNECTION OPTIMIZATION 24
32 CONNECTION REDESIGN The configuration of the existing bracing connections results in high labor costs associated with field welding. Therefore, in an effort to reduce costs, the HSS members were redesigned as W-shapes so that faster and cheaper bolted connections could be utilized. The reconfigured bracing connections use plates and double angles to connect the braces to the gusset plates using bolts as shown below in Figure Angles 2 plates Figure 16: Reconfigured Bracing Connection CONCLUSIONS: CONNECTION REDESIGN While connections only account for a small percentage of a steel structure s weight, they can contribute to a large amount of the structure s cost. Therefore, by reducing the cost of the connections considerable savings can be produced. It is recommended that the Market Square Plaza s moment connections are eliminated and the welded HSS brace connections are converted to bolted W- shape connections. While these result in larger steel members and consequent costs, the connections changes can save a sizeable amount of money. STRUCTURAL SYSTEM REDESIGN: CONNECTION OPTIMIZATION 25
33 BUILDING ENCLOSURE STUDY: PRECAST PANEL REDESIGN
34 EXISTING BUILDING ENCLOSURE Market Square Plaza s existing building enclosure consists primarily of nonloadbearing precast concrete panels. The 7 thick precast panels were chosen primarily for the system s economy, durability, and quick erection. A variety of finishing techniques such as sandblast finishing, colors, and reveals were used to create architectural interest. Also, openings in the panels were in-filled with an aluminum and glass window system. The majority of the panels span from floor to floor with two combination bearing/tieback connections affixing them to the buildings exterior columns. Three additional tieback connections provide further attachment to both the columns and the concrete slabs. Some of the largest panels had to be cast with recessed areas in order to lighten the panel so that it could be lifted into place with a crane. Finally, a secondary building enclosure system, an aluminum and glass curtain wall, was utilized on the first two levels of the southwest quadrant. REDESIGN CRITERIA The redesign of Market Square Plaza s building enclosure focused on the primary enclosure system, the precast concrete panels. The aim of the redesign was to increase the quality of the system while maintaining or reducing the cost of the system. The following factors were desired in the new system: Maintain or decrease the overall initial cost of the system. Maintain fast erection. Increase durability and quality while maintaining architectural considerations. Lower long term costs by increasing insulation values. Reduce the weight of the system. BUILDING ENLCOSURE STUDY: PRECAST PANEL REDESIGN 26
35 BUILDING ENCLOSURE REDESIGN A new building enclosure was selected based on research and recommendations made by industry professionals. However, a detailed design was not performed due to the specialized nature of the selected product. Carbon fiber reinforced concrete panels, a new building enclosure system, has recently emerged into the building market. Carbon fiber reinforced panels have the advantages of traditional precast panels while improving upon many of the disadvantages. While carbon fiber reinforced panels are still new to the building industry, the product has been developed and rigorously tested to ensure high long-term performance. Additionally, over 20 million square feet of panels was sold during the first eight months of the products introduction by AltusGroup, Inc. The panels have thus far met or exceeded testing expectations in the field. Carbon fiber reinforced concrete panels utilize epoxy-coated carbon fiber reinforcing in place of the secondary steel reinforcement. The carbon fiber used in this application is non-corrosive and has a tensile strength of approximately six times that of steel. The carbon fiber forms a superior bond with the concrete, requiring only ¼ of concrete cover. Therefore, lighter panels can be manufactured. CarbonCast, a carbon fiber reinforced panel suitable for this application, is manufactured by AltusGroup, Inc., a group of precast manufacturers who have united in order to promote the product. A typical panel section is shown in Figure 17. According to its manufacturer, AltusGroup, Inc., this panel can be used for walls up to 15 feet high and 40 feet long or more, well within the scope of this project. BUILDING ENLCOSURE STUDY: PRECAST PANEL REDESIGN 27
36 Foam Structural or Architectural Concrete Carbon Fiber Shear Grid Rebar 7" Carbon Fiber Grid Reinforcement Architectural Concrete Figure 17: Typical CarbonCast Section BUILDING ENCLOSURE REDESIGN EVALUATION The suitability of any building system for a project in determined by three factors: cost, quality, and time. Therefore, the carbon fiber reinforced concrete panel enclosure was evaluated based on these factors. Cost Carbon fiber reinforced panels can be manufactured up to 66 percent lighter than traditional precast panels, allowing for lighter supporting members and subsequent cost savings. Lighter panels reduce shipping costs. Additionally, High Concrete Structures, a manufacturer of carbon fiber reinforced panels, is located approximately 50 miles from Market Square Plaza. Architectural Precast, LLC, the project s precast panel manufacturer is also located 50 miles from the project site. Therefore, no additional travel distance is required, and because the carbon fiber reinforced panels are lighter, transportation costs will be reduced. Recent advancements in the manufacturing of carbon fiber products have made carbon fiber an economical means of reinforcing. Because the reinforcing steel is thermally separated, higher insulation values of R-8 to R-13 can be produced, resulting in energy savings. Finally, although carbon fiber reinforced panels are slightly more expensive to produce than traditional precast panels, the cost can be offset by savings on shipping costs, a lighter supporting structure, and energy savings over time. BUILDING ENLCOSURE STUDY: PRECAST PANEL REDESIGN 28
37 Quality Carbon fiber reinforcing is non-corrosive, eliminating problems such as rusting, spalling, and staining which can occur with steel reinforcing. Carbon fiber reinforcement produces a superior bond with concrete, better controlling shrinkage cracking by up to 50%, as compared with traditional precast concrete. Architectural precast finishes such as brick insets, colors, textures, reveals, and other details can also be produced with carbon fiber reinforced panels. The same high level of quality control associated with precast concrete is also associated with carbon fiber reinforced panels. Time Because carbon fiber reinforced panels are manufactured using very similar procedures to traditional precast panels, lead times remain the same as with in the original design. The same erection procedures exist for carbon fiber reinforced panels as for traditional precast panels. Therefore, no changes are needed in the construction schedule Below, Figure 18 summarizes how CarbonCast compares to other building enclosure systems. Figure 18: How CarbonCast Compares (from 1 ) BUILDING ENLCOSURE STUDY: PRECAST PANEL REDESIGN 29
38 CONCLUSIONS: BUILDING ENCLOSURE REDESIGN Carbon fiber reinforced concrete panels have recently entered the building industry as an alternative to traditional precast concrete panels. Because carbon fiber reinforcement requires only ¼ of concrete cover, lighter panels can be designed while eliminating problems such as concrete spalling and rust stains. While carbon fiber reinforced panels can cost slightly more, this cost is outweighed by lower shipping charges, reduced supporting structure weights, and energy savings resulting from higher insulation values. While carbon fiber reinforced panels are a new product, the system has undergone much testing. Additionally, installed panels are performing as predicted by testing. Therefore, because of the savings associated with the lower panel weights and better insulation values, it is recommended that carbon fiber reinforced concrete panels are a suitable alternative to the existing precast concrete panels for Market Square Plaza. BUILDING ENLCOSURE STUDY: PRECAST PANEL REDESIGN 30
39 CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT EVALUATION BUDGET & SCHEDULE
40 GRAVITY SYSTEM REDESIGN EVALUATION Budget In order to evaluate the changes made to the gravity system, cost information was taken from various sources. Recommendations from the American Institute of Steel Construction were used to estimate steel material costs. Steel W-shape material costs were estimated at $500/ton, and each shear stud was taken as equivalent to 10 pounds of steel, or $2.50 each. Also, cambering was approximated at $50 per beam. In order to approximate the change to a heavier gauge of composite metal decking in the office floors, values were estimated using R.S. Means The change from 20 gauge to 19 gauge decking resulted in a change of $0.21 per square foot. R.S. Means was also used to estimate the labor savings involved in the elimination of one beam per bay. Overall, the gravity system redesign resulted in a cost savings of approximately $60,400. A summary of the cost differences between the original design and the redesign of the gravity system is shown below in Table 1. Note that a negative value represents a reduction in material or cost. Cost Differences: Gravity Framing Redesign Level Beams (lb) Decking (sf) Cambered Beams Shear Studs 2nd Floor rd Floor No Change Parking Levels (8) No Change Office Levels (8) Total Unit Costs $570/ton $.21/sf difference $50/beam $2.50/stud Material Cost -$48,535 $31,743 $21,850 $705 Erection Cost $777/ton lb -$66,161 Total Cost Difference: -$60,400 Table 1: Gravity Redesign Estimate Summary CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT EVALUATION: BUDGET & SCHEDULE 31
41 Schedule The changes made to Market Square Plaza s gravity system result in an overall improvement of the construction schedule. By eliminating one beam per bay, or approximately 255 beams, time can be saved during steel erection. Because the steel structure is on the critical path, this schedule reduction is noteworthy. LATERAL SYSTEM REDESIGN EVALUATION Budget In estimating the cost implications of the lateral system redesign, steel material costs were determined using values given by the American Institute of Steel Construction. Additionally, the cost of the moment connections was estimated at $400 per connection based on recommendations given by industry professionals. Estimates for the reconfigured bolted W-shape braces connections, as compared with the original HSS welded brace connections, were not able to be obtained. In general, bolted connections are assumed to be less expensive than field welded connections. However, in this case the two can not easily be compared because the design forces are not equal due to the loading increases. While the bolted connections are generally cheaper, they must resist higher loads. Therefore, for the purposes of this evaluation the two connections will be considered at equal cost. In all, updating the lateral system to resist the higher loads dictated by the most recent codes results in an increase of approximately $61,700. Cost Differences: Lateral Framing Redesign Member Orginal Design (lb) Redesign (lb) Unit Cost ($/ton) Cost Difference Columns $570 $409 Beams $570 $55,769 HSS Braces $700 -$67,137 W-Shape Braces $570 $130,296 Moment Connections $400 each -$57,600 Total Cost Difference: $61,700 Table 2: Lateral Redesign Estimate Summary CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT EVALUATION: BUDGET & SCHEDULE 32
42 Schedule The lateral system redesign will also reduce the critical path of the construction schedule. The redesign does not change the number of members which need to be erected. However, it does eliminate time-consuming moment connections. Additionally, replacing the welded bracing connections with bolted connections will further increase the time savings. CONCLUSIONS: CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT EVALUATION In all, the redesign of Market Square Plaza s gravity and lateral systems adds very little cost to the structure. The quality of the structure has been improved by redesigning to resist increased lateral loads as specified by the latest design codes. While the new lateral system s cost is approximately $61,700 more than the original, the majority of this cost has been recovered by changing the floor framing configurations, saving $60,400. In addition to increasing the quality of the structure with very little increase in cost, the redesign of the structural system also improves the construction schedule. Fewer beams per bay results in fewer members which must be erected, thus condensing the schedule. Finally, additional time is saved by eliminating the moment connections and converting the welded bracing connections to bolted connections. CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT EVALUATION: BUDGET & SCHEDULE 33
43 CONCLUSIONS, REFERENCES, & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
44 CONCLUSIONS Market Square Plaza is an 18 story, multi-use parking/office building currently under construction in downtown Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. At approximately 240 tall, Market Square Plaza will be the second tallest building in the city. The building is approximately 105 by 160 and will provide about 270,000 square feet of space. First, the building s composite steel floor framing system was economically reconfigured. One beam per bay was eliminated, and levels of composite action and camber were selected based on the most economical configuration. The floor framing redesign would save approximately $60,400 and also condense the schedule because fewer members would need to be erected. Secondly, Market Square Plaza was designed according to the 1996 BOCA Building Code. However, upon analysis of the building, according to the most recent design code, IBC 2003, it was found that significant changes have been made to the lateral loads in recent publications. Therefore, Market Square Plaza s lateral system was redesigned to meet the most current codes. In addition to updating the lateral system to resist larger lateral loads, the North- South frames were also reconfigured to eliminate costly moment connections. The bracing members in all frames were redesigned as W-shapes instead of the original HSS members in order to allow for bolted bracing connections in place of the existing field welded bracing connections. The cost of updating the lateral system is estimated at $61,700 and also allows for a reduction of the construction schedule. Finally, carbon fiber reinforced concrete panels were selected to replace the buildings traditional precast panel enclosure. The carbon fiber reinforced panels maintain the benefits of precast concrete such as high quality control, fast erection, and low cost, while improving upon some of precast concrete s disadvantages. The carbon fiber reinforced panels are lighter, have better insulating properties, and are more resistant to staining, spalling, and cracking. CONCLUSIONS 34
45 REFERENCES Building Enclosures 1. A New Partnership. An Innovation in Precast Concrete Technology. AltusGroup, Inc The website of the leading group of carbon fiber reinforced concrete manufactures provides information and links to articles regarding these products. 2. Graziano, Gary and Ken Baur. Carbon Fiber Takes Precast to a New Level. The Construction Specifier. May 2004: The article provides details regarding the design and application of carbon fiber reinforced concrete products. 3. Innovation in Building Envelopes and Environmental Systems. Harvard Design School. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. < The website provides links and information about building envelope systems. It was used to research and evaluate alternative building enclosures. 14. Klemens, Tom. Carbon Fiber Reinforcement Requires Less Cover. Concrete Construction. April 2004: 52. The article summarizes the benefits of using carbon fiber reinforcing in conrete. Design Codes & Design Aids 5. International Building Code. Falls Church, VA: The International Code Council, Manual of Steel Construction. Load and Resistance Factor Design, Third Edition. Chicago, IL: American Institute of Steel Construction, Inc., Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers, REFERENCES 35
46 8. Steel Roof and Floor Deck. Vulcraft, The above design codes and aids were used as a guide and reference in the redesign of Market Square Plaza s structural and enclosure components. Economical Steel Design 19. Carter, Charles J, Thomas M. Murray, and William A. Thornton. Economy in Steel. Modern Steel Construction. April The article contains a wealth of ideas and recommendations for producing economical steel structures. 10. Eckmann, David E. Column-Free Office Space Rises In Chicago s Loop. Modern Steel Construction. April The article describes methods used to produce an economical 18-story steel office building in Chicago. Because this building is very similar in size and function to Market Square Plaza, many of the same design methods and goals could be utilized. 11. Steel Solutions Center. American Institute of Steel Construction, Inc The website contains tools, resources, and information which can be used to produce economical and innovative steel designs. Additional Resources 12. Means Building Construction Cost Data. Kingston, MA. R.S. Means Company, The reference provided a resource for estimating changes. REFERENCES 36
47 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I would like to thank everyone who has helped make this thesis project possible. Special recognition is given to the following people who have answered questions, given recommendations, and provided resources. Faculty Consultant M. Kevin Parfitt Industry Sponsors Mike Fry Murray Associates Architects, PC G.R. Sponaugle & Sons Industry Consultants High Concrete Structures Charlie Carter American Institute of Steel Construction ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS 37
48 APPENDIX: CALCULATIONS & RESULTS SUMMARY
49 ROOF SNOW LOAD CALCULATIONS Terrain Category B C e = C t = I = 1.0 p g =30 psf p f =(.7)(C e )(C t )(I)(P g ) = (.7)(1.0)(1.0)(1.0)(30) = 21 psf Rain on snow surcharge=5psf Drifts on Lower Roof Leeward h d =1.5 controls w=4(h d )=6 γ=(.13)(21)+14=16.7 p d= (h d )( γ )=(1.5)(16.7)=25psf Windward h d =1.125 Drift surcharge of 25 psf reducing linearly to 0 at 6 WIND LOAD CALCULATIONS Basic Wind Speed, V = 90 mph Wind Directionality Factor, K d =.85 Importance Factor, I = 1.0 (Category II) Velocity Pressure Exposure Coefficient, K z Exposure B, Case 2 Topographic Factor, Kzt = 1.0 q z = K z K zt K d V 2 I p = qgc p -q i (GC pi ) Rigid Structure, G =.85 C p =.8 GC pi =.18 q h = APPENDIX: z (ft) K z q z (psf) CALCULATIONS & RESULTS SUMMARY A.1
50 Wind Direction L B L/B C p (leeward) North-South East-West Table A.2 North-South Wind Pressures Story Elevation (ft) Elev. Ref 0 Lower H Upper H Trib Height p wind (lb/ft) p lee (lb/ft) p (lb/ft) P (k) Ground Roof EMR EMR Roof Table A.3 East-West Wind Pressures (X-Bracing) Story Elevation (ft) Elev. Ref 0 Lower H Upper H Trib Height p wind (lb/ft) p lee (lb/ft) p (lb/ft) P (k) Ground Roof EMR EMR Roof Table A.4 APPENDIX: CALCULATIONS & RESULTS SUMMARY A.2
51 SEISMIC LOAD CALCULATIONS Category II Structure Seismic Use Group I Occupancy Importance Factor, I = 1.0 Site Class B Site Coefficients, F a = 1.0, F v = s Spectral Response Acceleration = 7.5%g.2s = 20%g S 1 =.075, S s =.2 S MS = F a S s = (1.0)(.2) =.2 S M1 = F v S 1 = (1.0)(.075) =.075 S DS = 2/3 S MS = (2/3)(.2) =.133 S D1 = 2/3 S M1 = (2/3)(.075) =.05 Use Equivalent Lateral Force Procedure Seismic Base Shear, V = CsW Seismic Design Category B R = 5 ρ = 1.0 C s = S DS /(R/I) =.133/(5/1.0) =.0267 S D1 /(RT/I E ) =.05/((5)(1.22/1) =.0082 Controls.044 S DS I E = (.044)(.133)(1.0) = Building Period, T a = C t h n x = (.02)(240).75 = 1.22 APPENDIX: CALCULATIONS & RESULTS SUMMARY A.3
52 Seismic Story Forces C s = V = Level Weight Height k w x h x C vx F i (k) Ground Roof EMR EMR Roof Table A.5 DRIFT RESULTS North-South Direction Level Height (ft) Story Height (ft) Drift (in) Relative Drift (in) Drift Limit (in) Roof Table A.7 APPENDIX: CALCULATIONS & RESULTS SUMMARY A.4
OVERALL STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The at the Pittsburgh International Airport, PA, is a 275,000 square foot multi-use building located directly adjacent to the airport s landside terminal. The building consists of an
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The at the Pittsburgh International Airport, PA, is a 275,000 square foot multi-use building located directly adjacent to the airport s landside terminal. The building consists of an
William W. Wilkins Professional Building Columbus, Ohio
 William W. Wilkins Professional Building Columbus, Ohio Technical Assignment 1 October 5, 2006 Michelle Structural Option AE 481W Senior Thesis Faculty Advisor: Dr. Boothby Table of Contents Executive
William W. Wilkins Professional Building Columbus, Ohio Technical Assignment 1 October 5, 2006 Michelle Structural Option AE 481W Senior Thesis Faculty Advisor: Dr. Boothby Table of Contents Executive
[TECHNICAL REPORT 3] Lateral System Analysis
![[TECHNICAL REPORT 3] Lateral System Analysis [TECHNICAL REPORT 3] Lateral System Analysis](/thumbs/96/126531717.jpg) Science Center Research Park 3711 Market St. The Pennsylvania State University Department of Architectural Engineering Senior Thesis 2009-2010 Prepared by: November 30, 2009 [TECHNICAL REPORT 3] Lateral
Science Center Research Park 3711 Market St. The Pennsylvania State University Department of Architectural Engineering Senior Thesis 2009-2010 Prepared by: November 30, 2009 [TECHNICAL REPORT 3] Lateral
TECHNICAL REPORT 1. Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions. Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital. Hershey, Pennsylvania
 TECHNICAL REPORT 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital Matthew V Vandersall The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering
TECHNICAL REPORT 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital Matthew V Vandersall The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering
MOUNTAIN STATE BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD HEADQUARTERS
 MOUNTAIN STATE BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD HEADQUARTERS PARKERSBURG, WEST VIRGINIA DOMINIC MANNO STRUCTURAL OPTION FACULTY CONSULTANT: DR. ANDRES LEPAGE Technical Report 3 11-21-08 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF
MOUNTAIN STATE BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD HEADQUARTERS PARKERSBURG, WEST VIRGINIA DOMINIC MANNO STRUCTURAL OPTION FACULTY CONSULTANT: DR. ANDRES LEPAGE Technical Report 3 11-21-08 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF
STRUCTURAL TECHNICAL REPORT 1
 Technical Report 1 Page 1 David Lee AE 481W Structural Option Advisor: Andres Lepage URS Office Building October 5, 2006 STRUCTURAL TECHNICAL REPORT 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions
Technical Report 1 Page 1 David Lee AE 481W Structural Option Advisor: Andres Lepage URS Office Building October 5, 2006 STRUCTURAL TECHNICAL REPORT 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions
Technical Report #2. Matthew R Peyton
 Technical Report #2 This Document is Technical Report #2 for 5th year senior thesis in the Architectural Engineering Departments at The Pennsylvania State University. This Report is to prepare a study
Technical Report #2 This Document is Technical Report #2 for 5th year senior thesis in the Architectural Engineering Departments at The Pennsylvania State University. This Report is to prepare a study
Technical Report #1. Matthew R Peyton
 Technical Report #1 This Document is Technical Report #1 for 5th year senior thesis in the Architectural Engineering Departments at The Pennsylvania State University. This Report will include structural
Technical Report #1 This Document is Technical Report #1 for 5th year senior thesis in the Architectural Engineering Departments at The Pennsylvania State University. This Report will include structural
Brent Ellmann Structural Option 200 Minuteman Park, Andover, MA Structural Consultant: Dr. Hanagan
 Brief Building Overview: 200 Minuteman Park stands as a 200,000 square foot Class A office building in Andover, Massachusetts, worth roughly $15,000,000. Although the building has a large square footage,
Brief Building Overview: 200 Minuteman Park stands as a 200,000 square foot Class A office building in Andover, Massachusetts, worth roughly $15,000,000. Although the building has a large square footage,
Rutgers University Law School Building Addition and Renovation Camden, NJ
 Building Addition and Renovation Camden, NJ Technical Assignment 1 October 5, 2007 Nathan E. Reynolds Structural Option Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Consultant: Professor M.
Building Addition and Renovation Camden, NJ Technical Assignment 1 October 5, 2007 Nathan E. Reynolds Structural Option Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Consultant: Professor M.
Technical Assignment 3 December 3, 2007
 Technical Assignment 3 December 3, 2007 101 Eola Drive, Orlando, FL Justin Raducha Pennsylvania State University Faculty Advisor: M. Kevin Parfitt Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Executive Summary...
Technical Assignment 3 December 3, 2007 101 Eola Drive, Orlando, FL Justin Raducha Pennsylvania State University Faculty Advisor: M. Kevin Parfitt Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Executive Summary...
Structural Redesign Gravity System
 Redesign Gravity System Design Considerations A composite floor system was used for this design to maximize the efficiency of the material being used. This type of system requires less material and provides
Redesign Gravity System Design Considerations A composite floor system was used for this design to maximize the efficiency of the material being used. This type of system requires less material and provides
1000 CONTINENTAL SQUARE
 1000 CONTINENTAL SQUARE KING OF PRUSSIA, PENNSYLVANIA Carter Davis Hayes Structural Option January 13, 2008 Advisor: Dr. Hanagan TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 I. STRUCTURAL
1000 CONTINENTAL SQUARE KING OF PRUSSIA, PENNSYLVANIA Carter Davis Hayes Structural Option January 13, 2008 Advisor: Dr. Hanagan TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 I. STRUCTURAL
Danielle Shetler - Structural option Courtyard by Marriott Lancaster, PA
 Structural Analysis Overview: During the structural analysis of the in Lancaster, Pa, a redesign of the lateral and gravity system from masonry bearing and shear walls to a staggered truss system was performed.
Structural Analysis Overview: During the structural analysis of the in Lancaster, Pa, a redesign of the lateral and gravity system from masonry bearing and shear walls to a staggered truss system was performed.
Crossroads at Westfields Building II
 Crossroads at Westfields Building II Chantilly, Va STEPHEN LUMPP Structural option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Andres Lepage Technical Report 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report is a study of alternate floor systems
Crossroads at Westfields Building II Chantilly, Va STEPHEN LUMPP Structural option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Andres Lepage Technical Report 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report is a study of alternate floor systems
Structural Technical Report #2 Pro/Con Study of Alternate Floor Systems
 Christopher McCune Structural Option Eight Tower Bridge Faculty Advisor: Dr. Hanagan October 31 st, 2005 Structural Technical Report #2 Pro/Con Study of Alternate Floor Systems Executive Summary This technical
Christopher McCune Structural Option Eight Tower Bridge Faculty Advisor: Dr. Hanagan October 31 st, 2005 Structural Technical Report #2 Pro/Con Study of Alternate Floor Systems Executive Summary This technical
Table of Contents.2. Introduction...3 Gravity Loading and Deflections..4. Existing Structural System..8
 WISCONSIN PLACE RESIDENTIAL TECHNICAL ASSIGNMENT 2 OCTOBER 29, 2007 KURT KRASAVAGE THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY STRUCTURAL OPTION FACULTY ADVISOR: DR. ALI MEMARI 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents.2
WISCONSIN PLACE RESIDENTIAL TECHNICAL ASSIGNMENT 2 OCTOBER 29, 2007 KURT KRASAVAGE THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY STRUCTURAL OPTION FACULTY ADVISOR: DR. ALI MEMARI 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents.2
Technical Report #1. Indiana Regional Medical Center Indiana, PA. Cody A. Scheller. Structural Concepts & Existing Conditions Report
 Technical Report #1 Technical Report #1 Structural Concepts & Existing Conditions Report Indiana Regional Medical Center Cody A. Scheller The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Faculty
Technical Report #1 Technical Report #1 Structural Concepts & Existing Conditions Report Indiana Regional Medical Center Cody A. Scheller The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Faculty
HIGH RISE CONDO SOHO, NEW YORK, NY
 HIGH RISE CONDO SOHO, NEW YORK, NY TECHNICAL ASSIGNMENT 1 October 5, 2006 Joseph The Pennsylvania State University Structural Option Faculty Advisor: Andres Lepage TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 2
HIGH RISE CONDO SOHO, NEW YORK, NY TECHNICAL ASSIGNMENT 1 October 5, 2006 Joseph The Pennsylvania State University Structural Option Faculty Advisor: Andres Lepage TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 2
Best Buy Corporate Building D (4) Richfield, MN
 Best Buy Corporate Building D (4) Thesis Proposal Professor Boothby December 12 th, 2008 Executive Summary: The Best Buy Corporate Building D is a 6 story building with a total area of 304,610 square feet.
Best Buy Corporate Building D (4) Thesis Proposal Professor Boothby December 12 th, 2008 Executive Summary: The Best Buy Corporate Building D is a 6 story building with a total area of 304,610 square feet.
Southwest Housing, Arizona State University
 Prepared by KSENIA TRETIAKOVA Structural Option 01.09.2012 Architectural Engineering Pennsylvania State University 2012 Southwest Housing, Arizona State University Technical Report #3 Lateral System 01.09.2012
Prepared by KSENIA TRETIAKOVA Structural Option 01.09.2012 Architectural Engineering Pennsylvania State University 2012 Southwest Housing, Arizona State University Technical Report #3 Lateral System 01.09.2012
ECMC Skilled Nursing Facility
 ECMC Skilled Nursing Facility 462 Grider Street Buffalo, NY 14215 Brian Brunnet Structural Option AE 482 Senior Thesis Dr. Ali Memari Presentation Outline Project Background Building Statistics: Location:
ECMC Skilled Nursing Facility 462 Grider Street Buffalo, NY 14215 Brian Brunnet Structural Option AE 482 Senior Thesis Dr. Ali Memari Presentation Outline Project Background Building Statistics: Location:
Temecula Medical Center Temecula, CA
 Temecula Medical Center Temecula, CA Technical Assignment #2 Sean F. Beville The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Structural Option Senior Thesis Project Student Advisor: Thomas
Temecula Medical Center Temecula, CA Technical Assignment #2 Sean F. Beville The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Structural Option Senior Thesis Project Student Advisor: Thomas
Technical Report #3. Matthew R Peyton
 Technical Report #3 This Document is Technical Report #3 for 5th year senior thesis in the Architectural Engineering Departments at The Pennsylvania State University. In this report the existing reinforced
Technical Report #3 This Document is Technical Report #3 for 5th year senior thesis in the Architectural Engineering Departments at The Pennsylvania State University. In this report the existing reinforced
North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building
 North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building Phoenix, Arizona Michael Hopple Technical Assignment 2 October 29 th, 2007 AE 481W-Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Adviser: Dr. Ali Memari,
North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building Phoenix, Arizona Michael Hopple Technical Assignment 2 October 29 th, 2007 AE 481W-Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Adviser: Dr. Ali Memari,
Technical Report 1. Kingstowne Section 36A 5680 King Center Drive Kingstowne, VA James Chavanic. Structural Option. Advisor: Dr.
 Technical Report 1 Rendering provided by DCS Design 5680 King Center Drive Kingstowne, VA 22315 Advisor: Dr. Boothby September 17, 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary 3 Building Introduction 4 Structural
Technical Report 1 Rendering provided by DCS Design 5680 King Center Drive Kingstowne, VA 22315 Advisor: Dr. Boothby September 17, 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary 3 Building Introduction 4 Structural
Brent Ellmann Structural Option 200 Minuteman Park, Andover, MA Structural Consultant: Dr. Hanagan
 Structural Design: Goals: The original design of 200 Minuteman Drive was dictated largely by Brickstone Properties, the building s owner. The new design of 200 Minuteman Drive, with additional floors,
Structural Design: Goals: The original design of 200 Minuteman Drive was dictated largely by Brickstone Properties, the building s owner. The new design of 200 Minuteman Drive, with additional floors,
Executive Summary Building Description: Introduction... 13
 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 2 Building Description:... 2 Report Summary:... 2 Introduction... 3 Building Description:... 3 Current Framing Layout... 4 Report Topics:... 4 Loads and Load Cases...
Table of Contents Executive Summary... 2 Building Description:... 2 Report Summary:... 2 Introduction... 3 Building Description:... 3 Current Framing Layout... 4 Report Topics:... 4 Loads and Load Cases...
David A. Walenga Technical Assignment #1
 Executive Summary Contained in this report is design information related to the structural system of the Residence Inn by Marriot located in Stamford, Connecticut. Specifically, this report covers: code
Executive Summary Contained in this report is design information related to the structural system of the Residence Inn by Marriot located in Stamford, Connecticut. Specifically, this report covers: code
John Jay College Expansion Project
 Technical Report #1 Michael Hopper Mike AE Consultant: Dr. Lepage [Type the company name] September 29 th, 2008 Technical Report #1 Table of Contents Executive Summary.3 Introduction.4 Structural System.6
Technical Report #1 Michael Hopper Mike AE Consultant: Dr. Lepage [Type the company name] September 29 th, 2008 Technical Report #1 Table of Contents Executive Summary.3 Introduction.4 Structural System.6
North Shore at Canton Baltimore, MD Beau Menard Technical Report 1
 North Shore at Canton Baltimore, MD Beau Menard Technical Report 1 Structural Schneider 10/05/05 Structural Concepts Executive Summary North Shore at Canton is a 4 story town home and parking garage structure
North Shore at Canton Baltimore, MD Beau Menard Technical Report 1 Structural Schneider 10/05/05 Structural Concepts Executive Summary North Shore at Canton is a 4 story town home and parking garage structure
Dead Loads (psf): Concrete Floor Slab on Metal Deck 45 psf Mechanical and Ceiling 7 psf Miscellaneous 5 psf Exterior Wall 80 psf
 CODES AND REQUIREMENTS The structural design of Northbrook Corporate Center was based on the International Building Code 2003, which incorporates many of the provisions of ASCE 7. The lateral load design
CODES AND REQUIREMENTS The structural design of Northbrook Corporate Center was based on the International Building Code 2003, which incorporates many of the provisions of ASCE 7. The lateral load design
Technical Report 1. Seneca Allegany Casino Hotel Addition. Salamanca, NY
 Technical Report 1 Seneca Allegany Casino Hotel Addition Salamanca, NY Nicholas Reed Structural Option Advisor: Prof. Parfitt Executive Summary The purpose of this technical report was to analyze the existing
Technical Report 1 Seneca Allegany Casino Hotel Addition Salamanca, NY Nicholas Reed Structural Option Advisor: Prof. Parfitt Executive Summary The purpose of this technical report was to analyze the existing
Table of Contents 2. Structural Systems.4 Foundations.4 Floor System...4 Columns..5 Lateral System...5
 WISCONSIN PLACE RESIDENTIAL TECHNICAL ASSIGNMENT 1 OCTOBER 5, 2007 KURT KRASAVAGE THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY STRUCTURAL OPTION FACULTY ADVISOR: DR. ALI MEMARI Table of Contents Table of Contents
WISCONSIN PLACE RESIDENTIAL TECHNICAL ASSIGNMENT 1 OCTOBER 5, 2007 KURT KRASAVAGE THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY STRUCTURAL OPTION FACULTY ADVISOR: DR. ALI MEMARI Table of Contents Table of Contents
Global Village Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester, New York
 Presentation Outline Welcome Introduction Architecture Existing Structure Problem Statement Arch. Breadth Structural Depth Conclusion Questions Global Village Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester,
Presentation Outline Welcome Introduction Architecture Existing Structure Problem Statement Arch. Breadth Structural Depth Conclusion Questions Global Village Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester,
Belmont Executive Center; Building A
 Nicholas L. Ziegler: Structural Advisor: Professor M. Kevin Parfitt December 1, 2009 1 Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Introduction...3 Structural System...4 Foundation System... 4 Column System...
Nicholas L. Ziegler: Structural Advisor: Professor M. Kevin Parfitt December 1, 2009 1 Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Introduction...3 Structural System...4 Foundation System... 4 Column System...
Thesis Proposal 12/13/06
 Photo courtesy of OTO Development, http://www.otodevelopment.com/ Dr. Memari Thesis Advisor Thesis Proposal 12/13/06 Executive Summary Structural System The in, is an eleven story hotel complex which reaches
Photo courtesy of OTO Development, http://www.otodevelopment.com/ Dr. Memari Thesis Advisor Thesis Proposal 12/13/06 Executive Summary Structural System The in, is an eleven story hotel complex which reaches
111 MORGAN ST. Ryan Friis
 Technical Report No. 1 September 30, 2002 Executive Summary: 111 Morgan St. is a 9 story cast-in-place concrete condominium building being constructed in Chicago, Illinois. The building s floor system
Technical Report No. 1 September 30, 2002 Executive Summary: 111 Morgan St. is a 9 story cast-in-place concrete condominium building being constructed in Chicago, Illinois. The building s floor system
Park Potomac Office Building E
 Technical Assignment 1 Kyle Wagner (IP) AE Consultant: Professor Kevin Parfitt October 05, 2009 Table of Contents I. Executive Summary 3 II. Introduction... 4 III. Structural System Overview..... 4 Foundation
Technical Assignment 1 Kyle Wagner (IP) AE Consultant: Professor Kevin Parfitt October 05, 2009 Table of Contents I. Executive Summary 3 II. Introduction... 4 III. Structural System Overview..... 4 Foundation
THE PLAZA AT PPL CENTER HAMILTON BOULEVARD AT 9 TH STREET - ALLENTOWN, PA
 THE PLAZA AT PPL CENTER HAMILTON BOULEVARD AT 9 TH STREET - ALLENTOWN, PA Amy Graver, Structural Option - Dr. Hanagan, Advisor 12.16.2002 THESIS PROPOSAL Executive Summary Architecture The Plaza at PPL
THE PLAZA AT PPL CENTER HAMILTON BOULEVARD AT 9 TH STREET - ALLENTOWN, PA Amy Graver, Structural Option - Dr. Hanagan, Advisor 12.16.2002 THESIS PROPOSAL Executive Summary Architecture The Plaza at PPL
Pro-Con Structural Study for Alternative Floor Systems October 27, 2004
 Ismail Al-Hadhrami Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Thomas Boothby Agricultural Hall and Annex East Lansing, MI Pro-Con Structural Study for Alternative Floor Systems October 27, 2004 Executive
Ismail Al-Hadhrami Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Thomas Boothby Agricultural Hall and Annex East Lansing, MI Pro-Con Structural Study for Alternative Floor Systems October 27, 2004 Executive
Christopher McCune Structural Option 2006 Senior Thesis Penn State Architectural Engineering. Eight Tower Bridge Conshohocken, Pennsylvania
 Christopher McCune Structural Option 2006 Senior Thesis Penn State Architectural Engineering Outline Project Original Proposal Structural Design Proposal Design Objectives Design Criteria Presentation
Christopher McCune Structural Option 2006 Senior Thesis Penn State Architectural Engineering Outline Project Original Proposal Structural Design Proposal Design Objectives Design Criteria Presentation
School of Engineering and Applied Science Building Miami University, Oxford, OH Technical Assignment 3 December 3, 2007
 School of Engineering and Applied Science Building Miami University, Oxford, OH Technical Assignment 3 December 3, 2007 Jonathan Kirk AE 481W Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Advisor:
School of Engineering and Applied Science Building Miami University, Oxford, OH Technical Assignment 3 December 3, 2007 Jonathan Kirk AE 481W Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Advisor:
Structural System. Design Criteria Fire Resistance Concrete designed for 2 HR rating (worst case) Geotechnical Report Allowable Bearing Capacity
 System Codes and Criteria Design Codes and Standards The design code used is the Wisconsin Administrative Code along with the State of Wisconsin Department of Commerce-Safety & Buildings Chapters Comm
System Codes and Criteria Design Codes and Standards The design code used is the Wisconsin Administrative Code along with the State of Wisconsin Department of Commerce-Safety & Buildings Chapters Comm
151 First Side. Technical Assignment 2 November 16 th, William J. Buchko. AE 481w Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University
 November 16 th, 2007 William J. Buchko AE 481w Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Thesis Advisor: Kevin Parfitt Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Structural System Overview Foundation...
November 16 th, 2007 William J. Buchko AE 481w Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Thesis Advisor: Kevin Parfitt Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Structural System Overview Foundation...
LIFE SCIENCES BUILDING STRUCTURAL CONCEPTS AND EXISTING CONDITIONS
 Structural Technical Report 1 LIFE SCIENCES BUILDING STRUCTURAL CONCEPTS AND EXISTING CONDITIONS Prepared for: Dr. Aly M. Said Dr. Thomas Boothby Professor Kevin Parfitt Dr. Charles D. Cox Prepared by:
Structural Technical Report 1 LIFE SCIENCES BUILDING STRUCTURAL CONCEPTS AND EXISTING CONDITIONS Prepared for: Dr. Aly M. Said Dr. Thomas Boothby Professor Kevin Parfitt Dr. Charles D. Cox Prepared by:
Hilton Baltimore Convention Center Hotel Western Podium
 Hilton Baltimore Convention Center Hotel Western Podium CHRIS SIMMONS Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Ali M. Memari Technical Report 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Page 3 INTRODUCTION..
Hilton Baltimore Convention Center Hotel Western Podium CHRIS SIMMONS Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Ali M. Memari Technical Report 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Page 3 INTRODUCTION..
Kevin Wigton Structural Option. Technical Report III. Simmons College School of Management, Boston, Ma
 Kevin Wigton Structural Option Technical Report III Simmons College School of Management, Boston, Ma Advisor: Professor Parfitt 12/1/2009 Table of Contents Executive Summary: Technical Report III... 3
Kevin Wigton Structural Option Technical Report III Simmons College School of Management, Boston, Ma Advisor: Professor Parfitt 12/1/2009 Table of Contents Executive Summary: Technical Report III... 3
Structural Design Engineers 120 Montgomery Street, Suite 1410 San Francisco, California / Fax 415/
 120 Montgomery Street, Suite 1410 San Francisco, California 94104 415/781-1505 Fax 415/781-2718 sde@sdesf.com Rajendra Sahai, SE Principal John W. Laws, SE Principal Steven Lepisto, SE Principal STRUCTURAL
120 Montgomery Street, Suite 1410 San Francisco, California 94104 415/781-1505 Fax 415/781-2718 sde@sdesf.com Rajendra Sahai, SE Principal John W. Laws, SE Principal Steven Lepisto, SE Principal STRUCTURAL
These systems are evaluated on the basis of serviceability issues such as:
 1 Traci Peterson Option: Structural Faculty Consultant: Memari The Del Monte Center at The North Shore Pittsburgh, PA Structural Technical Report 2 Pro Con Structural Study of Alternate Floor Systems Date
1 Traci Peterson Option: Structural Faculty Consultant: Memari The Del Monte Center at The North Shore Pittsburgh, PA Structural Technical Report 2 Pro Con Structural Study of Alternate Floor Systems Date
THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER
 THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER Image courtesy of Gaudreau, Inc. TECHNICAL REPORT #1 OCTOBER 5, 2007 KEENAN YOHE STRUCTURAL OPTION DR. MEMARI FACULTY ADVISOR EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Image courtesy of Gaudreau, Inc.
THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER Image courtesy of Gaudreau, Inc. TECHNICAL REPORT #1 OCTOBER 5, 2007 KEENAN YOHE STRUCTURAL OPTION DR. MEMARI FACULTY ADVISOR EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Image courtesy of Gaudreau, Inc.
REVISED PROPOSAL. University Academic Center. Eastern USA. Alexander Altemose. Structural Option. Advisor: Thomas E. Boothby
 REVISED PROPOSAL University Academic Center Eastern USA Alexander Altemose Structural Option Advisor: Thomas E. Boothby January 11, 2013 Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 Introduction 4 Structural
REVISED PROPOSAL University Academic Center Eastern USA Alexander Altemose Structural Option Advisor: Thomas E. Boothby January 11, 2013 Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 Introduction 4 Structural
Visteon Village Corporate Center
 Visteon Village Corporate Center Van Buren Township, MI Technical Assignment #1 Jamison Morse Structural Option Advisor: Dr. Andres Lapage Jamison Morse Structural Option Visteon Village Center Advisor:
Visteon Village Corporate Center Van Buren Township, MI Technical Assignment #1 Jamison Morse Structural Option Advisor: Dr. Andres Lapage Jamison Morse Structural Option Visteon Village Center Advisor:
Fairfield Inn and Suites Pittsburgh, PA
 Existing Building Information Presentation Outline Construction Management Breadth Study Existing Building Information Location: Downtown Pittsburgh 228 Federal St, Building Statistics: Occupancy - Hotel
Existing Building Information Presentation Outline Construction Management Breadth Study Existing Building Information Location: Downtown Pittsburgh 228 Federal St, Building Statistics: Occupancy - Hotel
Xyston Inn. NY. Proposal. Xiaodong Jiang. Structure Option. Advisor: Dr. Linda Hanagan
 Proposal Xiaodong Jiang Structure Option Advisor: Dr. Linda Hanagan December 12, 2014 Executive Summary Xyston Inn is a 17-story hotel building that will be located in Brooklyn, New York. The design of
Proposal Xiaodong Jiang Structure Option Advisor: Dr. Linda Hanagan December 12, 2014 Executive Summary Xyston Inn is a 17-story hotel building that will be located in Brooklyn, New York. The design of
Xyston Inn. NY. Proposal. Xiaodong Jiang. Structure Option. Advisor: Dr. Linda Hanagan
 Proposal Xiaodong Jiang Structure Option Advisor: Dr. Linda Hanagan December 12, 2014 Executive Summary Xyston Inn is a 17-story hotel building that will be located in Brooklyn, New York. The design of
Proposal Xiaodong Jiang Structure Option Advisor: Dr. Linda Hanagan December 12, 2014 Executive Summary Xyston Inn is a 17-story hotel building that will be located in Brooklyn, New York. The design of
Boyds Bear Country Pigeon Forge, TN
 Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Report Executive Summary:, located in Pigeon Forge, Tennessee, is designed as a multifunctional space and tourist attraction for
Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Report Executive Summary:, located in Pigeon Forge, Tennessee, is designed as a multifunctional space and tourist attraction for
Technical Report #3: Lateral System Analysis. Executive Summary
 ERIC MUELLER STRUCTURAL OPTION ADVISOR DR. LEPAGE AE 481W DECEMBER 19, 2006 555 12 TH STREET OAKLAND, CALIFORNIA Technical Report #3: Lateral System Analysis Executive Summary 555 12 th Street is a 21
ERIC MUELLER STRUCTURAL OPTION ADVISOR DR. LEPAGE AE 481W DECEMBER 19, 2006 555 12 TH STREET OAKLAND, CALIFORNIA Technical Report #3: Lateral System Analysis Executive Summary 555 12 th Street is a 21
Point Pleasant Apartments Point Pleasant, NJ Ryan P. Flynn Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Hanagan
 Point Pleasant Apartments Point Pleasant, NJ Ryan P. Flynn Structural Option Faculty Technical Report #3: Lateral System Analysis and Confirmation Design Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Executive Summary...
Point Pleasant Apartments Point Pleasant, NJ Ryan P. Flynn Structural Option Faculty Technical Report #3: Lateral System Analysis and Confirmation Design Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Executive Summary...
Executive Summary...2 Introduction...3 Structural System Overview Buffalo,...4 Foundation...4 Floor System...4 Gravity System...4 Lateral System...
 Table of Contents University at Buffalo CTRC/Incubator Executive Summary...2 Introduction...3 Structural System Overview Buffalo,...4 New York Foundation...4 Floor System...4 Gravity System...4 Lateral
Table of Contents University at Buffalo CTRC/Incubator Executive Summary...2 Introduction...3 Structural System Overview Buffalo,...4 New York Foundation...4 Floor System...4 Gravity System...4 Lateral
181 Fremont San Francisco, CA. Tech Report 3 10/17/2014. PSUAE Structural Option Advisor: Dr. Thomas Boothby
 181 Fremont San Francisco, CA Tech Report 3 10/17/2014 PSUAE Structural Option Advisor: Dr. Thomas Boothby Caroline Klatman cjk5258@psu.edu October 17, 2014 Dr. Thomas Boothby The Pennsylvania State University
181 Fremont San Francisco, CA Tech Report 3 10/17/2014 PSUAE Structural Option Advisor: Dr. Thomas Boothby Caroline Klatman cjk5258@psu.edu October 17, 2014 Dr. Thomas Boothby The Pennsylvania State University
TECHNICAL REPORT III LATERAL STRUCTURAL SYSTEM ANALYSIS
 TECHNICAL REPORT III LATERAL STRUCTURAL SYSTEM ANALYSIS Chris Vanaskie Structural Peninsula Regional Medical Center Salisbury, MD January 10, 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary... 3 Introduction...
TECHNICAL REPORT III LATERAL STRUCTURAL SYSTEM ANALYSIS Chris Vanaskie Structural Peninsula Regional Medical Center Salisbury, MD January 10, 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary... 3 Introduction...
Franklin Square Hospital Center Patient Tower
 Thomas Weaver Structural Option Franklin Square Hospital Center Patient Tower Baltimore, MD Thomas Weaver Structural Option AE 481W Senior Thesis Consultant: Professor M. Kevin Parfitt 12/14/2009 Page
Thomas Weaver Structural Option Franklin Square Hospital Center Patient Tower Baltimore, MD Thomas Weaver Structural Option AE 481W Senior Thesis Consultant: Professor M. Kevin Parfitt 12/14/2009 Page
90% Design Submittal Structural Calculations Parking Garage CDRL
 NORTH METRO RAIL LINE PROJECT Thornton Crossroads at 104 th Avenue Station 90% Design Submittal Structural Calculations Parking Garage CDRL 03-037.11.06 June 2, 2017 Prepared by: Regional Rail Partners
NORTH METRO RAIL LINE PROJECT Thornton Crossroads at 104 th Avenue Station 90% Design Submittal Structural Calculations Parking Garage CDRL 03-037.11.06 June 2, 2017 Prepared by: Regional Rail Partners
Simplified Building Schematic for Typical Floor (Levels 9 through 22):
 Introduction to Structural System Simplified Building Schematic for Typical Floor (Levels 9 through 22): Key: - Tower Columns - Tower Shear Walls - Parking Garage Columns - Parking Garage Shear Walls Solid
Introduction to Structural System Simplified Building Schematic for Typical Floor (Levels 9 through 22): Key: - Tower Columns - Tower Shear Walls - Parking Garage Columns - Parking Garage Shear Walls Solid
Thesis Proposal. Executive Summary:
 Executive Summary: Thesis Proposal Contained in this report are the following items: Building background related to proposal topics Investigation topics with their proposed solutions Solutions methods
Executive Summary: Thesis Proposal Contained in this report are the following items: Building background related to proposal topics Investigation topics with their proposed solutions Solutions methods
Letter of Transmittal
 Letter of Transmittal November 17, 2014 Ali Said Structural Thesis Advisor The Pennsylvania State University aus59@psu.edu Dear Doctor Said, The following technical report fulfills the fourth Technical
Letter of Transmittal November 17, 2014 Ali Said Structural Thesis Advisor The Pennsylvania State University aus59@psu.edu Dear Doctor Said, The following technical report fulfills the fourth Technical
TECHNICAL REPORT III. University Academic Center. Eastern USA. Alexander Altemose. Structural Option. Advisor: Thomas E. Boothby
 TECHNICAL REPORT III University Academic Center Eastern USA Alexander Altemose Structural Option Advisor: Thomas E. Boothby November 12, 2012 Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 Introduction 4 Structural
TECHNICAL REPORT III University Academic Center Eastern USA Alexander Altemose Structural Option Advisor: Thomas E. Boothby November 12, 2012 Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 Introduction 4 Structural
Stephan Northrop Structural Option Dr. Linda Hanagan. North Shore Equitable Building Pittsburgh, PA Senior Thesis Proposal
 Stephan Northrop NORTHROP THESIS PROPOSAL PAGE - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary.. 3 1. Introduction.. 4 2. Structural Systems.. 5 Foundation.. 5 General Floor Framing.. 6 Turret Framing.. 7 Roof
Stephan Northrop NORTHROP THESIS PROPOSAL PAGE - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary.. 3 1. Introduction.. 4 2. Structural Systems.. 5 Foundation.. 5 General Floor Framing.. 6 Turret Framing.. 7 Roof
Caitlin Ferrell Structural Option Dr. Boothby, AE Faculty Consultant. Erie Convention Center and Sheraton Hotel
 Caitlin Ferrell Structural Option Dr. Boothby, AE Faculty Consultant Erie Convention Center and Sheraton Hotel Erie, Pennsylvania Technical Report #2: Pro-Con Structural Study of Alternate Floor Systems
Caitlin Ferrell Structural Option Dr. Boothby, AE Faculty Consultant Erie Convention Center and Sheraton Hotel Erie, Pennsylvania Technical Report #2: Pro-Con Structural Study of Alternate Floor Systems
WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC COMPANY CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS CRANBERRY, PA
 WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC COMPANY CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS CRANBERRY, PA Technical Assignment 3 November 21, 2008 Advisor: Dr. Linda Hanagan Page 2 of 57 TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 INTRODUCTION...
WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC COMPANY CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS CRANBERRY, PA Technical Assignment 3 November 21, 2008 Advisor: Dr. Linda Hanagan Page 2 of 57 TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 INTRODUCTION...
Hilton Baltimore Convention Center Hotel Western Podium
 Hilton Baltimore Convention Center Hotel Western Podium CHRIS SIMMONS Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Ali M. Memari Technical Report 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Page 3 INTRODUCTION..
Hilton Baltimore Convention Center Hotel Western Podium CHRIS SIMMONS Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Ali M. Memari Technical Report 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Page 3 INTRODUCTION..
Park Potomac Office Building E
 Kyle Wagner (IP) Advisor: Professor Kevin Parfitt 12/11/2009 Table of Contents I. Executive Summary. 3 II. Introduction / Material Strengths. 4 III. Codes and Design Standards.. 5 IV. Existing Structural
Kyle Wagner (IP) Advisor: Professor Kevin Parfitt 12/11/2009 Table of Contents I. Executive Summary. 3 II. Introduction / Material Strengths. 4 III. Codes and Design Standards.. 5 IV. Existing Structural
Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts/ Structural Existing Conditions Report
 Kelly M. Sadusky The Food Science Building Oct. 6, 2004 Professor Parfitt University Park, PA Structural Option Executive Summery: Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts/ Structural Existing
Kelly M. Sadusky The Food Science Building Oct. 6, 2004 Professor Parfitt University Park, PA Structural Option Executive Summery: Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts/ Structural Existing
Project. San Jose City College Physical Education Building. Prepared For. Prepared By PLACE IMAGE HERE. Ken Bauer, AIA Principal
 Project San Jose City College Physical Education Building PLACE IMAGE HERE Prepared For Ken Bauer, AIA Principal LPAS 2484 Natomas Park Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 916.443.0335 Prepared By Steve Ratchye,
Project San Jose City College Physical Education Building PLACE IMAGE HERE Prepared For Ken Bauer, AIA Principal LPAS 2484 Natomas Park Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 916.443.0335 Prepared By Steve Ratchye,
Technical Report 1. Residence Inn By Marriott. Structural Option September 29, Existing Conditions / Structural Concepts.
 Katie Ritter Advisor: Dr. Ali Memari Structural Option September 29, 2008 Technical Report 1 Existing Conditions / Structural Concepts Residence Inn By Marriott Norfolk, Virginia 1 P age TABLE OF CONTENTS
Katie Ritter Advisor: Dr. Ali Memari Structural Option September 29, 2008 Technical Report 1 Existing Conditions / Structural Concepts Residence Inn By Marriott Norfolk, Virginia 1 P age TABLE OF CONTENTS
FINAL REPORT. Structural Redesign of Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital. Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital
 FINAL REPORT Structural Redesign of Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Adviser:
FINAL REPORT Structural Redesign of Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital Penn State Hershey Medical Center Children s Hospital The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Adviser:
Jonathan R. Torch Technical Report 2 Columbia University. Technical Report 2. Pro-Con Structural Study of Alternate Floor Systems
 Technical Report 2 Pro-Con Structural Study of Alternate Floor Systems Columbia University Broadway & 120 th Street, New York, NY Jonathan R. Torch Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering
Technical Report 2 Pro-Con Structural Study of Alternate Floor Systems Columbia University Broadway & 120 th Street, New York, NY Jonathan R. Torch Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering
La Jolla Commons Phase II Office Tower
 La Jolla Commons Phase II Office Tower San Diego, California Alyssa Stangl Structural Option Faculty Advisor Dr. Hanagan Preliminary Vibrations and Layout Building Introduction Location San Diego, California
La Jolla Commons Phase II Office Tower San Diego, California Alyssa Stangl Structural Option Faculty Advisor Dr. Hanagan Preliminary Vibrations and Layout Building Introduction Location San Diego, California
TEMECULA MEDICAL CENTER PRESENTATION OUTLINE
 TEMECULA MEDICAL CENTER TEMECULA, CA STRUCTURAL SYSTEM OPTIMIZATION IMAGE COUTESY OF THE HKS INC. THE DEPARTMENT OF ARCHITECTURAL ENGINEERING AT THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY DUCTION STRUCTURE CHANGES
TEMECULA MEDICAL CENTER TEMECULA, CA STRUCTURAL SYSTEM OPTIMIZATION IMAGE COUTESY OF THE HKS INC. THE DEPARTMENT OF ARCHITECTURAL ENGINEERING AT THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY DUCTION STRUCTURE CHANGES
The Harry and Jeanette Weinberg Center Mercy Hospital Medical Office Building Baltimore, MD. Thesis Proposal
 The Harry and Jeanette Weinberg Center Mercy Hospital Medical Office Building Baltimore, MD Thesis Proposal Kevin Clouser December 15, 2006 Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Boothby 1 Executive
The Harry and Jeanette Weinberg Center Mercy Hospital Medical Office Building Baltimore, MD Thesis Proposal Kevin Clouser December 15, 2006 Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Boothby 1 Executive
Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Report
 Michael A. Troxell Structural Option Advisor: Professor Parfitt College of Business Administration Oct. 5, 2005 Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Report
Michael A. Troxell Structural Option Advisor: Professor Parfitt College of Business Administration Oct. 5, 2005 Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Report
North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building
 North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building Phoenix, Arizona Michael Hopple Technical Assignment 1 October 5 th, 2007 AE 481W-Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Adviser: Dr. Ali Memari,
North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building Phoenix, Arizona Michael Hopple Technical Assignment 1 October 5 th, 2007 AE 481W-Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Adviser: Dr. Ali Memari,
Simplified Building Schematic for Typical Floor (Levels 9 through 22):
 Introduction to Structural System Simplified Building Schematic for Typical Floor (Levels 9 through 22): Key: - Tower Columns - Tower Shear Walls - Parking Garage Columns - Parking Garage Shear Walls Solid
Introduction to Structural System Simplified Building Schematic for Typical Floor (Levels 9 through 22): Key: - Tower Columns - Tower Shear Walls - Parking Garage Columns - Parking Garage Shear Walls Solid
THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER
 THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER Image courtesy of Gaudreau, Inc. TECHNICAL REPORT #2 OCTOBER 26, 2007 KEENAN YOHE STRUCTURAL OPTION DR. MEMARI FACULTY ADVISOR EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Image courtesy of Gaudreau,
THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER Image courtesy of Gaudreau, Inc. TECHNICAL REPORT #2 OCTOBER 26, 2007 KEENAN YOHE STRUCTURAL OPTION DR. MEMARI FACULTY ADVISOR EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Image courtesy of Gaudreau,
Kaleida Health Global Heart and Vascular Institute University at Buffalo CTRC/Incubator. Buffalo, New York. Technical Report #2
 University at Buffalo CTRC/Incubator Buffalo, New York William McDevitt October 27, 2010 Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Introduction...4 Structural System Overview...5 Foundation...5 Floor System...5
University at Buffalo CTRC/Incubator Buffalo, New York William McDevitt October 27, 2010 Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Introduction...4 Structural System Overview...5 Foundation...5 Floor System...5
Structural Technical Report I October 5, 2006 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Report
 1 THE ODYSSEY ARLINGTON, VA Aaron Snyder Structural Option Advisor: M. Kevin Parfitt, PE Structural Technical Report I October 5, 2006 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Report Executive
1 THE ODYSSEY ARLINGTON, VA Aaron Snyder Structural Option Advisor: M. Kevin Parfitt, PE Structural Technical Report I October 5, 2006 Structural Concepts / Structural Existing Conditions Report Executive
GEN*NY*SIS CENTER FOR EXCELLENCE IN CANCER GENOMICS Rensselaer, NY
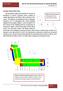 Existing Typical Floor Plan The typical floor plan of the Gen*NY*Sis Center for Excellence in Cancer Genomics (CFG) consists of mainly laboratories and offices with an atrium in the center. The hallway
Existing Typical Floor Plan The typical floor plan of the Gen*NY*Sis Center for Excellence in Cancer Genomics (CFG) consists of mainly laboratories and offices with an atrium in the center. The hallway
Outline. Introduction. Structural Redesign Gravity System Floor System Lateral System Weight Comparison Seismic Comparison
 Outline Breadth Conclusions, Acknowledgements, Questions & Comments Breadth Breadth Location: Wilmington Delaware Owned and managed by: Pettinaro Real Estate Development Company Delivery Method: Design-Bid-Build
Outline Breadth Conclusions, Acknowledgements, Questions & Comments Breadth Breadth Location: Wilmington Delaware Owned and managed by: Pettinaro Real Estate Development Company Delivery Method: Design-Bid-Build
Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts / Existing Conditions
 Chris Shelow Structural Advisor: M. Kevin Parfitt Koshland Integrated Natural Science Center 10/05/05 AE 481W Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts / Existing Conditions Executive Summary The
Chris Shelow Structural Advisor: M. Kevin Parfitt Koshland Integrated Natural Science Center 10/05/05 AE 481W Structural Technical Report 1 Structural Concepts / Existing Conditions Executive Summary The
Technical Report 1. Hakuna Resort Swift Water, Pennsylvania. Image Courtesy of LMN Development LLC
 Technical Report 1 Hakuna Resort Swift Water, Pennsylvania Image Courtesy of LMN Development LLC Young Jeon Structural Option Advisor: Heather Sustersic 13 September 2014 1 Table of Contents Technical
Technical Report 1 Hakuna Resort Swift Water, Pennsylvania Image Courtesy of LMN Development LLC Young Jeon Structural Option Advisor: Heather Sustersic 13 September 2014 1 Table of Contents Technical
Spring Hill Suites Marriott
 Spring Hill Suites Marriott Project Location: Amarillo, TX Prepared for: Girder Slab Technologies Contact: Daniel Fisher, Sr. January 15, 2008 Prepared by: Monica Stockmann Regional Engineer: Erika Winters-Downey
Spring Hill Suites Marriott Project Location: Amarillo, TX Prepared for: Girder Slab Technologies Contact: Daniel Fisher, Sr. January 15, 2008 Prepared by: Monica Stockmann Regional Engineer: Erika Winters-Downey
Boyds Bear Country Pigeon Forge, TN
 Technical Report 3 Lateral System Analysis and Confirmation Design Executive Summary:, located in Pigeon Forge, Tennessee, is designed as a multifunctional space and tourist attraction for Boyds Collections
Technical Report 3 Lateral System Analysis and Confirmation Design Executive Summary:, located in Pigeon Forge, Tennessee, is designed as a multifunctional space and tourist attraction for Boyds Collections
BWI Hilton Hotel. Thomas Sabol The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Structural Emphasis Advisor: Dr. Ali M.
 Thomas Sabol The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Structural Emphasis Advisor: Dr. Ali M. Memari Senior Thesis Presentations: Spring 2007 Presentation Overview Introduction Existing
Thomas Sabol The Pennsylvania State University Architectural Engineering Structural Emphasis Advisor: Dr. Ali M. Memari Senior Thesis Presentations: Spring 2007 Presentation Overview Introduction Existing
MOUNTAIN STATE BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD HEADQUARTERS
 MOUNTAIN STATE BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD HEADQUARTERS PARKERSBURG, WEST VIRGINIA DOMINIC MANNO STRUCTURAL OPTION FACULTY CONSULTANT: DR. ANDRES LEPAGE PROPOSAL 12-12-08 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS.
MOUNTAIN STATE BLUE CROSS BLUE SHIELD HEADQUARTERS PARKERSBURG, WEST VIRGINIA DOMINIC MANNO STRUCTURAL OPTION FACULTY CONSULTANT: DR. ANDRES LEPAGE PROPOSAL 12-12-08 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS.
181 Fremont San Francisco, CA. Proposal 12/12/2014. Caroline Klatman Structural Option Advisor: Dr. Thomas Boothby
 181 Fremont San Francisco, CA Proposal 12/12/2014 Caroline Klatman Structural Option Advisor: Dr. Thomas Boothby Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Introduction... 4 Purpose... 4 Building Summary...
181 Fremont San Francisco, CA Proposal 12/12/2014 Caroline Klatman Structural Option Advisor: Dr. Thomas Boothby Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Introduction... 4 Purpose... 4 Building Summary...
Arlington, Virginia December 3, 2007 TECHNICAL REPORT III LATERAL SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND CONFIRMATION DESIGN
 TECHNICAL REPORT III LATERAL SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND CONFIRMATION DESIGN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The is the practice facility for the NHL franchise, Washington Capitals. It is located in Arlington, Virginia just
TECHNICAL REPORT III LATERAL SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND CONFIRMATION DESIGN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The is the practice facility for the NHL franchise, Washington Capitals. It is located in Arlington, Virginia just
MITRE 3 Building McLean VA
 Executive Summary: The MITRE 3 building is an eight story office building. Its current frame is composed of A992 wide flange shapes. The lateral resisting system is a moment frame. This moment frame consists
Executive Summary: The MITRE 3 building is an eight story office building. Its current frame is composed of A992 wide flange shapes. The lateral resisting system is a moment frame. This moment frame consists
Traci Peterson Option: Structural Faculty Consultant: Memari. Executive Summary
 1 Traci Peterson Option: Structural Faculty Consultant: Memari The Del Monte Center at The North Shore Pittsburgh, PA Structural Technical Report 3 Lateral System Analysis and Confirmation Design Date
1 Traci Peterson Option: Structural Faculty Consultant: Memari The Del Monte Center at The North Shore Pittsburgh, PA Structural Technical Report 3 Lateral System Analysis and Confirmation Design Date
John Jay College Expansion Project
 Technical Report #3 Michael Hopper Mike AE Consultant: Dr. Lepage [Type the company name] November 21 st, 2008 Technical Report #3 Table of Contents Executive Summary.3 Introduction.4 Existing Composite
Technical Report #3 Michael Hopper Mike AE Consultant: Dr. Lepage [Type the company name] November 21 st, 2008 Technical Report #3 Table of Contents Executive Summary.3 Introduction.4 Existing Composite
