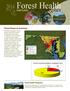
MAINE. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Health Programs in the Northeast
|
|
|
- Helena Flowers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2011 Foresthighlights Health MAINE Forest Resource Summary Almost all of the forest lands in Maine are privately owned approximately 94 percent with only 1 percent in Federal ownership that encompasses the eastern portion of the White Mountain National Forest. The latest Maine forest inventory estimates that there are approximately 17.7 million acres in the State that are forested. The forest resource is made up of a variety of forest types, mostly spruce and balsam fir, maples, other hardwoods, and pine. Maine s forests provide much of the raw materials to fuel the State s mills and serve as the backdrop for the recreation industry. These forest-based industries employ more than 12 percent of Maine s workforce and generate more than 11 percent of the State s payroll. The overall annual contribution of the forest resource to Maine s economy exceeds $8.5 billion. The forests of the State also Forest Land Ownership Federal 1% State 4% Local 1% Private 94% Forest Health Programs in the Northeast State forestry agencies work in partnership with the U.S. Forest Service to monitor forest conditions and trends in their State and respond to pest outbreaks to protect the forest resource.
2 Forest Species Type Spruce and balsam fir Maple Other Hardwoods Pine Other softwoods Eastern Hemlock Yellow birch Beech Oak Hickory million cubic feet provide watershed, environmental, wildlife, and recreational benefits. Forested parks and individual shade trees provide similar amenities in urban and suburban settings. Aerial Surveys Maine reported over 60,000 acres of damage. By far, the greatest impact continues to come from a complex of damage agents affecting northern white cedar. Hardwood defoliators also caused observable damage, including the browntail moth, oak leaftier, satin moth, and forest tent caterpillar. Other defoliators affected aspen stands and sugar maple sites. This map delineates aerial detection survey (ADS) results for Maine in 2011 and
3 Insect Damage The 2011 season began with extremely high browntail moth winter web counts in Bowdoinham, Bath, West Bath, Topsham (Sagadahoc County), and Brunswick (Cumberland County) at the southern terminus of Merry Meeting Bay. Feeding began normally in April and early May. The weather then turned cool and wet and the larvae slowed their feeding and spent more time than usual in their webs. The high population, reduced feeding, and cold wet weather probably contributed to the ensuing Entomophaga aulicae fungal outbreak that decimated the population (figure 1). Figure 1. Browntail moth larvae killed by the fungus Entomophaga aulicae. The browntail moth populations were reduced to the point where it was difficult to find any larvae at all within the core infested area. Trees that had been partially defoliated rapidly refoliated, and no defoliation was detected in these towns during the aerial survey. The Kennebunkport infestation also disappeared as did the infestations in Lewiston and Turner. There are still remnants of the Augusta (Kennebec County) population. Browntail numbers are increasing in Falmouth and parts of Freeport (Cumberland County) where 910 acres of moderate to severe defoliation were mapped in the two towns. Reports of an increase in browntail moth came from Peaks Island in Portland Harbor (Cumberland County) as well. Field trials with the naturally occurring BTM nucleopolyhedrovirus, EcNPV, were carried out in May in Bowdoinham and in September in Freeport (figure 2). The Bowdoinham browntail population was overwhelmed with the E. aulicae fungus after the EcNPV application, although the first post-spray sample did show virus present in larval cadavers. The results from the September application have not come in yet. These locations will be monitored for long-term control of the browntail by the virus. Figure 2. Applying EcNPV virus to browntail larvae. Hemlock woolly adelgid was first detected in native hemlocks in Maine in Until May of 2010, it had not been detected outside of York County, except where it was associated with infested nursery stock. In early May the adelgid was confirmed from a landowner report in Harpswell (Cumberland County). Subsequent survey and landowner reports in 2010 revealed infestations along the southern and midcoast region of the State. In 2011, surveys of high-risk sites in more than 80 towns outside the area known to have infestations of hemlock woolly adelgid produced one new detection of the 3
4 insect. Cape Elizabeth (Cumberland County) was added to the list of towns known to have established hemlock woolly adelgid infestations: Cumberland County: Brunswick, Cape Elizabeth, Cumberland, Falmouth, Freeport, Harpswell, Portland (Great Diamond Island), South Portland, Yarmouth Lincoln County: Boothbay, Boothbay Harbor, Bristol, Edgecomb, South Bristol, Westport Island, Wiscasset Sagadahoc County: Arrowsic, Bath, Georgetown, Phippsburg, West Bath, Woolwich York County: Eliot, Kennebunkport, Kittery, Ogunquit, Saco, South Berwick, Wells, and York An increase in inquiries from homeowners for advice on adelgid control reflects continued intensification of the problem in the towns of Kittery and York. Residents of this region frequently requested the list of licensed pesticide applicators that will treat for browntail moth and/or hemlock woolly adelgid, organized by region of operation. Infested planted trees continue to be located. In 2011, an arborist reported an infested hedgerow on a client s property in Mount Desert (Hancock County). Given the details the homeowner provided, the trees may have been part of infested shipments that entered the State in the late 1990s and early 2000s. The hedge was treated with imidacloprid and horticultural oil. Outreach will be focused in that area and the surrounding area will be surveyed for the adelgid. Efforts to establish biological controls continue in Maine. In 2011, through a grant from USDA APHIS, 10,000 Sasajiscymnus tsugae beetles were received from the North Carolina Department of Agriculture rearing lab. An additional 7,000 were purchased from a private supplier with money from a Maine Outdoor Heritage Fund grant and Departmental funds. Releases were conducted at Vaughan Woods (York County) and Wolfe Neck Woods (Cumberland County) State Parks, and on other conserved property in Kittery (York County), Harpswell (Cumberland County), and West Bath (Sagadahoc County) (figure 3). Figure 3. Releasing Sasajiscymnus tsugae predatory beetles. Spruce budworm catches in pheromone traps have increased significantly this year. New Brunswick budworm trap catches are rising as well, and Quebec is experiencing a large budworm outbreak north of the Saint Lawrence Seaway. There are still no reports of larval feeding, and no adults were caught in light traps in Maine. Highest trap catches are in the northwestern part of the State, particularly the far north. Only three 4
5 pheromone trap sites Downeast in Washington County continue to have zero moths; all other locations caught some number of budworm moths. The average moth catch from 66 sites across the northern half of the State was 7.3 moths, up from 2.5 moths in 2010, the highest it has been since The highest moth count was 58.7 moths (average of three traps) in Garfield, Aroostook County. Moth counts were highest in northern Maine. The Maine Forest Service will continue to monitor this serious pest. Forest Diseases An unusual disease of northern white-cedar (Arborvitae) was found in Scarborough (Cumberland County) and Kennebunk (York County), Maine. The needle disease, known as cedar leaf blight, is well known from western red-cedar (Thuja plicata) in the Western United States and Canada. It has also been reported previously on northern whitecedar from a few Eastern States, including Maine, but is considered to be uncommon. Damage in 2011 was reported from mature hedge plantings and was most severe where dense shading and high foliage moisture levels occurred. Symptoms first appear as light brown areas on the individual scalelike leaves. The fruiting bodies (apothecia) of the fungus appear in June on the upper surface of infected needles (figures 4a and b). The apothecia rupture through the needle epidermis, which then often stays attached to the needle. Heavily infected needles and twigs are shed later in the fall. The primary forest disease survey effort conducted in 2011 involved detecting and evaluating damage resulting from hemlock tip blight to eastern hemlock (figure 5). This disease, first recognized and reported on eastern hemlock in 2010, has been found in Androscoggin, Cumberland, Hancock, Kennebec, Knox, Lincoln, Oxford, Sagadahoc, Washington, and York Counties. A B Figures 4a and b. Cedar leaf blight, Didymascella thujina, on northern white-cedar, Maine. Figure 5. Hemlock tip blight survey crew in Bethel, ME. In cooperation with U.S. Forest Service employees at Durham, NH, personnel surveyed 11 stands across 9 towns in Maine. U.S. Forest Service and New Hampshire State personnel surveyed additional stands in New Hampshire. The hemlock tip blight pathogen was confirmed at all locations, with varying levels of severity. A preliminary analysis of stand conditions indicated that higher levels of infection occurred where hemlock regeneration was well shaded with a dense overstory than 5
6 in more open stands. Additional survey and evaluation work is scheduled for Several white pine needle cast diseases have long been known to occur in Maine. Three principal pathogens that result in needle infection and subsequent premature needle shedding are Mycosphaerella dearnessii (brown spot), Canavirgella banfieldii, and Bifusella linearis. During the past several years, an increased incidence and severity of needle casts has been observed. These diseases have been observed on white pine throughout the State, but have been most severe in western and southern counties. Management options are limited, but include maintaining healthy crown development with appropriate thinning protocols. Adequate spacing will also promote more rapid drying of needles, although in very wet years this may be of little help. Affected stands should be thinned either very cautiously or not at all during years of heavy defoliation, or for one or two years following excessive needle loss. Stands should be monitored to estimate crown density recovery before thinning and other stand disturbance operations can be safely resumed. The recent widespread distribution of needle casts and the intensity of infections appear to be without precedent in Maine and the Northeastern United States. These disease conditions are likely to have been fostered by the above-average precipitation during the spring and summer seasons that Maine has experienced for the past several consecutive years. Most damage in northern New England has been shown to be caused by the brown spot pathogen. For brown spot, current-season needles become infected and, over the course of a year, become yellow and eventually turn brown. The needles are then shed during the following spring. White pine normally retains needles for at least 2 years before they are shed; therefore, needle infections can result in the loss of up to 50 percent of the normal complement of foliage. To date, there has been no documented direct tree mortality from these diseases, but some trees do have very thin crowns (figure 6). Pine understory regeneration is also affected and may be more at risk of succumbing than mature overstory trees. Some trees on poor sites and those along shorelines of rivers and lakes may be most susceptible to mortality if significant needle loss occurs in successive years. Figure 6. White pine with heavy needle loss in the lower one-half of the crown from needlecast disease in Bethel, ME. 6
7 References Land Cover Map: U.S. Geological Survey National land cover dataset. Sioux Falls, SD. Forest Land Ownership, Forest Species Type: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Forest resources of the United States, Gen. Tech. Rep. WO 78. Washington, DC. 336 p. Forest Health Protection USDA Forest Service Northeastern Area State and Private Forestry 271 Mast Rd. Durham, NH Maine Department of Conservation Maine Forest Service 22 State House Station Augusta, ME January 2012 The USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. 7
MASSACHUSETTS. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Health Programs in the Northeast
 2011 Foresthighlights Health MASSACHUSETTS Forest Resource Summary The forest resource of Massachusetts has great demands placed on it. Although Massachusetts is thought of as an urban State, about half
2011 Foresthighlights Health MASSACHUSETTS Forest Resource Summary The forest resource of Massachusetts has great demands placed on it. Although Massachusetts is thought of as an urban State, about half
MASSACHUSETTS. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Health Programs in the Northeast
 Health 2013 Foresthighlights MASSACHUSETTS Forest Resource Summary The forest resource of Massachusetts has great demands placed on it. Although Massachusetts is thought of as an urban State, about half
Health 2013 Foresthighlights MASSACHUSETTS Forest Resource Summary The forest resource of Massachusetts has great demands placed on it. Although Massachusetts is thought of as an urban State, about half
NEW HAMPSHIRE. Forest Health Programs in the Northeast. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Land Ownership
 2010 Foresthighlights Health NEW HAMPSHIRE Forest Resource Summary 2001 Land Cover (%) Approximately three-quarters of the forest land in New Hampshire is privately owned. Only 16 percent is in Federal
2010 Foresthighlights Health NEW HAMPSHIRE Forest Resource Summary 2001 Land Cover (%) Approximately three-quarters of the forest land in New Hampshire is privately owned. Only 16 percent is in Federal
VERMONT. Forest Health Programs in the Northeast. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Land Ownership
 2008 Foresthighlights Health VERMONT Forest Resource Summary Vermont s forests, which encompass 4.6 million acres, offer valuable ecological, economic, and social benefits. Healthy forests are resilient
2008 Foresthighlights Health VERMONT Forest Resource Summary Vermont s forests, which encompass 4.6 million acres, offer valuable ecological, economic, and social benefits. Healthy forests are resilient
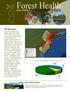
MAINE. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Health Programs in the Northeast
 2013 Foresthighlights Health MAINE Forest Resource Summary Almost all approximately 94 percent of the forest lands in Maine are privately owned. The 1 percent that is federally owned encompasses the eastern
2013 Foresthighlights Health MAINE Forest Resource Summary Almost all approximately 94 percent of the forest lands in Maine are privately owned. The 1 percent that is federally owned encompasses the eastern
RHODE ISLAND. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Health Programs in the Northeast
 2013 Foresthighlights Health RHODE ISLAND Forest Resource Summary Rhode Island s forests are 85 percent privately owned, primarily by individuals who view their land as a source of enjoyment and a resource
2013 Foresthighlights Health RHODE ISLAND Forest Resource Summary Rhode Island s forests are 85 percent privately owned, primarily by individuals who view their land as a source of enjoyment and a resource
Forest Health. highlights NEW YORK. Forest Resource Summary. Aerial Surveys. Forest Land Ownership in New York, 2012
 2015 Forest Health NEW YORK highlights Forest Resource Summary New York s forests are 75 percent privately owned. The remaining 25 percent is in public ownership, of which the State owns 21 percent, mostly
2015 Forest Health NEW YORK highlights Forest Resource Summary New York s forests are 75 percent privately owned. The remaining 25 percent is in public ownership, of which the State owns 21 percent, mostly
NEW JERSEY. The Resource. Forest Land Ownership (MD) Forest Land Ownership (OH) Forest Health Programs
 2011 Foresthighlights Health NEW JERSEY The Resource New Jersey is the most densely populated State in the Nation, yet its forests cover approximately 2 million acres (42 percent) of the State s 4.1 million
2011 Foresthighlights Health NEW JERSEY The Resource New Jersey is the most densely populated State in the Nation, yet its forests cover approximately 2 million acres (42 percent) of the State s 4.1 million
Kentucky. Forest Health Highlights The Resource
 Kentucky Forest Health Highlights 2017 The Resource Kentucky s forests cover an estimated 12.4 million acres, nearly 49% of the state s land area. The Cumberland Plateau and the Appalachians in the eastern
Kentucky Forest Health Highlights 2017 The Resource Kentucky s forests cover an estimated 12.4 million acres, nearly 49% of the state s land area. The Cumberland Plateau and the Appalachians in the eastern
highlights WEST VIRGINIA The Resource Forest Health Programs
 2010 Forest Health WEST VIRGINIA highlights The Resource The West Virginia landscape is dominated by more than 11.8 million acres of forest. Due in large part to its varied topography, the forest is a
2010 Forest Health WEST VIRGINIA highlights The Resource The West Virginia landscape is dominated by more than 11.8 million acres of forest. Due in large part to its varied topography, the forest is a
MARYLAND. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Health Programs
 2014 Foresthighlights Health MARYLAND Forest Resource Summary Maryland occupies a land area of 6,264,876 acres. Forest land comprises 2,709,062 acres, of which 72 percent is privately owned. Healthy, productive
2014 Foresthighlights Health MARYLAND Forest Resource Summary Maryland occupies a land area of 6,264,876 acres. Forest land comprises 2,709,062 acres, of which 72 percent is privately owned. Healthy, productive
highlights NEW JERSEY The Resource Forest Health Programs
 2013 Forest Health NEW JERSEY highlights The Resource New Jersey is the most densely populated State in the nation, and yet its forest covers approximately 2 million acres (42 percent) of the State s 4.1
2013 Forest Health NEW JERSEY highlights The Resource New Jersey is the most densely populated State in the nation, and yet its forest covers approximately 2 million acres (42 percent) of the State s 4.1
Aerial Survey Highlights for Colorado, 2016
 Aerial Survey Highlights for Colorado, 2016 Aerial detection surveys of tree-killing or damaging insects and diseases are conducted annually over Colorado s forestlands. This is a cooperative effort between
Aerial Survey Highlights for Colorado, 2016 Aerial detection surveys of tree-killing or damaging insects and diseases are conducted annually over Colorado s forestlands. This is a cooperative effort between
THE 6 STEPS IN THE MFS TGTL VALUATION. Kenneth M. Laustsen Biometrician, Maine Forest Service January 23, 2017
 THE 6 STEPS IN THE MFS TGTL VALUATION Kenneth M. Laustsen Biometrician, Maine Forest Service January 23, 2017 The 6 steps (all by respective geographic region ) The five geographic regions are Northern
THE 6 STEPS IN THE MFS TGTL VALUATION Kenneth M. Laustsen Biometrician, Maine Forest Service January 23, 2017 The 6 steps (all by respective geographic region ) The five geographic regions are Northern
Kentucky. Forest Health Highlights The Resource
 Kentucky Forest Health Highlights 2015 The Resource Kentucky s forests cover an estimated 12.4 million acres, nearly 49% of the state s land area. The Cumberland Plateau and the Appalachians in the eastern
Kentucky Forest Health Highlights 2015 The Resource Kentucky s forests cover an estimated 12.4 million acres, nearly 49% of the state s land area. The Cumberland Plateau and the Appalachians in the eastern
2/24/2009. The factors that determine what type of forest will grow in a region are temperature precipitation growing season soil land forms
 FOREST FACTS Forestry 37% of Canada's land area covered by forests. Stretches in a continuous band from BC to NL. Commercial forests are forests that could be easily be harvested for timber. Non-commercial
FOREST FACTS Forestry 37% of Canada's land area covered by forests. Stretches in a continuous band from BC to NL. Commercial forests are forests that could be easily be harvested for timber. Non-commercial
Major Forest Types Of Michigan
 Forests comprise 53% of the land area of the state, or about 19.3 million acres. These forests are a critical component of Michigan s environment and economy for the recreational opportunities and the
Forests comprise 53% of the land area of the state, or about 19.3 million acres. These forests are a critical component of Michigan s environment and economy for the recreational opportunities and the
Unity College Hemlock Ecosystem Management Study (HEMS)
 Unity College Hemlock Ecosystem Management Study (HEMS) A study of the ecological and socioeconomic implications of changes in mixed hemlock-hardwood forests Amy Arnett, Erika Latty, Alysa Remsburg, Kathleen
Unity College Hemlock Ecosystem Management Study (HEMS) A study of the ecological and socioeconomic implications of changes in mixed hemlock-hardwood forests Amy Arnett, Erika Latty, Alysa Remsburg, Kathleen
2015 Insect and Disease Update for Rocky Mountain. Region
 2015 Insect and Disease Update for Rocky Mountain Bob Cain USDA Forest Service State and Private Forestry and Tribal Relations Forest Health Protection Region Mountain Pine Beetle Spruce beetle Douglas-fir
2015 Insect and Disease Update for Rocky Mountain Bob Cain USDA Forest Service State and Private Forestry and Tribal Relations Forest Health Protection Region Mountain Pine Beetle Spruce beetle Douglas-fir
Forest Health Highlights 2015
 Forest Health Highlights 2015 Windbreaks, shelterbelts and narrow wooded riparian strips account for an additional 423,000 acres of tree-covered land. Community forests add 470,000 acres to the state s
Forest Health Highlights 2015 Windbreaks, shelterbelts and narrow wooded riparian strips account for an additional 423,000 acres of tree-covered land. Community forests add 470,000 acres to the state s
Mount Mansfield Monitoring Methods
 Introduction Damage to forest trees from insects, diseases and weather has played a major role in widespread tree declines in the past. Monitoring pest population trends and tree damage is conducted annually
Introduction Damage to forest trees from insects, diseases and weather has played a major role in widespread tree declines in the past. Monitoring pest population trends and tree damage is conducted annually
Insect and Disease Observations in Vermont Late Spring - Early Summer 2009
 Insect and Disease Observations in Vermont Late Spring - Early Summer 2009 Insects Red oak defoliation in Middlesex, Bolton, Jericho, Jamaica and other parts of Vermont, appears to be heavier and more
Insect and Disease Observations in Vermont Late Spring - Early Summer 2009 Insects Red oak defoliation in Middlesex, Bolton, Jericho, Jamaica and other parts of Vermont, appears to be heavier and more
USDA Forest Service Northeastern Area State & Private Forestry
 USDA Forest Service Northeastern Area State & Private Forestry NA-FR-01-94 HOW to Manage Jack Pine to Reduce Damage From Jack Pine Budworm Deborah G. McCullough, Steven Katovich, Robert L. Heyd, and Shane
USDA Forest Service Northeastern Area State & Private Forestry NA-FR-01-94 HOW to Manage Jack Pine to Reduce Damage From Jack Pine Budworm Deborah G. McCullough, Steven Katovich, Robert L. Heyd, and Shane
Activities of forest insects and diseases on the San Juan National Forest for 2015
 1 Activities of forest insects and diseases on the San Juan National Forest for 2015 Several insects and diseases which affect forest trees are currently influencing stands throughout the San Juan National
1 Activities of forest insects and diseases on the San Juan National Forest for 2015 Several insects and diseases which affect forest trees are currently influencing stands throughout the San Juan National
Western Spruce Budworm Management Strategies
 Western Spruce Budworm Management Strategies Introduction The western spruce budworm (Choristoneura occidentalis) is a very destructive native defoliator of western coniferous forests, which periodically
Western Spruce Budworm Management Strategies Introduction The western spruce budworm (Choristoneura occidentalis) is a very destructive native defoliator of western coniferous forests, which periodically
2016 Wyoming Forest Health Highlights
 2016 Wyoming Forest Health Highlights Figure 1. Orange trees toward bottom right indicate ponderosa pine mortality caused by bark beetles in the Black Hills of Wyoming. While mountain pine beetle has affected
2016 Wyoming Forest Health Highlights Figure 1. Orange trees toward bottom right indicate ponderosa pine mortality caused by bark beetles in the Black Hills of Wyoming. While mountain pine beetle has affected
Oklahoma. Forest Health Highlights 2015
 Oklahoma Forest Health Highlights 2015 The Resource Oklahoma s forests cover 12 million acres, about 25% of the state s land area. Some 6.9 million acres of the states forested land is in nonindustrial
Oklahoma Forest Health Highlights 2015 The Resource Oklahoma s forests cover 12 million acres, about 25% of the state s land area. Some 6.9 million acres of the states forested land is in nonindustrial
Oak and Tanoak Pest Issues. Tom Smith Forest Pest Management California Department of Forestry and Fire protection
 Oak and Tanoak Pest Issues Tom Smith Forest Pest Management California Department of Forestry and Fire protection California Oak Woodlands Issues Urbanization Fragmentation Fire Regimes Stand Structure
Oak and Tanoak Pest Issues Tom Smith Forest Pest Management California Department of Forestry and Fire protection California Oak Woodlands Issues Urbanization Fragmentation Fire Regimes Stand Structure
VERMONT. Forest Resource Summary. Forest Health Programs in the Northeast
 2010 Foresthighlights Health VERMONT These highlights summarize information from the Forest Insect and Disease Conditions in Vermont 2010 report. The complete annual report, as well as other Vermont forest
2010 Foresthighlights Health VERMONT These highlights summarize information from the Forest Insect and Disease Conditions in Vermont 2010 report. The complete annual report, as well as other Vermont forest
Spruce Budworm Choristoneura fumiferana (Clemens) Lepidoptera: Tortricidae
 Spruce Budworm Choristoneura fumiferana (Clemens) Lepidoptera: Tortricidae Montgomery, B. A.; Simmons, G. A.; Witter, J. A.; Flexner, J. L. 1982. The spruce budworm handbook: a management guide for spruce-fir
Spruce Budworm Choristoneura fumiferana (Clemens) Lepidoptera: Tortricidae Montgomery, B. A.; Simmons, G. A.; Witter, J. A.; Flexner, J. L. 1982. The spruce budworm handbook: a management guide for spruce-fir
Bartlett Experimental Forest Network
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Bartlett Experimental Forest Northern Research Station Experimental Forest Network NRS-INF-27-13 Bartlett Experimental Forest The Bartlett Experimental
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Bartlett Experimental Forest Northern Research Station Experimental Forest Network NRS-INF-27-13 Bartlett Experimental Forest The Bartlett Experimental
Adapting to Climate Change in the Northeast: Experiences from the Field. Climate Projections for Forests: A Quick Summary
 Adapting to Climate Change in the Northeast: Experiences from the Field NE SAF Annual Meeting, Nashua, NH 26 March 2014 Small Urban Mid coast Maine Large industrial Irving Woodlands Small woodlot Allen
Adapting to Climate Change in the Northeast: Experiences from the Field NE SAF Annual Meeting, Nashua, NH 26 March 2014 Small Urban Mid coast Maine Large industrial Irving Woodlands Small woodlot Allen
Adapting to Climate Change in the Northeast: Experiences from the Field
 Adapting to Climate Change in the Northeast: Experiences from the Field NE SAF Annual Meeting, Nashua, NH 26 March 2014 Small Urban Mid-coast Maine Large industrial Irving Woodlands Small woodlot Allen
Adapting to Climate Change in the Northeast: Experiences from the Field NE SAF Annual Meeting, Nashua, NH 26 March 2014 Small Urban Mid-coast Maine Large industrial Irving Woodlands Small woodlot Allen
REPORT. Parks and Open Space Department
 REPORT COMMUNITY SERVICES COMMITTEE MEETING DATE: NOVEMBER 13, 2017 FROM: Parks and Open Space Department DATE: September 15, 2017 SUBJECT: Gypsy Moth and Cankerworm Mitigation Plan LOCATION: Town Wide
REPORT COMMUNITY SERVICES COMMITTEE MEETING DATE: NOVEMBER 13, 2017 FROM: Parks and Open Space Department DATE: September 15, 2017 SUBJECT: Gypsy Moth and Cankerworm Mitigation Plan LOCATION: Town Wide
Contents. Do Not Delay. You Have a Choice
 Contents You Have a Choice Do Not Delay Benefits of Trees... 1 Emerald Ash Borer Facts... 2 TreeAzin Systemic Insecticide: Trees Saving Trees... 3 Having Your Tree Treated... 4 Other Insect Pests... 5
Contents You Have a Choice Do Not Delay Benefits of Trees... 1 Emerald Ash Borer Facts... 2 TreeAzin Systemic Insecticide: Trees Saving Trees... 3 Having Your Tree Treated... 4 Other Insect Pests... 5
Red Pine Management Guide A handbook to red pine management in the North Central Region
 Red Pine Management Guide A handbook to red pine management in the North Central Region This guide is also available online at: http://ncrs.fs.fed.us/fmg/nfgm/rp A cooperative project of: North Central
Red Pine Management Guide A handbook to red pine management in the North Central Region This guide is also available online at: http://ncrs.fs.fed.us/fmg/nfgm/rp A cooperative project of: North Central
Forest & Shade Tree Insect & Disease Conditions for Maine. A Summary of the 2013 Condition.
 Maine State Library Maine State Documents Forest Service Documents Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry 3-2014 Forest & Shade Tree Insect & Disease Conditions for Maine. A Summary of the 2013 Condition.
Maine State Library Maine State Documents Forest Service Documents Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry 3-2014 Forest & Shade Tree Insect & Disease Conditions for Maine. A Summary of the 2013 Condition.
Sustaining Northern Forests in the face of Climate Change
 Sustaining Northern Forests in the face of Climate Change USDA Forest Service Northern Research Station -Challenges -Opportunities -Actions Brian Palik, Ph.D. USDA Forest Service Northern Research Station
Sustaining Northern Forests in the face of Climate Change USDA Forest Service Northern Research Station -Challenges -Opportunities -Actions Brian Palik, Ph.D. USDA Forest Service Northern Research Station
Balsam Woolly Adelgid Adelges piceae. Glenn Kohler, Forest Entomologist Washington Department of Natural Resources
 Balsam Woolly Adelgid Adelges piceae Glenn Kohler, Forest Entomologist Washington Department of Natural Resources Hosts Only known on true fir (Abies) in North America Native to Europe where spruces (Picea)
Balsam Woolly Adelgid Adelges piceae Glenn Kohler, Forest Entomologist Washington Department of Natural Resources Hosts Only known on true fir (Abies) in North America Native to Europe where spruces (Picea)
Climate Change and Vermont s Forests
 Impacts and Vulnerabilities Climate Change and Vermont s Forests Sandy Wilmot, May 2011 Forests are an invaluable economic and environmental resource of Vermont. Climate change will likely affect many
Impacts and Vulnerabilities Climate Change and Vermont s Forests Sandy Wilmot, May 2011 Forests are an invaluable economic and environmental resource of Vermont. Climate change will likely affect many
Invasive Pests Threatening Western NC. Brian Heath Pest Control Forester NC Forest Service
 Invasive Pests Threatening Western NC Brian Heath Pest Control Forester NC Forest Service Gypsy Moth Leopold Trouvelot Introduced in 1868 - Boston, MA How d it get here? Host Trees Prefers oak and black
Invasive Pests Threatening Western NC Brian Heath Pest Control Forester NC Forest Service Gypsy Moth Leopold Trouvelot Introduced in 1868 - Boston, MA How d it get here? Host Trees Prefers oak and black
COUNTY FOREST COMPREHENSIVE LAND USE PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 600 PROTECTION
 COUNTY FOREST COMPREHENSIVE LAND USE PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 600 PROTECTION Section Subject Page 600 PROTECTION... 2 605 FIRE CONTROL... 2 605.1 COOPERATION WITH THE DEPARTMENT OF NATURA RESOURCES...
COUNTY FOREST COMPREHENSIVE LAND USE PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 600 PROTECTION Section Subject Page 600 PROTECTION... 2 605 FIRE CONTROL... 2 605.1 COOPERATION WITH THE DEPARTMENT OF NATURA RESOURCES...
State Forest Management: Pennsylvania
 State Forest Management: Pennsylvania April 14, 2010 Jim Grace Deputy Secretary for State Parks and Forestry Pennsylvania DCNR PENNSYLVANIA M Pennsylvania s Forests 16.6 million ac.(6.7 million ha.) of
State Forest Management: Pennsylvania April 14, 2010 Jim Grace Deputy Secretary for State Parks and Forestry Pennsylvania DCNR PENNSYLVANIA M Pennsylvania s Forests 16.6 million ac.(6.7 million ha.) of
2016 Wood Processor Report
 26 Wood Processor Report Including Import and Export Information Compiled from 26 Wood Processor Reports pursuant to 2 M.R.S. 8884 Published: April 27, 27 Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry
26 Wood Processor Report Including Import and Export Information Compiled from 26 Wood Processor Reports pursuant to 2 M.R.S. 8884 Published: April 27, 27 Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry
Proposed treatments of planted white pine in the Waynesville Watershed
 Proposed treatments of planted white pine in the Waynesville Watershed Peter Bates and Rob Lamb in collaboration with The Waynesville Watershed Advisory Committee September 14, 2010 Presentation overview
Proposed treatments of planted white pine in the Waynesville Watershed Peter Bates and Rob Lamb in collaboration with The Waynesville Watershed Advisory Committee September 14, 2010 Presentation overview
Forest Health Program
 Forest Health Program June 2007 www.for.gov.bc.ca/ hfp/health/ Library and Archives Canada Cataloguing in Publication Data British Columbia. Forest Health Program. Forest Health Program ISBN 978-0-7726-5814-2
Forest Health Program June 2007 www.for.gov.bc.ca/ hfp/health/ Library and Archives Canada Cataloguing in Publication Data British Columbia. Forest Health Program. Forest Health Program ISBN 978-0-7726-5814-2
Forest Health Highlights 2016
 Forest Health Highlights 2016 The Forest Resource Nebraska boasts a diverse array of forest resources. From the ponderosa pine forests of the Panhandle s Pine Ridge to the hardwood forests of the Missouri
Forest Health Highlights 2016 The Forest Resource Nebraska boasts a diverse array of forest resources. From the ponderosa pine forests of the Panhandle s Pine Ridge to the hardwood forests of the Missouri
Budworm/Insect & Disease Update
 Budworm/Insect & Disease Update Allison Kanoti Forest Entomologist Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry Maine Forest Service A. Steven Munson, USDA-FS, Bugwood.org Spruce Budworm Native
Budworm/Insect & Disease Update Allison Kanoti Forest Entomologist Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry Maine Forest Service A. Steven Munson, USDA-FS, Bugwood.org Spruce Budworm Native
Sugar Maple ( Acer ( saccharum ) saccharum Health Management Plan Brianne Looze Tree Tree Pests and Disease
 Sugar Maple (Acer saccharum) Health Management Plan Brianne Looze Tree Pests and Disease Outline Importance of Sugar Maple Management Objective Site Characteristics and Tree Biology Disease Complex: Asian
Sugar Maple (Acer saccharum) Health Management Plan Brianne Looze Tree Pests and Disease Outline Importance of Sugar Maple Management Objective Site Characteristics and Tree Biology Disease Complex: Asian
SUSTAINABLE FORESTRY INITIATIVE
 SAVAGE RIVER STATE FOREST ANNUAL WORK PLAN FISCAL YEAR 2018 FSC www.fsc.org FSC e C016194 The mark of responsible forestry SUSTAINABLE FORESTRY INITIATIVE Good for you. Good for our forests? SFI-00050
SAVAGE RIVER STATE FOREST ANNUAL WORK PLAN FISCAL YEAR 2018 FSC www.fsc.org FSC e C016194 The mark of responsible forestry SUSTAINABLE FORESTRY INITIATIVE Good for you. Good for our forests? SFI-00050
Introduction. Plot Methods
 54.06% of trees healthy in the 3800 foot elevation plot. The percentage of standing dead trees was also higher at the highest elevation plot, where 43.3% of trees were standing dead, compared with 8.0%
54.06% of trees healthy in the 3800 foot elevation plot. The percentage of standing dead trees was also higher at the highest elevation plot, where 43.3% of trees were standing dead, compared with 8.0%
Virginia Forest Type Distribution 13% 20% 61% Oak-hickory Loblolly-shortleaf pine Oak-pine Other
 Virginia Forest Health Highlights 2009 The Resource Virginia s forests cover 15.7 million acres, more than 62% of the state s land area. The majority of the state s forested land, some 10 million acres,
Virginia Forest Health Highlights 2009 The Resource Virginia s forests cover 15.7 million acres, more than 62% of the state s land area. The majority of the state s forested land, some 10 million acres,
Forest Health. highlights NEW JERSEY. Forest Resource Summary
 2015 Forest Health NEW JERSEY highlights Forest Resource Summary Even though New Jersey is the most densely populated State in the Nation, its forest covers approximately 2 million acres (42 percent) of
2015 Forest Health NEW JERSEY highlights Forest Resource Summary Even though New Jersey is the most densely populated State in the Nation, its forest covers approximately 2 million acres (42 percent) of
Envirothon New Brunswick
 Envirothon New Brunswick Forestry Workshop Part 1 of 2 February 18, 2017 Bernie Daigle 452-4133 Bernard.Daigle@nrcan-rncan.gc.ca Outline Forest Inventory Forest Succession Tree Identification/Dichotomous
Envirothon New Brunswick Forestry Workshop Part 1 of 2 February 18, 2017 Bernie Daigle 452-4133 Bernard.Daigle@nrcan-rncan.gc.ca Outline Forest Inventory Forest Succession Tree Identification/Dichotomous
Silviculture Art & science of establishing & tending trees & forests
 Silviculture Art & science of establishing & tending trees & forests Karen Bennett, karen.bennett@unh.edu Extension Forestry Professor & Specialist Presented to NH Coverts, May 2015 Silviculture Actions
Silviculture Art & science of establishing & tending trees & forests Karen Bennett, karen.bennett@unh.edu Extension Forestry Professor & Specialist Presented to NH Coverts, May 2015 Silviculture Actions
How to Measure a Tree
 How to Measure a Tree What to look for? When a forester is assessing a tree, they will look for many factors. These factors determine whether the tree is useful or ready to harvest. These include: Disease
How to Measure a Tree What to look for? When a forester is assessing a tree, they will look for many factors. These factors determine whether the tree is useful or ready to harvest. These include: Disease
LINCOLN COUNTY FOREST FIFTEEN-YEAR COMPREHENSIVE LAND USE PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 600 PROTECTION
 LINCOLN COUNTY FOREST FIFTEEN-YEAR COMPREHENSIVE LAND USE PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 600 PROTECTION Section Subject Page 600 PROTECTION... 3 605 FIRE CONTROL... 3 605.1 COOPERATION WITH THE DEPARTMENT
LINCOLN COUNTY FOREST FIFTEEN-YEAR COMPREHENSIVE LAND USE PLAN TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 600 PROTECTION Section Subject Page 600 PROTECTION... 3 605 FIRE CONTROL... 3 605.1 COOPERATION WITH THE DEPARTMENT
highlights NEW JERSEY The Resource Forest Health Programs
 2012 Forest Health NEW JERSEY highlights The Resource New Jersey is the most densely populated State in the Nation, and yet forest covers approximately 2 million acres (42 percent) of the State s 4.1 million
2012 Forest Health NEW JERSEY highlights The Resource New Jersey is the most densely populated State in the Nation, and yet forest covers approximately 2 million acres (42 percent) of the State s 4.1 million
Hillside Woods & Park
 Hillside Woods & Park Forest Inventory & Management Plan Public Meeting Thursday, June 7th @ 7pm Public Library, Hastings-On-Hudson Presentation Outline Who We Are DEC Community Forestry Program What is
Hillside Woods & Park Forest Inventory & Management Plan Public Meeting Thursday, June 7th @ 7pm Public Library, Hastings-On-Hudson Presentation Outline Who We Are DEC Community Forestry Program What is
Maine Spruce Budworm Task Force Update
 Maine Spruce Budworm Task Force Update Robert G. Wagner Nercofe 2016 Workshop March 14-15, 2016 Wells Conference Center, University of Maine The Eastern Spruce Budworm Choristoneura fumiferana Eastern
Maine Spruce Budworm Task Force Update Robert G. Wagner Nercofe 2016 Workshop March 14-15, 2016 Wells Conference Center, University of Maine The Eastern Spruce Budworm Choristoneura fumiferana Eastern
EMERALD ASH BORER IN SOUTH CAROLINA
 EMERALD ASH BORER IN SOUTH CAROLINA EMERALD ASH BORER DETECTED IN SOUTH CAROLINA The emerald ash borer (EAB), a beetle pest that has devastated ash trees throughout the midwestern and eastern United States,
EMERALD ASH BORER IN SOUTH CAROLINA EMERALD ASH BORER DETECTED IN SOUTH CAROLINA The emerald ash borer (EAB), a beetle pest that has devastated ash trees throughout the midwestern and eastern United States,
LAND AND USE. Figure 2. Land cover in Rhode Island, Forest land. Nonforest land and smaller forest patches predominate in the area surrounding
 Mountain laurel Kalmia latifolia Figure 2. Land cover in Rhode Island, 1992. Forest land Developed land Agricultural land Other land Water Source: U.S. Geologic Survey, National Land Cover Data LAND AND
Mountain laurel Kalmia latifolia Figure 2. Land cover in Rhode Island, 1992. Forest land Developed land Agricultural land Other land Water Source: U.S. Geologic Survey, National Land Cover Data LAND AND
6.9 DEER WINTERING AREAS
 6.9 DEER WINTERING AREAS BACKGROUND White-tailed deer in New Hampshire live near the northern limit of their geographic range. Because of severe winters, deer require special habitats to survive. The winter
6.9 DEER WINTERING AREAS BACKGROUND White-tailed deer in New Hampshire live near the northern limit of their geographic range. Because of severe winters, deer require special habitats to survive. The winter
Forest Health. highlights PENNSYLVANIA. Forest Resource Summary
 2017 Forest Health PENNSYLVANIA highlights Forest Resource Summary Pennsylvania covers a land area of 25,333 square miles and is 63 percent forested. Seventy percent of the forest land in the Commonwealth
2017 Forest Health PENNSYLVANIA highlights Forest Resource Summary Pennsylvania covers a land area of 25,333 square miles and is 63 percent forested. Seventy percent of the forest land in the Commonwealth
Proposal for Gypsy Moth Management St. Louis County, Minnesota, 2013
 Proposal for Gypsy Moth Management St. Louis County, Minnesota, 2013 The Minnesota Department of Agriculture (MDA), in collaboration with federal, state, and local partners, is proposing to slow the spread
Proposal for Gypsy Moth Management St. Louis County, Minnesota, 2013 The Minnesota Department of Agriculture (MDA), in collaboration with federal, state, and local partners, is proposing to slow the spread
Forest Health Protection Priorities
 Forest Health Protection Priorities in the US Forest Service Continental Dialogue November, 2016 Indianapolis, IN Rick Cooksey US Forest Service Washington, DC Forest Health Protection Outline -> Forest
Forest Health Protection Priorities in the US Forest Service Continental Dialogue November, 2016 Indianapolis, IN Rick Cooksey US Forest Service Washington, DC Forest Health Protection Outline -> Forest
TITLE: Occurrence of white pine blister rust on cultivated resistant varieties of Ribes species and the impact to local white pine resources
 TITLE: Occurrence of white pine blister rust on cultivated resistant varieties of Ribes species and the impact to local white pine resources LOCATION: New Hampshire (with implications to all regions with
TITLE: Occurrence of white pine blister rust on cultivated resistant varieties of Ribes species and the impact to local white pine resources LOCATION: New Hampshire (with implications to all regions with
North Shore Tree Concerns. Brian Schwingle Forest Insect & Disease Specialist Minnesota DNR
 North Shore Tree Concerns Brian Schwingle Forest Insect & Disease Specialist Minnesota DNR michael.parisio@state.mn.us 218-755-4024 jessica.hartshorn@state.mn.us 218-328-8897 DNR Forest Health staff responsible
North Shore Tree Concerns Brian Schwingle Forest Insect & Disease Specialist Minnesota DNR michael.parisio@state.mn.us 218-755-4024 jessica.hartshorn@state.mn.us 218-328-8897 DNR Forest Health staff responsible
Southern Pine Beetle (SPB)
 Southern Pine Beetle (SPB) SPB is the most destructive pest of pine forests in the South. SPB outbreaks are cyclic, with peaks usually every 6-9 years. Multiple-tree infestations (spots) may expand rapidly
Southern Pine Beetle (SPB) SPB is the most destructive pest of pine forests in the South. SPB outbreaks are cyclic, with peaks usually every 6-9 years. Multiple-tree infestations (spots) may expand rapidly
The Hardwood Resource and Sawmilling Industry. William Luppold USDA Forest Service
 The Hardwood Resource and Sawmilling Industry William Luppold USDA Forest Service Subjects to be Examined Change in forest composition some regional and state examples Changes in forest ownership, land
The Hardwood Resource and Sawmilling Industry William Luppold USDA Forest Service Subjects to be Examined Change in forest composition some regional and state examples Changes in forest ownership, land
Invasive Insects in Tennessee Forests
 Invasive Insects in Tennessee Forests Facing New Threats and Challenges Jerome F. Grant, UTIA Department of Entomology & Plant Pathology Invasive Insects in Tennessee Forests LEAVES OF CHANGE Invasive
Invasive Insects in Tennessee Forests Facing New Threats and Challenges Jerome F. Grant, UTIA Department of Entomology & Plant Pathology Invasive Insects in Tennessee Forests LEAVES OF CHANGE Invasive
Forest Health Monitoring in the Northeastern United States
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Northeastern Area State and Private Forestry NA-TP-01-04 Newtown Square, PA September 2004 Forest Health Monitoring in the Northeastern United States
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Northeastern Area State and Private Forestry NA-TP-01-04 Newtown Square, PA September 2004 Forest Health Monitoring in the Northeastern United States
Emerald Ash Borer: The Protection Option in Canada. J. Meating BioForest Technologies Inc. Sept. 28, 2011
 Emerald Ash Borer: The Protection Option in Canada J. Meating BioForest Technologies Inc. Sept. 28, 2011 EAB in North America EAB in Canada (Sept. 2011) EAB & DED Panic, doom & gloom! 2009 EAB Workshop
Emerald Ash Borer: The Protection Option in Canada J. Meating BioForest Technologies Inc. Sept. 28, 2011 EAB in North America EAB in Canada (Sept. 2011) EAB & DED Panic, doom & gloom! 2009 EAB Workshop
Managing Forested Wildlife Habitats
 Managing Forested Wildlife Habitats Matt Tarr Wildlife Specialist UNH Cooperative Extension What management activities are right for a given property? There is no one right way to manage any piece of land
Managing Forested Wildlife Habitats Matt Tarr Wildlife Specialist UNH Cooperative Extension What management activities are right for a given property? There is no one right way to manage any piece of land
Emerald Ash Borer Plan
 City of Bentwood Department of Parks and Recreation Emerald Ash Borer Plan Table of Contents Executive Summary..... 2 Background on the Emerald Ash Borer 3 Current Inventory...... 4 Recommendations......
City of Bentwood Department of Parks and Recreation Emerald Ash Borer Plan Table of Contents Executive Summary..... 2 Background on the Emerald Ash Borer 3 Current Inventory...... 4 Recommendations......
ASSESSING THE DIRECTION OF THE FOREST RESOURCE
 ASSESSING THE DIRECTION OF THE FOREST RESOURCE C U R T W I L S O N - R E G I O N A L F O R E S T R Y L E A D E R N O R T H E A S T R E G I O N - G R E E N B A Y, W D N R J U N E 2 0 1 2 QUESTIONS FOR TODAY
ASSESSING THE DIRECTION OF THE FOREST RESOURCE C U R T W I L S O N - R E G I O N A L F O R E S T R Y L E A D E R N O R T H E A S T R E G I O N - G R E E N B A Y, W D N R J U N E 2 0 1 2 QUESTIONS FOR TODAY
FIELD SURVEYS: HWA, EAB, ALB AERIAL SURVEY HIGHLIGHTS FEATURE ARTICLE: White Pine Blister Rust Revisited FEATURE CREATURE: Red Pine Scale
 IN THIS ISSUE: FIELD SURVEYS: HWA, EAB, ALB Page 1 AERIAL SURVEY HIGHLIGHTS Page 5 FEATURE ARTICLE: White Pine Blister Rust Revisited Page 7 FEATURE CREATURE: Red Pine Scale Page 9 OFFICE NOTES Page 12
IN THIS ISSUE: FIELD SURVEYS: HWA, EAB, ALB Page 1 AERIAL SURVEY HIGHLIGHTS Page 5 FEATURE ARTICLE: White Pine Blister Rust Revisited Page 7 FEATURE CREATURE: Red Pine Scale Page 9 OFFICE NOTES Page 12
Landscape-level biomass opportunities
 Forest insect and disease management: Implications for biomass production Outline Landscape-level opportunities Historic or mappable agents Invasive pests on the horizon Site-level opportunities By species/
Forest insect and disease management: Implications for biomass production Outline Landscape-level opportunities Historic or mappable agents Invasive pests on the horizon Site-level opportunities By species/
State and Private Forestry Fact Sheet
 State and Private Forestry Fact Sheet Oregon 2018 Investment in State's Cooperative Programs Program FY 2017 Final Community Forestry and Open Space $0 Cooperative Lands - Forest Health Management $797,131
State and Private Forestry Fact Sheet Oregon 2018 Investment in State's Cooperative Programs Program FY 2017 Final Community Forestry and Open Space $0 Cooperative Lands - Forest Health Management $797,131
A Characterization of Timber Salvage Operations on Public Forests in Minnesota and Wisconsin
 A Characterization of Timber Salvage Operations on Public Forests in Minnesota and Wisconsin Matthew Russell1, Michael Kilgore2, Charles Blinn3 Abstract Despite the common management practice and benefits
A Characterization of Timber Salvage Operations on Public Forests in Minnesota and Wisconsin Matthew Russell1, Michael Kilgore2, Charles Blinn3 Abstract Despite the common management practice and benefits
The Hemlock Crisis in Georgia (and the eastern U.S.)
 The Hemlock Crisis in Georgia (and the eastern U.S.) James Johnson Forest Health Coordinator Georgia Forestry Commission Thanks to the University of Georgia and the USDA Forest Service for review of this
The Hemlock Crisis in Georgia (and the eastern U.S.) James Johnson Forest Health Coordinator Georgia Forestry Commission Thanks to the University of Georgia and the USDA Forest Service for review of this
EMERALD ASH BORER MANAGEMENT PLAN
 EMERALD ASH BORER MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR THE CITY OF DODGEVILLE PREPARED MARCH, 2014 BY: GREG LEE TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY PAGE 3 PLAN ADMINISTRATION PAGE 4 PURPOSE PAGE 4 WHAT IS THE EMERALD ASH
EMERALD ASH BORER MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR THE CITY OF DODGEVILLE PREPARED MARCH, 2014 BY: GREG LEE TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY PAGE 3 PLAN ADMINISTRATION PAGE 4 PURPOSE PAGE 4 WHAT IS THE EMERALD ASH
FINAL REPORT NEW ENGLAND MAPLE SYRUP PEST MANAGEMENT SURVEY Glen W. Koehler University of Maine Cooperative Extension
 FINAL REPORT NEW ENGLAND MAPLE SYRUP PEST MANAGEMENT SURVEY Glen W. Koehler University of Maine Cooperative Extension Program: Partnership Project Title: New England Maple Syrup Pest Management Concerns
FINAL REPORT NEW ENGLAND MAPLE SYRUP PEST MANAGEMENT SURVEY Glen W. Koehler University of Maine Cooperative Extension Program: Partnership Project Title: New England Maple Syrup Pest Management Concerns
Hemlock Sawfly. Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 31. Forest Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture,
 Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 31 Forest Service U.S. Department of Agriculture defoliators, particularly the blackheaded budworm (Acleris gloverana Walsingham). Some trees, however, are top killed and
Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 31 Forest Service U.S. Department of Agriculture defoliators, particularly the blackheaded budworm (Acleris gloverana Walsingham). Some trees, however, are top killed and
Genomics & Canada s Trees Summer Street Halifax, NS B3H 0A8. genomeatlantic.ca
 Genomics & FORESTRY Producing and Protecting Canada s Trees genomics & FORESTRY Making the most of our forests in a sustainable way is a crucial economic and environmental challenge for Canada. With a
Genomics & FORESTRY Producing and Protecting Canada s Trees genomics & FORESTRY Making the most of our forests in a sustainable way is a crucial economic and environmental challenge for Canada. With a
3. The poor condition of Connecticut s forests in the late 1800s and early 1900s helped spur the conservation movement in CT.
 CT Envirothon Forestry Test - 2016 Where appropriate circle the correct answer(s) and be sure to answer questions on both sides of the page. Each correct answer is 2.5 points. Use two part common names
CT Envirothon Forestry Test - 2016 Where appropriate circle the correct answer(s) and be sure to answer questions on both sides of the page. Each correct answer is 2.5 points. Use two part common names
Part 2 Setting the Stage. Report of the New Brunswick Task Force on Forest Diversity and Wood Supply
 Part 2 Setting the Stage Report of the New Brunswick Task Force on Forest Diversity and Wood Supply The Acadian Forest The Acadian Forest is the name given to the forest region which encompasses northern
Part 2 Setting the Stage Report of the New Brunswick Task Force on Forest Diversity and Wood Supply The Acadian Forest The Acadian Forest is the name given to the forest region which encompasses northern
Defining Forests. forestry hardwood log native forest old-growth forest. E-unit: Defining Forests Page 1
 Defining Forests W HEN WE use the tree respectfully and economically, we have one of the greatest resources on the earth, said Frank Lloyd Wright. Clearly Mr. Wright placed value on trees and had sustainability
Defining Forests W HEN WE use the tree respectfully and economically, we have one of the greatest resources on the earth, said Frank Lloyd Wright. Clearly Mr. Wright placed value on trees and had sustainability
Virginia. Forest Health Highlights The Resource
 Virginia The Resource Forest Health Highlights 2012 Virginia s forests cover 15.7 million acres, more than 62% of the state s land area. The majority of the state s forested land, some 10 million acres,
Virginia The Resource Forest Health Highlights 2012 Virginia s forests cover 15.7 million acres, more than 62% of the state s land area. The majority of the state s forested land, some 10 million acres,
USDA FOREST SERVICE NORTHERN REGION State & Private Forestry Missoula, MT 59801
 5D// tio A3 FOREST (74INSECT & DISEASE MANAGEMENT USDA FOREST SERVICE NORTHERN REGION State & Private Forestry Missoula, MT 59801 3450 Report No. 79-6 February 1979 EVALUATION OF MOUNTAIN PINE BEETLE INFESTATION
5D// tio A3 FOREST (74INSECT & DISEASE MANAGEMENT USDA FOREST SERVICE NORTHERN REGION State & Private Forestry Missoula, MT 59801 3450 Report No. 79-6 February 1979 EVALUATION OF MOUNTAIN PINE BEETLE INFESTATION
Steve Munro - 21 August Westwind Forest Stewardship Inc. August 2016
 Steve Munro - 21 August 2016 - Westwind Forest Stewardship Inc. August 2016 Current Impacts on Canada s Forests Observed impacts already occurring Increasing length of growing season 12 days between 1981-1999
Steve Munro - 21 August 2016 - Westwind Forest Stewardship Inc. August 2016 Current Impacts on Canada s Forests Observed impacts already occurring Increasing length of growing season 12 days between 1981-1999
Diagnosing Spruce Problems
 1 White spruce with fungal needle cast Diagnosing Spruce Problems Table of Contents New or older needles eaten 2 Yellow-headed spruce sawfly New or older needles eaten 3 Spruce budworm New or older needles
1 White spruce with fungal needle cast Diagnosing Spruce Problems Table of Contents New or older needles eaten 2 Yellow-headed spruce sawfly New or older needles eaten 3 Spruce budworm New or older needles
Changing Climate, Changing Forests The Impacts of Climate Change on Forests of the Northeastern United States and Eastern Canada
 Changing Climate, Changing Forests The Impacts of Climate Change on Forests of the Northeastern United States and Eastern Canada Lindsey Rustad, US Forest Service NE March 26, 2014 Lindsey Rustad, US Forest
Changing Climate, Changing Forests The Impacts of Climate Change on Forests of the Northeastern United States and Eastern Canada Lindsey Rustad, US Forest Service NE March 26, 2014 Lindsey Rustad, US Forest
8) Which of the following species is best adapted to poorly drained sites? a) Bur oak b) Eastern red cedar c) Black ash d) Yellow birch
 School Score Wisconsin Envirothon 2004 Forestry Exam Answer the following questions based on the species description and graphic to the right. 1) This tree is the state tree of Wisconsin and is prized
School Score Wisconsin Envirothon 2004 Forestry Exam Answer the following questions based on the species description and graphic to the right. 1) This tree is the state tree of Wisconsin and is prized
2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES
 2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES BACKGROUND Quality timber trees are important to the region s wood products industry. Quality is determined by tree size and the amount of clear, knot-free lumber the
2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES BACKGROUND Quality timber trees are important to the region s wood products industry. Quality is determined by tree size and the amount of clear, knot-free lumber the
Spruce problem diagnosis for yard trees. by Jana and Mike Albers, MNDNR Division of Forestry
 Spruce problem diagnosis for yard trees by Jana and Mike Albers, MNDNR Division of Forestry Current or older needles eaten (1) Yellow-headed spruce sawfly Defoliation of leader and upper crown of trees
Spruce problem diagnosis for yard trees by Jana and Mike Albers, MNDNR Division of Forestry Current or older needles eaten (1) Yellow-headed spruce sawfly Defoliation of leader and upper crown of trees
Annual Report on Forest Management 2009/10
 Annual Report on Forest Management 2009/10 Annual Report on Forest Management For the year April 1, 2009 to March 31, 2010 Minister of Natural Resources of the Province of Ontario To his Honour The Lieutenant-Governor
Annual Report on Forest Management 2009/10 Annual Report on Forest Management For the year April 1, 2009 to March 31, 2010 Minister of Natural Resources of the Province of Ontario To his Honour The Lieutenant-Governor
Climate Change & New England Forests
 Climate Change & New England Forests Vulnerability Assessment and Other Resources Maria Janowiak mjanowiak02@fs.fed.us Northern Institute of Applied Climate Science USDA Forest Service www.nrs.fs.fed.us/niacs
Climate Change & New England Forests Vulnerability Assessment and Other Resources Maria Janowiak mjanowiak02@fs.fed.us Northern Institute of Applied Climate Science USDA Forest Service www.nrs.fs.fed.us/niacs
Black Spruce- Lowland. Tower Birch Clearcut-w/Reserves Adjacent 6/5/2019
 Minnesota Department of Natural Resource Division of Forestry 500 Lafayette Road St. Paul, MN 55155-4044 February 08, 2018 Notice of Annual Plan Additions Fiscal Year 2019 Harvest Plan Addition 4 This
Minnesota Department of Natural Resource Division of Forestry 500 Lafayette Road St. Paul, MN 55155-4044 February 08, 2018 Notice of Annual Plan Additions Fiscal Year 2019 Harvest Plan Addition 4 This
Forest Insect and Disease Highlights in Oregon, 2001
 United States Department of Agriculture Oregon Department of Forestry Forest Service Pacific Northwest Region Forest Insect and Disease Highlights in Oregon, 2001 Jerald E.Dewey June 2002 The U.S. Department
United States Department of Agriculture Oregon Department of Forestry Forest Service Pacific Northwest Region Forest Insect and Disease Highlights in Oregon, 2001 Jerald E.Dewey June 2002 The U.S. Department
