Stand age related differences in non-co 2 soil atmosphere GHG-exchange in wet temperate Eucalyptus forests of SE Australia
|
|
|
- Agatha Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Benedikt Fest Stand age related differences in non-co 2 soil atmosphere GHG-exchange in wet temperate Eucalyptus forests of SE Australia
2 Table of Content 1. Background 2. Research rationale/objectives 3. Case Studies 4. Discussion
3 Processes behind non-co2 soil GHG-flux CH4 NO NH2OH N2O NO2 NO2 CH4 CO2 H2O CH4 CH3OH HCHO CO2 HCOOH NO3 Anaerobic CH4 + O2 CH4 Oxidattion C N2O NH4 + O2 Nitrrification Denitrificattion D N2 Aerobic Aerobic Methanogen M nesis N2O Anaerobic
4 Table of Content 1. Background 2. Research rationale/objectives 3. Case Studies 4. Discussion
5 Research rationale after Dataur and Verchot 2007
6 Research rationale Uniqueness of Australian forest systems Old, weathered soils with a low nutrient t status t (especially nitrogen and phosphorous) Repeated changes to soil properties due to wildfire Direct fire effects: Physical: Increase in Bulk Density after fire Decrease in soil porosity Decrease in soil permeability Change in ph and EC Chemical: Quantity of organic matter decreases, quality changes Nutrient availability increases sometimes remarkably (NH 4 +) Biological: Composition of microbial community changes Microbial biomass decreases after Certini et al. 2005
7 Research objective Investigating the influence of the disturbance history (time since last disturbance) on soil CH 4 and N 2 O flux in wet temperate eucalypt forests of SE Australia
8 Table of Content 1. Background 2. Research rationale/objectives 3. Case Studies 4. Discussion
9 Case Study A King Lake NP Wallaby Creek, King Lake NP (ca mm precipitation y -1 ) - Chrono-sequence of 3 Eucalyptus regnans dominated forest stands that regenerated after stand replacing wildfires Young (30 years old) Mature (90 years old) Old growth (around 300+ years old)
10 Sampling approach Manual chamber incubations; to investigate seasonal variation of soil GHG exchange within forest stands and spatial variation between different aged forest stands King Lake NP: 2x10 chambers along two 50 m transects per forest stand (Project started in 2006 and seasonal measurements were taken in 2008 up to the bushfire in February 2009)
11 Additional measurements Established methods were used to determine: soil bulk density soil gravimetric, volumetric water content soil temperature soil ph and EC particle size analyses soil inorganic N status soil total N, C, litter quantity litter quality (N, C)
12 Case Study B Warra LTER Warra LTER (ca mm precipitation y -1 ) Chrono/disturbance sequence of 6 mixed Eucalyptus obliqua and Eucalyptus regnans forest stands ID History 01CS 2001 clear fell slash burn 66 CS 1966 clear fell slash burn 66S 34S 1966 wildfire 1934 wildfire 34/98S Mix of 1934 and 1898 wildfire OG Over 200 years old
13 Sampling approach Manual chamber incubations; to investigate seasonal variation of soil GHG exchange within forest stands and spatial variation between different aged forest stands Warra LTER 3 plots a 5 chambers per forest stand, seasonal (Project started t in 2009, seasonal measurements were taken until )
14 Additional measurements Established methods were used to determine: soil bulk density soil volumetric water content 2.5 soil temperature soil ph and EC particle size analyses 1 soil inorganic N status soil total N, C, litter quantity litter quality (N, C) [CH4], ppm Reaction/diffusion model (von Fischer et al. in press) Time, min Reactive gas [SF6], ppb Time, min Non-reactive gas A novel approach was used to determine soil diffusivity and methanotrophic activity at the Warra LTER (von Fischer et. al. 2009) Soil DNA extraction
15 Soil atmosphere non-co 2 GHG exchange between different age classes King Lake NP m -2 s Methan Nitrous Oxide mg CO 2 -e equivalents Y M O
16 Soil atmosphere non-co 2 GHG exchange between different age classes Warra LTER s -1 mg CO uivalents m equ Methane Nitrous Oxide CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG
17 Table of Content 1. Background 2. Research rationale/objectives 3. Case Studies 4. Discussion
18 Difference in soil-atmosphere nitrous oxide exchange between stands of different age/disturbance history ug N m -2 hr -1 2 O-N ug N m -2 hr -1 2 O-N CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG Y M O Warra LTER King Lake NP
19 Stand development after Ashton, 2000, Aust. J. Bot.
20 Forest soil C:N and nitrification Soil C/N ratio has been shown to determine the rate of nitrification ifi ti and mineralization in eucalypt forest soils C/N ratio can determine nitrification and mineralisation processes This might indirectly influence soil microbial activity After Attiwill & May 2001, Mar.Freshwater Res.
21 Difference in soil-atmosphere nitrous oxide exchange between stands of different age/disturbance history r -1 ug N 2 O-N m -2 hr r -1 ug N 2 O-N m -2 hr CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG 0 Y M O GWC g*g -1 mg*kg soil -1 NO mg*kgsoil -1 NH CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG 2001CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG 2001CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG GWC g*g NH mg*kg NO 3 mg*kg 4 soil soil Y M O Y M O Y M O
22 Difference in soil-atmosphere nitrous oxide exchange between stands of different age/disturbance history r -1 ug N 2 O-N m -2 hr CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG Model Adjusted R 2 GWC g*g -1 mg*kg soil -1 NO mg*kgsoil -1 NH CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG 2001CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG 2001CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG 8745 N 2 O flux = *NO
23 Differences in soil-atmosphere methane exchange between stands of different age/disturbance history ug CH 4 -C m -2 hr ug CH 4 -C m -2 hr CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG Y M O Warra LTER King Lake NP
24 Impact of fire on CH 4 oxidation Soil biophysical factors: pore volume pore distribution pore connectivity soil compaction soil moisture soil temperature CH 4, O 2 diffu usivity CH 4 assimilation Methanotrophic Biomass/Activiy Composition metabolism Soil biochemical factors: ph, EC, C/N nutrient status Methanotrophic traits: enzyme kinetics NH 4 tolerance nutrient demands (Cu, N, P?) ph tolerance desiccation tolerance temperature response
25 Differences in soil atmosphere methane exchange between stands at Warra LTER 0-10 Model Adjusted R 2 ug CH 4 -C m -2 hr CH 4 flux = * CH 4 flux = * 3.76*D CH CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG activity min -1 CH cm 2 min -1 4 diffusivity CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG 2001CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG Model Adjusted R 2 D CH4 = *S *Soil Temperature D CH4 = *Soil Temperature 6.866*VWC Model Adjusted R 2 = *Air filled porosity = *Air filled porosity *VWC 0.233
26 Summary Non-CO 2 soil atmosphere GHG fluxes are different in stands of different disturbance history for the same forest community in the same geographic area The differences can partly be attributed to stand development related changes in the soil structure and soil nutrient status For CH 4 differences in microbial activity between stands explains most of the observed differences in flux magnitude Differences in N 2 O flux magnitude between stands can be attributed to with stand development increasing soil NH 4 and NO 3 status probably due to lower soil C/N ratios. This with increased soil moisture probably leads to higher levels of denitrification ifi ti
27 Concluding Comments Þ Non-CO 2 soil atmosphere GHG fluxes are difficult to upscale due to their spatial variability Þ Better mechanistic understanding is needed to model these fluxes Þ approaches needed to characterize the soil status/and type for a given stand at one point in time that allows up scaling and modeling of Non-CO 2 GHG (this might be possible for CH 4 )
28 Soil GHG exchange in CO 2 equivalents Warra LTER King Lake NP ivalents m -2 s -1 mg CO 2 -equi CS 1966CS 1966S 1934S Tower OG Y M O Methane Nitrous Oxide Carbon Dioxide
29 Comparison with other forest systems kg N2O ha -1 y -1 kg CH4 ha -1 y CH4 ha -1 y -1 kg CH4 ha -1 y an forests (Duta taur & Verchot 2007) Northe ern Hemisphere (Smith et al. 2000) E. obliqua (Meyer et al. 1997) E. delegatensis (Khalil et al. 1990) E. delegatens sis (Fest et al. 2008) E. re egnans 30 yea ars old E. re egnans 90 yea ars old E. reg gnans 350 yea ars old Nativ ive woodland (Livesley et al. 2007) Mallee ecosystem (Galbally et al. 1996) Mou untain beech NZ (Price et al. 2003) Beech Germ many (Butterbac ach-bahl et al. 2002) Norwa way spruce (Bo orken & Beese e 2006) Rainforests OZ (Kiese et al. 2003) E. reg gnans/e.delega gatensis Warra a 01CS E. reg gnans/e.delega gatensis Warra a 66CS E. regnans/e.deleg egatensis Warr ra 66S E. regnans/e.deleg egatensis Warr ra 34S E. regn nans/e.delegat tensis Warra 89/34S E. regnans/e.dele legatensis War rra OG kg Global mean
30 Thank you! Copyright The University of Melbourne 2008
This presentation is on the value of reducing emissions and enhancing removals of greenhouse gases related to land use and land cover change in
 This presentation is on the value of reducing emissions and enhancing removals of greenhouse gases related to land use and land cover change in tropical wetland forests. 1 The objective of this presentation
This presentation is on the value of reducing emissions and enhancing removals of greenhouse gases related to land use and land cover change in tropical wetland forests. 1 The objective of this presentation
Wombat Flux Supersite
 Wombat Flux Supersite Department of Forest and Ecosystem Science Nina Hinko Najera, Anne Griebel, Benedikt Fest, Julio Najera Umana, Steve Livesley, Stefan Arndt Whroo & Wombat two nodes of the Victorian
Wombat Flux Supersite Department of Forest and Ecosystem Science Nina Hinko Najera, Anne Griebel, Benedikt Fest, Julio Najera Umana, Steve Livesley, Stefan Arndt Whroo & Wombat two nodes of the Victorian
CARBON, GREENHOUSE GASES, AND HOW WE MEASURE THEM
 CARBON, GREENHOUSE GASES, AND HOW WE MEASURE THEM Mila Bristow ENV1 Lecture 215 Mila.Bristow@nt.gov.au http://www.nt.gov.au/d/primary_industry/index.cfm?header=action%2on%2the%2ground Quiz 1. What are
CARBON, GREENHOUSE GASES, AND HOW WE MEASURE THEM Mila Bristow ENV1 Lecture 215 Mila.Bristow@nt.gov.au http://www.nt.gov.au/d/primary_industry/index.cfm?header=action%2on%2the%2ground Quiz 1. What are
EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND. Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella)
 EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella) Scales of meteorological processes: Synoptic scale, ~ 1000 km (weather predictions, 3-7days)
EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella) Scales of meteorological processes: Synoptic scale, ~ 1000 km (weather predictions, 3-7days)
Nutrients elements required for the development, maintenance, and reproduction of organisms.
 Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Advances in forest fire research in Australia Tina Bell
 Advances in forest fire research in Australia Tina Bell The University of Sydney Page 1 Australia is a fire-prone country 30 Area burnt in Australia (1996 2009) 25 Area burnt (Mha) 20 15 10 5 0 1996 1998
Advances in forest fire research in Australia Tina Bell The University of Sydney Page 1 Australia is a fire-prone country 30 Area burnt in Australia (1996 2009) 25 Area burnt (Mha) 20 15 10 5 0 1996 1998
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger,, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger,, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 24 September 2013 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 24 September 2013 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification
Greenhouse gas emissions from St. Emmanuel and the Holland Marsh in Joann Whalen McGill University January 22, 2018
 Greenhouse gas emissions from St. Emmanuel and the Holland Marsh in 2017 Joann Whalen McGill University January 22, 2018 80 0'0"W 75 0'0"W 70 0'0"W 65 0'0"W 55 0'0"N CANADA 55 0'0"N Québec 50 0'0"N 50
Greenhouse gas emissions from St. Emmanuel and the Holland Marsh in 2017 Joann Whalen McGill University January 22, 2018 80 0'0"W 75 0'0"W 70 0'0"W 65 0'0"W 55 0'0"N CANADA 55 0'0"N Québec 50 0'0"N 50
The next 2 weeks. Reading: IPCC (2007), Chap 7 (sections 7.4 and 7.5)
 PCC 588 Jan 15 The next 2 weeks Th. Jan 15: non-co 2 greenhouse gases CH 4 and N 2 O Tu. Jan 20: non-co 2 greenhouse gases: ozone, halocarbons Th. Jan 22: Aerosols and Climate Tu. Jan 27: Paper discussion
PCC 588 Jan 15 The next 2 weeks Th. Jan 15: non-co 2 greenhouse gases CH 4 and N 2 O Tu. Jan 20: non-co 2 greenhouse gases: ozone, halocarbons Th. Jan 22: Aerosols and Climate Tu. Jan 27: Paper discussion
The Australian flux and ecosystem research network. Presentation by Dr Helen Cleugh, Dr Eva van Gorsel and Dr Ray Leuning
 OzFlux The Australian flux and ecosystem research network Presentation by Dr Helen Cleugh, Dr Eva van Gorsel and Dr Ray Leuning Purpose of Facility Terrestrial ecosystems modulate climate Globally, terrestrial
OzFlux The Australian flux and ecosystem research network Presentation by Dr Helen Cleugh, Dr Eva van Gorsel and Dr Ray Leuning Purpose of Facility Terrestrial ecosystems modulate climate Globally, terrestrial
A generalized model of aquatic microbial metabolism based on thermodynamic, kinetic, and stoichiometric theory
 A generalized model of aquatic microbial metabolism based on thermodynamic, kinetic, and stoichiometric theory Robert A. Payn 1,2 Ashley M. Helton 3 Geoffrey C. Poole 1,2,4 Clemente Izurieta 2,4 Emily
A generalized model of aquatic microbial metabolism based on thermodynamic, kinetic, and stoichiometric theory Robert A. Payn 1,2 Ashley M. Helton 3 Geoffrey C. Poole 1,2,4 Clemente Izurieta 2,4 Emily
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 18 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 18 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions
Fluxing up the Deep North an update
 Fluxing up the Deep North an update Mila Bristow (CDU), Jason Beringer (Monash), Peter Isaac (TERN), Stephen Livesley (U Melb), Stefan Arndt (U Melb), Matthew Northwood (CDU), Benedict Fest (U Melb), Lindsay
Fluxing up the Deep North an update Mila Bristow (CDU), Jason Beringer (Monash), Peter Isaac (TERN), Stephen Livesley (U Melb), Stefan Arndt (U Melb), Matthew Northwood (CDU), Benedict Fest (U Melb), Lindsay
Nitrogen as a Contributor to Climate Change. Nitrogen and Climate Change
 Nitrogen as a Contributor to Climate Change Nitrogen and Climate Change Chris Evans Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Bangor, UK With contributions gratefully received from: Bridget Emmett, Gina Mills,
Nitrogen as a Contributor to Climate Change Nitrogen and Climate Change Chris Evans Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Bangor, UK With contributions gratefully received from: Bridget Emmett, Gina Mills,
John M. Marton Ellen R. Herbert Christopher B. Craft Ken W. Krauss. INTECOL 2012, Orlando, Florida
 John M. Marton Ellen R. Herbert Christopher B. Craft Ken W. Krauss INTECOL 2012, Orlando, Florida Wetland Services Effective nutrient (N,P) sinks and transformers C sequestration Flood abatement Biodiversity
John M. Marton Ellen R. Herbert Christopher B. Craft Ken W. Krauss INTECOL 2012, Orlando, Florida Wetland Services Effective nutrient (N,P) sinks and transformers C sequestration Flood abatement Biodiversity
Climate, Water, and Ecosystems: A Future of Surprises
 Climate, Water, and Ecosystems: A Future of Surprises Robert Harriss Houston Advanced Research Center Changsheng Li Steve Frolking University of New Hampshire Climate change is not uniform geographically
Climate, Water, and Ecosystems: A Future of Surprises Robert Harriss Houston Advanced Research Center Changsheng Li Steve Frolking University of New Hampshire Climate change is not uniform geographically
Brianna Richards Chris Craft
 Brianna Richards Chris Craft June 8, 2012 Wetland ecosystem services Flood abatement and water storage Nutrient Removal Biodiversity Habitat C sequestration Wetland Losses Conversion to ag Example: Great
Brianna Richards Chris Craft June 8, 2012 Wetland ecosystem services Flood abatement and water storage Nutrient Removal Biodiversity Habitat C sequestration Wetland Losses Conversion to ag Example: Great
Biogeochemistry of Wetlands
 Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS) Biogeochemistry of Wetlands Si Science and da Applications Biogeochemical Properties of Wetlands Wetland Biogeochemistry Laboratory Soil and Water Science
Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS) Biogeochemistry of Wetlands Si Science and da Applications Biogeochemical Properties of Wetlands Wetland Biogeochemistry Laboratory Soil and Water Science
Agriculture Practices on GHG Production: Adaptation and Mitigation of GHG Emission from Agriculture Sector
 Agriculture Practices on GHG Production: Adaptation and Mitigation of GHG Emission from Agriculture Sector R. Gowthami 1*, K. V. Raghavendra 2 and R. Shashank 3 1, 2 Ph. D. Student, AC & RI, Madurai, Tamil
Agriculture Practices on GHG Production: Adaptation and Mitigation of GHG Emission from Agriculture Sector R. Gowthami 1*, K. V. Raghavendra 2 and R. Shashank 3 1, 2 Ph. D. Student, AC & RI, Madurai, Tamil
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 23 September 2014 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2014 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 23 September 2014 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2014 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Development of a Microbial Module, CLM-Microbe in CESM: framework and preliminary results
 Development of a Microbial Module, CLM-Microbe in CESM: framework and preliminary results Xiaofeng Xu 1, Peter Thornton 1, Fengming Yuan 1, David Graham 2, Dwayne A. Elias 1,2, Santonu Goswami 1, Joshua
Development of a Microbial Module, CLM-Microbe in CESM: framework and preliminary results Xiaofeng Xu 1, Peter Thornton 1, Fengming Yuan 1, David Graham 2, Dwayne A. Elias 1,2, Santonu Goswami 1, Joshua
Biogeochemistry of C
 Biogeochemistry of C NREM 665 CO 2 CO 2 CH 4 diffusion & ebullition CO 2 Organic-C accretion DOC CH 4 methanogenesis C Biogeochemistry I.Forms of C in WTLs & Coastal Ecosystems Molecule Oxidation State
Biogeochemistry of C NREM 665 CO 2 CO 2 CH 4 diffusion & ebullition CO 2 Organic-C accretion DOC CH 4 methanogenesis C Biogeochemistry I.Forms of C in WTLs & Coastal Ecosystems Molecule Oxidation State
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils
 Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Contribution of Nitrous Oxide in Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Novel and Conventional Rice Production Technologies
 Contribution of Nitrous Oxide in Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Novel and Conventional Rice Production Technologies Md. Khairul Alam 1 ; Wahidul K. Biswas 2 and Richard W. Bell 1 1 Land Management
Contribution of Nitrous Oxide in Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Novel and Conventional Rice Production Technologies Md. Khairul Alam 1 ; Wahidul K. Biswas 2 and Richard W. Bell 1 1 Land Management
Maintaining soil fertility in biomass for bioenergy production systems
 Maintaining soil fertility in biomass for bioenergy production systems John Raison CSIRO Ecosystem Sciences Energy Transformed Flagship IEA Bioenergy, November 2011 Outline Central role of soils in ecosystem
Maintaining soil fertility in biomass for bioenergy production systems John Raison CSIRO Ecosystem Sciences Energy Transformed Flagship IEA Bioenergy, November 2011 Outline Central role of soils in ecosystem
Monitoring carbon budgets
 Monitoring carbon budgets Suess effect on 14 C/ 12 C in CO 2, from Stuiver and Quay, 1981, EPSL 53:349-362 1 Figure from IPCC 4 th assessment report 2 Biogeochemical cycling (on land) Living tissue C H
Monitoring carbon budgets Suess effect on 14 C/ 12 C in CO 2, from Stuiver and Quay, 1981, EPSL 53:349-362 1 Figure from IPCC 4 th assessment report 2 Biogeochemical cycling (on land) Living tissue C H
SARAWAK TROPICAL PEAT RESEARCH INSTITUTE (TROPI)
 SARAWAK TROPICAL PEAT RESEARCH INSTITUTE (TROPI) Workshop on Haze and Biomass Burning in Asia A Systems Perspective to Reveal Opportunities with Benefits for Long-term Transformations 4 th 5 th October
SARAWAK TROPICAL PEAT RESEARCH INSTITUTE (TROPI) Workshop on Haze and Biomass Burning in Asia A Systems Perspective to Reveal Opportunities with Benefits for Long-term Transformations 4 th 5 th October
Carbon Farming in Australia. Richard Eckard
 Carbon Farming in Australia Richard Eckard Australian Emissions Context DCCEE 2013 Australian Emissions Context Agriculture 57% of all methane 75% of all nitrous oxide Enteric Methane 11.5% of National
Carbon Farming in Australia Richard Eckard Australian Emissions Context DCCEE 2013 Australian Emissions Context Agriculture 57% of all methane 75% of all nitrous oxide Enteric Methane 11.5% of National
Contribution of Nitrous Oxide in Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Novel and Conventional Rice Production Technologies
 Contribution of Nitrous Oxide in Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Novel and Conventional Rice Production Technologies Md. Khairul Alam1; Wahidul K. Biswas2 and Richard W. Bell1 1Land Management Group
Contribution of Nitrous Oxide in Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Novel and Conventional Rice Production Technologies Md. Khairul Alam1; Wahidul K. Biswas2 and Richard W. Bell1 1Land Management Group
Application of biochar as a tool to mitigate non-co2 greenhouse gas emissions from soil
 Application of biochar as a tool to mitigate non-co2 greenhouse gas emissions from soil Per Ambus Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy Technical University of Denmark Biochar sequesters carbon
Application of biochar as a tool to mitigate non-co2 greenhouse gas emissions from soil Per Ambus Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy Technical University of Denmark Biochar sequesters carbon
Organic agriculture and climate change the scientific evidence
 Organic agriculture and climate change the scientific evidence >Andreas Fließbach >BioFach 2007, Nürnberg, 17.02.2007 Organic Agriculture and Climate Change > The report of the Intergovernmental Panel
Organic agriculture and climate change the scientific evidence >Andreas Fließbach >BioFach 2007, Nürnberg, 17.02.2007 Organic Agriculture and Climate Change > The report of the Intergovernmental Panel
David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology
 How does carbon influence nitrogen availability and losses? David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology Outline Carbon cycle Global carbon cycle Soil carbon 3
How does carbon influence nitrogen availability and losses? David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology Outline Carbon cycle Global carbon cycle Soil carbon 3
FORESTS, FIRE AND ECOLOGICAL PROCESSES MORE THAN JUST GOOD IN THEORY
 Bushfire Conference - Brisbane, 9 June FORESTS, FIRE AND ECOLOGICAL PROCESSES MORE THAN JUST GOOD IN THEORY A. K. York, T. L. Bell, F. J. Christie and K. E. C. Brennan School of Forest and Ecosystem Science,
Bushfire Conference - Brisbane, 9 June FORESTS, FIRE AND ECOLOGICAL PROCESSES MORE THAN JUST GOOD IN THEORY A. K. York, T. L. Bell, F. J. Christie and K. E. C. Brennan School of Forest and Ecosystem Science,
Determining the f ratio 11/16/2010. Incubate seawater in the presence of trace 15
 Plankton production is supported by 2 types of nitrogen: 1) new production supported by external sources of N (e.g. NO 3 and N 2 ), 2) recycled or regenerated production, sustained by recycling of N. Assumptions:
Plankton production is supported by 2 types of nitrogen: 1) new production supported by external sources of N (e.g. NO 3 and N 2 ), 2) recycled or regenerated production, sustained by recycling of N. Assumptions:
Managing Soils for Improved Pasture
 Managing Soils for Improved Pasture Jonathan Deenik, PhD Department of Tropical Plant and Soil Sciences University of Hawaii Rota Grazing and Livestock Management Workshop June 10-12, 12, 2010 1 Water
Managing Soils for Improved Pasture Jonathan Deenik, PhD Department of Tropical Plant and Soil Sciences University of Hawaii Rota Grazing and Livestock Management Workshop June 10-12, 12, 2010 1 Water
Greenhouse gas flux from green waste compost windrows and following application to soils in almonds and tomatoes
 Greenhouse gas flux from green waste compost windrows and following application to soils in almonds and tomatoes William R. Horwath Dept. Land, Air and Water Resources, Univ. California, Davis, CA, USA
Greenhouse gas flux from green waste compost windrows and following application to soils in almonds and tomatoes William R. Horwath Dept. Land, Air and Water Resources, Univ. California, Davis, CA, USA
Nutrient Cycles. Nutrient cycles involve flow of high quality energy from the sun through the environment & of elements.
 Nutrient Cycles Nutrient cycles (= biogeochemical cycles): natural processes that involve the flow of nutrients from the environment (air, water, soil, rock) to living organisms ( ) & back again. Nutrient
Nutrient Cycles Nutrient cycles (= biogeochemical cycles): natural processes that involve the flow of nutrients from the environment (air, water, soil, rock) to living organisms ( ) & back again. Nutrient
Manure-DNDC: Building a Process-Based Biogeochemical Tool for Estimating Ammonia and GHG Emissions from California Dairies
 Manure-DNDC: Building a Process-Based Biogeochemical Tool for Estimating Ammonia and GHG Emissions from California Dairies William Salas*, Applied Geosolutions, LLC Changsheng Li, University of New Hampshire,
Manure-DNDC: Building a Process-Based Biogeochemical Tool for Estimating Ammonia and GHG Emissions from California Dairies William Salas*, Applied Geosolutions, LLC Changsheng Li, University of New Hampshire,
Long Term Treatment and Disposal of Landfill Leachate. Debra R. Reinhart Nicole Berge Eyad Batarseh University of Central Florida
 Long Term Treatment and Disposal of Landfill Leachate Debra R. Reinhart Nicole Berge Eyad Batarseh University of Central Florida Presentation Brief introduction Debra Reinhart In Situ Nitrification/Denitrification
Long Term Treatment and Disposal of Landfill Leachate Debra R. Reinhart Nicole Berge Eyad Batarseh University of Central Florida Presentation Brief introduction Debra Reinhart In Situ Nitrification/Denitrification
Livestock and Poultry Environmental Learning Center Webcast Series October 17, 2008
 Contribution of Manure Amendments to Soil Fertility and Carbon Sequestration Animal wastes contain inorganic N (NH 4 + NO 3 -N) and organic N: Inorganic N is plant available Organic N is mineralized by
Contribution of Manure Amendments to Soil Fertility and Carbon Sequestration Animal wastes contain inorganic N (NH 4 + NO 3 -N) and organic N: Inorganic N is plant available Organic N is mineralized by
Assessing the impacts of intensive biomass removals and ash applications in the boreal forest
 Assessing the impacts of intensive biomass removals and ash applications in the boreal forest Paul Hazlett, Dave Morris, Rob Fleming Canadian Forest Service, Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources Why a
Assessing the impacts of intensive biomass removals and ash applications in the boreal forest Paul Hazlett, Dave Morris, Rob Fleming Canadian Forest Service, Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources Why a
DNDC-EUROPE. linking economic and mechanistic models
 DNDC-EUROPE linking economic and mechanistic models Adrian Leip, Giulio Marchi Joint Research Centre JRC-AL: CAPRI-DynaSpat final meeting, Bruxelles, 27.02.2007 - Approach CAPRI economic model with regional
DNDC-EUROPE linking economic and mechanistic models Adrian Leip, Giulio Marchi Joint Research Centre JRC-AL: CAPRI-DynaSpat final meeting, Bruxelles, 27.02.2007 - Approach CAPRI economic model with regional
Three-Dimensional Simulations of Methane Injection
 Three-Dimensional Simulations of Methane Injection Preliminary Modeling Study Using MIN3P-Dusty 6 th Annual International Conference on Soil, Water, Energy, and Air March 1-4, 016 San Diego, California
Three-Dimensional Simulations of Methane Injection Preliminary Modeling Study Using MIN3P-Dusty 6 th Annual International Conference on Soil, Water, Energy, and Air March 1-4, 016 San Diego, California
NUTRIENT CYCLES REVIEW
 52 Name A.P. Environmental Science Date Mr. Romano NUTRIENT CYCLES REVIEW 1. Which of the following chain of events would occur as a result of land clearing/deforestation? (vocabulary check: efflux means
52 Name A.P. Environmental Science Date Mr. Romano NUTRIENT CYCLES REVIEW 1. Which of the following chain of events would occur as a result of land clearing/deforestation? (vocabulary check: efflux means
N-cycle: biogeochemistry. Biological flows of Nitrogen
 N-cycle: biogeochemistry SWES 410/510 April 4, 2014 I. N cycling A. simplest possible B. Global N budget C. Effects of N-cycling ( the Nitrogen Cascade ) II. Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) budgets III. Data-Model
N-cycle: biogeochemistry SWES 410/510 April 4, 2014 I. N cycling A. simplest possible B. Global N budget C. Effects of N-cycling ( the Nitrogen Cascade ) II. Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) budgets III. Data-Model
River transport and chemistry. Lecture Outline
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.12.17) (Schlesinger & Bernhardt: Chapter 8) River transport and chemistry Lecture Outline 1. Introduction Overview 2. Soil Hydraulics & Stream Hydrology 3. Stream Load
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.12.17) (Schlesinger & Bernhardt: Chapter 8) River transport and chemistry Lecture Outline 1. Introduction Overview 2. Soil Hydraulics & Stream Hydrology 3. Stream Load
Hana Santruckova Introduction in the topic of the IP Soil & Water :
 ERASMUS Soil & Water Protokoll Montag 17.09.2012 Hana Santruckova Introduction in the topic of the IP Soil & Water : Soil-Water-Interactions water retention capacity of soil: water doesn't evaporate in
ERASMUS Soil & Water Protokoll Montag 17.09.2012 Hana Santruckova Introduction in the topic of the IP Soil & Water : Soil-Water-Interactions water retention capacity of soil: water doesn't evaporate in
Impact of forestry on soil quality in the UK
 Impact of forestry on soil quality in the UK Elena Vanguelova, Andy Moffat and Jim Lynch Forest Research, UK Processes and cycling in Forest Ecosystems Common forest soil chemical quality indicators Soil
Impact of forestry on soil quality in the UK Elena Vanguelova, Andy Moffat and Jim Lynch Forest Research, UK Processes and cycling in Forest Ecosystems Common forest soil chemical quality indicators Soil
How to measure soil health. Caley Gasch NDSU Soil Health Research
 How to measure soil health Caley Gasch NDSU Soil Health Research caley.gasch@ndsu.edu Ecosystem Soil Health Time Soil Function Biology Physics Chemistry What is soil health? Contamination Natural & industrial
How to measure soil health Caley Gasch NDSU Soil Health Research caley.gasch@ndsu.edu Ecosystem Soil Health Time Soil Function Biology Physics Chemistry What is soil health? Contamination Natural & industrial
BIOGEOCHEMISTRY BIOGEOCHEMISTR Y OF N NREM
 BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF N NREM 665 Dominant Pathways for N Cycling Plant Uptake: assimilation of NH + - 4 and NO 3 into biomass N Fixation: Conversion of gaseous N 2 to NH 3 Ammonia Volatilization: NH 4+ NH
BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF N NREM 665 Dominant Pathways for N Cycling Plant Uptake: assimilation of NH + - 4 and NO 3 into biomass N Fixation: Conversion of gaseous N 2 to NH 3 Ammonia Volatilization: NH 4+ NH
People and the Temperate Region n /-» _ r»» i r. i,,.._ ^^ fen and the Biosphere Program 1991
 United States Department of State People and the Temperate Region n /-» _ r»» i r. i,,.._ ^^ fen and the Biosphere Program 1991 United States Man and the Biosphere Program Nitrogen Transformation Processes
United States Department of State People and the Temperate Region n /-» _ r»» i r. i,,.._ ^^ fen and the Biosphere Program 1991 United States Man and the Biosphere Program Nitrogen Transformation Processes
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Modeling the Impacts of Different Agricultural Practices on Nitrogen Losses from Agricultural Soils in Haean Catchment
 Modeling the Impacts of Different Agricultural Practices on Nitrogen Losses from Agricultural Soils in Haean Catchment Kim, Youngsun (1,3); Kiese, Ralf (1); Berger, Sina (2); Gebauer, Gerhard (2); Tenhunen,
Modeling the Impacts of Different Agricultural Practices on Nitrogen Losses from Agricultural Soils in Haean Catchment Kim, Youngsun (1,3); Kiese, Ralf (1); Berger, Sina (2); Gebauer, Gerhard (2); Tenhunen,
N 2 O, CH 4 and CO 2 emissions from seasonal tropical rainforests and a rubber plantation in Southwest China
 Plant Soil (2006) 289:335 353 DOI 10.1007/s11104-006-9143-y ORIGINAL PAPER N 2 O, CH 4 and CO 2 emissions from seasonal tropical rainforests and a rubber plantation in Southwest China Christian Werner
Plant Soil (2006) 289:335 353 DOI 10.1007/s11104-006-9143-y ORIGINAL PAPER N 2 O, CH 4 and CO 2 emissions from seasonal tropical rainforests and a rubber plantation in Southwest China Christian Werner
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem
 Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem 2.1 Productivity 2.2 Oxygen 2.3 Salinity 2.4 Carbon 2.5 Nitrogen 2.6 Phosphorous 2.7 Iron 2.8 Sulphur 2.9 Silica 2.3 Salinity of Inland Waters The salinity of freshwaters
Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem 2.1 Productivity 2.2 Oxygen 2.3 Salinity 2.4 Carbon 2.5 Nitrogen 2.6 Phosphorous 2.7 Iron 2.8 Sulphur 2.9 Silica 2.3 Salinity of Inland Waters The salinity of freshwaters
Biochar Soil Amendment Opportunities
 Biochar Soil Amendment Opportunities Curtis Dell Research Soil Scientist, USDA ARS and Adjunct Associate Professor, Ecosystems Science and Management Department, PSU Soils 101 Important soil properties
Biochar Soil Amendment Opportunities Curtis Dell Research Soil Scientist, USDA ARS and Adjunct Associate Professor, Ecosystems Science and Management Department, PSU Soils 101 Important soil properties
The amount of fixed nitrogen (N that has chemically combined with other
 Chapter 1: Introduction The cycle of N is unique in that it consists of a massive, well-mixed, and (to most organisms) wholly unavailable pool of nitrogen gas (N 2 ) in the atmosphere; a relatively small
Chapter 1: Introduction The cycle of N is unique in that it consists of a massive, well-mixed, and (to most organisms) wholly unavailable pool of nitrogen gas (N 2 ) in the atmosphere; a relatively small
Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases
 Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases Content Atmospheric Composition Composition of the Earth s Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases The Radiative Forcing bar chart: AR5 version Natural Greenhouse Gases Water
Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases Content Atmospheric Composition Composition of the Earth s Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases The Radiative Forcing bar chart: AR5 version Natural Greenhouse Gases Water
Introduction of Dinghushan Forest Ecosystem Research Station
 Introduction of Dinghushan Forest Ecosystem Research Station Dinghushan Station Chinese Academy of Sciences Bayreuth, Germany 2010-04-13 Outline Location of Dinghushan History of Long-term ecological research
Introduction of Dinghushan Forest Ecosystem Research Station Dinghushan Station Chinese Academy of Sciences Bayreuth, Germany 2010-04-13 Outline Location of Dinghushan History of Long-term ecological research
EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND. Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella)
 EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella) Scales of meteorological processes: Synoptic scale, ~ 1000 km (weather predictions, ~ day) Mesoscale,
EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella) Scales of meteorological processes: Synoptic scale, ~ 1000 km (weather predictions, ~ day) Mesoscale,
Annual soil quality monitoring report for the Wellington region, 2007/08
 Annual soil quality monitoring report for the Wellington region, 27/8 Paul Sorensen Environmental Monitoring and Investigations Department FOR FURTHER INFORMATION Greater Wellington Regional Council Wellington
Annual soil quality monitoring report for the Wellington region, 27/8 Paul Sorensen Environmental Monitoring and Investigations Department FOR FURTHER INFORMATION Greater Wellington Regional Council Wellington
Legume-based catch crops can improve N-supply without increasing the N 2 O emission
 Legume-based catch crops can improve N-supply without increasing the N 2 O emission By Xiaoxi Li, Peter Sørensen, Søren O. Petersen and Jørgen E. Olesen, Department of Agroecology, Aarhus University Legume-based
Legume-based catch crops can improve N-supply without increasing the N 2 O emission By Xiaoxi Li, Peter Sørensen, Søren O. Petersen and Jørgen E. Olesen, Department of Agroecology, Aarhus University Legume-based
Legume-based catch crops can improve N-supply without increasing the N 2 O emission
 Legume-based catch crops can improve N-supply without increasing the N 2 O emission By Xiaoxi Li, Peter Sørensen, Søren O. Petersen and Jørgen E. Olesen, Department of Agroecology, Aarhus University Legume-based
Legume-based catch crops can improve N-supply without increasing the N 2 O emission By Xiaoxi Li, Peter Sørensen, Søren O. Petersen and Jørgen E. Olesen, Department of Agroecology, Aarhus University Legume-based
What s Happening in the Mud at the Bottom of the Bay?
 What s Happening in the Mud at the Bottom of the Bay? Sarah Q. Foster PhD Candidate Earth and Environment Department, Boston University Research at the Reserve Coffee House Series / WBNERR, East Falmouth,
What s Happening in the Mud at the Bottom of the Bay? Sarah Q. Foster PhD Candidate Earth and Environment Department, Boston University Research at the Reserve Coffee House Series / WBNERR, East Falmouth,
Influence of compost & wood chip mulch on greenhouse gas emissions, soil carbon & nutrient dynamics
 Influence of compost & wood chip mulch on greenhouse gas emissions, soil carbon & nutrient dynamics March 1, 2016 Compost Matters in British Columbia Biological activity Biological activity Bulk density,
Influence of compost & wood chip mulch on greenhouse gas emissions, soil carbon & nutrient dynamics March 1, 2016 Compost Matters in British Columbia Biological activity Biological activity Bulk density,
The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles
 OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles (12.1.11) The Contemporary N Cycle - Basic Facts - Reservoirs and Fluxes Global N and P Budgets - balance between N-fixation and
OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles (12.1.11) The Contemporary N Cycle - Basic Facts - Reservoirs and Fluxes Global N and P Budgets - balance between N-fixation and
Impact of Agricultural Production on Climate Change
 Impact of Agricultural Production on Climate Change Aaron J. Glenn Research Scientist - Micrometeorology Brandon Research & Development Centre March 22, 2017 What is micrometeorology? A part of meteorology
Impact of Agricultural Production on Climate Change Aaron J. Glenn Research Scientist - Micrometeorology Brandon Research & Development Centre March 22, 2017 What is micrometeorology? A part of meteorology
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES A biogeochemical cycle or cycling of substances is a pathway by which a chemical element or molecule moves through both biotic and abiotic compartments of Earth.
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES A biogeochemical cycle or cycling of substances is a pathway by which a chemical element or molecule moves through both biotic and abiotic compartments of Earth.
METHANE BIOFILTRATION: A COST-EFFECTIVE APPROACH TO ELIMINATE FUGITIVE METHANE EMISSIONS
 METHANE BIOFILTRATION: A COST-EFFECTIVE APPROACH TO ELIMINATE FUGITIVE METHANE EMISSIONS J. Patrick. A. HETTIARATCHI (1) (1) Professor, Center for Environmental Engineering Research and Education(CEERE),
METHANE BIOFILTRATION: A COST-EFFECTIVE APPROACH TO ELIMINATE FUGITIVE METHANE EMISSIONS J. Patrick. A. HETTIARATCHI (1) (1) Professor, Center for Environmental Engineering Research and Education(CEERE),
Production and Utilization of Compost and Greenhouse Emissions. Monica Ozores-Hampton, Ph.D University of Florida/IFAS
 Production and Utilization of Compost and Greenhouse Emissions Monica Ozores-Hampton, Ph.D University of Florida/IFAS Global Warming Increased CO 2 in the atmosphere has been implicated in the global warming.
Production and Utilization of Compost and Greenhouse Emissions Monica Ozores-Hampton, Ph.D University of Florida/IFAS Global Warming Increased CO 2 in the atmosphere has been implicated in the global warming.
FIGURE SET HEADER for Set #5. Figure Set 5: Global Warming Potential Temperate Agriculture
 FIGURE SET HEADER for Set #5 Figure Set 5: Global Warming Potential Temperate Agriculture Purpose: To teach students that land management can affect the amount of greenhouse gas emissions from temperate
FIGURE SET HEADER for Set #5 Figure Set 5: Global Warming Potential Temperate Agriculture Purpose: To teach students that land management can affect the amount of greenhouse gas emissions from temperate
Introduction. Objective: Livestock operations Current trend is towards large confined operations
 2 Introduction Optimizing feed and manure management to reduce methane and nitrous oxide emissions from livestock manure storage and composting Xiying Hao 1, Tim A. McAllister 1, Kim Stanford 2 1 Agriculture
2 Introduction Optimizing feed and manure management to reduce methane and nitrous oxide emissions from livestock manure storage and composting Xiying Hao 1, Tim A. McAllister 1, Kim Stanford 2 1 Agriculture
EFFECT OF PERSISTENT SUBSOIL COMPACTION ON N 2 O EMISSIONS FROM ARABLE SOILS
 EFFECT OF PERSISTENT SUBSOIL COMPACTION ON N 2 O EMISSIONS FROM ARABLE SOILS Kristiina Regina (Agrifood Research Finland) Asko Simojoki, Laura Alakukku (University of Helsinki) Hanna Silvennoinen, Peter
EFFECT OF PERSISTENT SUBSOIL COMPACTION ON N 2 O EMISSIONS FROM ARABLE SOILS Kristiina Regina (Agrifood Research Finland) Asko Simojoki, Laura Alakukku (University of Helsinki) Hanna Silvennoinen, Peter
Implementing APRIL s 4Cs on Peatland
 Implementing APRIL s 4Cs on Peatland APRIL-IPEWG Peatland Roadmap Version 3.2, June 2017 The Independent Peatland Expert Working Group (IPEWG) was established to support APRIL by providing science-based
Implementing APRIL s 4Cs on Peatland APRIL-IPEWG Peatland Roadmap Version 3.2, June 2017 The Independent Peatland Expert Working Group (IPEWG) was established to support APRIL by providing science-based
Relationships between nitrous oxide emissions from natural ecosystems and environmental factors
 Relationships between nitrous oxide emissions from natural ecosystems and environmental factors M. Bloemerts W. de Vries Alterra-report 1853, ISSN 1566-7197 Relationships between nitrous oxide emissions
Relationships between nitrous oxide emissions from natural ecosystems and environmental factors M. Bloemerts W. de Vries Alterra-report 1853, ISSN 1566-7197 Relationships between nitrous oxide emissions
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 19 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2017 Frank Sansone Outline 1. Nitrogen cycle
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 19 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2017 Frank Sansone Outline 1. Nitrogen cycle
Control of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from California Vineyards by Soil Carbon and Water and its Policy Implications
 2001-2006 Mission Kearney Foundation of Soil Science: Soil Carbon and California's Terrestrial Ecosystems Final Report: 2005225, 1/1/2006-12/31/2006 Control of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from California
2001-2006 Mission Kearney Foundation of Soil Science: Soil Carbon and California's Terrestrial Ecosystems Final Report: 2005225, 1/1/2006-12/31/2006 Control of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from California
A Genetic-Mitigation Strategy. GV Subbarao JIRCAS, Japan
 (BNI)-Technology Tackling Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Emissions A Genetic-Mitigation Strategy GV Subbarao JIRCAS, Japan Collaborators & Partners CIAT CIMMYT ICRISAT CCAF Global GHG emissions Monetization
(BNI)-Technology Tackling Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Emissions A Genetic-Mitigation Strategy GV Subbarao JIRCAS, Japan Collaborators & Partners CIAT CIMMYT ICRISAT CCAF Global GHG emissions Monetization
Major changes in forest carbon and nitrogen cycling caused by declining sulphur deposition
 Major changes in forest carbon and nitrogen cycling caused by declining sulphur deposition Filip Oulehle, Chris Evans, Henning Meesenburg, Jakub Hruska, Pavel Kram, Jiri Kopacek, Bridget Emmett, Jack Cosby,
Major changes in forest carbon and nitrogen cycling caused by declining sulphur deposition Filip Oulehle, Chris Evans, Henning Meesenburg, Jakub Hruska, Pavel Kram, Jiri Kopacek, Bridget Emmett, Jack Cosby,
Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers
 Symposium no. 65 Paper no. 246 Presentation: poster Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers KOZLOV A.E., STEPANOV A. and MANUCHAROVA N. Moscow
Symposium no. 65 Paper no. 246 Presentation: poster Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers KOZLOV A.E., STEPANOV A. and MANUCHAROVA N. Moscow
Land use change and the impact on greenhouse gas exchange in north Australian savanna soils
 Biogeosciences Discuss., 8, 9087 9123, 11 www.biogeosciences-discuss.net/8/9087/11/ doi:.194/bgd-8-9087-11 Author(s) 11. CC Attribution 3.0 License. This discussion paper is/has been under review for the
Biogeosciences Discuss., 8, 9087 9123, 11 www.biogeosciences-discuss.net/8/9087/11/ doi:.194/bgd-8-9087-11 Author(s) 11. CC Attribution 3.0 License. This discussion paper is/has been under review for the
FOREST BIOMASS FOR ENERGY PRODUCTION POTENTIALS, MANAGEMENT AND RISKS UNDER CLIMATE CHANGE
 FOREST BIOMASS FOR ENERGY PRODUCTION POTENTIALS, MANAGEMENT AND RISKS UNDER CLIMATE CHANGE Ashraful Alam, Antti Kilpeläinen, Seppo Kellomäki School of Forest Sciences, University of Eastern Finland, Joensuu
FOREST BIOMASS FOR ENERGY PRODUCTION POTENTIALS, MANAGEMENT AND RISKS UNDER CLIMATE CHANGE Ashraful Alam, Antti Kilpeläinen, Seppo Kellomäki School of Forest Sciences, University of Eastern Finland, Joensuu
TREATMENT OF DOMESTIC WASTEWATER WITH A MULTI-SOIL-LAYERING (MSL) SYSTEM IN A TEMPERATE AND A TROPICAL CLIMATE
 TREATMENT OF DOMESTIC WASTEWATER WITH A MULTI-SOIL-LAYERING (MSL) SYSTEM IN A TEMPERATE AND A TROPICAL CLIMATE S. Luanmanee, T. Attanandana 1, T. Masunaga 2 and T. Wakatsuki 2 Soil Chemistry Research Group
TREATMENT OF DOMESTIC WASTEWATER WITH A MULTI-SOIL-LAYERING (MSL) SYSTEM IN A TEMPERATE AND A TROPICAL CLIMATE S. Luanmanee, T. Attanandana 1, T. Masunaga 2 and T. Wakatsuki 2 Soil Chemistry Research Group
Discussion about Cause of Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) Emission in Wastewater Treatment Plant, Based on Long-Term Continuous Measurement
 Discussion about Cause of Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) Emission in Wastewater Treatment Plant, Based on Long-Term Continuous Measurement Tokyo Metropolitan Government, the Bureau of Sewerage Kiyoaki Kitamura
Discussion about Cause of Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) Emission in Wastewater Treatment Plant, Based on Long-Term Continuous Measurement Tokyo Metropolitan Government, the Bureau of Sewerage Kiyoaki Kitamura
Fires and hydrology of south eastern Australian mixed-species forests TARRYN TURNBULL RESEARCH FELLOW ECOPHYSIOLOGY ENSY
 Fires and hydrology of south eastern Australian mixed-species forests TARRYN TURNBULL RESEARCH FELLOW ECOPHYSIOLOGY ENSY 1002 2012 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Our project Fires and hydrology of south eastern
Fires and hydrology of south eastern Australian mixed-species forests TARRYN TURNBULL RESEARCH FELLOW ECOPHYSIOLOGY ENSY 1002 2012 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Our project Fires and hydrology of south eastern
The Global Nitrogen Cycle
 OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle (11.30.10) Fig. 12.2. Units are 10 12 g N/yr (Tg) Role of N in Biogeochemistry Bioavailability of N (and/or P) can limit NPP on land/oceans; controls size of biomass N
OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle (11.30.10) Fig. 12.2. Units are 10 12 g N/yr (Tg) Role of N in Biogeochemistry Bioavailability of N (and/or P) can limit NPP on land/oceans; controls size of biomass N
The Biology of Composting
 The Biology of Composting Mark King, Sustainability Division mark.a.king@maine.gov MAINE DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION Protecting Maine s Air, Land and Water Systems Covered First We ll Discuss
The Biology of Composting Mark King, Sustainability Division mark.a.king@maine.gov MAINE DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION Protecting Maine s Air, Land and Water Systems Covered First We ll Discuss
The SoilC&N model: simulating short- and long-term soil nitrogen supply to crops
 The SoilC&N model: simulating short- and long-term soil nitrogen supply to crops Marc Corbeels Agro-ecology and sustainable Intensification of annual crops AIDA - CIRAD, Montpellier, France Sustainable
The SoilC&N model: simulating short- and long-term soil nitrogen supply to crops Marc Corbeels Agro-ecology and sustainable Intensification of annual crops AIDA - CIRAD, Montpellier, France Sustainable
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea
 Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea NH 4 + N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 + Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations New, regenerated, and export production The processes: Assimilation, N 2 fixation,
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea NH 4 + N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 + Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations New, regenerated, and export production The processes: Assimilation, N 2 fixation,
PLANT-MEDIATED METHANE AND CANOPY EXCHANGE IN A BOREAL UPLAND FOREST
 Department of Agricultural Sciences & Institute for Atmospheric and Earth System Research INAR, University of Helsinki PLANT-MEDIATED METHANE AND CANOPY EXCHANGE IN A BOREAL UPLAND FOREST Mari Pihlatie,
Department of Agricultural Sciences & Institute for Atmospheric and Earth System Research INAR, University of Helsinki PLANT-MEDIATED METHANE AND CANOPY EXCHANGE IN A BOREAL UPLAND FOREST Mari Pihlatie,
N fertilizer placements and greenhouse gas emissions from continuously flooded rice systems
 N fertilizer placements and greenhouse gas emissions from continuously flooded rice systems M. Arlene Adviento-Borbe 1 and Bruce Linquist 2 1, USDA-ARS, Jonesboro, AR 2 Dept. of Plant Sciences, University
N fertilizer placements and greenhouse gas emissions from continuously flooded rice systems M. Arlene Adviento-Borbe 1 and Bruce Linquist 2 1, USDA-ARS, Jonesboro, AR 2 Dept. of Plant Sciences, University
TERRESTRIAL ECOLOGY PART DUEX. Biogeochemical Cycles Biomes Succession
 DO NOW: -GRAB PAPERS FOR TODAY -GET A HIGHLIGHTER -UPDATE HW FOR TONIGHT COMPLETE AQUATIC ECOLOGY PACKET (INCLUDES VIDEO) -BEGIN READING THROUGH THE LECTURE TERRESTRIAL ECOLOGY PART DUEX Biogeochemical
DO NOW: -GRAB PAPERS FOR TODAY -GET A HIGHLIGHTER -UPDATE HW FOR TONIGHT COMPLETE AQUATIC ECOLOGY PACKET (INCLUDES VIDEO) -BEGIN READING THROUGH THE LECTURE TERRESTRIAL ECOLOGY PART DUEX Biogeochemical
Soil, groundwater and surface water chemistry of nitrogen
 Soil, groundwater and surface water chemistry of nitrogen Shaun Watmough Trent University swatmough@trentu.ca Nitrogen Deposition Past and Present mg N/m 2 /yr 5000 2000 1000 750 500 250 100 50 25 5 1860
Soil, groundwater and surface water chemistry of nitrogen Shaun Watmough Trent University swatmough@trentu.ca Nitrogen Deposition Past and Present mg N/m 2 /yr 5000 2000 1000 750 500 250 100 50 25 5 1860
THE INTRODUCTION THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
 THE INTRODUCTION The earth is surrounded by atmosphere composed of many gases. The sun s rays penetrate through the atmosphere to the earth s surface. Gases in the atmosphere trap heat that would otherwise
THE INTRODUCTION The earth is surrounded by atmosphere composed of many gases. The sun s rays penetrate through the atmosphere to the earth s surface. Gases in the atmosphere trap heat that would otherwise
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment.
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
SEASONAL VARIATION OF MICROBIAL BIOMASS C AND SOIL RESPIRATION IN RICE PADDIES IN BLACK EARTH AND
 SEASONAL VARIATION OF MICROBIAL BIOMASS C AND SOIL RESPIRATION IN RICE PADDIES IN BLACK EARTH AND CORRELATION BETWEEN THEM AND CH 4 EMISSION W. Liang, J. Yue, J. Wu, Y. Shi and G.H. Huang Key Laboratory
SEASONAL VARIATION OF MICROBIAL BIOMASS C AND SOIL RESPIRATION IN RICE PADDIES IN BLACK EARTH AND CORRELATION BETWEEN THEM AND CH 4 EMISSION W. Liang, J. Yue, J. Wu, Y. Shi and G.H. Huang Key Laboratory
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
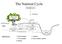 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
