Quiz Questions. For Process Integration. Fill in the blanks type Questions
|
|
|
- Clemence Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quiz Questions For Process Integration Fill in the blanks type Questions 1. is the key parameter used in the Pinch Technology. ( T min ) 2. In onion diagram pinch technology in applied at. (the boundary of separator and heat exchanger network) 3. works as a link between process and pinch analysis. (data extraction) 4. Composite curve consists of. (hot composite curve and cold composite curve) 5. To maintain temperature cross in a heat exchanger the value of F T factor should be more than or equal to. (0.8) 6. is a plot of the overall variation of heat supply and demand across the entire process. (Grand Composite Curve) 7. is used for designing heat exchanger network when feasibility criteria do not match. (stream splitting) 8. While designing heat exchanger network number of stream as well as CP criterion should be satisfied for. (Pinch match) 9. The temperature that a process stream is available at, before any heating or cooling is performed, is called. (Source Temperature) 10. The temperature up to which the process stream is to be heated or cooled is. (Target Temperature) 11. is the temperature at which the ability to transfer heat between the process streams is most constrained. (Pinch temperature) 12. In composite curves the areas where the hot and cold composite curves do not show the minimum utility requirements by reading the enthalpy axis. (overlap) 13. These are referred to when either heating or cooling utility is required, but not both. (threshold problems) 14. A source of heating or cooling that does not come from a process stream is known as. (utility) 15. The distillation column should not be placed with the background process. (across the pinch) 16. If does not meet in a pinch match the temperature difference between a hot and cold stream of that match becomes lesser than T min. (CP criterion) 17. For a case when feed temperature is equal to temperature of effect a single effect evaporator is represented by a in T-H diagram. (Rectangle) 18. In T-H diagram for a case when feed temperature is lower than the temperature of effect the upper line of trapezoid is than the below line. (longer)
2 19. When a pair of hot and cold process streams is matched a is created to handle the transfer of heat from the hot stream to the cold stream. (heat exchanger) 20. In hot stream moves from left to right whereas cold stream moves from right to left. (grid diagram) True/False Type Questions 1. Thermodynamics in process integration (PI) is used to analyze driving forces in the design and the existing driving forces are then reduced so that energy is saved while capital is spent 2. Thermodynamics in PI is not only used to analyze driving forces to reduce them but to distribute them differently to generate different options in design for lower capital cost at a constant level of energy recovery 3. Pinch technology identifies different options leading to: (i) Energy savings (ii) Capital savings (iii) Preferred integration alternatives in the interest of given constraints in plant layout, control, safety, etc. (iv) Optimal heat exchanger design (v) Optimal heat exchanger network design 4. In pinch technology the design task is to find the best network of exchangers, heaters and coolers that can handle exchange of heat amongst hot and cold streams and utilities at minimum operating and annualized capital cost 5. The total cost of a HEN tends to dominate by the amount of heating and cooling utility demands and by the number of capital items in the network 6. In pinch technology the prime aim is to produce a design which consumes minimum quantities of utilities (hot and cold) and employs the smallest possible number of units (heater, coolers and exchangers) 7. The hot composite curve can be shifted vertically but not horizontally 8. The pinch design method says that cold utility can be placed above the pinch 9. Capability to set performance target prior to design is the prime aim of targeting step in pinch design 10. Minimum hot utility requirement predicted by composite curve is a function of T min 11. Minimum cold utility requirement predicted by composite curve is a function of T min 12. Minimum cold utility requirement predicted by composite curve is not a function of T min 13. Because of the kinked nature of composite curves they approach most closely at one point of enthalpy axis called pinch 14. The point at which any composite curve experiences change in slope is either the supply or target temperature of a hot or cold stream 15. The section above the pinch in conventional composite curve is heat sink 16. The section below the pinch in conventional composite curve is heat source
3 17. For a minimum utility target to meet that should not be any heat flow through pinch 18. External heating in excess demands external cooling in excess of the same amount 19. An inefficient process requires more than the minimum external heating and therefore more than the minimum external cooling 20. An efficient process requires more than the minimum external heating and therefore more than the minimum external cooling 21. For every unit of external heat pushed to a process extra heat transfer area(proportional to heat pushed) to be provide in heaters as well as coolers 22. Composite curve indicate what type of site services (Boiler, cooling tower, steam heater, cooler, steam and gas turbine, etc.) should be used where (above the pinch or below the pinch) 23. Composite curve can never indicate what type of site services (Boiler, cooling tower, steam heater, cooler, steam and gas turbine, etc.) should be used where (above the pinch or below the pinch) 24. A simple relationship exists between a number of streams (process plus utilities) in a problem and the minimum number of heat exchanger unit (i.e. heaters, coolers, heat exchanger) 25. Once the hot and cold composite curves are known one can estimate exactly how much external heating and cooling are required for a given T min 26. If a designer goes for best energy recovery designing the (heat source) and (heat sink) sectional separately he will require more units than if the pinch division is ignored 27. There exists a trade-off between energy recovery and number of units 28. It is always possible to maintain T min in a heat exchanger network while loop breaking 29. In conventional problem (except threshold) increasing T min increases requirement of hot and cold utilities 30. For a given value of T min utilities predicted by composite curves are minimum that are required to solve the heat recovery problem 31. In general T min occurs at only one point termed the pinch and heat exchanger at the pinch need to operate at T values down to T min 32. The surplus heat in a problem table analysis can be cascaded down 33. The surplus heat in a problem table analysis can be cascaded up 34. In a problem table analysis full heat interchange within any temperature interval is possible 35. In a problem table analysis full heat interchange within any temperature interval is not possible 36. Problem table analysis ensures that within any interval hot streams and cold streams are at least T min apart 37. Problem table analysis ensures that within any interval hot streams and cold streams are less than T min apart
4 38. In a T-H diagram hot stream is represented by the line with the arrow head pointing to the left and cold stream vice-versa 39. In a T-H diagram hot stream is represented by the line with the arrow head pointing to the right and cold stream vice-versa 40. The T-H diagram is used to represent heat exchange as one is interested in enthalpy changes of streams and a given stream can be plotted anywhere on the enthalpy axis provided it has the same slope and runs between the same supply and target temperature 41. While placing composite curves hot composite curve is always kept above the cold composite curve 42. While placing composite curves cold composite curve is always kept below the hot composite curve 43. While placing composite curves hot composite curve is always kept below the cold composite curve 44. The pinch divides energy recovery problem into two thermodynamically distinct regions (Heat source and heat sink) in a MER design 45. Pinch Design Method starts the design where the problem is most constrained i.e. pinch point 46. Pinch Design Method starts the design where the problem is least constrained 47. Presence of a Loop in a HEN always introduces an extra unit over and above U min. 48. Presence of a Loop in a HEN always reduces U min value by one unity 49. Loop breaking invariably creates T min violation. 50. Loop breaking never creates T min violation. 51. T min restoration after loop breaking is done by energy relaxation through a relaxation path. 52. There exists a correlation between T min and utility usages. 53. There exists no correlation between T min and utility usages. 54. In a grand composite curve where zero heat flow occurs and where the process source profile meets the process sink profile is the pinch point. 55. Grand composite curve can be used to include multiple utilities in the design of HEN. 56. Grand composite curve cannot be used to include multiple utilities in the design of HEN. 57. In a multiple utility design more than one pinch point exists. 58. In a Threshold problem there is no trade-off between energy and capital for values of T min T threshold. 59. In a Threshold problem there is no trade-off between energy and capital for values of T min T threshold. 60. Stream splitting criterion for a HEN design depends on stream number criterion as well as CP criterion. 61. Stream splitting criterion for a HEN design depends on stream number criterion only.
5 62. For composite curves the criterion above pinch CP H < CP C and below the pinch CP H > CP C holds good. 63. For composite curves the criterion above pinch CP H > CP C and below the pinch CP H < CP C holds good. 64. During data extraction if simple linearization of CP value is not possible streams should be linearized in sections. 65. During data extraction most accurate CP value should be used in the neighborhood of pinch 66. Plus-Minus principle states that energy will be saved by increasing the proportion of the hot composite curve above the pinch or decreasing the proportion of the cold composite curve above the pinch. 67. Plus-Minus principle states that energy will be saved by decreasing the proportion of the hot composite curve above the pinch or increasing the proportion of the cold composite curve above the pinch. 68. The shifting of optimal T min occur for anything which changes the balance of capital cost and energy cost. 69. If capital becomes more expensive or energy becomes cheaper the optimum T min will increase. 70. The flat nature of most cost- T min curves indicates that there is not a single clear-cut best HEN but a range of good HENs. 71. For shell-and-tube exchangers, the number of shells required may be greater than the minimum number of units as the area required for a single heat exchanger may be inconveniently large or there may be temperature cross in a single shell. 72. The Bath formula which is most widely used assumes vertical heat transfer between the composite curves, and the prediction of a minimum value for area is valid only if all film heat transfer coefficients for the streams are equal 73. The Bath formula which is most widely used assumes vertical heat transfer between the composite curves, and the prediction of a minimum value for area is valid only if all film heat transfer coefficients for the streams are different 74. For cases where film heat transfer coefficients are significantly different, mathematical programming route which considers vertical as well as non-vertical heat transfer may be required to achieve a minimum area for the network. 75. For cases where film heat transfer coefficients of streams are almost equal, mathematical programming route which considers vertical as well as non-vertical heat transfer is a must to achieve a minimum area for the network. 76. Experimental and numerical results show that temperature crossover can be achieved in shell and tube heat exchangers(sthx) with L( length)/w(width) 4.62 and can t be achieved any more in STHXs with L/W 3.08.
6 77. To achieve the minimum capital cost target the design should be directed towards minimum number of units by using tick off heuristic while matches are selected for pinch heat exchanger. 78. The Tick off heuristic stems from the minimum number of units target equation. 79. The tick-off heuristic occasionally punishes the HEN design in terms of increased utility usage. 80. The Pinch Design Method(PDM) requires CPH CPC (for cold end design) and CPH CPC (for hot end design) for avoiding Tmin violation, in pinch matches. 81. The CP-rules of PDM(Pinch Design Method) ensure that the temperature profiles of exchangers at the pinch diverge away from the pinch. 82. The design relationship for approaching minimum area around the pinch can therefore be expressed as: (CPH/CPC)pinch match 1 (CPH/CPC)pinch match 2. (CPHot composite/cpcold composite)pinch 83. Away from the pinch there is exists more freedom regarding the choice of matches due to the availability of sufficient driving force. 84. The Driving Force Plot provides a rapid and easy to use guideline for designing networks which are close to minimum area. However, it is only a guideline and does not provide quantitative information. 85. Driving Force Plot is only a qualitative tool and does not provide quantitative information due to the fact that it works in temperatures only, neglecting the effect of duty on heat exchange area. 86. Maximum Energy Recovery based designed HENs are not the best HENs as far as total annual cost(tac) is concerned. 87. The placement of match is as important as the design itself as it can lead to a design which will direct to a higher heat transfer area of HEN than estimated by area target. 88. Remaining problem analysis(rpa) exploits the power of targeting ( Energy, Area, shells, cost, etc.) to steer the complete design in correct direction to achieve targets. 89. Maximum Energy Recovery based designed HENs are the best HENs as far as total annual cost(tac) is concerned. 90. Driving Force Plot is a quantitative tool for designing networks which are close to minimum area. 91. Away from the pinch there is exists less freedom regarding the choice of matches due to the unavailability of sufficient driving force. 92. The CP-rules of PDM(Pinch Design Method) ensure that the temperature profiles of exchangers at the pinch converge away from the pinch.
7 93. The Pinch Design Method(PDM) requires CPH CPC (for cold end design) and CPH CPC (for hot end design) for avoiding Tmin violation, in pinch matches. 94. The Tick off heuristic stems from the minimum area target equation. 95. The problem Table analysis(pta) of a problem provides the hot utility(qhmin) and cold utility(qcmin) consumption data a prior to the design of HEN. 96. Threshold problems either need hot utility or cold utility and not both. 97. Pinch Design Method (PDM) for HEN synthesis yield improved solutions by utilizing the Driving Force Plot (DFP) and Remaining Problem Analysis (RPA). 98. There are three Important steps in HEN design such as the targeting of utility and capital needs prior to synthesis of the HEN, synthesis and optimization of the network and, finally, analysts of network performance under network structure changes and varying operating conditions (i.e. feasibility and resilience analyses). 99. Threshold problems only need hot utility or both utilities Pinch Design Method (PDM) for HEN synthesis yield inferior solutions when it utilizes Driving Force Plot (DFP) and Remaining Problem Analysis (RPA) Low values of F T indicate inefficient use of the heat transfer area Low values of F T indicate efficient use of the heat transfer area The F T correction factor is usually correlated in terms of two dimensionless ratios, the ratio of the two heat capacity flowrates( R) and the thermal effectiveness of the exchanger(p): F T = f(r,p) 104. During data extraction Stream data should be linearized on the safe side 105. During data extraction utility should not be extracted with steam data 106. During data extraction heat loss from a cold stream can be accounted for by the inclusion of a fictitious cold stream 107. During data extraction heat loss from a hot stream can be accounted for by splitting the hot stream to represent the loss 108. During data extraction enforced matches can be accounted for by leaving parts of the stream data out of the problem 109. Non-isothermal mixing degrades temperature driving forces and might transfer heat across the pinch 110. Non-isothermal mixing improves temperature driving forces and but might transfer heat across the pinch 111. Use of complex columns(side strippers, side-rectifiers and thermally coupled prefractionators) reduce the overall heat duties for the separation at the expense of more extreme temperatures for reboiling and condensing. Multi-choice questions (tick the write answer/answers) 1. Grand composite curve can be directly plotted using a) Problem Table analysis data b) Stream data table c) Composite curve data
8 d) Grid diagram 2. Pinch technology is not applied in a) Hydrogen management b) Carbon-constrained planning c) Plant layout d) Emission targeting 3. Hot streams are those which have a) high enthalpy b) high temperature c) need to be cooled 4. Cold streams are those which have d) low enthalpy e) low temperature f) need to be heated 5. Area targeting can be carried out through a) Composite curve b) Balanced composite curves c) Balanced hot composite curve d) Grand composite curve 6. Over-shoot of the hot composite curve in composite curves represents a) Minimum amount of extra cooling required b) Minimum amount of extra heating required c) Minimum amount of cold utility required at specified T min for the composite curves 7. Over-shoot of the cold composite curve in composite curves represents d) Minimum amount of extra heating required e) Minimum amount of extra cooling required f) Minimum amount of hot utility required at specified T min for the composite curves 8. In section above the pinch a) The composite hot gives all its heat to composite cold and fully satisfies its requirement b) The composite hot gives all its heat to composite cold with only residual heating required c) The composite cold takes heat from composite hot with only residual cooling required 9. In section below the pinch a) The composite cold takes partial heat from composite hot and requires further heating b) The composite hot gives heat to composite cold with only residual cooling required c) The composite cold takes heat from composite hot with only residual heating required 10. For low temperature processes T min should be a) C b) 3-5 C c) C d) C 11. For integrating exhaust of gas turbine with the background process T min should be
9 a) C b) C c) 5-10 C d) C 12. Above the pinch which of the following equipments should not be placed a) Steam heaters b) Furnaces c) Coolers 13. Below the pinch which of the following equipments should be placed a) Steam heaters b) Furnaces c) Coolers 14. The recommended position of heat pump in background process is a) Above the pinch b) Below the pinch c) Across the pinch 15. The recommended position of heat engine in background process is a) Above the pinch b) Below the pinch c) Across the pinch 16. In background process the endothermic reactor should be placed a) Above the pinch b) Below the pinch c) Across the pinch 17. In background process the exothermic reactor should be placed a) Above the pinch b) Below the pinch c) Across the pinch 18. For a minimum utility design select appropriate statements a) Do transfer heat across the pinch b) Do not use cold utility above the pinch c) Do not transfer heat across the pinch d) Use cold utility above the pinch e) Do not use hot utility below the pinch 19. Select proper pinch design procedure for MER design a) Do not divide the problem at pinch and design as one problem b) Start at one end of the problem and move to the other end c) Immediately adjacent to the pinch obey following constraints: CP hot CP cold (above the pinch), CP hot CP cold (below the pinch) d) Immediately adjacent to the pinch obey following constraints: CP hot CP cold (above the pinch), CP hot CP cold (below the pinch) e) Divide the problem at the pinch and design each part separately
10 f) Starting the design at the pinch and move away g) Maximizing exchanger load where possible h) Supply external heating and external cooling only above and below pinch respectively i) Do not violate T min criterion 20. Select the correct statement a) U min U min MER b) U min < U min MER c) U min = U min MER d) U min U min MER 21. For units target select the proper rule a) U min = N+L-s b) U min = N-1 c) U min = N+L-1 d) U min = N+L 22. Stream splitting above the pinch takes place when: a) N H N C b) N H N C c) CP H CP C ( for every pinch match) d) CP H CP C ( for every pinch match) 23. Stream splitting below the pinch takes place when: e) N H N C f) N H N C g) CP H CP C ( for every pinch match) h) CP H CP C ( for every pinch match) 24. Select the correct statement of the Plus-Minus principle a) Increase the total hot stream heat load above the pinch b) Decrease the total hot stream heat load above the pinch c) Decrease the total cold stream load above the pinch d) Increase the total cold stream load above the pinch e) Decrease the total hot stream load below the pinch f) Increase the total hot stream load below the pinch g) Increase the total cold stream load below the pinch h) decrease the total cold stream load below the pinch 25. Select the proper placement for distillation column w.r.t. process a) Above the process pinch b) Below the process pinch c) Across the process pinch 26. Select correct statements favoring use of multiple utilities a) Power can be generated using high pressure steam and let down steam can be used for heating b) The driving forces between utility and process are reduced
11 c) Lower temperature steam is at low pressure and hence thickness of equipment will be less d) Each extra level increases complexity of design e) Steam can be raised more efficiently at a lower temperature level by recovering heat from boiler flue gases 27. Select the wrong sentence in regard to steam pressure and its utilization for a purpose a) 50 bar(g) is used for power generation b) 40 bar(g) is normal maximum pressure for distribution c) bar(g) are the conventional distribution pressure levels d) 2-5 bar(g0 are typically the lowest pressures used for distribution 28. Select the wrong sentence in regard to steam pressure and its utilization for a purpose e) 100 bar(g) is used for power generation f) 40 bar(g) is normal maximum pressure for distribution g) bar(g) are the conventional distribution pressure levels h) 2-5 bar(g) are typically the lowest pressures used for distribution 29. Select the wrong sentence in regard to use of steam for process heating. a) Energy can be generated at one place and then distributed b) It has a small range of operating temperature c) It has a low heat content through the latent heat d) It is non toxic and losses can be compensated easily. 30. Select the wrong sentence in regard to use of steam for process heating. e) It requires expensive material of construction for equipment f) It has a wide range of operating temperature g) It has a high heat content through the latent heat h) It is toxic and losses can be compensated easily
12
Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 27: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) 2 nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN
 Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 7: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN Some rules for pinch design methods such as Criteria for number of process streams
Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 7: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN Some rules for pinch design methods such as Criteria for number of process streams
3.17. PROCESS INTEGRATION AND PINCH TECHNOLOGY
 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES 111 pressure is expanded over the throttle value and fed to the condenser, to provide cooling to condense the vapour from the column. The vapour from the condenser is compressed
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES 111 pressure is expanded over the throttle value and fed to the condenser, to provide cooling to condense the vapour from the column. The vapour from the condenser is compressed
pinch 70 C 70 C 4 We want to cool both the hot streams to the pinch temperature. The next step is to find the duty for the two heat exchangers:
 Ene-47.5130 Process Integration (3 ECTS credits) P Espoo 2016 EXERCISE 2 SOLUTIONS 1 MER heat exchanger network First we draw the stream-grid and calculate the enthalpy rate change, Q, above and below
Ene-47.5130 Process Integration (3 ECTS credits) P Espoo 2016 EXERCISE 2 SOLUTIONS 1 MER heat exchanger network First we draw the stream-grid and calculate the enthalpy rate change, Q, above and below
Saturday 20 May C 180 C C 130 C C 60 C kw 50 C 30 C C 20 C
 Page 1 of 10 NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (NTNU) - TRONDHEIM DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND PROCESS ENGINEERING PROPOSED SOLUTION EXAMINATION IN COURSE TEP 4215 PROCESS INTEGRATION Saturday
Page 1 of 10 NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (NTNU) - TRONDHEIM DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND PROCESS ENGINEERING PROPOSED SOLUTION EXAMINATION IN COURSE TEP 4215 PROCESS INTEGRATION Saturday
Introduction to Pinch Technology
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 07, 2018 Introduction to Pinch Technology Rokni, Masoud Publication date: 2016 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Rokni,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 07, 2018 Introduction to Pinch Technology Rokni, Masoud Publication date: 2016 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Rokni,
TEP Energy Utilization and Process Integration in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process
 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
The Grid Diagram The Heat-Content Diagram Pinch Subnetworks Minimum Number of Heat-Exchange Units...
 3.1 INTRODUCTION... 2 3.2 DESIGN TOOLS: REPRESENTING HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORKS... 4 3.2.1. The Grid Diagram...4 3.2.2. The Heat-Content Diagram...7 3.3 PRELIMINARY HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORK DESIGN... 10 3.2.1
3.1 INTRODUCTION... 2 3.2 DESIGN TOOLS: REPRESENTING HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORKS... 4 3.2.1. The Grid Diagram...4 3.2.2. The Heat-Content Diagram...7 3.3 PRELIMINARY HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORK DESIGN... 10 3.2.1
Grand Composite Curve Module 04 Lecture 12
 Module 04: Targeting Lecture 12: Grand Composite Curve While composite curves provide overall energy targets, these do not indicate the amount of energy that should be supplied at different temperature
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 12: Grand Composite Curve While composite curves provide overall energy targets, these do not indicate the amount of energy that should be supplied at different temperature
Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH Technology. Lecture 07 : Hot and Cold Composite Curves and The Pinch
 Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH Technology Lecture 07 : Hot and Cold Composite Curves and The Pinch Key words: Pinch, T H diagram, Hot utility, Cold Utility, Composite Curve, T min Pinch analysis
Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH Technology Lecture 07 : Hot and Cold Composite Curves and The Pinch Key words: Pinch, T H diagram, Hot utility, Cold Utility, Composite Curve, T min Pinch analysis
Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant
 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): 39-49 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajee doi: 10.11648/j.ajee.20170505.13 ISSN: 2329-1648 (Print); ISSN: 2329-163X (Online) Debottlenecking
American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): 39-49 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajee doi: 10.11648/j.ajee.20170505.13 ISSN: 2329-1648 (Print); ISSN: 2329-163X (Online) Debottlenecking
Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency
 Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency S. R. Sunasara 1, J. J. Makadia 2 * 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, RK University Kasturbadham, Rajkot-Bhavngar highway,
Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency S. R. Sunasara 1, J. J. Makadia 2 * 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, RK University Kasturbadham, Rajkot-Bhavngar highway,
HDA Process. compressor. Reactor. Flash. heat. cool. Stabilizer. Recycle. Product
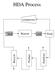 HDA Process compressor heat Reactor cool Flash Recycle Product Stabilizer Why Energy Integration? (ICI Experience) 20 case studies In every case, there was a reduction in energy In almost every case, the
HDA Process compressor heat Reactor cool Flash Recycle Product Stabilizer Why Energy Integration? (ICI Experience) 20 case studies In every case, there was a reduction in energy In almost every case, the
Researcher, 1(2), 2009, Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis
 Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis K.R. AJAO (Ph.D) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria e-mail: ajaomech@unilorin.edu.ng H. F. Akande
Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis K.R. AJAO (Ph.D) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria e-mail: ajaomech@unilorin.edu.ng H. F. Akande
Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison. Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner
 Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Introduction... 5 Paper Overview... 6 Example 1... 7 Example 2... 9 1. Mixed Integer
Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Introduction... 5 Paper Overview... 6 Example 1... 7 Example 2... 9 1. Mixed Integer
Energy Optimization Using Pinch Analysis
 Energy Optimization Using Pinch Analysis Practical Considerations By Richard Beaman, PE, and Cliff Reese, PE, SSOE Group Pinch analysis is a systematic method to maximize energy recovery from process streams
Energy Optimization Using Pinch Analysis Practical Considerations By Richard Beaman, PE, and Cliff Reese, PE, SSOE Group Pinch analysis is a systematic method to maximize energy recovery from process streams
Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery
 Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery Adnan A. Ateeq Engineering Technical College Southern Technical University Basra, Iraq
Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery Adnan A. Ateeq Engineering Technical College Southern Technical University Basra, Iraq
DESIGN OF A HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK BY GRAPH METHOD
 Tạp chí Khoa học và Công nghệ 49 (6) (2011) 117-126 DESIGN OF A HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK BY GRAPH METHOD Nguyen Huu Tung Hanoi University of Science and Technology Email: tungnguyenhu@gmail.com Received:
Tạp chí Khoa học và Công nghệ 49 (6) (2011) 117-126 DESIGN OF A HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK BY GRAPH METHOD Nguyen Huu Tung Hanoi University of Science and Technology Email: tungnguyenhu@gmail.com Received:
Utilization of THERMOPTIM Optimization Method
 Utilization of THERMOPTIM Optimization Method Thermoptim optimization method is dedicated to complex systems where a large number of fluids exchange heat, the overall behaviour of the system being governed
Utilization of THERMOPTIM Optimization Method Thermoptim optimization method is dedicated to complex systems where a large number of fluids exchange heat, the overall behaviour of the system being governed
Module 04 : Targeting. Lecture 11: PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM 1 st Part
 Module 04 : Targeting Lecture : PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM st Part Key words: Problem Table Algorithm, shifted temperature, composite curve, PTA, For a given ΔT min, Composite curves can be used to obtain
Module 04 : Targeting Lecture : PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM st Part Key words: Problem Table Algorithm, shifted temperature, composite curve, PTA, For a given ΔT min, Composite curves can be used to obtain
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant
 PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology
 Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology Ritesh Sojitra Srashti Dwivedi ITM University, Gwalior, India Abstract: Energy optimisation and process integration
Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology Ritesh Sojitra Srashti Dwivedi ITM University, Gwalior, India Abstract: Energy optimisation and process integration
Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology
 Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology Napredakul, D. a, Siemanond, K.a, Sornchamni, T.b, Laorrattanasak, S.b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok,
Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology Napredakul, D. a, Siemanond, K.a, Sornchamni, T.b, Laorrattanasak, S.b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok,
PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit
 PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water
PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design
 Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design The fixed cost of a heat exchanger network (HEN) depends upon the number of heat exchanger
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design The fixed cost of a heat exchanger network (HEN) depends upon the number of heat exchanger
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant
 PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
Heat Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit
 Review Paper Abstract Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit Padole Manjusha 1, Sapkal Pradyumna 2, Dawande S.D. 3 and Nitin Kanse 4 1, 3
Review Paper Abstract Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit Padole Manjusha 1, Sapkal Pradyumna 2, Dawande S.D. 3 and Nitin Kanse 4 1, 3
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit
 PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water
An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process
 An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process Alnouss M. Ahmed, and Al-Nuaimi A. Ibrahim Abstract In this paper, the energy performance of a selected UHDE Ammonia plant is optimized by conducting
An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process Alnouss M. Ahmed, and Al-Nuaimi A. Ibrahim Abstract In this paper, the energy performance of a selected UHDE Ammonia plant is optimized by conducting
A New Optimisation Based Retrofit Approach for Revamping an Egyptian Crude Oil Distillation Unit
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 36 (2013 ) 454 464 TerraGreen 13 International Conference 2013 - Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment A New Optimisation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 36 (2013 ) 454 464 TerraGreen 13 International Conference 2013 - Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment A New Optimisation
Steam balance optimisation strategies
 Steam balance optimisation strategies Publicado en Chemical Engineering, Noviembre 2002 Background Optimising a steam balance in a plant with several steam mains pressures is not always a simple intuitive
Steam balance optimisation strategies Publicado en Chemical Engineering, Noviembre 2002 Background Optimising a steam balance in a plant with several steam mains pressures is not always a simple intuitive
Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries
 National Seminar on Awareness and Implementation of Energy Management System Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries 19t h January- 2015 SCOPE Conversion centre, Lodhi
National Seminar on Awareness and Implementation of Energy Management System Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries 19t h January- 2015 SCOPE Conversion centre, Lodhi
On the use of heat pumps in total site heat integration
 Computers and Chemical Engineering 27 (2003) 1707/1719 www.elsevier.com/locate/compchemeng On the use of heat pumps in total site heat integration Miguel J. Bagajewicz *, Andrés F. Barbaro Department of
Computers and Chemical Engineering 27 (2003) 1707/1719 www.elsevier.com/locate/compchemeng On the use of heat pumps in total site heat integration Miguel J. Bagajewicz *, Andrés F. Barbaro Department of
Retrofitting Heat Exchanger Networks Based on Simple Pinch Analysis
 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 3967 3971 3967 Retrofitting Heat Exchanger Networks Based on Simple Pinch Analysis Bao-Hong Li Department of Chemical Engineering, Dalian Nationalities UniVersity, Dalian
Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 3967 3971 3967 Retrofitting Heat Exchanger Networks Based on Simple Pinch Analysis Bao-Hong Li Department of Chemical Engineering, Dalian Nationalities UniVersity, Dalian
Module 5: Process Integration of Heat and Mass Chapter 10. David R. Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University
 Module 5: Process Integration of Heat and Mass Chapter 10 David R. Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University 1 Module 5: Outline The environmental performance of a process
Module 5: Process Integration of Heat and Mass Chapter 10 David R. Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University 1 Module 5: Outline The environmental performance of a process
Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation
 Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation by James Gainey Mann, Jr. Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation by James Gainey Mann, Jr. Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery
 Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery J. Khorshidi, E. Zare, A.R. Khademi Abstract The reduction of energy consumption through improvements in energy efficiency
Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery J. Khorshidi, E. Zare, A.R. Khademi Abstract The reduction of energy consumption through improvements in energy efficiency
TEP Energy Utilization and Process Integration in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process
 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system
 Refrigeration System Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system A refrigerator is simply a heat pump where heat is rejected to atmosphere( the sink). Fig.41.3(lecture
Refrigeration System Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system A refrigerator is simply a heat pump where heat is rejected to atmosphere( the sink). Fig.41.3(lecture
Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method
 Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method 1) Objectives of the practical work The objective of the practical work is to study the implementation of the pinch
Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method 1) Objectives of the practical work The objective of the practical work is to study the implementation of the pinch
Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration
 Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration Stanislav Boldyryev, Goran Krajačić Department of Energy, Power Engineering and Environment, Faculty of Mechanical
Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration Stanislav Boldyryev, Goran Krajačić Department of Energy, Power Engineering and Environment, Faculty of Mechanical
Modification of Preheating Heat Exchanger Network in Crude Distillation Unit of Arak Refinery Based on Pinch Technology
 Modification of Preheating Heat Exchanger Network in Crude Distillation Unit of Arak Refinery Based on Pinch Technology Salomeh Chegini, Reza Dargahi, Afshin Mahdavi Abstract In this work, the Hint software
Modification of Preheating Heat Exchanger Network in Crude Distillation Unit of Arak Refinery Based on Pinch Technology Salomeh Chegini, Reza Dargahi, Afshin Mahdavi Abstract In this work, the Hint software
Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI
 Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI nasrmrj@ripi.ir 21 MAY 2015 HVAC AND HEATING & COOLING SYSTEM CONFERENCE TEHRAN, IRAN 1 Energy and economy savings in the process of
Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI nasrmrj@ripi.ir 21 MAY 2015 HVAC AND HEATING & COOLING SYSTEM CONFERENCE TEHRAN, IRAN 1 Energy and economy savings in the process of
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project. Production of Ethylbenzene
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Ethylbenzene We continue to investigate the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 80,000 tonne/y, ethylbenzene facility.
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Ethylbenzene We continue to investigate the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 80,000 tonne/y, ethylbenzene facility.
Combustion Chamber. Fig Schematic diagram of a simple gas turbine
 Module 06: Integration and placement of equipment Lecture 37: Integration of Gas turbine with process 1 st Part Key word: Gas turbine, Acid dew temperature, after burner, specific work In its non complicated
Module 06: Integration and placement of equipment Lecture 37: Integration of Gas turbine with process 1 st Part Key word: Gas turbine, Acid dew temperature, after burner, specific work In its non complicated
PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. NITROGEN-BASED FERTILIZER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at an Ammonia Plant
 PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen NITROGEN-BASED FERTILIZER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at an Ammonia Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen NITROGEN-BASED FERTILIZER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at an Ammonia Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
Application of Heat Integration Techniques on Extract Column Section to reduce the cold utility requirements
 Application of Heat Integration Techniques on Extract Column Section to reduce the cold utility requirements Deepa H A 1, Ravishankar R 2 1 Chemical Engineering Department, DSCE, Karnataka, India 2 Chemical
Application of Heat Integration Techniques on Extract Column Section to reduce the cold utility requirements Deepa H A 1, Ravishankar R 2 1 Chemical Engineering Department, DSCE, Karnataka, India 2 Chemical
Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy
 SECTION 1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy Ed Haack Duke Energy 1-1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy By Ed Haack, Duke Power Company The PEPSE model for the Catawba Units have been
SECTION 1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy Ed Haack Duke Energy 1-1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy By Ed Haack, Duke Power Company The PEPSE model for the Catawba Units have been
- 2 - SME Q1. (a) Briefly explain how the following methods used in a gas-turbine power plant increase the thermal efficiency:
 - 2 - Q1. (a) Briefly explain how the following methods used in a gas-turbine power plant increase the thermal efficiency: i) regenerator ii) intercooling between compressors (6 marks) (b) Air enters a
- 2 - Q1. (a) Briefly explain how the following methods used in a gas-turbine power plant increase the thermal efficiency: i) regenerator ii) intercooling between compressors (6 marks) (b) Air enters a
A Modified Energy Transfer Diagram for Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Bridge Analysis
 907 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
907 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
Advanced Process and Chemical Complex Analysis Systems
 157g Advanced Process and Chemical Complex Analysis Systems Derya Ozyurt b, Aimin Xu b, Thomas A Hertwig a, Janardhana R Punuru b, Ralph W Pike b, F. Carl Knopf b, Jack R Hopper c, and Carl L Yaws c a
157g Advanced Process and Chemical Complex Analysis Systems Derya Ozyurt b, Aimin Xu b, Thomas A Hertwig a, Janardhana R Punuru b, Ralph W Pike b, F. Carl Knopf b, Jack R Hopper c, and Carl L Yaws c a
PINCH ANALYSIS FOR EFFICIENT ENERGY UTILIZATION IN IGCC PLANTS: INCORPORATION OF CONTACT ECONOMISER
 PINCH ANALYSIS FOR EFFICIENT ENERGY UTILIZATION IN IGCC PLANTS: INCORPORATION OF CONTACT ECONOMISER Vhutshilo A. Madzivhandila a, Thokozani Majozi a,b*, and Toshko Zhelev c a Department of Chemical Engineering
PINCH ANALYSIS FOR EFFICIENT ENERGY UTILIZATION IN IGCC PLANTS: INCORPORATION OF CONTACT ECONOMISER Vhutshilo A. Madzivhandila a, Thokozani Majozi a,b*, and Toshko Zhelev c a Department of Chemical Engineering
Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and GAMS Technology.
 EngOpt 2012 3 rd International Conference on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 July 2012. Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and
EngOpt 2012 3 rd International Conference on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 July 2012. Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project. Production of Styrene
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Styrene The feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 100,000 tonne/y, styrene plant is being investigated. As part of
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Styrene The feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 100,000 tonne/y, styrene plant is being investigated. As part of
Optimized Heat Exchanger Network design of GTL (Gas-To-Liquid) process
 October 2014, Volume 5, No.5 International Journal of Chemical and Environmental Engineering Optimized Heat Exchanger Network design of GTL (Gas-To-Liquid) process Sangsun Lee a ; Dongju Moon b ; Sungwon
October 2014, Volume 5, No.5 International Journal of Chemical and Environmental Engineering Optimized Heat Exchanger Network design of GTL (Gas-To-Liquid) process Sangsun Lee a ; Dongju Moon b ; Sungwon
Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.9, No.06 pp 432-439, 2016 Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant K. Nagamalleswara Rao*
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.9, No.06 pp 432-439, 2016 Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant K. Nagamalleswara Rao*
Chapter Two. The Rankine cycle. Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah
 Chapter Two The Rankine cycle Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah 1 The Ideal Rankine Cycle Schematic Diagram of ideal simple Rankine 2 Superheater Economizer line 3 Heat Addition Types In The Steam Generator
Chapter Two The Rankine cycle Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah 1 The Ideal Rankine Cycle Schematic Diagram of ideal simple Rankine 2 Superheater Economizer line 3 Heat Addition Types In The Steam Generator
Multi-effect distillation applied to an industrial case study
 Chemical Engineering and Processing 44 (2005) 819 826 Multi-effect distillation applied to an industrial case study Hilde K. Engelien, Sigurd Skogestad Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU),
Chemical Engineering and Processing 44 (2005) 819 826 Multi-effect distillation applied to an industrial case study Hilde K. Engelien, Sigurd Skogestad Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU),
HYL III: Status And Trends
 HYL III: Status And Trends by Raúl Quintero, President HYL Technology Division, Hylsa, S.A. de C.V. presented at the Gorham/Intertech Conference on Iron & Steel Scrap, Scrap Substitutes and Direct Steel
HYL III: Status And Trends by Raúl Quintero, President HYL Technology Division, Hylsa, S.A. de C.V. presented at the Gorham/Intertech Conference on Iron & Steel Scrap, Scrap Substitutes and Direct Steel
Wastewater Minimization in Process Industry Through Pinch Technology:
 WASTEWATER MINIMIZATION IN PROCESS 101 Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 22 (1)(2006) pp 101-110 Enviromedia Printed in India. All rights reserved Wastewater Minimization in Process Industry Through
WASTEWATER MINIMIZATION IN PROCESS 101 Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 22 (1)(2006) pp 101-110 Enviromedia Printed in India. All rights reserved Wastewater Minimization in Process Industry Through
Reducing Hot and Cold Utility Requirements for Finishing Column Section Using Pinch Analysis Techniques
 Reducing Hot and Cold Utility Requirements for Finishing Column Section Using Pinch Analysis Techniques Deepa 1, Ravishankar 2 1, 2 Chemical Engineering Department, DSCE, Bangalore-78 ABSTRACT Pinch Analysis
Reducing Hot and Cold Utility Requirements for Finishing Column Section Using Pinch Analysis Techniques Deepa 1, Ravishankar 2 1, 2 Chemical Engineering Department, DSCE, Bangalore-78 ABSTRACT Pinch Analysis
The project goal is to design a process capable of converting methane, obtained from remote
 Introduction The project goal is to design a process capable of converting methane, obtained from remote sites, to a more easily transportable fuel, methanol. The design should focus on minimizing the
Introduction The project goal is to design a process capable of converting methane, obtained from remote sites, to a more easily transportable fuel, methanol. The design should focus on minimizing the
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project. Production of Phthalic Anhydride
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Phthalic Anhydride Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 75,000 tonne/y of phthalic anhydride
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Phthalic Anhydride Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 75,000 tonne/y of phthalic anhydride
Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter
 Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter Consider the separation of a mixture of 50 mol/hr of propane C 3 H 8 (1) and 50 mol/hr propene, C 3 H 6 (2) at a pressure of 1.1 bar and a
Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter Consider the separation of a mixture of 50 mol/hr of propane C 3 H 8 (1) and 50 mol/hr propene, C 3 H 6 (2) at a pressure of 1.1 bar and a
Canada. Iron and Steel Sector - PI Specifics
 How can process integration help me? Process integration (PI) is a very efficient approach to improving the energy efficiency of large and complex industrial facilities. PI refers to the application of
How can process integration help me? Process integration (PI) is a very efficient approach to improving the energy efficiency of large and complex industrial facilities. PI refers to the application of
TransPacific Energy Advantage: Case Studies
 TransPacific Energy Advantage: Case Studies Typical Power Plant TPE-ORC 0.60 KWh ORC 2.3 KWh LP steam 0.35 KWh 30% (maximum) 2.05 KWh CHP Typical Power Generated 1.1 KWh Typical Power Wasted 2.31 KWh Typical
TransPacific Energy Advantage: Case Studies Typical Power Plant TPE-ORC 0.60 KWh ORC 2.3 KWh LP steam 0.35 KWh 30% (maximum) 2.05 KWh CHP Typical Power Generated 1.1 KWh Typical Power Wasted 2.31 KWh Typical
Design Features of Combined Cycle Systems
 Design Features of Combined Cycle Systems 1.0 Introduction As we have discussed in class, one of the largest irreversibilities associated with simple gas turbine cycles is the high temperature exhaust.
Design Features of Combined Cycle Systems 1.0 Introduction As we have discussed in class, one of the largest irreversibilities associated with simple gas turbine cycles is the high temperature exhaust.
Effective Reduction of Industrial GHG Emissions via Energy Integration and Biomass Utilization
 Effective Reduction of Industrial GHG Emissions via Energy Integration and Biomass Utilization Eva Lovelady and Mahmoud El-Halwagi Department of Chemical Engineering Texas A & M University 1 1 Motivation
Effective Reduction of Industrial GHG Emissions via Energy Integration and Biomass Utilization Eva Lovelady and Mahmoud El-Halwagi Department of Chemical Engineering Texas A & M University 1 1 Motivation
HEAT INTEGRATION OF FERMENTATION AND RECOVERY STEPS FOR FUEL ETHANOL PRODUCTION FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC BIOMASS R. Grisales 1, C.A.
 HEAT INTEGRATION OF FERMENTATION AND RECOVERY STEPS FOR FUEL ETHANOL PRODUCTION FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC BIOMASS R. Grisales 1, C.A. Cardona 1 *, O.J. Sánchez 1,2, Gutiérrez L.F. 1 1 Department of Chemical
HEAT INTEGRATION OF FERMENTATION AND RECOVERY STEPS FOR FUEL ETHANOL PRODUCTION FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC BIOMASS R. Grisales 1, C.A. Cardona 1 *, O.J. Sánchez 1,2, Gutiérrez L.F. 1 1 Department of Chemical
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Fall Design Project. Production of Dimethyl Ether
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Fall 2001 Design Project Production of Dimethyl Ether We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 50,000 tonne/y, (1 tonne
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Fall 2001 Design Project Production of Dimethyl Ether We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 50,000 tonne/y, (1 tonne
Challenges in Industrial Waste Heat Recovery. Texas Technology 2006 Showcase Tony Dafft December 6 & 7, 2006
 Challenges in Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Texas Technology 2006 Showcase Tony Dafft December 6 & 7, 2006 Outline Plant Statistics and Energy History Tools Used to Identify Projects Sample of Projects
Challenges in Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Texas Technology 2006 Showcase Tony Dafft December 6 & 7, 2006 Outline Plant Statistics and Energy History Tools Used to Identify Projects Sample of Projects
Chapter 9: Applications of the Laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 9: Applications of the Laws of hermodynamics Goals of Period 9 Section 9.1: Section 9.2: Section 9.3: o review the first law of thermodynamics o discuss heat engines and their efficiency o discuss
Chapter 9: Applications of the Laws of hermodynamics Goals of Period 9 Section 9.1: Section 9.2: Section 9.3: o review the first law of thermodynamics o discuss heat engines and their efficiency o discuss
Opportunities for Energy Efficiency Improvement in a Renewable Fuels Process
 Opportunities for Energy Efficiency Improvement in a Renewable Fuels Process Master s Thesis within the Sustainable Energy Systems programme LISA LECEROF Department of Energy and Environment Division of
Opportunities for Energy Efficiency Improvement in a Renewable Fuels Process Master s Thesis within the Sustainable Energy Systems programme LISA LECEROF Department of Energy and Environment Division of
Chapter 10. Flowsheet Analysis for Pollution Prevention. by Kirsten Sinclair Rosselot and David T. Allen
 Chapter 10. Flowsheet Analysis for Pollution Prevention by Kirsten Sinclair Rosselot and David T. Allen The environmental performance of a process flowsheet depends on both the performance of the individual
Chapter 10. Flowsheet Analysis for Pollution Prevention by Kirsten Sinclair Rosselot and David T. Allen The environmental performance of a process flowsheet depends on both the performance of the individual
SYNTHESIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF DEMETHANIZER FLOWSHEETS FOR LOW TEMPERATURE SEPARATION PROCESSES
 Distillation Absorption 2010 A.B. de Haan, H. Kooijman and A. Górak (Editors) All rights reserved by authors as per DA2010 copyright notice SYNTHESIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF DEMETHANIZER FLOWSHEETS FOR LOW
Distillation Absorption 2010 A.B. de Haan, H. Kooijman and A. Górak (Editors) All rights reserved by authors as per DA2010 copyright notice SYNTHESIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF DEMETHANIZER FLOWSHEETS FOR LOW
WATER AND ENERGY INTEGRATION: A COMPREHENSIVE LITERATURE REVIEW OF NON-ISOTHERMAL WATER NETWORK SYNTHESIS
 WATER AND ENERGY INTEGRATION: A COMPREHENSIVE LITERATURE REVIEW OF NON-ISOTHERMAL WATER NETWORK SYNTHESIS Elvis Ahmetović a,b*, Nidret Ibrić a, Zdravko Kravanja b, Ignacio E. Grossmann c a University of
WATER AND ENERGY INTEGRATION: A COMPREHENSIVE LITERATURE REVIEW OF NON-ISOTHERMAL WATER NETWORK SYNTHESIS Elvis Ahmetović a,b*, Nidret Ibrić a, Zdravko Kravanja b, Ignacio E. Grossmann c a University of
ProSimPlus Library (Standard version + rate base option)
 ProSimPlus Library (Standard version + rate base option) Contents UNIT OPERATIONS... 5 Absorber... 5 Absorber with reboiler... 5 Rigorous two-phase distillation (L-V) with partial condenser and decanter...
ProSimPlus Library (Standard version + rate base option) Contents UNIT OPERATIONS... 5 Absorber... 5 Absorber with reboiler... 5 Rigorous two-phase distillation (L-V) with partial condenser and decanter...
Heat Integration Across Plants Considering Distance Factor
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
Does Your Application Call for an F-Shell Heat Exchanger?
 Heat Transfer Does Your Application Call for an F-Shell Heat Exchanger? Rajiv Mukherjee Consultant If the process has a temperature cross or a low flowrate, an F shell might prove beneficial. S EVERAL
Heat Transfer Does Your Application Call for an F-Shell Heat Exchanger? Rajiv Mukherjee Consultant If the process has a temperature cross or a low flowrate, an F shell might prove beneficial. S EVERAL
Exploring inter-process heat integration opportunities for increased energy efficiency in industrial process clusters
 Exploring inter-process heat integration opportunities for increased energy efficiency in industrial process clusters Simon Harvey Professor in Industrial Energy Systems Heat and Power Technology, Chalmers
Exploring inter-process heat integration opportunities for increased energy efficiency in industrial process clusters Simon Harvey Professor in Industrial Energy Systems Heat and Power Technology, Chalmers
Cost Effective Heat Exchangers Network of Total Site Heat Integration
 541 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
541 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
HIGHER EFFICIENCY TARGETING IN A STEAM POWER PLANT BY USING PINCH TECHNOLOGY
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 71, Iss. 4, 2009 ISSN 1454-2358 HIGHER EFFICIENCY TARGETING IN A STEAM POWER PLANT BY USING PINCH TECHNOLOGY Fazlollah ESKANDARI 1, Masoud BEHZAD 2 While energy productive
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 71, Iss. 4, 2009 ISSN 1454-2358 HIGHER EFFICIENCY TARGETING IN A STEAM POWER PLANT BY USING PINCH TECHNOLOGY Fazlollah ESKANDARI 1, Masoud BEHZAD 2 While energy productive
Pinch Analysis of an Industrial Milk Evaporator with Vapour Recompression Technologies
 Pinch Analysis of an Industrial Milk Evaporator with Vapour Recompression Technologies Energy Research Centre University of Waikato New Zealand Dr Tim Walmsley A.Prof Michael Walmsley Dr James Neale Dr
Pinch Analysis of an Industrial Milk Evaporator with Vapour Recompression Technologies Energy Research Centre University of Waikato New Zealand Dr Tim Walmsley A.Prof Michael Walmsley Dr James Neale Dr
Investigation of Heat Exchanger Network Flexibility of Distillation Unit for Processing Different Types of Crude Oil
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
Improving energy efficiency in an ammonia plant
 Improving energy efficiency in an ammonia plant D. Velázquez, F. Rossi and J. Rodríguez of DVA Global Energy Services and F.Galindo of Fertiberia present the results of an energy study carried out in an
Improving energy efficiency in an ammonia plant D. Velázquez, F. Rossi and J. Rodríguez of DVA Global Energy Services and F.Galindo of Fertiberia present the results of an energy study carried out in an
Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks
 Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks Topics: Heat Exchangers have (considerable) P Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop are related New Design: A new -way Trade-off Retrofit: Bottleneck Problems Basis:
Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks Topics: Heat Exchangers have (considerable) P Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop are related New Design: A new -way Trade-off Retrofit: Bottleneck Problems Basis:
Reboiler heat energy recovery using integration process industries to increase their efficiency
 International Journal of Advanced Biotechnology and Research IJBR ISSN 0976-61, Online ISSN 78 599X, Vol-7, Special Issue-March, 016, pp306-313 http://www.bipublication.com Research Article Reboiler heat
International Journal of Advanced Biotechnology and Research IJBR ISSN 0976-61, Online ISSN 78 599X, Vol-7, Special Issue-March, 016, pp306-313 http://www.bipublication.com Research Article Reboiler heat
Secondary Systems: Steam System
 Secondary Systems: Steam System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 10 Table of Contents 1 SECONDARY SYSTEM
Secondary Systems: Steam System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 10 Table of Contents 1 SECONDARY SYSTEM
Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics
 Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics 9-82 Air is used as the working fluid in a simple ideal Brayton cycle that has a pressure ratio of 12, a compressor inlet temperature of 300 K, and a turbine inlet
Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics 9-82 Air is used as the working fluid in a simple ideal Brayton cycle that has a pressure ratio of 12, a compressor inlet temperature of 300 K, and a turbine inlet
Locational Marginal Pricing (LMP): Basics of Nodal Price Calculation
 MRTU Locational Marginal Pricing (LMP): Basics of Nodal Price Calculation CRR Educational Class #2 CAISO Market Operations Why are LMPs important to the CRR Allocation & Settlement Process The CRR revenue
MRTU Locational Marginal Pricing (LMP): Basics of Nodal Price Calculation CRR Educational Class #2 CAISO Market Operations Why are LMPs important to the CRR Allocation & Settlement Process The CRR revenue
Utility-Heat Exchanger Grid Diagram: A Tool for Designing the Total Site Heat Exchanger Network
 7 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
7 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology: A Case Study of Orbit Chemicals Industry
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. I (May- Jun. 2014), PP 44-53 Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology:
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. I (May- Jun. 2014), PP 44-53 Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology:
PI Heat and Thermodynamics - Course PI 25 CRITERION TEST. of each of the following a. it
 Heat and Thermodynamics - Course PI 25 CRITERION TESTS PI 25-1 - 1. Define: heat temperature (c) enthalpy 2. State the applies to meaning water: of each of the following a. it saturation temperature subcooled
Heat and Thermodynamics - Course PI 25 CRITERION TESTS PI 25-1 - 1. Define: heat temperature (c) enthalpy 2. State the applies to meaning water: of each of the following a. it saturation temperature subcooled
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics Design Project. Production of Ethanol
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics Design Project Production of Ethanol Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 30,000 tonne/y of ethanol from ethylene.
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics Design Project Production of Ethanol Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 30,000 tonne/y of ethanol from ethylene.
Waste Heat to Power Economic Tradeoffs and Considerations
 Waste Heat to Power Economic Tradeoffs and Considerations By Dr. Arvind C. Thekdi E3M, Inc. Presented at 3 rd Annual Waste Heat to Power Workshop 2007 September 25, 2007 Houston, TX. Waste Heat Sources
Waste Heat to Power Economic Tradeoffs and Considerations By Dr. Arvind C. Thekdi E3M, Inc. Presented at 3 rd Annual Waste Heat to Power Workshop 2007 September 25, 2007 Houston, TX. Waste Heat Sources
Fundamental Investigation Of Whole-Life Power Plant Performance For Enhanced Geothermal Systems
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Fundamental Investigation Of Whole-Life Power Plant Performance For Enhanced
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Fundamental Investigation Of Whole-Life Power Plant Performance For Enhanced
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics. Design Project. Production of Ammonia
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Ammonia Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 50,000 tonne/y of ammonia from a syngas
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Ammonia Your assignment is to continue evaluating the details of a process to produce 50,000 tonne/y of ammonia from a syngas
IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production. Thorsten Spillmann
 IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production Thorsten Spillmann Content Introduction to IDRIST project Importance of pinch-methodology for energy demand reduction
IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production Thorsten Spillmann Content Introduction to IDRIST project Importance of pinch-methodology for energy demand reduction
CHAPTER 3 MODELLING AND SIMULATION
 58 CHAPTER 3 MODELLING AND SIMULATION 3.1 NEED FOR SIMULATION Simulation is the use of modeling to represent (but not replicate ) a system or process at an appropriate level of detail, and thereby help
58 CHAPTER 3 MODELLING AND SIMULATION 3.1 NEED FOR SIMULATION Simulation is the use of modeling to represent (but not replicate ) a system or process at an appropriate level of detail, and thereby help
CHAPTER 1 BASIC CONCEPTS
 GTU Paper Analysis CHAPTER 1 BASIC CONCEPTS Sr. No. Questions Jan 15 Jun 15 Dec 15 May 16 Jan 17 Jun 17 Nov 17 May 18 Differentiate between the followings; 1) Intensive properties and extensive properties,
GTU Paper Analysis CHAPTER 1 BASIC CONCEPTS Sr. No. Questions Jan 15 Jun 15 Dec 15 May 16 Jan 17 Jun 17 Nov 17 May 18 Differentiate between the followings; 1) Intensive properties and extensive properties,
A New Optimisation-based Design Methodology for Energyefficient Crude Oil Distillation Systems with Preflash Units
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 69, 2018 Guest Editors: Elisabetta Brunazzi, Eva Sorensen Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-66-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 69, 2018 Guest Editors: Elisabetta Brunazzi, Eva Sorensen Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-66-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
