Processes that can be Modeled with RT3D
|
|
|
- Martina Cummings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Natural attenuation of contaminants in aquifer Advanced Environmental Technology Dragan Kaludjerovic PhD Hydrogeologist Web site: Mobile: +381-(0) (0)
2 Theoretical Part
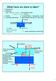
3 Processes that can be Modeled with RT3D Injection Well Extraction Well Ground Surface Flow Solid Solid Sorption NAPL Bacterial cells Sorption Flow Solid Attachment Detachment Growth
4 Natural attenuation of contaminants in aquifers relay on natural processes to achieve remediation goals in a time frame that is approximate to other more active remediation methods
5 Natural attenuation as method of aquifer remediation comprises of different physical, chemical and biological processes that act under favorable circumcises to reduce contaminant mass, concentration and toxicity without human intervention
6 These in-situ processes includes: Dilution of concentrations due to recharging with fresh water (precipitation, the river recharge.) Advection Hydrodynamic dispersion Adsorption Volatilization Biodegradation Abiotic transformation
7 Natural attenuation nondestructive processes they lower the concentrations but do not destroy the contamination, mass of contamination in aquifer remains the same Dilution of concentrations due to recharging with fresh water (precipitation, the river recharge.) Advection Hydrodynamic dispersion Adsorption
8 Natural attenuation destructive processes they lower the concentrations but also the mass of contamination by destroying it Biodegradation Chemical (abiotical) transformation Radioactive decay Volatilization
9 Advection- Dispersion Equation solved by MT3D [D ij C ] - (v i C ) + q s C s - λ [C + ρ b S] = R [ C ] x i x j x i θ θ t Dispersion Advection Sink/Source Reactions Retardation Only advection part solved differently by the different methods
10 Transport Mechanisms Advection C C s Slug Source - (v i C ) x i t c t Transport of dissolved solute at the same velocity of groundwater flow (t c = Distance/v i ) The dominant mechanism for most practical plume migration problems MT3D calculates v i using heads and K s from the MODFLOW modeling results
11 Transport Mechanisms C A 1 Dispersion (D ij C) x x i j Dissolved solute spreads more than predicted by advection alone (total mass constant, A 1 = A 2 ) Pore-scale mechanical dispersion of solute molecules, and molecular diffusion due to concentration gradients Scale dependent In theory, with a micro-scale grid and perfect information, we would not need dispersion Mechanisms well understood, but remains a difficult term to accurately measure t c A 2 t
12 Transport Mechanisms C A 1 Dispersion D = f(α i, v i, Diffusion) [L 2 /T] MT3D requires dispersivity (α) values and simulated flow velocities (v i from MODFLOW model) to calculate the Dispersion terms. Longitudinal Dispersivity (α L ) [L] Typically α L is 0.1 m < α L < 100 m or x plume length α L /α T ratio Typically 0.1 α L α L /α V ratio Typically 0.01 α L Diffusion (D * ) [L 2 /T] usually insignificant t c A 2 t
13 Transport Mechanisms C A 2 = A 1 A 1 Retardation R C t Desorption A 2 t c Adsorption t FLOW
14 Transport Mechanisms C A 1 A 2 = A 1 Retardation R C t t c A 2 t Adsorption caused by the affinity of hydrophobic organic solutes to bind with the organic coating of soil particles Equilibrium partitioning between solid phase and liquid phase As liquid phase concentration falls adsorbed molecules dissolve back into solution Retardation = transport delay caused by this partitioning
15 Transport Mechanisms C sb Linear F Retardation R Linear = 1 + ρ b K d θ K d = C sb /C aq C aq Retardation a function of the amount of solute adsorbed vs. the amount in solution = isotherm Linear isotherm (most common) Constant ratio of Conc. adsorbed vs. Conc. Dissolved = K d K d a function of contaminant (K oc ) and soil (f oc ) Non-linear isotherms (e.g. Freundlich and Langmuir) Variable ratio of Conc. adsorbed vs. Conc. Dissolved Often there is a maximum adsorbed conc. as dissolved concentrations become very high
16 Transport Mechanisms C sb Linear F Retardation R Linear = 1 + ρ b K d θ K d = C sb /C aq C aq Linear and non-linear isotherms assume instantaneous sorption/desorption MT3DMS and MT3D99 now allow kinetic mass transfer First-order, kinetic sorption/desorption Same as Linear isotherm but has a first-order rate constant First-order, kinetic dual-domain mass transfer Simulates diffusion into secondary porosity via a first-order rate constant
17 Transport Mechanisms Sources/Sinks + q s C s Source θ Dissolved solute concentration entering/leaving the model domain through sources/sinks MT3D boundary conditions allow both spatially distributed sources/sinks and point sources/sinks Constant Conc. Source Point Source Conc. Recharge/Evapo. Source Input for MT3D is concentration Flow (q s ) from MODFLOW (Type I - Dirichlet) (Type II - Neuman) (Type III - Cauchy) Sink
18 Transport C Mechanisms A 1 A 2 < A 1 Reactions - λ d C - λ s ρ b S θ t c A 2 t Simplest reaction is first-order irreversible decay C t = C o e λ t λ = degradation rate [1/day] assumes reaction not limited e.g. by oxygen half-life (t 1/2 ) = time for C t /C o to equal 1/2 = ln(1/2)/ λ For first-order decay MT3D requires: soil dry bulk density (ρ b [M/L 3 ]) degradation rate for the dissolved solute (λ d [T -1 ]) degradation rate for the sorbed solute (λ s [T -1 ])
19 Advective-Dispersive Transport Equation Solution Techniques [D ij C ] - (v i C ) + q s C s - λ [C + ρ b C] = R [ C ] ij i x x x θ θ t i j i Finite Difference MOC (Method of Characteristics) MMOC (Modified Method of Characteristics) HMOC (Hybrid Method of Characteristics) Explicit 3 rd -order TVD (ULTIMATE)
20 Biodegradation Biodegradation is a process where hydrocarbons and other contaminants are used as source of food and energy for bacteria and fungi (for grow and reproduction). As the end result contaminants are transformed into CO 2 and water.
21 Bacteria pictured by 3D microscope
22 Bacteria morphology Sperical shape Rod shape Spiral shape
23 Contaminant Microorganism Benzene Pseudomonas putida, P. rhodochrous, P. aeruginosa,acinetobacter sp., Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b, Nocardia sp., methanogens, anaerobes Biodegradation Potential Moderate to High Toluene Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b, Bacillus sp., High Pseudomonas putida, Cunninghamella elegans, P. aeruginosa, P. mildenberger, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas sp., Achromobacter sp., methanogens, anaerobes Ethylbenzene Pseudomonas putida High Xylene Pseudomonas putida, methanogens, anaerobes High Jet fuels Cladosporium, Hormodendrum High Kerozine Torulopsis, Candidatropicalis, Corynebacterium hydrocarboclastus, Candidaparapsilosis, C. guilliermondii, C. lipolytica, Trichosporon sp., Rhohosporidium toruloides, Cladosporium resinae High
24 Biodegradation of hydrocarbons BTEX (mineralization) Aerobic biodegradation C 6 H O 2 = 6CO 2 + 3H 2 O On a mass basis ratio between O2 and benzene = 240:78 = 3.08:1 which means that 3.08 mg of O2 is destroyed to mineralize 1 mg of benzene Anaerobic biodegradation - denitrification 6NO H + + C 6 H 6 = 6CO 2 (g) + 6H 2 O + N 2 (g) On a mass basis ratio between NO3 and benzene 372:78 = 4.77:1
25 Anaerobic biodegradation Fe (III) reduction 60H Fe(OH) 3 + C 6 H 6 = 6CO Fe H 2 O On a mass basis ratio between Fe2+ (produced) and benzene = 21.5:1 Anaerobic biodegradation sulfate reduction 7.5H SO C 6 H 6 = 6 CO 2 (g) H 2 S 0 + 3H 2 O On a mass basis ratio between SO4 and benzene = 4.6:1
26 Anaerobic biodegradation metanogenezis C 6 H H 2 O = 2.25CO CH 4 On a mass basis ratio between CH4 and benzene = 0.77:1
27 Amount of energy that is produced during biodegradation Proces G r (kj/mol benzene) Aerobic respiration Denitrification Fe 3+ reduction Sulfato (SO4) reduction -514 Metanogenezis -136
28 Fundamental concepts of Natural Attenuation. During last decade significant advance was made in understanding the natural processes that contribute to natural attenuation Intensive field investigation and desk studies have led to technical protocols and improved mathematical models
29 Fundamental concepts of Natural Attenuation. Implementation of N.A. is not do-nothing approach, this method of remediation requires: Complex investigation with aim to prove that natural processes rolled out in aquifer; Detail scientific documentation of processes in aquifer and prognosis how this processes can change; Long term monitoring to prove that this remediation technique is efficient; Alternative plan of remediation in a case that N.A is no more efficient
30 Influence of geochemical condition on biodegradation Biodegradation will occur only if geochemical conditions are favorable During biodegradation significant changes of geochemical condition occurs When evaluation natural attenuation it is important to predict future geochemical conditions that are favorably for biodegradation
31 Field investigation work One of the challenges in natural attenuation studies is to properly characterize geochemistry of groundwater low-flow sampling techniques are necessarily to obtain valid samples of dissolved O2 and other electron acceptors, ph, eh.
32 Field Application
33 Advanced Groundwater Technology AGT Dragan Kaludjerovic PhD Hydrogeologist Web site: mobile:
34 The River Sava Location of 45 t spill Renney wells 800 l/s
35 Location of 45 t spill
36 Xylene contaminant, spill of 45 tones
37 3D Geological model
38 3D Geological model
39 3D Hydrodynamic model
40 3D Local transport model Location of 45 t spill
41 3D Local transport model Location of 45 t spill
42 3D Local transport model Location of 45 t spill
43 Canals where the xylene spilled into and via which xylene is introduced into aquifer
44 Canals where the xylene spilled into and via which xylene is introduced into aquifer
45 Movement of dissolved xylene without processes of adsorption and biodegradation advection and dispersion only
46 Concentration of xylene after 912 days (~2.5 years)
47 Concentration of xylene after 1275 days (~3.5 years) Artificial boundary
48 Concentration of xylene after 1700 days (~4.65 years) Artificial boundary
49 Concentration of xylene after 2550 days (~7 years) Artificial boundary
50 Movement of dissolved xylene with advection, dispersion and microbial biodegradation
51 Concentration of xylene after 912 days (~2.5 years)
52 Concentration of xylene after 1425 days (~4 years)
53 Concentration of xylene after 1862 days (~5.1 years)
54 Concentration of xylene after 2550 days (~7 years)
55 Concentration of dissolved O2 after 1862 days (~5 years)
56 Concentration of dissolved NO3 after 1862 days (~5 years)
57 Concentration of dissolved Fe2+ after 1862 days (~5 years)
58 Concentration of dissolved SO4 after 1862 days (~5 years)
59 Concentration of dissolved CH4 after 1862 days (~5 years)
60 Movement of dissolved xylene with advection, dispersion, adsorption and microbial biodegradation high Kd
61 Koncentracija ksilena posle 912 dana (~2.5 godina)
62 Koncentracija ksilena posle 1425 dana (~4 godine)
63 Koncentracija ksilena posle 1862 dana (~4.65 godina)
64 Koncentracija ksilena posle 2550 dana (~7 godina)
65 Koncentracija ksilena posle 3650 dana (~10 godina)
66 Koncentracija ksilena posle 5000 dana (~13.7 godina)
67 Movement of dissolved xylene with advection, dispersion, adsorption and microbial biodegradation low Kd (calibrated case)
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77 Conclusion In this case it is not necessarily to introduce active method of groundwater remediation since it is shown that plume will not move toward well field Monitoring is necessarily
GMS 9.2 Tutorial RT3D BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors
 v. 9. GMS 9. Tutorial RT3D BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors Objectives Use GMS and RT3D to model BTEX degradation using a multiple electron acceptor model. Prerequisite Tutorials None
v. 9. GMS 9. Tutorial RT3D BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors Objectives Use GMS and RT3D to model BTEX degradation using a multiple electron acceptor model. Prerequisite Tutorials None
GMS 10.0 Tutorial RT3D BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial RTD BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors bjectives Use GMS and RTD to model BTEX degradation using a multiple electron acceptor model. Prerequisite Tutorials RTD
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial RTD BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors bjectives Use GMS and RTD to model BTEX degradation using a multiple electron acceptor model. Prerequisite Tutorials RTD
GMS 10.2 Tutorial RT3D BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors
 v. 10. GMS 10. Tutorial RT3D BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors bjectives Use GMS and RT3D to model BTEX degradation using a multiple electron acceptor model. Prerequisite Tutorials RT3D
v. 10. GMS 10. Tutorial RT3D BTEX Degradation with Multiple Electron Acceptors bjectives Use GMS and RT3D to model BTEX degradation using a multiple electron acceptor model. Prerequisite Tutorials RT3D
In Situ Remediation (ISR MT3DMS TM ) Features: Reactions
 In Situ Remediation (ISR MT3DMS TM ) Features: Reactions October 5, 2015 ISR MT3DMS TM Reactions 1 Introduction The core reaction framework in ISR MT3DMS TM was developed using the public domain reaction
In Situ Remediation (ISR MT3DMS TM ) Features: Reactions October 5, 2015 ISR MT3DMS TM Reactions 1 Introduction The core reaction framework in ISR MT3DMS TM was developed using the public domain reaction
Site Verified Contaminant Transport Model as a Mathematical Vehicle for Prevention of the Natural Aquifer Contamination
 PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., E-10 (406), 2008 Site Verified Contaminant Transport Model as a Mathematical Vehicle for Prevention of the Natural Aquifer Contamination Andrzej ANISZEWSKI Szczecin
PUBLS. INST. GEOPHYS. POL. ACAD. SC., E-10 (406), 2008 Site Verified Contaminant Transport Model as a Mathematical Vehicle for Prevention of the Natural Aquifer Contamination Andrzej ANISZEWSKI Szczecin
IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION EVALUATION USING THE WATERLOO EMITTER
 IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION EVALUATION USING THE WATERLOO EMITTER Douglas A. Sweeney, M.Sc., P.Eng. and Ian Mitchell, M.Sc., P.Geo. October 2004 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Introduction Case Study Waterloo Emitter
IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION EVALUATION USING THE WATERLOO EMITTER Douglas A. Sweeney, M.Sc., P.Eng. and Ian Mitchell, M.Sc., P.Geo. October 2004 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Introduction Case Study Waterloo Emitter
Groundwater Risk Assessment
 Groundwater Risk Assessment ELQF - 6 November 2012 Katy Baker Technical Director ARCADIS (UK) Limited Imagine the result Problem definition The importance of the CSM 2 The definition of the problem: 3
Groundwater Risk Assessment ELQF - 6 November 2012 Katy Baker Technical Director ARCADIS (UK) Limited Imagine the result Problem definition The importance of the CSM 2 The definition of the problem: 3
Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies
 Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies TASK Tersus Advanced Surface Kinetics NAPL Surfactants Tersus is the worldwide distributor of the
Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies TASK Tersus Advanced Surface Kinetics NAPL Surfactants Tersus is the worldwide distributor of the
Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies
 Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies TASK Tersus Advanced Surface Kinetics NAPL Surfactants Tersus is the worldwide distributor of the
Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies TASK Tersus Advanced Surface Kinetics NAPL Surfactants Tersus is the worldwide distributor of the
Groundwater Models and Modeling Considerations
 Groundwater Models and Modeling Considerations MPCA Industrial Landfill Guidance Workgroup April 30, 2009 Terry Johnson, P.G. Waste Management Inc., The Three Legs of the Stool 1. Engineering design and
Groundwater Models and Modeling Considerations MPCA Industrial Landfill Guidance Workgroup April 30, 2009 Terry Johnson, P.G. Waste Management Inc., The Three Legs of the Stool 1. Engineering design and
Groundwater Modeling Guidance
 Groundwater Modeling Guidance Richard J. Mandle Groundwater Modeling Program Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Draft 1.0 10/16/02 Executive Summary The use of groundwater models is prevalent
Groundwater Modeling Guidance Richard J. Mandle Groundwater Modeling Program Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Draft 1.0 10/16/02 Executive Summary The use of groundwater models is prevalent
Risk of well water pollution from the surface of a recharge area
 Water Pollution VIII: Modelling, Monitoring and Management 233 Risk of well water pollution from the surface of a recharge area J. Krivic Geological Survey of Slovenia Abstract An aquifer acts as a pollution
Water Pollution VIII: Modelling, Monitoring and Management 233 Risk of well water pollution from the surface of a recharge area J. Krivic Geological Survey of Slovenia Abstract An aquifer acts as a pollution
Lecture 6: In Situ Bioremediation and Natural Attenuation
 ENGI 7718 Environmental Geotechniques ENGI 9621 Soil Remediation Engineering Lecture 6: In Situ Bioremediation and Natural Attenuation Spring 2011 Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science 1 6.1 Introduction
ENGI 7718 Environmental Geotechniques ENGI 9621 Soil Remediation Engineering Lecture 6: In Situ Bioremediation and Natural Attenuation Spring 2011 Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science 1 6.1 Introduction
MODELING BIOREMEDIATON AT ABANDONED WASTE DUMPING AND LANDFILL SITE USING MODFLOW AND RT3D PACKAGES
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 19 2011 MODELING BIOREMEDIATON
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 19 2011 MODELING BIOREMEDIATON
Potential for the Bioremediation of Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE)
 Page 1 of 5 Potential for the Bioremediation of Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE) The Problem: The gasoline oxygenate, methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE), presents a serious complication in the remediation
Page 1 of 5 Potential for the Bioremediation of Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE) The Problem: The gasoline oxygenate, methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE), presents a serious complication in the remediation
MODELING NATURAL ATTENUATION OF CONTAMINATED AQUIFERS. Abstract
 MODELING NATURAL ATTENUATION OF CONTAMINATED AQUIFERS ii Abstract Characterizing the effects of subsurface wastewater effluent discharges remains as a significant challenge impacting both ground-water
MODELING NATURAL ATTENUATION OF CONTAMINATED AQUIFERS ii Abstract Characterizing the effects of subsurface wastewater effluent discharges remains as a significant challenge impacting both ground-water
Table of Contents. Overview of the Technical Protocol... Page 5. Overview of Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbon Biodegradation...
 Draft EPA Region 4 Suggested Practices for Evaluation of a Site For Natural Attenuation (Biological Degradation) of Chlorinated Solvents 1 November, 1999 http://www.epa.gov/region4/ Version 3.1 1 This
Draft EPA Region 4 Suggested Practices for Evaluation of a Site For Natural Attenuation (Biological Degradation) of Chlorinated Solvents 1 November, 1999 http://www.epa.gov/region4/ Version 3.1 1 This
Sections 5 & 6. Site Characterization and Lines of Evidence. Steve Posten
 Sections 5 & 6 Site Characterization and Lines of Evidence Steve Posten Overview Section 5 Site Characterization Conceptual site model Aquifer characteristics Hydraulic conductivity/gradient Porosity Organic
Sections 5 & 6 Site Characterization and Lines of Evidence Steve Posten Overview Section 5 Site Characterization Conceptual site model Aquifer characteristics Hydraulic conductivity/gradient Porosity Organic
6. Organic Compounds: Hydrocarbons. General Comments Borden, Canada, tracer test Laurens, SC, gasoline spill Bemidji, MN, crude oil spill
 6. Organic Compounds: Hydrocarbons General Comments Borden, Canada, tracer test Laurens, SC, gasoline spill Bemidji, MN, crude oil spill In the subsurface, biogeochemical processes that control contaminant
6. Organic Compounds: Hydrocarbons General Comments Borden, Canada, tracer test Laurens, SC, gasoline spill Bemidji, MN, crude oil spill In the subsurface, biogeochemical processes that control contaminant
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY - GEOL 406/506
 ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY - GEOL 406/506 Glossary of useful Terms: 1. Abiotic: not living. 2. A b s o r p t i o n: the penetration of atoms, ions, or molecules into the bulk mass of substrate. 3. Acclimation:
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY - GEOL 406/506 Glossary of useful Terms: 1. Abiotic: not living. 2. A b s o r p t i o n: the penetration of atoms, ions, or molecules into the bulk mass of substrate. 3. Acclimation:
Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies
 Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies RemBind Vadose Zone Treatment Tersus is the exclusive North American distributor for RemBind (US
Advancing the Science of In Situ Groundwater Remediation Petroleum Hydrocarbon Remediation Technologies RemBind Vadose Zone Treatment Tersus is the exclusive North American distributor for RemBind (US
Geology 627, Hydrogeology Review questions for final exam h t 1/ 2
 Geology 67, Hydrogeology Review questions for final exam 004 Multiple choice and fill in the blank. There may be more than one correct choice for each question. 1. Which hydrogeologic quantities are represented
Geology 67, Hydrogeology Review questions for final exam 004 Multiple choice and fill in the blank. There may be more than one correct choice for each question. 1. Which hydrogeologic quantities are represented
Guidance on Developing a Monitored Natural Attenuation Remedial Proposal for Chlorinated Organics in Ground Water
 Guidance on Developing a Monitored Natural Attenuation Remedial Proposal for Chlorinated Organics in Ground Water North Carolina Division of Waste Management Hazardous Waste Section Final Draft October
Guidance on Developing a Monitored Natural Attenuation Remedial Proposal for Chlorinated Organics in Ground Water North Carolina Division of Waste Management Hazardous Waste Section Final Draft October
Learning about Secondary Water Quality Impacts from the Bemidji Oil Spill
 Learning about Secondary Water Quality Impacts from the Bemidji Oil Spill Crystal Ng (gcng@umn.edu) Univ of Minnesota, Twin Cities Barbara Bekins Research Coordinator USGS, Menlo Park, CA Jard Trost Site
Learning about Secondary Water Quality Impacts from the Bemidji Oil Spill Crystal Ng (gcng@umn.edu) Univ of Minnesota, Twin Cities Barbara Bekins Research Coordinator USGS, Menlo Park, CA Jard Trost Site
Demonstrating Stormwater Infiltration to UICs is Protective of Groundwater Quality
 Demonstrating Stormwater Infiltration to UICs is Protective of Groundwater Quality GWPC Presentation September 28, 2010 Heidi Blischke, GSI Water Solutions, Inc. Barb Adkins, City of Portland, Oregon Rod
Demonstrating Stormwater Infiltration to UICs is Protective of Groundwater Quality GWPC Presentation September 28, 2010 Heidi Blischke, GSI Water Solutions, Inc. Barb Adkins, City of Portland, Oregon Rod
Enhanced Bioremediation Field Experience: Using Observed half Lives in Design and Prediction
 Enhanced Bioremediation Field Experience: Using Observed half Lives in Design and Prediction NDIA Environment, Energy & Sustainability Symposium & Exhibition. May 4-7, 2009, Denver, CO. Authors: Joanna
Enhanced Bioremediation Field Experience: Using Observed half Lives in Design and Prediction NDIA Environment, Energy & Sustainability Symposium & Exhibition. May 4-7, 2009, Denver, CO. Authors: Joanna
Enhanced bioremediation of gasoline contaminated groundwater in Finland by injection of humic acids
 In situ workshop, Stockholm 31.5.2011, Pirjo Tuomi Enhanced bioremediation of gasoline contaminated groundwater in Finland by injection of humic acids Enhanced Natural Attenuation Most organic contaminants
In situ workshop, Stockholm 31.5.2011, Pirjo Tuomi Enhanced bioremediation of gasoline contaminated groundwater in Finland by injection of humic acids Enhanced Natural Attenuation Most organic contaminants
Herb Levine EPA Region IX
 Opportunities to Integrate New Tools such as MBT and CSIA into Existing Policy and Guidance for Selection, Design and Performance Monitoring of Remedies at Chlorinated Solvent Sites Herb Levine EPA Region
Opportunities to Integrate New Tools such as MBT and CSIA into Existing Policy and Guidance for Selection, Design and Performance Monitoring of Remedies at Chlorinated Solvent Sites Herb Levine EPA Region
Evaluating Impoundment Closure Scenarios using Fate and Transport Modeling
 2017 World of Coal Ash (WOCA) Conference in Lexington, KY - May 9-11, 2017 http://www.flyash.info/ Evaluating Impoundment Closure Scenarios using Fate and Transport Modeling Jacob J. Walczak 1, Meng Wang
2017 World of Coal Ash (WOCA) Conference in Lexington, KY - May 9-11, 2017 http://www.flyash.info/ Evaluating Impoundment Closure Scenarios using Fate and Transport Modeling Jacob J. Walczak 1, Meng Wang
BIOVENTING. History. Where was the mass of contaminant going? The answer: Bacterial degradation!
 BIOVENTING History When SVE was implemented, progress of remediation was monitored by measuring the concentrations of contaminants in the extracted gas (Ca) and the depletion of contaminant mass in the
BIOVENTING History When SVE was implemented, progress of remediation was monitored by measuring the concentrations of contaminants in the extracted gas (Ca) and the depletion of contaminant mass in the
MTBE Fact Sheet #2 Remediation Of MTBE Contaminated Soil And Groundwater Background
 United States Office Of Solid Waste And EPA 510-F-98-002 Environmental Protection Emergency Response Agency (5401G) www.epa.gov/oust/mtbe/ Office Of Underground Storage Tanks MTBE Fact Sheet #2 Remediation
United States Office Of Solid Waste And EPA 510-F-98-002 Environmental Protection Emergency Response Agency (5401G) www.epa.gov/oust/mtbe/ Office Of Underground Storage Tanks MTBE Fact Sheet #2 Remediation
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND MINERAL ENGINEERING GEOEE 408 CONTAMINANT HYDROLOGY
 THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND MINERAL ENGINEERING GEOEE 408 CONTAMINANT HYDROLOGY Mid-term Examination Tuesday March 4 th, 2008 75 minutes Answer all three questions. For water
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND MINERAL ENGINEERING GEOEE 408 CONTAMINANT HYDROLOGY Mid-term Examination Tuesday March 4 th, 2008 75 minutes Answer all three questions. For water
Design Calculations for Groundwater and Soil Remediation
 Second Edition Practical Design Calculations for Groundwater and Soil Remediation Jeff Kuo ^ Ql*" CRC Press J Taylor& Francis Group Boca Raton CRC Press is an imprint of the London New York Taylor & Francis
Second Edition Practical Design Calculations for Groundwater and Soil Remediation Jeff Kuo ^ Ql*" CRC Press J Taylor& Francis Group Boca Raton CRC Press is an imprint of the London New York Taylor & Francis
PlumeStop Technical Bulletin 3.1: Post Sorption Contaminant Biodegradation
 Quick Reference: PlumeStop Technical Bulletin 3.1 Post Sorption Contaminant Biodegradation Post sorption contaminant biodegradation Net acceleration of contaminant biodegradation rate Background PlumeStop
Quick Reference: PlumeStop Technical Bulletin 3.1 Post Sorption Contaminant Biodegradation Post sorption contaminant biodegradation Net acceleration of contaminant biodegradation rate Background PlumeStop
Research Areas: Subsurface Flow & Transport (modified after Springer; YZ s expertise/interest marked by X )
 Research Areas: Subsurface Flow & Transport (modified after Springer; YZ s expertise/interest marked by X ) Classification Description A Fundamental of Transport in Porous Media A1 Phenomenological theory
Research Areas: Subsurface Flow & Transport (modified after Springer; YZ s expertise/interest marked by X ) Classification Description A Fundamental of Transport in Porous Media A1 Phenomenological theory
Dr. Robert Mitchell Ground Water Contamination. ES234 Winter
 Geology 474/574 Dr. Robert Mitchell Ground Water Contamination ES234 Winter 2017 650-3591 robert.mitchell@wwu.edu http://kula.geol.wwu.edu/rjmitch/ Office Hours: MWF from 9:00 to 10:00 am, or by arrangement
Geology 474/574 Dr. Robert Mitchell Ground Water Contamination ES234 Winter 2017 650-3591 robert.mitchell@wwu.edu http://kula.geol.wwu.edu/rjmitch/ Office Hours: MWF from 9:00 to 10:00 am, or by arrangement
Enhanced Bioremediation Field Experience: Using Observed Half Lives in Design and Prediction
 Enhanced Bioremediation Field Experience: Using Observed Half Lives in Design and Prediction Authors: Joanna Moreno, Tracy Bellehumeur, Jim Mueller, Fayaz Lakhwala, John Valkenburg, and Josephine Molin
Enhanced Bioremediation Field Experience: Using Observed Half Lives in Design and Prediction Authors: Joanna Moreno, Tracy Bellehumeur, Jim Mueller, Fayaz Lakhwala, John Valkenburg, and Josephine Molin
New England Storage Tank Conference
 New England Storage Tank Conference December 4, 2014 Richard Spiese Vermont Department of Environmental Conservation Waste Management & Prevention Division Sites Management Section 1 National Life Drive-Davis
New England Storage Tank Conference December 4, 2014 Richard Spiese Vermont Department of Environmental Conservation Waste Management & Prevention Division Sites Management Section 1 National Life Drive-Davis
Pump & Treat Remediation
 Pump & Treat Remediation Selection and Planning Pump & Treat Extraction of contaminated water Extraction of free product in the form of a NAPL Removal or destruction of the contaminant from the extracted
Pump & Treat Remediation Selection and Planning Pump & Treat Extraction of contaminated water Extraction of free product in the form of a NAPL Removal or destruction of the contaminant from the extracted
4.0 ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSPORT AND FATE PRINCIPAL FINDINGS
 4.0 ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSPORT AND FATE PRINCIPAL FINDINGS Both EDB and EDC: o Have low to moderate sorptive affinity for aquifer solids o Are relatively mobile in groundwater o Can volatilize from solution
4.0 ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSPORT AND FATE PRINCIPAL FINDINGS Both EDB and EDC: o Have low to moderate sorptive affinity for aquifer solids o Are relatively mobile in groundwater o Can volatilize from solution
22 TECHNICAL GUIDANCE
 22 TECHNICAL GUIDANCE ON CONTAMINATED SITES Version 1.0 Draft 15 vember 2014 Using Monitored Natural Attenuation and Enhanced Attenuation for Groundwater Remediation This document provides guidance on
22 TECHNICAL GUIDANCE ON CONTAMINATED SITES Version 1.0 Draft 15 vember 2014 Using Monitored Natural Attenuation and Enhanced Attenuation for Groundwater Remediation This document provides guidance on
Plume Cut-Off Treatment Example
 Page 1 of 5 H R C T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N # 2. 5. 2 Plume Cut-Off Treatment Example A biologically active barrier treatment zone can be constructed by applying HRC in rows of injection points.
Page 1 of 5 H R C T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N # 2. 5. 2 Plume Cut-Off Treatment Example A biologically active barrier treatment zone can be constructed by applying HRC in rows of injection points.
BREAKTHROUGH TREATMENT FOR PFAS. CASE STUDY: First Demonstrated In Situ Treatment Solution For PFOA/PFOS At Former Industrial Site
 BREAKTHROUGH TREATMENT FOR PFAS CASE STUDY: First Demonstrated In Situ Treatment Solution For PFOA/PFOS At Former Industrial Site www.regenesis.com 1011 Calle Sombra, San Clemente, CA 92673 T: 949.366.8000
BREAKTHROUGH TREATMENT FOR PFAS CASE STUDY: First Demonstrated In Situ Treatment Solution For PFOA/PFOS At Former Industrial Site www.regenesis.com 1011 Calle Sombra, San Clemente, CA 92673 T: 949.366.8000
Anaerobic Benzene Biodegradation - Insights from Treatability Studies and Molecular Tools. Sandra Dworatzek
 Anaerobic Benzene Biodegradation - Insights from Treatability Studies and Molecular Tools Sandra Dworatzek Outline Introduction BTEX degradation and bioremediation Aerobic vs anaerobic Benzene degrading
Anaerobic Benzene Biodegradation - Insights from Treatability Studies and Molecular Tools Sandra Dworatzek Outline Introduction BTEX degradation and bioremediation Aerobic vs anaerobic Benzene degrading
HW6 - MGP Site Bioremediation
 HW6 - MGP Site Bioremediation 1. Given the following group of compounds commonly found in coal tars at MGP sites, determine the relative concentration and total mass of each in the air, water, and soil
HW6 - MGP Site Bioremediation 1. Given the following group of compounds commonly found in coal tars at MGP sites, determine the relative concentration and total mass of each in the air, water, and soil
Field Performance of Dispersive Colloidal Activated Carbon
 .yalpsid rieht tropustonseod gnisu era uoy tahtnoisrevtnioprewop eht,revewoh ;stnof dedebme sniatnocnoitatneserp siht stnof-dedebme-on/moc.redebmetnofnoitatneserp.w tisiv noitamrofni eromrof.redebme tnofnoitatneserp
.yalpsid rieht tropustonseod gnisu era uoy tahtnoisrevtnioprewop eht,revewoh ;stnof dedebme sniatnocnoitatneserp siht stnof-dedebme-on/moc.redebmetnofnoitatneserp.w tisiv noitamrofni eromrof.redebme tnofnoitatneserp
August Prepared by:
 Case Study for the Use of a Decision Support Tool: Evaluating the Applicability of Remediation by Natural Attenuation Using BIOSCREEN at the Administration Area Naval Exchange (NEX) Gas Station, Naval
Case Study for the Use of a Decision Support Tool: Evaluating the Applicability of Remediation by Natural Attenuation Using BIOSCREEN at the Administration Area Naval Exchange (NEX) Gas Station, Naval
SUSTAINABILITY OF NATURAL ATTENUATION OF AROMATICS (BTEX) Final report
 SUSTAINABILITY OF NATURAL ATTENUATION OF AROMATICS (BTEX) Final report Client: NICOLE, Port of Rotterdam, Shell Global Solutions Project code: 2003.1969 Date: 20 July 2007 Client: Project title: NICOLE,
SUSTAINABILITY OF NATURAL ATTENUATION OF AROMATICS (BTEX) Final report Client: NICOLE, Port of Rotterdam, Shell Global Solutions Project code: 2003.1969 Date: 20 July 2007 Client: Project title: NICOLE,
Remediation of Petroleum LNAPL MSECA 2012
 Characterization Trap Instrumentation & Treat - Remediation BOS 200 Remediation of Petroleum LNAPL MSECA 2012 BOS 100 - Solvents BOS 200 Hydrocarbons Obstacles with Traditional In-Situ Remedial Methods
Characterization Trap Instrumentation & Treat - Remediation BOS 200 Remediation of Petroleum LNAPL MSECA 2012 BOS 100 - Solvents BOS 200 Hydrocarbons Obstacles with Traditional In-Situ Remedial Methods
Sediment Diagenesis. 1/61
 Sediment Diagenesis http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c542/ 1/61 Sequence of catabolic reactions In the presence of free O 2 : G (kj/mol) (1) Aerobic respiration: (CH 2 O) 106 (NH 3 ) 16 H 3 PO 4 + 138O 2
Sediment Diagenesis http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c542/ 1/61 Sequence of catabolic reactions In the presence of free O 2 : G (kj/mol) (1) Aerobic respiration: (CH 2 O) 106 (NH 3 ) 16 H 3 PO 4 + 138O 2
Bioremediation of Oil Spills
 Bioremediation of Oil Spills Moritz Becker Philip Eickenbusch 08.01.2013 Biofouling & Biocorrosion (Flemming/Sand) Bioremediation Process whereby bacteria, fungi or plants are used to remove pollutants
Bioremediation of Oil Spills Moritz Becker Philip Eickenbusch 08.01.2013 Biofouling & Biocorrosion (Flemming/Sand) Bioremediation Process whereby bacteria, fungi or plants are used to remove pollutants
Numerical Simulation of Variabledensity Groundwater Flow: Submarine Groundwater Discharge
 Numerical Simulation of Variabledensity Groundwater Flow: Submarine Groundwater Discharge Bill X. Hu and Xinya Li Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences Florida State University Submarine
Numerical Simulation of Variabledensity Groundwater Flow: Submarine Groundwater Discharge Bill X. Hu and Xinya Li Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences Florida State University Submarine
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Bench- and Pilot-Scale Treatability Testing of ISCO and Surfactant Enhanced Biodegradation of Long Chain Petroleum Hydrocarbons
 Bench- and Pilot-Scale Treatability Testing of ISCO and Surfactant Enhanced Biodegradation of Long Chain Petroleum Hydrocarbons Steven R. Hammer, P.E. SLR Consulting October 2014 Our Site Current site
Bench- and Pilot-Scale Treatability Testing of ISCO and Surfactant Enhanced Biodegradation of Long Chain Petroleum Hydrocarbons Steven R. Hammer, P.E. SLR Consulting October 2014 Our Site Current site
4.4 MODEL CODE DESCRIPTION 4.5 WATER SOURCES AND SINKS 4.6 MODEL DOMAIN AND BOUNDARIES. SLR South Africa
 Page 4-18 The developed model should therefore be seen as an initial site model which should be refined and recalibrated once more groundwater monitoring and other data become available. 4.4 MODEL CODE
Page 4-18 The developed model should therefore be seen as an initial site model which should be refined and recalibrated once more groundwater monitoring and other data become available. 4.4 MODEL CODE
Enhanced Anaerobic Biodegradation of a Refinery Benzene Groundwater Plume
 Enhanced Anaerobic Biodegradation of a Refinery Benzene Groundwater Plume Robert (Rory) S. Johnston, PE Michael Eberle SAWEA CONFERENCE DECEMBER 2007 Presentation Outline Go With the Flow Anaerobic Process
Enhanced Anaerobic Biodegradation of a Refinery Benzene Groundwater Plume Robert (Rory) S. Johnston, PE Michael Eberle SAWEA CONFERENCE DECEMBER 2007 Presentation Outline Go With the Flow Anaerobic Process
Development of Soil Cleanup Standards for Explosive Residues on Military Ranges
 Development of Soil Cleanup Standards for Explosive Residues on Military Ranges Jay Clausen AMEC Earth & Environmental Joe Robb AMEC Earth & Environmental Mahalingham Ravichandran AMEC Earth & Environmental
Development of Soil Cleanup Standards for Explosive Residues on Military Ranges Jay Clausen AMEC Earth & Environmental Joe Robb AMEC Earth & Environmental Mahalingham Ravichandran AMEC Earth & Environmental
FINAL REPORT Texas Hazardous Waste Research Center Project 412TAM0012H
 FINAL REPORT Texas Hazardous Waste Research Center Project 412TAM0012H In-situ Remediation of Hydrocarbon Contaminated Groundwater Using Polymeric Nanoparticles August 16, 2015 Principal Investigator:
FINAL REPORT Texas Hazardous Waste Research Center Project 412TAM0012H In-situ Remediation of Hydrocarbon Contaminated Groundwater Using Polymeric Nanoparticles August 16, 2015 Principal Investigator:
Natural Systems. Saumyen Guha Department of Civil Engineering
 Reach Symposium 2010 Remediation of Pollution in Natural Systems Saumyen Guha Department of Civil Engineering IIT Kanpur Outline Natural Systems Pollution in the Natural Systems Some Example Problems Overview
Reach Symposium 2010 Remediation of Pollution in Natural Systems Saumyen Guha Department of Civil Engineering IIT Kanpur Outline Natural Systems Pollution in the Natural Systems Some Example Problems Overview
**Water Resources Engineering, Royal Institute of Technology, S Stockholm, Sweden usu. edu
 Oxygen- and Nitrate-based Biodegradation of Aromatic Hydrocarbons Using Monod-kinetics: Application of a Simplified Numerical Algorithm Mamun Rashid* & Jagath J. Kaluarachchi** *Utah Water Research Laboratory,
Oxygen- and Nitrate-based Biodegradation of Aromatic Hydrocarbons Using Monod-kinetics: Application of a Simplified Numerical Algorithm Mamun Rashid* & Jagath J. Kaluarachchi** *Utah Water Research Laboratory,
Characterization and Remediation of Diesel in a Fractured Rock Aquifer with a Nutrient-Flushing System
 Characterization and Remediation of Diesel in a Fractured Rock Aquifer with a Nutrient-Flushing System Presentation by David Thomson and Stefan Humphries 31-Oct-07 Authors and Collaborators Presenting
Characterization and Remediation of Diesel in a Fractured Rock Aquifer with a Nutrient-Flushing System Presentation by David Thomson and Stefan Humphries 31-Oct-07 Authors and Collaborators Presenting
Wettability and Rock Diagenesis: Why Microbes are Important
 Wettability and Rock Diagenesis: Why Microbes are Important David B. Vance ARCADIS US, Inc. Presented at the 20 th Annual CO 2 Flooding Conference December 11-12, 2014 Midland, Texas Why Oil is in ROZs
Wettability and Rock Diagenesis: Why Microbes are Important David B. Vance ARCADIS US, Inc. Presented at the 20 th Annual CO 2 Flooding Conference December 11-12, 2014 Midland, Texas Why Oil is in ROZs
Chemical Reduction processes for In Situ Soluble Metals Remediation and Immobilization in Groundwater
 Chemical Reduction processes for In Situ Soluble Metals Remediation and Immobilization in Groundwater 2014 RPIC Federal Contaminated Sites National Workshop Ottawa 2014 Prepared by Jean Paré, P. Eng. Chemco
Chemical Reduction processes for In Situ Soluble Metals Remediation and Immobilization in Groundwater 2014 RPIC Federal Contaminated Sites National Workshop Ottawa 2014 Prepared by Jean Paré, P. Eng. Chemco
Upscaling retardation factors in 2-D porous media
 Calibration and eliability in Groundwater Modelling: From Uncertainty to Decision Making (Proceedings of ModelCAE 5, The Hague, The Netherlands, June 5). IAHS Publ.,. Upscaling retardation factors in -D
Calibration and eliability in Groundwater Modelling: From Uncertainty to Decision Making (Proceedings of ModelCAE 5, The Hague, The Netherlands, June 5). IAHS Publ.,. Upscaling retardation factors in -D
Monitored natural attenuation (MNA) as a long-term management technique for contaminated sites
 Monitored natural attenuation (MNA) as a long-term management technique for contaminated sites Application and experience Prof. Phil Morgan The Sirius Group phil.morgan@thesiriusgroup.com http://www.thesiriusgroup.com
Monitored natural attenuation (MNA) as a long-term management technique for contaminated sites Application and experience Prof. Phil Morgan The Sirius Group phil.morgan@thesiriusgroup.com http://www.thesiriusgroup.com
Modelling contamination of a drinking water supply well in the Sabarmati river bed aquifer, Ahmedabad, India
 Impacts of Urban Growth on Surface Water and Groundwater Quality (Proceedings of IUGG 99 Symposium HS5, Birmingham, July 1999). IAHS Publ. no. 259, 1999. 73 Modelling contamination of a drinking water
Impacts of Urban Growth on Surface Water and Groundwater Quality (Proceedings of IUGG 99 Symposium HS5, Birmingham, July 1999). IAHS Publ. no. 259, 1999. 73 Modelling contamination of a drinking water
C = W/a a = Q + v s A + kv C=C o e -λt. 7. Lakes (reactors) in series (SS)
 What have we done to date? 1. Regulations 2. Hydrology (ΔS = Rivers + Precip. + Groundwater disch. Outflow Evap. GW out ) 3. Kinetics 4. Eutrophication description, model 5. Limnology (field trips) 6.
What have we done to date? 1. Regulations 2. Hydrology (ΔS = Rivers + Precip. + Groundwater disch. Outflow Evap. GW out ) 3. Kinetics 4. Eutrophication description, model 5. Limnology (field trips) 6.
S.P. YIM Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute P.O.Box 150, Yusong, Daejon, Republic of Korea
 Hydrodynamic Dispersion Coefficients in a Porous Medium with Parallel Fractures - C.K. Lee Handong Global University 3 Namsong-ri, Heunghae-eub, Buk-gu, Pohang, Kyungbuk, 791-708 Republic of Korea S.P.
Hydrodynamic Dispersion Coefficients in a Porous Medium with Parallel Fractures - C.K. Lee Handong Global University 3 Namsong-ri, Heunghae-eub, Buk-gu, Pohang, Kyungbuk, 791-708 Republic of Korea S.P.
Enhanced removal of BTEX/TCE/cis-DCE mixture using waste scrap tires immobilized with indigenous Pseudomonas sp.
 Enhanced removal of BTEX/TCE/cis-DCE mixture using waste scrap tires immobilized with indigenous Pseudomonas sp. Q. Lu 1, R.A. de Toledo 1, F. Xie 1, J. Li 1,2, H. Shim 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental
Enhanced removal of BTEX/TCE/cis-DCE mixture using waste scrap tires immobilized with indigenous Pseudomonas sp. Q. Lu 1, R.A. de Toledo 1, F. Xie 1, J. Li 1,2, H. Shim 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental
Modeling the impact of ethanol on the persistence of benzene in gasoline-contaminated groundwater
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 1, 1003, 10.1029/2001WR000589, 2002 Modeling the impact of ethanol on the persistence of benzene in gasoline-contaminated groundwater J. W. Molson, J. F. Barker,
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 1, 1003, 10.1029/2001WR000589, 2002 Modeling the impact of ethanol on the persistence of benzene in gasoline-contaminated groundwater J. W. Molson, J. F. Barker,
Novel Activation Methods for Persulfate Oxidation: Cement and Calcium Peroxide. RE 3 Conference November 13, 2012
 Novel Activation Methods for Persulfate Oxidation: Cement and Calcium Peroxide RE 3 Conference November 13, 2012 Introduction to Activated Persulfate Oxidation Potentials In situ chemical oxidation ISCO
Novel Activation Methods for Persulfate Oxidation: Cement and Calcium Peroxide RE 3 Conference November 13, 2012 Introduction to Activated Persulfate Oxidation Potentials In situ chemical oxidation ISCO
Ashley Cedzo, Northwest District Technical Manager
 A TECHNOLOGY PLATFORM TO HARNESS SPEED AND CERTAINTY IN GROUNDWATER REMEDIATION: RAPID RISK REDUCTION AND ACCELERATED BIOREMEDIATION FACILITATED BY A COLLODIAL BIOMATRIX Ashley Cedzo, Northwest District
A TECHNOLOGY PLATFORM TO HARNESS SPEED AND CERTAINTY IN GROUNDWATER REMEDIATION: RAPID RISK REDUCTION AND ACCELERATED BIOREMEDIATION FACILITATED BY A COLLODIAL BIOMATRIX Ashley Cedzo, Northwest District
Dept. of Earth Sciences University of the Western Cape AVAP Project Steering Committee Meeting 22 September 2004
 Review of Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment Methods Unsaturated Zone Dept. of Earth Sciences University of the Western Cape AVAP Project Steering Committee Meeting 22 September 2004 Objectives Review
Review of Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment Methods Unsaturated Zone Dept. of Earth Sciences University of the Western Cape AVAP Project Steering Committee Meeting 22 September 2004 Objectives Review
7.0 GROUNDWATER AND STABILIZER TRANSPORT MODELING
 7.0 GROUNDWATER AND STABILIZER TRANSPORT MODELING 7.1 Introduction The concept of passive site remediation is the slow injection of stabilizing materials at the up gradient edge of a site and delivery
7.0 GROUNDWATER AND STABILIZER TRANSPORT MODELING 7.1 Introduction The concept of passive site remediation is the slow injection of stabilizing materials at the up gradient edge of a site and delivery
API SOIL & GROUNDWATER RESEARCH BULLETIN
 American Petroleum Institute API SOIL & GROUNDWATER RESEARC BULLETIN A summary of research results from APIÕs Soil and Groundwater Technical Task Force. August 998 No. 7 DAFfy Graphs An Innovative Approach
American Petroleum Institute API SOIL & GROUNDWATER RESEARC BULLETIN A summary of research results from APIÕs Soil and Groundwater Technical Task Force. August 998 No. 7 DAFfy Graphs An Innovative Approach
State of the Practice versus State of the Art in Chemical Oxidation / Reduction Technologies.
 State of the Practice versus State of the Art in Chemical Oxidation / Reduction Technologies. Presented by: Mike Marley Principal and Founder Advances in Oxidation and Reduction Technologies for Remediation
State of the Practice versus State of the Art in Chemical Oxidation / Reduction Technologies. Presented by: Mike Marley Principal and Founder Advances in Oxidation and Reduction Technologies for Remediation
Biological Reductive Dechlorination of Chlorinated Compounds. Barry Molnaa WSW Remediation Practice Manager ARCADIS
 Biological Reductive Dechlorination of Chlorinated Compounds Barry Molnaa WSW Remediation Practice Manager ARCADIS 1 Presentation Outline What are we trying to do? How is it supposed to work? What are
Biological Reductive Dechlorination of Chlorinated Compounds Barry Molnaa WSW Remediation Practice Manager ARCADIS 1 Presentation Outline What are we trying to do? How is it supposed to work? What are
New Applications of Current Methods to Assess and Monitor Natural Attenuation
 New Applications of Current Methods to Assess and Monitor Natural Attenuation Liz van Warmerdam Innovation that Provides Sustainable Solutions to Complex Local Challenges, Worldwide Outline What is Natural
New Applications of Current Methods to Assess and Monitor Natural Attenuation Liz van Warmerdam Innovation that Provides Sustainable Solutions to Complex Local Challenges, Worldwide Outline What is Natural
Modeling Intrinsic Remediation With Multiple Electron Acceptors: Results From Seven Sites
 Modeling Intrinsic Remediation With Multiple Electron Acceptors: Results From Seven Sites Charles J. Newell, J. A. Winters Groundwater Services, Inc., Houston, Texas Hanadi S. Rifai Energy and Environmental
Modeling Intrinsic Remediation With Multiple Electron Acceptors: Results From Seven Sites Charles J. Newell, J. A. Winters Groundwater Services, Inc., Houston, Texas Hanadi S. Rifai Energy and Environmental
CHAPTER 2. Objectives of Groundwater Modelling
 CHAPTER 2 Objectives of Groundwater Modelling In the last two decades mathematical modelling techniques have increasingly proved their value in furthering the understanding of groundwater systems and,
CHAPTER 2 Objectives of Groundwater Modelling In the last two decades mathematical modelling techniques have increasingly proved their value in furthering the understanding of groundwater systems and,
MNA PERFORMANCE EVALUATION FOR CONTAMINATED SITE REMEDIATION: FATE &TRANSPORT MODELING BASED APPROACH
 Congrès annuel de la Société canadienne de génie civil Annual Conference of the Canadian Society for Civil Engineering Montréal, Québec, Canada 5- juin / June 5-, MNA PERFORMANCE EVALUATION FOR CONTAMINATED
Congrès annuel de la Société canadienne de génie civil Annual Conference of the Canadian Society for Civil Engineering Montréal, Québec, Canada 5- juin / June 5-, MNA PERFORMANCE EVALUATION FOR CONTAMINATED
Biodegradation of Hydrocarbons under Nitrate and Sulfate Reducing Conditions
 Biodegradation of Hydrocarbons under Nitrate and Sulfate Reducing Conditions David Abranovic P.E., ERM, Scottsdale, AZ Paula Chang, ERM, Scottsdale, AZ Richard Brown, ERM, Ewing, NJ WaterTech 2008 Contents
Biodegradation of Hydrocarbons under Nitrate and Sulfate Reducing Conditions David Abranovic P.E., ERM, Scottsdale, AZ Paula Chang, ERM, Scottsdale, AZ Richard Brown, ERM, Ewing, NJ WaterTech 2008 Contents
Three-Dimensional Simulations of Methane Injection
 Three-Dimensional Simulations of Methane Injection Preliminary Modeling Study Using MIN3P-Dusty 6 th Annual International Conference on Soil, Water, Energy, and Air March 1-4, 016 San Diego, California
Three-Dimensional Simulations of Methane Injection Preliminary Modeling Study Using MIN3P-Dusty 6 th Annual International Conference on Soil, Water, Energy, and Air March 1-4, 016 San Diego, California
Surface Water and Seawater Interactions in the Coastal Environment of Biscayne Bay, Southeast Florida
 Surface Water and Seawater Interactions in the Coastal Environment of Biscayne Bay, Southeast Florida William C. Hutchings, MS, PG Nicholas Albergo, PE, DEE Paper No. 191-8 2005 Salt Lake City Annual Meeting
Surface Water and Seawater Interactions in the Coastal Environment of Biscayne Bay, Southeast Florida William C. Hutchings, MS, PG Nicholas Albergo, PE, DEE Paper No. 191-8 2005 Salt Lake City Annual Meeting
Conceptual Site Model Considerations - Terrestrial/Groundwater
 Site Description Site Conditions Location: Size: Site Status: Active Inactive Unknown Describe present site conditions using information obtained during property inspection or sitespecific documents to
Site Description Site Conditions Location: Size: Site Status: Active Inactive Unknown Describe present site conditions using information obtained during property inspection or sitespecific documents to
Tools for Monitoring Contaminant Biodegradation When Combined with Colloidal Activated Carbon
 Tools for Monitoring Contaminant Biodegradation When Combined with Colloidal Activated Carbon Ashley Cedzo Kristen Thoreson, Ph.D., Stephanie Rittenhouse, Craig Sandefur and Jeremy Birnstingl, Ph.D.- Regenesis
Tools for Monitoring Contaminant Biodegradation When Combined with Colloidal Activated Carbon Ashley Cedzo Kristen Thoreson, Ph.D., Stephanie Rittenhouse, Craig Sandefur and Jeremy Birnstingl, Ph.D.- Regenesis
FIELD IMPLIMENTATION OF ANAEROBIC DECHLORINATION UTILIZING ZERO-VALENT IRON WITH AN ORGANIC HYDROGEN DONOR
 FIELD IMPLIMENTATION OF ANAEROBIC DECHLORINATION UTILIZING ZERO-VALENT IRON WITH AN ORGANIC HYDROGEN DONOR Michael Scalzi (IET@IET-INC.NET) (Innovative Environmental Technologies, Pipersville, PA, USA)
FIELD IMPLIMENTATION OF ANAEROBIC DECHLORINATION UTILIZING ZERO-VALENT IRON WITH AN ORGANIC HYDROGEN DONOR Michael Scalzi (IET@IET-INC.NET) (Innovative Environmental Technologies, Pipersville, PA, USA)
Caesium-137 Transport in an Unconfined Aquifer
 Caesium-137 Transport in an Unconfined Aquifer 1 Introduction Caesium-137 is an anthropogenic radioactive isotope formed as a product of nuclear fission. Historically, Cs-137 was released into the environment
Caesium-137 Transport in an Unconfined Aquifer 1 Introduction Caesium-137 is an anthropogenic radioactive isotope formed as a product of nuclear fission. Historically, Cs-137 was released into the environment
PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL TREATMENT OF METALS AND RADIONUCLIDES IN THE SATURATED ZONE USING COLLOIDAL BUFFERS EOS Remediation, LLC.
 PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL TREATMENT OF METALS AND RADIONUCLIDES IN THE SATURATED ZONE USING COLLOIDAL BUFFERS - 12515 Yenjung Lai 1, Robert C. Borden 1, Ed Alperin 2 1 North Carolina State University, Raleigh,
PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL TREATMENT OF METALS AND RADIONUCLIDES IN THE SATURATED ZONE USING COLLOIDAL BUFFERS - 12515 Yenjung Lai 1, Robert C. Borden 1, Ed Alperin 2 1 North Carolina State University, Raleigh,
Section 5 Relative Effects of Manure Spreading and Confined Feeding Operations on Groundwater Quality
 Section 5 Relative Effects of Manure Spreading and Confined Feeding Operations on Groundwater Quality 5.1 Introduction The third objective of the Livestock Manure Impacts on Groundwater Quality in Alberta
Section 5 Relative Effects of Manure Spreading and Confined Feeding Operations on Groundwater Quality 5.1 Introduction The third objective of the Livestock Manure Impacts on Groundwater Quality in Alberta
Imagine the result. Ms. Jeannette DeBartolomeo Oil Control Program Maryland Department of Environment 1800 Washington Boulevard Baltimore, MD 21230
 Ms. Jeannette ebartolomeo Oil Control Program Maryland epartment of Environment 00 Washington Boulevard Baltimore, M 0 ARCAIS U.S., Inc. Benfield Boulevard Suite A Millersville Maryland 0 Tel 0..00 Fax
Ms. Jeannette ebartolomeo Oil Control Program Maryland epartment of Environment 00 Washington Boulevard Baltimore, M 0 ARCAIS U.S., Inc. Benfield Boulevard Suite A Millersville Maryland 0 Tel 0..00 Fax
Plume Area Treatment Example
 Page 1 of 5 H R C T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N # 2. 5. 1 Plume Area Treatment Example HRC injection grids are commonly employed at project sites where a localized plume of chlorinated solvent contamination
Page 1 of 5 H R C T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N # 2. 5. 1 Plume Area Treatment Example HRC injection grids are commonly employed at project sites where a localized plume of chlorinated solvent contamination
TECHNOLOGIES FOR BIOREMEDIATION OF SOILS CONTAMINATED WITH PETROLEUM PRODUCTS
 TECHNOLOGIES FOR BIOREMEDIATION OF SOILS CONTAMINATED WITH PETROLEUM PRODUCTS Lecturer PhD., Roxana Gabriela POPA, University Constantin Brâncuși of Tg-Jiu, roxanna_popa@yahoo.com Associate Professor PhD,
TECHNOLOGIES FOR BIOREMEDIATION OF SOILS CONTAMINATED WITH PETROLEUM PRODUCTS Lecturer PhD., Roxana Gabriela POPA, University Constantin Brâncuși of Tg-Jiu, roxanna_popa@yahoo.com Associate Professor PhD,
Before writing the discipline examinations, candidates must have passed, or have been exempted from, the Basic Studies Examinations.
 INTRODUCTION The Canadian Engineering Qualifications Board of Engineers Canada issues the Examination Syllabus that includes a continually increasing number of engineering disciplines. Each discipline
INTRODUCTION The Canadian Engineering Qualifications Board of Engineers Canada issues the Examination Syllabus that includes a continually increasing number of engineering disciplines. Each discipline
Comparison of Three Numerical Models for Chain-Decay Transport Simulation at a Closed AFB in Texas
 Comparison of Three Numerical Models for Chain-Decay Transport Simulation at a Closed AFB in Texas Ming-Shu Tsou 1, Kan Tu 1, Jan Kool 1, Christopher J. Neville 2, Steven C. Young 1* 1 HydroGeoLogic, Inc,
Comparison of Three Numerical Models for Chain-Decay Transport Simulation at a Closed AFB in Texas Ming-Shu Tsou 1, Kan Tu 1, Jan Kool 1, Christopher J. Neville 2, Steven C. Young 1* 1 HydroGeoLogic, Inc,
(,,,) = ( )exp ( + C(x,y,z,t) = the concentration of the contaminant at location x, y, z from the source at time t.
 INTRODUCTION Quick Domenico.xls (QD) is a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet application of An Analytical Model For Multidimensional Transport of a Decaying Contaminant Species, by P.A. Domenico, Journal of Hydrology,
INTRODUCTION Quick Domenico.xls (QD) is a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet application of An Analytical Model For Multidimensional Transport of a Decaying Contaminant Species, by P.A. Domenico, Journal of Hydrology,
MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL RESOURCES. Monitored Natural Attenuation of Groundwater Contamination at Voluntary Cleanup Program Sites
 MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL RESOURCES Monitored Natural Attenuation of Groundwater Contamination at Voluntary Cleanup Program Sites Technical Bulletin 1/2002 Hazardous Waste Program The chemical, physical
MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL RESOURCES Monitored Natural Attenuation of Groundwater Contamination at Voluntary Cleanup Program Sites Technical Bulletin 1/2002 Hazardous Waste Program The chemical, physical
PROOF-OF-CONCEPT EVALUATION PASSIVE IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION OF CHLORINATED-BENZENE GROUNDWATER CONTAMINANTS USING GREEN TECHNOLOGY
 PROOF-OF-CONCEPT EVALUATION PASSIVE IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION OF CHLORINATED-BENZENE GROUNDWATER CONTAMINANTS USING GREEN TECHNOLOGY Kent C. Armstrong BioStryke Remediation Products, LLC Robert Chimchirian,
PROOF-OF-CONCEPT EVALUATION PASSIVE IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION OF CHLORINATED-BENZENE GROUNDWATER CONTAMINANTS USING GREEN TECHNOLOGY Kent C. Armstrong BioStryke Remediation Products, LLC Robert Chimchirian,
The InSitu Remediation of PFAS-Impacted Groundwater Using Colloidal Activated Carbon
 The InSitu Remediation of PFAS-Impacted Groundwater Using Colloidal Activated Carbon R. McGregor InSitu Remediation Services RemTech 2018 Background Per & Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Emerging Compounds
The InSitu Remediation of PFAS-Impacted Groundwater Using Colloidal Activated Carbon R. McGregor InSitu Remediation Services RemTech 2018 Background Per & Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Emerging Compounds
