Impacts of Population On Water Resources in Libya
|
|
|
- Egbert Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impacts of Population On Water Resources in Libya Dr. Gadalmola Salem Mansor (Lecturer at Geograaphy department, Faculty of Arts and Science, Alkufra, University of Benghazi) 1
2 Impacts of Population On Water Resources in Libya Abstract This article deals with water situation in Libya generally in order to show the effect of population on water resources which included population growth and geographical distribution of population. The study describe the current water situation in Libya including water resources, water supply and water demand based on data collected from different resources such as literature, books, reports and journals. The study revealed that the population growth rate is the most important factor affecting water resources. Libya will be facing extreme deficit in water resources, among highly populated cities because of increase in consumption of drinkable water and in domestic purposes. The country s population has tripled since the 1950s. It was 1,888,730 in the first census in Libya in 1954 and it became 5,657,632 in the last census As a result of the population growth and the improvement of living standard, the country is facing a severe lack of water resources. Water shortages of about 1154 to 4339 Mm 3 have been estimated for the years 1998 and 2025, respectively. In respect to population distribution, the concentration of population in the north has led to increased demand for water, which in turn has led to the low level of water in some areas and vulnerability to pollution in other regions, while because of lack of population in the south part; these areas do not suffer from problems of water shortage or contamination. Keywords: water resources, water supply, water demand, population growth, distribution of population. 2
3 1. Introduction The world is entering a period of intense competition over limited supplies of water for multi uses in agriculture, industry, recreation, domestic, and environmental protection. The appearance of this competition and our present incapability to deal with it can be observed in many parts of the world. Gradually, water problem is extending universally but in some parts of the world it is turning out to be a major issue. Most of the Arab countries are located in arid and semi-arid zones well-known for their slight annual rainfall, very high rates of evaporation due to high temperatures around the year and therefore highly inadequate renewable water resources. Water scarcity is becoming more and more of a constraint in development, slowing down the economic growth of many countries in the region. Agriculture is the greatest single worldwide consumer of water (70%), followed by industry (20%) and homes (10%) (Wheida, E. 2004), Considerable efforts have been made to reduce consumption in industry and homes; but much remains to be done in improving the efficiency of irrigation. The proportion of water used in these three sectors varies region to region, and between levels of economic development. In Europe and North America, water is used primarily by industry. In Asia and Africa, agricultural irrigation is the primary consumer. In many semi-arid and arid regions about 30% of groundwater is extracted for irrigation, and the trend is increasing. The demand for fresh water in the mostly desert country of Libya to keep up its economy, especially in agriculture sector, go beyond its conventional supplies. Algeria, Tunisia and Libya share the consumption of the groundwater of the North Sahara Aquifer System, which over recent decades have seen their use increase from 0.6 to 2.2 billion m 3 per annum. Libya, which has very limited water resources, has been in a situation of imbalance between water resources and water needs. To equalize this imbalance, Libya has an alternative to non-conventional water and to mining as a means of making use of its underground water resources, which are non-renewable. In the 1950s and 1960s the search for new oilfields in the deserts of southern Libya led to the discovery of major oil reserves as well as of aquifers containing huge quantities of fresh groundwater. Most of this fossil water was collected over 35,000 years ago (Loucks, D. 2004), this article discusses the impacts of population increased anddistribution of population on water resources in Libya 3
4 2. Study area and methodology Libya is located on the northern coast of the continent of Africa; bounded by the Mediterranean to the north. Tunisia and Algeria to the west, Egypt and Sudan to the east and south-east, and by Chad and Niger to the south as shown in Figure 1, it is occupies vast area of 1,750,000 m 2 (Hamdan, J. 1993), so it ranks as the third Arab country in terms of area after Algeria and Saudi Arabia. It is also ranked third amongst African countries in terms of area after Algeria and Zaire (Congo), The geographical and astronomical location of Libya has a significant impact on water resources, as Libya is located between 19-32`'N latitude and 9-25 E longitude. This means that most of the country lies within the tropical environment, with the exception of some parts of the north which lie within the temperate zone. This means that there are desert conditions of high temperatures and severe drought and there is also a spread of the manifestations of desertification across around 90% of the country; the Mediterranean climate has limited impact: this is restricted to the coastal parts only. However, it should be noted that even the coastal portions of these areas do not escape the negative impacts of the desert climate; those parts are also exposed to climatic conditions very similar to those prevailing in the desert in the summer, such as severe high temperature and seasonal warm winds. The data was collected from different resources which include report and other locally exchanged documents, related studies in other areas, books and study journals. These collected from the nearby government offices, Libyan universities and from electronically available documents. In general the data sources can be divided as following a. Documents Documents viewed included books, reports of National Body for Information and Documentation, Libya. Libyan Statistic Agency, census 1973, 1984, 1995 and b. Literature review The literature review includes the studies that already done by other authors on water issue that includes water resources, water supply, and water demand. 4
5 Figure 1 location of Libya Source: location.com 3. Water resources Libya is considered among the countries which suffer from limited natural water resources availability because the majority parts of the country are either semi-arid or arid. This part of the world is located among the driest regions in the earth, with yearly average rainfall ranging from just ten millimeters to 500 mm. Just five per cent of the entire area of Libya exceeds 100 mm annually. Evaporation rates are also high due to high temperatures. Range of evaporation rates is estimated from 1,700 mm in the north to 6,000 mm in the south. Prevailing water conditions do not provide sustainable alternative to surface water development, thus create immense pressures on ground water resources. Much of the ground water resource is used in agriculture, which represents almost 80 % of the total consumption (Abdelrhem M., et al., 2008), Groundwater represents the main source of water supply in Libya. It is extracted through wells that vary in depth from few meters to more than 1,000 m. Groundwater is stored in aquifers that are either renewable or non-renewable. The renewable aquifers are those located in the northern zones and fall within areas under high precipitation rates. They contribute more than 2,400 5
6 million m 3 of water reserves per year against an annual recharge of less than 6.5 million m 3 per year. This imbalance has resulted in a continuous lowering of groundwater levels accompanied by deterioration in water quality due to mixing of seawater and addition of saline water from adjacent aquifers (Salem, O. 2007) The water researches indicate that Libya will be facing extreme deficit in water resources, among highly populated cities because of increase in consumption of drinkable water and in domestic purposes. Due to the shortage of feeding water and renewable resources to the ground water reservoirs different techniques are considered Man-Made River Project to save all the water demands in Libya. 4. Water supply Libya, as many other countries in the arid region, is heavily dependent on groundwater resources. The available groundwater supply is estimated at mm 3, which represents 95% of the total supply. Surface water supply is 2.3%, whereas the desalination of seawater and the re-use of waste water are minor resources with very small shares of 1.8% and 0.9%, respectively. Thus, the total water supply capacity equals Mm 3. The agricultural sector has the highest consumption quantity which is 85%. The domestic sector consume only 11.5%, and the industrial sector use only 3.5%, representing the lowest portion of the total water withdrawal. Figure 2 Available Water Resources in Libya Source: Salem (2007) Figure 2 gives an overview of available water compared to current consumption. The quantities show a disproportion between the total withdrawal and the annual available volume of 6
7 local water resources. Clearly there is a deficit, leading to deterioration of both water quantity and quality due to seawater intrusion. The state of Libya without any doubt is in front of a serious water shortage due to an imbalance between limited water resources and its demands. The country s population has tripled since the 1950s. As a result of the population growth and the improvement of living standard, the country is facing a severe lack of water resources. Water shortages of about 1154 to 4339 Mm 3 have been estimated for the years 1998 and 2025, respectively. There is a vital need to focus on this problem properly to avoid serious impact on the economic development of the country (Wheida, E. 2004) According to the reports published by the water resources institute (WRI), nine countries around the world are considered in water crisis as these countries are consuming water more than it can be replaced. Libya is the one of this country. In Libya rainfall (56 mm) generates an annual average flow of 98,000 Mm 3, but only small proportion of this rainfall is transformed into renewable water resources (Calzadilla, A., et al., 2005) Figure 3 Situation of water resources in Libya Source: Wheida (2004) 7
8 The underground water basins whose water is renewable are located at the north of Libya, Jifarah basin (200 mm 3, with an annual withdrawal of 1200 mm 3 ), Jabal Akhdar basin (200 mm 3 with a withdrawal of 600 mm 3 ), Hamada basin (475 mm 3 with a withdrawal of 150 mm 3 ) and three other basins (Murzuk, Sarir, and Kufra) contain substantial amount of water, but it is nonrenewable (Salem, O. 2007), The above statistics clearly shows that water demand in Libya far exceeds the amount of available ground water resources. Agriculture is the biggest water consuming sector but this consumption would decrease because of water scarcity in the region. That is why the Libyan government is looking forward on the Man-Made River Project for at least preserving the areas which are irrigated at the moment with a hope to extend them. 5. Water demand Libya has two choices to carry out its water demands: the Mediterranean Sea and groundwater from the Sahara Desert. Libya, neighboring the Mediterranean Sea in Northern Africa, is mostly desert. Large amounts of water and energy underlie much of that desert sand, that is, the groundwater accumulated from hydrological events that took place many thousands of years ago. Today Libya is making use of this water for the benefits of its people. Along the Mediterranean coast is the densely populated area and to enable the people of Libya to use the water, Libyan government has planned, designed, and implemented the world s largest and groundwater pumping and supply project. It is the Man-made River Project (Geriani, et al. 1998), Construction began in the mid -1980s and still continues. In Libya, the Man-Made River Project provides about 75% of Libya s annual water demand (agriculture) from 1,000 wells, with some surface water reservoirs for temporary water storage. Man-Made River Project s first aquifer, the Kufra Basin in southeast Libya, has an estimated groundwater storage capacity of nearly 21,000 km³ in the Libyan sector alone. Man- Made River Project s first stage supplies Benghazi and fills coastal reservoirs. Tripoli has been supplied since Ultimately Man-Made River Project is expected to provide 3,000 Mm³ annually from its 30,000 km³ aquifers. The goal is to supply 6Mm³ per day to coastal populations. Although two-thirds of Man-Made River Project water was originally allocated to irrigation, but due to increasing demand in domestic sector it is consumed in households. Pessimists believe that the Man-Made River Project has one century of function; optimists claim five centuries. (Superoptimists mention 4,000 years.) Man-Made River Project officials say it will last 50 years (Goodland, R. 2008), In fact, the Man-Made River Project aquifers are huge and much in number but are still finite. The aquifers contain fossil water many thousands of years old and are not being recharged. Water demand for irrigation is estimated at a volume of 4300 Mm 3 in This volume would increase to 6300 Mm 3 by Industry uses 4% of the Libyan water resources. Today the volume of water used by industries is 214 Mm 3, but it is expected that the demand will increase by the rate of 4%, which increases water demand for industry to 470 Mm 3 in Excessive extractions in ground water basins disturb salt levels, especially, when the basins are situated on 8
9 coast. It is a natural phenomenon which is likely to happen in the majority of the coastal basins of the countries. 6. Population and water resources in Libya 6.1. Population Growth The human factor is of great importance in terms of impact on water resources in Libya. Moreover, it can be said that the human factor is fundamental and comes in first place, because of the people who live in this land and invest in and use all of its resources to their benefit (NBID, 2000). This part of the study discusses population growth and distribution of population and its effect on water resources. Table 1 shows the evolution of population growth in Libya from the first official census in 1954 to the census of It can be seen that the population growth rate has increased from one census to another. It reached the rate of 3.70% in the period between 1954 to 1964, but that rate is not sufficiently accurate, because of the circumstances and conditions that surrounded the census in 1954; it was conducted during a bad economic situation and also when there was a lack of awareness among population, who were at the time mostly nomads. In addition, lack of mobility and rapid communication led to a large part of them not being covered by the census. However, it can be seen that the rate continued to rise during the period when it reached 4.30%. Possibly, the rate of population growth increased during this period due to the relative stability experienced by the country after the discovery of major oil reserves in early sixties of the last century. The growth rate of the population in Libya achieved its maximum during the period between reaching 4.48%. This is because it is during this period that the country began to invest oil revenues in the implementation of several development projects, and the population policy of the State in that period was designed to increase the population; the provision of housing for all citizens, many health facilities such as hospitals and polyclinics, added to the incentives that were given to families to encourage them to increase the number of children. There were also housing and family allowances, as well as free education and healthcare (NBID, 2000). There is no doubt that the high rate of population growth in that period led to increased demand on water resources. This may led to the idea for a Man-Made River Project to transfer water from the water basins in the south of Libya to the centers of population concentration in the north of Libya which appears to have emerged in that period, and hence it can be deduced that there may be a high correlation between the population growth in that period and the emergence of the idea concerning the Man-Made River Project. 9
10 During the period , the rate of population growth in Libya decreased (2.80%), but this rate reached its lowest level in the last census of the population in Libya in 2006, which covered the period from 1995 to The rate fell to 1.80% due to certain economic factors such as rising living standards and the difficulty of providing basic necessities of life, the most important of which is housing. Other factors include the high levels of education and cultural diversity of the population, and the entry of women in different areas of work which plays a role in the low birth rate, in addition to the tendency of some families to use birth control (GIA, Census 2006) Table 1 Population Growth for Libyan & Non-Libyan Population Census Libyan population Non-Libyan population Total population % ,041,599 47,274 1,888,730?? ,515,501 48,868 1,564, ,052, ,865 2,249, ,231, ,517 3,642, ,389, ,326 4,799, ,298, ,540 5,657, Source: GIA Census 2006, p 40. The country s population has tripled since the 1950s. As a result of the population growth and the improvement of living standard, the country is facing a severe lack of water resources. Water shortages of about 1154 to 4339 Mm 3 have been estimated for the years 1998 and 2025, respectively. Wheida (2004) illustrates that the water deficit was amounting to about 1154 million cubic meters in 1998 and estimates that the deficit will undoubtedly increase in the future in response to continuous population growth and corresponding increase in water requirements for the domestic, agriculture and industrial sectors. Depending on population growth, industrial and agriculture, water demand between (8200) and (8840) million cubic meters have been forecasted 10
11 for the year 2025 with deficits of about 4339 million cubic meters assuming the present water use practices Distribution of Population and Water Resources in Libya The distribution of population in Libya is characterized by the fact that is not equal over the country; the distribution of the population appears dispersed and chaotic, suggesting poor concentration and low population destiny. There are two distinct realms of population distribution, the first in the densely populated part in the north and the second is the low density part or the empty part in the south Densely populated part The densely population density part in the far north of the country covering a coastal strip that along the Mediterranean Sea. This part contains most of Libya s population; more than 80% of the total population is concentrated here is spite of the area good for human habitation being limited, which represented not more than 10% of the country. the population of this part is around 4,083,822 according to the 2006 census and is distributed in several cities and villages, especially around major cities such as Tripoli, Benghazi, Misurata, al-zawiah, and Darnah. The largest population in Libya is in the city of Tripoli; more than a million people are concentrated in this city, equivalent to about a quarter of Libya s population. The city of Benghazi is ranked second, where currently more than people are located, which represents 13.8% of the total population. In addition to Tripoli and Benghazi, there are some other cities where the population is concentrated, such as Misurata which has 10.1% of the total population and the city of al- Zawiah where currently 7.95 of the total population of Libya is located (GIA, Census 2006), Chia-Lin Ban (1949) stated that over 90% of the Libyan population were living in the coastal region It should be noted that the phenomenon of concentration of the population in the cities of Tripoli and Benghazi is not new, as is shown in the results of the population census in 1954, which was the first census in Libya. At that time, the proportion of population concentration in these two cities amounted to 34% of the total population (Alawar, A. 2002). The concentration of population in the northern part of Libya has to lead to an increased amount of water being consumed in the cities. Perhaps the best example to illustrate the effect of concentration of population in the northern part of Libya on water resource is what has happened in the plain of Benghazi, where the population concentration in this region and increased demand for water in different uses has led to a low level of water in the aquifer. It was observed that there has been a lower level of underground water in the plain of Benghazi by a distance of more than a meter and a half rate of decline of water supply in the reservoir after 1977 is nearly five times the rate of compensation (El-Deeb, M. 1997). 11
12 6.2.2 Low density part This range encompasses the greater part of Libya, as it represents about 90% of the total area. Al though the area is vast, the population is limited; not exceeding about 20% of the total population, and the population, and the population density is low in this part reaching.084 inhabitants per 1 km 2. The decrease in the proportion of people in this part is due to the ruling desert conditions. The Great African Desert covers most parts of this range, and it is one of the hottest deserts in the world, so being marked by harsh climatic conditions, it is not conducive to human settlement. The temperature rises during the day, rain is almost non-existent, and the soil in this part of the desert is poor, inadequate for agriculture. All these conditions have made this region's environment unsuitable for the population which has migrated and increased the concentration of population in the north of the country. Thus the rest of the country's total area is left virtually uninhabited except for some populations in small scattered areas of oases, where these populations live on ground water from these oases. Because of the low population in the south of Libya, these areas have not been exposed to the problems of pressure on water resources as has happened in the north (Hamdan, J. 1993). 7. Discussion The above overview discovered that the population growth rate is the most important factor affecting water resources; the more the population growth rate the greater the demand for water. Libya s population growth rates are among the highest in the world. In recent years however, a gradual decrease in the growth rates from over 4% to less than 3% was noticed. Accordingly, projection of future population based on past and present trends in growth rates could be generated as shown in Table 2 Table 2 Population Growth Year Population (10 6 ) Source: Miludi 1995 Table 3 shows the available water resources which amounts to 3,820 Mm 3 /yr of which 170 Mm 3 is in the form of surface water, 650 Mm 3 is the annual recharge to groundwater and 3000 Mm 3 is the acceptable reduction rate of the non-renewable aquifers. The latter is independently determined for each basin on the basis of its hydro geological characteristics 12
13 Table 3 Available Water Resources Source Potentially available water(mm 3 /yr) -Surface water 170 -Renewable groundwater 650 -Non-renewable groundwater Gefara Plain 25 Jabal Akhdar 25 Kufra & Sarir 1300 Hamada 150 Murzuk 1500 TOTAL 3820 Source: Miludi 1995 Table 4 The Overall Water Balance Projected for the Year 2025 Year Supply (Mm 3 ) Demand(Mm 3 ) Balance (Mm 3 ) Source: Miludi 1995 When calculated for each of the five regional water basins, the deficit in the water is more pronounced in the highly populated northern plains, namely Gefara, and Jabal Akhdar for the year Elhassadi (2007) estimated that if available resources remain constant at 2005 level the deficit will increase from around 76% of the total demand to about 86% by the year
14 With respect to the distribution of population in Libya, there are two ranges of main population; the first one is located in northern Libya, which is characterized by the overcrowding population, the same time bringing about a negative impact on water resources in northern Libya. The concentration of population in those areas has led to increased demand for water, which in turn has led to the low level of water in some areas and vulnerability to pollution in other regions. The second is in the central and southern parts of Libya, the uninhabited range, where there is a lack of population, and therefore these areas do not suffer from problems of water shortage or contamination. Therefore based on this study it is found that the population distribution in Libya tends to have a negative impact on water resources. 8. Conclusion This article almost clearly explains the deficiency of water that Libya is and will be facing in future. The data collected leave no doubt in understanding the overall dearth in water resource and water supply in Libya. The population growth and population distribution of Libya further explains the current insufficiency of water supply and demand. Most of the available water is consumed in agriculture; very less is available for industry and domestic use. Moreover, availability of water in Libya is mostly not subject to water reuse because most of the water sinks to river basins and flows to other countries. Existing condition of water do not provide sustainable alternative to surface water development, thus create enormous pressures on ground water resources. Groundwater represents the main source of water supply in Libya. population growth rate is the most important factor affecting water resources. In respect to population distribution, the concentration of population in the north has led to increased demand for water, which in turn has led to the low level of water in some areas and vulnerability to pollution in other regions, while because of lack of population in the south part; these areas do not suffer from problems of water shortage or contamination 14
15 References [1] Abdelrhem M., Rashid, K and Ismail, A., Integrated groundwater management for Great Man-Made River project in Libya, European. Journal of Scientific Research 22(4): [2] Alawar, A Indicators for sustainable development in the Mediterranean Coastal Regions. National Report of Libya: In Arabic [3] Calzadilla, A, A.B., Katrin, R. and Richard, S. J The economic impact of more sustainable water use in agriculture: A computable general equilibrium analysis. Journal of Hydrology 384(292). [4] Chia-Lin Ban The population of Libya. Population Investigation Committee 3(1):10 [5] El-Deeb, M Geo-political: a contemporary perspective. Cairo: Egyptian Anglo Library Publications, p 21. In Arabic [6] Elhassadi, A Pollution of water resources from industrial effluents a case study- Benghazi. Libya. Desalination 222(1-3): 287 [7] Geriani, A, Essamin, O. Gijsbers, P and Loucks, D., Cost-effectiveness analysis of Libya s water supply system, Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management [8] Goodland, R How Libya could become environmentally sustainable, Libyan Studies. [9] Hamdan, J The Libyan Arab Republic: a Study in Political Geography. Cairo: Alam al-kutub Publisher. Pp In Arabic [10] Libyan Statistic Agency, GIA Census 1973, 1984, 1995 and 2006 Libyan, Tripoli city. p 40 [11] Loucks, D The Great Man-Made River in Libya: Does it Make Sense?. Lecture in fluid Mechanics, Cornell University-USA [12] Miludi, A Water policies in the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, General Water Authority, Tripoli, Libyan Arab Jamahiriya [13] (NBID) National Body for Information and Documentation Report on population. Pp2-8. In Arabic [14] Salem, O Management of Shared Groundwater Basins in Libya, African Water Journal 1: 1. [15] Wheida, E Desalination as a water supply technique in Libya. Desalination 165:
Water resources and desalination: The Libyan perspective: a review
 المعمل المتقدم للتحاليل الكيمياي ية Water resources and desalination: The Libyan perspective: a review Presented by: Bashir Brika Instrumental analysis department Advanced Laboratory of Chemical Analysis
المعمل المتقدم للتحاليل الكيمياي ية Water resources and desalination: The Libyan perspective: a review Presented by: Bashir Brika Instrumental analysis department Advanced Laboratory of Chemical Analysis
Global Water Resources: Half Full or Half Empty?
 SAERC GGS 12 Mr. R. Allen Global Water Resources: Half Full or Half Empty? Essential for life, water is the most important natural resource in the world today. As with all resources, however, it is distributed
SAERC GGS 12 Mr. R. Allen Global Water Resources: Half Full or Half Empty? Essential for life, water is the most important natural resource in the world today. As with all resources, however, it is distributed
Survey of Sustainable Development to Make Great Man-Made River Producing Energy and Food
 Current World Environment Vol. 10(3), 758-763 (2015) Survey of Sustainable Development to Make Great Man-Made River Producing Energy and Food Mohamed Nasar Nasar Department Of Applied Ecology, Futura,
Current World Environment Vol. 10(3), 758-763 (2015) Survey of Sustainable Development to Make Great Man-Made River Producing Energy and Food Mohamed Nasar Nasar Department Of Applied Ecology, Futura,
Clean Water Scarcity and Solar energy opportunities in African and Middle East
 A Renewable Energy Company Clean Water Scarcity and Solar energy opportunities in African and Middle East Dr. Nabih Cherradi Facts on water Africa appears blessed with abundant water resources: large rivers
A Renewable Energy Company Clean Water Scarcity and Solar energy opportunities in African and Middle East Dr. Nabih Cherradi Facts on water Africa appears blessed with abundant water resources: large rivers
International Shared Aquifers in the Arab Region
 International Shared Aquifers in the Arab Region Chahra Ksia - Amb Chief of the Center of water Studies and Arab water Security, League of Arab States ABSTRACT The Arab countries are sharing many aquifers,
International Shared Aquifers in the Arab Region Chahra Ksia - Amb Chief of the Center of water Studies and Arab water Security, League of Arab States ABSTRACT The Arab countries are sharing many aquifers,
CHAPTER 6 MEDITERRANEAN WATERSHED MANAGEMENT: OVERCOMING WATER CRISIS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN
 Watershed Management: Water Resources for the Future CHAPTER 6 MEDITERRANEAN WATERSHED MANAGEMENT: OVERCOMING WATER CRISIS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN Luc Dassonville and Luca Fé d Ostiani Plan Bleu, FAO Water
Watershed Management: Water Resources for the Future CHAPTER 6 MEDITERRANEAN WATERSHED MANAGEMENT: OVERCOMING WATER CRISIS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN Luc Dassonville and Luca Fé d Ostiani Plan Bleu, FAO Water
Fadi Comair, Ph.D may 2018, Nicosia, Cyprus. Hydro-diplomacy and the Nexus: Climate Change Adaptation in the Middle-East
 Fadi Comair, Ph.D 18-19 may 2018, Nicosia, Cyprus Hydro-diplomacy and the Nexus: Climate Change Adaptation in the Middle-East The Geopolitics of water, energy and food -the most important strategic issues
Fadi Comair, Ph.D 18-19 may 2018, Nicosia, Cyprus Hydro-diplomacy and the Nexus: Climate Change Adaptation in the Middle-East The Geopolitics of water, energy and food -the most important strategic issues
N. Africa & S.W. Asia
 N. Africa & S.W. Asia CHAPTER #8, SECTION #1 Identifying Boundaries Three Regions North Africa (Border Mediterranean and Red Seas) Morocco, Western Sahara, Algeria, Egypt, Sudan, Tunisia, & Libya Southwest
N. Africa & S.W. Asia CHAPTER #8, SECTION #1 Identifying Boundaries Three Regions North Africa (Border Mediterranean and Red Seas) Morocco, Western Sahara, Algeria, Egypt, Sudan, Tunisia, & Libya Southwest
CLIMATE PROJECTIONS. More extreme weather, with increased and more severe sand and dust storms, floods and droughts KEY CLIMATE IMPACTS
 FACT SHEET CLIMATE CHANGE RISK PROFILE Libya COUNTRY OVERVIEW As a country with more than 90 percent desert and with limited governance capabilities since the overthrow of the Gaddafi government in 2011,
FACT SHEET CLIMATE CHANGE RISK PROFILE Libya COUNTRY OVERVIEW As a country with more than 90 percent desert and with limited governance capabilities since the overthrow of the Gaddafi government in 2011,
The Impact of Establishing the Ethiopian Dam Renaissance on Egypt
 2014, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com The Impact of Establishing the Ethiopian Dam Renaissance on Egypt Nagwa El Agroudy, Fatima Ahmed
2014, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com The Impact of Establishing the Ethiopian Dam Renaissance on Egypt Nagwa El Agroudy, Fatima Ahmed
H 2 O know-how. by Pradeep Aggarwal & Ali Boussaha
 H 2 O know-how by Pradeep Aggarwal & Ali Boussaha 38 IAEA BULLETIN 47/1 September 2005 The IAEA spreads the science for harnessing the world s aquifers. We know water is essential for life. Less known
H 2 O know-how by Pradeep Aggarwal & Ali Boussaha 38 IAEA BULLETIN 47/1 September 2005 The IAEA spreads the science for harnessing the world s aquifers. We know water is essential for life. Less known
Demographic Pressures in North Africa: Causes and Consequences
 The Euro-African Dialogue: Security Co-operation in Europe & North Africa Organized by The Royal United Services Institute for Defense Studies (RUSI), London In partnership with The Academy of Graduate
The Euro-African Dialogue: Security Co-operation in Europe & North Africa Organized by The Royal United Services Institute for Defense Studies (RUSI), London In partnership with The Academy of Graduate
Land Degradation Control in North Africa
 Land Degradation Control in North Africa By Dr. Ismail Hamdi El-Bagouri Emeritus Professor Soil and Water Conservation Desert Research Center Egypt International Workshop on Climate and Land Degradation
Land Degradation Control in North Africa By Dr. Ismail Hamdi El-Bagouri Emeritus Professor Soil and Water Conservation Desert Research Center Egypt International Workshop on Climate and Land Degradation
Cool waters and atmospheric high pressure
 QU: How does human activity contribute to drought risk? AIM: To evaluate the human influence of drought events in Africa's Sahel region. ST: What part of the ENSO cycle is at work here? What does it mean
QU: How does human activity contribute to drought risk? AIM: To evaluate the human influence of drought events in Africa's Sahel region. ST: What part of the ENSO cycle is at work here? What does it mean
Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa
 Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa Shawki Barghouti Director General International Center for Biosaline Agriculture 1 water scarcity
Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa Shawki Barghouti Director General International Center for Biosaline Agriculture 1 water scarcity
The role of dams in securing the surface water in the northern and eastern parts of the United Arab Emirates (UAE)
 Changes in Water Resources Systems: Methodologies to Maintain Water Security and Ensure Integrated Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS at IUGG, Perugia, July ). IAHS Publ.,. The role of dams in securing
Changes in Water Resources Systems: Methodologies to Maintain Water Security and Ensure Integrated Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS at IUGG, Perugia, July ). IAHS Publ.,. The role of dams in securing
Water Management in South Africa: Are we headed towards a crisis? By Tony Coetzer
 Water Management in South Africa: Are we headed towards a crisis? By Tony Coetzer Contents Facts & Resources Challenges facing South Africa Expedition H 2 O Water saving practices Obligations Conclusion
Water Management in South Africa: Are we headed towards a crisis? By Tony Coetzer Contents Facts & Resources Challenges facing South Africa Expedition H 2 O Water saving practices Obligations Conclusion
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions
 Intended Nationally Determined Contributions Objective: The State of Kuwait - November 2015 In accordance with Decision 1/CP.19 and based on the information mentioned in decision 1/CP.20 which invites
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions Objective: The State of Kuwait - November 2015 In accordance with Decision 1/CP.19 and based on the information mentioned in decision 1/CP.20 which invites
Water and Sustainability: A Global Perspective
 Check Against Delivery. Embargoed until 11:45 AM, 5 November 2010 Water and Sustainability: A Global Perspective by Wolfgang Kinzelbach, Institute of Environmental Engineering ETH Zürich, Switzerland Session
Check Against Delivery. Embargoed until 11:45 AM, 5 November 2010 Water and Sustainability: A Global Perspective by Wolfgang Kinzelbach, Institute of Environmental Engineering ETH Zürich, Switzerland Session
Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin
 Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin Spain and Algeria are active members of the United Nations, the Union for the Mediterranean and the 5+5 Dialogue for
Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin Spain and Algeria are active members of the United Nations, the Union for the Mediterranean and the 5+5 Dialogue for
DISCUSSION PAPER INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN ISRAEL
 DISCUSSION PAPER INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN ISRAEL Nir KEDMI Economics and Standard Division Ministry of the Environment P.O.Box 34033 Jerusalem 95464 Israel Tel: 972-2-6495838 Fax: 972-2-6495894
DISCUSSION PAPER INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN ISRAEL Nir KEDMI Economics and Standard Division Ministry of the Environment P.O.Box 34033 Jerusalem 95464 Israel Tel: 972-2-6495838 Fax: 972-2-6495894
Rashid Ali Khan, FAO (Ret.) Gurgaon, Haryana
 Sustainability and Water Conservation mentioned in the draft strategic plan of DDWS was not provided adequate coverage, though important for improving the supply. In view of the unpredictable rainfall,
Sustainability and Water Conservation mentioned in the draft strategic plan of DDWS was not provided adequate coverage, though important for improving the supply. In view of the unpredictable rainfall,
The Future of Food and Water Security in New Egypt
 22 November 2012 The Future of Food and Water Security in New Egypt Jay Vella Research Analyst Key Points Fifteen million Egyptians do not earn a sufficient income to purchase an adequate level of nutrition.
22 November 2012 The Future of Food and Water Security in New Egypt Jay Vella Research Analyst Key Points Fifteen million Egyptians do not earn a sufficient income to purchase an adequate level of nutrition.
DAMPAK KEGIATAN MANUSIA TERHADAP KUALITAS LINGKUNGAN
 DAMPAK KEGIATAN MANUSIA TERHADAP KUALITAS LINGKUNGAN IMPACT OF HUMAN ACTIVITIES ON ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY 1 Since Homo sapiens live on the planet of earth c.a.180,000 years ago, human activities have been
DAMPAK KEGIATAN MANUSIA TERHADAP KUALITAS LINGKUNGAN IMPACT OF HUMAN ACTIVITIES ON ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY 1 Since Homo sapiens live on the planet of earth c.a.180,000 years ago, human activities have been
Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health
 Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health Land degradation and desertification The spread of land degradation and desertification
Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health Land degradation and desertification The spread of land degradation and desertification
Global Desalination Market: Trends & Opportunities ( )
 Global Desalination Market: Trends & Opportunities (2013-18) Country Coverage Saudi Arabia United States India China Company Coverage DHI Veolia Water Solutions & Technologies Hyflux IDE GHD Scope of the
Global Desalination Market: Trends & Opportunities (2013-18) Country Coverage Saudi Arabia United States India China Company Coverage DHI Veolia Water Solutions & Technologies Hyflux IDE GHD Scope of the
Lecture 14. Water: A Limited Resource. Lecture 14
 Lecture 14 Water: A Limited Resource Lecture 14 1. Importance of Water 2. Water Use and Resource Problems 3. Water Problems in U.S. and Canada 4. Global Water Problems 5. Water Management 6. Water Conservation
Lecture 14 Water: A Limited Resource Lecture 14 1. Importance of Water 2. Water Use and Resource Problems 3. Water Problems in U.S. and Canada 4. Global Water Problems 5. Water Management 6. Water Conservation
Environmental and Climate change in Mongolia
 Environmental and Climate change in Mongolia D. Azzaya Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology (IMH), Mongolia Juulchny gudamj-5, Ulaanbaatar-46, 210646, Mongolia A.Khaulenbek Desertification study center,
Environmental and Climate change in Mongolia D. Azzaya Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology (IMH), Mongolia Juulchny gudamj-5, Ulaanbaatar-46, 210646, Mongolia A.Khaulenbek Desertification study center,
Effective Water Demand Management in the GCC Countries
 Effective Water Demand Management in the GCC Countries Dr. Mohamed A. Dawoud Manager Water Resources Department Environment Agency Abu Dhabi P.O. Box 45553, UAE Overview Water Resources in the Arab Region
Effective Water Demand Management in the GCC Countries Dr. Mohamed A. Dawoud Manager Water Resources Department Environment Agency Abu Dhabi P.O. Box 45553, UAE Overview Water Resources in the Arab Region
Water Resources. Israel, Jordan and the United States a case study
 World Geography TEK (12) Economics. The student understands the economic importance of, and issues related to, the location and management of resources. The student is expected to: (A) analyze how the
World Geography TEK (12) Economics. The student understands the economic importance of, and issues related to, the location and management of resources. The student is expected to: (A) analyze how the
Kariz(Qanat); An Eternal Friendly System For Harvesting Groundwater
 Kariz(Qanat); An Eternal Friendly System For Harvesting Groundwater An evaluation of the sustainability of Qanats under changing socio economic and climatic conditions in Iran This article has been prepared
Kariz(Qanat); An Eternal Friendly System For Harvesting Groundwater An evaluation of the sustainability of Qanats under changing socio economic and climatic conditions in Iran This article has been prepared
Environmental Studies
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Environmental Studies Unit 2 The Physical Environment Thursday 23 May 2013 You
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Environmental Studies Unit 2 The Physical Environment Thursday 23 May 2013 You
Impacts of Climate Change on Ecosystems
 Introduction The main objective of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change is to stabilise greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level which will avoid dangerous human interference
Introduction The main objective of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change is to stabilise greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level which will avoid dangerous human interference
Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- China
 Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- China EarthTrends Country Profiles Internal Renewable Water Resources (IRWR),1977-2001, in cubic km China Asia (excl. Middle East) Surface water produced internally
Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- China EarthTrends Country Profiles Internal Renewable Water Resources (IRWR),1977-2001, in cubic km China Asia (excl. Middle East) Surface water produced internally
1. Introduction to water issues and water accounting in Southern Africa
 1. Introduction to water issues and water accounting in Southern Africa Glenn-Marie Lange and Rashid Hassan 1.1 INTRODUCTION Global water demand has been growing rapidly over the past few decades owing
1. Introduction to water issues and water accounting in Southern Africa Glenn-Marie Lange and Rashid Hassan 1.1 INTRODUCTION Global water demand has been growing rapidly over the past few decades owing
Water Development and Management Strategy of China
 Water Development and Management Strategy of China Li Yuanyuan Deputy Chief Engineer, General Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Planning and Design General Institute, MWR Abstract: Water is not
Water Development and Management Strategy of China Li Yuanyuan Deputy Chief Engineer, General Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Planning and Design General Institute, MWR Abstract: Water is not
Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- Armenia
 Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- Armenia EarthTrends Country Profiles Internal Renewable Water Resources (IRWR),1977-2001, in cubic km Armenia Asia (excl. Middle East) Surface water produced
Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- Armenia EarthTrends Country Profiles Internal Renewable Water Resources (IRWR),1977-2001, in cubic km Armenia Asia (excl. Middle East) Surface water produced
TRANS-BOUNDARY WATER MANAGEMENT IN WESTEREN PART OF JORDAN CHALLENGES & SOLUTIONS
 Enhancing Water Management Capacity in a Changing World Transboundary Waters and Conflicts: Managing Water for Peace TRANS-BOUNDARY WATER MANAGEMENT IN WESTEREN PART OF JORDAN CHALLENGES & SOLUTIONS Nisreen
Enhancing Water Management Capacity in a Changing World Transboundary Waters and Conflicts: Managing Water for Peace TRANS-BOUNDARY WATER MANAGEMENT IN WESTEREN PART OF JORDAN CHALLENGES & SOLUTIONS Nisreen
13 Water: A Limited Resource
 13 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 13 Importance of Water Water Use and Resource Problems Water Problems in U.S. and Canada Global Water Problems Water Management Water Conservation Water
13 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 13 Importance of Water Water Use and Resource Problems Water Problems in U.S. and Canada Global Water Problems Water Management Water Conservation Water
Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- Madagascar
 Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- Madagascar EarthTrends Country Profiles Sub- Internal Renewable Water Resources (IRWR),1977-2001, in cubic km Madagascar Saharan Africa Surface water produced
Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems-- Madagascar EarthTrends Country Profiles Sub- Internal Renewable Water Resources (IRWR),1977-2001, in cubic km Madagascar Saharan Africa Surface water produced
Prof. Dr. Yousef Abu Mayla Al-Azhar University - Gaza Mobile: (0)
 Prof. Dr. Yousef Abu Mayla Al-Azhar University - Gaza Mobile: 00972 (0) 599 704465 E-mail: abumayla@hotmail.com 1 365 sq. Km Egypt 11 Km, Israel 51 Km Population: 2,000,000 2 Gaza Humanitarian Facts 10
Prof. Dr. Yousef Abu Mayla Al-Azhar University - Gaza Mobile: 00972 (0) 599 704465 E-mail: abumayla@hotmail.com 1 365 sq. Km Egypt 11 Km, Israel 51 Km Population: 2,000,000 2 Gaza Humanitarian Facts 10
Desalination of brackish groundwater in Zahedan city in Iran
 PROOF DES 2784 Desalination 17x (2005) 000 000 Desalination of brackish groundwater in Zahedan city in Iran G.R. Lashkaripour a *, M. Zivdar b a Department of Geology, University of Sistan and Baluchestan,
PROOF DES 2784 Desalination 17x (2005) 000 000 Desalination of brackish groundwater in Zahedan city in Iran G.R. Lashkaripour a *, M. Zivdar b a Department of Geology, University of Sistan and Baluchestan,
Chapter 13 Water: A Limited Resource
 Chapter 13 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 13 Importance of Water Water Use and Resource Problems Water Problems in US and Canada Global Water Problems Water Management Water Conservation
Chapter 13 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 13 Importance of Water Water Use and Resource Problems Water Problems in US and Canada Global Water Problems Water Management Water Conservation
Prof. Harvey Shear Department of Geography University of Toronto Mississauga. February 5, 2013
 Prof. Harvey Shear Department of Geography University of Toronto Mississauga February 5, 2013 Water, water, everywhere, And all the boards did shrink; Water, water, everywhere, Nor any drop to drink. Rime
Prof. Harvey Shear Department of Geography University of Toronto Mississauga February 5, 2013 Water, water, everywhere, And all the boards did shrink; Water, water, everywhere, Nor any drop to drink. Rime
Challenges & Opportunities in the Water Sector (Mauritius) Manta Devi Nowbuth (Dr) University of Mauritius
 Challenges & Opportunities in the Water Sector (Mauritius) By Manta Devi Nowbuth (Dr) University of Mauritius The island of Mauritius Mauritius The island of Mauritius Geographical location: between longitude
Challenges & Opportunities in the Water Sector (Mauritius) By Manta Devi Nowbuth (Dr) University of Mauritius The island of Mauritius Mauritius The island of Mauritius Geographical location: between longitude
RESERVOIR HYDROLOGIC ROUTING FOR WATER BALANCE OF AL-BURULLUS WETLAND, EGYPT
 RESERVOIR HYDROLOGIC ROUTING FOR WATER BALANCE OF AL-BURULLUS WETLAND, EGYPT Ibrahim Abdelmagid El-Shinnawy Associate Prof., Environment and Climate Research Institute (ECRI) National Water Research Center
RESERVOIR HYDROLOGIC ROUTING FOR WATER BALANCE OF AL-BURULLUS WETLAND, EGYPT Ibrahim Abdelmagid El-Shinnawy Associate Prof., Environment and Climate Research Institute (ECRI) National Water Research Center
Non-Conventional Resources for Irrigation Water Demand in Egypt
 Non-Conventional Resources for Irrigation Water Demand in Egypt This presentation comprises four parts 1- Introduction 2- Egypt and Challenges 3- Water resources of Egypt 4- Conclusions and recommendations
Non-Conventional Resources for Irrigation Water Demand in Egypt This presentation comprises four parts 1- Introduction 2- Egypt and Challenges 3- Water resources of Egypt 4- Conclusions and recommendations
Water Supply Development in Iran during Recent Drought
 Water Supply Development in Iran during Recent Drought Farid Karimpour 1, Seyed Hamed Alemohammad 2 Abstract Iran is located in one of the arid and semi-arid regions of the world and due to a dry weather,
Water Supply Development in Iran during Recent Drought Farid Karimpour 1, Seyed Hamed Alemohammad 2 Abstract Iran is located in one of the arid and semi-arid regions of the world and due to a dry weather,
Water Scarcity Research opportunities for competing and conflicting demands
 Water Scarcity Research opportunities for competing and conflicting demands Prof. Dionysis Assimacopoulos School of Chemical Engineering National Technical University of Athens Greece What is Scarcity?
Water Scarcity Research opportunities for competing and conflicting demands Prof. Dionysis Assimacopoulos School of Chemical Engineering National Technical University of Athens Greece What is Scarcity?
water resources action project, inc.
 water resources action project, inc. www.wrapdc.org A Comparative Study of Water Data Across Israel, West Bank, and Jordan Water Resources Action Project (WRAP) December 2013 Introduction Water is necessary
water resources action project, inc. www.wrapdc.org A Comparative Study of Water Data Across Israel, West Bank, and Jordan Water Resources Action Project (WRAP) December 2013 Introduction Water is necessary
tes I. SOIL AND FORESTS (pupil Edition pages 87-88)
 ! I......... C H P'T ER Resources and Environmental Change Lee tes I. SOIL AND FORESTS (pupil Edition pages 87-88) A. Soil 1. Throughout history, people have developed ways to conserve and enrich the soil.
! I......... C H P'T ER Resources and Environmental Change Lee tes I. SOIL AND FORESTS (pupil Edition pages 87-88) A. Soil 1. Throughout history, people have developed ways to conserve and enrich the soil.
Review of Saudi Arabia Municipal Water Tariff
 World Environment 213, 3(2): 66-7 DOI: 1.5923/j.env.21332.5 Review of Saudi Arabia Municipal Water Tariff Omar K M Ouda Department of Civil Engineering, Prince Mohamed Bin Fahd University, Al Khobar, Kingdom
World Environment 213, 3(2): 66-7 DOI: 1.5923/j.env.21332.5 Review of Saudi Arabia Municipal Water Tariff Omar K M Ouda Department of Civil Engineering, Prince Mohamed Bin Fahd University, Al Khobar, Kingdom
CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT
 Convention on Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes SEMINAR ON THE ROLE OF ECOSYSTEMS AS WATER SUPPLIERS (Geneva, 13-14 December 2004) CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT Water Management
Convention on Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes SEMINAR ON THE ROLE OF ECOSYSTEMS AS WATER SUPPLIERS (Geneva, 13-14 December 2004) CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT Water Management
In the name of God. Country Level Presentation Iran Country Report. Rome, Italy, December 15 th, 2015
 In the name of God Country Level Presentation Iran Country Report Rome, Italy, December 15 th, 2015 Area Population No of provinces Average Rainfall Neighboring Countries 1.648 million km 2 >78 million
In the name of God Country Level Presentation Iran Country Report Rome, Italy, December 15 th, 2015 Area Population No of provinces Average Rainfall Neighboring Countries 1.648 million km 2 >78 million
Fresh Water Treaty. International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development
 Fresh Water Treaty Preamble International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development 1. In recent years most countries have faced a grave economic crisis which generated a great decrease
Fresh Water Treaty Preamble International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development 1. In recent years most countries have faced a grave economic crisis which generated a great decrease
The Water Crisis with Nile Basin Countries and its Impact on the Water Security of Egypt
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.9, No.05 pp 101-107, 2016 The Water Crisis with Nile Basin Countries and its Impact on the Water
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.9, No.05 pp 101-107, 2016 The Water Crisis with Nile Basin Countries and its Impact on the Water
Section 1: Hydropower: Dams
 Water As a Resource EARTH SCIENCE EARTH S RESOURCES WATER AS A RESOURCE Section 1: Hydropower: Dams Where does water gain its energy from? Hydropower is the electricity generated by the energy of moving
Water As a Resource EARTH SCIENCE EARTH S RESOURCES WATER AS A RESOURCE Section 1: Hydropower: Dams Where does water gain its energy from? Hydropower is the electricity generated by the energy of moving
6. Africa. 6.1 Overview
 6. Africa This chapter presents water and sanitation data. Urban and rural water and sanitation figures are shown by country, area or territory for both 199 and 2. Maps of current are also presented. Graphs
6. Africa This chapter presents water and sanitation data. Urban and rural water and sanitation figures are shown by country, area or territory for both 199 and 2. Maps of current are also presented. Graphs
70% OF EARTH SURFACE IS OCEAN WATER
 70% OF EARTH SURFACE IS OCEAN WATER A man may die, nations may rise and fall, but an idea lives on. John F. Kennedy 1961 John F. Kennedy said: If mankind will find a way to desalinate the ocean water in
70% OF EARTH SURFACE IS OCEAN WATER A man may die, nations may rise and fall, but an idea lives on. John F. Kennedy 1961 John F. Kennedy said: If mankind will find a way to desalinate the ocean water in
Regional Workshop Use of Brackish Water for Agricultural Production in the Near East and North Africa:
 Regional Workshop Use of Brackish Water for Agricultural Production in the Near East and North Africa: Status, Good Agricultural Practices and New Developments Cairo Egypt / June 10-12, 2013 Case study
Regional Workshop Use of Brackish Water for Agricultural Production in the Near East and North Africa: Status, Good Agricultural Practices and New Developments Cairo Egypt / June 10-12, 2013 Case study
Evaluation of Groundwater Part B. Water Quality in the Gaza Strip Municipal Wells. Water Resources Directorate
 State of Palestine دولة فلسطين سلطة المياه الفلسطينية Evaluation of Groundwater Part B Water Quality in the Gaza Strip Municipal Wells Water Resources Directorate Sept, 2013 i Table of Content List of
State of Palestine دولة فلسطين سلطة المياه الفلسطينية Evaluation of Groundwater Part B Water Quality in the Gaza Strip Municipal Wells Water Resources Directorate Sept, 2013 i Table of Content List of
Green Water Assessment in the Arab Region An Approach to Virtual Water Evaluation
 برنامج إدارة الموارد الماي ية Green Water Assessment in the Arab Region An Approach to Virtual Water Evaluation Khaled AbuZeid PhD, PE, PMP Regional Water Resources Manager, CEDARE Centre for Environment
برنامج إدارة الموارد الماي ية Green Water Assessment in the Arab Region An Approach to Virtual Water Evaluation Khaled AbuZeid PhD, PE, PMP Regional Water Resources Manager, CEDARE Centre for Environment
APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran
 APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran Purpose: Conduct research to analyze the effects of water diversions on surrounding ecosystems and human communities. Compare and contrast the problems and successes
APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran Purpose: Conduct research to analyze the effects of water diversions on surrounding ecosystems and human communities. Compare and contrast the problems and successes
of Tunis (CITET) Institutional and Economic instruments for sustainable The deterioration of available Groundwater resources in Tunisia
 1 International Center For Environmental Technologie of Tunis (CITET) INECO Institutional and Economic instruments for sustainable management of water resources in the Mediterranean Region The deterioration
1 International Center For Environmental Technologie of Tunis (CITET) INECO Institutional and Economic instruments for sustainable management of water resources in the Mediterranean Region The deterioration
Water and Climate Change. David Coates Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Montreal Canada
 Water and Climate Change David Coates Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Montreal Canada Water and climate change How important is water? What do ecosystems have to do with it? How important
Water and Climate Change David Coates Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Montreal Canada Water and climate change How important is water? What do ecosystems have to do with it? How important
COUNTRY LEVEL IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE (CLICC) PILOT PROJECT- GHANA
 COUNTRY LEVEL IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE (CLICC) PILOT PROJECT- GHANA National Circumstances: Major Developments Since 2006 Ghana s population has tripled, from 6.7million in 1960 to 24.9million in 2010
COUNTRY LEVEL IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE (CLICC) PILOT PROJECT- GHANA National Circumstances: Major Developments Since 2006 Ghana s population has tripled, from 6.7million in 1960 to 24.9million in 2010
WATER VOLATILITY - IT S A GLOBAL PROBLEM
 WATER VOLATILITY - IT S A GLOBAL PROBLEM 19 June 2015 Volume 1 Issue 11 Water volatility is a world-wide phenomenon. Increasing pressure on water resources from population growth, increased competition
WATER VOLATILITY - IT S A GLOBAL PROBLEM 19 June 2015 Volume 1 Issue 11 Water volatility is a world-wide phenomenon. Increasing pressure on water resources from population growth, increased competition
International Symposium on Solar Physics and Solar Eclipses (SPSE) 2006 R. Ramelli, O. M. Shalabiea, I. Saleh, and J.O. Stenflo, eds.
 International Symposium on Solar Physics and Solar Eclipses (SPSE) 2006 R. Ramelli, O. M. Shalabiea, I. Saleh, and J.O. Stenflo, eds. PROSPECTS OF RENEWABLE ENERGY IN LIBYA IBRAHIM M. SALEH Faculty of
International Symposium on Solar Physics and Solar Eclipses (SPSE) 2006 R. Ramelli, O. M. Shalabiea, I. Saleh, and J.O. Stenflo, eds. PROSPECTS OF RENEWABLE ENERGY IN LIBYA IBRAHIM M. SALEH Faculty of
Water industry Caring for a precious resource
 Background information Water industry Water is the basis of life. As the world s population grows and its standards of living increase, the world s finite water resources must be carefully managed. ABB
Background information Water industry Water is the basis of life. As the world s population grows and its standards of living increase, the world s finite water resources must be carefully managed. ABB
4.7 What happens when we divert water?
 4.7 What happens when we divert water? Many of the world s greatest lakes are shrinking, and large rivers such as the Colorado, Rio Grande, Indus, Ganges, Nile and Murray discharge very little water into
4.7 What happens when we divert water? Many of the world s greatest lakes are shrinking, and large rivers such as the Colorado, Rio Grande, Indus, Ganges, Nile and Murray discharge very little water into
Home to about 56 million people, the Southwest includes Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado and most of California.
 Climate change in the U.S. Southwest U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Overview The Southwest is the hottest and driest region in the nation. Extending from the Pacific Ocean east to the Rocky Mountains
Climate change in the U.S. Southwest U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Overview The Southwest is the hottest and driest region in the nation. Extending from the Pacific Ocean east to the Rocky Mountains
ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES-II
 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES-II MODULE III HUMAN POPULATION & THE ENVIRONMENT LECTURE 19 HUMAN POPULATION CONTENTS Introduction Population Growth Population Explosion Causes of Rapid Population Growth Effect
ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES-II MODULE III HUMAN POPULATION & THE ENVIRONMENT LECTURE 19 HUMAN POPULATION CONTENTS Introduction Population Growth Population Explosion Causes of Rapid Population Growth Effect
Uncontrolled Urban Expansion of Amman City and the Disintegration of the Rainfed Lands
 Architecture Research 2017, 7(1): 24-28 DOI: 10.5923/j.arch.20170701.03 Uncontrolled Urban Expansion of Amman City and the Disintegration of the Rainfed Lands Numan Abu Hammad Department of Civil Engineering,
Architecture Research 2017, 7(1): 24-28 DOI: 10.5923/j.arch.20170701.03 Uncontrolled Urban Expansion of Amman City and the Disintegration of the Rainfed Lands Numan Abu Hammad Department of Civil Engineering,
Water Resources Data APPENDIX 1. Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region. Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region
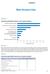 APPENDIX 1 Water Resources Data FIGURE A1.1 Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region Australia and New Zealand Latin America and the Caribbean North America Europe and Central Asia Sub-Saharan
APPENDIX 1 Water Resources Data FIGURE A1.1 Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region Australia and New Zealand Latin America and the Caribbean North America Europe and Central Asia Sub-Saharan
Europe - IMBO th European Conference on the Implementation of the WFD
 Europe - IMBO 2006 4th European Conference on the Implementation of the WFD Megeve 21 September 2006 The consideration of Qualitative and Quantitative aspects in the WFD Implementation Giorgio Pineschi
Europe - IMBO 2006 4th European Conference on the Implementation of the WFD Megeve 21 September 2006 The consideration of Qualitative and Quantitative aspects in the WFD Implementation Giorgio Pineschi
Ministry for the Environment, Land and Sea of Italy. Bruxelles, 8th December 2011
 Ministry for the Environment, Land and Sea of Italy Bruxelles, 8th December 2011 Basic Data Reference of the Call for Proposals EuropeAid/131046/C/ACT/Multi Title of the Call for Proposals Sustainable
Ministry for the Environment, Land and Sea of Italy Bruxelles, 8th December 2011 Basic Data Reference of the Call for Proposals EuropeAid/131046/C/ACT/Multi Title of the Call for Proposals Sustainable
Country Profile - Republic of Korea INFORMATION
 INFORMATION Geography The Republic of Korea occupies the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula, which extends some 1,100 km from the Asian mainland. This mountainous peninsula is flanked by the Yellow
INFORMATION Geography The Republic of Korea occupies the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula, which extends some 1,100 km from the Asian mainland. This mountainous peninsula is flanked by the Yellow
Transboundary Water Cooperation in the Arab Region. Chahra Ksia President Center of Water Studies and Arab Water Security League of Arab States
 Transboundary Water Cooperation in the Arab Region Chahra Ksia President Center of Water Studies and Arab Water Security League of Arab States Water is an increasingly scarce resource in the Arab region
Transboundary Water Cooperation in the Arab Region Chahra Ksia President Center of Water Studies and Arab Water Security League of Arab States Water is an increasingly scarce resource in the Arab region
Texas Water Resources Institute
 Texas Water Resources Institute April 1975 Volume 1 No. 5 Opportunities for Artificial Recharge By Jim Valliant, Research Engineer, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Put "dirty" water back underground--i'd
Texas Water Resources Institute April 1975 Volume 1 No. 5 Opportunities for Artificial Recharge By Jim Valliant, Research Engineer, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Put "dirty" water back underground--i'd
Improvement of Water Resources Planning in Egypt s Agricultural Sector using the LIBRA-River Basin Simulation Game
 1 Improvement of Water Resources Planning in Egypt s Agricultural Sector using the LIBRA-River Basin Simulation Game Mohie M. Omar, Researcher, Nile Research Institute, National Water Research Center (NWRC),
1 Improvement of Water Resources Planning in Egypt s Agricultural Sector using the LIBRA-River Basin Simulation Game Mohie M. Omar, Researcher, Nile Research Institute, National Water Research Center (NWRC),
Report of the Governor s Advisory Committee on the Management and Protection of the State s Water Supply
 Department of the Environment Report of the Governor s Advisory Committee on the Management and Protection of the State s Water Supply MDE Ground Water Symposium September 25, 2008 The Advisory Committee
Department of the Environment Report of the Governor s Advisory Committee on the Management and Protection of the State s Water Supply MDE Ground Water Symposium September 25, 2008 The Advisory Committee
The Arab world is facing one of the severest water scarcities in the world.
 Water Harvesting Techniques in the Arab Region By Abdelaziz Zaki UNESCO Cairo Office Water Resources in the Arab region The Arab world is facing one of the severest water scarcities in the world. According
Water Harvesting Techniques in the Arab Region By Abdelaziz Zaki UNESCO Cairo Office Water Resources in the Arab region The Arab world is facing one of the severest water scarcities in the world. According
SOLUTIONS FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER USE AND MANAGEMENT IN DA NANG CITY
 MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT DEPARTMENT OF WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER USE AND MANAGEMENT IN DA NANG CITY September 2018 DR. NGUYEN MINH KHUYEN DEPUTY DIRECTOR
MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT DEPARTMENT OF WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER USE AND MANAGEMENT IN DA NANG CITY September 2018 DR. NGUYEN MINH KHUYEN DEPUTY DIRECTOR
Water Status in the Gaza Strip and Future Plans
 ` Water Status in the Gaza Strip and Future Plans April 2010 1.0 Background and Introduction Gaza Strip is one of the semi-arid area where rainfall is falling in the winter season from September to April,
` Water Status in the Gaza Strip and Future Plans April 2010 1.0 Background and Introduction Gaza Strip is one of the semi-arid area where rainfall is falling in the winter season from September to April,
Chapter 14 Water: A Limited Resource
 Chapter 14 Water: A Limited Resource I. Importance of Water A. Cooking & washing B. Agriculture C. Manufacturing D. Mining E. Energy production F. Waste disposal G. There are more people and individual
Chapter 14 Water: A Limited Resource I. Importance of Water A. Cooking & washing B. Agriculture C. Manufacturing D. Mining E. Energy production F. Waste disposal G. There are more people and individual
URBAN SYSTEMS IN AREAS OF EXTREME ARIDITY. PROPOSALS FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER MANAGEMENT
 URBAN SYSTEMS IN AREAS OF EXTREME ARIDITY. PROPOSALS FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER MANAGEMENT Mario Molina Center Abstract The objective of this study was to identify the most appropriate actions, from an environmental,
URBAN SYSTEMS IN AREAS OF EXTREME ARIDITY. PROPOSALS FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER MANAGEMENT Mario Molina Center Abstract The objective of this study was to identify the most appropriate actions, from an environmental,
Battle for the Biosphere
 Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
Climate Change, Dams, Reservoirs and Water Resources
 Climate Change, Dams, Reservoirs and Water Resources Dr. Denis Aelbrecht (EDF-CIH, France) Chairman of ICOLD Technical Committee on Climate Change, Dams and Reservoirs Conférence Internationale Eau et
Climate Change, Dams, Reservoirs and Water Resources Dr. Denis Aelbrecht (EDF-CIH, France) Chairman of ICOLD Technical Committee on Climate Change, Dams and Reservoirs Conférence Internationale Eau et
The Potential Scenarios of the Impacts of Climate Change on Egyptian Resources and Agricultural Plant Production
 Open Journal of Applied Sciences, 2016, 6, 270-286 Published Online April 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojapps http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojapps.2016.64027 The Potential Scenarios of the
Open Journal of Applied Sciences, 2016, 6, 270-286 Published Online April 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojapps http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojapps.2016.64027 The Potential Scenarios of the
Abdul-Karim Sadik. Sixth Zayed Seminar 8-9 May 2013
 Agriculture, Wt Water and Food Security in GCC Countries Abdul-Karim Sadik Sixth Zayed Seminar 8-9 May 2013 Arabian Gulf lfuniversity, it Manama INTRODUCTION GCC Countries (Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar,
Agriculture, Wt Water and Food Security in GCC Countries Abdul-Karim Sadik Sixth Zayed Seminar 8-9 May 2013 Arabian Gulf lfuniversity, it Manama INTRODUCTION GCC Countries (Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar,
Water Scarcity, Human Security and Democratization: Aspects and Impacts of the Syrian Crisis
 Water Scarcity, Human Security and Democratization: Aspects and Impacts of the Syrian Crisis April 19 th, 2016 Nebraska Innovation Campus Conference Center - Lincoln, Nebraska Clive Lipchin. PhD, director,
Water Scarcity, Human Security and Democratization: Aspects and Impacts of the Syrian Crisis April 19 th, 2016 Nebraska Innovation Campus Conference Center - Lincoln, Nebraska Clive Lipchin. PhD, director,
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS
 WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
ABDULRAHMN ALDAKHEEL. King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 ABDULRAHMN ALDAKHEEL King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia OVERVIEW OF WATER RESOURCES Groundwater : Fossil aquifers (non-renewable) Alluvial aquifers (renewable) Desalination: More than 30 plants
ABDULRAHMN ALDAKHEEL King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia OVERVIEW OF WATER RESOURCES Groundwater : Fossil aquifers (non-renewable) Alluvial aquifers (renewable) Desalination: More than 30 plants
Key words: World Water Distribution, System Dynamics, Continental Scope, Economic Activities, Water Utilization, Global Worming
 J. Japan Soc. Hydrol. & Water Resour. Vol. 20, No.1, Jan. 2007 pp. 47-54 This research addresses the problem of growing shortage of water resources from the world-wide viewpoints by modeling of the socio-environmental
J. Japan Soc. Hydrol. & Water Resour. Vol. 20, No.1, Jan. 2007 pp. 47-54 This research addresses the problem of growing shortage of water resources from the world-wide viewpoints by modeling of the socio-environmental
Sustainable Water Resources Management - Safeguarding the Future
 Sustainable Water Resources Management - Safeguarding the Future Er. J. Lordwin Girisb Kumar Assistant Professor Dept!. ofsoil Water Land Engg & Mgt AllahabadAgricultural Institute - Deemed University
Sustainable Water Resources Management - Safeguarding the Future Er. J. Lordwin Girisb Kumar Assistant Professor Dept!. ofsoil Water Land Engg & Mgt AllahabadAgricultural Institute - Deemed University
Water ressources in Tunisiaare limitedand characterised by high spatial disparities.
 Tunisia ranks in the category of countries with the least resources water in the Mediterranean. For a population of 11 million, the total renewable water resources per capita is estimated to 415 m 3 (2014)
Tunisia ranks in the category of countries with the least resources water in the Mediterranean. For a population of 11 million, the total renewable water resources per capita is estimated to 415 m 3 (2014)
U.S. Water Budget. Figure Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources , Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council.
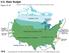 U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
Groundwater Management of the South Al Batinah/Interior Governorates in the Sultanate of Oman
 Muscat, 28/10/2014 Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Groundwater Management Institute Groundwater Management of the South Al Batinah/Interior Governorates in the Sultanate of Oman By Eng. Saif Al Amri
Muscat, 28/10/2014 Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Groundwater Management Institute Groundwater Management of the South Al Batinah/Interior Governorates in the Sultanate of Oman By Eng. Saif Al Amri
The Earth as a Planet. The Earth's Structure
 The Earth as a Planet Earth's age: formed 4.6 billion years old from particles orbiting the Sun To determine the age of the Earth, you cannot simply measure the age of the oldest rocks - most of them have
The Earth as a Planet Earth's age: formed 4.6 billion years old from particles orbiting the Sun To determine the age of the Earth, you cannot simply measure the age of the oldest rocks - most of them have
NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES
 UNESCO IHP VI NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES basic concepts & management approaches DR STEPHEN FOSTER GW-MATE Director (IAH President) a GWP Associate Program NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES relative
UNESCO IHP VI NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES basic concepts & management approaches DR STEPHEN FOSTER GW-MATE Director (IAH President) a GWP Associate Program NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES relative
