Evaluation of a CFD modeling approach by means of an intensive experimental campaign using passive samplers in an urban area of Madrid
|
|
|
- Megan Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of a CFD modeling approach by means of an intensive experimental campaign using passive samplers in an urban area of Madrid Jose Luis Santiago 1, Rafael Borge 2, Fernando Martin 1, David de la Paz 2, Alberto Martilli 1, Julio Lumbreras 2 1 Air Pollution Division, Environmental Department, CIEMAT, Madrid, Spain, addresses: jl.santiago@ciemat.es ; fernando.martin@ciemat.es; alberto.martilli@ciemat.es 2 Laboratory of Environmental Modelling, Technical University of Madrid (UPM), Madrid, Spain, addresses: rborge@etsii.upm.es ; dpaz@etsii.upm.es ; jlumbreras@etsii.upm.es 1. Introduction dated: 8 June 2015 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) models, based on the resolution of the Reynolds Average Navier Stokes (RANS) Equations are being increasingly used to simulate the dispersion of air pollutants in urban areas. Their ability to reproduce the air flow modifications induced by the buildings at a fraction of the computational time required by Large Eddy Simulations (LES) models, make them an attractive choice for real world applications (air quality assessment or network design, microscale air pollution abatement strategies, etc.). Parra et al. (2010), Santiago et al. (2011) and Santiago et al. (2013) developed a methodology based on a set of steady state simulations for a range of wind directions, that allowed to compute average concentration maps over large periods of time (weeks, months). In this work, this methodology is further validated using measurements of NO 2 from two intensive experimental campaigns lasting several weeks that were carried out deploying a large number of passive samplers distributed in a heavily trafficked district in the city center of Madrid. The CFD-RANS simulations were done assuming that: a) road traffic is the dominant air pollutant source, b) chemical reactions can be neglected, and c) thermal induced circulations can be also neglected. Data of daily mean traffic intensity, used as proxy of the traffic emission, were provided by the Madrid City Council. The methodology to obtain average concentration maps is evaluated by comparing measured values with the time averaged NO 2 predictions in the locations of passive sampler tubes. 2. Numerical methodology High resolution maps of average concentration over a large period of time are necessary for air quality management and the assessment of abatement measures. Due to computational loads, it is not possible (within a reasonable CPU time) to run an unsteady CFD simulation of several weeks or months. The solution proposed (Parra et al., 2010; Santiago et al., 2011; Santiago et al., 2013) is to run only a set of scenarios (16 inlet wind directions) using steady CFD-RANS simulations (STAR-CCM+ code from CD-Adapco). The pollutant emissions are modelled with a line source inside each street and several tracers (one for each street) are emitted in each simulation. The final map of average concentration is made by means of a combination of the simulated scenarios considering concurrent wind patterns within the period analyzed. Pollutant concentration is computed assuming: 1) non-reactive pollutants, thermal effects negligible in comparison with dynamical effects, 2) emissions inside each street at a given hour are proportional to the number of cars at that hour and tracer concentration at a certain hour depend only on emissions and background pollution at that hour. It should be noted that the two periods simulated in this study correspond to winter conditions, where the pollutant concentrations are less affected by atmospheric chemistry and thermal effects are not important. In addition, the dynamic effects of vegetation are included in CFD simulations assuming the trees as a porous medium (Santiago et al., 2013). The background concentration at each hour from an urban background station is added to the results of the simulations as they only represent the local traffic contribution. Finally, some modifications to the methodology of Parra et al. (2010) are introduced to take into account weak winds. For these cases, several assumptions are not fulfilled (e.g. thermal effects have more importance, concentration is not proportional to 1/v, etc). Taking into account all of these assumptions, for wind speed higher than 2 m s -1 at 10 m height a concentration proportional to the observed one at time t is computed using CFD results and Eq. 1. Note that we do not obtain the observed concentration because the number of vehicles inside each street is used as proxy of traffic emissions. Li 1 CObserved ( t) Cbackground Ccomputed ( Sector ( t)) Ci ( Sector ( t)) Ni( t) (1) Vsource v () t i i in where C () t Observed and C () background t are the observed and background concentration at time t, Sector() t is the
2 wind direction sector at time t, i indicates the tracer emitted inside each street, Ci ( Sector ( t )) is the concentration computed for Sector() t for a given emission from street i and for a given inlet wind speed, L i is the length of the street i, Vsource is the volume of the row of computational cells where emission of the street i is located, N () t i is the number of cars per unit time in street i and v () t is the inlet wind speed. In the case of weak winds (lower in than 2 m s -1 ) the methodology was modified. For these cases, thermal effects are not negligible and we assume that the pollutant concentration is independent of wind direction and it is modelled depending on traffic intensity and mixing height along the day. This assumption allows taking into account indirectly the thermal effects. As for emission sources, only those of road traffic are considered. According to previous source contribution analysis, NO 2 ambient concentration levels in Madrid, particularly in the innermost area of the city where de modelling domain is located, are strongly dominated by road traffic (Borge et al., 2014). i 3. Description of modeling domain, experimental campaigns and simulation setup The methodology presented in the previous section was evaluated by Parra et al. (2010) for an urban area of Pamplona using measurements from experimental campaigns using passive samplers and monitoring data. However in this work the evaluation is done by means of a denser network of passive samplers providing more information about the spatial distribution of the time averaged NO 2 concentrations. Two different experimental campaigns were carried out and simulated in the same urban area in Madrid. 3.1 Location and urban environment The urban area analyzed is located in Madrid City close to El Retiro park. In this zone there are several streets and avenues with intense road traffic and also there is a large green urban area (El Retiro). Buildings with different heights are located in this area; most of them have a height between 18 m and 24 m, although the tallest building is 90 m high approximately. A traffic air quality monitoring station (EA) is located in a garden very close to the sidewalk in the intersection of the two more important avenues (Figure 1). Meteorological data were provided by AEMET (Spanish Meteorological Agency) from the meteorological station located in El Retiro (the urban park South of EA station), approximately 200 m outside of the numerical domain (Figure1). The urban park produces not negligible dynamical effects on pollutant dispersion. 350 m Fig. 1. Escuelas Aguirre a) district. Left: Aerial picture of the b) modeling domain (red line) including the location of the air quality monitoring station (blue dot)). Right: Modeled geometry of the domain including street and park vegetation. 3.2 Simulation set-up The size of the modelling domain is 700 m x 800 m, approximately (Fig. 1). Hourly traffic data inside each street is estimated from the daily average traffic intensity (TI) data provided by the city council of Madrid, considering typical traffic patterns for different types of days (working days and weekend days) and the corresponding diurnal variation (TF). 29 passive tracers were released (one for each street) within the modelling domain. An irregular mesh of grid points with a resolution of about 1 m 3 close to the buildings is used. The dynamical effects of the vegetation are modelled considering trees as porous medium. More details can be found in Santiago et al. (2013), Santiago et al. (2014) and Krayenhoff et al. (2015). Inside the park, vegetation is represented in the numerical cells located from the ground to 18 meters-height (average height of trees) but for the trees within the street only the canopy level is considered. 3.3 Experimental campaigns Two different campaigns were carried out in this zone. The first campaign was took place from January 26 th to February 16 th passive samplers were deployed in the simulation domain (Fig. 2). The second campaign was done from November 6 th to December 1 st In this campaign the number of passive samplers deployed
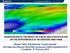
3 within the modelling domain was increased to 95 (Figure 3).. Fig.2. Daily mean traffic intensity for 2011 campaign (vehicles day -1 ), location of passive samplers, and the zone B (dashed line). Fig.3. Daily mean traffic intensity for 2014 campaign (vehicles day -1 ), location of passive samplers and and the zone B (dashed line). 4. Results The two different campaigns are modelled following the methodology described in section 2. Firstly, modelled hourly data for NO 2 were compared with observed data in the air quality monitoring station (Figs. 4 and 5) for both periods. The results were quite good showing that the simulated data fit well the observations.
4 Fig. 4. Comparison between modeled and measured hourly NO 2 concentrations recorded at EA air quality monitoring station for the 2011 campaign. Left: Time series. Right: Scatter-plot. Fig. 5. Comparison between modeled and measured hourly NO 2 concentrations recorded at EA air quality monitoring station for the 2014 campaign. Left: Time series. Right: Scatter-plot. Following the methodology described in the previous sections, maps of the time averaged NO 2 concentrations were produced for the two experimental campaigns (Fig. 6 and 7). Higher concentrations in 2011 campaign were observed are essentially due to a higher background concentration. Comparing modelled concentrations with passive sampler measurements, a good correlation agreement is found. However, model performance varies spatially. It was found that the correlation improves if measurements in the locations within the zone marked with a dash line (hereinafter, zone B) in Figs. 2 and 3 are not considered. Figs 8 and 9 show the scatter plots of NO 2 modelled concentration against NO 2 experimental concentration with and without measurements in zone B for the two campaigns. The problem found in the comparison with the zone B could be due to unrealistic emission representation in this particular area. In Fig. 10, it can be observed that the real distribution of the street in this zone which is more complex than the distribution of the emissions (a triangle) used in the simulations (Fig 3 and 4). In addition, the number of the vehicles in the street close to the park is not very high but usually there are traffic jams in this street. This fact may imply that the emissions are not proportional to the number of vehicles that is one of the assumptions made and then, our emissions estimates would not be correct for this zone. For this reasons, passive sampler number 22 is not considered in 2011 campaign and numbers 9, 12, 25, 35, 36, 38 y 164 in 2014 campaigns.taking into account the correlation obtained in the comparison, we can conclude that the methodology using CFD simulations provides realistic NO 2 averaged concentration maps.
5 Fig. 6. Map of the time averaged NO 2 concentration in μg m -3 (508 hours) and location of passive samplers for 2011 campaign Fig. 7. Map of the time averaged NO 2 concentration in μg m -3 (602 hours) and location of passive samplers for 2014 campaign Fig. 8.Left: Scatter plot with all measurements. Rigth: Scatter plot without passive sampler number 22.
6 Fig. 9. Left: Scatter plot with all measurements within domain. Rigth: Scatter plot without passive samplers in zone with tunnels and street forks not modeled by emissions (without 9, 12, 25, 35, 36, 38 y 164). 5. Conclusions Fig. 10. Image from google maps of the zone B. In the comparison with experimental data from two different campaigns, a good correlation between model estimates and measurements was obtained showing that this methodology, based on the CFD-RANS modelling is able to reproduce the main aspects of several-week averaged pollutant distribution, with resolution of the order of meters. It was observed that in a zone where the traffic distribution was not well estimated due to the complexity (tunnels, street forks,..), the model provided worse results in comparison with passive measurements. We can conclude that the methodology proposed is able to reproduce satisfactorily week-averaged pollutant concentration distribution in an urban area with heavy traffic and shows promising potential to support the analysis of streetscale measures to improve air quality. However, additional research efforts should be done to improve the representation of traffic emissions and the contributions from other sources though dynamic boundary conditions. Acknowledgment This study has been supported by the project TECNAIRE (S2013/MAE-2972) funded by The Regional Government of Madrid. References Borge, R, Lumbreras, J, Pérez, J, de la Paz, D, Vedrenne, M, de Andrés, JM, Rodríguez, ME, 2014: Emission inventories and modeling requirements for the development of air quality plans. Application to Madrid (Spain). Science of the Total Environment , Parra MA, Santiago JL, Martín F, Martilli A, Santamaría JM, 2010: A methodology to urban air quality assessment during large time periods of winter using computational fluid dynamic models. Atmospheric Environment 44, Santiago JL, Martín F, Martilli A, 2011: Representativeness of urban monitoring stations. 14th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Kos (Greece) 2-6 October. Santiago JL, Martín F, Martilli A, 2013: A computational fluid dynamic modelling approach to assess the representativeness of urban monitoring stations. Science of the Total Environment , Santiago JL Martilli A, Martín F, 2014: Estimating the impact of street vegetation on air quality: a simple case with different types and position of vegetation. In: 16th International Conference on Harmonization within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Varna (Bulgaria), 8-11 September Krayenhoff ES, Santiago JL, Martilli A, Christen A, Oke TR, 2015: Parametrization of drag and turbulence for urban neighbourhoods with trees. Boundary-Layer Meteorology (In press) DOI: /s
REPRESENTATIVENESS OF URBAN MONITORING STATIONS
 REPRESENTATIVENESS OF URBAN MONITORING STATIONS JL Santiago, F Martín, A Martilli Atmospheric Pollution Division, Environmental Department, CIEMAT, Spain jl.santiago@ciemat.es fernando.martin@ciemat.es
REPRESENTATIVENESS OF URBAN MONITORING STATIONS JL Santiago, F Martín, A Martilli Atmospheric Pollution Division, Environmental Department, CIEMAT, Spain jl.santiago@ciemat.es fernando.martin@ciemat.es
ESTIMATING THE IMPACT OF URBAN VEGETATION ON AIR QUALITY IN A NEIGHBORHOOD: REAL CASE VS NEW VEGETATION SCENARIOS
 17th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, 9-12 May 2016 Budapest, Hungary ESTIMATING THE IMPACT OF URBAN VEGETATION ON AIR QUALITY
17th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, 9-12 May 2016 Budapest, Hungary ESTIMATING THE IMPACT OF URBAN VEGETATION ON AIR QUALITY
CFD Modeling of Reactive Pollutants in an Urban Street Canyon using Different Chemical Mechanisms
 CFD Modeling of Reactive Pollutants in an Urban Street Canyon using Different Chemical Mechanisms B Sanchez a,b, JL Santiago a, A Martilli a, M Palacios a, F Kirchner c a Center for Energy, Environment
CFD Modeling of Reactive Pollutants in an Urban Street Canyon using Different Chemical Mechanisms B Sanchez a,b, JL Santiago a, A Martilli a, M Palacios a, F Kirchner c a Center for Energy, Environment
Session A4: Healthy-Polis Workshop on Climate Change and Urban Health II
 Session A4: Healthy-Polis Workshop on Climate Change and Urban Health II Experimental Campaign in a Heavily Trafficked Roundabout in Madrid for the Assessment of Air Quality Monitoring Station Representativeness
Session A4: Healthy-Polis Workshop on Climate Change and Urban Health II Experimental Campaign in a Heavily Trafficked Roundabout in Madrid for the Assessment of Air Quality Monitoring Station Representativeness
Impact of measures to improve urban air quality in Spain. Studies to estimate impact of measures for improving air quality in Spain and in some cities
 Impact of measures to improve urban air quality in Spain. Studies to estimate impact of measures for improving air quality in Spain and in some cities Fernando Martín, Marta G. Vivanco, José Luis Santiago,
Impact of measures to improve urban air quality in Spain. Studies to estimate impact of measures for improving air quality in Spain and in some cities Fernando Martín, Marta G. Vivanco, José Luis Santiago,
Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM
 Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM Márton Balczó 1, Tamás Faragó 2, Tamás Lajos 3 PhD Student 1, Student 2, Professor 3 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of
Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM Márton Balczó 1, Tamás Faragó 2, Tamás Lajos 3 PhD Student 1, Student 2, Professor 3 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of
H AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL. Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi
 H13-198 AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi FLUIDYN France, Saint-Denis, France Abstract: The air
H13-198 AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi FLUIDYN France, Saint-Denis, France Abstract: The air
EXAMINATION OF TRAFFIC POLLUTION DISTRIBUTION IN A STREET CANYON USING THE NANTES 99 EXPERIMENTAL DATA AND COMPARISON WITH MODEL RESULTS
 EXAMINATION OF TRAFFIC POLLUTION DISTRIBUTION IN A STREET CANYON USING THE NANTES 99 EXPERIMENTAL DATA AND COMPARISON WITH MODEL RESULTS R. BERKOWICZ 1, M. KETZEL 1, G. VACHON 2, P. LOUKA 2, J.-M. ROSANT
EXAMINATION OF TRAFFIC POLLUTION DISTRIBUTION IN A STREET CANYON USING THE NANTES 99 EXPERIMENTAL DATA AND COMPARISON WITH MODEL RESULTS R. BERKOWICZ 1, M. KETZEL 1, G. VACHON 2, P. LOUKA 2, J.-M. ROSANT
3D Simulation of a fire inside a river tunnel and optimisation of the ventilation using Computational Fluid Dynamics
 3D Simulation of a fire inside a river tunnel and optimisation of the ventilation using Computational Fluid Dynamics Authors: B. TRUCHOT, A. TRIPATHI Fluidyn-France Abstract CFD simulation is used to predict
3D Simulation of a fire inside a river tunnel and optimisation of the ventilation using Computational Fluid Dynamics Authors: B. TRUCHOT, A. TRIPATHI Fluidyn-France Abstract CFD simulation is used to predict
A multi-layer urban canopy model for neighbourhoods with trees Scott Krayenhoff, Andreas Christen, Alberto Martilli, Tim Oke
 A multi-layer urban canopy model for neighbourhoods with trees Scott Krayenhoff, Andreas Christen, Alberto Martilli, Tim Oke ICUC-9 Toulouse - July 21, 2015 Mesoscale atmospheric modelling Oke et al. (2014),
A multi-layer urban canopy model for neighbourhoods with trees Scott Krayenhoff, Andreas Christen, Alberto Martilli, Tim Oke ICUC-9 Toulouse - July 21, 2015 Mesoscale atmospheric modelling Oke et al. (2014),
TECNAIRE NEWS, OCTOBER 2016
 ISSUE 2, OCTOBER 2016 TECNAIRE NEWS, OCTOBER 2016 http://tecnaire-cm.org UNIÓN EUROPEA Fondos Estructurales Programas de Actividades de I + D entre grupos de investigación de la Comunidad de Madrid en
ISSUE 2, OCTOBER 2016 TECNAIRE NEWS, OCTOBER 2016 http://tecnaire-cm.org UNIÓN EUROPEA Fondos Estructurales Programas de Actividades de I + D entre grupos de investigación de la Comunidad de Madrid en
CODASC: A DATABASE FOR THE VALIDATION OF STREET CANYON DISPERSION MODELS. Christof Gromke
 CODASC: A DATABASE FOR THE VALIDATION OF STREET CANYON DISPERSION MODELS Christof Gromke Building Physics and Services, Department of the Built Environment, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven,
CODASC: A DATABASE FOR THE VALIDATION OF STREET CANYON DISPERSION MODELS Christof Gromke Building Physics and Services, Department of the Built Environment, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven,
Vipac Engineers & Scientists Ltd
 Vipac Engineers & Scientists Ltd COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS Simulation of Turbulent Flows and Pollutant Dispersion Around Groups of Buildings presented by Dr. Neihad Al-Khalidy Specialist Consultant
Vipac Engineers & Scientists Ltd COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS Simulation of Turbulent Flows and Pollutant Dispersion Around Groups of Buildings presented by Dr. Neihad Al-Khalidy Specialist Consultant
MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD
 MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD J. Allegrini 1,2 ; J. Kämpf 3 ; V. Dorer 1 ; J. Carmeliet 1,2 1: Empa, Laboratory for Building Science
MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD J. Allegrini 1,2 ; J. Kämpf 3 ; V. Dorer 1 ; J. Carmeliet 1,2 1: Empa, Laboratory for Building Science
CFD modelling of dispersion in neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layers:
 Health and Safety Executive CFD modelling of dispersion in neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layers: Results for Prairie Grass and Thorney Island 9 th May 2016 Rachel Batt, Simon Gant, Jean-Marc
Health and Safety Executive CFD modelling of dispersion in neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layers: Results for Prairie Grass and Thorney Island 9 th May 2016 Rachel Batt, Simon Gant, Jean-Marc
Near-Road Air Quality Monitoring and Modeling: Towards a Mechanistic Understanding
 Near-Road Air Quality Monitoring and Modeling: Towards a Mechanistic Understanding K. Max Zhang Energy and the Environment Research Laboratory Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Outline
Near-Road Air Quality Monitoring and Modeling: Towards a Mechanistic Understanding K. Max Zhang Energy and the Environment Research Laboratory Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Outline
Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion
 Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion S. M. Salim, K. C. Ong, S. C. Cheah Abstract The performance of three different numerical techniques, i.e. RANS,
Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion S. M. Salim, K. C. Ong, S. C. Cheah Abstract The performance of three different numerical techniques, i.e. RANS,
Smoke Dispersion from Stacks on Pitched-Roof Buildings: Model Calculations Using MISKAM in Comparison with Wind Tunnel Results
 Smoke Dispersion from Stacks on Pitched-Roof Buildings: Model Calculations Using MISKAM in Comparison with Wind Tunnel Results Konstantinos E. Kakosimos 1 Marc J. Assael 1 Matthias Ketzel 2 Helge Rørdam
Smoke Dispersion from Stacks on Pitched-Roof Buildings: Model Calculations Using MISKAM in Comparison with Wind Tunnel Results Konstantinos E. Kakosimos 1 Marc J. Assael 1 Matthias Ketzel 2 Helge Rørdam
Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol II, WCE, July -,, London, U.K. Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies S. M. Kwa, S. M. Salim Abstract Fluctuating
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol II, WCE, July -,, London, U.K. Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies S. M. Kwa, S. M. Salim Abstract Fluctuating
Aerosol transport and deposition modelling. Tim Foat Fluid Dynamics and Indoor Dispersion Team Detection Department
 Aerosol transport and deposition modelling Tim Foat Fluid Dynamics and Indoor Dispersion Team Detection Department Introduction Work of the team focuses on three main areas Indoor dispersion Transport,
Aerosol transport and deposition modelling Tim Foat Fluid Dynamics and Indoor Dispersion Team Detection Department Introduction Work of the team focuses on three main areas Indoor dispersion Transport,
H POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH. Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu*
 H14-117 POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu* Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong
H14-117 POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu* Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong
ASSESSMENT OF AIR CHANGE RATE AND CONTRIBUTION RATIO IN IDEALIZED URBAN CANOPY LAYERS BY TRACER GAS SIMULATIONS
 Topic B4: Ventilation ASSESSMENT OF AIR CHANGE RATE AND CONTRIBUTION RATIO IN IDEALIZED URBAN CANOPY LAYERS BY TRACER GAS SIMULATIONS Qun WANG 1, Mats SANDBERG 2, Jian HANG 1* 1 Department of Atmospheric
Topic B4: Ventilation ASSESSMENT OF AIR CHANGE RATE AND CONTRIBUTION RATIO IN IDEALIZED URBAN CANOPY LAYERS BY TRACER GAS SIMULATIONS Qun WANG 1, Mats SANDBERG 2, Jian HANG 1* 1 Department of Atmospheric
5.39 AN EVALUATION OF THE URBAN DISPERSION MODELS SIRANE AND ADMS URBAN, USING FIELD DATA FROM LYON.
 5.39 AN EVALUATION OF THE URBAN DISPERSION MODELS SIRANE AND ADMS URBAN, USING FIELD DATA FROM LYON. Soulhac, L. 1., Pradelle, F. 2 & Perkins, R.J. 1 1 Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d Acoustique,
5.39 AN EVALUATION OF THE URBAN DISPERSION MODELS SIRANE AND ADMS URBAN, USING FIELD DATA FROM LYON. Soulhac, L. 1., Pradelle, F. 2 & Perkins, R.J. 1 1 Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d Acoustique,
Modeling of pollutant dispersion in street canyon by means of CFD
 Modeling of pollutant dispersion in street canyon by means of CFD Davide Meschini a, Valentina Busini * a, Sjoerd W. van Ratingen b, Renato Rota a a Department of Chemistry, Materials and Chemical Engineering
Modeling of pollutant dispersion in street canyon by means of CFD Davide Meschini a, Valentina Busini * a, Sjoerd W. van Ratingen b, Renato Rota a a Department of Chemistry, Materials and Chemical Engineering
WG1 ASSESSMENT: KEY TOPICS & RECOMMENDATIONS STIJN JANSSEN & JOOST WESSELING
 WG1 ASSESSMENT: KEY TOPICS & RECOMMENDATIONS STIJN JANSSEN & JOOST WESSELING CONTENT» Fitness for purpose and quality objectives in assessment modelling WG1 recommendation» Spatial representativeness of
WG1 ASSESSMENT: KEY TOPICS & RECOMMENDATIONS STIJN JANSSEN & JOOST WESSELING CONTENT» Fitness for purpose and quality objectives in assessment modelling WG1 recommendation» Spatial representativeness of
COMPARISON OF WIND TUNNEL MEASUREMENT AND NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DISPERSION OF POLLUTANTS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENT
 COMPARISON OF WIND TUNNEL MEASUREMENT AND NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DISPERSION OF POLLUTANTS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENT I. Goricsán Department of Fluid Mechanics Budapest University of Technology and Economics
COMPARISON OF WIND TUNNEL MEASUREMENT AND NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DISPERSION OF POLLUTANTS IN URBAN ENVIRONMENT I. Goricsán Department of Fluid Mechanics Budapest University of Technology and Economics
Study of microscale urban air dispersion by ADMS - Urban
 Study of microscale urban air dispersion by ADMS - Urban Jason P.L. Huang Atmospheric, Marine and Coastal Environment Program (AMCE), The Hong Kong University of Science & Technology Jimmy C.H. Fung Department
Study of microscale urban air dispersion by ADMS - Urban Jason P.L. Huang Atmospheric, Marine and Coastal Environment Program (AMCE), The Hong Kong University of Science & Technology Jimmy C.H. Fung Department
18th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 9-12 October 2017, Bologna, Italy
 18th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 9-12 October 2017, Bologna, Italy COMBINING GAUSSIAN AND CFD MODELLING TO ASSESS THE IMPACT
18th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 9-12 October 2017, Bologna, Italy COMBINING GAUSSIAN AND CFD MODELLING TO ASSESS THE IMPACT
THE DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM FOR NESTING ADMS-URBAN IN REGIONAL PHOTOCHEMICAL MODELS
 THE DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM FOR NESTING URBAN IN REGIONAL PHOTOCHEMICAL MODELS Jenny Stocker, Christina Hood*, David Carruthers, Martin Seaton and Kate Johnson Cambridge Environmental
THE DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM FOR NESTING URBAN IN REGIONAL PHOTOCHEMICAL MODELS Jenny Stocker, Christina Hood*, David Carruthers, Martin Seaton and Kate Johnson Cambridge Environmental
Fotios Barmpas, Nicolas Moussiopoulos, Ioannis Ossanlis and Vassilis Akylas
 H14-292 DISPERSION OF TRAFFIC EMISSIONS IN THE LEOPOLD II ROAD TUNNEL IN BRUSSELS UNDER THE COMBINED INFLUENCE OF THE VENTILATION SYSTEM AND THE VEHICLE MOTION Fotios Barmpas, Nicolas Moussiopoulos, Ioannis
H14-292 DISPERSION OF TRAFFIC EMISSIONS IN THE LEOPOLD II ROAD TUNNEL IN BRUSSELS UNDER THE COMBINED INFLUENCE OF THE VENTILATION SYSTEM AND THE VEHICLE MOTION Fotios Barmpas, Nicolas Moussiopoulos, Ioannis
Riccardo Buccolieri 1, Mats Sandberg 2
 STUDY OF TE EFFECTS OF BUILDING DENSITY AND OVERALL SAPE OF A CITY ON POLLUTANT DISPERSION BY COMBINATION OF WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND CFD SIMULATIONS Riccardo Buccolieri 1, Mats Sandberg 2 1 Dipartimento
STUDY OF TE EFFECTS OF BUILDING DENSITY AND OVERALL SAPE OF A CITY ON POLLUTANT DISPERSION BY COMBINATION OF WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND CFD SIMULATIONS Riccardo Buccolieri 1, Mats Sandberg 2 1 Dipartimento
3D numerical modeling of the flow over a gravel river bed due to hydropower peaking
 Technische Universität Dresden Fakultät Bauingenieurwesen Institut für Wasserbau und Technische Hydromechanik 37. Dresdner Wasserbaukolloquium 2014 Simulationsverfahren und Modelle für Wasserbau und Wasserwirtschaft
Technische Universität Dresden Fakultät Bauingenieurwesen Institut für Wasserbau und Technische Hydromechanik 37. Dresdner Wasserbaukolloquium 2014 Simulationsverfahren und Modelle für Wasserbau und Wasserwirtschaft
ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE PASSIVE CONTROL OF AIR POLLUTION IN ASYMMETRICAL URBAN STREET CANYONS USING REFINED MESH
 Accepted Manuscript Numerical modelling of the passive control of air pollution in asymmetrical urban street canyons using refined mesh discretization schemes J. Gallagher, L.W. Gill, A. McNabola PII:
Accepted Manuscript Numerical modelling of the passive control of air pollution in asymmetrical urban street canyons using refined mesh discretization schemes J. Gallagher, L.W. Gill, A. McNabola PII:
CFD SIMULATION OF HEAVY GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS AND VALIDATION BY TRACING EXPERIMENTS
 CFD SIMULATION OF HEAVY GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS AND VALIDATION BY TRACING EXPERIMENTS L. Ricciardi, C. Prévost, L. Bouilloux, R. Sestier-Carlin Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire,
CFD SIMULATION OF HEAVY GAS DISPERSION IN VENTILATED ROOMS AND VALIDATION BY TRACING EXPERIMENTS L. Ricciardi, C. Prévost, L. Bouilloux, R. Sestier-Carlin Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire,
Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
A Modelling-Mapping Approach for Fine-Scale Natural Ventilation Evaluation in High Density Cities
 A Modelling-Mapping Approach for Fine-Scale Natural Ventilation Evaluation in High Density Cities Chao Yuan 1, 2, Leslie Norford 3, Rex Britter 4, Steve Yim 5, Edward Ng 6, 1 Massachusetts Institute of
A Modelling-Mapping Approach for Fine-Scale Natural Ventilation Evaluation in High Density Cities Chao Yuan 1, 2, Leslie Norford 3, Rex Britter 4, Steve Yim 5, Edward Ng 6, 1 Massachusetts Institute of
EMISSION NEEDS AT LOCAL SCALE FOR AIR QUALITY MODELLING
 Emission needs at local scale for AQ modelling Lumbreras, J., Borge, R., Tarrason, L., and Rodriguez, M.E. Parallel session FAIRMODE 5th October 2011 EMISSION NEEDS AT LOCAL SCALE FOR AIR QUALITY MODELLING
Emission needs at local scale for AQ modelling Lumbreras, J., Borge, R., Tarrason, L., and Rodriguez, M.E. Parallel session FAIRMODE 5th October 2011 EMISSION NEEDS AT LOCAL SCALE FOR AIR QUALITY MODELLING
A Numerical Investigation on bubble formation in Coolant channel with various Ethylene Glycol and water compositions and change in contact angle
 2016 IEEE 23rd International Conference on High Performance Computing Workshops A Numerical Investigation on bubble formation in Coolant channel with various Ethylene Glycol and water compositions and
2016 IEEE 23rd International Conference on High Performance Computing Workshops A Numerical Investigation on bubble formation in Coolant channel with various Ethylene Glycol and water compositions and
Verification and validation of a real-time 3D-CFD wake model for large wind farms
 Verification and validation of a real-time 3D-CFD wake model for large wind farms Presented by: Wolfgang Schlez 1,2 Co-Authors: Philip Bradstock 2, Michael Tinning 2, Staffan Lindahl 2 (1) ProPlanEn GmbH;
Verification and validation of a real-time 3D-CFD wake model for large wind farms Presented by: Wolfgang Schlez 1,2 Co-Authors: Philip Bradstock 2, Michael Tinning 2, Staffan Lindahl 2 (1) ProPlanEn GmbH;
A three-dimensional numerical model of air pollutant dispersion
 Air Pollution XIII 39 A three-dimensional numerical model of air pollutant dispersion K. Kaminski, W. Kaminski & J. Petera Faculty of Process and Environmental Engineering, Technical University of Lodz,
Air Pollution XIII 39 A three-dimensional numerical model of air pollutant dispersion K. Kaminski, W. Kaminski & J. Petera Faculty of Process and Environmental Engineering, Technical University of Lodz,
Scott Reynolds, PE M/E Engineering Syracuse NY
 Scott Reynolds, PE M/E Engineering Syracuse NY What is Wind Modeling? Wind modeling studies are used to determine: The flow of pollutants from exhaust stacks on buildings. The determination of pollutant
Scott Reynolds, PE M/E Engineering Syracuse NY What is Wind Modeling? Wind modeling studies are used to determine: The flow of pollutants from exhaust stacks on buildings. The determination of pollutant
16th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 8-11 September 2014, Varna, Bulgaria
 16th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 8-11 September 2014, Varna, Bulgaria UPDATES ON COST ACTION ES1006. EVALUATION, IMPROVEMENT
16th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 8-11 September 2014, Varna, Bulgaria UPDATES ON COST ACTION ES1006. EVALUATION, IMPROVEMENT
Urban greenery: increasing resilience to climate change through green roofs and urban forestry
 Urban greenery: increasing resilience to climate change through green roofs and urban forestry Author: Saiz Alcazar, Susana; Arup, Madrid, Spain Abstract: This study evaluates the impact of green roofs
Urban greenery: increasing resilience to climate change through green roofs and urban forestry Author: Saiz Alcazar, Susana; Arup, Madrid, Spain Abstract: This study evaluates the impact of green roofs
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF URBAN CANOPY LAYER FLOW AND DISPERSION
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF URBAN CANOPY LAYER FLOW AND DISPERSION Schatzmann, M. 1, Bächlin, W. 2,Emeis, S. 3, Kühlwein, J. 4, Leitl, B. 1, Müller, W.J. 5, Schäfer, K. 3 1 University of Hamburg, Centre
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF URBAN CANOPY LAYER FLOW AND DISPERSION Schatzmann, M. 1, Bächlin, W. 2,Emeis, S. 3, Kühlwein, J. 4, Leitl, B. 1, Müller, W.J. 5, Schäfer, K. 3 1 University of Hamburg, Centre
Vehicle Simulation With STAR-CCM+ Frederick J. Ross CD-adapco USA
 Vehicle Simulation With STAR-CCM+ Frederick J. Ross CD-adapco USA Vehicle Simulation with STAR-CCM+ Aero Acoustics Vehicle Aerodynamics Front End Cooling Vehicle Aerodynamics Passenger Thermal Comfort
Vehicle Simulation With STAR-CCM+ Frederick J. Ross CD-adapco USA Vehicle Simulation with STAR-CCM+ Aero Acoustics Vehicle Aerodynamics Front End Cooling Vehicle Aerodynamics Passenger Thermal Comfort
The effect of vegetative buffers on wind and dispersion of particulate matter around poultry barns
 The effect of vegetative buffers on wind and dispersion of particulate matter around poultry barns Andreas Christen (1), Daryll Pauls (2), Shabtai Bittman (3) (1) Department of Geography, University of
The effect of vegetative buffers on wind and dispersion of particulate matter around poultry barns Andreas Christen (1), Daryll Pauls (2), Shabtai Bittman (3) (1) Department of Geography, University of
Air Pollution Estimation from Traffic Flows in Tehran Highways
 Current World Environment Vol. 7(1), 01-06 (2012) Air Pollution Estimation from Traffic Flows in Tehran Highways KEIVAN SAEB¹, MARYAM MALEKZADEH¹ and SAEED KARDAR² ¹Department of Environment, Tonekabon
Current World Environment Vol. 7(1), 01-06 (2012) Air Pollution Estimation from Traffic Flows in Tehran Highways KEIVAN SAEB¹, MARYAM MALEKZADEH¹ and SAEED KARDAR² ¹Department of Environment, Tonekabon
MODELLING OF AMMONIA CONCENTRATIONS AND DEPOSITION OF REDUCED NITROGEN IN THE UNITED KINGDOM
 MODELLING OF AMMONIA CONCENTRATIONS AND DEPOSITION OF REDUCED NITROGEN IN THE UNITED KINGDOM Anthony Dore 1, Mark Theobald 1, Massimo Vieno 2 Sim Tang 1 and Mark Sutton 1 1 Centre for Ecology and Hydrology,
MODELLING OF AMMONIA CONCENTRATIONS AND DEPOSITION OF REDUCED NITROGEN IN THE UNITED KINGDOM Anthony Dore 1, Mark Theobald 1, Massimo Vieno 2 Sim Tang 1 and Mark Sutton 1 1 Centre for Ecology and Hydrology,
40-Ton Articulated Truck Cooling System Modelling Using STAR-CCM+
 40-Ton Articulated Truck Cooling System Modelling Using STAR-CCM+ Gary Yu, Martin Timmins and Mario Ciaffarafa DENSO Marston Ltd, Bradford, BD17 7JR, UK DENSO Marston Founded in 1904 Acquired by DENSO
40-Ton Articulated Truck Cooling System Modelling Using STAR-CCM+ Gary Yu, Martin Timmins and Mario Ciaffarafa DENSO Marston Ltd, Bradford, BD17 7JR, UK DENSO Marston Founded in 1904 Acquired by DENSO
2. SOBEK-river model on River Vuoksi SOBEK 1D/2D model [3] is all-in-one software suite for modelling river hydrodynamics and water quality. The SOBEK
![2. SOBEK-river model on River Vuoksi SOBEK 1D/2D model [3] is all-in-one software suite for modelling river hydrodynamics and water quality. The SOBEK 2. SOBEK-river model on River Vuoksi SOBEK 1D/2D model [3] is all-in-one software suite for modelling river hydrodynamics and water quality. The SOBEK](/thumbs/92/109590151.jpg) Transport model application in River Vuoksi Janne Ropponen * and Timo Huttula * * Freshwater Centre, Finnish Environment Institute, Finland Janne.Ropponen@ymparisto.fi Abstract: We describe our recent
Transport model application in River Vuoksi Janne Ropponen * and Timo Huttula * * Freshwater Centre, Finnish Environment Institute, Finland Janne.Ropponen@ymparisto.fi Abstract: We describe our recent
u and Yoshie (2013) investigate the effect of building geometry and they revealed that the ventilation efficiency strongly depended on the level of bu
 Effect of upstream building arrangement and setback distance on air flow around idealized cubical building arrays A. Abd Razak 1*, R.. usam 1, T. Liyana 1, S. A. Zaki 2 and A. F. Mohammad 2 1 Faculty of
Effect of upstream building arrangement and setback distance on air flow around idealized cubical building arrays A. Abd Razak 1*, R.. usam 1, T. Liyana 1, S. A. Zaki 2 and A. F. Mohammad 2 1 Faculty of
Flow Induced Vibration A Review of Current Assessment Methods
 Flow Induced Vibration A Review of Current Assessment Methods David Fielding, Matt Straw (Norton Straw Consultants) Alex Graham, Phil Shorter (CD-adapco) Introduction Presenting a joint study into flow-induced
Flow Induced Vibration A Review of Current Assessment Methods David Fielding, Matt Straw (Norton Straw Consultants) Alex Graham, Phil Shorter (CD-adapco) Introduction Presenting a joint study into flow-induced
Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study
 Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study Stéphane SANQUER (1), Julien Berthaut-Gerentes (1), Luis Cosculluela Soteras (2) (1) Meteodyn (2) Iberdrola Renovables Introduction Forested areas
Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study Stéphane SANQUER (1), Julien Berthaut-Gerentes (1), Luis Cosculluela Soteras (2) (1) Meteodyn (2) Iberdrola Renovables Introduction Forested areas
Urban Heat Island modelling with ADMS-Urban: London case study
 Urban Heat Island modelling with ADMS-Urban: London case study Stephen Smith ADMS-Urban & ADMS-Roads User Group Meeting 10 th November 2016 London Contents Motivation Theory & model overview Model applications
Urban Heat Island modelling with ADMS-Urban: London case study Stephen Smith ADMS-Urban & ADMS-Roads User Group Meeting 10 th November 2016 London Contents Motivation Theory & model overview Model applications
Modelling of air pollutants released from highway traffic in Hungary
 Air Pollution XVI 77 Modelling of air pollutants released from highway traffic in Hungary Gy. Baranka Hungarian Meteorological Service, Hungary Abstract The aim of study is to determine the CO and NO 2
Air Pollution XVI 77 Modelling of air pollutants released from highway traffic in Hungary Gy. Baranka Hungarian Meteorological Service, Hungary Abstract The aim of study is to determine the CO and NO 2
XVII th World Congress of the International Commission of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (CIGR)
 XVII th World Congress of the International Commission of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (CIGR) Hosted by the Canadian Society for Bioengineering (CSBE/SCGAB) Québec City, Canada June 13-17, 2010
XVII th World Congress of the International Commission of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (CIGR) Hosted by the Canadian Society for Bioengineering (CSBE/SCGAB) Québec City, Canada June 13-17, 2010
Dispersion Modelling Tools for Urban Air Quality and Climate Amy Stidworthy, Jenny Stocker and David Carruthers
 Dispersion Modelling Tools for Urban Air Quality and Climate Amy Stidworthy, Jenny Stocker and David Carruthers 28 th April 2016 London CERC Software ADMS 5 ADMS-Urban ADMS-Roads ADMS-Airport EMIT FLOWSTAR-Energy
Dispersion Modelling Tools for Urban Air Quality and Climate Amy Stidworthy, Jenny Stocker and David Carruthers 28 th April 2016 London CERC Software ADMS 5 ADMS-Urban ADMS-Roads ADMS-Airport EMIT FLOWSTAR-Energy
A comparison of CALPUFF air quality simulation results with monitoring data for Krakow Poland
 A comparison of CALPUFF air quality simulation results with monitoring data for Krakow Poland John S. Irwin 1, Joanna Niedzialek 2, Jerzy Burzynski 3 1 Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division (Mail Drop
A comparison of CALPUFF air quality simulation results with monitoring data for Krakow Poland John S. Irwin 1, Joanna Niedzialek 2, Jerzy Burzynski 3 1 Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division (Mail Drop
On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation
 On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong,
On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong,
College of Science and Engineering. Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Numerical analysis of CO concentration distribution on extraction ventilation type tunnel Tao Guo 1,a, Jun Zhou 2,b, Xiaonan Liu 3,c and Bo Shang 4
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-10-15 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 444-445, pp 277-280 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.444-445.277 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Numerical analysis
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-10-15 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 444-445, pp 277-280 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.444-445.277 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Numerical analysis
CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas
 2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas Qiao Yan, Dalong Li,
2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas Qiao Yan, Dalong Li,
Modelling Airport Air Quality
 Modelling Airport Air Quality David Carruthers Cambridge Environmental Research Consultants Safeguarding Airport Air Quality Manchester 12 April 27 Outline of talk Key factors affecting air quality at
Modelling Airport Air Quality David Carruthers Cambridge Environmental Research Consultants Safeguarding Airport Air Quality Manchester 12 April 27 Outline of talk Key factors affecting air quality at
To whom it may concern
 Department of the Built Environment Building Physics and Services Den Dolech 2, 5612 AZ Eindhoven Postbus 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven Internal address: Vertigo 6.B14 www.urbanphysics.net To whom it may concern
Department of the Built Environment Building Physics and Services Den Dolech 2, 5612 AZ Eindhoven Postbus 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven Internal address: Vertigo 6.B14 www.urbanphysics.net To whom it may concern
Oil&Gas I N S I G H T Volume
 Oil&Gas I N S I G H T Volume 4 2016 Gas Extraction from Lake Kivu: Safety Considerations Introduction Lake Kivu, located between Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of Congo, is unique among several East
Oil&Gas I N S I G H T Volume 4 2016 Gas Extraction from Lake Kivu: Safety Considerations Introduction Lake Kivu, located between Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of Congo, is unique among several East
ACPD. Interactive comment. Lars Gidhagen et al.
 Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-2018-1094-ac1, 2019 Author(s) 2019. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. on Experimental and model assessment
Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-2018-1094-ac1, 2019 Author(s) 2019. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. on Experimental and model assessment
17th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 9-12 May 2016, Budapest, Hungary
 17th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 9-12 May 2016, Budapest, Hungary A REVIEW OF DISPERSION MODELLING OF AGRICULTURAL AND BIOAEROSOL
17th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes 9-12 May 2016, Budapest, Hungary A REVIEW OF DISPERSION MODELLING OF AGRICULTURAL AND BIOAEROSOL
THE IMPACT OF ROADSIDE BARRIERS ON NEAR-ROAD CONCENTRATIONS OF TRAFFIC RELATED POLLUTANTS Nico Schulte 1 and Akula Venkatram 1
 THE IMPACT OF ROADSIDE BARRIERS ON NEAR-ROAD CONCENTRATIONS OF TRAFFIC RELATED POLLUTANTS Nico Schulte 1 and Akula Venkatram 1 1 Mechanical Engineering, University of California, Riverside, USA Abstract:
THE IMPACT OF ROADSIDE BARRIERS ON NEAR-ROAD CONCENTRATIONS OF TRAFFIC RELATED POLLUTANTS Nico Schulte 1 and Akula Venkatram 1 1 Mechanical Engineering, University of California, Riverside, USA Abstract:
COMSOL Multiphysics Simulation of Flow in a Radial Flow Fixed Bed Reactor (RFBR)
 COMSOL Multiphysics Simulation of Flow in a Radial Flow Fixed Bed Reactor (RFBR) Anthony G. Dixon *,1, Dominic Polcari 1, Anthony Stolo 1 and Mai Tomida 1 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Worcester
COMSOL Multiphysics Simulation of Flow in a Radial Flow Fixed Bed Reactor (RFBR) Anthony G. Dixon *,1, Dominic Polcari 1, Anthony Stolo 1 and Mai Tomida 1 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Worcester
Effects of Climate Change on Pedestrian Comfort: Madrid Case Study
 International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, V0l. 101 (2017) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2017. V101. 14 Effects of Climate Change on Pedestrian Comfort: Madrid Case Study Roberto
International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, V0l. 101 (2017) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2017. V101. 14 Effects of Climate Change on Pedestrian Comfort: Madrid Case Study Roberto
UMA APROXIMAÇÃO METODOLÓGICA PARA O ESTUDO TEMPORAL E ESPACIAL DA QUALIDADE DO AR RELACIONADA ÀS EMISSÕES DE VEÍCULOS EM MADRI E SÃO PAULO
 UMA APROXIMAÇÃO METODOLÓGICA PARA O ESTUDO TEMPORAL E ESPACIAL DA QUALIDADE DO AR RELACIONADA ÀS EMISSÕES DE VEÍCULOS EM MADRI E SÃO PAULO Pedro José Pérez-Martínez lapat-nuance.iag.usp.br Marie Curie
UMA APROXIMAÇÃO METODOLÓGICA PARA O ESTUDO TEMPORAL E ESPACIAL DA QUALIDADE DO AR RELACIONADA ÀS EMISSÕES DE VEÍCULOS EM MADRI E SÃO PAULO Pedro José Pérez-Martínez lapat-nuance.iag.usp.br Marie Curie
9 th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes
 9 th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Germany June 1-4, 24 Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory
9 th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Germany June 1-4, 24 Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory
Large-Eddy Simulation of Porous-Like Canopy Forest Flows Using Real. Field Measurement Data for Wind Energy Application
 Large-Eddy Simulation of Porous-Like Canopy Forest Flows Using Real Field Measurement Data for Wind Energy Application *Zeinab Ahmadi Zeleti¹, Antti Hellsten1,2, Ashvinkumar Chaudhari¹, Heikki Haario1
Large-Eddy Simulation of Porous-Like Canopy Forest Flows Using Real Field Measurement Data for Wind Energy Application *Zeinab Ahmadi Zeleti¹, Antti Hellsten1,2, Ashvinkumar Chaudhari¹, Heikki Haario1
Bruyères-le-Châtel France
 3D SIMULATIONS OF POLLUTANTS ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION AROUND THE BUILDINGS OF AN INDUSTRIAL SITE COMPARISON OF MERCURE CFD APPROACH WITH MICRO-SWIFT-SPRAY SEMI-EMPIRICAL APPROACH Patrick Armand 1, Julien
3D SIMULATIONS OF POLLUTANTS ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION AROUND THE BUILDINGS OF AN INDUSTRIAL SITE COMPARISON OF MERCURE CFD APPROACH WITH MICRO-SWIFT-SPRAY SEMI-EMPIRICAL APPROACH Patrick Armand 1, Julien
Lungs of the city of Eindhoven
 Lungs of the city of Eindhoven ir. Rob Vervoort (r.p.m.vervoort@tue.nl), Eindhoven University of Technology, PDEng-trainee Smart Buildings & Cities, Department of the Built Environment, Building Physics
Lungs of the city of Eindhoven ir. Rob Vervoort (r.p.m.vervoort@tue.nl), Eindhoven University of Technology, PDEng-trainee Smart Buildings & Cities, Department of the Built Environment, Building Physics
Ecole Centrale de Lyon. Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d'acoustique
 Ecole Centrale de Lyon Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d'acoustique Pollutant dispersion through an obstacle array: numerical modelling and experimental investigation Soulhac L., Rios I., Garbero
Ecole Centrale de Lyon Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d'acoustique Pollutant dispersion through an obstacle array: numerical modelling and experimental investigation Soulhac L., Rios I., Garbero
Prediction of Pollutant Emissions from Industrial Furnaces Using Large Eddy Simulation
 Paper # B03 Topic: Turbulent Flames 5 th US Combustion Meeting Organized by the Western States Section of the Combustion Institute and Hosted by the University of California at San Diego March 25-28, 2007.
Paper # B03 Topic: Turbulent Flames 5 th US Combustion Meeting Organized by the Western States Section of the Combustion Institute and Hosted by the University of California at San Diego March 25-28, 2007.
Analysis of the corrosion test process for heat exchangers in corrosion test chambers by CFD simulation
 Analysis of the corrosion test process for heat exchangers in corrosion test chambers by CFD simulation STAR Global Conference, Wien, March 17-19, 2014 R. Stauch, F. Brändle, M. Pfitzer, W. Kühnel MAHLE
Analysis of the corrosion test process for heat exchangers in corrosion test chambers by CFD simulation STAR Global Conference, Wien, March 17-19, 2014 R. Stauch, F. Brändle, M. Pfitzer, W. Kühnel MAHLE
Extensions of TerrSysMP-CO 2 to resolve dynamic processes induced by tall vegetation
 Extensions of TerrSysMP-CO 2 to resolve dynamic processes induced by tall vegetation Markus Übel and Andreas Bott Meteorological Institute, University of Bonn TerrSysMP-CO 2 model domain General Meeting,
Extensions of TerrSysMP-CO 2 to resolve dynamic processes induced by tall vegetation Markus Übel and Andreas Bott Meteorological Institute, University of Bonn TerrSysMP-CO 2 model domain General Meeting,
Volume 7 - Number 12 - November 2011 (29-34) Numerical Modeling of Wind Effect on Plume Dispersion from a Point Source around Buildings
 ISESCO JOURNAL of Science and Technology Volume 7 - Number 12 - November 2011 (29-34) Abstract Dispersion from the polluted point source within the atmosphere is the major concern in the urban areas. The
ISESCO JOURNAL of Science and Technology Volume 7 - Number 12 - November 2011 (29-34) Abstract Dispersion from the polluted point source within the atmosphere is the major concern in the urban areas. The
Flow and heat distribution analysis of different transformer sub-stations
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Flow and heat distribution analysis of different transformer sub-stations To cite this article: H Hasini et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Flow and heat distribution analysis of different transformer sub-stations To cite this article: H Hasini et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
An update from the UK: the CLEAN AIR STRATEGY
 An update from the UK: the CLEAN AIR STRATEGY 1. Slides from Defra presentation on the UK s Clean Air Strategy : under development with draft due in summer 2018 Focus on pollutants SO2, NOx, NH3, VOCs,
An update from the UK: the CLEAN AIR STRATEGY 1. Slides from Defra presentation on the UK s Clean Air Strategy : under development with draft due in summer 2018 Focus on pollutants SO2, NOx, NH3, VOCs,
Spatial Extent of Mobile Source Air Pollution
 Spatial Extent of Mobile Source Air Pollution Ying Zhou, Sc.D. Harvard School of Public Health Northern Transportation and Air Quality Summit Baltimore, MD August 13 1, 28 1 Introduction Hot spot Spatial
Spatial Extent of Mobile Source Air Pollution Ying Zhou, Sc.D. Harvard School of Public Health Northern Transportation and Air Quality Summit Baltimore, MD August 13 1, 28 1 Introduction Hot spot Spatial
Assessment of Toxic Gas Dispersion using Phast and Panache
 Assessment of Toxic Gas Dispersion using Phast and Panache Tejeswi Ramprasad 1, Madhavi Gaonkar 2, Diptendu Das 3 1 ME Research Student, Department of Chemical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering
Assessment of Toxic Gas Dispersion using Phast and Panache Tejeswi Ramprasad 1, Madhavi Gaonkar 2, Diptendu Das 3 1 ME Research Student, Department of Chemical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering
Modeling a Novel Shallow Ground Heat Exchanger
 Modeling a Novel Shallow Ground Heat Exchanger Michele Bottarelli* 1, Marco Bortoloni 1 1 Università degli Studi di Ferrara, Dipartimento di Architettura, Ferrara, Italia *Corresponding author: via Quartieri,
Modeling a Novel Shallow Ground Heat Exchanger Michele Bottarelli* 1, Marco Bortoloni 1 1 Università degli Studi di Ferrara, Dipartimento di Architettura, Ferrara, Italia *Corresponding author: via Quartieri,
Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Greenhouses with Artificial Heat Tube
 World Journal of Mechanics, 2012, 2, 181-187 doi:10.4236/wjm.2012.24022 Published Online August 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjm) Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Greenhouses with Artificial
World Journal of Mechanics, 2012, 2, 181-187 doi:10.4236/wjm.2012.24022 Published Online August 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjm) Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Greenhouses with Artificial
Experiments and volume-of-fluid (VOF) simulations of a three-fluid dam-break
 Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 363 Experiments and volume-of-fluid (VOF) simulations of a three-fluid dam-break M. Furuya 1, Y. Oka 2, M. Satoh 3, S. Lo 4 & T. Arai
Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 363 Experiments and volume-of-fluid (VOF) simulations of a three-fluid dam-break M. Furuya 1, Y. Oka 2, M. Satoh 3, S. Lo 4 & T. Arai
768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES
 768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES Sue Ellen Haupt 1,2, Susan W. Stewart 2, Julia A. Cole 2, Frank J. Zajaczkowski, and Kerrie J. Schmehl 2
768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES Sue Ellen Haupt 1,2, Susan W. Stewart 2, Julia A. Cole 2, Frank J. Zajaczkowski, and Kerrie J. Schmehl 2
modeling using the Pollution Climate Mapping (PCM) model UK NO X and NO 2
 UK NO X and NO 2 modeling using the Pollution Climate Mapping (PCM) model Susannah Grice, John Stedman, Sally Cooke, Andrew Kent, Daniel Brookes, Helen Walker and Keith Vincent 8th December 2010 Presentation
UK NO X and NO 2 modeling using the Pollution Climate Mapping (PCM) model Susannah Grice, John Stedman, Sally Cooke, Andrew Kent, Daniel Brookes, Helen Walker and Keith Vincent 8th December 2010 Presentation
CFD Projects at the Energy Systems Laboratory IIT Gandhinagar
 CFD Projects at the Energy Systems Laboratory IIT Gandhinagar Atul Bhargav atul.bhargav@iitgn.ac.in Assistant Professor Energy Systems Research Overview Hydrocarbon based Fuel Cell Systems collaborations
CFD Projects at the Energy Systems Laboratory IIT Gandhinagar Atul Bhargav atul.bhargav@iitgn.ac.in Assistant Professor Energy Systems Research Overview Hydrocarbon based Fuel Cell Systems collaborations
2.3 A PHOTOCHEMICAL MODEL COMPARISON STUDY: CAMx AND CMAQ PERFORMANCE IN CENTRAL CALIFORNIA
 2.3 A PHOTOCHEMICAL MODEL COMPARISON STUDY: CAMx AND CMAQ PERFORMANCE IN CENTRAL CALIFORNIA Jinyou Liang *, Philip T. Martien, Su-Tzai Soong, and Saffet Tanrikulu Bay Area Air Quality Management District,
2.3 A PHOTOCHEMICAL MODEL COMPARISON STUDY: CAMx AND CMAQ PERFORMANCE IN CENTRAL CALIFORNIA Jinyou Liang *, Philip T. Martien, Su-Tzai Soong, and Saffet Tanrikulu Bay Area Air Quality Management District,
Wind Effects on Retention Time in Highway Ponds Bentzen, Thomas Ruby; Larsen, Torben; Rasmussen, Michael Robdrup
 Aalborg Universitet Wind Effects on Retention Time in Highway Ponds Bentzen, Thomas Ruby; Larsen, Torben; Rasmussen, Michael Robdrup Published in: Proceedings 11th International Conference on Diffuse Pollution
Aalborg Universitet Wind Effects on Retention Time in Highway Ponds Bentzen, Thomas Ruby; Larsen, Torben; Rasmussen, Michael Robdrup Published in: Proceedings 11th International Conference on Diffuse Pollution
Dr. J. Wolters. FZJ-ZAT-379 January Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ
 Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ ZAT-Report FZJ-ZAT-379 January 2003 Benchmark Activity on Natural Convection Heat Transfer Enhancement in Mercury with Gas Injection authors Dr. J. Wolters abstract A
Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ ZAT-Report FZJ-ZAT-379 January 2003 Benchmark Activity on Natural Convection Heat Transfer Enhancement in Mercury with Gas Injection authors Dr. J. Wolters abstract A
Evaluation of Gaussian Plume Model against CFD Simulations through the Estimation of CO and NO Concentrations in an Urban Area
 American Journal of Environmental Sciences Original Research Paper Evaluation of Gaussian Plume Model against CFD Simulations through the Estimation of CO and NO Concentrations in an Urban Area 1,2 Mahmoud
American Journal of Environmental Sciences Original Research Paper Evaluation of Gaussian Plume Model against CFD Simulations through the Estimation of CO and NO Concentrations in an Urban Area 1,2 Mahmoud
CFD Analysis of Earth-Air Heat Exchanger to Evaluate the Effect of Parameters on Its Performance
 PP 14-19 CFD Analysis of Earth-Air Heat Exchanger to Evaluate the Effect of Parameters on Its Performance Arpit Thakur 1, Aashish Sharma 2 1,2 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Lovely Professional
PP 14-19 CFD Analysis of Earth-Air Heat Exchanger to Evaluate the Effect of Parameters on Its Performance Arpit Thakur 1, Aashish Sharma 2 1,2 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Lovely Professional
Environmental Modelling for Air Pollution
 18 UNCONVENTIONAL ANNIVERSARY Environmental Modelling for Air Pollution Giuseppe Brusasca - ARIANET S.r.l. Milano 1 Numerical MODELS allow to represent on the screen the fate of pollutants released into
18 UNCONVENTIONAL ANNIVERSARY Environmental Modelling for Air Pollution Giuseppe Brusasca - ARIANET S.r.l. Milano 1 Numerical MODELS allow to represent on the screen the fate of pollutants released into
TREES IN URBAN STREET CANYONS AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DISPERSION OF AUTOMOBILE EXHAUSTS. Christof Gromke*, Bodo Ruck
 TREES IN URBAN STREET CANYONS AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DISPERSION OF AUTOMOBILE EXHAUSTS Christof Gromke*, Bodo Ruck Laboratory of Building- and Environmental Aerodynamics Institute for Hydromechanics,
TREES IN URBAN STREET CANYONS AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DISPERSION OF AUTOMOBILE EXHAUSTS Christof Gromke*, Bodo Ruck Laboratory of Building- and Environmental Aerodynamics Institute for Hydromechanics,
INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM
 INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM Mandar Tabib, Adil Rasheed, Trond Kvamsdal 12th Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, EERA DeepWind'2015,
INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM Mandar Tabib, Adil Rasheed, Trond Kvamsdal 12th Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, EERA DeepWind'2015,
THE ACTUAL CONTRIBUTION OF WTE PLANTS EMISSIONS TO AIR QUALITY: A CASE STUDY FROM NORTHERN ITALY
 THE ACTUAL CONTRIBUTION OF WTE PLANTS EMISSIONS TO AIR QUALITY: A CASE STUDY FROM NORTHERN ITALY Alberto Cambiaghi 1, Giovanni Lonati 2 1 Brianza Energia Ambiente S.p.A., via Gaetana Agnesi 272, 20832
THE ACTUAL CONTRIBUTION OF WTE PLANTS EMISSIONS TO AIR QUALITY: A CASE STUDY FROM NORTHERN ITALY Alberto Cambiaghi 1, Giovanni Lonati 2 1 Brianza Energia Ambiente S.p.A., via Gaetana Agnesi 272, 20832
Clean Air. for. Kaliningrad
 Clean Air for Kaliningrad Clean Air for Kaliningrad The urban air pollution induced by traffic in Kaliningrad is raising increasing concern. KALAIR is a LIFE-Third Countries Project, co-funded by the European
Clean Air for Kaliningrad Clean Air for Kaliningrad The urban air pollution induced by traffic in Kaliningrad is raising increasing concern. KALAIR is a LIFE-Third Countries Project, co-funded by the European
