UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS. Cambridge International Diploma in Management Professional Level
|
|
|
- Shana Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Diploma in Management Professional Level Scheme of Work 4250 Managing Operations Optional Module
2 MODULE NUMBER (OPTIONAL) 4250: MANAGING OPERATIONS BRIEF INTRODUCTION AND MODULE OUTLINE This optional module deals with the importance of having efficient operations, whether this is in a manufacturing or service environment. It asks candidates to consider the different approaches to operational management and the increasing emphasis on customers and their requirements. Being aware of the different approaches will enable candidates to appraise their own organisations and identify areas for improvement. The module encourages candidates to explore the links between organisational objectives and operations, the customer-supplier chain, the concept of internal and external customers and how operations need to be geared to meet their needs. It also looks at how to set performance standards and manage the operations to ensure these are being maintained. This provides an opportunity to explore a range of quality monitoring approaches and how to plan and schedule work to meet demands. The importance of effective resource planning and management is a key feature of this module. Assessment objectives: 1. Identify operational strategy and its position within the organisation 2. Identify supply chains in the organisation 3. Plan, schedule and manage operational capacity 4. Set and control operational standards 5. Manage resource requirements and use RECOMMENDED PRIOR KNOWLEDGE No prior knowledge is required for this module, but the Unit Introductions do make suggestions about preparatory work and background reading which would help to promote understanding. SUGGESTED TEACHING ORDER / SUMMARY SCHEME OF WORK Apart from the need to ensure that any requirements for prior knowledge are addressed, the module sits comfortably at any point in the Programme. Indeed, this is an optional module and may not be taken by all candidates, but for those that do select it, there are strong links between this and Managing for Quality and it may be advisable to position these two modules together. The Managing Operations module is made up of 5 assessment objectives which follow a logical order from identifying processes to planning and scheduling work and resources. The teaching should follow this logical progression, although there are areas of overlap and tutors may choose to exercise some flexibility here. The column headed Explanation of competence criteria is designed to give an indication of the main content to be covered and should help with this planning detail. UNITS / ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES: SUGGESTED ORDER 1 Identify operational strategy and its position within the organisation This unit requires candidates to identify the link between strategic objectives and operational objectives at department level. It looks at different types of operation and how to set objectives in line with strategy. 2 Identify supply chains in the organisation This helps the candidate to differentiate between internal and external customers and suppliers. It also explores the flow of information between different parts of the process. Supply chain models are introduced and used to show how value can be added at different parts of the process. 3 Plan, schedule and manage operational capacity UCLES
3 This unit looks at how managers can plan and schedule operations to meet objectives. The concept of push and pull systems is introduced and a range of planning tools are made available to the candidates. Capacity planning and scheduling tools, such as Gantt charts are a feature of this unit. The candidates are also required to use various techniques to forecast resource requirements. 4 Set and control operational standards Having established the customer requirements, this unit looks at how standards of performance can be defined and monitored. A range of analytical tools are introduced and candidates are encouraged to explore these with different types of operation. Monitoring systems are introduced and suggestions made for recording findings. The importance of communicating the quality procedures is explored, bringing in the role of the team or individual in maintaining standards. 5 Manage resource requirements and use This unit requires candidates to consider the issues around resource management to support operations. It looks at the human resource, the material resource and the capital resource. Issues such as the skills mix, task allocation and staff planning are explored, as are inventory control, purchasing, facilities layout, maintenance and wastage. Other aspects, such as health and safety and the environment are also included, as these directly affect operations. LIST OF RESOURCES There is a wealth of accessible and readable material about managing operations and resource management. Most general management books include sections on managing operations and there are websites available on the subject too. Some suggestions are included in the Cambridge International Diploma (CID) in Management recommended reading list and the Biz Ed website may be a useful source of information ( ). Candidates should be encouraged to read around the subject and in particular to look at Operations Management by Slack, N., Chambers, S., Harland, C., Harrison, A. and Johnston, R (2003). This established work is published by Financial Times Prentice Hall and supports this module very well and includes small case studies for each section. Other notable works include: Waller, D. (2003), Operations Management: A Supply Chain Approach, Thomson Business Press, Naylor, J. (1996), Introduction to Operations Management, FT Prentice Hall, Bicheno, J. (2000) The Lean Toolbox, Picsie Press, Pande, P., Holpp, L. (2001) What is Six Sigma?, McGraw-Hill. UCLES
4 Unit 1: Identify operational strategy and its position within the organisation Recommended prior knowledge: No prior knowledge is required for this unit although awareness of simple analysis tools such as PESTLE and SWOT would be useful. An awareness of the issues of change management, such as that covered in the core module, Managing Change would also be of assistance. Candidates should be encouraged to read around the subject, particularly in the area of objectives. Operations Management by Slack et al is an excellent resource. In addition, the internet contains a range of sites that look at objective setting and a number of case studies are available. It is useful to look at the Times 100 website, the Biz Ed website or the Chartered Management Institute (CMI). Using the search facility case studies and operational management also brings up useful information. Outline: Identify operational strategy and its position within the organisation requires candidates to analyse the link between strategic objectives and operational objectives and the types of operations that best meet customer requirements. 1.1 Identify the vertical alignment of strategies within the organisation EXPLANATION OF organisational strategy or business objectives and how departmental strategies directly contribute to these SUGGESTED TEACHING ACTIVITIES Ask candidates to write down the mission, key strategy or business objectives of their own organisations. They should then identify the objectives or strategy for each department or business unit. Using a code or a series of + and signs, get them to assess how well each strategy fits with the one above and below it. Alternatively, you could give the candidates some examples to work on, including those that show good vertical alignment and those that do not. Use discussion to bring out the importance of alignment and the possible effects of mismatch. UCLES
5 1.2 Identify appropriate performance objectives of operational strategy identifying the key purposes or performance objectives and the meaning of these to the operation and the enduser Introduce the concept of Quality, Speed, Dependability, Flexibility and Cost as the basis of objectives. Ask the candidates to identify what each these means for operations (for example, quality means error-free processes) and the benefits for the end-user or customer (for example, quality means products/services will meet the specification). 1.3 Identify the type of operation most effective within the organisation to meet customer requirements 1.4 Define and evaluate operational strategy within the organisation different types of operation or systems and how these may differ for manufacturing and service organisations defining the operational strategy using SMART objectives and evaluating these in line with organisational objectives Discuss the importance of prioritising objectives, in terms of customer needs, competitor activities and the position of the product/service in its life cycle. Generate discussion on the relative importance their organisations place on Quality, Speed, Dependability, Flexibility and Cost and use some examples of well known organisations, such as MacDonalds, Body Shop, a car manufacturer and a major airline, for example. Introduce the five main types of operation for manufacturing: Project, Job shop, Batch flow, Line flow and Continuous flow. Discuss when each of these might be used, bringing out the effects of quantity required and the range of different products being produced. Then compare this with a service operation, bringing out the flow of people rather than materials and how the degree of customer involvement impacts on the operation (for example, a restaurant, a bank, a government department or charity), whether the organisation is offering a service package for a range of customers or a specific service for a specific customer. It may be useful to refer back to the organisations used in 1.2 and get candidates to categorise them. Return to the work done earlier on objectives and ask the candidates to write objectives using SMART. At this stage it is useful to provide them with a couple of strategic objectives, perhaps taken from one of the organisations used previously, and ask them to devise some operational objectives that are aligned to these. From this, introduce the concept of operational plans to achieve objectives, again using SMART. Explain the importance of evaluating objectives to ensure that the organisational strategy will be met. Ask the group to identify some evaluation criteria that might be used; you may wish to introduce the 5 criteria suggested by Slack and others: appropriate, comprehensive, coherent, consistent over time and credible. UCLES
6 1.5 Position operations within the organisation identifying links across different operational areas and the importance of having these work in synergy Return to the original activity where candidates looked at vertical alignment. Through discussion, bring out that organisations are not just linear, rather they will have different departments or functions that create horizontal links. Discuss why these functions link and whether this link is formal or informal, leading to the concept of synergy between departments or functions to achieve quality products/services. Using an example from the organisations previously used, select three or more departments and ask the candidates to write down a principal objective for each, then ask them to identify the conflict that might exist between these. (Operations, Finance and Marketing are useful departments to use). Discuss who is responsible for maintaining these links and how this can be encouraged. Bring out the importance of communication here. It is useful at this stage to get the candidates to apply this exercise to their own organisations and share their findings. Using any of the weak links that have been brought out in the above exercises, get the candidates, in small groups, to identify why these have arisen and what can be done about it. UCLES
7 UNIT 2: Identify supply chains in the organisation Recommended prior knowledge: No prior knowledge is required for this unit, but candidates should be encouraged to reflect on the work done in the previous unit, which focuses on different types of operation, strategic and operational objectives and the importance of internal links. Candidates should be encouraged to read around the subject and, in particular to look at the work of Slack et al, referred to in Unit 1. Equally, the web sites referred to in Unit 1 also apply here. Outline: Identify supply chains in the organisation builds on the work done in Unit 1 and explores the concept of each section of the chain being both a supplier and customer of another part of the chain. In order to meet customer requirements and achieve a competitive edge, the concept of adding value is also explored. 2.1 Explain the concept of the customer-supplier chains EXPLANATION OF an awareness of all the stages in the operation both within the organisation and beyond, to customers and suppliers. How this can be used to identify disruptions or to add value SUGGESTED TEACHING ACTIVITIES Introduce Waller s definition of a supply chain (or similar). Link to the importance of the flow of information as well as products or services. Use real examples, possibly taken from the earlier organisations, to illustrate this diagrammatically. Bring out the concept of webs of supply chains, as illustrated by Slack and others. Introduce different types of supply chain, such as Naylor s inventorybased models. Ask candidates to consider the management responsibilities at each stage of the chain, then use group discussion to bring out the importance of working closely with all parties in the chain, both internal and external. UCLES
8 2.2 Identify the supply chains within and outside an organisation applying the above understanding in practice and identifying supply chains Select a couple of organisations known to the candidates and ask them to devise a supply chain, then consider how effective this is and the implications for management at each stage. If there is time, you may wish to get the candidates to do this for their own organisations and share results. Look at key objectives: strategically the organisation should aim to drive the entire chain in the direction of satisfying customers. Now get candidates to consider the objectives to achieve this aim and what barriers are likely to arise. Extend the barriers to the global market and bring out the effects of external pressures. Introduce the concept of adding value to each stage in the chain, considering the different levels, then discuss value-added cells and the main ways to add value. You may wish to introduce Porter s value chain analysis, then get the group to apply this to one of the earlier examples used. Get them to identify what value-added effect each transformation has. Conclude this section by linking Porter s value chain concept with gaining competitive advantage. Get the candidates to now consider this for the previous activity. UCLES
9 UNIT 3: Plan, schedule and manage operational capacity Recommended prior knowledge: No prior knowledge is required other than that covered in Units 1 to 4 and candidates should be encouraged to reflect on the work done so far on suppliers and customers and the different types of operation. The use of Gantt charts is included, so the ability to use computer software to produce such charts would be helpful. The following are useful resources to assist: Microsoft Project 2000 Step by Step, Microsoft Press International, Chatfield, C., (2000); Operations Management, FT Prentice Hall, Slack et al (2000; revised version 2003). Outline: This Unit requires candidates to review different systems of planning and forecasting to achieve operational objectives, then to use scheduling tools, such as Gantt charts and other appropriate IT applications for planning operational activities. Techniques of forecasting are covered, as well as risk analysis and contingency planning. 3.1 Plan operations to achieve performance objectives EXPLANATION OF approaches to planning operations SUGGESTED TEACHING ACTIVITIES Introduce the concept of capacity and get the group to come up with some examples for the case study organisations. Differentiate between demand and load. Ask the group to identify what is meant by resources, bringing out: equipment and facilities, materials, staff and information and the effect of resources on capacity. Explain MRP (Materials requirement planning) and JIT (Just in time) and MRP2 (manufacturing resource planning) and how technology has enhanced these as planning techniques. Explain the difference between push and pull systems and use your case study organisations to illustrate these. Link this to waste reduction. Explain the concept of Kanban as a planning and control technique. Explore different approaches to capacity planning, such as chase demand planning, demand management, level capacity planning etc, again linking to the case study organisations. UCLES
10 3.2 Schedule operations scheduling tools and techniques 3.3 Forecast resource requirements techniques for forecasting the resources required to meet demand Explain the MPS (master production schedule) and its importance in an organisation. Ask the candidates to identify the information required to devise an MPS. Link this to MRP. Differentiate between forward and backward scheduling, then introduce the Gantt chart as a planning tool. Get the candidates in small groups to devise a Gantt chart for a simple operation, such as a fast food outlet. Ask the group what could go wrong, leading to contingency planning. Ask the group what is meant by forecasting and why it is used. Introduce techniques for forecasting, including judgemental, customer-based, predictive and causal. Using their own organisation or an example provided, ask the candidates to appraise the forecasting techniques used in terms of why they are used, what information they provide and the degree of accuracy. Explain how statistical analysis can be used in forecasting, giving examples from the case studies used. UCLES
11 UNIT 4: Set and control operational standards Recommended prior knowledge: No prior knowledge is required for this unit, other than that covered in Units 1 to 3, however, it might be useful if candidates were aware of national and international control systems, such as ISO 9000, although this is not essential. Much of the content of this unit will have been covered in the Managing for Quality module, so, if this has already been completed, the candidates should be encouraged to review the work done, as it can be applied directly here. Outline: Setting and controlling operational standards requires candidates to analyse processes, set standards of performance and develop processes and procedures for monitoring purposes. Established process control models are looked at and the communicating of such procedures is also covered. Candidates will be expected to identify the most appropriate process control and monitoring system for different operations. Introduce the 4-stage approach of: identifying the PROCESSES, setting the STANDARDS, MEASURING performance against standards and writing PROCEDURES to describe how the processes should be carried out. Use this model to address the requirements of Unit Analyse processes and set standards of performance EXPLANATION OF using analysis techniques to identify strengths and weaknesses in the chain and set performance standards SUGGESTED TEACHING ACTIVITIES Discuss what is meant by a process, then describe how to flow chart a typical process; again it is useful to use the previous case studies. Get the candidates to analyse a process, either from a case study you have provided, or from their own organisation, by creating a flow chart, then analysing it to identify the purpose of what is done, where, its sequence, who does it and the methods used. The aim here is to identify what is working well and what needs improving. 4.2 Control operational standards of performance using quality control methods to ensure standards are being maintained Introduce established analysis models, such as Ishikawa fishbone, variation analysis, critical path and bottleneck identification and apply these to the activity above. Explain the importance of having quality standards as a basis for measuring operational performance. Using previous case studies, work with the group to identify some known standards of performance, then introduce the concept of externally set process control standards, such as TQM, ISO 9000, Health and Safety etc. Include here any local or national standards and explain that these are often in addition to the customer-led UCLES
12 4.3 Create and document procedures for systems and processes 4.4 Communicate Quality Standards identifying and Establishing appropriate monitoring procedures and systems ensuring everyone is aware of the standards of performance expected standards. Having set the standards, it is then important to have a monitoring system. Introduce Statistical Process Control (SCP) as a means of getting individual departments or teams to take responsibility for standards of performance. Ask the candidates to identify how this could be used and the benefits to be gained. Explore process capability and the concept of tolerance levels, then ask the group to devise some monitoring systems for your case study example. Lead them into the use of control charts. Explain that once a process is working satisfactorily, it can be incorporated into a procedure. Refer back to established procedures, such as ISO Ask the group to identify what should be in a procedure, then get them to create one for the case study you have been working on. Discuss who should have access to the procedure and how it should be communicated. Lead into the importance of giving people the responsibility for quality of performance. This may involve issues such as team briefs, delegation, empowerment, a customer-led or quality culture. The key issue is communication and you may wish to get the candidates to consider issues of communication in the case study example and their own organisations. Bring out: quality circles, improvement groups and Kaizen as ways of communicating and controlling quality. You may also introduce the five Ss from Japan as a quality improvement tool. UCLES
13 UNIT 5: Manage resource requirements and use Recommended prior knowledge: No prior knowledge is required, but candidates should be encouraged to reflect on the work done in the previous units. Issues of managing people are included here and the work done on the Managing Teams module will be useful here. It might be useful to encourage candidates to review the work done on Evaluating Team Performance, as much of it will apply here. Equally, work done in the Managing Finance module could be useful when looking at inventory costs. Outline: This unit looks at all the resource implications of managing operations: the human resource, the material resource and the capital resource. Candidates are required to review the skill mix of the staff in order to allocate tasks, control inventory in a cost-efficient manner and purchase and maintain equipment and facilities in line with operational demands and health and safety considerations. 5.1 Manage people, the human resource EXPLANATION OF planning the staff to meet the demands, including matching skills to tasks SUGGESTED TEACHING ACTIVITIES Using one of the case study organisations, get the group to list the key people skills required to meet the operational demands. Group the responses into technical competence, management skills and interpersonal skills. Discuss the relative importance of each of these according to the operational demands. Introduce a skills matrix and show how this can be used to plan staff needs and manage it. Link to utilisation of strengths and the need for training and development. Explore key issues around allocation of tasks to individuals in terms of the nature of the task, the customer relationship, the level of skill required and the equipment to be used. Devise a team activity for the group with clear outcomes and ask them to complete a skills matrix and allocate tasks. Having completed this and the team activity, ask them to review how well their people planning skills were. Use this exercise to explore flexible approaches to managing the people, such as multi-skilling and changes in work practices. Link all of this to the forecasting activities carried out previously. UCLES
14 5.2 Manage inventory or stock, the material resource 5.3 Manage equipment and facilities, the capital resource planning and maintaining the materials and stock required to meet the demands planning and managing the facilities, including equipment, to meet the demands Using the case study organisations, ask the group to list examples of inventory, stock or materials held by them. Distinguish between different types of inventory and why these are held. Return to the case studies and get the candidates to identify inventory and why it is held. Generate discussion around the costs associated with inventory and ask the group to come up with ideas for controlling costs. Here you can link to JIT and introduce EOQ (economic order quantity) and the importance of having good relationships with suppliers. Brainstorm what is meant by equipment and facilities. Discuss how equipment is selected and what the trends are towards automation. Discuss the links between equipment and the layout of facilities and the effect on operations; bring out functional and cellular layouts, assembly lines and continuous flow. Again you will be able to draw on the case study organisations. Compare this with service layouts. Get the candidates to appraise some familiar layouts in terms of effectiveness, utilisation of space, safety and customer requirements. Stress the importance of having all equipment working properly and introduce different approaches to maintenance, including scheduling, preventative maintenance and total productive maintenance (TPM). Here you could introduce relevant rules and regulations regarding health and safety. Discuss the need to reduce cost and waste and the different approaches to this; using the case study organisations, get the candidates to identify possible sources of waste and strategies for reducing this. Explore cost savings to the organisation as well as the positive impact on the environment (internal and external). UCLES
The senior assessor s report aims to provide the following information: An indication of how to approach the examination question
 INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES The senior assessor s report is written in order to provide candidates with feedback relating to the examination. It is designed as a tool for candidates - both those who have
INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES The senior assessor s report is written in order to provide candidates with feedback relating to the examination. It is designed as a tool for candidates - both those who have
Strategic Quality and Systems Management
 Unit 11: Strategic Quality and Systems Management Unit code: QCF Level 7: H/602/2327 BTEC Professional Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 30 Unit aim This unit provides the learner with an understanding
Unit 11: Strategic Quality and Systems Management Unit code: QCF Level 7: H/602/2327 BTEC Professional Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 30 Unit aim This unit provides the learner with an understanding
Diploma in Management (890) Operations Management
 Diploma in Management (890) Operations Management Prerequisites: Basic business knowledge. Corequisites: Completion of Certificate in Business Studies or equivalence. Aim: Examines the concepts for designing,
Diploma in Management (890) Operations Management Prerequisites: Basic business knowledge. Corequisites: Completion of Certificate in Business Studies or equivalence. Aim: Examines the concepts for designing,
LearningZone Mapping Against ILM Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership
 LearningZone Mapping Against ILM Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership ILM Learning Zone Mapping Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership 1 of 23 Develop a Strategic
LearningZone Mapping Against ILM Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership ILM Learning Zone Mapping Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership 1 of 23 Develop a Strategic
Producing Quality Goods and Services
 Producing Quality Goods and Services Prentice Hall, 2004 Business In Action 2e Chapter 8-1 What Is Production? Leading Planning Production Operations Management (POM) Organizing Controlling Prentice Hall,
Producing Quality Goods and Services Prentice Hall, 2004 Business In Action 2e Chapter 8-1 What Is Production? Leading Planning Production Operations Management (POM) Organizing Controlling Prentice Hall,
Producing Quality Goods and Services. What Is Production? The Conversion Process. Production Operations Management (POM) The Value Chain.
 Producing Quality Goods and Services Prentice Hall, 2007 Excellence in Business, 3e Chapter 9-1 What Is Production? Leading Planning Production Operations Management (POM) Organizing Controlling Prentice
Producing Quality Goods and Services Prentice Hall, 2007 Excellence in Business, 3e Chapter 9-1 What Is Production? Leading Planning Production Operations Management (POM) Organizing Controlling Prentice
Strategic Marketing is a 15-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules.
 Module Specification: Strategic Marketing Strategic Marketing is a 15-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules. To gain the CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing a
Module Specification: Strategic Marketing Strategic Marketing is a 15-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules. To gain the CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing a
King Saud University College Of Business Administration Management Department Course: Operations Management
 King Saud University College Of Business Administration Management Department Course: Section: 35003 ادا 371 Second Semester - 1432/1433 Instructor: Dr. Abdullah M. Aldakhil Office Hours: Saturday & Sunday
King Saud University College Of Business Administration Management Department Course: Section: 35003 ادا 371 Second Semester - 1432/1433 Instructor: Dr. Abdullah M. Aldakhil Office Hours: Saturday & Sunday
Manufacturing Environment
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Meaning and Definition... 1 Operations Management in Organization Chart... 2 Objectives of Operations Management... 3 Functions of Operations Management... 3 1.2 Operations
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Meaning and Definition... 1 Operations Management in Organization Chart... 2 Objectives of Operations Management... 3 Functions of Operations Management... 3 1.2 Operations
Supply chain management theory, NQF level 6, Credits 10
 SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGER Knowledge modules 132401-001-01-00 KM-01 Supply chain theory, NQF level 6, Credits 10 132401-001-01-00 KM-02 Supply chain service delivery operational planning, NQF level 6, Credits
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGER Knowledge modules 132401-001-01-00 KM-01 Supply chain theory, NQF level 6, Credits 10 132401-001-01-00 KM-02 Supply chain service delivery operational planning, NQF level 6, Credits
YOUR TRAINING PARTNER
 YOUR TRAINING PARTNER CIPS International Certificate (CIPS Exam Preparatory Course) 2011 Baku, Azerbaijan PRO LOG Training Center is Registered International Study Centre with The Chartered Institute of
YOUR TRAINING PARTNER CIPS International Certificate (CIPS Exam Preparatory Course) 2011 Baku, Azerbaijan PRO LOG Training Center is Registered International Study Centre with The Chartered Institute of
Resource Portal for Management Sciences Students, Teachers and Business Professionals. Visit
 Resource Portal for Management Sciences Students, Teachers and Business Professionals Visit www.accountancyknowledge.com MCQs 1-50 1. Which of the following statements is correct? (a) Marketing is the
Resource Portal for Management Sciences Students, Teachers and Business Professionals Visit www.accountancyknowledge.com MCQs 1-50 1. Which of the following statements is correct? (a) Marketing is the
Masters Degree in Business Administration & Diploma in Management Studies. Vasiliki Kazantzi, PhD
 Technological Education Institute of Larissa Department of Project Management School of Business Administration Staffordshire University, Business School Masters Degree in Business Administration & Diploma
Technological Education Institute of Larissa Department of Project Management School of Business Administration Staffordshire University, Business School Masters Degree in Business Administration & Diploma
Question Paper Code: 60837
 Reg.NO: Question Paper Code: 60837 B.E / B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER / DECEMBER 2016 Eighth Semester Mechanical Engineering ME2036 / ME802 / 10122 ME E144 PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL (Common
Reg.NO: Question Paper Code: 60837 B.E / B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER / DECEMBER 2016 Eighth Semester Mechanical Engineering ME2036 / ME802 / 10122 ME E144 PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL (Common
Technical specifications for City & Guilds Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership (8624)
 Technical specifications for City & Guilds Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership (8624) Version: 1.0 (March 2017) Version 1.0 (March 2017) Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management
Technical specifications for City & Guilds Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership (8624) Version: 1.0 (March 2017) Version 1.0 (March 2017) Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Quality Management: An Introduction. Unit code: DT8Y 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Quality Management: An Introduction Unit code: DT8Y 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to allow candidates to explain
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Quality Management: An Introduction Unit code: DT8Y 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to allow candidates to explain
INSTRUCTORS GUIDE FOR USING THE THE ENCYCLOPEDIA OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT by Professor Arthur V. Hill Revised November 21, 2018
 INSTRUCTORS GUIDE FOR USING THE THE ENCYCLOPEDIA OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT by Professor Arthur V. Hill Revised November 21, 2018 Introduction Many instructors have found the Encyclopedia of Operations Management
INSTRUCTORS GUIDE FOR USING THE THE ENCYCLOPEDIA OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT by Professor Arthur V. Hill Revised November 21, 2018 Introduction Many instructors have found the Encyclopedia of Operations Management
APS1028 Operations and Production Management - 10 Day Spring 2018 (9AM- Noon) Weeks; 4 th June to 8 th June 2017 and 18 th June to 22 nd June 2018.
 - 10 Day Spring 2018 (9AM- Noon) Weeks; 4 th June to 8 th June 2017 and 18 th June to 22 nd June 2018. Course Outline Operations Management is the systematic approach and control of the processes that
- 10 Day Spring 2018 (9AM- Noon) Weeks; 4 th June to 8 th June 2017 and 18 th June to 22 nd June 2018. Course Outline Operations Management is the systematic approach and control of the processes that
Lean Manufacturing. Introduction & Background to Lean
 Lean Manufacturing Introduction & Background to Lean Professor Trevor Spedding P160 t.spedding@gre.ac.uk 01634 883425 Grahame Baker P237 g.baker@gre.ac.uk 01634 883302 Sam Berkhauer P345 BS983@gre.ac.uk
Lean Manufacturing Introduction & Background to Lean Professor Trevor Spedding P160 t.spedding@gre.ac.uk 01634 883425 Grahame Baker P237 g.baker@gre.ac.uk 01634 883302 Sam Berkhauer P345 BS983@gre.ac.uk
MCQ: Unit-1: introduction to Operations and Supply Chain management
 MCQ: Unit-1: introduction to Operations and Supply Chain management 1."Quality is defined by the customer" is : An unrealistic definition of quality A user-based definition of quality A manufacturing-based
MCQ: Unit-1: introduction to Operations and Supply Chain management 1."Quality is defined by the customer" is : An unrealistic definition of quality A user-based definition of quality A manufacturing-based
ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam: Operations Management Name Total Scors: ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Planning is the process of coping with changes
Exam: Operations Management Name Total Scors: ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Planning is the process of coping with changes
Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership. Qualification Specification
 Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership Qualification Specification ProQual 2014 Contents Page Introduction 3 The Qualifications and Credit Framework (QCF) 3 Qualification profile 4
Level 7 NVQ Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership Qualification Specification ProQual 2014 Contents Page Introduction 3 The Qualifications and Credit Framework (QCF) 3 Qualification profile 4
Chart 1.1 The business planning process
 1 1 Introduction This book is designed for those with an inspired idea who wish to translate it into a successful new business or incorporate it in an existing business. Usually, the first challenge for
1 1 Introduction This book is designed for those with an inspired idea who wish to translate it into a successful new business or incorporate it in an existing business. Usually, the first challenge for
5) To understand how Enterprise Resource Planning and MRPII CAD / CAM/CIM and automated factory systems are used in managing operations
 - Fall 2018-100% Online starting 10 th September 2018: There is only one inclass seminar Room RS208 (9AM Noon) Course Outline Operations Management is the systematic approach and control of the processes
- Fall 2018-100% Online starting 10 th September 2018: There is only one inclass seminar Room RS208 (9AM Noon) Course Outline Operations Management is the systematic approach and control of the processes
Level 5. Nov Senior Assessor s Report. Advanced Diploma Purchasing and Supply. Operations Management in the Supply Chain L5-12
 Advanced Diploma Purchasing and Supply Operations Management in the Supply Chain L5-12 Level 5 Senior Assessor s Report Nov 2008 L5-12/SA report/nov 2008 1 INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES The senior assessor
Advanced Diploma Purchasing and Supply Operations Management in the Supply Chain L5-12 Level 5 Senior Assessor s Report Nov 2008 L5-12/SA report/nov 2008 1 INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES The senior assessor
CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing
 CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing Mastering Metrics (2201) April 2019 Assignment The assignment comprises THREE compulsory tasks Task 1 is worth 30 marks Task 2 is worth 40 marks Task 3 is
CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing Mastering Metrics (2201) April 2019 Assignment The assignment comprises THREE compulsory tasks Task 1 is worth 30 marks Task 2 is worth 40 marks Task 3 is
ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam: Operations Management Name Total Scors: ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Aggregated demand forecasts are a key element
Exam: Operations Management Name Total Scors: ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Aggregated demand forecasts are a key element
CHARTERED BANKER DIPLOMA 2016 MODULE SPECIFICATION Operations Management Credit Value: SCQF Level 10 / EQF Level 6 SCQF Credit Points 10
 Title: CHARTERED BANKER DIPLOMA 2016 MODULE SPECIFICATION Operations Management Credit Value: SCQF Level 10 / EQF Level 6 SCQF Credit Points 10 Aim: Access Statement: Programmes of study to which unit
Title: CHARTERED BANKER DIPLOMA 2016 MODULE SPECIFICATION Operations Management Credit Value: SCQF Level 10 / EQF Level 6 SCQF Credit Points 10 Aim: Access Statement: Programmes of study to which unit
Unit: Strategic Operations Management Assignment title: An Evaluation of Rolls Royce December Marking Scheme
 Unit: Strategic Operations Management Assignment title: An Evaluation of Rolls Royce December 2015 Marking Scheme Markers are advised that, unless a task specifies that an answer be provided in a particular
Unit: Strategic Operations Management Assignment title: An Evaluation of Rolls Royce December 2015 Marking Scheme Markers are advised that, unless a task specifies that an answer be provided in a particular
MTP_ Intermediate _Syllabus 2016_Dec 2017_Set 2. Paper 9 OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT & STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
 Paper 9 OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT & STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 9- OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT &
Paper 9 OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT & STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 9- OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT &
CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing
 CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing Digital Strategy (2203) April 2019 Assignment The assignment comprises THREE compulsory tasks Task 1 is worth 30 marks Task 2 is worth 40 marks Task 3 is worth
CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing Digital Strategy (2203) April 2019 Assignment The assignment comprises THREE compulsory tasks Task 1 is worth 30 marks Task 2 is worth 40 marks Task 3 is worth
LEAN PROCUREMENT.
 LEAN PROCUREMENT www.fourprinciples.com BACKGROUND Procurement s core responsibilities have traditionally provided purchased materials and services on time, at the lowest costs, and highest quality to
LEAN PROCUREMENT www.fourprinciples.com BACKGROUND Procurement s core responsibilities have traditionally provided purchased materials and services on time, at the lowest costs, and highest quality to
CAD/CAM CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION. Dr. Ibrahim Naimi
 CAD/CAM CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Production System Facilities The facilities in the production system are the factory, production machines and tooling, material handling equipment,
CAD/CAM CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Production System Facilities The facilities in the production system are the factory, production machines and tooling, material handling equipment,
Manufacturing Information Systems. deden08m.com 1
 Manufacturing Information Systems deden08m.com 1 Computers in the Physical System CAD (computer-aided design) Design database CAM (computer aided manufacturing) Robotics deden08m.com 2 Reorder Point (ROP)
Manufacturing Information Systems deden08m.com 1 Computers in the Physical System CAD (computer-aided design) Design database CAM (computer aided manufacturing) Robotics deden08m.com 2 Reorder Point (ROP)
Part 3 : 11/10/10 21:33:42. The four factors that derive from a company's distinctive competencies and which create competitive advantage are
 Question 1 - HOCK CMA P3A H45 - Strategic Planning The four factors that derive from a company's distinctive competencies and which create competitive advantage are A. the value (utility) customers place
Question 1 - HOCK CMA P3A H45 - Strategic Planning The four factors that derive from a company's distinctive competencies and which create competitive advantage are A. the value (utility) customers place
7/8/2017 CAD/CAM. Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi. Chapter one. Introduction
 CAD/CAM Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter one Introduction 1 2 3 Production System Facilities The facilities in the production system are the factory, production machines and tooling, material handling equipment,
CAD/CAM Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter one Introduction 1 2 3 Production System Facilities The facilities in the production system are the factory, production machines and tooling, material handling equipment,
L3 Certificate in Leadership and Management Candidate Pack
 L3 Certificate in Leadership and Management Candidate Pack 2013/14 Clive Betts Centre Co-ordinator ILM Candidate Pack L3 Certificate L&M 2013/14 July 2013 Page 1 of 25 Qualification flowchart Complete
L3 Certificate in Leadership and Management Candidate Pack 2013/14 Clive Betts Centre Co-ordinator ILM Candidate Pack L3 Certificate L&M 2013/14 July 2013 Page 1 of 25 Qualification flowchart Complete
Graded Unit Title: Electronic Engineering: Graded Unit 2
 General information for centres This d Unit has been validated as part of the SQA Advanced Diploma in Electronic Engineering award. Centres are required to develop the assessment instrument in accordance
General information for centres This d Unit has been validated as part of the SQA Advanced Diploma in Electronic Engineering award. Centres are required to develop the assessment instrument in accordance
THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS NOVEMBER 2015 PROFESSIONAL EXAMINATIONS BUSINESS MANAGEMENT & INFORMATION SYSTEMS EXAMINERS GENERAL COMMENTS
 THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS NOVEMBER 2015 PROFESSIONAL EXAMINATIONS BUSINESS MANAGEMENT & INFORMATION SYSTEMS EXAMINERS GENERAL COMMENTS GENERAL PERFORMANCE The performance of candidates was
THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS NOVEMBER 2015 PROFESSIONAL EXAMINATIONS BUSINESS MANAGEMENT & INFORMATION SYSTEMS EXAMINERS GENERAL COMMENTS GENERAL PERFORMANCE The performance of candidates was
Chapter 11. In-Time and Lean Production
 Chapter 11 Just-In In-Time and Lean Production What is JIT? Producing only what is needed, when it is needed A philosophy An integrated management system JIT s mandate: Eliminate all waste Basic Elements
Chapter 11 Just-In In-Time and Lean Production What is JIT? Producing only what is needed, when it is needed A philosophy An integrated management system JIT s mandate: Eliminate all waste Basic Elements
Understanding the Management Process
 Chapter 6 Understanding the Management Process 1 Define what management is. 2 Describe the four basic management functions: planning, organizing, leading and motivating, and controlling. 3 Distinguish
Chapter 6 Understanding the Management Process 1 Define what management is. 2 Describe the four basic management functions: planning, organizing, leading and motivating, and controlling. 3 Distinguish
9707 BUSINESS STUDIES
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9707 BUSINESS STUDIES
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9707 BUSINESS STUDIES
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Level BUSINESS 9609/32 Paper 3 Case Study MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 100 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Level BUSINESS 9609/32 Paper 3 Case Study MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 100 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to
Digital Strategy is a 15-credit elective module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules.
 Module Specification: Digital Strategy Digital Strategy is a 15-credit elective module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules. To gain the CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing a pass in
Module Specification: Digital Strategy Digital Strategy is a 15-credit elective module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules. To gain the CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing a pass in
20 SUBJECT AREA: MODULE TYPE: Double SEMESTER OFFERED: 1 through 2. Course(s) for which module is acceptable and status in course:
 BRIGHTON BUSINESS SCHOOL MOULSECOOMB MODULAR SCHEME OP282 TITLE: Business Operations & Systems LEVEL: 2 CREDIT RATING: 20 SUBJECT AREA: Business Systems MODULE TYPE: Double SEMESTER OFFERED: 1 through
BRIGHTON BUSINESS SCHOOL MOULSECOOMB MODULAR SCHEME OP282 TITLE: Business Operations & Systems LEVEL: 2 CREDIT RATING: 20 SUBJECT AREA: Business Systems MODULE TYPE: Double SEMESTER OFFERED: 1 through
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level BUSINESS STUDIES 9707/03 Paper 3 Case Study For Examination from 2011 SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME 3 hours MAXIMUM
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level BUSINESS STUDIES 9707/03 Paper 3 Case Study For Examination from 2011 SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME 3 hours MAXIMUM
ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam: Operations Management Name Total Scors: ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The EOQ formula has been criticised in a
Exam: Operations Management Name Total Scors: ID Class MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The EOQ formula has been criticised in a
Higher National Unit specification: general information. Graded Unit 2
 Higher National Unit specification: general information This Graded Unit has been validated as part of the Coaching and Developing Sport Award. Centres are required to develop the assessment instrument
Higher National Unit specification: general information This Graded Unit has been validated as part of the Coaching and Developing Sport Award. Centres are required to develop the assessment instrument
SEG Awards ABC Level 5 Diploma in Procurement
 SEG Awards ABC Level 5 Diploma in Procurement Qualification Guidance [60140252] D7043-C5 Issue 3 60140252 August 2018 About Us At the Skills and Education SEG Awards (ABC) 1 we continually invest in high
SEG Awards ABC Level 5 Diploma in Procurement Qualification Guidance [60140252] D7043-C5 Issue 3 60140252 August 2018 About Us At the Skills and Education SEG Awards (ABC) 1 we continually invest in high
1. (a) What factors have contributed to the 10
 MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME Term-End Examination 00 December, 2009 (Y) CD : PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 (Weightage 70%) Note : Section A has five questions carrying 20
MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME Term-End Examination 00 December, 2009 (Y) CD : PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Time : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 (Weightage 70%) Note : Section A has five questions carrying 20
APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS
 APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS About this Topic Outline This outline details the concepts and applications coved in all five of the APICS Principles of
APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS About this Topic Outline This outline details the concepts and applications coved in all five of the APICS Principles of
Operations Management and Quality
 Slide 1 BA-101 Introduction to Business Operations Management and Quality Chapter Seven 1-1 Slide 2 What Does Operations Mean Today? Operations (Production) activities involved in making products goods
Slide 1 BA-101 Introduction to Business Operations Management and Quality Chapter Seven 1-1 Slide 2 What Does Operations Mean Today? Operations (Production) activities involved in making products goods
Organizational Effectiveness
 Organizational Effectiveness Second Edition Donna C. S. Summers I niwrsity of Dayton Columbus, O Contents Organizational Effectiveness. ' 2 What is an effective organization? 4 ' How is an effective organization
Organizational Effectiveness Second Edition Donna C. S. Summers I niwrsity of Dayton Columbus, O Contents Organizational Effectiveness. ' 2 What is an effective organization? 4 ' How is an effective organization
Chapter Eight. Learning Objectives
 Chapter Eight Production Management 8 1 Learning Objectives 1. Explain the nature of production. 2. Outline how the conversion process transforms raw materials, labor, and other resources into finished
Chapter Eight Production Management 8 1 Learning Objectives 1. Explain the nature of production. 2. Outline how the conversion process transforms raw materials, labor, and other resources into finished
A marked improvement in the overall standard of work was shown for this session.
 Module report Level: Diploma in Professional Marketing Module: Strategic Marketing Please refer to the December 2015 assessment Most candidates produced a solid strategic plan using a SOSTAC (PR Smith)
Module report Level: Diploma in Professional Marketing Module: Strategic Marketing Please refer to the December 2015 assessment Most candidates produced a solid strategic plan using a SOSTAC (PR Smith)
Content Specification Outline
 Content Specification Outline Copyright 2017 Institute of Certified Management Accountants Updated 8/25/17 Institute of Certified Management Accountants Content Specification Outline Certified in Strategy
Content Specification Outline Copyright 2017 Institute of Certified Management Accountants Updated 8/25/17 Institute of Certified Management Accountants Content Specification Outline Certified in Strategy
a2 applied business UNIT 10 PROMOTIONAL ACTIVITIES
 a2 applied business UNIT 10 PROMOTIONAL ACTIVITIES YEAR 13 A2 APPLIED BUSINESS UNIT 10: PROMOTIONAL ACTIVITIES Coursework Task How much is this coursework worth? Unit 8 Unit 10 Unit 15 Business Planning
a2 applied business UNIT 10 PROMOTIONAL ACTIVITIES YEAR 13 A2 APPLIED BUSINESS UNIT 10: PROMOTIONAL ACTIVITIES Coursework Task How much is this coursework worth? Unit 8 Unit 10 Unit 15 Business Planning
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE ( Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai)
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE ( Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE ( Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
MSc Management (International Standards) Programme Design. Academic Year
 MSc Management (International Standards) Programme Design Academic Year 2014-15 1 MSc Management (International Standards) The MSc Management programme is divided into three distinct sections: The first
MSc Management (International Standards) Programme Design Academic Year 2014-15 1 MSc Management (International Standards) The MSc Management programme is divided into three distinct sections: The first
Principles of Production & Inventory Management PPIM
 Principles of Production & Inventory Management PPIM PPIM course sessions. 1. Manufacturing Strategies & Resource Management 2. Product Development Cycle 3. Forecasting and Forecasting Techniques 4. Production
Principles of Production & Inventory Management PPIM PPIM course sessions. 1. Manufacturing Strategies & Resource Management 2. Product Development Cycle 3. Forecasting and Forecasting Techniques 4. Production
Level 5 5SK. Valid for December 2015 exams. TP 2.2 / advice / 6:2011 / V1
 Skills for the SME Manager Level 5 5SK Valid for December 2015 exams Institute of Financial Accountants The Podium, 1 Eversholt Street Euston London NW1 2DN T: +44 (0)20 7554 0730 F: +44(0)20 7554 0731
Skills for the SME Manager Level 5 5SK Valid for December 2015 exams Institute of Financial Accountants The Podium, 1 Eversholt Street Euston London NW1 2DN T: +44 (0)20 7554 0730 F: +44(0)20 7554 0731
Contents Introduction to Logistics... 6
 CONTENTS Contents... 3 1. Introduction to Logistics... 6 1.1 Interfaces between Logistics Manufacturing....7 1.2 Logistics: Manufacturing issues in Customer Service...9 I.3 Production scheduling...10 1.4
CONTENTS Contents... 3 1. Introduction to Logistics... 6 1.1 Interfaces between Logistics Manufacturing....7 1.2 Logistics: Manufacturing issues in Customer Service...9 I.3 Production scheduling...10 1.4
Level: Diploma In Professional Marketing. Module: Strategic Marketing. Please refer to the July 2016 assessment
 Module report Level: Diploma In Professional Marketing Module: Strategic Marketing Please refer to the July 2016 assessment Overarching performance and key points: Organisational summaries were generally
Module report Level: Diploma In Professional Marketing Module: Strategic Marketing Please refer to the July 2016 assessment Overarching performance and key points: Organisational summaries were generally
Global Management Academy
 Global Management Academy ILM LEVEL 3 QUALIFICATIONS HANDBOOK Global Management Academy www.globalmanagementacademy.co.uk CONTENTS Global Management Academy ILM Level 3 Program... 5 Qualification Specifications...
Global Management Academy ILM LEVEL 3 QUALIFICATIONS HANDBOOK Global Management Academy www.globalmanagementacademy.co.uk CONTENTS Global Management Academy ILM Level 3 Program... 5 Qualification Specifications...
Planning. Planning Horizon. Stages of Planning. Dr. Richard Jerz
 Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate-range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate-range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Advanced Diploma in Banking and Leadership in a Digital Age Module Specification: Bank Strategy, Operations and Technology
 Advanced Diploma in Banking and Leadership in a Digital Age Module Specification: Bank Strategy, Operations and Technology Title: Bank Strategy, Operations and Technology Level: SCQF Level 10/EQF Level
Advanced Diploma in Banking and Leadership in a Digital Age Module Specification: Bank Strategy, Operations and Technology Title: Bank Strategy, Operations and Technology Level: SCQF Level 10/EQF Level
Digital Strategy is a 15-credit elective module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules.
 Module Specification: Digital Strategy Digital Strategy is a 15-credit elective module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules. To gain the CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing a pass in
Module Specification: Digital Strategy Digital Strategy is a 15-credit elective module which sits within the suite of Level 6 modules. To gain the CIM Level 6 Diploma in Professional Marketing a pass in
THE CONVERSION CYCLE
 Accounting Information Systems, 3rd. Ed. The Conversion Cycle 7 CHAPTER 7 THE CONVERSION CYCLE This is perhaps the most complex chapter so far. The first section presents a discussion of a traditional
Accounting Information Systems, 3rd. Ed. The Conversion Cycle 7 CHAPTER 7 THE CONVERSION CYCLE This is perhaps the most complex chapter so far. The first section presents a discussion of a traditional
Principles of Operations Management
 Unit 25: Unit code Principles of Operations Management H/508/0539 Unit level 5 Credit value 30 Introduction The aim of this unit is to introduce students to the role of the operations in an organisation
Unit 25: Unit code Principles of Operations Management H/508/0539 Unit level 5 Credit value 30 Introduction The aim of this unit is to introduce students to the role of the operations in an organisation
UNIT 3 BUSINESS MANAGEMENT AREA OF STUDY 3 OPTIMISING OPERATIONS
 UNIT 3 BUSINESS MANAGEMENT AREA OF STUDY 3 OPTIMISING OPERATIONS DISCUSS AND ANALYSE STRATEGIES RELATED TO OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT. STUDY DESIGN OVERVIEW The operations management function In area of study
UNIT 3 BUSINESS MANAGEMENT AREA OF STUDY 3 OPTIMISING OPERATIONS DISCUSS AND ANALYSE STRATEGIES RELATED TO OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT. STUDY DESIGN OVERVIEW The operations management function In area of study
Credit value: 15 Guided learning hours: 45. Unit aim. Unit introduction
 Unit 12: Strategic Planning Unit code: Level 7: H/602/2330 BTEC Professional Credit value: 15 Guided learning hours: 45 Unit aim This unit provides the learner with an understanding of how to review current
Unit 12: Strategic Planning Unit code: Level 7: H/602/2330 BTEC Professional Credit value: 15 Guided learning hours: 45 Unit aim This unit provides the learner with an understanding of how to review current
INSTRUMENT DEVELOPMENT, RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY TESTS
 41 CHAPTER 4 INSTRUMENT DEVELOPMENT, RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY TESTS 4.1 INSTRUMENT DEVELOPMENT The research instrument used in the study consists of nine constructs. Each construct consists of set of items
41 CHAPTER 4 INSTRUMENT DEVELOPMENT, RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY TESTS 4.1 INSTRUMENT DEVELOPMENT The research instrument used in the study consists of nine constructs. Each construct consists of set of items
LEVEL 5 DIPLOMA IN PROCUREMENT QUALIFICATION GUIDANCE
 LEVEL 5 DIPLOMA IN PROCUREMENT QUALIFICATION GUIDANCE [60140252] D7043-C5 Issue 2 60140252 Sep 17 About ABC Awards ABC Awards is a leading national awarding organisation which has a long-established reputation
LEVEL 5 DIPLOMA IN PROCUREMENT QUALIFICATION GUIDANCE [60140252] D7043-C5 Issue 2 60140252 Sep 17 About ABC Awards ABC Awards is a leading national awarding organisation which has a long-established reputation
P2 Performance Management
 DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO Performance Pillar P2 Performance Management 22 May 2013 Wednesday Afternoon Session Instructions to candidates You are allowed three hours to
DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO Performance Pillar P2 Performance Management 22 May 2013 Wednesday Afternoon Session Instructions to candidates You are allowed three hours to
0471 TRAVEL AND TOURISM
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 0471 TRAVEL AND TOURISM 0471/02 Paper 2 (Alternative
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 0471 TRAVEL AND TOURISM 0471/02 Paper 2 (Alternative
Company Business Excellence Self-Assessment
 Company Business Excellence Self-Assessment Assessment Review Date: Danbury ISR Updated: 7/21/2011 1 Completing this Self-Assessment 1. Review each section as a separate assessment of your current state
Company Business Excellence Self-Assessment Assessment Review Date: Danbury ISR Updated: 7/21/2011 1 Completing this Self-Assessment 1. Review each section as a separate assessment of your current state
COURSE CODE:01BMBAD17261 CREDITS: 4
 COURSE TITLE: STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT COURSE CODE:01BMBAD17261 CREDITS: 4 Unit 1 Strategic Management: An introduction, meaning, need and process of strategic management; business policy. Corporate Planning
COURSE TITLE: STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT COURSE CODE:01BMBAD17261 CREDITS: 4 Unit 1 Strategic Management: An introduction, meaning, need and process of strategic management; business policy. Corporate Planning
Operations Management Competitiveness, Operations strategy and Productivity
 1/11/2018 Operations Management Competitiveness, Operations strategy and Productivity Session 2 Leaning outcome Understand the importance of Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity in todays global
1/11/2018 Operations Management Competitiveness, Operations strategy and Productivity Session 2 Leaning outcome Understand the importance of Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity in todays global
2. Ofqual level 6 descriptors
 Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria The learning outcomes and assessment criteria for the Chartered Manager Degree Apprenticeship have been based upon the following: 1. DfEdefinition - level 6 descriptor
Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria The learning outcomes and assessment criteria for the Chartered Manager Degree Apprenticeship have been based upon the following: 1. DfEdefinition - level 6 descriptor
E1 Enterprise Operations
 DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO Enterprise Pillar E1 Enterprise Operations 20 November 2012 Tuesday Morning Session Instructions to candidates You are allowed three hours to
DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO Enterprise Pillar E1 Enterprise Operations 20 November 2012 Tuesday Morning Session Instructions to candidates You are allowed three hours to
Quality and Process Improvement
 Unit 17: Unit code Quality and Process Improvement H/615/1491 Unit level 4 Credit value 15 Introduction Quality has always been the key to business success and survivability, but it requires organisations
Unit 17: Unit code Quality and Process Improvement H/615/1491 Unit level 4 Credit value 15 Introduction Quality has always been the key to business success and survivability, but it requires organisations
Operations and Processes
 Operations and Processes Operations and process management is about how organisations create goods and services. All organisations are made up of processes; the operations function is the part of the organization
Operations and Processes Operations and process management is about how organisations create goods and services. All organisations are made up of processes; the operations function is the part of the organization
Courses offered for Postgraduate Program in AEM
 Courses offered for Postgraduate Program in AEM Course No Course Title Credit Hours AEM 6102 Quality Management Techniques 3 AEM 6111 Business Statistics 3 AEM 6112 Quantitative Analysis 3 AEM 6113 Business
Courses offered for Postgraduate Program in AEM Course No Course Title Credit Hours AEM 6102 Quality Management Techniques 3 AEM 6111 Business Statistics 3 AEM 6112 Quantitative Analysis 3 AEM 6113 Business
Site Safety Plus. Site Management Safety Training Scheme (SMSTS) Course appendix G
 Site Safety Plus Site Management Safety Training Scheme (SMSTS) Course appendix G 1. Introduction 2. Aims and objectives 3. Entry requirements 4. Assessment 5. Delegate numbers 6. Course duration and attendance
Site Safety Plus Site Management Safety Training Scheme (SMSTS) Course appendix G 1. Introduction 2. Aims and objectives 3. Entry requirements 4. Assessment 5. Delegate numbers 6. Course duration and attendance
Site Safety Plus. Site Management Safety Training Scheme (SMSTS) Course appendix G
 Page 1 of 21 Site Safety Plus Site Management Safety Training Scheme (SMSTS) Course appendix G 1. Introduction... 2 2. Aims and objectives... 2 3. Entry requirements... 2 4. Assessment... 2 5. Delegate
Page 1 of 21 Site Safety Plus Site Management Safety Training Scheme (SMSTS) Course appendix G 1. Introduction... 2 2. Aims and objectives... 2 3. Entry requirements... 2 4. Assessment... 2 5. Delegate
Qualification Specification. HABC Level 2 Certificate in Business Improvement Techniques (QCF) Qualification Number: 601/3198/6
 wwwhighfieldabccom Qualification Specification HABC Level 2 Certificate in Business Improvement Techniques (QCF) Qualification Number: 601/3198/6 Highfield House Heavens Walk Lakeside Doncaster South Yorkshire
wwwhighfieldabccom Qualification Specification HABC Level 2 Certificate in Business Improvement Techniques (QCF) Qualification Number: 601/3198/6 Highfield House Heavens Walk Lakeside Doncaster South Yorkshire
Logistics Strategy Leagile Thinking
 Logistics Strategy Leagile Thinking Kate Hughes & John Whiteley 1 Managing the Lead Time Frontier Time is a simple measure By following the flow through a process we can see where is lost. data can be
Logistics Strategy Leagile Thinking Kate Hughes & John Whiteley 1 Managing the Lead Time Frontier Time is a simple measure By following the flow through a process we can see where is lost. data can be
Presented by Renaldo de Jager 11-1
 Operations & Innovations Management Presented by Renaldo de Jager 11-1 Vendor Selection 11-2 VENDOR SELECTION A firm that decides to buy components rather than make them, must select suitable vendors.
Operations & Innovations Management Presented by Renaldo de Jager 11-1 Vendor Selection 11-2 VENDOR SELECTION A firm that decides to buy components rather than make them, must select suitable vendors.
Product, Service & Process Design
 Strategies for new product introduction market pull we make what we can sell example: food industry technology push we sell what we can make example: electronics inter-functional view example: personal
Strategies for new product introduction market pull we make what we can sell example: food industry technology push we sell what we can make example: electronics inter-functional view example: personal
(Assignment) Master of Business Administration (MBA) PGDPM Subject : Management Subject Code : PGDPM
 (Assignment) 2017-2018 Master of Business Administration (MBA) PGDPM Subject : Management Subject Code : PGDPM Subject Title : Operation Research Course Code : PGDPM-01 Maximum Marks: 30 Note: Long Answer
(Assignment) 2017-2018 Master of Business Administration (MBA) PGDPM Subject : Management Subject Code : PGDPM Subject Title : Operation Research Course Code : PGDPM-01 Maximum Marks: 30 Note: Long Answer
Marketing Plan. Business Group : Period : Business Unit : Prepared by : Product/Product Line : Date :
 Marketing Plan Business Group : Period : Business Unit : Prepared by : Product/Product Line : Date : Marketing Plan Contents : Terms Of Reference... 3 Executive Summary... 3 Business Mission and Vision...
Marketing Plan Business Group : Period : Business Unit : Prepared by : Product/Product Line : Date : Marketing Plan Contents : Terms Of Reference... 3 Executive Summary... 3 Business Mission and Vision...
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science
 Topic Support Guide Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 9608 For examination from 2017 Topic 4.4.3 Project management PERT and GANTT charts Cambridge International Examinations retains
Topic Support Guide Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 9608 For examination from 2017 Topic 4.4.3 Project management PERT and GANTT charts Cambridge International Examinations retains
UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI
 AC. 6.6.2012 Item No.4.109 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Revised Syllabus for the MHRDM Program: MHRDM Course: MHRDM Second Year (Semester II) & Third Year (Semester I &II) (Part Time) (As per Credit Based Semester
AC. 6.6.2012 Item No.4.109 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Revised Syllabus for the MHRDM Program: MHRDM Course: MHRDM Second Year (Semester II) & Third Year (Semester I &II) (Part Time) (As per Credit Based Semester
Advanced Diploma in Purchasing and Supply IMPROVING SUPPLY CHAIN PERFORMANCE. L5-03/Jan12 LEVEL 5 MARKING SCHEME. January 2012 AULTRO
 Advanced Diploma in Purchasing and Supply IMPROVING SUPPLY CHAIN PERFORMANCE L5-03/Jan12 LEVEL 5 MARKING SCHEME January 2012 AULTRO SECTION A You are strongly advised to read carefully and analyse the
Advanced Diploma in Purchasing and Supply IMPROVING SUPPLY CHAIN PERFORMANCE L5-03/Jan12 LEVEL 5 MARKING SCHEME January 2012 AULTRO SECTION A You are strongly advised to read carefully and analyse the
Higher National Unit specification: general information. Graded Unit 3
 Higher National Unit specification: general information This Graded Unit has been validated as part of the the HND in Sports Coaching with Sport Development. Centres are required to develop the assessment
Higher National Unit specification: general information This Graded Unit has been validated as part of the the HND in Sports Coaching with Sport Development. Centres are required to develop the assessment
Define 6. Improve 80. Measure 20. Control 100. Analyse 46. Analyse cont... Hypothesis Testing Correlation & Regression 74-79
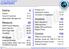 CONTENT Define 6 Charter 8-11 Voice Of Customer 12-15 Stakeholder Management 16-19 Measure 20 VSM/Process Mapping 22-27 Data Collection 28-31 MSA/Gage R&R 32-39 Capability 40-45 Analyse 46 Graphical Analysis
CONTENT Define 6 Charter 8-11 Voice Of Customer 12-15 Stakeholder Management 16-19 Measure 20 VSM/Process Mapping 22-27 Data Collection 28-31 MSA/Gage R&R 32-39 Capability 40-45 Analyse 46 Graphical Analysis
Level: Diploma in Professional Marketing. Unit/Module: Mastering Metrics. Please refer to the December 2015 assessment. Overarching performance:
 Module report Level: Diploma in Professional Marketing Unit/Module: Mastering Metrics Please refer to the December 2015 assessment Overarching performance: The overall performance for this session of the
Module report Level: Diploma in Professional Marketing Unit/Module: Mastering Metrics Please refer to the December 2015 assessment Overarching performance: The overall performance for this session of the
Duration of online examination will be of 1 Hour 20 minutes (80 minutes).
 Program Name: PGDBA Subject: Production and Operations Management Assessment Name: POM - Exam Weightage: 70 Total Marks: 70 Duration: 80 mins Online Examination: Online examination is a Computer based
Program Name: PGDBA Subject: Production and Operations Management Assessment Name: POM - Exam Weightage: 70 Total Marks: 70 Duration: 80 mins Online Examination: Online examination is a Computer based
Unit title: Marketing Planning: Domestic Market (SCQF level 8)
 General information Unit title: Marketing Planning: Domestic Market (SCQF level 8) Unit code: HP09 48 Superclass: BA Publication date: June 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit
General information Unit title: Marketing Planning: Domestic Market (SCQF level 8) Unit code: HP09 48 Superclass: BA Publication date: June 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit
Examiner s Report March 2013
 Examiner s Report March 2013 Level 3 Diploma Paper 4: Human Resource Management International. Introduction Candidates were required to answer six questions from a choice of ten questions. The most popular
Examiner s Report March 2013 Level 3 Diploma Paper 4: Human Resource Management International. Introduction Candidates were required to answer six questions from a choice of ten questions. The most popular
