Thin Film Evaporation Guide
|
|
|
- Octavia Mills
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vacuum Engineering & Materials 390 Reed Street Santa Clara, CA USA Revision 2017 Thin Film Evaporation Guide Toll Free: Phone: Fax: Copyright 2017 Vacuum Engineering and Materials, all rights reserved
2 Al ebeam (Xlnt) TiB 2 -TiC, TiB 2 -BN,, BN High deposition rates possible. Al wets IMCS Antimonide Arsenide 2% Copper Nitride (Alumina) 2% Silicon AlSb ebeam (fair) AlAs ~1300 ebeam (poor) TiB 2 -BN, BN, C, TiB 2 -BN, BN, AlBr ~50 ebeam (poor), W Al 4 C ~800 ebeam (fair), W Al2%Cu ebeam (fair) TiB 2 -TiC, BN AlF AlN ~1750 ebeam (fair) Co-evaporation is the best approach Co-evaporation can work but typically done with MBE ebeam or thermal evaporation of anhydrous AlBr 3 powder ebeam evaporation from powder, but CVD is a better approach ebeam evaporation of Al-Cu alloys is possible, but sputter deposition is a better approach ebeam (fair), Mo, W Films tend to be porous, but smooth TiB 2 -TiC,, BN ebeam (Xlnt) W, Al2%Si ebeam (fair) TiB 2 -TiC, BN Antimony Sb Antimony Telluride Antimony Trioxide Antimony Triselenide Antimony Trisulphide ebeam (fair) BN,, Sb 2 Te ebeam (fair), BN, W Sb or 5.76 ~300 Sb 2 Se ebeam (fair) Sb 2 S ~200, Mo, Ta Arsenic As Arsenic Selenide Arsenic Trisulphide Arsenic Tritelluride Reactive evaporation of Al in N 2 or ammonia partial pressure Swept beam with low deposition rates (< 3 Å/sec) ebeam evaporation of Al-Si alloys is possible, but sputter deposition is a better approach As the deposition rate is increased from 3-5 Å/s the grain size decreases and film coverage improves Best results are achieved with powdered source material, relatively high deposition rates can be achieved BN, ebeam evaporation from powder or granules ebeam (poor), BeO, As 2 Se ebeam (poor) As 2 S ~400 ebeam (fair) Mo As 2 Te ebeam (poor) Barium Ba ebeam (fair) W, Ta, Mo Barium BaCl ~650 ebeam (poor) W, Mo Barium BaF ~700 ebeam (fair) Barium BaO or 5.32 ~1300 ebeam (fair) Barium W, Mo BaS ebeam (poor) W, Mo Barium Titanate BaTi Decomposes 6 Decomposes ebeam (poor) W, Mo Can be co-evaporated with Se to overcome variable stoichiometric effects Films without substrate heating are amorphous, while polycrystalline films form on heated substrates Sputter deposition is the preferred method for deposition of elemental arsenic Deposition efficiency increases with deposition rate Thin films tend to be richer in As compared to the source material CVD is the preferred deposition technique for this material Reacts with ceramics. Ba evaporation pellets are often shipped with protective coatings which must be removed Swept beam and slow power ramp to precondition and outgas the source material Better consistency in refractive index is achieved via CVD Swept beam and slow power ramp to precondition and outgas the source material Sputter deposition is the preferred deposition technique BaTi will decompose as single source. Co-evaporate with Ti to maintain Ba/Ti ratio
3 Beryllium Be ebeam (Xlnt) Beryllium Beryllium BeCl ~150 ebeam (poor) BeF ~200 Very high deposition rates are possible. Avoid Be powder sources due to toxicity CVD is the preferred deposition technique for this material ebeam (fair) Avoid powder sources due to toxicity Beryllium BeO ebeam (fair), Thin films can also be produced via reactive evaporation of Be with O 2 Bismuth Bi ebeam (Xlnt), Bismuth BiF ~300 ebeam (poor) Bismuth Bi ~1400 ebeam (poor) Bismuth Selenide Bismuth Telluride Bismuth Titanate Bismuth Trisulphide Bi 2 Se ~650 ebeam (fair) Bi 2 Te ~600 ebeam (fair) Bi 2 Ti 2 O 7 Decomposes ebeam (poor) Bi 2 S ebeam (poor), W Boron B ebeam (Xlnt), W Post deposition thermal annealing significantly enhances film properties. However, vapors are toxic Sublimes at relatively low temperature, so reasonable vapor pressure can be achieved ebeam evaporation from Bi 2 source is possible, but variations in thin film stoichiometry may occur Sputter deposition is preferred, but co-evaporation using Bi and Se sources is possible Sputter deposition is preferred, but co-evaporation using Bi and Te sources is possible Decomposes when evaporated. Sputter deposition is preferred, but can be reactively co-evaporated in O 2 partial pressure Can be co-evaporated from Bi and S sources Can react with and tungsten crucible liners. Requires high power to evaporate Boron B 4 C , W ~1600 Boron Nitride BN ebeam (poor), W Boron B ~1400 W, Mo Ion assisted ebeam deposition with Ar can improve film adhesion Ion assisted ebeam deposition with N 2 produces stoichiometric thin films, but sputter deposition is preferred ebeam evaporation from bulk source material produces stoichiometric thin films Boron Trisulphide B 2 S ebeam (poor) Cd ebeam (fair) Dedicated system is recommended, since Cd can contaminate other purity sensitive depositions Antimonide CdSb Arsenide Iodide Cd 3 As ebeam (poor) quartz Thin films can be produced by ebeam evaporation from bulk source material, but CVD is a preferred deposition method CdBr ~300 CdCl ~400 CdF ~500 CdI ~250 CdO ~530 ebeam (poor) Selenide CdSe CdI 2 films have been deposited by thermal evaporation on glass substrates using stoichiometric powders Can be produced by reactive evaporation of Cd in partial pressure of O 2 or reactive sputtering with O 2 ebeam evaporation from bulk source material produces uniform films
4 Siliside Telluride CdSiO 2 ~600 CdS ebeam (fair) CdTe ebeam (fair) Calcium Ca ebeam (poor) Reports in the literature of deposition by CVD Substrate heating improves film adhesion. Deposition rates of 15 Å/sec are possible High quality CdTe thin films on glass substrates at 100 C have been fabricated with ebeam deposition Low partial pressure of O 2 in the vacuum chamber is required to avoid oxidizing the Ca Calcium CaF ~1100 ebeam (Xlnt) quartz, Ta Deposition rate of 20 Å/sec are easily achieved with ebeam deposition. Substrate heating improves film quality Calcium CaO ~1700 ebeam (poor) ZrO 2, Forms volatile oxides with W and Mo Calcium Silicate CaO-SiO quartz Calcium Calcium Titanate Calcium Tungstate Carbon (diamond) CaS ebeam (poor) ZrO 2, CaTi ebeam (poor) Post deposition thermal annealing at 500 C improves film quality and adhesion Decomposition of CaS bulk source material can be overcome by coevaporation with S Sputter deposition is the preferred method CaWO W, ZrO 2 Substrate heating improves the crystallinity of the deposit C ebeam (Xlnt) Cerium Ce Ceric CeO , W, BeO,, Ta Cerium CeF ~900 Mo, Ta, W Cerium Ce ebeam (fair), Ta Better film adhesion results from ebeam evaporation compared to vacuum arc deposition Ce deposits readily oxidize when exposed to air Stoichiometric films are best achieved using reactive evaporation with O 2. Substrate heating improves film quality Can be produced using bulk source material. Substrate heating from C improves adhesion and film quality Mixed CeO 2 -Ce 2 films can be reduced to Ce 2 by heating in UHV at 725 C Cesium Cs ebeam (poor) quartz Cesium Cesium Cesium Cesium Hydroxide CsBr ~400 CsCl ~500 CsF ~500 CsOH ~550 Cesium Iodide CsI ~500 ebeam (poor) quartz, Pt Stoichiometric CsI films are possible from bulk, source material, but good film coverage can be a challenge Chiolote Na 5 Al 3 F ~800 ebeam (poor) Stoichiometric chiolite films are difficult to fabricate with ebeam evaporation Chromium Cr Chromium Boride Chromium Chromium Chromium W, Films are very adherent. High deposition rates possible, but uniformity can be an issue CrB CrBr Cr 3 C ~2000 ebeam (fair) W Can be fabricated by co-evaporation of Cr and C CrCl
5 Chromium Chromium Siliside Chromium Silicon Monoxide Cr ~2000 W Stoichiometry can be maintained by reactive evaporation in O 2 Cr 3 Si Cr-SiO Influenced by Composition W Cobalt Co ebeam (Xlnt) Cobalt CoBr Cobalt CoCl , BeO, Cobalt CoO ebeam (fair) Copper Cu ebeam (Xlnt) Copper The quality Cr-SiO cermet films fabricated with ebeam evaporation improves with annealing at 425 C Pellets or powder both work well as source material, Mo Ta, CuCl ~600 ebeam (poor) quartz Copper Cu 2 O Copper Sulfide CuS ~600 ~500,, Ta Cryolite Na 3 AlF W, Dyprosium Dy W Dyprosium Dyprosium DyF ~800 CoO can be fabricated by reactive evaporation with O 2, but sputter deposition is the preferred fabrication method Poor adhesion on most substrates. Use thin adhesion layer of Cr or Ti Stoichiometric CuCl films have been produced from pellets and powder source material Thin films have been fabricated from stoichiometric Cu 2 O powder Dy ~1400 ebeam (fair) W Erbium Er W, Ta Good films can be fabricated using pellets or powder source material. Quality thin films can be fabricated from bulk source material Bulk source material is available in pellets and powder form Thin films have been fabricated from bulk source material W, Ta Erbium ErF ~950 Erbium Er ~1600 ebeam (fair) W Europium Eu Europium Europium Europium Reactive evaporation of bulk material in O 2 atmosphere maintains stoichiometry. ebeam (fair) EuF ~950 Eu ~1600 W EuS 5.75 W Gadolinium Gd ebeam (Xlnt) 0 3, W Gadolinium Gd ebeam (fair) 0 3, W Gallium Ga Gallium Antimonide,, BeO GaSb ebeam (fair) W, Ta Reactive evaporation of Eu 2 powder or granules in O 2 atmosphere maintains stoichiometry. ebeam evaporation of EuS powder in UHV (10-8 torr base vacuum) has been in the literature ebeam evaporation of Gd directly from the water cooled Cu hearth has been Reactive evaporation of Gd 2 pellets in O 2 maintains thin film stoichiometry. Refractive index increases with substrate heating Alloys with refractory metals ebeam evaporation from bulk source material is possible
6 Gallium Arsenide Gallium Nitride Gallium (ß) Gallum Phosphide GaAs , W GaN 6.1 ~200 ebeam (fair),, BeO Ga ebeam (fair), W GaP ebeam (fair) quartz, W Gemanium Ge ebeam (Xlnt) Germanium Nitride Germanium Germanium Telluride Ge 3 N ~650, Ni ebeam (poor) GeO ~625,, quartz Film quality is improved with ion assisted evaporation Reactive evaporation of Ga in 10-3 N 2 Reactive evaporation of Ga 2 in O 2 partial pressure maintains stoichiometry Co-evaporation of Ga and P has been Uniform films achieved with slow power ramp and swept beam Sputtering is the preferred method of fabrication GeO 2 stoichiometry can be maintained by reactive evaporation of bulk source material in O 2 GeTe Gold Au ebeam (Xlnt) W,,, BN Metal spitting can be an issue. Mitigate by slow power ramp with swept beam and low carbon content in source material Hafnium Hf W Hafnium Boride HfB Hafnium HfC ~2600 Hafnium Nitride HfN Hafnium HfO ~2500 ebeam (fair), W Hafnium Silicide HfSi ebeam (fair) W Holmium Ho Holmium Fabrication of HfB 2 films by CVD has been HfN films have been produced by reactive RF sputtering of Hf in N 2 + Ar Can be fabricated by reactive evaporation in O 2 or using bulk source material. Post process annealing at 500 C improves film quality HfSi 2 thin films have been fabricated by ebeam evaporation of Hf on Si substrates followed by annealing at 750 C for an hour W HoF ~800 quartz Holmium Ho ebeam (fair) W Indium In ebeam (Xlnt) Indium Antimonide Indium Arsenide Mo,, InSb ~400 ebeam (fair), W InAs Indium In ~1200 Ho 2 thin films have been fabricated by ebeam evaporation of powdered source material or reactive evaporation of Ho in O 2 Wets Cu and W. Mo liner is preferred Thin films fabricated using powdered source material Sputter deposition is the preferred thin film fabrication technique reactive evaporation of powdered In 2 Thin films have been produced by in O 2 partial pressure. Indium Phosphide InP ebeam (fair), W Deposits are P rich Indium Selenide In 2 Se ebeam (fair), W Thin films have been fabricated by ebeam evaporation from powdered InSe. Post process annealing improves crystallinity Indium Sesquisulphide In 2 S ,9 850
7 Indium In 2 S Indium Telluride In 2 Te Indium Tin In 2 - SnO Iridium Ir ebeam (fair) W Iron Fe ebeam (Xlnt), BeO, Thin films from co-evaporation of In and Te sources has been. Thin films have been produced from 90% In 2-10%SnO 2 powder in O 2 partial pressure. Substrate temperature of 250 C improves electrical conductivity of resulting films Better uniformity and adhesion can be achieved using sputter deposition Molten Fe will attack and adhere to, severely limiting crucible liner life Iron FeBr Iron FeCl Iron Iodide FeI Iron FeO ebeam (poor) Sputter deposition preferred. Iron Fe , BeO, Fe 2 thin films fabricated by reactive evaporation of Fe in 0.1 Pa O 2 partial pressure has been Iron FeS Lanthanum La ebeam (Xlnt) W, Ta Lanthanum Boride Lanthanum Lanthanum Lanthanum LaB ebeam (fair) LaB 6 films and coatings are more commonly produced with sputter deposition. LaBr LaF Ta, Mo La W, Lead Pb ebeam (Xlnt), W Ion assisted ebeam evaporation improves film density and adhesion C contamination can occur with crucible liners Lead PbBr ~300 Lead PbCl ~325 Lead PbF ~400 Lead Iodide PbI ~500 Lead PbO ~550 ebeam (fair) W Lead Stannate PbSn ebeam (poor), W Disproportionates Lead Selenide PbSe Lead PbS ~ Stoichiometric PbO thin films can be produced using powdered source material ebeam (fair), ebeam (fair) Lead Telluride PbTe ebeam (poor), Lead Titanate PbTi 7.52 ebeam (fair) W, Ta Post deposition annealing at 150 C improves the crystallinity of the films Films produced from bulk PbTe tend to be Te rich. Sputter deposition is preferred Thin films of PbTi with reactive coevaporation of PbO powder and TiO 2 pellets in O 2 partial pressure has been Lithium Li Ta,, BeO Li films oxidize readily in air Lithium LiBr ~500
8 Lithium LiCl Lithium LiF W, Mo, Ta, Outgas prior to deposition rastered Rate control important for optical films. beam Lithium Iodide LiI Lithium Li 2 O Lutetium Lu ebeam (Xlnt) Lutetuim Lu ebeam (fair) material results in stoichiometric films by post deposition rapid thermal anneal ebeam evaporation of powdered source in O 2 at C Magnesium Mg Magnesium Aluminate Magnesium Magnesium Magnesium Magnesium Iodide Magnesium W,, Mg O Powder is flammable. High deposition rates are possible ebeam deposition from Mg O 4 powder has been MgBr ~450 MgCl MgF ebeam (Xlnt),, Mo Best optical properties result from substrate heating at 300 C and a deposition rate of 5 Å/sec MgI MgO , Manganese Mn Manganese Manganese Manganese IV Manganese Stoichiometric films result from reactive evaporation in partial pressure of 10-3 torr O 2 W,, BeO MnBr MnCl MnO ebeam (poor) W, Mo, produced by reactive evaporation of Mn Stoichiometric thin films have been powder in 10-3 torr O 2 MnS Mercury Hg Mercury HgS Toxic, not recommended for evaporation processes ebeam (poor) recommended for evaporation Toxic and decomposes, not processes Molybdenum Mo ebeam (Xlnt), W Films are smooth, hard and adherent Molybdenum Boride Molybdenum Molybdenum Disulphide Molybdenum Silicide Molybdenum Trioxide MoB Mo 2 C MoS ~50 MoSi ~50 Mo ~900 ebeam (fair),, BN, Mo Thin films of Mo 2 C by sputter deposition and CVD have been Fabrication of MoS 2 by CVD has been MoSi 2 films have been produced by sputter deposition Substrate heating improves film crystallinity Neodymium Nd ebeam (Xlnt), Ta Neodymium Neodymium NdF ~900 W, Mo, Substrate heating at 360 C improved film quality Nd ~1400 W, Ta Films may be oxygen deficient. Refractive index increases with increasing substrate temperature
9 Nickel Ni ebeam (Xlnt) Nickel NiBr Nickel NiCl , BeO, W, Nickel NiO ~1470, W Niobium (Columbium) Nb (Cb) ebeam (Xlnt) Differential thermal expansion between Ni and can cause crucible liners to crack on cooling Substrate temperature of 125 C improves film adhesion and quality. Use of NiO powder as source material mitigates spitting Ion assisted ebeam evaporation modifies Nb film stress from tensile to compressive at a substrate temperature of 400 C Niobium Boride NbB Niobium NbC ebeam (fair) NbC thin films on Ti has been Niobium Nitride NbN ebeam (fair), W NbN films have been fabricated using reactive evaporation and reactive sputtering in N 2. NbN films by ion assisted evaporation have also been Niobium NbO Niobium Pentoxide Niobium Telluride Nb 2 O Nb 2 O 5 films produced by RF magnetron sputtering using a stoichiometric target have been NbTe 7.6 Niobium-Tin Nb 3 Sn ebeam (Xlnt), Ta Niobium Trioxide Films produced by co-evaporation of Nb and Sn have been. Substrate heating improves film homogeneity Nb Osmium Os Palladium Pd ebeam (Xlnt) Palladium W,, PdO ebeam (poor) Decomposes Susceptible to metal spitting. Mitigate with slow power ramp and longer soak before deposition Phosphorus P ebeam (poor) Reacts violently in air Platinum Pt ebeam (Xlnt) W,, Low deposition rates (< 5 Å/sec) preferred for film uniformity. Carbon contamination with liners is possible at high power Plutonium Pu Toxic. Radioactive Polonium Po Toxic. Radioactive Potassium K quartz Highly reactive in air Potassium Potassium Potassium Potassium Hydroxide Potassum Iodide KBr ~450 quartz Use gentle preheat to outgas KCl ~510 ebeam (fair) Ta Mo Use gentle preheat to outgas KF ~500 ebeam (poor) quartz Use gentle preheat to outgas KOH ~400 KI ~500 Praseodymium Pr W,, Ta Pr films will oxidize in air Praseodymium Pr W,, ThO 2 Loses oxygen. Reports of Pr 2 thin films grown by MBE
10 Radium Ra Rhenium Re W, Rhenium Re ~100 W, Substrate heating at 600 C improves film properties Films produced by reactive evaporation of Re in 10-3 torr O 2 Rhodium Rh W, Rubidium Rb quartz Rubidium Rubidium Iodide RbCl ~500 quartz RbI ~400 quartz Ruthenium Ru ebeam (poor) W Material spits using ebeam. Sputter deposition is preferred Samarium Sm Samarium Samarium Sm W Loses oxygen. Sputter deposition is preferred Sm 2 S Scandium Sc ebeam (Xlnt) W, Mo, Alloys with Ta Scandium Sc ~400 ebeam (fair) W Selenium Se Silicon Si ebeam (fair) W, Mo,, Ta,, BeO Loses oxygen. Films produced by reactive sputtering in O 2 have been Toxic. Can contaminate vacuum systems High deposition rates possible. Molten Si can attack liners limiting crucible liner life Silicon Boride SiB Silicon SiC ebeam (fair) W Silicon Dioxide SiO Silicon Monoxide Silicon Nitride Si 3 N 4 SiO ~1025 Influenced by composition 850 ebeam (Xlnt) ebeam (fair), Ta,, W W, Ta, 3.44 ~800 Sputter deposition is the preferred thin film fabrication technique Swept beam is critical to avoid hole drilling, since the source material will have a shallow melt pool Thin films from bulk SiO material has been Thin films of Si 3 N 3 by reactive sputter deposition have been Silicon Selenide SiSe 550 Silicon Sillicon Telluride SiS SiTe Silver Ag ebeam (Xlnt) W,, Ta, Mo, Swept beam during melt and focused beam during deposition is recommended for higher deposition rates Silver AgBr ~380 Silver AgCl ~520 Silver Iodide AgI ~500 Sodium Na quartz Sodium Sodium Sodium Cyanide Thin films of AgI fabricated by thermal evaporation have been Use gentle preheat to outgas. Metal reacts violently in air NaBr ~400 NaCl Thin films of NaCl fabricated by thermal evaporation in Knudsen cells with quartz crucibles have been NaCN 563 ~550
11 Sodium Sodium Hydroxide NaF ~700 W, Ta,, BeO Use gentle preheat to outgas. NaF thin films produced from powder source material and 230 C substrate heating have been NaOH ~470 Strontium Sr ebeam (poor) Strontium Strontium Strontium SrF ~1000 ebeam (poor), W SrO Wets refractory metals. May react strongly in air Thin films of SrF 2 produced by ebeam and thermal evaporation have been ebeam (poor) Loses oxygen. Reacts with W and Mo SrS > Decomposes Sulphur S ebeam (poor) quartz Can contaminate vacuum systems Tantalum Ta ebeam (Xlnt) Tantalum Boride Tantalum Tantalum Nitride Tantalum Pentoxide Tantalum High melting point of Ta limits crucible liner selection. High vacuum is required to mitigate oxygen incorporation in films TaB TaC ~2500 TaN ebeam (fair) Ta 2 O , Ta Thin films of TaN can be produced by reactive evaporation in 10-3 torr N 2 Swept beam to avoid hole drilling. A thin Ti layer will improve adhesion to the substrate TaS Technetium Tc Tellurium Te ebeam (poor) Terbium Tb ebeam (Xlnt) Terbium,, Ta Wets refractory metals Thin films produced by sputter deposition and thermal evaporation have also been TbF ~800 Sputter deposition is preferred Terbium Tb Terbium Peroxide Tb 4 O Thallium Tl ebeam (poor) Thallium Thallium Thallium Iodide (ß) Tlbr TlCl TlI ~250 ~150 ~250 Thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition have been Annealing of Tb 2 films at 800 C in air to produce stable Tb 4 O 7 has been Thallium and its compounds are very toxic. Wets freely Thermal evaporation of TlBr thin films has been ebeam (poor) Low stress thin films can be produced by ebeam evaporation with a substrate temperature of 100 C Thallium Tl Disproportionates at 850 C to Tl 2 O Thorium Th ebeam (Xlnt) W, Ta, Mo Toxic and mildly radioactive Thorium Thorium ThBr ThC ~2300 Thorium Dioxide ThO ~2100 W Stable stoichiometric films of ThO 2 produced from powdered source material have been
12 Thorium Thorium Oxyfluoride Thorium ThF ~750 ebeam (fair) Ta, Mo, ThOF ebeam (poor) W, Ta, Mo, Use gentle preheat to outgas. Substrate temperature of 175 C improves film adhesion and quality Does not evaporate stoichiometrically, resulting films are primarily ThF 4 ThS Thulium Tm Thulium Tm Tin Sn ebeam (Xlnt) Tin SnO ~1000 ebeam (Xlnt), Ta,, W Tin Selenide SnSe ~400 Tin SnS ~450 ebeam (poor) quartz, W Tin Telluride SnTe ~450 ebeam (poor) quartz Titanium Ti ebeam (Xlnt) W,, TiC Titanium Boride TiB Titanium Titanium Dioxide Titanium Monoxide TiC ~2300 ebeam (fair) W, TiO ~1300 W,, Ta TiO 1750 ~1500 W,, Ta Titanium Nitride TiN W,, TiC Titanium Sesquioxide Ti W, Ta, Tungsten W W Tungsten Boride Tungsten Tungsten Telluride Tungsten Trioxide Thin films of Tm 2 by ebeam evaporation and MBE have been High deposition rates possible, but uniformity may suffer. Slow power ramp to mitigate cavitation of melt pool Substrate temperature above 200 C improves film crystallinity Stoichiometric thin films of SnSe produced by thermal evaporation of powdered source material have been Thin films prepared by ebeam evaporation of SnS powder and reactive co-evaporation of Sn and S have been Thin films of SnTe produced with ebeam evaporation at a substrate temperature of 300 C have been Films are very adherent to almost any substrate Sputter deposition is the preferred thin film fabrication technique ebeam evaporation of TiC thin films with and without ion beam assistance have been Stoichiometric thin films of TiO 2 have been produced from powder source material and a substrate temperature of 600 C Outgas with gentle preheat prior to deposition Thin films have been prepared by reactive evaporation of Ti in N 2 partial pressure Stoichiometric films have been produced by reactive evaporation of Ti 2 powder in 2.5 x 10-4 torr O 2 Long, slow preheat is required to condition the source material. Raster the electron beam to avoid hole drilling WB W 2 C W, Thin films prepared by ebeam evaporation of powdered source material have been. RF Sputter deposition is widely WTe W Uranium U W, Mo, Uranium W Thin films are most commonly prepared using W powder source material Depleted uranium thin films oxidize easily even in low partial pressure of O 2 UC
13 Uranium Dioxide Uranium UO ebeam (fair) W UF 4 ~ Uranium U 3 O 8 Decomposes 8.3 Uranium Phosphide Uranium Stoichiometric thin films produced by reactive evaporation of depleted uranium in O 2 partial pressure have been Thin films fabricated by sputter deposition of depleted uranium by F - ions has been Thin films produced by reactive sputter deposition of depleted uranium targets in O 2 have been. UP U 2 S Vanadium V ebeam (Xlnt) W,, Ta Vanadium Boride Vanadium Vanadium Dioxide Vanadium Nitride Vanadium Pentoxide Vanadium Silicide Wets Mo. ebeam evaporation is preferred VB VC ~1800 VO ~575 ebeam (poor) W, Difficult to maintain stoichiometry by ebeam evaporation, sputter deposition is preferred VN V 2 O ~500 W, Thin films prepared from powdered source material are nearly stoichiometric. Post process annealing at 280 in O 2 restores full stoichiometry VSi Ytterbium Yb Ytterbium Ytterbium , W, Ta YbF ~800 ebeam (fair) Ta, Mo, W Yb ~1500 ebeam (fair), W, Ta Store Yb evaporation source material in N 2 desiccator to mitigate oxidation Preheat slowly and evaporate at 10Å/sec to mitigate dissociation Thin films produced by reactive evaporation in 8 x 10-5 torr O 2 have been. Yttrium Y ebeam (Xlnt) W, Substrate heating at 300 C improves adhesion and film smoothness Yttrium Yttrium Y 3 Al 5 O W, material, typically with dopants. YAG films post deposition annealed at Films prepared from powdered source 1100 C in vacuum improves crystallinity YF W, Ta, Mo, 10Å/sec and substrate temperature of 200 C produces crystalline films with ebeam evaporation at a rate of good adhesion Yttrium Y ~2000 Zinc Zn ebeam (Xlnt) Zinc Antimonide, W W, ebeam evaporated films can be oxygen deficient, post deposition annealing in 10-3 torr O 2 at 525 C results in stoichiometric films. Evaporates well under a wide range of conditions Zn 3 Sb Zinc ZnBr ~300 Zinc ZnF ~800 ebeam (fair) quartz, W Zinc Nitride Zn 3 N Thin films prepared by ebeam evaporation of powdered source material have been. Substrate heating at 400 C improved crystallinity Reactive sputter deposition in N 2 has been
14 Zinc ZnO ~1800 ebeam (fair) quartz, W Quality thin films fabricated using ebeam evaporation at a rate of 8Å/sec and a substrate temperature of 300 C has been Zinc Selenide ZnSe ebeam (fair) Zinc ZnS ~800 Zinc Telluride ZnTe ~600 ebeam (fair) W, Ta, Mo, quartz W, Ta, Mo, quartz W, Ta, Mo, quartz Deposition rate of 5 Å/sec. Thin films are polycrystalline and a substrate temperature of 300 C improves adhesion and size of crystallites Thin films produced by ebeam evaporation display a preferred (111) orientation and best optical properties result from a 400 C substrate temperature Stoichiometric thin films produced by ebeam evaporation have good crystallinity with a substrate temperature of 230 C. Optical properties are thickness dependent Zircon ZrSiO Zirconium Zr ebeam (Xlnt) W Alloys with W. Thin films oxidize readily Zirconium Boride Zirconium Zirconium Nitride ZrB W ZrC ~2500 ebeam (poor) ZrN Stoichiometric films prepared by co-evaporation of Zr and B have been Quality thin films of ZrC using pulsed laser deposition have been Thin films of ZrN prepared by N 2 ion assisted evaporation of Zr have been Zirconium Zirconium Silicide ZrO ~220 W, ZrSi Reactive evaporation in 10-3 torr O 2 produce as deposited stoichiometric films. For ebeam evaporated films, post deposition annealing in O 2 restores stoichiometry ebeam evaporated Zr on Si substrates forms ZrSi 2 following post deposition thermal annealing at 600 C
MATERIALS H 01. Liners...H 03 Crucible Liners Selection Table...H 06. MATERIALS / Inorganics & thin films guide
 H MATERIALS CRUCIBLES, LINERS & Cones H Liners...H 03 Crucible Liners Selection Table...H 06 H 01 MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners Crucible liners protect the water-cooled copper hearth
H MATERIALS CRUCIBLES, LINERS & Cones H Liners...H 03 Crucible Liners Selection Table...H 06 H 01 MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners Crucible liners protect the water-cooled copper hearth
MATERIALS H 01. Temescal & Telemark Liners... H 03 Satis Liners... H 05 Crucible Liners Selection Table... H 06
 MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners... 03 Satis Liners... 05 Crucible Liners Selection Table... 06 01 MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners Crucible liners protect the water-cooled
MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners... 03 Satis Liners... 05 Crucible Liners Selection Table... 06 01 MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners Crucible liners protect the water-cooled
Crucible MATERIALS H 01. Temescal & Telemark Liners...H 03 Satis Liners...H 05 Crucible Liners Selection Table...H 06
 MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners... 03 Satis Liners... 05 Crucible Liners Selection Table... 06 01 MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners Crucible liners protect the water-cooled
MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners... 03 Satis Liners... 05 Crucible Liners Selection Table... 06 01 MATERIALS Crucible Liners Temescal & Telemark Liners Crucible liners protect the water-cooled
Material Evaporation Application Comment MP P / Optical films, Oxide films, Electrical contacts. Doping, Electrical contacts.
 for vapour Aluminum (Al) -, Optical, Oxide, Electrical BN liners with lid are recommended due to the reactivity and the fact that Al creeps out. Cooling down of the cell with 1K per minute. 660 972 Antimony
for vapour Aluminum (Al) -, Optical, Oxide, Electrical BN liners with lid are recommended due to the reactivity and the fact that Al creeps out. Cooling down of the cell with 1K per minute. 660 972 Antimony
Formula Density Z-Ratio Material Name Ca Calcium CaF Calcium Fluoride CaO *1.000 Calcium Oxide CaO-SiO *1.
 Material Parameters In the table below, an * is used to indicate that the material s Z Factor is not known. A method of determining Z Factor empirically follows the materials table. Formula Density Z-Ratio
Material Parameters In the table below, an * is used to indicate that the material s Z Factor is not known. A method of determining Z Factor empirically follows the materials table. Formula Density Z-Ratio
VACUUM DEPOSITION GUIDE
 A A MATERIALS VACUUM DEPOSITION GUIDE Technical Guide about Thin Films Deposition... A 02 Vapor Pressures Table... A 27 MATERIALS / Inorganics & thin films guide A 01 MATERIALS VACUUM DEPOSITION GUIDE
A A MATERIALS VACUUM DEPOSITION GUIDE Technical Guide about Thin Films Deposition... A 02 Vapor Pressures Table... A 27 MATERIALS / Inorganics & thin films guide A 01 MATERIALS VACUUM DEPOSITION GUIDE
SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "FOUNDRY-MASTER UV"
 SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "FOUNDRY-MASTER UV" Fe 100 low alloy steel Fe 150 free cutting steel Fe 200 cast iron Fe 250 Cr-Hard/Ni.Resist Fe 300 stainless steel Fe 400 tool steel Fe 500
SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "FOUNDRY-MASTER UV" Fe 100 low alloy steel Fe 150 free cutting steel Fe 200 cast iron Fe 250 Cr-Hard/Ni.Resist Fe 300 stainless steel Fe 400 tool steel Fe 500
BAPE Memoire ~ Exhibit B. Partial List of Radionuclides in 10-year-old CANDU fuel irradiated in a power reactor 207 DM44-2. Bécancour
 207 DM44-2 BAPE Memoire ~ Exhibit B Projet de modification des installations de stockage des déchets radioactifs et réfection de Gentilly-2 Bécancour 6212-02-005 Partial List of Radionuclides in 10-year-old
207 DM44-2 BAPE Memoire ~ Exhibit B Projet de modification des installations de stockage des déchets radioactifs et réfection de Gentilly-2 Bécancour 6212-02-005 Partial List of Radionuclides in 10-year-old
This resource contains three different versions of the periodic table, including a blank one for colouring!
 Teaching notes This resource contains three different versions of the periodic table, including a blank one for colouring! It also contains tables of the Group 0, 1 and 7 elements with a few columns for
Teaching notes This resource contains three different versions of the periodic table, including a blank one for colouring! It also contains tables of the Group 0, 1 and 7 elements with a few columns for
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION 2.0 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
 300 Technology Drive Christiansburg, VA 24073. USA inorganicventures.com CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS tel: 800.669.6799. 540.585.3030 fax: 540.585.3012 info@inorganicventures.com 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION
300 Technology Drive Christiansburg, VA 24073. USA inorganicventures.com CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS tel: 800.669.6799. 540.585.3030 fax: 540.585.3012 info@inorganicventures.com 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION
Periodic Table Of The Elements
 H Hydrogen NOTE: The classification of some elements, especially METALLOIDS and OTHER METALS, is often artbitrary because these elements have characteristics of both 8 9 0 Li Be metals and nonmetals. As
H Hydrogen NOTE: The classification of some elements, especially METALLOIDS and OTHER METALS, is often artbitrary because these elements have characteristics of both 8 9 0 Li Be metals and nonmetals. As
September 30, IB Syllabus. So, here's the order and you will have to memorize the order! But we can also use the periodic table!
 So, here's the order and you will have to memorize the order! 1 H Hydrogen 3 4 Li Na Be Lithium Beryllium 11 12 Mg Sodium Magnesium But we can also use the periodic table! 5 6 7 8 9 10 B Al C Si N P O
So, here's the order and you will have to memorize the order! 1 H Hydrogen 3 4 Li Na Be Lithium Beryllium 11 12 Mg Sodium Magnesium But we can also use the periodic table! 5 6 7 8 9 10 B Al C Si N P O
Standard Operating Procedures
 CENTER FOR NANOSCALE SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Standard Operating Procedures Edwards Thermal Evaporator Matt Deye and Brian Wajdyk Page 1 of 13 Important Gloves should be worn while handling substrate and
CENTER FOR NANOSCALE SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Standard Operating Procedures Edwards Thermal Evaporator Matt Deye and Brian Wajdyk Page 1 of 13 Important Gloves should be worn while handling substrate and
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION 2.0 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
 300 Technology Drive Christiansburg, VA 24073. USA inorganicventures.com CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS tel: 800.669.6799. 540.585.3030 fax: 540.585.3012 info@inorganicventures.com 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION
300 Technology Drive Christiansburg, VA 24073. USA inorganicventures.com CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS tel: 800.669.6799. 540.585.3030 fax: 540.585.3012 info@inorganicventures.com 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION
Name: 1: /33 Grade: /100 2: /33 3: /33 +1 point. Midterm Exam 2. CHEM 181: Introduction to Chemical Principles October 13, 2015
 Name: 1: /33 Grade: /100 2: /33 3: /33 +1 point Directions: Do all three problems. Midterm Exam 2 CHEM 181: Introduction to Chemical Principles October 13, 2015 Show all of your work neatly and clearly.
Name: 1: /33 Grade: /100 2: /33 3: /33 +1 point Directions: Do all three problems. Midterm Exam 2 CHEM 181: Introduction to Chemical Principles October 13, 2015 Show all of your work neatly and clearly.
Appendix 4a: PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS (full)
 Appendix 4a: PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS (full) 1 18 IA VIIIA 1 2 H He hydrogen 2 13 14 15 16 17 helium 1.008 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 4.003 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Li Be B C N O F Ne lithium beryllium boron
Appendix 4a: PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS (full) 1 18 IA VIIIA 1 2 H He hydrogen 2 13 14 15 16 17 helium 1.008 IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 4.003 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Li Be B C N O F Ne lithium beryllium boron
An essential element. N o u r i s h i n g t h e P l a n e t i n t h e 21s t C e n t u r y
 Master 1.1, Essential Nutrients An essential element 1. is required for a plant to complete its life cycle; 2. cannot be replaced by another element; 3. is directly involved in the plant s metabolism;
Master 1.1, Essential Nutrients An essential element 1. is required for a plant to complete its life cycle; 2. cannot be replaced by another element; 3. is directly involved in the plant s metabolism;
Center for By-Products Utilization
 Center for By-Products Utilization DRAFT Evaluation of Biron #5 Boiler Ash from Stora Enso North America By Tarun R. Naik and Rudolph N. Kraus REP-500 February 2003 Submitted to Mr. John Michalsen, Stora
Center for By-Products Utilization DRAFT Evaluation of Biron #5 Boiler Ash from Stora Enso North America By Tarun R. Naik and Rudolph N. Kraus REP-500 February 2003 Submitted to Mr. John Michalsen, Stora
CHA E-Beam Evaporator Operation Manual
 CHA E-Beam Evaporator Operation Manual Description: The CHA is a multi-pocket electron beam evaporator. It is a high vacuum (10-6 Torr) e- beam evaporation system that can be used to deposit metals and
CHA E-Beam Evaporator Operation Manual Description: The CHA is a multi-pocket electron beam evaporator. It is a high vacuum (10-6 Torr) e- beam evaporation system that can be used to deposit metals and
Atomic Properties. Atomic weight amu Face centered cubic Rn 6d 1 7s , 3
 Actinium Ac Aluminium Al Americium Am Antimony Sb Argon Ar Arsenic As Astatine At Barium Ba Berkelium Bk Beryllium Be Bismuth Bi Bohrium Bh Boron B Bromine Br Cadmium Cd Caesium Cs Calcium Ca Californium
Actinium Ac Aluminium Al Americium Am Antimony Sb Argon Ar Arsenic As Astatine At Barium Ba Berkelium Bk Beryllium Be Bismuth Bi Bohrium Bh Boron B Bromine Br Cadmium Cd Caesium Cs Calcium Ca Californium
ICP/ICP-MS Standards. High Purity Standards for ICP/ICP-MS
 ICP/ICP-MS Fisher Brand AA/ICP MS Fisherbrand ICP/ICP-MS Catalog No. Catalog No. Concentrationion Size ml Concentration Size ml 36 102 7820 Aluminum 36 102 7821 Antimony 36 102 7823 Arsenic 36 102 7824
ICP/ICP-MS Fisher Brand AA/ICP MS Fisherbrand ICP/ICP-MS Catalog No. Catalog No. Concentrationion Size ml Concentration Size ml 36 102 7820 Aluminum 36 102 7821 Antimony 36 102 7823 Arsenic 36 102 7824
High Purity Acids Trace Elemental Analysis. Detect as low as 1 to 100 ppt
 High Purity Acids Trace Elemental Analysis Detect as low as 1 to 100 ppt High purity acids If you are looking for acids, look no further. Whether you are analyzing environmental samples, etching glass,
High Purity Acids Trace Elemental Analysis Detect as low as 1 to 100 ppt High purity acids If you are looking for acids, look no further. Whether you are analyzing environmental samples, etching glass,
Technical References General Catalog A
 Technical References General Catalog 2015-2017 A TAILOR MADE REAGENTS LF Values / C for Conductivity standard solutions Conductivity Standard Solutions Type 1 0.01mol/l KCl 0.1 mol/l KCl mol/l KCl CL
Technical References General Catalog 2015-2017 A TAILOR MADE REAGENTS LF Values / C for Conductivity standard solutions Conductivity Standard Solutions Type 1 0.01mol/l KCl 0.1 mol/l KCl mol/l KCl CL
Standard Operating Procedures
 CENTER FOR NANOSCALE SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Standard Operating Procedures Electron Beam Evaporator Ross Levine With revisions by: Brian Wajdyk Page 1 of 17 Important Gloves should be worn while handling
CENTER FOR NANOSCALE SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Standard Operating Procedures Electron Beam Evaporator Ross Levine With revisions by: Brian Wajdyk Page 1 of 17 Important Gloves should be worn while handling
Standard Operating Procedures
 CENTER FOR NANOSCALE SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Standard Operating Procedures Electron Beam Evaporator Ross Levine With revisions by: Brian Wajdyk Page 1 of 17 Important Gloves should be worn while handling
CENTER FOR NANOSCALE SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Standard Operating Procedures Electron Beam Evaporator Ross Levine With revisions by: Brian Wajdyk Page 1 of 17 Important Gloves should be worn while handling
Standard Operating Procedures
 CENTER FOR NANOSCALE SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Standard Operating Procedures Small Sputtering Machine Ross Levine With revisions by: Brian Wajdyk Page 1 of 17 Important Gloves should be worn while handling
CENTER FOR NANOSCALE SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Standard Operating Procedures Small Sputtering Machine Ross Levine With revisions by: Brian Wajdyk Page 1 of 17 Important Gloves should be worn while handling
Chemistry Senior External Examination. Paper Two Resource book. Wednesday 28 October :00 pm to 3:10 pm. Directions.
 Directions You may write in this book during perusal time. Contents Table of constants Simple rules for solubility of salts in water Standard reduction potentials for half-reactions Periodic classification
Directions You may write in this book during perusal time. Contents Table of constants Simple rules for solubility of salts in water Standard reduction potentials for half-reactions Periodic classification
AIM: SWBAT determine the location of metals, nonmetals and metalloids on the periodic table. What is another name for a column in the periodic table?
 th Grade Science Metals, nonmetals and metalloids Name Date: UNIT 1 LESSON 1 Do Now AIM: SWBAT determine the location of metals, nonmetals and metalloids on the periodic table Directions: Answer the following
th Grade Science Metals, nonmetals and metalloids Name Date: UNIT 1 LESSON 1 Do Now AIM: SWBAT determine the location of metals, nonmetals and metalloids on the periodic table Directions: Answer the following
Unit 3 Earth Materials
 Unit 3 Earth Materials (35 hrs 10 weeks) Minerals, Rocks, Rock Cycle, Rock Classification Unit 3 Outline: 1. Mineral Chemistry 2. Minerals > Core lab 3 mineral id and specific gravity Mineral quiz 3. Rock
Unit 3 Earth Materials (35 hrs 10 weeks) Minerals, Rocks, Rock Cycle, Rock Classification Unit 3 Outline: 1. Mineral Chemistry 2. Minerals > Core lab 3 mineral id and specific gravity Mineral quiz 3. Rock
SCIENCE 5124/3, 5126/3 PAPER 3 Chemistry OCTOBER/NOVEMBER SESSION 2001
 Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE Joint Examination for the School Certificate and General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level SCIENCE
Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE Joint Examination for the School Certificate and General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level SCIENCE
SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "PMI-MASTER Pro" Spark - mode Fe 000
 SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "PMI-MASTER Pro" Spark - mode Fe 100 Fe 200 *** Fe 250 *** Fe 300 Fe 400 Fe 500 Fe 000 Fe low alloy steel cast iron Cr hard / Ni resist stainless steel tool
SUB-Programs - Calibration range Fe Base for "PMI-MASTER Pro" Spark - mode Fe 100 Fe 200 *** Fe 250 *** Fe 300 Fe 400 Fe 500 Fe 000 Fe low alloy steel cast iron Cr hard / Ni resist stainless steel tool
ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 S15-4472-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. THURSDAY, 14 May 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 S15-4472-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. THURSDAY, 14 May 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY. A.M. TUESDAY, 14 January hour
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CEMISTRY CEMISTRY 2 IGER TIER A.M. TUESDAY, 14 January 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 8
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CEMISTRY CEMISTRY 2 IGER TIER A.M. TUESDAY, 14 January 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 8
ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY. A.M. TUESDAY, 14 January hour
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CEMISTRY CEMISTRY 2 IGER TIER A.M. TUESDAY, 14 January 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 8
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CEMISTRY CEMISTRY 2 IGER TIER A.M. TUESDAY, 14 January 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 8
Using the Periodic Table
 Lesson Outline LESSON A. What is the periodic table?. The is a chart of the elements arranged into rows and columns according to their chemical and physical properties.. The table can be used to determine
Lesson Outline LESSON A. What is the periodic table?. The is a chart of the elements arranged into rows and columns according to their chemical and physical properties.. The table can be used to determine
Info Bulletin Laboratory Chemicals, Molecular Biology Culture Media for Microbiology
 Info Bulletin September 26th 2014 NEW FAMILY OF SCHARLAU ICP STANDARDS Scharlau is glad to announce the introduction of the new family of ICP standards. From now, this range of products replaces the current
Info Bulletin September 26th 2014 NEW FAMILY OF SCHARLAU ICP STANDARDS Scharlau is glad to announce the introduction of the new family of ICP standards. From now, this range of products replaces the current
Practice General Chemistry Speaking Test (I. Gould) (Questions from Chapter 1 of the textbook) hydrogen 1 H
 Practice General hemistry Speaking Test (I. Gould) (Questions from hapter 1 of the textbook) hydrogen 1 1.0079 helium 2 e 4.0026 lithium 3 Li 6.941 beryllium 4 Be 9.012 boron 5 B 10.811 carbon 6 12.0107
Practice General hemistry Speaking Test (I. Gould) (Questions from hapter 1 of the textbook) hydrogen 1 1.0079 helium 2 e 4.0026 lithium 3 Li 6.941 beryllium 4 Be 9.012 boron 5 B 10.811 carbon 6 12.0107
General Certificate of Secondary Education ADDITIONAL SCIENCE. FOUNDATION TIER (Grades G-C) P.M. FRIDAY, 18 January 2008 (45 minutes)
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 24/1 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER (Grades G-C) CHEMISTRY 2 P.M. FRIDAY, 18 January 28 (45 minutes) For Examiner
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 24/1 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER (Grades G-C) CHEMISTRY 2 P.M. FRIDAY, 18 January 28 (45 minutes) For Examiner
Company. Applications. Quality Assurance
 Company Nivo Technology, Inc. is a leading evaporation chemical manufacturer for thin film coating. We have developed a range of high quality products suitable for vacuum coating. Our products include
Company Nivo Technology, Inc. is a leading evaporation chemical manufacturer for thin film coating. We have developed a range of high quality products suitable for vacuum coating. Our products include
A.M. MONDAY, 18 January minutes
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 240/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE IGER TIER CEMISTRY 2 A.M. MONDAY, 18 January 2010 45 minutes ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you may require
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 240/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE IGER TIER CEMISTRY 2 A.M. MONDAY, 18 January 2010 45 minutes ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you may require
Mendeleev Modern Periodic Table Classes of Elements Alkali Metals
 The Periodic Table Name: Mendeleev Russian chemist in Arranged elements in rows with similar and increasing Left blanks for elements Modern Periodic Table Elements arranged by Periods- across the table
The Periodic Table Name: Mendeleev Russian chemist in Arranged elements in rows with similar and increasing Left blanks for elements Modern Periodic Table Elements arranged by Periods- across the table
New GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 2
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 2 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. MONDAY, 21 May 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you will
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 2 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. MONDAY, 21 May 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you will
236/02 SCIENCE. HIGHER TIER (Grades D-A*) CHEMISTRY 1. P.M. FRIDAY, 19 January (45 minutes)
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number WELSH JOINT EDUCATION COMMITTEE General Certificate of Secondary Education CYD-BWYLLGOR ADDYSG CYMRU Tystysgrif Gyffredinol Addysg Uwchradd 236/02 SCIENCE
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number WELSH JOINT EDUCATION COMMITTEE General Certificate of Secondary Education CYD-BWYLLGOR ADDYSG CYMRU Tystysgrif Gyffredinol Addysg Uwchradd 236/02 SCIENCE
Part 1. Preparation and Color of Solutions. Experiment 1 (2 session lab) Electrons and Solution Color. Pre-lab Report, page 29
 Experiment 1 (2 session lab) Electrons and Solution Color Pre-lab Report, page 29 Session 1 One hour discussion (E2) Two hour lab (E1) Aim to complete Parts 1, 2, and 3 of E1. Part 1. Preparation and Color
Experiment 1 (2 session lab) Electrons and Solution Color Pre-lab Report, page 29 Session 1 One hour discussion (E2) Two hour lab (E1) Aim to complete Parts 1, 2, and 3 of E1. Part 1. Preparation and Color
Periodic Table of the Elements
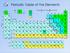 Period ydrogen.0 Name Symbol gas liquid solid Li Be Lithium Beryllium synthetic Sodium Magnesium.0. 9 0 Potassium lcium Scandium Titanium 9. 0. Group.0.9 8 9 0 Rubidium Strontium Yttrium Zirconium 8. 8.
Period ydrogen.0 Name Symbol gas liquid solid Li Be Lithium Beryllium synthetic Sodium Magnesium.0. 9 0 Potassium lcium Scandium Titanium 9. 0. Group.0.9 8 9 0 Rubidium Strontium Yttrium Zirconium 8. 8.
P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January minutes
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 236/01 SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 1 P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January 2009 45 minutes For Examiner s use Total Mark ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 236/01 SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 1 P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January 2009 45 minutes For Examiner s use Total Mark ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition
Chemistry I. Final Examination Reference Materials
 Chemistry I Final Examination Reference Materials DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BOOKLET Chemistry I: final Exam REFERENCE 2013 April 13 Miscellaneous 1 mole = 6.02 x 10 23 representative particles 1 mole = 22.4
Chemistry I Final Examination Reference Materials DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BOOKLET Chemistry I: final Exam REFERENCE 2013 April 13 Miscellaneous 1 mole = 6.02 x 10 23 representative particles 1 mole = 22.4
P.M. FRIDAY, 12 June hour For Examiner s use only
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4462/02 S15-4462-02 SCIENCE A/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1 HIGHER TIER P.M. FRIDAY, 12 June 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1.
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4462/02 S15-4462-02 SCIENCE A/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1 HIGHER TIER P.M. FRIDAY, 12 June 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1.
ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 S16-4472-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. THURSDAY, 19 May 2016 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 S16-4472-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 2 HIGHER TIER A.M. THURSDAY, 19 May 2016 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
XIX. Chemistry, High School
 XIX. Chemistry, High School High School Chemistry Test The spring 08 high school Chemistry test was based on learning standards in the Chemistry content strand of the October 006 version of the Massachusetts
XIX. Chemistry, High School High School Chemistry Test The spring 08 high school Chemistry test was based on learning standards in the Chemistry content strand of the October 006 version of the Massachusetts
Appendix: Periodic Table of the Elements
 Appendix: Periodic-Table-of-the-Elements In this chapter, we present some data on the chemical elements. The periodic table lists all the known chemical elements, arranged by atomic number (that is, the
Appendix: Periodic-Table-of-the-Elements In this chapter, we present some data on the chemical elements. The periodic table lists all the known chemical elements, arranged by atomic number (that is, the
GCSE 4472/02 CHEMISTRY 2 HIGHER TIER ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY. P.M. MONDAY, 20 May hour For Examiner s use only Question Maximum Mark 1.
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 2 HIGHER TIER P.M. MONDAY, 20 May 2013 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 8 Mark Awarded
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 2 HIGHER TIER P.M. MONDAY, 20 May 2013 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 8 Mark Awarded
Periodic Table of the Elements
 Group 1 Periodic Table of the Elements 18 1 H Hydrogen 1.01 2 13 14 15 16 17 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Li Be B C N O F Lithium Beryllium Boron Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Fluorine 6.94 9.01 10.8 12.0 14.0 16.0 19.0 11
Group 1 Periodic Table of the Elements 18 1 H Hydrogen 1.01 2 13 14 15 16 17 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Li Be B C N O F Lithium Beryllium Boron Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Fluorine 6.94 9.01 10.8 12.0 14.0 16.0 19.0 11
A.M. MONDAY, 18 January minutes
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 240/01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 2 A.M. MONDAY, 18 January 2010 45 minutes ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you may
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 240/01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 2 A.M. MONDAY, 18 January 2010 45 minutes ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you may
CH141, Fall 2016 Practice Exam 1. Name: Part I. Circle your answers
 Part I. Circle your answers Name: 1. If a sample of matter is uniform throughout and cannot be separated into other substances by physical means, it is. A) a compound B) either a compound or an element
Part I. Circle your answers Name: 1. If a sample of matter is uniform throughout and cannot be separated into other substances by physical means, it is. A) a compound B) either a compound or an element
EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF SWAZILAND Swaziland General Certificate of Secondary Education
 EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF SWAZILAND Swaziland General Certificate of Secondary Education CANDIDATE NAME CENTRE NUMBER CANDIDATE NUMBER PHYSICAL SCIENCE 6888/01 Paper 1 Short Answers October/November 2016
EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF SWAZILAND Swaziland General Certificate of Secondary Education CANDIDATE NAME CENTRE NUMBER CANDIDATE NUMBER PHYSICAL SCIENCE 6888/01 Paper 1 Short Answers October/November 2016
GCSE 0236/02 SCIENCE HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 0236/02 SCIENCE IGER TIER CEMISTRY 1 A.M. TUESDAY, 12 June 2012 45 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 7 Mark Awarded 2. 8 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 0236/02 SCIENCE IGER TIER CEMISTRY 1 A.M. TUESDAY, 12 June 2012 45 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 7 Mark Awarded 2. 8 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
Traceable Reference Standards for Plasma Emission Spectroscopy
 AccuStandard s Single Element Standards for Metal Analysis ICP IPC/MS AA Our most popular line and best value with comprehensive certificates for all applications For specialized ICP / MS analysis Lowest
AccuStandard s Single Element Standards for Metal Analysis ICP IPC/MS AA Our most popular line and best value with comprehensive certificates for all applications For specialized ICP / MS analysis Lowest
Name: 1: /33 Grade: /100 2: /33 3: /33 +1 point. Midterm Exam 2. CHEM 181: Introduction to Chemical Principles October 13, 2015
 Name: 1: /33 Grade: /100 2: /33 3: /33 +1 point Directions: Do all three problems. Midterm Exam 2 EM 181: Introduction to hemical Principles ctober 13, 2015 Show all of your work neatly and clearly. Do
Name: 1: /33 Grade: /100 2: /33 3: /33 +1 point Directions: Do all three problems. Midterm Exam 2 EM 181: Introduction to hemical Principles ctober 13, 2015 Show all of your work neatly and clearly. Do
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *8965824072* SCIENCE 5124/03 Paper 3 Chemistry October/November 2011 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *8965824072* SCIENCE 5124/03 Paper 3 Chemistry October/November 2011 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January minutes
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 236/02 SCIENCE HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1 P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January 2009 45 minutes For Examiner s use Total Mark ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 236/02 SCIENCE HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1 P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January 2009 45 minutes For Examiner s use Total Mark ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this
2018 No. 42 NUCLEAR ENERGY. The Nuclear Installations (Prescribed Sites and Transport) Regulations 2018
 S T A T U T O R Y I N S T R U M E N T S 2018 No. 42 NUCLEAR ENERGY The Nuclear Installations (Prescribed Sites and Transport) Regulations 2018 Made - - - - 16th January 2018 Laid before Parliament 16th
S T A T U T O R Y I N S T R U M E N T S 2018 No. 42 NUCLEAR ENERGY The Nuclear Installations (Prescribed Sites and Transport) Regulations 2018 Made - - - - 16th January 2018 Laid before Parliament 16th
GCSE 4782/02 SCIENCE B UNIT 2: Science and Life in the Modern World HIGHER TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4782/02 SCIENCE B UNIT 2: Science and Life in the Modern World HIGHER TIER P.M. WEDNESDAY, 15 June 2016 1 hour S16-4782-02 For s use Question Maximum
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4782/02 SCIENCE B UNIT 2: Science and Life in the Modern World HIGHER TIER P.M. WEDNESDAY, 15 June 2016 1 hour S16-4782-02 For s use Question Maximum
Chemistry/Additional Science
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry/Additional Science Unit C2: Discovering Chemistry Higher Tier Wednesday 14 June 2017 Morning Time:
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry/Additional Science Unit C2: Discovering Chemistry Higher Tier Wednesday 14 June 2017 Morning Time:
Atomic Masses (amu) IA IIA IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB VIIIB VIIIB VIIIB IB IIB IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIA
 Atomic Masses (amu) 1 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 18 1 1.008.00 8 9 10.91 9.01 10.81 1.01 1.01 1.00 19.00 0.18 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 18.99.1.98 8.09 0.9.0. 9.9 19 0 1 8 9 0 1 9.10 0.08.9.8 0.9.00.9.8 8.9 8.9..1 9...9
Atomic Masses (amu) 1 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 18 1 1.008.00 8 9 10.91 9.01 10.81 1.01 1.01 1.00 19.00 0.18 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 18.99.1.98 8.09 0.9.0. 9.9 19 0 1 8 9 0 1 9.10 0.08.9.8 0.9.00.9.8 8.9 8.9..1 9...9
SUPPLEMENTAL ALPHABETICAL LISTING OF ISOTOPES ATOMLAB DOSE CALIBRATORS. FOR CALIBRATORS WITH 6.0 V and HIGHER SOFTWARE updated 3/8/06
 Page 1 of 7 Ac-5 Actinium 44.0 Alpha, Beta-, etc 10 days. In equilibrium with daughters until Bi-09 (stable Am-41 Americium 40.4 Alpha 434.7 years As-76 Arsenic 5.1 Beta - 1068 1.1 days Au-198 Gold 3.0
Page 1 of 7 Ac-5 Actinium 44.0 Alpha, Beta-, etc 10 days. In equilibrium with daughters until Bi-09 (stable Am-41 Americium 40.4 Alpha 434.7 years As-76 Arsenic 5.1 Beta - 1068 1.1 days Au-198 Gold 3.0
A.M. WEDNESDAY, 26 May minutes
 andidate Name entre Number 0 andidate Number GSE 240/02 ADDITIONAL SIENE IGER TIER EMISTRY 2 A.M. WEDNESDAY, 26 May 2010 45 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 4 2. 6 Mark Awarded 3. 8 4. 3 5. 4
andidate Name entre Number 0 andidate Number GSE 240/02 ADDITIONAL SIENE IGER TIER EMISTRY 2 A.M. WEDNESDAY, 26 May 2010 45 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 4 2. 6 Mark Awarded 3. 8 4. 3 5. 4
MATERIALS. pellets. Vacuum Deposition Grade Pellets... C 03 C 01. MATERIALS / Inorganics & thin films guide
 C C MATERIALS pellets Vacuum Deposition Grade Pellets.... C 03 C 01 MATERIALS pellets Vacuum Deposition Grade Pellets Granules, pellets, pieces, tablets and shaped sources are available in virtually any
C C MATERIALS pellets Vacuum Deposition Grade Pellets.... C 03 C 01 MATERIALS pellets Vacuum Deposition Grade Pellets Granules, pellets, pieces, tablets and shaped sources are available in virtually any
GCSE 4462/02 CHEMISTRY 1 HIGHER TIER SCIENCE A/CHEMISTRY. A.M. FRIDAY, 17 June hour JUN S PMT.
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4462/02 S16-4462-02 SCIENCE A/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1 HIGHER TIER A.M. FRIDAY, 17 June 2016 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1.
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4462/02 S16-4462-02 SCIENCE A/CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1 HIGHER TIER A.M. FRIDAY, 17 June 2016 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1.
Periodic Table of the Elements Current View MCHS Periodic Table of the Elements
 Periodic Table of the Elements Current View MCHS Periodic Table of the Elements 1 18 1 H hydrogen 1.0 2 13 14 15 16 17 2 He helium 4.0 3 Li lithium 7.0 4 Be beryllium 9.0 5 B boron 10.8 6 C carbon 12.0
Periodic Table of the Elements Current View MCHS Periodic Table of the Elements 1 18 1 H hydrogen 1.0 2 13 14 15 16 17 2 He helium 4.0 3 Li lithium 7.0 4 Be beryllium 9.0 5 B boron 10.8 6 C carbon 12.0
New GCSE 4462/02 SCIENCE A HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4462/02 SCIENCE A HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. WEDNESDAY, 18 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may require
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4462/02 SCIENCE A HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. WEDNESDAY, 18 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may require
The Periodic Table 5.3
 The Periodic Table 5.3 Objectives Students will be able to explain atomic structure and have a general understanding of how atomic structure relates to the periodic table of elements Students will be able
The Periodic Table 5.3 Objectives Students will be able to explain atomic structure and have a general understanding of how atomic structure relates to the periodic table of elements Students will be able
GCSE 4782/01 SCIENCE B UNIT 2: Science and Life in the Modern World FOUNDATION TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4782/01 SCIENCE B UNIT 2: Science and Life in the Modern World FOUNDATION TIER P.M. TUESDAY, 9 June 2015 1 hour S15-4782-01 For s use Question
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4782/01 SCIENCE B UNIT 2: Science and Life in the Modern World FOUNDATION TIER P.M. TUESDAY, 9 June 2015 1 hour S15-4782-01 For s use Question
Recommended List of Common Impurities for Metallic Fixed-point Materials of the ITS-90
 Recommended List of Common Impurities for Metallic Fixedpoint Materials of the ITS90 Dean Ripple 1, Anatoly Pokhodun 2, Peter Steur 3, Gregory Strouse 1 and Osamu Tamura 4 1 National Institute of Standards
Recommended List of Common Impurities for Metallic Fixedpoint Materials of the ITS90 Dean Ripple 1, Anatoly Pokhodun 2, Peter Steur 3, Gregory Strouse 1 and Osamu Tamura 4 1 National Institute of Standards
New GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Higher Tier CHEMISTRY 2 A.M. MONDAY, 14 January 2013 1 hour ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you will
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4472/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Higher Tier CHEMISTRY 2 A.M. MONDAY, 14 January 2013 1 hour ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you will
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC C COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY (S omitted) METALLURGY C22 METALLURGY (of iron C21); FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS (production of
CPC C COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY (S omitted) METALLURGY C22 METALLURGY (of iron C21); FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS (production of
Chemistry A Level Transition
 Chemistry A Level Transition Name: We are delighted that you will be joining us in September and are looking forward to helping you become amazing Chemists. Chemistry is brilliant when you get it and,
Chemistry A Level Transition Name: We are delighted that you will be joining us in September and are looking forward to helping you become amazing Chemists. Chemistry is brilliant when you get it and,
Edexcel Chemistry: Model Test Paper-10. Index Number
 Edexcel Chemistry: Model Test Paper-10 Chemistry: Unit 4 Index Number Name Advance Level Subject code: 6244 Time: 1 hour 30 min. Instruction to the candidates In the box above write your name and index
Edexcel Chemistry: Model Test Paper-10 Chemistry: Unit 4 Index Number Name Advance Level Subject code: 6244 Time: 1 hour 30 min. Instruction to the candidates In the box above write your name and index
Paper Reference (complete below) Edexcel GCSE Additional Science (5018H) Chemistry (5038H) C2 Topics 5 to 8
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. H 1 H Signature Paper Reference(s) 5018H/1H 5038H/1H Edexcel GCSE Additional Science (5018H) Chemistry (5038H) C2 Topics 5 to
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. H 1 H Signature Paper Reference(s) 5018H/1H 5038H/1H Edexcel GCSE Additional Science (5018H) Chemistry (5038H) C2 Topics 5 to
Chemistry Paper One Resource book
 2017 Senior External Examination Chemistry Paper One Resource book Directions You may write in this book during perusal time. Contents Table of constants Simple rules for solubility of salts in water Periodic
2017 Senior External Examination Chemistry Paper One Resource book Directions You may write in this book during perusal time. Contents Table of constants Simple rules for solubility of salts in water Periodic
Chemistry Friday 28 October 2016 Paper Two Resource book
 2016 Senior External Examination Chemistry Friday 28 October 2016 Paper Two Resource book 1 pm to 3:10 pm Directions You may write in this book during perusal time. Contents Table of constants Simple rules
2016 Senior External Examination Chemistry Friday 28 October 2016 Paper Two Resource book 1 pm to 3:10 pm Directions You may write in this book during perusal time. Contents Table of constants Simple rules
CHM1. General Certificate of Education January 2008 Advanced Subsidiary Examination. Unit 1 Atomic Structure, Bonding and Periodicity
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2008 Advanced Subsidiary Examination CHEMISTRY Unit 1 Atomic Structure,
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2008 Advanced Subsidiary Examination CHEMISTRY Unit 1 Atomic Structure,
ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CEMISTRY CEMISTRY 2 FOUNDATION TIER A.M. TURSDAY, 15 May 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1.
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CEMISTRY CEMISTRY 2 FOUNDATION TIER A.M. TURSDAY, 15 May 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1.
ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CEMISTRY CEMISTRY 2 FOUNDATION TIER A.M. TURSDAY, 15 May 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1.
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4472/01 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/CEMISTRY CEMISTRY 2 FOUNDATION TIER A.M. TURSDAY, 15 May 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1.
CHM2. General Certificate of Education January 2008 Advanced Subsidiary Examination. Unit 2 Foundation Physical and Inorganic Chemistry
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2008 Advanced Subsidiary Examination CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Foundation Physical
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2008 Advanced Subsidiary Examination CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Foundation Physical
Chemistry Data Booklet Access 3 and Intermediate 1
 Chemistry Data Booklet Access 3 and Intermediate 1 For use in National Qualification Courses leading to the 2007 examinations and beyond. Published date: January 2007 Publication code: BB3572 ISBN: 978
Chemistry Data Booklet Access 3 and Intermediate 1 For use in National Qualification Courses leading to the 2007 examinations and beyond. Published date: January 2007 Publication code: BB3572 ISBN: 978
AAS - Atomic Absorption Mono Element ppm Standard Solutions (Spectro ECON)
 CL01.0105 CL01.0106 CL01.0107 CL01.0126 CL01.0127 CL01.0135 CL01.0136 CL01.0137 CL01.0138 CL01.0205 CL01.0206 CL01.0207 CL01.0216 Aluminium standard solution (Spectro ECON) 8.948 g AlCl3.6H2O / l H2O Solution
CL01.0105 CL01.0106 CL01.0107 CL01.0126 CL01.0127 CL01.0135 CL01.0136 CL01.0137 CL01.0138 CL01.0205 CL01.0206 CL01.0207 CL01.0216 Aluminium standard solution (Spectro ECON) 8.948 g AlCl3.6H2O / l H2O Solution
METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK
 METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK FOURTH EDITION Robert B. Ross Ross Materials Technology Ltd, East Kilbride, Glasgow Volume I SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS
METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK METALLIC MATERIALS SPECIFICATION HANDBOOK FOURTH EDITION Robert B. Ross Ross Materials Technology Ltd, East Kilbride, Glasgow Volume I SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS
CHM2. General Certificate of Education June 2006 Advanced Subsidiary Examination. Unit 2 Foundation Physical and Inorganic Chemistry
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2006 Advanced Subsidiary Examination CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Foundation Physical and Inorganic
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2006 Advanced Subsidiary Examination CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Foundation Physical and Inorganic
Standard Solutions (Traceable to NIST)
 Standard Solutions (Traceable to NIST) - Multi Element ICP Standard Solutions (Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy) - Single Element ICP Standard Solutions (Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy)
Standard Solutions (Traceable to NIST) - Multi Element ICP Standard Solutions (Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy) - Single Element ICP Standard Solutions (Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy)
EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF SWAZILAND Swaziland General Certificate of Secondary Education
 EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF SWAZILAND Swaziland General Certificate of Secondary Education PHYSICAL SCIENCE 6888/01 Paper 1 Short Answers October/November 2013 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL OF SWAZILAND Swaziland General Certificate of Secondary Education PHYSICAL SCIENCE 6888/01 Paper 1 Short Answers October/November 2013 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
*16GSD2201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier THURSDAY 19 MAY 2016, MORNING [GSD22] *GSD22* TIME 1 hour.
![*16GSD2201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier THURSDAY 19 MAY 2016, MORNING [GSD22] *GSD22* TIME 1 hour. *16GSD2201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier THURSDAY 19 MAY 2016, MORNING [GSD22] *GSD22* TIME 1 hour.](/thumbs/85/92047421.jpg) Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2015 2016 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C1 Higher Tier [GSD22] *GSD22* *G5802* *GSD22* THURSDAY 19 MAY 2016, MORNING TIME
Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2015 2016 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C1 Higher Tier [GSD22] *GSD22* *G5802* *GSD22* THURSDAY 19 MAY 2016, MORNING TIME
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7761599169* CHEMISTRY 0620/31 Paper 3 (Extended) October/November 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7761599169* CHEMISTRY 0620/31 Paper 3 (Extended) October/November 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
GCSE 4493/02 CHEMISTRY 3 HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY. A.M. THURSDAY, 19 May hour S PMT. Candidate Number. Centre Number.
 Surname entre Number andidate Number Other Names 0 GSE 4493/02 S16-4493-02 EMISTRY EMISTRY 3 IGER TIER A.M. TURSDAY, 19 May 2016 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 8 2. 7 4493 020001
Surname entre Number andidate Number Other Names 0 GSE 4493/02 S16-4493-02 EMISTRY EMISTRY 3 IGER TIER A.M. TURSDAY, 19 May 2016 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 8 2. 7 4493 020001
Naming and Classifying the Elements. nobelium antimony. oxygen arsenic. phosphorus beryllium. platinum bismuth. plutonium boron.
 6.2 Naming and Classifying the Elements To learn more about the origins of the names of the elements, visit www.science.nelson.com GO The names of the elements have varied origins. Some elements are named
6.2 Naming and Classifying the Elements To learn more about the origins of the names of the elements, visit www.science.nelson.com GO The names of the elements have varied origins. Some elements are named
Standard Solutions (Traceable to NIST)
 Standard Solutions (Traceable to NIST) - Multi Element ICP Standard Solutions (Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy) - Single Element ICP Standard Solutions (Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy)
Standard Solutions (Traceable to NIST) - Multi Element ICP Standard Solutions (Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy) - Single Element ICP Standard Solutions (Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy)
New GCSE 4462/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 1
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4462/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. WEDNESDAY, 18 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4462/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. WEDNESDAY, 18 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may
Chemistry Monday 4 November 2013 Paper One Resource book
 2013 Senior External Examination Chemistry Monday 4 November 2013 Paper One Resource book 9 am to 11:40 am Directions You may write in this book during perusal time. Contents Table of constants Simple
2013 Senior External Examination Chemistry Monday 4 November 2013 Paper One Resource book 9 am to 11:40 am Directions You may write in this book during perusal time. Contents Table of constants Simple
Title: Feb 14 11:20 AM (1 of 58)
 Title: Feb 14 11:20 AM (1 of 58) Introduction to Chemistry What is chemistry? Title: Feb 12 6:47 PM (2 of 58) Title: Dec 3 11:24 AM (3 of 58) Introduction to Chemistry What is chemistry? Definition: The
Title: Feb 14 11:20 AM (1 of 58) Introduction to Chemistry What is chemistry? Title: Feb 12 6:47 PM (2 of 58) Title: Dec 3 11:24 AM (3 of 58) Introduction to Chemistry What is chemistry? Definition: The
49 CFR Ch. I ( Edition)
 TABLE 1 TO APPENDIX A HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCES OTHER THAN RADIONUCLIDES Hazardous substance Reportable quantity (RQ) pounds (kilograms) K125... Filtration, evaporation, and centrifugation solids from the production
TABLE 1 TO APPENDIX A HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCES OTHER THAN RADIONUCLIDES Hazardous substance Reportable quantity (RQ) pounds (kilograms) K125... Filtration, evaporation, and centrifugation solids from the production
