A REVIEW OF EXPERIENCES WITH AL-6XN AND ZERON 100 ALLOYS IN AIR POLLUTION CONTROL SYSTEMS
|
|
|
- Piers Jordan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A REVIEW OF EXPERIENCES WITH AL-6XN AND ZERON 100 ALLOYS IN AIR POLLUTION CONTROL SYSTEMS D. Wachow iak J. Wilson Rolled Alloys 125 West Sterns Road Temperance, M I 48182
2 A REVIEW OF EXPERIENCES WITH AL-6XN AND ZERON 100 ALLOYS IN AIR POLLUTION CONTROL SYSTEMS D. Wachow iak J. Wilson Rolled Alloys 125 West Sterns Road Temperance, M I Abstract Coal fired power plants are faced with increasingly strict air quality control laws and EPA rules. New multi-pollutant legislation is controlling a wider range of emissions, especially sulfur compounds. A significant number of flue gas desulfurization (FGD) units worldwide employ wet scrubbing to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions by more than 90 percent. Wet scrubbing has also been found to be effective at removing mercury in many cases. Due to the inherent contaminants generated by the combustion of coal, wet FGD s require the use of corrosion resistant materials in their construction. A variety of metallic corrosion resistant alloys are currently used in these pollution control systems. This paper will review the use of AL-6XN and ZERON 100 alloys in various FGD applications around the world. Examples of AL-6XN and ZERON 100 in actual service in FGD units will be presented. AL-6XN and ZERON 100 are alloys that have been chosen for these systems when conditions are too severe for either 317L stainless steel or 2205 duplex stainless steel. Experimental data will be reviewed that supports the use of these alloys in the high chloride containing environments encountered by the many components of the pollution control systems. AL-6XN and ZERON 100 alloys have proven to be cost effective materials of construction that fill the gap between the lower alloyed stainless steels such as 317L, and 2205, and the high molybdenum and nickel based alloys such as C-276. As AL-6XN and ZERON 100 alloys are established materials of construction that are readily available in product forms necessary to complete an FGD system. Introduction Coal fired power plants currently generate nearly half of the electric power in the United States. Combustion of coal generates NOx, SO2, particulates, and other pollutants that contaminate the environment. These coal fired power plants are being faced with increasingly stricter air quality control laws and EPA rules mandating the reduction of a wide range of pollutants especially
3 sulfur compounds. Thus, it is clear that pollution control will remain a major concern for the power generation industry for many years. The most effective way to significantly reduce emissions of SO2, and in some cases mercury, is through the use of flue gas desulfurization (FGD). There are several FGD methods available, examples include various dry scrubbing methods, sea water scrubbing, and wet scrubbing with lime or limestone. The majority of the scrubbers currently being installed use the wet limestone technology. This method is the best suited to scrubbing the high volume of flue gas emitted by large power plants. In addition, this method has the added advantage of allowing for the production of wallboard quality gypsum, which can be sold to partially offset the cost of scrubbing. The corrosive conditions within an FGD are complex, with many factors contributing to the severity of the environment. The selection of an appropriate material will depend on the operating parameters of the system as well as the environment surrounding the specific components. The most important corrosive species generated during the combustion of coal are chlorides and fluorides along with sulfur bearing species. Contributing to the corrosive environment is the temperature, acid dew point, ph, crevice forming deposits, slurry additives, etc. Typically, several alloys are used in a system, which will be matched to the conditions under which a component is operating. Fortunately, extensive operating experience has been generated which can be used as guide to selecting appropriate materials of construction. The purpose of this paper is to review the properties and corrosion resistance of the 6% Mo alloy, AL-6XN alloy (UNS N08367) and the super duplex ZERON 100 (S32760), in relation to pollution control systems. In addition, typical current applications of the N08367 and S32760 alloys in the FGD systems are described. Backgr ound Several alloys have been used in FGD systems ranging from the 300 series stainless steels to the high nickel based alloys. Some of these alloys are listed below in Table 1. The appropriate alloy of construction will depend on the operating conditions and location within the equipment. In the case of the absorber inlet, shown in Figure 1, the hot flue gas passes through the sulfuric acid dew point, leading to the condensation of hot, concentrated sulfuric acid. In this aggressive environment, a nickel alloy with a high content of molybdenum is necessary. The vast majority of absorber inlets in the world are made of N10276 alloy. The material of construction for the absorber tower is largely dependent on the chloride content of the slurry. Fluorides may also be present, which can be considered to be approximately the same as chlorides with regard to their effect on pitting of stainless steels. Since the fluoride content is usually very low, discussion of the effect of halides will be limited to chloride content. The chloride content of the slurry is largely determined by the chloride concentration of the coal being burned, and the rate at which fresh water is added to the slurry (blow down). In cases where a high blow down rate is not possible, e.g. where water treatment is inadequate, the slurry chloride content may become very concentrated.
4 Table 1: Nominal Composition (wt. %) of Stainless Steels and Nickel Based Alloys used in FGD Systems UNS Number Alloy Cr Mo Ni Fe Other Duplex S Bal 0.16N S32760 ZERON Bal 0.22N Austenitic S L Bal S LMN Bal 0.15N Superaustenitic N08367 AL-6XN Bal 0.22N Ni Based N Bal 4 4(Cb+Ta) N Bal 5.5 4W N Bal 4 3W, 1.7Co Table 2: Temperature for Initiation of Crevice Corrosion in 10% Ferric Chloride (FeCl 3 6H 2 O) Solution per ASTM G 48 Practice B; PRE N = Cr + 3.3Mo + 16N UNS Number F ( C) PRE N S (2) 28 S (20) 35 S (20) 35 S (40) 41 N (43) 45 N (45) 51 N (55) 69 N (55) 65
5 A useful way of ranking the resistance of a material to chlorides is through the Pitting Resistance Equivalent, PREN. Equation 1 gives a common formula for calculating the PREN for austenitic and duplex stainless steels. The elements Cr, Mo, and N provide resistance, especially when present together (1-3). Nitrogen is particularly effective in the superaustenitic alloys with high Mo content (4-6). PREN = Cr + 3.3Mo + 16N (1) The higher the PREN, the more resistant the alloy is to pitting and crevice corrosion in the presence of chlorides. Typical PREN values for various alloys are shown in Table 2 on the previous page. By listing the alloys by decreasing PREN, the 6% Mo alloys and super duplex stainlesses are positioned above (more resistant than) the conventional stainless steels and approaching the nickel alloys. Figure 1. Schematic of an FGD system The absorber outlet ducting will be exposed to some slurry carry over from the absorber as well as residual SO3 from the flue gas. Since the temperature in the absorber outlet is typically well
6 below the sulfuric acid dew point, low ph condensates containing chlorides are often present. Thus, a Ni-Cr-Mo alloy, such as N10276 or N06022, is often employed. However, the increased efficiency and improved design of modern scrubbers somewhat alleviates this issue, allowing for the application of stainless steels in some cases. A plot demonstrating the corrosion resistance of various alloys in sulfuric acid is given in Figure 2. The presence of chlorides in conjunction with sulfuric acid will generally increase the corrosion rate. Figure 2. Corrosion resistance of alloys in sulfuric acid. Lines indicate a corrosion rate of 0.1mm/yr (4mpy) A general guide for alloy selection for FGD absorber towers is presented in Figure 3. This table applies to a temperature range of 50 C 60 C (120 F 150 F) and a fluoride content of less than 50 ppm. This table is based on the open literature on the subject and is intended to be used as a guide only. Factors such as deposit formation, fabrication procedures, contaminants, additives, etc., must also be taken into consideration when selecting the appropriate material.
7 N08637 Superaustenitic Figure 3. Alloy selection chart for FGD absorber towers In the early 1970s UNS N08366 alloy, containing 6.3Mo, along with 20Cr and 24Ni, was introduced (7). Used primarily as welded power plant condenser tube in seawater, this material performed well in the high chloride environment (8-9). High Cr and Mo provided excellent resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion but also promoted intermetallic phases. This limited the thickness at which the material could be produced to thin gauges, such as that used for condenser tubing. Nitrogen suppresses intermetallic phases (10-11) and 0.2 percent was shown to be beneficial to the 20Cr 24Ni 6.3Mo alloy. Nitrogen also improves pitting resistance and increases strength. These benefits, incorporated into the N08367 alloy in the early 1980s, permitted a full range of product forms and much broader applicability. The N08367 alloy has found may uses in power plants (12-13), oil refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants, and pulp mills, as well as in a variety of seawater applications. Not all alloys in the 6Mo family contain N, and some have a higher or lower nickel content than N08367 alloy. Some other 6Mo alloys also contain Cu which may cause intergranular attack in high chloride environments. All of these alloys have a low carbon content ( L grades), and thus, are highly resistant to sensitization and intergranular corrosion. S32760 Super Duplex The first duplex stainless steels, developed in the 1920 s, lacked toughness and ductility, and thus, were of little utility. Development of modern duplex stainless steels began in the late 1970 s with the expanded commercial use of the AOD (Argon Oxygen Decarburization) process, which among other things permitted the controlled addition of nitrogen. The wide spread usage of duplex alloys was further driven by the sharp escalation in raw material prices during the mid 2000 s, resulting in their wide spread use as a cost effective upgrade over traditional austenitic alloys. The standard duplex alloy, namely UNS S32205, has been the chosen alloy for many FGD systems in the past decade. The 25Cr alloy, known commercially as 255, saw its first extensive FGD application in the United States at Gibson Station in the mid 1980 s. The good performance of this alloy in this application has lead to more widespread use elsewhere. The Super Duplex alloys S32750 and S32760, commercially know as 2507 and ZERON 100, respectively, have been widely and successfully applied in Oil and Gas and Desalination applications for many years. More recently, these alloys have gained acceptance in the FGD community and are being applied in environments where excellent corrosion resistance is needed.
8 The duplex name comes from the fact that the alloys develop a microstructure containing approximately equal amounts of austenite and ferrite phases. The duplex microstructure results in properties that are a combination of those of ferritic and austenitic alloys. The first widely available super duplex stainless steel was developed by Gradwell and coworkers in the mid 1980 s. This alloy was called ZERON 100 and was developed as a casting alloy (J93380) for pump applications in the oil and gas industry. The performance of the steel in this application generated a demand for the alloy in wrought product forms also. As demand for the steel grew, clients called for ASTM, NACE, British Standards and other codes to include and cover the ZERON 100 range of products. Moreover, with the introduction of the EC Procurement Directive in 1993, it became an exception for clients to specify any trade name in requests for quotation and a generic description for the alloy was required for the business to continue. In , ASTM considered the properties of several heats of ZERON 100 in a range of product forms and on the basis of this designated the code UNS S32760 to the alloy and introduced this number into several standards. Finally, in 1997, UNS S32760 was listed in ASME complete with applicable design stresses. These listings were again based upon the properties of the proprietary alloy. Fabr ication Char acter istics Both the N08367 and S32760 alloys are readily welded to itself, other stainless steels, nickel based alloys, and carbon steel. Segregation occurs in as-cast matching-composition weld metal, leaving areas which are low in Cr and Mo, making them susceptible to pitting. For this reason a weld filler metal with -higher Mo content is needed for proper as welded corrosion resistance. Nickel alloy 625 (AWS ERNiCrMo-3) filler metal and 112 (AWS ENiCrMo-3) electrodes provide welds with corrosion resistance and mechanical properties generally comparable to the N08367 alloy base metal. Other high-mo, nickel-base filler metals, such as N01276 alloy are also suitable. S32760 can also be readily welded using a matching composition ZERON 100X filler metal, which overmatches the base metal with more nickel to ensure proper phase balance after welding in complete without the need to anneal afterwards. Both the N08367 and S32760 also have good ductility to be formed into various shapes and sizes needed to fabricate equipment necessary within the FGD absorber. L abor ator y Testing Both the N08367 and S32760 alloys have been tested in various conditions that represent conditions that can be seen in FGD environments, including high chloride and fluoride environments, sulfuric acid mixed with chloride environments and other severe environments that take into effect the elevated temperatures, lower ph and various amounts of chloride and acid levels within the FGD system.
9 N08367 Laboratory Testing Extensive testing has been performed comparing N08367 alloys to stainless steels and higher Ni- Mo alloys. The testing includes standard ASTM corrosion testing as well as specialized testing intended to simulate FGD environments. Data from some of these tests are shown in the following tables. An indication of the pitting resistance is given by the ferric chloride crevice corrosion data shown in Table 2, which is generated using test method ASTM G48-B. The capability of the N08367 alloy with 6.2Mo is seen to be close to that of nickel-base N06625 alloy (9Mo) and significantly better than S32205 and S31726 alloys. In the ferric chloride test without crevices, ASTM G48-A, the N08367 alloy withstands pitting at 62 C (145 F). There is a good correlation between the ferric chloride test results and the calculated value of the PREN for the various alloys. Test data for N08367 alloy exposed to 24,000 ppm chloride water with temperature varied from 43 C (110 F) to 71 C (160 F) and ph varied from 4 to 0.5 with H2SO4 are presented in Table 3. No corrosion was observed at ph 4 or 2. With ph adjusted to 1.0, corrosion was not observed up to and including 66 C (150 F). However, at 71 C (160 F) crevice corrosion was observed. With ph 0.5, no corrosion was observed at 60 C (140 F) but crevice attack was observed at 66 C (150 F). The strong influence of the temperature on corrosion rate should be noted. Crevice corrosion data for exposure to a severe acid-chloride solution, the Green Death solution, are given in Table 4. This test is commonly used to compare materials in reducing environments, such as that of the inlet duct of an absorber. Crevice corrosion is observed on S31603 and S31703 at room temperature. At 50 C (122 F) alloys with up to 4.4Mo are corroded. The N08367 (6.2Mo) alloy and higher Mo nickel-base materials resist attack. Further increase in temperature to 70 C (158 F) resulted in significant crevice corrosion on all alloys through the 9Mo N06625 alloy. The 16Mo N10276 alloy exhibited only superficial crevice corrosion. Testing has also been performed under actual service conditions at various locations. Field testing data was presented in 2000 (14). Again, a generic 6 Mo sample was used in the testing. The testing above indicates that N08367 alloy is expected to perform similarly. The most severe test conditions were found at the Orlando Utilities Stanton Energy Plant. Various samples were exposed for 270 days. The slurry average chloride content was ~70,000 ppm, the ph was 5.6, and the temperature was ~130 F (54 C). Figure 4 shows the alloy samples after testing. Note the 6 Mo and N10276 displayed very good corrosion resistance. Crevice corrosion on a S31603 specimen was severe. Localized attack incurred by the S31726 stainless steel was considerably less than that suffered by S31603 stainless steel, but nevertheless still quite severe. One of the duplex stainless steel specimens exhibited under-scale type etching. The results demonstrate the superior resistance of the 6Mo stainless steels to the FGD environment compared to the lower alloyed stainless steels.
10 Table 3: 24,000ppm Chloride Water with ph and Temperature Varied (1) Temperature Weight Loss, g/cm 2 (2) F ( C) ph 0.5 (3) ph 1 ph 2 ph (43) (49) (54) (60) (66) (71) (1) 30 day tests, procedures per ASTM G 48-B (2) Average of two tests (3) ph adjusted with H 2 SO 4 Table 4: Crevice Corrosion Testing in Simulated Scrubber Environment (Green Death (1)) Weight Loss g/cm 2 (2) Alloy 75 F (25 C) 122 F (50 C) 158 F (70 C) S S N N N (1) 7 Vol. % H 2 SO 4, 3 Vol. % HCl, 1 Wt. % CuCl 2, 1 Wt. % FeCl 3 (2) Tests per ASTM G48-b procedures, 72 hour duration
11 Figure 4. Results of exposure to ~70,000 ppm chlorides at a ph of 5.6 and a temperature of ~130F (54C) for 270 days. Exposure to slurry at Orlando Utilities Stanton Energy Center (FL) S32760 Laboratory Testing There is obvious concern that alloys for use in FGD scrubber systems may suffer from crevice corrosion, as crevices abound in all commercial designs. Early laboratory tests (15) were conducted in simple sulphate/ chloride solutions and the results suggested that ph had little effect on the critical crevice corrosion temperature (CCCT). However, more recent work by Weir Materials & Foundries (16) in more realistic slurries has shown that ph has a strong effect and the CCCT can decrease over 20 C as the ph decreases from ph 5 to ph 3. During normal operation ph levels are generally from 4.5 to 6, but under adverse conditions ph values as low as 4 are possible. Hence, WM&F has carried out a series of electrochemical tests in simulated FGD slurries at this ph. Table 5 shows the results of CCCT tests in simulated anthracite slurry at ph of 4. In this environment normal operating temperatures are about 122 F (50 C). The results show that wrought S32760 is superior to the older cast 25Cr duplex. Welded and cast S32760 and J93380 (cast version of ZERON 100) are also suitable in this application. Table 6 shows the CCCT data for simulated lignite slurry, where operating temperatures are typically F (60 65 C). These results show that both cast and welded ZERON 100 are suitable, but the older 25Cr duplex alloy is not. They also show the excellent resistance of ZERON 100 to crevice corrosion, particularly the wrought product. Erosion corrosion can be a significant problem in FGD systems, especially in areas in direct contact with the slurry. These areas include the absorber sump, slurry piping, pumps, valves, and agitators. The calcium sulphate and limestone in FGD slurries are not particularly erosive. It has been found that fly ash causes most of the erosion.
12 Table 5: Critical crevice temperature for some stainless steels in simulated anthracite FGD slurry at ph of 4 Form Alloy CCCT F ( C) Wrought S32760 > 176 (80) Wrought S (64.7) Welded S (58.5) Cast J (57.8) Cast 25Cr Duplex (42) Slurry composition CaSO 4 10 wt. % Chloride 40,000ppm Fluoride 50ppm Dithionate 200ppm Fe 3+ 10ppm A13+ 30ppm Table 6: Critical crevice temperature for some stainless steels in simulated lignite FGD slurry at ph of 4 Form Alloy CCCT F ( C) Wrought S32760 > 181 (83) Wrought S (66.7) Welded S (63.4) Cast J (62.6) Cast S (39.6) Slurry composition CaSO 4 10 wt. % Chloride 15,000ppm Fluoride 200ppm Dithionate 200ppm Fe 3+ 10ppm A13+ 30ppm
13 Tests have been conducted in simulated FGD brines including fly ash in a recirculating erosion test rig (17). Results from pin erosion tests showed that S32760 offered superior erosion resistance to austenitic alloys such as 316L as well as more highly alloyed materials. Figure 6 shows the erosion resistance of several alloys including Z100 as a function of ph. It can be seen that Z100 has the best erosion resistance, which is not affected by ph i.e. the alloy does not corrode significantly at low ph. Applications Figure 5. Pin erosion rig test results in a simulated FGD slurry Both N08367 and S32760 have been used successfully for over 20 years in several areas on the FGD system around the world. Below are highlights of many of the successful applications where these two alloys have been used over the years. N08367 Applications The following section gives several examples of the application of N08367 in actual pollution control applications. Northern Indiana Public Service Company (NIPSCO) Bailly Generating Station. This station uses 2 to 4.5% sulfur bituminous coal. Pure Air on the Lake manages this FGD system. N08367 alloy has been used in several applications in this system. The successful performance of N08367 alloy in earlier applications has led to its utilization in other areas. Estimated conditions of the absorber are ~11,000 ppm chlorides, ph of 6, and 125 F (52 C).
14 Original construction consisting of N08367 alloy recirculation piping, spray piping system, and rotary sparger unit (submerged in the limestone scrubber tank) have been in service for over 16 years. See Figures 5 & 6. In 1997, N alloy w as fabricated into top hats to protect flanged connections in rubber lined steel pipe for slurry pipe headers and the spray piping systems. Top hats w ere also installed in other areas in more recent times. See Figure 7. In 2003, N alloy box beams replaced rubber coated carbon steel beams. These beams, located in the absorber tower, support a 28,000 piece grid packing system. See Figures Figure 5 & 6. N08367 Alloy Rotary Sparger (left), N08367 Alloy Spray Piping (right) Figure 7. N08367 Alloy Top Hats
15 Figure 8 & 9. N08376 Alloy Box Beams (left) replaced rubber coated steel beams (right) Figure 10. N08376 Alloy Box Beams Installed Louisville Gas & Electric (LG&E) Cane Run Station. This station burns 3.5% sulfur coal. N08367 has been used in several applications in this system. The estimated chloride levels in the Unit #6 absorbers are ~5500 ppm. Unit #5 absorber is ~800ppm. In 1990, N alloy replaced S31726 lining in two FGD downcomer ducts. See Figure 11. The S31726 liner failed in less than 3 years due to perforation from pitting. 14ga and 16ga sheet w as used to w allpaper the duct. The N alloy is still in service after 21 years. In 1999, N alloy replaced a 16 coated carbon steel pipe for the pump suction system used to recirculate the scrubber liquor that quenches the flue gas in the absorber tower. The carbon steel supporting beams that support the absorber trays w ere w allpapered w ith N alloy.
16 In 2003, N alloy w as fabricated into liquid distribution rings in the absorber tow er. These w ere installed to protect the absorber tow er w alls. Figure 11. N08376 Alloy used in Absorber Tower and Downcomer Duct Korea Electric Power Company (KEPCO) Taean Units 1-4, Hadong Units 1-6. A total of 10 absorbers were installed for KEPCO, with start-up of eight units in 1998 and two in No problems have been reported since the installation. Each of the 10 wet limestone absorber towers was 16.8m (55 ft.) in diameter and serviced a 500MW boiler. N08367 alloy was used for absorber tower plates, internals including stiffeners and structurals, piping systems, and the absorber trays. Inlet SO 2 concentration was 645 ppm and chloride levels were ~20,000 ppm maximum. The N08367 alloy for this project was produced to a minimum PREN of 47.5 in order to meet the demanding requirements for corrosion resistance. One of the absorber towers may be seen in Figure 12. Figure 12. N08376 Alloy used in Absorber Tower at KEPCO Hadong Power Station
17 Indianapolis Power & Light (IP&L) Petersburg Station. N08367 alloy was used for the wallpapering of a carbon steel duct connecting the electrostatic precipitator to the flue stack. Lower than expected temperatures led to condensation in the bottom of the 12 foot (3.7m) wide duct. The duct was approximately 150 feet (45.7m) long. 35,000 pounds (15,909 kg) of 14ga N08367 alloy sheet were supplied to wallpaper the bottom of the duct to protect against corrosion by the condensate which would include sulfurous acid and chlorides. Gas estimates through the duct were 33 lbs/hour of Cl- and 29 lbs/hr of SO2. The lining and duct are shown in Figure 13. After 5 years in service the duct was removed from service with no reported problems. Reason for removal was the installation of the of a wet FGD system. Due to the success of N08367 in this application, it was selected for portions of the absorber tower contacted after the quench section. Figure 13. N08376 Alloy used for Duct Lining at IP&L Ameren Energy Generating Company Newton Station. N08367 alloy was fabricated into a turning vane for a flue gas stack. The turning vane was installed to address an undesirable cyclone effect at the base of the flue gas stack. Excellent resistance to pitting and crevice attack was demonstrated by the N08367 alloy, necessary for this plant which burns high sulfur coal. The N08367 alloy was chosen based on corrosion testing. The scrubber was decommissioned in 1994, but CIPS (operator at the time) reported that the N08367 performed well in resisting corrosion over several years of service. The vane can be seen in Figure 14.
18 Figure 14. N08376 Alloy used for turning vane Duke Energy Zimmer Station. N08367 alloy 14ga sheet was chosen to line six bypass ducts for each of the absorber modules. The carbon steel bypass ducts were corroding due to the condensation of acid. Installation was performed in early A photo of the duct may be seen in Figure 15. Figure 15. N08376 Alloy used to line bypass ducting
19 New Brunswick Power Coleson Cove Power Plant. Over 14,000 feet (4267m) of N08367 box beams were furnished for use in a wet electrostatic precipitator (WESP). These beams were drawn to an overall size of 1.0 x 6.0 x (25.4mm x 152mm x 3.2mm) average wall for the application. Over 300,000 lbs (136,364 kg) of N08367 alloy sheet was also supplied for use as collector plates, which were hung from the box beams. Over 42,000 lugs were also fabricated from plate. The schematic of this WESP can be seen in Figure 16 below. Figure 16. N08376 Alloy used for collector plates, box beams, and lug clips Westar Energy Jeffrey Energy Center. Westar Energy used over 500 ton of N08367 plate to upgrade their FGD units in N08367 was chosen due to its track record in similar FGD environments. The alloy was mainly used for ductwork to connect the three existing FGD units as well as for modifications to the FGD units in order to increase the SO 2 removal rate to 95%. N10276 was also used in these modifications and new installations where environments were more severe and required a higher corrosion resistant alloy. A section of this ducting can be seen below in Figure 17.
20 Figure 17. N08376 Alloy used for ductwork connecting existing FGD units San Miguel Electric Cooperative. San Miguel Electric has used the N08367 alloy in few areas within their FGD System. Over 5 years ago, they tested both S32205 and N08367for turning vanes in their ductwork. After inspection, they noticed that both the S32205 and AL-6XN looked brand new after several months in service. N08367was also selected for the walls and ceiling of the outlet ducting downstream of the reheater where acid concentration are higher. N08367was also used in some areas on the floor of the ducting along with N It was noticed that where the acids pool on the floor, the N08367did not hold up as well as the N10276, but on the walls and ceiling where the acids could run down the walls, N08367has held up great for nearly 5 years now. Hoosier Energy Merom Station. Hoosier Energy has relined their FGD absorbers with N The original FGD s were constructed from a lower corrosion resistant alloy and after detecting some corrosion, it was determined to reline all of the absorbers using N08367.
21 S32760 Applications The following section gives several examples of the application of S32760 in actual pollution control applications. The excellent corrosion resistance of S32760 combined with its high strength makes it suitable for a wide range of applications in FGD plants. Cast ZERON 100 can be used for pumps, valves, and agitators, while the wrought product can be used for ducting, where acid condensation may occur, up to 300 C. Other applications include gas distribution plates, sprinkler heads, fasteners, centrifuges, and absorber towers. With absorber towers, the high strength of super duplex stainless steel means it is more economic to make absorber vessels from solid alloy rather than clad steel. One power station in the USA has changed from clad to solid super duplex for absorber vessels because of the economics. Ratcliffe Power Station - UK. The slurry centrifuges at Ratcliffe FGD plant were supplied in S32760 in After fifteen years operation, they are in excellent condition. After a short time of operation, the GRP slurry return lines at Ratcliffe FGD plant were suffering severe erosion. These have now been replaced with spools of S32760 and have given no further problems. A picture of the S32760 centrifuges at Ratcliffe can be seen in Figure 19. Figure 19. S32760 slurry centrifuge at Ratcliffe Power Plant Drax Power Station - UK. S32760 has been used successfully for the slurry pumps, agitator stools and gas distribution plates at the Drax FGD plant in the UK since A picture of the FGD slurry recirluation pumps at Drax can be seen in Figure 20. The pumps are lasting 30,000 to 40,000 hours between major overhauls. ZERON 100 has also had the advantage that minor damage can be weld repaired, while white cast irons, also used for FGD pumps, cannot.
22 Figure 20. S32760 slurry recirculation pump fitted at Drax FGD Plant in the UK Power Plant in Texas. S32760 was selected for the fabrication of three FGD outlet duct dampers for a power plant in the state of Texas. The fabricator worked with Rolled Alloys to learn to weld and form the ZERON 100, which was a new alloy to the fabricator. The strength and cost savings vs a higher nickel alloy was the criteria used for material selection as well as it proven corrosion resistance in testing and in FGD environments. Figure 21. S32760 used for three FGD outlet duct dampers at a Texas power plant
23 Summary Alloys N08367 and S32760 are currently being successfully used for many applications in FGD systems. These include absorber bodies, ducting, mixers, spargers, spray piping, turning vanes, dampers, wallpaper lining, reheaters, spray absorbers, structural supports, agitators, and centrifuges. These two alloys have been employed for over 20 years and have demonstrated excellent performance. N08367 and S32760 alloys are shown to be cost effective materials of construction to fill the gap between the 300 series stainless steels and duplex S32205 and the higher molybdenum and nickel based alloys. Both materials are available in a wide variety of product forms (plate, sheet, round bar, pipe, fittings, and flanges) needed to meet the requirements of all FGD system components.
24 References 1. R. J. Brigham, Corrosion, 28 (5), (1972), p R. J. Brigham, E. W. Tozer, Corrosion, 29 (1), (1973), p R. J. Brigham, E. W. Tozer, Corrosion, 30 (5), (1974), p H. E. Deverell, J.R. Maurer, Materials Performance, 17, (3), (1978), p J. R. Kearns, J. Mater. Energy Sys., 7 (1), (1985) p R. Bandy, Y. C. Lu, R. C. Newman, C. R. Clayton, Proc. Equilibrium Diagrams and Localized Corrosion Symposium, P. Frankenthal and J. Kruger, Eds., (Electrochem. Soc., Pennington, NJ, 1984) p J. E. Truman, M. J. Coleman, K. R. Pirt, Brit. Corrosion J., 12 (4), 1977, p H. E. Deverell, J. R. Maurer, Materials Performance, 17, (3), A. H. Tuthill, Materials Performance, 27, (7), H. E. Deverell, C. R. Finn, G. E. Moller, Corrosion/88, Paper No. 313, (Houston, TX: NACE, 1988). 10. A. E. Baumel, M. Horn, H. Grafen, Proc. Fifth International Congress Metall. Corrosion, (NACE, Houston, TX, 1974), p H. Their, A. Baumel, E. Schmidtmann, Archiv. Eisenhutt, 40 (4), (1969), p I. A. Franson, Joint ASME/IEEE Power Gen Conf., 85-JPGC-Pwr-15, (Milwaukee, WI, October, 1985). 13. I. A. Franson, J. R. Maurer, Joint ASME/IEEE Power Gen Conf., 87-JPGC-Pwr-27, (Miami, FL, October, 1987). 14. J. F. Grubb, Proc. of the Mega Symposium, NACE, J P Audouard, P Soulignac and F Dupoiron, Materials Selection for Wet FGD Systems, Presented at "Airpol '90", Louisville, USA Oct 1990.
25 16. R Francis, WM&F Technical Note TN 1235 February J T Dallas and T A McConnell, "Solids Pumping" Seminar, I Mech E London, UK Oct C Stinner, J Wilson, AIRPOL 2007 Conference Proceedings AL-6XN is a registered trademark of ATI Technologies ZERON is a registered trademark of Rolled Alloys
A REVIEW OF EXPERIENCES WITH AL-6XN AND ZERON 100 IN AIR POLLUTION CONTROL EQUIPMENT. *Devin M. Wachowiak and Jason D. Wilson
 A REVIEW OF EXPERIENCES WITH AL-6XN AND ZERON 100 IN AIR POLLUTION CONTROL EQUIPMENT *Devin M. Wachowiak and Jason D. Wilson Rolled Alloys 125 West Sterns Road Temperance, MI 48182 USA (*Corresponding
A REVIEW OF EXPERIENCES WITH AL-6XN AND ZERON 100 IN AIR POLLUTION CONTROL EQUIPMENT *Devin M. Wachowiak and Jason D. Wilson Rolled Alloys 125 West Sterns Road Temperance, MI 48182 USA (*Corresponding
AL-6XN ALLOY: ALLOY OF THE 21 ST CENTURY FOR AIR POLLUTION CONTROL TIM CARNEY JASON WILSON ROLLED ALLOYS TEMPERANCE, MI 48182
 AL-6XN ALLOY: ALLOY OF THE 21 ST CENTURY FOR AIR POLLUTION CONTROL TIM CARNEY JASON WILSON ROLLED ALLOYS TEMPERANCE, MI 48182 PAPER TO BE PRESENTED AT: POWERGEN 2003 DECEMBER 9-11 LAS VEGAS, NV USA ENVIRONMENTAL
AL-6XN ALLOY: ALLOY OF THE 21 ST CENTURY FOR AIR POLLUTION CONTROL TIM CARNEY JASON WILSON ROLLED ALLOYS TEMPERANCE, MI 48182 PAPER TO BE PRESENTED AT: POWERGEN 2003 DECEMBER 9-11 LAS VEGAS, NV USA ENVIRONMENTAL
UNS N08367 Alloy Superaustenitic Stainless Steel for Air Pollution Control Equipment. Charles Stinner ATI Allegheny Ludlum Brackenridge, PA 15014
 UNS N08367 Alloy Superaustenitic Stainless Steel for Air Pollution Control Equipment Charles Stinner ATI Allegheny Ludlum Brackenridge, PA 15014 Jason Wilson Rolled Alloys Temperance, MI 48182 ABSTRACT
UNS N08367 Alloy Superaustenitic Stainless Steel for Air Pollution Control Equipment Charles Stinner ATI Allegheny Ludlum Brackenridge, PA 15014 Jason Wilson Rolled Alloys Temperance, MI 48182 ABSTRACT
Accelerated Crevice Corrosion of Duplex Stainless Steels in Wet Limestone FGD Environments. Deba Maitra, Special Metals Corporation PCC Energy Group
 Accelerated Crevice Corrosion of Duplex Stainless Steels in Wet Limestone FGD Environments Deba Maitra, Special Metals Corporation PCC Energy Group Outline General comments on alloy crevice corrosion and
Accelerated Crevice Corrosion of Duplex Stainless Steels in Wet Limestone FGD Environments Deba Maitra, Special Metals Corporation PCC Energy Group Outline General comments on alloy crevice corrosion and
HASTELLOY ALLOYS: SOLUTIONS TO SEVERE WET FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION ENVIRONMENTS
 HASTELLOY ALLOYS: SOLUTIONS TO SEVERE WET FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION ENVIRONMENTS H. J. White Haynes International 1020 West Park A venue Kokomo, Indiana 46904-9013 HASTELLOY ALLOYS: SOLUTIONS TO SEVERE
HASTELLOY ALLOYS: SOLUTIONS TO SEVERE WET FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION ENVIRONMENTS H. J. White Haynes International 1020 West Park A venue Kokomo, Indiana 46904-9013 HASTELLOY ALLOYS: SOLUTIONS TO SEVERE
Overmatching Superalloy Consumable Inco-weld 686CPT Broadens its Applications to Include Welding Super Austenitic and Super Duplex Stainless Steels
 Overmatching Superalloy Consumable Inco-weld 686CPT Broadens its Applications to Include Welding Super Austenitic and Super Duplex Stainless Steels P0468 Authors: Ph.D C. Thornton, B.Sc C. Cooper Special
Overmatching Superalloy Consumable Inco-weld 686CPT Broadens its Applications to Include Welding Super Austenitic and Super Duplex Stainless Steels P0468 Authors: Ph.D C. Thornton, B.Sc C. Cooper Special
ZERON 100 FOR DOWNSTREAM PROCESSING IN ACID LEACH MINING. Park Works Manchester M40 2BA UK (*Corresponding author:
 ZERON 100 FOR DOWNSTREAM PROCESSING IN ACID LEACH MINING *Roger Francis 1 and Devin M. Wachowiak 2 1 RA Materials Park Works Manchester M40 2BA UK (*Corresponding author: rfrancis@rolledalloys.com) 2 Rolled
ZERON 100 FOR DOWNSTREAM PROCESSING IN ACID LEACH MINING *Roger Francis 1 and Devin M. Wachowiak 2 1 RA Materials Park Works Manchester M40 2BA UK (*Corresponding author: rfrancis@rolledalloys.com) 2 Rolled
Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers
 Materials Selection for Condensing Economizers Gary M. Carinci, Ph.D. Outokumpu Stainless Outokumpu Stainless Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers Temperature ph control Sulfur
Materials Selection for Condensing Economizers Gary M. Carinci, Ph.D. Outokumpu Stainless Outokumpu Stainless Factors Influencing Materials Selection in Condensing Economizers Temperature ph control Sulfur
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING
 DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS
 DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS corrosion resistant alloys ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS corrosion resistant alloys ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
STAINLESS STEEL SELECTION FOR FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION EQUIPMENT
 STAINLESS STEEL SELECTION FOR FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION EQUIPMENT Gary M. Carinci William A. Pratt Outokumpu Stainless 3209 McKnight East Drive Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15237 gcarinci@tmr-inc.com Abstract
STAINLESS STEEL SELECTION FOR FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION EQUIPMENT Gary M. Carinci William A. Pratt Outokumpu Stainless 3209 McKnight East Drive Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15237 gcarinci@tmr-inc.com Abstract
AL 29-4C AL 29-4C. Technical Data Sheet. Stainless Steel: Superferritic INTRODUCTION (UNS S44735)
 AL 29-4C Stainless Steel: Superferritic (UNS S44735) INTRODUCTION AL 29-4C alloy, is a superferritic stainless steel developed by ATI in the early 1980s specifically for power plant surface condenser tubing.
AL 29-4C Stainless Steel: Superferritic (UNS S44735) INTRODUCTION AL 29-4C alloy, is a superferritic stainless steel developed by ATI in the early 1980s specifically for power plant surface condenser tubing.
Special Alloys for Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems
 Special Alloys for Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems Figure 1-Flue Gas Desulfurization Sytem structure Introduction Flue gas desulfurization is a process of elimination of sulfur oxides from gas products
Special Alloys for Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems Figure 1-Flue Gas Desulfurization Sytem structure Introduction Flue gas desulfurization is a process of elimination of sulfur oxides from gas products
Special Alloys and Overmatching Welding Products Solve FGD Corrosion Problems
 Special Alloys and Overmatching Welding Products Solve FGD Corrosion Problems J. R. Crum. L. E. Shoemaker Special s Corporation 3200 Riverside Drive Huntington, WV 25705-1771 and S. D. Kiser, P.E. Special
Special Alloys and Overmatching Welding Products Solve FGD Corrosion Problems J. R. Crum. L. E. Shoemaker Special s Corporation 3200 Riverside Drive Huntington, WV 25705-1771 and S. D. Kiser, P.E. Special
Stainless steels for flue gas cleaning Dear Reader
 acom 4-2007 A corrosion management and applications engineering magazine from Outokumpu Stainless steels for flue gas cleaning Dear Reader Flue gas cleaning is inherently linked to expansion of industrial
acom 4-2007 A corrosion management and applications engineering magazine from Outokumpu Stainless steels for flue gas cleaning Dear Reader Flue gas cleaning is inherently linked to expansion of industrial
Nickel containing materials in flue gas desulfurization equipment
 flue gas desulfurization equipment By: W.H.D. Plant and W.L. Mathay Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) is the removal of the sulfur oxides from gaseous products produced by the combustion of fossil fuels.
flue gas desulfurization equipment By: W.H.D. Plant and W.L. Mathay Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) is the removal of the sulfur oxides from gaseous products produced by the combustion of fossil fuels.
Outokumpu 2507 UNS S32750
 UNS S32750 North American Version Imperial Units Design Features Very high strength High resistance to pitting, crevice, and general corrosion Very high resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking
UNS S32750 North American Version Imperial Units Design Features Very high strength High resistance to pitting, crevice, and general corrosion Very high resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking
ATI 2205 ATI Technical Data Sheet. Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES. (UNS S31803 and S32205)
 ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
Area of Use for Z100 (UNS S32760) Superduplex Stainless Steel Wireline.
 Area of Use for Z100 (UNS S32760) Superduplex Stainless Steel Wireline. R Francis and G Warburton Weir Materials & Foundries Abstract Wirelines or slicklines are routinely used in the oil and gas industry
Area of Use for Z100 (UNS S32760) Superduplex Stainless Steel Wireline. R Francis and G Warburton Weir Materials & Foundries Abstract Wirelines or slicklines are routinely used in the oil and gas industry
ATI ATI 2205 Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel. Technical Data Sheet
 Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogenenhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly improve
Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogenenhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly improve
SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3RE60 is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: High resistance to stress corrosion cracking (SCC)
SANDVIK 3RE60 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3RE60 is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: High resistance to stress corrosion cracking (SCC)
Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD)
 Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) In most developed countries, wet scrubber (flue-gas desulfurization; FGD) technology is a well-established process for removing SO2. Also, costs have been reduced significantly
Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) In most developed countries, wet scrubber (flue-gas desulfurization; FGD) technology is a well-established process for removing SO2. Also, costs have been reduced significantly
STAINLESS STEEL WORLD CONFERENCE EXPERIENCES WITH ZERON 100 SUPER DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL IN THE PROCESS INDUSTRIES Paper No.
 STAINLESS STEEL WORLD CONFERENCE 1999 EXPERIENCES WITH ZERON 100 SUPER DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL IN THE PROCESS INDUSTRIES Paper No. 99007 R FRANCIS, G BYRNE, G R WARBURTON Weir Materials & Foundries Park
STAINLESS STEEL WORLD CONFERENCE 1999 EXPERIENCES WITH ZERON 100 SUPER DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL IN THE PROCESS INDUSTRIES Paper No. 99007 R FRANCIS, G BYRNE, G R WARBURTON Weir Materials & Foundries Park
SANDVIK 254 SMO TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 254 SMO TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 254 SMO is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel developed for use in seawater and other aggressive chloride-bearing media. The steel is characterized
SANDVIK 254 SMO TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 254 SMO is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel developed for use in seawater and other aggressive chloride-bearing media. The steel is characterized
Epoxy Vinyl Ester Polymer Lining for Duplex UNS S32205/S31803 Alloy FGD Absorber Modules
 Epoxy Vinyl Ester Polymer Lining for Duplex UNS S32205/S31803 Alloy FGD Absorber Modules Heather M. Ramsey Sauereisen, Inc. 160 Gamma Drive Pittsburgh, PA 15238 USA Thom L. Johnson Ashland, Inc. 5200 Blazer
Epoxy Vinyl Ester Polymer Lining for Duplex UNS S32205/S31803 Alloy FGD Absorber Modules Heather M. Ramsey Sauereisen, Inc. 160 Gamma Drive Pittsburgh, PA 15238 USA Thom L. Johnson Ashland, Inc. 5200 Blazer
Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets)
 Datasheet updated 2013 11 28 14:13:21 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets) Sandvik SAF 2205 is a duplex (austenitic ferritic) stainless steel characterized by: High resistance
Datasheet updated 2013 11 28 14:13:21 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik SAF 2205 (Billets) Sandvik SAF 2205 is a duplex (austenitic ferritic) stainless steel characterized by: High resistance
by David Crowe and Randy Nixon Corrosion Probe, Inc.
 by David Crowe and Randy Nixon Corrosion Probe, Inc. Introduction to Stainless Steels Austenitic 300 Series 304/304L and 316/316L Are Most Common Face-Centered Cubic Arrangement of Atoms We Call This Microstructure
by David Crowe and Randy Nixon Corrosion Probe, Inc. Introduction to Stainless Steels Austenitic 300 Series 304/304L and 316/316L Are Most Common Face-Centered Cubic Arrangement of Atoms We Call This Microstructure
ATI 904L ATI 904L. Technical Data Sheet. Stainless Steel: Superaustenitic INTRODUCTION COMPOSITION CORROSION RESISTANCE (UNS N08904)
 ATI 904L Stainless Steel: Superaustenitic (UNS N08904) INTRODUCTION ATI 904L alloy (UNS N08904) is an austenitic stainless steel designed for a middle to high level of corrosion resistance. The alloy contains
ATI 904L Stainless Steel: Superaustenitic (UNS N08904) INTRODUCTION ATI 904L alloy (UNS N08904) is an austenitic stainless steel designed for a middle to high level of corrosion resistance. The alloy contains
Wet FGD Materials of Construction. Gregory T. Bielawski Manager, Environmental Aftermarket Services
 Wet FGD Materials of Construction Gregory T. Bielawski Manager, Environmental Aftermarket Services Wet FGD Absorber Zones Inlet fluework and dampers Inlet wet/dry interface Recirculation tank Spray zone
Wet FGD Materials of Construction Gregory T. Bielawski Manager, Environmental Aftermarket Services Wet FGD Absorber Zones Inlet fluework and dampers Inlet wet/dry interface Recirculation tank Spray zone
WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS
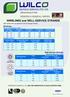 WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS High quality wire and strand for the oil and gas industry. Wirelines Minimum Breaking Loads Diameter in mm HT Carbon EHT Carbon ZERON 100VHX 0.092 2.34 1,950 1,980 1,350
WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS High quality wire and strand for the oil and gas industry. Wirelines Minimum Breaking Loads Diameter in mm HT Carbon EHT Carbon ZERON 100VHX 0.092 2.34 1,950 1,980 1,350
Special Metals Co., 3200 Riverside Dr., Huntington, WV U.S.A.
 A Comparison of the Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Alloys and : An Aid for Specifying the Most Cost Effective Materials for Demanding Applications (Revision 2, August 30, 2005) While commercially pure
A Comparison of the Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Alloys and : An Aid for Specifying the Most Cost Effective Materials for Demanding Applications (Revision 2, August 30, 2005) While commercially pure
409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL
 409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Superior Corrosion Resistance to Mild and Low-Alloy Steels Cost Effective Alternative to Austenitic Stainless AK Steel 409 Ni Stainless Steel
409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL P R O D U C T D ATA B U L L E T I N Superior Corrosion Resistance to Mild and Low-Alloy Steels Cost Effective Alternative to Austenitic Stainless AK Steel 409 Ni Stainless Steel
ATI 825 ATI 825. Technical Data Sheet. Nickel-base Alloy INTRODUCTION PRODUCT FORMS SPECIFICATIONS & CERTIFICATES (UNS N08825)
 ATI 825 Nickel-base (UNS N08825) INTRODUCTION ATI 825 alloy (UNS N08825) is an austenitic nickel-iron-chromium-molybdenum-copper alloy containing high levels of chromium, nickel, molybdenum and copper
ATI 825 Nickel-base (UNS N08825) INTRODUCTION ATI 825 alloy (UNS N08825) is an austenitic nickel-iron-chromium-molybdenum-copper alloy containing high levels of chromium, nickel, molybdenum and copper
CEMENT PLANT ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY FOR ACHIEVING HIGH SO 2 REMOVAL
 CEMENT PLANT ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY FOR ACHIEVING HIGH SO 2 REMOVAL Sara Safariyeganeh sara.safariyeganeh@mecsglobal.com Cary Joe Lovett, PE joe.lovett@holcim.com Abstract - The EPA has adopted revised
CEMENT PLANT ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY FOR ACHIEVING HIGH SO 2 REMOVAL Sara Safariyeganeh sara.safariyeganeh@mecsglobal.com Cary Joe Lovett, PE joe.lovett@holcim.com Abstract - The EPA has adopted revised
Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes
 Cast materials Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes Our customer-focused R&D and continuous research on new material options enable us to develop equipment with a strong
Cast materials Rely on our material competence for your demanding industrial processes Our customer-focused R&D and continuous research on new material options enable us to develop equipment with a strong
SANDVIK 5R60 FOR WIRELINES WIRE
 SANDVIK 5R60 FOR WIRELINES WIRE DATASHEET Sandvik 5R60 is an austenitic stainless steel alloy suitable for service in less severe oil and gas wells. The grade is characterized by: Good resistance to general
SANDVIK 5R60 FOR WIRELINES WIRE DATASHEET Sandvik 5R60 is an austenitic stainless steel alloy suitable for service in less severe oil and gas wells. The grade is characterized by: Good resistance to general
Nominal Composition. Weight %
 HASTELLOY HYBRID-BC1 Principal Features High Resistance to Hydrochloric Acid, Sulfuric Acid, Pitting, and Crevice Corrosion HASTELLOY HYBRID-BC1 (UNS N10362) alloy possesses much higher resistance to hydrochloric
HASTELLOY HYBRID-BC1 Principal Features High Resistance to Hydrochloric Acid, Sulfuric Acid, Pitting, and Crevice Corrosion HASTELLOY HYBRID-BC1 (UNS N10362) alloy possesses much higher resistance to hydrochloric
STAINLESS STEELS. Experience has shown that, at least for stainless. for Corrosion Resistance
 STAINLESS STEELS for Corrosion Resistance Newly developed stainless steels provide increased corrosion resistance, improved mechanical properties, easier forming and fabrication, and/or improved economy.
STAINLESS STEELS for Corrosion Resistance Newly developed stainless steels provide increased corrosion resistance, improved mechanical properties, easier forming and fabrication, and/or improved economy.
Hastelloy C-2000 (UNS N06200)
 Hastelloy C-2000 (UNS N06200) Hastelloy C-2000 is a versatile alloy that provides high resistance to variety of chemicals including sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and other strong acidic media. It offers
Hastelloy C-2000 (UNS N06200) Hastelloy C-2000 is a versatile alloy that provides high resistance to variety of chemicals including sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and other strong acidic media. It offers
SANDVIK SAF 2507 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK SAF 2507 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik SAF 2507 is a super-duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel for service in highly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized by: Excellent
SANDVIK SAF 2507 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik SAF 2507 is a super-duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel for service in highly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized by: Excellent
J2101 UNS S32101 EN
 J2101 UNS S32101 EN 1.4162 DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL General Characteristics: Lean Duplex Stainless steel 2101 (UNS S32101) possesses high strength coupled with corrosion resistance comparable to austenitic
J2101 UNS S32101 EN 1.4162 DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL General Characteristics: Lean Duplex Stainless steel 2101 (UNS S32101) possesses high strength coupled with corrosion resistance comparable to austenitic
Nickel & Stainless Steel. Product Range
 Nickel & Stainless Steel Product Range General Index ITEM BRAND SIZE Inconel 600 Inconel 601 Inconel alloy Inconel 625 Inconel 718 Monel 400 Monel alloy Monel K500 Nickel 52 Nickel alloy Nickel 200 Nickel
Nickel & Stainless Steel Product Range General Index ITEM BRAND SIZE Inconel 600 Inconel 601 Inconel alloy Inconel 625 Inconel 718 Monel 400 Monel alloy Monel K500 Nickel 52 Nickel alloy Nickel 200 Nickel
Minimizing FGD Costs Mr. Bryan D. Hansen, P.E., Burns & McDonnell
 Title: Author: Minimizing FGD Costs Mr. Bryan D. Hansen, P.E., Burns & McDonnell With nearly every utility in the United States adding or upgrading their Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) system, it is crucial
Title: Author: Minimizing FGD Costs Mr. Bryan D. Hansen, P.E., Burns & McDonnell With nearly every utility in the United States adding or upgrading their Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) system, it is crucial
HASTELLOY G-35 alloy. Nominal Composition. Weight % O 5
 HASTELLOY G-35 alloy Principal Features A nickel alloy with exceptional resistance to wet process phosphoric acid HASTELLOY G-35 alloy (UNS N06035) was designed to resist wet process phosphoric acid (P
HASTELLOY G-35 alloy Principal Features A nickel alloy with exceptional resistance to wet process phosphoric acid HASTELLOY G-35 alloy (UNS N06035) was designed to resist wet process phosphoric acid (P
Zero Liquid Discharge Effluent Guidelines Compliance Strategies for Coal-Fired Power Plants FGD Wastewater
 Zero Liquid Discharge Effluent Guidelines Compliance Strategies for Coal-Fired Power Plants FGD Wastewater Author: Holly Hills, Sargent & Lundy L.L.C, 55 E. Monroe Street, Chicago IL 60603 holly.m.hills@sargentlundy.com
Zero Liquid Discharge Effluent Guidelines Compliance Strategies for Coal-Fired Power Plants FGD Wastewater Author: Holly Hills, Sargent & Lundy L.L.C, 55 E. Monroe Street, Chicago IL 60603 holly.m.hills@sargentlundy.com
HASTELLOY G-30 alloy Principal Features
 HASTELLOY G-30 alloy Principal Features 30 years of proven performance in wet process phosphoric acid HASTELLOY G-30 alloy (UNS # N06030) is a nickel-chromium-iron material highly resistant to wet process
HASTELLOY G-30 alloy Principal Features 30 years of proven performance in wet process phosphoric acid HASTELLOY G-30 alloy (UNS # N06030) is a nickel-chromium-iron material highly resistant to wet process
Worldwide Pollution Control Association. August 3-4, 2010
 Worldwide Pollution Control Association IL Regional Technical Seminar August 3-4, 2010 Visit our website at www.wpca.infowpca An Unbiased Comparison of FGD Technologies: Wet, Spray Dry and CDS WPCA Conference
Worldwide Pollution Control Association IL Regional Technical Seminar August 3-4, 2010 Visit our website at www.wpca.infowpca An Unbiased Comparison of FGD Technologies: Wet, Spray Dry and CDS WPCA Conference
The Use of FRP (Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic) in Phosphate Fertilizer and Sulfuric Acid Processes
 The Use of FRP (Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic) in Phosphate Fertilizer and Sulfuric Acid Processes Don Kelley Ashland Performance Materials 5200 Blazer Parkway Dublin, OH 43017 ABSTRACT The demand for
The Use of FRP (Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic) in Phosphate Fertilizer and Sulfuric Acid Processes Don Kelley Ashland Performance Materials 5200 Blazer Parkway Dublin, OH 43017 ABSTRACT The demand for
Density, lb/in g/cm Table 3 - Thermal and Electrical Properties
 www.specialmetals.com INCONEL alloy 686 (UNS N6686/W.Nr. 2.466) is a single-phase, austenitic Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy offering outstanding corrosion-resistance in a range of severe environments. Its high nickel
www.specialmetals.com INCONEL alloy 686 (UNS N6686/W.Nr. 2.466) is a single-phase, austenitic Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy offering outstanding corrosion-resistance in a range of severe environments. Its high nickel
Stainless Steels for Desalination Plants
 Stainless Steels for Desalination Plants Tersainox in Olive Oil Production The 3CR12 in Different Applications and Equipment Transport Equipment, Designed According to Customer Requirements Tersainox -
Stainless Steels for Desalination Plants Tersainox in Olive Oil Production The 3CR12 in Different Applications and Equipment Transport Equipment, Designed According to Customer Requirements Tersainox -
SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES
 SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES A02 (Identical with ASTM Specification A 276-97.) 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers hot-finished or coldfinished bars except bars for reforging (Note
SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES A02 (Identical with ASTM Specification A 276-97.) 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers hot-finished or coldfinished bars except bars for reforging (Note
CENTRAL ELECTRICITY AUTHORITY NEW DELHI
 AMENDMENT TO STANDARD TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR RETROFIT OF WET LIMESTONE BASED FLUE GAS DESULPHURISATION (FGD) SYSTEM IN A TYPICAL 2 x 500 MW THERMAL POWER PLANT CENTRAL ELECTRICITY AUTHORITY NEW DELHI
AMENDMENT TO STANDARD TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR RETROFIT OF WET LIMESTONE BASED FLUE GAS DESULPHURISATION (FGD) SYSTEM IN A TYPICAL 2 x 500 MW THERMAL POWER PLANT CENTRAL ELECTRICITY AUTHORITY NEW DELHI
SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX SF SPRING WIRE WIRE
 SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX SF SPRING WIRE WIRE DATASHEET Sandvik Springflex SF is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel especially designed for spring applications with extremely high fatigue requirements.
SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX SF SPRING WIRE WIRE DATASHEET Sandvik Springflex SF is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel especially designed for spring applications with extremely high fatigue requirements.
Table 2 - Physical Properties. Table 3 - Thermal and Electrical Properties. a Mean coefficient of linear expansion between room temperature and
 www.specialmetals.com INCONEL alloy 686 (UNS N6686/W.Nr. 2.466) is a single-phase, austenitic Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy offering outstanding corrosion-resistance in a range of severe environments. Its high nickel
www.specialmetals.com INCONEL alloy 686 (UNS N6686/W.Nr. 2.466) is a single-phase, austenitic Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy offering outstanding corrosion-resistance in a range of severe environments. Its high nickel
Fluid Bed Scrubbing TECHNOLOGY
 CIRCULATING Fluid Bed Scrubbing TECHNOLOGY Circulating fluid bed scrubbing technology is a flexible multi-pollutant technology quickly gaining recognition. >> BY BOB GIGLIO, VICE PRESIDENT OF STRATEGIC
CIRCULATING Fluid Bed Scrubbing TECHNOLOGY Circulating fluid bed scrubbing technology is a flexible multi-pollutant technology quickly gaining recognition. >> BY BOB GIGLIO, VICE PRESIDENT OF STRATEGIC
family of stainless steels can be divided into five (5) categories:
 Welcome to the fifth issue of Tech Talk. This newsletter covers a range of topics on various welding products, applications, metallurgy, techniques, and economics. Previous issues are archived at www.unibraze.com.
Welcome to the fifth issue of Tech Talk. This newsletter covers a range of topics on various welding products, applications, metallurgy, techniques, and economics. Previous issues are archived at www.unibraze.com.
WET FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION (FGD) SYSTEMS ADVANCED MULTI-POLLUTANT CONTROL TECHNOLOGY
 WET FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION (FGD) SYSTEMS ADVANCED MULTI-POLLUTANT CONTROL TECHNOLOGY B&W WET FGD SYSTEMS FLEXIBILITY OF DESIGN AND ADVANCED FEATURES TO MEET CUSTOMER NEEDS When performance counts SINCE
WET FLUE GAS DESULFURIZATION (FGD) SYSTEMS ADVANCED MULTI-POLLUTANT CONTROL TECHNOLOGY B&W WET FGD SYSTEMS FLEXIBILITY OF DESIGN AND ADVANCED FEATURES TO MEET CUSTOMER NEEDS When performance counts SINCE
SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sanicro 29 is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel (CRA) for OCTG downhole applications in particularly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized
SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sanicro 29 is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel (CRA) for OCTG downhole applications in particularly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized
Sandvik SAF 2205 (Tube and pipe, seamless)
 Datasheet updated 2012 10 14 10:38:02 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik SAF 2205 (Tube and pipe, seamless) Sandvik SAF 2205 is a duplex (austenitic ferritic) stainless steel characterized by:
Datasheet updated 2012 10 14 10:38:02 (supersedes all previous editions) Sandvik SAF 2205 (Tube and pipe, seamless) Sandvik SAF 2205 is a duplex (austenitic ferritic) stainless steel characterized by:
AL 29-4C For Heating and Ventilating
 AL 29-4C Alloy For Heating and Ventilating Stainless Steel (UNS S44735) TYPICAL COMPOSITION Element Carbon Manganese Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Chromium Nickel Molybdenum Nitrogen Titanium+Columbium (Niobium)
AL 29-4C Alloy For Heating and Ventilating Stainless Steel (UNS S44735) TYPICAL COMPOSITION Element Carbon Manganese Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Chromium Nickel Molybdenum Nitrogen Titanium+Columbium (Niobium)
Chlorimet 2 and 3. DC2 and DC3. Bulletin A/3k
 Chlorimet 2 and 3 DC2 and DC3 Bulletin A/3k DC2 & DC3 Introduction Chlorimet 2 Chlorimet 2 and Chlorimet 3 are Flowserve developed Mo-Ni and Cr-Mo-Ni alloys that have been in use since the early 1950s.
Chlorimet 2 and 3 DC2 and DC3 Bulletin A/3k DC2 & DC3 Introduction Chlorimet 2 Chlorimet 2 and Chlorimet 3 are Flowserve developed Mo-Ni and Cr-Mo-Ni alloys that have been in use since the early 1950s.
SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R65 is a molybdenum-alloyed austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content. STANDARDS ASTM: TP316L, TP316 UNS: S31603, S31600
SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R65 is a molybdenum-alloyed austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content. STANDARDS ASTM: TP316L, TP316 UNS: S31603, S31600
Stainless Steel - St St Introduction
 Stainless steel is not a single material but the name for a family of corrosion resistant steels. Like many scientific discoveries the origins of stainless steel lies in a serendipitous accident. In 1913
Stainless steel is not a single material but the name for a family of corrosion resistant steels. Like many scientific discoveries the origins of stainless steel lies in a serendipitous accident. In 1913
Duplex stainless steels for chemical tankers
 Duplex Stainless Steels 97-5th World Conference D97-018 PAGE 727 Home page by Jacques Charles and Bruno Vincent (CREUSOT-LOIRE INDUSTRIE, France) Abstract Material selection for chemical tanks is of prime
Duplex Stainless Steels 97-5th World Conference D97-018 PAGE 727 Home page by Jacques Charles and Bruno Vincent (CREUSOT-LOIRE INDUSTRIE, France) Abstract Material selection for chemical tanks is of prime
ATI 20 ATI 20. Technical Data Sheet. Stainless Steel: Superaustenitic INTRODUCTION TYPICAL COMPOSITION (UNS N08020)
 ATI 20 Stainless Steel: Superaustenitic (UNS N08020) INTRODUCTION ATI 20 alloy (UNS N08020) has been available for many years and has found applications in many environments, such as in chlorides and in
ATI 20 Stainless Steel: Superaustenitic (UNS N08020) INTRODUCTION ATI 20 alloy (UNS N08020) has been available for many years and has found applications in many environments, such as in chlorides and in
SANDVIK SAF 2304 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK SAF 2304 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik SAF 2304 is a lean duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: Very good resistance to stress corrosion
SANDVIK SAF 2304 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik SAF 2304 is a lean duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel characterized by the following properties: Very good resistance to stress corrosion
Energy Production Systems Engineering
 Welcome to Energy Production Systems Engineering USF Polytechnic Engineering tom@thomasblairpe.com Session 10: Environmental Controls Spring 2012 Plant Environmental Control Systems Power plant Environmental
Welcome to Energy Production Systems Engineering USF Polytechnic Engineering tom@thomasblairpe.com Session 10: Environmental Controls Spring 2012 Plant Environmental Control Systems Power plant Environmental
Dual Flow Tray Technology for Wet FGD Performance Upgrades
 Dual Flow Tray Technology for Wet FGD Performance Upgrades Michael T Hoydick Amec Foster Wheeler Pittsburgh, PA / USA Aydra R Kalynchuk Amec Foster Wheeler Pittsburgh, PA / USA Robert Giglio Amec Foster
Dual Flow Tray Technology for Wet FGD Performance Upgrades Michael T Hoydick Amec Foster Wheeler Pittsburgh, PA / USA Aydra R Kalynchuk Amec Foster Wheeler Pittsburgh, PA / USA Robert Giglio Amec Foster
FABRICATION OF SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FOR OPTIMUM SEAWATER CORROSION RESISTANCE
 FABRICATION OF SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FOR OPTIMUM SEAWATER CORROSION RESISTANCE Authors: G. Byrne, G. Warburton, J. Wilson and R. Francis. Presenter: G Warburton, Technical Director, Rolled Alloys
FABRICATION OF SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL FOR OPTIMUM SEAWATER CORROSION RESISTANCE Authors: G. Byrne, G. Warburton, J. Wilson and R. Francis. Presenter: G Warburton, Technical Director, Rolled Alloys
409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL
 409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL Bus Frames Dryer Component Intermodal Containers Rail Cars Trailers AK STEEL 409 Ni is an ideal material for applications requiring weldability and toughness superior to standard
409 Ni STAINLESS STEEL Bus Frames Dryer Component Intermodal Containers Rail Cars Trailers AK STEEL 409 Ni is an ideal material for applications requiring weldability and toughness superior to standard
Types 316 (S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700), 317L (S31703)
 Types 316 (S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700), 317L (S31703) GENERAL PROPERTIES Types 316 (UNS S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700) and 317L (S31703) are molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steels
Types 316 (S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700), 317L (S31703) GENERAL PROPERTIES Types 316 (UNS S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700) and 317L (S31703) are molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steels
Stainless Steels. Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum Types 316 (S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700), 317L (S31703) GENERAL PROPERTIES CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum Types 316 (S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700), 317L (S31703) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI Allegheny Ludlum Types 316 (UNS S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700) and 317L (S31703) are
Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum Types 316 (S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700), 317L (S31703) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI Allegheny Ludlum Types 316 (UNS S31600), 316L (S31603), 317 (S31700) and 317L (S31703) are
Think Stainless, Think Encore STAINLESS STEEL FOR SPECIALTY APPLICATIONS. Specialty Metals to Support Innovative Manufacturing
 STAINLESS STEEL FOR SPECIALTY APPLICATIONS Specialty Metals to Support Innovative Manufacturing Specialty Metals to Support Innovative Manufacturing Encore Metals is a specialist supplier of high grade
STAINLESS STEEL FOR SPECIALTY APPLICATIONS Specialty Metals to Support Innovative Manufacturing Specialty Metals to Support Innovative Manufacturing Encore Metals is a specialist supplier of high grade
Worldwide Pollution Control Association
 Worldwide Pollution Control Association ESKOM Scrubber Seminar April 12 th 13 th, 2007 Visit our website at www.wpca.info Duke Carolinas Scrubbers Scott Williams Background North Carolina Clean Air Plan
Worldwide Pollution Control Association ESKOM Scrubber Seminar April 12 th 13 th, 2007 Visit our website at www.wpca.info Duke Carolinas Scrubbers Scott Williams Background North Carolina Clean Air Plan
Ultra 6XN EN , ASTM UNS N08926
 Ultra 6XN EN 1.4529, ASTM UNS N08926 General characteristics 6% Mo, high Ni, and N alloyed austenitic grade with extremely high resistance to both uniform and localized corrosion. Commonly used in applications
Ultra 6XN EN 1.4529, ASTM UNS N08926 General characteristics 6% Mo, high Ni, and N alloyed austenitic grade with extremely high resistance to both uniform and localized corrosion. Commonly used in applications
Welding Consumables for Lean Duplex Stainless Steels
 Welding Consumables for Lean Duplex Stainless Steels Graham Holloway, Adam Marshall & Zhuyao Zhang Metrode Products Ltd, UK Presenter: Presenter - Graham Holloway Graham Holloway has been at Metrode Products
Welding Consumables for Lean Duplex Stainless Steels Graham Holloway, Adam Marshall & Zhuyao Zhang Metrode Products Ltd, UK Presenter: Presenter - Graham Holloway Graham Holloway has been at Metrode Products
Stainless Steel St St Introduction
 Stainless steel is not a single material but the name for a family of corrosion resistant steels. Like many scientific discoveries the origins of stainless steel lies in a serendipitous accident. In 1913
Stainless steel is not a single material but the name for a family of corrosion resistant steels. Like many scientific discoveries the origins of stainless steel lies in a serendipitous accident. In 1913
Arcos Has You Covered
 Arcos is the company with the reputation and experience you can rely on for a comprehensive line of superior quality bare and covered electrodes for high nickel alloys. Our wide selection of high nickel
Arcos is the company with the reputation and experience you can rely on for a comprehensive line of superior quality bare and covered electrodes for high nickel alloys. Our wide selection of high nickel
Forta SDX 2507 EN , ASTM UNS S32750
 Forta SDX 2507 EN 1.4410, ASTM UNS S32750 General characteristics Forta SDX 2507 is a super duplex product with higher corrosion resistance and mechanical strength than Forta DX 2205. Often used in extremely
Forta SDX 2507 EN 1.4410, ASTM UNS S32750 General characteristics Forta SDX 2507 is a super duplex product with higher corrosion resistance and mechanical strength than Forta DX 2205. Often used in extremely
ATI Datalloy HP TM Alloy
 ATI Datalloy HP TM Alloy UNS N08830 INTRODUCTION ATI Datalloy HP TM alloy is a Ni-Cr-Mo-Fe non-magnetic high strength alloy with exceptional pitting and crevice corrosion resistance, while maintaining
ATI Datalloy HP TM Alloy UNS N08830 INTRODUCTION ATI Datalloy HP TM alloy is a Ni-Cr-Mo-Fe non-magnetic high strength alloy with exceptional pitting and crevice corrosion resistance, while maintaining
UR 2202 is a low nickel, low molybdenum stainless steel designed to match the corrosion resistance of 304L in most environments.
 Industeel URANUS 2202 The alternative to 304L UR 2202 is a low nickel, low molybdenum stainless steel designed to match the corrosion resistance of 304L in most environments. Its higher strength allows
Industeel URANUS 2202 The alternative to 304L UR 2202 is a low nickel, low molybdenum stainless steel designed to match the corrosion resistance of 304L in most environments. Its higher strength allows
SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES FOR USE IN BOILERS AND OTHER PRESSURE VESSELS
 2007 SECTION II, PART A SA-479/SA-479M SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES FOR USE IN BOILERS AND OTHER PRESSURE VESSELS SA-479/SA-479M (Identical with ASTM Specification A 479/A 479M-04
2007 SECTION II, PART A SA-479/SA-479M SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES FOR USE IN BOILERS AND OTHER PRESSURE VESSELS SA-479/SA-479M (Identical with ASTM Specification A 479/A 479M-04
WELDING CONSUMABLES FOR DUPLEX AND SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEELS OPTIMISING PROPERTIES AFTER HEAT TREATMENT
 WELDING CONSUMABLES FOR DUPLEX AND SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEELS OPTIMISING PROPERTIES AFTER HEAT TREATMENT by G B Holloway & J C M Farrar Metrode Products Limited ABSTRACT The first 50 years of duplex
WELDING CONSUMABLES FOR DUPLEX AND SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEELS OPTIMISING PROPERTIES AFTER HEAT TREATMENT by G B Holloway & J C M Farrar Metrode Products Limited ABSTRACT The first 50 years of duplex
Nickel-Chrome Alloy Inconel 625 (UNS N06625)
 NickelChrome Alloy Inconel 625 (UNS N06625) Inconel Alloy 625 is a corrosion and oxidation resistant nickel alloy that is employed for its high strength and good aqueous corrosion resistance properties.
NickelChrome Alloy Inconel 625 (UNS N06625) Inconel Alloy 625 is a corrosion and oxidation resistant nickel alloy that is employed for its high strength and good aqueous corrosion resistance properties.
SEASTROM Manufacturing Co., Inc Seastrom Street Twin Falls, Idaho Fax (208)
 MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS - METAL Aluminum 2024 Aircraft Grade 1/3 the weight of steel Heat treat to increase hardness Good electrical conductivity (30% of copper) Good heat conductivity (70 btu/hr/ft²/
MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS - METAL Aluminum 2024 Aircraft Grade 1/3 the weight of steel Heat treat to increase hardness Good electrical conductivity (30% of copper) Good heat conductivity (70 btu/hr/ft²/
THE PERFORMANCE OF Z100 (UNS S32760) SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL IN SULPHURIC ACID.
 THE PERFORMANCE OF (UNS S32760) SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL IN SULPHURIC ACID. R Francis and G Byrne Weir Materials & Foundries Park Works Newton Heath Manchester M40 2BA U.K. ABSTRACT The history and
THE PERFORMANCE OF (UNS S32760) SUPERDUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL IN SULPHURIC ACID. R Francis and G Byrne Weir Materials & Foundries Park Works Newton Heath Manchester M40 2BA U.K. ABSTRACT The history and
Ultra 904L EN , ASTM UNS N08904
 Ultra 904L EN 1.4539, ASTM UNS N08904 General characteristics High Ni and Mo austenitic grade with very high resistance to corrosion. Commonly used in chemical and petrochemical industry for handling medium
Ultra 904L EN 1.4539, ASTM UNS N08904 General characteristics High Ni and Mo austenitic grade with very high resistance to corrosion. Commonly used in chemical and petrochemical industry for handling medium
STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS
 STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS Alloys: 304 304L 310 316 316L 316LN 316Ti 316LVM 6Mo 21-6-9 22-13-5 904L Alloys 304 / 304L Alloys 304 / 304L (UNS S30400 / S30403) Alloys 304 (S30400) and 304L (S30403) stainless
STAINLESS STEEL DATASHEETS Alloys: 304 304L 310 316 316L 316LN 316Ti 316LVM 6Mo 21-6-9 22-13-5 904L Alloys 304 / 304L Alloys 304 / 304L (UNS S30400 / S30403) Alloys 304 (S30400) and 304L (S30403) stainless
HASTELLOY C-2000 alloy
 HASTELLOY C-2000 alloy Principal Features A copper-bearing Ni-Cr-Mo material with exceptional resistance to sulfuric acid HASTELLOY C-2000 alloy (UNS N06200) is unique among the versatile nickel-chromium-molybdenum
HASTELLOY C-2000 alloy Principal Features A copper-bearing Ni-Cr-Mo material with exceptional resistance to sulfuric acid HASTELLOY C-2000 alloy (UNS N06200) is unique among the versatile nickel-chromium-molybdenum
THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STAINLESS STEEL
 THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STAINLESS STEEL Stainless steel is primarily utilised on account of its corrosion resistance. However, the scope of excellent mechanical properties the within the family of
THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STAINLESS STEEL Stainless steel is primarily utilised on account of its corrosion resistance. However, the scope of excellent mechanical properties the within the family of
Hastelloy G-30 (UNS N06030) Chemical Composition
 Hastelloy G-30 (UNS N06030) Hastelloy G-30 is commonly used for providing excellent resistance to chemical conditions. It offers resistance to nitric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric
Hastelloy G-30 (UNS N06030) Hastelloy G-30 is commonly used for providing excellent resistance to chemical conditions. It offers resistance to nitric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric
The ATI 17-4 precipitation hardening stainless steel (S17400) is covered by the following wrought product specifications.
 ATI 17-4 Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel (UNS S17400) INTRODUCTION ATI 17-4 precipitation hardening stainless steel (S17400), Type 630, is a chromium-nickel-copper precipitation hardening stainless
ATI 17-4 Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel (UNS S17400) INTRODUCTION ATI 17-4 precipitation hardening stainless steel (S17400), Type 630, is a chromium-nickel-copper precipitation hardening stainless
Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service
 SA-268/SA-268M ASME BPVC.II.A-2015 Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers a number of
SA-268/SA-268M ASME BPVC.II.A-2015 Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Tubing for General Service 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers a number of
Heat and corrosion resistant alloys for chemical processing systems
 Heat and corrosion resistant alloys for chemical processing systems Regular advancement in metallurgical and fabrication procedures had led to the development of broad range of nickel alloys and their
Heat and corrosion resistant alloys for chemical processing systems Regular advancement in metallurgical and fabrication procedures had led to the development of broad range of nickel alloys and their
ATI 45Nb Alloy. ATI 45Nb Alloy. Technical Data Sheet. Titanium Alloy
 ATI 45Nb Alloy Titanium Alloy INTRODUCTION Originally developed for application as an aerospace alloy because of its relative ease of formability, high strength and ductility at temperatures up to 427
ATI 45Nb Alloy Titanium Alloy INTRODUCTION Originally developed for application as an aerospace alloy because of its relative ease of formability, high strength and ductility at temperatures up to 427
The Convenience Stores For Metal
 STEEL Data and Specifications 303 Chromium-nickel stainless steel with added sulfur or selenium and phosphorus to improve machinability and non-seizing properties. It is the most free machining of the
STEEL Data and Specifications 303 Chromium-nickel stainless steel with added sulfur or selenium and phosphorus to improve machinability and non-seizing properties. It is the most free machining of the
Fireside Corrosion: Implications and Solutions for Oxy-combustion Boilers. Jo hn E. Oakey
 Fireside Corrosion: Implications and Solutions for Oxy-combustion Boilers Jo hn E. Oakey Tanvir Hussain Adnan U. Syed Nigel J. Simms Nelia Jurado Hamid G Darabkhani Outline Introduction What we think we
Fireside Corrosion: Implications and Solutions for Oxy-combustion Boilers Jo hn E. Oakey Tanvir Hussain Adnan U. Syed Nigel J. Simms Nelia Jurado Hamid G Darabkhani Outline Introduction What we think we
Evaporative Gas Cooling and Emissions Control Solutions
 Evaporative Gas Cooling and Emissions Control Solutions for the Iron and Steel Industry MEGTEC ENERGY ENVIRONMENTAL B&W MEGTEC Solutions for the Iron & Steel Industry Our Pedigree Babcock & Wilcox MEGTEC
Evaporative Gas Cooling and Emissions Control Solutions for the Iron and Steel Industry MEGTEC ENERGY ENVIRONMENTAL B&W MEGTEC Solutions for the Iron & Steel Industry Our Pedigree Babcock & Wilcox MEGTEC
GLORIA STEEL LIMITED Web:www.gloriasteel.com Fax: (UNS S32205/S31803) EN duplex stainless steel
 2205 (UNS S32205/S31803) EN 1.4462 duplex stainless steel A 22Cr-3Mo Stainless Steel Alloy 2205 is a 22% Chromium, 3% Molybdenum, 5-6% Nickel, nitrogen alloyed duplex stainless steel with high general,
2205 (UNS S32205/S31803) EN 1.4462 duplex stainless steel A 22Cr-3Mo Stainless Steel Alloy 2205 is a 22% Chromium, 3% Molybdenum, 5-6% Nickel, nitrogen alloyed duplex stainless steel with high general,
Alloy 20 29Ni-20.5Cr-3.5Cu-2.5Mo A351 CN7M J Mo 20Cr-18Ni-6.5Mo-N-Cu A351 CK3MCuN J93254
 The typical Austentic Stainless Steel 18%Cr + 10% Ni have been adopted in corrosion resistant application for decades. In accordance with more and more application, the typical Austentic stainless steel
The typical Austentic Stainless Steel 18%Cr + 10% Ni have been adopted in corrosion resistant application for decades. In accordance with more and more application, the typical Austentic stainless steel
