Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Change. 3. The weight of a body varies according to the force of gravity exerted on the body.
|
|
|
- Amos Anderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Change 1- T/F 1. The boiling point of a liquid is an example of a physical property. (a) True (b) False 2. The density of a substance is an example of a chemical property. (a) True (b) False 3. The weight of a body varies according to the force of gravity exerted on the body. (a) True (b) False 4. The SI base unit of length is the centimeter. (a) True (b) False 5. Mass, length, and volume are extensive properties, but density is an intensive property. (a) True (b) False C is colder than 40 F. (a) True (b) False megagrams (Mg) is equal to g. (a) True (b) False 8. The conversion of water into steam is an example of a chemical change. (a) True (b) False 2- M C Q 9. After carrying out the operations below, how many significant figures are appropriate to show in the result? ( ) (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) Select the answer with correct number of significant figures for the following calculation: g / (15.4 ml 13.2 ml) = (a) g/ml (b) 2.12 g/ml (c) 2 g/ml (d) 2.1 g/ml 11. The distance between carbon atoms in ethylene is 134 picometers. Which of the following expresses this distance in meters? (a) 1.34 x m (b) 1.34 x m (c) 1.34 x 10 7 m (d) 1.34 x 10 6 m 12. The diameter of an atom is approximately cm. What is this diameter when expressed in nanometers? (a) nm (b) nm (c) nm (d) nm km is how many micrometers? (a) µm (b) µm (c) µm (d) µm km is how many millimeters? (a) 2,400 mm (b) mm (c) mm (d) mm 15. How many milliliters is L? (a) 0.5 ml (b) 5 ml (c) 0.50 ml (d) ml 1
2 16. Express 7,500 nm as picometers. (a) 7.50 pm (b) 75.0 pm (c) 750 pm (d) pm 17. Which of these quantities represents the largest mass? (a) mg (b) kg (c) µg (d) cg 18. The number has how many significant figures? (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) How many cubic inches are in 1.00 liter? (a) 61.0 in 3 (b) 155 in 3 (c) 394 in 3 (d) in Convert 500. milliliters to quarts. (1L = 1.06 qt) (a) 1.88 qt (b) qt (c) qt (d) qt 21. A US barrel is 4.21 cubic feet. Express this volume in liters. (a) L (b) L (c) 105 L (d) 119 L 22. A barrel of oil contains 42.0 gallons. How many liters is this? (1L = 1.06 qt) (a) 9.9 L (b) 11 L (c) 142 L (d) 158 L 23. The average distance from Earth to the sun is miles. How many kilometers is this? (a) km (b) km (c) km (d) km 24. What is the area, in square centimeters, of a rectangle that is 6.0 inches by 7/8 inch? (a) 0.81 cm 2 (b) 5.3 cm 2 (c) 13 cm 2 (d) 34 cm Suppose a house has a floor area of 2,250 square feet. What is this area in units of square centimeters? (a) 2.42 cm 2 (b) cm 2 (c) cm 2 (d) cm The diameter of an atom is approximately mm. What is this diameter when expressed in nanometers? (a) nm (b) nm (c) nm (d) nm 27. What is the volume, in cubic centimeters, of a brick that is 12.0 in. 20 mm 2.0 cm? (a) 10 cm 3 (b) 48 cm 3 (c) 120 cm 3 (d) 480 cm How many square kilometers are equivalent to 28.5 cm2? (a) km 2 (b) km 2 (c) 285 km 2 (d) km How many cubic centimeters are there in exactly one cubic meter? (a) cm 3 (b) cm 3 (c) cm 3 (d) cm If a car has an EPA mileage rating of 30 miles per gallon, what is this rating in kilometers per liter? (1 L = 1.06 qt) (a) 200 km/l (b) 180 km/l (c) 70 km/l (d) 13 km/l 31. If the price of gasoline is $1.14 per U.S. gallon, what is the cost per liter? (1 L = 1.06 qt) (a) $0.0434/L (b) $4.83/L (c) $0.302/L (d) $0.269/L 32. An aluminum beverage can contains 12.0 fluid ounces of liquid. Express this volume in microliters. (1 fl oz = 29.6 ml) (a) µl (b) 355 µl (c) µl (d) µl 2
3 troy oz of silver were used in the United States in How many gigagrams is this? (1 troy oz = 31.1 g) (a) Gg (b) 4.89 Gg (c) Gg (d) 3.12 Gg 34. Table salt (sodium chloride) is 39.1% sodium. How many grams of salt contains 72.0 g of sodium? (a) 28.2 g salt (b) 72.0 g salt (c) 184 g salt (d) 2,820 g salt 35. Some molecules move with speeds approaching the "escape velocity" from Earth, which is 7.0 miles per second. What is this speed in cm/h? (1 mile = 1609 m) (a) 313 cm/h (b) cm/h (c) cm/h (d) cm/h 36. Which of the following speeds is the greatest? (a) 40 mi/h (b) mm/min (c) 40 km/h (d) 0.74 km/min 37. The diameter of Earth is 12.7 Mm. Express this diameter in centimeters. (a) cm (b) cm (c) cm (d) cm 38. Iron has a density of 7.87 g/cm 3. What mass of iron would be required to cover a football playing surface of 120 yds 60 yds to a depth of 1.0 mm? (1 inch = 2.54 cm) (a) 76 kg (b) 47 Mg (c) g (d) g 39. How many significant figures are there in g? (a) 6 (b) 5 (c) 4 (d) How many significant figures does the product contain? (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) How many significant figures does the sum contain? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) How many significant figures does the sum contain? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) How many significant figures does the difference contain? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) Do the indicated arithmetic and give the answer to the correct number of significant figures. ( ) = (a) (b) 2.0 (c) (d) When 7.02 C is converted to the Fahrenheit scale, how many significant figures are there in the F result? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) Which of the following measurements has five significant figures? (a) 4867 mi (b) 56 ml (c) 60,104 ton (d) cm 47. What is expressed as a decimal? (a) (b) (c) 152 (d) Lead melts at C. What temperature is this in F? (a) 302 F (b) 1,114 F (c) 1,082 F (d) 365 F 49. Ammonia boils at C. What temperature is this in F? (a) F (b) F (c) F (d) F 3
4 50. Many home freezers maintain a temperature of 0 F. Express this temperature in C. (a) -32 C (b) -18 C (c) 0 C (d) 18 C 51. The highest temperature ever recorded in Phoenix, Arizona, was 122 F. Express this temperature in C. (a) 50.0 C (b) 64.4 C (c) 67.8 C (d) C 52. Dry ice (carbon dioxide) changes from a solid to a gas at C. What is this temperature in F? (a) -173 F (b) F (c) -109 F (d) F 53. The density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm3. How many liters does 251 g of Hg occupy? (a) 18.5 L (b) 54.9 L (c) L (d) L 54. The density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm3. How many quarts does 100. g of Hg occupy?(1 L = 1.06 qt) (a) 144 qt (b) 7.35 qt (c) 7.79 qt (d) qt 55. A person walking fast requires 5.0 kcal of energy per minute. How many minutes of such exercise are required to consume 520 kcal, the energy in a large bag of French fries? (a) min (b) 100 min (c) 130 min (d) 520 min 56. Acetic acid boils at o F. What is the boiling point in degrees Celsius? (a) o C (b) o C (c) o C (d) o C 57. Normally the human body can endure a temperature of 105 F for only short periods of time without permanent damage to the brain and other vital organs. What is this temperature in degrees Celsius? (a) 26.3 C (b) 40.6 C (c) 131 C (d) 83.5 C 58. What temperature is 14 F when converted to degrees Celsius? (a) 18 C (b) 287 C (c) 10 C (d) 44 C 59. A piece of metal with a mass of 125 g is placed into a graduated cylinder that contains ml of water, raising the water level to ml. What is the density of the metal? (a) 5.00 g/cm 3 (b) 4.03 g/cm 3 (c) 2.23 g/cm 3 (d) 1.51 g/cm A piece of metal with a mass of 114 g was placed into a graduated cylinder that contained ml of water, raising the water level to ml. What is the density of the metal? (a) g/cm 3 (b) g/cm 3 (c) 2.68 g/cm 3 (d) 6.51 g/cm Given the following densities at 25oC:magnesium: 1.7 g/cm 3 graphite: 1.8 g/cm 3 iron: 7.9 g/cm 3 A block of iron has a mass of 826 g. What is the mass of a block of magnesium that has the same volume as the block of iron? (a) 1,400 g (b) 3,800 g (c) 830 g (d) 180 g 62. Given the following densities at 25 o C:magnesium: 1.7 g/cm 3 graphite: 1.8 g/cm 3 iron: 7.9 g/cm 3 A block of iron has a mass of 483 g. What is the mass of a block of graphite that has the same volume as the block of iron? (a) 110 g (b) 2,120 g (c) 6,870 g (d) 34 g 4
5 63. Calculate the mass of the air contained in a room that measures 2.50 m 5.50 m 3.00 m (density of air = 1.29 g/dm3 at 25 C). (a) g (b) 32.0 kg (c) 53.2 kg (d) 53.2 g 64. The density of lead is 11.4 g/cm3 at 25 C. Calculate the volume occupied by 25.0 g of lead. (a) 2.19 cm 3 (b) cm 3 (c) 285 cm 3 (d) 1.24 cm Iron has a density of 7.86 g/cm3. The volume occupied by g of iron is (a) cm 3 (b) 7.11 cm 3 (c) 2.8 cm 3 (d) 439 cm Bromine is a red liquid at 25 C. Its density is 3.12 g/cm 3. What is the volume of 28.1 g of liquid bromine? (a) 87.7 cm 3 (b) cm 3 (c) 9.01 cm 3 (d) 28.1 cm The Hope diamond weighs 44.0 carats. Determine the volume occupied by the diamond, given that its density is 3.5 g/cm3 at 20 C, and that 1 carat = g. (a) 2.5 cm 3 (b) 0.40 cm 3 (c) cm 3 (d) 63 cm What is the volume of a 2.5 g block of metal if its density is 4.75 g/cm 3? (a) 0.53 cm 3 (b) 1.9 cm 3 (c) 2.5 cm 3 (d) 4.75 cm Which of the following is not an SI base unit? (a) kilometer (b) kilogram (c) second (d) kelvin 70. Which of the following SI base units is not commonly used in chemistry? (a) kilogram (b) kelvin (c) candela (d) mole 71. Which of the following prefixes means 1/1000? (a) kilo (b) deci (c) centi (d) milli 72. Which one of these represents a physical change? (a) water, when heated, forms steam (b) bleach turns hair yellow (c) sugar, when heated, becomes brown (d) milk turns sour 73. Which one of these represents a physical change? (a) sugar, if heated enough, turns black and loses its sweetness (b) battery cables corrode (c) lard, when heated, changes to liquid (d) bleach turns hair yellow 74. Which of the following is not a chemical change? (a) burning coal (b) making bread rise using baking soda (c) boiling an egg (d) boiling water 75. All of these statements describe properties of tin. Which one describes a chemical property of tin? (a) Tin can be hammered into a thin sheet. (b) At -40 C a sheet of tin crumbles to a gray powder. (c) When a bar of tin is bent, it emits an audible "cry". (d) Tin dissolves slowly in cold, dilute hydrochloric acid, but it dissolves readily in concentrated hydrochloric acid. 5
6 76. All of these statements describe properties of sodium. Which one describes a physical property of sodium? (a) Sodium's surface turns black when first exposed to air. (b) Sodium is a solid at 25 C and changes to a liquid when heated to 98 C (c) When placed in water, sodium sizzles and a gas is formed. (d) When placed in contact with chlorine, sodium forms a compound that melts at 801 C. 77. Which one of these represents a chemical change? (a) boiling water to form steam (b) turning hair yellow with bleach (c) melting butter (d) mixing powdered charcoal and oxygen at room temperature 78. Which one of these represents a chemical change? (a) lard when heated changes to liquid (b) water disappears from a beaker in a few days at room temperature (c) sugar dissolving in water (d) milk turns sour in a few days at room temperature 79. Which one of these represents a chemical change? (a) heating water to form steam (b) sliced apples, in contact with air, turning brown (c) sugar dissolving in hot coffee (d) mixing sugar and cinnamon 80. Which of these does not represent a chemical change? (a) a freshly cut apple turns brown (b) milk turns sour on standing at room temperature (c) when cooled, liquid water becomes ice (d) bread rises when baking 81. Which of the following is an extensive property? (a) volume (b) boiling point (c) density (d) freezing point 82. A set of measurements has good precision if (a) the average is close to the true value (b) the measurements are in close agreement with each other but are not necessarily correct (c) a large number of measurements are made (d) a small number of measurements are made 83. Condensation refers to which conversion? (a) solid gas (b) solid liquid (c) gas liquid (d) gas solid 84. Radio waves travel at the speed of light, which is m/s. How many minutes does it take for a radio message to reach Earth from Saturn if Saturn is km from Earth? (a) min (b) min (c) min (d) 44 min 85. Americans combined drive about miles per day and their vehicles get an average of 20 miles per gallon of fuel used. For each 1 kg of gasoline that is burned, about 3.0 kg of carbon dioxide are produced. How many kilograms of CO2 are emitted into the atmosphere each day by cars in the U.S.? One gallon of gas weighs about 3.5 kg. (a) kg (b) kg (c) kg (d) 93 kg 6
7 86. How many cubic centimeters of ore containing 0.22% by mass gold must be processed to obtain $100 worth of gold? The density of the ore is 8.0 g/cm3 and the price of gold is $418 per troy ounce. (14.6 troy oz = 1.0 ordinary pound, called an avoirdupois pound; 1 lb = 454 g) (a) 42 cm 3 (b) cm 3 (c) cm 3 (d) 6,200 cm Radio waves travel at the speed of light, which is m/s. How many kilometers will radio messages to outer space travel in exactly one year? (a) km (b) km (c) km (d) km 88. The city of Los Angeles is now approximately 2400 miles south of Alaska. It is moving slowly northward as the San Andreas fault slides along. If Los Angeles is to arrive near Anchorage, Alaska, in 76 million years, at what average rate will it have to move in mm per month? (a) mm/mo (b) mm/mo (c) 4.2 mm/mo (d) 9.5 mm/mo 89. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of calcium is 1.2 g. Calcium carbonate contains 12.0% calcium by mass. How many grams of calcium carbonate are needed to provide the RDA of calcium? (a) 0.10 g (b) 0.14 g (c) 1.2 g (d) 10 g 90. One of the common intravenous fluids, called physiological saline, is a homogeneous mixture of NaCl in water. In this mixture, 0.89% of the mass is contributed by the NaCl. What mass of NaCl is found in 450. ml of physiological saline?(given: density of physiological saline = g/cm 3 ) (a) 2.0 g (b) 4.0 g (c) 5.1 g (d) 508 g 91. The radius of the Earth is approximately 6370 km. If one could dig down straight towards the center of the Earth, one would find that the outermost 2890 km (the crust and the mantle) has an average density of about 4.5 g/cm3. Farther down is the core. If the average density of the Earth is 5.5 g/cm3, what is the average density of the Earth's core? (Recall that the volume of a sphere is given by V = (4/3)πr 3.) (a) 11. g/cm 3 (b) 57. g/cm 3 (c) 6.2 g/cm 3 (d) 1.9 g/cm The radius of the Earth is approximately 6370 km. If one could dig down straight towards the center of the Earth, one would find that the innermost 3480 km (the core) has an average density of about 11. g/cm3. Above that are the mantle and crust. If the average density of the Earth is 5.5 g/cm3, what is the average density of the Earth's mantle and crust? (Recall that the volume of a sphere is given by V = (4/3)πr 3.) (a) 57. g/cm 3 (b) 4.5 g/cm 3 (c) 8.7 g/cm 3 (d) 5.3 g/cm An object sinks when placed in water if the mass of the object is greater than the mass of the water that the object displaces. Which of these objects will not sink when dropped into a bucket of water? (Given: density of water = 1.00 g/cm 3 ) (a) a cube of aluminum (density = g/cm 3 ) (b) a diamond (density = 3.51 g/cm 3 ) (c) a chunk of dry ice (density = 1.56 g/cm 3 ) (d) a chunk of sodium (density = 0.91 g/cm 3 ) 94. An object will float at the surface of a liquid if the mass of the object is less than the mass of the liquid that it displaces. A spherical vessel (diameter = 2.00 cm) when empty has a mass of 2.00 g. What is the greatest volume of water that can be placed in the vessel and still have the vessel float at the surface of water?(given: density of water = 1.00 g/cm 3 ) (a) 2.00 ml (b) 31.5 ml (c) 2.19 ml (d) 4.19 ml 7
8 95. An object will float at the surface of a liquid if the mass of the object is less than the mass of the liquid that it displaces. A spherical vessel (diameter = 5.00 cm) when empty has a mass of g. What is the greatest volume of water that can be placed in the vessel and still have the vessel float at the surface of benzene? (Given: density of water = 1.00 g/cm 3 ; density of benzene = g/cm 3 ) (a) 45.5 ml (b) 448 ml (c) 53.4 ml (d) 57.5 ml 96. A special flask used in the determination of densities, called a pycnometer, has a mass of g when empty, and it has a mass of g when filled with water at 20.0 C. When this same pycnometer is filled with ethyl alcohol at 20.0 C, it is found to have a mass of g. Find the density of ethyl alcohol at 20.0 C. (Given: at 20.0 C, the density of water is g/ml) (a) g/ml (b) g/ml (c) g/ml (d) g/ml 97. A particular flask has a mass of g when empty. When filled with ordinary water at 20.0 C (density = g/ml), the mass of the flask is now g. The density of so-called "heavy water" at 20.0 C is g/ml. What will the mass of the flask be when filled with heavy water at 20.0 C? (a) g (b) g (c) g (d) g ا سي لة كتاب -3 CHANG 98. (1-4) All matter is composed of very small particles called atoms is an example of a law (a) True (b) False 99. (1-5) Choose the response that includes all the items listed below that are pure substances. i. orange juice ii. steam iii. wine iv. oxygen v. vegetable soup (a) i, iii, v (b) ii, iv (c) i, iii, iv (d) iv only 100. (1-6) Grape juice is an example of a: (a) substance (b) heterogeneous mixture (c) element (d) homogeneous mixture 101. (1-7)Which of these is an example of a physical property? (a) corrosiveness of sulfuric acid (b) flammability of gasoline (c) neutralization of stomach acid with an antacid (d) lead becomes a liquid when heated to 601 C 102. (1-7)Which one of these is an example of a physical property? (a) dynamite explodes (b) meat rots if it is not refrigerated (c) honey tastes sweet (d) ice floats on top of liquid water 103. (1-8)Which of the following is an intensive property? (a) mass (b) volume (c) density (d) length 104. (1-9)Which of the following is an element? (a) water (b) oxygen (c) sugar (d) carbon dioxide 105. (1-9)Which of the following is a compound? (a) iron (b) ammonia (c) cobalt (d) gold 8
9 106. (1-12)Which of the following is a chemical change? (a) helium gas leaking from a balloon (b) frozen orange juice is reconstituted by the addition of water (c) a flashlight beam slowly dims and goes out (d) a spoonful of salt is dissolved in a bowl of soup 107. (1-15)Water is an example of a: (a) compound (b) heterogeneous mixture (c) element (d) homogeneous mixture 108. (1-17)The SI unit of time is the (a) hour (b) second (c) minute (d) ampere 109. (1-18)The SI prefixes kilo and centi represent, respectively: (a) 10 3 and 10-2 (b) 10 6 and 10-1 (c) 10-3 and 10-2 (d) 10-6 and (1-18)The SI prefixes milli and mega represent, respectively: (a) 10 6 and (b) 10-3 and 10 6 (c) 10 3 and (d) 10-3 and (1-18)The SI prefixes giga and micro represent, respectively: (a) 10-9 and 10-6 (b) 10 6 and 10-3 (c) 10 3 and 10-3 (d) 10 9 and (1-21)If 586 g of bromine occupies 188 ml, what is the density of bromine in g/ml? (a) 31.2 g/ml (b) g/ml (c) 4.53 g/ml (d) 3.12 g/ml 113. (1-22)The density of ethanol, a colorless liquid that is commonly known as grain alcohol, is g/ml. Calculate the mass of 17.4 ml of the liquid? (a) 13.9 g (b) 21.8 g (c) g (d) g 114. (1-23)What temperature is 95 F when converted to degrees Celsius? (a) 63 C (b) 35 C (c) 127 C (d) 15 C 115. (1-23)Convert C (theoretically the lowest attainable temperature) to degrees Fahrenheit. (a) F (b) F (c) F (d) F 116. (1-24)Ethylene glycol is a liquid organic compound that is used as antifreeze in car radiators. It freezes at 11.5 C. Calculate the freezing temperature in degrees Fahrenheit? (a) 11.3 F (b) 36.9 F (c) 25.6 F (d) 44.2 F 117. (1-24)The temperature on the surface of the sun is about 6300 C. What is this temperature in degrees Fahrenheit? (a) F (b) F (c) F (d) F 118. (1-24)The ignition temperature of paper is 451 F. What is the temperature in degrees Celcius? (a) 844 C (b) 268 C (c) 233 C (d) 214 C 119. (1-25)What temperature is 37 C when converted to kelvin? (a) 310 K (b) 99 K (c) 236 K (d) 67 K 9
10 120. (1-25)What temperature is 113 C when converted to kelvin? (a) 160 K (b) 239 K (c) 45 K (d) 386 K 121. (1-26)What temperature is 77 K when converted to degrees Celsius? (a) 296 C (b) 105 C (c) 196 C (d) 25 C 122. (1-26)What temperature is 601 K when converted to degrees Celsius? (a) 874 C (b) 633 C (c) 328 C (d) 215 C 123. (1-29)What is expressed in scientific notation? (a) (b) (c) (d) (1-29)What is 356 expressed in scientific notation? (a) (b) (c) (d) (1-30)What is ? (a) (b) (c) (d) (1-31)For which of the following calculations is the correct answer? (a) ( ) (b) 79,500 ( ) (c) ( ) ( ) (d) ( ) ( ) 127. (1-32)For which of the following calculations is the correct answer? (a) ( ) (b) 653 ( ) (c) 850,000 ( ) (d) ( ) ( ) 128. (1-33)How many significant figures are there in 60,104 ton? (a) 6 (b) 5 (c) 4 (d) (1-34)How many significant figures are there in L? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) (1-34)How many significant figures are there in cm 2? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) (1-35)What is m m m expressed in the correct units with the correct number of significant figures? (a) 10.6 m (b) 10.6 m (c) m (d) m 132. (1-36)What is km 5.70 km expressed in the correct units with the correct number of significant figures? (a) km (b) 1.28 km (c) km (d) 1.28 km 133. (1-37)Convert 556 ml to liters. (a) L (b) L (c) 5.56 L (d) (1-37)What is 22.6 m when converted to decimeters? (a) dm (b) 2.26 dm (c) 226 dm (d) dm 135. (1-37)What is 25.4 mg when converted to kilograms? (a) 2540 kg (b) kg (c) 2.54 kg (d) kg 10
11 136. (1-37)Convert 10.6 kg/m 3 to g/cm 3 (a) (b) (c) (d) (1-38)Convert 7.2 m 3 to liters. (a) 720 L (b) L (c) 0.72 L (d) (1-38)Convert 28.3 µg to pounds (a) lbs (b) lbs (c) lbs (d) lbs 139. (1-40)How many seconds are there in a solar year ( days), expressed in the correct number of significant figures? (a) s (b) s (c) s (d) s 140. (1-41)How many minutes does it take light from the sun to reach Earth, given that the distance from the sun to Earth is 93 million mi, and the speed of light is m/s? (a) 500 min (b) min (c) 8.3 min (d) 8.26 min 141. (1-42)A slow jogger runs a mile in 13 min. Calculate the speed in km/h. (1 mi = 1609 m) (a) 3.5 km/hr (b) 0.74 km/hr (c) 2.9 km/hr (d) 7.4 km/hr 142. (1-43)6.0-ft person weighs 168 lb. What is this person's height in meters and weight in kilograms? (1 lb = g; 1 m = 3.28 ft.) (a) 1.8 m, 76.2 kg (b) 1.8 m, 7620 kg (c) 5.4 m, 76.2 kg (d) 2.3 m, 43.2 kg 143. (1-44)The speed limit in some states in the United States is 55 miles per hour. What is the speed limit in kilometers per hour? (1 mi = 1609 m.) (a) 65 km/hr (b) 88 km/hr (c) 100 km/hr (d) 34 km/hr 144. (1-45)For a fighter jet to take off from the deck of an aircraft carrier, it must reach a speed of 62 m/s. What is this speed in miles per hour (mph)? (a) 120 mph (b) mph (c) mph (d) 300 mph 145. (1-46)The normal'' lead content in human blood is about 0.40 part per million (that is, 0.40 g of lead per million grams of blood). A value of 0.80 part per million (ppm) is considered to be dangerous. How many grams of lead are contained in g of blood (the amount in an average adult) if the lead content is 0.62 ppm? (a) g Pb (b) g Pb (c) g Pb (d) g Pb 146. (1-47)What is cm/s when converted to ft/s? (a) ft/s (b) ft/s (c) ft/s (d) ft/s 147. (1-49)Aluminum is a lightweight metal (density = 2.70 g/cm 3 ) used in aircraft construction, high-voltage transmission lines, beverage cans, and foils. What is its density in kg/m 3? (a) kg/m 3 (b) kg/m 3 (c) kg/m 3 (d) kg/m (1-50)The density of ammonia gas under certain conditions is g/l. What is its density in g/cm 3? (a) g/cm 3 (b) g/cm 3 (c) g/cm 3 (d) g/cm 3 11
12 149. (1-51)Which of the following statements is qualitative? (a) Water freezes at 0 C (b) Table salt melts at 801 C (c) Mercury is a liquid at room temperature (d) Gold contains 20% oxygen by volume 150. (1-52)Which of the following statements describes a chemical property? (a) Iron has a tendency to rust. (b) Rainwater in industrialized regions tends to be acidic. (c) Hemoglobin molecules have a red color. (d) When a glass of water is left out in the sun, the water gradually disappears 151. (1-53)In 2002, about 95.0 billion lb of sulfuric acid were produced in the United States. What is this quantity in tons? (a) ton (b) tons (c) tons (d) tons 152. (1-54)In determining the density of a rectangular metal bar, a student made the following measurements: length, 8.53 cm; width, 2.4 cm; height, 1.0 cm; mass, g. What is the density of the metal, expressed in the correct number of significant figures? (a) 2.57 g/cm 3 (b) g/cm 3 (c) g/cm 3 (d) 2.6 g/cm (1-55)Calculate the mass of a cube of platinum of edge length mm (the density of platinum = 21.4 g/cm 3 ). (a) g (b) g (c) g (d) g 154. (1-56)A cylindrical glass tube 12.7 cm in length is filled with mercury. The mass of mercury needed to fill the tube is g. What is the inner diameter of the tube? (The density of mercury = 13.6 g/ml.) (a) 1.34 cm (b) 1.00 cm (c) cm (d) cm 155. (1-57)The following procedure was used to determine the volume of a flask. The flask was weighed dry and then filled with water. If the masses of the empty flask and filled flask were g and g, respectively, and the density of water is g/cm 3, what is the volume of the flask in cm 3? (a) cm 3 (b) cm 3 (c) cm 3 (d) cm (1-58)The speed of sound in air at room temperature is about 343 m/s. What is this speed in miles per hour? (1 mi = 1609 m.) (a) 767 mph (b) 12.8 mph (c) mph (d) 343 mph 157. (1-59)A piece of silver (Ag) metal weighing g is placed in a graduated cylinder containing ml of water. The volume of water now reads ml. From these data calculate the density of silver. (a) 21.0 g/cm 3 (b) 1.25 g/cm 3 (c) g/cm 3 (d) 10.5 g/cm (1-61)A lead sphere has a mass of g, and its volume is cm 3. What is the density of lead? (a) g/cm 3 (b) 11.4 g/cm 3 (c) g/cm 3 (d) 1.14 g/cm (1-62)Lithium is the least dense metal known (density: 0.53 g/cm 3 ). What is the volume occupied by g of lithium? (a) cm 3 (b) cm 3 (c) cm 3 (d) cm 3 12
13 160. (1-63)The medicinal thermometer used in a doctor's office may be accurate to ± 0.1 C. In degrees Celsius, what is the percent error expected from such a thermometer in measuring a person's body temperature of 38.9 C? (a) 2.6 % (b) 0.1 % (c) 0.3 % (d) 1.4 % 161. (1-64)Vanillin (used to flavor vanilla ice cream and other foods) is the substance whose aroma the human nose detects in the smallest amount. The threshold limit is g per liter of air. If the current price of 50 g of vanillin is $112, determine the cost to supply enough vanillin so that the aroma could be detected in a large aircraft hangar with a volume of ft 3. (a) 6.3 ($0.063) (b) $15 (c) 63 ($0.63) (d) $ (1-65)At what temperature does the numerical reading on a Celsius thermometer equal that on a Fahrenheit thermometer? (a) 0 C (b) 40 C (c) 100 C (d) 32 C 163. (1-66)Suppose that a new temperature scale has been devised on which the melting point of ethanol ( C) and the boiling point of ethanol (78.3 C) are taken as 0 S and 100 S, respectively, where S is the symbol for the new temperature scale. Derive an equation relating a reading on this scale to a reading on the Celsius scale. What would this thermometer read at 25 C? (a) S (b) 10.0 S (c) 25 S (d) 72.8 S 164. (1-67)A resting adult requires about 240 ml of pure oxygen/min and breathes about 12 times every minute. If inhaled air contains 20 percent oxygen by volume and exhaled air 16 percent, what is the volume of air per breath? (Assume that the volume of inhaled air is equal to that of exhaled air.) (a) ml (b) ml (c) ml (d) ml 165. (1-68)A resting adult requires about 240 ml of pure oxygen/min and breathes about 12 times every minute. If inhaled air contains 20 percent oxygen by volume and exhaled air 16 percent, calculate the total volume (in liters) of air an adult breathes in a day. (a) L (b) L (c) L (d) L 166. (1-69)The total volume of seawater is L. Assume that seawater contains 3.1 percent sodium chloride by mass and that its density is 1.03 g/ml. Calculate the total mass of sodium chloride in kilograms. (a) kg (b) kg (c) kg (d) kg 167. (1-70)Magnesium (Mg) is a valuable metal used in alloys, in batteries, and in the manufacture of chemicals. It is obtained mostly from seawater, which contains about 1.3 g of Mg for every kilogram of seawater. Assume that seawater has a density is 1.03 g/ml. Calculate the volume of seawater (in liters) needed to extract tons of Mg, which is roughly the annual production in the United States. (a) L (b) L (c) L (d) L 168. (1-71)A student is given a crucible and asked to determine its density. She first weighs the crucible in air and then weighs it suspended in water (density = g/ml). The readings are g and g, respectively. What is the density of the crucible? (Hint: An object suspended in a fluid is buoyed up by the mass of the fluid displaced by the object. Neglect the buoyancy of air.) (a) 3.55 g/cm 3 (b) g/cm 3 (c) 40.0 g/cm 3 (d) g/cm 3 13
14 169. (1-72)The surface area and average depth of the Pacific Ocean are km 2 and m, respectively. Calculate the volume of water in the ocean in liters. (a) L (b) L (c) L (d) L 170. (1-73)The unit troy ounce'' is often used for precious metals such as gold (Au) and platinum (Pt). (1 troy ounce = g.) A gold coin weighs 2.41 troy ounces. What is its mass in grams? (a) 12.9 g (b) 52.3 g (c) 25.6 g (d) 75.0 g 171. (1-74)Osmium (Os) is the densest element known (density = g/cm 3 ). Calculate the mass in pounds and in kilograms of an Os sphere 15 cm in diameter (about the size of a grapefruit; V = (4/3) r 3 for a sphere of radius r). (a) 90 kg, 41 lb (b) kg, lb (c) 40 kg, 88 lb (d) 10 kg, 22 lb 172. (1-75)Percent error is often expressed as the absolute value of the difference between the true value and the experimental value, divided by the true value, multiplied by 100. Calculate the percent error for the following measurement: The density of alcohol (ethanol) is found to be g/ml. (True value: g/ml.) (a) 0.5 % (b) 5 % (c) % (d) 22 % 173. (1-76)The natural abundances of elements in the human body, expressed as percent by mass, are: oxygen (O), 65 percent; carbon (C), 18 percent; hydrogen (H), 10 percent; nitrogen (N), 3 percent; calcium (Ca), 1.6 percent; phosphorus (P), 1.2 percent; all other elements, 1.2 percent. What is the mass (in grams) of oxygen, carbon and hydrogen in the body of a 62-kg person? (a) g O; g C; g H (b) g O; g C; g H (c) g O; g C; g H (d) g O; g C; g H (1-77)The men's world record for running a mile outdoors (as of 1997) is 3 min s. At this rate, how long would it take to run a 1500-m race? (1 mi = 1609 m.) (a) s (b) s (c) s (d) s 176. (1-78)Venus, the second closest planet to the sun, has a surface temperature of K. Convert this temperature to C and F. (a) C; F (b) C; F (c) C; F (d) C; F 177. (1-79)Chalcopyrite, the principal ore of copper (Cu), contains percent Cu by mass. How many grams of Cu can be obtained from kg of the ore? (a) 147 kg (b) g (c) 147 g (d) g 178. (1-80)It has been estimated that tons of gold (Au) have been mined. Assume gold costs $350 per ounce. What is the total worth of this quantity of gold? (a) $ (b) $ (c) $ (d) $ (1-81)A 1.0-mL volume of seawater contains about g of gold. The total volume of ocean water is L. Calculate the total amount of gold (in grams) that is present in seawater, and the worth of the gold in dollars. (Assume gold costs $350 per ounce.) (a) g, $ (b) g, $ (c) g, $ (d) g, $
15 180. (1-82)Measurements show that 1.0 g of iron (Fe) contains Fe atoms. How many Fe atoms are in 4.9 g of Fe, which is the total amount of iron in the body of an average adult? (a) Fe atoms (b) Fe atoms (c) Fe atoms (d) Fe atoms 181. (1-83)The thin outer layer of Earth, called the crust, contains only 0.50 percent of Earth's total mass and yet is the source of almost all the elements (the atmosphere provides elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and a few other gases). Silicon (Si) is the second most abundant element in Earth's crust (27.2 percent by mass). Calculate the mass of silicon in kilograms in Earth's crust. (The mass of Earth is tons. 1 ton = 2000 lb; 1 lb = g.) (a) kg (b) kg (c) kg (d) kg 182. (1-84)The diameter of a copper (Cu) atom is roughly m. How many times can you divide evenly a piece of 10-cm copper wire until it is reduced to two separate copper atoms? (Assume there are appropriate tools for this procedure and that copper atoms are lined up in a straight line, in contact with each other. Round off your answer to an integer.) (a) 28 times (b) 29 times (c) 30 times (d) 31times 183. (1-85)One gallon of gasoline in an automobile's engine produces on the average 9.5 kg of carbon dioxide, which is a greenhouse gas, that is, it promotes the warming of Earth's atmosphere. Calculate the annual production of carbon dioxide in kilograms if there are 40 million cars in the United States and each car covers a distance of 5000 mi at a consumption rate of 20 miles per gallon. (a) kg (b) kg (c) kg (d) kg 184. (1-86)A sheet of aluminum (Al) foil has a total area of ft 2 and a mass of g. What is the thickness of the foil in millimeters? (Density of Al = g/cm 3.) (a) mm (b) mm (c) mm (d) mm 185. (1-87)Which of the following describes a closed bottle of air? (a) compound (b) heterogeneous mixture (c) element (d) homogeneous mixture 186. (1-88)Chlorine is used to disinfect swimming pools. The accepted concentration for this purpose is 1 ppm chlorine, or 1 g of chlorine per million grams of water. Calculate the volume of a chlorine solution (in milliliters) a homeowner should add to her swimming pool if the solution contains 6.0% chlorine by mass and there are gallons of water in the pool. (1 gallon = 3.79 L; density of liquids = 1.0 g/ml.) (a) ml of solution (b) 1.3 ml of solution (c) ml of solution (d) ml of solution 187. (1-89)The world's total petroleum reserve is estimated at J (joule is the unit of energy where 1 J = 1 kg m 2 /s 2 ). At the present rate of consumption, J/yr, how long would it take to exhaust the supply? (a) yr (b) yr (c) yr (d) yr 15
16 188. (1-90)In water conservation, chemists spread a thin film of certain inert material over the surface of water to cut down the rate of evaporation of water in reservoirs. Benjamin Franklin pioneered this technique three centuries ago. Franklin found that 0.10 ml of oil could spread over the surface of water of about 40 m 2 in area. Assuming that the oil forms a monolayer, that is, a layer that is only one molecule thick, estimate the length of each oil molecule in nanometers. (1 nm = m.) (a) 8.4 nm (b) 2.5 nm (c) 6.3 nm (d) 12.5 nm 189. (1-91)Fluoridation is the process of adding fluorine compounds to drinking water to help fight tooth decay. A concentration of 1 ppm of fluorine is sufficient for the purpose. (1 ppm means one part per million, or 1 g of fluorine per 1 million g of water.) The compound normally chosen for fluoridation is sodium fluoride, which is also added to some toothpaste. Calculate the quantity of sodium fluoride in kilograms needed per year for a city of 50,000 people if the daily consumption of water per person is 150 gallons. What percent of the sodium fluoride is wasted'' if each person uses only 6.0 L of water a day for drinking and cooking? (Sodium fluoride is 45.0% fluorine by mass. 1 gallon = 3.79 L; 1 year = 365 days; 1 ton = 2000 lb; 1 lb = g; density of water = 1.0 g/ml.) (a) 1% (b) 49% (c) 75% (d) 99% 190. (1-92)A gas company in Massachusetts charges $1.30 for 15.0 ft 3 of natural gas. If it takes ft 3 of gas to boil a liter of water, starting at room temperature (25 C), how much would it cost to boil a 2.1-L kettle of water? (a) $18 (b) 18 ($0.18) (c) 45 ($0.45) (d) 5.5 ($0.055) 191. (1-93)Pheromones are compounds secreted by females of many insect species to attract mates. Typically, g of a pheromone is sufficient to reach all targeted males within a radius of 0.50 mi. Calculate the density of the pheromone (in grams per liter) in a circular air space having a radius of 0.50 mi and a height of 40 ft. (a) g/l (b) g/l (c) g/l (d) g/l 16
CHAPTER 1. Conversions. General Plan for Converting Measurements. State the relationship between the unit given and the unit sought as an equality.
 CHAPTER 1 Conversions One of the aims of chemistry is to describe changes to tell what changed, how it changed, and what it changed into. Another aim of chemistry is to look at matter and its changes and
CHAPTER 1 Conversions One of the aims of chemistry is to describe changes to tell what changed, how it changed, and what it changed into. Another aim of chemistry is to look at matter and its changes and
This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use.
 This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use. Density & Dimensional Analysis Density - the volume which is occupied by a specific
This slide show has been prepared under fair use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law and are restricted from further use. Density & Dimensional Analysis Density - the volume which is occupied by a specific
There are 2 different types of numbers Exact -Measured
 Significant Figures When measuring or using our calculators we must determine the correct answer; our calculators are mindless drones and don t know the correct answer. There are 2 different types of numbers
Significant Figures When measuring or using our calculators we must determine the correct answer; our calculators are mindless drones and don t know the correct answer. There are 2 different types of numbers
CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 1 Matter and Change HOMEWORK. Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70)
 Name KEY Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 1 Matter and Change HOMEWORK Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70) 1.1 1.2 1.3 Warm Ups Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic
Name KEY Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 1 Matter and Change HOMEWORK Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70) 1.1 1.2 1.3 Warm Ups Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic
Corresponding Physical or Chemical Property bread rising through the use of baking soda carbonates decompose to form CO 2
 Substance = a chemical (element or mixture) Substance mixture chemical process = chemical reaction (new substances result) physical process = same substances present through out Physical or chemical processes?
Substance = a chemical (element or mixture) Substance mixture chemical process = chemical reaction (new substances result) physical process = same substances present through out Physical or chemical processes?
2.3 Density and Density Calculations
 2.3 Density and Density Calculations When people say that lead is heavier than wood, they do not mean that a pea sized piece of lead weighs more than a truckload of pine logs. What they mean is that a
2.3 Density and Density Calculations When people say that lead is heavier than wood, they do not mean that a pea sized piece of lead weighs more than a truckload of pine logs. What they mean is that a
D =? D = M = 10 g = 5 g/cm 3 M = 10 g V 2 cm 3 V = 2 cm 3 5 g/cm 3
 Using the formula for density, answer the following calculation problems. M D = (g/ml or g/cm 3 ) Density = Mass D = M M = (g) Volume V D V V = (ml or cm 3 ) For all of your problems, please complete them
Using the formula for density, answer the following calculation problems. M D = (g/ml or g/cm 3 ) Density = Mass D = M M = (g) Volume V D V V = (ml or cm 3 ) For all of your problems, please complete them
Experiment #3. Density and Specific Gravity.
 Experiment #3. Density and Specific Gravity. Goals 1. To measure and calculate the density and specific gravity of various substances. 2. To use significant figures correctly in calculations. Background
Experiment #3. Density and Specific Gravity. Goals 1. To measure and calculate the density and specific gravity of various substances. 2. To use significant figures correctly in calculations. Background
Chapter 3 - Energy and Matter Practice Problems
 Chapter 3 - Energy and Matter Practice Problems 1) Helium is a(n) A) compound. B) heterogeneous mixture. C) element. D) homogeneous mixture. E) electron. 2) Air is a(n) A) compound. B) heterogeneous mixture.
Chapter 3 - Energy and Matter Practice Problems 1) Helium is a(n) A) compound. B) heterogeneous mixture. C) element. D) homogeneous mixture. E) electron. 2) Air is a(n) A) compound. B) heterogeneous mixture.
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET
 SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET PART 1 - Determine the number of significant figures in the following numbers. 1.) 0.02 2.) 0.020 3.) 501 4.) 501.0 5.) 5,000 6.) 5,000. 7.) 6,051.00 8.) 0.0005 9.) 0.1020
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES WORKSHEET PART 1 - Determine the number of significant figures in the following numbers. 1.) 0.02 2.) 0.020 3.) 501 4.) 501.0 5.) 5,000 6.) 5,000. 7.) 6,051.00 8.) 0.0005 9.) 0.1020
1. Elemental mercury is a shiny, silver-colored, dense liquid that flows easily. Are these characteristics of mercury physical or chemical properties?
 Chemistry Dr. Saulmon 2014-15 School Year Unit 2: Basics of Chemistry Problem Set 3 Wednesday, September 3, 2014 1. Elemental mercury is a shiny, silver-colored, dense liquid that flows easily. Are these
Chemistry Dr. Saulmon 2014-15 School Year Unit 2: Basics of Chemistry Problem Set 3 Wednesday, September 3, 2014 1. Elemental mercury is a shiny, silver-colored, dense liquid that flows easily. Are these
Year 7 Chemistry HW Questions
 Year 7 Chemistry HW Questions 37 minutes 56 marks Page 1 of 15 Q1. Molly used a ph sensor to test different liquids. She dipped the probe of the sensor into each liquid and recorded the ph value in a table.
Year 7 Chemistry HW Questions 37 minutes 56 marks Page 1 of 15 Q1. Molly used a ph sensor to test different liquids. She dipped the probe of the sensor into each liquid and recorded the ph value in a table.
1 Elements. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Look at the illustration and identify one source of iron that comes to Earth from somewhere else.
 CHAPTER 4 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
CHAPTER 4 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
Homework for Unit Vocab for Unit 6; due: 2. Pg 333 (1-5), Pg 335 (1-4), Pg 337 (1-4), Pg 339 (1-6), No sentences; due:
 Unit 6 Heat Homework for Unit 6 1. Vocab for Unit 6; due: 2. Pg 333 (1-5), Pg 335 (1-4), Pg 337 (1-4), Pg 339 (1-6), No sentences; due: 3. Temperature change activity; due: 4. Heat Transfer Homework; due:
Unit 6 Heat Homework for Unit 6 1. Vocab for Unit 6; due: 2. Pg 333 (1-5), Pg 335 (1-4), Pg 337 (1-4), Pg 339 (1-6), No sentences; due: 3. Temperature change activity; due: 4. Heat Transfer Homework; due:
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS
 ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS Note: This worksheet is for additional practice. It is not due for a grade. Note: Unless specifically told otherwise, assume that percentage-by-mass
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE WITH WRITING CONVERSION FACTORS Note: This worksheet is for additional practice. It is not due for a grade. Note: Unless specifically told otherwise, assume that percentage-by-mass
Iron filings (Fe) 56g IRON + SULPHUR IRON SULPHIDE
 W.S.51. Chemical reactions. All of the different materials around us have been formed by chemical reactions from about one hundred simple elements. The diagram below shows a chemical reaction between the
W.S.51. Chemical reactions. All of the different materials around us have been formed by chemical reactions from about one hundred simple elements. The diagram below shows a chemical reaction between the
Density What is density? How do you measure density?
 Density What is density? How do you measure density? What is density? Density describes how much mass is in a given volume of a material. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. Volume: the amount of
Density What is density? How do you measure density? What is density? Density describes how much mass is in a given volume of a material. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. Volume: the amount of
Name Honors Chemistry / /
 Name Honors Chemistry / / SOL Questions Chapter 1 Each of the following questions below appeared on an SOL Chemistry Exam. For each of the following bubble in the correct answer on your scantron. 1. The
Name Honors Chemistry / / SOL Questions Chapter 1 Each of the following questions below appeared on an SOL Chemistry Exam. For each of the following bubble in the correct answer on your scantron. 1. The
THE PERIODIC TABLE. Chapter 15
 THE PERIODIC TABLE Chapter 15 MENDELEEV 1869 The first version of the periodic table was published by Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass This
THE PERIODIC TABLE Chapter 15 MENDELEEV 1869 The first version of the periodic table was published by Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass This
Name Class Date. mass of lithium 534 g Li molar mass of lithium 6.94 g/mol Li Unknown:
 Skills Worksheet Math Skills Converting Mass to Amount After you study each sample problem and solution, work out the practice problems on a separate sheet of paper. Write your answers in the spaces provided.
Skills Worksheet Math Skills Converting Mass to Amount After you study each sample problem and solution, work out the practice problems on a separate sheet of paper. Write your answers in the spaces provided.
Name: 2017 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment
 P a g e 1 Name: 2017 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment The Summer Assignment is due on the first day of class. P a g e 2 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment (This assignment is due on the
P a g e 1 Name: 2017 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment The Summer Assignment is due on the first day of class. P a g e 2 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment (This assignment is due on the
The table shows the students suggestions about the identity of P.
 1 Three students, X, Y and Z, were told that solid P reacts with dilute acids and also conducts electricity. The table shows the students suggestions about the identity of P. Which of the students are
1 Three students, X, Y and Z, were told that solid P reacts with dilute acids and also conducts electricity. The table shows the students suggestions about the identity of P. Which of the students are
Physics 171, Physics and Society Quiz 1 1pm Thurs Sept 14, 2017 Each question has one correct answer, or none (choose e on the clicker). 1.
 Physics 171, Physics and Society Quiz 1 1pm Thurs Sept 14, 2017 Each question has one correct answer, or none (choose e on the clicker). 1. Maria is riding her bicycle on a flat road at 10 mi/hr. Then
Physics 171, Physics and Society Quiz 1 1pm Thurs Sept 14, 2017 Each question has one correct answer, or none (choose e on the clicker). 1. Maria is riding her bicycle on a flat road at 10 mi/hr. Then
Science Class 8 Topic: Elements And Compounds Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Elements And Compounds Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1.Choose the best answer. 1. Which of the following is an element? a) steam b) sugar c)dry ice d) sulphur 2. Which
Science Class 8 Topic: Elements And Compounds Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1.Choose the best answer. 1. Which of the following is an element? a) steam b) sugar c)dry ice d) sulphur 2. Which
Chapter 12 Reactivity of Metals 12.1 Different Reactivities of Metals Recall an experiment performed in F.3
 Chapter 12 Reactivity of Metals 12.1 Different Reactivities of Metals Recall an experiment performed in F.3 p.1/9 When freshly cut, potassium has a shiny surface and it reacts vigorously with water, giving
Chapter 12 Reactivity of Metals 12.1 Different Reactivities of Metals Recall an experiment performed in F.3 p.1/9 When freshly cut, potassium has a shiny surface and it reacts vigorously with water, giving
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 22 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the layers of Earth s atmosphere? How has Earth s atmosphere
CHAPTER 22 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the layers of Earth s atmosphere? How has Earth s atmosphere
OC30 Conduct a qualitative experiment to detect the presence of dissolved solids in water samples, and test water for hardness (soap test)
 Chemistry: 6. Water Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OC14 Use cobalt chloride paper or anhydrous copper sulfate to test
Chemistry: 6. Water Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OC14 Use cobalt chloride paper or anhydrous copper sulfate to test
1 Elements. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Look at the illustration and identify one source of iron that comes to Earth from somewhere else.
 CHAPTER 3 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
CHAPTER 3 1 Elements SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an element? How do elements differ from
NCERT solutions for Metals and Non Metals
 NCERT solutions for Metals and Non Metals 1 Question 1 Give an example of a metal which (i) is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) can be easily cut with a knife. (iii) is the best conductor of heat. (iv)
NCERT solutions for Metals and Non Metals 1 Question 1 Give an example of a metal which (i) is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) can be easily cut with a knife. (iii) is the best conductor of heat. (iv)
Zinc 17. Part 2 Practical work
 Zinc 17 Part 2 Practical work 18 Zinc and Zirconia (per group) Teacher s notes Using carbon to extract copper from copper oxide could be used as an introduction to extracting less-reactive metals by displacement.
Zinc 17 Part 2 Practical work 18 Zinc and Zirconia (per group) Teacher s notes Using carbon to extract copper from copper oxide could be used as an introduction to extracting less-reactive metals by displacement.
Suggest one reason why spoons are electroplated. ... Why is hydrogen produced at the negative electrode and not sodium?
 Q1.This question is about electrolysis. (a) Metal spoons can be coated with silver. This is called electroplating. Suggest one reason why spoons are electroplated. (b) When sodium chloride solution is
Q1.This question is about electrolysis. (a) Metal spoons can be coated with silver. This is called electroplating. Suggest one reason why spoons are electroplated. (b) When sodium chloride solution is
85 Q.51 Which of the following carbonates would give the metal when heated with carbon? (1) MgCO 3 (2) PbCO 3 (3) K 2 CO 3 (4) CuCO 3
 Metal and metal reactivity / Section 2 / Sect2pp.doc / S. W. Tse / P.1 85 Q.51 Which of the following carbonates would give the metal when heated with carbon? (1) MgCO 3 (2) PbCO 3 (3) K 2 CO 3 (4) CuCO
Metal and metal reactivity / Section 2 / Sect2pp.doc / S. W. Tse / P.1 85 Q.51 Which of the following carbonates would give the metal when heated with carbon? (1) MgCO 3 (2) PbCO 3 (3) K 2 CO 3 (4) CuCO
Density Answers to the End of module questions
 IDS 101 Density Answers to the End of module questions 1. You are experimenting with the mysterious substance X. You carefully measure the mass of a uniform 2 ml sample of pure substance X. You slice it
IDS 101 Density Answers to the End of module questions 1. You are experimenting with the mysterious substance X. You carefully measure the mass of a uniform 2 ml sample of pure substance X. You slice it
Chapter: The Periodic Table
 Table of Contents Chapter: The Periodic Table Section 1: Introduction to the Periodic Table Section 2: Representative Elements Section 3: Transition Elements 1 Introduction to the Periodic Table Development
Table of Contents Chapter: The Periodic Table Section 1: Introduction to the Periodic Table Section 2: Representative Elements Section 3: Transition Elements 1 Introduction to the Periodic Table Development
Introduction to Density
 Introduction to Density INTRODUCTION Which is heavier, a pound of aluminum or a pound of lead? The answer, of course, is neither, but many people confuse the words "heavy" and "dense". "Heavy" refers to
Introduction to Density INTRODUCTION Which is heavier, a pound of aluminum or a pound of lead? The answer, of course, is neither, but many people confuse the words "heavy" and "dense". "Heavy" refers to
EOC 7th Grade District Common Assessment
 EOC 7th Grade District Common Assessment 1. Todd needs to measure 50 grams of table salt for an experiment. Which measuring device will most accurately measure 50 grams? 2. What is the length (in millimeters)
EOC 7th Grade District Common Assessment 1. Todd needs to measure 50 grams of table salt for an experiment. Which measuring device will most accurately measure 50 grams? 2. What is the length (in millimeters)
Physical Science Chapter 19. Elements and Their Properties Quick Notes
 Physical Science Chapter 19 Elements and Their Properties Quick Notes 1 19:1 A.Metals conduct heat and electricity, reflect light (luster); are malleable ( ) Can be hammered or rolled into sheets are ductile
Physical Science Chapter 19 Elements and Their Properties Quick Notes 1 19:1 A.Metals conduct heat and electricity, reflect light (luster); are malleable ( ) Can be hammered or rolled into sheets are ductile
Methods for determination of mercury in LP gas
 (JLPGA-S-07) Methods for determination of mercury in LP gas 1. Scope This standard specifies the methods for determination of gaseous mercury in vaporized liquid liquefied petroleum (LP) gas. Remarks 1
(JLPGA-S-07) Methods for determination of mercury in LP gas 1. Scope This standard specifies the methods for determination of gaseous mercury in vaporized liquid liquefied petroleum (LP) gas. Remarks 1
Covered with a thin layer of oxide at ordinary temperatures.
 1 More about Metals Physical properties of metals In general metals have luster, are malleable and ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity and have high boiling and melting points and nonmetals
1 More about Metals Physical properties of metals In general metals have luster, are malleable and ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity and have high boiling and melting points and nonmetals
Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3
 Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3 Directions to Students: Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. Please respond to the following items by marking the best answer
Chemistry Attitudes, Skills, & Knowledge Survey (CASKS) Form 3 Directions to Students: Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. Please respond to the following items by marking the best answer
4. Where do the names of the elements come from? Some were named as substances before they were known to be elements. sulfur 16
 4. Where do the names of the elements come from? Some were named as substances before they were known to be elements. silver 47 sulfur 16 copper 29 Some are named from the natural substance that they are
4. Where do the names of the elements come from? Some were named as substances before they were known to be elements. silver 47 sulfur 16 copper 29 Some are named from the natural substance that they are
SAMPLE PAGES PAGES. Extraction of metals from metal oxides. mixture of iron sand and coal are heated as they move down kiln, by force of gravity
 Unit 11.5 Metals and Non-metals Topic 3: Extraction of metals and corrosion In the previous two Topics we looked at the physical and chemical properties of metals. In Topic 3 we now examine how metals
Unit 11.5 Metals and Non-metals Topic 3: Extraction of metals and corrosion In the previous two Topics we looked at the physical and chemical properties of metals. In Topic 3 we now examine how metals
Today. Terrestrial Planets. Atmospheres Climate. Factors affecting atmospheres. Earth, Venus, Mars. Greenhouse effect from planetary perspective
 Today Terrestrial Planets Earth, Venus, Mars Atmospheres Climate Greenhouse effect from planetary perspective Factors affecting atmospheres EXAM NEXT TIME Why the sky is blue Atmosphere scatters blue light
Today Terrestrial Planets Earth, Venus, Mars Atmospheres Climate Greenhouse effect from planetary perspective Factors affecting atmospheres EXAM NEXT TIME Why the sky is blue Atmosphere scatters blue light
EXPERIMENT 3: Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties
 EXPERIMENT 3: Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties Materials: Hot plate Digital balance Capillary tubes (3) Thermometer Beakers (250 ml) Watch glass Graduated Cylinder (10 ml) Mel-Temp
EXPERIMENT 3: Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties Materials: Hot plate Digital balance Capillary tubes (3) Thermometer Beakers (250 ml) Watch glass Graduated Cylinder (10 ml) Mel-Temp
Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill
 Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill Lesson Overview: Students use the dimensions of the cargo hold of a ship s hull to calculate the volume of material that can be contained. Students will then use the
Calculating Ballast By Troy Averill Lesson Overview: Students use the dimensions of the cargo hold of a ship s hull to calculate the volume of material that can be contained. Students will then use the
Chemistry Quiz #1 Review
 Name: Chemistry Quiz 1 Review Page 1 of 6 Date: Please check your answers at http://leetz.weebly.com Chemistry Quiz #1 Review Part A: Density Calculations 1. The density of sodium is 0.97 g/cm 3. A sample
Name: Chemistry Quiz 1 Review Page 1 of 6 Date: Please check your answers at http://leetz.weebly.com Chemistry Quiz #1 Review Part A: Density Calculations 1. The density of sodium is 0.97 g/cm 3. A sample
Salinity in Seawater
 Salinity in Seawater Objective To familiarize students with the different methods used for measuring salinity of water. Introduction: Salinity exerts profound impacts on the marine environment. It controls
Salinity in Seawater Objective To familiarize students with the different methods used for measuring salinity of water. Introduction: Salinity exerts profound impacts on the marine environment. It controls
OCN 201 Chemical Oceanography Class Notes, Fall 2014 The origin of sea salt Chris Measures, Department of Oceanography
 OCN 201 Chemical Oceanography Class Notes, Fall 2014 The origin of sea salt Chris Measures, Department of Oceanography 1 Introduction Everyone knows that the sea is salty but what exactly is the salt in
OCN 201 Chemical Oceanography Class Notes, Fall 2014 The origin of sea salt Chris Measures, Department of Oceanography 1 Introduction Everyone knows that the sea is salty but what exactly is the salt in
Measurement and Density - Experiment 1
 Measurement and Density - Experiment 1 Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to acquaint you with some common metric units of length, volume, and mass. You will also measure the density of an unknown
Measurement and Density - Experiment 1 Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to acquaint you with some common metric units of length, volume, and mass. You will also measure the density of an unknown
COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER
 COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER Ocean water is a combination of freshwater and a variety of dissolved substances. Salinity is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in seawater, measured in parts per thousand
COMPOSITION OF SEAWATER Ocean water is a combination of freshwater and a variety of dissolved substances. Salinity is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in seawater, measured in parts per thousand
Overview of Climate Science
 1 Overview of Climate Science This overview of climate science is written to support the development of a K- 14 climate education plan for the Pacific Islands Climate Education Partnership (PCEP). It aims
1 Overview of Climate Science This overview of climate science is written to support the development of a K- 14 climate education plan for the Pacific Islands Climate Education Partnership (PCEP). It aims
(A) Copper. (B) Zinc. (C) Iron. (D) Wood. (A) Zinc. (B) Wood. (C) Rubber. (D) Plastic.
 Downloaded from MATERIALS : METALS AND NON-METALS 1.Give one example of each: metals and non-metals. 2.Name the metal, which is the best conductor of heat and electricity. 3.Name the property by which
Downloaded from MATERIALS : METALS AND NON-METALS 1.Give one example of each: metals and non-metals. 2.Name the metal, which is the best conductor of heat and electricity. 3.Name the property by which
Metal and Non Metals
 Metal and Non Metals Malleable Ductile Sonorous Conductor Insulator KEYWORDS Rusting Brass Calcium Chloride Galvanising Reactivity Metals on the Periodic table Metals Non Metals Metals and their properties
Metal and Non Metals Malleable Ductile Sonorous Conductor Insulator KEYWORDS Rusting Brass Calcium Chloride Galvanising Reactivity Metals on the Periodic table Metals Non Metals Metals and their properties
Biomass. Coal. 10 Intermediate Energy Infobook Activities. Description of biomass: Renewable or nonrenewable: Description of photosynthesis:
 Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Year 9 Science. 9C5: Energy Changes in Reactions and the Reactions of Metals. Home-Learning Challenge
 Year 9 Science 9C5: Energy Changes in Reactions and the Reactions of Metals Home-Learning Challenge Name: Form: 9C5 Module Overview and Home-Learning Subject: Science - Chemistry Year: 9 Half-Term: 1,
Year 9 Science 9C5: Energy Changes in Reactions and the Reactions of Metals Home-Learning Challenge Name: Form: 9C5 Module Overview and Home-Learning Subject: Science - Chemistry Year: 9 Half-Term: 1,
1. Marie mixed 5 g of carbon with 5 g of lead oxide. She heated the mixture strongly for 15 minutes in a fume cupboard.
 1. Marie mixed 5 g of carbon with 5 g of lead oxide. She heated the mixture strongly for 15 minutes in a fume cupboard. After 15 minutes, Marie found some shiny beads in the mixture. a. (i) Marie collected
1. Marie mixed 5 g of carbon with 5 g of lead oxide. She heated the mixture strongly for 15 minutes in a fume cupboard. After 15 minutes, Marie found some shiny beads in the mixture. a. (i) Marie collected
5-4 Chemical changes Trilogy
 5-4 Chemical changes Trilogy.0 A student investigated the reaction of sodium carbonate with dilute hydrochloric acid. The student used the apparatus shown in Figure. Figure Sodium carbonate This is the
5-4 Chemical changes Trilogy.0 A student investigated the reaction of sodium carbonate with dilute hydrochloric acid. The student used the apparatus shown in Figure. Figure Sodium carbonate This is the
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
 Q 1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry What weight of AgCI will be precipitated when a solution containing 4.77 g of NaCI is added to a solution of 5.77 g of AgNO 3? (IIT JEE 1978 3 Marks) Q 2. One gram
Q 1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry What weight of AgCI will be precipitated when a solution containing 4.77 g of NaCI is added to a solution of 5.77 g of AgNO 3? (IIT JEE 1978 3 Marks) Q 2. One gram
ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2004
 ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2004 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
ICSE-Science 2 (Chemistry) 2004 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter.
 1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of this object? A) 0.5 g B) 2 g C) 18 g D) 36 g Base your answers to questions 2 through
1. The diagram below represents a solid object with a density of 3 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of this object? A) 0.5 g B) 2 g C) 18 g D) 36 g Base your answers to questions 2 through
Closed Systems A closed system is a system in which energy, but not matter is exchanged with the surroundings.
 2.2 Notes Objectives Compare an open system with a closed system. List the characteristics of Earth s four major spheres. Identify the two main sources of energy in the Earth system. Identify four processes
2.2 Notes Objectives Compare an open system with a closed system. List the characteristics of Earth s four major spheres. Identify the two main sources of energy in the Earth system. Identify four processes
TREATMENT PLANT OPERATOR TRAINEE Examination Study Guide
 TREATMENT PLANT OPERATOR TRAINEE Examination Study Guide Mobile County Personnel Board 1809 Government St., Mobile AL 36606 May, 2018 A calculator and this page will be made available to examinees when
TREATMENT PLANT OPERATOR TRAINEE Examination Study Guide Mobile County Personnel Board 1809 Government St., Mobile AL 36606 May, 2018 A calculator and this page will be made available to examinees when
Stoichiometry Practice Related to Climate Change LESSON 6
 Stoichiometry Practice Related to Climate Change LESSON 6 Homework Assignment 1 Calculate the number of pounds of CO2 added to the atmosphere with the combustion of 1 gallon of gasoline. Conversions needed:
Stoichiometry Practice Related to Climate Change LESSON 6 Homework Assignment 1 Calculate the number of pounds of CO2 added to the atmosphere with the combustion of 1 gallon of gasoline. Conversions needed:
What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what. conduction is. Does conduction happen best in solids, liquids or gases?
 What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what conduction is What type of materials are good conductors and what type of materials are bad conductors (good insulators)? Does conduction happen
What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what conduction is What type of materials are good conductors and what type of materials are bad conductors (good insulators)? Does conduction happen
The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel.
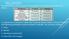 BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
Boiling point in C. Colour in aqueous solution. Fluorine 188 colourless. Chlorine 35 pale green. Bromine X orange.
 Q1.This question is about halogens and their compounds. The table below shows the boiling points and properties of some of the elements in Group 7 of the periodic table. Element Boiling point in C Colour
Q1.This question is about halogens and their compounds. The table below shows the boiling points and properties of some of the elements in Group 7 of the periodic table. Element Boiling point in C Colour
AP Chemistry Reaction Set
 Class: Date: AP Chemistry Reaction Set 2009-2010 Other 1. Pure solid phosphorus (white form) is burned in air. (2002) 2. Sulfur dioxide gas is bubbled into distilled water. (2001) 3. A drop of potassium
Class: Date: AP Chemistry Reaction Set 2009-2010 Other 1. Pure solid phosphorus (white form) is burned in air. (2002) 2. Sulfur dioxide gas is bubbled into distilled water. (2001) 3. A drop of potassium
TWEED RIVER HIGH SCHOOL 2006 PRELIMINARY CHEMISTRY. Unit 2 Metals
 TWEED RIVER HIGH SCHOOL 2006 PRELIMINARY CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Metals Part 2 Metals differ in their reactivity with other chemicals and this influences their uses. Describe observable changes when metals react
TWEED RIVER HIGH SCHOOL 2006 PRELIMINARY CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Metals Part 2 Metals differ in their reactivity with other chemicals and this influences their uses. Describe observable changes when metals react
The Earth s Global Energy Balance
 The Earth s Global Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Insolation over the Globe World Latitude Zones Composition of the Atmosphere Sensible Heat and Latent Heat Transfer The Global Energy System
The Earth s Global Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Insolation over the Globe World Latitude Zones Composition of the Atmosphere Sensible Heat and Latent Heat Transfer The Global Energy System
Copper Odyssey. Chemical Reactions of Copper
 Name Lab Partner(s) Copper Odyssey Chemical Reactions of Copper Date Period Elemental copper metal will be converted into copper (II) ion and then brought through a series of compound conversions until
Name Lab Partner(s) Copper Odyssey Chemical Reactions of Copper Date Period Elemental copper metal will be converted into copper (II) ion and then brought through a series of compound conversions until
The names and formulae of three hydrocarbons in the same homologous series are: Which homologous series contains ethane, propane and butane?
 Q1.This question is about hydrocarbons. (a) The names and formulae of three hydrocarbons in the same homologous series are: Ethane C 2 H 6 Propane C 3 H 8 Butane C 4 H 10 The next member in the series
Q1.This question is about hydrocarbons. (a) The names and formulae of three hydrocarbons in the same homologous series are: Ethane C 2 H 6 Propane C 3 H 8 Butane C 4 H 10 The next member in the series
ATOM STRUCTURE AND BONDING OF METALS
 ATOM STRUCTURE AND BONDING OF METALS The atom is composed of a small, central nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons. Shells, or energy levels of electrons surround this nucleus. These electrons
ATOM STRUCTURE AND BONDING OF METALS The atom is composed of a small, central nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons. Shells, or energy levels of electrons surround this nucleus. These electrons
Oxidation and Reduction
 Oxidation and Reduction An oxidation reaction is one in which oxygen is added to a substance. Example: Methane is oxidised when it burns in air. Oxygen is added to the carbon in methane, forming carbon
Oxidation and Reduction An oxidation reaction is one in which oxygen is added to a substance. Example: Methane is oxidised when it burns in air. Oxygen is added to the carbon in methane, forming carbon
Environmental Life Cycle Assessment PSE 476/FB 576
 Environmental Life Cycle Assessment PSE 476/FB 576 Lecture 4: Life Cycle Inventory: Units and Material and Energy Balances Fall 2016 Richard A. Venditti Forest Biomaterials North Carolina State University
Environmental Life Cycle Assessment PSE 476/FB 576 Lecture 4: Life Cycle Inventory: Units and Material and Energy Balances Fall 2016 Richard A. Venditti Forest Biomaterials North Carolina State University
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Lab: Ocean Salinity and Density M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Page 2. Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon. Methane. Nitrogen.
 Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. (a) Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon Methane Nitrogen Oxygen (b) An increase in global temperature will cause climate change.
Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. (a) Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon Methane Nitrogen Oxygen (b) An increase in global temperature will cause climate change.
DETERMINATION OF DENSITY
 DETERMINATION OF DENSITY Dr. Barbara B. Bunn. Adapted from Experiments in General Chemistry ; Wiley 1996J.G. Wardeska, T.T-S. Huang, R.W. Kopp; used by permission. Tested by Ms. Janice Orr s Chemistry
DETERMINATION OF DENSITY Dr. Barbara B. Bunn. Adapted from Experiments in General Chemistry ; Wiley 1996J.G. Wardeska, T.T-S. Huang, R.W. Kopp; used by permission. Tested by Ms. Janice Orr s Chemistry
Chemistry CH1HP. (Jan13CH1Hp01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier January Unit Chemistry C1. Unit Chemistry C1 TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Science A Unit Chemistry C1 Chemistry Unit Chemistry C1 Monday 14 January 2013 For this paper
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Science A Unit Chemistry C1 Chemistry Unit Chemistry C1 Monday 14 January 2013 For this paper
EMG 807 Post-test. 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of
 EMG 807 Post-test 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of a. Energy that we use. b. Power that we use. c. Force that we use. a. i only
EMG 807 Post-test 1. Workers from the electric company regularly read the meters on houses. These meters measure the amount of a. Energy that we use. b. Power that we use. c. Force that we use. a. i only
CHY1H (JUN08CHY1H01) General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June Unit Chemistry C1. CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1.
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June 2008 SCIENCE B Unit Chemistry C1 CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1 CHY1H
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June 2008 SCIENCE B Unit Chemistry C1 CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1 CHY1H
Earth as a System. Chapter 2. Table of Contents. Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet. Section 2 Energy in the Earth System.
 Earth as a System Table of Contents Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet Section 2 Energy in the Earth System Section 3 Ecology Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet Objectives Describe the size and shape of Earth.
Earth as a System Table of Contents Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet Section 2 Energy in the Earth System Section 3 Ecology Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet Objectives Describe the size and shape of Earth.
NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90933) 2012 page 1 of 5. Q Evidence Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5 M6 E7 E8
 Assessment Schedule 2012 NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90933) 2012 page 1 of 5 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of selected elements (90933) Evidence Statement Q Evidence with Merit with Excellence
Assessment Schedule 2012 NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90933) 2012 page 1 of 5 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of selected elements (90933) Evidence Statement Q Evidence with Merit with Excellence
» Talc is a native, hydrous magnesium silicate, sometimes containing a small proportion of aluminum silicate.
 Change to read: Talc» Talc is a native, hydrous magnesium silicate, sometimes containing a small proportion of aluminum silicate. Packaging and storage Preserve in well closed containers. Identification
Change to read: Talc» Talc is a native, hydrous magnesium silicate, sometimes containing a small proportion of aluminum silicate. Packaging and storage Preserve in well closed containers. Identification
Properties A Metal B Non- metal Electronic configuration?? Nature of oxides?? Oxidizing or reducing action?? Conduction of heat and electricity??
 CLASS: X NCERT (CBSE) SCIENCE: Chemistry Page: 1 Question 1: Compare the properties of a typical metal and a non-metal on the basis of the following. Fill in Column A, B. Properties A Metal B Non- metal
CLASS: X NCERT (CBSE) SCIENCE: Chemistry Page: 1 Question 1: Compare the properties of a typical metal and a non-metal on the basis of the following. Fill in Column A, B. Properties A Metal B Non- metal
Melting the Ice: Energy Transfer
 Melting the Ice: Energy Transfer Overview: Students observe a discrepant event, explore thermal energy and energy transfer, and apply their knowledge of energy transfer to sea ice processes. Objectives:
Melting the Ice: Energy Transfer Overview: Students observe a discrepant event, explore thermal energy and energy transfer, and apply their knowledge of energy transfer to sea ice processes. Objectives:
AP* CHEMISTRY EQUATIONS BY TYPE
 AP* CHEMISTRY EQUATIONS BY TYPE Double Replacement 1. Hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate. 2. An excess of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a solution of magnesium nitrate.
AP* CHEMISTRY EQUATIONS BY TYPE Double Replacement 1. Hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate. 2. An excess of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a solution of magnesium nitrate.
SIMPLE CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 SIMPLE CHEMICAL REACTIONS 1. Magnesium burns in air giving a very bright light. (a) Complete the word equation below to show this reaction. magnesium +...... The diagram shows four gas-jars. Each contains
SIMPLE CHEMICAL REACTIONS 1. Magnesium burns in air giving a very bright light. (a) Complete the word equation below to show this reaction. magnesium +...... The diagram shows four gas-jars. Each contains
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 18 - The Representative Elements: Groups 1A through 4A
 AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 18 - The Representative Elements: Groups 1A through 4A 18.1 A Survey of the Representative Elements A. Basic Trends 1. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations 2. Nonmetals
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 18 - The Representative Elements: Groups 1A through 4A 18.1 A Survey of the Representative Elements A. Basic Trends 1. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations 2. Nonmetals
not to be republished NCERT Every day you come across many Physical and Chemical Changes 6.1 PHYSICAL CHANGES Activity 6.1 Activity 6.2 Activity 6.
 6 Physical and Chemical Changes Every day you come across many changes in your surroundings. These changes may involve one or more substances. For example, your mother may ask you to dissolve sugar in
6 Physical and Chemical Changes Every day you come across many changes in your surroundings. These changes may involve one or more substances. For example, your mother may ask you to dissolve sugar in
Determination of the Empirical Formula of an Unknown Lead Oxide
 Determination of the Empirical Formula of an Unknown Lead Oxide by: Student Name Abstract Using a process known as smelting, 1 the empirical formula of an unknown lead oxide was determined 2 to be PbO
Determination of the Empirical Formula of an Unknown Lead Oxide by: Student Name Abstract Using a process known as smelting, 1 the empirical formula of an unknown lead oxide was determined 2 to be PbO
Electricity and Chemistry
 Electricity and Chemistry Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the reactions involving the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice-versa. Electrochemical
Electricity and Chemistry Electrochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that deals with the reactions involving the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice-versa. Electrochemical
Skills in Science. Lab equipment. (Always draw 2D) Drawings below are NOT to scale. Beaker - A general purpose container with a pouring lip.
 Skills in Science Safety: Do NOT enter or leave the lab without permission from a teacher. Keep the gaps between tables clear of stools and bags. Never run in the lab. Do not throw things around in the
Skills in Science Safety: Do NOT enter or leave the lab without permission from a teacher. Keep the gaps between tables clear of stools and bags. Never run in the lab. Do not throw things around in the
METALS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS
 METALS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS Metals are elements whose atoms ionize by electron loss, while non-metals are elements whose atoms ionize by electron gain. Metals are in groups 1, 2 and 3 of the periodic table.
METALS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS Metals are elements whose atoms ionize by electron loss, while non-metals are elements whose atoms ionize by electron gain. Metals are in groups 1, 2 and 3 of the periodic table.
1 Exam Prep Neon Techniques Questions
 1 Exam Prep Neon Techniques Questions 1. For the average neon sign or cold cathode tubing, a temperature of to degrees C is required for good heating. A. 150 to 200 B. 100 to 300 C. 200 to 250 D. 200 to
1 Exam Prep Neon Techniques Questions 1. For the average neon sign or cold cathode tubing, a temperature of to degrees C is required for good heating. A. 150 to 200 B. 100 to 300 C. 200 to 250 D. 200 to
Station 1 Dry Ice Experiments / Producing CO 2 in a reaction
 Station 1 Dry Ice Experiments / Producing CO 2 in a reaction 1. WHAT IS DRY ICE Put a flat chunk of dry ice on the counter and see how easy it "floats" on top of the counter when you give it a small push.
Station 1 Dry Ice Experiments / Producing CO 2 in a reaction 1. WHAT IS DRY ICE Put a flat chunk of dry ice on the counter and see how easy it "floats" on top of the counter when you give it a small push.
SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example,
 SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example, density, thermal or electrical conductivity, solubility,
SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured; for example, density, thermal or electrical conductivity, solubility,
Basics Course. Montana. Introduction to Drinking Water Systems. for small public drinking water systems serving less than 3,300 people
 Basics Course for small public drinking water systems serving less than 3,300 people Montana Montana Basics Course for Small Public Drinking Water Systems -1 Introduction to Drinking Water Systems Welcome
Basics Course for small public drinking water systems serving less than 3,300 people Montana Montana Basics Course for Small Public Drinking Water Systems -1 Introduction to Drinking Water Systems Welcome
Composition of Air. Air is a mixture of different gases. Gas % Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Argon 1% Carbon Dioxide 0.04%
 The Atmosphere Composition of Air Air is a mixture of different gases Gas % Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Argon 1% Carbon Dioxide 0.04% Water Vapour Varies day to day Experiment to show 1/5 of air is oxygen
The Atmosphere Composition of Air Air is a mixture of different gases Gas % Nitrogen 78% Oxygen 21% Argon 1% Carbon Dioxide 0.04% Water Vapour Varies day to day Experiment to show 1/5 of air is oxygen
CARBON. Carbon is an element of symbol C, with atomic number 6 (this means it has 6. available to form covalent bonds (tetravalent).
 CARBON Carbon is an element of symbol C, with atomic number 6 (this means it has 6 protons in its core or nuclei), is a non-metallic element, with available electrons available to form covalent bonds (tetravalent).
CARBON Carbon is an element of symbol C, with atomic number 6 (this means it has 6 protons in its core or nuclei), is a non-metallic element, with available electrons available to form covalent bonds (tetravalent).
