Research of Evaluation on Cultivated Land Fertility in Xinjiang Desert Oasis Based on GIS Technology- Taking No.22 State Farm as the Example 1
|
|
|
- Baldwin Booker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Research of Evaluation on Cultivated Land Fertility in Xinjiang Desert Oasis Based on GIS Technology- Taking No.22 State Farm as the Example 1 Ling Wang 1, Xin Lv 2, *, Hailong Liu 3 1 Department of Geography, Teachers College, Shihezi University, Shihezi, Xinjiang Province, P. R. China Key Laboratory of Oasis Ecological Agriculture of Xinjiang Production & Construction Corps(XPCC), Shihezi University, Shihezi, Xinjiang Province, P. R. China * Corresponding author, Address: Key Laboratory of Oasis Ecological Agriculture of Xinjiang Production & Construction Corps(XPCC), Shihezi University, Shihezi, , Xinjiang Province, P. R. China, Tel: , lxshz@126.com 3 College of Water Conservancy Construction Engineering, Shihezi University, Shihezi, Xinjiang Province, P. R. China Abstract. This paper, with No.22 State Farm, Agricultural Division No.2, XPCC as the example and under support of GIS, takes cultivated land plot as the evaluation unit and chooses 13 influence factors from five aspects of nutrient of cultivation layer, physical and chemical properties of cultivation layer, soil management, climate conditions and obstacle factor to establish desert oasis cultivated land fertility evaluation system and model. On the basis of a great quantity of information related to cultivated land fertility through field sampling and laboratory analysis, and supported by GIS, the papers takes advantages of mathematics method and mathematical model such as hierarchical analysis process and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation process to realize automatic and quantitative evaluation on cultivated land fertility, analyze area statistics and distribution characteristics of cultivated land fertility at different levels and main attribute of cultivated land at various classes in State Farm No.22, and give analysis of the space distribution. Results show that cultivated land in state farm No.22 can be divided into six classes, of which Class 1 Land IFI (integrated fertility index) is 0.74~1.00, area hm2, accounting for 7.67% of the total area; Class 2 - Class 6 Land for36.45%, 43.47%, 12.32%, 0.089%and % of the total area respectively. Research results are of significance in guiding local cultivated land quality management and promoting construction of new rural area. Keywords: Geographical information system (GIS), Cultivated land fertility, Desert oasis 1 Introduction Cultivated land is the foundation of agriculture and one of important resources guaranteeing sustainable development of the society and national economy. Evaluation on cultivated land fertility means a process assessing production potential and suitability of cultivated land for better utilization of land, so as to reveal bio-productivity capacity and potential productivity[1]. For recent decades, several surveys of land resources and general surveys of soil have been made in China. However, with social and economic development, great changes have taken place in quality and quantity of land utilizations and agricultural land(particularly cultivated land), existing data have become outdated and traditional survey method backward, failing to meet the need of modern agricultural production. GIS technology, however, can realize effective management of cultivated land resources with space characteristics. In recent years, with application of 3S technology, management and use of cultivated land resources have become more reasonable. For example, Zhang 1 *Foundation project: the Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region for Philosophy and Social Sciences(07JYB027) Primary author: Ling Wang, (1974-), F, Associate Professor, Department of Geography, Teachers School, Shihezi University, mainly in study of land quality evaluation, rain_ling@163.com Corresponding author: Xin Lv, Address: Key Laboratory of Oasis Ecological Agriculture of Xinjiang Production & Construction Corps(XPCC), Shihezi University, Shihezi, , Xinjiang Province, P. R. China, Tel: , lxshz@126.com 1
2 Haitao and others, by using GIS, introduced hierarchical analysis principle and method into evaluation on cultivated land fertility, for determining weight of involved factors, quickly and accurately completing comprehensive evaluation on natural fertility of cultivated land in Houhu Area in Jianghan Plain [2]; Zhou Hongyi and others, with SORER database as the foundation, made evaluation on fertility class of 53 cultivated land units in the typical area (Pengzhou) in upstream Yangtz River [3]; Wang Ruiyan and others took Qingzhou, Shandong Province as the test area and comprehensively used hierarchical cluster method, hierarchical analysis process, fuzzy evaluation method and mathematical model, realizing automatic and quantitative evaluation on cultivated land fertility[4]; Lin Bishan and others took soil species as the unit and adopted limiting factors method and the inductive method to made systematic analysis and appraisal of cultivated land fertility factors and evaluation on cultivated land (soil species ) Ilk force class [5]; He Yurong and others used soil quality coefficient to make evaluation on cultivated land fertility of Chuanjiang River Basin and several typical ecological agricultural zones in the surrounding area, to direct ecological environment construction and agricultural structure adjustment [6]; Liu Youzhao and others, taking Pizhou City, Jiangsu Province as the study-covered area and under support of GIS, made research of evaluation on cultivated land fertility, realizing automatic cultivated land classification and improving results scientificalness [7]. Therefore, the scientific research and practice using GIS technology to carry out cultivated land fertility survey and quality evaluation, on the one hand, can prepare information reserve for establishment of China s soil fertility information system and precision agriculture system, and help realize global soil information exchange and sharing; on the other hand, will be of great theoretical and practice significance in sounding out about what China has got in soil resources, reasonably utilizing and scientifically administrating land resources, promoting sustained, steady and concerted development of China in population, resources, environment, society and economy[8]. This paper mainly takes State Farm No.22, Agricultural Division No.2 as the example to analyze its cultivated land fertility situations, so as to make contributions to high quality and high yield of grain and economic crops in the Regiment. 2 General Description of the Study-covered Area The State Farm No.22 in Yanqi, Ba-Prefecture, Xinjiang, located at the hinterland of Eurasian Continent and southern foot of Tianshan Mountains, with Kaidu River passing through the center and geographical position E and N, enjoys typical continental North Temperate Zone cold climate, with annual accumulated temperature of 3379, annual average sunshine of 2973hours, annual precipitation of 93.7mm, annual average temperature of 7.9, extremely highest temperature of 37.7, extremely lowest temperature of minus 26.5 ; accumulated temperature 10 of 3353, frost-free period of 160~180. The Regiment neighbors Bosteng Lake in the east, is encircled by mountains in the south, borders Hular Mountain in the west and is against Tianshan Mountains in the north, making a typical basin area. The Regiment has a square topography, higher in the north and lower in the south, with slope of l/1000 and altitude of 1057m. The Regiment has land area of million hm 2. Of which cultivated land area is 9530 hm 2 ; mountain meadow area is 50, 000 hm 2 ; forest and fruits area 2467 hm 2 ; water area hm 2 ; and town-administrated area 3240 hm 2. In the Regiment soil is fertile and mainly consists of Quaternary-System sand loam soil, moisture soil, meadow soil, clay, salty soil and humult, etc, belonging to the ancient- past shallow marsh zone of Kaidu River and ancient Bosteng Lake delta. In terms of texture, the soil has sandy loam as the primary part and light loam as the secondary; moderate grain size, organic matter content average of 1.85%, total nitrogen of 0.11%, hydrolyzable nitrogen of 76mg/kg, rapid available phosphorus of 63mg/kg, rapid available potassium of 178mg/kg and PH of 7.7~8.1, suitable for planting wheat, tomato, pepper, beet, chrysanthemum, oil sunflower, confectionery sunflower, Black Seed Melon and maize, etc as agronomic crop. 2
3 3 Data and Research Method 3.1 Data Sources Collecting Data. Social and economic statistical data, including social and economic index data of population and land area on the basis of basic unit of administrative division; basic and thematic maps data, including relief map, administrative division map, current land utilization map and soil map, etc. Field Survey Data. Including topography, landforms, soil parent material, soil layer thickness, cultivation layer texture, current utilization of cultivated land and irrigation and drainage conditions, etc. Soil Laboratory Analysis Data. According to actual situations of the study-covered area, we decide to arrange points for sampling on the basis of strip field and by the same density (interval). And we give full considerations to utilization of factors of current situations, type of soil species and fertility level, and concurrent consideration to uniformity. Our sampling works are mainly carried out in autumn, with some samplings in summer. On the basis of indoor point arrangement, we select a representative plot in the field, position it with GPS positioner, and adopt S method, X method or chessboard method to randomly specify 10~15 sampling points. Each sampling point s earth borrow depth and sampling volume should be even and identical, with sampling depth of 0~20cm. After full mixing of soil samples, reserve sample by quartering, with 1.5kg for key point and 1kg for common point. In the State Farm No.22 total 917 soil samples have been collected. Soil sample analysis and determination items consist of: organic matter, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, rapid available phosphorus, rapid available potassium, effective zinc, effective iron, effective manganese, effective copper, salt content and ph value. Analysis method is subject to the Technical Regulations for National Cultivated Land Fertility Survey and Quality Evaluation. 3.2 Cultivated Land Fertility Evaluation Method This paper, by using geographical information system software ArcGIS and establishing the basic database for State Farm No.22 s cultivated land fertility evaluation, comprehensively analyzes factors influencing the State Farm No.22 s cultivated land fertility, so as to establish the State Farm No.22 s cultivated land fertility evaluation system and model. Determination of Evaluation Unit. Evaluation unit is the basic space unit for carrying out cultivated land class appraisal and division. The unit has uniform internal quality but big difference between units. Unit division needs comprehensive considerations of natural factors and social and economic factors. According to specific situations of the study-covered area, all sampling points in the State Farm No.22 are divided into evaluation units by strip field. Determination of Evaluation Index and Its Weight. The substance of cultivated land fertility evaluation is the evaluation on how natural elements such as topography and soil limit growth of local major agronomic crops. Cultivated land fertility evaluation factors consist of climate, topography, soil, vegetation, hydrologic and hydrogeological factors and social and economic factors. Many factors can influence cultivated land quality, involving various aspects of natural ecological conditions and social, economic and regional conditions. Our research, on the principle of stability, leading, comprehensiveness, difference, quantitation and reality, by referring to the index system of the National Cultivated Land Fertility Survey and Quality Evaluation by the Ministry of Agriculture, considering characteristics of the cultivated land resources in Agricultural Division No.2 and following the principle of availability, difference, importance, stability and combination of qualitative and quantitative indexes, selects five standard levels (nutrient of cultivation layer, cultivation layer s physical and chemical properties, soil management, climate conditions and obstacle factor), and 13 indexes (texture, PH, organic matter, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, rapid available phosphorus, rapid available potassium, effective zinc, effective copper, effective iron, effective manganese, accumulated temperature, irrigation guarantee rate and salt 3
4 content) from the national cultivated land fertility survey and quality evaluation index system, to establish Agricultural Division No.2 s cultivated land fertility evaluation index system, which is arranged in manner of target level (A), standard level (B) and index level (C) (See Table 1). Our research is carried out according to actual situations of the cultivated land soil in Agricultural Division No.2 and on the basis of opinions from relevant experts and technicians with practice experience. And weight of every factor is determined as shown in Table 1 according to actual situations of cultivated land soil in the Division and to influence of various factors, and by using hierarchical analysis process and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation process (See Table 1). Table 1. Cultivated Land Fertility Evaluation Factor and Weight of the State Farm No.22, Agricultural Division No.2 Target Level A Cultivated Land Fertility Standard Level B Index Level C Single Factor Weight Combined Weight Nutrient of cultivation layer Cultivation layer s physical and chemical properties Soil management Climate conditions Obstacle factor Nutrient of cultivation layer Organic matter Alkalihydr-olyzable nitrogen Rapid available phosphorus Rapid available potassium Effective copper Effective iron Effective zinc Effective manganese Cultivation layer s physical and chemical PH value properties Texture Soil management Irrigation guarantee rate Climate conditions Accumulated temperature Obstacle factor Cultivation layer s salt content Quantizing Treatment of Evaluation Index. According to land fertility and geological survey in Xinjiang, combining specific experiment and expert judgment, we process the quantitative data through combination of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation process and membership function to determine membership function of various evaluation indexes, and introduce evaluation factor value into the membership function, so as to calculate its membership value. For organic matter, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, rapid available phosphorus and rapid available potassium, etc, Type S membership function is established;for qualitative index, the method of grading by multiple experts but taking value on average is adopted. Quantizing treatment of concept factors. Concept factors such as soil texture, irrigation guarantee rate and accumulated temperature, etc are valuated as follows by adopting experts grading according to their influence on fertility, namely taking their characteristic value as the membership function (See Table 2.). Table 2. Membership Function of Concept Evaluation Index Accumulated temperature membership ~ ~2400 > Irrigation guarantee rate Fully met Basically met Generally met Not met membership
5 Soil texture membership loam clay sandy loam sandy soil Membership function of quantitative index. By using others research achievements [3], and through induction, feedback, gradual shrinkage and concentration, membership function of the following indexes is established. 1 Determining Type S membership function of organic matter, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, rapid available phosphorus and rapid available potassium membership: 1.0 x x 2 f(x)= 0.9(x-x 1 )/(x 2 -x 1 )+0.1 x 1 x<x 2 (1) 0.1 x>x 1 2 Determining Type S membership function of cultivation layer salt content membership: 1.0 x x 1 f(x)= 0.9(x-x 1 )/(x 2 -x 1 )+0.1 x 1 <x x 2 (2) 0.1 x>x 2 3 Determining Type S membership function of effective copper, effective iron, effective zinc, effective manganese membership: 1.0 x x 2 f(x) = (x-x 1 )/(x 2 -x 1 ) x 1 x<x 2 (3) 0 x<x 1 Break for value-taking of factors is shown as Table 3. Table 3. Value Taking of Type S Membership Function s Curve Break Break X1 X2 Organic matter % Alkalihydrolyzable nitrogen mg/kg Rapid available phosphorus mg/kg 5 25 Rapid available potassium mg/kg Salt content % Effective copper mg/kg Effective iron mg/kg Effective zinc mg/kg Effective manganese mg/kg Determination of ph membership The corresponding membership function for ph value, etc in soil is a med-type (trapezoid) membership function. The closer the index to certain range, the better the quality of the evaluation object; the farther the index from the range, the poorer the quality of the evaluation object. (x-3.5)/3 3.5<x<6.5 f(x)= (9.5-x)/2 7.5<x<9. (4) x x 3.5 or X 9.5 Comprehensive Evaluation on Cultivated Land Fertility. Using weighted summation formula to calculate IFI(Integrated Fertility Index) reflecting cultivated land fertility situations. The formula is: 5
6 IFI= Wi Ni. (5) Where, Ni and Wi respectively mean membership value and weight coefficient of No. i fertility index. 4 Evaluation Results and the Analysis 4.1 Quantity of Cultivated Land of Various Classes According to the above-mentioned cultivated land fertility evaluation method to calculate IFI of cultivated land fertility in State Farm No.22, Agricultural Division No.2. Using equidistance method to divide IFI into six classes (See Table 4.) ; calculate area of plot at various levels and the proportion (Table 5.). IFI 0.74~ 1.00 Class Class 1 Table 4. Division of Agricultural Division No.2 s Cultivated Land Fertility 0.68~ 0.73 Class ~ 0.67 Class ~ 0.62 Class ~ 0.56 Class 5 0~ 0.51 Class 6 Table 5. Class of Cultivated Land Fertility in State Farm No.22, Agricultural Division No.2 Unit Fertility Class Area Proportion % (hm 2 ) State Farm No.22 Class 1 Land Class 2 Land Class 3 Land Class 4 Land Class 5 Land Class 6 Land From Table 5. it can be found that the cultivated land in State Farm No.22 s hm 2 basic farmland can be divided into six classes, of which Class 1 Land has IFI(integrated fertility) of 0.74~1.00 and area of hm 2, accounting for 7.67% of the total area ; Class 2 Land has IFI of 0.68~0.73 and area of hm 2, accounting for 36.45%; Class 3 Land has IFI of 0.63~0.67 and area of hm 2, accounting for 43.47%; Class 4 Land has IFI of 0.57~0.62 and area of hm 2, accounting for 12.32% ; Class 5 Land has IFI of 0.51~0.56 and area of hm 2, accounting for 0.089%; Class 6 Land has IFI of 0~0.51 and area of hm 2, accounting for %. 4.2 Space Distribution of Cultivated Land at Various Levels With support of GIS software ArcGIS 9.2, on the basis of evaluation unit map and according to cultivated land fertility evaluation of the units, same-class and neighboring units are merged to get polygon of cultivated land fertility classes (See Fig. 1). In State Farm No.22, Agricultural Division No.2, Class 1 Land, within 10% of the total, is mainly distributed in Company 3, Company 6, Company 7, Company 8 and Company 9. The Class 1 Land belongs to high/stable-yield field, characterized by highest fertility, flat land, assured irrigation andconcerted water and air, where high yield is common for crops. In the Class 1 Land, soil has good arability, long cultivation period, good permeability and irrigation and quick fertilizer effect. However, attentions should be paid to application of more organic fertilizer and phosphorus/potassium fertilizers to prevent fertility from decreasing. 6
7 Fig. 1. Cultivated Land Fertility Class of State Farm No.22, Agricultural Division No.2 Class 2 Land accounts for about 35% of the total, and is distributed in all companies, with the most in Company 1 and the least in Company 2; Class 2 Land boasts higher content of alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, rapid available phosphorus, effective iron, effective manganese and effective copper, but lower content of organic matter and effective zinc that average of other classes, and soil mainly consisting of loam and sandy loam. In the project area Class 2 Land is characterized by high fertility, flat land, basically-matched irrigation system, concerted water and air, good arability and high nutrient content. Class 3 Land accounts for up to 43.47%, the highest proportion, and is distributed evenly, with the most in Company 1 and the least in Company 10. Class 3 Land has high content of organic matter and rapid available potassium, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, low content of rapid available phosphorus, and soil mainly consisting of sandy loam and little loam. In the area utilization of soil under Class 3 Land is limited to certain extent, soil s physical property is poor, and irrigation conditions are common, making crop subject to selection. In production, some improvement tests are needed to guarantee yield. The soil here has nutrient under med. level or short partially, needing more organic fertilizer and deepened mature cultivation layer to improve overall growth in soil. Class 4 Land is mainly distributed in Company 12, Company 13, Company 14 and Company 15. Class 4 Land boasts high organic matter and effective zinc content but low effective iron content, and soil mainly consists of sandy loam. Class 4 Land in the project area is more selective to agronomic crop and poor in soil quality and has considerable part of low-yield field as obstacle level. Class 4 Land has soil characterized by short arable period, hard control, poor overall quality (influencing germination), poor permeability, physical performance and ability against floodwater and drought. Proportion of Class 5 Land is slightly higher than that of Class 6 Land, very little compared with other classes and only in Company 14. Class 5 Land has average content of rapid available phosphorus and effective zinc the highest, and of other factors the lowest, compared with the average in other classes respectively. Its soil consists of sandy soil and sandy loam. Class 5 Land mainly belongs to low-yield field, basically has obstacle level and is badly limited for agricultural production and more selective to agronomic crop. The soil is poor in quality, fertility, physical performance and permeability. Soil in Class 5 Land should be applied with more organic fertilizer and supported with phosphorus potassium fertilizer. There is only a plot of Class 6 Land. Class 6 Land is characterized by obviously lower organic matter content and lower content of nutrient factors than those in land of other classes. Its soil mainly consists of sandy soil. Class 6 Land basically belongs to low-yield field, and the soil has poor fertility and physical performance. Yield of crop from the land 7
8 is very low. Overall content of nutrients is not low, but difference of nutrients is higher, meaning uneven distribution of nutrients. Meanwhile, main limiting factor of Class 6 Land lies in the soil s site conditions and obstacle factor, and the Land needs long-term comprehensive treatment and improvement. 5 Conclusion (1) From the above-mentioned researches it can be found that using GIS technology can quickly and effectively make quantitative and scientific evaluation on cultivated land fertility and the space distribution, saving time, work and effort compared with traditional evaluation method. (2) Application of hierarchical analysis process and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in cultivated land fertility evaluation can to certain extent reduce influence of subjective factors from evaluator, better reflect fertility difference of cultivated land and improve precision of cultivated land fertility evaluation results. (3) Using cultivated land plot as evaluation unit means clear space boundary and relationship of administrative subordination, accurate area, identical landforms type and soil type, and basically same utilization mode and cultivation method, making evaluation results more comprehensive and objective and implemented more directly in practice. (4) The results of evaluation on the basis of cultivated land fertility index of State Farm No.22, Agricultural Division No.2 are in line with actual conditions very much, and have very high guiding significance and practical value. Acknowledgments. Funding for this research was provided by the Social Science Fund program. The first authors are grateful to Dr. Xin Lv for his insightful comments on this manuscript. We wish to thank Dr. Hailong Liu for his help in organizing the data. The authors also appreciate other members of the Research on the Social Science Fund Project for their assistance. References 1. Lu Mingxing, He Liyuan and Wu Shuli. GIS-based Research of Evaluation on Cultivated Land Fertility in Central China Hilly Area. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering. 2006, 22 ( 8 ): (in Chinese) 2. Zhang Haitao, Zhou Yong and Wang Shanqin. Comprehensive Evaluation on Natural Fertility of Cultivated Land in Houhu Area, Jianghan Plain by Using GIS, RS Data and Hierarchical Analysis Process. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2003, 19(2): (in Chinese) 3. Wang Ruiyan, Zhao Gengxing and Li Tao. GIS-supported Evaluation on Cultivated Land Fertility Class. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2004, 20(1): (in Chinese) 4. Lin Bishan, Tang Jiandong and Zhang Manhong. Research and Evaluation on Cultivated Land Fertility Class in Guangdong. Ecological Environment, 2005, 14(1): (in Chinese). 5. He Yurong, Zhou Hongyi and Zhang Baohua. Cultivated Land Fertility and Agricultural Structure Adjustment in Typical Area of Upstream Yangtz River -- Taking Chuanjiang River Basin and its Surrounding Area as the Example. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2003, 17(3): 86 88, 92 (in Chinese) 6. Bi Rutian, Wang Bin and Wang Jinmin. Establishment and Application of MAPGIS-based Cultivated Land Fertility Evaluation System. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University, 2005, 25(2): (in Chinese) 7. Liu Youzhao, Wang Jun and Liu Jijun. Research of County-level Cultivated Land Classification und er Support of Geographical Information System. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2001, 24(3): (in Chinese) 8. Niu Yanbin, Xu Hui and Qin Shuangyue. Research of GIS-supported Cultivated Land Fertility Evaluation Method. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2004, 2 7(3):85 88 (in Chinese) 8
A Study of Agricultural Zoning of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain Based on GIS 1
 A Study of Agricultural Zoning of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain Based on GIS 1 Manping Hou 1, Jinmin Hao 2, Ying Shi 3, Jun Yang 4, Qian Wen 5, Mingzhu Cha 3, Lingkun Xiong 4 ( 1 China Institute of Defense Science
A Study of Agricultural Zoning of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain Based on GIS 1 Manping Hou 1, Jinmin Hao 2, Ying Shi 3, Jun Yang 4, Qian Wen 5, Mingzhu Cha 3, Lingkun Xiong 4 ( 1 China Institute of Defense Science
BioTechnology. An Indian Journal FULL PAPER ABSTRACT KEYWORDS. Trade Science Inc.
 [Type text] [Type text] [Type text] ISSN : 0974-745 Volume 0 Issue 6 04 BioTechnology An Indian Journal FULL PAPER BTAIJ, 0(6), 04 [9094-9098] Effects of comprehensive land consolidation on land quality
[Type text] [Type text] [Type text] ISSN : 0974-745 Volume 0 Issue 6 04 BioTechnology An Indian Journal FULL PAPER BTAIJ, 0(6), 04 [9094-9098] Effects of comprehensive land consolidation on land quality
Suitability Evaluation of Cold Water Paddy Field for Rice Planting. in Jianghan Plain
 International Conference on Advances in Energy and Environmental Science (ICAEES 2015) Suitability Evaluation of Cold Water Paddy Field for Rice Planting in Jianghan Plain Qingjun Deng1, a *, Yuru Chen2,b
International Conference on Advances in Energy and Environmental Science (ICAEES 2015) Suitability Evaluation of Cold Water Paddy Field for Rice Planting in Jianghan Plain Qingjun Deng1, a *, Yuru Chen2,b
A Dynamic Knowledge Models of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Computer System for Cotton
 A Dynamic Knowledge Models of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Computer System for Cotton ChunJing Si College of Information Engineering, Tarim University, Xinjiang 843300, China smallx1002@sina.com Abstract. Through
A Dynamic Knowledge Models of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Computer System for Cotton ChunJing Si College of Information Engineering, Tarim University, Xinjiang 843300, China smallx1002@sina.com Abstract. Through
Research Article Effects of Water-retention and Slow-release Fertilizers on Photosynthetic Rate of Summer Maize and Winter Wheat
 Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 10(4): 292-296, 2016 DOI: 10.19026/ajfst.10.2071 ISSN: 2042-4868; e-issn: 2042-4876 2016 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: February 3, 2015
Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 10(4): 292-296, 2016 DOI: 10.19026/ajfst.10.2071 ISSN: 2042-4868; e-issn: 2042-4876 2016 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: February 3, 2015
Managing Soil Fertility for Sustainable Agriculture in Taihang Mountain Piedmont, North China
 12 Managing Soil Fertility for Sustainable Agriculture in Taihang Mountain Piedmont, North China Chunsheng Hu* Abstract Soil fertility the ability of soil reserves to supply adequate levels of essential
12 Managing Soil Fertility for Sustainable Agriculture in Taihang Mountain Piedmont, North China Chunsheng Hu* Abstract Soil fertility the ability of soil reserves to supply adequate levels of essential
Discussion on Post - evaluation of Land Reclamation Project in Coal Mining Subsidence Land
 07 5th International Civil Engineering, Architecture and Machinery Conference(ICEAMC 07) Discussion on Post - evaluation of Land Reclamation Project in Coal Mining Subsidence Land Hui Zhang, Feng Gao Department
07 5th International Civil Engineering, Architecture and Machinery Conference(ICEAMC 07) Discussion on Post - evaluation of Land Reclamation Project in Coal Mining Subsidence Land Hui Zhang, Feng Gao Department
Changes in Area and Quality of Cultivated Land in China
 1 Changes in Area and Quality of Cultivated Land in China Qinxue WANG* and Kuninori OTSUBO* * National Institute for Environmental Studies, 16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506, Japan Abstract: In this
1 Changes in Area and Quality of Cultivated Land in China Qinxue WANG* and Kuninori OTSUBO* * National Institute for Environmental Studies, 16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506, Japan Abstract: In this
Cold-humid effect of Baiyangdian wetland
 Water Science and Engineering, 2012, 5(1): 1-10 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2012.01.001 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com Cold-humid effect of Baiyangdian wetland Hui-yun LI, Shi-guo
Water Science and Engineering, 2012, 5(1): 1-10 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2012.01.001 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com Cold-humid effect of Baiyangdian wetland Hui-yun LI, Shi-guo
Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and irrigation rate on nitrate present in the profile of a sandy farmland in Northwest China
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 11 (2011) 726 732 Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and irrigation rate on nitrate present in the profile of a sandy farmland in Northwest
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 11 (2011) 726 732 Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and irrigation rate on nitrate present in the profile of a sandy farmland in Northwest
Research in crop land suitability analysis based on GIS
 Research in crop land suitability analysis based on GIS Guobing Pan 1,2 Jianping Pan 2 (1 Structure Engineering Lab, Chongqing Jiaotong University, No.66 Xuefu Road Nan an District Chongqing China,China,400074)
Research in crop land suitability analysis based on GIS Guobing Pan 1,2 Jianping Pan 2 (1 Structure Engineering Lab, Chongqing Jiaotong University, No.66 Xuefu Road Nan an District Chongqing China,China,400074)
Optimal cattle manure application rate to maximise crop yield and minimise risk of N loss to the environment in a wheat-maize rotation cropping system
 Optimal cattle manure application rate to maximise crop yield and minimise risk of N loss to the environment in a wheat-maize rotation cropping system Yongping Jing 1,2, Yan Li 1,2,4, Yingpeng Zhang 1,2,
Optimal cattle manure application rate to maximise crop yield and minimise risk of N loss to the environment in a wheat-maize rotation cropping system Yongping Jing 1,2, Yan Li 1,2,4, Yingpeng Zhang 1,2,
APPLICATION OF 3S TECHNOLOGY TO LAND CONSOLIDATION IN CHERNOZEM REGION OF CHINA a case study of Hulun Buir
 APPLICATION OF 3S TECHNOLOGY TO LAND CONSOLIDATION IN CHERNOZEM REGION OF CHINA a case study of Hulun Buir Boqi Wang 1, Nan Li 2, Wei Li 1, Jinmin Hao 1,* 1 College of Resources and Environmental Sciences,
APPLICATION OF 3S TECHNOLOGY TO LAND CONSOLIDATION IN CHERNOZEM REGION OF CHINA a case study of Hulun Buir Boqi Wang 1, Nan Li 2, Wei Li 1, Jinmin Hao 1,* 1 College of Resources and Environmental Sciences,
A Case Study For Evaluating Sustainable Saline Soil Management Un exemple d évaluation de la gestion d un sol salin en vue d une agriculture durable
 Scientific registration number: 2524 Symposium n : 29 Presentation: poster A Case Study For Evaluating Sustainable Saline Soil Management Un exemple d évaluation de la gestion d un sol salin en vue d une
Scientific registration number: 2524 Symposium n : 29 Presentation: poster A Case Study For Evaluating Sustainable Saline Soil Management Un exemple d évaluation de la gestion d un sol salin en vue d une
Effects of irrigation on groundwater recharge under deep buried depth condition
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of on groundwater recharge under deep buried depth condition To cite this article: DONG Qiguang et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of on groundwater recharge under deep buried depth condition To cite this article: DONG Qiguang et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.:
DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM OF VARIABLE RATE IRRIGATION BASED ON MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND GIS
 DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM OF VARIABLE RATE IRRIGATION BASED ON MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND GIS Jianjun Zhou 1, Gang Liu 1 *, Su Li 2, Xiu Wang 3, Man Zhang 1 1 Key Laboratory of Modern Precision Agriculture System
DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM OF VARIABLE RATE IRRIGATION BASED ON MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND GIS Jianjun Zhou 1, Gang Liu 1 *, Su Li 2, Xiu Wang 3, Man Zhang 1 1 Key Laboratory of Modern Precision Agriculture System
Development Mode of Cold-chain Logistics of Guangxi Agricultural Products and Innovation Strategies. Weiyu Zhong
 International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2015) Development Mode of Cold-chain Logistics of Guangxi Agricultural Products and Innovation Strategies Weiyu Zhong
International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2015) Development Mode of Cold-chain Logistics of Guangxi Agricultural Products and Innovation Strategies Weiyu Zhong
Research Article. The effect of irrigation amount on soil salinity and the yield of drip irrigated cotton in saline-alkaline soils
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 14, 6(1):71-75 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effect of irrigation amount on soil salinity and
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 14, 6(1):71-75 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effect of irrigation amount on soil salinity and
TWO WITHIN-FIELD RAINWATER HARVESTING MEASURES AND THEIR EFFECTS ON INCREASING SOIL MOISTURE AND CROP PRODUCTION IN NORTH CHINA ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 TWO WITHIN-FIELD RAINWATER HARVESTING MEASURES AND THEIR EFFECTS ON INCREASING SOIL MOISTURE AND CROP PRODUCTION IN NORTH CHINA Jianxin Zhang 1,2, Dawei Zheng 1, Yantian Wang 1, Yu Duan 3, Yanhua Su 1
TWO WITHIN-FIELD RAINWATER HARVESTING MEASURES AND THEIR EFFECTS ON INCREASING SOIL MOISTURE AND CROP PRODUCTION IN NORTH CHINA Jianxin Zhang 1,2, Dawei Zheng 1, Yantian Wang 1, Yu Duan 3, Yanhua Su 1
System Dynamics Modeling for Sustainable Water Management of a Coastal Area in Shandong Province, China
 Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 4 (2016) 226-234 doi: 10.17265/2159-581X/2016.04.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING System Dynamics Modeling for Sustainable Water Management of a Coastal Area in Shandong
Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 4 (2016) 226-234 doi: 10.17265/2159-581X/2016.04.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING System Dynamics Modeling for Sustainable Water Management of a Coastal Area in Shandong
Impact of agricultural development on variation in surface runoff in arid regions: a case of the Aksu River Basin
 Journal of Arid Land Science Press 2012, 4(4): 399 410 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1227.2012.00399 jal.xjegi.com; www.chinasciencejournal.com Impact of agricultural development on variation in surface runoff in
Journal of Arid Land Science Press 2012, 4(4): 399 410 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1227.2012.00399 jal.xjegi.com; www.chinasciencejournal.com Impact of agricultural development on variation in surface runoff in
Overview of Water and Fertilizer Integration Development
 Overview of Water and Fertilizer Integration Development Huaiguo Zheng a, Limin Chuan b,*, Jingjuan Zhao c, Sufen Sun d and Junfeng Zhang e Institute of Information on Science and Technology of Agriculture,
Overview of Water and Fertilizer Integration Development Huaiguo Zheng a, Limin Chuan b,*, Jingjuan Zhao c, Sufen Sun d and Junfeng Zhang e Institute of Information on Science and Technology of Agriculture,
Analysis on Vegetation Growth Characteristics of Manas River Basin in Sinkiang. Wang Xiuyan, Liu Shaoyu, Han Shangping, liu Zhimin
 Analysis on Vegetation Growth Characteristics of Manas River Basin in Sinkiang Wang Xiuyan, Liu Shaoyu, Han Shangping, liu Zhimin Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of
Analysis on Vegetation Growth Characteristics of Manas River Basin in Sinkiang Wang Xiuyan, Liu Shaoyu, Han Shangping, liu Zhimin Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of
Effects of Burning Crop Residues on Soil Quality in Wenshui, Shanxi of China
 IJERD International Journal of Environmental and Rural Development (212) 3-1 Research article erd Effects of Burning Crop Residues on Soil Quality in Wenshui, Shanxi of China LIEXIANG LI Graduate School
IJERD International Journal of Environmental and Rural Development (212) 3-1 Research article erd Effects of Burning Crop Residues on Soil Quality in Wenshui, Shanxi of China LIEXIANG LI Graduate School
Study on Economies of Scale in Xinjiang Cotton Production Based on. Small Sample Survey. Yuyong Xia1, Qiong Ma2
 2nd International Conference on Economy, Management and Education Technology (ICEMET 2016) Study on Economies of Scale in Xinjiang Cotton Production Based on Small Sample Survey Yuyong Xia1, Qiong Ma2
2nd International Conference on Economy, Management and Education Technology (ICEMET 2016) Study on Economies of Scale in Xinjiang Cotton Production Based on Small Sample Survey Yuyong Xia1, Qiong Ma2
A FUZZY CONTROL IRRIGATION SYSTEM FOR COTTON FIELD
 A FUZZY CONTROL IRRIGATION SYSTEM FOR COTTON FIELD Jun Zhang 1, Yandong Zhao 2, Yiming Wang 3, Jinping Li 1,* 1 College of Information, Beijing Union University, Beijing, P. R. China 100101 2 College of
A FUZZY CONTROL IRRIGATION SYSTEM FOR COTTON FIELD Jun Zhang 1, Yandong Zhao 2, Yiming Wang 3, Jinping Li 1,* 1 College of Information, Beijing Union University, Beijing, P. R. China 100101 2 College of
Study on the Evaluation Index System and Standard of Arable Land Health Mei Shan 1,2,a, Xun Wang 3,b
 Study on the Evaluation Index System and Standard of Health Mei Shan 1,2,a, Xun Wang 3,b 1 College of Resources and Environment,Shandong Agricultural University,China,Shandong Taian 271018 2 Department
Study on the Evaluation Index System and Standard of Health Mei Shan 1,2,a, Xun Wang 3,b 1 College of Resources and Environment,Shandong Agricultural University,China,Shandong Taian 271018 2 Department
 Effects of water and soil conservation works on runoff and sediment variation in the areas with high and coarse sediment yield of the middle Yellow River Wei Ying SUN, Pan ZHANG, Li LI, and Jiang Nan CHEN
Effects of water and soil conservation works on runoff and sediment variation in the areas with high and coarse sediment yield of the middle Yellow River Wei Ying SUN, Pan ZHANG, Li LI, and Jiang Nan CHEN
Rationally Utilizing Water Resources to Control Soil Salinity in Irrigation Districts
 This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages 1134-1138. In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds). 2001. Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 10th International
This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages 1134-1138. In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds). 2001. Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 10th International
Mapping an inland-valley catchment area
 The inland-valley bottom or lowland is the lowest part of an Place a sheet of strong inland-valley catchment area, which includes from top to bottom: packing paper on the ground, preferably in the The
The inland-valley bottom or lowland is the lowest part of an Place a sheet of strong inland-valley catchment area, which includes from top to bottom: packing paper on the ground, preferably in the The
Evaluation of the Green Sustainable Development Ability of Chengdu Agriculture Based on Entropy Method Yuejie Xiao a and Hong Tang b,*
 2018 3rd International Conference on Society Science and Economics Development (ICSSED 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-031-0 Evaluation of the Green Sustainable Development Ability of Chengdu Agriculture Based
2018 3rd International Conference on Society Science and Economics Development (ICSSED 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-031-0 Evaluation of the Green Sustainable Development Ability of Chengdu Agriculture Based
WEB-BASED EXPERT SYSTEM OF WHEAT AND CORN GROWTH MANAGEMENT
 WEB-BASED EXPERT SYSTEM OF WHEAT AND CORN GROWTH MANAGEMENT Xuesong Suo 1,*, Nan Shi 2 1 School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding 071001, China 2 College
WEB-BASED EXPERT SYSTEM OF WHEAT AND CORN GROWTH MANAGEMENT Xuesong Suo 1,*, Nan Shi 2 1 School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding 071001, China 2 College
Rice-rice-potato rotation system
 Rice-rice-potato rotation system Potato likes to grow in the cool environment. The suitable temperature for potato development ranges from 15-18 0 C.If temperature is higher than 25 0 C, potato growth
Rice-rice-potato rotation system Potato likes to grow in the cool environment. The suitable temperature for potato development ranges from 15-18 0 C.If temperature is higher than 25 0 C, potato growth
Effects of Nitrogen Application Levels on Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrogen Utilization during Rice Growing Season
 Rice Science, 2012, 19(2): 125 134 Copyright 2012, China National Rice Research Institute Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved Effects of Nitrogen Application Levels on Ammonia Volatilization
Rice Science, 2012, 19(2): 125 134 Copyright 2012, China National Rice Research Institute Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved Effects of Nitrogen Application Levels on Ammonia Volatilization
Prospects on Drip Irrigation Development in Xinjiang, China
 Prospects on Drip Irrigation Development in Xinjiang, China Shalamu Abudu 1, Zhuping Sheng 1, Jiancun He 2, Chunliang Cui 2, Bayinmengke 2 1.Texas A&M AgriLife Research Center at El Paso, 1380 A&M Circle,
Prospects on Drip Irrigation Development in Xinjiang, China Shalamu Abudu 1, Zhuping Sheng 1, Jiancun He 2, Chunliang Cui 2, Bayinmengke 2 1.Texas A&M AgriLife Research Center at El Paso, 1380 A&M Circle,
Benefit assessment of soil and water conservation from cropland to forest in hilly Loess Plateau at Qinghai
 a SpringerOpen Journal PROCEEDINGS Open Access Benefit assessment of soil and water conservation from cropland to forest in hilly Loess Plateau at Qinghai Chuanchuan Zhao 1*, Ninggui Yang 1, Zhen Wang
a SpringerOpen Journal PROCEEDINGS Open Access Benefit assessment of soil and water conservation from cropland to forest in hilly Loess Plateau at Qinghai Chuanchuan Zhao 1*, Ninggui Yang 1, Zhen Wang
China. Keywords: Automotive manufacturing, Servitization, Total factor productivity (TFP), Research and development (R&D).
 2016 3 rd International Conference on Social Science (ICSS 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-410-3 The SWOT and Countermeasures Analysis about Automotive Manufacturing Servitization in Guangxi Based on the Perspective
2016 3 rd International Conference on Social Science (ICSS 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-410-3 The SWOT and Countermeasures Analysis about Automotive Manufacturing Servitization in Guangxi Based on the Perspective
Utilization of winter fallowed cotton fields in the Huang Huai Hai Plain 1
 Utilization of winter fallowed cotton fields in the Huang Huai Hai Plain 1 Niu Ling an, Lu Zhenyu, Yan Yong, Yang He fa, Shen Guangcheng, Zhang Shukui and Hao Jin min Quzhou Experimental Station, China
Utilization of winter fallowed cotton fields in the Huang Huai Hai Plain 1 Niu Ling an, Lu Zhenyu, Yan Yong, Yang He fa, Shen Guangcheng, Zhang Shukui and Hao Jin min Quzhou Experimental Station, China
Utilization of water resources and its effects on the hydrological environment of the Tarim River basin in Xinjiang, China
 Water Resources Systems Water Availability and Global Change (Proceedings of symposium HS02n held during IUGG2003 al Sapporo. July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 280. 2003. 23 Utilization of water resources and
Water Resources Systems Water Availability and Global Change (Proceedings of symposium HS02n held during IUGG2003 al Sapporo. July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 280. 2003. 23 Utilization of water resources and
Analysis of agricultural input-output based on Cobb Douglas production function in Hebei Province, North China
 African Journal of Microbiology Research Vol. 5(32), pp. 5916-5922, 30 December, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajmr ISSN 1996-0808 2011 Academic Journals DOI: 10.5897/AJMR11.961
African Journal of Microbiology Research Vol. 5(32), pp. 5916-5922, 30 December, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajmr ISSN 1996-0808 2011 Academic Journals DOI: 10.5897/AJMR11.961
CONSTRUCTION STANDARD OF FARMLAND LANDSCAPE PATTERN IN CHINA BASED ON PRECISION AGRICULTURE
 CONSTRUCTION STANDARD OF FARMLAND LANDSCAPE PATTERN IN CHINA BASED ON PRECISION AGRICULTURE Meichen Fu 1,*, Jianjun Zhang 1 1 School of Land Sciences and Technology, China University of Geosciences,Beijing,
CONSTRUCTION STANDARD OF FARMLAND LANDSCAPE PATTERN IN CHINA BASED ON PRECISION AGRICULTURE Meichen Fu 1,*, Jianjun Zhang 1 1 School of Land Sciences and Technology, China University of Geosciences,Beijing,
Journal of Integrative Agriculture 2016, 15(11): Available online at ScienceDirect
 Journal of Integrative Agriculture 216, (11): 2639 2646 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect RESEARCH ARTICLE The status and distribution characteristics of residual mulching film in
Journal of Integrative Agriculture 216, (11): 2639 2646 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect RESEARCH ARTICLE The status and distribution characteristics of residual mulching film in
Flood forecasting model based on geographical information system
 192 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Flood forecasting model based on geographical information
192 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Flood forecasting model based on geographical information
Effect of Irrigation System Basin and Furrow in Saline Distributions Patterns and Productivity Corn (Zea Mays L.)
 IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. II (May. 2016), PP 31-38 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Irrigation System Basin
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. II (May. 2016), PP 31-38 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Irrigation System Basin
Flood forecasting model based on geographical information system
 doi:10.5194/piahs-368-192-2015 192 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Flood forecasting model
doi:10.5194/piahs-368-192-2015 192 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Flood forecasting model
THE SIMULATION OF AGRICULTURAL NON- POINT SOURCE POLLUTION IN SHUANGYANG RIVER WATERSHED
 THE SIMULATION OF AGRICULTURAL NON- POINT SOURCE POLLUTION IN SHUANGYANG RIVER WATERSHED Yongsheng Ma 1, Xiucui Tan 1,*, Qiuyue Shi 1 School of Water Conservancy & Civil Engineering, Northeast Agricultural
THE SIMULATION OF AGRICULTURAL NON- POINT SOURCE POLLUTION IN SHUANGYANG RIVER WATERSHED Yongsheng Ma 1, Xiucui Tan 1,*, Qiuyue Shi 1 School of Water Conservancy & Civil Engineering, Northeast Agricultural
How Does Utah Lake Measure Up?
 How Does Measure Up? This lesson plan has been created as a resource for fourth grade teachers to teach their students the new core standards. It integrates math, social studies, and science standards
How Does Measure Up? This lesson plan has been created as a resource for fourth grade teachers to teach their students the new core standards. It integrates math, social studies, and science standards
Demonstration Zones of Agricultural Modernization by Mr. Qian (chief agroeconomist
 Disclaimer: This translation by the DCZ is provided as a working tool, and is provided "as is." No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, correctness, or reliability
Disclaimer: This translation by the DCZ is provided as a working tool, and is provided "as is." No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, correctness, or reliability
Suitable oasis scales under a government plan in the Kaidu-Konqi
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Suitable oasis scales under a government plan in the Kaidu-Konqi River Basin of northwest
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Suitable oasis scales under a government plan in the Kaidu-Konqi River Basin of northwest
Water Pollution Characteristics and Assessment of Lower Reaches in Haihe River Basin
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 2 (2010) 199 206 International Society for Environmental Information Sciences 2010 Annual Conference (ISEIS) Water Pollution Characteristics
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 2 (2010) 199 206 International Society for Environmental Information Sciences 2010 Annual Conference (ISEIS) Water Pollution Characteristics
The comprehensive evaluation on resource environmental bearing capacity of central cities in the Yellow River Delta-A case study on Dongying City
 Journal Journal of Groundwater of Science Science and and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.5 No.4 No.4 Dec. Dec. 2017 2017 The comprehensive evaluation on resource environmental bearing capacity of central cities
Journal Journal of Groundwater of Science Science and and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.5 No.4 No.4 Dec. Dec. 2017 2017 The comprehensive evaluation on resource environmental bearing capacity of central cities
Land use structural optimization of Lilin based on GMOP ESV
 Trans. Nonferrous et. Soc. China 21(2011 s738-s742 and use structural optimization of ilin based on GOP ESV ZHANG He bing, ZHANG Xiao hu School of Surveying & and Information Engineering, Henan Polytechnic
Trans. Nonferrous et. Soc. China 21(2011 s738-s742 and use structural optimization of ilin based on GOP ESV ZHANG He bing, ZHANG Xiao hu School of Surveying & and Information Engineering, Henan Polytechnic
International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID) WATSAVE AWARDS 2012
 International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID) WATSAVE AWARDS 2012 Technology Award ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID) WATSAVE AWARDS 2012 Technology Award ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Soils Soil Formation Soils of Hungary Land Degradation and Soil Fertility
 Soils Soil Formation Soil is the uppermost part of the weathered surface layer of Earth, developed within the interaction zone of the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere under the integrated
Soils Soil Formation Soil is the uppermost part of the weathered surface layer of Earth, developed within the interaction zone of the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere under the integrated
Regional Groundwater Flow Modeling of Yarkant Basin in West China
 Conference on Environmental Pollution and Public Health Regional Groundwater Flow Modeling of Yarkant Basin in West China Sun Jinyu Zhang Qiang Xu Mo College of Environment and Civil Engineering, Chengdu
Conference on Environmental Pollution and Public Health Regional Groundwater Flow Modeling of Yarkant Basin in West China Sun Jinyu Zhang Qiang Xu Mo College of Environment and Civil Engineering, Chengdu
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Drip Irrigation in Cotton Production in Northwestern China
 1 Cost-Benefit Analysis of Drip Irrigation in Cotton Production in Northwestern China Til Feike 1,2 *, Thomas Lang 2, Heinrich Hagel 2, Yusuyunjiang Mamitimin 2, Reiner Doluschitz 2 1 Julius Kühn-Institute
1 Cost-Benefit Analysis of Drip Irrigation in Cotton Production in Northwestern China Til Feike 1,2 *, Thomas Lang 2, Heinrich Hagel 2, Yusuyunjiang Mamitimin 2, Reiner Doluschitz 2 1 Julius Kühn-Institute
Water Resources CHOIR in China
 Water Resources CHOIR in China Strategic research and innovation priorities for water Liu Dengwei 水利部发展研究中心 Development Research Center of the Ministry of Water Resources of China Water Resources CHOIR
Water Resources CHOIR in China Strategic research and innovation priorities for water Liu Dengwei 水利部发展研究中心 Development Research Center of the Ministry of Water Resources of China Water Resources CHOIR
Assessing the role of agri-environmental measures to enhance the environment in the Veneto Region with a model based-approach
 Assessing the role of agri-environmental measures to enhance the environment in the Veneto Region with a model based-approach Francesco Morari Department of Agronomy Food Natural resources Animals Environment
Assessing the role of agri-environmental measures to enhance the environment in the Veneto Region with a model based-approach Francesco Morari Department of Agronomy Food Natural resources Animals Environment
The Game Between Companies and Farmers in Controlling Pig Environmental Pollution
 Management Science and Engineering Vol. 10, No. 3, 2016, pp. 35-40 DOI:10.3968/8620 ISSN 1913-0341 [Print] ISSN 1913-035X [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The Game Between Companies and Farmers
Management Science and Engineering Vol. 10, No. 3, 2016, pp. 35-40 DOI:10.3968/8620 ISSN 1913-0341 [Print] ISSN 1913-035X [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The Game Between Companies and Farmers
Keywords: Water Resources Carrying Capacity; The Arid and Semi-arid Regions of Northwest China; Research Progress.
 2016 2 nd International Conference on Social Science and Development (ICSSD 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-356-4 Current Research Status and Perspective of Water Resources Carrying Capacity in the Arid and Semi-arid
2016 2 nd International Conference on Social Science and Development (ICSSD 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-356-4 Current Research Status and Perspective of Water Resources Carrying Capacity in the Arid and Semi-arid
Lift irrigation Using man or Animal power Using Mechanical or Electrical Power Flow irrigation a)inundation Irrigation b) Perennial Irrigation Direct
 Lift irrigation Using man or Animal power Using Mechanical or Electrical Power Flow irrigation a)inundation Irrigation b) Perennial Irrigation Direct irrigation Storage irrigation a)flow irrigation system:
Lift irrigation Using man or Animal power Using Mechanical or Electrical Power Flow irrigation a)inundation Irrigation b) Perennial Irrigation Direct irrigation Storage irrigation a)flow irrigation system:
Institute of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(CAAS)
 Institute of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(CAAS) The Integration of Export Coefficient Method and SWAT Model for Identifying the Contribution of
Institute of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(CAAS) The Integration of Export Coefficient Method and SWAT Model for Identifying the Contribution of
FERTILIZER RECOMMENDATIONS for the Lower Rio Grande Valley
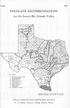 L-222 1957 FERTILIZER RECOMMENDATIONS for the Lower Rio Grande Valley SOIL AREAS: A B C D E F G H I J K East Texas Timber Country Gulf Coast Prairie Blackland Prairie Grand Prairie West Cross Timbers Central
L-222 1957 FERTILIZER RECOMMENDATIONS for the Lower Rio Grande Valley SOIL AREAS: A B C D E F G H I J K East Texas Timber Country Gulf Coast Prairie Blackland Prairie Grand Prairie West Cross Timbers Central
Mixed-Oak Forest On A Fine-Textured Alfisol
 NRE 430 / EEB 489 D.R. Zak 2003 Lab #3 Mixed-Oak Forest On A Fine-Textured Alfisol Radrick Forest is typical of many of the hardwood forests that occupy dry-mesic to wet-mesic sites in southern Michigan,
NRE 430 / EEB 489 D.R. Zak 2003 Lab #3 Mixed-Oak Forest On A Fine-Textured Alfisol Radrick Forest is typical of many of the hardwood forests that occupy dry-mesic to wet-mesic sites in southern Michigan,
Study of Interactive Development Model of Producer Services and Manufacturing Industry Based on Symbiotic Theory
 International Journal of Economics, Finance and Management Sciences 2016; 4(5): 292-297 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijefm doi: 10.11648/j.ijefm.20160405.19 ISSN: 2326-9553 (Print); ISSN: 2326-9561
International Journal of Economics, Finance and Management Sciences 2016; 4(5): 292-297 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijefm doi: 10.11648/j.ijefm.20160405.19 ISSN: 2326-9553 (Print); ISSN: 2326-9561
08. WATER BUDGETING AND ITS IMPORTANCE - IRRIGATION SCHEDULING - APPROACHES
 08. WATER BUDGETING AND ITS IMPORTANCE - IRRIGATION SCHEDULING - APPROACHES Water budgeting: Allocation of the water receipt including anticipated within the crop period and its detailed account of expenditure
08. WATER BUDGETING AND ITS IMPORTANCE - IRRIGATION SCHEDULING - APPROACHES Water budgeting: Allocation of the water receipt including anticipated within the crop period and its detailed account of expenditure
Simulation of soil moisture for typical plain region using the Variable Infiltration Capacity model
 doi:10.5194/piahs-368-215-2015 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). 215 Simulation of soil
doi:10.5194/piahs-368-215-2015 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). 215 Simulation of soil
href=" 1d3227ea7bfd4d1085ec1738dce6dd611d">Pr esentation<
 SMALL GRAINS SEEDBED PREPARATION AND RESIDUE Pr
SMALL GRAINS SEEDBED PREPARATION AND RESIDUE Pr
Special Seminar on Food Security: Focusing on Water management and Sustainable Agriculture
 Special Seminar on Food Security: Focusing on Water management and Sustainable Agriculture Kyi Myint Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation Location Latitude 9 58-28 31 N Longitude 92 9-100 10 E Country
Special Seminar on Food Security: Focusing on Water management and Sustainable Agriculture Kyi Myint Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation Location Latitude 9 58-28 31 N Longitude 92 9-100 10 E Country
ARKANSAS WHEAT Jason Kelley - Wheat and Feed Grains Extension Agronomist September 13, 2017
 2017 Wheat Crop Summary and Outlook for 2018 The 2017 Arkansas wheat crop was small in acreage but many producers reported exceptional yields with intensive management. Acreage was at or near record lows
2017 Wheat Crop Summary and Outlook for 2018 The 2017 Arkansas wheat crop was small in acreage but many producers reported exceptional yields with intensive management. Acreage was at or near record lows
Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria
 Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria 131 132 Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria A. Bader, N.
Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria 131 132 Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria A. Bader, N.
FERTILIZER RECOMMENDATIONS for the Gulf Coast Prairie
 L-224 1958 FERTILIZER RECOMMENDATIONS for the Gulf Coast Prairie SOIL AREAS: A East Texas Timber Country B Gulf Coast Prairie C Blackland Prairie o Grand PraIrie E West Cross Timbers f Central Basin G
L-224 1958 FERTILIZER RECOMMENDATIONS for the Gulf Coast Prairie SOIL AREAS: A East Texas Timber Country B Gulf Coast Prairie C Blackland Prairie o Grand PraIrie E West Cross Timbers f Central Basin G
Influences of Agricultural Irrigation on Regional Salinity Balance in Arid Areas of Northwestern China
 Research article erd Influences of Agricultural Irrigation on Regional Salinity Balance in Arid Areas of Northwestern China ABDISALAM JALALDIN* College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, Xinjiang
Research article erd Influences of Agricultural Irrigation on Regional Salinity Balance in Arid Areas of Northwestern China ABDISALAM JALALDIN* College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, Xinjiang
Correlation analysis on water resources utilization and the sustainable development of economy in Minqin of Gansu Province
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(4):157-161 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Correlation analysis on water utilization and the
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(4):157-161 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Correlation analysis on water utilization and the
Developing Quick Guides for fertilizing hybrid maize in large areas
 Developing Quick Guides for fertilizing hybrid maize in large areas This document provides you with An overview of a Quick Guide The information required to develop a Quick Guide The steps involved in
Developing Quick Guides for fertilizing hybrid maize in large areas This document provides you with An overview of a Quick Guide The information required to develop a Quick Guide The steps involved in
The Route of Informationization to Promote Agricultural Modernization of Yunnan Province of China
 China-USA Business Review, January 2016, Vol. 15, No. 1, 50-54 doi: 10.17265/1537-1514/2016.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING The Route of Informationization to Promote Agricultural Modernization of Yunnan Province
China-USA Business Review, January 2016, Vol. 15, No. 1, 50-54 doi: 10.17265/1537-1514/2016.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING The Route of Informationization to Promote Agricultural Modernization of Yunnan Province
Comprehensive Evaluation of Regional Agricultural Water and Land Resources Carrying Capacity Based on DPSIR Concept Framework and PP Model
 Comprehensive Evaluation of Regional Agricultural Water and Land Resources Carrying Capacity Based on DPSIR Concept Framework and PP Model Qiang Fu, Qiuxiang Jiang, Zilong Wang College of Water Conservancy
Comprehensive Evaluation of Regional Agricultural Water and Land Resources Carrying Capacity Based on DPSIR Concept Framework and PP Model Qiang Fu, Qiuxiang Jiang, Zilong Wang College of Water Conservancy
VI SUMMARY. and maize-sunflower sequential cropping systems
 Summary VI SUMMARY Agronomic investigation on System based nutrient management for maize and groundnut cropping sequences was carried out on sandy loam soils at farmer s field, Nulugummanahalli, Gauribidnur
Summary VI SUMMARY Agronomic investigation on System based nutrient management for maize and groundnut cropping sequences was carried out on sandy loam soils at farmer s field, Nulugummanahalli, Gauribidnur
Cropland Mapping and area estimation method in CropWatch. Nana Yan, Miao Zhang, Bingfang Wu, Bo Chen RADI, CAS June, 2015
 Cropland Mapping and area estimation method in CropWatch Nana Yan, Miao Zhang, Bingfang Wu, Bo Chen RADI, CAS June, 2015 Outline Background Methodology in CropWatch Recent updates of crop classification
Cropland Mapping and area estimation method in CropWatch Nana Yan, Miao Zhang, Bingfang Wu, Bo Chen RADI, CAS June, 2015 Outline Background Methodology in CropWatch Recent updates of crop classification
Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.
 Cropping 101 Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.edu This overview provides summaries of 1. Key
Cropping 101 Prepared by Mark Bell, Amanda Crump, Nick Madden and Maria Paz Santibanez 2012 For more information visit: International Programs ip.ucdavis.edu This overview provides summaries of 1. Key
Study on Development Status and Countermeasures of Cold Chain Logistics in Blue and Yellow Economic Zone. Changgang Xiao
 3rd International Conference on Science and Social Research (ICSSR 2014) Study on Development Status and Countermeasures of Cold Chain Logistics in Blue and Yellow Economic Zone Changgang Xiao Shandong
3rd International Conference on Science and Social Research (ICSSR 2014) Study on Development Status and Countermeasures of Cold Chain Logistics in Blue and Yellow Economic Zone Changgang Xiao Shandong
The Governmental Environmental Investment Project Performance Audit Index System Research Jinyu Tian1, a and Ziyuan Zhang2, b
 International Conference on Education, E-learning and Management Technology (EEMT 2016) The Governmental Environmental Investment Project Performance Audit Index System Research Jinyu Tian1, a and Ziyuan
International Conference on Education, E-learning and Management Technology (EEMT 2016) The Governmental Environmental Investment Project Performance Audit Index System Research Jinyu Tian1, a and Ziyuan
Optimization of Water Allocation in Canal Systems of Chengai Irrigation Area
 Optimization of Water Allocation in Canal Systems of Chengai Irrigation Area Zhiliang Wang, Zhenmin Zhou (North China College of WRHP, Zhengzhou, Henan 450045, China) Abstract: Chengai Yellow River Irrigation
Optimization of Water Allocation in Canal Systems of Chengai Irrigation Area Zhiliang Wang, Zhenmin Zhou (North China College of WRHP, Zhengzhou, Henan 450045, China) Abstract: Chengai Yellow River Irrigation
Chapter 4. China. 4.1 Overview
 70 Chapter 4. China Chapter 4 presents a detailed CropWatch analysis for China, focusing on the seven most productive agroecological regions of the east and south. After a brief overview including a production
70 Chapter 4. China Chapter 4 presents a detailed CropWatch analysis for China, focusing on the seven most productive agroecological regions of the east and south. After a brief overview including a production
Effects of Zinc on variety performance in terms of Yield and Yield Attributing Characters of Rice at Karma R & D Center, Jyotinagar
 A RESEARCH REPORT ON: Effects of Zinc on variety performance in terms of Yield and Yield Attributing Characters of Rice at Karma R & D Center, Jyotinagar Principal Researcher Mr. Amit Raj Adhikari R &
A RESEARCH REPORT ON: Effects of Zinc on variety performance in terms of Yield and Yield Attributing Characters of Rice at Karma R & D Center, Jyotinagar Principal Researcher Mr. Amit Raj Adhikari R &
Kamskiy. Presentation
 Kamskiy sapropel LLC Presentation Sapropel a unique gift of nature Main fields of sapropel application Eco-friendly fertilizers for any crops and soils Feeding additives for farm animals and birds Sorbent
Kamskiy sapropel LLC Presentation Sapropel a unique gift of nature Main fields of sapropel application Eco-friendly fertilizers for any crops and soils Feeding additives for farm animals and birds Sorbent
Analysis on Composition and Pattern of Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution in Liaohe River Basin, China
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 8 (2011) 26 33 ICESB 2011: 25-26 November 2011, Maldives Analysis on Composition and Pattern of Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 8 (2011) 26 33 ICESB 2011: 25-26 November 2011, Maldives Analysis on Composition and Pattern of Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution
SinoTropia The background data analysis of Yuqiao reservoir
 SinoTropia The background data analysis of Yuqiao reservoir Ph.D. candidate: Zhou Bin The background data analysis The future monitoring plan The background data analysis Soil background data analysis
SinoTropia The background data analysis of Yuqiao reservoir Ph.D. candidate: Zhou Bin The background data analysis The future monitoring plan The background data analysis Soil background data analysis
Comparison of water drainage and nitrate leaching under three land use types in the North China Plain
 1 Comparison of water drainage and nitrate leaching under three land use types in the North China Plain 2016 SWAT Conference Reporter: Sun Chengchun Co-worker: Chen Shufeng; Wu Wenliang Email: sunspringer@gmail.com
1 Comparison of water drainage and nitrate leaching under three land use types in the North China Plain 2016 SWAT Conference Reporter: Sun Chengchun Co-worker: Chen Shufeng; Wu Wenliang Email: sunspringer@gmail.com
Long-Term Fertilization Effects on Crop Yield and Nitrate-N Accumulation in Soil in Northwestern China
 Long-Term Fertilization Effects on Crop Yield and Nitrate-N Accumulation in Soil in rthwestern China Shengmao Yang 1, Fengmin Li 2, Ping Wang 3 Sukhdev S. Malhi 4 and Shuying Liu 5 1 State Key Laboratory
Long-Term Fertilization Effects on Crop Yield and Nitrate-N Accumulation in Soil in rthwestern China Shengmao Yang 1, Fengmin Li 2, Ping Wang 3 Sukhdev S. Malhi 4 and Shuying Liu 5 1 State Key Laboratory
15. Soil Salinity SUMMARY THE ISSUE
 15. Soil Salinity AUTHORS: B.H. Wiebe, R.G. Eilers, W.D. Eilers and J.A. Brierley INDICATOR NAME: Risk of Soil Salinization STATUS: Provincial coverage (AB, SK, MB), 1981 to 2001 SUMMARY At very low levels,
15. Soil Salinity AUTHORS: B.H. Wiebe, R.G. Eilers, W.D. Eilers and J.A. Brierley INDICATOR NAME: Risk of Soil Salinization STATUS: Provincial coverage (AB, SK, MB), 1981 to 2001 SUMMARY At very low levels,
Effect of EM Bokashi application on control of secondary soil salinization
 Water Science and Engineering, Dec. 2008, Vol. 1, No. 4, 99-106 ISSN 1674-2370, http://kkb.hhu.edu.cn, e-mail: wse@hhu.edu.cn Effect of EM Bokashi application on control of secondary soil salinization
Water Science and Engineering, Dec. 2008, Vol. 1, No. 4, 99-106 ISSN 1674-2370, http://kkb.hhu.edu.cn, e-mail: wse@hhu.edu.cn Effect of EM Bokashi application on control of secondary soil salinization
Aquifer water abundance evaluation using a fuzzy- comprehensive weighting method
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS water abundance evaluation using a fuzzy- comprehensive weighting method To cite this article: Z Wei 016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS water abundance evaluation using a fuzzy- comprehensive weighting method To cite this article: Z Wei 016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
Chapter 7.2. AFFIRM and Alberta MMP Software. learning objectives
 AFFIRM and Alberta MMP Software learning objectives Identify information required to use the Alberta Farm Fertilizer Information and Recommendation Manager (AFFIRM). Identify information required to use
AFFIRM and Alberta MMP Software learning objectives Identify information required to use the Alberta Farm Fertilizer Information and Recommendation Manager (AFFIRM). Identify information required to use
APPENDIX E. LESA Models
 APPENDIX E LESA Models LESA ASSESSMENT CALEXICO SOLAR FARM I PHASE A PROJECT AREA CALEXICO SOLAR FARM I PHASE A PROJECT (SW/4 Section 13, S/2 Section 14, S/2 NE/4 Section 15, NW/4 Section 15, T17S, R13E,
APPENDIX E LESA Models LESA ASSESSMENT CALEXICO SOLAR FARM I PHASE A PROJECT AREA CALEXICO SOLAR FARM I PHASE A PROJECT (SW/4 Section 13, S/2 Section 14, S/2 NE/4 Section 15, NW/4 Section 15, T17S, R13E,
Measurements for Forest Ecological Benefit in China
 Marsland Press World Rural Observations 2009;1(2):25-30 Measurements for Forest Ecological Benefit in China 1 Ming Liang, 2 Changsheng Li 1. Institute of Natural Resource & Ecology of Heilongjiang Provincial
Marsland Press World Rural Observations 2009;1(2):25-30 Measurements for Forest Ecological Benefit in China 1 Ming Liang, 2 Changsheng Li 1. Institute of Natural Resource & Ecology of Heilongjiang Provincial
Application of Maize Precision Fertilizer Expert System in the Maize Production Yao Yuxia, Zhang Yun
 4th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Computing Technology (ICMMCT 2016) Application of Maize Precision Fertilizer Expert System in the Maize Production Yao Yuxia, Zhang Yun The Information
4th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Computing Technology (ICMMCT 2016) Application of Maize Precision Fertilizer Expert System in the Maize Production Yao Yuxia, Zhang Yun The Information
Research and Development on Wheat No-Tillage Seeders in Annual Double Cropping System in Central China
 Research and Development on Wheat No-Tillage Seeders in Annual Double Cropping System in Central China Li Hongwen, Gao Huanwen, Yao Zonglu, Li Wenying, Zhang Xuemin, He Jin, and Ma Hongliang 1 ABSTRACT
Research and Development on Wheat No-Tillage Seeders in Annual Double Cropping System in Central China Li Hongwen, Gao Huanwen, Yao Zonglu, Li Wenying, Zhang Xuemin, He Jin, and Ma Hongliang 1 ABSTRACT
LESA ASSESSMENT MOUNT SIGNAL SOLAR FARM I PROJECT AREA
 LESA ASSESSMENT MOUNT SIGNAL SOLAR FARM I PROJECT AREA MOUNT SIGNAL SOLAR FARM I PROJECT (SW/4 Section 16, S/2 Section 15, NE/4 Section 14 (portion), N/2 Section 13 (portion) and SE/4 Section 13, T17S,
LESA ASSESSMENT MOUNT SIGNAL SOLAR FARM I PROJECT AREA MOUNT SIGNAL SOLAR FARM I PROJECT (SW/4 Section 16, S/2 Section 15, NE/4 Section 14 (portion), N/2 Section 13 (portion) and SE/4 Section 13, T17S,
5.5 Improving Water Use Efficiency of Irrigated Crops in the North China Plain Measurements and Modelling
 183 5.5 Improving Water Use Efficiency of Irrigated Crops in the North China Plain Measurements and Modelling H.X. Wang, L. Zhang, W.R. Dawes, C.M. Liu Abstract High crop productivity in the North China
183 5.5 Improving Water Use Efficiency of Irrigated Crops in the North China Plain Measurements and Modelling H.X. Wang, L. Zhang, W.R. Dawes, C.M. Liu Abstract High crop productivity in the North China
