Some years ago, farming, mainly in the form of wheat production, comprised:
|
|
|
- Caroline Lee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE CONSERVATION FARMING SYSTEM J.E. Pratley Director, Centre for Conservation Farming, Charles Sturt University. Wagga Wagga. NSW 2678 Introduction Some years ago, farming, mainly in the form of wheat production, comprised: - several passes with cultivation implements prior to sowing; - pre-emergent weed control involving herbicide incorporation; - fertiliser inputs at suboptimal levels; - acceptance of whatever yields were obtained. Surveys at the time (e.g. A Basis for Soil Conservation Policy in Australia, AGPS 1978) showed that soils were in a state of structural decline. Table 1 shows the extent of degradation in NSW in that study. Table 1. Extent of soil degradation in the cropping zone of NSW in 1976 % of area Management changes needed 49 Treatment with works 44 Total needing treatment 93 Further, farmers were experiencing problems with soil crusting, erosion was rife and waterlogging was common. Acidification was apparent and dryland salting was about to impact. The capacity of our soils to absorb this abuse had been reached and change was inevitable if future productivity was to be preserved. Out of these circumstances emerged the system of conservation farming.
2 Development Of A New Farming System The development of this new system was facilitated by the availability of the 'knockdown' herbicides Spray.Seed and Roundup and the post-emergent herbicide, Hoegrass, for annual ryegrass and wild oats control. The success of adoption of conservation farming has been variable but, in general, farmers have adapted the philosophy to develop a system that suits their soils, machinery and management. It is worth reflecting that in the 1970s, some farmers cultivated their soils times per crop, most farmers cultivating at least four times. This represented a considerable waste of manhours, fuel, machinery wearout and unnecessary soil destruction. In 1992 we can acknowledge the considerable progress made. Farmers cultivate 1-3 times, if at all, the outcome being much improved soil structure particularly on the surface. As a consequence soil structure has improved and there is a greater number and diversity of soil organisms. There is now greater harvesting of water through infiltration, thus less runoff and less surface soil erosion - a very positive result, at least in theory. Life, however, can never be that simple. The improvement in water infiltration provides a reservoir for use by crops and pastures. It is now well recognised that yield is directly related to crop water use. However, in circumstances where the water is not used, it contributes eventually to a rise in the watertable, subsequently to be expressed by dryland salting downslope in the catchment. Fortunately, technology allows us to monitor groundwater levels relatively easily through electro-magnetic survey techniques so that early warning signals can be given (Figure 1). Figure 1. Electro-magnetic survey of Charles Sturt University farm. The percolation through the soil provides the opportunity for leaching, creating a more acid soil and adding nutrients to the groundwater. Thus the problems of soil acidification and of eutrophication causing algal bloom result significantly from poor soil water use. The lesson from this experience, therefore, is that simple low output agriculture is not environmentally sustainable, particularly from a catchment perspective. Because of the inherently low fertility status of most Australian soils, it follows that simple low input systems also cannot be sustainable. Such systems, in any case, even on the most fertile soils, are mining operations. For example, crop production on the very fertile black earth soils of the Liverpool Plains occurred for decades without fertiliser inputs but now rely heavily on fertiliser contributions. Even rice production in the MIA now requires phosphate inputs, having previously done without. Low input systems can be financially rewarding provided product prices are high enough but the resource base deteriorates over time. It follows from the previous arguments therefore, that high productivity is sustainable and highly desirable. Clearly however, it requires high inputs under Australian conditions.
3 Potential Yield - A Performance Indicator How, then, does a farmer know what system he operates? What benchmarks can be used to measure the performance of a farmer or a paddock? The 1990s is the era of performance indicators and farming should be no different. Given that water is the factor over which we have least control, we can expect that water availability will be the ultimate limiting factor to yield attainment. Through the efforts of French (1987) in South Australia and Cornish and Murray (1989) in Wagga Wagga, we now have a benchmark - water limited potential yield. Experience has since shown the concept to be reasonable and attainable by farmers. Thus in a year of 5 t/ha potential yield, a farmer attaining 4.5 t/ha can be well satisfied, whereas another achieving only 3.5 t/ha (considered by many to be a good yield) should undertake a critical analysis of performance. In a less favourable year with a potential yield of 2.5 t/ha, a 2.3 t/ha crop is a top performer. It has long been known that farmers are likely to attain near potential yields in seasons of poor rainfall, whereas in good seasons actual yields vary markedly from the potential (Figure 2). Figure 2. A survey of farm yields under different potential yield conditions (Cornish and Murray, 1989) experimental yields district yields for Wagga Wagga Thus the opportunity to make profits from good seasons is not taken, or at least not maximised. Further, the unused water resource in these seasons contributes to the watertable problem previously discussed. Raising productivity uses this water and therefore improves the prospect of sustainability. Agricultural Chemicals Dependance (a) Fertilisers In order that productivity be maximised, inputs of agricultural chemicals are necessary. In particular fertiliser phosphate additions are essential to balance the removal of phosphorus in farm product. The phosphorus cycle is of great ecological significance due to the scarcity of the element and due to it being exported from the site of use to the site of consumption and subsequently disposed of through sewers into river systems and oceans. The cycle is thus broken and the process is unidirectional creating long-term concerns. Nitrogen fertilisers are also regularly used, often for raising quality of product through increased protein levels. Much nitrogen availability for plants is achieved through the process of nitrogen fixation of legumes, a natural process, and improved methods of managing this form of nitrogen are needed. (b) Herbicides The development of conservation farming has also increased the dependance by farmers on herbicides, an area where the philosophies of the conservation farmers and the organics diverge. It must be said in the defence of herbicides that their availability has allowed us to successfully address the issues of soil structure decline and improved productivity. It must also be said that most herbicides are relatively safe if used as directed. New chemicals have shorter residual life and are much safer to use. The group of sulfonyl
4 ureas, for example, target an enzyme in plants which is not present in mammalian metabolic systems. This is not to say that caution is not needed in their use. Training of users also becomes an imperative. As well as their effectiveness, herbicides have become increasingly important because their cost has remained more than competitive with alternate practices. They are easy to use and farmers have become more familiar and experienced with the technology. Their ready acceptance has brought its own problems, the development of herbicide resistance being of greatest concern. In any population there will be individuals who react differently to the rest. Thus an effective herbicide will remove the susceptible weeds and allow the resistant subpopulation to dominate. Subsequent applications of the same or related herbicide will be increasingly ineffective. Farmers need to be aware of this issue and implement strategies, particularly herbicide rotation, to reduce its buildup. Regular testing for resistance of weeds that escape control should be done to reduce unnecessary use of chemicals which do not work. Such a process is environmentally and economically sensible. (c) Reduced Chemical Inputs It is fair to say that most farmers would like to reduce their inputs of farm chemicals, both on cost and environmental grounds. The reality is, however, that farmers will be dependant on their use into the foreseeable future. Prospects for reducing their use are strong. Technology will soon be available through remote sensing technology such as aerial video to map the weed distribution in paddocks and only spray the infested areas. Already similar technology exists for fallow weed control. Known as the WASP, the machine uses red and infra-red reflectance to discriminate green vegetation from soil or litter such that individual nozzles release herbicide only where green material is detected (Felton et al. 1987). (d) Integrated Pest Management Numerous actions by farmers can reduce the need for chemical inputs. Factors such as disease resistant cultivars, early sowing, weed management in the pasture phase and crop rotations all play a part in the process. These factors are addressed elsewhere in the conference. (e) Natural chemicals A new term for farmers is allelopathy, the chemical control of one plant on another. Natural allelochemicals exist in both growing plants and in dry residues of the plants and are commonly effectively used by weed species. In silvergrass, for example, such chemicals in the dried residues inhibit the germination and establishment of crop and pasture species (Pratley, 1989; Pratley and Ingrey, 1990). Some crop and pasture plants and their stubbles also have allelopathic capacity. Canola is noted for its ability to produce a clean seedbed for a succeeding crop. Cereal stubbles, where retained, have interfered with establishment of crops being sown into them. Litter of phalaris is known to inhibit the germination of subterranean clover. The phenomenon of allelopathy currently acts negatively by inhibiting production. Greater knowledge of how it operates and which compounds are involved may allow farmers of the future to effectively counteract the inhibition of productive plants or to use the process positively to limit dependance on chemical inputs. So-called 'natural' herbicides may be an outcome of the research. However, will these allelochemicals be any safer than those used now?
5 What Is The Best Farming System? In ecological systems there are no simple answers. Simple solutions are always unstable solutions. Consequently, there is no one best farming system. Such systems evolve as our knowledge base increases, and as technology develops. Attitudes also change and farmers are now more environmentally conscious than ever before, in line with community expectations. However, all of us have to operate within the constraints imposed on us at the time - be they economic, regulatory, or knowledge. But, evolving farming systems must be intensively monitored to measure performance and to make adjustments where undesirable trends are identified. Objective Measures Decision making on the farm must be made as objective a possible. Good record keeping of both financial and physical data will enable an analysis of "what went right/wrong". It will also provide the basis for more accurate forward planning. Many objective tests already are available or will be in the near future. Farmers will test for or have tested: - root zone soil moisture through the season; get regular soil tests for fertility and ph. Plant tissue testing may substitute in some cases; - groundwater over time to monitor watertables; - herbicide resistance; - soil structural stability; and may make regular use of remote sensing technology such as aerial video mapping. Crop and pasture monitoring will be routine. It is important to note that the top performers are those who get all the factors of production right. This has been shown regularly in farm monitoring groups and is shown in Figure 3. Figure 3. The relationship between yield, profitability and the adoption of key factors by farmers in a crop monitoring group at Finley, NSW (J. Lacy, personal communication) Getting it right becomes easier because priorities become clearer due to the sound platform of information. Conclusion Conservation farming has come a long way in a short time. It embraces many of the aspects of the organics and is empathetic with much of the philosophy. It clearly differs in its approach
6 to pesticides and fertilisers which remain an integral part of the system as it endeavours to obtain profitable yields of good quality produce. References 1. Cornish, P.S. and Murray, G.M. (1989). Low rainfall rarely limits wheat yields in southern New South Wales. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 29: Felton, W.L., McCloy, K.R., Doss, A.F. and Burger, A.E. (1987). Evaluation of a weed detector. Proceedings 8th Australian Weeds Conference, Sydney, French, R.J. (1987). Future productivity on our farmlands. Proceedings 4th Australian Agronomy Conference, Melbourne, Pratley, J.E. (1989). Silvergrass residue effects on wheat. Proceedings 5th Australian Agronomy Conference, Perth, Pratley, J.E. and Ingrey, J.D. (1990). Silvergrass allelopathy on crop and pasture species. Proceedings 9th Australian Weeds Conference, Adelaide.
ORGANIC AND CONSERVATION FARMING - BRIDGING THE GAP - TO THE FUTURE. NSW Agriculture, Horticultural Research and Advisory Station. Gosford.
 ORGANIC AND CONSERVATION FARMING - BRIDGING THE GAP - TO THE FUTURE P.S. Cornish NSW Agriculture, Horticultural Research and Advisory Station. Gosford. NSW 2250 I well remember my first, and last, attempt
ORGANIC AND CONSERVATION FARMING - BRIDGING THE GAP - TO THE FUTURE P.S. Cornish NSW Agriculture, Horticultural Research and Advisory Station. Gosford. NSW 2250 I well remember my first, and last, attempt
Perennial Cover Cropping Colin Seis
 Perennial Cover Cropping Colin Seis 2015 Annual SANTFA conference Winona Myself and son Nick Granite soil, Ph 5.5-6.0 2000 acres (840 Ha) 650 mm annual Rainfall 300 km NW of Sydney Central Tablelands NSW
Perennial Cover Cropping Colin Seis 2015 Annual SANTFA conference Winona Myself and son Nick Granite soil, Ph 5.5-6.0 2000 acres (840 Ha) 650 mm annual Rainfall 300 km NW of Sydney Central Tablelands NSW
Integrating pastures into farming systems soil health and the benefits to crops
 Tropical Grasslands (2009) Volume 43, 212 216 212 Integrating pastures into farming systems soil health and the benefits to crops DAVID LAWRENCE 1, MIKE BELL 2, BRIAN JOHNSON 1 and DAVID LLOYD 1 1 Queensland
Tropical Grasslands (2009) Volume 43, 212 216 212 Integrating pastures into farming systems soil health and the benefits to crops DAVID LAWRENCE 1, MIKE BELL 2, BRIAN JOHNSON 1 and DAVID LLOYD 1 1 Queensland
B.1.5 Sodic and acidic soils
 B.1.5 Sodic and acidic soils Alice Thompson * Sodicity The effects of soil salinity have been well publicised, with dramatic images of bare and badly gullied land glistening with salt crystals, and of
B.1.5 Sodic and acidic soils Alice Thompson * Sodicity The effects of soil salinity have been well publicised, with dramatic images of bare and badly gullied land glistening with salt crystals, and of
Effective Integration of Livestock & Cropping. Simon Vogt Rural Directions Pty Ltd
 Effective Integration of Livestock & Cropping Simon Vogt Rural Directions Pty Ltd Background MLA Profitable Integration of Cropping and Livestock project Currently collecting and analysing 100 x multi-year
Effective Integration of Livestock & Cropping Simon Vogt Rural Directions Pty Ltd Background MLA Profitable Integration of Cropping and Livestock project Currently collecting and analysing 100 x multi-year
KEYWORD Stubble retention, canola, hypocotyl, direct drilling, seedling
 WHEAT STUBBLE AND CANOLA GROWTH- IDENTIFYING AND OVERCOMING LIMITATIONS S. Bruce 1,2, M.H. Ryan 1, J.Kirkegaard 1 and J.Pratley 2. 1. CSIRO Plant Industry, GPO Box 16, Canberra, ACT. 2. Charles Sturt University,
WHEAT STUBBLE AND CANOLA GROWTH- IDENTIFYING AND OVERCOMING LIMITATIONS S. Bruce 1,2, M.H. Ryan 1, J.Kirkegaard 1 and J.Pratley 2. 1. CSIRO Plant Industry, GPO Box 16, Canberra, ACT. 2. Charles Sturt University,
Profitable regenerative Agriculture. Colin Seis
 Profitable regenerative Agriculture Colin Seis Winona Myself and son Nick 2000 acres (840 Ha) Granite soil, Ph 4.5-5.0, 650 ml av. Rainfall Central Tablelands NSW 4000 Merino sheep 500 acres of pasture
Profitable regenerative Agriculture Colin Seis Winona Myself and son Nick 2000 acres (840 Ha) Granite soil, Ph 4.5-5.0, 650 ml av. Rainfall Central Tablelands NSW 4000 Merino sheep 500 acres of pasture
Economics of Increasing Wheat Competitiveness as a Weed Control Weapon
 Economics of Increasing Wheat Competitiveness as a Weed Control Weapon John P. Brennan A, Deirdre Lemerle AB and Peter Martin A A Senior Research Scientist (Economics), Principal Research Scientist (Weeds)
Economics of Increasing Wheat Competitiveness as a Weed Control Weapon John P. Brennan A, Deirdre Lemerle AB and Peter Martin A A Senior Research Scientist (Economics), Principal Research Scientist (Weeds)
An overview of the benefits delivered by research and new technology to farmers in South-Eastern-Australia
 An overview of the benefits delivered by research and new technology to farmers in South-Eastern-Australia I.M. MacKinnon Chairman, Grains Research and Development Corporation, Southern Regional Panel.
An overview of the benefits delivered by research and new technology to farmers in South-Eastern-Australia I.M. MacKinnon Chairman, Grains Research and Development Corporation, Southern Regional Panel.
Re-evaluating cover crops in semi-arid cropping in Australia
 Re-evaluating cover crops in semi-arid cropping in Australia John Kirkegaard, James Hunt, Jeremy Whish, Mark Peoples, Tony Swan SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE FLAGSHIP 1 Introduction and talk outline Background
Re-evaluating cover crops in semi-arid cropping in Australia John Kirkegaard, James Hunt, Jeremy Whish, Mark Peoples, Tony Swan SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE FLAGSHIP 1 Introduction and talk outline Background
Long Term tillage and. Merriwagga FARMERS ADVANCING RESEARCH
 Long Term tillage and rotation trial Merriwagga 1999-2014 FARMERS ADVANCING RESEARCH LONG TERM TILLAGE & ROTATION TRIAL key points * treatments have been higher yielding and more profitable in continuous
Long Term tillage and rotation trial Merriwagga 1999-2014 FARMERS ADVANCING RESEARCH LONG TERM TILLAGE & ROTATION TRIAL key points * treatments have been higher yielding and more profitable in continuous
Dealing with sown pasture run-down
 Department of Agriculture and Fisheries Fact sheet 2 Dealing with sown pasture run-down When a paddock is first developed and a new pasture is sown, the amount of plant-available nitrogen (N) in the soil
Department of Agriculture and Fisheries Fact sheet 2 Dealing with sown pasture run-down When a paddock is first developed and a new pasture is sown, the amount of plant-available nitrogen (N) in the soil
Dealing with sown pasture run-down
 Department of Agriculture and Fisheries Fact sheet 2 Dealing with sown pasture run-down When a paddock is first developed and a new pasture is sown, the amount of plant-available nitrogen (N) in the soil
Department of Agriculture and Fisheries Fact sheet 2 Dealing with sown pasture run-down When a paddock is first developed and a new pasture is sown, the amount of plant-available nitrogen (N) in the soil
Cadiz French serradella : a new pasture variety for deep acid soils
 Cadiz French serradella : a new pasture variety for deep acid soils Farmnote 12/97 By Bradley Nutt and Janet Paterson, Centre for Legumes in Mediterranean Agriculture (CLIMA) and staff of the Pasture Improvement
Cadiz French serradella : a new pasture variety for deep acid soils Farmnote 12/97 By Bradley Nutt and Janet Paterson, Centre for Legumes in Mediterranean Agriculture (CLIMA) and staff of the Pasture Improvement
Improving the performance of canola
 The challenge - Keeping canola in the rotation Description Authors Collaborators Research Update - Southern Region (High Rainfall) - July 2004 John Kirkegaard, Susie Sprague CSIRO Plant Industry, Canberra
The challenge - Keeping canola in the rotation Description Authors Collaborators Research Update - Southern Region (High Rainfall) - July 2004 John Kirkegaard, Susie Sprague CSIRO Plant Industry, Canberra
ENVIRONMENTAL POSITIONING STATEMENT
 ENVIRONMENTAL POSITIONING STATEMENT CSBP s commitment to sustainable agriculture. June 2018 CSBP STRATEGIES Introduction At CSBP, we are more than just a fertiliser supplier. From field research to the
ENVIRONMENTAL POSITIONING STATEMENT CSBP s commitment to sustainable agriculture. June 2018 CSBP STRATEGIES Introduction At CSBP, we are more than just a fertiliser supplier. From field research to the
WHY GROW MEDIC? Training Kit No. 1
 Training Kit No. 1 WHY GROW MEDIC? Script: Brian and Lynne Chatterton. Photos: Florita Botts. Additional Photos: Brian Chatterton. Production: Florita Botts. THE FAILURE OF THE CEREAL - FALLOW ROTATION
Training Kit No. 1 WHY GROW MEDIC? Script: Brian and Lynne Chatterton. Photos: Florita Botts. Additional Photos: Brian Chatterton. Production: Florita Botts. THE FAILURE OF THE CEREAL - FALLOW ROTATION
Maintaining profitability in retained stubble systems on upper Eyre Peninsula
 Maintaining profitability in retained stubble systems on upper Eyre Peninsula A joint EPARF and GRDC funded project. Guideline 12: Economic and risk analysis of break crops compared to continuous wheat
Maintaining profitability in retained stubble systems on upper Eyre Peninsula A joint EPARF and GRDC funded project. Guideline 12: Economic and risk analysis of break crops compared to continuous wheat
Understanding Lucerne
 Farming System Understanding Lucerne How to increase the value of the feed produced Break through developments in grazing tolerance How to choose a lucerne Pest and disease ratings Best management practices
Farming System Understanding Lucerne How to increase the value of the feed produced Break through developments in grazing tolerance How to choose a lucerne Pest and disease ratings Best management practices
LONG TERM TILLAGE AND ROTATION TRIAL. Merriwagga INDEPENDENT AGRONOMY ADVICE + CUTTING EDGE RESEARCH
 LONG TERM TILLAGE AND ROTATION TRIAL Merriwagga 1999-2015 INDEPENDENT AGRONOMY ADVICE + CUTTING EDGE RESEARCH LONG TERM TILLAGE & ROTATION TRIAL 2015 Results KEY POINTS treatments, for all rotations, were
LONG TERM TILLAGE AND ROTATION TRIAL Merriwagga 1999-2015 INDEPENDENT AGRONOMY ADVICE + CUTTING EDGE RESEARCH LONG TERM TILLAGE & ROTATION TRIAL 2015 Results KEY POINTS treatments, for all rotations, were
Sorghum, innovative, management, practices, reliability, Central Queensland.
 Innovative Management of Grain Sorghum in Central Queensland. G.B. Spackman 1, K.J. McCosker 2, A.J. Farquharson 3 and M.J. Conway 4 1. Agricultural consultant, Graham Spackman & Associates, Emerald, Queensland.
Innovative Management of Grain Sorghum in Central Queensland. G.B. Spackman 1, K.J. McCosker 2, A.J. Farquharson 3 and M.J. Conway 4 1. Agricultural consultant, Graham Spackman & Associates, Emerald, Queensland.
Presentation by Mark Branson 2004 Nuffield Scholar. Using Precision and Conservation Agriculture to Improve Farm Profits and the Environment.
 Presentation by Mark Branson 2004 Nuffield Scholar Using Precision and Conservation Agriculture to Improve Farm Profits and the Environment. Sponsored By: My Family Farm Area: 1000 ha Lower North of South
Presentation by Mark Branson 2004 Nuffield Scholar Using Precision and Conservation Agriculture to Improve Farm Profits and the Environment. Sponsored By: My Family Farm Area: 1000 ha Lower North of South
A Case Study to Reduce Dryland Salinity on a Temora Farm. M.H. McCallum 1, J.S. Salmon 2 and J.F. Angus 1 ABSTRACT
 A Case Study to Reduce Dryland Salinity on a Temora Farm M.H. McCallum 1, J.S. Salmon 2 and J.F. Angus 1 1 CSIRO Plant Industry, Canberra, ACT. 2 NSW Department of Land and Water Conservation, Temora,
A Case Study to Reduce Dryland Salinity on a Temora Farm M.H. McCallum 1, J.S. Salmon 2 and J.F. Angus 1 1 CSIRO Plant Industry, Canberra, ACT. 2 NSW Department of Land and Water Conservation, Temora,
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION AGRICULTURE. 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) SECTION I (20 Marks)
 STUDENT NUMBER CENTRE NUMBER N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 1996 AGRICULTURE 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) SECTION I (20 Marks) Total time allowed for Sections I, II, III, and IV Three
STUDENT NUMBER CENTRE NUMBER N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 1996 AGRICULTURE 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) SECTION I (20 Marks) Total time allowed for Sections I, II, III, and IV Three
Origin Winter Active Tall Fescue
 Origin Winter Active Tall Fescue Festuca arundinacea Derived from North African germplasm, Origin exhibits excellent persistence and production in summer-dry regions of Australia, and can be used as an
Origin Winter Active Tall Fescue Festuca arundinacea Derived from North African germplasm, Origin exhibits excellent persistence and production in summer-dry regions of Australia, and can be used as an
PAGE 1 SOUTHERN AND WESTERN REGION
 PAGE 1 water use efficiency fact sheet SOUTHERN AND WESTERN REGION 2009 Converting rainfall to grain Growers can improve crop water use efficiency by using strategies to increase stored soil moisture prior
PAGE 1 water use efficiency fact sheet SOUTHERN AND WESTERN REGION 2009 Converting rainfall to grain Growers can improve crop water use efficiency by using strategies to increase stored soil moisture prior
ROW SPACING fact sheet
 CROP PLACEMENT AND ROW SPACING fact sheet January 2011 southern region A systems approach to row spacing The depth of seed placement and the distance from the adjacent row both influence crop performance.
CROP PLACEMENT AND ROW SPACING fact sheet January 2011 southern region A systems approach to row spacing The depth of seed placement and the distance from the adjacent row both influence crop performance.
4 Sustainability in Dryland Farming Systems
 4 Sustainability in Dryland Farming Systems Elias Fereres Introduction Dryland farming systems are very fragile because of their dependence on an uncertain water supply. Traditionally, dryland farmers
4 Sustainability in Dryland Farming Systems Elias Fereres Introduction Dryland farming systems are very fragile because of their dependence on an uncertain water supply. Traditionally, dryland farmers
NORTHERN MARCH 2017 SAFFLOWER CONTENTS
 MARCH 2017 SAFFLOWER CONTENTS safflowers What s new Introduction A.1 Safflower agronomy at a glance...xiv A.2 Crop overview...xv A.2.1 Marketing safflower... xvi Seed...xvi Linoleic oil...xvii A.2.2 Potential
MARCH 2017 SAFFLOWER CONTENTS safflowers What s new Introduction A.1 Safflower agronomy at a glance...xiv A.2 Crop overview...xv A.2.1 Marketing safflower... xvi Seed...xvi Linoleic oil...xvii A.2.2 Potential
GRDC project code: CSA Keywords: Cover-crop, seed coat, financial risk. Take home messages
 EverCrop: Improving establishment of perennial pastures Richard C. Hayes 1, Guangdi D. Li 1, Tony D. Swan 3, Tim R. Hutchings 2, Geoff Casburn 1, Matthew T. Newell 1, Helen Burns 1, and Tom L. Nordblom
EverCrop: Improving establishment of perennial pastures Richard C. Hayes 1, Guangdi D. Li 1, Tony D. Swan 3, Tim R. Hutchings 2, Geoff Casburn 1, Matthew T. Newell 1, Helen Burns 1, and Tom L. Nordblom
Refining Silverleaf Nightshade Best Management Strategies
 Tips and Tactics Refining Silverleaf Nightshade Best Management Strategies Keeping sorghum safe Northern Region Improving long-term silverleaf nightshade control Silverleaf nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium
Tips and Tactics Refining Silverleaf Nightshade Best Management Strategies Keeping sorghum safe Northern Region Improving long-term silverleaf nightshade control Silverleaf nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium
Agriculture and Society: Part II. PA E & E Standards 4.4
 Agriculture and Society: Part II PA E & E Standards 4.4 Let s get Dirty! 1. All agriculture ultimately depends on the soil. What is soil? Soil is the upper layer of the land surface that contains pieces
Agriculture and Society: Part II PA E & E Standards 4.4 Let s get Dirty! 1. All agriculture ultimately depends on the soil. What is soil? Soil is the upper layer of the land surface that contains pieces
Educational Farm Walk Aldinga 15 October 2016
 Educational Farm Walk Aldinga 15 October 2016 1 Landholder: Deb Ophof Event Program (9.30am to 12.00noon) Introductions The importance of soil testing Observe horse keeping facilities and welfare of horses
Educational Farm Walk Aldinga 15 October 2016 1 Landholder: Deb Ophof Event Program (9.30am to 12.00noon) Introductions The importance of soil testing Observe horse keeping facilities and welfare of horses
Farmer s decision parameters on diversification and supply responses to dryland salinity - modelling across the Australian wheat-sheep zone
 Farmer s decision parameters on diversification and supply responses to dryland salinity - modelling across the Australian wheat-sheep zone Paper presented at the Australian Agricultural and Resource Economics
Farmer s decision parameters on diversification and supply responses to dryland salinity - modelling across the Australian wheat-sheep zone Paper presented at the Australian Agricultural and Resource Economics
No Tillage Challenges and Solutions for Soybeans in Australia
 No Tillage Challenges and Solutions for s in Australia J.D Sykes 1, P. Desborough 2, L. Gaynor 3, M.J. Bell 4, A.L Garside 5 1,2,3 NSW Agriculture, Dubbo, Grafton and Yanco. 4,5 Agency for Food and Fibre
No Tillage Challenges and Solutions for s in Australia J.D Sykes 1, P. Desborough 2, L. Gaynor 3, M.J. Bell 4, A.L Garside 5 1,2,3 NSW Agriculture, Dubbo, Grafton and Yanco. 4,5 Agency for Food and Fibre
Weed management in the southern region mixed farming systems Strategies to combat herbicide resistance. Charles Sturt University
 Weed management in the southern region mixed farming systems Strategies to combat herbicide resistance Dr. William B. Brown Lecturer in Precision Agriculture Senior Research Fellow School of Agricultural
Weed management in the southern region mixed farming systems Strategies to combat herbicide resistance Dr. William B. Brown Lecturer in Precision Agriculture Senior Research Fellow School of Agricultural
Agronomy for early sown canola
 Yield gain from March sown canola (%) Agronomy for early sown canola Martin Harries, Mark Seymour, Jackie Bucat, Bob French, Sally Sprigg: DAFWA Key messages Agronomic management of canola changes considerably
Yield gain from March sown canola (%) Agronomy for early sown canola Martin Harries, Mark Seymour, Jackie Bucat, Bob French, Sally Sprigg: DAFWA Key messages Agronomic management of canola changes considerably
RESULTS OF 7 FERTILISER PROGRAMS ON CEREAL CROPS
 Beverley Land Conservation District Committee (LCDC) Trial 1997 to 2001 RESULTS OF 7 FERTILISER PROGRAMS ON CEREAL CROPS 5-Year Completely Randomised Trial July 20, 2015 Introduction This is an historical
Beverley Land Conservation District Committee (LCDC) Trial 1997 to 2001 RESULTS OF 7 FERTILISER PROGRAMS ON CEREAL CROPS 5-Year Completely Randomised Trial July 20, 2015 Introduction This is an historical
Pastures in crop sequencing (SFS 00022) Final report on trialling conducted through the project
 Pastures in crop sequencing (SFS 00022) Final report on trialling conducted through the project December 2015 1 Contents Insights from trials using pastures and fodders in a crop rotation... 3 Dry matter
Pastures in crop sequencing (SFS 00022) Final report on trialling conducted through the project December 2015 1 Contents Insights from trials using pastures and fodders in a crop rotation... 3 Dry matter
Harvesting pasture cropped oats on Winona with summer perennial grass emerging beneath the crop. Pasture Cropping. Profitable Regenerative Agriculture
 Harvesting pasture cropped oats on Winona with summer perennial grass emerging beneath the crop Pasture Cropping Profitable Regenerative Agriculture Colin Seis Concerns about declining profitability, increased
Harvesting pasture cropped oats on Winona with summer perennial grass emerging beneath the crop Pasture Cropping Profitable Regenerative Agriculture Colin Seis Concerns about declining profitability, increased
Soil Fertility Management on the Teagasc Tillage BETTER Farms Williamsons in Wexford
 Soil Fertility Management on the Teagasc Tillage BETTER Farms By Mark lunkett and David Wall, Teagasc, Crops Environment and Land Use Centre, Johnstown Castle Cereal crop yields in Ireland are amongst
Soil Fertility Management on the Teagasc Tillage BETTER Farms By Mark lunkett and David Wall, Teagasc, Crops Environment and Land Use Centre, Johnstown Castle Cereal crop yields in Ireland are amongst
Sunflower in the Central Queensland Farming System
 Sunflower in the Central Queensland Farming System Kevin McCosker 1 & Andrew Farquharson 2 1 Agency for Food & Fibre Sciences, Qld. Dept. Primary Industries, LMB 6, Emerald, Qld., 4720 2 Pioneer Hi-Bred
Sunflower in the Central Queensland Farming System Kevin McCosker 1 & Andrew Farquharson 2 1 Agency for Food & Fibre Sciences, Qld. Dept. Primary Industries, LMB 6, Emerald, Qld., 4720 2 Pioneer Hi-Bred
Of vital importance..
 Soil moisture Of vital importance.. Low and erratic rainfall form a significant cause of low crop production and crop failure in rainfed agriculture in the tropics However, crop and land management do
Soil moisture Of vital importance.. Low and erratic rainfall form a significant cause of low crop production and crop failure in rainfed agriculture in the tropics However, crop and land management do
Tower Summer Active Tall Fescue
 Tower Summer Active Tall Fescue Festuca arundinacea Tower is a continental fescue that has a soft and palatable leaf and is being released after excellent performance in production trials. The late heading
Tower Summer Active Tall Fescue Festuca arundinacea Tower is a continental fescue that has a soft and palatable leaf and is being released after excellent performance in production trials. The late heading
WHITBREAD Anthony (1), BLAIR Graeme J. (1), LEFROY Rod (2)
 Scientific registration n o : 457 Symposium n o : 20 Presentation: poster Management of legume leys, residues and fertilisers to enhance the sustainability of wheat cropping systems Gestion des fertilisants
Scientific registration n o : 457 Symposium n o : 20 Presentation: poster Management of legume leys, residues and fertilisers to enhance the sustainability of wheat cropping systems Gestion des fertilisants
Plant: winter growing annual, with multiple laterals branching from near the base. Initial growth is slow.
 Purple vetch Scientific name(s) Vicia benghalensis Strengths Purple vetch is an annual pasture/forage/green manure plant. Palatable as green and dry matter. Vetches have the ability to offer substantial
Purple vetch Scientific name(s) Vicia benghalensis Strengths Purple vetch is an annual pasture/forage/green manure plant. Palatable as green and dry matter. Vetches have the ability to offer substantial
Climate decision-support tools
 August 2008 Climate decision-support tools Australian Rainman Description: A seasonal climate analysis tool containing monthly and daily rainfall for 3800 Australian locations, monthly rainfall and streamflow
August 2008 Climate decision-support tools Australian Rainman Description: A seasonal climate analysis tool containing monthly and daily rainfall for 3800 Australian locations, monthly rainfall and streamflow
HERBICIDES AND LIFE IN THE SOIL
 HERBICIDES AND LIFE IN THE SOIL By V.V.S.R Gupta, CSIRO Land & Water A diverse range of organism types and species carry out one function Please note: Pesticides are an essential in modern agriculture.
HERBICIDES AND LIFE IN THE SOIL By V.V.S.R Gupta, CSIRO Land & Water A diverse range of organism types and species carry out one function Please note: Pesticides are an essential in modern agriculture.
Nutrient Cycles. & how Humans impact nutrient cycling. Accel Bio. Where do energy & nutrients come from?
 Nutrient Cycles & how Humans impact nutrient cycling Accel Bio Where do energy & nutrients come from? What are nutrients? What else do organisms need to survive and grow? Organisms need, Energy, water
Nutrient Cycles & how Humans impact nutrient cycling Accel Bio Where do energy & nutrients come from? What are nutrients? What else do organisms need to survive and grow? Organisms need, Energy, water
Potassium responses in wheat and canola, Glenthompson, 2016
 Potassium responses in wheat and canola, Glenthompson, 2016 Rob Norton 1 and Claudia Gebert 2 1 International Plant Nutrition Institute, Horsham, Vic. 2 Southern Farming Systems, Inverleigh, Vic. Key messages
Potassium responses in wheat and canola, Glenthompson, 2016 Rob Norton 1 and Claudia Gebert 2 1 International Plant Nutrition Institute, Horsham, Vic. 2 Southern Farming Systems, Inverleigh, Vic. Key messages
2010 Survey results Nadine Hollamby (Liebe Group) Roy Murray-Prior (Curtin University)
 Grower s Attitudes and Practices towards Soil Health in the Liebe Area 2010 Survey results Nadine Hollamby (Liebe Group) Roy Murray-Prior (Curtin University) Report to GRDC as part of the Improved stubble
Grower s Attitudes and Practices towards Soil Health in the Liebe Area 2010 Survey results Nadine Hollamby (Liebe Group) Roy Murray-Prior (Curtin University) Report to GRDC as part of the Improved stubble
Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science. Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices
 Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices 1 Terms Conservation tillage Continuous cropping Conventional tillage Crop rotation Double cropping Organic farming
Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices 1 Terms Conservation tillage Continuous cropping Conventional tillage Crop rotation Double cropping Organic farming
Incorporating stubble as climate change adaptation strategy by spatial estimation of soil organic carbon in NSW wheat belt
 Incorporating stubble as climate change adaptation strategy by spatial estimation of soil organic carbon in NSW wheat belt De Li Liu, Muhuddin Anwar and Mark K. Conyers NSW Department of Primary Industries
Incorporating stubble as climate change adaptation strategy by spatial estimation of soil organic carbon in NSW wheat belt De Li Liu, Muhuddin Anwar and Mark K. Conyers NSW Department of Primary Industries
Role of Soils in Water Quality. Mike Marshall Extension Associate Texas A&M-Institute of Renewable Natural Resources
 Role of Soils in Water Quality Mike Marshall Extension Associate Texas A&M-Institute of Renewable Natural Resources Water Quality in Texas Water is a finite resource that can be impaired by pollution from
Role of Soils in Water Quality Mike Marshall Extension Associate Texas A&M-Institute of Renewable Natural Resources Water Quality in Texas Water is a finite resource that can be impaired by pollution from
NQF Level: 4 US No:
 NQF Level: 4 US No: 116320 Assessment Guide Primary Agriculture Plan & maintain environmentally sound agricultural processes Assessor:.......................................... Workplace / Company:.................................
NQF Level: 4 US No: 116320 Assessment Guide Primary Agriculture Plan & maintain environmentally sound agricultural processes Assessor:.......................................... Workplace / Company:.................................
2010 State FFA Crops Contest Written Exam
 1. The Economic Optimum N rate for corn is: a) The rate where the corn yield is at the maximum level b) The rate where the last unit of N returns a grain yield high enough to pay for the N c) The rate
1. The Economic Optimum N rate for corn is: a) The rate where the corn yield is at the maximum level b) The rate where the last unit of N returns a grain yield high enough to pay for the N c) The rate
Mungbean - Recommended Cultural Practices
 Mungbean - Recommended Cultural Practices Introduction Grain legumes are concentrated sources of protein and unlike many other crops, they can adapt to nitrogen-deficient soils. Virtually all of the grain
Mungbean - Recommended Cultural Practices Introduction Grain legumes are concentrated sources of protein and unlike many other crops, they can adapt to nitrogen-deficient soils. Virtually all of the grain
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices Interest Approach Ask students what challenges the first farmers faced as colonists moved across North America. Some of the challenges involved
Animal, Plant & Soil Science D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices Interest Approach Ask students what challenges the first farmers faced as colonists moved across North America. Some of the challenges involved
CROP PLACEMENT AND ROW SPACING fact sheet
 CROP PLACEMENT AND ROW SPACING fact sheet JANUARY 2011 northern region A systems approach to row spacing The depth of seed placement and the distance from the adjacent row both influence crop performance.
CROP PLACEMENT AND ROW SPACING fact sheet JANUARY 2011 northern region A systems approach to row spacing The depth of seed placement and the distance from the adjacent row both influence crop performance.
Cobra Balansa Clover. Trifolium michelianum
 Cobra Balansa Clover Trifolium michelianum Cobra is an early to very early flowering hardseeded Balansa Clover. It is an aerial seeded type, suitable for self regeneration in the long-term pasture phase.
Cobra Balansa Clover Trifolium michelianum Cobra is an early to very early flowering hardseeded Balansa Clover. It is an aerial seeded type, suitable for self regeneration in the long-term pasture phase.
Biogeochemical Cycles
 Biogeochemical Cycles Biogeochemical Cycles refers to the cycling of materials between living things and the environment. Text Pages 50 51, 62 69 1 The Oxygen Cycle the movement of oxygen between the atmosphere
Biogeochemical Cycles Biogeochemical Cycles refers to the cycling of materials between living things and the environment. Text Pages 50 51, 62 69 1 The Oxygen Cycle the movement of oxygen between the atmosphere
Soil Degradation. Lesson Plan NRES B2-9
 Soil Degradation Lesson Plan NRES B2-9 Objectives 1. What is soil degradation? 2. How can construction result in soil degradation? 3. What are the sources of contamination, and how do they result in soil
Soil Degradation Lesson Plan NRES B2-9 Objectives 1. What is soil degradation? 2. How can construction result in soil degradation? 3. What are the sources of contamination, and how do they result in soil
8. Weed management. Weed management. Andrew Storrie, Steve Sutherland, NSW DPI; and Chris Preston, University of Adelaide
 8. Weed management Andrew Strie, Steve Sutherland, NSW DPI; and Chris Preston, University of Adelaide Canola is highly susceptible to weed competition during the early stages of growth, making early weed
8. Weed management Andrew Strie, Steve Sutherland, NSW DPI; and Chris Preston, University of Adelaide Canola is highly susceptible to weed competition during the early stages of growth, making early weed
ROW SPACING fact sheet
 CROP PLACEMENT AND ROW SPACING fact sheet january 2011 Western region A systems approach to row spacing The depth of seed placement and the distance from the adjacent row both influence crop performance.
CROP PLACEMENT AND ROW SPACING fact sheet january 2011 Western region A systems approach to row spacing The depth of seed placement and the distance from the adjacent row both influence crop performance.
Domesticating and transforming nature to produce food
 5. Ecology and food economy 5.1 The rise of agriculture: Challenges for our diet and the environment 5.1.1 Domesticating and transforming nature to produce food Human beings have always used nature to
5. Ecology and food economy 5.1 The rise of agriculture: Challenges for our diet and the environment 5.1.1 Domesticating and transforming nature to produce food Human beings have always used nature to
THE POTENTIAL IMPACT AND OPPORTUNITIES FROM NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT REGULATION ON THE NEW ZEALAND HERBAGE SEED INDUSTRY
 Pyke, N., Chynoweth, R. and Mathers, D., 2016. The potential impact and opportunities from nutrient management regulation on the New Zealand herbage seed industry. In: Integrated nutrient and water management
Pyke, N., Chynoweth, R. and Mathers, D., 2016. The potential impact and opportunities from nutrient management regulation on the New Zealand herbage seed industry. In: Integrated nutrient and water management
Cover Crops (Section 6.3)
 Cover Crops (Section 6.3) Conceptually they are meant to provide cover to prevent erosion during fallow periods between cash crops. They can provide a variety of benefits to the crop rotation. The intended
Cover Crops (Section 6.3) Conceptually they are meant to provide cover to prevent erosion during fallow periods between cash crops. They can provide a variety of benefits to the crop rotation. The intended
THE BENEFITS OF ROTATION CROPPING TO COTTON
 463 THE BENEFITS OF ROTATION CROPPING TO COTTON ohn Marshall and Sarah Thomson CRC for Sustainable Cotton Production, QDPI, Dalby Ian Rochester and Greg Constable CRC for Sustainable Cotton Production,
463 THE BENEFITS OF ROTATION CROPPING TO COTTON ohn Marshall and Sarah Thomson CRC for Sustainable Cotton Production, QDPI, Dalby Ian Rochester and Greg Constable CRC for Sustainable Cotton Production,
Crop Rotations Under Irrigation. Irrigation Agronomy Workshop April 9, 2013 Outlook, SK Gary Kruger PA CCA Irrigation Agrologist
 Crop Rotations Under Irrigation Irrigation Agronomy Workshop April 9, 2013 Outlook, SK Gary Kruger PA CCA Irrigation Agrologist Crop Rotation A planned sequence of crops repeated over time on the same
Crop Rotations Under Irrigation Irrigation Agronomy Workshop April 9, 2013 Outlook, SK Gary Kruger PA CCA Irrigation Agrologist Crop Rotation A planned sequence of crops repeated over time on the same
Pty Limited ABN area of. Mark Harris Chris Minehan (02)
 RURAL MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES Pty Limited ABN 73 352 656 360 AGRICULTURAL CONSULTANTS www.rmsag.com.au Southern Agribusiness Trial Extension Network GRDC Project 03.07.20133 2013 Improving Nitrogen application
RURAL MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES Pty Limited ABN 73 352 656 360 AGRICULTURAL CONSULTANTS www.rmsag.com.au Southern Agribusiness Trial Extension Network GRDC Project 03.07.20133 2013 Improving Nitrogen application
TALL FESCUE MANAGEMENT GUIDE
 TALL FESCUE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Introduction Where is Tall Fescue Suited? Tall fescue is an exciting grass species that has proven itself to be an answer to pasture persistence and performance in hot summer
TALL FESCUE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Introduction Where is Tall Fescue Suited? Tall fescue is an exciting grass species that has proven itself to be an answer to pasture persistence and performance in hot summer
SOIL CULTIVATION AND CONSERVATION AGRICULTURE
 SOIL CULTIVATION AND CONSERVATION AGRICULTURE Soil cultivation Soil is cultivated to combat weeds, pests and diseases, to incorporate crop residues, and chemicals and to create a favourable seedbed for
SOIL CULTIVATION AND CONSERVATION AGRICULTURE Soil cultivation Soil is cultivated to combat weeds, pests and diseases, to incorporate crop residues, and chemicals and to create a favourable seedbed for
33. Fate of pesticides in soil and plant.
 33. Fate of pesticides in soil and plant. What Happens to Pesticides When a pesticide is released into the environment many things happen to it. Sometimes what happens is beneficial. For example, the leaching
33. Fate of pesticides in soil and plant. What Happens to Pesticides When a pesticide is released into the environment many things happen to it. Sometimes what happens is beneficial. For example, the leaching
Opportunity to increase phosphorus efficiency through co-application of organic amendments with monoammonium
 Opportunity to increase phosphorus efficiency through co-application of organic amendments with monoammonium phosphate (MAP) Gale DL, Condon JR, Conyers MK, Southwell AF EH Graham Centre for Agricultural
Opportunity to increase phosphorus efficiency through co-application of organic amendments with monoammonium phosphate (MAP) Gale DL, Condon JR, Conyers MK, Southwell AF EH Graham Centre for Agricultural
Climate Risk Management through Structural Adjustment and Regional Relocation: A Case of Rice Industry in Australia Shahbaz Mushtaq
 Climate Risk Management through Structural Adjustment and Regional Relocation: A Case of Rice Industry in Australia Shahbaz Mushtaq Climate Risk Management Symposium Guayaquil, Ecuador October 10-12, 2011
Climate Risk Management through Structural Adjustment and Regional Relocation: A Case of Rice Industry in Australia Shahbaz Mushtaq Climate Risk Management Symposium Guayaquil, Ecuador October 10-12, 2011
Agriculture. Paper 1. Centre Number. Student Number. Total marks 70
 Centre Number Student Number 2008 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Agriculture Paper 1 Total marks 70 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 2 hours Write using black or blue pen
Centre Number Student Number 2008 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Agriculture Paper 1 Total marks 70 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 2 hours Write using black or blue pen
Grain & Graze National Feedbase Project. Production vs ground cover tradeoffs in the Murrumbidgee region
 Grain & Graze National Feedbase Project Production vs ground cover tradeoffs in the Murrumbidgee region JM Lilley & AD Moore 18 May 2007 Enquiries should be addressed to: Dr Julianne Lilley CSIRO Plant
Grain & Graze National Feedbase Project Production vs ground cover tradeoffs in the Murrumbidgee region JM Lilley & AD Moore 18 May 2007 Enquiries should be addressed to: Dr Julianne Lilley CSIRO Plant
Lesson Overview. Cycles of Matter. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so..where do essential
Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so..where do essential
ROUNDUP READY CANOLA CROP MANAGEMENT PLAN (CMP)
 ROUNDUP READY CANOLA CROP MANAGEMENT PLAN (CMP) Objective. The Roundup Ready canola Crop Management Plan details strategies that can be implemented on-farm to manage risks to the integrity of grain supply-chains
ROUNDUP READY CANOLA CROP MANAGEMENT PLAN (CMP) Objective. The Roundup Ready canola Crop Management Plan details strategies that can be implemented on-farm to manage risks to the integrity of grain supply-chains
John Kirkegaard CSIRO Plant Industry, Canberra
 Canola & its role in Australia s conservation farming revolution John Kirkegaard CSIRO Plant Industry, Canberra Why invite an Aussie? An oilseed (canola) is most important non-cereal crop (3 rd most important
Canola & its role in Australia s conservation farming revolution John Kirkegaard CSIRO Plant Industry, Canberra Why invite an Aussie? An oilseed (canola) is most important non-cereal crop (3 rd most important
Agronomic Insight 8 August 2017
 Topdressing trials and tribulations By Lee Menhenett -Technical Agronomist Page 1 of 5 Topdressing nitrogen can be difficult to get right with respect to timing and rate. Given that nitrogen is the biggest
Topdressing trials and tribulations By Lee Menhenett -Technical Agronomist Page 1 of 5 Topdressing nitrogen can be difficult to get right with respect to timing and rate. Given that nitrogen is the biggest
Managing heavy clay soils to improve grain cropping in a high rainfall environment
 GROWER SOLUTIONS FOR COASTAL/HINTERLAND QLD AND NSW NORTH COAST 2018 PRACTICE CHANGE CASE STUDY GRDC PROJECT CODE: DAQ00204 Managing heavy clay soils to improve grain cropping in a high rainfall environment
GROWER SOLUTIONS FOR COASTAL/HINTERLAND QLD AND NSW NORTH COAST 2018 PRACTICE CHANGE CASE STUDY GRDC PROJECT CODE: DAQ00204 Managing heavy clay soils to improve grain cropping in a high rainfall environment
CHAPTER 8. CROP ESTABLISHMENT AND MANAGEMENT Jim Pratley and Rex Stanton
 CHAPTER 8 CROP ESTABLISHMENT AND MANAGEMENT Jim Pratley and Rex Stanton Farming systems in Australia differ according to the climatic (Chapter 2) and soil (Chapter 5) constraints of the environment. In
CHAPTER 8 CROP ESTABLISHMENT AND MANAGEMENT Jim Pratley and Rex Stanton Farming systems in Australia differ according to the climatic (Chapter 2) and soil (Chapter 5) constraints of the environment. In
SEED
 PROTECTS THE SOIL SAVES YOU MONEY www.pennington.com 1-800-285-SEED WHO IS PENNINGTON SEED? Pennington has a long history in the farming industry starting with the first members of the Pennington family
PROTECTS THE SOIL SAVES YOU MONEY www.pennington.com 1-800-285-SEED WHO IS PENNINGTON SEED? Pennington has a long history in the farming industry starting with the first members of the Pennington family
February Mg Magnesium
 February 2015 INTERPRETING SOIL TEST INFORMATION C Carbon Ca Calcium K Potassium Mg Magnesium N Nitrogen P Phosphorous S - Sulphur Most Australian soils are deficient in one or more nutrients in their
February 2015 INTERPRETING SOIL TEST INFORMATION C Carbon Ca Calcium K Potassium Mg Magnesium N Nitrogen P Phosphorous S - Sulphur Most Australian soils are deficient in one or more nutrients in their
Is there potential value in more precise broadacre cropping system management? Brett Whelan
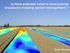 Is there potential value in more precise broadacre cropping system management? Brett Whelan Is there potential value in more precise agricultural management? Site-specific gross margin Wheat crop uniformly
Is there potential value in more precise broadacre cropping system management? Brett Whelan Is there potential value in more precise agricultural management? Site-specific gross margin Wheat crop uniformly
4. Crop rotation and paddock selection
 4. Crop rotation and paddock selection Paul Parker, NSW DPI Crop rotation Any crop rotation should be based on sound principles but remain flexible to allow for variations in the seasonal break, commodity
4. Crop rotation and paddock selection Paul Parker, NSW DPI Crop rotation Any crop rotation should be based on sound principles but remain flexible to allow for variations in the seasonal break, commodity
SUMMER FALLOW PRACTICES DEMONSTRATION
 6 SUMMER FALLOW PRACTICES DEMONSTRATION By Duane D. Hauck Assoc. Ext. Eg. Eng. INTRODUCTION: Summer Fallow Practices Demonstration trials were conducted during the summer of 1983 in cooperation with the
6 SUMMER FALLOW PRACTICES DEMONSTRATION By Duane D. Hauck Assoc. Ext. Eg. Eng. INTRODUCTION: Summer Fallow Practices Demonstration trials were conducted during the summer of 1983 in cooperation with the
CHAPTER # 4. Fate of Pollutants in the Environment
 CHAPTER # 4 Fate of Pollutants in the Environment Once a pesticide is introduced into the environment, whether through an application, a disposal or a spill, it is influenced by many processes. These processes
CHAPTER # 4 Fate of Pollutants in the Environment Once a pesticide is introduced into the environment, whether through an application, a disposal or a spill, it is influenced by many processes. These processes
RF Brennan A, MDA Bolland B and JW Bowden C. Abstract. Introduction. Material and methods
 Post canola syndrome: burning swathed canola stubbles enables potassium deficiency and induced molybdenum deficiency and aluminium toxicity to be expressed in the next cereal crop RF Brennan A, MDA Bolland
Post canola syndrome: burning swathed canola stubbles enables potassium deficiency and induced molybdenum deficiency and aluminium toxicity to be expressed in the next cereal crop RF Brennan A, MDA Bolland
7.0 - nutrient uptake, removal and budgeting
 7.0 - nutrient uptake, removal and budgeting - nutrient uptake - nutrient removal - nutrient budgeting 7.0 nutrient uptake, removal and budgeting NUTRIENT UPTAKE The generalised relationship between plant
7.0 - nutrient uptake, removal and budgeting - nutrient uptake - nutrient removal - nutrient budgeting 7.0 nutrient uptake, removal and budgeting NUTRIENT UPTAKE The generalised relationship between plant
soil carbon, erosion + moisture conservation
 soil carbon, erosion + moisture conservation in stubble retained systems in Central West NSW Project code CWF00018 KEY MESSAGES Soil carbon and microbial health are positively correlated. Carbon is influenced
soil carbon, erosion + moisture conservation in stubble retained systems in Central West NSW Project code CWF00018 KEY MESSAGES Soil carbon and microbial health are positively correlated. Carbon is influenced
Water use efficiency of dryland canola
 1 Water use efficiency of dryland canola Michael J Robertson A and John A Kirkegaard B A CSIRO Sustainable Ecosystems, Private Bag, PO Wembley, WA 6913, Australia B CSIRO Plant Industry, GPO Box 16, Canberra,
1 Water use efficiency of dryland canola Michael J Robertson A and John A Kirkegaard B A CSIRO Sustainable Ecosystems, Private Bag, PO Wembley, WA 6913, Australia B CSIRO Plant Industry, GPO Box 16, Canberra,
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE. Professor PhD GABRIELA TEODORESCU, Romania
 SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE Professor PhD GABRIELA TEODORESCU, Romania INTRODUCTION The main objective of this project is to promote the sustainable agriculture has become key words to horticultural and agricultural
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE Professor PhD GABRIELA TEODORESCU, Romania INTRODUCTION The main objective of this project is to promote the sustainable agriculture has become key words to horticultural and agricultural
Potential for cover crops in Northern Ireland. Shay Phelan Teagasc Crops Specialist Oak Park Carlow
 Potential for cover crops in Northern Ireland Shay Phelan Teagasc Crops Specialist Oak Park Carlow What Name Various names used Cover crops cover the ground Catch crops catch nutrients preventing them
Potential for cover crops in Northern Ireland Shay Phelan Teagasc Crops Specialist Oak Park Carlow What Name Various names used Cover crops cover the ground Catch crops catch nutrients preventing them
User guide. Ryegrass Integrated Management. Ryegrass Integrated Management
 Ryegrass Integrated Management A tool to evaluate the profitability of ryegrass (Lolium rigidum Gaud.) control methods in the no-till broadacre cropping systems of the Southern Australian grainbelt, short
Ryegrass Integrated Management A tool to evaluate the profitability of ryegrass (Lolium rigidum Gaud.) control methods in the no-till broadacre cropping systems of the Southern Australian grainbelt, short
Land management practice trends in Australia s northern and remote agricultural industries
 Land management practice trends in Australia s northern and remote agricultural industries Introduction Northern and remote Australia includes 11 Natural Resource Management (NRM) regions in Western Australia,
Land management practice trends in Australia s northern and remote agricultural industries Introduction Northern and remote Australia includes 11 Natural Resource Management (NRM) regions in Western Australia,
germinal.com Catch Crops The benefits, management and their role in compliance
 germinal.com Catch Crops The benefits, management and their role in compliance Contents Contents Introduction 01 The benefits of catch crops 02 GLAS 05 Greening 06 Mixture Options 07 Catch crop options
germinal.com Catch Crops The benefits, management and their role in compliance Contents Contents Introduction 01 The benefits of catch crops 02 GLAS 05 Greening 06 Mixture Options 07 Catch crop options
Establishing small seeded pasture legumes into existing grass pastures. Gavin Peck, Stuart Buck, Brian Johnson.
 Establishing small seeded pasture legumes into existing grass pastures Gavin Peck, Stuart Buck, Brian Johnson. Overview Section 1: Background &trial results Legumes production benefits The challenge of
Establishing small seeded pasture legumes into existing grass pastures Gavin Peck, Stuart Buck, Brian Johnson. Overview Section 1: Background &trial results Legumes production benefits The challenge of
Northwest Regional Certified Crop Adviser
 Northwest Regional Certified Crop Adviser Performance Objectives Prepared by Northwest Regional CCA Board CONTENTS Introduction... iii Soil Fertility Competency Areas...1 1 Basic concepts of soil fertility...2
Northwest Regional Certified Crop Adviser Performance Objectives Prepared by Northwest Regional CCA Board CONTENTS Introduction... iii Soil Fertility Competency Areas...1 1 Basic concepts of soil fertility...2
