Thermal Responsive Release of a Model Drug, Rhoadmine B, from Alginate Bead System
|
|
|
- Shanna Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The University of Akron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2016 Thermal Responsive Release of a Model Drug, Rhoadmine B, from Alginate Bead System Heather F. Fairbairn Miss The University of Akron, hff2@zips.uakron.edu Please take a moment to share how this work helps you through this survey. Your feedback will be important as we plan further development of our repository. Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Biochemical and Biomolecular Engineering Commons Recommended Citation Fairbairn, Heather F. Miss, "Thermal Responsive Release of a Model Drug, Rhoadmine B, from Alginate Bead System" (2016). Honors Research Projects This Honors Research Project is brought to you for free and open access by The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College at IdeaExchange@UAkron, the institutional repository of The University of Akron in Akron, Ohio, USA. It has been accepted for inclusion in Honors Research Projects by an authorized administrator of IdeaExchange@UAkron. For more information, please contact mjon@uakron.edu, uapress@uakron.edu.
2 Thermal Responsive Release of A Model Drug, Rhodamine B, from Alginate Bead System 4200:497:001 The Williams Honors College Heather Fairbairn April 29, 2016
3 Executive Summary Stimuli responsive drug release vehicles have become of increased interest in recent years. Common stimuli that have been investigated include light, ph, and temperature. The goal of this project was to investigate the drug release profiles of alginate beads that have PNIPAAm, a thermal responsive polymer, incorporated into the matrix. The purpose of doing this was to create a drug delivery system that can be tuned to have a specific release profile or specific release time by varying the amount of PNIPAAm in the delivery matrix. The drug used for delivery was rhodamine B. The project was designed to investigate the release speed and mechanism of beads made with differing ratios of alginate to PNIPAAm. After obtaining data, the percent of drug released versus time can be fitted to a power law curve. This power law curve and its corresponding constant and exponent can be classified using a simplified form of Fick s 2nd Law of Diffusion. The constant k describes the speed of the diffusion and is a function of bead thickness, while the exponent n describes the diffusion case, which has four distinct regions: zero-order constant diffusion, anomalous, Fickian, and pseudo-fickian. After analysis, it was determined that the mixed PNIPAAm beads had significantly higher k values than the pure alginate beads. This shows that the PNIPAAm speeds the drug release. This is due to the hydrophobic behavior displayed by PNIPAAm above its lower critical solution temperature (LCST), which causes the pores of the network to collapse and expel the drug. The n values for the different systems showed that the release changes from a zero order release for pure alginate to a Fickian diffusion case for the 50/50 mixture of alginate and PNIPAAm.
4 One of the largest impacts of my work was on my personal and career goals. In the fall, I will be attending the University of Michigan to begin my PhD in Chemical Engineering. I plan to pursue a career in academia upon completion of my doctorate. Completing this project has increased my confidence in my ability to conduct, analyze, and report original research. I have also gained experience in using literature surveys to trouble shoot, explain results, and provide supporting evidence. I also had the opportunity to refine my technical skills through using laboratory equipment, practicing safe laboratory procedures, and learning to use specific equipment, such as the microscope and the plate reader. This project will contribute to the body of work being done by researchers around the world to create stimuli responsive drug delivery systems to overcome obstacles and improve the efficiency of release systems. One application of using thermal responsive drug delivery systems can lead to advances in topical delivery systems that respond to the body s temperature change, creating a consistent release profile. This could lead to a reduction in required dosages. This would increase patient compliance to the recommended treatment procedures, which could improve his or her quality of life. The next step for this project would be to confirm the result by obtaining additional data sets at the same experimental conditions. If concise results are obtained that show an appreciable difference between the n and k values for each ratio of PNIPAAm to Alginate, then it would be recommended to continue investigation into tuning the release profile by varying the overall % of polymer in the beads. Also, it would be beneficial to test the release profile in PBS to give an initial confirmation of the viability of using these beads in vivo. The biggest
5 improvements that are needed for success in this project are consistent morphology and an improved sampling procedure that ensures the samples obtained are not only of the localized concentration. As an undergraduate, I have had the opportunity to explore three different research projects. Through these experiences, I would advise other students to choose their advisor carefully. An advisor that is highly supportive, easily accessible, and sufficiently able to answer questions makes beginning researcher less daunting and more enjoyable. Choose a project that excites you, because you are quickly going to become an expert in your project topic! When your hard work returns faulty or meaningless results, and you start to get discouraged, remind yourself that failure is a key portion of the research process, and often more is learned through failure than success. I wish students the best as they embark on these endeavors!
6 Introduction Controlled and targeted drug release has become a topic of great interest among the academic and medical community. Conventional drug release systems can be inadequate and ineffective for special circumstances. For example, research in administering drugs orally that are normally injected necessitates the design of a smart release vehicle. [1] Insulin, a protein based drug that is typically administered to diabetic patients through a pump or an injection, is one such drug. Oral delivery would be preferred to injection to increase patient compliance and comfort, [1] but bypassing the stomach and releasing in the intestines for uptake into the blood stream can prove to be a difficult task. During the digestive process, proteins are broken down into their constituents in the highly acidic stomach environment, which would prove fatal for the needed insulin proteins. This type of delivery quandary would warrant the use of a smart release system that can be activated by environmental stimuli, such as the ph change between the stomach and the intestines. Another medical opportunity that can be addressed with smart polymers is topical applications of drugs. Obtaining the correct distribution of medication in a topical application can be particularly challenging if the drug seeps through the skin into the blood stream. 2 The negative outcomes of this scenario can range in severity. In the best case, the quickly leaching drug would necessitate frequent applications of the medication, decreasing effectiveness of the treatment. More severe cases would include local toxicity in the blood because of the leached drug. To approach this issue, research has been done into infusing electrospun PVA mats with PNIPAAm, a thermal responsive polymer, to allow for the topical applicator to respond to the temperature change on the body surface. 2 The study found this to prolong the release and
7 promote even distribution of the drug in the affected area while decreasing leaching. Advances in using smart materials for topical applications will increase treatment effectiveness and promote patient compliance. Hydrogels are excellent candidates for environmentally sensitive releases because they have properties that allow them to achieve rapid transition between swelling and shrinking or gel and solid, depending on the type of polymer used. [3] The transition can be initiated by relatively small changes in physical or chemical stimuli. Some of the common stimuli that are investigated for use in drug delivery include temperature, electric field, light, and ph. The following report will introduce investigations into temperature stimulated drug delivery. The purpose of this project was to design and test experimental methods to determine the impact that incorporating a thermal responsive polymer, PNIPAAm, into alginate beads would have on the release of a small molecule model drug, rhodamine B. It was hypothesized that the release profile, which is evaluated by fitting the time versus total drug released (up to 60%) [4] to a Fickian model, can be tuned by varying the ratio of alginate to PNIPAAm in the drug delivery matrix. Release behavior was recorded using a modified Franz diffusion cell setup. This investigation into incorporating thermal responsive materials into bead carriers for targeted drug release is part of a larger investigation into controlled drug release for wound healing applications. Work has been conducted on polyelectrolyte beads, which produce ph responsive behavior. Better bead synthesis methods are also being developed under this project heading to improve the consistency and customizability of bead size and morphology. During this project, many recommendations for further investigation were created. Future studies should focus on varying the overall weight percent of polymer, as well as evaluating the
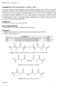
8 efficiency of the release profile for wet beads at 37 C and the release profile of wet and dry beads at room temperature. The beads should also be released into PBS. A better drug loading determination method should be investigated, preferably one that degrades the polymer matrices, allowing for complete release of incorporated rhodamine B. Background To exploit the temperature responsive nature of hydrogels as drug delivery vehicles, poly(n-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) is a commonly used polymer. [5] The structure of PNIPAAm is shown in Figure 1. Synthesized via free radical polymerization from N- isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm) monomer, PNIPAAm exhibits swelling-shrinking response when heated above its lower critical solution temperature (LCST), which occurs at 32 C. [6] Since this is close to body temperature (37 ⁰C), PNIPAAm is used in many biomedical investigations. PNIPAAm can be easily dissolved into an aqueous solution at temperatures below the LCST. If a crosslinking agent is added, PNIPAAM can exist as a loose, transparent gel at room temperature that becomes hard and opaque when the LCST is exceeded (Figure 2). This transitioning behavior is due to the unique constituents of the PNIPAAM molecule, which consist of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components. When the temperature is lower, the hydrogen bonds in the side-chain amide group interact strongly with the surrounding water molecules. As the temperature is increased, the hydrophobic segments increase intramolecular interactions between the polymer chain and other polymer chains. The increase in temperature
9 also weakens the hydrogen bonding between the water and the polymer chains.[3] These two phenomena cause the network to tighten, expel any interspersed water molecules, and decrease in volume. The collapsed network can be observed by a visual change from transparent to opaque (See Figure 2). The transition is considered completely reversible and almost instantaneous when the material temperature crosses the 32 C LCST. One of the downsides of using PNIPAAm in drug release systems is that it is not biodegradable.[5] Although it is not biodegradable, a cursory study done by Malonne, Eeckman, and Fontaine et al. showed that PNIPAAm and its common copolymers do not appear to cause acute or subacute toxicity in mice. The research group asserted that further toxicity studies should be conducted prior to approving PNIPAAm for use in human drug delivery systems. Despite the possibility of negative effects on the body and the lack of biodegradability, PNIPAAm is used frequently in biomedical investigations. Because of the biodegradability issues, it is beneficial to combine PNIPAAm with a known biodegradable matrix, such as alginic acid (alginate). Alginate is a natural polymer extracted from brown seaweed.[8] It is commonly used in the medical field because it is non-toxic, biocompatible, and biodegradable. One interesting application of alginate in the medical field is
10 the creation of molds for orthodontic applications. Aqueous alginate solutions can be easily crosslinked by addition to a dilute calcium chloride solution. The resulting hydrogel is commonly used in orally delivered drugs, and can be combined with other polymers and chemicals to create non-gelatinous soft capsules. [9] Based off of the work done by Shi, Alves, and Mano, it was decided to investigate if controllable drug release profiles could be achieved by incorporating temperature responsive PNIPAAm into alginate beads. Expanding off of their original investigation, it was determined that a standard 3 wt.% polymer solution would be used and that the ratio of alginate to PNIPAAm would be varied to research the feasibility of creating a tunable release profile. The chosen ratios of polymer weight percent of alginate to PNIPAAm included 90/10, 75/25, 66/33, and 50/50. Pure alginate beads were used as a control for every drug release conducted. In order to economically research the effectiveness of drug release matrices, a model drug is commonly used. Rhodamine B was selected as the model drug for this investigation. This small molecule is assumed to accurately mimic the release of actual small molecule medications. Rhodamine B is fluorescent magenta, which allows for facile absorbance readings and convenient visual representation of amount released with respect to time. For rhodamine B at low concentrations, the Beer-Lambert law can be used to model the absorbance as a function of concentration. [11] This relationship
11 can be utilized to create a connection between absorbance of a sample and the amount of drug released in the solution. This relationship can be used to model the drug release behavior over time. Drug release from polymeric beads is a well investigated field. These delivery vehicles can be comprised of a degradable matrix or a non-degradable matrix. The kinetics and transport mechanisms of the release system are unique to the type of matrix. The alginate and PNIPAAm delivery system used for this study is considered to be non-degradable during the chosen release period of up to 3 days and in the chosen release medium, DI water (ph 5.5). To model the unsteady state small molecule drug release behavior of a non-biodegradable system, Fick s 2 nd Law can be used. To utilize Fick s 2 nd Law of Diffusion for a one-dimensional system (xdirection shown), the concentration (c) is found with respect to time as shown in Equation 1 below. Equation 1: = ( ) Upon substitution and approximations, an alternate form of Fick s 2 nd Law can be derived that relates released mass at time t ( ) to the equilibrium mass ( ). This equation makes use of the constant k, which represents the diffusion coefficient (D) and the film thickness (L)(i.e., = ( ). ). [12] The k constant can be used as a metric to understand how fast the drug will release in the system. The exponent n can be used to determine the main mechanism for diffusion that the system is following. Descriptions of the possible values for n can be found in Table 1. Equation 2: =
12 Table 1: Exponential values for modeling systems using Fick s 2 nd Law of Diffusion. [12] n Case Zero Order diffusion (Constant rate of diffusion after initial n <= 1 penetration of drug) [8] 1 > n > 0.5 Anomalous diffusion 0.5 > n Pseudo-Fickian Diffusion n = 0.5 Fickian Diffusion Experimental Methods Materials Materials used for this project included PNIPAAm (Polysciences, Inc- M n 40,000), rhodamine B (Sigma- 95% (HPLC)), alginic acid sodium salt from brown algae (Sigma), and calcium chloride (EMD Millipore- anhydrous). DI water used was purified in house and has a conductivity of < 1 µs/cm. Method To test the drug release profile, beads were synthesized. To begin, stock solutions of aqueous alginate (3 wt. %) and aqueous PNIPAAm (10 wt. %) were created by dissolving the respective polymers in DI water. A stock solution of dissolved rhodamine B was also created. Because rhodamine B has limited solubility in water (8 mg/ml), [13] it was important to create an aqueous solution of rhodamine B prior to introducing it to the viscous alginate solution. This step aids in creating a more uniform drug loading in the beads. Rhodamine B was added on top of the measured water, and then stirred magnetically to create a 1.4 wt. % solution. These solutions were then combined to create a bead stock solution for each of the four desired ratios of alginate to PNIPAAm: 90/10, 75/25, 66/33, and 50/50. Each solution contained a total of 2 wt. % polymer. After the solutions were combined, each beads solution was vortexed for 10
13 seconds to ensure uniform mixing before making the beads. A bath of weak CaCl 2 (3 wt. %) and rhodamine B (1 wt. %) solution was prepared by dissolving 3 g of CaCl 2 in 100 g of water. After the CaCl 2 was dissolved, additional rhodamine B (1 g) was dissolved in the bath. The addition of rhodamine B was used to decrease the likelihood of rhodamine B leaching out of the beads during preparation. Beads were formed by adding the alginate, PNIPAAm, and rhodamine B solution dropwise to the CaCl 2 bath, which was being magnetically stirred rapidly. The bead solution was added to a 3 CC syringe, and then extruded by hand with a consistent pressure at a rate of two drops per second through a 20 G surgical needle. The needle was held approximately 2 cm from the surface of the liquid. After exhausting the solution in the syringe, beads were immediately removed from the solution by filtering through a wire mesh. The beads were then rinsed with ~5 ml of DI water to remove excess CaCl 2. The mesh was set on KimWipes to absorb excess moisture before photographing the beads. Bead photographs were taken prior to drying so that the morphology could be observed (Figure 7). Beads were then transferred to a fume hood, where they were allowed to dry for approximately 1 week. Beads were photographed again post drying (Figure 8). The drug release was done using a modified Franz diffusion cell release chamber (Fig. 5 & 6). The chamber consists of a 50 ml centrifuge tube with a modified lid that accepts a G14 surgical needle. A second hole in the lid minimizes pressure issues during sampling. This chamber was created by Dr. Bi-min Newby and Eric
14 Brink (The University of Akron, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering). To begin the release, a water bath was prepared at 37 C using an incubator (PolyScience). The incubator was filled with water deep enough to submerge the centrifuge tubes up to their 45 ml mark. Needle tips were wrapped in cotton gauze to provide a physical barrier to prevent uptake of beads during sampling. Beads were weighed and recorded, in groups of 5, and then added to the bottom of the chamber. Once all chambers were filled with 5 beads, the first chamber was filled with DI water to the 45 ml mark, then immediately placed in the water bath. To maintain accuracy of timing between sampling periods, one chamber was filled per minute. In order to obtain a standard deviation and ensure the accuracy of results, each different alginate to PNIPAAm ratio was tested in triplicate and tested at the same time as a pure alginate control. Once the chambers were filled, samples of the release environment were taken at regular intervals. For the first hour, samples were taken every 15 minutes. For the second hour, samples were taken every 30 minutes. For the next four hours, the samples were taken every hour. Longer time samples were taken to use as the drug loading measurement. For each sample, a 1 ml syringe was inserted into the chamber s port, the syringe was pumped 5 times, and approximately 0.5 ml of solution was removed. The solution-filled syringe was set on a scale, which was then tared. The solution was emptied into a microcentrifuge tube, then the syringe was placed back on the scale and the difference in weight was recorded. To prevent contamination between sampling, the sampling syringe was rinsed with DI water between
15 samples. To maintain a constant volume release environment, 0.5 ml of DI water was added to the chamber with a clean syringe after each sample was taken. After completing the sampling cycle, with the final measurement after 120 hours to determine drug loading, the samples were analyzed for drug content. Any sample that had a rhodamine B concentration higher than 5 ppm was diluted with DI water to maintain the accuracy of the Beer-Lambert law calibration. [11] The weight of added water was recorded. For accurate readings, the concentration of rhodamine B in aqueous solution also had to remain at a level where the absorbance would not exceed 1. For each sample, 200 µl of solution were removed from each centrifuge vial and placed in a 96-well plate. The Tecan Infinite M200 Plate Reader was used to read the absorbance of each well at a wavelength of 554 nm. [11] These absorbance readings, along with the sample weights, dilution weights, and sampling times, were used to calculate the amount of drug released at each sample time. The amount released at each sample time was converted into a percentage by using the total amount of drug released. As mentioned previously, rhodamine B can be analyzed via absorbance measurements, and at low concentrations (5 ppm or less), can be evaluated using Beer-Lambert law. The Beer- Lambert law is shown in Equation 3, where A is the absorbance (no units), c is the concentration in ppm, ε is the molar absorptivity in L*mol -1 *cm -1, and b is the path length in cm. Equation 3: = The Beer-Lambert law is only valid in linear regions, with the εb term representing the slope of the line. This constant was previously determined for rhodamine B in water by creating
16 a serial dilution of samples, taking absorbance readings at 554 nm wavelength light, then performing a linear regression on that data. The value of the calibration curve slope (εb) was found to be The concentration of rhodamine B in each sample was obtained via Equation 4, which is a rearrangement of Equation 3, using the calibration curve slope for εb. Equation 4: h The path length, l, was assumed to be constant, and was thus reported analyzed data was assumed to be independent of path length. To find the gram amount of drug in each representative sample, Equation 5 was used. To determine the gram/gram concentration of rhodamine in the representative sample, Equation 6 was used. This g/g concentration was then multiplied by the amount of solution in the sampling environment (45 ml) to find the total gram amount of rhodamine B in the sampling environment at the time of sampling. These values, along with the drug loading, were used to find a percentage release at each sampling time Equation 5: =,, After calculations, the percent drug released was then plotted as a function of time. The graph was truncated after 60% drug release. For a polymeric matrix, the simplified version of Fick law shown in Equation 2 is only applicable up to 60% release from a polymeric matrix. [4] The data was fitted to a power law curve, and the coefficients and exponents were recorded in Table 2. Correct safety and waste disposal procedures were followed to dispose of chamber liquid and remaining beads.
17 Data and Results The synthesis of the drug release beads was quantified by taking photographs of the wet beads (Figure 7) and dry beads (Figure 8). From these pictures, assessment of the size and surface morphology can be made. The release behavior of the beads was analyzed using Excel. The percent drug released with respect to time was calculated via the method outlined above. The percent drug released was graphed versus time, and then fitted to a power law trend line. (Figure 9) The equation for the trend line was used to determine the n and k values, as shown in Equation 2. As previously mentioned, the constant k represents the speed of diffusion, and the exponent n explains the release behavior. Values for k, n, and the assumed release case for each type of bead can be found in Table 2.
18 Figure 9: Graph of drug released versus time for all 6 types of beads. Error bars are shown to show standard error for each data point. Each point is the average of three data readings. The
19 trend lines shown were obtained using a power law fit. The dotted red line represents the 60% release threshold for modeling diffusion using Equation 2. Table 2: A summary of the coefficient k and exponent n for each type of bead. The case, based off of the exponent n as defined in Table 1, is also listed. k n Case Alg Ct Constant Rate of Diffusion Alg Ct Anomalous / Constant Rate of Diffusion 90/ Anomalous Diffusion 75/ Pseudo-Fickian Diffusion 66/ Pseudo-Fickian Diffusion 50/ Fickian Diffusion Table 3: Summary of estimated times for 60% release and drug loading for each type of bead. 60% release time (h) Std Dev Drug Loading (mg) Std Dev Alg Ct % % Alg Ct % % 90/ % % 75/ % % 66/ % % 50/ % % Discussion / Analysis An analysis of the efficiency and behavior of a drug release system can be evaluated from the n and k constants produced from fitting the experimental data to a Fickian diffusion model. Based off of the n and k values, it can be seen that the addition of PNIPAAm to the system can significantly alter the release profile. In general, the addition of PNIPAAm speeds the release, as seen by the significantly larger k values for the mixed beads as compared to the pure alginate beads. This behavior can be attributed to the LCST behavior of PNIPAAm. Since the PNIPAAm is fully incorporated into the crosslinked alginate network, the pores of the network will collapse
20 when the LCST is reached, promoting the expulsion of the rhodamine D molecules and accelerating the drug release. Previous investigations into drug release from PNIPAAM and alginate beads has shown similar behavior, with the drug releasing more rapidly when the beads were brought above the LCST of the PNIPAAm. [10] It can also be observed that the addition of PNIPAAm quickly moves the release system from exhibiting a constant diffusion profile when no PNIPAAm is added towards exhibiting Fickian diffusion for the highest percentage of PNIPAAm (50/50). With increasing polymer percentage of PNIPAAm, the release profile starts to behave according to a Fickian model. It would be of interest to determine if pure PNIPAAm beads exhibit Fickian diffusion. The 60% release threshold for modeling shows the upper end of the range over which the Fickian diffusion model holds. [4] There was not a discernable trend to relate the 60% release time with the amount of PNIPAAm added, which could be attributed to experimental errors. Since both alginate control bead data sets were created using the same batch of beads, the significantly variable k values and 60% release times may be due to environmental variation between the two release recordings. One such investigation variable could be non-uniform temperature in the incubator. The release environment was kept open for the duration of sampling, which could allow for non-uniform change in heat in the water bath. During further investigations, a better way to sample the release environment should be developed. Because the tip of the needle in the modified diffusion cell is close to where the beads are located (~2 cm above), the local concentration during sampling may be higher than the overall environment, despite attempts to distribute the drug by pumping the syringe prior to removing sample. Evidence of this being an issue could be observed during absorbance
21 readings, where an unexpected spike in absorbance would be seen early in the sampling process. A possible remedy could be inducing agitation during the release period, perhaps through addition of magnetic stirring or a shaker plate. For future investigation into the usefulness of alginate and PNIPAAm matrices for drug release, it is necessary to go beyond investigating the release profile at only body temperature and incorporate a study of the release at other body conditions, such as ph. Release studies must be conducted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) since PBS mimics the body environment through providing a ph similar to blood. Also, alginate responds to ph stimulation, and it would be important to understand how the incorporation of PNIPAAM influences its behavior in a modified ph. Further investigations and improvements should be done to confirm and reinforce the behavior observed. Many of the discrepancies may be remedied by incorporating additional data. One of the biggest improvements to the experimental method that can be made is increasing the number of samples taken during the diffusion modeling stage (before 60% release is achieved). For example, the 75/25 bead system has only four data points that were measured prior to the 60% release point. More data points in this region will increase the accuracy of the model, perhaps clarifying some of the cases where the n is near an expected case, such as the difference in n values seen between the two alginate controls. To increase the accuracy of drug loading measurement, a matrix degradation technique should be used to measure the total amount of drug in each bead. Because release profile can be influenced by morphology, investigations should be made into techniques that will create a uniform bead morphology for every bead solution.
22 During observations of the release environment, it was noted that the dry beads often released rhodamine immediately upon addition of water. This may be attributed to residual rhodamine B being on the surface of the beads. Beads should be rinsed thoroughly prior to drying to promote uniform drug loading and prevent spikes in release profile due to initial drug loading. In conclusion, the addition of PNIPAAm to alginate beads tends to decrease the release time, therefore speeding up the drug delivery of the small molecule model drug, rhodamine B, into a body-temperature aqueous release environment. Further investigations should include the collection of more data to confirm the behavior observed in this experiment. Further investigations should also include improvements to the consistency of bead morphology and to the release procedure, as well as modeling in PBS as a proof-of-concept for viability as a drug release matrix. Literature Cited [1] Lowman, A. M., Morishita, M., Kajita, M., Nagai, T., & Peppas, N. A. (1999). Oral delivery of insulin using ph-responsive complexation gels. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 88(9), [2] Azarbayjani, A. F., Venugopal, J. R., Ramakrishna, S., Lim, F. C., Chan, Y. W., & Chan, S. Y. (2010). Smart polymeric nanofibers for topical delivery of levothyroxine. Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences, 13(3), [3] Qiu, Y., & Park, K. (2012). Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 64, [4] Ritger, P. L., & Peppas, N. A. (1987). A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. Journal of controlled release, 5(1), [5] Bromberg, L. E., & Ron, E. S. (1998). Temperature-responsive gels and thermogelling polymer matrices for protein and peptide delivery. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 31(3),
23 [6] Almeida, H., Amaral, M. H., & Lobão, P. (2012). Temperature and ph stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications in controlled and self-regulated drug delivery. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 2(6), [7] Malonne, H., Eeckman, F., Fontaine, D., Otto, A., De Vos, L., Moës, A.,... & Amighi, K. (2005). Preparation of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymers and preliminary assessment of their acute and subacute toxicity in mice. European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics, 61(3), [8] Lee, K. Y., & Mooney, D. J. (2012). Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Progress in polymer science, 37(1), [9] Nussinovitch, A. Polymer macro-and micro-gel beads fundamentals and applications, physical properties of beads and their estimation Chapter 8 [10] Shi, J., Alves, N. M., & Mano, J. F. (2008). Chitosan coated alginate beads containing poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) for dual-stimuli-responsive drug release. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 84(2), [11] Van der Auweraer, M., Verschuere, B., & De Schryver, F. C. (1988). Absorption and fluorescence properties of rhodamine B derivatives forming Langmuir-Blodgett films. Langmuir, 4(3), [12] Karimi, M. (2011). Diffusion in polymer solids and solutions. INTECH Open Access Publisher. Chapter 2 [13] Berkland, C., Kipper, M. J., Narasimhan, B., Kim, K. K., & Pack, D. W. (2004). Microsphere size, precipitation kinetics and drug distribution control drug release from biodegradable polyanhydride microspheres. Journal of Controlled Release, 94(1),
Polymeric hydrogels are of special importance in polymeric biomaterials because of
 POLYMERIC HYDROGELS Polymeric hydrogels are of special importance in polymeric biomaterials because of their favorable biocompatibility. Hydrogels are cross-linked macromolecular networks formed by hydrophilic
POLYMERIC HYDROGELS Polymeric hydrogels are of special importance in polymeric biomaterials because of their favorable biocompatibility. Hydrogels are cross-linked macromolecular networks formed by hydrophilic
Experiment 11. DNA Composition by HPLC 1,2
 Experiment 11 DNA Composition by HPLC 1,2 Introduction This experiment illustrates quantitative analysis by high performance liquid chromatography and biochemical methods of sample preparation. The sample
Experiment 11 DNA Composition by HPLC 1,2 Introduction This experiment illustrates quantitative analysis by high performance liquid chromatography and biochemical methods of sample preparation. The sample
BME Polymer Lab
 BME 383 - Polymer Lab Background Information Hydrogels, which are water-swollen, cross-linked polymer networks, have emerged as an important class of materials in biomedical engineering. Methods of preparation
BME 383 - Polymer Lab Background Information Hydrogels, which are water-swollen, cross-linked polymer networks, have emerged as an important class of materials in biomedical engineering. Methods of preparation
Supplementary Figure S1. Swelling and mechanical properties as a function of the PS-b- PAA block copolymer composition. a, Swelling kinetics of PAA
 Supplementary Figure S1. Swelling and mechanical properties as a function of the PS-b- PAA block copolymer composition. a, Swelling kinetics of PAA homopolymer and PS-b-PAAs (4 mm disc with 1 mm thickness)
Supplementary Figure S1. Swelling and mechanical properties as a function of the PS-b- PAA block copolymer composition. a, Swelling kinetics of PAA homopolymer and PS-b-PAAs (4 mm disc with 1 mm thickness)
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Controlled drug delivery systems, which are intended to deliver drugs at predetermined rates for predefined periods of time, have been used to overcome the shortcomings of conventional
Chapter 1 Introduction Controlled drug delivery systems, which are intended to deliver drugs at predetermined rates for predefined periods of time, have been used to overcome the shortcomings of conventional
The research work highlights the development and evaluation of. bioavailability of drugs. The buccal route can bypass the first-pass
 212 9. Summary, conclusion and recommendation 9.1 Summary and conclusion The research work highlights the development and evaluation of novel transbuccal drug antagonist of Famotidine. route have a rapid
212 9. Summary, conclusion and recommendation 9.1 Summary and conclusion The research work highlights the development and evaluation of novel transbuccal drug antagonist of Famotidine. route have a rapid
nanoprecipitation mpeg-pla 2 nd Emulsion mpeg-pla in DCM
 THERAPEUTIC NANOTECHNOLOGY LAB MODULE Location: BioNano Lab, 3119 Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory (MNTL) Instructor: Jianjun Cheng, Assistant Professor of Materials Science and Engineering Lab Assistants:
THERAPEUTIC NANOTECHNOLOGY LAB MODULE Location: BioNano Lab, 3119 Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory (MNTL) Instructor: Jianjun Cheng, Assistant Professor of Materials Science and Engineering Lab Assistants:
VitroGel ready-to-use tunable hydrogel for 3D cell culture and beyond
 VitroGel ready-to-use tunable hydrogel for 3D cell culture and beyond Cat No: TWG001 VItroGel 3D (10 ml high concentration) Cat No: TWG002 VitroGel 3D-RGD (10 ml high concentration) Handbook Rev. June
VitroGel ready-to-use tunable hydrogel for 3D cell culture and beyond Cat No: TWG001 VItroGel 3D (10 ml high concentration) Cat No: TWG002 VitroGel 3D-RGD (10 ml high concentration) Handbook Rev. June
Thermoresponsive Membranes from Electrospun. Mats with Switchable Wettability for Efficient
 Thermoresponsive Membranes from Electrospun Mats with Switchable Wettability for Efficient Oil/Water Separations Yan Liu, a,b Sinem Tas, b Kaihuan Zhang, b, Wiebe M. de Vos, c Jinghong Ma, a,* and G. Julius
Thermoresponsive Membranes from Electrospun Mats with Switchable Wettability for Efficient Oil/Water Separations Yan Liu, a,b Sinem Tas, b Kaihuan Zhang, b, Wiebe M. de Vos, c Jinghong Ma, a,* and G. Julius
Controlled Release Drug Delivery from Hydrogels
 Controlled Release Drug Delivery from Hydrogels Teacher s Guide Keith Neeves CSIP Graduate Fellow Cornell University 1 Overview The objective of this project is to introduce students to the concepts of
Controlled Release Drug Delivery from Hydrogels Teacher s Guide Keith Neeves CSIP Graduate Fellow Cornell University 1 Overview The objective of this project is to introduce students to the concepts of
EXPERIMENT 5. Molecular Absorption Spectroscopy: Determination of Iron with 1,10-Phenanthroline
 EXPERIMENT 5 Molecular Absorption Spectroscopy: Determination of Iron with 1,10-Phenanthroline UNKNOWN Submit a clean, labeled 100-mL volumetric flask to the instructor so that your unknown iron solution
EXPERIMENT 5 Molecular Absorption Spectroscopy: Determination of Iron with 1,10-Phenanthroline UNKNOWN Submit a clean, labeled 100-mL volumetric flask to the instructor so that your unknown iron solution
SensoLyte AMC Calpain Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte AMC Calpain Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72150 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect calpain activity Enhanced Value: It provides
SensoLyte AMC Calpain Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72150 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect calpain activity Enhanced Value: It provides
DNA Purification Magnetic Beads
 DNA Purification Magnetic Beads Catalog #: 801-109 User Manual Last revised December 17 th, 2018 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information enclosed ISO 13485 Certified 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 100 Norcross,
DNA Purification Magnetic Beads Catalog #: 801-109 User Manual Last revised December 17 th, 2018 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information enclosed ISO 13485 Certified 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 100 Norcross,
Applications of self-assembling peptides in controlled drug delivery
 Applications of self-assembling peptides in controlled drug delivery Sotirios Koutsopoulos, Ph.D. Problems associated with drug administration Drug concentration in blood C toxic C effective Time 1 The
Applications of self-assembling peptides in controlled drug delivery Sotirios Koutsopoulos, Ph.D. Problems associated with drug administration Drug concentration in blood C toxic C effective Time 1 The
Soft Fabrication and Polymers
 Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices Soft Fabrication and Polymers Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/ R012408
Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices Soft Fabrication and Polymers Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/ R012408
THE DISSOLUTION PROCEDURE: DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION
 THE DISSOLUTION PROCEDURE: DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION Pharmacopeial Forum Vol. 31(5)(Sept.-Oct. 2005) By : Mr. Seubpong Kumpusiri Mrs. Patima Maneesatid 26 May 2006 THE DISSOLUTION PROCEDURE: DEVELOPMENT
THE DISSOLUTION PROCEDURE: DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION Pharmacopeial Forum Vol. 31(5)(Sept.-Oct. 2005) By : Mr. Seubpong Kumpusiri Mrs. Patima Maneesatid 26 May 2006 THE DISSOLUTION PROCEDURE: DEVELOPMENT
Chem 2115 Experiment #9. Consumer Chemistry: Determining the Iron Content in Supplements
 Chem 2115 Experiment #9 Consumer Chemistry: Determining the Iron Content in Supplements OBJECTIVE: The goal of this experiment is to use the quantitative technique of spectrophotometry to determine the
Chem 2115 Experiment #9 Consumer Chemistry: Determining the Iron Content in Supplements OBJECTIVE: The goal of this experiment is to use the quantitative technique of spectrophotometry to determine the
Swelling Behavior of Acrylamide-2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate Hydrogels
 Turk J Chem 24 (2000), 147 156. c TÜBİTAK Swelling Behavior of Acrylamide-2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate Hydrogels Belma IŞIK Hacettepe University, Chemistry Department, 06532, Beytepe, Ankara-TURKEY Received
Turk J Chem 24 (2000), 147 156. c TÜBİTAK Swelling Behavior of Acrylamide-2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate Hydrogels Belma IŞIK Hacettepe University, Chemistry Department, 06532, Beytepe, Ankara-TURKEY Received
International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research
 International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research www.ijipsr.com SMART POLYMERS: A SMART APPROACH FOR DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS 1 Devendra G. Kapadnis*, 1 Mahendra G. Sonule, 1 Dhiraj
International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research www.ijipsr.com SMART POLYMERS: A SMART APPROACH FOR DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS 1 Devendra G. Kapadnis*, 1 Mahendra G. Sonule, 1 Dhiraj
AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72053 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate 5-FAM SE (5-carboxyfluorescein) to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72053 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate 5-FAM SE (5-carboxyfluorescein) to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
NETosis Assay Kit. Item No Customer Service Technical Support
 NETosis Kit Item No. 601010 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied
NETosis Kit Item No. 601010 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 750 Microscale Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 750 Microscale Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72044 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 750 SE to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 750 Microscale Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72044 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 750 SE to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample
Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ashley B. Allen, Hazel Y. Stevens, Robert E. Guldberg. Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA. Disclosures:
Cross-Linker Modulation to Maintain Phenotype of RGD-Alginate-Embedded Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ashley B. Allen, Hazel Y. Stevens, Robert E. Guldberg. Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA. Disclosures:
MST Starting Guide Monolith NT.115
 MST Starting Guide Monolith NT.115 Contents 1. How to design an experiment 2. Before you start 3. Assay Setup Pretests 4. Assay Setup 5. MST-experiment using temperature control 6. Data Interpretation
MST Starting Guide Monolith NT.115 Contents 1. How to design an experiment 2. Before you start 3. Assay Setup Pretests 4. Assay Setup 5. MST-experiment using temperature control 6. Data Interpretation
Robert Wiegmann, Yiyun Zhang, Alexander Yarin. 31 July Contact:
 Investigation of flow through P[NIPAM/MMA] copolymer coated glass capillary tubes, and glass copolymer adhesion improvements with hydrofluoric acid etching Robert Wiegmann, Yiyun Zhang, Alexander Yarin
Investigation of flow through P[NIPAM/MMA] copolymer coated glass capillary tubes, and glass copolymer adhesion improvements with hydrofluoric acid etching Robert Wiegmann, Yiyun Zhang, Alexander Yarin
Zinc Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 1 15ppm
 Document: AND Zinc 100 10 2012 Zinc Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 1 15ppm October, 2012 Edition 2 ANDalyze, Inc., 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in USA. Table of
Document: AND Zinc 100 10 2012 Zinc Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 1 15ppm October, 2012 Edition 2 ANDalyze, Inc., 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in USA. Table of
Uranium Testing and Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 2 60ppb
 Document: AND Uranium 100 10 2012 Uranium Testing and Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 2 60ppb October, 2012 Edition 1 ANDalyze, Inc., 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in USA. Table
Document: AND Uranium 100 10 2012 Uranium Testing and Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 2 60ppb October, 2012 Edition 1 ANDalyze, Inc., 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in USA. Table
Experimental Characterisation of the Alginate Gelation Process for Rapid Prototyping
 Experimental Characterisation of the Alginate Gelation Process for Rapid Prototyping R.A. Rezende 1,2, P.J. Bártolo 1, A. Mendes 1, R. Maciel Filho 2 1 Centre for Rapid and Sustainable Product Development
Experimental Characterisation of the Alginate Gelation Process for Rapid Prototyping R.A. Rezende 1,2, P.J. Bártolo 1, A. Mendes 1, R. Maciel Filho 2 1 Centre for Rapid and Sustainable Product Development
BIODEGRADABLE HYDROGEL- ANALYZING THE IMPACT AND SENSITIVITY OF TEMPERATURE AND ph CHANGE
 BIODEGRADABLE HYDROGEL- ANALYZING THE IMPACT AND SENSITIVITY OF TEMPERATURE AND ph CHANGE Aayush Goel Department of Polymer Science Chemical Technology Delhi Technological University (Formerly Delhi College
BIODEGRADABLE HYDROGEL- ANALYZING THE IMPACT AND SENSITIVITY OF TEMPERATURE AND ph CHANGE Aayush Goel Department of Polymer Science Chemical Technology Delhi Technological University (Formerly Delhi College
Institute of Science & Technology in Medicine Control of Substance Hazardous to Health COSHH assessment
 Institute of Science & Technology in Medicine Control of Substance Hazardous to Health COSHH assessment Title of Experiment/Procedure: Cell counting and viability using FACS, counting beads and propidium
Institute of Science & Technology in Medicine Control of Substance Hazardous to Health COSHH assessment Title of Experiment/Procedure: Cell counting and viability using FACS, counting beads and propidium
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72049 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 647 SE to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72049 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 647 SE to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
Regenerez Degradation and Release Kinetics White Paper
 R Regenerez Degradation and Release Kinetics White Paper A White Paper by Carissa Smoot, Scientist, Secant Group, Jeremy Harris, Ph.D, Secant Group and Stephanie Reed, Ph.D, Secant Group Introduction Implantable
R Regenerez Degradation and Release Kinetics White Paper A White Paper by Carissa Smoot, Scientist, Secant Group, Jeremy Harris, Ph.D, Secant Group and Stephanie Reed, Ph.D, Secant Group Introduction Implantable
Swelling Behavior Study of γ-irradiated Gelatin Hydrogels Prepared in Organic/Aqueous Mixtures
 J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 13, No. 6, (2007) 997-1001 Swelling Behavior Study of γ-irradiated Gelatin Hydrogels Prepared in Organic/Aqueous Mixtures Junhwa Shin, Youn Mook Lim, Joon-Pyo Jeun, and Young Chang
J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 13, No. 6, (2007) 997-1001 Swelling Behavior Study of γ-irradiated Gelatin Hydrogels Prepared in Organic/Aqueous Mixtures Junhwa Shin, Youn Mook Lim, Joon-Pyo Jeun, and Young Chang
MyBioSource.com. Human Vitamin K2 ELISA USER INSTRUCTION
 Human Vitamin K2 ELISA USER INSTRUCTION Cat.No MBS163021 Standard Curve Range: 5ng/ml - 1000ng/ml Sensitivity: 2.52ng/ml Size: 96 wells Storage: Store the reagents at 2-8 C. For over 6-month storage refer
Human Vitamin K2 ELISA USER INSTRUCTION Cat.No MBS163021 Standard Curve Range: 5ng/ml - 1000ng/ml Sensitivity: 2.52ng/ml Size: 96 wells Storage: Store the reagents at 2-8 C. For over 6-month storage refer
MyBioSource.com. Human Osteoprotegerin ELISA USER INSTRUCTION
 Human Osteoprotegerin ELISA USER INSTRUCTION Cat.No MBS162588 Standard Curve Range: 0.05ng/ml - 15ng/ml Sensitivity: 0.023ng/ml Size: 96 wells Storage: Store the reagents at 2-8 C. For over 6-month storage
Human Osteoprotegerin ELISA USER INSTRUCTION Cat.No MBS162588 Standard Curve Range: 0.05ng/ml - 15ng/ml Sensitivity: 0.023ng/ml Size: 96 wells Storage: Store the reagents at 2-8 C. For over 6-month storage
MyBioSource.com. Rat Hydroxyproline ELISA USER INSTRUCTION
 Rat Hydroxyproline ELISA USER INSTRUCTION Cat.No MBS162747 Standard Curve Range: 10ng/L - 4000ng/L Sensitivity: 4.99ng/L Size: 96 wells Storage: Store the reagents at 2-8 C. For over 6-month storage refer
Rat Hydroxyproline ELISA USER INSTRUCTION Cat.No MBS162747 Standard Curve Range: 10ng/L - 4000ng/L Sensitivity: 4.99ng/L Size: 96 wells Storage: Store the reagents at 2-8 C. For over 6-month storage refer
1. Methacrylated poly(lactic acid) functionalized poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) 2. Methacrylated sebacic acid
 LAB MODULE 2: Materials Degradation Surface vs. Bulk In this lab students will investigate how polymeric chemical structure can be used to control the degradation properties of the crosslinked network.
LAB MODULE 2: Materials Degradation Surface vs. Bulk In this lab students will investigate how polymeric chemical structure can be used to control the degradation properties of the crosslinked network.
Multiwell plates loaded with fluorescent hydrogel sensors for
 Multiwell plates loaded with fluorescent hydrogel sensors for measuring ph and glucose concentration Boaz Vilozny, Alexander Schiller, a * Ritchie A. Wessling, and Bakthan Singaram* Department of Chemistry
Multiwell plates loaded with fluorescent hydrogel sensors for measuring ph and glucose concentration Boaz Vilozny, Alexander Schiller, a * Ritchie A. Wessling, and Bakthan Singaram* Department of Chemistry
Environmental Water Testing: Surface Water, Groundwater, Hard Water, Wastewater, & Seawater
 Document: AND Sol Env 08 2013 Environmental Water Testing: Surface Water, Groundwater, Hard Water, Wastewater, & Seawater Matrix specific sample preparation and testing methods for environmental waters
Document: AND Sol Env 08 2013 Environmental Water Testing: Surface Water, Groundwater, Hard Water, Wastewater, & Seawater Matrix specific sample preparation and testing methods for environmental waters
Oral Delivery of Drugs
 Oral Delivery of Drugs 1 S E S S I O N O N E O F T I P P R O J E C T Advantages of taking oral drugs Convenient (storage, portability, premeasured dose) economical non-invasive, often safer route requires
Oral Delivery of Drugs 1 S E S S I O N O N E O F T I P P R O J E C T Advantages of taking oral drugs Convenient (storage, portability, premeasured dose) economical non-invasive, often safer route requires
SAMPLE LITERATURE Please refer to included weblink for correct version.
 REVISED & UPDATED Edvo-Kit #269 Introduction to ELISA Reactions Experiment Objective: This experiment introduces concepts and methodologies of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). See page 3 for
REVISED & UPDATED Edvo-Kit #269 Introduction to ELISA Reactions Experiment Objective: This experiment introduces concepts and methodologies of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). See page 3 for
Enzyme-mediated preparation of hydrogels composed of poly(ethylene glycol) and gelatin as cell culture platforms
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances Enzyme-mediated preparation of hydrogels composed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances Enzyme-mediated preparation of hydrogels composed
RayBio Genomic DNA Magnetic Beads Kit
 RayBio Genomic DNA Magnetic Beads Kit Catalog #: 801-112 User Manual Last revised January 4 th, 2017 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information enclosed ISO 13485 Certified 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 100
RayBio Genomic DNA Magnetic Beads Kit Catalog #: 801-112 User Manual Last revised January 4 th, 2017 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information enclosed ISO 13485 Certified 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 100
Effect of Nanofiber Morphology on PVDF Air Filter Performance
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Effect of Nanofiber Morphology on PVDF Air Filter Performance Andrew
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Effect of Nanofiber Morphology on PVDF Air Filter Performance Andrew
IgG1 (Mouse) ELISA Kit
 IgG1 (Mouse) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA1011 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
IgG1 (Mouse) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA1011 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
Cadmium Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: ppm
 Document: AND016 04 2014 Cadmium Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 0.1 1.0ppm April, 2014 Edition 3 ANDalyze, Inc., 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in USA. Table of
Document: AND016 04 2014 Cadmium Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 0.1 1.0ppm April, 2014 Edition 3 ANDalyze, Inc., 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in USA. Table of
Implantable hydrogel beads entrapping PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres: Exploring the effects of nearzero-order drug release for intracranial chemotherapy
 Implantable hydrogel beads entrapping PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres: Exploring the effects of nearzero-order drug release for intracranial chemotherapy Abstract ID: 123910 Sudhir H. Ranganath, Alvin Yang,
Implantable hydrogel beads entrapping PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres: Exploring the effects of nearzero-order drug release for intracranial chemotherapy Abstract ID: 123910 Sudhir H. Ranganath, Alvin Yang,
BIODEGRADABLE INJECTABLE IMPLANT SYSTEMS FOR SUSTAINED DELIVERY USING POLY (LACTIDE-CO-GLYCOLIDE) COPOLYMERS
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article BIODEGRADABLE INJECTABLE IMPLANT SYSTEMS FOR SUSTAINED DELIVERY USING POLY (LACTIDE-CO-GLYCOLIDE)
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article BIODEGRADABLE INJECTABLE IMPLANT SYSTEMS FOR SUSTAINED DELIVERY USING POLY (LACTIDE-CO-GLYCOLIDE)
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 555 Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 555 Protein Labeling Kit Revision number: 1.3 Last updated: April 2018 Catalog # AS-72045 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 555 SE to
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 555 Protein Labeling Kit Revision number: 1.3 Last updated: April 2018 Catalog # AS-72045 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 555 SE to
NIDS DIY Digoxigenin-NHS Antibody Labeling Kit
 ANP Technologies Inc. Part no. 90-1024-01 For Research Use Only This procedure must be read in its entirety before using this product Intended use The purpose of the kit is to provide a rapid way to efficiently
ANP Technologies Inc. Part no. 90-1024-01 For Research Use Only This procedure must be read in its entirety before using this product Intended use The purpose of the kit is to provide a rapid way to efficiently
Rat / Mouse Amylin EIA Kit
 Rat / Mouse Amylin EIA Kit Catalog No: IRAPKT2052 Lot No: SAMPLE INTENDED USE This Enzyme Immunoassay kit is designed to detect a specific peptide and its related peptides based on the principle of competitive
Rat / Mouse Amylin EIA Kit Catalog No: IRAPKT2052 Lot No: SAMPLE INTENDED USE This Enzyme Immunoassay kit is designed to detect a specific peptide and its related peptides based on the principle of competitive
Evaluating Microplate Detection Instruments
 AppNote Evaluating Microplate Detection Instruments Introduction Important features to consider when evaluating a microplate reader are the following: sensitivity, dynamic range, throughput, integration
AppNote Evaluating Microplate Detection Instruments Introduction Important features to consider when evaluating a microplate reader are the following: sensitivity, dynamic range, throughput, integration
Get the most out of Pure PRP
 Get the most out of Pure PRP The Basic Science of PRP Platelets are small non-nucleated bodies in peripheral blood known for role in hemostasis Platelets contain proteins, cytokines & other bioactive factors
Get the most out of Pure PRP The Basic Science of PRP Platelets are small non-nucleated bodies in peripheral blood known for role in hemostasis Platelets contain proteins, cytokines & other bioactive factors
Electrospinning and Polarization of PVDF Fiber Mats for Adsorption of NaCl
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Electrospinning and Polarization of PVDF Fiber Mats for Adsorption of NaCl Michael
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Electrospinning and Polarization of PVDF Fiber Mats for Adsorption of NaCl Michael
Alanine Transaminase ELISA Kit
 Alanine Transaminase ELISA Kit Cat.No: CEIA-H005 Lot. No. (See product label) Intended Use The Alanine Transaminase Assay Kit provides a convenient method of detecting ALT activity in serum, plasma, tissue
Alanine Transaminase ELISA Kit Cat.No: CEIA-H005 Lot. No. (See product label) Intended Use The Alanine Transaminase Assay Kit provides a convenient method of detecting ALT activity in serum, plasma, tissue
Human CRP Precoated ELISA kit
 Absorption 450 nm CL76153K-48/CL76153K-96 Human CRP Precoated ELISA kit Product Description: 2.4 The Human CRP ELISA kit is to be used for the in-vitro quantitative determination of CRP in human serum,
Absorption 450 nm CL76153K-48/CL76153K-96 Human CRP Precoated ELISA kit Product Description: 2.4 The Human CRP ELISA kit is to be used for the in-vitro quantitative determination of CRP in human serum,
or A. thaliana). After cell lysis is complete, centrifugation, the Bradford assay, and possibly
 BIOSC147: Lab 3c Use of protein extraction, purification and quantitation of with spectrophotometry and standard curves to investigate protein expression, structure, and function. Cell lysis to generate
BIOSC147: Lab 3c Use of protein extraction, purification and quantitation of with spectrophotometry and standard curves to investigate protein expression, structure, and function. Cell lysis to generate
Procine CRP ELISA Kit
 Procine CRP ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Procine C-Reactive Protein concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Procine CRP ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Procine C-Reactive Protein concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Guinea pig PGI2 ELISA Kit
 Guinea pig PGI2 ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Guinea pig PGI2 concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY.
Guinea pig PGI2 ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Guinea pig PGI2 concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY.
Canine PHA ELISA Kit
 Canine PHA ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Canine Phytohaemagglutinin concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE
Canine PHA ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Canine Phytohaemagglutinin concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE
Human LENK ELISA Kit
 Human LENK ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Human Leu-enkephalin concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY.
Human LENK ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Human Leu-enkephalin concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY.
Human High sensitivity C Reactive Protein ELISA KIT
 Distribuito in ITALIA da Li StarFish S.r.l. Via Cavour, 35 20063 Cernusco S/N (MI) telefono 02-92150794 fax 02-92157285 info@listarfish.it www.listarfish.it Optimize Your Research Human High sensitivity
Distribuito in ITALIA da Li StarFish S.r.l. Via Cavour, 35 20063 Cernusco S/N (MI) telefono 02-92150794 fax 02-92157285 info@listarfish.it www.listarfish.it Optimize Your Research Human High sensitivity
Mouse RF IgM ELISA Kit
 Mouse RF IgM ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Mouse rheumatoid factor IgM concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Mouse RF IgM ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Mouse rheumatoid factor IgM concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Chicken VEGF ELISA Kit
 Chicken VEGF ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Chicken Vascular Endothelial cell Growth Factor concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR
Chicken VEGF ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Chicken Vascular Endothelial cell Growth Factor concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR
ADVANCED ELECTROPHORESIS
 Ref. ELECAVANZADA (4 practices) 1. EXPERIMENT OBJETIVE ADVANCED ELECTROPHORESIS The aim of this experiment is to introduce students to the knowledge of electrophoretic theory and to familiarize themselves
Ref. ELECAVANZADA (4 practices) 1. EXPERIMENT OBJETIVE ADVANCED ELECTROPHORESIS The aim of this experiment is to introduce students to the knowledge of electrophoretic theory and to familiarize themselves
Rat GLO ELISA Kit. For the quantitative in vitro determination of Rat Glyoxalase concentrations in
 Rat GLO ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Rat Glyoxalase concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR
Rat GLO ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Rat Glyoxalase concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR
CHAPTER 4 WATER ABSORPTION BEHAVIOR AND ACCELERATED AGING EFFECTS
 1 CHAPTER WATER ABSORPTION BEHAVIOR AND ACCELERATED AGING EFFECTS.1 INTRODUCTION The mechanical properties of the polymer matrix composites depend on the properties of their constituents and their interaction
1 CHAPTER WATER ABSORPTION BEHAVIOR AND ACCELERATED AGING EFFECTS.1 INTRODUCTION The mechanical properties of the polymer matrix composites depend on the properties of their constituents and their interaction
Bovine IgG-Ab ELISA Kit
 Bovine IgG-Ab ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Bovine Immunoglobulin G Antibody concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Bovine IgG-Ab ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Bovine Immunoglobulin G Antibody concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Validation of a Dual Wavelength Size Exclusion HPLC Method with Improved Sensitivity to Detect Aggregates of a Monoclonal Antibody Biotherapeutic
 Validation of a Dual Wavelength Size Exclusion HPLC Method with Improved Sensitivity to Detect Aggregates of a Monoclonal Antibody Biotherapeutic By J. Tompkins1, T. Spurgeon 1, R. Tobias 1, J. Anders1,
Validation of a Dual Wavelength Size Exclusion HPLC Method with Improved Sensitivity to Detect Aggregates of a Monoclonal Antibody Biotherapeutic By J. Tompkins1, T. Spurgeon 1, R. Tobias 1, J. Anders1,
Guinea pig TIMP-1 ELISA Kit
 Guinea pig TIMP-1 ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Guinea pig tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase 1 concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body
Guinea pig TIMP-1 ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Guinea pig tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase 1 concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body
Human CoxV-A16 ELISA Kit
 Human CoxV-A16 ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Human Coxsackie virus A16 concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Human CoxV-A16 ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Human Coxsackie virus A16 concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Guinea pig Hyp ELISA Kit
 Guinea pig Hyp ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Guinea pig hydroxyproline concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Guinea pig Hyp ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Guinea pig hydroxyproline concentrations in serum - plasma - celiac fluid - tissue homogenate - body fluid FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 488 Microscale Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 488 Microscale Protein Labeling Kit Revision number: 1.3 Last updated: April 2018 Catalog # AS-72048 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 488 Microscale Protein Labeling Kit Revision number: 1.3 Last updated: April 2018 Catalog # AS-72048 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor
Human CTRP5 ELISA Kit
 Human CTRP5 ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Human C1q And Tumor Necrosis Factor Related Protein 5 concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids
Human CTRP5 ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Human C1q And Tumor Necrosis Factor Related Protein 5 concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids
Complete kit for the systematic 3-D conformational comparability analysis of Simponi biosimilar molecule to Golimumab (Simponi trade name).
 GoliBridge ELISA Kit 1 Plate Kit Catalog # AB000215 Complete kit for the systematic 3-D conformational comparability analysis of Simponi biosimilar molecule to Golimumab (Simponi trade name). Please read
GoliBridge ELISA Kit 1 Plate Kit Catalog # AB000215 Complete kit for the systematic 3-D conformational comparability analysis of Simponi biosimilar molecule to Golimumab (Simponi trade name). Please read
Kit Components Product # (50 samples) Wash Solution A Elution Buffer B
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cells and Tissue DNA Isolation Kit Product # 53100 Product Insert
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cells and Tissue DNA Isolation Kit Product # 53100 Product Insert
INTERDISCIPLINARY INVESTIGATION (IDI)-LAB LABORATORY HANDOUT
 INTERDISCIPLINARY INVESTIGATION (IDI)-LAB LABORATORY HANDOUT Research-based Interdisciplinary Science Education ION CHROMATOGRAPHY TO INVESTIGATE WATER QUALITY ISSUES: FLUORIDE IN DRINKING WATER Introduction
INTERDISCIPLINARY INVESTIGATION (IDI)-LAB LABORATORY HANDOUT Research-based Interdisciplinary Science Education ION CHROMATOGRAPHY TO INVESTIGATE WATER QUALITY ISSUES: FLUORIDE IN DRINKING WATER Introduction
Monkey hs-tnt ELISA Kit
 Monkey hs-tnt ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Monkey Hypersensitive troponin T concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Monkey hs-tnt ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Monkey Hypersensitive troponin T concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH
Determination of the Mass Percentage of Copper in a Penny
 Determination of the Mass Percentage of Copper in a Penny Introduction This experiment will cost you one penny ($0.01). The penny must be minted after 1983. Any penny will do; for best results the penny
Determination of the Mass Percentage of Copper in a Penny Introduction This experiment will cost you one penny ($0.01). The penny must be minted after 1983. Any penny will do; for best results the penny
PHARMACEUTICAL PRINCIPLES OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS
 PHARMACEUTICAL PRINCIPLES OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS J. T. Carstensen, Ph.D. Professor of Pharmacy University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin TECHNOMIC ^PUBLISHING CO.. INC J 1.ANCASTER BASET, TABLE OF CONTENTS
PHARMACEUTICAL PRINCIPLES OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS J. T. Carstensen, Ph.D. Professor of Pharmacy University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin TECHNOMIC ^PUBLISHING CO.. INC J 1.ANCASTER BASET, TABLE OF CONTENTS
Guinea pig 25-OH-VD ELISA Kit
 Guinea pig 25-OH-VD ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Guinea pig 25-Dihydroxy vitamin D concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids FOR LABORATORY
Guinea pig 25-OH-VD ELISA Kit For the quantitative in vitro determination of Guinea pig 25-Dihydroxy vitamin D concentrations in serum - plasma - tissue homogenates - other biological fluids FOR LABORATORY
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Label-Free Detection of Tear Biomarkers Using Hydrogel Coated Gold Nanoshells in a Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based Biosensor Heidi R. Culver a,b,, Marissa E. Wechsler a,b,,
Supporting Information Label-Free Detection of Tear Biomarkers Using Hydrogel Coated Gold Nanoshells in a Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based Biosensor Heidi R. Culver a,b,, Marissa E. Wechsler a,b,,
Polyhexamethylene Biguanide Release by Chitosan-Heparin Nanoparticles
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2018 Polyhexamethylene Biguanide Release by Chitosan-Heparin Nanoparticles
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2018 Polyhexamethylene Biguanide Release by Chitosan-Heparin Nanoparticles
Human IgG ELISA Kit. Strip well format. Reagents for up to 96 tests
 Human IgG ELISA Kit Strip well format. Reagents for up to 96 tests Catalog No. CS222A Quantity: 1 x 96 tests CS222B 5 x 96 tests Intended Use: Background: Assay Principle: This human immunoglobulin G antigen
Human IgG ELISA Kit Strip well format. Reagents for up to 96 tests Catalog No. CS222A Quantity: 1 x 96 tests CS222B 5 x 96 tests Intended Use: Background: Assay Principle: This human immunoglobulin G antigen
4.4 MICROBIOLOGICAL METHOD FOR THE ESTIMATION OF. The microbiological assay was performed by using the test
 109 4.4 MICROBIOLOGICAL METHOD FOR THE ESTIMATION OF AMOXICILLIN The microbiological assay was performed by using the test organism Staphylococcus aureus. The strain was isolated from soil and allowed
109 4.4 MICROBIOLOGICAL METHOD FOR THE ESTIMATION OF AMOXICILLIN The microbiological assay was performed by using the test organism Staphylococcus aureus. The strain was isolated from soil and allowed
HUMAN LBP Quantification ELISA
 HUMAN LBP Quantification ELISA For the quantitative determination of natural and recombinant human LBP in serum, plasma and culture medium Cat. No. KT-1004 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic
HUMAN LBP Quantification ELISA For the quantitative determination of natural and recombinant human LBP in serum, plasma and culture medium Cat. No. KT-1004 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic
Quantify protein stability with ΔG
 Technical Note Quantify protein stability with ΔG Introduction Biologics stability determinations often rely on forced degradation methods to rank constructs or optimize formulations. The most well-established
Technical Note Quantify protein stability with ΔG Introduction Biologics stability determinations often rely on forced degradation methods to rank constructs or optimize formulations. The most well-established
Human Fibrinogen Antigen Assay
 Catalog # FIBKT 0 Human Fibrinogen Antigen Assay Strip well format. Reagents for up to 96 tests. For Research Use Only. INTENDED USE This human fibrinogen antigen assay is intended for the quantitative
Catalog # FIBKT 0 Human Fibrinogen Antigen Assay Strip well format. Reagents for up to 96 tests. For Research Use Only. INTENDED USE This human fibrinogen antigen assay is intended for the quantitative
igem 2018 InterLab Study Protocol Before You Begin
 igem 2018 InterLab Study Protocol Before You Begin Read through this entire protocol sheet carefully before you start your experiment and prepare any materials you may need. In order to improve reproducibility,
igem 2018 InterLab Study Protocol Before You Begin Read through this entire protocol sheet carefully before you start your experiment and prepare any materials you may need. In order to improve reproducibility,
NADP + /NADPH Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 Product Manual NADP + /NADPH Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number MET-5018 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Product Manual NADP + /NADPH Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number MET-5018 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Innovative Materials and Separations Science
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC 2006 Conference Proceedings 7-20-2006 Innovative Materials and Separations Science William L. Bourcier et al. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Follow
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC 2006 Conference Proceedings 7-20-2006 Innovative Materials and Separations Science William L. Bourcier et al. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Follow
BIOO RESEARCH PRODUCTS. Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) Color Endpoint Assay Kit Manual Catalog #:
 BIOO RESEARCH PRODUCTS Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) Color Endpoint Assay Kit Manual Catalog #: 3460-09 BIOO Scientific Corp. 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Procedure
BIOO RESEARCH PRODUCTS Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) Color Endpoint Assay Kit Manual Catalog #: 3460-09 BIOO Scientific Corp. 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Procedure
LavaDigest Protease Monitoring Kit
 LavaDigest Protease Monitoring Kit Ordering LP-031020 LavaDigest protease monitoring kit for up to 2000 assays Order from http://www.fluorotechnics.com.au L.avaDigest Protocol March 2013 Content 2 LavaDigest
LavaDigest Protease Monitoring Kit Ordering LP-031020 LavaDigest protease monitoring kit for up to 2000 assays Order from http://www.fluorotechnics.com.au L.avaDigest Protocol March 2013 Content 2 LavaDigest
Product datasheet. Note: This protocol was modified as of July All previous protocols are obsolete.
 Product datasheet Note: This protocol was modified as of July 2017. All previous protocols are obsolete. Human GM-CSF ELISA Kit Product #: 0008 Storage recommendations Store the kit at 2-8 C. The kit is
Product datasheet Note: This protocol was modified as of July 2017. All previous protocols are obsolete. Human GM-CSF ELISA Kit Product #: 0008 Storage recommendations Store the kit at 2-8 C. The kit is
Benzothiazole Sulfinate: a Water Soluble and Slow Releasing Sulfur Dioxide Donor
 Benzothiazole Sulfinate: a Water Soluble and Slow Releasing Sulfur Dioxide Donor Supporting Information Jacob J. Day, a, Zhenhua Yang, b, Wei Chen, a Armando Pacheco, a and Ming Xian a,b, * a Department
Benzothiazole Sulfinate: a Water Soluble and Slow Releasing Sulfur Dioxide Donor Supporting Information Jacob J. Day, a, Zhenhua Yang, b, Wei Chen, a Armando Pacheco, a and Ming Xian a,b, * a Department
Product datasheet. Storage recommendations Store the kit at 2-8 C. The kit is stable for a period of up to 3 months from the date of receipt.
 Product datasheet Human VEGF-A ELISA Kit Product #: 0028 Storage recommendations Store the kit at 2-8 C. The kit is stable for a period of up to 3 months from the date of receipt. Description This human
Product datasheet Human VEGF-A ELISA Kit Product #: 0028 Storage recommendations Store the kit at 2-8 C. The kit is stable for a period of up to 3 months from the date of receipt. Description This human
HCT-116 InstaCell Proliferation Assay with XTT - CE-111
 HCT-116 InstaCell Proliferation Assay with XTT - CE-111 Background With InstaCell Proliferation Assays you gain a tool that will help you to increase the efficacy in your screenings. The ready-touse assay
HCT-116 InstaCell Proliferation Assay with XTT - CE-111 Background With InstaCell Proliferation Assays you gain a tool that will help you to increase the efficacy in your screenings. The ready-touse assay
E.Z.N.A. HP Viral RNA/DNA Kit. R preps R preps
 E.Z.N.A. HP Viral RNA/DNA Kit R6873-00 5 preps R6873-01 50 preps August 2013 E.Z.N.A. HP Viral RNA/DNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Preparing
E.Z.N.A. HP Viral RNA/DNA Kit R6873-00 5 preps R6873-01 50 preps August 2013 E.Z.N.A. HP Viral RNA/DNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Preparing
4. PREPARATION OF GELATIN MICROSPHERES. Intra-articular delivery of drug loaded microspheres has been developed by
 64 4. PREPARATION OF GELATIN MICROSPHERES Intra-articular delivery of drug loaded microspheres has been developed by many authors (Ratcliffe et al., 1987; Pavanetto et al., 1994; Tuncay et al., 2000a;
64 4. PREPARATION OF GELATIN MICROSPHERES Intra-articular delivery of drug loaded microspheres has been developed by many authors (Ratcliffe et al., 1987; Pavanetto et al., 1994; Tuncay et al., 2000a;
