Subcellular fractionation of dystrophin to the triads of skeletal muscle
|
|
|
- Bertram Lang
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 754 Subcellular fractionation of dystrophin to the triads of skeletal muscle Eric P. Hoffman*, C. Michael Knudson, Kevin P. Campbell & Louis M. Kunkel* * Department of Pediatrics, Harvard Medical School and Division of Genetics, Children's Hospital, and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa 52242, USA Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a human X-linked biochemical defect resulting in the progressive wasting of skeletal muscle of affected individuals 1. It is the most common and is considered to be the most devastating of the muscular dystrophies, affecting about 1 in 3,500 live-born males 2. The gene that, when defective, results in this disorder was recently isolated 3-6. Using the cloned complementary DNA sequences corresponding to the DMD gene, antibodies have been produced that react with a protein species of relative molecular mass (M r ) ~400,000 (400K) which was absent in two DMD-affected individuals and in mdx mice 7. This protein species is called dystrophin because of its identification by molecular-genetic analysis of affected individuals. Here we show that dystrophin is associated with the triadic junctions in skeletal muscle, and is therefore probably involved with Ca 2+ homoeostasis. We also show that the ~450K ryanodine receptor/sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ channel 8, which has the large size and subcellular distribution characteristics of dystrophin, is an immunologically distinct protein species. Dystrophin messenger RNA 3,5,6,9 and protein 7 are present in all types of mature, terminally differentiated muscle tissue.
2 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of subcellular fractionations, showing the procedure for fractionation of mouse skeletal muscle. Methods. For detergent-insoluble myofibrils, freshly dissected muscle (2 g) was homogenized in a Waring blender at full speed in 15ml homogenization buffer (10 mm HEPES ph 7.1, 10 mm EGTA, 1 mm iodoacetamide, 0.8 mm benzamidine, 0.5 µg ml -1 aprotinin, 0.5 µg ml -1 leupeptin, 0.25 µg ml -1 pepstatin A, supplemented with solid phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride) containing either 0.25% Triton X-100 or 0.1% N-lauryl sarcosyl. Insoluble proteins were pelleted at 10,000 r.p.m. in a Beckman JA-13 rotor, pellets resuspended in homogenization buffer, and the protein concentration of the suspension determined using the Bio-Rad protein assay. Samples were diluted with sample buffer and boiled before fractionation (see Fig. 2, lanes 2,3,11). Sucrose homogenate fractions (see Fig. 2, lanes 4-9,12-13) were prepared as described 11. Mouse rear-leg skeletal muscle and heart was dissected and immediately homogenized as above, supplemented with 0.25% sucrose. Myofibrillar fractions were isolated by centrifugation as above for 20 min. The skeletal muscle myofibrillar pellet contained two layers (Fig. 2; lanes 4, 5), whereas the heart myofibrillar pellet was homogeneous (Fig. 2; lane 12). The pellets were resuspended in homogenization buffer without sucrose. An aliquot of the lowspeed supernatant was reserved (Fig. 2; lane 6) and the remainder was centrifuged at 40,000 r.p.m. in a Beckman SW-40 rotor for 20 min. An aliquot of the pellet was resuspended in homogenization buffer and reserved (microsomes. Fig. 2; lanes 7, 13). The rest of the microsomal pellets were resuspended and fractionated on a discontinuous sucrose gradient for the isolation of light and heavy microsomes (Fig. 2; lanes 8, 9) as described for mouse skeletal muscle 12, except that protease inhibitors were added. Dystrophin is thought to have a structural role in myofibres because of its high degree of conservation between mice and humans, the structural characteristics of the amino-terminal one-third of the primary amino-acid sequence 4,5, and the significant similarity of the amino terminus to the actin-binding site of the cytoskeletal protein α-actinin 10. Consistent with this hypothesis, the protein is generally insoluble in the detergent Triton, but the very low abundance of dystrophin in myofibres (~0.002% of total muscle protein 7 ) indicates that it is probably not a prominent component of the myofibrillar matrix. We sought to determine the subcellular compartment in which dystrophin is localized. We decided to perform fractionation of subcellular components followed by Western analysis rather than immunofluorescent localization because of the artefacts inherent to immunocytological techniques when detecting very low abundance proteins with polyclonal antisera. We dissected skeletal muscle from normal, adult mice and fractionated it into detergent-insoluble (Triton X-100, N-lauryl sarcosyl) and sucrose-homogenized myofibrillar, soluble and microsomal fractions 11. We further separated the microsomal fraction into light and heavy microsomes using a sucrose-step gradient 12 (see Fig. 1). We also performed similar fractionations for mouse heart. We incubated identical Western blots with antibodies directed against dystrophin 7 (Fig. 2a); the (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )ATPase 13 (Fig. 2b); the ryanodine receptor 8,14 (Fig. 2c); or tropomyosin (Fig. 2d). As expected, tropomyosin and crossreacting myosin are enriched in the myofibrillar fractions 15 (Fig. 2d; lanes 2-5, 11-12), whereas the (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )ATPase and ryanodine receptor are both enriched in the microsomal fractions (Fig. 2b,c; lanes 7-9, 13) 12,14,16. The ATPase monoclonal antibodies used do not cross-react with the cardiac form of this protein (Fig. 2b; lanes 10-13) 13. Dystrophin parallels the localization of the ryanodine receptor and (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )ATPase, being enriched in the microsomal fractions (Fig. 2a; lanes 7-9, 13), with a particularly strong enrichment in the heavy fraction (Fig. 2a; lane 9). The heavy microsomal fraction was originally developed to enrich sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles derived from the terminal cisternae of the triad junction. Proteins known to be contained in this fraction are the (Ca 2+ +Mg 2+ )ATPase 16, calsequestrin 16 and the ryanodine receptor 14. The enrichment of dystrophin in the same fraction, and the lack of enrichment in other fractions, suggests a similar association with the triad region. To define further the subcellular compartmentalization of dystrophin within the triad junctional region of skeletal muscle, and to determine whether dystrophin and the ryanodine receptor are the same protein, we performed a second subcellular fractionation series using rabbit skeletal muscle. Triadic fractions can be efficiently isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle using the pyrophosphate variant protocol 11. Such fractions have been found to be enriched in high-affinity [ 3 H]PN (radiolabelled dihydropyridine) binding 17,18 (a junctional T-system marker) and high-affinity [ 3 H]ryanodine binding 14 (a junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum marker). We collected aliquots from all steps of the purification to demonstrate the co-purification of ryanodine receptor, the dihydropyridine receptor and dystrophin in all fractions. Figure 3a shows the Coomassie blue staining of the fractionated muscle, with the myofibrillar proteins myosin, nebulin and titin indicated, as well as the sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine receptor, (Ca 2+ +Mg 2+ )ATPase and calsequestrin. Western blot analysis of gels identical to Fig. 3a using affinity-purified anti-dystrophin antibodies, monoclonal antibody against the 170K subunit of the dihydropyridine receptor or polyclonal antibodies against the ryanodine receptor indicate that ail three detected proteins have a very similar subcellular fractionation pattern (Fig. 3b-d). All three of these proteins were highly concentrated within fractions enriched for triadic structures, [ 3 H]ryanodine binding and [ 3 H]PN binding (Fig. 3b-d; lanes 4-6). Our additional experiments (not shown) show that extraction of triads with 0.6 M KCl does not remove dystrophin; and immunoblot analysis of heavy sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles 16 compared with isolated triads 11 shows the enrichment of dystrophin and the ryanodine receptor in isolated triads. The co-purification of dystrophin with other, well-characterized triad-associated proteins indicates that dystrophin is tightly associated with the triad structures of skeletal muscle. To test the relationship between the ryanodine receptor and dystrophin directly, we performed further immunoblot experiments using an affinity-purified ryanodine receptor preparation containing Ca 2+ -channel activity 8. We stained isolated triads and the purified ryanodine receptor with polyclonal antiryanodine receptor and anti-dystrophin antibodies (Fig. 4b,c). We found that anti-dystrophin antibodies do not react with the affinity-purified 450K. ryanodine receptor and we did not detect dystrophin in the purified ryanodine receptor preparation. Also, the polyclonal antibodies to the ryanodine receptor do not react with dystrophin (Fig. 4b; lane 1). The comparison of the immunostaining (Fig. 4b,c) and amido black staining (Fig. 4a) of the triadic fractions also reveals that the ryanodine receptor is larger and much more abundant than 755
3 756 Fig. 2 Localization of dystrophin to the microsomal fractions of mouse skeletal and cardiac muscle by Western blot analysis of the subcellular protein fractions described in Fig. 1. Mouse skeletal muscle. lane 1, total SDS-solubilized (50 µg) (total); lane 2, Triton X-100- insoluble myofibrils (50 µg) (triton); lane 3, N-lauryl sarcosyl-insoluble myofibrils (50 µg) (sarcosyl); lane 4, sucrose-insoluble myofibrils (dense fraction) (50 µg) (sucrose 1); lane 5, sucrose-insoluble myofibrils (50 µg) (sucrose 2); lane 6, soluble/microsomes (50 µg) (soluble); lane 7, microsomes (50 µg) (membranes); lane 8, light microsomes (25 µg) (light SR); lane 9, heavy microsomes (50 µg) (heavy SR). Mouse cardiac muscle: lane 10, total SDS-solubilized (50 µg) (total); lane 11, Triton X-100- insoluble myofibrils (50 µg)(triton); lane 12, sucrose-insoluble myofibrils (50 µg) (sucrose); lane 13, microsomes (25 µg) (membranes). Antibodies used: a, anti-mouse dystrophin (affinity-purified sheep anti-60k and rabbit anti-30k polyclonals 7 ; b, mouse anti-chicken fast (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ ) ATPase monoclonal (sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ pump) 13 ; c, guinea pig anti-rabbit ryanodine receptor polyclonal (sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ channel); d, rabbit anti-chicken smooth-muscle tropomyosin antisera (myofibrillar marker with cross-reacting myosin shown). Dystrophin (400K) (a) parallels the localization of the sarcoplasmic reticulum markers, the 105K (Ca 2+ +Mg 2+ )ATPase 13 (b) and the 450K. ryanodine receptor 8,14 (c). Disassociation of the triads from myofibrils is very inefficient 27, explaining the presence of the sarcoplasmic reticulum markers in myofibrillar preparations. Also in a is the 100K, skeletal muscle-specific, myofibrillar protein species that cross-reacts with the rabbit anti-30k dystrophin antibodies 7. The ATPase monoclonal is specific for the fast muscle form of this protein and does not react with the cardiac muscle form (panel b, lanes 10-13). Methods. Total SDS-solubilized muscle (lanes 1,10). Freshly dissected muscle was minced, boiled in 10 vol sample-loading buffer (10% SDS, 50 mm dithiothreitol, 0.1 M Tris ph 8.0, 10 mm EDTA). SDS-insoluble proteins were precipitated and discarded. All other samples were prepared as described in Fig. 1. Samples were boiled and SDS-insoluble proteins precipitated before gel loading. Protein samples were fractionated on % gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gels 30, using a 3% stacking gel. Western blotting was as described 7. Polyclonal antibodies against the purified ryanodine receptor were prepared according to Tung 29 by immunization of guinea pigs with gel slices of the purified 450K ryanodine receptor protein. Fig. 3 Association of dystrophin with triadic junctions of rabbit skeletal muscle. Shown are the following subcellular protein fractions from rabbit skeletal muscle. Numbers in parentheses represent [ 3 H]PN and [ 3 H]ryanodine binding, respectively. Binding (in pmol mg -1 ) was performed as described 12,15. Lane 1, initial muscle homogenate (0.39, 0.09); lane 2, soluble/microsomal fraction of initial homogenate (0-32, 0.12); lane 3, rehomogenized myofibrillar fraction (second homogenate) (0.51,0.15); lane 4, heavy microsomes from initial homogenate (7.61, 2.53); lane 5, heavy microsomes from second homogenate (10.60,3.27); lane 6, isolated triads (12.03, 4.25); lane 7, soluble/microsomal fraction from second homogenate (0.46, 1.62); lane 8, soluble/light microsomal fraction from lane 7 (0, 0.05); lane 9, myofibrillar fraction of second homogenate (0.41, 0.11); lane 10, light microsomes from lane 8 (2.50, 0.78); lane 11, soluble fraction (cytosol) (0,0). a, Coomassie blue-stained gel (100 µg protein per lane); b, Western blot using affinity-purified sheep anti-mouse dystrophin antibodies with alkaline phosphatase conjugated donkey anti-sheep IgG secondary. (50 µg per lane); c, Western blot using monoclonal antibody IIF7 directed against the 170K subunit of the dihydropyridine receptor with peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG secondary (50 µg per lane). d, Western blot using polyclonal guinea pig anti-rabbit ryanodine receptor antibodies with peroxidase-conjugated rabbit antiguinea pig IgG secondary. (50 µg per lane). In a, myofibrillar markers are titin (apparent M r ~1,500K 31 ), nebulin (apparent M r ~700K 32 ), myosin (205K) and the sarcoplasmic reticulum marker (Ca 2+ +Mg 2+ ATPase (105K). Dystrophin (b) parallels the localization of the ryanodine receptor (sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ channel, c), being most highly concentrated in the purified triad fraction (lane 6). Because of differences in the second antibodies used and differences in the sensitivities of the various antisera, the intensity of the bands does not reflect the relative quantity of dystrophin present. Methods. Total rabbit skeletal muscle was dissected and fractionated into myofibrils, heavy microsomes and triads using a modification 18 of the pyrophosphate-variant procedure 11. Light microsomes were isolated as described 16. Protein content of samples was determined 33, and aliquots were solubilized in SDS and fractionated using 3-12% gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gels 30 using a 3% stacking gel. Western blot analysis was performed as described 14.
4 Fig. 4 Dystrophin is unrelated to the ryanodine receptor. Shown are three similar Western blots containing isolated triad structures and purified ryanodine receptor 8. a, Amido black staining. Lane 1, triads (50 µg); lane 2, purified ryanodine receptor (1.5 µg), b, Ryanodine receptor seen using guinea pig anti-rabbit ryanodine receptor antibodies with peroxidase-conjugated rabbit anti-guinea pig IgG secondary antibodies. Lane 1, triads (10 µg); lane 2, purified ryanodine receptor (0.7 µg). c, Dystrophin seen using sheep anti-mouse dystrophin antibodies with alkaline phosphataseconjugated donkey anti-sheep IgG. Lane 1, triads (50 µg); lane 2, purified ryanodine receptor (1.5 µg). dystrophin. The amido black-stained protein species migrating immediately below the abundant ryanpdine receptor (Fig. 4a; see also Fig. 3a) could potentially represent dystrophin. But there are differences between the fractionation of this amido black-stained protein species and the fractionation of dystrophin; the stained protein is not evident in lane 9 of Fig. 3a, whereas dystrophin is present in this lane (Fig. 3b). Furthermore, in contrast to dystrophin (Fig. 3b), the stained protein shows a substantial enrichment in the light microsomal fraction (Fig. 3a; lane 10) relative to the heavy microsomal fractions (Fig. 3a; lanes 4-6). Dystrophin either co-migrates with this amido black-stained protein species, or is not abundant enough to be stained at all. In either case, dystrophin presumably is a very minor component of the triads. This observation is consistent with previous estimates of the very low relative abundance of dystrophin in striated muscle 5,7. The differences in size and abundance between the ryanodine receptor and dystrophin indicate that they are indeed distinct, immunologically unrelated proteins. The triadic structures of muscle consist of transverse sarcolemmal invaginations (t-tubules) interdigitated between two terminal cisternae of the longitudinally oriented sarcoplasmic reticulum (junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum). These structures occur at the A-I junction of every half sarcomere in higher vertebrates and are responsible for the signal transduction of membrane depolarization into sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ release, resulting in myofibrillar contraction (excitationcontraction coupling). Membrane depolarizations triggered by motomeurons are transmitted to the internal portions of myofibres via the t-tubule system, where voltage sensors in the triadic structures (possibly the dihydropyridine receptor of the t-tubules ) are thought to initiate Ca 2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum through the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ channel (the ryanodine receptor) 8,22, resulting in myofibril contraction. The junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum is also responsible, together with the non-junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum, for the active uptake and storage of intracellular Ca 2+, which is accomplished via the very abundant intrinsic (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )ATPase and calsequestrin, the extrinsic Ca 2+ -binding protein. Here we have shown that the protein product of the DMD locus, dystrophin, is a protein associated with triadic structures in myofibres. Because these structures are essential for the maintenance of calcium homoeostasis within the muscle fibre, one can speculate that the absence of one of its potential components, dystrophin, would disrupt this process. It has been reported 23 that increased iritracellular Ca 2+ levels could initiate myofibre death by the activation of phospholipase A, resulting in sarcolemmal dissolution. It is possible that altered Ca 2+ homoeostasis resulting from dystrophin deficiency leads to such a Ca 2+ -mediated phospholipase activation. This process could explain the very high. levels of soluble sarcoplasmic enzymes in the serum of the DMD-affected individual 23. The ammo-terminal 200 amino acids of dystrophin exhibit striking similarity to the actin filament-binding domain of chicken cytoskeletal α-actinin 10. This actin filament-binding domain is highly conserved between the widely divergent Dictyostelium and chicken α-actinin, presumably due to the highly conserved nature of the actin filaments to which both proteins bind 24. The similarity of the amino terminus of dystrophin to this same conserved region suggests -that this similarity represents a functional homology. It is therefore probable that dystrophin interacts with actin filaments in myofibres. We have shown that dystrophin is associated with the triadic Structures of muscle. It is tempting to suggest that dystrophin might serve as an anchor for the triads to the myofibrillar cytpskeleton through the binding of actin filaments at its amino terminus. Supporting this hypothesis, DMD-affected muscle (which lacks dystrophin) has been seen to contain poorly aligned triads 25 and disorganized t-tubule system networks 26. Clearly there are many other hypothetical roles for dystrophin in the triads. The localization of dystrophin to the triadic junctions, however, implies that Ca 2+ homoeostasis is the most likely process disrupted in DMD. The precise function of dystrophin should soon be elucidated, as its subcellular localization is refined by immunoelectron microscopy and production of monoclonal antibodies, and as its biochemistry is defined by more extensive purifications and binding studies. We thank Zaven Kaprielian and Douglas Fambrough for (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )ATPase antibodies; Toshiaki Imagawa and Albert Leung for the anti-ryanodine receptor antibody and anti-dihydropyridine receptor antibody, respectively; Michel Koenig for discussions; Angelika Noegel and Walter Witke for communication of Dictyostelium α-actinin data; and Steven Kahl for technical assistance. Supported by grants from NIH (L.M.K. and K.P.C.) and MDA (L.M.K. and K.P.C.). E.P.H. is the Harry Zimmerman postdoctoral Fellow of the MDA; K.P.C. is an established investigator of the AHA; L.M.K. is an associate investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Received 6 November; accepted 17 November Walton, J. N. & Gardner-Medwin, D. in Disorders of Voluntary Muscle (ed. Walton, S. J.) (Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 1981). 2. Moser, H. Hum. Genet. 66, (1984). 3. Monaco, A. P. et al. Nature 323, (1986). 4. Koenig, M. et al Cell 50, (1987). 5. Hoffman, E. P., Monaco, A. P., Feener, C. C. & Kunkel, L. M. Science 238, (1987). 6. Burghes, A. H. et al. Nature 328, (1987). 7. Hoffman, E. P., Brown, R. H. & Kunkel, L. M. Cell (in the press). 8. Imagawa, T., Smith, J. S., Coronado, R. & Campbell, K. P. J. biol. Chem. 262, (1987). 9. Lev, A., Feener, C., Kunkel, L. M. & Brown, R. H. J. biol. Chem. (in the press). 10. Hammonds, R. G. Cell 51, 1 (1987). 11. Mitchell, R. D., Palade, P. & Fleischer, S. J. Cell Biol. 96, (1983). 12. Mrak, R. E. & Fleischer, S. Muscle Nerve 5, (1982). 13. Kaprielian, Z. & Fambrough, D. M. Devl Biol. (in the press). 14. Campbell, K. P. et al. J. biol. Chem. 262, (1987). 15. Stone, D. & Smillie, L. B. J. biol. Chem. 253, (1978). 16. Campbell, K. P., Franzini-Armstrong, C. & Shamoo, A. E. Biochim. biophys. Acta 602, (1980). 17. Leung, A. T., Imagawa, T. & Campbell, K. P. J. biol. Chem. 253, (1978). 18. Sharp, A. H., Imagawa, T., Leung, A. T. & Campbell, K. P. J. biol. Chem. 262, (1987). 19. Bios, E. & Brum, G. Nature 325, (1987). 20. Tanabe, T. et al. Nature 328, (1987). 21. Leung, A. T., Imagawa, T., Block, B., Franzini-Armstrong, C. & Campbell, K. P. J. biol. Chem. (in the press). 22. Smith, J. S., Coronado, R. & Meissner, G. Nature 316, (1985). 757
5 Jackson, M. J., Jones, D. A. & Edwards, R. H. Eur. J. clin. Invest. 13, (1984). 24. Noegel, A., Witke, W. & Schleicher, M. Fedn Eur. Biochem. Sci. 221, (1987). 25. Watkins, S. C. & Cullen, M. J. J. neurol. Sci. (in the press). 26. Oguchi, K., Yanagisawa, N. & Tsukagoshi, H. J. neurol. Sci. 57, (1982). 27. Rodemann, H. P., Waxman, L. & Goldberg, A. L. J. biol. Chem. 257, (1982). 28. Martonosi, A. N. in Myology (eds Engel, A. G. & Banker, B. Q.) (McGraw Hill, New York, 1986). 29. Tung, A. S. Meth. Enzym. 93, (1983). 30. Laemmli, U. K. Nature 227, (1970). 31. Wang, K. Cell Muscle Motil. 6, (1985). 32. Sugita, H. et al. Proc. Jap. Acad. 63, (1987). 33. Peterson, G. L. Analyt. Biochem. 83, (1977).
SDS-PAGE and Western Blot. Molecular Basis of Evolution
 1 SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Molecular Basis of Evolution Homology high level of DNA and protein sequence similarity due to common ancestry. Evidence Genomes of related organisms are very similar. Even
1 SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Molecular Basis of Evolution Homology high level of DNA and protein sequence similarity due to common ancestry. Evidence Genomes of related organisms are very similar. Even
Immunoprecipitation Protocol
 Immunoprecipitation Protocol Immunoprecipitation is a general method to obtain the enrichment of a specific protein from tissue lysate and cell lysate. It can be used to purify a specific protein, to identify
Immunoprecipitation Protocol Immunoprecipitation is a general method to obtain the enrichment of a specific protein from tissue lysate and cell lysate. It can be used to purify a specific protein, to identify
WesternMAX Alkaline Phosphatase Chemiluminescent Detection Kits
 WesternMAX Alkaline Phosphatase Chemiluminescent Detection Kits Code N221-KIT N220-KIT Description WesternMAX Chemiluminescent AP Kit, Anti-Mouse Includes: Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) Conjugated Anti-Mouse
WesternMAX Alkaline Phosphatase Chemiluminescent Detection Kits Code N221-KIT N220-KIT Description WesternMAX Chemiluminescent AP Kit, Anti-Mouse Includes: Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) Conjugated Anti-Mouse
ab Ran Activation Assay Kit
 ab173247 Ran Activation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the simple and fast measurement of Ran activation. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last
ab173247 Ran Activation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the simple and fast measurement of Ran activation. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last
1. Cross-linking and cell harvesting
 ChIP is a powerful tool that allows the specific matching of proteins or histone modifications to regions of the genome. Chromatin is isolated and antibodies to the antigen of interest are used to determine
ChIP is a powerful tool that allows the specific matching of proteins or histone modifications to regions of the genome. Chromatin is isolated and antibodies to the antigen of interest are used to determine
ab G alpha i Activation Assay Kit
 ab173234 G alpha i Activation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the simple and fast measurement of G alpha i activation. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab173234 G alpha i Activation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the simple and fast measurement of G alpha i activation. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
Viral RNAi suppressor reversibly binds sirna to. outcompete Dicer and RISC via multiple-turnover
 Supplementary Data Viral RNAi suppressor reversibly binds sirna to outcompete Dicer and RISC via multiple-turnover Renata A. Rawlings 1,2, Vishalakshi Krishnan 2 and Nils G. Walter 2 * 1 Biophysics and
Supplementary Data Viral RNAi suppressor reversibly binds sirna to outcompete Dicer and RISC via multiple-turnover Renata A. Rawlings 1,2, Vishalakshi Krishnan 2 and Nils G. Walter 2 * 1 Biophysics and
Table of Contents. Catalog No
 Table of Contents Catalog No. 54-11-50 Section Page Introduction 2 Materials and Equipment 3 Warnings and Precautions 4 Protocols Western Blotting Protocol At A Glance 5 PAGE and Western Blotting 6-7 Detection
Table of Contents Catalog No. 54-11-50 Section Page Introduction 2 Materials and Equipment 3 Warnings and Precautions 4 Protocols Western Blotting Protocol At A Glance 5 PAGE and Western Blotting 6-7 Detection
Rabbit (monoclonal) Anti-FAK [py 397 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated
![Rabbit (monoclonal) Anti-FAK [py 397 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated Rabbit (monoclonal) Anti-FAK [py 397 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated](/thumbs/78/77450403.jpg) Rabbit (monoclonal) Anti-FAK [py 397 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated PRODUCT ANALYSIS SHEET Catalog Number: Lot Number: Volume: 44-625G (10 mini-blot size) See product label 100 μl Clone Number:
Rabbit (monoclonal) Anti-FAK [py 397 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated PRODUCT ANALYSIS SHEET Catalog Number: Lot Number: Volume: 44-625G (10 mini-blot size) See product label 100 μl Clone Number:
SensoLyte Anti-alpha-Synuclein Quantitative ELISA Kit (Human/Mouse/Rat) *Colorimetric*
 Catalog # Kit Size SensoLyte Anti-alpha-Synuclein Quantitative ELISA Kit (Human/Mouse/Rat) *Colorimetric* AS-55550 One 96-well strip plate This kit is optimized to detect human/mouse/rat alpha-synuclein
Catalog # Kit Size SensoLyte Anti-alpha-Synuclein Quantitative ELISA Kit (Human/Mouse/Rat) *Colorimetric* AS-55550 One 96-well strip plate This kit is optimized to detect human/mouse/rat alpha-synuclein
Electrophoresis and transfer
 Electrophoresis and transfer Electrophoresis Cation = positively charged ion, it moves toward the cathode (-) Anion = negatively charged ion, it moves toward the anode (+) Amphoteric substance = can have
Electrophoresis and transfer Electrophoresis Cation = positively charged ion, it moves toward the cathode (-) Anion = negatively charged ion, it moves toward the anode (+) Amphoteric substance = can have
IMMUNOPRECIPITATION (IP)
 1 IMMUNOPRECIPITATION (IP) Overview and Technical Tips 2 CONTENTS 3 7 8 9 12 13 17 18 19 20 Introduction Factors Influencing IP General Protocol Modifications Of IP Protocols Troubleshooting Contact Us
1 IMMUNOPRECIPITATION (IP) Overview and Technical Tips 2 CONTENTS 3 7 8 9 12 13 17 18 19 20 Introduction Factors Influencing IP General Protocol Modifications Of IP Protocols Troubleshooting Contact Us
SUMOylated protein capture kit
 SUMOylated protein capture kit Cat no. A010-100 Capture and detect SUMOylated proteins High capacity, high specificity SUMO binding matrix Fast, convenient protein isolation using purification system provided
SUMOylated protein capture kit Cat no. A010-100 Capture and detect SUMOylated proteins High capacity, high specificity SUMO binding matrix Fast, convenient protein isolation using purification system provided
IMMUNOPRECIPITATION TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS
 IMMUNOPRECIPITATION TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS Creative Diagnostics Abstract Immunoprecipitation (IP) is the technique of precipitating a protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that specifically binds
IMMUNOPRECIPITATION TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS Creative Diagnostics Abstract Immunoprecipitation (IP) is the technique of precipitating a protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that specifically binds
Week 1: Protein isolation and quantification
 Week 1: Protein isolation and quantification Objective The objective of this lab exercise is to obtain protein samples from fruit fly larvae, BCS and FBS, all of which are then quantitated in the preparation
Week 1: Protein isolation and quantification Objective The objective of this lab exercise is to obtain protein samples from fruit fly larvae, BCS and FBS, all of which are then quantitated in the preparation
Purification of Lactate Dehydrogenase
 Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Scholarly & Creative Works Conference 2018 Scholarly and Creative Works Conference 2016 Apr 15th, 1:30 PM - 2:00 PM Purification of Lactate Dehydrogenase
Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Scholarly & Creative Works Conference 2018 Scholarly and Creative Works Conference 2016 Apr 15th, 1:30 PM - 2:00 PM Purification of Lactate Dehydrogenase
Custom Antibodies Services. GeneCust Europe. GeneCust Europe
 GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 2 route de Remich L-5690 Ellange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com Custom
GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 2 route de Remich L-5690 Ellange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com Custom
Cellular Fractionation
 Cellular Fractionation Lamond Lab Protocol 2007 More detailed protocol can be found here: http://www.lamondlab.com/f7nucleolarprotocol.htm This protocol has been adapted to fractionate a variety of different
Cellular Fractionation Lamond Lab Protocol 2007 More detailed protocol can be found here: http://www.lamondlab.com/f7nucleolarprotocol.htm This protocol has been adapted to fractionate a variety of different
Purification Kits. Fast and Convenient PROSEP -A and PROSEP-G Spin Column Kits for Antibody Purification DATA SHEET
 Â Montage Antibody Purification Kits Fast and Convenient PROSEP -A and PROSEP-G Spin Column Kits for Antibody Purification DATA SHEET Available with immobilized Protein A or Protein G Easy-to-use Antibody
 Montage Antibody Purification Kits Fast and Convenient PROSEP -A and PROSEP-G Spin Column Kits for Antibody Purification DATA SHEET Available with immobilized Protein A or Protein G Easy-to-use Antibody
Presto Stool DNA Extraction Kit
 Instruction Manual Ver. 10.21.17 For Research Use Only Presto Stool DNA Extraction Kit Advantages STLD004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) STLD050 (50 Preparation Kit) STLD100 (100 Preparation Kit) Sample: 180-200
Instruction Manual Ver. 10.21.17 For Research Use Only Presto Stool DNA Extraction Kit Advantages STLD004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) STLD050 (50 Preparation Kit) STLD100 (100 Preparation Kit) Sample: 180-200
Orexin A (HUMAN, MOUSE, RAT, PORCINE, OVINE,
 Orexin A (HUMAN, MOUSE, RAT, PORCINE, OVINE, BOVINE) Western Blot Kit Protocol (Catalog #WBK-003-30) PHOENIX PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Kit Contents...2 2. Storage...2 3. Introduction...3
Orexin A (HUMAN, MOUSE, RAT, PORCINE, OVINE, BOVINE) Western Blot Kit Protocol (Catalog #WBK-003-30) PHOENIX PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Kit Contents...2 2. Storage...2 3. Introduction...3
Technical Note Detection of post-immunoprecipitation proteins by Western blot using the Quick Western Kit IRDye 680RD
 Technical Note Detection of post-immunoprecipitation proteins by Western blot using the Quick Western Kit IRDye 680RD Developed for: Aerius, Odyssey Classic, Odyssey CLx and Odyssey Sa Imaging Systems
Technical Note Detection of post-immunoprecipitation proteins by Western blot using the Quick Western Kit IRDye 680RD Developed for: Aerius, Odyssey Classic, Odyssey CLx and Odyssey Sa Imaging Systems
PROCEDURE FOR USE NICKEL NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads (5%)
 1 AFFINITY HIS-TAG PURIFICATION PROCEDURE FOR USE NICKEL NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads (5%) DESCRIPTION Nickel NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads are products that allow rapid and easy small-scale purification of
1 AFFINITY HIS-TAG PURIFICATION PROCEDURE FOR USE NICKEL NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads (5%) DESCRIPTION Nickel NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads are products that allow rapid and easy small-scale purification of
ab Ubiquitylation Assay Kit (HeLa lysate-based)
 ab139471 Ubiquitylation Assay Kit (HeLa lysate-based) Instructions for Use For the generation of ubiquitin-conjugated lysate proteins This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139471 Ubiquitylation Assay Kit (HeLa lysate-based) Instructions for Use For the generation of ubiquitin-conjugated lysate proteins This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Protein Electrophoresis EZ-Run Protein Gel Solution EZ-Run Protein Standards EZ-Run Gel Staining Solution Traditional SDS-PAGE Reagents
 Protein Electrophoresis EZ-Run Protein Gel Solution EZ-Run Protein Standards EZ-Run Gel Staining Solution Traditional SDS-PAGE Reagents Reliability. Purity. Certainty. Introduction Sodium dodecyl sulfate
Protein Electrophoresis EZ-Run Protein Gel Solution EZ-Run Protein Standards EZ-Run Gel Staining Solution Traditional SDS-PAGE Reagents Reliability. Purity. Certainty. Introduction Sodium dodecyl sulfate
Porablot PVDF membranes
 Porablot PVDF membranes User manual Porablot PVDF March 2018 / Rev. 03 www.mn-net.com Table of contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Membrane handling and preparation 5 3 Buffers and solutions 6 4 Protein transfer
Porablot PVDF membranes User manual Porablot PVDF March 2018 / Rev. 03 www.mn-net.com Table of contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Membrane handling and preparation 5 3 Buffers and solutions 6 4 Protein transfer
RNA extraction from tissue - using Bioruptor (Standard/Plus) and RNA extraction kit
 RNA extraction from tissue - using Bioruptor (Standard/Plus) and RNA extraction kit Introduction Isolation of intact RNA is essential for many techniques used in gene expression analysis. Efficient disruption
RNA extraction from tissue - using Bioruptor (Standard/Plus) and RNA extraction kit Introduction Isolation of intact RNA is essential for many techniques used in gene expression analysis. Efficient disruption
Ral Activation Assay Kit
 Product Manual Ral Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number STA-408 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Small GTP-binding proteins (or GTPases) are a family of
Product Manual Ral Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number STA-408 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Small GTP-binding proteins (or GTPases) are a family of
3.1 PREPARATION OF SYNAPTOSOMES AND SYNAPTIC VESICLES FROM RAT BRAIN
 3 METHODS 3.1 PREPARATION OF SYNAPTOSOMES AND SYNAPTIC VESICLES FROM RAT BRAIN 3.1.3 PREPARATION OF SYNAPTOSOMES Isolated nerve terminals (synaptosomes) were prepared from adult and embryonic Wistar rat
3 METHODS 3.1 PREPARATION OF SYNAPTOSOMES AND SYNAPTIC VESICLES FROM RAT BRAIN 3.1.3 PREPARATION OF SYNAPTOSOMES Isolated nerve terminals (synaptosomes) were prepared from adult and embryonic Wistar rat
Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous
 Preparation and purification of polyclonal antibodies Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous injections of glutathione S-transferase-ARHGAP25-(509-619) (GST-coiled
Preparation and purification of polyclonal antibodies Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous injections of glutathione S-transferase-ARHGAP25-(509-619) (GST-coiled
Electro refers to electron flow or current. Thus Electrophoresis is movement under electric current.
 ELECTROPHORESIS Electrophoresis Electro refers to electron flow or current. Phoresis refers to movement. Thus Electrophoresis is movement under electric current. This technique therefore can separate molecules
ELECTROPHORESIS Electrophoresis Electro refers to electron flow or current. Phoresis refers to movement. Thus Electrophoresis is movement under electric current. This technique therefore can separate molecules
Azure Biosystems Western Blotting Workflow
 Azure Biosystems Western Blotting Workflow PROBE PLAN SEPARATE ANALYZE VISUALIZE PLAN Plan your experiment and choose your detection method Chemiluminescent Western Blotting The most common method for
Azure Biosystems Western Blotting Workflow PROBE PLAN SEPARATE ANALYZE VISUALIZE PLAN Plan your experiment and choose your detection method Chemiluminescent Western Blotting The most common method for
PROTOCOL 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon
 PROTOCOL Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Enzyme Activity Dipstick Assay Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP30 Rev.4 DESCRIPTION Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Enzyme Activity Dipstick
PROTOCOL Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Enzyme Activity Dipstick Assay Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP30 Rev.4 DESCRIPTION Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Enzyme Activity Dipstick
High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No
 for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No. 1 796 88 Principle Cells are lysed during a short incubation with Proteinase K in the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), which immediately
for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No. 1 796 88 Principle Cells are lysed during a short incubation with Proteinase K in the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), which immediately
ab K-Ras Activation Assay Kit
 Version 1 Last updated 7 July 2016 ab211159 K-Ras Activation Assay Kit For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of active K-Ras in cell or tissue lysates from human, mouse or rat. This product
Version 1 Last updated 7 July 2016 ab211159 K-Ras Activation Assay Kit For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of active K-Ras in cell or tissue lysates from human, mouse or rat. This product
E.Z.N.A. Tissue RNA Kit. R preps R preps
 E.Z.N.A. Tissue RNA Kit R6688-00 5 preps R6688-01 50 preps May 2015 E.Z.N.A. Tissue RNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Important Notes...4 Homogenization
E.Z.N.A. Tissue RNA Kit R6688-00 5 preps R6688-01 50 preps May 2015 E.Z.N.A. Tissue RNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Important Notes...4 Homogenization
Production of Antisera to Synthetic Decapeptide of the Cooh-Terminus of Rat Glut2
 Production of Antisera to Synthetic Decapeptide of the Cooh-Terminus of Rat Glut2 Sandro Vestri 1, Hideki Nikami 2, Masayuki Saito 2 and Ubiratan F. Machado 1* 1 Department of Physiology and Biophysics,
Production of Antisera to Synthetic Decapeptide of the Cooh-Terminus of Rat Glut2 Sandro Vestri 1, Hideki Nikami 2, Masayuki Saito 2 and Ubiratan F. Machado 1* 1 Department of Physiology and Biophysics,
The preparation of native chromatin from cultured human cells.
 Native chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol The preparation of native chromatin from cultured human cells. All solutions need to be ice cold. Sucrose containing solutions must be made up fresh on the
Native chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol The preparation of native chromatin from cultured human cells. All solutions need to be ice cold. Sucrose containing solutions must be made up fresh on the
western blotting tech
 western blotting tech note 6148 Transfer of High Molecular Weight Proteins to Membranes: A Comparison of Transfer Efficiency Between Blotting Systems Nik Chmiel, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., 6000 James
western blotting tech note 6148 Transfer of High Molecular Weight Proteins to Membranes: A Comparison of Transfer Efficiency Between Blotting Systems Nik Chmiel, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., 6000 James
RayBio Phospho- Stat 3 (Tyr705) ELISA Kit
 RayBio Phospho- Stat 3 (Tyr705) ELISA Kit For Measuring Phosphorylated Stat3 (Tyr705) in Human, Mouse and Rat Cell Lysates User Manual (Revised Mar 1, 2012) RayBio Stat3 (Tyr705) ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat#:
RayBio Phospho- Stat 3 (Tyr705) ELISA Kit For Measuring Phosphorylated Stat3 (Tyr705) in Human, Mouse and Rat Cell Lysates User Manual (Revised Mar 1, 2012) RayBio Stat3 (Tyr705) ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat#:
Multiplex Fluorescent Western Blot Starter Kit for the Bio- Rad ChemiDoc MP
 Page 1 of 7 INSTRUCTIONS: Z-310 Multiplex Fluorescent Western Blot Starter Kit for the Bio- Rad ChemiDoc MP Rockland Immunochemicals and Bio-Rad Laboratories have jointly developed an easy to use multiplex
Page 1 of 7 INSTRUCTIONS: Z-310 Multiplex Fluorescent Western Blot Starter Kit for the Bio- Rad ChemiDoc MP Rockland Immunochemicals and Bio-Rad Laboratories have jointly developed an easy to use multiplex
Strep-tag detection in Western blots
 Strep-tag detection in Western blots General protocol for the detection of Strep-tag fusion proteins Last date of revision April 2012 Version PR07-0010 www.strep-tag.com For research use only Important
Strep-tag detection in Western blots General protocol for the detection of Strep-tag fusion proteins Last date of revision April 2012 Version PR07-0010 www.strep-tag.com For research use only Important
Species predicted to react based on 100% sequence homology: Chicken, Bovine, Dog.
 1 of 5 11/1/2013 10:25 PM Product Pathways - Jak/Stat Pathway Phospho-Stat3 (Tyr705) Antibody #9131 Have you tried your application using our XP monoclonal antibodies? Try products: 9145 PhosphoSitePlus
1 of 5 11/1/2013 10:25 PM Product Pathways - Jak/Stat Pathway Phospho-Stat3 (Tyr705) Antibody #9131 Have you tried your application using our XP monoclonal antibodies? Try products: 9145 PhosphoSitePlus
Mitochondria/Cytosol Fractionation Kit
 Mitochondria/Cytosol Fractionation Kit Sufficient for analysis of 50 samples Cat. No. MIT1000 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures. USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951)
Mitochondria/Cytosol Fractionation Kit Sufficient for analysis of 50 samples Cat. No. MIT1000 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures. USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951)
Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing. 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology
 Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Immunization Chapter Reading pp. 505-511 What is Immunization? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 17: Immunization & Immune Testing 1. Immunization 2. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Immunization Chapter Reading pp. 505-511 What is Immunization? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Amersham * ECL * Gel horizontal electrophoresis system
 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Data file 28-9970-20 AB Electrophoresis products Amersham * ECL * Gel horizontal electrophoresis system Amersham ECL Gel and Amersham ECL Gel Box constitute a horizontal mini-gel
GE Healthcare Life Sciences Data file 28-9970-20 AB Electrophoresis products Amersham * ECL * Gel horizontal electrophoresis system Amersham ECL Gel and Amersham ECL Gel Box constitute a horizontal mini-gel
Presto Soil DNA Extraction Kit
 Instruction Manual Ver. 02.23.17 For Research Use Only Presto Soil DNA Extraction Kit Advantages SLD004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) SLD050 (50 Preparation Kit) SLD100 (100 Preparation Kit) Sample: 250-500
Instruction Manual Ver. 02.23.17 For Research Use Only Presto Soil DNA Extraction Kit Advantages SLD004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) SLD050 (50 Preparation Kit) SLD100 (100 Preparation Kit) Sample: 250-500
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. MEK Activity Assay Kit. Product Code CS0490 Storage Temperature 20 C
 MEK Activity Assay Kit Product Code CS0490 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The MAP kinase kinases (MAPKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, also termed MEK) are a
MEK Activity Assay Kit Product Code CS0490 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The MAP kinase kinases (MAPKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, also termed MEK) are a
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling
 Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Microtubule associated proteins of goat brain
 J. Biosci., Vol. 4, Number 1, March 1982, pp. 61-68. Printed in India. Microtubule associated proteins of goat brain A. MAJUMDER, S. K. BANERJEE and P. K. SARKAR Department of Cell Biology, Indian Institute
J. Biosci., Vol. 4, Number 1, March 1982, pp. 61-68. Printed in India. Microtubule associated proteins of goat brain A. MAJUMDER, S. K. BANERJEE and P. K. SARKAR Department of Cell Biology, Indian Institute
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit
 Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
BCH 462. Western Blot
 BCH 462 Western Blot Blotting Immunoassay: A test that uses antibody and antigen complexes [immuno-complexes] as a means of generating measurable results. Antigens [Ag]: A substance that when introduced
BCH 462 Western Blot Blotting Immunoassay: A test that uses antibody and antigen complexes [immuno-complexes] as a means of generating measurable results. Antigens [Ag]: A substance that when introduced
How to run Alpha assay: How to setup an Alpha assay Make your own assay!
 How to run Alpha assay: How to setup an Alpha assay Make your own assay! 1 2009 PerkinElmer AlphaLISA kits - recommendations before starting the assay Samples: Phenol red and hemoglobin: choose AlphaLISA
How to run Alpha assay: How to setup an Alpha assay Make your own assay! 1 2009 PerkinElmer AlphaLISA kits - recommendations before starting the assay Samples: Phenol red and hemoglobin: choose AlphaLISA
electrophoresis tech Mini-PROTEAN TGX Precast Gel: A Gel for SDS-PAGE with Improved Stability Comparison with Standard Laemmli Gels
 electrophoresis tech note 591 Mini-PROTEAN Precast Gel: A Gel for SDS-PAGE with Improved Stability Comparison with Standard Laemmli Gels Tom Berkelman, Shane Petersen, Chengjun Sun, and Sean Cater, Bio-Rad
electrophoresis tech note 591 Mini-PROTEAN Precast Gel: A Gel for SDS-PAGE with Improved Stability Comparison with Standard Laemmli Gels Tom Berkelman, Shane Petersen, Chengjun Sun, and Sean Cater, Bio-Rad
Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-Rac1/cdc42 [ps 71 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated
![Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-Rac1/cdc42 [ps 71 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-Rac1/cdc42 [ps 71 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated](/thumbs/78/77178502.jpg) Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-Rac1/cdc42 [ps 71 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated PRODUCT ANALYSIS SHEET Catalog Number: Lot Number: 0101 Volume: 100 µl (10 mini-blot size) Form of Antibody: Rabbit polyclonal
Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-Rac1/cdc42 [ps 71 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated PRODUCT ANALYSIS SHEET Catalog Number: Lot Number: 0101 Volume: 100 µl (10 mini-blot size) Form of Antibody: Rabbit polyclonal
GST Fusion Protein Purification Kit
 Glutathione Resin GST Fusion Protein Purification Kit Cat. No. L00206 Cat. No. L00207 Technical Manual No. TM0185 Version 01042012 Index 1. Product Description 2. Related Products 3. Purification Procedure
Glutathione Resin GST Fusion Protein Purification Kit Cat. No. L00206 Cat. No. L00207 Technical Manual No. TM0185 Version 01042012 Index 1. Product Description 2. Related Products 3. Purification Procedure
MEK1/2 (MAPK Kinase) Activity Assay Kit
 MEK1/2 (MAPK Kinase) Activity Assay Kit For 96 tests Cat. No. SGT440 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0)
MEK1/2 (MAPK Kinase) Activity Assay Kit For 96 tests Cat. No. SGT440 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0)
Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde
 Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
Product Datasheet. TGN38 Antibody NBP Unit Size: 0.5 mg
 Product Datasheet TGN38 Antibody NBP1-03495 Unit Size: 0.5 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
Product Datasheet TGN38 Antibody NBP1-03495 Unit Size: 0.5 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
MATERIAL DATA SHEET. NOTE: Kit contains reagents sufficient for 10 x 30 μl reactions and 5 Western Blots (minigel. Reagents Provided in Kit
 Lot # XXXXX ITCH/AIP4 Ubiquitin Ligase Kit Cat. # K-270 MATERIAL DATA SHEET The mammalian Itchy homolog, or ITCH, (also known as Atrophin-1-interacting protein 4 or AIP4) is a HECT domain class ubiquitin
Lot # XXXXX ITCH/AIP4 Ubiquitin Ligase Kit Cat. # K-270 MATERIAL DATA SHEET The mammalian Itchy homolog, or ITCH, (also known as Atrophin-1-interacting protein 4 or AIP4) is a HECT domain class ubiquitin
Note: for laboratory research use only. RNA High-purity Total RNA Rapid Extraction Kit (Spin-column) Signalway Biotechnology
 Note: for laboratory research use only RNA High-purity Total RNA Rapid Extraction Kit (Spin-column) Cat. #: RP1202 (50preps) Signalway Biotechnology I. Kit Content, Storage Condition and Stability Content
Note: for laboratory research use only RNA High-purity Total RNA Rapid Extraction Kit (Spin-column) Cat. #: RP1202 (50preps) Signalway Biotechnology I. Kit Content, Storage Condition and Stability Content
SANTA CRUZ BIOTECHNOLOGY, INC.
 TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa)
 Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0377 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0377 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
KPL LumiGLO Reserve Chemiluminescent Substrate
 DESCRIPTION KPL LumiGLO Reserve contains a luminol-based chemiluminescent substrate designed for use with peroxidase-labeled (HRP) reporter molecules. KPL LumiGLO Reserve offers improvements in the way
DESCRIPTION KPL LumiGLO Reserve contains a luminol-based chemiluminescent substrate designed for use with peroxidase-labeled (HRP) reporter molecules. KPL LumiGLO Reserve offers improvements in the way
Fisher (Fairlawn, NJ) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and were used without further. (Promega) and DpnI (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA).
 175 Appendix III Chapter 4 Methods General. Unless otherwise noted, reagents were purchased from the commercial suppliers Fisher (Fairlawn, NJ) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and were used without further
175 Appendix III Chapter 4 Methods General. Unless otherwise noted, reagents were purchased from the commercial suppliers Fisher (Fairlawn, NJ) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and were used without further
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
special offers from your protein biology resource
 special offers from your protein biology resource Pop open your cells, extract your proteins, purify, quantify and express them. Seeking knowledge about proteins with Thermo Scientific Protein Research
special offers from your protein biology resource Pop open your cells, extract your proteins, purify, quantify and express them. Seeking knowledge about proteins with Thermo Scientific Protein Research
KPL SignaLOCK ChemiWestern Kits (Film and Imager Analysis)
 KPL SignaLOCK ChemiWestern Kits (Film and Imager Analysis) SignaLOCK HRP ChemiWestern Kit (Film) Catalog No. 54-53-00 SignaLOCK HRP ChemiWestern Kit (Imager) Catalog No. 54-54-00 SignaLOCK AP ChemiWestern
KPL SignaLOCK ChemiWestern Kits (Film and Imager Analysis) SignaLOCK HRP ChemiWestern Kit (Film) Catalog No. 54-53-00 SignaLOCK HRP ChemiWestern Kit (Imager) Catalog No. 54-54-00 SignaLOCK AP ChemiWestern
OPPF-UK Standard Protocols: Mammalian Expression
 OPPF-UK Standard Protocols: Mammalian Expression Joanne Nettleship joanne@strubi.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents 1. Materials... 3 2. Cell Maintenance... 4 3. 24-Well Transient Expression Screen... 5 4. DNA
OPPF-UK Standard Protocols: Mammalian Expression Joanne Nettleship joanne@strubi.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents 1. Materials... 3 2. Cell Maintenance... 4 3. 24-Well Transient Expression Screen... 5 4. DNA
RayBio Phospho- Akt (Ser473) ELISA Kit
 RayBio Phospho- Akt (Ser473) ELISA Kit For Measuring Phosphorylated Akt (Ser473) in Human, Mouse and Rat Cell Lysates User Manual (Revised Mar 1, 2012) RayBio Akt (Ser473) ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat#: PEL-Akt-S473-001)
RayBio Phospho- Akt (Ser473) ELISA Kit For Measuring Phosphorylated Akt (Ser473) in Human, Mouse and Rat Cell Lysates User Manual (Revised Mar 1, 2012) RayBio Akt (Ser473) ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat#: PEL-Akt-S473-001)
Expression and Purification of Large Nebulin Fragments and Their Interaction with Actin
 Biophysical Journal Volume 74 January 1998 349 359 349 Expression and Purification of Large Nebulin Fragments and Their Interaction with Actin Jian Q. Zhang,* Andrea Weisberg, # and Robert Horowits* *National
Biophysical Journal Volume 74 January 1998 349 359 349 Expression and Purification of Large Nebulin Fragments and Their Interaction with Actin Jian Q. Zhang,* Andrea Weisberg, # and Robert Horowits* *National
Figure 1. Schematic of Ats1p expression plasmid.
 Abstract: Anita Corbett page 2 The goal of my rotation project was to express, purify, and examine the exchange activity of a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor, Ats1p. The S. cerevisiae ATS1
Abstract: Anita Corbett page 2 The goal of my rotation project was to express, purify, and examine the exchange activity of a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor, Ats1p. The S. cerevisiae ATS1
Dolphin-Chemi Plus. Aim: To visualise and evaluate the performance of chemiluminescent immunoblots using Wealtec s Dolphin-Chemi plus image system
 Application Note 03 Dolphin-Chemi plus 8/22/2007 Dolphin-Chemi Plus Aim: To visualise and evaluate the performance of chemiluminescent immunoblots using Wealtec s Dolphin-Chemi plus image system INTRODUCTION
Application Note 03 Dolphin-Chemi plus 8/22/2007 Dolphin-Chemi Plus Aim: To visualise and evaluate the performance of chemiluminescent immunoblots using Wealtec s Dolphin-Chemi plus image system INTRODUCTION
Purification of alpha-1 antitrypsin using an antibody based affinity chromatography medium
 Purification of alpha-1 antitrypsin using an antibody based affinity chromatography medium Ulrika Meyer a, Hanna Wlad a, Sven Blokland b, Frank J.M. Detmers b and Henrik Ihre a a GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences
Purification of alpha-1 antitrypsin using an antibody based affinity chromatography medium Ulrika Meyer a, Hanna Wlad a, Sven Blokland b, Frank J.M. Detmers b and Henrik Ihre a a GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences
EZ-10 SPIN COLUMN GENOMIC DNA MINIPREPS KIT HANDBOOK
 EZ-0 SPIN COLUMN GENOMIC DNA MINIPREPS KIT HANDBOOK (Bacteria, Plant, Animal, Blood) Version 8 Rev 05/0/03 EZ-0 Genomic DNA Kit Handbook Table of Contents Introduction Limitations of Use Features Applications
EZ-0 SPIN COLUMN GENOMIC DNA MINIPREPS KIT HANDBOOK (Bacteria, Plant, Animal, Blood) Version 8 Rev 05/0/03 EZ-0 Genomic DNA Kit Handbook Table of Contents Introduction Limitations of Use Features Applications
ab Antibody Serum Purification Kit (Protein A) Protocol
 ab109209 Antibody Serum Purification Kit (Protein A) Protocol For preparing antibodies for conjugation The components of Ab109209 are fully compatible with our Conjugation kits however they are not compatible
ab109209 Antibody Serum Purification Kit (Protein A) Protocol For preparing antibodies for conjugation The components of Ab109209 are fully compatible with our Conjugation kits however they are not compatible
Jan 25, 05 His Bind Kit (Novagen)
 Jan 25, 05 His Bind Kit (Novagen) (1) Prepare 5ml of 1X Charge buffer (stock is 8X= 400mM NiSO4): 0.625ml of the stock + 4.375ml DH2O. (2) Prepare 13ml of 1X Binding buffer (stock is 8X = 40mM imidazole,
Jan 25, 05 His Bind Kit (Novagen) (1) Prepare 5ml of 1X Charge buffer (stock is 8X= 400mM NiSO4): 0.625ml of the stock + 4.375ml DH2O. (2) Prepare 13ml of 1X Binding buffer (stock is 8X = 40mM imidazole,
Can be prepared in advance and stored at -80º
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay Protocol Can be prepared in advance and stored at -80º Wash Staph A Cells: 1. Resuspend 1 gram of lyophilized Staph A cells (Pansorbin, Calbiochem Cat#507862)
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay Protocol Can be prepared in advance and stored at -80º Wash Staph A Cells: 1. Resuspend 1 gram of lyophilized Staph A cells (Pansorbin, Calbiochem Cat#507862)
EZ-DNA. Instructions for Use. Genomic DNA Isolation Reagent. Product Description. Kit Reagent. Reagent Required But Not Supplied.
 EZ-DNA Genomic DNA Isolation Reagent Cat. No.: 20-600-50 Store at: Room Temperature Instructions for Use Protocol for Genomic DNA Isolation Tissue Specific Recommendations for the Use of EZ-DNA Assessing
EZ-DNA Genomic DNA Isolation Reagent Cat. No.: 20-600-50 Store at: Room Temperature Instructions for Use Protocol for Genomic DNA Isolation Tissue Specific Recommendations for the Use of EZ-DNA Assessing
DETERMINATION OF SERUM FERRITIN GLYCOSYLATION IN HYPERFERRITINEMIA
 DETERMINATION OF SERUM FERRITIN GLYCOSYLATION IN HYPERFERRITINEMIA ASSOCIATED TO IRON OVERLOAD AND INFLAMMATION. Bethina Isasi Gasser 1,2 1 Medical University of Innsbruck, Department of Medicine II Gastroenterology
DETERMINATION OF SERUM FERRITIN GLYCOSYLATION IN HYPERFERRITINEMIA ASSOCIATED TO IRON OVERLOAD AND INFLAMMATION. Bethina Isasi Gasser 1,2 1 Medical University of Innsbruck, Department of Medicine II Gastroenterology
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
ab Ubiquitylation Assay Kit
 ab139467 Ubiquitylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the activation of ubiquitin for use in ubiquitylation experiments This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
ab139467 Ubiquitylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the activation of ubiquitin for use in ubiquitylation experiments This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
AFFINITY HIS-TAG PURIFICATION
 DESCRIPTION Nickel NTA Agarose Cartridges 5ml are used for purification of histidine-tagged proteins in native or denaturing conditions. This cartridge can be used with an automated chromatography system,
DESCRIPTION Nickel NTA Agarose Cartridges 5ml are used for purification of histidine-tagged proteins in native or denaturing conditions. This cartridge can be used with an automated chromatography system,
One-Step Western TM Kit using TMB
 Technical Manual No. 0203 Version 03272008 I Description.. 1 II Kit Contents.. 2 III Applications 3 IV Key Features.. 3 V Storage.. 3 VI One-Step Western TM Protocol. 3 VII Examples. 3 VIII Troubleshooting..
Technical Manual No. 0203 Version 03272008 I Description.. 1 II Kit Contents.. 2 III Applications 3 IV Key Features.. 3 V Storage.. 3 VI One-Step Western TM Protocol. 3 VII Examples. 3 VIII Troubleshooting..
IP 3 receptor function and localization in myotubes: an unexplored Ca 2+ signaling pathway in skeletal muscle
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 3673 IP 3 receptor function and localization in myotubes: an unexplored Ca 2+ signaling pathway in skeletal muscle Jeanne A. Powell 1, *,, Maria Angelica Carrasco 2, *, Dany S. Adams 1,
RESEARCH ARTICLE 3673 IP 3 receptor function and localization in myotubes: an unexplored Ca 2+ signaling pathway in skeletal muscle Jeanne A. Powell 1, *,, Maria Angelica Carrasco 2, *, Dany S. Adams 1,
A General Protocol for GST Pull-down Lili Jing *
 A General Protocol for GST Pull-down Lili Jing * Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA *For correspondence: lilijingcn@gmail.com [Abstract] GST pull-down
A General Protocol for GST Pull-down Lili Jing * Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA *For correspondence: lilijingcn@gmail.com [Abstract] GST pull-down
Standards for Electrophoresis and Blotting
 Electrophoresis and Blotting for Electrophoresis and Blotting A Diverse Portfolio for All Applications A Diverse Portfolio of Bio-Rad s standards provide an excellent means of monitoring electrophoresis
Electrophoresis and Blotting for Electrophoresis and Blotting A Diverse Portfolio for All Applications A Diverse Portfolio of Bio-Rad s standards provide an excellent means of monitoring electrophoresis
Protein A Mag Sepharose Xtra Protein G Mag Sepharose Xtra
 GE Healthcare Data file 28-9768-1 AA Protein sample preparation Protein A Mag Sepharose Xtra Xtra products are magnetic beads designed for efficient, high capacity small-scale purification/screening of
GE Healthcare Data file 28-9768-1 AA Protein sample preparation Protein A Mag Sepharose Xtra Xtra products are magnetic beads designed for efficient, high capacity small-scale purification/screening of
Rotation Report Sample Version 2. Due Date: August 9, Analysis of the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Activity of the S. cerevisiae Ats1 Protein
 Rotation Report Sample Version 2 Due Date: August 9, 1998 Analysis of the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Activity of the S. cerevisiae Ats1 Protein Anita H. Corbett Advisor: Amy Jones Rotation 1 Abstract:
Rotation Report Sample Version 2 Due Date: August 9, 1998 Analysis of the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Activity of the S. cerevisiae Ats1 Protein Anita H. Corbett Advisor: Amy Jones Rotation 1 Abstract:
Instant-Bands Protein Sample Loading Buffer for SDS-PAGE. User s Manual. View Protein Bands in an SDS Gel. Instantly. EZBiolab.
 Instant-Bands Protein Sample Loading Buffer for SDS-PAGE User s Manual View Protein Bands in an SDS Gel Instantly www.ezbiolab.com 2 Instant-Bands User s Manual Table of Contents Introduction 3 Storage
Instant-Bands Protein Sample Loading Buffer for SDS-PAGE User s Manual View Protein Bands in an SDS Gel Instantly www.ezbiolab.com 2 Instant-Bands User s Manual Table of Contents Introduction 3 Storage
Strep-tag Technology for Molecular Weight (MW) Determinations on Blots Using Precision Plus Protein Standards
 blotting tech note 2847 Strep-tag Technology for Molecular Weight (MW) Determinations on Blots Using Precision Plus Protein Standards Introduction Bio-Rad has consistently provided innovative standards
blotting tech note 2847 Strep-tag Technology for Molecular Weight (MW) Determinations on Blots Using Precision Plus Protein Standards Introduction Bio-Rad has consistently provided innovative standards
BCH 462. Single Radial Immunodiffusion and Immuno-electrophoresis
 BCH 462 Single Radial Immunodiffusion and Immuno-electrophoresis Immunoassays tests include: 1. Precipitation. 2. Agglutination. 3. Immunofluorescence. 4. Radioimmunoassay (RIA). 5. Enzyme-Linked Immuno
BCH 462 Single Radial Immunodiffusion and Immuno-electrophoresis Immunoassays tests include: 1. Precipitation. 2. Agglutination. 3. Immunofluorescence. 4. Radioimmunoassay (RIA). 5. Enzyme-Linked Immuno
Rho activation kit. Catalog Number: ADI-EKS-465. Table of Contents
 Rho activation kit Catalog Number: ADI-EKS-465 Table of Contents Assay Design Page 1 Scientific Overview 2 Precautions 2 Materials Provided 3 Storage of Materials 3 Materials Required but Not Provided
Rho activation kit Catalog Number: ADI-EKS-465 Table of Contents Assay Design Page 1 Scientific Overview 2 Precautions 2 Materials Provided 3 Storage of Materials 3 Materials Required but Not Provided
ANAT Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales. UNSW Copyright Notice
 ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales The actin cytoskeleton Prof Peter Gunning Oncology Research Unit Room 502A Wallace Wurth Building Email:
ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales The actin cytoskeleton Prof Peter Gunning Oncology Research Unit Room 502A Wallace Wurth Building Email:
Allergy Warning: Students with know shellfish allergies should avoid all potential contact with shellfish samples.
 Biology 3A Laboratory Protein Fingerprinting using SDS-PAGE Objectives: To use polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) to compare protein profiles derived from muscle tissue of different seafood items.
Biology 3A Laboratory Protein Fingerprinting using SDS-PAGE Objectives: To use polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) to compare protein profiles derived from muscle tissue of different seafood items.
electrophoresis (100-A filaments/muscle contractile proteins/two-dimensional isoelectric focusing/sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis)
 Proc. Nat!. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 74, No. 4, pp. 1450-1454, April 1974 Biochemistry Invariance and heterogeneity in the major structural and regulatory proteins of chick muscle cells revealed by two-dimensional
Proc. Nat!. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 74, No. 4, pp. 1450-1454, April 1974 Biochemistry Invariance and heterogeneity in the major structural and regulatory proteins of chick muscle cells revealed by two-dimensional
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
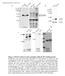 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
HiPer Immunoprecipitation Teaching Kit
 HiPer Immunoprecipitation Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI016 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment Storage Instructions The kit is stable for 6 months from the date of receipt
HiPer Immunoprecipitation Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI016 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment Storage Instructions The kit is stable for 6 months from the date of receipt
RNA EXTRACTION KIT DIAGENODE. Instruction Manual. RNA Extraction kit. Cat. No. C (AL ) Version 1 /
 RNA EXTRACTION KIT Instruction Manual RNA Extraction kit Cat. No. C20000010 (AL-001-0050) Version 1 / 21.05.12 Content Principle 4 General remarks before starting 5 Required materials and reagents 5 Standard
RNA EXTRACTION KIT Instruction Manual RNA Extraction kit Cat. No. C20000010 (AL-001-0050) Version 1 / 21.05.12 Content Principle 4 General remarks before starting 5 Required materials and reagents 5 Standard
Binding and Phosphorylation of Tubulin by G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinases*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 273, No. 32, Issue of August 7, pp. 20308 20316, 1998 1998 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Binding and Phosphorylation
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 273, No. 32, Issue of August 7, pp. 20308 20316, 1998 1998 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Binding and Phosphorylation
