WHITE PAPER Understanding Linux Deployment Strategies: The Business Case for Standardizing on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
|
|
|
- Anthony Park
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WHITE PAPER Understanding Linux Deployment Strategies: The Business Case for Standardizing on Red Hat Enterprise Linux Sponsored by: Red Hat Al Gillen April 2011 Randy Perry Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA USA P F EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Commercial products based on open source software have long enjoyed a symbiotic relationship with the open source world that is both cooperative and competitive. In the end, users benefit with a variety of product choices that range from free to commercially supported, enterprise-grade fee-based solutions. Across that range of solutions, it is easy to presume that free solutions are by definition cheaper to own simply because the original acquisition cost ($0 out of pocket) is so compelling. While this might be a valid assumption if IT labor costs were also zero, as soon as an hourly value is attached to IT labor and end-user productivity, the cost associated with free products suddenly becomes much higher. IDC research typically finds that the cost of operating system software is a relatively minor component of an overall total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis but that IT labor costs are generally a far greater contributor to TCO calculations. As a result, products that offer efficiency and productivity improvements for IT staff generally end up with competitive and often lower TCO metrics when all costs are considered. This IDC White Paper compares organizations using a commercial Linux subscription from Red Hat to support their Linux servers with organizations that are using a mixed environment of both commercially supported and nonpaid Linux distributions and organizations that are primarily using nonpaid Linux distributions aboard their servers. The result of this analysis is clear: Organizations that have standardized on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) recover up-front subscription costs through more efficient operations, higher ratios of servers and users per administrator, and a significantly lower annual downtime cost compared with organizations that maintain a Linux server infrastructure that is either mixed or primarily nonpaid. Specific observations include:! Organizations standardized on RHEL have more efficient IT staffs. Shops standardized on RHEL average 174 servers per administrator, while mixed shops average 115 servers per administrator and primarily nonpaid shops average only 97 servers per administrator.
2 ! In terms of end users per administrator, shops standardized on RHEL average 422 users per administrator compared with 373 users per administrator in mixed shops and 358 users per administrator in primarily nonpaid shops. This efficiency, combined with lower downtime and fewer help desk issues, means that RHEL shops incur $18,960 in annual IT labor costs per 100 users, while primarily nonpaid shops experience annual IT labor costs of $37,099 per 100 users.! Downtime was another real differentiator. Shops standardized on RHEL average 0.4 hours per year per user, or about one-fifth the amount of downtime experienced by shops that are mixed and slightly less for shops using primarily nonpaid Linux distributions on their Linux servers. The cost for downtime adds up quickly, with annual downtime user productivity cost for RHEL shops at $12 per year per 100 users compared with mixed shops at $63 per year per 100 users and primarily nonpaid shops at $67 per year per 100 users.! Hardware and management software savings were also noted. The combination of more end users per server and more standardized maintenance operations, together with a longer useful life cycle (i.e., less frequent replacement), resulted in lower hardware costs. Hardware savings, combined with less need for management software tools, means shops standardized on RHEL are spending $12,029 per year per 100 users, while mixed shops spend $19,201 per year per 100 users and primarily nonpaid shops are spending $25,206 per year per 100 users.! Our findings indicate that organizations that heavily use nonpaid Linux end up with higher total operational costs of $62,305 per year per 100 users compared with $37,494 per year per 100 users for shops standardized on RHEL with the up-front subscription cost for RHEL being recovered through lower operational costs in as little as 7 months. IN THIS WHITE PAPER This IDC White Paper considers the operational experiences of customer sites that are highly standardized on RHEL, using the product on over 70% of their Linux servers, and contrasts these organizations with customer sites that have a mixed environment of commercially supported and nonpaid Linux server operating systems on their servers (between 45% and 69% of their Linux operating systems are commercially supported) and sites that are running primarily nonpaid Linux distributions (on a minimum of 70% of their Linux servers). These categories of sites are used to establish a comparison of operational cost metrics using common measurement criteria. We take the two extremes primarily nonpaid shops and shops standardized on RHEL and calculate the differential of the TCO, and from that, we calculate the return on investment (ROI) for sites standardized on using RHEL from a primarily nonpaid environment. 2 # IDC
3 METHODOLOGY IDC identified, screened, and qualified multiple end-user organizations and used their experiences as a representative model of the effect of acquiring and deploying Linux. Our research included organizations that are highly standardized on using RHEL and its associated subscription support on over 70% of their company's Linux servers and organizations that primarily use nonpaid Linux distributions on at least 70% of their Linux servers. In addition, IDC interviewed a number of organizations that had a more heterogeneous collection of Linux operating system solutions in place (categorized as mixed). As part of this work, IDC conducted a series of interviews with these companies about their use of and experience in supporting their Linux installations. This analysis included capturing the operational characteristics of their environments, including the size and nature of their deployments; the mix of Linux operating systems in use; the frequency of system and end-user problems, system outages, and help desk calls; and the time spent by IT professionals to support end users within the organization who are accessing applications deployed on servers running Linux. This information is used to create a comparison between organizations that are using commercially supported Linux deployments relying on RHEL and a RHEL support subscription and organizations that are using primarily nonpaid Linux solutions. Comparisons on many metrics were also made between shops standardized on RHEL versus mixed environments, but TCO and ROI calculations used these values only as a checkpoint for the data at the two extremes of the analysis to validate the contrasts found between shops standardized on RHEL and shops that are using primarily nonpaid Linux deployments. For more details on IDC's methodology, see the Appendix. Study Demographics Table 1 introduces the demographics of the organizations interviewed and analyzed to develop the study presented in this IDC White Paper. As noted in Table 1, the commercial customers interviewed, on average, were relatively large organizations with over 1,000 Linux operating systems in use, which includes both virtual servers and physical servers. As noted in Table 1, a high percentage of mission-critical applications are running on Linux servers, with 34% of the users at shops standardized on RHEL accessing applications on Linux and 50% of users at shops that are primarily nonpaid accessing applications on Linux. Virtualization rates were slightly higher at RHEL standardized and mixed shops than at shops that were primarily nonpaid IDC #
4 TABLE 1 Demographics of Companies Studied Standardized on RHEL Mixed Primarily Nonpaid Employees 53,436 88,831 42,850 Percentage of employees using IT services Servers 7,667 15,850 3,363 Linux environment Users of applications running on Linux 18,059 10,610 21,615 Linux servers (virtual and physical) 1,219 1,363 1,730 Percentage of mission-critical applications running on Linux Percentage of Linux instances virtualized Sites with Linux servers IT staff supporting Linux Average experience of Linux staff (years) n = Source: IDC, 2011 One of the interesting differences that emerge from Table 1 is the relative level of staff experience with Linux. The average experience level is directly reflective of the portion of nonpaid Linux that is in use. The amount of staff expertise necessary to support a primarily nonpaid Linux environment is considerably higher than the amount of staff expertise needed to support either a mixed shop or a shop that is standardized on RHEL. The comparison also shows the primarily nonpaid shops with 17.8 IT staff supporting 1,730 virtual and physical Linux servers, mixed shops with 11.8 staff supporting 1,363 virtual and physical servers, and shops standardized on RHEL with 7 IT staff supporting 1,219 virtual and physical servers. IDC notes that larger IT organizations at shops that are primarily nonpaid are likely influenced by the need to have a broader set of skills on staff, including the ability to support the Linux kernel with on-staff expertise. This also contributes to having more experienced (and presumably more expensive) assets in place to do that work. 4 # IDC
5 SITUATION OVERVIEW In the late 1990s and early 2000s, open source software emerged and established itself as a credible system infrastructure software solution to many server workloads that previously had been addressed by Unix/RISC servers or Windows/x86 servers. Initially there was skepticism among some larger enterprise customers about Linux adoption, but open source software solutions proved to be reliable and cost-effective. Although GPL open source solutions long preceded Linux, widespread exposure to and experience with Linux really changed the acceptability of broadly using open source solutions, and before long, open source developed middleware solutions, database solutions, and even some application solutions entered the market. Today, dozens of examples of open source software are in the mainstream, and concerns over the viability, sustainability, and reliability of the solutions built on open source software have ceased to be an impediment to adoption. Open source proponents have long asserted that software should be freely available, and accordingly, mainstream open source based products are accompanied by available source code. This licensing requirement means that for every commercial product built from open source software, the source code for that commercial product is available, without any acquisition cost. At the same time, alongside most open source communities, commercial entities have formed to offer a commercialized version of open source software. The commercial entities generally support a specific snapshot of an open source technology and serve the needs of enterprise customers that demand long support life cycles; API stability; and level 1, 2, and 3 technical support for problems that may occur. IDC believes the availability of commercialized versions of open source solutions to be a critical dimension in making the greater open source development successful. Without high-quality, commercially packaged versions of open source solutions, large portions of the total available customer market simply would not be accessible to open source software solutions. Large customers see value in commercialized open source solutions for multiple reasons, including that for many organizations, technical adoption barriers and business adoption barriers remain that are easily overcome by a commercialized version of the software. Using Linux as an example, we note that system management solutions, database, middleware, and commercial applications are required for a healthy, robust, and complete Linux ecosystem to exist. And for these secondary solutions to be developed and supported on Linux, a predictable, versionstable release of Linux must be available for these secondary products to build upon. Cooperative and Competitive IDC research has found that 58% of worldwide Linux deployments use a commercially supported distribution, while the balance is made up of nonpaid Linux solutions. The nonpaid solutions include community Linux distributions (CentOS, Debian, Fedora, etc.), while some of the deployments use commercial Linux distributions that either have expired from a previous subscription support contract or are simply deployed inconsistently with contractual requirements (sometimes 2011 IDC #
6 intentionally, sometimes unintentionally). Some regions tend to run at higher penetration rates of paid distribution use; for example, the average paid usage for the United States was 68% in In various research projects over the years, IDC has found that customers tend to perceive free versions of open source software as a meaningful contributor to a lower TCO. However, we have long found that TCO is consistently far more influenced by labor costs than by acquisition costs of a singular software product such as the operating system. IDC notes that commercial products based on open source software have long enjoyed a symbiotic relationship with the open source world that is both cooperative and competitive. In the end, users benefit with a variety of product choices that range from free to commercially supported, enterprise-grade fee-based solutions. However, when solutions for commercial workloads are considered, multiple factors suggest that a commercially supported solution is the better option. First, for both end customers and ISVs that write applications, the concept of a fast-revving mainline Linux kernel is seen as a negative feature, simply because once an application is developed or ported to a Linux distribution, or once an enterprise customer makes a deployment, the return on that investment happens only if the investment can stay in place for a long enough time typically three to five years, often longer. Commercially supported Linux distributions enable customers to enjoy that long period of return after making the initial investment to deploy without making customers feel like they are at risk from a security or reliability standpoint because they have fallen so far behind the mainline release version. Behind the Models: Shops using either a mixed environment or a primarily nonpaid environment are 20 to 25 percentage points more likely to say they believe their choice of software helps reduce costs. BUSINESS VALUE OF A RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX SUBSCRIPTION Fully understanding the benefit of commercially supported software requires taking a look at quantifiable metrics. This section presents such data, including IT administrative efficiency and productivity and business agility. The Impact on IT Productivity As previously noted, shops standardized on RHEL have a higher number of servers and IT users per administrator. However, the use of a highly standardized environment and the use of management tools across that environment lead to other benefits, including the ability to deploy a virtual machine far faster than mixed and primarily nonpaid shops that are presumably less automated. The result is that a RHEL shop can deploy a virtual server in less than half the time it takes for other shops to deploy a new virtual server. The capability to deploy quickly also reveals itself in the ability to deploy new applications more quickly, with a RHEL shop able to roll out an application in half the time that a primarily nonpaid Linux shop would take to do the same rollout. IDC refers to the ability to deploy applications quickly as "business agility," meaning an organization can respond to changing needs quickly and efficiently. Behind the Models: The percentage of the budget associated with "keeping the lights on" is 20 points higher for shops that support mixed environments or primarily nonpaid environments. Shops standardized on RHEL allocate less of their budget to this area. 6 # IDC
7 Organizations standardized on RHEL have more efficient IT staffs. As shown in Table 2, shops standardized on RHEL average 174 servers per administrator, while mixed shops average 115 servers per administrator and primarily nonpaid shops average 97 servers per administrator. In terms of end users per administrator, shops standardized on RHEL average 422 users per administrator compared with 373 users per administrator in mixed shops and 358 users per administrator in primarily nonpaid shops. TABLE 2 IT Productivity Key Performance Metrics for Shops Standardized on RHEL Versus Mixed Shops Versus Primarily Nonpaid Linux Shops IT Productivity Standardized on RHEL Mixed Primarily Nonpaid Servers per administrator (virtual and physical) IT users per administrator Hours to deploy a virtual server Days to deploy an application Source: IDC, 2011 We believe that one of the reasons for the more efficient staffs at shops standardized on RHEL is the reduced need for IT professionals with deep kernel and operating systems expertise; instead, they can apply their skills (and workdays) toward their organization's core competency its line-of-business applications. As noted earlier, shops that support their own Linux distributions still need line-of-business expertise, but they also need operating system level technical expertise. Simply stated, shops that support their own Linux distributions have more IT infrastructure to support and therefore need larger staffs with more diversified skill sets. Behind the Models: Shops standardized on RHEL tend to have higher percentages of virtual instances of Linux running. In addition to more efficient operations, this study found that RHEL shops experienced 82% less time dealing with server downtime and 92% less time dealing with help desk activities associated with applications running on Linux servers. We believe that downtime costs are lower for a number of reasons, including a higher level of consistency, better management practices (allowed because of the consistency), and external factors such as the regression testing that is being done not only by Red Hat but also by Red Hat's ISV partner community, which likely culls most potential issues long before patches and application updates are distributed to customer organizations. The ISVs also benefit because Red Hat delivers enhancements and hardens code so that they have a solid platform to build on IDC #
8 Ultimately, IT staffers not only are relieved from the responsibility of identifying and resolving conflicts caused by patches and updates but also benefit from the wealth of input that a single central vendor has from other customer experiences that can lead to identifying and resolving problems before other shops experience them. Because of their more efficient IT staffs, RHEL shops in our study averaged 49% lower IT staffing costs than primarily nonpaid shops, with annual IT staff labor costs at $18,960 per 100 users compared with $22,009 for mixed shops and $37,099 for primarily nonpaid shops (see Figure 1). These savings are made up of lower server administration costs, lower help desk costs, and a modest contribution from new server deployment costs. Behind the Models: More than half of the shops (57%) standardized on RHEL engage with Red Hat for architecture and design services, which likely helps improve their overall system performance. FIGURE 1 Annual IT Staff Labor Cost Comparison of Shops Standardized on RHEL Versus Mixed Shops Versus Primarily Nonpaid Linux Shops 35,000 ($ per year per 100 users) 30,000 25,000 20,000 15,000 10,000 5,000 0 Server administration Help desk/downtime response Server deployment Standardized on RHEL Mixed Primarily nonpaid Source: IDC, 2011 The takeaway from Table 2 and Figure 1 is to recognize that real business value is associated with a consistent, standardized infrastructure. It is important to note that this is not a Linux phenomenon; IDC research has found the same results in other operating systems. For instance, a mixed Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 client environment typically proves to be far more expensive to operate and maintain than a client environment that uses only one of the three products. 8 # IDC
9 Another important point is that IT shops should focus on cost avoidance and savings in key areas. For example, IT staff should focus on core IT competency requirements rather than on developing deep expertise in an area such as operating system configuration and support a topic that requires deep expertise but in the end adds little competitive advantage to business operations. The Impact on Infrastructure Costs Table 3 presents costs associated with the deployment of and maintenance of infrastructure, including hardware costs, management tool costs, and IT labor costs associated with infrastructure support (excluding server administrative costs). Of particular note is that even with the higher Linux software costs associated with RHEL solutions, overall annual infrastructure and operating system subscription costs for environments standardized on RHEL are 52% lower than those for nonpaid environments $12,029 compared with $25,206 per year per 100 users and 37% lower than those for mixed environments. The reduced infrastructure cost is driven by two primary factors:! Because of a more standardized operating and support environment, the RHEL shops were able to adopt a more standardized hardware environment to deliver service. The benefits of the standardized environment compared with the primarily nonpaid environment were 18% more end users per server and 13% more users compared with the mixed environment. In addition, we found that shops standardized on RHEL had longer useful replacement cycles, slightly higher incidence of virtualized servers, and standardized maintenance operations, which ameliorated dramatic per-server costs associated with nonstandard environments. IDC believes that strong OEM partnerships help RHEL offer these benefits. By contrast, many nonpaid Linux distributions have no direct OEM certification. Behind the Models: Shops standardized on RHEL have longer life cycles, probably the result of greater standardization; this behavior adds to ROI and TCO benefits IDC #
10 TABLE 3 IT Hardware, Software, and Labor Costs for Shops Standardized on RHEL Versus Mixed Shops Versus Primarily Nonpaid Linux Shops Infrastructure Costs Standardized on RHEL Mixed Primarily Nonpaid Hardware ($ per year per 100 users) Additional management tools ($ per year per 100 users) Total infrastructure costs ($ per year per 100 users) 11,029 15,670 20,265 1,000 3,437 4,941 12,029 19,106 25,206 IT Labor Costs Standardized on RHEL Mixed Primarily Nonpaid Savings (Hours per Year per 100 Users) % Savings per Year per 100 Users Server administration (hours per year per 100 users) Help desk/ downtime response (hours per year per 100 users) Server deployment (hours per year per 100 users) Total (hours per year per 100 users) 445 NA NA NA NA Source: IDC, 2011! Not surprisingly, secondary management tool costs were 80% higher for nonpaid Linux, presumably because the tools supplied with the distribution were less comprehensive than the tools available with Red Hat subscriptions. 10 # IDC
11 Figure 2 presents a graphical view of IT costs related to infrastructure, using data from Table 3. In Figure 2, we see comparisons between IT staffing, infrastructure, and subscription costs for the Linux operating system in use and an allowance for RHEL Linux subscription costs. Behind the Models: Shops using primarily nonpaid Linux and mixed shops have dramatically higher third-party management software costs than shops standardized on RHEL. FIGURE 2 Annual IT Cost Comparison of Shops Standardized on RHEL Versus Primarily Nonpaid Linux Shops 70,000 ($ per year per 100 users) 60,000 50,000 40,000 30,000 20,000 10,000 0 Standardized on RHEL Primarily nonpaid RHEL subscription Infrastructure IT staffing Source: IDC, 2011 The Impact on End-User Productivity Finally, we take a look at end-user productivity in shops that are standardized on RHEL compared with shops that are primarily nonpaid. We measure user productivity by calculating the number of hours that IT users have access to the applications they need to do their jobs. Unplanned downtime is the major disruption of user productivity. Downtime is one of the metrics that are often difficult for many organizations to quantify. In this study, it was one of the real differentiators for shops standardized on RHEL at 0.4 hours per user per year, or about one-fifth the amount of downtime experienced by shops that were running primarily nonpaid Linux distributions on their Linux servers (see Table 4). Time spent dealing with application-related issues also impacts user productivity IDC #
12 TABLE 4 User Productivity Key Performance Metrics for Shops Standardized on RHEL Versus Mixed Shops Versus Primarily Nonpaid Linux Shops User Productivity Standardized on RHEL Mixed Primarily Nonpaid Downtime (hours per year per user) Help desk (hours per year per user) Source: IDC, 2011 It may not be surprising that organizations with Linux deployments heavily dominated by a commercially supported Linux distribution experience less downtime. But what can be surprising is how high the cost of downtime is. The cost for downtime adds up quickly just over $12 per year per 100 users for RHEL shops compared with $63 per year per 100 users for mixed shops and over $67 per year per 100 users for primarily nonpaid shops. (See the Methodology section in the Appendix for more detail on calculating user downtime costs.) End-user costs associated with help desk requests also have a ratio of similar magnitude, with RHEL environments at $4 per year per 100 users compared with $8 per year per 100 users for mixed environments and a meaningful total of $44 per year per 100 users, or about 10 times the cost, albeit on a much lower number, for primarily nonpaid environments (see Figure 3). 12 # IDC
13 FIGURE 3 Annual User Downtime Cost Comparison of Shops Standardized on RHEL Versus Mixed Shops Versus Primarily Nonpaid Linux Shops ($ per year per 100 users) Help desk Standardized on RHEL Mixed Primarily nonpaid Downtime Source: IDC, 2011 ROI ANALYSIS While few organizations are likely to make a sudden move from being primarily nonpaid to being standardized on RHEL, the data suggests that even moving to a mixed environment has some benefits, though the greatest benefit comes from moving to a unified infrastructure that incorporates a single Linux distribution. While the metric defined for this paper describes an environment that is standardized on a single commercially supported operating system, such standardization includes more than merely the value of a consistent singular distribution. If pure consistency delivered the benefit to users, the spread between a primarily nonpaid environment and a shop that is standardized on RHEL would be far less dramatic. It is really a combination of this standardization bolstered by the inherent value that a commercial Linux distribution brings to the table through management tools, training, support, and other service offerings. To be certain, nonpaid, open source software solutions make good business sense and may not lead to higher costs for some workloads, but we believe that those solutions tend to be concentrated around installations where there are few or no application workloads, with the server mainly using services normally included with the Linux operating system. One good example is virtualized infrastructure or Web workload servers, which do not have mission-critical dependencies. Using virtualization management tools, it is possible to follow a destructive management paradigm that a failed server operating system is simply destroyed and replaced by a new image spun up from the virtualization management tools IDC #
14 For the rest of mainstream commercial IT workloads, where daily or hourly business activities take place that depend on accessing these applications, the conclusion of this study is that the best approach is to absorb the up-front capex investment in exchange for lower long-term operation cost improvements. IDC uses the net present value (NPV) of the savings and increased revenue over three years in calculating the ROI and payback period for the deployment. The NPV of the savings is determined by subtracting the amount that would have been earned by investing the original sum in an instrument yielding a 12% return (to allow for the missed opportunity cost that could have been realized using that capital). This accounts for both the assumed cost of money and the assumed rate of return. The ROI analysis is shown in Table 5. On average, companies identified discounted benefits of $79,480 per 100 users for a three-year period at a total discounted investment of $16,851 per 100 users. The investment yields a return of 372% over three years. Companies included in this study on average were able to pay back their initial investment in 7 months. TABLE 5 Three-Year ROI Analysis per 100 Users Benefit (discounted) $79,480 Investment (discounted) $16,851 Net present value (NPV) $62,629 ROI = NPV/investment 372% Payback 7 months Discount rate 12% Source: IDC, 2011 FUTURE OUTLOOK IDC believes that the industry is increasingly moving toward modular solutions. Over the past decade, many application programs have made a dramatic shift away from utilizing operating system APIs to a more abstracted deployment model on a Java layer, which insulates and virtualizes the application from the underlying operating system. Hardware vendors are increasingly integrating operating systems into their hardware platforms to give customers a turnkey deployment experience, lowering initial deployment costs. This trend directly aligns with a movement to embrace cloud computing over the longer term. As this transition happens, organizations increasingly will focus on the application layers and turn over the day-to-day management of the operating system and related infrastructure management to a qualified partner the hardware vendor, the operating system vendor, or the cloud provider. 14 # IDC
15 This transition is happening first in mature geographies, where IT labor costs tend to be highest. Not surprisingly, mature geographies are also where the penetration of commercially supported Linux tends to be highest. By contrast, emerging geographies, where IT labor costs continue to be comparatively low, are trailing on this trend and will be a bigger challenge to convince of the real value associated with the broad use of a commercially supported Linux distribution. Mature geographies are likely to latch onto opportunities to reduce costs, boost staff efficiency, and equally important, reduce user downtime and the productivity losses that accompany that downtime. Management is a dimension that has not been explicitly broken out in this study, but there is an implicit connection between a well-managed system and lower IT costs. CHALLENGES/OPPORTUNITIES Users considering their Linux options will easily grasp the benefits and efficiencies associated with the use of a single commercial Linux distribution, and why, outsourcing much of the effort of keeping that distribution current, secure, and operationally complete to a commercial vendor. However, users and commercial vendors such as Red Hat still face challenges and opportunities, including:! Opportunity: Better ISV support. The use of a commercial distribution, especially one with the dominant market share that Red Hat enjoys, is particularly attractive to ISVs. As a result, end-user organizations will likely have far better ISV support and choices for a commercial Linux deployment than for a noncommercial distribution. In fact, in many cases, ISVs offer no support for noncommercial distributions simply because they have to limit their test and support matrix. On a related note, a service partner that provides more value than pure break/fix can likewise bring incremental value to user organizations.! Challenge: Overcoming the perception that free is less expensive. In study after study, IDC finds that customers still associate low- or no-cost software with automatically offering a lower cost of ownership than a commercial product that requires an up-front acquisition and/or annual maintenance subscription. Studies such as this one clearly discredit that concept, but IT professionals continue to buy into the concept of using free software as a cost reduction strategy.! Opportunity: Easy migration to RHEL. One of the great benefits of using Linux is that compatibility is good between distributions, and moving from a nonpaid distribution to RHEL preserves most of the existing IT investment. Tools, scripts, management practices, and most application code will move relatively painlessly to a different distribution.! Challenge: Getting customers to remain under subscription and stay in compliance. Red Hat's approach to subscriptions requires that RHEL customers carry subscription coverage for all RHEL servers in their organization. In many cases, we find shops that carry a subscription for only a portion of their RHEL instances. In fact, IDC research finds that RHEL is the single most commonly used nonpaid Linux in the industry. IDC notes that most customers, particularly in mature geographies, want to be in compliance, and when they are out of compliance, it 2011 IDC #
16 often is because of a misunderstanding of the contractual terms rather than the result of any malicious intent. Curiously, this is not a Linux-only phenomenon; indeed, it is a problem that even companies like Microsoft struggle with today.! Opportunity: Users can lower operational costs by using RHEL rather than nonpaid Linux. Most importantly, this study clearly identifies the benefit associated with the broad use of a commercially supported Linux distribution such as RHEL in organizations. CONCLUSION Labor costs often are not readily obvious and even harder to measure and track, and they usually get buried in larger operational expense metrics that larger organizations track. As a result, it becomes difficult, if not impossible, for many IT managers to really understand the cost associated with supporting free software. For many organizations, these operational costs are relatively invisible compared with a line item on a purchase order that pays for a product license or subscription a cost item that ultimately is accounted for as a capital expense investment. But tapping an expert organization to support a critical layer of the corporate infrastructure not only is justified but also is an investment that pays dividends over the long term. Users should carefully consider Red Hat's position in the industry, its ability to deliver a strong suite of related management tools and middleware, and its ability to be a strategic partner that can provide a technology road map and deliver on that road map so that IT professionals can focus on their key value-add to their business: maximizing their organization's competitive capabilities and delivering maximum value to corporate and end customer users. APPENDIX Methodology IDC's standard ROI methodology was utilized for this project. This methodology is based on gathering data from current users of the technology as the foundation for the model. As part of this study, IDC identified, screened, and qualified 18 end-user organizations and used the experiences of these organizations as a representative model of the effect of acquiring and deploying Linux. The qualified organizations included those that are highly standardized, using RHEL and its associated subscription support on over 70% of the company's Linux servers and for organizations that primarily use nonpaid Linux distributions on at least 70% of their Linux servers. In addition, IDC interviewed a number of organizations that had a mixture of solutions in place (categorized as mixed). In these interviews, IDC asked these companies about their use of Linux and carefully probed customers about their experience with the use of RHEL and the use of nonpaid Linux, and for mixed shops, the use of commercially supported solutions in 16 # IDC
17 use that are supported by vendors including Red Hat and other Linux server operating system providers. This analysis included capturing the operational characteristics of these organizations' environments, including the frequency of end-user problems, outages, and help desk calls and the time spent by IT professionals to support servers and server applications within the organization. No comparison was made with organizations that have mixed infrastructure, although data collected from these organizations was directly utilized to validate the contrasts found between shops standardized on RHEL and shops that are primarily nonpaid Linux deployments. The data collected from these two groups, and the differences between them, is used to calculate TCO and ROI. Based on these interviews, IDC performs a three-step process to calculate the ROI and payback period: 1. Measure the savings from reduced IT costs (staff, hardware, software, maintenance, and IT support), increased user productivity, and improved revenue over the term of the deployment. 2. Ascertain the investment made in deploying the solution and the associated training and support costs. 3. Project the costs and savings over a three-year period and calculate the ROI and payback for the deployed solution. IDC uses the NPV of the savings and increased revenue over three years in calculating the ROI and payback period for the deployment. The NPV of the savings is determined by subtracting the amount that would have been earned by investing the original sum in an instrument yielding a 12% return (to allow for the missed opportunity cost that could have been realized using that capital). IDC bases the payback period and ROI calculations on a number of assumptions, which are summarized as follows: 1. Time values are multiplied by burdened salary (salary + 28% for benefits and overhead) to quantify efficiency and manager productivity savings. 2. Downtime values are a product of the number of hours of downtime multiplied by the number of users affected. 3. The impact of unplanned downtime is quantified in terms of impaired end-user productivity and lost revenue. 4. Lost productivity is a product of downtime multiplied by burdened salary. 5. Lost revenue is a product of downtime multiplied by the average revenue generated per hour. 6. The NPV of the three-year savings is calculated by subtracting the amount that would have been realized by investing the original sum in an instrument yielding a 12% return to allow for the missed opportunity cost. This accounts for both the assumed cost of money and the assumed rate of return IDC #
18 Because every hour of downtime does not equate to a lost hour of productivity or revenue generation, IDC attributes only a fraction of the result to savings. As part of our assessment, we asked each company what fraction of downtime hours to use in calculating productivity savings and the reduction in lost revenue. IDC then taxes the revenue at that rate. Further, because IT solutions require a deployment period, the full benefits of the solution are not available during deployment. To capture this reality, IDC prorates the benefits on a monthly basis and then subtracts the deployment time from the first-year savings. Note: All numbers in this document may not be exact due to rounding. Definitions Table 6 presents definitions for the categories of user organizations that were analyzed in this IDC White Paper. TABLE 6 Definitions for Categories Used in This IDC White Paper Number Average Linux Use (% of Total Servers in Use) Nonpaid (general definition): Linux servers not under a current commercial support subscription or Linux server operating systems that are free or nonpaid NA NA Primarily nonpaid: Minimum of 70% of Linux servers using nonpaid Linux 6 84 Mixed: Includes 45 69% of Linux servers using a paid distribution from one or more vendors, which may or may not include Red Hat Standardized on RHEL: Minimum of 70% of Linux servers covered by RHEL subscription Source: IDC, 2011 Copyright Notice External Publication of IDC Information and Data Any IDC information that is to be used in advertising, press releases, or promotional materials requires prior written approval from the appropriate IDC Vice President or Country Manager. A draft of the proposed document should accompany any such request. IDC reserves the right to deny approval of external usage for any reason. Copyright 2011 IDC. Reproduction without written permission is completely forbidden. 18 # IDC
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA USA P F
 Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com W H I T E P A P E R D e s k t o p O p t i m i z a t i o n U s i n g M D O P : C o n t i n u e d I
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com W H I T E P A P E R D e s k t o p O p t i m i z a t i o n U s i n g M D O P : C o n t i n u e d I
WHITE PAPER Demonstrating Return on Investment with Enterprise-Class Identity and Access Management Technology
 WHITE PAPER Demonstrating Return on Investment with Enterprise-Class Identity and Access Management Technology Sponsored by: Novell Sally Hudson November 2007 Randy Perry EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Global Headquarters:
WHITE PAPER Demonstrating Return on Investment with Enterprise-Class Identity and Access Management Technology Sponsored by: Novell Sally Hudson November 2007 Randy Perry EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Global Headquarters:
W H I T E P A P E R B u s i n e s s V a l u e o f A u t o m a t e d O u t p u t M a n a g e m e n t
 Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com W H I T E P A P E R B u s i n e s s V a l u e o f A u t o m a t e d O u t p u t M a n a g e m e n
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com W H I T E P A P E R B u s i n e s s V a l u e o f A u t o m a t e d O u t p u t M a n a g e m e n
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA USA P F
 Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com WHITE PAPER Why Linux Is Good for ISVs Sponsored by: Red Hat and Intel Julie Tiley August 2005 IDC
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com WHITE PAPER Why Linux Is Good for ISVs Sponsored by: Red Hat and Intel Julie Tiley August 2005 IDC
Global Media and Entertainment Company Uses IBM Cloud for Skytap Solutions to Deliver More Cost-Effective, Functional, and Timely Application Releases
 IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT Global Media and Entertainment Company Uses IBM Cloud for Skytap Solutions to Deliver More Cost-Effective, Functional, and Timely Application Releases Sponsored by: Skytap Inc.
IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT Global Media and Entertainment Company Uses IBM Cloud for Skytap Solutions to Deliver More Cost-Effective, Functional, and Timely Application Releases Sponsored by: Skytap Inc.
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA USA P F
 WHITE PAPER Dell Client Migration and Deployment Services Sponsored by: Dell Matt Healey October 2009 Katie Broderick IDC OPINION Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200
WHITE PAPER Dell Client Migration and Deployment Services Sponsored by: Dell Matt Healey October 2009 Katie Broderick IDC OPINION Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200
S U R V E Y I D C O P I N I O N. Cushing Anderson
 S U R V E Y I m p a c t o f T r a i n i n g o n N e t w o r k A d m i n i s t r a t i o n : C e r t i f i c a t i o n L e a d s t o O p e r a t i o n a l P r o d u c t i v i t y Cushing Anderson I D C
S U R V E Y I m p a c t o f T r a i n i n g o n N e t w o r k A d m i n i s t r a t i o n : C e r t i f i c a t i o n L e a d s t o O p e r a t i o n a l P r o d u c t i v i t y Cushing Anderson I D C
The Business Value of Red Hat CloudForms
 White Paper The Business Value of Red Hat CloudForms Sponsored by: Red Hat Stephen Elliot October 2017 Matthew Marden EXECUTIVE SUMMARY IDC's research shows that the majority of enterprise-scale organizations
White Paper The Business Value of Red Hat CloudForms Sponsored by: Red Hat Stephen Elliot October 2017 Matthew Marden EXECUTIVE SUMMARY IDC's research shows that the majority of enterprise-scale organizations
Cloud Skills and Organizational Influence: How Cloud Skills Are Accelerating the Careers of IT Professionals
 White Paper Cloud Skills and Organizational Influence: How Cloud Skills Are Accelerating the Careers of IT Professionals Sponsored by: Microsoft Cushing Anderson May 2017 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Cloud is becoming
White Paper Cloud Skills and Organizational Influence: How Cloud Skills Are Accelerating the Careers of IT Professionals Sponsored by: Microsoft Cushing Anderson May 2017 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Cloud is becoming
The Business Value of Microsoft Premier Support Services
 WHITE PAPER The Business Value of Microsoft Premier Support Services Sponsored by: Microsoft Matthew Marden Randy Perry June 2014 Elaina Stergiades EXECUTIVE SUMMARY An IDC analysis demonstrates that Microsoft's
WHITE PAPER The Business Value of Microsoft Premier Support Services Sponsored by: Microsoft Matthew Marden Randy Perry June 2014 Elaina Stergiades EXECUTIVE SUMMARY An IDC analysis demonstrates that Microsoft's
Critical Application And Business KPIs For Successful Cloud Migration. An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by AppDynamics
 Critical Application And Business KPIs For Successful Cloud Migration An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by AppDynamics Authors: Mary Johnston Turner, Tim Grieser August 2017 Sponsored by: AppDynamics Authors:
Critical Application And Business KPIs For Successful Cloud Migration An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by AppDynamics Authors: Mary Johnston Turner, Tim Grieser August 2017 Sponsored by: AppDynamics Authors:
An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by Red Hat Authors: Maureen Fleming, Matthew Marden
 The Business Value of Red Hat Integration Products An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by Red Hat Authors: Maureen Fleming, Matthew Marden Sponsored by: Red Hat Authors: Maureen Fleming Matthew Marden The Business
The Business Value of Red Hat Integration Products An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by Red Hat Authors: Maureen Fleming, Matthew Marden Sponsored by: Red Hat Authors: Maureen Fleming Matthew Marden The Business
The Business Value of Cisco UCS as a Platform for SAP HANA and Other SAP Mission-Critical Applications
 Sponsored by: Cisco Authors: Matthew Marden Jed Scaramella Carl W. Olofson September 2014 The Business Value of Cisco UCS as a Platform for SAP HANA and Other SAP Mission-Critical Applications EXECUTIVE
Sponsored by: Cisco Authors: Matthew Marden Jed Scaramella Carl W. Olofson September 2014 The Business Value of Cisco UCS as a Platform for SAP HANA and Other SAP Mission-Critical Applications EXECUTIVE
Developing a Cloud Strategy for Digital Transformation: Hybrid Cloud and Beyond
 White Paper Developing a Cloud Strategy for Digital Transformation: Hybrid Cloud and Beyond Sponsored by: DellEMC Richard L. Villars September 2016 IDC OPINION For organizations undertaking digital transformation
White Paper Developing a Cloud Strategy for Digital Transformation: Hybrid Cloud and Beyond Sponsored by: DellEMC Richard L. Villars September 2016 IDC OPINION For organizations undertaking digital transformation
Using Avanade s Managed Services to Unlock Business Value. An IDC InfoBrief Sponsored by Avanade March 2017
 Using Avanade s Managed Services to Unlock Business Value March 2017 Business Value Highlights IDC s research and analysis demonstrates that Avanade s managed services deliver an average payback period
Using Avanade s Managed Services to Unlock Business Value March 2017 Business Value Highlights IDC s research and analysis demonstrates that Avanade s managed services deliver an average payback period
Driving Strategic Value with IBM Supply Chain Business Network
 Sponsored by: IBM Authors: Chandana Gopal Matthew Marden Driving Strategic Value with IBM Supply Chain Business Network January 2018 Business Value Highlights More than $4 in business benefits per $1 invested*
Sponsored by: IBM Authors: Chandana Gopal Matthew Marden Driving Strategic Value with IBM Supply Chain Business Network January 2018 Business Value Highlights More than $4 in business benefits per $1 invested*
Next Generation Services for Digital Transformation: An Enterprise Guide for Prioritization
 IDC Executive Brief Sponsored by: Computacenter Authors: Chris Barnard, Francesca Ciarletta, Leslie Rosenberg, Roz Parkinson March 2019 Next Generation Services for Digital Transformation: An Enterprise
IDC Executive Brief Sponsored by: Computacenter Authors: Chris Barnard, Francesca Ciarletta, Leslie Rosenberg, Roz Parkinson March 2019 Next Generation Services for Digital Transformation: An Enterprise
Enterprise Voice Transformation: Migration from TDM to IP
 White Paper Enterprise Voice Transformation: Migration from TDM to IP Sponsored by: AT&T Amy Lind February 2018 IDC OPINION Voice has been the primary method of business communication for more than a century.
White Paper Enterprise Voice Transformation: Migration from TDM to IP Sponsored by: AT&T Amy Lind February 2018 IDC OPINION Voice has been the primary method of business communication for more than a century.
Mediaocean Empowers Better Customer Support Teams and Content with Zendesk
 IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT Mediaocean Empowers Better Customer Support Teams and Content with Zendesk Sponsored by: Zendesk Harsh Singh November 2018 OVERVIEW Mediaocean is an advertising service and software
IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT Mediaocean Empowers Better Customer Support Teams and Content with Zendesk Sponsored by: Zendesk Harsh Singh November 2018 OVERVIEW Mediaocean is an advertising service and software
Ensuring Data Protection and Recovery in the 3rd Platform Era
 WHITE PAPER Ensuring Data Protection and Recovery in the 3rd Platform Era Sponsored by: CommVault and HDS Robert Amatruda August 2014 IDC OPINION Today, the IT industry is experiencing enormous change
WHITE PAPER Ensuring Data Protection and Recovery in the 3rd Platform Era Sponsored by: CommVault and HDS Robert Amatruda August 2014 IDC OPINION Today, the IT industry is experiencing enormous change
Changing IT Leadership: Part 5 Partnering with Vendors and Suppliers
 IDC PERSPECTIVE Changing IT Leadership: Part 5 Partnering with Vendors and Suppliers Serge Findling Aaron Polikaitis EXECUTIVE SNAPSHOT FIGURE 1 Executive Snapshot: Partnering with Vendors and Suppliers
IDC PERSPECTIVE Changing IT Leadership: Part 5 Partnering with Vendors and Suppliers Serge Findling Aaron Polikaitis EXECUTIVE SNAPSHOT FIGURE 1 Executive Snapshot: Partnering with Vendors and Suppliers
IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT
 IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT Global Program Management Firm Improves Project Delivery with Meridian's Proliance Software Suite Sponsored by Meridian Systems Randy Perry October 2012 Overview As one of the largest
IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT Global Program Management Firm Improves Project Delivery with Meridian's Proliance Software Suite Sponsored by Meridian Systems Randy Perry October 2012 Overview As one of the largest
A CIOview White Paper by Scott McCready
 A CIOview White Paper by Scott McCready 1 Table of Contents How to Craft an Effective ROI Analysis... 3 ROI Analysis is Here to Stay... 3 When is an ROI Analysis Not Necessary?... 3 It s More About the
A CIOview White Paper by Scott McCready 1 Table of Contents How to Craft an Effective ROI Analysis... 3 ROI Analysis is Here to Stay... 3 When is an ROI Analysis Not Necessary?... 3 It s More About the
Consolidating on iseries
 Avneesh Saxena VP, Computing Systems Consolidating on iseries www.idc.com CIO Challenges Today Restructuring Emerging Applications Drive Costs Down Security Performance Mobility Capacity Increase Responsiveness
Avneesh Saxena VP, Computing Systems Consolidating on iseries www.idc.com CIO Challenges Today Restructuring Emerging Applications Drive Costs Down Security Performance Mobility Capacity Increase Responsiveness
RunKeeper's Applications Run Better with Applause's In-the-Wild Testing
 IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT RunKeeper's Applications Run Better with Applause's In-the-Wild Testing Sponsored by: Applause Matthew Marden December 2014 Overview RunKeeper of Boston, Massachusetts, develops
IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT RunKeeper's Applications Run Better with Applause's In-the-Wild Testing Sponsored by: Applause Matthew Marden December 2014 Overview RunKeeper of Boston, Massachusetts, develops
Support Services: The Value of Technical Account Managers
 Survey Support Services: The Value of Technical Account Managers Rob Brothers IDC OPINION IDC conducted a worldwide survey of enterprises to determine what value technical account managers (TAMs) brought
Survey Support Services: The Value of Technical Account Managers Rob Brothers IDC OPINION IDC conducted a worldwide survey of enterprises to determine what value technical account managers (TAMs) brought
WHITE PAPER Improving the Services Experience by Injecting Network Intelligence Into the Model
 WHITE PAPER Improving the Services Experience by Injecting Network Intelligence Into the Model Sponsored by: Cisco Leslie Rosenberg July 2011 Chris Barnard Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham,
WHITE PAPER Improving the Services Experience by Injecting Network Intelligence Into the Model Sponsored by: Cisco Leslie Rosenberg July 2011 Chris Barnard Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham,
Dignity Health Transforms the Process of Developing Compensation Plans Through Salary.com's CompAnalyst Platform
 IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT Dignity Health Transforms the Process of Developing Compensation Plans Through Salary.com's CompAnalyst Platform Sponsored by: Salary.com Utsav Arora February 2017 Lisa Rowan OVERVIEW
IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT Dignity Health Transforms the Process of Developing Compensation Plans Through Salary.com's CompAnalyst Platform Sponsored by: Salary.com Utsav Arora February 2017 Lisa Rowan OVERVIEW
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA USA P F
 Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com WHITE PAPER A I D T O R E C O V E R Y : T H E E C O N O M I C I M P A C T O F I T, S O F T W A R E,
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com WHITE PAPER A I D T O R E C O V E R Y : T H E E C O N O M I C I M P A C T O F I T, S O F T W A R E,
WHITE PAPER Quantifying the Return on Investment from Deploying Configuration Management Solutions
 WHITE PAPER Quantifying the Return on Investment from Deploying Configuration Management Solutions Sponsored by: HP Frederick W. Broussard July 2006 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street
WHITE PAPER Quantifying the Return on Investment from Deploying Configuration Management Solutions Sponsored by: HP Frederick W. Broussard July 2006 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street
The Economic Benefits of Puppet Enterprise
 Enterprise Strategy Group Getting to the bigger truth. ESG Economic Value Validation The Economic Benefits of Puppet Enterprise Cost- effectively automating the delivery, operation, and security of an
Enterprise Strategy Group Getting to the bigger truth. ESG Economic Value Validation The Economic Benefits of Puppet Enterprise Cost- effectively automating the delivery, operation, and security of an
ExtraHop Delivers Better User Experience and Security for Enterprises
 Sponsored by: ExtraHop Authors: Tim Grieser Harsh Singh August 2018 Business Value Highlights 740% three-year ROI 4 months to break even 95% reduction in time to detect threats 59% less time to resolve
Sponsored by: ExtraHop Authors: Tim Grieser Harsh Singh August 2018 Business Value Highlights 740% three-year ROI 4 months to break even 95% reduction in time to detect threats 59% less time to resolve
The Benefits of Modern BI: Strategy Companion's Analyzer with Recombinant BI Functionality
 WHITE PAPER The Benefits of Modern BI: Strategy Companion's Analyzer with Recombinant BI Functionality Sponsored by: Strategy Companion Brian McDonough November 2013 IDC OPINION Widespread use of business
WHITE PAPER The Benefits of Modern BI: Strategy Companion's Analyzer with Recombinant BI Functionality Sponsored by: Strategy Companion Brian McDonough November 2013 IDC OPINION Widespread use of business
CLOUDCHECKR ON AWS AND AZURE: A GUIDE TO PUBLIC CLOUD COST MANAGEMENT
 ebook CLOUDCHECKR ON AWS AND AZURE: A GUIDE TO PUBLIC CLOUD COST MANAGEMENT Guide to Cost Management CloudCheckr 2017 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 7 9 10 Intro Optimization Requires Visibility Cost Management
ebook CLOUDCHECKR ON AWS AND AZURE: A GUIDE TO PUBLIC CLOUD COST MANAGEMENT Guide to Cost Management CloudCheckr 2017 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 7 9 10 Intro Optimization Requires Visibility Cost Management
IDC White Paper. The Business Value of the Connected Mainframe for Digital Transformation
 IDC White Paper The Business Value of the Connected Mainframe for Digital Transformation Sponsored by CA Technologies and IBM December 2016 The Business Value of the Connected Mainframe for Digital Transformation
IDC White Paper The Business Value of the Connected Mainframe for Digital Transformation Sponsored by CA Technologies and IBM December 2016 The Business Value of the Connected Mainframe for Digital Transformation
Manufacturing: Small and Midsize Industrial Machinery and Components Manufacturers Are Using Technology to Make a Difference
 Sponsored by: SAP Authors: Raymond Boggs Jeffrey Hojlo August 2016 Manufacturing: Small and Midsize Industrial Machinery and Components Manufacturers Are Using Technology to Make a Difference THE BRIEF
Sponsored by: SAP Authors: Raymond Boggs Jeffrey Hojlo August 2016 Manufacturing: Small and Midsize Industrial Machinery and Components Manufacturers Are Using Technology to Make a Difference THE BRIEF
Taking a Holistic View of the Total Cost of Data Helps CIOs Optimize IT and Business Gains
 WHITE PAPER Taking a Holistic View of the Total Cost of Data Helps CIOs Optimize IT and Business Gains Sponsored by: Delphix Matthew Marden Randy Perry April 2014 Carl W. Olofson EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Data
WHITE PAPER Taking a Holistic View of the Total Cost of Data Helps CIOs Optimize IT and Business Gains Sponsored by: Delphix Matthew Marden Randy Perry April 2014 Carl W. Olofson EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Data
Business Value of Building Apps on the Salesforce Lightning Platform. An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by Salesforce
 Business Value of Building Apps on the Salesforce Lightning Platform An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by Salesforce Authors: Larry Carvalho, Matthew Marden Sponsored by: Salesforce Authors: Larry Carvalho
Business Value of Building Apps on the Salesforce Lightning Platform An IDC White Paper, Sponsored by Salesforce Authors: Larry Carvalho, Matthew Marden Sponsored by: Salesforce Authors: Larry Carvalho
AN EXECUTIVE S GUIDE TO BUDGETING FOR SECURITY INFORMATION & EVENT MANAGEMENT
 WHITE PAPER AN EXECUTIVE S GUIDE TO BUDGETING FOR SECURITY INFORMATION & EVENT MANAGEMENT COST ANALYSIS OF TWO DELIVERY MODELS: SELF-MANAGED SIEM VS. MANAGED SIEM SERVICES AN EXECUTIVE S GUIDE TO BUDGETING
WHITE PAPER AN EXECUTIVE S GUIDE TO BUDGETING FOR SECURITY INFORMATION & EVENT MANAGEMENT COST ANALYSIS OF TWO DELIVERY MODELS: SELF-MANAGED SIEM VS. MANAGED SIEM SERVICES AN EXECUTIVE S GUIDE TO BUDGETING
SAS Is Helping Standard Chartered Comply with IFRS 9 Quickly and Cost Effectively
 IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT SAS Is Helping Standard Chartered Comply with IFRS 9 Quickly and Cost Effectively Sponsored by: SAS Kevin Permenter March 2018 Overview Harsh Singh Standard Chartered PLC is a leading
IDC ExpertROI SPOTLIGHT SAS Is Helping Standard Chartered Comply with IFRS 9 Quickly and Cost Effectively Sponsored by: SAS Kevin Permenter March 2018 Overview Harsh Singh Standard Chartered PLC is a leading
Why a Digital-Ready Network Makes Business Sense. IDC White Paper Sponsored by Cisco IDC#US
 Why a Digital-Ready Network Makes Business Sense IDC White Paper Sponsored by Cisco IDC#US42176917 Why a Digital-Ready Network Makes Business Sense Sponsored by: Cisco Authors: Nolan Greene Robert Parker
Why a Digital-Ready Network Makes Business Sense IDC White Paper Sponsored by Cisco IDC#US42176917 Why a Digital-Ready Network Makes Business Sense Sponsored by: Cisco Authors: Nolan Greene Robert Parker
Ensuring Petabyte-Scale Data Consistency in a Multicloud Environment
 Sponsored by: WANdisco Mission-critical and business-critical applications are becoming distributed across private and public clouds, making data consistency a challenge. IT organizations need to take
Sponsored by: WANdisco Mission-critical and business-critical applications are becoming distributed across private and public clouds, making data consistency a challenge. IT organizations need to take
Dynamic Publishing: Compliance and Risk Management in the Digital World
 Dynamic Publishing: Compliance and Risk Management in the Digital World WHITE PAPER Sponsored by: Quark Marc DeCastro October 2012 Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.620.5533
Dynamic Publishing: Compliance and Risk Management in the Digital World WHITE PAPER Sponsored by: Quark Marc DeCastro October 2012 Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.620.5533
Worldwide IT Operations Management Software Market Shares, 2017: Hybrid Management Drives Growth
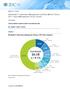 MARKET SHARE Worldwide IT Operations Management Software Market Shares, 2017: Hybrid Management Drives Growth Tim Grieser THIS IDC MARKET SHARE EXCERPT FEATURES SPLUNK IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1
MARKET SHARE Worldwide IT Operations Management Software Market Shares, 2017: Hybrid Management Drives Growth Tim Grieser THIS IDC MARKET SHARE EXCERPT FEATURES SPLUNK IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1
BMC REMEDYFORCE AMERITAS
 ROI CASE STUDY May 2014 BMC REMEDYFORCE AMERITAS THE BOTTOM LINE Ameritas adopted BMC Remedyforce to provide its IT support center with a consistent and standardized process to address IT incidents. Nucleus
ROI CASE STUDY May 2014 BMC REMEDYFORCE AMERITAS THE BOTTOM LINE Ameritas adopted BMC Remedyforce to provide its IT support center with a consistent and standardized process to address IT incidents. Nucleus
Driving Business Value Through Travel and Expense Management Maturity
 WHITE PAPER Driving Business Value Through Travel and Expense Management Maturity Sponsored by: Concur Christopher Chute January 2016 Matthew Marden EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Today's modern organizations are deploying
WHITE PAPER Driving Business Value Through Travel and Expense Management Maturity Sponsored by: Concur Christopher Chute January 2016 Matthew Marden EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Today's modern organizations are deploying
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculator
 Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculator Hardware & Software Management Support Implementation Communications fees Direct Costs The capital expenditures and lease fees for servers, client computers, peripherals,
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculator Hardware & Software Management Support Implementation Communications fees Direct Costs The capital expenditures and lease fees for servers, client computers, peripherals,
BUSINESS VALUE SPOTLIGHT
 BUSINESS VALUE SPOTLIGHT Using Information Lifecycle Management to Retire Legacy Applications and Slash Information Retention Costs: A Case Study on Adelphia April 2010 Sponsored by: Informatica, Inc.
BUSINESS VALUE SPOTLIGHT Using Information Lifecycle Management to Retire Legacy Applications and Slash Information Retention Costs: A Case Study on Adelphia April 2010 Sponsored by: Informatica, Inc.
Simplifying Data Protection with Next-Generation Converged Infrastructure
 Sponsored by: Veritas Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) and secondary storage connected to the cloud are changing the way IT organizations approach data protection. These systems offer greater usability
Sponsored by: Veritas Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) and secondary storage connected to the cloud are changing the way IT organizations approach data protection. These systems offer greater usability
Quantifying the Value of Investing In VM Explorer
 White Paper Business Continuity Quantifying the Value of Investing In VM Explorer Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Benefit Categories... 1 The Micro Focus Approach to VM Explorer: An Easy To Use
White Paper Business Continuity Quantifying the Value of Investing In VM Explorer Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Benefit Categories... 1 The Micro Focus Approach to VM Explorer: An Easy To Use
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculator
 Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculator Hardware & Software Management Support Implementation Communications fees Direct Costs The capital expenditures and lease fees for servers, client computers, peripherals,
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculator Hardware & Software Management Support Implementation Communications fees Direct Costs The capital expenditures and lease fees for servers, client computers, peripherals,
Contents. Introduction. What is Cloud Computing? Temenos and Azure. Enterprise-level banking from anywhere. Benefits.
 Banking in the Cloud Contents Introduction 03 The rise of cloud computing What is Cloud Computing? 04 The concept explained Temenos and Azure 06 A powerful combination Enterprise-level banking from anywhere
Banking in the Cloud Contents Introduction 03 The rise of cloud computing What is Cloud Computing? 04 The concept explained Temenos and Azure 06 A powerful combination Enterprise-level banking from anywhere
AppDynamics Launches Business iq
 MARKET NOTE AppDynamics Launches Business iq Mary Johnston Turner EXECUTIVE SNAPSHOT FIGURE 1 Executive Snapshot: AppDynamics Launches Business iq Source: IDC, 2016 January 2017, IDC #US42196817 IN THIS
MARKET NOTE AppDynamics Launches Business iq Mary Johnston Turner EXECUTIVE SNAPSHOT FIGURE 1 Executive Snapshot: AppDynamics Launches Business iq Source: IDC, 2016 January 2017, IDC #US42196817 IN THIS
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA USA P F
 L e an IT: The Time for Transformation I s N o w W H I T E P A P E R Sponsored by: CA Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.620.5533 F.508.988.6761 www.financial-insights.com
L e an IT: The Time for Transformation I s N o w W H I T E P A P E R Sponsored by: CA Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.620.5533 F.508.988.6761 www.financial-insights.com
Worldwide IT Automation and Configuration Management Software Market Shares, 2017: Hybrid IT Drives Growth
 Market Share Worldwide IT Automation and Configuration Management Software Market Shares, 2017: Hybrid IT Drives Growth Stephen Elliot Tim Grieser THIS IDC MARKET SHARE EXCERPT FEATURES VMWARE IDC MARKET
Market Share Worldwide IT Automation and Configuration Management Software Market Shares, 2017: Hybrid IT Drives Growth Stephen Elliot Tim Grieser THIS IDC MARKET SHARE EXCERPT FEATURES VMWARE IDC MARKET
An Overview of the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework
 An Overview of the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework Version 2 February 2017 2017, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Notices This document is provided for informational purposes
An Overview of the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework Version 2 February 2017 2017, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Notices This document is provided for informational purposes
Using Avanade s Managed Services to Unlock Business Value
 Sponsored by: Avanade Authors: Matthew Marden Peter Marston Randy Perry Robert Parker March 2017 Business Value Highlights 433% Five-year ROI $5 in benefits for every $1 invested 10 month payback period
Sponsored by: Avanade Authors: Matthew Marden Peter Marston Randy Perry Robert Parker March 2017 Business Value Highlights 433% Five-year ROI $5 in benefits for every $1 invested 10 month payback period
Managed Cloud storage. Turning to Storage as a Service for flexibility
 Managed Cloud storage Turning to Storage as a Service for flexibility Table of contents Encountering problems? 2 Get an answer 2 Check out cloud services 2 Getting started 3 Understand changing costs 4
Managed Cloud storage Turning to Storage as a Service for flexibility Table of contents Encountering problems? 2 Get an answer 2 Check out cloud services 2 Getting started 3 Understand changing costs 4
Connected Banking Through Enhanced B2B
 White Paper Connected Banking Through Enhanced B2B Sponsored by: IBM Jerry Silva October 2017 IN THIS WHITE PAPER Digital transformation is the driving force behind new initiatives in financial services
White Paper Connected Banking Through Enhanced B2B Sponsored by: IBM Jerry Silva October 2017 IN THIS WHITE PAPER Digital transformation is the driving force behind new initiatives in financial services
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA USA P F
 W H I T E P A P E R L a c k o f O p e r a t i o n a l R e s i l i e n c e W i l l U n d e r m i n e E n t e r p r i s e C o m p e t i t i v e n e s s : A S t r a t e g y f o r A v a i l a b i l i t y Sponsored
W H I T E P A P E R L a c k o f O p e r a t i o n a l R e s i l i e n c e W i l l U n d e r m i n e E n t e r p r i s e C o m p e t i t i v e n e s s : A S t r a t e g y f o r A v a i l a b i l i t y Sponsored
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA USA P F
 Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com W H I T E P A P E R T h e G r o w i n g I r r e l e v a n c y o f t h e B l a c k R e c t a n g l
Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015 www.idc.com W H I T E P A P E R T h e G r o w i n g I r r e l e v a n c y o f t h e B l a c k R e c t a n g l
The Economics of the Cloud: A View from the Field
 The Economics of the Cloud: A View from the Field By Paul Lidbetter Enterprise Architect Cloud computing is being hailed as the biggest change in business IT since client/server. But what are the hard
The Economics of the Cloud: A View from the Field By Paul Lidbetter Enterprise Architect Cloud computing is being hailed as the biggest change in business IT since client/server. But what are the hard
THE ECONOMIC IMPACT OF IT, SOFTWARE, AND THE MICROSOFT ECOSYSTEM ON THE GLOBAL ECONOMY
 Addendum THE ECONOMIC IMPACT OF IT, SOFTWARE, AND THE MICROSOFT ECOSYSTEM ON THE GLOBAL ECONOMY METHODOLOGY AND DEFINITIONS Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015
Addendum THE ECONOMIC IMPACT OF IT, SOFTWARE, AND THE MICROSOFT ECOSYSTEM ON THE GLOBAL ECONOMY METHODOLOGY AND DEFINITIONS Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015
HOW SOFTWARE-AS-A-SERVICE (SAAS) LOWERS THE TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP (TCO) FOR PHYSICAL SECURITY SYSTEMS
 HOW SOFTWARE-AS-A-SERVICE (SAAS) LOWERS THE TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP (TCO) FOR PHYSICAL SECURITY SYSTEMS www.brivo.com Table of Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 INTRODUCTION... 4 HOW SAAS IS A GAME CHANGER...
HOW SOFTWARE-AS-A-SERVICE (SAAS) LOWERS THE TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP (TCO) FOR PHYSICAL SECURITY SYSTEMS www.brivo.com Table of Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 INTRODUCTION... 4 HOW SAAS IS A GAME CHANGER...
Solving the Top 5 Enterprise IT Infrastructure Software Management Challenges
 White Paper Solving the Top 5 Enterprise IT Infrastructure Software Management Challenges Sponsored by: Cisco Nolan Greene Elaina Stergiades November 2017 Rohit Mehra IDC OPINION As enterprises move quickly
White Paper Solving the Top 5 Enterprise IT Infrastructure Software Management Challenges Sponsored by: Cisco Nolan Greene Elaina Stergiades November 2017 Rohit Mehra IDC OPINION As enterprises move quickly
W i p r o : V e n d o r P r o f i l e S e r i e s f o r C l o u d P r o f e s s i o n a l S e r v i c e O f f e r i n g s
 V E N D O R P R O F I L E W i p r o : V e n d o r P r o f i l e S e r i e s f o r C l o u d P r o f e s s i o n a l S e r v i c e O f f e r i n g s Gard Little Rebecca Segal I D C O P I N I O N Global
V E N D O R P R O F I L E W i p r o : V e n d o r P r o f i l e S e r i e s f o r C l o u d P r o f e s s i o n a l S e r v i c e O f f e r i n g s Gard Little Rebecca Segal I D C O P I N I O N Global
Migrate with Altiris.
 Migrate with Altiris. ARE YOU PREPARED? Migrating to a new operating system may seem like a daunting task. You want to take advantage of the improved security and reliability of Windows Vista, but how
Migrate with Altiris. ARE YOU PREPARED? Migrating to a new operating system may seem like a daunting task. You want to take advantage of the improved security and reliability of Windows Vista, but how
The Economic Benefits of Migrating Apache Spark and Hadoop to Amazon EMR
 Sponsored by: Amazon Web Services Authors: Carl W. Olofson Harsh Singh November 2018 Business Value Highlights 57% reduced cost of ownership 342% five-year ROI 8 months to breakeven 33% more efficient
Sponsored by: Amazon Web Services Authors: Carl W. Olofson Harsh Singh November 2018 Business Value Highlights 57% reduced cost of ownership 342% five-year ROI 8 months to breakeven 33% more efficient
I D C M A R K E T S P O T L I G H T. S i l o s a n d Promote Business Ag i l i t y
 I D C M A R K E T S P O T L I G H T E f f e c t i ve M u l ticloud Str ategies B reak Dow n S i l o s a n d Promote Business Ag i l i t y August 2016 Adapted from IDC's Multicloud Management Survey by
I D C M A R K E T S P O T L I G H T E f f e c t i ve M u l ticloud Str ategies B reak Dow n S i l o s a n d Promote Business Ag i l i t y August 2016 Adapted from IDC's Multicloud Management Survey by
The Business Value of Oracle SuperCluster
 Sponsored by: Oracle Authors: Ashish Nadkarni Matthew Marden The Business Value of Oracle SuperCluster November 2017 Business Value Highlights 393% five-year ROI 49% lower five-year cost of operations
Sponsored by: Oracle Authors: Ashish Nadkarni Matthew Marden The Business Value of Oracle SuperCluster November 2017 Business Value Highlights 393% five-year ROI 49% lower five-year cost of operations
I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T
 I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T E f f e c t i ve M u l t i c l o u d, H yb r i d I T Operations D e p e n d o n Au tomation and An a l yt i c s April 2017 Adapted from Effective Multicloud
I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T E f f e c t i ve M u l t i c l o u d, H yb r i d I T Operations D e p e n d o n Au tomation and An a l yt i c s April 2017 Adapted from Effective Multicloud
Worldwide Virtual Machine Software Market Shares, 2017: Virtualization Still Showing Positive Growth
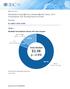 Market Share Worldwide Virtual Machine Software Market Shares, 2017: Virtualization Still Showing Positive Growth Gary Chen IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide Virtual Machine Software 2017 Share
Market Share Worldwide Virtual Machine Software Market Shares, 2017: Virtualization Still Showing Positive Growth Gary Chen IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide Virtual Machine Software 2017 Share
Worldwide IT Event and Log Management Software Market Shares, 2016: Year of Strong Growth
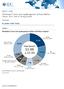 MARKET SHARE Worldwide IT Event and Log Management Software Market Shares, 2016: Year of Strong Growth Tim Grieser IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide IT Event and Log Management Software 2016 Share
MARKET SHARE Worldwide IT Event and Log Management Software Market Shares, 2016: Year of Strong Growth Tim Grieser IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide IT Event and Log Management Software 2016 Share
Hosted UC: the Total Cost of Ownership
 Hosted UC: the Total Cost of Ownership WITH HOSTED UC, NO TWO SYSTEMS ARE ALIKE. FEATURES CAN BE ENABLED OR DISABLED ACROSS THE ENTERPRISE OR PER USER. A STUDY FROM INFONETICS RESEARCH FOUND THAT NEARLY
Hosted UC: the Total Cost of Ownership WITH HOSTED UC, NO TWO SYSTEMS ARE ALIKE. FEATURES CAN BE ENABLED OR DISABLED ACROSS THE ENTERPRISE OR PER USER. A STUDY FROM INFONETICS RESEARCH FOUND THAT NEARLY
Changing the way businesses buy technology
 New Business Models Changing the way businesses buy technology Organizations have reached a complex and transformative stage in digital business as the pace of innovation accelerates every day. Technology
New Business Models Changing the way businesses buy technology Organizations have reached a complex and transformative stage in digital business as the pace of innovation accelerates every day. Technology
On-Premise or Cloud? The Choice is Yours
 Empowering ERP Asset Management Solutions On-Premise or Cloud? The Choice is Yours Premier EAM add-on software providers offer both delivery methods By Chris McIntosh and Sean Licata, VIZIYA Corp. Enterprise
Empowering ERP Asset Management Solutions On-Premise or Cloud? The Choice is Yours Premier EAM add-on software providers offer both delivery methods By Chris McIntosh and Sean Licata, VIZIYA Corp. Enterprise
Quantifying the Value of Investments in Micro Focus Quality Center Solutions
 Dynamic Value Brief Application Delivery Management Quantifying the Value of Investments in Micro Focus Quality Center Solutions Manage software testing and IT quality management with consistent processes
Dynamic Value Brief Application Delivery Management Quantifying the Value of Investments in Micro Focus Quality Center Solutions Manage software testing and IT quality management with consistent processes
An IT Briefing produced by. How CA Clarity PPM On Demand Delivers Value: Building the Business Case. Sponsored By:
 An IT Briefing produced by By Jose Mora and Randy Perry 2009 TechTarget BIOS Jose Mora is Senior Director of Product Marketing, CA Clarity PPM at CA. Randy Perry is Vice-President of Business Value Consulting
An IT Briefing produced by By Jose Mora and Randy Perry 2009 TechTarget BIOS Jose Mora is Senior Director of Product Marketing, CA Clarity PPM at CA. Randy Perry is Vice-President of Business Value Consulting
IBM Tivoli Service Desk
 Deliver high-quality services while helping to control cost IBM Tivoli Service Desk Highlights Streamline incident and problem management processes for more rapid service restoration at an appropriate
Deliver high-quality services while helping to control cost IBM Tivoli Service Desk Highlights Streamline incident and problem management processes for more rapid service restoration at an appropriate
Select Plus. Commercial Licensing guide
 Select Plus Commercial Licensing guide Select Plus has been retired New Select Plus commercial agreements will no longer be sold starting July 1, 2015. Customers will Select Plus agreements that have not
Select Plus Commercial Licensing guide Select Plus has been retired New Select Plus commercial agreements will no longer be sold starting July 1, 2015. Customers will Select Plus agreements that have not
ECONOMIC AND STRATEGIC BENEFITS
 THE ECONOMIC AND STRATEGIC BENEFITS OF CLOUD COMPUTING Grab a seat and enjoy. Read Time: 12 minutes THE ECONOMIC AND STRATEGIC BENEFITS OF CLOUD COMPUTING Does SaaS save money? Traditional vendors of IT
THE ECONOMIC AND STRATEGIC BENEFITS OF CLOUD COMPUTING Grab a seat and enjoy. Read Time: 12 minutes THE ECONOMIC AND STRATEGIC BENEFITS OF CLOUD COMPUTING Does SaaS save money? Traditional vendors of IT
Service management solutions White paper. Six steps toward assuring service availability and performance.
 Service management solutions White paper Six steps toward assuring service availability and performance. March 2008 2 Contents 2 Overview 2 Challenges in assuring high service availability and performance
Service management solutions White paper Six steps toward assuring service availability and performance. March 2008 2 Contents 2 Overview 2 Challenges in assuring high service availability and performance
WHITEPAPER WHITEPAPER. Processing Invoices in the Cloud or On Premises Pros and Cons
 WHITEPAPER WHITEPAPER Processing Invoices in the Cloud or On Premises Pros and Cons Table of Contents What and Where is the Cloud?...1 Some Business Reasons for and Against Cloud Deployment...2 Security
WHITEPAPER WHITEPAPER Processing Invoices in the Cloud or On Premises Pros and Cons Table of Contents What and Where is the Cloud?...1 Some Business Reasons for and Against Cloud Deployment...2 Security
An Oracle White Paper January Upgrade to Oracle Netra T4 Systems to Improve Service Delivery and Reduce Costs
 An Oracle White Paper January 2013 Upgrade to Oracle Netra T4 Systems to Improve Service Delivery and Reduce Costs Executive Summary... 2 Deploy Services Faster and More Efficiently... 3 Greater Compute
An Oracle White Paper January 2013 Upgrade to Oracle Netra T4 Systems to Improve Service Delivery and Reduce Costs Executive Summary... 2 Deploy Services Faster and More Efficiently... 3 Greater Compute
THE IMPACT OF OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE ON DEVELOPING IoT SOLUTIONS
 THE IMPACT OF OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE ON DEVELOPING IoT SOLUTIONS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Worldwide IoT spending is projected to surpass $1 trillion in 2020, with annual growth of 15 percent over the next several
THE IMPACT OF OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE ON DEVELOPING IoT SOLUTIONS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Worldwide IoT spending is projected to surpass $1 trillion in 2020, with annual growth of 15 percent over the next several
IBM _` iseries systems Retail
 iseries systems delivering technology innovations and maximum business productivity to retailers for their On Demand Business IBM _` iseries systems Retail Highlights Helps simplify IT environments by
iseries systems delivering technology innovations and maximum business productivity to retailers for their On Demand Business IBM _` iseries systems Retail Highlights Helps simplify IT environments by
Worldwide Cloud Systems Management Software 2012 Vendor Shares
 COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS Worldwide Cloud Systems Management Software 2012 Vendor Shares Mary Johnston Turner IDC OPINION Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015
COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS Worldwide Cloud Systems Management Software 2012 Vendor Shares Mary Johnston Turner IDC OPINION Global Headquarters: 5 Speen Street Framingham, MA 01701 USA P.508.872.8200 F.508.935.4015
Leveraging Effective Application Discovery, Delivery, Change, and Quality Strategies for Digital Transformation
 White Paper Leveraging Effective Application Discovery, Delivery, Change, and Quality Strategies for Digital Transformation Sponsored by: IBM Melinda-Carol Ballou March 2018 IDC OPINION As part of digital
White Paper Leveraging Effective Application Discovery, Delivery, Change, and Quality Strategies for Digital Transformation Sponsored by: IBM Melinda-Carol Ballou March 2018 IDC OPINION As part of digital
I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T
 I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T H ow T o d a y' s I T C h a l lenges Ar e C r e a t i n g N ew R e q u i r e m e n ts in Support Servi c e s D elive r y May 2012 Adapted from Converging Infrastructure
I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T H ow T o d a y' s I T C h a l lenges Ar e C r e a t i n g N ew R e q u i r e m e n ts in Support Servi c e s D elive r y May 2012 Adapted from Converging Infrastructure
Assessing the Business Value of VDI in the Public Cloud
 IDC Solution Brief Sponsored by: Microsoft and Citrix Authors: Michael Ceroici Andrew Buss Giorgio Nebuloni Mathew Marden Harsh Singh March 2018 VDI is one of the solutions that organisations are adopting
IDC Solution Brief Sponsored by: Microsoft and Citrix Authors: Michael Ceroici Andrew Buss Giorgio Nebuloni Mathew Marden Harsh Singh March 2018 VDI is one of the solutions that organisations are adopting
Value Beyond Virtualization
 An Executive To-Do List for Moving from Virtualization to a Private Cloud Executive Summary To thrive in competitive times, there is no room for lag. This has CIOs steadfastly focused on driving IT efficiencies
An Executive To-Do List for Moving from Virtualization to a Private Cloud Executive Summary To thrive in competitive times, there is no room for lag. This has CIOs steadfastly focused on driving IT efficiencies
Insurance Carrier Core Systems in the Cloud. A Novarica Research Partners Program Report Underwritten by OneShield Software
 Insurance Carrier Core Systems in the Cloud A Novarica Research Partners Program Report Underwritten by OneShield Software Executive Summary The insurance industry is past the tipping point. Cloud adoption
Insurance Carrier Core Systems in the Cloud A Novarica Research Partners Program Report Underwritten by OneShield Software Executive Summary The insurance industry is past the tipping point. Cloud adoption
The Time Is Now for Considering Workload Automation
 I D C V E N D O R S P O T L I G H T The Time Is Now for Considering Workload Automation August 2008 Adapted from IT Organizations Are Maturing from Job Scheduling to Workload Automation by Stephen Elliot,
I D C V E N D O R S P O T L I G H T The Time Is Now for Considering Workload Automation August 2008 Adapted from IT Organizations Are Maturing from Job Scheduling to Workload Automation by Stephen Elliot,
Why You Should Take a Holistic Approach
 Why You Should Take a Holistic Approach to ITIL and Service Support best practices WHITE PAPER Table of Contents Executive Summary...1 Moving to a Holistic Service Support Approach...2 Optimize and Integrate
Why You Should Take a Holistic Approach to ITIL and Service Support best practices WHITE PAPER Table of Contents Executive Summary...1 Moving to a Holistic Service Support Approach...2 Optimize and Integrate
Transforming software delivery with cloud
 IBM Software Thought Leadership White Paper August 2011 Transforming software delivery with cloud 2 Transforming software delivery with cloud Contents 2 Cloud: An opportunity 2 Increasing pressure from
IBM Software Thought Leadership White Paper August 2011 Transforming software delivery with cloud 2 Transforming software delivery with cloud Contents 2 Cloud: An opportunity 2 Increasing pressure from
Engaging in Big Data Transformation in the GCC
 Sponsored by: IBM Author: Megha Kumar December 2015 Engaging in Big Data Transformation in the GCC IDC Opinion In a rapidly evolving IT ecosystem, "transformation" and in some cases "disruption" is changing
Sponsored by: IBM Author: Megha Kumar December 2015 Engaging in Big Data Transformation in the GCC IDC Opinion In a rapidly evolving IT ecosystem, "transformation" and in some cases "disruption" is changing
How do I simplify, accelerate and scale application testing in my Microsoft Azure development environments?
 SOLUTION BRIEF CA SERVICE VIRTUALIZATION ON DEMAND ON MICROSOFT AZURE How do I simplify, accelerate and scale application testing in my Microsoft Azure development environments? SOLUTION BRIEF CA DATABASE
SOLUTION BRIEF CA SERVICE VIRTUALIZATION ON DEMAND ON MICROSOFT AZURE How do I simplify, accelerate and scale application testing in my Microsoft Azure development environments? SOLUTION BRIEF CA DATABASE
IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Subscription Relationship Management 2017 Vendor Assessment
 IDC MarketScape IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Subscription Relationship Management 2017 Vendor Assessment Jordan Jewell Eric Newmark THIS EXCERPT PREPARED FOR: GOTRANSVERSE IDC MARKETSCAPE FIGURE FIGURE 1
IDC MarketScape IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Subscription Relationship Management 2017 Vendor Assessment Jordan Jewell Eric Newmark THIS EXCERPT PREPARED FOR: GOTRANSVERSE IDC MARKETSCAPE FIGURE FIGURE 1
Title: HP OpenView Configuration Management Overview Session #: 87 Speaker: Loic Avenel Company: HP
 Title: HP OpenView Configuration Management Overview Session #: 87 Speaker: Loic Avenel Company: HP What we will cover in this session What is the HP OpenView configuration management solution for enterprises?
Title: HP OpenView Configuration Management Overview Session #: 87 Speaker: Loic Avenel Company: HP What we will cover in this session What is the HP OpenView configuration management solution for enterprises?
SOLUTION BRIEF MAINFRAME SERVICES FROM CA TECHNOLOGIES
 SOLUTION BRIEF MAINFRAME SERVICES FROM CA TECHNOLOGIES Can You Make Your Mainframe Platform the Strongest Player in a Team Computing Environment, Supporting Mobile, Big Data, Massive Transaction Processing
SOLUTION BRIEF MAINFRAME SERVICES FROM CA TECHNOLOGIES Can You Make Your Mainframe Platform the Strongest Player in a Team Computing Environment, Supporting Mobile, Big Data, Massive Transaction Processing
