KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS
|
|
|
- Madeleine Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Soil Columns 40- to minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW 4 L A B O R AT O R Y Students investigate the composition of two different types of soil by separating the soils with water. By creating and observing a water-and-soil column, they gather evidence to show that soils are made from a mixture of different-sized materials. They learn how to use a graduated cylinder to quantify the height of the different sections. Comparison of this data shows that soils have different types and proportions of these materials. KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS (with correlation to NSE 5 8 Content Standards) 1. One way to gather data is through direct observation. Accurate and complete observations are important for making conclusions about the natural world. (Inquiry: 1) 2. Scientists use common units of measurement to collect data. This system is known as the metric or international system (SI). (Inquiry: 1) 3. Soil consists of weathered rocks and decomposed organic material from dead plants, animals, and bacteria. (Earth Science: 1) 4. Soils from different environments have different compositions and properties. (Earth Science: 1) KEY VOCABULARY centimeters (cm) composition evidence milliliter (ml) observation A-33
2 Activity 4 Soil Columns MATERIALS AND ADVANCE PREPARATION For the teacher * 2 3 large containers or tubs 1 Science Skills Transparency 1, How to Read a Graduated Cylinder (optional) For each group of four students 1 sample of Soil A (labeled) 1 sample of Soil B (labeled) * 1 sample of local soil (optional) * 1 cup of water 1 SEPUP tray 2 3 large clear plastic tubes with caps 1 30-mL graduated cup 1 50-mL graduated cylinder 1 plastic spoon 1 ruler 1 magnifying lens (3x/6x, optional) For each student 1 Student Sheet 4.1, Soil Column Observations 1 Science Skills Student Sheet 1, Understanding Measurement: Length (optional) 1 Science Skills Student Sheet 2, Understanding Measurement: Volume (optional) *Not supplied in kit A local soil can be added to the two provided in the equipment kit as a third soil for student investigation. There is enough equipment and supplies for the inclusion of a third sample. The local soil can be introduced as a known basis of comparison or as an unknown soil that is part of the garden problem. Gather large containers or tubs for soil set up and clean up. Provide them in a common area where students can collect and return the soil. Have access to running water for cleaning out the soil tubes. You can reuse the soils in this activity with subsequent classes. The silt in the mixtures is easily washed away, so be on the lookour for a change in the composition of soils that have been mixed with water and dried. The soils from this activity will NOT dry out enough overnight to work well in the next activity, so you will need to reserve some soil for Activity 5, Soil Composition. Activity 6, Describing Soil Scientifically and Activity 10, Organic Matter Test require soil that has not yet been wet and dried, so you will need to reserve some of each soil sample for these activities as well. A-34
3 Soil Columns Activity 4 In the next activity, students are asked to reflect back on this activity and apply their new knowledge. If possible, keep at least a few soil columns from this activity available until the completion of Activity 5. Masters for the Science Skills transparency and student sheets can be found in the Science Skills section of Teacher Resources II: Diverse Learners. TEACHING SUMMARY Getting Started 1. Introduce soil composition. 2. Students predict what will happen when soil and water are mixed. Doing the Activity 3. Students construct and observe soil columns. Follow-Up 4. Let tubes stand overnight and make further observations. 5. Students revisit their predictions and construct a definition of soil.if t BACKGROUND INFORMATION Settling Many students know that large particles will settle to the bottom of a mixture. However, there is a common misconception that this is due solely to its weight or density. Settling patterns are due to many factors, but in particular, to the ratio of mass to frictional resistance as the particle travels through the water. The shape, or aerodynamic profile, of the particle affects the amount of friction. A higher mass to friction ratio will travel through the water faster and therefore settle down to the bottom faster. A-35
4 Activity 4 Soil Columns TEACHING SUGGESTIONS GETTING STARTED 1. Introduce soil composition. Review the definitions of soil developed in the last activity. Let students know they will revise their definitions after this and other activities as their knowledge and understanding of soil continues to expand. Explain that in this activity they will further investigate the composition of the two soils previously examined. Clarify the meaning of the term composition and relate it to the observations of Soils A and B. Simply define composition as what something is made of or its specific ingredients. It may help to use the term composition in an everyday example such as, The composition of chocolate milk is milk, chocolate, and sugar. 2. Students predict what will happen when soil and water are mixed. Ask students to predict what will happen when water is mixed with the soils and is left to stand for a while. Provide a framework for the prediction by describing, in general terms, the procedure of creating the soil columns. Have students write down their prediction and ask them to explain. DOING THE ACTIVIT Y 3. Students construct and observe soil columns. Before starting the activity, review how to read the markings on the graduated cylinder by using Science Skills Transparency 1, How to Read a Graduated Cylinder. The SEPUP 50-mL graduated cylinder is marked by a short line (starting at 4 ml) at every milliliter, a long line at every 5 milliliters, and is numbered every 10 milliliters. Show students how to interpolate the measurement when the liquid falls in between lines. If appropriate, let students practice reading a graduated cylinder and ruler with optional Science Skills Student Sheet 1, Understanding Measurement: Length and/or Student Sheet 2, Understanding Measurement: Volume. Note that although the Student Sheets show a meniscus, students may have difficulty identifying the meniscus for this activity, as the water and soil mixture may not form a clearly visible curve. In this activity, students measure soil using a 30-mL graduated cup (instead of a balance, which is what most scientists would use). This is done for convenience because the amount of soil used may be difficult to accurately measure on a balance. The soils provided in this kit are reasonably consistent. In an actual test, however, soils have different levels of compactness and mass is a more accurate way to measure it. If students are curious about this, ask them why they think the experiment uses a measure of volume (ml) instead a measure of mass (g) for measuring soil amounts. Use the discussion to review the use of units in measurement. You may want to review some other aspects of the Procedure, such as using the SEPUP tray to keep the two tubes separated and identified, e.g., the tube containing Soil A is in Cup A, the tube containing Soil B is in Cup B. Have students complete the activity. After mixing with water, the soils should split into differentiated strata in about 5 minutes. Teacher s Note: Because the different strata in the tubes are not correlated to the soil layers found in the earth, this activity refers to differentiated soil particles in the soil columns as sections (and not layers). Soil layers are introduced in the next activity. One misconception related to this activity is the idea that the soil sections created by the settling action in the tubes corresponds to soil layers found under the surface of the earth. This is not true; the columns merely reflect varying settle rates of the different particles. Without getting into a lesson on the physics of fluid dynamics (see Background Information), avoid perpetuating this misconception with students. A sample student response to Student Sheet 4.1, Soil Column Observations, is shown on the next page. Actual student results may be slightly different as the soils in the kit may vary. Use Analysis Question 2 as an opportunity to discuss the different particle sizes found in soil. Without getting into the details of why particles have different fall rates, discuss the fact that the columns give clear observational evidence that soil is composed of different-sized particles. The next activity introduces sand, silt, and clay (and their differing size) as one of the major aspects of describing and differentiating soil composition. A-36
5 Soil Columns Activity 4 Sample Response to Student Sheet 4.1, Soil Column Observations Observations: Top getting darker Bottom getting lighter Particles moving downward Particles floating Splitting into sections FOLLOW-UP 4. Let tubes stand overnight and make further observations. Let the tubes stand overnight and have students make observations the following day. If it is not possible to keep individual tubes set up, keep a few for groups or the class to share. Give students an opportunity to compare their observations to the ones they made the first day. They should find even more separation of the soil components on the second day; the water should appear clearer and the sections more distinct. 5. Students revisit their predictions and construct a definition of soil. After completing the investigation, have students revisit their prediction from the start of the activity. Ask them to compare their first-hand observations to their predictions. Students should be able to articulate which parts of their predictions were accurate and which parts were not. For example, a student might have predicted that the water will get all muddy, when, in fact, observations indicate that the water was muddy for only a short time and that the water and soil were clearly observable as separate entities after settling occurred. Ask students to analyze the inconsistencies between predictions and observations. An accurate observation would note that a lot of the soil settled to the bottom of the tube over time, while some particles floated into various sections. This icon indicates questions for formative assessment. See Teacher Resources III: Assessment for more information. Lead a short discussion about the definition of soil that students constructed in the previous activity. Ask students to add to their initial ideas about soil. At A-37
6 Activity 4 Soil Columns this point, let students offer their ideas and words, since they are still building knowledge about soil composition. The reading in the next activity will further develop their understanding of soil. At that time, they will be asked again to revise their working definition of soil and will be assessed on a more complete understanding of soil composition. EXTENSION Students can estimate the percentage of the overall composition by taking the section height and dividing it by the overall column height of soil. A sample calculation is as shown below: This calculation is an estimate in that it does not account for the varying amount of water between the soil particles. In particular, the volume of floating organic material in column B is likely to be overestimated. SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. How were the sections in Tube A similar to or different from the sections in Tube B? Support your answer with your observations. The sections are similar in that both soils have more than one section and that the particles in the bottom section of Soil B look identical to the second from the bottom section of Soil A. The bottom section of soil A is different because it does not look like any particles in Soil B. Likewise, the material floating on the top only appears in Soil B. 2. Were the particles on the bottom of Tube A larger, smaller, or the same size as the particles at the top? The particles on the bottom looked larger than those above it. This is because the larger particles settle to the bottom first. Students may try to explain this because they are heavier but this is not entirely accurate. The reason is complicated and due to a number of factors (see Background Information). Because the physics behind different settling rates is difficult to understand, focus the response of this question on the resulting sections and not the actual mechanics of settling. 3. Is the composition of Soil A the same as that of Soil B? Support your answer with evidence from this activity. Students should be able to point out that since some of the soil sections revealed different types of particles when separated, the soil compositions are not the same. Encourage students to cite evidence to support their conclusions (for example, by describing the height and composition of a particular section and comparing the sections between the two soils). Students may also cite similarities between the soils (for example, they both contained silt). A-38
7 Name Date Soil Column Observations Observations 2012 The Regents of the University of California Issues and Earth Science Student Sheet 4.1 A-39
Heating Earth Surfaces
 Heating Earth Surfaces 55 40- to 2-3 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y Students design an experiment to measure how the Sun s energy heats land and water as well as how quickly both
Heating Earth Surfaces 55 40- to 2-3 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y Students design an experiment to measure how the Sun s energy heats land and water as well as how quickly both
KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS
 A Cell So Small 41 40- to 1 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW M OD E L I N G Students model the relative size of cells to determine why cells are so small. This activity is used to reinforce the concept
A Cell So Small 41 40- to 1 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW M OD E L I N G Students model the relative size of cells to determine why cells are so small. This activity is used to reinforce the concept
GOAL STATEMENT: Students will learn about soil as a natural resource, what its components are, how it is used, and whether it is renewable.
 STATE SCIENCE STANDARDS: 6 th, 7 th, 8 th Grade Skills and Processes 1.0.A.1.h Use mathematics to interpret and communicate data. 1.0.B.1 Review data from a simple experiment, summarize the data, and construct
STATE SCIENCE STANDARDS: 6 th, 7 th, 8 th Grade Skills and Processes 1.0.A.1.h Use mathematics to interpret and communicate data. 1.0.B.1 Review data from a simple experiment, summarize the data, and construct
Lesson Plan: Stream Table Investigation By: Lauri Dahlin
 Lesson Plan: Stream Table Investigation By: Lauri Dahlin Target Grade: 4 th Teacher Prep Time: 1 hour Lesson Time: 3½ hours (We recommend doing this lesson over 4 days.) Day 1 o 15 min. Beginning Thoughts
Lesson Plan: Stream Table Investigation By: Lauri Dahlin Target Grade: 4 th Teacher Prep Time: 1 hour Lesson Time: 3½ hours (We recommend doing this lesson over 4 days.) Day 1 o 15 min. Beginning Thoughts
Teacher Resources. Survey of a Biome s Biotic and Abiotic Factors. Teacher Prep Student Setup Concept Level Cleanup
 Teacher Resources Edit File FIELD LAB AND Survey of a Biome s Biotic and Abiotic Factors Small groups Three 45-minute class periods LAB RATINGS Teacher Prep Student Setup Concept Level Cleanup SAFETY INFORMATION
Teacher Resources Edit File FIELD LAB AND Survey of a Biome s Biotic and Abiotic Factors Small groups Three 45-minute class periods LAB RATINGS Teacher Prep Student Setup Concept Level Cleanup SAFETY INFORMATION
The Varying Density of Sea Water Based on
 Based on http://www.maine.gov/doc/nrimc/mgs/education/lessons/act37.htm Focus on Inquiry The student will collect and analyze data to determine the effects of temperature and dissolved on sea water. Lesson
Based on http://www.maine.gov/doc/nrimc/mgs/education/lessons/act37.htm Focus on Inquiry The student will collect and analyze data to determine the effects of temperature and dissolved on sea water. Lesson
Diluting the Problem KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS KEY VOCABULARY ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y B-137
 Diluting the Problem 40- to 3 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW 24 L A B O R ATO R Y Students explore dilution as a disposal method for copper-containing solutions produced during circuit-board manufacturing.
Diluting the Problem 40- to 3 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW 24 L A B O R ATO R Y Students explore dilution as a disposal method for copper-containing solutions produced during circuit-board manufacturing.
Interactive Science Grade
 A Correlation of Interactive Science 2012 To the Michigan Science Grade Level Content Expectations v.1.09 Introduction This document demonstrates the close alignment between, and the Michigan Science Standards
A Correlation of Interactive Science 2012 To the Michigan Science Grade Level Content Expectations v.1.09 Introduction This document demonstrates the close alignment between, and the Michigan Science Standards
Warm up # 5. Warm up # 4
 Warm up # 5 What is 1 lab safety rule? Warm up # 4 What 3 things are harming the suisun marsh? 1 Warm up # 5 What are each of these used to measure? 1. ruler 2. Stopwatch 3. Scale 4. Thermometer 5. Graduated
Warm up # 5 What is 1 lab safety rule? Warm up # 4 What 3 things are harming the suisun marsh? 1 Warm up # 5 What are each of these used to measure? 1. ruler 2. Stopwatch 3. Scale 4. Thermometer 5. Graduated
The students will be able to: define porosity and relate it to the capacity of a common object's TEKS ADDRESSED:
 AUTHORS NAMES: TITLE OF THE LESSON: Porosity and Permeability TECHNOLOGY LESSON : No DATE OF LESSON: TIME LESSON: 2 (60 min class) NAME OF COURSE Biology SOURCE OF THE LESSON: Lynn Kirby TEKS ADDRESSED:
AUTHORS NAMES: TITLE OF THE LESSON: Porosity and Permeability TECHNOLOGY LESSON : No DATE OF LESSON: TIME LESSON: 2 (60 min class) NAME OF COURSE Biology SOURCE OF THE LESSON: Lynn Kirby TEKS ADDRESSED:
DENSITY of Solids and Liquids
 Regents Earth Science Name: Date: Lab # DENSITY of Solids and Liquids Introduction: Density is the term used to describe the relationship between the mass of an object and its volume. Under given conditions
Regents Earth Science Name: Date: Lab # DENSITY of Solids and Liquids Introduction: Density is the term used to describe the relationship between the mass of an object and its volume. Under given conditions
Soil Ecology and Nutrient Cycling
 MODULE 3 NGSS TEACHER S GUIDE Soil Ecology and Nutrient Cycling Keego Technologies LLC. All rights reserved. NGSS Alignment CORE IDEAS Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
MODULE 3 NGSS TEACHER S GUIDE Soil Ecology and Nutrient Cycling Keego Technologies LLC. All rights reserved. NGSS Alignment CORE IDEAS Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Waterworks. QUT Extreme Science
 Waterworks QUT Extreme Science Glossary QUT Extreme Science Contaminants Dependent variable Fair test Filtration Independent variable Microbes ph indicator Salinity Turbidity Something that contaminates
Waterworks QUT Extreme Science Glossary QUT Extreme Science Contaminants Dependent variable Fair test Filtration Independent variable Microbes ph indicator Salinity Turbidity Something that contaminates
Rockets Describe space explorations and the understandings gained from them including: Technologies used to explore space.
 Rockets Overview In this exercise, students learn how to build a simple rocket fueled by an effervescent antacid tablet in water. They will explore adjusting variables (e.g., tube size, amount of water,
Rockets Overview In this exercise, students learn how to build a simple rocket fueled by an effervescent antacid tablet in water. They will explore adjusting variables (e.g., tube size, amount of water,
Just Passing Through. Suggested Grade Level 6-8. Estimated Time 45 minutes. Objectives Students will be able to:
 Just Passing Through Overview Students will investigate soils and observe how water moves through soil, how soil properties affect flow rate and water holding capacity. Students time the flow of water
Just Passing Through Overview Students will investigate soils and observe how water moves through soil, how soil properties affect flow rate and water holding capacity. Students time the flow of water
Rich Soil or Poor Soil?
 This investigation will help us to examine how water drains through different kinds of soil. Think about how each of the soils are different and try to predict which soil will allow the water to drain
This investigation will help us to examine how water drains through different kinds of soil. Think about how each of the soils are different and try to predict which soil will allow the water to drain
7. The diagram below represents cross sections of equal-size beakers A, B, and C filled with beads.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents four tubes, labeled A, B, C, and D, each containing 150 ml of sediments. Tubes
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents four tubes, labeled A, B, C, and D, each containing 150 ml of sediments. Tubes
Filtering Out Pollution Lowering Turbidity to Increase Water Quality
 Filtering Out Pollution Lowering Turbidity to Increase Water Quality Authors: Tara Cornelisse, PhD student and SCWIBLES Graduate Fellow, Environmental Studies, University of California, Santa Cruz; Ruben
Filtering Out Pollution Lowering Turbidity to Increase Water Quality Authors: Tara Cornelisse, PhD student and SCWIBLES Graduate Fellow, Environmental Studies, University of California, Santa Cruz; Ruben
Density. The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the topic of density by determining the densities of some materials.
 Density Goals The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the topic of density by determining the densities of some materials. Introduction There is a lesson in the old bromide: Which is heavier,
Density Goals The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the topic of density by determining the densities of some materials. Introduction There is a lesson in the old bromide: Which is heavier,
Effective January 2008 All indicators in Standard / 11
 Scientific Inquiry 6-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of technological design and scientific inquiry, including the process skills, mathematical thinking, controlled investigative design
Scientific Inquiry 6-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of technological design and scientific inquiry, including the process skills, mathematical thinking, controlled investigative design
Energy TEACHER EDITION
 Energy TEACHER EDITION 1 Home Energy Use i n v e s t i g at i o n 1 2 c l a s s sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW NGSS CONNECTIONS Students begin exploring concepts about energy transfer by analyzing qualitative
Energy TEACHER EDITION 1 Home Energy Use i n v e s t i g at i o n 1 2 c l a s s sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW NGSS CONNECTIONS Students begin exploring concepts about energy transfer by analyzing qualitative
Item 36 has not been slated for public release in 2011.
 S Use the power-plant diagrams and information below to answer questions 35 37. Power Plants 35. Which describes a chemical change and a physical change that take place during the production of electricity
S Use the power-plant diagrams and information below to answer questions 35 37. Power Plants 35. Which describes a chemical change and a physical change that take place during the production of electricity
The Science of Maryland Agriculture
 The Science of Maryland Agriculture GOAL STATEMENT: Students will learn about soil as a natural resource, what its components are, how it is used, and whether it is renewable. OBJECTIVES: Students will
The Science of Maryland Agriculture GOAL STATEMENT: Students will learn about soil as a natural resource, what its components are, how it is used, and whether it is renewable. OBJECTIVES: Students will
BACKGROUND: Porosity permeability. PART I Materials Procedure EMPTY the tube.
 Name: Water Movement (adapted from Wards) LAB BACKGROUND: While some precipitation falls to the earth and runs off into streams and river, another portion seeps slowly through the soil into the upper layers
Name: Water Movement (adapted from Wards) LAB BACKGROUND: While some precipitation falls to the earth and runs off into streams and river, another portion seeps slowly through the soil into the upper layers
Lesson 1 Introduction to Unit
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Unit Teacher instructions for Lesson One Overview Lesson One introduces sedimentation as a nonpoint source of pollution involving soils in runoff from the watershed into the surface
Lesson 1 Introduction to Unit Teacher instructions for Lesson One Overview Lesson One introduces sedimentation as a nonpoint source of pollution involving soils in runoff from the watershed into the surface
T. Trimpe Lesson 1: Length
 T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ Lesson 1: Length Metric Units The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter and is represented by a lowercase m. Metric Units 1 Kilometer (km) = 1000
T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ Lesson 1: Length Metric Units The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter and is represented by a lowercase m. Metric Units 1 Kilometer (km) = 1000
LESSON hat is density? 24
 LESSON hat is density? 24 Rocks are heavy. A small box of rocks has a large. Yet a box of the same size containing corks has a small. How can objects that are the same size have different es? Scientists
LESSON hat is density? 24 Rocks are heavy. A small box of rocks has a large. Yet a box of the same size containing corks has a small. How can objects that are the same size have different es? Scientists
Class 4J Spring Term Unit 4D Solids, liquids and how they can be separated Adapted from QCA Science Unit 4D
 Class 4J Spring Term 2003 Science Unit 4D Solids, liquids and how they can be separated Adapted from QCA Science Unit 4D ABOUT THE UNIT In this unit children learn about the differences between solids
Class 4J Spring Term 2003 Science Unit 4D Solids, liquids and how they can be separated Adapted from QCA Science Unit 4D ABOUT THE UNIT In this unit children learn about the differences between solids
Particle Size Distribution Analysis for Ceramic Pot Water filter production
 Particle Size Distribution Analysis for Ceramic Pot Water filter production Maria del Mar Duocastella and Kai Morrill Potters Without Borders, Enderby, British Columbia, Canada - September 2012 Abstract:
Particle Size Distribution Analysis for Ceramic Pot Water filter production Maria del Mar Duocastella and Kai Morrill Potters Without Borders, Enderby, British Columbia, Canada - September 2012 Abstract:
Rain and Flood. Materials: Clear jar or mason jar or a clear glass that is heat resistant Stove or microwave to heat water Plate Ice cubes (optional)
 Lesson Plan for Grades 2-3 Length of Lesson: 1 hr Authored by: Maisha_Rumman for UT Environmental Science Institute Date created: 11/21/2014 Subject area/course: Science Materials: Clear jar or mason jar
Lesson Plan for Grades 2-3 Length of Lesson: 1 hr Authored by: Maisha_Rumman for UT Environmental Science Institute Date created: 11/21/2014 Subject area/course: Science Materials: Clear jar or mason jar
JEFFERSON PARISH PUBLIC SCHOOL SYSTEM. Grade 2 Science Scope, Sequence, Timeline
 JEFFERSON PARISH PUBLIC SCHOOL SYSTEM Grade 2 Science 2015 Scope, Sequence, Timeline Correlation to s, Benchmarks, the Louisiana and Instructions for use: The book used in the 2 nd grade curriculum is:
JEFFERSON PARISH PUBLIC SCHOOL SYSTEM Grade 2 Science 2015 Scope, Sequence, Timeline Correlation to s, Benchmarks, the Louisiana and Instructions for use: The book used in the 2 nd grade curriculum is:
Science Grade 07 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 03: Effects of Human Activity on Water
 Unit: 04 Lesson: 03 Suggested Duration: 7 days Grade 07 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 03: Effects of Human Activity on Water This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit.
Unit: 04 Lesson: 03 Suggested Duration: 7 days Grade 07 Unit 04 Exemplar Lesson 03: Effects of Human Activity on Water This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit.
Dirty Water. Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, Grade Level: all. Duration: 1-2 class periods
 Dirty Water Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, 1997. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Grade Level: all Duration: 1-2 class periods Setting: classroom or laboratory Summary:
Dirty Water Adapted from: Dirty Water in Living in Water. National Aquarium in Baltimore, 1997. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Grade Level: all Duration: 1-2 class periods Setting: classroom or laboratory Summary:
Science in the Schoolyard Guide: FOSS California Water Planet. Investigation 3 Evaporation Locations
 Water Planet Water Planet > Investigation 3: Water Vapor > Part 2: Evaporation Locations, page 120 Evaporation Locations Following Part 2, take students outside to expand this investigation. Refer to the
Water Planet Water Planet > Investigation 3: Water Vapor > Part 2: Evaporation Locations, page 120 Evaporation Locations Following Part 2, take students outside to expand this investigation. Refer to the
Exploring the Geographical Region and Ecosystems of the Tar-Pamlico Watershed. The River Food Web. Overview. Background
 Alignment to NC Essential Standards Science 4.L.1, 4.L.2, 5.L.2 Learning Objectives Students will explain the role of bacteria as primary consumers in the food web. Students will describe how energy moves
Alignment to NC Essential Standards Science 4.L.1, 4.L.2, 5.L.2 Learning Objectives Students will explain the role of bacteria as primary consumers in the food web. Students will describe how energy moves
STUDENT NAME. Science Grade 4. Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers.
 FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS Third Grading Period 2010-11 March 21-24 STUDENT NAME DATE Science Grade 4 Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. 1 In the circuit
FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS Third Grading Period 2010-11 March 21-24 STUDENT NAME DATE Science Grade 4 Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. 1 In the circuit
esources / ^ Vocabulary Process Skill
 / ^ Vocabulary natural resource, C38 renewable resource, C40 nonrenewable resource, C41 pollution, C42 esources Why do miners dig deep into Earth? They are looking for useful materials, such as metals,
/ ^ Vocabulary natural resource, C38 renewable resource, C40 nonrenewable resource, C41 pollution, C42 esources Why do miners dig deep into Earth? They are looking for useful materials, such as metals,
Permeability Field Investigation
 Permeability Field Investigation Using the scientific method to guide this outdoor investigation, students test the permeability of different school-ground areas, record and organize the results with maps
Permeability Field Investigation Using the scientific method to guide this outdoor investigation, students test the permeability of different school-ground areas, record and organize the results with maps
Analyzing Groundwater
 Analyzing Groundwater SUBJECTS: Science GRADE LEVELS: 7 th DURATION: approximately two 60 minute periods ACTIVITY SUMMARY: Students will compare the properties of different soil types including texture
Analyzing Groundwater SUBJECTS: Science GRADE LEVELS: 7 th DURATION: approximately two 60 minute periods ACTIVITY SUMMARY: Students will compare the properties of different soil types including texture
Water: A Valuable, Yet Limited Resource
 Water: A Valuable, Yet Limited Resource Subject: Science Target Grades 4-5 Duration: One class period Materials per class 3 100-ml graduated cylinders container of water (10-ml/student) Water Cycle with
Water: A Valuable, Yet Limited Resource Subject: Science Target Grades 4-5 Duration: One class period Materials per class 3 100-ml graduated cylinders container of water (10-ml/student) Water Cycle with
metric 1.2 (Compare/contrast characteristics in a given set) beaker hotplate stopwatch hand lens rain gauge greatest least fewest closest slowest
 Observe/Measure 1.1 (Observe and measure using SI units) mass length time appropriate type of unit, appropriate type of tool volume temperature International System of Units grams milligrams meters millimeters
Observe/Measure 1.1 (Observe and measure using SI units) mass length time appropriate type of unit, appropriate type of tool volume temperature International System of Units grams milligrams meters millimeters
Permeability Tests. Geotechnical Engineering, Laboratory 7
 1. General Notes Permeability Tests Geotechnical Engineering, Laboratory 7 Be prepared to get wet. All stations, benches, and tables must be cleaned before your group leaves the lab. Please clean all glassware
1. General Notes Permeability Tests Geotechnical Engineering, Laboratory 7 Be prepared to get wet. All stations, benches, and tables must be cleaned before your group leaves the lab. Please clean all glassware
Professional Development Documents: Developing Learning Progressions
 Professional Development Documents: Developing Learning Progressions In this packet you will find a set of handouts and support materials for the Developing Learning Progressions professional development
Professional Development Documents: Developing Learning Progressions In this packet you will find a set of handouts and support materials for the Developing Learning Progressions professional development
Standard Test Procedures Manual
 STP 205-10 Standard Test Procedures Manual Section: 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test This method describes the quantitative determination of the distribution of particle sizes in soils. The distribution
STP 205-10 Standard Test Procedures Manual Section: 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test This method describes the quantitative determination of the distribution of particle sizes in soils. The distribution
Measuring Turbidity with Filters
 Measuring Turbidity with Filters Adapted from: It s Sedimentary, My Dear Watson in Environmental Resource Guide: Nonpoint Source Pollution Prevention Grades 9-12. Tennessee Valley Authority and Air and
Measuring Turbidity with Filters Adapted from: It s Sedimentary, My Dear Watson in Environmental Resource Guide: Nonpoint Source Pollution Prevention Grades 9-12. Tennessee Valley Authority and Air and
Module 2, Add on Lesson Turbidity Sensor. Teacher. 90 minutes
 Module 2, Add on Lesson Turbidity Sensor Teacher 90 minutes Purpose Construct a sensor to measure the turbidity of water Graph data and reason about curves and linear relationships Calibrate the turbidity
Module 2, Add on Lesson Turbidity Sensor Teacher 90 minutes Purpose Construct a sensor to measure the turbidity of water Graph data and reason about curves and linear relationships Calibrate the turbidity
WATER UNDER GROUND. Pore space is the space between particles in a sample. It can be filled with air or water depending on the conditions.
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) WATER UNDER GROUND You have decided to plant an azalea bush in a bare spot in your yard. You dig an appropriate hole and plant the bush. Despite sufficient rain and sun, the bush dies.
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) WATER UNDER GROUND You have decided to plant an azalea bush in a bare spot in your yard. You dig an appropriate hole and plant the bush. Despite sufficient rain and sun, the bush dies.
ECOS Inquiry Template
 ECOS Inquiry Template 1. Contributor s Name: NATHAN GORDON 2. Name of Inquiry: NOT TOO HOT, NOT TOO COLD: THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON SOIL BACTERIA 3. Goals and Objectives: a. Inquiry Questions: 1. How
ECOS Inquiry Template 1. Contributor s Name: NATHAN GORDON 2. Name of Inquiry: NOT TOO HOT, NOT TOO COLD: THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON SOIL BACTERIA 3. Goals and Objectives: a. Inquiry Questions: 1. How
Ohio s Learning Standards Grade 1 Science: Earth and Space Science - Sun, Energy and Weather The physical properties of water change.
 TEACHER GUIDE WATER: H 2 O IS AWESOME! 60 Minute Physical Science Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: 1-3 Water: H 2 O is Awesome! Description Studying science takes on a Splash Factor as we introduce
TEACHER GUIDE WATER: H 2 O IS AWESOME! 60 Minute Physical Science Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: 1-3 Water: H 2 O is Awesome! Description Studying science takes on a Splash Factor as we introduce
The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel.
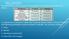 BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
To have students identify the layering of material according to their separate densities.
 Elizabeth Youngs DeLaura Middle School Satellite Beach, Florida 29 July 05 Lesson Plans/Activities from TESI 05 Lesson 1 Density To have students identify the layering of material according to their separate
Elizabeth Youngs DeLaura Middle School Satellite Beach, Florida 29 July 05 Lesson Plans/Activities from TESI 05 Lesson 1 Density To have students identify the layering of material according to their separate
Interactive Science Grade
 A Correlation of Interactive Science 2012 To the Michigan Science Grade Level Content Expectations v.1.09 Introduction This document demonstrates the close alignment between and the Michigan Science Standards
A Correlation of Interactive Science 2012 To the Michigan Science Grade Level Content Expectations v.1.09 Introduction This document demonstrates the close alignment between and the Michigan Science Standards
T. Trimpe Lesson 1: Length
 T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ Lesson 1: Length Metric Units The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter and is represented by a lowercase m. Metric Units 1 Kilometer (km) = 1000
T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ Lesson 1: Length Metric Units The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter and is represented by a lowercase m. Metric Units 1 Kilometer (km) = 1000
Student Learning Objectives
 M. Slone 2018 Lesson Title: THE ROLE OF SOIL IN THE FIGHT AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE Targeted Grade Level: GRADES 4 AND 5 MA STE Frameworks: 4-LS1-1. Construct an argument that animals and plants have internal
M. Slone 2018 Lesson Title: THE ROLE OF SOIL IN THE FIGHT AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE Targeted Grade Level: GRADES 4 AND 5 MA STE Frameworks: 4-LS1-1. Construct an argument that animals and plants have internal
LABORATORY 3 SOIL ANALYSIS
 VEGETATION DESCRIPTION AND ANALYSIS 2017 LABORATORY 3 SOIL ANALYSIS OBJECTIVE This lab will obtain four key soil parameters from the samples collected from Shawnee Gowan s Grizzly Glacier project relevés.
VEGETATION DESCRIPTION AND ANALYSIS 2017 LABORATORY 3 SOIL ANALYSIS OBJECTIVE This lab will obtain four key soil parameters from the samples collected from Shawnee Gowan s Grizzly Glacier project relevés.
TE Activity: Break the Tension
 TE Activity: Break the Tension Summary Students learn about and experiment with the concept of surface tension. How can a paper clip "float" on top of water? How can a paper boat be powered by soap in
TE Activity: Break the Tension Summary Students learn about and experiment with the concept of surface tension. How can a paper clip "float" on top of water? How can a paper boat be powered by soap in
Module 2, Add on Lesson Turbidity Sensor. Student. 90 minutes
 Module 2, Add on Lesson Turbidity Sensor Student 90 minutes Purpose Construct a sensor to measure the turbidity of water Graph data and reason about curves and linear relationships Calibrate the turbidity
Module 2, Add on Lesson Turbidity Sensor Student 90 minutes Purpose Construct a sensor to measure the turbidity of water Graph data and reason about curves and linear relationships Calibrate the turbidity
Soil Particle Density Protocol
 Soil Particle Density Protocol Purpose To measure the soil particle density of each horizon in a soil profile Overview Students weigh a sample of dry, sieved soil from a horizon, mix it with distilled
Soil Particle Density Protocol Purpose To measure the soil particle density of each horizon in a soil profile Overview Students weigh a sample of dry, sieved soil from a horizon, mix it with distilled
Microhabitats #1: Quantitative Study of Microhabitats
 Microhabitats #1: Quantitative Study of Microhabitats Adapted from: Microhabitats in Environmental Science Activities Kit by Michael Roa. The Center for Applied Research in Education, 1993. Microhabitats
Microhabitats #1: Quantitative Study of Microhabitats Adapted from: Microhabitats in Environmental Science Activities Kit by Michael Roa. The Center for Applied Research in Education, 1993. Microhabitats
Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology
 Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology 2013 Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 education.ti.com Science Objectives Identify characteristics of different soils to demonstrate that a suspect has been at a scene.
Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology 2013 Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 education.ti.com Science Objectives Identify characteristics of different soils to demonstrate that a suspect has been at a scene.
AQUIFERS OF THE SAN ANTONIO RIVER BASIN
 AQUIFERS OF THE SAN ANTONIO RIVER BASIN OBJECTIVES Explain what an aquifer is Identify the major aquifers located in the San Antonio River Basin Explain the difference between porosity and permeability
AQUIFERS OF THE SAN ANTONIO RIVER BASIN OBJECTIVES Explain what an aquifer is Identify the major aquifers located in the San Antonio River Basin Explain the difference between porosity and permeability
Activity Descriptions
 Activity Descriptions Celestial Dome Planisphere A planisphere, or a star chart, allows you to see which constellations are up on a given day or time. This activity, developed by Ken Wilson at the Science
Activity Descriptions Celestial Dome Planisphere A planisphere, or a star chart, allows you to see which constellations are up on a given day or time. This activity, developed by Ken Wilson at the Science
Step-by-Step Instructions for Lesson and Materials List
 Step-by-Step Instructions for Lesson and Materials List Materials: Modeling clay (beige, terra cotta, dark brown, green) 1 - Roll the beige, dark brown, and green modeling clay into flat layers using a
Step-by-Step Instructions for Lesson and Materials List Materials: Modeling clay (beige, terra cotta, dark brown, green) 1 - Roll the beige, dark brown, and green modeling clay into flat layers using a
(1) 45-minute lesson This activity is to be done by half the class at the same time as Activity Seven is done by the other half of the class.
 ACTIVITY SIX: TIME: SCIENCE PROCESS SKILL: SCIENCE CONCEPT: (1) 45-minute lesson This activity is to be done by half the class at the same time as Activity Seven is done by the other half of the class.
ACTIVITY SIX: TIME: SCIENCE PROCESS SKILL: SCIENCE CONCEPT: (1) 45-minute lesson This activity is to be done by half the class at the same time as Activity Seven is done by the other half of the class.
LESSON 8 GRADE 8 BRIDGE UP! ENGINEERING LESSON 8 GRADE 8
 LESSON 8 GRADE 8 BRIDGE UP! ENGINEERING LESSON 8 GRADE 8 LESSON 8 GRADE 8: Making Concrete Big Idea How do concrete and cement work? Use concrete to make parts of bridges to see how they work together.
LESSON 8 GRADE 8 BRIDGE UP! ENGINEERING LESSON 8 GRADE 8 LESSON 8 GRADE 8: Making Concrete Big Idea How do concrete and cement work? Use concrete to make parts of bridges to see how they work together.
Science Unit: Surface Water and Groundwater
 Science Unit: Lesson 2: Water Surface Water and Groundwater School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School
Science Unit: Lesson 2: Water Surface Water and Groundwater School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School
Lakewood City Schools Standards Based Science Course of Study FIRST GRADE
 FIRST GRADE Scope and Sequence Welcome to First Grade. Science instruction in the first grade builds upon the science skills developed in kindergarten and from the child s life experiences. Students have
FIRST GRADE Scope and Sequence Welcome to First Grade. Science instruction in the first grade builds upon the science skills developed in kindergarten and from the child s life experiences. Students have
Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science. Subchapter A. Elementary
 Text of Proposed Amendments to 19 TAC Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science Subchapter A. Elementary 112.10. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science,
Text of Proposed Amendments to 19 TAC Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science Subchapter A. Elementary 112.10. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science,
Bulk Density Protocol
 Bulk Density Protocol Purpose To measure the soil bulk density of each horizon in your soil profile. Overview Students obtain a soil sample in the field using a container with a measured volume. The soil
Bulk Density Protocol Purpose To measure the soil bulk density of each horizon in your soil profile. Overview Students obtain a soil sample in the field using a container with a measured volume. The soil
Lesson Title: How Natural Areas Filter Water
 Lesson Title: How Natural Areas Filter Water Essential question: Science Topic: Natural Resources How do paved areas impact the filtration of rainwater? Lesson Overview: Students learn about the importance
Lesson Title: How Natural Areas Filter Water Essential question: Science Topic: Natural Resources How do paved areas impact the filtration of rainwater? Lesson Overview: Students learn about the importance
Jennifer A. Keller Earth and Space Science Center for Math, Science and Technology Education SUNY at Stony Brook
 77 FLOW-THROUGH ANALOG GROUNDWATER MODELS: LESSON PLANS AND ACTMTIES FOR TEACHERS Jennifer A. Keller Earth and Space Science Center for Math, Science and Technology Education SUNY at Stony Brook This project's
77 FLOW-THROUGH ANALOG GROUNDWATER MODELS: LESSON PLANS AND ACTMTIES FOR TEACHERS Jennifer A. Keller Earth and Space Science Center for Math, Science and Technology Education SUNY at Stony Brook This project's
DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF
 DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF THE LEAKY FAUCET Outcome (lesson objective) Students will gather scientific data and be able to utilize the data to generalize the results over a long period of time. Student/Class
DRIP, DRIP, DRIP OR THE CASE OF THE LEAKY FAUCET Outcome (lesson objective) Students will gather scientific data and be able to utilize the data to generalize the results over a long period of time. Student/Class
SCIENCE Grade 1 Strand 1: Inquiry Process
 Strand 1: Inquiry Process s 1: 2: 3: 4: Science as inquiry is basic to science education and a controlling principle in the continuing organization and selection of students activities. Students at all
Strand 1: Inquiry Process s 1: 2: 3: 4: Science as inquiry is basic to science education and a controlling principle in the continuing organization and selection of students activities. Students at all
Deinking Recycled Paper through Flotation. Table of Contents 1. Objectives 2. Content Standards 3. Materials 3. Safety 4. Background Information 4
 1 Deinking Recycled Paper through Flotation Page Table of Contents 1 Activity Overview 2 Objectives 2 Content Standards 3 Materials 3 Safety 4 Background Information 4 Time Requirements and Preparation
1 Deinking Recycled Paper through Flotation Page Table of Contents 1 Activity Overview 2 Objectives 2 Content Standards 3 Materials 3 Safety 4 Background Information 4 Time Requirements and Preparation
Copyright 2014 Science Doodles
 Copyright 2014 Science Doodles If a scientist comes across an unknown element, could she use density to identify the element? A. Yes, because each element has a specific density. B. No, because density
Copyright 2014 Science Doodles If a scientist comes across an unknown element, could she use density to identify the element? A. Yes, because each element has a specific density. B. No, because density
Make Every Breath Count
 QuickLab Make Every Breath Count MATERIALS beaker, 250 ml bromthymol blue Elodea, sprig graduated cylinder stopper straw test tube,large water, 100 ml SAFETY PROCEDURE 1. Pour 100 ml of water from a graduated
QuickLab Make Every Breath Count MATERIALS beaker, 250 ml bromthymol blue Elodea, sprig graduated cylinder stopper straw test tube,large water, 100 ml SAFETY PROCEDURE 1. Pour 100 ml of water from a graduated
4th Grade Science GLEs
 4th Grade GLEs as Inquiry The Abilities to Do Scientific Inquiry 1. Ask questions about objects and events in the environment (e.g., plants, rocks, storms) (SI-E-A1) 2. Pose questions that can be answered
4th Grade GLEs as Inquiry The Abilities to Do Scientific Inquiry 1. Ask questions about objects and events in the environment (e.g., plants, rocks, storms) (SI-E-A1) 2. Pose questions that can be answered
Curriculum Map: Elementary Science Grade 3 Course: Gr 3 Science
 Curriculum Map: Elementary Science Grade 3 Course: Gr 3 Science Course Description: Science & Technology & Engineering Education: Science & Technology & Engineering Education is taught through the inquiry
Curriculum Map: Elementary Science Grade 3 Course: Gr 3 Science Course Description: Science & Technology & Engineering Education: Science & Technology & Engineering Education is taught through the inquiry
BASIS Lesson Plan. *Note to teachers: Detailed standards connections can be found at the end of this lesson plan.
 BASIS Lesson Plan Lesson Name: It s Just a Phase! Grade Level Connection(s) NGSS Standards: Grade 2, Physical Science FOSS CA Edition: Grade 3 Physical Science: Matter and Energy Module *Note to teachers:
BASIS Lesson Plan Lesson Name: It s Just a Phase! Grade Level Connection(s) NGSS Standards: Grade 2, Physical Science FOSS CA Edition: Grade 3 Physical Science: Matter and Energy Module *Note to teachers:
Science Curriculum. Saint Gerard Majella. Updated August 2016
 Science Curriculum Saint Gerard Majella Updated August 2016 GRADE: K 1. Identify non living things and the habitats and needs of living things. 2. Identify how plants and animals grow and change in their
Science Curriculum Saint Gerard Majella Updated August 2016 GRADE: K 1. Identify non living things and the habitats and needs of living things. 2. Identify how plants and animals grow and change in their
Deciding how to handle waste produced from manufacturing
 27 Reclaiming the Metal l a b o r at o ry Deciding how to handle waste produced from manufacturing is challenging. It can be diluted or incinerated, as you saw in previous activities. In some cases, it
27 Reclaiming the Metal l a b o r at o ry Deciding how to handle waste produced from manufacturing is challenging. It can be diluted or incinerated, as you saw in previous activities. In some cases, it
Science Supply Lists
 2014-2015 Science Supply Lists Earth Science 2014 Glynlyon, Inc Table of Contents UNIT 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH... 1 UNIT 2: FORCES AND FEATURES OF EARTH... 1 UNIT 3: FEATURES OF EARTH'S CRUST...
2014-2015 Science Supply Lists Earth Science 2014 Glynlyon, Inc Table of Contents UNIT 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH... 1 UNIT 2: FORCES AND FEATURES OF EARTH... 1 UNIT 3: FEATURES OF EARTH'S CRUST...
Orange Grove ISD Science Scope and Sequence 7th Grade 1 st Six Weeks # of Days Instructional Planning Information and Process Standards
 1 st Six Weeks # of Days Instructional Planning Information and Process Standards Unit 1 Scientific Investigations 15 Days 7.1 Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student, for at least 40% of the
1 st Six Weeks # of Days Instructional Planning Information and Process Standards Unit 1 Scientific Investigations 15 Days 7.1 Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student, for at least 40% of the
Science TEKS Verification Grade 7
 (1) Scientific investigation and reasoning. he student, for at least 40% of the instructional time, conducts laboratory and field investigations following safety procedures and environmentally appropriate
(1) Scientific investigation and reasoning. he student, for at least 40% of the instructional time, conducts laboratory and field investigations following safety procedures and environmentally appropriate
LAB National Science Teachers Association. Lab Handout. Introduction
 Lab Handout Lab 16. Surface Materials and Temperature Change: How Does the Nature of the Surface Material Covering a Specific Location Affect Heating and Cooling Rates at That Location? Introduction Inner
Lab Handout Lab 16. Surface Materials and Temperature Change: How Does the Nature of the Surface Material Covering a Specific Location Affect Heating and Cooling Rates at That Location? Introduction Inner
NATIONAL SCIENCE STANDARDS. TIME FRAME 1 class period (50 minutes) Grade Level
 GOAL Students assess whether the Martian surface around high latitude regions is more like dirty ice, icy dirt, or something else based on both Mars data and student-made physical models. OBJECTIVE Based
GOAL Students assess whether the Martian surface around high latitude regions is more like dirty ice, icy dirt, or something else based on both Mars data and student-made physical models. OBJECTIVE Based
DNA The Stuff of Life
 DNA Extraction 1 Name DNA The Stuff of Life Materials: Pea soup Rubbing alcohol Small beaker or cup Measuring spoon Meat tenderizer Detergent Test tube Coffee stirrer Procedure: 1. Fill your cup ½ full
DNA Extraction 1 Name DNA The Stuff of Life Materials: Pea soup Rubbing alcohol Small beaker or cup Measuring spoon Meat tenderizer Detergent Test tube Coffee stirrer Procedure: 1. Fill your cup ½ full
Observing Cells. 2.3 Explore
 1.1 Understand the 2.3 Challenge Explore 2.3 Explore Observing Cells What structure do all living things, whether they are germs or humans, have in common? The cell is the basic unit common to all living
1.1 Understand the 2.3 Challenge Explore 2.3 Explore Observing Cells What structure do all living things, whether they are germs or humans, have in common? The cell is the basic unit common to all living
Materials. Materials. NOTE Delta Education Customer Service can be reached at
 w Weather and Water Measuring Matter Materials Materials Contents Kit Inventory List... 42 Materials Supplied by the Teacher... 45 Preparing the Kit for Your Classroom... 47 Care, Reuse, and Recycling...
w Weather and Water Measuring Matter Materials Materials Contents Kit Inventory List... 42 Materials Supplied by the Teacher... 45 Preparing the Kit for Your Classroom... 47 Care, Reuse, and Recycling...
Module 4.3. Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? CT Science Framework Topics
 Module 4.3 Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? Science Content Standard 4.3 CT Science Framework Topics 1. Water is continuously moving
Module 4.3 Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? Science Content Standard 4.3 CT Science Framework Topics 1. Water is continuously moving
Overview. Learning Objectives: This module provides step-by-step instructions in how to do the Bulk Density Protocol.
 Overview This module provides step-by-step instructions in how to do the Bulk Density Protocol. Learning Objectives: After completing this module, you will be able to: Explain why bulk density is worth
Overview This module provides step-by-step instructions in how to do the Bulk Density Protocol. Learning Objectives: After completing this module, you will be able to: Explain why bulk density is worth
The Dynamic Density Bottle: A Make-and-Take, Guided Inquiry Activity on Density
 Supporting Information for: The Dynamic Density Bottle: A Make-and-Take, Guided Inquiry Activity on Density Thomas S. Kuntzleman, Department of Chemistry, Spring Arbor University, Spring Arbor, MI Information
Supporting Information for: The Dynamic Density Bottle: A Make-and-Take, Guided Inquiry Activity on Density Thomas S. Kuntzleman, Department of Chemistry, Spring Arbor University, Spring Arbor, MI Information
It is not essential for students to conduct an investigation for every question they generate or generate questions based on prior investigations.
 Scientific Inquiry 5-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific inquiry, including the foundations of technological design and the processes, skills, and mathematical thinking necessary
Scientific Inquiry 5-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific inquiry, including the foundations of technological design and the processes, skills, and mathematical thinking necessary
Crystal Growth and Buoyancy- Driven Convection Currents
 Crystal Growth and Buoyancy- Driven Convection Currents Objective: To observe buoyancy-driven covection currents that are created as crystals grow in a crystal growing solution. Science Standards: Science
Crystal Growth and Buoyancy- Driven Convection Currents Objective: To observe buoyancy-driven covection currents that are created as crystals grow in a crystal growing solution. Science Standards: Science
Florida Sunshine State Standards Benchmarks & Grade Level Expectations
 A Correlation of 2007 to the Florida Sunshine State Standards Benchmarks & Grade Level Expectations Grade Five T/S 44A_G5 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Florida
A Correlation of 2007 to the Florida Sunshine State Standards Benchmarks & Grade Level Expectations Grade Five T/S 44A_G5 Introduction This document demonstrates how Scott Foresman Science meets the Florida
Global Warming and Sea Level Rise
 MATERIALS SUITABLE FOR GRADES 1-8 This activity will show how increased temperatures will hasten the melting of ice in the environment, contributing to a rise in sea level and subsequent flooding of coastal
MATERIALS SUITABLE FOR GRADES 1-8 This activity will show how increased temperatures will hasten the melting of ice in the environment, contributing to a rise in sea level and subsequent flooding of coastal
Name: Date: Obi-Wan Adobe Design Worksheet
 Example Answers Obi-Wan Adobe Design Worksheet Adobe Brick Construction. Your teacher will assign one of the following variables for your team to test: water content, straw content or sand content. Circle
Example Answers Obi-Wan Adobe Design Worksheet Adobe Brick Construction. Your teacher will assign one of the following variables for your team to test: water content, straw content or sand content. Circle
Climate Change - Teacher Resource
 Climate Change - Teacher Resource Harnessing energy from wind and water This is a follow-up resource with some simple activites you might like to run with the students after their visit to Lab in a Lorry.
Climate Change - Teacher Resource Harnessing energy from wind and water This is a follow-up resource with some simple activites you might like to run with the students after their visit to Lab in a Lorry.
Science Is A Verb! Elementary. Part 1 LET S DO IT! ISBN
 LET S DO IT! Science Is A Verb! Elementary Part 1 ISBN 978-1-847003-56-0 Contents INTRODUCTION Lab Title How bright can you make the light bulbs? Students know how to design and build simple series and
LET S DO IT! Science Is A Verb! Elementary Part 1 ISBN 978-1-847003-56-0 Contents INTRODUCTION Lab Title How bright can you make the light bulbs? Students know how to design and build simple series and
Ordering Information and Guidelines
 TM 201 West Michigan Avenue Battle Creek, MI 49017 Ph: (269) 213-3907 Fax: (269) 965-9540 www.cerealcityscience.org Ordering Information and Guidelines February 2018 - January 2019 Ordering Order by fax:
TM 201 West Michigan Avenue Battle Creek, MI 49017 Ph: (269) 213-3907 Fax: (269) 965-9540 www.cerealcityscience.org Ordering Information and Guidelines February 2018 - January 2019 Ordering Order by fax:
