Assessment of Domestic Pollution Load from Urban Agglomeration in Ganga Basin:
|
|
|
- Shonda Horton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Assessment of Domestic Pollution Load from Urban Agglomeration in Ganga Basin: Ramganga, Kali and Gomati Sub-Basin GRBMP: Ganga River Basin Management Plan by Indian Institutes of Technology IIT Bombay IIT Delhi IIT Guwahati IIT Kanpur IIT Kharagpur IIT Madras IIT Roorkee
2 Preface In exercise of the powers conferred by sub-sections (1) and (3) of Section 3 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 (29 of 1986), the Central Government has constituted National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA) as a planning, financing, monitoring and coordinating authority for strengthening the collective efforts of the Central and State Government for effective abatement of pollution and conservation of the river Ganga. One of the important functions of the NGRBA is to prepare and implement a Ganga River Basin Management Plan (GRBMP). A Consortium of 7 Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) has been given the responsibility of preparing Ganga River Basin Environment Management Plan (GRBMP) by the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF), GOI, New Delhi. Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) has been signed between 7 IITs (Bombay, Delhi, Guwahati, Kanpur, Kharagpur, Madras and Roorkee) and MoEF for this purpose on July 6, This report is one of the many reports prepared by IITs to describe the strategy, information, methodology, analysis and suggestions and recommendations in developing Ganga River Basin Management Plan (GRB EMP). The overall Frame Work for documentation of GRBMP and Indexing of Reports is presented on the inside cover page. There are two aspects to the development of GRB EMP. Dedicated people spent hours discussing concerns, issues and potential solutions to problems. This dedication leads to the preparation of reports that hope to articulate the outcome of the dialog in a way that is useful. Many people contributed to the preparation of this report directly or indirectly. This report is therefore truly a collective effort that reflects the cooperation of many, particularly those who are members of the IIT Team. Lists of persons who have contributed directly and those who have taken lead in preparing this report is given on the reverse side. DrVinod Tare Professor and Coordinator Development of GRBMP IIT Kanpur
3 The Team 1. A AKazmi, IIT Roorkee kazmifce@iitr.ernet.in 2. A K Gupta, IIT Kharagpur akgupta18@rediffmail.com,akgupta@iitkgp.ac.in 3. A K Mittal, IIT Delhi akmittal@civil.iitd.ernet.in 4. A K Nema, IIT Delhi aknema@gmail.com 5. Ajay Kalmhad, IIT Guwahati kajay@iitg.ernet.in 6. Anirban Gupta, BESU Shibpur guptaanirban@hotmail.com 7. Arun Kumar, IIT Delhi arunku@civil.iitd.ac.in 8. G J Chakrapani, IIT Roorkkee gjcurfes@iitr.ernet.in 9. GazalaHabib, IIT Delhi gazalahabib@gmail.com 10. Himanshu Joshi, IIT Roorkee himanshujoshi58@gmail.com 11. InduMehrotra, IIT Roorkee indumfce@iitr.ernet.in 12. I M Mishra, IIT Roorkee imishfch@iitr.ernet.in 13. Ligy Philip, IIT Madras ligy@iitm.ac.in 14. M MGhangrekar, IIT Kharagpur ghangrekar@civil.iitkgp.ernet.in 15. MukeshDoble, IIT Bombay mukeshd@iitm.ac.in 16. P K Singh, IT BHU dr_pksingh1@rediffmail.com 17. Purnendu Bose, IIT Kanpur pbose@iitk.ac.in 18. R Ravi Krishna, IIT Madras rrk@iitm.ac.in 19. Rakesh Kumar, NEERI Nagpur r_kumar@neeri.res.in 20. S M Shivnagendra, IIT Madras snagendra@iitm.ac.in 21. SaumyenGuha, IIT Kanpur sguha@iitk.ac.in 22. Shyam R Asolekar, IIT Bombay asolekar@iitb.ac.in 23. SudhaGoel, IIT Kharagpur sudhagoel@civil.iitkgp.ernet.in 24. Suparna Mukherjee, IIT Bombay mitras@iitb.ac.in 25. T R Sreekrishanan, IIT Delhi sree@dbeb.iitd.ac.in 26. Vinod Tare, IIT Kanpur vinod@iitk.ac.in 27. Vivek Kumar, IIT Roorkee vivekfpt@iitr.ernet.in 1. Vinod Tare, IIT Kanpur 2. Purnendu Bose, IIT Kanpur 3. Shashikant Patel, IIT Kanpur Lead Persons
4 Ramganga River is a tributary of river Ganga. It originates at a place known as Diwali Khal at an elevation of 2926 meters in the Himalayas. The total length of the river course from its origin up to its confluence with Ganga River is about 600 km. The river flows though the districts of Bijnor, Moradabad, Rampur, Shajahanpur, Farukhabad and Hardoi before joining with Ganga River. The catchment area of the basin is about 32,493 sq. km. The major tributaries which join Ramganga river are the Khoh, Gagan, Kosi, Dhela, Bhakara, East Begul, West Begul and Deoha (Garra). These tributaries carry the wastewater and industrial effluents from different towns and industrial units in the basin. Table 1 shows the demography of the major cities situated along river Ramganga and its tributaries. City Tributary Area (sq.km) Population (as in 2011) in lakhs Moradabad Bareilly Shahjhanpur Garra Rampur Koshi Major Dam Table 1: Demography of major cities on river Ramganga and its tributaries Ramganga River Valley Project s dam is situated about 3 km upstream of Kalagarh village in the district of Pauri Garhwal of the present Uttarakhand state. The reservoir has a live storage of m cu.m. Utilizable for the development of command area of and drinking water supplies to Delhi Nagar Nigam. The water is being utilized for irrigating 5.90 lakh hectares of command area in the Ganga Yamuna basins through a network of canals. This added irrigation is spread over 16 Districts of Uttar Pradesh extending from Saharanpur to Allahabad. Pollution Load on River Ramganga As per the data available from Jal Nigam/Nagar Nigam, all the major cities situated on the river Ramganga use ground water as the sole source for meeting the domestic demand. Figure 1 shows the ground water extracted and the corresponding sewage generated in all the major cities
5 Pollution Load (kg/day) Pollution Load kg/day MLD Report Code: 066_GBP_IIT_EQP_S&R_16_Ver 1_DEC Groundwater Supply Sewage Generated (MLD) Untreated sewage Rampur Moradabad Bareilly Shahjhanpur Major Cities (Source to Mouth) Figure 1: Ground water utilization and Sewage Generation (in MLD) Estimated BOD Estimated COD Rampur Moradabad Bareilly Shahjhanpur Major Cities (Source to Mouth) Figure 2a: Spatial distribution of estimated pollution load on Ramganga River TKN Rampur Moradabad Bareilly Shahjhanpur Major Cities(Source to Mouth) Figure 2b: Spatial distribution of estimated pollution load on Ramganga River.
6 As per the data available from Jal Nigam/Nagar Nigam none of the major cities situated along the river Ramganga have an installed STP. Based on the actual field survey and flow measurements of sewage in major drains in the major cities the total untreated sewage discharge into the river Ramganga is estimated to be about 342 MLD. The river receives the domestic sewage through a network of 29 major drains. Due to the discharge of rainwater runoff in the domestic drains the sewage generated is more than the groundwater supply in the cities of Rampur and Bareilly. The pollution load on the river in terms of BOD 5, COD and TKN is estimated based on the per capita contribution for all the major cities. Figure 2a & 2b shows the spatial distribution of the pollution load on the river from source to mouth. Figure3: Major drains disposing sewage into River Ramganga
7 Figure4: Major Cities on River Ramganga
8 City: Bareilly 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 70 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 10,286 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 17 Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd)* Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) BOD 5 NIL (kg/d) COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Ramganga River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal Number of Water Bodies Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 13 July, 2011 at 3:30 PM. Remark- Because of rainy season flow in drain is more than water supply into the city.
9 City: Moradabad 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 70 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 12,712 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD 5 NIL COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Ramganga 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 7 33 Number of Water Bodies Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on July, 2011 at 06:30 PM to 07:30 PM & 09:30 AM to 10:30 AM.
10 City: Rampur 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 43 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 6,546 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) NA 21 Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD 5 NIL COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Koshi River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 5 33 Number of Water Bodies NIL 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) NIL 35 Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 20 July, 2011 at 6:30 PM. Remark- Because of rainy season flow in drain is more than water supply into the city.
11 City: Shahjahanpur 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 44 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 6,750 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL BO NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) CO NIL TK NIL 29 BO Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) CO (kg/d) TK Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Khanaut &Garra 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 9 33 Number of Water Bodies 1 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 07 July, 2011 at 5:30 PM Remark- Because of rainy season flow in drain is more than water supply into the city.
12 Kali river Basin: The Kali River is a tributary of river Ganga. It originates near Khatholi town and flows through the districts of Muzaffarnagar, Modinagar, Meerut, Hapur, Bulandshahr, and Kasganj finally merges with river Ganga at Kannauj. The river has a total length of approximately 550 km from origin till confluence. Muzaffarnagar, Modinagar, Meerut, Hapur, Bulandshahr, Kasganj, Kannauj are the major urban settlements along the course of the river Table 1 shows the demography of the major cities situated along river Kali. City Area (sq.km) Population (as in 2011) in lakhs Muzaffarnagar Modinagar Meerut Hapur Bulandshar Kasganj Kannauj Table 2: Demography of major cities on Kali River Pollution Load on the River Kali As per the data available from Jal Nigam/Nagar Nigam, all the major cities situated on the river Kali use ground water as the sole source for meeting the domestic demand. Figure 1 shows the ground water extracted and the corresponding sewage generated in all the major cities. Based on the actual field survey and flow measurements of sewage in major drains in the major cities the total untreated sewage discharge into the river Kali is estimated to be about 346MLD. The river receives the sewage through a network of 24 major drains along its course. As observed in Modinagar, the sewage flow in the domestic drains was very high as compared to the ground water supply. This is due to the discharge of industrial wastewater into the domestic drains. As per the data available from Jal Nigam/Nagar Nigam Muzaffarnagar is the only city on the river that has one operating STP which handles about 75% of the generated sewage. None of the other major cities situated along the river Kali have an installed STP. All the sewage carried by the domestic drains is discharged into the river without any treatment. The pollution load on the river in terms of BOD 5, COD and TKN is estimated based on the per capita contribution for all the major cities. Figure 2a & 2b shows the spatial distribution of the pollution load on the river from source to mouth.
13 Pollution Load (kg/day) Pollution Load(kg/day) MLD Report Code: 066_GBP_IIT_EQP_S&R_16_Ver 1_DEC Groundwater supply Sewage Generated Untreated Sewage Major Cities (Source to Mouth) Figure 1: Ground water utilization and sewage generation (in MLD) BOD COD Major Cities(Source to Mouth) Figure 2a: Spatial distribution of estimated pollution load on Kali River. TKN Major Cities (Source to Mouth) Figure 2b: Spatial distribution of estimated pollution load on Kali River.
14 Figure3: Major drains in various cities along River Kali
15 Figure4: Major Cities on River Kali
16 City: Muzaffarnagar 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 45 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 10,995 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD) Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) Number of STPs 1 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) BOD 5 NIL (kg/d) COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Kali 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 2 33 Number of Water Bodies 2 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 19 April, 2012 at 01:00 PM to 02:00 PM.
17 City: Modinagar 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 26 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 7,031 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd)* Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) BOD 5 NIL (kg/d) COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Kali River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 2 33 Number of Water Bodies NIL 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) NIL 35 Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 30 June, 2011 at 09:04 Note:-Due to Industrial wastewater discharge into the domestic drains the flows in drains were very high.
18 City: Meerut 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 80 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 17,811 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD 5 NIL COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Kali River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 4 33 Number of Water Bodies Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on August, 2011 at 05:30 PM.
19 City: Hapur 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 36 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 7,300 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) BOD 5 NIL (kg/d) COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Kali River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 3 33 Number of Water Bodies NIL 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) NIL 35 Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 30 June, 2011 at 09:04 Note:-Due to Industrial wastewater discharge into the domestic drains the flows in
20 City: Bulandshahar 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 32 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 6,963 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) BOD 5 NIL (kg/d) COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Kali River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 8 33 Number of Water Bodies Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 17 August, 2011 at 05:30 PM.
21 City: Kasganj 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 30 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 3,375 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD 5 NIL COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means Land/ River 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Land/ Kali River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 4 33 Number of Water Bodies 0 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 20 October, 2011 at 3.30 PM.
22 City: Kannauj 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2001 (%) Total Number of Wards 30 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 2,391 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells 8 13 Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) BOD (kg/d) COD Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) TKN 0.0 BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River & Land 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Kali River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 4 33 Number of Water Bodies Gross Area of Water Bodies (sq km) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<<1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 11 November, 2011 at 04:00 PM.
23 Gomti River Basin: The Gomti is one of the tributaries of the Ganga. It originates near Mainkot, from a lake Fulhar Jheel in Madhotanda about 30 km east of the Pilibhit town in Uttar Pradesh. The river flows through the districts of Sitapur, Lucknow, Barabanki, Sultanpur, Jaunpur and confluences with River Ganga in Kaithi, Ghazipur bordering Varanasi. The total length of the river from source to mouth is about 960km. The total catchment area of the river is 30,437 sq. km. The main tributaries of the river are Kathina, Bhainsi, Sarayan, Gon, Reth, Sai, Pili,Ull and Kalyani. Sai River is its major tributary having catchment area of 12,900 sq. km, approximately 43% of the total catchment area of River Gomti. On the banks of the river, Sitapur, Lucknow, Sultanpur, and Jaunpur, are the major urban settlements. Among these Lucknow is a major city with the highest population as well as the administrative capital of the state of Uttarpradesh. Table 1 shows the demography of the major cities situated along river Kali. City Tributary Area (sq.km) Population (as in 2011) in lakhs Lakhimpur Ull Sitapur Sarayan Lucknow Barabanki Sultanpur Sar Jaunpur Faizabad Sai RaeBareily Sai Pollution Load on the River Gomati As observed from Table 1, the city of Lucknow has an area and population greater than all the other cities combined. Therefore, it can reasonably be assumed that Lucknow is a major contributor to the pollution load on the River Gomati. Pollution Load on the River Gomati from Lucknow: As per the data available from Jal Nigam/Nagar Nigam, both groundwater and surface water from River Gomati are used for meeting the domestic demand of Lucknow City. Figure 1 shows the ground and surface water extracted and the corresponding sewage generated in Lucknow. Based on the actual field survey and flow measurements of sewage in major drains in Lucknow the total sewage generation is estimated to be about 1010 MLD. As per the data available from Jal Nigam there are two sewage treatment plants operative in Lucknow. The details of both the STPs are provided in Table 2. The combined treatment capacity of the STPs is about 400 MLD which is about 40% of the total sewage generation. The remaining untreated sewage is discharged into the River Gomati through a network of 23 major drains. The pollution load on the river in terms of BOD5, COD and TKN is estimated based on the per capita contribution. Figure 2a & 2b shows the pollution load on the river Gomati from Lucknow.
24 kg/day kg/day MLD Report Code: 066_GBP_IIT_EQP_S&R_16_Ver 1_DEC Lucknow Surface water Supply Groundwater Supply Total Sewage Generation Treated Sewage Figure 1: Surface and ground water utilization and sewage generation (in MLD) BOD COD Lucknow City Figure 2a: Pollution load on Gomati River TKN Lucknow City Figure 2b: Pollution load on Gomati River
25 SNo. Place Details of Sewage Treatment Plants: (Source: Jal Nigam/Parallel Organization) Location Current Year of Year of Installed Utilized Constructi Commissionin Capacity Latitude (N) Longitude (E) Capacity on g (MLD) (MLD) Adopted Technology 1 Bharwara 26 50'16.0"N 81 02'17.4"E UASB 2 Daulatganj 26 52'58.1"N 80 54'5.4"E FAB Effluent Disposa l Gomti River Gomti River Figure 5: Major cities situated on River Gomati
26 MLD Report Code: 066_GBP_IIT_EQP_S&R_16_Ver 1_DEC 2014 Pollution load on River Gomati from Other Cities As per the data available from Jal Nigam/Nagar Nigam, barring Jaunpur all the major cities situated on the river Gomati use ground water as the sole source for meeting the domestic demand. Jaunpur city is supplied with both ground and surface water from the River Gomati to meet the domestic demand. Figure 3 shows the ground water extracted and the corresponding sewage generated in all the major cities. Based on the actual field survey and flow measurements of sewage in major drains in the major cities the total untreated sewage discharge into the river Gomati is estimated to be about 100 MLD. The river receives the sewage (directly and indirectly from its tributaries) through a network of 25 major drains along its course. As per the data available from Jal Nigam/Nagar Nigam Sultanpur is the only city on the river that has one operating oxidation pond which handles about 5 MLD of the generated sewage. None of the other major cities situated along the river Gomati have an installed STP/treatment facility. All the sewage carried by the domestic drains is discharged into the river without any treatment. The pollution load on the river in terms of BOD5, COD and TKN is estimated based on the per capita contribution for all the major cities. Figure 4a & 4b shows the spatial distribution of the pollution load on the river from source to mouth Groundwater Supply Total Sewage Generation 0.0 Lakhimpur Sitapur Barabanki Sultanpur Jaunpur Faizabad Raebarielly Major Cities (Source to Mouth) Figure 3: Water utilization and sewage generation (in MLD)
27 kg/day kg/day Report Code: 066_GBP_IIT_EQP_S&R_16_Ver 1_DEC BOD COD Lakhimpur Sitapur Barabanki Sultanpur Jaunpur Faizabad Raebarielly Major Cities(Source to Mouth) Figure 4b: Spatial distribution of estimated pollution load on Gomati River TKN Lakhimpur Sitapur Barabanki Sultanpur Jaunpur Faizabad Raebarielly Major cities (Source to Mouth) Figure 4b: Spatial distribution of estimated pollution load on Gomati River. The pollution load on the river in terms of BOD5, COD and TKN is estimated based on the per capita contribution for all the major cities. Figure 4a & 4b shows the spatial distribution of the pollution load on the river from source to mouth.
28 Figure5: Major drains disposing sewage into River Gomati
29 City: Lakhimpur S. No. Items Value 1 Total Area (sq km) : Population as in 2011 : Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) : Total Number of Wards : 27 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) : 6,108 6 Total Number of Household as in 2011 : Number of Household per Ward : Surface Water Supply (MLD) : NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) : Number of Bore Wells : Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) : Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells : Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) : Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply : NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) : NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) : Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) : Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) : Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* : Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) : Sewage Collection (MLD) : NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) : NIL 23 Number of STPs : NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) : NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) : NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) : NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) : NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD5 : 0.0 COD : 0.0 TKN : Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD5 : COD : TKN : Wastewater Disposal Means : River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal : Ull River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal : 1 33 Number of Water Bodies : 9 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (sq km) : Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area : <<<1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 17 November, 2011 at 05:00 PM.
30 City: Sitapur 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 30 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 6,274 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL BOD Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) COD 0.0 TKN BOD Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita COD Contribution) (kg/d) TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Sarien River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 6 33 Number of Water Bodies 6 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (sq km) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<<1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 16 November, 2011 at 03:00 PM to 04:00 PM.
31 City: Lucknow 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards Population per Ward (Thousands) 26,377 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) NIL 10 Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) NIL 12 Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD) 20 Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) 21 Sewage Collection (MLD) 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) 23 Number of STPs 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP & YAP I & II (MLD) 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) BOD5 NIL (kg/d) COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River & Land 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Gomati 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal Number of Water Bodies Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1
32 City: Barabanki 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 25 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 6,188 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD) Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD5 NIL COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Reth River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 1 33 Number of Water Bodies 2 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 15 May, 2012 at 09:40 AM to 10:40 AM.
33 City: Faizabad 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 28 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 9,256 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD) Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD5 0.0 COD 0.0 TKN Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Sai River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 3 33 Number of Water Bodies 1 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area << 1
34 City: Jaunpur 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 31 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 5,423 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps/ Tubewells Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) BOD5 NIL (kg/d) COD NIL TKN NIL 29 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River Disposal 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Gomti River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 9 33 Number of Water Bodies 3 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) 35 Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area <<< 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IT,BHU team on 18 Nov, 2011 at 1:30 PM.
35 City: Raibareily 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 31 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 6,181 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD)* Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) NIL 22 Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) NIL 23 Number of STPs NIL 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) NIL 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) NIL 26 Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) NIL 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD5 0.0 COD 0.0 TKN Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Sai River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 1 33 Number of Water Bodies Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area >> 1 *Estimation based on one time survey by IIT, Kanpur team on 19 November, 2011 at 03:30 PM.
36 City: Sultanpur 1 Total Area (sq km) Population as in Population Growth Rate as in 2011 (%) Total Number of Wards 25 5 Population per Ward (Thousands) 4,648 6 Total Number of Household as in Number of Household per Ward Surface Water Supply (MLD) NIL 9 Ground Water (GW) Supply (MLD) 9 10 Number of Bore Wells Ground Water Extraction per Bore Well (MLD) Number of Hand Pumps Ground Water Extraction per Hand Pump (lpd) Number of Pumping Stations for Water Supply NIL 15 Total Pumping Capacity (MLD) NIL 16 Average Water Supply Rate from ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Water Supply from ULB and Non-ULB Sources (MLD) Average Water Supply Rate from ULB & Non-ULB Sources (lpcd) Total Sewage Generation (MLD) Per Capita Sewage Generation (lpcd) Sewage Collection (MLD) Percentage of Sewage Collection (%) Number of STPs 1 24 Total Installed Capacity of STPs under GAP I & II (MLD) 5 25 Current Utilized Capacity of STPs (MLD) Percentage Utilization of Installed Capacity (%) 0 27 Capacity of STPs Sanctioned under JNNURM & Others (MLD) NIL 28 Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 1: Actual Flow) (kg/d) BOD5 0.0 COD 0.0 TKN Pollution Load (Domestic) (Method 2: Per Capita Contribution) (kg/d) BOD COD TKN Wastewater Disposal Means River 31 Name of River/Streams for Wastewater Disposal Sai River 32 Number of Drains/Nallah for Wastewater Disposal 4 33 Number of Water Bodies 1 34 Gross Area of Water Bodies (Hectare) Area of Water Bodies as % of Total Area << 1.0
Assessment of Domestic Pollution Load from Urban Agglomeration in Ganga Basin: Gandak and Kosi Sub-Basin
 Report Code: 067_GBP_IIT_EQP_S&R_17_Ver 1_DEC 2014 Assessment of Domestic Pollution Load from Urban Agglomeration in Ganga Basin: Gandak and Kosi Sub-Basin GRBMP: Ganga River Basin Management Plan by Indian
Report Code: 067_GBP_IIT_EQP_S&R_17_Ver 1_DEC 2014 Assessment of Domestic Pollution Load from Urban Agglomeration in Ganga Basin: Gandak and Kosi Sub-Basin GRBMP: Ganga River Basin Management Plan by Indian
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF DRINKING WATER & SANITATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.450 TO BE ANSWERED ON Piped Water Supply
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF DRINKING WATER & SANITATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.450 TO BE ANSWERED ON 19.07.2018 Piped Water Supply 450. SHRI BHAIRON PRASAD MISHRA: Will the Minister of DRINKING
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF DRINKING WATER & SANITATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.450 TO BE ANSWERED ON 19.07.2018 Piped Water Supply 450. SHRI BHAIRON PRASAD MISHRA: Will the Minister of DRINKING
Assessment of Water Quality Index of River Gomti Using Weighted Arithmetic Index Method
 Assessment of Water Quality Index of River Gomti Using Weighted Arithmetic Index Method Nusrat Ali 1, Sh. Runa Oraon 2, Sh. Aviral Saxsena 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Integral
Assessment of Water Quality Index of River Gomti Using Weighted Arithmetic Index Method Nusrat Ali 1, Sh. Runa Oraon 2, Sh. Aviral Saxsena 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Integral
Study on performance evaluation of. sustainability
 Study on performance evaluation of STPs in Lucknow and dissue of wastewater t sustainability REGIONAL WORKSHOP Sustainable Water and Sanitation: Best management Practices Potential and Challenges May 1,
Study on performance evaluation of STPs in Lucknow and dissue of wastewater t sustainability REGIONAL WORKSHOP Sustainable Water and Sanitation: Best management Practices Potential and Challenges May 1,
Steps to Conserve the Water Quality of River Ganga (Upto Kanpur) UP Pollution Control Board TC-12V, Vibhuti Khand, Gomti Nagar, Lucknow
 Steps to Conserve the Water Quality of River Ganga (Upto Kanpur) 2016-17 UP Pollution Control Board TC-12V, Vibhuti Khand, Gomti Nagar, Lucknow 31-08-2016 Steps taken in U.P. for overall improvement of
Steps to Conserve the Water Quality of River Ganga (Upto Kanpur) 2016-17 UP Pollution Control Board TC-12V, Vibhuti Khand, Gomti Nagar, Lucknow 31-08-2016 Steps taken in U.P. for overall improvement of
Review of Wastewater Reuse Projects Worldwide
 Review of Wastewater Reuse Projects Worldwide Collation of Selected International Case Studies and Experiences GRB EMP : Ganga River Basin Environment Management Plan by Indiann Institutes of Technology
Review of Wastewater Reuse Projects Worldwide Collation of Selected International Case Studies and Experiences GRB EMP : Ganga River Basin Environment Management Plan by Indiann Institutes of Technology
Excreta Matters: 7 th Citizens Report on the state of India s Environment. An agenda for water-prudent and waste-wise India.
 Excreta Matters: 7 th Citizens Report on the state of India s Environment An agenda for water-prudent and waste-wise India Need to reinvent Rapid urbanization is creating new water stresses Violence is
Excreta Matters: 7 th Citizens Report on the state of India s Environment An agenda for water-prudent and waste-wise India Need to reinvent Rapid urbanization is creating new water stresses Violence is
Javier Mateo-Sagasta, International Water Management Institute, Sri Lanka
 Javier Mateo-Sagasta, International Water Management Institute, Sri Lanka This article is the first in a special series looking at water quality issues in the River Ganga (also known as the Ganges). The
Javier Mateo-Sagasta, International Water Management Institute, Sri Lanka This article is the first in a special series looking at water quality issues in the River Ganga (also known as the Ganges). The
Status of Urbanization and Industrialization
 Status of Urbanization and Industrialization in Middle Ganga Basin GRBMP: Ganga River Basin Management Plan by Indian Institutes of Technology IIT Bombay IIT Delhi IIT Guwahati IIT Kanpur IIT Kharagpur
Status of Urbanization and Industrialization in Middle Ganga Basin GRBMP: Ganga River Basin Management Plan by Indian Institutes of Technology IIT Bombay IIT Delhi IIT Guwahati IIT Kanpur IIT Kharagpur
India Water and Wastewater Report
 India Water and Wastewater Report Industry Report India Water and Wastewater Overview Water and wastewater management in India has emerged as an issue relatively recent priority at the national, state,
India Water and Wastewater Report Industry Report India Water and Wastewater Overview Water and wastewater management in India has emerged as an issue relatively recent priority at the national, state,
RIVER BASIN TAPI [ INDIA
 RIVER BASIN TAPI [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names); Tapi,
RIVER BASIN TAPI [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names); Tapi,
WATER QUALITY MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR GANGA RIVER BASIN COLLABORATION BETWEEN THE GOVERNMENT OF JAPAN AND GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
 WATER QUALITY MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR GANGA RIVER BASIN COLLABORATION BETWEEN THE GOVERNMENT OF JAPAN AND GOVERNMENT OF INDIA BRIJESH SIKKA Additional Director, Ministry of Environment and Forests, National
WATER QUALITY MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR GANGA RIVER BASIN COLLABORATION BETWEEN THE GOVERNMENT OF JAPAN AND GOVERNMENT OF INDIA BRIJESH SIKKA Additional Director, Ministry of Environment and Forests, National
RIVER BASIN GHAGARA [ INDIA
 RIVER BASIN GHAGARA [ INDIA ] Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names. 1.2 Relief Map and Index Map of RB with Country/ State/ Province
RIVER BASIN GHAGARA [ INDIA ] Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names. 1.2 Relief Map and Index Map of RB with Country/ State/ Province
QUANTITATIVE ASSESSMENT OF KALI RIVER WATER POLLUTION
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2261-2266 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com QUANTITATIVE ASSESSMENT OF KALI RIVER WATER POLLUTION D. K. SINHA *, RAMAKANT RAM a and NAVNEET KUMAR b Department
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2261-2266 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com QUANTITATIVE ASSESSMENT OF KALI RIVER WATER POLLUTION D. K. SINHA *, RAMAKANT RAM a and NAVNEET KUMAR b Department
CHAPTER 6 PROFILE OF URBAN PUNJAB WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO LUDHIANA CITY
 CHAPTER 6 PROFILE OF URBAN PUNJAB WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO LUDHIANA CITY Access to clean drinking water is a fundamental right in India as cited in right to life under Article 21 of the Constitution of
CHAPTER 6 PROFILE OF URBAN PUNJAB WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO LUDHIANA CITY Access to clean drinking water is a fundamental right in India as cited in right to life under Article 21 of the Constitution of
Energy and resource efficiency in Urban Water Management : Challenges & potential ti for enabling paradigm shift
 Energy and resource efficiency in Urban Water Management : Challenges & potential ti for enabling paradigm shift Dr Suresh Kumar Rohilla Programme Director Water Management, CSE February 28, 2013 CSE CCBP
Energy and resource efficiency in Urban Water Management : Challenges & potential ti for enabling paradigm shift Dr Suresh Kumar Rohilla Programme Director Water Management, CSE February 28, 2013 CSE CCBP
Status of River Ganga and Action Plan to improve its water quality
 Status of River Ganga and Action Plan to improve its water quality in Phase-II (District Unnao D/S to District Balia) for Chamber Meeting at NGT on 15 September, 2017 UP Pollution Control Board TC-12V,
Status of River Ganga and Action Plan to improve its water quality in Phase-II (District Unnao D/S to District Balia) for Chamber Meeting at NGT on 15 September, 2017 UP Pollution Control Board TC-12V,
THE STUDY ON WATER QUALITY MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR GANGA RIVER IN THE REPUBLIC OF INDIA
 No. JAPAN INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION AGENCY (JICA) NATIONAL RIVER CONSERVATION DIRECTORATE (NRCD) MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT AND FORESTS THE STUDY ON WATER QUALITY MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR GANGA RIVER IN THE REPUBLIC
No. JAPAN INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION AGENCY (JICA) NATIONAL RIVER CONSERVATION DIRECTORATE (NRCD) MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT AND FORESTS THE STUDY ON WATER QUALITY MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR GANGA RIVER IN THE REPUBLIC
Monitoring Systems to manage Water Quality of River Ganga
 Monitoring Systems to manage Water Quality of River Ganga By Mrinal Kanti Biswas Scientist D Central Pollution Control Board Delhi biswasmrinal@gmail.com Content Layout Why Ganga an introduction Criteria
Monitoring Systems to manage Water Quality of River Ganga By Mrinal Kanti Biswas Scientist D Central Pollution Control Board Delhi biswasmrinal@gmail.com Content Layout Why Ganga an introduction Criteria
Environmental implication of new agricultural technology in Uttar Pradesh
 2017; 3(8): 713-718 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(8): 713-718 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 13-06-2017 Accepted: 14-07-2017 Dr. Naima Umar Department
2017; 3(8): 713-718 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(8): 713-718 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 13-06-2017 Accepted: 14-07-2017 Dr. Naima Umar Department
Study of Waste Water Characteristics and its pollution for the stretch of Krishna River from Sangli to Haripur
 Study of Waste Water Characteristics and its pollution for the stretch of Krishna River from Sangli to Haripur Wagh C.H 1, Kamat R.S 2 1, 2 Civil Department, Walchand College of Engineering; Sangli (Maharashtra),
Study of Waste Water Characteristics and its pollution for the stretch of Krishna River from Sangli to Haripur Wagh C.H 1, Kamat R.S 2 1, 2 Civil Department, Walchand College of Engineering; Sangli (Maharashtra),
Impact of Regional Disparities on Agricultural Development in Uttar Pradesh- A Geographical Analysis
 Global Journal of HUMN SOCIL SCIENCE Geography, Geo-Sciences, Environmental Disaster Management Volume 13 Issue 5 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher:
Global Journal of HUMN SOCIL SCIENCE Geography, Geo-Sciences, Environmental Disaster Management Volume 13 Issue 5 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher:
UTILIZATION OF AVAILABLE WATER RESOURCES IN UTTARANCHAL: AN APPRAISAL OF CURRENT STATUS AT THE DISTRICT SCALE INTRODUCTION
 UTILIZATION OF AVAILABLE WATER RESOURCES IN UTTARANCHAL: AN APPRAISAL OF CURRENT STATUS AT THE DISTRICT SCALE V. N. Sharda and P.R. Ojasvi* INTRODUCTION The study on water as a natural resource is inclusive
UTILIZATION OF AVAILABLE WATER RESOURCES IN UTTARANCHAL: AN APPRAISAL OF CURRENT STATUS AT THE DISTRICT SCALE V. N. Sharda and P.R. Ojasvi* INTRODUCTION The study on water as a natural resource is inclusive
Namami Gange Programme
 Namami Gange Programme National Mission for Clean Ganga -> Implementation wing of National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA). Registered society originally formed by Ministry of Environment, Forests
Namami Gange Programme National Mission for Clean Ganga -> Implementation wing of National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA). Registered society originally formed by Ministry of Environment, Forests
THE WATER-WASTE PORTRAIT The city just needs to protect and recharge its groundwater. Instead, it is eyeing Ganga waters
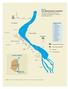 MASANI STP To Vrindavan MATHURA THE WATER-WASTE PORTRAIT The city just needs to protect and recharge its groundwater. Instead, it is eyeing Ganga waters Bhuteshwar RS CIS-YAMUNA 1 Masani RS Shri Krishna
MASANI STP To Vrindavan MATHURA THE WATER-WASTE PORTRAIT The city just needs to protect and recharge its groundwater. Instead, it is eyeing Ganga waters Bhuteshwar RS CIS-YAMUNA 1 Masani RS Shri Krishna
6. ENVIRONEMNTAL IMPACT
 6. ENVIRONEMNTAL IMPACT 6.1 Introduction Any development activity invariably involves some changes in the existing natural environment. Of late, there has been a considerable awareness regarding the need
6. ENVIRONEMNTAL IMPACT 6.1 Introduction Any development activity invariably involves some changes in the existing natural environment. Of late, there has been a considerable awareness regarding the need
SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA
 SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names used in different countries, states
SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names used in different countries, states
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF WATER RESOURCES, RIVER DEVELOPMENT & GANGA REJUVENATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO. 801 ANSWERED ON
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF WATER RESOURCES, RIVER DEVELOPMENT & GANGA REJUVENATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO. 801 ANSWERED ON 21.07.2016 801. SHRI DUSHYANT SINGH SHRIMATI MEENAKASHI LEKHI NAMAMI
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF WATER RESOURCES, RIVER DEVELOPMENT & GANGA REJUVENATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO. 801 ANSWERED ON 21.07.2016 801. SHRI DUSHYANT SINGH SHRIMATI MEENAKASHI LEKHI NAMAMI
RIVER BASIN MANJARA [ INDIA
 RIVER BASIN MANJARA [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. Details No. 1 Physical Features - General Information Response 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional
RIVER BASIN MANJARA [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. Details No. 1 Physical Features - General Information Response 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional
RIVER BASIN PENNAR [ INDIA
 RIVER BASIN PENNAR [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS ORGANISATIONS (RBOs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. Details No. 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional
RIVER BASIN PENNAR [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS ORGANISATIONS (RBOs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. Details No. 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional
Suggestions for a Modified Approach Towards Implementation and Assessment of Ganga Action Plan and Other Similar River Action Plans in India
 Water Qual. Res. J. Canada, 2003 Volume 38, No. 4, 607 626 Copyright 2003, CAWQ Suggestions for a Modified Approach Towards Implementation and Assessment of Ganga Action Plan and Other Similar River Action
Water Qual. Res. J. Canada, 2003 Volume 38, No. 4, 607 626 Copyright 2003, CAWQ Suggestions for a Modified Approach Towards Implementation and Assessment of Ganga Action Plan and Other Similar River Action
THE 3R S FOR CLEAN WATER - SAVING INDIA S RIVERS: INDIAN EXPERIENCES
 THE 3R S FOR CLEAN WATER - SAVING INDIA S RIVERS: INDIAN EXPERIENCES NATIONAL MISSION FOR CLEAN GANGA MINISTRY OF WATER RESOURCES, RIVER DEVELOPMENT & GANGA REJUVENATION Central Water Commission India
THE 3R S FOR CLEAN WATER - SAVING INDIA S RIVERS: INDIAN EXPERIENCES NATIONAL MISSION FOR CLEAN GANGA MINISTRY OF WATER RESOURCES, RIVER DEVELOPMENT & GANGA REJUVENATION Central Water Commission India
Susmita Sengupta, DPM, CSE
 Susmita Sengupta, DPM, CSE Ganga: Everyone lives downstream 2 3 How polluted is the river? 5 Ga ga s jou ey: Ga got i to Dia o d Ha ou Even the cleaner stretches are becoming polluted 6 Key problems The
Susmita Sengupta, DPM, CSE Ganga: Everyone lives downstream 2 3 How polluted is the river? 5 Ga ga s jou ey: Ga got i to Dia o d Ha ou Even the cleaner stretches are becoming polluted 6 Key problems The
Research Article Water Quality of River Kosi and Rajera System at Rampur (India): Impact Assessment
 Chemistry Volume 2013, Article ID 618612, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/618612 Research Article Water Quality of River Kosi and Rajera System at Rampur (India): Impact Assessment Ashish Kumar,
Chemistry Volume 2013, Article ID 618612, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/618612 Research Article Water Quality of River Kosi and Rajera System at Rampur (India): Impact Assessment Ashish Kumar,
Ganga River Basin Environment Management Plan
 Tuesday, August 9, 2011 WWF-India Conference Hall, New Delhi River Basin Planning-Viewpoints Ganga River Basin Environment Management Plan by IIT Bombay IIT Delhi IIT Guwahati IIT Kanpur IIT Kharagpur
Tuesday, August 9, 2011 WWF-India Conference Hall, New Delhi River Basin Planning-Viewpoints Ganga River Basin Environment Management Plan by IIT Bombay IIT Delhi IIT Guwahati IIT Kanpur IIT Kharagpur
CHEMICALLY ENHANCED PRIMARY TREATMENT AN ALTERNATE PARADIGM FOR BASIN-WIDE RIVER WATER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
 CHEMICALLY ENHANCED PRIMARY TREATMENT AN ALTERNATE PARADIGM FOR BASIN-WIDE RIVER WATER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT Asit Nema 1 and Dr. Vinod Tare 2 ABSTRACT In view of limited resources available for water pollution
CHEMICALLY ENHANCED PRIMARY TREATMENT AN ALTERNATE PARADIGM FOR BASIN-WIDE RIVER WATER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT Asit Nema 1 and Dr. Vinod Tare 2 ABSTRACT In view of limited resources available for water pollution
AN NGO FOR ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION, PROTECTION AND SECURITY
 AN NGO FOR ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION, PROTECTION AND SECURITY Contact at: 0512-2402986/2405229 Mob: 9415129482 Website: www.ecofriends.org e-mail : rakjai@sancharnet.in, info@ecofriends.org, rakesh@ecofriends.org
AN NGO FOR ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION, PROTECTION AND SECURITY Contact at: 0512-2402986/2405229 Mob: 9415129482 Website: www.ecofriends.org e-mail : rakjai@sancharnet.in, info@ecofriends.org, rakesh@ecofriends.org
Rural Non-Farm Employment in Uttar Pradesh
 Study No. 121 Publication No.168 Preliminary Draft report Rural Non-Farm Employment in Uttar Pradesh B. K. Mishra 2003 Agro- Economic Research Centre University of Allahabad Allahabad 211002 PREFACE The
Study No. 121 Publication No.168 Preliminary Draft report Rural Non-Farm Employment in Uttar Pradesh B. K. Mishra 2003 Agro- Economic Research Centre University of Allahabad Allahabad 211002 PREFACE The
Linkage between rural poverty and agricultural productivity across the districts of Uttar Pradesh in India
 Journal of Development and Agricultural Economics Vol. (), pp. 06-040, February, 00 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/jdae ISSN 006-9774 00 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper
Journal of Development and Agricultural Economics Vol. (), pp. 06-040, February, 00 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/jdae ISSN 006-9774 00 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper
Performance Evaluation of Sewage Treatment Plants in Lucknow City
 Performance Evaluation of Sewage Treatment Plants in Lucknow City Mansi Tripathi and K. Singal Mansi Tripathi K. Singal Abstract: The present study was conducted to evaluate the performance of existing
Performance Evaluation of Sewage Treatment Plants in Lucknow City Mansi Tripathi and K. Singal Mansi Tripathi K. Singal Abstract: The present study was conducted to evaluate the performance of existing
SOCIO-ECONOMIC ASPECTS OF MENTHOL MINT CULTIVATION IN THE DISTRICTS OF UTTAR PRADESH
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) SOCIO-ECONOMIC ASPECTS OF MENTHOL MINT CULTIVATION IN THE DISTRICTS OF UTTAR PRADESH ANIL KUMAR 1 Department of Biotechnology, FET, Rama University, Kanpur,
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) SOCIO-ECONOMIC ASPECTS OF MENTHOL MINT CULTIVATION IN THE DISTRICTS OF UTTAR PRADESH ANIL KUMAR 1 Department of Biotechnology, FET, Rama University, Kanpur,
1.0 STATEMENT OF PROPOSAL
 MEMORANDUM FOR EMPOWERED STEERING COMMITTEE (ESC) ON THE PROPOSAL OF WATER QUALITY MONITORING SYSTEM FOR RIVER GANGA UNDER NATIONAL GANGA RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY (NGRBA) 1.0 STATEMENT OF PROPOSAL 1(a) 1(b)
MEMORANDUM FOR EMPOWERED STEERING COMMITTEE (ESC) ON THE PROPOSAL OF WATER QUALITY MONITORING SYSTEM FOR RIVER GANGA UNDER NATIONAL GANGA RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY (NGRBA) 1.0 STATEMENT OF PROPOSAL 1(a) 1(b)
QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF GANGA RIVER AT HARIDWAR WITH REFERENCE TO VARIOUS PHYSICO-CHEMICAL PARAMETERS
 Biotechnology Society www.bti.org.in ISSN 0974-1453 Research Article QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF GANGA RIVER AT HARIDWAR WITH REFERENCE TO VARIOUS PHYSICO-CHEMICAL PARAMETERS ABSTRACT R. Bhutiani*, D.R. Khanna,
Biotechnology Society www.bti.org.in ISSN 0974-1453 Research Article QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF GANGA RIVER AT HARIDWAR WITH REFERENCE TO VARIOUS PHYSICO-CHEMICAL PARAMETERS ABSTRACT R. Bhutiani*, D.R. Khanna,
Regional Plan-2021 and Other Transport Proposals under Implementation
 13 Regional Plan-2021 and Other Transport Proposals under Implementation Regional Plan-2021 proposals are being implemented and are at various stages of implementation by the concerned Central Ministries
13 Regional Plan-2021 and Other Transport Proposals under Implementation Regional Plan-2021 proposals are being implemented and are at various stages of implementation by the concerned Central Ministries
RIVER BASIN INDRAVATI [ INDIA
 RIVER BASIN INDRAVATI [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names)
RIVER BASIN INDRAVATI [ INDIA ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. No. Details 1 Physical Features - General Information 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional names)
Energy and Resource Efficiency in Urban Water Management Challenges & potential for enabling paradigm shift under NURM
 Energy and Resource Efficiency in Urban Water Management Challenges & potential for enabling paradigm shift under NURM Dr Suresh Kumar Rohilla Programme Director Water Management, CSE June 20, 2013 CSE
Energy and Resource Efficiency in Urban Water Management Challenges & potential for enabling paradigm shift under NURM Dr Suresh Kumar Rohilla Programme Director Water Management, CSE June 20, 2013 CSE
RIVER BASIN CHENAB [ INDIA
 + RIVER BASIN CHENAB [ INDIA ] Sr. No. SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Details 1 Physical Features :- General Information Response 1.1 Name of River; Chenab ( Moon river). The
+ RIVER BASIN CHENAB [ INDIA ] Sr. No. SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Details 1 Physical Features :- General Information Response 1.1 Name of River; Chenab ( Moon river). The
Water Allocation and the Economic Dimension in the Ganga River Basin Management Plan
 IEWP Workshop Water Allocation, Water Economics and Ecological Flows in River Basin Management 14 15 September 2016, New Delhi (India) Water Allocation and the Economic Dimension in the Ganga River Basin
IEWP Workshop Water Allocation, Water Economics and Ecological Flows in River Basin Management 14 15 September 2016, New Delhi (India) Water Allocation and the Economic Dimension in the Ganga River Basin
REPORT ON PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT TIRUNELVELI, TAMILNADU
 REPORT ON PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT TIRUNELVELI, TAMILNADU As per mandate of Ministry of Environment & Forest, New Delhi, Central Pollution Control Board has taken up study on performance
REPORT ON PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT TIRUNELVELI, TAMILNADU As per mandate of Ministry of Environment & Forest, New Delhi, Central Pollution Control Board has taken up study on performance
Rajneesh K. Gautam 1, Islamuddin 2, Nandkishor More 3, Saumya Verma 4, Spriha Pandey 5, Neha Mumtaz 6, Rajesh Kumar 7, Md.
 Sewage Generation and Treatment Status for the City of Delhi, its Past, Present and Future Scenario- A Statistical Analysis Rajneesh K. Gautam 1, Islamuddin 2, Nandkishor More 3, Saumya Verma 4, Spriha
Sewage Generation and Treatment Status for the City of Delhi, its Past, Present and Future Scenario- A Statistical Analysis Rajneesh K. Gautam 1, Islamuddin 2, Nandkishor More 3, Saumya Verma 4, Spriha
STATE URBAN DEVELOPMENT AGENCY (SUDA), Uttar Pradesh
 STATE URBAN DEVELOPMENT AGENCY (SUDA), Uttar Pradesh Expression of Interest (EOI) Expression of Interest (EoI) for short listing / selection of HR Agencies as service provider (for procurement of Experts
STATE URBAN DEVELOPMENT AGENCY (SUDA), Uttar Pradesh Expression of Interest (EOI) Expression of Interest (EoI) for short listing / selection of HR Agencies as service provider (for procurement of Experts
11. Area specific mineral mixture formulation for the state of Area specific mineral mixture formulation for the state of 13
 Area specific mineral mixture formulations developed based on the mineral mapping programme taken up by NDDB and various centres under the ICAR Micro-Nutrients Network Programme Content Page Number 1.
Area specific mineral mixture formulations developed based on the mineral mapping programme taken up by NDDB and various centres under the ICAR Micro-Nutrients Network Programme Content Page Number 1.
Wastewater treatment and reuse in Bangalore: complexities and challenges
 Wastewater treatment and reuse in Bangalore: complexities and challenges Priyanka Jamwal Fellow, Center for Environment and Development, ATREE (based on joint work with Bejoy K Thomas, Sharachchandra Lele
Wastewater treatment and reuse in Bangalore: complexities and challenges Priyanka Jamwal Fellow, Center for Environment and Development, ATREE (based on joint work with Bejoy K Thomas, Sharachchandra Lele
Excreta Matters: 7 th Citizens Report on the state of India s Environment. An agenda for water-prudent and waste-wise India
 Excreta Matters: 7 th Citizens Report on the state of India s Environment An agenda for water-prudent and waste-wise India Water for growth? Cities-industries need water for growth Vague old water sums
Excreta Matters: 7 th Citizens Report on the state of India s Environment An agenda for water-prudent and waste-wise India Water for growth? Cities-industries need water for growth Vague old water sums
Dr Sanjay Kumar Shukla PhD (IITK), MTech (IITK), BSc Eng (BIT Sindri), FIEAust, FIE(India), FIGS, MASCE, MIGS, MIFAI, MIRC, MISRMTT, MISTE, MCAII
 Dr Sanjay Kumar Shukla PhD (IITK), MTech (IITK), BSc Eng (BIT Sindri), FIEAust, FIE(India), FIGS, MASCE, MIGS, MIFAI, MIRC, MISRMTT, MISTE, MCAII Founding Editor-in-Chief, International Journal of Geosynthetics
Dr Sanjay Kumar Shukla PhD (IITK), MTech (IITK), BSc Eng (BIT Sindri), FIEAust, FIE(India), FIGS, MASCE, MIGS, MIFAI, MIRC, MISRMTT, MISTE, MCAII Founding Editor-in-Chief, International Journal of Geosynthetics
Looking beyond the boundaries: An approach for Water Neutral Electricity Production
 Looking beyond the boundaries: An approach for Water Neutral Electricity Production Shresth Tayal 1 *, Dharmesh Kumar Singh 1,Shiv Kumar Dube 1,GopiKanta Nayak 2 and Sonia Grover 1 * Corresponding Author;
Looking beyond the boundaries: An approach for Water Neutral Electricity Production Shresth Tayal 1 *, Dharmesh Kumar Singh 1,Shiv Kumar Dube 1,GopiKanta Nayak 2 and Sonia Grover 1 * Corresponding Author;
Design of a Prototype Sewage Treatment Plant for SHIATS Campus
 Design of a Prototype Sewage Treatment Plant for SHIATS Campus Rupesh Kumar Patel 1, Deepak Lal 2 PG Scholar, Department of SWLEM Sam Higginbottom Institute of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences ALLAHABAD,
Design of a Prototype Sewage Treatment Plant for SHIATS Campus Rupesh Kumar Patel 1, Deepak Lal 2 PG Scholar, Department of SWLEM Sam Higginbottom Institute of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences ALLAHABAD,
NEED FOR GROUNDWATER UTILIZATION AND MANAGEMENT IN AURANGABAD CITY, MAHARASHTRA ABSTRACT
 NEED FOR GROUNDWATER UTILIZATION AND MANAGEMENT IN AURANGABAD CITY, MAHARASHTRA S.M.Deshpande Junior Geologist, Groundwater Surveys and Development Agency, Shivajinagar, Pune 411 005 ABSTRACT Aurangabad
NEED FOR GROUNDWATER UTILIZATION AND MANAGEMENT IN AURANGABAD CITY, MAHARASHTRA S.M.Deshpande Junior Geologist, Groundwater Surveys and Development Agency, Shivajinagar, Pune 411 005 ABSTRACT Aurangabad
Water Pollution and its effects on human health: A case study of Dehradun City
 ` ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Volume VII: No. 2 2016 [17 24] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Water Pollution and its effects on human health:
` ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Volume VII: No. 2 2016 [17 24] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Water Pollution and its effects on human health:
Hydro Chemical Changes in two Eutrophic Tapti Pond of Madhya Pradesh (Multai) after Immersion of Durga and Ganesh idol
 Hydro Chemical Changes in two Eutrophic Tapti Pond of Madhya Pradesh (Multai) after Immersion of Durga and Ganesh idol Thakre Gajanand, Jain Vikrant, and Gawande Sandeep Department of Chemistry, Patel
Hydro Chemical Changes in two Eutrophic Tapti Pond of Madhya Pradesh (Multai) after Immersion of Durga and Ganesh idol Thakre Gajanand, Jain Vikrant, and Gawande Sandeep Department of Chemistry, Patel
Physiochemical Analysis of River Ganges at Mirzapur In Uttar Pradesh, India
 IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736.Volume 7, Issue 12 Ver. II. (Dec. 2014), PP 61-67 Physiochemical Analysis of River Ganges at Mirzapur In Uttar Pradesh, India Shahid Khan
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736.Volume 7, Issue 12 Ver. II. (Dec. 2014), PP 61-67 Physiochemical Analysis of River Ganges at Mirzapur In Uttar Pradesh, India Shahid Khan
Progressive deteriortaion of groundwater quality in Vrishabhavathi Valley Basin, Bangalore, India
 Progressive deteriortaion of groundwater quality in Vrishabhavathi Valley Basin, Bangalore, India Dr.Balasubramanya N Professor & Dean, Civil Dept Acharya Institute of Technology, Bangalore Dr Shankar
Progressive deteriortaion of groundwater quality in Vrishabhavathi Valley Basin, Bangalore, India Dr.Balasubramanya N Professor & Dean, Civil Dept Acharya Institute of Technology, Bangalore Dr Shankar
Ex-ante Evaluation - 1 -
 Ex-ante Evaluation 1. Name of the Project Country: India Project: Orissa Integrated Sanitation Improvement Project (Loan Agreement: 03/30/2007; Loan Amount: 19,061 million yen; Borrower: The President
Ex-ante Evaluation 1. Name of the Project Country: India Project: Orissa Integrated Sanitation Improvement Project (Loan Agreement: 03/30/2007; Loan Amount: 19,061 million yen; Borrower: The President
R.B. PANDA, D. PRADHAN AND L.K. PANDA. Department of Environment Science, Fakir Mohan University, Vyas Vihar, Balasore, Orissa.
 Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 25 (1) (2009) pp 1- Enviromedia Printed in India. All rights reserved WATER QUALITY OF THE BRAHMANI RIVER- AN ANALYTICAL STUDY UPSTREAM, MID STREAM, DOWN STREAM AT EFFLUENT
Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 25 (1) (2009) pp 1- Enviromedia Printed in India. All rights reserved WATER QUALITY OF THE BRAHMANI RIVER- AN ANALYTICAL STUDY UPSTREAM, MID STREAM, DOWN STREAM AT EFFLUENT
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HYDERABAD
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HYDERABAD SUSTAINABLE ARCOP LARGE ASSOCIATES DEVELOPMENT PRIVATE LIMITED SUSTAINABILITY AND THE CITY WHAT ARE WE TALKING ABOUT THE LINK KNOWN COMPONENTS OF AN URBAN FABRIC
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HYDERABAD SUSTAINABLE ARCOP LARGE ASSOCIATES DEVELOPMENT PRIVATE LIMITED SUSTAINABILITY AND THE CITY WHAT ARE WE TALKING ABOUT THE LINK KNOWN COMPONENTS OF AN URBAN FABRIC
Water quality analysis of Disposal site and its adjacent area of Guwahati, Assam, India
 International Research Journal of Environment Sciences ISSN 2319 1414 Water quality analysis of Disposal site and its adjacent area of Guwahati, Assam, India Abstract Ali Sayed, Singh Raghvendra Kumar
International Research Journal of Environment Sciences ISSN 2319 1414 Water quality analysis of Disposal site and its adjacent area of Guwahati, Assam, India Abstract Ali Sayed, Singh Raghvendra Kumar
The NGT, Ganga, U.P. And Uttaranchal-Implications for the Sugar & Distillery Sector by: Dr. Yashpal Singh. Environmental Counselor
 The NGT, Ganga, U.P. And Uttaranchal-Implications for the Sugar & Distillery Sector by: Dr. Yashpal Singh Environmental Counselor IF ALL THE WATER ON EARTH WERE STORED IN A 18 LITER BOTTLE. FRESH WATER
The NGT, Ganga, U.P. And Uttaranchal-Implications for the Sugar & Distillery Sector by: Dr. Yashpal Singh Environmental Counselor IF ALL THE WATER ON EARTH WERE STORED IN A 18 LITER BOTTLE. FRESH WATER
NAME OF ULB BASTI. Location of source of drinking water
 Water Supply NAME OF ULB BASTI 1. Assess the Service Level Gap The first step is to assess the existing situation and service levels gaps for Water Supply (AMRUT Guidelines; para 3 & 6). This will also
Water Supply NAME OF ULB BASTI 1. Assess the Service Level Gap The first step is to assess the existing situation and service levels gaps for Water Supply (AMRUT Guidelines; para 3 & 6). This will also
Presentation Covers: 1. Regulatory Framework in
 Presentation Covers: 1. Regulatory Framework in 1 downstream Petroleum & Natural Gas Sector; and 2. Development of Natural Gas Transmission & Distribution Networks in Uttar Pradesh K. Rajeswara Rao, OSD
Presentation Covers: 1. Regulatory Framework in 1 downstream Petroleum & Natural Gas Sector; and 2. Development of Natural Gas Transmission & Distribution Networks in Uttar Pradesh K. Rajeswara Rao, OSD
Water quality assessment of Ajay River with reference to suitability for agricultural purposes
 Water quality assessment of Ajay River with reference to suitability for agricultural purposes BALWANT KUMAR 1, UMESH KUMAR SINGH 1 *, PRATAP KUMAR PADHY 2 1. Department of Integrated Science Education
Water quality assessment of Ajay River with reference to suitability for agricultural purposes BALWANT KUMAR 1, UMESH KUMAR SINGH 1 *, PRATAP KUMAR PADHY 2 1. Department of Integrated Science Education
NAME OF ULB- PILIBHIT
 Water Supply NAME OF ULB- PILIBHIT 1. Assess the Service Level Gap The first step is to assess the existing situation and service levels gaps for Water Supply (AMRUT Guidelines; para 3 & 6). This will
Water Supply NAME OF ULB- PILIBHIT 1. Assess the Service Level Gap The first step is to assess the existing situation and service levels gaps for Water Supply (AMRUT Guidelines; para 3 & 6). This will
Stockholm World Water Week, August Dr. Arne Panesar, Dr. Regina Dube, Dirk Walther, Sanjay Kumar Srivastava IFS (GIZ) Dayanand Panse (ESF)
 Case India: Supporting the Indian National Urban Sanitation Policy (BMZ-GIZ) - Policy development - City Sanitation Plans - School Sanitation from Plan to Implementation Dr. Arne Panesar, Dr. Regina Dube,
Case India: Supporting the Indian National Urban Sanitation Policy (BMZ-GIZ) - Policy development - City Sanitation Plans - School Sanitation from Plan to Implementation Dr. Arne Panesar, Dr. Regina Dube,
Aao Jal Sanchay Karein. Boond - Boond se Dharti Bharein.
 Aao Jal Sanchay Karein Boond - Boond se Dharti Bharein Ravindra Kumar ravindra53@yahoo.co.in Major GW Issues Quality Problems Declining Water Levels & Depleting first aquifer Over Exploitation of Ground
Aao Jal Sanchay Karein Boond - Boond se Dharti Bharein Ravindra Kumar ravindra53@yahoo.co.in Major GW Issues Quality Problems Declining Water Levels & Depleting first aquifer Over Exploitation of Ground
RIVER BASIN SATLUJ [ PAKISTAN
 RIVER BASIN SATLUJ [ PAKISTAN ] Sr. Details No. 1 Physical Features - General Information SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Response 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional
RIVER BASIN SATLUJ [ PAKISTAN ] Sr. Details No. 1 Physical Features - General Information SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Response 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional
GOVERNMENT OF MADHYA PRADESH WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENT
 GOVERNMENT OF MADHYA PRADESH WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENT SUTHALIYA PROJECT PRE FEASIBILITY REPORT ( PFR ) 2018 CHIEF ENGINEER CHAMBAL BETWA BASIN WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENT BHOPAL (M.P) SUTHALIYA PROJECT
GOVERNMENT OF MADHYA PRADESH WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENT SUTHALIYA PROJECT PRE FEASIBILITY REPORT ( PFR ) 2018 CHIEF ENGINEER CHAMBAL BETWA BASIN WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENT BHOPAL (M.P) SUTHALIYA PROJECT
Strategy and Methodology for Improved IWRM
 Strategy and Methodology for Improved IWRM A Case Study of Tungabhadra River Basin in India S. Puttaswamaiah H. L. Shashidhara K. V. Raju Centre for Ecological Economics and Natural Resources Institute
Strategy and Methodology for Improved IWRM A Case Study of Tungabhadra River Basin in India S. Puttaswamaiah H. L. Shashidhara K. V. Raju Centre for Ecological Economics and Natural Resources Institute
UASB TECHNOLOGY EXPECTATIONS AND REALITY
 UASB TECHNOLOGY EXPECTATIONS AND REALITY Dr. Vinod Tare 1 and Asit Nema 2 INTRODUCTION Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) technology was introduced in India in late eighties during the Ganga Action
UASB TECHNOLOGY EXPECTATIONS AND REALITY Dr. Vinod Tare 1 and Asit Nema 2 INTRODUCTION Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) technology was introduced in India in late eighties during the Ganga Action
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(6):265-270 Assessment of seasonal variation in physico-chemical
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(6):265-270 Assessment of seasonal variation in physico-chemical
8.1 BACKGROUND 8.2 EXISTING SITUATION AND ISSUES
 WATER 8.1 BACKGROUND Water is an essential component in every aspect of life and must be valued and safeguarded. The NCR is a water scarce region, but can have sufficient water if this resource is conserved
WATER 8.1 BACKGROUND Water is an essential component in every aspect of life and must be valued and safeguarded. The NCR is a water scarce region, but can have sufficient water if this resource is conserved
BRIHANMUMBAI MAHANAGARPALIKA
 BRIHANMUMBAI MAHANAGARPALIKA PROJECTS SANCTIONED UNDER JNNURM A] IV Mumbai - Middle Vaitarna Water Supply Project :- Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM) has undertaken the Middle Vaitarana Water
BRIHANMUMBAI MAHANAGARPALIKA PROJECTS SANCTIONED UNDER JNNURM A] IV Mumbai - Middle Vaitarna Water Supply Project :- Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM) has undertaken the Middle Vaitarana Water
Hindon 2030: Vision to Action Plan
 Hindon 2030: Vision to Action Plan This document is subject to discussion and updates can be made as and when required. Submitted to Divisional Commissioner Meerut during Hindon Committee meeting on 8
Hindon 2030: Vision to Action Plan This document is subject to discussion and updates can be made as and when required. Submitted to Divisional Commissioner Meerut during Hindon Committee meeting on 8
SHAKUNTHALA BAI and S.SRIKANTASWAMY Department of Studies in Environmental Science, Manasagangotri, Mysore
 Lake 2008 Conference, IISc, Bangalore 22-24,December 2008 WASTE WATER TREATMENT AND MANAGEMENT IN URBAN AREAS A CASE STUDY OF MYSORE CITY. SHAKUNTHALA BAI and S.SRIKANTASWAMY Department of Studies in Environmental
Lake 2008 Conference, IISc, Bangalore 22-24,December 2008 WASTE WATER TREATMENT AND MANAGEMENT IN URBAN AREAS A CASE STUDY OF MYSORE CITY. SHAKUNTHALA BAI and S.SRIKANTASWAMY Department of Studies in Environmental
7 th REPORT ON PK KAUL COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS In Writ Petition{C} No 914/1996 in response to the letter from the Amicus Curiae
 7 th REPORT ON PK KAUL COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS In Writ Petition{C} No 914/1996 in response to the letter from the Amicus Curiae January, 2007 ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION (PREVENTION AND CONTROL) AUTHORITY
7 th REPORT ON PK KAUL COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS In Writ Petition{C} No 914/1996 in response to the letter from the Amicus Curiae January, 2007 ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION (PREVENTION AND CONTROL) AUTHORITY
NAME OF ULB - BALLIA
 Water Supply NAME OF ULB - BALLIA 1. Assess the Service Level Gap The first step is to assess the existing situation and service levels gaps for Water Supply (AMRUT Guidelines; para 3 & 6). This will also
Water Supply NAME OF ULB - BALLIA 1. Assess the Service Level Gap The first step is to assess the existing situation and service levels gaps for Water Supply (AMRUT Guidelines; para 3 & 6). This will also
Arghyam s Inputs to the Pre-Budget Consultation of the Finance Minister with Social Sector related groups
 Arghyam s Inputs to the Pre-Budget Consultation of the Finance Minister with Social Sector related groups 4 January, 2013 Launch a Research Initiative to Mainstream Groundwater into Urban Water Supply
Arghyam s Inputs to the Pre-Budget Consultation of the Finance Minister with Social Sector related groups 4 January, 2013 Launch a Research Initiative to Mainstream Groundwater into Urban Water Supply
Modulatory Effect of Tannery Effluents on Physicochemical Quality of River Water
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2014.617 2014, 3(1), 73-78 RESEARCH ARTICLE Modulatory Effect of Tannery Effluents on Physicochemical Quality of River Water VINAY
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2014.617 2014, 3(1), 73-78 RESEARCH ARTICLE Modulatory Effect of Tannery Effluents on Physicochemical Quality of River Water VINAY
Action taken (NGT Order dated 07 th August vide OA No. 138, 139/2018)
 Action taken (NGT Order dated 07 th August vide OA No. 138, 139/2018) Till date, eight meetings of the Executing Committee have been conducted i.e. one at Shimla and seven at Chandigarh where HPPCB participated
Action taken (NGT Order dated 07 th August vide OA No. 138, 139/2018) Till date, eight meetings of the Executing Committee have been conducted i.e. one at Shimla and seven at Chandigarh where HPPCB participated
Department of Tourism Audit on Up-gradation and extension of facilities in State Tourism Circuits Chapter 3 Compliance Audit
 Table of contents Reference to Particulars Paragraph (s) Page (s) Preface v Overview vii-x Chapter 1 Introduction About this Report 1.1 1 Budget Profile 1.2 1 Application of Resources of the State Government
Table of contents Reference to Particulars Paragraph (s) Page (s) Preface v Overview vii-x Chapter 1 Introduction About this Report 1.1 1 Budget Profile 1.2 1 Application of Resources of the State Government
WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF VRISHABHAVATHI RIVER, BIDADI A CASE STUDY
 WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF VRISHABHAVATHI RIVER, BIDADI A CASE STUDY Vidya. B. R 1, Ashfaq T M 2, Chaitra M V 3 Dodda Basappa S 4, Soumya Bhuti 5 1, Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 U G Students, Department
WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF VRISHABHAVATHI RIVER, BIDADI A CASE STUDY Vidya. B. R 1, Ashfaq T M 2, Chaitra M V 3 Dodda Basappa S 4, Soumya Bhuti 5 1, Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 U G Students, Department
WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF VRISHABHAVATHI RIVER, BIDADI A CASE STUDY
 WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF VRISHABHAVATHI RIVER, BIDADI A CASE STUDY Vidya. B. R 1, Ashfaq T M 2, Chaitra M V 3 Dodda Basappa S 4, Soumya Bhuti 5 1, Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 U G Students Department
WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF VRISHABHAVATHI RIVER, BIDADI A CASE STUDY Vidya. B. R 1, Ashfaq T M 2, Chaitra M V 3 Dodda Basappa S 4, Soumya Bhuti 5 1, Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 U G Students Department
main target of the AHP is to decide and help decision makers in making resolutions for the complex problems by
 Application of Analytical Hierarchy Process in Evaluation of Best Sewage Treatment Plant Kshitij Upadhyay Civil Engineering Department Rajkiya Engineering College, Bijnor Abstract: This paper presents
Application of Analytical Hierarchy Process in Evaluation of Best Sewage Treatment Plant Kshitij Upadhyay Civil Engineering Department Rajkiya Engineering College, Bijnor Abstract: This paper presents
RIVER BASIN PADMA [ BANGLADESH ]
![RIVER BASIN PADMA [ BANGLADESH ] RIVER BASIN PADMA [ BANGLADESH ]](/thumbs/94/118208652.jpg) RIVER BASIN PADMA [ BANGLADESH ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. No Details Response 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional The Ganges-Padma River (known as the Ganges
RIVER BASIN PADMA [ BANGLADESH ] SCHEDULE A ASSESSMENT OF RIVER BASINS (RBs) IN SOUTH ASIA Sr. No Details Response 1.1 Name of River basin (also indicate regional The Ganges-Padma River (known as the Ganges
ENVIRONMENTAL AND SOCIAL SAFEGUARD DUE DILLIGENCE FOR SEWERAGE SYSTEM IN MUNGER TOWN, BIHAR
 ENVIRONMENTAL AND SOCIAL SAFEGUARD DUE DILLIGENCE FOR SEWERAGE SYSTEM IN MUNGER TOWN, BIHAR 1. INTRODUCTION Increasing population, haphazard urbanization and industrial growth in Ganga river basin has
ENVIRONMENTAL AND SOCIAL SAFEGUARD DUE DILLIGENCE FOR SEWERAGE SYSTEM IN MUNGER TOWN, BIHAR 1. INTRODUCTION Increasing population, haphazard urbanization and industrial growth in Ganga river basin has
Water Rights: A Case Study of Rural Areas of Allahabad. Firdaus Fatima Rizvi Indian Institute of Dalit Studies New Delhi
 Water Rights: A Case Study of Rural Areas of Allahabad Firdaus Fatima Rizvi Indian Institute of Dalit Studies New Delhi HPI Measures poverty in three dimensions- Longevity- not surviving to age 40 Knowledge-
Water Rights: A Case Study of Rural Areas of Allahabad Firdaus Fatima Rizvi Indian Institute of Dalit Studies New Delhi HPI Measures poverty in three dimensions- Longevity- not surviving to age 40 Knowledge-
Speed Post. F.No.B-23012/1/PCI-III Date:
 Speed Post F.No.B-23012/1/PCI-III Date: 24.02.2015 To, The Chairman, SPCBs (Uttarakhand/ ) DIRECTIONS UNDER SECTION 18(1)(b) OF THE WATER (PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF POLLUTION) ACT, 1974 AND SECTION 18(1)(b)
Speed Post F.No.B-23012/1/PCI-III Date: 24.02.2015 To, The Chairman, SPCBs (Uttarakhand/ ) DIRECTIONS UNDER SECTION 18(1)(b) OF THE WATER (PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF POLLUTION) ACT, 1974 AND SECTION 18(1)(b)
GANGA ACTION PLAN IN INDIA AN OVERVIEW
 GANGA ACTION PLAN IN INDIA AN OVERVIEW PRESENTATION BY BRIJESH SIKKA, DIRECTOR MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT & FORESTS, GOVT. OF INDIA SABESP INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AT SAO PAULO, BRAZIL 7 TH TO 8 TH NOVEMBER,
GANGA ACTION PLAN IN INDIA AN OVERVIEW PRESENTATION BY BRIJESH SIKKA, DIRECTOR MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT & FORESTS, GOVT. OF INDIA SABESP INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AT SAO PAULO, BRAZIL 7 TH TO 8 TH NOVEMBER,
Water Supply. Yes we have collected Census 2011 data table is mentions below:- S.No Source Particulars Numbers Tap Water Connection
 1. Assess the Service Level Gap Water Supply City Name Bareilly The first step is to assess the existing situation and service levels gaps for Water Supply (AMRUT Guidelines; para 3 & 6). This will also
1. Assess the Service Level Gap Water Supply City Name Bareilly The first step is to assess the existing situation and service levels gaps for Water Supply (AMRUT Guidelines; para 3 & 6). This will also
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development EFFECT OF NEARBY CITIES ON WATER QUALITY OF CHAMBAL RIVER
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 6, June -217 e-issn (O): 2348-447 p-issn (P): 2348-646 EFFECT OF NEARBY
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 6, June -217 e-issn (O): 2348-447 p-issn (P): 2348-646 EFFECT OF NEARBY
INTRODUCTION. Latitude ' N ' N Longitude ' E ' E Area 147,181 km 2
 INTRODUCTION Country Location Between China and India Latitude 26 0 22' N - 30 0 27' N Longitude 80 0 04' E - 88 0 12' E Area 147,181 km 2 Population 28.8 millions Access to Electricity 67% Per capita
INTRODUCTION Country Location Between China and India Latitude 26 0 22' N - 30 0 27' N Longitude 80 0 04' E - 88 0 12' E Area 147,181 km 2 Population 28.8 millions Access to Electricity 67% Per capita
Focus on environmental assessment needs for water resources development projects in India
 River Basin Management IV 425 Focus on environmental assessment needs for water resources development projects in India L. S. Deshpande & P. S. Kelkar Geo-Environment Management Division, National Environmental
River Basin Management IV 425 Focus on environmental assessment needs for water resources development projects in India L. S. Deshpande & P. S. Kelkar Geo-Environment Management Division, National Environmental
