ENERGY CONSERVATION & ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR PRODUCTION OF MT/ANNUM ISOBUTYLENE PLANT USING PINCH ANALYSIS MOHD FAIRUZ BIN MOHD JAIS
|
|
|
- Jason Booker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 i ENERGY CONSERVATION & ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR PRODUCTION OF MT/ANNUM ISOBUTYLENE PLANT USING PINCH ANALYSIS MOHD FAIRUZ BIN MOHD JAIS A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirement for the award of the degree of Bachelor Chemical Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Natural Resources Engineering Universiti Malaysia Pahang MAY 2010
2 v ABSTRACT Pinch technology is the state of the art-technique for design of energy efficient processing that allows the calculation of theoretically minimum data utilities consumption for a process based on the thermal data of process stream. The goal of Pinch analysis is to maximize the process to process heat recovery and minimize the utility requirements of heat exchanger system which offers maximum scope for energy and cost saving. The main factor that must be considered here is the determination of the stream utility used in the plant for extraction process of thermal data in the system that requires optimization. This analysis on production of MT/Annum isobutylene plant establishes the Grand Composite Curve of the process as a function of temperature and it is important to determine the Pinch point that can be defined as the temperature where the net deficit or surplus is equal to zero. This analysis is based on thermodynamic principle that set energy savings and cost targets prior to the design of a Heat Exchanger Network with T min =13 C and T min =14 C, where the process to design and implement is complicated and critical part in order to minimizing the energy consumption and maximizing the heat and energy recovery. From this research, it can be seen that the application of heat integration using Pinch analysis method can minimize the energy usage besides lowering the production cost of MT/A isobutylene. By using T min =13 C, the payback period for investment in this new heat exchanger network in this plant are 4.2 months while T min =14 C result in lesser payback period of 2.3 months.
3 vi ABSTRAK Teknologi jepitan adalah merupakan satu teknik untuk menganalisa penggunaan tenaga secara efektif mengikut kaedah pengiraan secara teori daripada data utiliti yang digunakan di dalam loji untuk kesinambungan proses berdasarkan data terma proses aliran. Proses ini adalah berdasarkan prinsip termodinamik yang mensasarkan penjimatan tenaga dan penjimatan kos dalam sesebuah jaringan alat penukar haba. Justeru, tujuan utama analisa jepitan ini adalah untuk memaksimumkan proses penjimatan tenaga dan meminimumkan lagi keperluan utiliti dalam sesebuah sistem dengan menganalisa sistem alat penukar haba. Perkara permulaan yang perlu dibuat dalam proses analisa ini adalah penentuan utiliti yang digunakan di dalam alat penukar haba dan proses pengekstrakan data terma di kawasan sistem ini. Berdasarkan analisa dalam proses penghasilan Metrik tan tahunan isobutylene, ia berkonsepkan lengkungan komposit utama yang terhasil daripada proses yang berkaitan secara langsung dengan suhu. Kewujudan lengkungan ini adalah penting untuk menentukan di mana berlakunya titik jepitan yang menjadi titik tolak permulaan proses integrasi tenaga, dan titik jepitan ini boleh didefinisikan sebagai satu nilai suhu di mana nilai defisit dan surplus adalah bersamaan sifar. Analisa ini adalah berdasarkan prinsip penjimatan tenaga yang terhasil daripada konsep termodinamik untuk merangka jaringan alat penukar haba, dan proses ini merupakan satu proses yang rumit dan perlu dibuat secara teliti supaya penjimatan yang dapat dihasilkan adalah semaksimum yang mungkin dengan menggunakan perbezaan suhu minimum bersamaan 13 C dan 14 C. Hasil daripada kajian ini didapati bahawa pengaplikasian integrasi haba ini dengan menggunakan kaedah analisa jepitan mampu untuk meminimumkan penggunaan tenaga di samping dapat menjimatkan lagi kos dalam penghasilan isobutylene ini. Keputusannya, dengan menggunakan perbezaan suhu minimum 13 C, tempoh pulangan modal untuk alat penukar haba dalam loji ini adalah selama 4.2 bulan dan 2.3 bulan diperlukan untuk tempoh pulangan modal dengan menggunakan perbezaan suhu minimum 14 C.
4 vii TABLE OF CONTENTS DECLARATION OF ORIGINAL WORK DEDICATION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ABSTRACT ABSTRAK TABLE OF CONTENT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS AND NOMENCLATURES LIST OF APPENDICES ii iii iv v vi vii xi xii xiv xvi CHAPTER TITLE PAGE 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background of Study Current Scenario Process Flow Diagram (PFD) Problem Statement Research Objectives Scopes of Study Significance of the Study 8 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Research Background History and Background Basic Pinch Analysis Concepts 10
5 viii The Grid Representation Threshold Problems Composite Curves (CC) Concepts Grand Composite Curves (GCC) Concepts Advantages of Pinch Analysis Literature Review Application of Pinch Technology The Pinch Design Method for New Heat Exchanger Network Design The Pinch Design Method for Heat Exchanger Network Process Heat Integration 25 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 Introduction Analyze the Process Flow Diagram Data Identification of Hot, Cold and Utility Stream in the Process Thermal Data Extraction for Process and Utility Stream Pinch Analysis Selection of Initial T min Value Construction of Composite Curve & Grand Composite Curve Design of Heat Exchanger Network Heat Exchanger Sizing Economic analysis Total Capital Investment Cost Operating Labor Cost Utilities Cost Payback Period 38
6 ix 4 RESULTS & DISCUSSIONS 4.1 Thermal Data Extraction for Process & Utility Streams Temperature Intervals of Hot and Cold Streams Pinch Analysis Determination of T min and Construction of Composite Curves Construction of Grand Composite Curves Shifted Temperature Scale Problem Table Algorithm Cascade Diagram Grand Composite Curve Heat Exchanger Network ( T min =13 o C) Overall Analysis on Heat Exchanger Network Analysis on Above and Below Pinch Region Heat Exchanger Network ( T min =14 o C) Overall Analysis on Heat Exchanger Network Analysis on Above and Below Pinch Region Heat Exchanger Sizing Economic Analysis Costing of Heat Exchangers Costing of Utilities Costing of Operating Labor Payback Period Payback Period for T min =13 o C Payback Period for T min =14 o C 64
7 x 5 CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 5.1 Conclusion Recommendations 67 REFERENCES 68 APPENDICES 71
8 xi LIST OF TABLES TABLE NO. TITLE PAGE 1.1 Summary of Heat Exchanger Thermal data for process stream The problem table for data given in Table Stream process data Typical T min value Operator requirements for various process equipment Utilities provide by off sites for a plant with multiple 38 process unit 4.1 Stream process data for heat exchanger Stream for hot composite Stream for cold composite Shifting temperature for hot composite ( T min =13 C) Shifting temperature for cold composite ( T min =13 C) Shifting temperature for hot composite ( T min =14 C) Shifting temperature for cold composite ( T min =14 C) Problem Table Algorithm ( T min =13 C) Problem Table Algorithm ( T min =14 C) Cascade diagram ( T min =13 C) Cascade diagram ( T min =14 C) Sizing of heat exchanger Costing of heat exchanger Costing of utilities Costing of operating labor Payback period ( T min =13 C) Payback period ( T min =14 C) 64
9 xii LIST OF FIGURES FIGURE NO. TITLE PAGE 1.1 Process Flow Diagram (PFD) of isobutylene plant Heat exchanger stream flow Cross section of heat exchanger Cross section of heat exchanger Cross section of heat exchanger Cross section of heat exchanger (a) Transshipment heat flow diagram for data in Table (b) Sub-networks combined into a hot and cold region (a) Effect of heat transfer across the Pinch 14 (b) Effect of utility cooling above the Pinch 14 (c) Effect of utility heating below the Pinch Grid representation Heat exchanger representation in grid diagram (a) A threshold problem 16 (b) A Pinch problem 17 (c) The threshold T min Utility requirement versus T min plot Construction of composite curve Prediction of energy targets using Composite Curve Construction of the Grand Composite Curve Flow Analyze PFD Composite Curve Grand Composite Curve Above Pinch region Below Pinch region Overall Heat Exchanger Network 35
10 xiii 4.1 Temperature interval diagram Composite Curve ( T min =13 C) Composite Curve ( T min =14 C) Shifted temperature scale ( T min =13 C) Shifted temperature scale ( T min =14 C) Grand Composite Curve ( T min =13 C) Grand Composite Curve ( T min =14 C) Composite curve with respect to the value of T min ( T min =13 C) Overall stream temperature with respect to the value of T min ( T min =13 C) Above Pinch region ( T min =13 C) Below Pinch region ( T min =13 C) Heat Exchanger Network ( T min =13 C) Composite curve with respect to the value of T min ( T min =14 C) Overall stream temperature with respect to the value of T min ( T min =14 C) Above Pinch region ( T min =14 C) Below Pinch region ( T min =14 C) Heat Exchanger Network ( T min =14 C) Payback period graph ( T min =13 C) Payback period graph ( T min =14 C) 65
11 xiv ABBREVIATIONS CC GCC GHG HEN MT SN PA PDM PFD PI PT PTA STS T-H Composite Curve Grand Composite Curve Green House Green Heat Exchanger Network Metric Tonne Sub-networking Pinch Analysis Pinch Design Method Process Flow Diagram Process Integration Pinch Technology Problem Table Algorithm Shifted Temperature Scale Temperature-Enthalpy
12 xv NOMENCLATURES H Enthalpy Change T Difference Temperature T m Mean Temperature Difference T lm T min T in T thresh A U Log Mean Temperature Difference Minimum Temperature Difference Difference of Temperature Interval Difference Threshold Temperature Area Fouling Factor C Celcius C BM Bare Module Cost C TM Total Module Cost F BM Bare Module Factor F m F p K CP CP interval T cold T hot T ci T co T hi T ho T in T out T s T t Material Factor Pressure Factor Kelvin Heat Capacity Flow Rate Interval Heat Capacity Cold Temperature Hot Temperature Inlet Temperature of Cold Fluid Outlet Temperature of Cold Fluid Inlet Temperature of Hot Fluid Outlet Temperature of Hot Fluid Inlet Temperature Outlet Temperature Supply Temperature Target Temperature
13 xvi LIST OF APPENDICES APPENDIX TITLE PAGE A Process Flow Diagram 71 B Heat Exchanger Sizing 72 C Economic Analysis 77 D Table & Graph 83
14 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background of Study Current Scenario Isobutylene is produced commercially to used as chemical intermediate in the production of variety of products. Based on its usage, application and demand, these scenarios enhance the growth of isobutylene plant in entire world. Observed from economical perspective, the total capital investment for isobutylene plant is about RM and the total production cost is RM This high production and investment cost maybe reduced through an effective optimization method and technique applied to this plant. Based on data, since 1971 until 2004, energy use in petrochemical plant has increased by 206% to 33.6EJ/year and CO 2 emissions increased by 160 % to 1.0Gt/year. Petrochemicals industries has some energy relevance (accounting for approximately 10%) represent the bulk of the energy and feed stock use in this sector. Most industrial energy consumption occurs in industries that produce raw material such as chemical, petrochemicals, iron and steel, nonmetallic minerals and nonferrous metals industries. Together, these four materials groups consumed 69.9 EJ of final energy in 2004 (62% of total final industrial energy use). The chemicals and petrochemical industry alone accounts for 30% of industrial energy use (Phil Thompson C.Eng. M.I.Chem.E., UK). According to these facts, it is predicted that the world s energy will be exhausted within a century.
15 2 In Malaysia, the government has issued many energy conservation plans for reducing the energy consumption. With the latest plan, the energy consumption is being cut down in factories and buildings, and promoting the use of renewable energy. The industrial sector, which consumes a large amount of energy, is looking for the way to use the energy efficiently in order to reduce the plant cost. A lot of researchers in the entire world had done different studies in order to find the suitable optimization methods in the management of energy for chemical plants. Pinch technology is one of the energy optimization methods. Pinch Technology is the most practical method for applying process integration. Process Integration is a very important means of improving energy efficiency of industrial and manufacturing processes as well as minimizing their environment impact. By analyzing the thermodynamics of a process, an engineer can qualify the thermodynamic efficiency of the process, identify the regions where energy can be better utilized and define the minimum targets for energy consumption. Pinch technology is used mostly for the Heat Exchanger Network (HEN). The process pinch point refers to the energy optimum point in the process design, the temperature level above this point acts as heat sink, and the one below acts as heat source. Based on rigorous thermodynamic principles, Pinch technology matches cold streams that need to be heated with hot streams which need to be cooled, causing high degree of energy recovery. Thus pinch technology can be used to determine the minimum requirements for both hot and cold utilities in a process. In the present energy crisis scenario all over the world, this project will optimize this isobutylene plant by applying pinch technology on 4 heat exchangers for retrofitting the heat exchanger network to obtain the best design which posses high degree of energy recovery beside reduce the cost of plant production, operating, and utilities.
16 Process Flow Diagram (PFD) Figure 1.1 : Process Flow Diagram (PFD) of isobutylene plant From Figure 1.1, it can be observed and summarized that the process flow diagram for this isobutylene plant consists of 4 heat exchangers where two of it are used for cooling down of the process stream and the other two heat exchangers are used for heating up. The transfer of heat in a process fluid is an essential part of most chemical processes where heat can be transferred between two fluids. The most common type is one in which the hot and the cold fluid do not come into direct contact with each other but are separated by a tube wall or flat or curved. The transfer of heat accomplished from the hot fluid to the wall or tube surface by convection through tube wall or plate conduction and by convection to the cold fluid. It is important to determine whether the stream is cold or hot stream. Generally, hot and cold streams can be defined as: Hot Stream : The stream that must be cooled or are available to be cooled. Cold Stream : The stream that must be heated.
17 4 In addition, utility stream are used to heat or cool process streams, when heat exchange between process streams is not practical or economic, a number of different hot utilities (steam, hot water, flue gas, etc.) and cold utilities (cooling water, air, refrigerant, etc.) are used in this plant. The basic concept of a heat exchanger is based on the premise that the loss of heat on the high temperature side is exactly the same as the heat gained in the low temperature side after the heat and mass flows through the heat exchanger. Figure 1.2 : Heat Exchanger stream flow HEAT EXCHANGER 1 t out = K T in = 300K T out = 394K t in = 588.8K Figure 1.3 : Cross section of Heat Exchanger 1 From figure 1.3, the stream process at 300K was supplied. This stream needs to be heated to 394K to proceed for the oxidation reactor which requires higher
18 5 temperature. This first Heat Exchanger was applied on that stream for this purpose. The inlet flowrate of the Heat Exchanger 1 is kg/hr of water steam at 588.8K. As the result, the outlet temperature of the process stream increase to 394K with decreasing t out of the Heat Exchanger 1 to K. HEAT EXCHANGER 2 t out = 375K T in = 380K T out = 394K t in = 400K Figure 1.4 : Cross section of Heat Exchanger 2 From figure 1.4, shows the initial temperature of steam process is 380K. Similar with the previous steam, it needs to be heated to 394K to proceed with the oxidation reactor which requires higher temperature for oxidation process. The second Heat Exchanger was applied on that stream with inlet flowrate of the Heat Exchanger 2 is kg/hr of water steam at 400K. As the result, the outlet temperature of the process stream increase to 394K with decreasing the t out of the Heat Exchanger 2 to 375K.
19 6 HEAT EXCHANGER 3 t out = 353K T in = 394K T out = 363K t in = 300K Figure 1.5 : Cross section of Heat Exchanger 3 In figure 1.5, the temperature of entering stream process is 394K. It was then lowered down to 363K before entering the flash distillation column to proceed with the separation of homogeneous mixture. The third Heat Exchanger was installed to this stream with the inlet flowrate of kg/hr of water steam at 300K. The outlet temperature of the process stream increase to 363K with the t out of the heat exchanger 3 is 353K. HEAT EXCHANGER 4 t out = 358K T in = 373K T out = 363K t in = 373K Figure 1.6 : Cross section of Heat Exchanger 4 Figure 1.6 simulate the purpose of Heat exchanger 4. It shows that the entering stream prior the Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) which require
20 7 lower temperature of 363K, the forth heat exchanger was applied on that stream. The inlet flowrate of the Heat Exchanger 4 is kg/hr of water steam at 373K. The outlet of process stream is 363K which while for the leaving water steam, it was decreased to 358K. The overall heat exchanger used in this plant can be summarized in the following table: Table 1.1 : Summary of Heat Exchanger No. of Heat Process Stream Utility Stream Exchanger T in (K) T out (K) t in (K) t out (K) Heat Exchanger Heat Exchanger Heat Exchanger Heat Exchanger Problem Statement The importance of heat exchangers as a medium of heat transfer between specific equipments has given more good reasons for energy usage for the continuity of plant processes. The situation where most of the energy that are being used in a plant gone to waste without being recovered has led to the increasing cost of production of a plant. Basically, the energy used should not exceed the energy required in a process. The use of excessive energy will rise to environmental problems which is highly potential to increase the carbon emission to atmosphere. The increasing of carbon in atmosphere will contribute to greenhouse effect. The initial study shows that the plant process is not very efficient based on the usage of energy and high capital and production cost of the plant. The total usage energy of all heat exchangers in this plant is kw which shows significantly high energy consumption thus have a potential for energy recovery analysis. Therefore, with respect of the scenario discussed, this research is done to optimize this petrochemical plant. The main objectives is to ensure total energy used
21 8 for production is being minimized and reduced without disrupting the plant process performance. To achieve this target, Pinch technology will be applied to analyze for potential energy saving. For further analysis, this research will analyze the impacts and effects of this technique towards the plant s economics. 1.3 Research Objectives (1) To minimize the cost of utility for a chemical plant. (2) To optimize the energy usage of the plant. (3) To observe the effect of energy optimization to plant economy. 1.4 Scopes of the Study (1) Performing Pinch Analysis on energy conservation in isobutylene plant using T min =13 C and T min =14 C. (2) To obtain stream data on the process stream in the plant. (3) Studying on heat exchangers. 1.5 Significance of the Study (1) Optimizing the energy usage of an existing plant. (2) Decrease quantity of the carbon emission that can contribute to the global warming. (3) To improve the plant economy through energy saving.
22 9 CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Background Research History and Background Pinch technology is a relatively modern engineering tool developed in the late 1970's and early 1980's by Phd student Bodo Linnhoff from Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) under the supervision of Professor John Flower from the University of Leeds This new approach to evaluating the energy requirements of a site quickly identified ways of improving the overall energy use. The name Pinch Technology was applied because the technique identified the point or points in the energy flow where restrictions applied and hence limited one s ability to re-use low grade energy. The major difference between this new technology and previous engineering approaches was the formalized methodology involving the rigorous application of thermodynamic principles. Pinch technology was initially adopted by major chemical companies and the petrochemical energy (Phil Thompson C.Eng. M.I.Chem.E., UK). Pinch analysis is a methodology for minimizing energy consumption of chemical processes by calculating thermodynamically feasible energy targets (or minimum energy consumption) and achieving them by optimizing heat recovery systems, energy supply methods and process operating conditions. It is also known as process integration, heat integration, energy integration or pinch technology. The process data is represented as a set of energy flows, or streams, as a function of heat load (kw) against temperature (deg C). These data are combined for
23 10 all the streams in the plant to give composite curves, one for all hot streams (releasing heat) and one for all cold streams (requiring heat). The point of closest approach between the hot and cold composite curves is the pinch temperature (pinch point or just pinch), and is where design is most constrained. Hence, by finding this point and starting design there, the energy targets can be achieved using heat exchangers to recover heat between hot and cold streams. In practice, during the pinch analysis, often cross-pinch exchanges of heat are found between a stream with its temperature above the pinch and one below the pinch. Removal of those exchanges by alternative matching makes the process reach its energy target Basic Pinch Analysis Concepts The pinch analysis concept is originated to design the heat recovery network for a specified design task. The pinch analysis starts with the heat and material balances data of the process which is obtained after the core process, i.e. reaction and separation system, has been designed. Using thermal data from the process, we can set the target for energy saving prior to the design of the heat exchanger networks. The necessary thermal data is source and target temperature and heat capacity flow rate for each stream as shown in Table 2.1. Table 2.1 : Thermal data for process streams (Linnhoff and Hindmarsh,1983) No Type Temperature (T s ), Temperature (T t ), Flowrate (CP), C C kw/ C 1 Hot Hot Cold Cold Here, the hot streams are referred to the streams that required cooling, i.e. the source temperature is higher than the target. While the cold streams are referred to those required heating, i.e. the target temperature is higher than the supply. Heat
24 11 capacity flow rate is defined as specific heat capacity times mass flow rate as shown below: CP = Cp x F (2.1) Where CP = heat capacity flow rate (kw/ C) Cp = specific heat capacity of the stream (kj/ C.kg) F = mass flow rate of the stream (kg/s) The data using here is based on the assumption that the heat capacity flow rate is constant. In practice, this assumption is valid because every streams with or without phase change can easily be described in terms of linearized temperatureenthalpy data (i.e. CP is constant). The location of pinch and the minimum utility requirement can be calculated by using the problem table algorithm (Linnhoff and Flower, 1979) for a specified minimum temperature different, T min. For a T min of 20 C, the results from this method are shown in Table 2.2: Table 2.2 : The problem table for data given in Table 2.1 (Linnhoff and Hindmarsh, 1983) Streams & Temperatures Heat Accumulated Heat Flows Subnetwork Cold T ( C) Hot Deficit Input Output Input Output Stream Stream (3) (4) 150 (2) SN SN SN SN SN SN In the table the stream data are shown on the left. The network is divided into six sub-networks (SN1-SN6) corresponding to the temperature interval. The interval is defined by process stream supply and target temperatures. For example, SN2 is defined by the target temperature of stream No.3 and No. 4. The important feature of this method is the separation between hot and cold streams by T min. This feature ensures the feasibility of complete heat exchange between the hot and cold streams.
25 12 In other words, for each sub-network there will be either a net heat deficit or surplus as shown in Heat Deficit column (column 1) in Table 2.2. The sign convention for heat deficit is positive while the negative is used for heat surplus. Another important feature of the problem table algorithm is the heat cascade, i.e. heat is transferred from the high to low temperature sub-networks. This idea is used in calculation of accumulated heat as shown in column 2 and 3 of Table 2.2. Initially, it is assumed that no heat supply from external utilities. The output for each sub-network is obtained by adding the surplus to the input of that sub-network. The output is then used as an input for the next sub-networks. The procedure is repeated until all of the network heat flows are calculated as shown in equation Heat flow input = Heat flow output + Heat deficit (2.2) To be feasible, the flow of heat from sub-network to sub-network must not be negative. Therefore, the heat has to be added into a network to ensure that the heat flows are non-negative. The minimum utility usage is observed when heat flows in the network are zero. The input to the hottest interval for this case is the minimum hot utility requirement for the network, while the cold utility usage is the output from the coldest sub-network. The results of the problem table algorithm can be shown diagrammatically called Transshipment heat flow diagram as shown in Figure 2.1(a). All heat flows are calculated by problem table algorithm. It can be seen from this diagram, the heat flow from SN3 to SN4 is zero while other flows are positive. The point where value of the heat flow is zero represents the pinch point.
26 13 Q Hmin = Q Hmin = SN SN HOT END SN SN Pinch SN SN (a) COLD END Q Hmin = 40 Q Hmin = 40 (b) Figure 2.1 : (a) Transshipment heat flow diagram for data in table 2.1 (b) Sub-networks combined into a hot and cold region (Linnhoff and Hindmarsh, 1983). The significance of the pinch is shown in Figure 2.1(b). The pinch separates the problem into two thermodynamic regions, namely, hot end and cold end. The hot end is the region comprising all streams or parts of streams above the pinch temperature. Only hot utility is required in this region but not cold utility. The cold end is the region comprising all streams or parts of streams below the pinch temperature. Cold utility is required in this region but not for hot utility. There is no heat transferring across the pinch, therefore, the utility requirement is the minimum. As described previously, the hot end requires only hot utility so it acts as a heat sink while the cold end requires only cold utility so it acts as a heat source. To achieve this minimum requirement, the design has to obey the pinch principle. The pinch principle comprises of : (1) There must not be heat across the pinch. (2) There must not be external utility cooling above the pinch. (3) There must not be external utility heating below the pinch.
Introduction to Pinch Technology
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 07, 2018 Introduction to Pinch Technology Rokni, Masoud Publication date: 2016 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Rokni,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 07, 2018 Introduction to Pinch Technology Rokni, Masoud Publication date: 2016 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Rokni,
ESTIMATION IN SPOT WELDING PARAMETERS USING GENETIC ALGORITHM HAFIZI BIM LUKMAN
 iii ESTIMATION IN SPOT WELDING PARAMETERS USING GENETIC ALGORITHM HAFIZI BIM LUKMAN A report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering (Mechanical)
iii ESTIMATION IN SPOT WELDING PARAMETERS USING GENETIC ALGORITHM HAFIZI BIM LUKMAN A report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering (Mechanical)
AN EFFICIENT MICROCONTROLLER-BASED ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR HIGH PRESSURE SODIUM LAMPS USED IN STREET LIGHTING MOHD HAMIZAN BIN OMAR
 AN EFFICIENT MICROCONTROLLER-BASED ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR HIGH PRESSURE SODIUM LAMPS USED IN STREET LIGHTING MOHD HAMIZAN BIN OMAR A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the award of
AN EFFICIENT MICROCONTROLLER-BASED ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR HIGH PRESSURE SODIUM LAMPS USED IN STREET LIGHTING MOHD HAMIZAN BIN OMAR A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the award of
Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency
 Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency S. R. Sunasara 1, J. J. Makadia 2 * 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, RK University Kasturbadham, Rajkot-Bhavngar highway,
Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency S. R. Sunasara 1, J. J. Makadia 2 * 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, RK University Kasturbadham, Rajkot-Bhavngar highway,
Grand Composite Curve Module 04 Lecture 12
 Module 04: Targeting Lecture 12: Grand Composite Curve While composite curves provide overall energy targets, these do not indicate the amount of energy that should be supplied at different temperature
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 12: Grand Composite Curve While composite curves provide overall energy targets, these do not indicate the amount of energy that should be supplied at different temperature
Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant
 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): 39-49 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajee doi: 10.11648/j.ajee.20170505.13 ISSN: 2329-1648 (Print); ISSN: 2329-163X (Online) Debottlenecking
American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): 39-49 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajee doi: 10.11648/j.ajee.20170505.13 ISSN: 2329-1648 (Print); ISSN: 2329-163X (Online) Debottlenecking
Researcher, 1(2), 2009, Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis
 Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis K.R. AJAO (Ph.D) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria e-mail: ajaomech@unilorin.edu.ng H. F. Akande
Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis K.R. AJAO (Ph.D) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria e-mail: ajaomech@unilorin.edu.ng H. F. Akande
Quiz Questions. For Process Integration. Fill in the blanks type Questions
 Quiz Questions For Process Integration Fill in the blanks type Questions 1. is the key parameter used in the Pinch Technology. ( T min ) 2. In onion diagram pinch technology in applied at. (the boundary
Quiz Questions For Process Integration Fill in the blanks type Questions 1. is the key parameter used in the Pinch Technology. ( T min ) 2. In onion diagram pinch technology in applied at. (the boundary
The Grid Diagram The Heat-Content Diagram Pinch Subnetworks Minimum Number of Heat-Exchange Units...
 3.1 INTRODUCTION... 2 3.2 DESIGN TOOLS: REPRESENTING HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORKS... 4 3.2.1. The Grid Diagram...4 3.2.2. The Heat-Content Diagram...7 3.3 PRELIMINARY HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORK DESIGN... 10 3.2.1
3.1 INTRODUCTION... 2 3.2 DESIGN TOOLS: REPRESENTING HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORKS... 4 3.2.1. The Grid Diagram...4 3.2.2. The Heat-Content Diagram...7 3.3 PRELIMINARY HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORK DESIGN... 10 3.2.1
Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery
 Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery Adnan A. Ateeq Engineering Technical College Southern Technical University Basra, Iraq
Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery Adnan A. Ateeq Engineering Technical College Southern Technical University Basra, Iraq
AVAILABLE TRANSFER CAPABILITY BASED ON RANDOMLY GENERATED PROBABILISTIC DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF WIND SPEED USING MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
 AVAILABLE TRANSFER CAPABILITY BASED ON RANDOMLY GENERATED PROBABILISTIC DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF WIND SPEED USING MONTE CARLO SIMULATION NOR AMIRA BINTI A. BAKAR UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA AVAILABLE
AVAILABLE TRANSFER CAPABILITY BASED ON RANDOMLY GENERATED PROBABILISTIC DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF WIND SPEED USING MONTE CARLO SIMULATION NOR AMIRA BINTI A. BAKAR UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA AVAILABLE
Signature :... Supervisor s Name: Mohd Saifuzam Bin Jamri. Date :...
 I hereby declare that I have read through this report entitle Modeling and Control Stand Alone PV system by using Voltage mode control converter method and found that it has comply the partial fulfillment
I hereby declare that I have read through this report entitle Modeling and Control Stand Alone PV system by using Voltage mode control converter method and found that it has comply the partial fulfillment
3.17. PROCESS INTEGRATION AND PINCH TECHNOLOGY
 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES 111 pressure is expanded over the throttle value and fed to the condenser, to provide cooling to condense the vapour from the column. The vapour from the condenser is compressed
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES 111 pressure is expanded over the throttle value and fed to the condenser, to provide cooling to condense the vapour from the column. The vapour from the condenser is compressed
TITLE PAGE DEVELOPMENT OF A COMPUTER SOFTWARE FOR OPTIMAL DESIGN AND RETROFIT OF HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK IN A CHEMICAL PROCESS PLANT OOI BOON LEE
 TITLE PAGE DEVELOPMENT OF A COMPUTER SOFTWARE FOR OPTIMAL DESIGN AND RETROFIT OF HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK IN A CHEMICAL PROCESS PLANT OOI BOON LEE A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for
TITLE PAGE DEVELOPMENT OF A COMPUTER SOFTWARE FOR OPTIMAL DESIGN AND RETROFIT OF HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK IN A CHEMICAL PROCESS PLANT OOI BOON LEE A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for
SCHEDULE RISK ANALYSIS IN OFFSHORE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT BUDI HERMANTO
 SCHEDULE RISK ANALYSIS IN OFFSHORE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT BUDI HERMANTO A project report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Science in Construction
SCHEDULE RISK ANALYSIS IN OFFSHORE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT BUDI HERMANTO A project report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Science in Construction
SIMULATION ON EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF CHANNEL/DRAIN ENGINEERING STRUCTURE ON MOS DEVICE PERFORMANCE NORAZLINA BINTI MOHD AMIN
 SIMULATION ON EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF CHANNEL/DRAIN ENGINEERING STRUCTURE ON MOS DEVICE PERFORMANCE NORAZLINA BINTI MOHD AMIN SCHOOL OF MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS 2007
SIMULATION ON EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF CHANNEL/DRAIN ENGINEERING STRUCTURE ON MOS DEVICE PERFORMANCE NORAZLINA BINTI MOHD AMIN SCHOOL OF MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS 2007
SIZING OF ENERGY STORAGE BASED ON LOSS OF LOAD PROBABILITY OF STANDALONE PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS RAZMAN BIN AYOP UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
 SIZING OF ENERGY STORAGE BASED ON LOSS OF LOAD PROBABILITY OF STANDALONE PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS RAZMAN BIN AYOP UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SIZING OF ENERGY STORAGE BASED ON LOSS OF LOAD PROBABILITY OF
SIZING OF ENERGY STORAGE BASED ON LOSS OF LOAD PROBABILITY OF STANDALONE PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS RAZMAN BIN AYOP UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SIZING OF ENERGY STORAGE BASED ON LOSS OF LOAD PROBABILITY OF
FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT MODEL USING COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS NOR AZLIZA BINTI AKBAR
 FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT MODEL USING COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS NOR AZLIZA BINTI AKBAR A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering
FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT MODEL USING COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS NOR AZLIZA BINTI AKBAR A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering
Module 04 : Targeting. Lecture 11: PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM 1 st Part
 Module 04 : Targeting Lecture : PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM st Part Key words: Problem Table Algorithm, shifted temperature, composite curve, PTA, For a given ΔT min, Composite curves can be used to obtain
Module 04 : Targeting Lecture : PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM st Part Key words: Problem Table Algorithm, shifted temperature, composite curve, PTA, For a given ΔT min, Composite curves can be used to obtain
OPTIMIZATION OF A MULTI-OBJECTIVE-MULTI-PERIOD TRAVELING SALESMAN PROBLEM WITH PICKUP AND DELIVERY USING GENETIC ALGORITHM SEYED POURYA POURHEJAZY
 OPTIMIZATION OF A MULTI-OBJECTIVE-MULTI-PERIOD TRAVELING SALESMAN PROBLEM WITH PICKUP AND DELIVERY USING GENETIC ALGORITHM SEYED POURYA POURHEJAZY A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the
OPTIMIZATION OF A MULTI-OBJECTIVE-MULTI-PERIOD TRAVELING SALESMAN PROBLEM WITH PICKUP AND DELIVERY USING GENETIC ALGORITHM SEYED POURYA POURHEJAZY A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the
THICKNESS EFFECT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF COMPOSITE TUBE ABDULLAH OMAR BIN ABDUL AZIZ UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG
 THICKNESS EFFECT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF COMPOSITE TUBE ABDULLAH OMAR BIN ABDUL AZIZ UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG THICKNESS EFFECT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF COMPOSITE TUBE ABDULLAH OMAR BIN ABDUL AZIZ Report submitted
THICKNESS EFFECT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF COMPOSITE TUBE ABDULLAH OMAR BIN ABDUL AZIZ UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG THICKNESS EFFECT ON THE PERFORMANCE OF COMPOSITE TUBE ABDULLAH OMAR BIN ABDUL AZIZ Report submitted
 v ABSTRACT Many strategies have been formulated to help a company in achieving it s objectives. One of the most popular strategy that has been adopted among researchers and business sponsor nowadays is
v ABSTRACT Many strategies have been formulated to help a company in achieving it s objectives. One of the most popular strategy that has been adopted among researchers and business sponsor nowadays is
OPTIMUM UTILIZATION OF QUARRY DUST AS PARTIAL REPLACEMENT OF SAND IN GREEN CONCRETE
 OPTIMUM UTILIZATION OF QUARRY DUST AS PARTIAL REPLACEMENT OF SAND IN GREEN CONCRETE JAHARATUL DINI KAREN LEE BINTI ABDULLAH UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA OPTIMUM UTILIZATION OF QUARRY DUST AS PARTIAL REPLACEMENT
OPTIMUM UTILIZATION OF QUARRY DUST AS PARTIAL REPLACEMENT OF SAND IN GREEN CONCRETE JAHARATUL DINI KAREN LEE BINTI ABDULLAH UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA OPTIMUM UTILIZATION OF QUARRY DUST AS PARTIAL REPLACEMENT
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL ROUGHNESS INDEX (IRI) AND PRESENT SERVICEABILITY INDEX (PSI)
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL ROUGHNESS INDEX (IRI) AND PRESENT SERVICEABILITY INDEX (PSI) AMMINUDIN BIN AB. LATIF UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL ROUGHNESS INDEX
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL ROUGHNESS INDEX (IRI) AND PRESENT SERVICEABILITY INDEX (PSI) AMMINUDIN BIN AB. LATIF UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL ROUGHNESS INDEX
EXERCISE BIKE ELECTROLYSER AS THE HYDROGEN PRODUCTION SYSTEM MUHAMAD NASIRUDDIN BIN MOHD SAMSI
 EXERCISE BIKE ELECTROLYSER AS THE HYDROGEN PRODUCTION SYSTEM MUHAMAD NASIRUDDIN BIN MOHD SAMSI A thesis submitted in the fulfilment of the requirement for the award of degree of Bachelor of Engineering
EXERCISE BIKE ELECTROLYSER AS THE HYDROGEN PRODUCTION SYSTEM MUHAMAD NASIRUDDIN BIN MOHD SAMSI A thesis submitted in the fulfilment of the requirement for the award of degree of Bachelor of Engineering
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING FOR DEGRADATION OF WATER POLLUTION BY EFFECTIVE MICROORGANISM (EM) IN RIVER
 1 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING FOR DEGRADATION OF WATER POLLUTION BY EFFECTIVE MICROORGANISM (EM) IN RIVER MUHAMMAD SYARIFUDDIN HILMI BIN YUSUF UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA 3 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING FOR DEGRADATION
1 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING FOR DEGRADATION OF WATER POLLUTION BY EFFECTIVE MICROORGANISM (EM) IN RIVER MUHAMMAD SYARIFUDDIN HILMI BIN YUSUF UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA 3 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING FOR DEGRADATION
Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology
 Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology Napredakul, D. a, Siemanond, K.a, Sornchamni, T.b, Laorrattanasak, S.b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok,
Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology Napredakul, D. a, Siemanond, K.a, Sornchamni, T.b, Laorrattanasak, S.b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok,
GENDER PREFERENCES AND INSTAGRAM HASHTAG USAGE ON #MALAYSIANFOOD ZHANG YE
 GENDER PREFERENCES AND INSTAGRAM HASHTAG USAGE ON #MALAYSIANFOOD ZHANG YE A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Management (Technology) Faculty
GENDER PREFERENCES AND INSTAGRAM HASHTAG USAGE ON #MALAYSIANFOOD ZHANG YE A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Management (Technology) Faculty
ANALYSIS OF PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE FOR PROCESSING PLANT ( GASSIFICATION PROCESS UNIT )
 ANALYSIS OF PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE FOR PROCESSING PLANT ( GASSIFICATION PROCESS UNIT ) ABDUL PAIZAL BIN MOHD ZAIN B041210141 BMCL Email: abdpaizal@gmail.com Draft Final Report Projek Sarjana Muda II Supervisor:
ANALYSIS OF PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE FOR PROCESSING PLANT ( GASSIFICATION PROCESS UNIT ) ABDUL PAIZAL BIN MOHD ZAIN B041210141 BMCL Email: abdpaizal@gmail.com Draft Final Report Projek Sarjana Muda II Supervisor:
APPLICATION OF THE TRAVEL COST METHOD TO URBAN FORESTS IN JOHOR BAHRU NURUL SHAHIRAWATI BINTI MOHAMED ROSLI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
 APPLICATION OF THE TRAVEL COST METHOD TO URBAN FORESTS IN JOHOR BAHRU NURUL SHAHIRAWATI BINTI MOHAMED ROSLI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA APPLICATION OF THE TRAVEL COST METHOD TO URBAN FORESTS IN JOHOR
APPLICATION OF THE TRAVEL COST METHOD TO URBAN FORESTS IN JOHOR BAHRU NURUL SHAHIRAWATI BINTI MOHAMED ROSLI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA APPLICATION OF THE TRAVEL COST METHOD TO URBAN FORESTS IN JOHOR
BERASAS KOMPUTER. Oleh Mohamad Rodzizan b. Hj. Ahmad Tajuddin. 0 MOHAMAD RODZIZAN TAJUDDIN, Hak Cipta Terpelihara.
 LATIHAN PERAKAUNAN BERASAS KOMPUTER Tesis ini dikemukakan kepada Sekolah Siswazah sebagai memenuhi sebahagian daripada syarat pengijazahan Sarjana Sains (Teknologi Maklumat) Universiti Utara Malaysia Oleh
LATIHAN PERAKAUNAN BERASAS KOMPUTER Tesis ini dikemukakan kepada Sekolah Siswazah sebagai memenuhi sebahagian daripada syarat pengijazahan Sarjana Sains (Teknologi Maklumat) Universiti Utara Malaysia Oleh
HDA Process. compressor. Reactor. Flash. heat. cool. Stabilizer. Recycle. Product
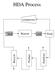 HDA Process compressor heat Reactor cool Flash Recycle Product Stabilizer Why Energy Integration? (ICI Experience) 20 case studies In every case, there was a reduction in energy In almost every case, the
HDA Process compressor heat Reactor cool Flash Recycle Product Stabilizer Why Energy Integration? (ICI Experience) 20 case studies In every case, there was a reduction in energy In almost every case, the
STUDY ON IRON AND MANGANESE REMOVAL IN RIVER WATER FOR TEXTILES INDUSTRY USAGE ZAITON BIN SAMAD UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
 STUDY ON IRON AND MANGANESE REMOVAL IN RIVER WATER FOR TEXTILES INDUSTRY USAGE ZAITON BIN SAMAD UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA iii STUDY ON IRON AND MANGANESE REMOVAL IN RIVER WATER FOR TEXTILES INDUSTRY
STUDY ON IRON AND MANGANESE REMOVAL IN RIVER WATER FOR TEXTILES INDUSTRY USAGE ZAITON BIN SAMAD UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA iii STUDY ON IRON AND MANGANESE REMOVAL IN RIVER WATER FOR TEXTILES INDUSTRY
SIMULATION AND MEASUREMENT FOR INDOOR AIR FLOW LIM DA PING UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
 SIMULATION AND MEASUREMENT FOR INDOOR AIR FLOW LIM DA PING UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA i SUPERVISOR DECLARATION I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my opinion this report is sufficient
SIMULATION AND MEASUREMENT FOR INDOOR AIR FLOW LIM DA PING UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA i SUPERVISOR DECLARATION I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my opinion this report is sufficient
POLYSILICON PROCESS DEVELOPMENT THE EFFECT OF PECVD PROCESS PARAMETERS ON THE FILM CHARACTERISTICS MUJAHIDUN BIN MASHURI
 POLYSILICON PROCESS DEVELOPMENT THE EFFECT OF PECVD PROCESS PARAMETERS ON THE FILM CHARACTERISTICS MUJAHIDUN BIN MASHURI SCHOOL OF MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS 2007 POLYSILICON
POLYSILICON PROCESS DEVELOPMENT THE EFFECT OF PECVD PROCESS PARAMETERS ON THE FILM CHARACTERISTICS MUJAHIDUN BIN MASHURI SCHOOL OF MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS 2007 POLYSILICON
SIMULATION PERFORMANCE OF LOW DAMAGE BASE CONNECTION ON ABAQUS MAHDI HATAMI
 SIMULATION PERFORMANCE OF LOW DAMAGE BASE CONNECTION ON ABAQUS MAHDI HATAMI A project report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering (Civil-Structure)
SIMULATION PERFORMANCE OF LOW DAMAGE BASE CONNECTION ON ABAQUS MAHDI HATAMI A project report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering (Civil-Structure)
THE DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF POST TENSIONED FLAT SLAB NURHIDAYAH BINTI ZAKARIA
 THE DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF POST TENSIONED FLAT SLAB NURHIDAYAH BINTI ZAKARIA A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering
THE DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF POST TENSIONED FLAT SLAB NURHIDAYAH BINTI ZAKARIA A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering
SUPERVISOR VALIDATION
 SUPERVISOR VALIDATION I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my opinion this project is sufficient in terms of scope and quality for the award of Bachelor of Technology Management (Innovation)
SUPERVISOR VALIDATION I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my opinion this project is sufficient in terms of scope and quality for the award of Bachelor of Technology Management (Innovation)
MASOUD GHEISARI A WEB BASED ENVIRONMENT FOR BUILDINGS LIFE CYCLE COST ANALYSIS 2007/2009
 MASOUD GHEISARI 07.26.1984 A WEB BASED ENVIRONMENT FOR BUILDINGS LIFE CYCLE COST ANALYSIS 2007/2009 / Z11003383 DR. ARHAM BIN ABDULLAH MAY 2009 MAY 2009 2 I hereby declare that I have read this project
MASOUD GHEISARI 07.26.1984 A WEB BASED ENVIRONMENT FOR BUILDINGS LIFE CYCLE COST ANALYSIS 2007/2009 / Z11003383 DR. ARHAM BIN ABDULLAH MAY 2009 MAY 2009 2 I hereby declare that I have read this project
Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system
 Refrigeration System Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system A refrigerator is simply a heat pump where heat is rejected to atmosphere( the sink). Fig.41.3(lecture
Refrigeration System Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system A refrigerator is simply a heat pump where heat is rejected to atmosphere( the sink). Fig.41.3(lecture
THE INFLUENCE OF CELEBRITY ENDORSEMENT AND CONSUMER TRUST TOWARD PURCHASE INTENTION IN DOTIC DONUT INSTAGRAM IN MALANG.
 THE INFLUENCE OF CELEBRITY ENDORSEMENT AND CONSUMER TRUST TOWARD PURCHASE INTENTION IN DOTIC DONUT INSTAGRAM IN MALANG Thesis for S-1 BY : YOSUA SENDI SASONGKO 3303014006 INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT
THE INFLUENCE OF CELEBRITY ENDORSEMENT AND CONSUMER TRUST TOWARD PURCHASE INTENTION IN DOTIC DONUT INSTAGRAM IN MALANG Thesis for S-1 BY : YOSUA SENDI SASONGKO 3303014006 INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT
TABLE OF CONTENTS DECLARATION DEDICATION ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABSTRACT
 vi ABSTRACT Post tensioning flat slab are not complex where the construction technique, structure behavior and design are all simple. The tendon install provide a suspension system within the slab and
vi ABSTRACT Post tensioning flat slab are not complex where the construction technique, structure behavior and design are all simple. The tendon install provide a suspension system within the slab and
PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION SIMULATION OF HIGH POWER YTTERBIUM DOPED DOUBLE-CLAD FIBER LASER KHAIROL BARIYAH BINTI MAAMUR
 PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION SIMULATION OF HIGH POWER YTTERBIUM DOPED DOUBLE-CLAD FIBER LASER KHAIROL BARIYAH BINTI MAAMUR A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirement for the award of the degree of
PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION SIMULATION OF HIGH POWER YTTERBIUM DOPED DOUBLE-CLAD FIBER LASER KHAIROL BARIYAH BINTI MAAMUR A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirement for the award of the degree of
IMPROVE MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEM IN HIROTAKO ACOUSTIC SDN.BHD S LOGISTIC DEPARTMENT AREA LINGENTHIRAN A/L SAMYLINGAM
 IMPROVE MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEM IN HIROTAKO ACOUSTIC SDN.BHD S LOGISTIC DEPARTMENT AREA LINGENTHIRAN A/L SAMYLINGAM Report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree
IMPROVE MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEM IN HIROTAKO ACOUSTIC SDN.BHD S LOGISTIC DEPARTMENT AREA LINGENTHIRAN A/L SAMYLINGAM Report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree
STUDY OF MICRO PITS ON BILLET EXPERIMENTAL SURFACE IN EXTRUSION PROCESS MAK KAM WONG
 1 STUDY OF MICRO PITS ON BILLET EXPERIMENTAL SURFACE IN EXTRUSION PROCESS MAK KAM WONG UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA 3 STUDY OF MICRO PITS ON BILLET EXPERIMENTAL SURFACE IN EXTRUSION PROCESS MAK KAM WONG
1 STUDY OF MICRO PITS ON BILLET EXPERIMENTAL SURFACE IN EXTRUSION PROCESS MAK KAM WONG UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA 3 STUDY OF MICRO PITS ON BILLET EXPERIMENTAL SURFACE IN EXTRUSION PROCESS MAK KAM WONG
Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery
 Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery J. Khorshidi, E. Zare, A.R. Khademi Abstract The reduction of energy consumption through improvements in energy efficiency
Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery J. Khorshidi, E. Zare, A.R. Khademi Abstract The reduction of energy consumption through improvements in energy efficiency
Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison. Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner
 Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Introduction... 5 Paper Overview... 6 Example 1... 7 Example 2... 9 1. Mixed Integer
Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Introduction... 5 Paper Overview... 6 Example 1... 7 Example 2... 9 1. Mixed Integer
COMMUNICATION Mass Transfer in a Closed-cycle Solid-liquid Extraction Unit
 Pertanika J. Sci. & Techno!. 2(2): 237-241 (1994) ISSN: 0128-7680 Universiti Pertanian Malaysia Press OMMUNIATION Mass Transfer in a losed-cycle Solid-liquid Extraction Unit B.A.Asbi Department offood
Pertanika J. Sci. & Techno!. 2(2): 237-241 (1994) ISSN: 0128-7680 Universiti Pertanian Malaysia Press OMMUNIATION Mass Transfer in a losed-cycle Solid-liquid Extraction Unit B.A.Asbi Department offood
DESIGN AND FABRICATE WELDING MACHINE CART ZULFADLI ADHA BIN NADZRI. Report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the
 DESIGN AND FABRICATE WELDING MACHINE CART ZULFADLI ADHA BIN NADZRI Report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the Diploma of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Mechanical
DESIGN AND FABRICATE WELDING MACHINE CART ZULFADLI ADHA BIN NADZRI Report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the Diploma of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Mechanical
Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 27: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) 2 nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN
 Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 7: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN Some rules for pinch design methods such as Criteria for number of process streams
Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 7: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN Some rules for pinch design methods such as Criteria for number of process streams
Application of Heat Integration Techniques on Extract Column Section to reduce the cold utility requirements
 Application of Heat Integration Techniques on Extract Column Section to reduce the cold utility requirements Deepa H A 1, Ravishankar R 2 1 Chemical Engineering Department, DSCE, Karnataka, India 2 Chemical
Application of Heat Integration Techniques on Extract Column Section to reduce the cold utility requirements Deepa H A 1, Ravishankar R 2 1 Chemical Engineering Department, DSCE, Karnataka, India 2 Chemical
Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and GAMS Technology.
 EngOpt 2012 3 rd International Conference on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 July 2012. Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and
EngOpt 2012 3 rd International Conference on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 July 2012. Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and
BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS TESIS
 UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS TESIS JUDUL: EVALUATION AND OPTIMIZATION OF HEAT EXTRACTION DEVICE SESI PENGAJIAN: 2010/2011 Saya AZRI AMZARI BIN RAMLI (880613-35-5401) (HURUF BESAR)
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS TESIS JUDUL: EVALUATION AND OPTIMIZATION OF HEAT EXTRACTION DEVICE SESI PENGAJIAN: 2010/2011 Saya AZRI AMZARI BIN RAMLI (880613-35-5401) (HURUF BESAR)
LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF AN INTEGRATED SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN JOHOR BAHRU SITI NADZIRAH BINTI OTHMAN UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
 LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF AN INTEGRATED SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN JOHOR BAHRU SITI NADZIRAH BINTI OTHMAN UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF AN INTEGRATED SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT
LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF AN INTEGRATED SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN JOHOR BAHRU SITI NADZIRAH BINTI OTHMAN UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT OF AN INTEGRATED SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT
EFFECT OF PRECIPITATE HARDENING TREATMENT ON MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CAST ALUMINUM SILICON ALLOY (A356) BENJUNIOR BINDAMIN
 EFFECT OF PRECIPITATE HARDENING TREATMENT ON MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CAST ALUMINUM SILICON ALLOY (A356) BENJUNIOR BINDAMIN UNIVERSITY MALAYSIA PAHANG UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG BORANG
EFFECT OF PRECIPITATE HARDENING TREATMENT ON MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CAST ALUMINUM SILICON ALLOY (A356) BENJUNIOR BINDAMIN UNIVERSITY MALAYSIA PAHANG UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG BORANG
ESTIMATING THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF CARBON EMISSIONS FROM FUEL CONSUMPTION DURING CONSTRUCTION ACTIVITIES PEZHMAN SHAHID
 ESTIMATING THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF CARBON EMISSIONS FROM FUEL CONSUMPTION DURING CONSTRUCTION ACTIVITIES PEZHMAN SHAHID A project report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
ESTIMATING THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF CARBON EMISSIONS FROM FUEL CONSUMPTION DURING CONSTRUCTION ACTIVITIES PEZHMAN SHAHID A project report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
NATURAL GAS DEHYDRATION USING TRIETHYLENE GLYCOL (TEG) AHMAD SYAHRUL BIN MOHAMAD UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG
 NATURAL GAS DEHYDRATION USING TRIETHYLENE GLYCOL (TEG) AHMAD SYAHRUL BIN MOHAMAD UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS TESIS PSZ 19:16 (Pind. 1/97) JUDUL : NATURAL
NATURAL GAS DEHYDRATION USING TRIETHYLENE GLYCOL (TEG) AHMAD SYAHRUL BIN MOHAMAD UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS TESIS PSZ 19:16 (Pind. 1/97) JUDUL : NATURAL
EFFECTIVENESS OF CRM SYSTEM FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE REPRESENTATIVES (CSR) TRAINING AT TELEKOM MALAYSIA
 EFFECTIVENESS OF CRM SYSTEM FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE REPRESENTATIVES (CSR) TRAINING AT TELEKOM MALAYSIA BADRUL AZIZ BIN MUHAMMAD UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA iii EFFECTIVENESS OF CRM SYSTEM FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE
EFFECTIVENESS OF CRM SYSTEM FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE REPRESENTATIVES (CSR) TRAINING AT TELEKOM MALAYSIA BADRUL AZIZ BIN MUHAMMAD UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA iii EFFECTIVENESS OF CRM SYSTEM FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE
Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation
 Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation by James Gainey Mann, Jr. Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation by James Gainey Mann, Jr. Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method
 Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method 1) Objectives of the practical work The objective of the practical work is to study the implementation of the pinch
Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method 1) Objectives of the practical work The objective of the practical work is to study the implementation of the pinch
Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI
 Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI nasrmrj@ripi.ir 21 MAY 2015 HVAC AND HEATING & COOLING SYSTEM CONFERENCE TEHRAN, IRAN 1 Energy and economy savings in the process of
Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI nasrmrj@ripi.ir 21 MAY 2015 HVAC AND HEATING & COOLING SYSTEM CONFERENCE TEHRAN, IRAN 1 Energy and economy savings in the process of
ASSESSMENT OF KETCHUP COMPANIES PERFORMANCE IN MALAYSIA AFAGH MALEK UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
 ASSESSMENT OF KETCHUP COMPANIES PERFORMANCE IN MALAYSIA AFAGH MALEK UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA i ASSESSMENT OF KETCHUP COMPANIES PERFORMANCE IN MALAYSIA AFAGH MALEK A project report submitted in partial
ASSESSMENT OF KETCHUP COMPANIES PERFORMANCE IN MALAYSIA AFAGH MALEK UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA i ASSESSMENT OF KETCHUP COMPANIES PERFORMANCE IN MALAYSIA AFAGH MALEK A project report submitted in partial
OPTIMAL DESIGN OF WATER NETWORK WITH IMPOVED OPERABILITY MOHAMMADREZA DEHGHANI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
 OPTIMAL DESIGN OF WATER NETWORK WITH IMPOVED OPERABILITY MOHAMMADREZA DEHGHANI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA OPTIMAL DESIGN OF WATER RECOVERY NETWORK WITH IMPROVED OPERABILITY MOHAMMADREZA DEHGHANI A dissertation
OPTIMAL DESIGN OF WATER NETWORK WITH IMPOVED OPERABILITY MOHAMMADREZA DEHGHANI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA OPTIMAL DESIGN OF WATER RECOVERY NETWORK WITH IMPROVED OPERABILITY MOHAMMADREZA DEHGHANI A dissertation
FEASIBILITY STUDY ON EFFECTIVENESS LARGE SURFACE AREA OF ELECTRODE FOR EARTH BATTERY MUHAMMAD IZZUDDEEN BIN KHAZALI
 FEASIBILITY STUDY ON EFFECTIVENESS LARGE SURFACE AREA OF ELECTRODE FOR EARTH BATTERY MUHAMMAD IZZUDDEEN BIN KHAZALI A report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirement for the degree of Bachelor
FEASIBILITY STUDY ON EFFECTIVENESS LARGE SURFACE AREA OF ELECTRODE FOR EARTH BATTERY MUHAMMAD IZZUDDEEN BIN KHAZALI A report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirement for the degree of Bachelor
AIR-CONDITIONING & MECHANICAL VENTILATION AND LIGHTING RETROFIT THROUGH BUILDING SIMULATION CHEW CHIN ONG UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
 AIR-CONDITIONING & MECHANICAL VENTILATION AND LIGHTING RETROFIT THROUGH BUILDING SIMULATION CHEW CHIN ONG UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA AIR-CONDITIONING & MECHANICAL VENTILATION AND LIGHTING RETROFIT
AIR-CONDITIONING & MECHANICAL VENTILATION AND LIGHTING RETROFIT THROUGH BUILDING SIMULATION CHEW CHIN ONG UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA AIR-CONDITIONING & MECHANICAL VENTILATION AND LIGHTING RETROFIT
MANAGING GREENNESS IN FIRM MARKETING TO ENHANCE BUSINESS PERFORMANCE CHONG KAH JUAN UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
 MANAGING GREENNESS IN FIRM MARKETING TO ENHANCE BUSINESS PERFORMANCE CHONG KAH JUAN UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA SUPERVISOR CONFIRMATION I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my
MANAGING GREENNESS IN FIRM MARKETING TO ENHANCE BUSINESS PERFORMANCE CHONG KAH JUAN UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA SUPERVISOR CONFIRMATION I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my
SUBCRITICAL WATER EXTRACTION WITH COMPACTED NATURAL CALCIUM CARBONATE COLUMN FOR THE EXTRACTION OF NATURAL PRODUCTS
 SUBCRITICAL WATER EXTRACTION WITH COMPACTED NATURAL CALCIUM CARBONATE COLUMN FOR THE EXTRACTION OF NATURAL PRODUCTS YOUSIF JUMAA ABDO ALRAHMAN ADAM UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SUBCRITICAL WATER EXTRACTION
SUBCRITICAL WATER EXTRACTION WITH COMPACTED NATURAL CALCIUM CARBONATE COLUMN FOR THE EXTRACTION OF NATURAL PRODUCTS YOUSIF JUMAA ABDO ALRAHMAN ADAM UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SUBCRITICAL WATER EXTRACTION
FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT MODEL USING COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS NOR AZLIZA BINTI AKBAR
 FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT MODEL USING COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS NOR AZLIZA BINTI AKBAR A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering
FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT MODEL USING COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS NOR AZLIZA BINTI AKBAR A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering
An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process
 An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process Alnouss M. Ahmed, and Al-Nuaimi A. Ibrahim Abstract In this paper, the energy performance of a selected UHDE Ammonia plant is optimized by conducting
An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process Alnouss M. Ahmed, and Al-Nuaimi A. Ibrahim Abstract In this paper, the energy performance of a selected UHDE Ammonia plant is optimized by conducting
IDENTIFICATION OF PUBLIC PLACE ATTRIBUTES USING MEAN-END CHAIN RESEARCH MODEL BENTALHODA FOOLADIVANDA UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
 IDENTIFICATION OF PUBLIC PLACE ATTRIBUTES USING MEAN-END CHAIN RESEARCH MODEL BENTALHODA FOOLADIVANDA UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA Identification of Public Place Attributes Using mean-end Chain Research
IDENTIFICATION OF PUBLIC PLACE ATTRIBUTES USING MEAN-END CHAIN RESEARCH MODEL BENTALHODA FOOLADIVANDA UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA Identification of Public Place Attributes Using mean-end Chain Research
OPTIMIZATION OF EXTRACTION AND SPRAY DRYING PROCESSES OF TONGKAT ALI EXTRACTS USING RESPONSE SURFACE METHODOLOGY
 OPTIMIZATION OF EXTRACTION AND SPRAY DRYING PROCESSES OF TONGKAT ALI EXTRACTS USING RESPONSE SURFACE METHODOLOGY WAN MASTURA BT WAN ZAMRI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA OPTIMIZATION OF EXTRACTION AND SPRAY
OPTIMIZATION OF EXTRACTION AND SPRAY DRYING PROCESSES OF TONGKAT ALI EXTRACTS USING RESPONSE SURFACE METHODOLOGY WAN MASTURA BT WAN ZAMRI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA OPTIMIZATION OF EXTRACTION AND SPRAY
SIMULATION OF NON-POINT SOURCES OF POLLUTION IN A HETEROGENEOUS MEDIA BY USING 2D REGIONAL GROUNDWATER FLOW MODEL HAMID ASGARI
 SIMULATION OF NON-POINT SOURCES OF POLLUTION IN A HETEROGENEOUS MEDIA BY USING 2D REGIONAL GROUNDWATER FLOW MODEL HAMID ASGARI A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the
SIMULATION OF NON-POINT SOURCES OF POLLUTION IN A HETEROGENEOUS MEDIA BY USING 2D REGIONAL GROUNDWATER FLOW MODEL HAMID ASGARI A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the
WIND EFFECTS ON SYMMETRICAL MULTIPLE CORE WALL SYSTEM OF HIGH-RISE BUILDING HAZWANI BINTI SAMSUDIN
 WIND EFFECTS ON SYMMETRICAL MULTIPLE CORE WALL SYSTEM OF HIGH-RISE BUILDING HAZWANI BINTI SAMSUDIN A project report submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of
WIND EFFECTS ON SYMMETRICAL MULTIPLE CORE WALL SYSTEM OF HIGH-RISE BUILDING HAZWANI BINTI SAMSUDIN A project report submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of
pinch 70 C 70 C 4 We want to cool both the hot streams to the pinch temperature. The next step is to find the duty for the two heat exchangers:
 Ene-47.5130 Process Integration (3 ECTS credits) P Espoo 2016 EXERCISE 2 SOLUTIONS 1 MER heat exchanger network First we draw the stream-grid and calculate the enthalpy rate change, Q, above and below
Ene-47.5130 Process Integration (3 ECTS credits) P Espoo 2016 EXERCISE 2 SOLUTIONS 1 MER heat exchanger network First we draw the stream-grid and calculate the enthalpy rate change, Q, above and below
IMPACT OF WORK LIFE BALANCE ON EMPLOYEES LOYALTY, SATISFACTION, AND PRODUCTIVITY KADARKO ESTHER DIZAHO
 i IMPACT OF WORK LIFE BALANCE ON EMPLOYEES LOYALTY, SATISFACTION, AND PRODUCTIVITY KADARKO ESTHER DIZAHO A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree
i IMPACT OF WORK LIFE BALANCE ON EMPLOYEES LOYALTY, SATISFACTION, AND PRODUCTIVITY KADARKO ESTHER DIZAHO A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree
WASTED HEAT RECOVERY SYSTEM: HOW TO GAIN ENERGY ABDUL MUHAIMIN BIN MOHD SHAFIE UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
 WASTED HEAT RECOVERY SYSTEM: HOW TO GAIN ENERGY ABDUL MUHAIMIN BIN MOHD SHAFIE UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA SUPERVISOR DECLARATION I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my opinion
WASTED HEAT RECOVERY SYSTEM: HOW TO GAIN ENERGY ABDUL MUHAIMIN BIN MOHD SHAFIE UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA SUPERVISOR DECLARATION I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my opinion
Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology
 Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology Ritesh Sojitra Srashti Dwivedi ITM University, Gwalior, India Abstract: Energy optimisation and process integration
Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology Ritesh Sojitra Srashti Dwivedi ITM University, Gwalior, India Abstract: Energy optimisation and process integration
ENERGY EFFICIENT RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS ASSESSMENT USING BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING AMIN FAKHKHAR ZADEH
 ENERGY EFFICIENT RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS ASSESSMENT USING BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING AMIN FAKHKHAR ZADEH A project report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree
ENERGY EFFICIENT RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS ASSESSMENT USING BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING AMIN FAKHKHAR ZADEH A project report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree
ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF A 3-CHLOROPROPIONIC ACID (3CP) DEGRADING ASPERGILLUS ACULEATUS STRAIN MBS_179 SALAR KADHUM ALI ZANGANA
 ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF A 3-CHLOROPROPIONIC ACID (3CP) DEGRADING ASPERGILLUS ACULEATUS STRAIN MBS_179 SALAR KADHUM ALI ZANGANA A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF A 3-CHLOROPROPIONIC ACID (3CP) DEGRADING ASPERGILLUS ACULEATUS STRAIN MBS_179 SALAR KADHUM ALI ZANGANA A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
EFFECT OF DRY MACHINING ON TOOL WEAR MADIHAH BINTI ZUBIR
 EFFECT OF DRY MACHINING ON TOOL WEAR MADIHAH BINTI ZUBIR This thesis is submitted as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the bachelor of mechanical engineering with manufacturing
EFFECT OF DRY MACHINING ON TOOL WEAR MADIHAH BINTI ZUBIR This thesis is submitted as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the bachelor of mechanical engineering with manufacturing
AN INTEGRATED STOCHASTIC-FUZZY METHOD FOR SUPPLY CHAIN LEANNESS EVALUATION IN IRANIAN AUTOMOTIVE SMALL AND MEDIUM ENTEPRISES
 AN INTEGRATED STOCHASTIC-FUZZY METHOD FOR SUPPLY CHAIN LEANNESS EVALUATION IN IRANIAN AUTOMOTIVE SMALL AND MEDIUM ENTEPRISES FARZAD BEHROUZI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA AN INTEGRATED STOCHASTIC-FUZZY
AN INTEGRATED STOCHASTIC-FUZZY METHOD FOR SUPPLY CHAIN LEANNESS EVALUATION IN IRANIAN AUTOMOTIVE SMALL AND MEDIUM ENTEPRISES FARZAD BEHROUZI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA AN INTEGRATED STOCHASTIC-FUZZY
TRANSITION OF ENGINE POWERED AIR-CONDITIONING SYSTEM TO THE SOLAR POWERED AIR- CONDITIONING SYSTEM IN A BUS: A FEASIBILITY STUDY
 TRANSITION OF ENGINE POWERED AIR-CONDITIONING SYSTEM TO THE SOLAR POWERED AIR- CONDITIONING SYSTEM IN A BUS: A FEASIBILITY STUDY MUHD ZULPATTAH BIN MOHD YUSOFF This report is submitted to Faculty of Technology
TRANSITION OF ENGINE POWERED AIR-CONDITIONING SYSTEM TO THE SOLAR POWERED AIR- CONDITIONING SYSTEM IN A BUS: A FEASIBILITY STUDY MUHD ZULPATTAH BIN MOHD YUSOFF This report is submitted to Faculty of Technology
BUSINESS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT (BPI) IN AN ENTERPRISE COMPANY NORASIKIN BINTI SALIM. A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the
 BUSINESS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT (BPI) IN AN ENTERPRISE COMPANY NORASIKIN BINTI SALIM A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering
BUSINESS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT (BPI) IN AN ENTERPRISE COMPANY NORASIKIN BINTI SALIM A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG
 1 OPTIMAL DESIGN OF HEAT RECOVERY SYSTEM AZRI BIN MARMOH A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Bachelor (Hons.) of Chemical Engineering MARCH
1 OPTIMAL DESIGN OF HEAT RECOVERY SYSTEM AZRI BIN MARMOH A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Bachelor (Hons.) of Chemical Engineering MARCH
A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR WATER AND ENERGY NETWORKS MOHAMMAD REZA ABBASI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
 A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR WATER AND ENERGY NETWORKS MOHAMMAD REZA ABBASI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA 5 A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR MINIMUM WATER AND ENERGY NETWORKS MOHAMMAD REZA ABBASI A dissertation submitted
A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR WATER AND ENERGY NETWORKS MOHAMMAD REZA ABBASI UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA 5 A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR MINIMUM WATER AND ENERGY NETWORKS MOHAMMAD REZA ABBASI A dissertation submitted
Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration
 Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration Stanislav Boldyryev, Goran Krajačić Department of Energy, Power Engineering and Environment, Faculty of Mechanical
Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration Stanislav Boldyryev, Goran Krajačić Department of Energy, Power Engineering and Environment, Faculty of Mechanical
INVENTORY MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL AT AN IN-FLIGHT CATERING COMPANY NOR LIAWATI BINTI ABU OTHMAN
 INVENTORY MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL AT AN IN-FLIGHT CATERING COMPANY NOR LIAWATI BINTI ABU OTHMAN A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master
INVENTORY MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL AT AN IN-FLIGHT CATERING COMPANY NOR LIAWATI BINTI ABU OTHMAN A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master
POLLUTION INVESTIGATION AND EMISSION INVENTORY FOR RESTAURANT IN MBMB REGION SHARMEEZAM BIN MAT UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
 POLLUTION INVESTIGATION AND EMISSION INVENTORY FOR RESTAURANT IN MBMB REGION SHARMEEZAM BIN MAT UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA SHARMEEZAM BIN MAT BACH. OF MECHANICAL ENG. (PLANT & MAINTENANCE) 2015
POLLUTION INVESTIGATION AND EMISSION INVENTORY FOR RESTAURANT IN MBMB REGION SHARMEEZAM BIN MAT UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA SHARMEEZAM BIN MAT BACH. OF MECHANICAL ENG. (PLANT & MAINTENANCE) 2015
FOREST ENCROACHMENT MAPPING IN CAMERON HIGHLANDS, USING CADASTRAL PARCEL AND REMOTE SENSING DATASETS
 FOREST ENCROACHMENT MAPPING IN CAMERON HIGHLANDS, USING CADASTRAL PARCEL AND REMOTE SENSING DATASETS MOHD HAYYI BIN MAT ZIN UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA FOREST ENCROACHMENT MAPPING IN CAMERON HIGHLANDS,
FOREST ENCROACHMENT MAPPING IN CAMERON HIGHLANDS, USING CADASTRAL PARCEL AND REMOTE SENSING DATASETS MOHD HAYYI BIN MAT ZIN UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA FOREST ENCROACHMENT MAPPING IN CAMERON HIGHLANDS,
PRODUCT DESIGN IMPROVEMENT THROUGH DESIGN FOR MANUFACTURE AND ASSEMBLY (DFMA) AND THEORY OF INVENTIVE PROBLEM SOLVING (TRIZ) AFZAN BINTI ROZALI
 PRODUCT DESIGN IMPROVEMENT THROUGH DESIGN FOR MANUFACTURE AND ASSEMBLY (DFMA) AND THEORY OF INVENTIVE PROBLEM SOLVING (TRIZ) AFZAN BINTI ROZALI A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements
PRODUCT DESIGN IMPROVEMENT THROUGH DESIGN FOR MANUFACTURE AND ASSEMBLY (DFMA) AND THEORY OF INVENTIVE PROBLEM SOLVING (TRIZ) AFZAN BINTI ROZALI A project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements
DEFLECTION MONITORING OF CAST IN-SITU BALANCED CANTILEVER PRESTRESSED CONCRETE BOX GIRDER BRIDGE MOHD KHAIRUL AZMAN BIN HAMBALI
 DEFLECTION MONITORING OF CAST IN-SITU BALANCED CANTILEVER PRESTRESSED CONCRETE BOX GIRDER BRIDGE MOHD KHAIRUL AZMAN BIN HAMBALI A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the
DEFLECTION MONITORING OF CAST IN-SITU BALANCED CANTILEVER PRESTRESSED CONCRETE BOX GIRDER BRIDGE MOHD KHAIRUL AZMAN BIN HAMBALI A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the
MINIMIZING CONFLICTS DURING CONSTRUCTION STAGE BY USING BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING MOHD FAIZ BIN SHAPIAI
 MINIMIZING CONFLICTS DURING CONSTRUCTION STAGE BY USING BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING MOHD FAIZ BIN SHAPIAI A capstone project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of
MINIMIZING CONFLICTS DURING CONSTRUCTION STAGE BY USING BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING MOHD FAIZ BIN SHAPIAI A capstone project report submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of
CARBON EMISSION STRATEGY FOR MALAYSIA (GREEN BUILDING COMMERCIAL) TINA ZAHANI ZAINUDDIN
 CARBON EMISSION STRATEGY FOR MALAYSIA (GREEN BUILDING COMMERCIAL) TINA ZAHANI ZAINUDDIN A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Electrical Engineering in fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the
CARBON EMISSION STRATEGY FOR MALAYSIA (GREEN BUILDING COMMERCIAL) TINA ZAHANI ZAINUDDIN A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Electrical Engineering in fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the
DEVELOPMENT OF BRICK FROM MUD FLOOD: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND MORPHOLOGY CHANGES MUHAMMAD IRFAN BIN SHAHRIN
 DEVELOPMENT OF BRICK FROM MUD FLOOD: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND MORPHOLOGY CHANGES MUHAMMAD IRFAN BIN SHAHRIN A project report submitted in fulfilment ofthe requirements for the award ofthe degree of Master
DEVELOPMENT OF BRICK FROM MUD FLOOD: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND MORPHOLOGY CHANGES MUHAMMAD IRFAN BIN SHAHRIN A project report submitted in fulfilment ofthe requirements for the award ofthe degree of Master
UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA CHANGE DETECTION IN MANGROVE FOREST AREA USING LOCAL MUTUAL INFORMATION
 UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA CHANGE DETECTION IN MANGROVE FOREST AREA USING LOCAL MUTUAL INFORMATION MAHIRAH BINTI JAHARI ITMA 2010 5 CHANGE DETECTION IN MANGROVE FOREST AREA USING LOCAL MUTUAL INFORMATION
UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA CHANGE DETECTION IN MANGROVE FOREST AREA USING LOCAL MUTUAL INFORMATION MAHIRAH BINTI JAHARI ITMA 2010 5 CHANGE DETECTION IN MANGROVE FOREST AREA USING LOCAL MUTUAL INFORMATION
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project. Production of Allyl Chloride
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Allyl Chloride We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 20,000 metric tons/year, allyl chloride
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, Thermodynamics Design Project Production of Allyl Chloride We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 20,000 metric tons/year, allyl chloride
COMBINED EMPIRICAL MODE DECOMPOSITION AND DYNAMIC REGRESSION MODEL FOR FORECASTING ELECTRICITY LOAD DEMAND NURAMIRAH BINTI AKROM
 i COMBINED EMPIRICAL MODE DECOMPOSITION AND DYNAMIC REGRESSION MODEL FOR FORECASTING ELECTRICITY LOAD DEMAND NURAMIRAH BINTI AKROM A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of
i COMBINED EMPIRICAL MODE DECOMPOSITION AND DYNAMIC REGRESSION MODEL FOR FORECASTING ELECTRICITY LOAD DEMAND NURAMIRAH BINTI AKROM A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of
A NOVEL HYBRID GREY-INTERVAL TYPE-2 FUZZY LOGIC SYSTEM : FORECASTING OF CO 2 EMISSIONS
 A NOVEL HYBRID GREY-INTERVAL TYPE-2 FUZZY LOGIC SYSTEM : FORECASTING OF CO 2 EMISSIONS MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA TERENGGANU 2015 A NOVEL HYBRID GREY-INTERVAL TYPE-2 FUZZY LOGIC SYSTEM : FORECASTING
A NOVEL HYBRID GREY-INTERVAL TYPE-2 FUZZY LOGIC SYSTEM : FORECASTING OF CO 2 EMISSIONS MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA TERENGGANU 2015 A NOVEL HYBRID GREY-INTERVAL TYPE-2 FUZZY LOGIC SYSTEM : FORECASTING
Combustion Chamber. Fig Schematic diagram of a simple gas turbine
 Module 06: Integration and placement of equipment Lecture 37: Integration of Gas turbine with process 1 st Part Key word: Gas turbine, Acid dew temperature, after burner, specific work In its non complicated
Module 06: Integration and placement of equipment Lecture 37: Integration of Gas turbine with process 1 st Part Key word: Gas turbine, Acid dew temperature, after burner, specific work In its non complicated
MULTI-OBJECTIVES OPTIMIZATION OF POWER CONSUMPTION OF A BUILDING TOWARDS ENERGY SAVING MHD ISWANDI BIN KATUTU
 MULTI-OBJECTIVES OPTIMIZATION OF POWER CONSUMPTION OF A BUILDING TOWARDS ENERGY SAVING MHD ISWANDI BIN KATUTU A project report submitted in partial fullfilment of the requirements for the award of the
MULTI-OBJECTIVES OPTIMIZATION OF POWER CONSUMPTION OF A BUILDING TOWARDS ENERGY SAVING MHD ISWANDI BIN KATUTU A project report submitted in partial fullfilment of the requirements for the award of the
