THE PROBLEM OF EXTRANEOUS WATER IN SANITARY SEWER SYSTEMS IN POLAND AND FRANCE
|
|
|
- Bruno Franklin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/3/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: THE PROBLEM OF EXTRANEOUS WATER IN SANITARY SEWER SYSTEMS IN POLAND AND FRANCE Grzegorz Kaczor 1, Léo Pujol 2, Błażej Stęplewski 1 1 Uniwersytet Rolniczy im. H. Kołłątaja w Krakowie 2 National Engineering School in Water and Environment of Strasbourg (ENGEES) Abstract The objective of this research was to compare the amount of extraneous water flowing into selected gravitational separate sewer systems which discharge domestic sewage from the settlement of single-family houses in Poland and France during a year with a standard annual amount of precipitation. The study included a total of four sewer systems, including two operating in Poland and discharging the sewage from settlements near Krakow in the Malopolska Province and two systems operating in France and discharging the sewage from settlements of single-family houses near Lorient, Brittany, Morbihan Department. As part of the analysis, an average daily tributaries of extraneous water into sewers under the research, values of addition and share of this water were compared. Analysis of the research results demonstrated that the hydraulic load of sewer systems with extraneous water does not depend on the age of the sewer system, but mainly on the number of house drains, and to a lesser extent its length. It was also determined that the average daily amount of extraneous -1 water flowing into sanitary sewer systems in wet weather is 0,107 m3 d per 1 sewer connection. The study showed that tributaries of extraneous water into the separate sewer system occurring during the intense precipitation are a major operating problem both in Poland and France. Key words: sewage, sewer system, i/i, extraneous water 1661
2 Grzegorz Kaczor, Léo Pujol, Błażej Stęplewski INTRODUCTION The implementation of Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 started general efforts aimed at setting in order the wastewater management in countries of the European Union. 14 billion was allocated for this purpose in the years In the existing EU Member States (EU-15) with the participation of this support good standards of waste treatment were maintained and the situation in terms of the protection of the so-called sensitive water resources was improved. While in new Member States (EU-12), first and foremost, the condition of technical infrastructure used for the disposal and treatment of the sewage was thoroughly improved. In Poland, as part of the National Programme for Municipal Waste Water Treatment ( ), a number of measures was taken, most important of which involved the modernization or construction of 1163 sewage treatment plants for the disposal of municipal waste. The last update of the above mentioned programme carried out in 2015 adopts the construction of 119 new sewage treatment plants, including 91 after 2015 (Krajowy Program Oczyszczania..., 2015). All newly built and modernized sewage treatment plants are prepared for biological removal of biogenic compounds. In France, after the introduction of Directive 91/271/EEC there was observed an increase by 72% of the sewage discharged to mechanical and biological sewage treatment plants in the years Since 2007, 146 major sewage treatment plants in France are included in the government project, within which these facilities began to be adapted to the current requirements. There were difficulties with the implementation of the objectives of Directive 91/271/EEC in France and Poland which is confirmed by the fact that in 2014 still 3260 sewage treatment plants out of a total number of 19,688 did not meet established requirements for their effective operation. In 2009 alone, 2.6 billion was allocated for the development of wastewater management, of which more than 1.9 billion were funds intended for the sewage treatment ( All activities taken in Poland and France in order to protect the quality of surface and ground water should not, however, focus exclusively on the construction of new and modernization of existing systems for sewage disposal and treatment. It is equally essential to keep the appropriate effectiveness and reliability of the operation of sewer systems and sewage treatment plants already existing but not yet economically eligible for the modernization. With regard to the existing sewage treatment plants, one should have in mind maintaining the proper technical condition of all mechanical as well as structural equipment of these facilities and acquiring planned effectiveness of removing individual pollutants. While in the case of existing and operating sewer systems their tightness and required capacity should be maintained. The aspect of tightness is under- 1662
3 The problem of extraneous water in sanitary sewer systems... stood as the protection of sewer channels against tributaries of infiltrating water and possible exfiltration of wastewater from their interior as well as the ongoing elimination of potential sources of extraneous water (Pujol, 2017). Infiltration (French: d infiltration) means tributaries of mainly ground water to the sewer system caused by a damage of pipes, their connections and leaky walls and bottom of the sewage well (Pujol, 2017). Tributaries of infiltrating water to the sewer system occur when pipes are arranged below groundwater table. The intensity of the flow of infiltrating water to sewer channels is directly proportional to the height of water column above the pipe (Madryas and all, 2010). Tributaries of infiltrating water into sewage collectors gain in strength after intense precipitation and are the largest in the early spring and late autumn due to the high position of groundwater table (Błażejewski, 2003). Exfiltration (French: exfiltration) is defined as underground sewage outflow from sanitary sewer systems or sewage wells as a result of damaged or leaky connections of individual elements of the sewer system (Ellis and Bertrand-Krajewski, 2010). Serious problems in the operation of sewer systems, and particularly sewage treatment plants are due to tributaries of extraneous water (De Bénédittis, 2004). Extraneous water (French: eaux parasites / eaux accidentel) is mostly rainwater (rain or snowmelt) penetrating into sanitary systems through manhole covers of sewage wells or illegally introduced into the sewer system by inhabitants through the inclusion of the gutter outlets (Butler and Davis, 2011), yard drains (Kaczor, 2012) or drainage outlets used for drainage of water from the property to house drains (Pecher, 1999). Extraneous water also includes water directed into the sewer system, intentionally or unintentionally, discharged during construction or renovation works, cooling water as well as water penetrating into the sewer system through manhole covers after washing streets or vehicles (Strategien..., 2005). During the operation of sewer systems, extraneous water most often occurs in the course of intense precipitation and causes overflow of channels, overload of sewage pumping stations, periodic flow of the sewage in gravitational channels under pressure conditions or in extreme situations even a flow of the sewage out of sewage wells on the land surface. Extraneous water has the most negative impact on sewage treatment plants. Primarily, it is the cause of hydraulic overloads of technological equipment of sewage treatment plants such as grids, sand separators, primarily and secondary settlement tanks. It also affects negatively the operation of biological reactors causing decreased temperature of the sewage (especially when the snow melts) and reduces the retention time of the sewage in individual chambers or zones of the reactor. Not without significance is also lowering concentrations of pollutants in the sewage by their dilution with rain water, thus their depletion in substances necessary for the growth of microorganisms of the activated sludge (Kaczor et all., 2015). The influence of extraneous water on 1663
4 Grzegorz Kaczor, Léo Pujol, Błażej Stęplewski numerous aspects of the functioning of the sewage treatment plant consequently leads to reduced effectiveness of its operation, and thus is a significant risk for the water quality of the sewage receiver. In recent years, the problem of extraneous water has lost some of its importance both in Poland and France due to the presence of chiefly dry or average years, characterized by a relatively low annual sum of precipitation. The amount of extraneous water flowing into the sewer system during the year is highly correlated with the intensity and frequency of precipitation which in recent years occurs less common, but can be very intense (Kaczor, 2011; Ziernicka-Wojtaszek i Kaczor, 2013). Intense precipitation results in strong, but short-term hydraulic overloads of the sewage treatment plant. In such situation technological facilities of the plant are protected by throttling the flow of the sewage. In the short term, such actions with the appropriate retention of channels can to some extent protect especially small facilities from the maximum flows (Kaczor, 2012). There are performed many activities in Poland and France aimed at eliminating or at least limiting the flow of extraneous water into the sewer system (Monnier, 2006; Cieślak and Pawełek, 2014). The most common are smoke tests, dye tests, water or air tightness tests, thermal performance, soundproof, ultrasonic and geoelectric tests as well as detailed inspections of the channel interiors using modern automatically controlled video cameras. As part of the exchange of experience and knowledge as well as Polish and French research it was undertaken to compare in this paper the amount of extraneous water flowing into sewer systems used for discharging sanitary sewage from the settlement of single-family houses in Poland and France. OBJECTIVE, SCOPE AND METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH The objective of this research was to compare the amount of extraneous water flowing into selected gravitational separate sewer systems which discharge domestic sewage from the settlement of single-family houses in Poland and France during a year with average annual amount of precipitation. In view of the fact that the volume of extraneous water flowing into sanitary sewer systems depends largely on the annual sum of precipitation, it was decided that the comparative analysis will be based only on years characterized by a standard annual sum of precipitation as the most frequently occurring. Humidity of a given year was estimated on the basis of the criterion of Kaczorowska (1962) with mean annual precipitation totals from the years This archival data was used to determine the extent of an annual amount of precipitation at which a given year can be assessed as an average wet one. In case of Krakow, a year is considered as an average when the annual amount of precipitation is between % of the mean annual precipitation from the years
5 The problem of extraneous water in sanitary sewer systems... amounting to 662 mm, that is in the range from 596 to 728 mm. Research of the overload of sewage systems with extraneous water was carried out in Krakow from 2000 to During this period, a year average humidity whose total annual precipitation is from 90 to 110% of the average mean annual precipitation occurred 7 times, which is at a frequency of every 2.3 year. An average annual precipitation for France has been obtained from online database ( For the region of Lorient analyzed in the following paper this value is 951 mm. Therefore, for the analyzed area of France the year in terms of precipitation can be considered as an average if its total annual precipitation is in the range from 856 to 1046 mm. The annual volume of extraneous water was determined based on the difference of domestic sewage outflow from sewer systems under the research during dry and wet weather.. A daily sewage outflow was classified to dry weather if in that day and five previous days there was no precipitation or it occurred, but its daily amount did not exceed 1 mm. The average daily outflow of the sewage from the sewer system during dry weather was used to determine the average amount of the proper sewage (not including extraneous water). Due to the fact that in dry weather the daily outflows of the sewage were subject to cyclical weekly fluctuations, it was assumed that the maximum daily outflow of the sewage during this period is equal to the average value increased using standard deviation. A value calculated by means of this method represented the limit above which the sewage outflow contained only extraneous water. Such calculations were carried out separately for each of 4 facilities under research. In comparative analyses the amount of extraneous water flowing into the sewer system is expressed most often using two indicators represented in percentage value: extraneous water share and extraneous water addition (Pecher, 1999). Extraneous water share (SEW) in the daily inflow to the sewer system can be computed using the following formula: where: Q dew daily inflow of extraneous water to the sewer system [m 3 d -1 ], Q d total daily inflow of the sewage and extraneous water to the sewer system [m 3 d -1 ]. Extraneous water addition (DWP) to the daily inflow to the sewer system is calculated using the following formula: (1) (2) 1665
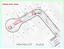
6 Grzegorz Kaczor, Léo Pujol, Błażej Stęplewski where: Q ds daily inflow of the sewage to the sewer system in dry weather [m 3 d -1 ]. SEW and AEW parameters are used as standard to compare the overload with extraneous water of various sewer systems. DESCRIPTION OF SUBJECT OF RESEARCH The research included separate sewer systems made of the same material and discharging domestic sewage from the settlement of single-family houses. There were difficulties in finding facilities operating for a similar period of time as well as serving a similar number of inhabitants. However, bearing in mind that extraneous water is not directly associated with the age of the sewer system, but mainly its length and a number of house drains, two sewer systems operating in Poland and discharging the sewage from settlements near Krakow in the Malopolska Province and two systems operating in France and discharging the sewage from settlements of single-family houses near Lorient, Brittany, Morbihan Department were ultimately chosen for the research (fig. 1). Figure 1. Location of sewer systems under the study in France and Poland General characteristics of sewer systems analysed comparatively are presented in Table 1. The longest of the analysed sewer systems is the one in Keryado (France), while the shortest is in Bielany (Poland). Sewer systems included in the study are operated for 17 years (Wadów) up to 47 years (Keryado and Boisdu-Château). The greatest number of houses is operated by the sewer system in 1666
7 The problem of extraneous water in sanitary sewer systems... Keryado (3 309), while the smallest number in Bielany (330). Sewer systems in French were characterized by the greatest daily flow of the sewage in dry weather ranging from 1175 m 3 d -1 in Keryado to 1138 m 3 d -1 in Bois-du-Château. In Polish sewer systems included in the analysis a daily flow of the sewage in dry weather ranged from 182 m 3 d -1 in Bielany up to 469 m 3 d -1 in Wadów. All sewer systems under the research are made of stoneware. Table 1. General characteristics of sewer systems under the study in France and Poland Parameter Location Keryado Bois-du-Château (near Lorient) (near Lorient) Wadów (near Krakow) Bielany (near Krakow) Length [km] Material [ ] Stoneware Stoneware Stoneware Stoneware Exploitation time [years] Number of houses [ ] Number of inhabitants [ ] Average flow in dry weather [m 3 d -1 ] RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Analysis of the results was based on data covering daily outflow of the sewage from individual sewer systems and precipitation data. The first stage of the research involved periods of dry weather, including information on daily amount of precipitation. Then, the average daily flow of the proper sewage (not including extraneous water) was calculated for these periods. Subsequently, on the basis of the calculation procedure described in the methodology of the research the daily outflows of the proper sewage and extraneous water were determined for each facility under the research. Exemplary result of the calculation for the sewer system in Wadów (Poland) is presented in Fig. 2. Black colour indicates a daily inflows of extraneous water to the sewer system, while white colour shows a daily inflows of domestic sewage. Detailed results of the calculation of the average daily outflows of the sewage, extraneous water and their share and addition in daily flows for the year with the average annual amount of precipitation are presented in the Table 2. Relevant in the context of this analysis values of share (SEW) and addition (AEW) of extraneous water turned out to be very similar for all facilities under the study. The greatest amount of extraneous water during the year with a standard annual sum of precipitation reached the sewer system in Keryado (annually 21.5% of 1667
8 Grzegorz Kaczor, Léo Pujol, Błażej Stęplewski the outflow from this sewer was extraneous water). Whereas the smallest amount of extraneous water during (annually 15.7% of the outflow from this sewer was extraneous water) in the year with the average amount of precipitation reached the sewer system in Wadów. While calculated and presented in Table 2 values of addition of extraneous water indicate the percentage increase of the sewage outflow from a given sewer system during wet weather in relation to the sewage outflow from this sewer during dry weather. Achieved results show that it increased in Keryado by 27.5% in relation to the flow in dry weather, while in Wadów only by 17.5%. Figure 2. Proper sewage and extraneous water in the daily outflow from the sewer system in Wadów in 2014 To sum up this part of the analysis, it can be stated that all four tested sewer systems are in a similar degree loaded with extraneous water during intense precipitation. There is also a visible and strong correlation which indicates that the amount of extraneous water increases with the length of the sewer system (correlation coefficient R = 0.71) and the number of house drains (correlation coefficient R = 0.99). Having in mind achieved correlation dependence it was attempted to determine indicative unit values such as the amount of extraneous water in relation to 1 km of the sewer system and the amount of extraneous water in relation to 1 sewer connection. Calculation results are presented in Table 3. Results summarized in Table 3 clearly indicate that the amount of extraneous water flowing into sewer systems under the research depends primarily on the number of connections to buildings, and to a lesser extent on the length of the sewer system. It can be assumed based on these dependencies that the main 1668
9 The problem of extraneous water in sanitary sewer systems... source of extraneous water in all examined sewer systems are illegal connections to house drains of gutter outlets. This is confirmed by video inspections of sewer systems performed in France, Poland as well as other countries (Pecher, 1999; Butler and Davis, 2011; Kaczor, 2012; Pujol, 2017). Table 2. Characteristics of the sewage outflow from sewer systems included in the research along with addition and share of extraneous water in the year with the average amount of precipitation Parameter Average daily outflow of the sewage and extraneous water from the sewer system [m 3 d -1 ] Average daily outflow of the proper sewage from the sewer system [m 3 d -1 ] Average daily outflow of extraneous water from the sewer system [m 3 d -1 ] Value of individual parameters for analysed sewer systems Keryado Bois-du-Château Wadów Bielany SEW [%] 21,5 19,2 15,7 16,4 AEW [%] 27,5 23,7 17,5 19,4 Table 3. Indicative unit values to describe the load of individual systems with extraneous water Parameter Average daily outflow of extraneous water from the sewer system in relation to 1 km length of the system [m 3 d -1 km -1 ] Average daily outflow of extraneous water from the sewer system in relation to 1 sewer connection [m 3 d -1 ] Value of individual parameters for analysed sewer systems Keryado Bois-du-Château Wadów Bielany Average value 9,0 15,9 3,7 3,6 8,05 0,100 0,108 0,112 0,109 0,107 Whereas, nearly constant unit value of the tributary of extraneous water in relation to one sewer connection is a surprising fact. The average value for four analysed sewer systems is 0,107 m 3 d -1 per 1 sewer connection with a standard deviation of only 0,0051 m 3 d -1. The analysis presented in this paper is based 1669
10 Grzegorz Kaczor, Léo Pujol, Błażej Stęplewski on a small sample, but the results achieved provide the basis to continue the research with correspondingly reliable number of facilities. CONCLUSIONS 1. Based on review of the literature and performed tests and analyses, it was concluded that tributaries of extraneous water into separate sewer systems occurring during the intense precipitation are a major operating problem both in Poland and France. 2. Hydraulic load of sewer systems with extraneous water does not depend on the age of the sewer system, but mainly on the number of connections. This may indicate that the main source of extraneous water in Poland and France are illegal connections of roof gutters to sanitary drains. 3. The average amount of extraneous water flowing into the sanitary system during wet weather is 0,107 m 3 d -1 with a standard deviation of 0,0051 m 3 d -1 in relation to one house drain (sewer connection). 4. All activities taken in Poland and France in order to protect the quality of surface and ground water should not, however, focus exclusively on the construction of new and modernization of existing systems for sewage disposal and treatment. It is equally essential to keep the appropriate effectiveness and reliability of the operation of sewer systems and sewage treatment plants already existing but not yet economically eligible for the modernization. REFERENCES Błażejewski R. (2003). Kanalizacja wsi. PZITS Oddział Wielkopolski. Butler D., Davies J.W. (2011). Urban Drainage. 3rd Edition. Spon Press an imprint of Taylor & Francis, London and New York. Cieślak O., Pawełek J. (2014). Dopływ wód obcych do kanalizacji sanitarnej na przykładzie gminy Mézos we Francji. Instal, Z. 7-8, De Bénédittis J. (2004). Mesurage de l infiltration et de l exfiltration dans les réseaux d assainissement. Le grade de docteur. INSA de Lyon, Villeurbanne, France. Ellis J.B., Bertrand-Krajewski J.L. (2010). Assessing Infiltration and Exfiltration on the Performance of Urban Sewer Systems. IWA Publishing. Kaczor G. (2011). The Effect of heavy precipitation on the infiltration and inflow into small sewage treatment plants in Infrastruktura i Ekologia Terenów Wiejskich, English Edition. PAN Oddział w Krakowie, Kraków,
11 The problem of extraneous water in sanitary sewer systems... Kaczor G. (2012). Wpływ wód infiltracyjnych i przypadkowych na funkcjonowanie małych systemów kanalizacyjnych. Zeszyty Naukowe Uniwersytetu Rolniczego w Krakowie, zeszyt nr 495, rozprawy, nr 372, ss Kaczor G., Bergel T., Bugajski P. (2015). Impact of extraneous waters on the proportion of sewage pollution indices regarding its biological treatment. Infrastruktura i Ekologia Terenów Wiejskich, No. IV/3/2015, PAN Oddział w Krakowie, Kraków, Kaczorowska Z. (1962). Opady w Polsce w przekroju wieloletnim. Polska Akademia Nauk, Instytut Geografii, Prace Geograficzne nr 33, Warszawa, 112. Krajowy Program Oczyszczania Ścieków Komunalnych z aktualizacjami ( ). (dostęp: ). Madryas C., Przybyła B., Wysocki L. (2010). Badania i ocena stanu technicznego przewodów kanalizacyjnych. Dolnośląskie Wydawnictwo Edukacyjne, Wrocław. Monnier H. (2006). Diagnostic permanent en réseau d assainissement: mesures et calculs sur sites pilotes de la Région Ouest. ENGEES. Pecher R. (1999). Wody przypadkowe w sieci kanalizacyjnej-problem gospodarki wodnej. Gaz, Woda i Technika Sanitarna, SIGMA-NOT Sp. z o. o., nr 12/1999, 1 6. Pujol L. (2017). Evaluation de l influence des eaux de pluie et d infiltration sur les coûts d exploitation de petites stations d épuration. Rapport de Stage Pratique de l Ingénierie. National Engineering School in Water and Environment of Strasbourg (ENGEES), ss. 34. Strategien zur effizienten Fremdwassererkennung und Schadensbehebung in Abwasserkanälen Handlungsanleitung für eine effektive Eigenkontrolle. (2005). Ministerium für Landwirtschaft, Naturschutz und Umwelt. Freistaat Thüringen. www. thueringen.de (dostęp: ). (dostęp: ) ). Ziernicka-Wojtaszek A., Kaczor G. (2013). Wysokość i natężenie opadów atmosferycznych podczas powodzi w okresie maj-czerwiec Acta Scientiarum Polonorum, Formatio Circumiectus, 12 (2). Wydawnictwo UR w Krakowie,
12 Grzegorz Kaczor, Léo Pujol, Błażej Stęplewski dr hab. ing. Grzegorz Kaczor, mail: mgr ing. Błażej Stęplewski mail: Uniwersytet Rolniczy w Krakowie Katedra Inżynierii Sanitarnej i Gospodarki Wodnej Kraków, al. Mickiewicza 24/28 tel ing. Léo Pujol, mail: lpujol@engees.eu National Engineering School in Water and Environment of Strasbourg (ENGEES) 1 quai Koch BP Strasbourg Cedex, FRANCE Received: Accepted:
THE EFFECT OF HEAVY PRECIPITATION ON THE INFILTRATION AND INFLOW INTO SMALL SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANTS IN 2010
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr 12/2011, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddzia w Krakowie, s. 69 77 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi Commission of
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr 12/2011, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddzia w Krakowie, s. 69 77 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi Commission of
Influence of extraneous waters on the quality and loads of pollutants in wastewater discharged into the treatment plant
 DOI: 10.1515/jwld-2017-0021 Polish Academy of Sciences (PAN), Committee on Agronomic Sciences JOURNAL OF WATER AND LAND DEVELOPMENT Section of Land Reclamation and Environmental Engineering in Agriculture,
DOI: 10.1515/jwld-2017-0021 Polish Academy of Sciences (PAN), Committee on Agronomic Sciences JOURNAL OF WATER AND LAND DEVELOPMENT Section of Land Reclamation and Environmental Engineering in Agriculture,
THE EFFICIENCY OF POLLUTANT ELIMINATION IN THE DOBRA TREATMENT PLANT
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr III/1/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 737 747 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2016.3.1.054
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr III/1/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 737 747 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2016.3.1.054
Environment Protection Engineering EVALUATION OF A BIOCOMPACT SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT OPERATING UNDER LOW HYDRAULIC LOADING CONDITIONS
 Environment Protection Engineering Vol. 34 2008 No. 3 GRZEGORZ KACZOR*, PIOTR BUGAJSKI* EVALUATION OF A BIOCOMPACT SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT OPERATING UNDER LOW HYDRAULIC LOADING CONDITIONS The aim of the
Environment Protection Engineering Vol. 34 2008 No. 3 GRZEGORZ KACZOR*, PIOTR BUGAJSKI* EVALUATION OF A BIOCOMPACT SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT OPERATING UNDER LOW HYDRAULIC LOADING CONDITIONS The aim of the
T. Bergel, P. Bugajski, J. Pawełek. Geomatics, Landmanagement and Landscape No , 15 24
 T. Bergel, P. Bugajski, J. Pawełek GLL http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/gll/2013.2.15 Geomatics, Landmanagement and Landscape No. 2 2013, 15 24 Water supply network expansion in the commune of Mściwojów as relates
T. Bergel, P. Bugajski, J. Pawełek GLL http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/gll/2013.2.15 Geomatics, Landmanagement and Landscape No. 2 2013, 15 24 Water supply network expansion in the commune of Mściwojów as relates
EVALUATION OF WASTEWATER TREATMENT EFFICIENCY IN WOLBROM
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/4/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 1889 1897 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2016.4.4.142
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/4/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 1889 1897 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2016.4.4.142
Infiltration in sewer systems: comparison of measurement methods
 Infiltration in sewer systems: comparison of measurement methods J. De Bénédittis *, J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski * *URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, 34 avenue des Arts, 69621 Villeurbanne cedex, France
Infiltration in sewer systems: comparison of measurement methods J. De Bénédittis *, J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski * *URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, 34 avenue des Arts, 69621 Villeurbanne cedex, France
Transfer reservoir as a new solution for transfer of stormwater to water receivers
 Transfer reservoir as a new solution for transfer of stormwater to water receivers Robert Malmur 1,* 1 Institute of Environmental Engineering, ul. Brzeźnicka 60a, 42-200 zęstochowa, Poland Abstract. With
Transfer reservoir as a new solution for transfer of stormwater to water receivers Robert Malmur 1,* 1 Institute of Environmental Engineering, ul. Brzeźnicka 60a, 42-200 zęstochowa, Poland Abstract. With
APPENDIX 14. Inflow and Infiltration in the CRD
 APPENDIX 14 Inflow and Infiltration in the CRD As documented in the CRD-published discussion paper Cost versus Benefit of Reducing Inflow and Infiltration inflow and infiltration refers to rainwater and
APPENDIX 14 Inflow and Infiltration in the CRD As documented in the CRD-published discussion paper Cost versus Benefit of Reducing Inflow and Infiltration inflow and infiltration refers to rainwater and
THE ENERGY COST VERSUS ENERGY ABSORPTION OF SINGLE FAMILY HOUSES A CASE STUDY OF CITY OF JASŁO
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/3/2015, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 1377 1385 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2015.4.3.099
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/3/2015, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 1377 1385 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2015.4.3.099
COMPOSITIONAL ANALYSIS OF THE SEWAGE INCOMING TO AND DISCHARGED FROM THE SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT IN KOLBUSZOWA DOLNA
 Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 17, Issue 5, Nov. 2016, pages 9 16 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/64446 Research Article COMPOSITIONAL ANALYSIS OF THE SEWAGE INCOMING TO AND DISCHARGED FROM THE SEWAGE
Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 17, Issue 5, Nov. 2016, pages 9 16 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/64446 Research Article COMPOSITIONAL ANALYSIS OF THE SEWAGE INCOMING TO AND DISCHARGED FROM THE SEWAGE
Verification of the combined sewage system simulation model based on the example of the city of Głogów
 Verification of the combined sewage system simulation model based on the example of the city of Głogów Ireneusz Nowogoński 1,*, and Ewa Ogiołda 1 1 University of Zielona Góra, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Verification of the combined sewage system simulation model based on the example of the city of Głogów Ireneusz Nowogoński 1,*, and Ewa Ogiołda 1 1 University of Zielona Góra, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Estimating groundwater infiltration into sewerages by using the moving minimum method a survey in Austria
 Estimating groundwater infiltration into sewerages by using the moving minimum method a survey in Austria Th. Ertl 1 *, G. Spatzierer², St. Wildt³ 1 University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences
Estimating groundwater infiltration into sewerages by using the moving minimum method a survey in Austria Th. Ertl 1 *, G. Spatzierer², St. Wildt³ 1 University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences
CE 370. Wastewater Characteristics. Quantity. The design of a wastewater treatment plant requires knowledge of: Quantity or flowrate of wastewater.
 CE 370 Wastewater Characteristics Quantity 1 Introduction The design of a wastewater treatment plant requires knowledge of: Quantity or flowrate of wastewater. Required to determine the size of the various
CE 370 Wastewater Characteristics Quantity 1 Introduction The design of a wastewater treatment plant requires knowledge of: Quantity or flowrate of wastewater. Required to determine the size of the various
DEVELOPMENT OF TECHNICAL INFRASTRUCTURE IN RURAL AREAS OF POLAND IN THE YEARS
 Development of technical infrastructure... INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr 1/4/2012, POKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 93 101 Komisja Technicznej
Development of technical infrastructure... INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr 1/4/2012, POKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 93 101 Komisja Technicznej
ANALYSIS OF EXISTING CONCRETE TILES ROOFING IN AGRICULTURAL HOLDINGS ON A SELECTED EXAMPLE
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr II/2/2015, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 385 392 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2015.2.2.031
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr II/2/2015, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 385 392 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2015.2.2.031
NEW TECHNOLOGIES OF SMALL DOMESTIC SEWAGE VOLUME TREATMENT APPLIED IN POLAND
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND EKOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr 3/2007, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 69 78 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi New technologies
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND EKOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr 3/2007, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 69 78 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi New technologies
HSA SEWER PROJECT FAQs
 HSA SEWER PROJECT FAQs Q1: Why do some residents in the Phase II project area have only 45 days to comply with the HSA water tightness regulations? A1: Some homeowners in the Phase II project area are
HSA SEWER PROJECT FAQs Q1: Why do some residents in the Phase II project area have only 45 days to comply with the HSA water tightness regulations? A1: Some homeowners in the Phase II project area are
THE GROUNDWATER LEVEL CHANGES CAUSED BY MODERNIZATION OF WATER DEVICES IN THE POMORZE FOREST DISTRICT
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr III/1/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 715 723 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2016.3.1.052
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr III/1/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 715 723 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2016.3.1.052
ONTARIO CENTRE FOR MUNICIPAL BEST PRACTICES 200 University Ave., Suite 801, Toronto, Ontario, M5H 3C6. BEST PRACTICE SUMMARY REPORT February, 2008
 ONTARIO CENTRE FOR MUNICIPAL BEST PRACTICES 200 University Ave., Suite 801, Toronto, Ontario, M5H 3C6 BEST PRACTICE SUMMARY REPORT February, 2008 Water and Wastewater PROJECT APPROACH The focus of the
ONTARIO CENTRE FOR MUNICIPAL BEST PRACTICES 200 University Ave., Suite 801, Toronto, Ontario, M5H 3C6 BEST PRACTICE SUMMARY REPORT February, 2008 Water and Wastewater PROJECT APPROACH The focus of the
Dynamics of the Surface Water Circulation between a River and Fishponds in a Sub-Mountain Area
 Dynamics of the Surface Water Circulation between a River and Fishponds in a Sub-Mountain Area Maria Anna Szumiec, Danuta Augustyn Polish Academy of Sciences Institute of Ichthyobiology and Aquaculture,
Dynamics of the Surface Water Circulation between a River and Fishponds in a Sub-Mountain Area Maria Anna Szumiec, Danuta Augustyn Polish Academy of Sciences Institute of Ichthyobiology and Aquaculture,
CHAPTER 4 SYSTEM DESIGN CRITERIA
 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 4 SYSTEM DESIGN CRITERIA Adequate design of the District s wastewater conveyance facilities requires the determination of the quantity of wastewater from contributing sources. The
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 4 SYSTEM DESIGN CRITERIA Adequate design of the District s wastewater conveyance facilities requires the determination of the quantity of wastewater from contributing sources. The
IMPACT OF TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE ON TRANSPORT ACCESSIBILITY OF FARMS
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr III/1/2017, POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES, Cracow Branch, pp. 1053 1060 Commission of Technical Rural Infrastructure
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr III/1/2017, POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES, Cracow Branch, pp. 1053 1060 Commission of Technical Rural Infrastructure
SEASONAL CHANGES IN NITROGEN, PHOSPHORUS, BOD AND COD REMOVAL IN BYSTRE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT
 Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 18, Issue 4, July 2017, pages 185 191 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/74361 Research Article SEASONAL CHANGES IN NITROGEN, PHOSPHORUS, BOD AND COD REMOVAL IN BYSTRE WASTEWATER
Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 18, Issue 4, July 2017, pages 185 191 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/74361 Research Article SEASONAL CHANGES IN NITROGEN, PHOSPHORUS, BOD AND COD REMOVAL IN BYSTRE WASTEWATER
NIAGARA REGION. Pollution Prevention Control Plan for the Town of Niagara-On-The-Lake Wastewater Collection System
 Welcome to the NIAGARA REGION Pollution Prevention Control Plan for the Town of Niagara-On-The-Lake Wastewater Collection System MUNICIPAL CLASS ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT Public Information Centre Please
Welcome to the NIAGARA REGION Pollution Prevention Control Plan for the Town of Niagara-On-The-Lake Wastewater Collection System MUNICIPAL CLASS ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT Public Information Centre Please
Fractionation of Infiltration and Inflow (I/I) components in urban sewer systems with regression analysis
 Fractionation of Infiltration and Inflow (I/I) components in urban sewer systems with regression analysis Détermination de l'origine de l'infiltration et des apports dans un système d'assainissement urbain
Fractionation of Infiltration and Inflow (I/I) components in urban sewer systems with regression analysis Détermination de l'origine de l'infiltration et des apports dans un système d'assainissement urbain
WASTEWATER DEPARTMENT CITY OF MANNHEIM
 WASTEWATER DEPARTMENT CITY OF MANNHEIM TABLE OF CONTENTS Key dates Locations und employees Organisation Distribution of staff Wastewater charges and expenses Expense distribution Sewage disposal Sewerage
WASTEWATER DEPARTMENT CITY OF MANNHEIM TABLE OF CONTENTS Key dates Locations und employees Organisation Distribution of staff Wastewater charges and expenses Expense distribution Sewage disposal Sewerage
Water supply components
 Water supply components Water sources structures (Dams, wells, reservoirs) Surface water Groundewater Pipelines from source Water treatment plant components Pumping stations Storage (elevated tanks) Distribution
Water supply components Water sources structures (Dams, wells, reservoirs) Surface water Groundewater Pipelines from source Water treatment plant components Pumping stations Storage (elevated tanks) Distribution
Original Research Aspects of Sewage Disposal from Tourist Facilities in National Parks and Other Protected Areas
 Pol. J. Environ. Stud. Vol. 24, No. 1 (215), 17-114 DOI: 1.15244/pjoes/28355 Original Research Aspects of Sewage Disposal from Tourist Facilities in National Parks and Other Protected Areas Grzegorz Kaczor
Pol. J. Environ. Stud. Vol. 24, No. 1 (215), 17-114 DOI: 1.15244/pjoes/28355 Original Research Aspects of Sewage Disposal from Tourist Facilities in National Parks and Other Protected Areas Grzegorz Kaczor
Lynn Township Sewer Authority. Corrective Action Plan. March 2007
 Lynn Township Sewer Authority Corrective Action Plan March 2007 4130.00 Prepared By: ARRO Consulting, Inc. 400 Washington Street, Suite 602 Reading, Pennsylvania 19610 610 374 5285 Corrective Action Plan
Lynn Township Sewer Authority Corrective Action Plan March 2007 4130.00 Prepared By: ARRO Consulting, Inc. 400 Washington Street, Suite 602 Reading, Pennsylvania 19610 610 374 5285 Corrective Action Plan
City of Grosse Pointe Park Sanitary Sewer System Inflow and Infiltration Investigation Smoke Testing
 City of Grosse Pointe Park Sanitary Sewer System Inflow and Infiltration Investigation Smoke Testing August 2017 Definitions Sanitary Sewer System Sanitary sewer pipes and pump stations that collect wastewater
City of Grosse Pointe Park Sanitary Sewer System Inflow and Infiltration Investigation Smoke Testing August 2017 Definitions Sanitary Sewer System Sanitary sewer pipes and pump stations that collect wastewater
CHAPTER 12: SANITARY SEWER SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 12: SANITARY SEWER SYSTEM Chapter 12 includes the following information: 1. System Overview 2. On Site Sewage Treatment 3. Inter Community Services 4. Future Demand Forecast 5. Infiltration and
CHAPTER 12: SANITARY SEWER SYSTEM Chapter 12 includes the following information: 1. System Overview 2. On Site Sewage Treatment 3. Inter Community Services 4. Future Demand Forecast 5. Infiltration and
CHAPTER 12: SANITARY SEWER SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 12: SANITARY SEWER SYSTEM Chapter 12 includes the following information: 1. System Overview 2. On-Site Sewage Treatment 3. Inter-Community Services 4. Future Demand Forecast 5. Infiltration and
CHAPTER 12: SANITARY SEWER SYSTEM Chapter 12 includes the following information: 1. System Overview 2. On-Site Sewage Treatment 3. Inter-Community Services 4. Future Demand Forecast 5. Infiltration and
Risk management of urban rain events in a coastal city. The case of Marseille
 Risk management of urban rain events in a coastal city The case of Marseille Jean Claude GONDART General Secretary of the municipality of Marseille Dominique LAPLACE Manager engineering department SERAM
Risk management of urban rain events in a coastal city The case of Marseille Jean Claude GONDART General Secretary of the municipality of Marseille Dominique LAPLACE Manager engineering department SERAM
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 TECHNICAL REPORT RAPPORT TECHNIQUE TECHNISCHER BERICHT CEN/TR 12566-2 June 2005 ICS 13.060.30 English version Small wastewater treatment systems for up to 50 PT - Part 2: Soil infiltration systems Petites
TECHNICAL REPORT RAPPORT TECHNIQUE TECHNISCHER BERICHT CEN/TR 12566-2 June 2005 ICS 13.060.30 English version Small wastewater treatment systems for up to 50 PT - Part 2: Soil infiltration systems Petites
Sanitary Sewer Design. Sanitary Sewers, Page 1
 Sanitary Sewer Design Sanitary Sewers, Page 1 Sanitary Sewers, Page 2 Sanitary Sewer Design sanitary sewers collect and transport domestic and industrial wastes via gravity flow the ultimate destination
Sanitary Sewer Design Sanitary Sewers, Page 1 Sanitary Sewers, Page 2 Sanitary Sewer Design sanitary sewers collect and transport domestic and industrial wastes via gravity flow the ultimate destination
SANITARY SEWER BACKUP
 SANITARY SEWER BACKUP Causes & Prevention A. PURPOSE The purpose of this publication is twofold: 1. It provides homeowners with basic information on the causes of sanitary sewer backups. 2. It provides
SANITARY SEWER BACKUP Causes & Prevention A. PURPOSE The purpose of this publication is twofold: 1. It provides homeowners with basic information on the causes of sanitary sewer backups. 2. It provides
Environment Protection Engineering THE PHENOMENON OF SIMULTANEOUS WORK OF PUMPS IN A PRESSURISED SEWERAGE SYSTEM
 Environment Protection Engineering Vol. 34 2008 No. 3 TOMASZ SIONKOWSKI*, RYSZARD ŚLIZOWSKI** THE PHENOMENON OF SIMULTANEOUS WORK OF PUMPS IN A PRESSURISED SEWERAGE SYSTEM The occurrence of simultaneous
Environment Protection Engineering Vol. 34 2008 No. 3 TOMASZ SIONKOWSKI*, RYSZARD ŚLIZOWSKI** THE PHENOMENON OF SIMULTANEOUS WORK OF PUMPS IN A PRESSURISED SEWERAGE SYSTEM The occurrence of simultaneous
Rainwater management for urban drainage, groundwater recharge and storage
 Rainwater management for urban drainage, groundwater recharge and storage M. Jekel Technical University of Berlin Dept. of Water Quality Control H. Sieker Ingenieurgesellschaft Prof. Sieker (IPS), Berlin,
Rainwater management for urban drainage, groundwater recharge and storage M. Jekel Technical University of Berlin Dept. of Water Quality Control H. Sieker Ingenieurgesellschaft Prof. Sieker (IPS), Berlin,
6.1 Introduction to Wastewater Issues
 Section 6: Water Pollution This Section will help you: Understand if you generate industrial wastewater; Understand where your wastewater goes; Make sure you meet requirements for floor drains; Properly
Section 6: Water Pollution This Section will help you: Understand if you generate industrial wastewater; Understand where your wastewater goes; Make sure you meet requirements for floor drains; Properly
RECOMMENDATION PREVIOUS REPORTS PERTINENT TO THIS MATTER STRATEGIC PLAN
 TO: FROM: SUBJECT: CHAIR AND MEMBERS CIVIC WORKS COMMITTEE MEETING ON NOVEMBER 21, 2017 KELLY SCHERR, P.ENG., MBA, FEC MANAGING DIRECTOR, ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES & CITY ENGINEER WASTEWATER
TO: FROM: SUBJECT: CHAIR AND MEMBERS CIVIC WORKS COMMITTEE MEETING ON NOVEMBER 21, 2017 KELLY SCHERR, P.ENG., MBA, FEC MANAGING DIRECTOR, ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES & CITY ENGINEER WASTEWATER
ENERGY INTENSITY OF GDP IN THE LIGHT OF ENERGY POLICY OBJECTIVES IN POLAND UNTIL 2030
 ENERGY INTENSITY OF GDP IN THE LIGHT OF ENERGY POLICY OBJECTIVES IN POLAND UNTIL 2030 Krzysztof Adam Firlej Cracow University of Economics chriskrk2@yahoo.pl Keywords: energy intensity of GDP, Poland's
ENERGY INTENSITY OF GDP IN THE LIGHT OF ENERGY POLICY OBJECTIVES IN POLAND UNTIL 2030 Krzysztof Adam Firlej Cracow University of Economics chriskrk2@yahoo.pl Keywords: energy intensity of GDP, Poland's
Effects of precipitation on the amount and quality of raw sewage entering a sewage treatment plant in Wodzisław Śląski
 DOI: 10.1515/jwld-2017-0041 Polish Academy of Sciences (PAN), Committee on Agronomic Sciences JOURNAL OF WATER AND LAND DEVELOPMENT Section of Land Reclamation and Environmental Engineering in Agriculture,
DOI: 10.1515/jwld-2017-0041 Polish Academy of Sciences (PAN), Committee on Agronomic Sciences JOURNAL OF WATER AND LAND DEVELOPMENT Section of Land Reclamation and Environmental Engineering in Agriculture,
A simplified dimensioning method for highefficiency
 A simplified dimensioning method for highefficiency retention tanks Kamil Pochwat 1,* Kristijan Iličić 2, 1 Rzeszow University of Technology, Department of Infrastructure and Water Management, al. Powstańców
A simplified dimensioning method for highefficiency retention tanks Kamil Pochwat 1,* Kristijan Iličić 2, 1 Rzeszow University of Technology, Department of Infrastructure and Water Management, al. Powstańców
Rainfall Event of September 29, Public Works & Environmental Services
 Rainfall Event of September 29, 2016 Rainfall Recorded on Revland Street Rain Gauge 220 mm of rain in 24 hours between 6:00 pm September 28 th and 6:00 am September 29 th 195 mm of rain in 12 hours between
Rainfall Event of September 29, 2016 Rainfall Recorded on Revland Street Rain Gauge 220 mm of rain in 24 hours between 6:00 pm September 28 th and 6:00 am September 29 th 195 mm of rain in 12 hours between
Construction of first wastewater treatment plant in Kosovo: an EU pilot project
 Water Utility Journal 14: 41-46, 2016. 2016 E.W. Publications Construction of first wastewater treatment plant in Kosovo: an EU pilot project B.Sh. Kajtazi European Union Office in Kosovo, Kosovo Street
Water Utility Journal 14: 41-46, 2016. 2016 E.W. Publications Construction of first wastewater treatment plant in Kosovo: an EU pilot project B.Sh. Kajtazi European Union Office in Kosovo, Kosovo Street
GERMAN ATV-DVWK RULES AND STANDARDS. STANDARD ATV-DVWK-A 157E Sewer System Structures
 GERMAN ATV-DVWK RULES AND STANDARDS STANDARD ATV-DVWK-A 157E Sewer System Structures GERMAN ATV-DVWK RULES AND STANDARDS STANDARD ATV-DVWK-A 157E Sewer System Structures ISBN 978-3-937758-46-6 Publisher/Marketing:
GERMAN ATV-DVWK RULES AND STANDARDS STANDARD ATV-DVWK-A 157E Sewer System Structures GERMAN ATV-DVWK RULES AND STANDARDS STANDARD ATV-DVWK-A 157E Sewer System Structures ISBN 978-3-937758-46-6 Publisher/Marketing:
THE LOGISTIC COST ANALYSIS IN AGRIBUSINESS CASE STUDY OF FOOD SECTOR COMPANY
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/3/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 1535 1545 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2016.4.3.114
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/3/2016, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 1535 1545 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2016.4.3.114
AUTHORITY OF THE BOROUGH OF CHARLEROI WASHINGTON COUNTY, PENNSYLVANIA ACT 537 SEWAGE FACILITIES PLAN UPDATE
 PLAN SUMMARY AUTHORITY OF THE BOROUGH OF CHARLEROI WASHINGTON COUNTY, PENNSYLVANIA ACT 537 SEWAGE FACILITIES PLAN UPDATE The Pennsylvania Sewage Facilities Act (Act 537) was enacted by the Pennsylvania
PLAN SUMMARY AUTHORITY OF THE BOROUGH OF CHARLEROI WASHINGTON COUNTY, PENNSYLVANIA ACT 537 SEWAGE FACILITIES PLAN UPDATE The Pennsylvania Sewage Facilities Act (Act 537) was enacted by the Pennsylvania
THE USE OF MULTIPLE-CRITERIA RANKING METHODS FOR DESIGNING PUBLIC TRANSPORT SYSTEMS
 INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/3/2014, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 1477 1486 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2014.4.3.112
INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr IV/3/2014, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddział w Krakowie, s. 1477 1486 Komisja Technicznej Infrastruktury Wsi DOI: http://dx.medra.org/10.14597/infraeco.2014.4.3.112
Council Directive 91/271/EEC The National Programme for Municipal Waste Water Treatment
 Council Directive 91/271/EEC The National Programme for Municipal Waste Water Treatment Regional Water Management Board Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 concerning urban waste-water treatment
Council Directive 91/271/EEC The National Programme for Municipal Waste Water Treatment Regional Water Management Board Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 concerning urban waste-water treatment
THE STUDY ON INTEGRATED URBAN DRAINAGE IMPROVEMENT FOR MELAKA AND SUNGAI PETANI IN MALAYSIA FINAL REPORT
 THE GOVERNMENT OF MALAYSIA PRIME MINISTER S DEPARTMENT ECONOMIC PLANNING UNIT THE STUDY ON INTEGRATED URBAN DRAINAGE IMPROVEMENT FOR MELAKA AND SUNGAI PETANI IN MALAYSIA FINAL REPORT VOL. 5: TECHNICAL
THE GOVERNMENT OF MALAYSIA PRIME MINISTER S DEPARTMENT ECONOMIC PLANNING UNIT THE STUDY ON INTEGRATED URBAN DRAINAGE IMPROVEMENT FOR MELAKA AND SUNGAI PETANI IN MALAYSIA FINAL REPORT VOL. 5: TECHNICAL
Environmental Task Force SSSMP Summary, September 18, 2011 Scheduled for City Council Approval September 26, 2017
 Attachment 1 Environmental Task Force SSSMP Summary, September 18, 2011 Scheduled for City Council Approval September 26, 2017 Sanitary Sewer System Master Plan Summary Points - City s sanitary system
Attachment 1 Environmental Task Force SSSMP Summary, September 18, 2011 Scheduled for City Council Approval September 26, 2017 Sanitary Sewer System Master Plan Summary Points - City s sanitary system
SMOKE TESTING SMOKING ON THE JOB
 SMOKE TESTING SMOKING ON THE JOB A LITTLE HISTORY ORIGINALLY INSTALLED IN 1958-1959 ORIGINAL DESIGN CAPACITY OF 2500 PEOPLE 500 GPM PUMPING CAPACITY ABOUT 18 ACRES OF PONDS POPULATION OF 2000 IN 1960 CURRENT
SMOKE TESTING SMOKING ON THE JOB A LITTLE HISTORY ORIGINALLY INSTALLED IN 1958-1959 ORIGINAL DESIGN CAPACITY OF 2500 PEOPLE 500 GPM PUMPING CAPACITY ABOUT 18 ACRES OF PONDS POPULATION OF 2000 IN 1960 CURRENT
Design flow = PDWF + GWI + RDI
 WSA 02 2014 3.1 1 Appendix C C1 GENERAL APPENDIX C FLOW ESTIMATION FOR UNDEVELOPED AREAS The use of this Appendix requires Water Agency approval. Design flow estimates are required for designing pipe networks
WSA 02 2014 3.1 1 Appendix C C1 GENERAL APPENDIX C FLOW ESTIMATION FOR UNDEVELOPED AREAS The use of this Appendix requires Water Agency approval. Design flow estimates are required for designing pipe networks
9th IWA Symposium on Systems Analysis and Integrated Assessment June 2015 Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia
 9th IWA Symposium on Systems Analysis and Integrated Assessment 14-17 June 2015 Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia Haiwei Huang, Siyu Zeng, Xin Dong, Pengfei Du School of Environment Tsinghua University,
9th IWA Symposium on Systems Analysis and Integrated Assessment 14-17 June 2015 Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia Haiwei Huang, Siyu Zeng, Xin Dong, Pengfei Du School of Environment Tsinghua University,
IDDE From the Regulatory Perspective. Chris Kallis IEPA
 IDDE From the Regulatory Perspective Chris Kallis IEPA What is an Illicit discharge? A discharge to an MS4 that is not composed entirely of storm water Exceptions: NPDES Permitted discharges Discharges
IDDE From the Regulatory Perspective Chris Kallis IEPA What is an Illicit discharge? A discharge to an MS4 that is not composed entirely of storm water Exceptions: NPDES Permitted discharges Discharges
Energy efficiency in wastewater treatment
 Energy efficiency in wastewater treatment Armin Müller Industry Segment Management Water/ Wastewater Festo AG & Co KG Esslingen, Germany Festo an independent family-owned company Some Facts & Figures Pneumatic
Energy efficiency in wastewater treatment Armin Müller Industry Segment Management Water/ Wastewater Festo AG & Co KG Esslingen, Germany Festo an independent family-owned company Some Facts & Figures Pneumatic
Homeowner s Guide Foundation Water PenetrationTips TIPS TO IDENTIFY WATER PENETRATION PROBLEMS / CRACKING BASEMENTS
 Homeowner s Guide Foundation Water PenetrationTips TIPS TO IDENTIFY WATER PENETRATION PROBLEMS / CRACKING BASEMENTS MAINTAINING YOUR HOME BASEMENT FOUNDATION BY HOMEOWNER PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE LUX WATERPROOF
Homeowner s Guide Foundation Water PenetrationTips TIPS TO IDENTIFY WATER PENETRATION PROBLEMS / CRACKING BASEMENTS MAINTAINING YOUR HOME BASEMENT FOUNDATION BY HOMEOWNER PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE LUX WATERPROOF
Town of New Castle, New Hampshire Sewer Infrastructure Evaluation
 Town of New Castle, New Hampshire Sewer Infrastructure Evaluation March 2016 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Town of New Castle (Town) is working collaboratively with the City of Portsmouth (City) to consider options
Town of New Castle, New Hampshire Sewer Infrastructure Evaluation March 2016 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Town of New Castle (Town) is working collaboratively with the City of Portsmouth (City) to consider options
European Water and Sanitation Services vs. Sustainable Development Example Germany. ATHENS European Week, Autumn 2013 Paris, November 19 th, 2013
 1G e r m a n I n s t i t u t e o f U r b a n A f f a i r s European Water and Sanitation Services vs. Sustainable Development Example Germany ATHENS European Week, Autumn 2013 Paris, November 19 th, 2013
1G e r m a n I n s t i t u t e o f U r b a n A f f a i r s European Water and Sanitation Services vs. Sustainable Development Example Germany ATHENS European Week, Autumn 2013 Paris, November 19 th, 2013
SEWAGE TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL
 SEWAGE TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL QUANTITY OF SANITARY SEWAGE AND STORM WATER Zerihun Alemayehu Unpolluted cooling water Intercept or sewer Sources of Sewage Residential and commercial sewage Industrial wastewater
SEWAGE TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL QUANTITY OF SANITARY SEWAGE AND STORM WATER Zerihun Alemayehu Unpolluted cooling water Intercept or sewer Sources of Sewage Residential and commercial sewage Industrial wastewater
 You can help protect our water from pharmaceuticals and personal care products! Tel. 1-800-666-0206 Fax. 1-703-684-2492 www.wef.org a Printed on 100% recycled paper. HS1802 6/2008 You can help protect
You can help protect our water from pharmaceuticals and personal care products! Tel. 1-800-666-0206 Fax. 1-703-684-2492 www.wef.org a Printed on 100% recycled paper. HS1802 6/2008 You can help protect
Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes
 Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes J. De Bénédittis (1), J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski (1) (1) URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, Bâtiment Coulomb, 34 avenue
Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes J. De Bénédittis (1), J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski (1) (1) URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, Bâtiment Coulomb, 34 avenue
UNIVERSITà DEGLI STUDI DI NAPOLI FEDERICO II
 UNIVERSITà DEGLI STUDI DI NAPOLI FEDERICO II FACOLTÀ DI INGEGNERIA CORSO DI LAUREA IN INGEGNERIA PER L AMBIENTE E IL TERRITORIO (CLASSE DELLE LAUREE IN INGEGNERIA CIVILE E AMBIENTALE) DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA
UNIVERSITà DEGLI STUDI DI NAPOLI FEDERICO II FACOLTÀ DI INGEGNERIA CORSO DI LAUREA IN INGEGNERIA PER L AMBIENTE E IL TERRITORIO (CLASSE DELLE LAUREE IN INGEGNERIA CIVILE E AMBIENTALE) DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA
Sewage Management Changes in the Northeastern Poland After Accession to the European Union
 Sewage Management Changes in the Northeastern Poland After Accession to the European Union Szymon Skarżyński 1,*, and Izabela Bartkowska 2 1,2 Bialystok University of Technology, Faculty of Civil and Environmental
Sewage Management Changes in the Northeastern Poland After Accession to the European Union Szymon Skarżyński 1,*, and Izabela Bartkowska 2 1,2 Bialystok University of Technology, Faculty of Civil and Environmental
10 Inflow and Infiltration Reduction Strategy Update
 Clause 10 in Report No. 4 of Committee of the Whole was adopted, without amendment, by the Council of The Regional Municipality of York at its meeting held on March 24, 2016. 10 Inflow and Infiltration
Clause 10 in Report No. 4 of Committee of the Whole was adopted, without amendment, by the Council of The Regional Municipality of York at its meeting held on March 24, 2016. 10 Inflow and Infiltration
SECTION 1 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 SECTION 1 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS This Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) Master Plan was prepared to meet the conditions set forth in Special Condition A, Paragraph 4 of the February 6, 2009
SECTION 1 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS This Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) Master Plan was prepared to meet the conditions set forth in Special Condition A, Paragraph 4 of the February 6, 2009
MULTIDIMENSIONAL COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF OTHER GAINFUL ACTIVITIES OF AGRICULTURAL HOLDINGS IN EU COUNTRIES
 Multidimensional comparative analysis INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr 7/2009, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddzia w Krakowie, s. 129137 Komisja Technicznej
Multidimensional comparative analysis INFRASTRUKTURA I EKOLOGIA TERENÓW WIEJSKICH INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECOLOGY OF RURAL AREAS Nr 7/2009, POLSKA AKADEMIA NAUK, Oddzia w Krakowie, s. 129137 Komisja Technicznej
Evaluation of Collection System Design Standards
 Wastewater Master Plan DWSD Project No. CS-1314 Evaluation of Collection System Design Standards Technical Memorandum Original Date: August 9, 2001 Revision Date: September 2003 Author: CDM Table of Contents
Wastewater Master Plan DWSD Project No. CS-1314 Evaluation of Collection System Design Standards Technical Memorandum Original Date: August 9, 2001 Revision Date: September 2003 Author: CDM Table of Contents
Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes
 Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes J. De Bénédittis (1), J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski (1) (1) URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, 34 avenue des Arts, 69621
Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes J. De Bénédittis (1), J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski (1) (1) URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, 34 avenue des Arts, 69621
Public Information Centre No. 1
 Public Information Centre No. 1 City of Timmins Schedule B Class Environmental Assessment for the WHITNEY TISDALE SANITARY SYSTEM UPGRADES Welcome Please Sign In Class EA Process & Public Consultation
Public Information Centre No. 1 City of Timmins Schedule B Class Environmental Assessment for the WHITNEY TISDALE SANITARY SYSTEM UPGRADES Welcome Please Sign In Class EA Process & Public Consultation
Storm Water and Sanitary Sewer
 Public Works Department Summary Report on Planned Capital Improvements Storm Water and Sanitary Sewer Introduction Public Works has assembled this summary report to highlight major capital improvements
Public Works Department Summary Report on Planned Capital Improvements Storm Water and Sanitary Sewer Introduction Public Works has assembled this summary report to highlight major capital improvements
A reliable solution for ditching, underpassing and rainwater drainage
 PIPES AND CHAMBERS CULVERT PIPES A reliable solution for ditching, underpassing and rainwater drainage Culvert pipes are used to convey drain pipe water or rainwater under the ground. The smallest (110
PIPES AND CHAMBERS CULVERT PIPES A reliable solution for ditching, underpassing and rainwater drainage Culvert pipes are used to convey drain pipe water or rainwater under the ground. The smallest (110
GENERAL MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
 IS BASEMENT FLOODING A COMMON PROBLEM? Basement flooding is unfortunately a common occurrence in many parts of Canada. Basement flooding related insurance claims in Canada are estimated to be in the order
IS BASEMENT FLOODING A COMMON PROBLEM? Basement flooding is unfortunately a common occurrence in many parts of Canada. Basement flooding related insurance claims in Canada are estimated to be in the order
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management
 The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management Husam Al-Najar Storm water management : Collection System Design principles The Objectives
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management Husam Al-Najar Storm water management : Collection System Design principles The Objectives
OLD DUNDAS ROAD SEWAGE PUMPING STATION (HC005) EMERGENCY OVERFLOW SCHEDULE C MUNICIPAL CLASS ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT (EA)
 OLD DUNDAS ROAD SEWAGE PUMPING STATION (HC005) EMERGENCY OVERFLOW SCHEDULE C MUNICIPAL CLASS ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT (EA) Agency Meeting #1 Meeting Minutes Location: 77 James Street North, Suite 400,
OLD DUNDAS ROAD SEWAGE PUMPING STATION (HC005) EMERGENCY OVERFLOW SCHEDULE C MUNICIPAL CLASS ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT (EA) Agency Meeting #1 Meeting Minutes Location: 77 James Street North, Suite 400,
Key I/I Reduction Plan Components
 MARCH 24, 2015 Brad D. Werner, P.E. Key I/I Reduction Plan Components Understanding of the Collection System Developing solid Ordinances and Policies Long-Range Plan Development Capital Project Implementation
MARCH 24, 2015 Brad D. Werner, P.E. Key I/I Reduction Plan Components Understanding of the Collection System Developing solid Ordinances and Policies Long-Range Plan Development Capital Project Implementation
MWRD Infiltration and Inflow Control Program Compliance Update. Committee of the Whole Meeting April 3, 2018
 MWRD Infiltration and Inflow Control Program Compliance Update Committee of the Whole Meeting April 3, 2018 Presentation Outline Background on MWRD s Watershed Management Ordinance Wastewater, Infiltration
MWRD Infiltration and Inflow Control Program Compliance Update Committee of the Whole Meeting April 3, 2018 Presentation Outline Background on MWRD s Watershed Management Ordinance Wastewater, Infiltration
Commonwealth of Massachusetts Title 5 Official Inspection Form Subsurface Sewage Disposal System Form - Not for Voluntary Assessments
 Inspection results must be submitted on this form. Inspection forms may not be altered in any way. Important: When filling out forms on the computer, use only the tab key to move your cursor - do not use
Inspection results must be submitted on this form. Inspection forms may not be altered in any way. Important: When filling out forms on the computer, use only the tab key to move your cursor - do not use
Design and Construction of Local Public and Private Sewers and Ancillary Facilities
 Chapter 2 Design and Construction of Local Public and Private Sewers and Ancillary Facilities Subchapter I - General 2.101 Purpose...1 2.102 Applicability...1 2.103 Electronic data...1 2.104 Effect of
Chapter 2 Design and Construction of Local Public and Private Sewers and Ancillary Facilities Subchapter I - General 2.101 Purpose...1 2.102 Applicability...1 2.103 Electronic data...1 2.104 Effect of
APPENDIX E APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS
 APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method
APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method
Changes in surface water microflora caused by discharge of purified sewage into rivers
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 75 (2017) 26-32 EISSN 2392-2192 Changes in surface water microflora caused by discharge of purified sewage into rivers Agnieszka Godela*, Monika Lewańska,
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 75 (2017) 26-32 EISSN 2392-2192 Changes in surface water microflora caused by discharge of purified sewage into rivers Agnieszka Godela*, Monika Lewańska,
City of Leadwood Wastewater System Engineering Report
 City of Leadwood Wastewater System Engineering Report DRAFT H2O C Engneering www.h2oc.com 877-22-WATER Background The purpose of this report is to describe the City of Leadwood s wastewater system (System
City of Leadwood Wastewater System Engineering Report DRAFT H2O C Engneering www.h2oc.com 877-22-WATER Background The purpose of this report is to describe the City of Leadwood s wastewater system (System
STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT. Dundas Square Gardens Inc. High Rise Residential/Commercial Development
 STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT Dundas Square Gardens Inc. Revised: April 6, 2016 Revised: January 12, 2016 Revised: July 10, 2015 OUR FILE: 14-RE-352 June 16, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE 1.0 Scope of work
STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT Dundas Square Gardens Inc. Revised: April 6, 2016 Revised: January 12, 2016 Revised: July 10, 2015 OUR FILE: 14-RE-352 June 16, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE 1.0 Scope of work
Managing Salt Impacted Water at Maintenance Yards
 Managing Salt Impacted Water at Maintenance Yards Presented to the: Transportation Association of Canada Calgary 2005 Abstract Managing Salt Impacted Water at Maintenance Yards The Code of Practice for
Managing Salt Impacted Water at Maintenance Yards Presented to the: Transportation Association of Canada Calgary 2005 Abstract Managing Salt Impacted Water at Maintenance Yards The Code of Practice for
APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS
 ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS June 2011 THIS PAGE LEFT BLANK INTENTIONALLY. June 2011 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method Values June 2011
ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS June 2011 THIS PAGE LEFT BLANK INTENTIONALLY. June 2011 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method Values June 2011
INTEGRATED MEASURES FOR THE REDUCTION OF STORM WATER AND COMBINED SEWER OVERFLOW IMPACT ON AN URBAN LAKE
 Hydrological Processes and Water Management in Urban Areas (Proceedings of the Duisberg Symposium, April 1988). IAHS Publ. no. 198, 1990. INTEGRATED MEASURES FOR THE REDUCTION OF STORM WATER AND COMBINED
Hydrological Processes and Water Management in Urban Areas (Proceedings of the Duisberg Symposium, April 1988). IAHS Publ. no. 198, 1990. INTEGRATED MEASURES FOR THE REDUCTION OF STORM WATER AND COMBINED
RAINWATER MANAGEMENT IN PROTECTED AREAS
 Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 18, Issue 2, March 2017, pages 69 77 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/67858 Research Article RAINWATER MANAGEMENT IN PROTECTED AREAS Wioletta Żarnowiec 1, Andrzej Bogdał
Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 18, Issue 2, March 2017, pages 69 77 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/67858 Research Article RAINWATER MANAGEMENT IN PROTECTED AREAS Wioletta Żarnowiec 1, Andrzej Bogdał
Stormwater Awareness Training
 Stormwater Awareness Training 2014 Purpose of Stormwater Awareness Training To educate City of Aurora employees on the importance of identifying non stormwater discharges and reducing pollution through
Stormwater Awareness Training 2014 Purpose of Stormwater Awareness Training To educate City of Aurora employees on the importance of identifying non stormwater discharges and reducing pollution through
INFLOW AND INFILTRATION REDUCTION STRATEGY
 INFLOW AND INFILTRATION REDUCTION STRATEGY ANNUAL REPORT MARCH 31, 2016 Table of Contents Highlights of program activities and accomplishments 2015... 2 1. 2015 Inflow and Infiltration Reduction... 2 2.
INFLOW AND INFILTRATION REDUCTION STRATEGY ANNUAL REPORT MARCH 31, 2016 Table of Contents Highlights of program activities and accomplishments 2015... 2 1. 2015 Inflow and Infiltration Reduction... 2 2.
S.O.P. No. HMD
 Page: 1 of 9 PURPOSE: To establish (SOP) for submission requirements, review process and approval of applications for Non-vehicular Access Permits for the purpose of connection or discharge to any MassDOT
Page: 1 of 9 PURPOSE: To establish (SOP) for submission requirements, review process and approval of applications for Non-vehicular Access Permits for the purpose of connection or discharge to any MassDOT
Town of Madawaska, ME. CSO Success Overcoming Funding & Design Challenges
 Town of Madawaska, ME CSO Success Overcoming Funding & Design Challenges Town of Madawaska - Introduction Madawaska is in rural Aroostook County, Maine Northeastern Most Point In U.S. Population: 4,035
Town of Madawaska, ME CSO Success Overcoming Funding & Design Challenges Town of Madawaska - Introduction Madawaska is in rural Aroostook County, Maine Northeastern Most Point In U.S. Population: 4,035
5 CONSULTANT SELECTION FOR INFLOW AND INFILTRATION AUDIT AND FLOW MONITORING PROGRAM
 5 CONSULTANT SELECTION FOR INFLOW AND INFILTRATION AUDIT AND FLOW MONITORING PROGRAM The Environmental Services Committee recommends the adoption of the recommendation contained in the following report
5 CONSULTANT SELECTION FOR INFLOW AND INFILTRATION AUDIT AND FLOW MONITORING PROGRAM The Environmental Services Committee recommends the adoption of the recommendation contained in the following report
Settling of Solids in Primary Clarifiers / Storm Water Tanks
 Settling of Solids in Primary Clarifiers / Storm Water Tanks M. T. Aslam 1*, H. Kainz 1 and G. Gruber 1 1 Institute of Urban Water Management and Landscape Water Engineering, Graz University of Technology,
Settling of Solids in Primary Clarifiers / Storm Water Tanks M. T. Aslam 1*, H. Kainz 1 and G. Gruber 1 1 Institute of Urban Water Management and Landscape Water Engineering, Graz University of Technology,
WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL
 CVE 471 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus CVE
CVE 471 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus CVE
Commonwealth of Massachusetts Title 5 Official Inspection Form. Subsurface Sewage Disposal System Form - Not for Voluntary Assessments
 Inspection results must be submitted on this form. Inspection forms may not be altered in any way. Please see completeness checklist at the end of the form. Important: When filling out forms on the computer,
Inspection results must be submitted on this form. Inspection forms may not be altered in any way. Please see completeness checklist at the end of the form. Important: When filling out forms on the computer,
Chapter 8 Addressing I/I Issues and High Flows
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Addressing I/I Issues and High Flows This chapter is organized into the following sections: Introduction Background Estimation of Infiltration Volume Conveyance Costs Effect of
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Addressing I/I Issues and High Flows This chapter is organized into the following sections: Introduction Background Estimation of Infiltration Volume Conveyance Costs Effect of
Infiltration and Inflow. Michael Sassaman Phone
 Infiltration and Inflow Michael Sassaman msassaman@entecheng.com Phone 610-373-3345 Inflow and Infiltration PA DEP Learning Objectives Do you have Excessive I/I? Sources of Inflow and Infiltration I/I
Infiltration and Inflow Michael Sassaman msassaman@entecheng.com Phone 610-373-3345 Inflow and Infiltration PA DEP Learning Objectives Do you have Excessive I/I? Sources of Inflow and Infiltration I/I
Damaged Lines in Morro Bay s Wastewater Collection System
 Damaged Lines in Morro Bay s Wastewater Collection System Causes and Effects Richard E. T. Sadowski and Marla Jo Bruton B. S. Mechanical Engineering; CWEA Grade IV Wastewater Collection System Operator
Damaged Lines in Morro Bay s Wastewater Collection System Causes and Effects Richard E. T. Sadowski and Marla Jo Bruton B. S. Mechanical Engineering; CWEA Grade IV Wastewater Collection System Operator
