Principles of Economics
|
|
|
- Abel Floyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Economics 2nd edition by Fred M Gottheil PowerPoint lides prepared by Ken Long Chapter 16 Wages and Employment: Monopsony & Labor Unions 2/26/ What is a Labor Union? An association of workers, each of whom transfers the right to negotiate wage rates, work hours, and working conditions to the association 3 Types of Unions Craft or trade union--members practice the same craft--plumbers, etc. Industrial union, workers in the same industry--auto, steel Public employees union, members are government employees--teachers, police, etc. Employee Associations: American medical association, etc--not really unions but similar in many ways 4 Brief History of Unions Early unions, groups of craft workers Knights of Labor, early attempt at a national union of all workers Problems faced by the Knights, skilledunskilled debate In early days, courts very anti-union 5 AFL, American Federation of Labor, formed in 1883 Attempted to organize the skilled craft unions 6
2 Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) Formed in 1938, attempt to organize the industrial workers Auto and teel industries among their first successes AFL-CIO merged in the 1950 s 7 What are the major Acts? Norris-La Guardia Act of 1932 Wagner Act of 1935 Taft-Hartley Act of 1947 Labor Management Reporting & Landrum-Griffin Act 1959 Civil Rights Act of Norris-LaGuardia Act, 1932 Outlawed yellow-dog contracts in which workers agreed to not join unions in order to get a job Restricted injunctions against unions 9 Wagner Act, 1935 (national labor relations act) Gave workers the right to join unions if majority of workers vote to Required management to engage in good faith bargaining Created national labor relations 10 board Taft-Hartley Act, 1947 Closed shops illegal, union shops illegal if state passes right to work law Certain strikes illegal Cooling off period can be ordered in national emergency cases 11 What is a Closed hop? An arrangement in which a firm may hire only union labor 12
3 What is a Union hop? An arrangement in which a firm may hire nonunion labor, but every worker hired must join the union by a certain date Landrum-Griffin Act, 1959 Unions must hold elections, keep financial records Union Behavior, Ways of Raising Wages Increase the demand for labor Decrease the supply of labor Collective bargaining Wages Increasing the demand for labor D1 D2 Labor 15 L 1 L Increasing the demand for Union Labor Wages Decreasing the supply of labor 2 Trying to increase the demand for the product produced Look for the Union Label Improve the productivity of union labor Restrict the supply of non-union made goods, such as via import restrictions Featherbedding, trying to require more work than necessary L 2 L 1 D 1 Labor 18
4 Decreasing the supply of labor Exclusive unions, such as the craft unions, via initiation fees, apprenticeship programs Employee associations such as AMA often accused of restricting supply Usually requires help from the government 19 Wage Rate ' 0 B A Q 2 Q 1 Q 3 Quantity of Labor '. This is the supply curve the union may want management to believe exists. It says no one will work for less than. D uccessful Collective Bargaining by Union What is a Monopsony? A labor market with only one buyer Why is the upply Curve for Labor upward sloping? Because as the wage rate increases the incentive for more people wanting to work increases W2 W1 What is Marginal Labor Cost? The MLC is the cost of hiring one more worker Q1 Q
5 Why does the MLC Curve lie above the upply Curve? When the Monopsonist increases employment, it must offer a higher wage to all workers W MLC Q What is Marginal Revenue Product? MRP is the addition to total revenue that one more worker contributes How many workers will a firm hire? It continues hiring workers as long as MRP > MLC and stops when MRP = MLC Why is the MRP Curve downward sloping? Because each additional worker hired adds less and less to total product W W c 16 MLC MRP (D) 29 6,000 L Labor c 30 30
6 Comparison of Monopsony and Competition Monopsony wages are lower, hire less labor than in a perfectly competitive market 31 W $26 $16 MRP = MLC Return to Monopsony Power 6,000 MLC MRP Q When workers are unionized, who is the supplier of labor? The Union For more information about labor disputes: employment/index.html pg.html What happens if the company offers a lower wage than $26? Collective bargaining ensues where the company and the labor union negotiate What is a trike? The withholding of labor by a union when the collective bargaining process is unacceptable to the union 35 36
7 What problem does the union have at $26? It must control the supply of labor or it will have too many workers and weaken its bargaining power For more information about labor unions: Union Impact on wages tudies by Lewis and others find average union wage 10-15% higher than comparable nonunion labor In some industries, this is higher, others lower Does not include fringe benefits 39 Union Impact on nonunion waqes, 2 possibilities pillover effect--fewer jobs in the union sector means a greater supply of labor to nonunion jobs, lowers wages in the nonunion sector Threat effect--do nonunion firms pay more due to the threat of unionization? 40 Effect of Labor Unions on Union and Nonunion Wages (spillover effect) Changes in supplyconditions and wagerates in the unionizedsector can bring on changes in supplyand wage rates in thenonunionized sector. Wage Rate ' U Q' Q U U Quantity of Labor (a) Unionized ector U D U Wage Rate 0 1 NU Q NU Q' NU Quantity of Labor (b) Nonunionized ector 2 ' NU D NU Union Impact on Productivity, 2 different views Traditional, sees unions as harming productivity via strikes, restrictive work rules, etc. New view (Freeman and Medoff)-sees unions as giving workers a collective voice, reduces turnover of workers, lowering training costs, worker married to the firm 42
8 What is a Monopsony? Why is the upply Curve for Labor upward sloping? What is Marginal Labor Cost? What is Marginal Resource Product? How many workers will a firm hire? Why is the MRP Curve downward sloping? What wage rate will the union agree to work? What is a trike? What is a Closed hop? What is a Union hop? END 45
Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power
 29 Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. outline the essential history of the labor union movement; 2. discuss the current
29 Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. outline the essential history of the labor union movement; 2. discuss the current
Labor, Employment and Wages. Chapter 9
 Labor, Employment and Wages Chapter 9 The Unit 3 Test Thursday for periods 2 and 4; Friday for period 7 Chapters 7-9 and 16 (100 points possible) 60 multiple choice and 4 short answer questions Approximately
Labor, Employment and Wages Chapter 9 The Unit 3 Test Thursday for periods 2 and 4; Friday for period 7 Chapters 7-9 and 16 (100 points possible) 60 multiple choice and 4 short answer questions Approximately
EMPLOYMENT AND WAGES BEFORE YOU BEGIN. Looking at the Chapter. Date Period. Chapter. Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words.
 EMPLOYMENT AND WAGES BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words. of labor of labor What Determines Wages? for labor Demand for the labor produces for labor Practices
EMPLOYMENT AND WAGES BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words. of labor of labor What Determines Wages? for labor Demand for the labor produces for labor Practices
What Is a Labor Union? Less than 14% of U.S. workers belong to a labor union.
 LABOR What Is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers that tries to improve working conditions, wages, and benefits for its members. Less than 14% of U.S. workers belong to a labor union.
LABOR What Is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers that tries to improve working conditions, wages, and benefits for its members. Less than 14% of U.S. workers belong to a labor union.
Chapter 14. Labor Law. Statutory Basis. Coming Together on Issues 1/12/2009. Employment Law for Business, 6 th ed.
 Employment Law for Business, 6 th ed. Bennett-Alexander Chapter 14 Labor Law Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Statutory Basis Employees shall have the right to selforganization,
Employment Law for Business, 6 th ed. Bennett-Alexander Chapter 14 Labor Law Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Statutory Basis Employees shall have the right to selforganization,
Labor Market Trends. Chapter 9 Section Main Menu
 Labor Market Trends How do economists define the labor force? What occupational trends exist in the U.S. economy? What is temporary employment? What are the current trends in wages and benefits? The United
Labor Market Trends How do economists define the labor force? What occupational trends exist in the U.S. economy? What is temporary employment? What are the current trends in wages and benefits? The United
Chapter Eleven. Learning Objectives
 Chapter Eleven Enhancing Union Management Relations Learning Objectives 1. Explain how and why labor unions came into being. 2. Discuss the sources of unions negotiating power and trends in union membership.
Chapter Eleven Enhancing Union Management Relations Learning Objectives 1. Explain how and why labor unions came into being. 2. Discuss the sources of unions negotiating power and trends in union membership.
Test Yourself: Labor
 Test Yourself: Labor If the workers took a notion they could stop all speeding trains; every ship upon the ocean they could tie with mighty chains. Every wheel in the creation every mine and every mill;
Test Yourself: Labor If the workers took a notion they could stop all speeding trains; every ship upon the ocean they could tie with mighty chains. Every wheel in the creation every mine and every mill;
Review Questions. Unions and Collective Bargaining. Choose the letter that represents the BEST response.
 192 Ehrenberg/Smith Modern Labor Economics: Theory and Public Policy, Tenth Edition Review Questions Choose the letter that represents the BEST response. Unions and Collective Bargaining 1. Which of the
192 Ehrenberg/Smith Modern Labor Economics: Theory and Public Policy, Tenth Edition Review Questions Choose the letter that represents the BEST response. Unions and Collective Bargaining 1. Which of the
Test Yourself: Labor
 Test Yourself: Labor If the workers took a notion they could stop all speeding trains; every ship upon the ocean they could tie with mighty chains. Every wheel in the creation every mine and every mill;
Test Yourself: Labor If the workers took a notion they could stop all speeding trains; every ship upon the ocean they could tie with mighty chains. Every wheel in the creation every mine and every mill;
Differing Philosophies of Unions and Management
 Differing Philosophies of Unions and Management Unions generally believe that management exploits labor and is more interested in making a profit than in furthering the welfare of its employees Management
Differing Philosophies of Unions and Management Unions generally believe that management exploits labor and is more interested in making a profit than in furthering the welfare of its employees Management
Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining
 15 Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining 15-1 Learning Objectives 1. Give a brief history of the American labor movement. 2. Discuss the main features of at least three major pieces of labor legislation.
15 Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining 15-1 Learning Objectives 1. Give a brief history of the American labor movement. 2. Discuss the main features of at least three major pieces of labor legislation.
Chapter 21: 1/28/2014. Demand. Changes in Demand. Supply
 Demand Chapter 21: Demand and Supply Desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or service Law of Demand Buy more at lower prices Buy less at higher prices Diminishing Marginal Utility satisfaction
Demand Chapter 21: Demand and Supply Desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or service Law of Demand Buy more at lower prices Buy less at higher prices Diminishing Marginal Utility satisfaction
Labor Unions
 Labor Unions 11.05.2010 Labor Unions Def.: A labor union is an organization of workers, which through its leadership, bargains with the employer on behalf of union members and negotiates labor contracts
Labor Unions 11.05.2010 Labor Unions Def.: A labor union is an organization of workers, which through its leadership, bargains with the employer on behalf of union members and negotiates labor contracts
Labor Management Relationship
 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Right Reserved The Legal & Regulatory Environment of Business 16e Labor Management Relationship Chapter 22 Reed Pagnattaro Cahoy
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Right Reserved The Legal & Regulatory Environment of Business 16e Labor Management Relationship Chapter 22 Reed Pagnattaro Cahoy
Types of Unions. Craft or Trade Unions. Industrial Unions. Workers who perform the same kind of work. All workers in the same industry
 The Labor Movement In 2003 there were approximately 291 million people in the United States. Slightly less than half or about 146 million belong to the civilian labor force. Excludes armed forces and prisoners.
The Labor Movement In 2003 there were approximately 291 million people in the United States. Slightly less than half or about 146 million belong to the civilian labor force. Excludes armed forces and prisoners.
Chapter 13 Unions and the Labor Market
 Chapter 13 nions and the Labor Market ummary Chapter 12 introduced an objective framework for analyzing the earnings differences that accompany gender, race, and ethnicity. This framework was then used
Chapter 13 nions and the Labor Market ummary Chapter 12 introduced an objective framework for analyzing the earnings differences that accompany gender, race, and ethnicity. This framework was then used
Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY
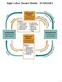 Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY 1 Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market 3. Monopsony
Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY 1 Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market 3. Monopsony
SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4
 SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4 Chapter 13: Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market
SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4 Chapter 13: Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market
causing MARGINAL PRODUCT OF LABOR to fall beyond some point. iv. PRODUCT PRICE : Because this is a competitive market, the PRODUCT PRICE = MARKET
 WAGE DETERMINATION I. A FOCUS ON LABOR a. The basic principles for labor also apply to other factors of production b. About 70% of all income in the U.S. flows to households in the form of wages and salaries.
WAGE DETERMINATION I. A FOCUS ON LABOR a. The basic principles for labor also apply to other factors of production b. About 70% of all income in the U.S. flows to households in the form of wages and salaries.
Unit 4 Labor and Careers
 Unit 4 Labor and Careers - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1. Describe our Labor force 2. Learning Effect 3. Equilibrium wage 4. Labor pool 5. White Collar 6. Blue Collar 7. Skilled
Unit 4 Labor and Careers - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1. Describe our Labor force 2. Learning Effect 3. Equilibrium wage 4. Labor pool 5. White Collar 6. Blue Collar 7. Skilled
Managing Labor Relations
 11 Managing Labor Relations Copyright 2016 Cengag e Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. LEARNING OUTCOMES
11 Managing Labor Relations Copyright 2016 Cengag e Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. LEARNING OUTCOMES
Chapter 11 Work with Labor Unions
 Chapter 11 Work with Labor Unions Section One True/False Questions 1. Trade unions were developed in Europe during the Industrial Revolution. 2. The National Labor Union can be credited with the implementation
Chapter 11 Work with Labor Unions Section One True/False Questions 1. Trade unions were developed in Europe during the Industrial Revolution. 2. The National Labor Union can be credited with the implementation
Markets for Factor Inputs
 C H A P T E R 14 Markets for Factor Inputs Prepared by: Fernando & Yvonn Quijano CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE 14.1 Competitive Factor Markets 14.2 Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market 14.3 Factor Markets with
C H A P T E R 14 Markets for Factor Inputs Prepared by: Fernando & Yvonn Quijano CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE 14.1 Competitive Factor Markets 14.2 Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market 14.3 Factor Markets with
COMMON LABOR TERMS. Arbitration A way of settling disputes by calling in an impartial third party whose decision is final and binding on both parties.
 COMMON LABOR TERMS Agency Shop A union security clause providing that an employee in the bargaining unit refusing to join the union must pay a service fee to the union equal to union dues. Arbitration
COMMON LABOR TERMS Agency Shop A union security clause providing that an employee in the bargaining unit refusing to join the union must pay a service fee to the union equal to union dues. Arbitration
Learning Objectives. The Labor Relations Framework. The Labor Relations Framework. Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage
 Handout 6-1 Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage Chapter 14 Collective Bargaining and Labor Relations Learning Objectives After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe
Handout 6-1 Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage Chapter 14 Collective Bargaining and Labor Relations Learning Objectives After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe
Air Transport Labor Relations
 Air Transport Labor Relations Robert W. Kaps Southern Illinois University Press Carbondale and Edwardsville List of Figures ix List of Tables x Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Abbreviations xiv Parti 1.
Air Transport Labor Relations Robert W. Kaps Southern Illinois University Press Carbondale and Edwardsville List of Figures ix List of Tables x Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Abbreviations xiv Parti 1.
LO AGENDA Tues 12/1. QOD #37: Work with benefits Wage Determination Monopsony Unions (Effect of Unions wksht) HW: Read pp Q #7,9
 LO1 13-1 AGENDA Tues 12/1 QOD #37: Work with benefits Wage Determination Monopsony Unions (Effect of Unions wksht) HW: Read pp 273-282 Q #7,9 10-2 QOD #37: Work with Benefits Workers are compensated by
LO1 13-1 AGENDA Tues 12/1 QOD #37: Work with benefits Wage Determination Monopsony Unions (Effect of Unions wksht) HW: Read pp 273-282 Q #7,9 10-2 QOD #37: Work with Benefits Workers are compensated by
Labor Unions Part II
 Labor Unions Part II The role of a labor union is to ensure that the balance is not tipped in favor of the employer when employees do not receive wages and benefits commensurate with their contribution.
Labor Unions Part II The role of a labor union is to ensure that the balance is not tipped in favor of the employer when employees do not receive wages and benefits commensurate with their contribution.
Refer to the given data. At the profit-maximizing level of employment, this firm's total labor cost will be: A. $16. B. $30. C. $24. D. $32.
 1. The more work people do, all other things unchanged, the: A) more their free time. B) greater their nonmarket use of time. C) less income they have. D) less leisure they have. 2. A wage will the leisure.
1. The more work people do, all other things unchanged, the: A) more their free time. B) greater their nonmarket use of time. C) less income they have. D) less leisure they have. 2. A wage will the leisure.
13 Wage Determination
 13 Wage Determination Labor, Wages,and Earnings Wages Price paid for labor Direct pay plus fringe benefits Wage rate Nominal wage Real wage General level of wages LO1 13-2 Global Perspective LO1 13-3 Role
13 Wage Determination Labor, Wages,and Earnings Wages Price paid for labor Direct pay plus fringe benefits Wage rate Nominal wage Real wage General level of wages LO1 13-2 Global Perspective LO1 13-3 Role
Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining
 Gary Dessler t e n t h e d i t i o n Chapter 15 Part 5 Employee Relations Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook
Gary Dessler t e n t h e d i t i o n Chapter 15 Part 5 Employee Relations Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook
Chapter 02. The Evolution of American Labor
 Chapter 02. The Evolution of American Labor True / False Questions 1. (p. 27) Corporatism still prevails in some parts of the United States, but it has eroded in the European Union since the 1960s. 2.
Chapter 02. The Evolution of American Labor True / False Questions 1. (p. 27) Corporatism still prevails in some parts of the United States, but it has eroded in the European Union since the 1960s. 2.
Labor markets and wage determination
 Labor markets and wage determination LABOR, WAGES, AND EARNINGS Wages Defined... Wages - - Salary - - Earnings Wage Rate Nominal Wages Real Wages International differences... GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE Hourly
Labor markets and wage determination LABOR, WAGES, AND EARNINGS Wages Defined... Wages - - Salary - - Earnings Wage Rate Nominal Wages Real Wages International differences... GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE Hourly
Economics Unit 8. Labor and Unions
 Economics Unit 8 Labor and Unions These documents are being distributed for educational discussion purposes only. They do not reflect any attempt by the North East Independent School District, its trustees,
Economics Unit 8 Labor and Unions These documents are being distributed for educational discussion purposes only. They do not reflect any attempt by the North East Independent School District, its trustees,
Edexcel (B) Economics A-level
 Edexcel (B) Economics A-level Theme 4: Making Markets Work 4.2 Market Power and Market Failure 4.2.1 Market failure Notes Significance of market power: o Cartels, collusion, restrictive practices and tacit
Edexcel (B) Economics A-level Theme 4: Making Markets Work 4.2 Market Power and Market Failure 4.2.1 Market failure Notes Significance of market power: o Cartels, collusion, restrictive practices and tacit
Labor supply is the willingness and ability to work specific amounts of time at alternative wage rates in a given time period, ceteris paribus.
 Labor Unions Part I The role of a labor union is to ensure that the balance is not tipped in favor of the employer when employees do not receive wages and benefits commensurate with their contribution.
Labor Unions Part I The role of a labor union is to ensure that the balance is not tipped in favor of the employer when employees do not receive wages and benefits commensurate with their contribution.
LABOR RELATIONS Professor Bruce Fortado MAN 4301/6305 University of North Florida
 LABOR RELATIONS Professor Bruce Fortado MAN 4301/6305 University of North Florida In the early years of US history, there was no legislative framework to manage labor relations. In general, employers did
LABOR RELATIONS Professor Bruce Fortado MAN 4301/6305 University of North Florida In the early years of US history, there was no legislative framework to manage labor relations. In general, employers did
LABOR RELATIONS Professor Bruce Fortado MAN 4301/6305 University of North Florida
 LABOR RELATIONS Professor Bruce Fortado MAN 4301/6305 University of North Florida In the early years of US history, there was no legislative framework to manage labor relations. In general, employers did
LABOR RELATIONS Professor Bruce Fortado MAN 4301/6305 University of North Florida In the early years of US history, there was no legislative framework to manage labor relations. In general, employers did
CHAPTER 8. Human Resource Management: From Recruitment to Labor Relations
 CHAPTER 8 Human Resource Management: From Recruitment to Labor Relations Chapter Summary: Key Concepts Human Resource: The People Behind the People Human resource management The function of attracting,
CHAPTER 8 Human Resource Management: From Recruitment to Labor Relations Chapter Summary: Key Concepts Human Resource: The People Behind the People Human resource management The function of attracting,
UNIT 4 PRACTICE EXAM
 UNIT 4 PRACTICE EXAM 1. The prices paid for resources affect A. the money incomes of households in the economy B. the allocation of resources among different firms and industries in the economy C. the
UNIT 4 PRACTICE EXAM 1. The prices paid for resources affect A. the money incomes of households in the economy B. the allocation of resources among different firms and industries in the economy C. the
Imaging you were one of these workers. What would you do?
 Imaging you were one of these workers. What would you do? Monopsony and Trades Unions Trades Unions in Labour Markets In this lesson we will Investigate how trades unions seek to protect the welfare of
Imaging you were one of these workers. What would you do? Monopsony and Trades Unions Trades Unions in Labour Markets In this lesson we will Investigate how trades unions seek to protect the welfare of
Labor Relations. John A. Fossum. Center for Human Resources and Labor Studies Carlson School of Management University of Minnesota
 Labor Relations Development, Structure, Process Eleventh Edition John A. Fossum Center for Human Resources and Labor Studies Carlson School of Management University of Minnesota Table of Contents About
Labor Relations Development, Structure, Process Eleventh Edition John A. Fossum Center for Human Resources and Labor Studies Carlson School of Management University of Minnesota Table of Contents About
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY The City University of New York School of Arts & Sciences Department of Social Science Course Outline
 Course code: ECON 2403 Course title: Labor Management Relations Class hours/credits: 3 class hours, 3 credits Prerequisite: ECON 1101 Pathways: US Experience in Its Diversity NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY
Course code: ECON 2403 Course title: Labor Management Relations Class hours/credits: 3 class hours, 3 credits Prerequisite: ECON 1101 Pathways: US Experience in Its Diversity NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY
Chapter 8 The Labor Market: Employment, Unemployment, and Wages
 Chapter 8 The Labor Market: Employment, Unemployment, and Wages Multiple Choice Questions Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If the price of a factor
Chapter 8 The Labor Market: Employment, Unemployment, and Wages Multiple Choice Questions Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If the price of a factor
Unit 4: The Factor Market
 Unit 4: The Factor Market (aka: The Resource Market or Input Market) - Factor Wages - Perfect Competition vs. Monopsonies - Optional Combination of Factors - Income Inequality - Taxation 7 Market in which
Unit 4: The Factor Market (aka: The Resource Market or Input Market) - Factor Wages - Perfect Competition vs. Monopsonies - Optional Combination of Factors - Income Inequality - Taxation 7 Market in which
This is Work with Labor Unions, chapter 11 from the book Beginning Human Relations (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Work with Labor Unions, chapter 11 from the book Beginning Human Relations (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Work with Labor Unions, chapter 11 from the book Beginning Human Relations (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
MGT 3500 Exam 1 Study Guide, Part I
 MGT 3500 Exam 1 Study Guide, Part I Chapter 1 1. What are labor relations about from the worker s perspective & from the employer s? Workers perspective- equity and voice, higher wages, collective workrelated
MGT 3500 Exam 1 Study Guide, Part I Chapter 1 1. What are labor relations about from the worker s perspective & from the employer s? Workers perspective- equity and voice, higher wages, collective workrelated
Unit V: Factor Markets. Problem Set #5 Points Distribution
 Unit V: Factor Markets Problem Set #5 Points Distribution Question #1 Real World Application of Key Concepts 5 Points EACH 2 Points Definition 3 Points Clear Example 1. Derived Demand Definition (2 points):
Unit V: Factor Markets Problem Set #5 Points Distribution Question #1 Real World Application of Key Concepts 5 Points EACH 2 Points Definition 3 Points Clear Example 1. Derived Demand Definition (2 points):
Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing
 Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. define marginal factor cost, marginal physical product of
Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. define marginal factor cost, marginal physical product of
Choose the one alternative that BEST completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHAPTER 3 The Demand for Labor In addition to the multiple choice and quantitative problems listed here, you should answer review questions 1, 3, 5, and 7 and problems 1-4 at the end of chapter 3. Multiple-Choice
CHAPTER 3 The Demand for Labor In addition to the multiple choice and quantitative problems listed here, you should answer review questions 1, 3, 5, and 7 and problems 1-4 at the end of chapter 3. Multiple-Choice
Application: the effect of immigration on domestic wages
 LABOUR DEMAND Application: the effect of igration on domestic wages Case 1. Immigrants and nonigrants are perfect substitutes in production W S 0 S 1 Law of one price: all workers earn the same wage W
LABOUR DEMAND Application: the effect of igration on domestic wages Case 1. Immigrants and nonigrants are perfect substitutes in production W S 0 S 1 Law of one price: all workers earn the same wage W
AS and A-level Economics podcast transcript Podcast two: The Labour Market
 AS and A-level Economics podcast transcript Podcast two: The Labour Market In this podcast, we will be talking about: The Labour Market. Particularly; the demand for labour and marginal productivity theory,
AS and A-level Economics podcast transcript Podcast two: The Labour Market In this podcast, we will be talking about: The Labour Market. Particularly; the demand for labour and marginal productivity theory,
Narrator: In this presentation, you will be introduced to some concepts regarding labor relations.
 MGT 441 Module 1 AVP Transcript Title: Introduction to Labor Relations Slide 1 Narrator: In this presentation, you will be introduced to some concepts regarding labor relations. Slide 2 What is labor relations?
MGT 441 Module 1 AVP Transcript Title: Introduction to Labor Relations Slide 1 Narrator: In this presentation, you will be introduced to some concepts regarding labor relations. Slide 2 What is labor relations?
Chapter 17: Labor Markets
 Chapter 17: Labor Markets Econ 102: Introduction to Microeconomics 1 1.1 Goals of this class Goals of this class Learn how employment and wages are determined in equilibrium. Learn what can shift labor
Chapter 17: Labor Markets Econ 102: Introduction to Microeconomics 1 1.1 Goals of this class Goals of this class Learn how employment and wages are determined in equilibrium. Learn what can shift labor
Table of Contents Unit 1 Introduction to Economics TB Section TB Pages Chapter 1 What is Economics? 2 Section A 2 Parts of Economics 2 18.
 Table of Contents Unit 1 Introduction to Economics TB Section TB Pages Chapter 1 What is Economics? 2 Section A 2 Parts of Economics 2 18.1 499-500 Section B Other Basic Definitions 2 Chapter 2 Fundamental
Table of Contents Unit 1 Introduction to Economics TB Section TB Pages Chapter 1 What is Economics? 2 Section A 2 Parts of Economics 2 18.1 499-500 Section B Other Basic Definitions 2 Chapter 2 Fundamental
Labor notes. Chapter 9
 Labor notes Chapter 9 I. The Civilian Labor Force: the total number of people 16 years and older who are either employed or ac@vely seeking work. It is nearly 156 million people. A. Classifica@on 1 1.
Labor notes Chapter 9 I. The Civilian Labor Force: the total number of people 16 years and older who are either employed or ac@vely seeking work. It is nearly 156 million people. A. Classifica@on 1 1.
LESSON FIVE. Finance, Marketing Distribution, and Labor. CHAPTER 10 Financing and Producing. CHAPTER 11 Marketing and Distribution
 ECON (ENT) COURSE LESSON FIVE Finance, Marketing Distribution, and Labor CHAPTER 10 Financing and Producing CHAPTER 11 Marketing and Distribution CHAPTER 12 The American Labor Force Lesson Four Competition
ECON (ENT) COURSE LESSON FIVE Finance, Marketing Distribution, and Labor CHAPTER 10 Financing and Producing CHAPTER 11 Marketing and Distribution CHAPTER 12 The American Labor Force Lesson Four Competition
BACHELOR OF BUSINESS. Sample FINAL EXAMINATION
 BACHELOR OF BUSINESS Sample FINAL EXAMINATION Subject Code : ECO201 Subject Name : LABOUR ECONOMICS This examination carries 50% of the total assessment for this subject. Examiner(s) Moderator(s) Joyce
BACHELOR OF BUSINESS Sample FINAL EXAMINATION Subject Code : ECO201 Subject Name : LABOUR ECONOMICS This examination carries 50% of the total assessment for this subject. Examiner(s) Moderator(s) Joyce
Labor Unions: Membership, Wages, Competition, and Performance in the Private and Public Sectors
 Labor Unions: Membership, Wages, Competition, and Performance in the Private and Public Sectors Barry Hirsch Economics 8220 Human Resources & Labor Markets April 2013 0 1. The labor demand curve D L as
Labor Unions: Membership, Wages, Competition, and Performance in the Private and Public Sectors Barry Hirsch Economics 8220 Human Resources & Labor Markets April 2013 0 1. The labor demand curve D L as
MARKETS FOR LABOR Microeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.), 3 rd Edition
 Chapter 9 MARKETS FOR LABOR Microeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.), 3 rd Edition Chapter Overview This chapter deals with supply and demand for labor. You will learn about why the supply curve for
Chapter 9 MARKETS FOR LABOR Microeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.), 3 rd Edition Chapter Overview This chapter deals with supply and demand for labor. You will learn about why the supply curve for
STRIKES! Functions of Strikes
 STRIKES! Functions of Provide information to both sides Persuade to modify or negotiate Influence bargainer-constituent relationships May force budget changes Change bargaining structure (e.g., number
STRIKES! Functions of Provide information to both sides Persuade to modify or negotiate Influence bargainer-constituent relationships May force budget changes Change bargaining structure (e.g., number
Chapter 10. Labour Unions. Introduction. to maximise the well-being of their members. Unions can flourish only when firms earn abovenormal
 Chapter 10 Labour Unions McGraw-Hill/Irwin Labor Economics, 5 th edition Copyright 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 11-2 Introduction Unions choose among different options in an
Chapter 10 Labour Unions McGraw-Hill/Irwin Labor Economics, 5 th edition Copyright 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 11-2 Introduction Unions choose among different options in an
Factors of Prodution. Unit 3: The Nature and Function of Factor Markets
 Factors of Prodution Unit 3: The Nature and Function of Factor Markets 4 Factors of Production Labor Capital Land Entrepreneurship Factor Markets Factors of production (labor, capital, and land) are paid
Factors of Prodution Unit 3: The Nature and Function of Factor Markets 4 Factors of Production Labor Capital Land Entrepreneurship Factor Markets Factors of production (labor, capital, and land) are paid
CIE Economics A-level
 CIE Economics A-level Topic 3: Government Microeconomic Intervention c) Labour market forces and government intervention Notes Demand for and supply of labour The labour market is a factor market. The
CIE Economics A-level Topic 3: Government Microeconomic Intervention c) Labour market forces and government intervention Notes Demand for and supply of labour The labour market is a factor market. The
ECON 230-D2-002 Version 2. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ECON 230-D2-002 Version 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The two largest auto manufacturers, Toyota and GM, have experimented
ECON 230-D2-002 Version 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The two largest auto manufacturers, Toyota and GM, have experimented
LABOR UNIONS AND COLLECTIVE BARGAINING
 1 LABOR UNIONS AND COLLECTIVE BARGAINING LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this appendix, you will be able to LO1 Describe how unions in the United States are organized LO2 Discuss the key provisions
1 LABOR UNIONS AND COLLECTIVE BARGAINING LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this appendix, you will be able to LO1 Describe how unions in the United States are organized LO2 Discuss the key provisions
SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP. Business that is organized by one single owner.
 BUSINESS & LABOR Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation Non-Profit Organization Types of Workers Labor Unions Labor Unions (Organization) Collective Bargaining SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP Business that is
BUSINESS & LABOR Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation Non-Profit Organization Types of Workers Labor Unions Labor Unions (Organization) Collective Bargaining SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP Business that is
Chapter 9: Labor Section 1
 Chapter 9: Labor Section 1 Key Terms labor force: all nonmilitary people who are employed or unemployed outsourcing: the practice of contracting with another company to do a specific job that would otherwise
Chapter 9: Labor Section 1 Key Terms labor force: all nonmilitary people who are employed or unemployed outsourcing: the practice of contracting with another company to do a specific job that would otherwise
CHAPTER 2 The History of Labor Management Relationships
 CHAPTER 2 The History of Labor Management Relationships TRUEFALSE 1. The Haymarket Riot, Homestead Incident, and the Pullman Strike eliminated Samuel Gompers' leadership effectiveness in the AFL. 2. The
CHAPTER 2 The History of Labor Management Relationships TRUEFALSE 1. The Haymarket Riot, Homestead Incident, and the Pullman Strike eliminated Samuel Gompers' leadership effectiveness in the AFL. 2. The
Unit 5: The Resource Market
 February AP Microeconomics Unit : Resource Market. Resource Demand Curve Unit : The Resource Market Review. Give an example of Derived Demand.. Define MRP.. Explain the difference between MRP and MR..
February AP Microeconomics Unit : Resource Market. Resource Demand Curve Unit : The Resource Market Review. Give an example of Derived Demand.. Define MRP.. Explain the difference between MRP and MR..
Answers To Chapter 13
 nswers To Chapter 13 Review Questions 1. nswer c. ote that bargaining often takes place simultaneously with a number of employers. The FL-CIO is largely a political action group. It is not involved directly
nswers To Chapter 13 Review Questions 1. nswer c. ote that bargaining often takes place simultaneously with a number of employers. The FL-CIO is largely a political action group. It is not involved directly
Unit 5: The Resource Market. (aka: The Factor Market or Input Market)
 Unit 5: The Resource Market (aka: The Factor Market or Input Market) 1 Perfect Competition Resource Markets Monopsony Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Characteristics: Many small firms are hiring workers
Unit 5: The Resource Market (aka: The Factor Market or Input Market) 1 Perfect Competition Resource Markets Monopsony Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Characteristics: Many small firms are hiring workers
CHAPTER 2 Evolution of Labor-Management Relationships
 CHAPTER 2 Evolution of Labor-Management Relationships TRUE/FALSE 1. Strikes have a long history in the United States; they were frequently employed in the 1600s. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p.38 TOP:
CHAPTER 2 Evolution of Labor-Management Relationships TRUE/FALSE 1. Strikes have a long history in the United States; they were frequently employed in the 1600s. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p.38 TOP:
The Role of Unions. COMM 203 Flex at the Sauder School of Business, University of British Columbia
 Last updated: May 4, 2017 The Role of Unions COMM 203 Flex at the Sauder School of Business, University of British Columbia W:\Learning Services\Courses\COMM 203\Siobhan Flex Work with Brian The Role of
Last updated: May 4, 2017 The Role of Unions COMM 203 Flex at the Sauder School of Business, University of British Columbia W:\Learning Services\Courses\COMM 203\Siobhan Flex Work with Brian The Role of
Economics Unit 2. The United States Economic System
 Economics Unit 2 The United States Economic System Demand Objective 2.01: Illustrate how supply and demand affects prices. What is Demand? Demand: The desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or
Economics Unit 2 The United States Economic System Demand Objective 2.01: Illustrate how supply and demand affects prices. What is Demand? Demand: The desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or
Case: An Increase in the Demand for the Product
 1 Appendix to Chapter 22 Connecting Product Markets and Labor Markets It should be obvious that what happens in the product market affects what happens in the labor market. The connection is that the seller
1 Appendix to Chapter 22 Connecting Product Markets and Labor Markets It should be obvious that what happens in the product market affects what happens in the labor market. The connection is that the seller
Economics Challenge Online State Qualification Practice Test. 1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from
 1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from A. an increase in tax rates. B. a decrease in consumer spending. C. a decrease in net export spending. D. an increase in business investment.
1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from A. an increase in tax rates. B. a decrease in consumer spending. C. a decrease in net export spending. D. an increase in business investment.
Labor Market Equilibrium. Labor Economics VŠE March 2010
 Labor Market Equilibrium Labor Economics VŠE March 2010 Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Assumptions: Perfect Information: o All workers know relevant details about all jobs; o All employers know relevant
Labor Market Equilibrium Labor Economics VŠE March 2010 Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Assumptions: Perfect Information: o All workers know relevant details about all jobs; o All employers know relevant
(CAPE, AFL-CIO). CAPE
 Dear Candidate: Thank you for your interest in endorsement by the California Association of Professional Employees (CAPE, AFL-CIO). CAPE is honored to support candidates who demonstrate their dedication
Dear Candidate: Thank you for your interest in endorsement by the California Association of Professional Employees (CAPE, AFL-CIO). CAPE is honored to support candidates who demonstrate their dedication
EOCT Test Semester 2 final
 EOCT Test Semester 2 final 1. The best definition of Economics is a. The study of how individuals spend their money b. The study of resources and government c. The study of the allocation of scarce resources
EOCT Test Semester 2 final 1. The best definition of Economics is a. The study of how individuals spend their money b. The study of resources and government c. The study of the allocation of scarce resources
Labour Demand Lecturer: Dr. Priscilla T. Baffour
 Lecture 3 Labour Demand Lecturer: Dr. Priscilla T. Baffour Determinants of Short Run Demand for Labour The wage rate: The wage rate is a very important determinant of labour demand. Thus the higher the
Lecture 3 Labour Demand Lecturer: Dr. Priscilla T. Baffour Determinants of Short Run Demand for Labour The wage rate: The wage rate is a very important determinant of labour demand. Thus the higher the
Practice Problems II EC Questions
 Practice Problems II EC 102.03 Questions 1. What do the following terms mean and how are they calculated? i. The unemployment rate ii. The labor force participation rate Answer: i.the unemployment rate
Practice Problems II EC 102.03 Questions 1. What do the following terms mean and how are they calculated? i. The unemployment rate ii. The labor force participation rate Answer: i.the unemployment rate
GLOSSARY OF LABOR TERMS
 GLOSSARY OF LABOR TERMS Accretion The addition or consolidation of new employees to or with an existing bargaining unit. Across The Board Increases A raise in wages, in terms of dollars or a percentage,
GLOSSARY OF LABOR TERMS Accretion The addition or consolidation of new employees to or with an existing bargaining unit. Across The Board Increases A raise in wages, in terms of dollars or a percentage,
Demand & Supply of Resources
 Resource Markets 1 Demand & Supply of Resources Resource demand Firms demand resources As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost To maximize profit Resource supply People supply resources To the
Resource Markets 1 Demand & Supply of Resources Resource demand Firms demand resources As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost To maximize profit Resource supply People supply resources To the
OCR Economics A-level
 OCR Economics A-level Microeconomics Topic 4: Labour Market 4.1 Wage determination Notes The main influences on demand and supply in labour markets The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour
OCR Economics A-level Microeconomics Topic 4: Labour Market 4.1 Wage determination Notes The main influences on demand and supply in labour markets The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour
Collective Bargaining And Wage Formation Performance And Challenges
 Collective Bargaining And Wage Formation Performance And Challenges We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on
Collective Bargaining And Wage Formation Performance And Challenges We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on
Practice Problem Set 5 (ANSWERS)
 Economics 370 Professor H.J. Schuetze Practice Problem Set 5 (ANSWERS) 1. Autos Slope=-1 Slope = -2 40 A1 U2 U1 F1 F2 20 Food a) The opportunity cost of producing one more unit of food is 2 autos foregone.
Economics 370 Professor H.J. Schuetze Practice Problem Set 5 (ANSWERS) 1. Autos Slope=-1 Slope = -2 40 A1 U2 U1 F1 F2 20 Food a) The opportunity cost of producing one more unit of food is 2 autos foregone.
FACTORS AFFECTING WAGE DETERMINATION. Regional Management Services Inc
 FACTORS AFFECTING WAGE DETERMINATION Regional Management Services Inc DEFINITION It is the process of setting wage rates or establishing wage structure in particular situations. It is linked to a pay scale
FACTORS AFFECTING WAGE DETERMINATION Regional Management Services Inc DEFINITION It is the process of setting wage rates or establishing wage structure in particular situations. It is linked to a pay scale
Not For Sale. Relations. The Historical Development of Unions. Early History
 Appendix C Enhancing Union-Management Relations Southwest Airlines, like a number of other business organizations, has been unionized for years, and both management and the unions have experienced ups
Appendix C Enhancing Union-Management Relations Southwest Airlines, like a number of other business organizations, has been unionized for years, and both management and the unions have experienced ups
Topic 4.1 Outcomes in a Single Market. Professor H.J. Schuetze Economics 370
 Topic 4.1 Outcomes in a ingle Market Professor H.J. chuetze Economics 370 upply and emand Let s put labour supply and demand together to look at ho ages and employment might be determined eoclassical model
Topic 4.1 Outcomes in a ingle Market Professor H.J. chuetze Economics 370 upply and emand Let s put labour supply and demand together to look at ho ages and employment might be determined eoclassical model
Factors of Production and Factor Markets
 Factors of Production and Factor Markets Factors of production: the inputs used to produce goods and services. Labor Land Capital: the equipment and structures used to produce goods and services. Prices
Factors of Production and Factor Markets Factors of production: the inputs used to produce goods and services. Labor Land Capital: the equipment and structures used to produce goods and services. Prices
EMPLOYEE PARTICIPATION IN THE USA: A LEGAL AND MANAGERIAL CONSIDERATION
 EMPLOYEE PARTICIPATION IN THE USA: A LEGAL AND MANAGERIAL CONSIDERATION Mahmut YAVAŞĐ Ph.D. (Leeds) in Business Law, LL.M. (Hertfordshire) in Commercial Law, BA (Marmara) in Business Administration, HND
EMPLOYEE PARTICIPATION IN THE USA: A LEGAL AND MANAGERIAL CONSIDERATION Mahmut YAVAŞĐ Ph.D. (Leeds) in Business Law, LL.M. (Hertfordshire) in Commercial Law, BA (Marmara) in Business Administration, HND
Chapter 9: Labor Section 3
 Chapter 9: Labor Section 3 Objectives 1. Describe why American workers have formed labor unions. 2. Summarize the history of the labor movement in the United States. 3. Analyze reasons for the decline
Chapter 9: Labor Section 3 Objectives 1. Describe why American workers have formed labor unions. 2. Summarize the history of the labor movement in the United States. 3. Analyze reasons for the decline
Chapter 14. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 Labor Chapter Outline A Perfectly Competitive Firm s Demand for Labor Market Demand Curve for Labor An Imperfect Competitor s Demand for Labor Labor Supply Market Supply Curve Monopsony Minimum
Chapter 14 Labor Chapter Outline A Perfectly Competitive Firm s Demand for Labor Market Demand Curve for Labor An Imperfect Competitor s Demand for Labor Labor Supply Market Supply Curve Monopsony Minimum
Chapter Outline McGraw Hill Education. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 14 Labor Chapter Outline A Perfectly Competitive Firm s Demand for Labor Market Demand Curve for Labor An Imperfect Competitor s Demand for Labor Labor Supply Market Supply Curve Monopsony Minimum
Chapter 14 Labor Chapter Outline A Perfectly Competitive Firm s Demand for Labor Market Demand Curve for Labor An Imperfect Competitor s Demand for Labor Labor Supply Market Supply Curve Monopsony Minimum
UNIONS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER OBJECTIVES. At the end of this chapter you will INTRODUCTION
 UNIONS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES At the end of this chapter you will understand why labor unions exist and how they alter the bargaining relationship between employers and employees. You will understand how a
UNIONS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES At the end of this chapter you will understand why labor unions exist and how they alter the bargaining relationship between employers and employees. You will understand how a
VA SHRM. Dr. Lou Pugliese Bridgewater College School of Economics and Business Administration. Labor Pains?
 VA SHRM Dr. Lou Pugliese Bridgewater College School of Economics and Business Administration Labor Pains? How are unions in the United States organized? What are the key provisions of the laws that govern
VA SHRM Dr. Lou Pugliese Bridgewater College School of Economics and Business Administration Labor Pains? How are unions in the United States organized? What are the key provisions of the laws that govern
Managerial Economics Prof. Trupti Mishra S.J.M School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture -29 Monopoly (Contd )
 Managerial Economics Prof. Trupti Mishra S.J.M School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture -29 Monopoly (Contd ) In today s session, we will continue our discussion on monopoly.
Managerial Economics Prof. Trupti Mishra S.J.M School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture -29 Monopoly (Contd ) In today s session, we will continue our discussion on monopoly.
Federal Labor Laws. Paul K. Rainsberger, Director University of Missouri Labor Education Program Revised, February 2004
 Federal Labor Laws Paul K. Rainsberger, Director University of Missouri Labor Education Program Revised, February 2004 XXVII. Primary and Secondary Activity A. Regulation of Secondary Pressure 1. In an
Federal Labor Laws Paul K. Rainsberger, Director University of Missouri Labor Education Program Revised, February 2004 XXVII. Primary and Secondary Activity A. Regulation of Secondary Pressure 1. In an
