A Guide To Successful Damage And Needs Assessment
|
|
|
- Regina Miles
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 South Pacific Disaster Reduction Programme (SPDRP) A Guide To Successful Damage And Needs Assessment Prepared by Angelika Planitz March 97 (Updated October 99)
2 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -1- Table of Contents: 1. PRINCIPALS FOR RELIEF PLANNING 1 2. ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES 1 3. ASSESSMENT TYPES 1 4. INITIAL ASSESSMENT 1 5. DETAILED ASSESSMENT 2 6. SITUATION AND NEEDS ASSESSMENT 2 7. KEYS TO SUCCESSFUL ASSESSMENT 3 8. ELEMENTS OF THE ASSESSMENT PROCESS 3 9. ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY ASSESSMENT TEAMS SOURCES OF INFORMATION ASSESSMENT TOOLS ASSESSMENT ORGANIZATION & ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES DAMAGE ASSESSMENT ACTIVIATION SYSTEM 14 Annex 1 12 Annex 2 13 Annex 3 15
3 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -2- A GUIDE TO SUCCESSFUL DAMAGE AND NEEDS ASSESSMENT The clear and concise assessment of damages, losses and injuries in the aftermath of a disaster is a prerequisite for the effective planning and implementation of relief and recovery. 1. PRINCIPALS FOR RELIEF PLANNING the primary responsibility for disaster relief lies with the affected government country response capacity has to be preferred over outside assistance, in order not to destroy self-help capacities the same princ iple applies to the local situation: community response capacities have to be preferred over government assistance assistance is based on priority humanitarian needs, which have to be determined prior to the disaster relief measures have to be planned in the context of long-term development. This gives an opportunity to reduce vulnerability to future disasters 2. ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES The objectives of damage and needs assessments are to determine: nature and extent of a disaster damage and secondary threats needs of the population resource availability and local response capacity options for relief assistance, longer-term recovery and development needs for international assistance 3. ASSESSMENT TYPES initial assessment detailed assessment 4. INITIAL ASSESSMENT aims at determining relief and immediate response requirements is conducted immediately in the early and critical stage of a disaster, as soon as the conditions allow survey teams to operate (about two to three days after the event) is broad in scope and focuses on overall patterns and trends
4 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -3- identifies: the magnitude of a disaster (without necessarily delivering exact figures) the impact of a disaster on society people s capacity to cope the most urgent relief needs and potential methods for delivery priorities for action the utilisation of resources for immediate response the need for detailed assessment of specific geographical areas or substantive sectors the level of continuing or emerging threats the need for international assistance 5. DETAILED ASSESSMENT aims at determining the longer-term recovery and development requirements is conducted two to four weeks after a disaster, depending on the accessibility of the affected area covers critical sectors in terms of the country s future economic and social development strategy is carried out by specialists in the sectors concerned identifies: recovery programme options estimates on financial and material recovery requirements estimates on value loss through damage damage to the social structure links between relief and development continuing need for relief assistance the need for international assistance 6. SITUATION AND NEEDS ASSESSMENT Both, initial and detail assessments contain: a situation assessment, that depicts a picture of the situation by describing the magnitude of the disaster and the impact on population and infrastructure (what has happened?) a needs assessment, that defines the level and type assistance required for the affected population (what needs to be done?) 7. KEYS TO SUCCESSFUL ASSESSMENT
5 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -4- information has to be accurate - the best sources to obtain information need to be accessed and biased information be avoided information has to be timely - assessments should be carried out as soon as possible after the disaster information has to be continuously updated, in order to re-evaluate the needs and the appropriateness of response and recovery actions emergency and chronic needs have to be distinguished, in order to know what is normal for the location and what is the result of the disaster survey methods, terminologies, ratings and classifications have to be used in a standard manner surveyors have to be sensitive towards the local situation to prevent unrealistic expectations on the part of the affected population information has to be presented in a manner that suits the needs of the respective addressees assessment results have to be presented in a way that makes implications for prioritization and action very clear assessments hardly reflect the full picture of the situation and surveyors have to be aware, that intangible things can be equally important resources to carry out assessments (i.e.: teams, transportation, logistical support) have to be immediately available 8. ELEMENTS OF THE ASSESSMENT PROCESS Every assessment process comprises of five basic elements or activities: Planning and Preparation: Assessments need thorough planning, design and preparation well in advance of a disaster. Most information needs can be identified well in advance. The means for collecting data and the formats in which it is to be presented should be established well in advance during the predisaster planning period. Seek advice widely from survey specialists, statisticians, epidemiologists and people with local knowledge. By preparing to undertake assessments well in advance of a disaster, both the data required and the process most appropriate for its accurate and speedy collection can be identified and refined prior to the disaster. Proper design of sampling and survey methods can increase substantially the accuracy and usefulness of assessment data. Standard survey techniques, questionnaires, checklists and procedures should be prepared to ensure that all areas are examined and that the information is reported using standard terminology and classifications. Please refer to the checklist below:
6 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -5- collect and maintain baseline and background data (for details see annex 1) prepare survey forms for data collection and formats for presentation of results (see annex 2 for lists of available pilot forms) prepare standard survey techniques and procedures pre-identify survey teams know available personnel, resources and stocks pre-identify likely problem areas and indicators develop standards for minimal performance requirements on living conditions, human services, life-sustaining elements, safety (based on baseline data) establish standing agreements for emergency coordination among agencies concerning staff, communication, transport etc. and clarifying roles & responsibilities during the assessment phase Survey and Data Collection: The collection of data about the extent of damage caused by a disaster is the basis upon which decisions on relief and recovery are taken. Information gathering must proceed rapidly and thoroughly. Surveyors should look for patterns and indicators of potential problems. Using procedures developed earlier, key problems should be checked more thoroughly. Sources of information should be identified (e.g. whether the information was observed by the surveyor himself, reported by an informant, collected through a randomly sampled population, or heard by rumor). The information will be more meaningful to those who interpret it if the source is indicated, especially when there are conflicting reports. Please refer to the checklist below: data collection is an ongoing process, which ensures that up-to-date information is always available information requirements and the level of detail of information vary at different times, therefore, different types of assessments are conducted such as initial and detailed assessments the main subjects on which disaster management authorities need information on are: The Disaster Situation: area affected number of people affected mortality rates injuries and illnesses condition of the affected population damage to all sectors level of local response response by NGOs and other agencies secondary threats The Needs of the Population: search and rescue medical and health matters water supplies evacuation clothing shelter and housing administration, transport and communication food supplies agriculture lifelines and critical facilities
7 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -6- Interpretation and Forecasting: Incoming assessment data has to be thoroughly analysed and interpreted in order to become meaningful and useful information for decision-makers. Those performing the analysis must be trained to detect and recognize trends and indicators of problems, to interpret the information and to link it to action programs. Estimates must be constructed of how the situation might develop so that contingency plans can be drawn up. Forecasting requires inputs from many specialists. People with previous disaster experience are likely to be especially helpful. Please refer to the checklist below: cross check and compare reports, check against baseline for validity differentiate chronic and disaster-related needs consider information sources and survey methods avoid generalisation detect and recognise trends and indicators of problems link information to action programmes estimate how the situation might develop in the future. This requires input of specialists who have had extensive experience in previo us emergencies. Reporting: Information and results of the analysis process need to be disseminated in a format that enables disaster managers and decision-makers to formulate action programmes (see annex 3 for a possible format). Monitoring: Assessments must be seen as a continuos process of re-evaluating the needs and the appropriateness of response and recovery interventions. 9. ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY The data collection methods depicted below are some of the most commonly used during emergencies: Initial Self-Assessment: automatically done by key elements in the system, i.e. staff of lifeline facilities, such as power, water or telecom. Visual Inspection: through overflights or sample surveys to achieve a rapid appraisal of the damage. Sample Surveying: through specialist teams which focus on specific characteristics of the affected population. Sentinel Surveillance:
8 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -7- is used predominantly in health emergency monitoring and consists of a reporting system that detects early signs of particular problems in specific areas. Such an early warning system can be introduced also for other context. Detailed Critical Sector Assessments by Specialists: involves technical inspections and assessments by experts. Interviews with Key Informants: as for example village leaders, head-teachers, hospital management or the like. 10. ASSESSMENT TEAMS initial assessments should be carried out by multi-disciplinary assessment teams comprising of four to five members the characteristics of a team are: common interest clear allocation of responsibilities among team members complementary of tasks shared commitment inputs of all members are important to fulfill the task
9 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -8- the skills and competence assessment teams should have are in the fields of: team leader agriculture public works & logistics health (environmental health specialist, epidemiologist, nutritionist) education regional development or other local expertise gender communication assessment teams should be pre-identified and their contact details held at the District Office or Division and be regularly updated assessment staff can be drawn from: national ministries and government departments at all levels national military and navy units local and international NGOs international organisations team members should be adequately trained and familiar with: damage and needs assessments completion of assessment survey forms reporting channels procedures, roles & responsibilities safety & security instructions Prior to the field mission team members should be briefed on: the current situation (whatever is known about the disaster situation) the mission objectives (time frame, sectors to focus on, geographical area to be covered) local particularities their roles, specific tasks and responsibilities available resources (equipment, transport, communication) to whom to report to and how to transmit reports team members should be equipped with: pen or pencils official report forms a board or a file to write on protection of papers from water and dirt blank paper maps of the area food and water for the team fuel supplies spare clothes and first aid supplies for longer missions
10 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page SOURCES OF INFORMATION district or regional government officials sectoral specialists chiefs and other community leaders crews of ships and air-crafts police and other officials in the affected areas individuals living in, coming out or going to the affected area satellite imagery aerial photographs 12. ASSESSMENT TOOLS Standard Field Assessment Reporting Forms standardised, pre-defined reporting forms help national authorities which are responsible for damage assessment to collect, collate and report essential information on the disaster situation depending on the features of the administrative system the types of forms required are: initial assessment reporting forms detailed assessment reporting forms district summary forms these forms should be prepared for the following sectors: rural villages/settlements public works agriculture, fisheries & forestry health education (An overview of all pilot survey forms developed through SPDRP is displayed in annex 2. These forms can be obtained from the project team for in -country adaptation) the structure of the reporting forms should cover about thirteen areas and is similar for various sectors:
11 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -10- The Structure of Assessment Forms: 1. Disaster Identification 2. Location and/or Facility Details 3. Communication Details 4. Access D etails 5. Human & Operational Details 6. Structural Damages 7. Production Damages 8. Equipment Damages 9. Water Supply Damages 10. Power Supply Damages 11. Remaining Threats 12. Source of Information 13. Reporting Officer Details Additional areas for detailed assessments: 14. Estimates on the monetary loss of damage 15. Rehabilitation Requirements National Disaster Situation Report the compilation of all incoming damage information at the national level has the purpose of creating a picture of the overall situation. This supports: decision-making setting of priorities coordination mobilisation of resources (national and international) note the following rules for report writing: reports should be frequently updated and not repeat information that has already been provided (if necessary emphasise since last report ) reports should be instantaneously disseminated, even if certain information is lacking. Missing information can be provided in the update provide a list of unmet needs be explicit and precise and double check figures avoid vague and ambiguous words and phrases follow the instructions and definitions for filling out reporting forms (see bottom or backside of forms) when summarising numbers of people affected, houses destroyed, area affected - try not to present only actual numbers, but also the percentages! Only then it is possible for decision-makers to get a picture of the severeness or extent of the situation. Information such as houses destroyed has little value without knowing whether these are 10% or 80% of the total number of houses. Although the survey forms do not always explicitly ask for percentages, the total numbers can be derived for example by adding houses undamaged + slightly damaged + severely damaged +
12 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -11- destroyed. Also, baseline information could deliver total numbers for deriving percentages. specify the source of information. The information will be more meaningful to those who interpret it if the source is indicated, especially when there are conflicting reports. a standard format for national disaster situation reports is attached (see annex 3) Reports to the International Donor Community If the national response capacities and unmet needs exceed the government s abilities and international assistance is sought, donors want to be informed about the current situation and needs. However, the National Disaster Situation Report does not fully satisfy potential donors information needs. The following background information should be provided, which can already be compiled during the planning phase: National Disaster Management Organisation: authorities responsible for response and rehabilitation, coordinating structures, focal points for international assistance channels for delivery of international assistance: cash contributions: institutions, bank account details etc. in-kind contributions: clearance formalities and costs, details of airport facilities, accessibility of disaster zones, location and capacity of storage facilities etc. baseline information on: population, social structure, political & cultural & religious particularities, consumption patterns of population, food marketing system, agricultural system, and economy. 13. ASSESSMENT ORGANIZATION & ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES Effective disaster assessment requires the coordinated allocation of roles and responsibilities to all entities involved in the assessment process and well-functioning arrangements for information handling and analysis. This can be achieved by designing operational procedures for damage assessment, which establish areas of responsibility and accountability, guidelines and standard working procedures and reporting channels. The first step towards developing assessment procedures is to identify each and every task during the assessment process (see elements of the assessment process). Then allocate for each task the responsible organization. It should be stated whether this organization needs assistance in carrying out assigned responsibilities and who could provide this assistance. Draft procedures will be developed during the workshop that will be finalized and completed succeeding the workshop. Please refer to the following checklist: list each assessment task, then check whether the total of these tasks can achieve the assessment objectives. This is important to ensure that all relevant tasks are covered.
13 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -12- examine each task to see if it can be broadly subdivided. This will help in identifying the tasks that need the involvement of more than one organization. alongside each task, list the organization responsible for it and which one(s) should provide assistance. involve all organizations in this process likely to play a role to make sure that they agree to that role.
14 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page DAMAGE ASSESSMENT ACTIVIATION SYSTEM Pre-Impact work on activities listed under planning and preparation of assessments Stage One - Readiness contact assessment team members and hold them on stand-by; identify replacements where necessary hold assessment reporting forms ready recapitulate procedures for damage assessment Stage Two - Stand -by depending on the prognosis of future development of the disaster threat: identify vulnerable areas, where impacts are likely examine availability of personnel to support collation and analysis of assessment forms examine availability of transportation and communication facilities as well as other equipment in case assessment teams will be mobilised (this includes provisions for search and rescue) Stage Three - Activation complete stage one and stage two activities Post -Impact activate damage assessment teams brief teams teams carry out field assessments teams submit assessment data interpret incoming information compile and disseminate reports (see roles and responsibilities) monitor assessment process SOURCES: Disaster Assessment: United Nations Training Programme, UNDP, United Nations Disaster Assessment and Coordination (UNDAC) Field Handbook, UNOCHA, Field Operations Guide for Disaster Assessment and Response, OFDA, FOG version 2.0. Module Four Organizational Plan and Operational Procedure Development, UNDHA SPPO/EMA. Brian Ward: Post Disaster Assessment, ADPC.
15 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -14-
16 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -15- ANNEX 1: Disaster Management Baseline Data Baseline and background data that is relevant for dis aster management purposes is listed below: Baseline Data Population Village/settlement details Health sector details Agricultural sector details Educational facility details Transportation network details Plant and equipment Commercial sector Food supply Critical government stockpiles Social system Lifelines Communication Critical facilities Manpower Shelter and evacuation facilities air sea roads/bridges location of central economic sectors or high risk sectors food fuel energy building material relief materials pharmaceuticals water power sewage waste broadcasting radio government buildings critical persons in emergency phase Location capacity Specific baseline data reporting forms may be developed.
17 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -16- ANNEX 2: Pilot Damage Assessment & Baseline Data Forms Developed through SPDRP Baseline Data Time Form By Contents Baseline Data Form - Rural Village / Settlement Before a disaster strikes; updates on a yearly basis prior to the cyclone season as soon as possible after the disaster Baseline Data Form - Rural Health Facility Baseline Data Form - Educational Institution Baseline Data Forms - Agriculture: crop and fruit trees livestock Sectoral baseline & background data about the conditions in the rural areas: resources general problems and needs Sectoral baseline & background data: resources & personnel general problems and needs Sectoral baseline & background data: resources & personnel general problems and needs Sectoral baseline & background data: resources & personnel general problems and needs Initial Needs and Damage Assessment Time Form By Contents Initial Damage Report - Rural Village / Settlement Initial Damage Report -Rural Health Facility Initial Damage Report -Educational Institution Initial picture of: immediate needs of community; esp. life support and safety -> rationing, evacuation etc. extent of damage & losses Early identification of threats to public health epidemiological surveillance immediate needs of village health facilities Initial picture of: immediate needs damage and losses suitability for shelter
18 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -17- Initial Damage Reports - Transportation Infrastructure: Road / Bridge Airfield Wharf Detailed Needs and Damage Assessment Initial picture of: access situation, damages & losses Time Form By Contents Within 14 days Detailed Damage Detailed picture of: Report - Rural Village / long-term needs of Settlement: through household households and communities surveys rehabilitation requirements damage & estimated loss costs Detailed Damage Report - Rural Health Facility Detailed Damage Report -Educational Institution Detailed picture of health facilities : long-term needs rehabilitation requirements damage & estimated loss costs Detailed picture of: long-term needs rehabilitation requirements damage & estimated loss costs District Summary Forms Time Form By Contents District Summary - Rural Village / Summary of initial assessments Settlement District Summary - Rural Health Facility Summary of initial assessments District Summary - Educational Institution Summary of initial assessments AP/info/assessment/frm/list.doc/96 District Summary - Agriculture crop and fruit trees livestock fisheries & forestry District Summary - Transportation Infrastructure Summary of initial assessments Summary of initial assessments
19 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -18- TYPE OF DISASTER AND NAME: DATE OF REPORT: NATIONAL DISASTER SITUATION REPORT A. SITUATION: 1. Nature of the Disaster Specify: - event, cause, intensity, date, time, place. 2. Area Affected Specify: - name, size, climate, topography - estimated total number of population of affected area - worst affected areas 3. Impact 3.1. Damage by Sector: - buildings (type of construction) - lifelines and critical facilities: - transport and infrastructure (roads, railways, bridges, ports, airports) - telecommunications - health facilities - public utilities (electricity, gas, fuel, water supply, sanitation) - agriculture and fisheries (crops, livestock, irrigation, fishing boats and equipment) 3.2. Effects on Population Specify: - number of dead, missing, injured - number of people affected in specific ways, e.g. homeless, evacuated 4. Projected Evolution/Secondary Threats Specify: - how is situation expected to develop (further flooding, population movements, potentially hazardous sites, release of toxic substances etc.) B. NATIONAL RESPONSE 5. Administrative Measures Specify: - nature and expected outcome of measures taken; e.g. declaration of emergency, requisition of means of transport, restrictions on movements 6. Operations/Mobilization of Resources Specify: - search and rescue actions, evacuations, assessment, mobilization of local resources, distribution of relief, allocation of emergency funds etc. 7. Constraints Specify: - areas where national response capacity seems to be overburdened C. IN -COUNTRY INTERNATIONAL RESPONSE 8. Priority needs Specify: - unmet priority needs under the following sub-headings: search and rescue, medical teams and supplies, shelter, blankets, clothing, household utensils, water and sanitation s, food items, logistics, communications, repairs to infrastructure, expertise for assessment and coordination. - quantities etc. 9. Assistance items which are not needed Specify and explain why 10. Government requests Specify: - by whom and to whom - whether provisions have been assured 11. Resources mobilized Specify: - funds, materials, transport, personnel - origin, amount, destination, expected duration 12. Coordination Specify: - mechanisms for coordination of teams, donors and government (e.g. meetings, significant decisions etc.) 13. International pledges and contributions Specify: - list of new pledges/contributions - whether delivered - estimated arrival time
20 SPDRP A Guide to Successful Damage and Needs Assessment Page -19- ANNEX 3:
CONSOLIDATED APPEAL PROCESS GUIDELINES [As endorsed by the Inter-Agency Standing Committee on 13 April 1994]
![CONSOLIDATED APPEAL PROCESS GUIDELINES [As endorsed by the Inter-Agency Standing Committee on 13 April 1994] CONSOLIDATED APPEAL PROCESS GUIDELINES [As endorsed by the Inter-Agency Standing Committee on 13 April 1994]](/thumbs/73/68460929.jpg) CONSOLIDATED APPEAL PROCESS GUIDELINES [As endorsed by the Inter-Agency Standing Committee on 13 April 1994] A. INTRODUCTION The Consolidated Appeal is one of four main components of General Assembly Resolution
CONSOLIDATED APPEAL PROCESS GUIDELINES [As endorsed by the Inter-Agency Standing Committee on 13 April 1994] A. INTRODUCTION The Consolidated Appeal is one of four main components of General Assembly Resolution
International Workshop on Research on Impacts of Tsunamis and Natural Disasters May 2005, Brussels
 International Workshop on Research on Impacts of Tsunamis and Natural Disasters 25-26 May 2005, Brussels Report on Main Recommendations 1.0 Introduction... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Issues raised... 3 4.0
International Workshop on Research on Impacts of Tsunamis and Natural Disasters 25-26 May 2005, Brussels Report on Main Recommendations 1.0 Introduction... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Issues raised... 3 4.0
Declarations. Director s Guidelines for the CDEM Sector (DGL13/12) Resilient New Zealand Aotearoa Manahau
 Declarations Director s Guidelines for the CDEM Sector (DGL13/12) Resilient New Zealand Aotearoa Manahau Declarations Director s Guidelines for the CDEM Sector (DGL13/12) March 2012 ISBN 978-0-478-35560-4
Declarations Director s Guidelines for the CDEM Sector (DGL13/12) Resilient New Zealand Aotearoa Manahau Declarations Director s Guidelines for the CDEM Sector (DGL13/12) March 2012 ISBN 978-0-478-35560-4
Review of information needs after natural disaster Key findings
 Review of information needs after natural disaster Key findings Introduction Following a sudden onset disaster there is typically limited comprehensive information on what the impact of the disaster has
Review of information needs after natural disaster Key findings Introduction Following a sudden onset disaster there is typically limited comprehensive information on what the impact of the disaster has
BRITISH RED CROSS EMERGENCY RESPONSE UNITS CANDIDATE GUIDE
 BRITISH RED CROSS EMERGENCY RESPONSE UNITS CANDIDATE GUIDE 1 Refusing to ignore people in crisis 2 Introduction Thank you for your interest in joining our international Emergency Response Units (ERUs).
BRITISH RED CROSS EMERGENCY RESPONSE UNITS CANDIDATE GUIDE 1 Refusing to ignore people in crisis 2 Introduction Thank you for your interest in joining our international Emergency Response Units (ERUs).
Provincial Disaster Risk Management Planning Guidelines
 Provincial Disaster Risk Management Planning GUIDELINES JULY 2007 Sindh AJK NWFP Balochistan Northern Area Punjab National Disaster Management Authority 1. Introduction The Provincial Disaster Management
Provincial Disaster Risk Management Planning GUIDELINES JULY 2007 Sindh AJK NWFP Balochistan Northern Area Punjab National Disaster Management Authority 1. Introduction The Provincial Disaster Management
WELLINGTON EARTHQUAKE NATIONAL INITIAL RESPONSE PLAN (WENIRP)
 WELLINGTON EARTHQUAKE NATIONAL INITIAL RESPONSE PLAN (WENIRP) T.H. Woodley Ministry of Civil Defence and Emergency Management 2010 NZSEE Conference ABSTRACT The objective of this paper is to describe the
WELLINGTON EARTHQUAKE NATIONAL INITIAL RESPONSE PLAN (WENIRP) T.H. Woodley Ministry of Civil Defence and Emergency Management 2010 NZSEE Conference ABSTRACT The objective of this paper is to describe the
ISASTER RISK REDUCTION EFFORTS IN ZIMBABWE
 D ISASTER RISK REDUCTION EFFORTS IN ZIMBABWE GOVERNANCE - POLITICAL COMMITMENT AND INSTITUTIONAL ASPECTS In Zimbabwe, political will is amply demonstrated by the existence of the legal enabling statute,
D ISASTER RISK REDUCTION EFFORTS IN ZIMBABWE GOVERNANCE - POLITICAL COMMITMENT AND INSTITUTIONAL ASPECTS In Zimbabwe, political will is amply demonstrated by the existence of the legal enabling statute,
1. Introduction 1. INTRODUCTION. Summary
 1. Introduction Summary Civil defence emergency management (CDEM) planning is essential if the impacts of emergencies on people and our communities are to be managed and reduced. Contents The section contents
1. Introduction Summary Civil defence emergency management (CDEM) planning is essential if the impacts of emergencies on people and our communities are to be managed and reduced. Contents The section contents
Delivering and Tracking Climate Change Related ODA
 Delivering and Tracking Climate Change Related ODA Author/Owner: Principal Development Manager - Environment and Climate Change Policy approved: 21/10/2010 by DLT Guidelines approved by: Deputy Director,
Delivering and Tracking Climate Change Related ODA Author/Owner: Principal Development Manager - Environment and Climate Change Policy approved: 21/10/2010 by DLT Guidelines approved by: Deputy Director,
WFP MADAGASCAR SPECIAL OPERATION SO
 WFP MADAGASCAR SPECIAL OPERATION SO 201070 Country: Madagascar Type of project: Special Operation Title: Logistics and Emergency Telecommunications Augmentation and Coordination in Response to the Cyclone
WFP MADAGASCAR SPECIAL OPERATION SO 201070 Country: Madagascar Type of project: Special Operation Title: Logistics and Emergency Telecommunications Augmentation and Coordination in Response to the Cyclone
Briefing Note: Checklist on Law and Disaster Risk Reduction IFRC-UNDP Project (updated 22 October 2014)
 Briefing Note: Checklist on Law and Disaster Risk Reduction IFRC-UNDP Project 2012-2015 (updated 22 October 2014) Overview In 2012, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies
Briefing Note: Checklist on Law and Disaster Risk Reduction IFRC-UNDP Project 2012-2015 (updated 22 October 2014) Overview In 2012, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies
Analysing client requirements
 Analysing client requirements Before you can start to analyse the information you have gathered you should think about what you are trying to achieve . The client has presented you with a business problem.
Analysing client requirements Before you can start to analyse the information you have gathered you should think about what you are trying to achieve . The client has presented you with a business problem.
31. International assistance for New Zealand
 31. International assistance for New Zealand Summary Offers of international assistance or requests for international assistance may result from an emergency. When these occur they are to be considered
31. International assistance for New Zealand Summary Offers of international assistance or requests for international assistance may result from an emergency. When these occur they are to be considered
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Forecast-Based Financing
 MEAL guide Cost-Benefit Analysis for Forecast-Based Financing Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) is a tool used to compare the benefits and costs of a project, program or action. The conclusions drawn from a
MEAL guide Cost-Benefit Analysis for Forecast-Based Financing Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) is a tool used to compare the benefits and costs of a project, program or action. The conclusions drawn from a
Chapter 3. Principles of assessment
 PRINCIPLES OF ASSESSMENT Manual Chapter 1 2 Principles of assessment This section is designed to describe the methods that can be used in the rapid assessment process. It does not cover the interactive
PRINCIPLES OF ASSESSMENT Manual Chapter 1 2 Principles of assessment This section is designed to describe the methods that can be used in the rapid assessment process. It does not cover the interactive
Handbook Basics of Indicators, Targets and Data Sources. 11/30/2011 Produced by Poverty and Environment Initiative (PEI) Project Tajikistan-Phase 1
 Handbook Basics of Indicators, Targets and Data Sources 11/30/2011 Produced by Poverty and Environment Initiative (PEI) Project Tajikistan-Phase 1 1. HOW WILL WE KNOW IF WE VE GOT THERE? 1.1 Laying the
Handbook Basics of Indicators, Targets and Data Sources 11/30/2011 Produced by Poverty and Environment Initiative (PEI) Project Tajikistan-Phase 1 1. HOW WILL WE KNOW IF WE VE GOT THERE? 1.1 Laying the
Chapter 17. Outline programme design
 OUTLINE PROGRAMME DESIGN Chapter Outline programme design The outline programme design is a rapidly produced plan of action for the selected sanitation sectors. This is developed by key agency staff and
OUTLINE PROGRAMME DESIGN Chapter Outline programme design The outline programme design is a rapidly produced plan of action for the selected sanitation sectors. This is developed by key agency staff and
REPORT OF WORKING GROUP 3 AWARENESS AND PREPAREDNESS ACTIONS FOR AN INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI WARNING SYSTEM
 SC/IOC/2005/TSUNAMI/WORK/GP.3 International Coordination Meeting for the Development of a Tsunami Warning and Mitigation System for the Indian Ocean within a global framework UNESCO Headquarters, Paris,
SC/IOC/2005/TSUNAMI/WORK/GP.3 International Coordination Meeting for the Development of a Tsunami Warning and Mitigation System for the Indian Ocean within a global framework UNESCO Headquarters, Paris,
Emergency preparedness and response handbook. Saving lives and protecting rights
 Emergency preparedness and response handbook Saving lives and protecting rights Thirteen-year-old Malik Aman practises using his loudspeaker to warn of fl oods as part of emergency preparedness training
Emergency preparedness and response handbook Saving lives and protecting rights Thirteen-year-old Malik Aman practises using his loudspeaker to warn of fl oods as part of emergency preparedness training
Byblos, Lebanon. Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle)
 Byblos, Lebanon Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Organization: Title/Position: Tony Sfeir Byblos Municipality Municipal member
Byblos, Lebanon Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Organization: Title/Position: Tony Sfeir Byblos Municipality Municipal member
WFP (Ecuador) SPECIAL OPERATION SO (200972)
 WFP (Ecuador) SPECIAL OPERATION SO (200972) Country: Type of project: Title: Total cost (US$): Duration: Ecuador Special Operation Logistics Augmentation and Coordination in Response to the Earthquake
WFP (Ecuador) SPECIAL OPERATION SO (200972) Country: Type of project: Title: Total cost (US$): Duration: Ecuador Special Operation Logistics Augmentation and Coordination in Response to the Earthquake
Elements of EMPRES Food Safety Strategic Plan
 lements of MPRS Food Safety Strategic Plan MPRS Food Safety is a holistic and multidisciplinary programme that aims to prevent and deal with food safety emergencies at a global level by partnering with
lements of MPRS Food Safety Strategic Plan MPRS Food Safety is a holistic and multidisciplinary programme that aims to prevent and deal with food safety emergencies at a global level by partnering with
Shelter and settlement
 Shelter and settlement Executive summary The wide range of natural disasters in the past two years and the scale of the resulting shelter need has continued to highlight the demands on the humanitarian
Shelter and settlement Executive summary The wide range of natural disasters in the past two years and the scale of the resulting shelter need has continued to highlight the demands on the humanitarian
Module 6 Introduction to Measurement
 Module 6 Introduction to Measurement 1 Module Objectives By the end of this module participants will be able to: 1 2 Make initial decisions regarding when you need to collect data and on whom or what you
Module 6 Introduction to Measurement 1 Module Objectives By the end of this module participants will be able to: 1 2 Make initial decisions regarding when you need to collect data and on whom or what you
Briefing for the Minister of Civil Defence
 Briefing for the Minister of Civil Defence Resilient New Zealand Contents 3 Foreword 5 Sector Overview 6 Strategic and Legislative Framework 7 Minister s Role 9 The ministry s Role 10 Key Issues and Themes
Briefing for the Minister of Civil Defence Resilient New Zealand Contents 3 Foreword 5 Sector Overview 6 Strategic and Legislative Framework 7 Minister s Role 9 The ministry s Role 10 Key Issues and Themes
Checklist for RCs and HCs on Emergency Preparedness and Response
 Checklist for RCs and HCs on Emergency Preparedness and Response 2 ABOUT THIS CHECKLIST This checklist provides guidance to RCs and HCs who are confronted with any type of humanitarian emergency. It maps
Checklist for RCs and HCs on Emergency Preparedness and Response 2 ABOUT THIS CHECKLIST This checklist provides guidance to RCs and HCs who are confronted with any type of humanitarian emergency. It maps
NDMO NEOC. Fiji Disaster Management Cluster Framework #1. Preparedness. Response. Early Recovery WASH. Shelter. Education
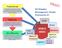 Preparedness The arrangements and systems to ensure that communities are prepared should an emergency occur and that all those resources and systems which are needed to cope with the affects can be efficiently
Preparedness The arrangements and systems to ensure that communities are prepared should an emergency occur and that all those resources and systems which are needed to cope with the affects can be efficiently
joint Joint UNEP/OCHA Environment Unit At Environmental and Humanitarian Crossroads Wendy Cue Chief of Section
 Joint UNEP/OCHA Environment Unit At Environmental and Humanitarian Crossroads joint Wendy Cue Chief of Section Joint UNEP/OCHA Environment Unit OCHA Emergency Services Branch Geneva, Switzerland Vision
Joint UNEP/OCHA Environment Unit At Environmental and Humanitarian Crossroads joint Wendy Cue Chief of Section Joint UNEP/OCHA Environment Unit OCHA Emergency Services Branch Geneva, Switzerland Vision
National Forest Plan
 National Forest Plan Guyana Forestry Commission February, 2001 Contents National Forest Plan objectives 1. Introduction...1 1.1 Forest Policy...1 1.2 Forest legislation...2 1.3 National Forest Plan...2
National Forest Plan Guyana Forestry Commission February, 2001 Contents National Forest Plan objectives 1. Introduction...1 1.1 Forest Policy...1 1.2 Forest legislation...2 1.3 National Forest Plan...2
Participatory rural planning processes
 Rural Transport Training Materials Module 2: Planning, Design, Appraisal and Implementation Participatory rural planning processes Session 2.1 Part 1 Presentation 2.1a The Training Modules Module1. Policies
Rural Transport Training Materials Module 2: Planning, Design, Appraisal and Implementation Participatory rural planning processes Session 2.1 Part 1 Presentation 2.1a The Training Modules Module1. Policies
Terms of Reference. Innovative Models of Livelihood Interventions in Diyala and KRI
 Terms of Reference Household Economy Analysis (HEA) and Baseline Assessment for Building Resilience through Innovative Models of Livelihoods and Market Interventions in Iraq Organization Oxfam GB Country
Terms of Reference Household Economy Analysis (HEA) and Baseline Assessment for Building Resilience through Innovative Models of Livelihoods and Market Interventions in Iraq Organization Oxfam GB Country
HEALTH AND POPULATION b) Water Supply and Sanitation
 HEALTH AND POPULATION b) Water Supply and Sanitation Demand driven approaches Project quality and sustainability are improved by including men and women Water Supply and Sanitation projects are increasingly
HEALTH AND POPULATION b) Water Supply and Sanitation Demand driven approaches Project quality and sustainability are improved by including men and women Water Supply and Sanitation projects are increasingly
Chapter 19. Detailed programme design
 DETAILED PROGRAMME DESIGN Chapter Detailed programme design Note: This section assumes that the outline programme design (described in Chapter 17) has already been conducted. After the initial programme
DETAILED PROGRAMME DESIGN Chapter Detailed programme design Note: This section assumes that the outline programme design (described in Chapter 17) has already been conducted. After the initial programme
TUKASTANTIMES. Massive Earthquake Strikes Tukastan
 SIMULATION ONLY Monday 14 November $2,50 TUKASTANTIMES Massive Earthquake Strikes Tukastan Tukastan Times. The President s office posted a statement on its website calling on the international community
SIMULATION ONLY Monday 14 November $2,50 TUKASTANTIMES Massive Earthquake Strikes Tukastan Tukastan Times. The President s office posted a statement on its website calling on the international community
FAO and Disaster Risk Management. IASC Weekly Meeting 29 April 2009
 FAO and Disaster Risk Management IASC Weekly Meeting 29 April 2009 Agenda 1. What is the DRM Working Group? 2. FAO and Disaster Risk Management 3. Guidance, Toolkits and Technical Expertise 4. DRM Good
FAO and Disaster Risk Management IASC Weekly Meeting 29 April 2009 Agenda 1. What is the DRM Working Group? 2. FAO and Disaster Risk Management 3. Guidance, Toolkits and Technical Expertise 4. DRM Good
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar. The Union Government. The Ministry of Social Welfare, Relief and Resettlement. Notification No.
 The Republic of the Union of Myanmar The Union Government The Ministry of Social Welfare, Relief and Resettlement Notification No. 22 / 2014 The 4 th Waning Day of Tagu, 1376, M.E. ( 7 th April, 2015)
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar The Union Government The Ministry of Social Welfare, Relief and Resettlement Notification No. 22 / 2014 The 4 th Waning Day of Tagu, 1376, M.E. ( 7 th April, 2015)
Significant Service Contracts Framework
 1 Significant Service Contracts Framework The Significant Service Contracts Framework is delivered by New Zealand Government Procurement (NZGP). NZGP delivers on the Ministry of Business Innovation and
1 Significant Service Contracts Framework The Significant Service Contracts Framework is delivered by New Zealand Government Procurement (NZGP). NZGP delivers on the Ministry of Business Innovation and
2. Consultancy assignment to conduct baseline assessment of Building
 TOR Household Economy Analysis (HEA) and Baseline assessment for the building resilience through Social Safety Nets in South-Central Somalia Project Organization Social Safety nets consortium (SSNP consortium)
TOR Household Economy Analysis (HEA) and Baseline assessment for the building resilience through Social Safety Nets in South-Central Somalia Project Organization Social Safety nets consortium (SSNP consortium)
Programming Guide for Strategy Papers
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Programming Guide for Strategy Papers Programming Fiche Urban development Date: November 2008 Programming guidelines The programming exercise will serve to assess whether and in what
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Programming Guide for Strategy Papers Programming Fiche Urban development Date: November 2008 Programming guidelines The programming exercise will serve to assess whether and in what
Bau-Bau, Indonesia. Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action ( )
 Bau-Bau, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical Support Consultant
Bau-Bau, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical Support Consultant
A gender-responsive approach to disaster risk reduction (DRR) planning in the agriculture sector
 A gender-responsive approach to disaster risk reduction (DRR) planning in the agriculture sector Guidance for supporting rural women and men to build resilience in the face of disasters Introduction In
A gender-responsive approach to disaster risk reduction (DRR) planning in the agriculture sector Guidance for supporting rural women and men to build resilience in the face of disasters Introduction In
THE HOUSEHOLD ECONOMY APPROACH: WHAT IS IT AND WHAT CAN IT BE USED FOR?
 THE HOUSEHOLD ECONOMY APPROACH: WHAT IS IT AND WHAT CAN IT BE USED FOR? Introduction The Household Economy Approach is a way of assessing and describing how different types of households get their food,
THE HOUSEHOLD ECONOMY APPROACH: WHAT IS IT AND WHAT CAN IT BE USED FOR? Introduction The Household Economy Approach is a way of assessing and describing how different types of households get their food,
Insert a short description of any ongoing response and assessments already conducted:
 DNA 2 Terms of Reference Template for Completion Note on the ToR: This document has been prepared to guide agencies responsible for a Disaster Needs Assessment (DNA) in preparing a ToR for the assessment.
DNA 2 Terms of Reference Template for Completion Note on the ToR: This document has been prepared to guide agencies responsible for a Disaster Needs Assessment (DNA) in preparing a ToR for the assessment.
Asia and Pacific Commission on Agricultural Statistics
 February 2016 APCAS/16/5.1.1 Asia and Pacific Commission on Agricultural Statistics Twenty-Sixth Session Thimphu, Bhutan, 15-19 Feb 2016 Agenda Item 5 Global Strategy: An Overview and Summary of Progress
February 2016 APCAS/16/5.1.1 Asia and Pacific Commission on Agricultural Statistics Twenty-Sixth Session Thimphu, Bhutan, 15-19 Feb 2016 Agenda Item 5 Global Strategy: An Overview and Summary of Progress
ESF 11 - Agriculture and Natural Resources
 Coordinating Agency: Harvey County Extension Office Primary Agency: Harvey County Extension Office ESF - Agriculture and Natural Resources Support Agencies: Adjutant General's Office, Kansas Division of
Coordinating Agency: Harvey County Extension Office Primary Agency: Harvey County Extension Office ESF - Agriculture and Natural Resources Support Agencies: Adjutant General's Office, Kansas Division of
Developing, Appraising and Approving an Activity Design
 Developing, Appraising and Approving an Activity Design Guideline Last updated: 22 September 2016 Approver: PDLT Contents Overview... 2 Drafting Terms of Reference... 3 Terms of Reference drafted by MFAT...
Developing, Appraising and Approving an Activity Design Guideline Last updated: 22 September 2016 Approver: PDLT Contents Overview... 2 Drafting Terms of Reference... 3 Terms of Reference drafted by MFAT...
MONITORING AND EVALUATION
 MONITORING AND EVALUATION 16 January, 2004 The Federation s mission is to improve the lives of vulnerable people by mobilizing the power of humanity. It is the world s largest humanitarian organization
MONITORING AND EVALUATION 16 January, 2004 The Federation s mission is to improve the lives of vulnerable people by mobilizing the power of humanity. It is the world s largest humanitarian organization
INTER-AGENCY CONTINGENCY PLANNING GUIDELINES FOR HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE. November 2007 IASC. Inter-Agency Standing Committee
 INTER-AGENCY CONTINGENCY PLANNING GUIDELINES FOR HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE November 2007 IASC Inter-Agency Standing Committee INTER-AGENCY CONTINGENCY PLANNING GUIDELINES FOR HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE Endorsed
INTER-AGENCY CONTINGENCY PLANNING GUIDELINES FOR HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE November 2007 IASC Inter-Agency Standing Committee INTER-AGENCY CONTINGENCY PLANNING GUIDELINES FOR HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE Endorsed
Evaluation Inception Report Draft Template
 Decentralized evaluation for evidence-based decision making WFP Office of Evaluation Evaluation Inception Report Draft Template This template provides a suggested structure and guidance on content for
Decentralized evaluation for evidence-based decision making WFP Office of Evaluation Evaluation Inception Report Draft Template This template provides a suggested structure and guidance on content for
Terms of Reference Outcome Evaluation: Disaster Risk Management Programme
 Terms of Reference Outcome Evaluation: Disaster Risk Management Programme Background and Context UNDP has been working with the Government of (GoSL) in the area of disaster risk management (DRM) since
Terms of Reference Outcome Evaluation: Disaster Risk Management Programme Background and Context UNDP has been working with the Government of (GoSL) in the area of disaster risk management (DRM) since
PAKISTAN: CYCLONE. The context. appeal no. 13/99 situation report no. 1 (Revised budget) period covered: 26 May - 5 June 1999.
 PAKISTAN: CYCLONE 11 June 1999 appeal no. 13/99 situation report no. 1 (Revised budget) period covered: 26 May - 5 June 1999 Cyclone victims are now returning home, after being given shelter in public
PAKISTAN: CYCLONE 11 June 1999 appeal no. 13/99 situation report no. 1 (Revised budget) period covered: 26 May - 5 June 1999 Cyclone victims are now returning home, after being given shelter in public
Community-based Early Warning System: The SC UK Experience By Aden Tekle, Early Warning Technical Manager, Ethiopia
 Community-based Early Warning System: The SC UK Experience By Aden Tekle, Early Warning Technical Manager, Ethiopia The early warning system in Ethiopia was created in the aftermath of the 1973 famine.
Community-based Early Warning System: The SC UK Experience By Aden Tekle, Early Warning Technical Manager, Ethiopia The early warning system in Ethiopia was created in the aftermath of the 1973 famine.
SURVIVAL SUPPLY. Procedures and selection 13. Flowchart S1: Steps for assessing survival supply 13
 : SURVIVAL SUPPLY 11 SURVIVAL SUPPLY Procedures and selection 13 Flowchart S1: Steps for assessing survival supply 13 Flowchart S: Source and water treatment process selection for survival supply 14 Checklists
: SURVIVAL SUPPLY 11 SURVIVAL SUPPLY Procedures and selection 13 Flowchart S1: Steps for assessing survival supply 13 Flowchart S: Source and water treatment process selection for survival supply 14 Checklists
The total budget is CHF 12,195,240 (USD 11,147,386 or EUR 7,767,669). Click here to go directly to the summary budget of the plan.
 Logistics Executive summary The Logistics and Resource Mobilisation department s strategic approach over the next two years will focus on sustainably increasing and then stabilizing, the coverage and accessibility
Logistics Executive summary The Logistics and Resource Mobilisation department s strategic approach over the next two years will focus on sustainably increasing and then stabilizing, the coverage and accessibility
Asia: Earthquake and Tsunami Operation Evaluation Framework
 Asia: Earthquake and Tsunami Operation Evaluation Framework International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies Monitoring and Evaluation Department Introduction Following the Asia Earthquake
Asia: Earthquake and Tsunami Operation Evaluation Framework International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies Monitoring and Evaluation Department Introduction Following the Asia Earthquake
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Capacity Assessment Report of the National Disaster Risk Management System in Namibia. 1 P a g e
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Capacity Assessment Report of the National Disaster Risk Management System in Namibia 1 P a g e September 2016 Introduction At the request of the Government of Namibia, an inter-agency
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Capacity Assessment Report of the National Disaster Risk Management System in Namibia 1 P a g e September 2016 Introduction At the request of the Government of Namibia, an inter-agency
Monitoring and Evaluating Social Protection Programs Efforts to Respond to Natural Disasters and Climate Change-Related Shocks
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Why Is It Important to Monitor and Evaluate Disaster- and Climate Shock-sensitive Components
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Why Is It Important to Monitor and Evaluate Disaster- and Climate Shock-sensitive Components
Initiative for Disaster Reduction through ODA
 Initiative for Disaster Reduction through ODA January 18, 2005 Government of Japan Ⅰ Japan s basic position on disaster reduction The disaster caused by the major earthquake off the coast of Sumatra and
Initiative for Disaster Reduction through ODA January 18, 2005 Government of Japan Ⅰ Japan s basic position on disaster reduction The disaster caused by the major earthquake off the coast of Sumatra and
Workshop II Project Management
 Workshop II Project Management UNITAR-HIROSHIMA FELLOWSHIP FOR AFGHANISTAN 2007 Introduction to Project Management 15 17 August 2007, Dehradun, India Presented by: Jobaid Kabir, Ph.D. Fellowship Program
Workshop II Project Management UNITAR-HIROSHIMA FELLOWSHIP FOR AFGHANISTAN 2007 Introduction to Project Management 15 17 August 2007, Dehradun, India Presented by: Jobaid Kabir, Ph.D. Fellowship Program
Framework for the establishment of a Protection Cluster strategy
 Framework for the establishment of a Protection Cluster strategy I. Summary The protection of civilians during armed conflict and natural disaster is a complex and bold endeavour, requiring a multidimensional
Framework for the establishment of a Protection Cluster strategy I. Summary The protection of civilians during armed conflict and natural disaster is a complex and bold endeavour, requiring a multidimensional
1. You should attempt all 60 questions. Each question is worth one mark. 3. Mark your answers on the answer sheet provided. Use a pencil (NOT pen).
 The PRINCE2 Foundation Examination Sample Paper 1 Question Booklet Multiple Choice Exam Duration: 1 hour Instructions 1. You should attempt all 60 questions. Each question is worth one mark. 2. There is
The PRINCE2 Foundation Examination Sample Paper 1 Question Booklet Multiple Choice Exam Duration: 1 hour Instructions 1. You should attempt all 60 questions. Each question is worth one mark. 2. There is
Haiti Earthquake 2010 Response and Recovery Programme Final Evaluation
 Haiti Earthquake 2010 Response and Recovery Programme Final Evaluation Terms of Reference (TOR) Summary > Purpose: the British Red Cross seeks to evaluate its Haiti Earthquake 2010 Response and Recovery
Haiti Earthquake 2010 Response and Recovery Programme Final Evaluation Terms of Reference (TOR) Summary > Purpose: the British Red Cross seeks to evaluate its Haiti Earthquake 2010 Response and Recovery
TIER II STANDARD FOR TECHNICAL COOPERATION ADMINISTRATORS INTRODUCTION
 Job Classification Manual Page 1 of 49 TIER II STANDARD FOR TECHNICAL COOPERATION ADMINISTRATORS INTRODUCTION 1. This grade level standard illustrates the application of the ICSC Master Standard (Tier
Job Classification Manual Page 1 of 49 TIER II STANDARD FOR TECHNICAL COOPERATION ADMINISTRATORS INTRODUCTION 1. This grade level standard illustrates the application of the ICSC Master Standard (Tier
United Nations Development Programme GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATORS CONTENTS
 United Nations Development Programme GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATORS CONTENTS PREFACE 1. BASIC DEFINITIONS 2. POLICY FRAMEWORK FOR EVALUATION 3. PURPOSES OF EVALUATION 4. TYPES OF PROJECT EVALUATIONS 5. BASIC
United Nations Development Programme GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATORS CONTENTS PREFACE 1. BASIC DEFINITIONS 2. POLICY FRAMEWORK FOR EVALUATION 3. PURPOSES OF EVALUATION 4. TYPES OF PROJECT EVALUATIONS 5. BASIC
National Civil Defence Emergency Management Plan
 The Guide to the National Civil Defence Emergency Management Plan 2006 Revised June 2009 Approved by Cabinet 12 June 2006 First published June 2006 Revised November 2007 This edition June 2009 ISBN 0-478-25470-0
The Guide to the National Civil Defence Emergency Management Plan 2006 Revised June 2009 Approved by Cabinet 12 June 2006 First published June 2006 Revised November 2007 This edition June 2009 ISBN 0-478-25470-0
Presentation to the National Climate Change Country Team and Other Stakeholders. Suva, 29 March, John E. Hay (GOPA Team Leader)
 Presentation to the National Climate Change Country Team and Other Stakeholders Suva, 29 March, 2011 John E. Hay (GOPA Team Leader) Presentation to the National Climate Change Country Team and Other Stakeholders
Presentation to the National Climate Change Country Team and Other Stakeholders Suva, 29 March, 2011 John E. Hay (GOPA Team Leader) Presentation to the National Climate Change Country Team and Other Stakeholders
Information on national contact and provider of info:
 Information on national contact and provider of info: Name: B.O. Swai Position: Director Organization, Disaster Management Department Address: Prime Minister s Office, P.O. Box 3021 DAR ES SALAAM Country
Information on national contact and provider of info: Name: B.O. Swai Position: Director Organization, Disaster Management Department Address: Prime Minister s Office, P.O. Box 3021 DAR ES SALAAM Country
Sri Lanka: National Water Resources Authority
 Sri Lanka: National Water Resources Authority I. Description of NWASAB (i) Introduction Sri Lanka s water sector reforms are influenced by number of warning signs related to water and non-availability
Sri Lanka: National Water Resources Authority I. Description of NWASAB (i) Introduction Sri Lanka s water sector reforms are influenced by number of warning signs related to water and non-availability
The WHO Global CODE of Practice on the International Recruitment of Health Personnel Implementation by the Secretariat
 The WHO Global CODE of Practice on the International Recruitment of Health Personnel Implementation by the Secretariat WHO/HSS/HRH/HMR/2010.1 The WHO Global Code of Practice on the International Recruitment
The WHO Global CODE of Practice on the International Recruitment of Health Personnel Implementation by the Secretariat WHO/HSS/HRH/HMR/2010.1 The WHO Global Code of Practice on the International Recruitment
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION PUBLIC WEATHER SERVICES PROGRAMME. Guidance on Developing Service Delivery Mechanisms in NMHSs
 WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION PUBLIC WEATHER SERVICES PROGRAMME Guidance on Developing Service Delivery Mechanisms in NMHSs Guidance on Developing Service Delivery Mechanisms in NMHSs 1. Introduction
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION PUBLIC WEATHER SERVICES PROGRAMME Guidance on Developing Service Delivery Mechanisms in NMHSs Guidance on Developing Service Delivery Mechanisms in NMHSs 1. Introduction
Country Report Myanmar
 Regional Expert Workshop on Land Accounting for SDG Monitoring and Reporting Bangkok, Thailand 25-27 September 2017 Country Report Myanmar Mrs. Khin Swe Latt Director Central Statistical Organization Outlines
Regional Expert Workshop on Land Accounting for SDG Monitoring and Reporting Bangkok, Thailand 25-27 September 2017 Country Report Myanmar Mrs. Khin Swe Latt Director Central Statistical Organization Outlines
FIJI NATIONAL DISASTER MANAGEMENT OFFICE CSO DRM NADI WORKSHOP 13 TH NOVEMBER,2013
 FIJI NATIONAL DISASTER MANAGEMENT OFFICE CSO DRM NADI WORKSHOP 13 TH NOVEMBER,2013 FIJI Once known as the Cannibal Isles, because of its ferocious natives. Fiji comprises of about 322 islands and only
FIJI NATIONAL DISASTER MANAGEMENT OFFICE CSO DRM NADI WORKSHOP 13 TH NOVEMBER,2013 FIJI Once known as the Cannibal Isles, because of its ferocious natives. Fiji comprises of about 322 islands and only
Annual Outcome Survey: An Effective Tool for Project Management
 Annual Outcome Survey: The Leasehold Forestry and Livestock Programme (LFLP) has been implemented by the Government of Nepal under the Department of Forests (DoF) and the Department of Livestock Services
Annual Outcome Survey: The Leasehold Forestry and Livestock Programme (LFLP) has been implemented by the Government of Nepal under the Department of Forests (DoF) and the Department of Livestock Services
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council E/ESCAP/CST(5)/6 Distr.: General 12 October 2016 Original: English Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific Committee on Statistics Fifth session
United Nations Economic and Social Council E/ESCAP/CST(5)/6 Distr.: General 12 October 2016 Original: English Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific Committee on Statistics Fifth session
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
 Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Afghanistan National Disaster Management Authority (ANDMA) Director General Dr. Mohammad Daim Kakar Expert Group Meeting, India, New Delhi Date:16-April-2014, 1 Background
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Afghanistan National Disaster Management Authority (ANDMA) Director General Dr. Mohammad Daim Kakar Expert Group Meeting, India, New Delhi Date:16-April-2014, 1 Background
TRAINING Seminar POVERTY ENVIRONMENT MAINSTREAMING IN TAJIKISTAN
 + TRAINING Seminar POVERTY ENVIRONMENT MAINSTREAMING IN TAJIKISTAN + Outline of the Seminar Introduction P-E Mainstreaming and MDGs Relevance to Tajikistan P-E Mainstreaming Process Responsibilities for
+ TRAINING Seminar POVERTY ENVIRONMENT MAINSTREAMING IN TAJIKISTAN + Outline of the Seminar Introduction P-E Mainstreaming and MDGs Relevance to Tajikistan P-E Mainstreaming Process Responsibilities for
Ref. Ares(2014) /11/2014. Resilience Marker. General Guidance (November 2014) Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection
 Ref. Ares(2014)3883617-21/11/2014 Resilience Marker General Guidance (November 2014) Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection 2 / RESILIENCE MARKER / 3 1. What is resilience and why is it important? 2. What
Ref. Ares(2014)3883617-21/11/2014 Resilience Marker General Guidance (November 2014) Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection 2 / RESILIENCE MARKER / 3 1. What is resilience and why is it important? 2. What
Long Term Planning Framework Shelter and Settlement
 Long Term Planning Framework Shelter and Settlement 2012-2015 Photo: Training in building safer roofs provided to affected community members in St Vincent in the aftermath of Hurricane Tomas. 1. Who are
Long Term Planning Framework Shelter and Settlement 2012-2015 Photo: Training in building safer roofs provided to affected community members in St Vincent in the aftermath of Hurricane Tomas. 1. Who are
Module 5: POST-DISASTER REHABILITATION AND RECOVERY
 Module 5: POST-DISASTER REHABILITATION AND RECOVERY July 2013 Knowledge and Training Resource Center on Climate Change and Disaster Risk Reduction Cordillera Studies Center University of the Philippines
Module 5: POST-DISASTER REHABILITATION AND RECOVERY July 2013 Knowledge and Training Resource Center on Climate Change and Disaster Risk Reduction Cordillera Studies Center University of the Philippines
Candidate Brief. Project Coordinator Syria Resilience Project - 3 year fixed term contract
 Candidate Brief Project Coordinator Syria Resilience Project - 3 year fixed term contract November 2016 Dear Candidate, Thank you for your interest in the role of Project Coordinator for the CARE Syria
Candidate Brief Project Coordinator Syria Resilience Project - 3 year fixed term contract November 2016 Dear Candidate, Thank you for your interest in the role of Project Coordinator for the CARE Syria
Patika, Pakistan. Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle)
 Patika, Pakistan Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Habib Mughal Organization: UN-HABITAT - Pakistan Title/Position: Manager
Patika, Pakistan Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Habib Mughal Organization: UN-HABITAT - Pakistan Title/Position: Manager
Ex-Post Evaluation of Japanese Technical Cooperation Project
 Senegal Ex-Post Evaluation of Japanese Technical Cooperation Project Integrated Forestry Community Development Project (PRODEFI) External Evaluator: Keiichi Takaki, Foundation for Advanced Studies on International
Senegal Ex-Post Evaluation of Japanese Technical Cooperation Project Integrated Forestry Community Development Project (PRODEFI) External Evaluator: Keiichi Takaki, Foundation for Advanced Studies on International
Social Aspects and Stakeholder Involvement in Integrated Flood Management
 Social Aspects and Stakeholder Involvement in Integrated Flood Management Presentation by Simeon Otieno Dulo, Lecturer Department of Civil and Construction Engineering, University of Nairobi Training Workshop
Social Aspects and Stakeholder Involvement in Integrated Flood Management Presentation by Simeon Otieno Dulo, Lecturer Department of Civil and Construction Engineering, University of Nairobi Training Workshop
Terms of Reference (ToR) Livelihood and Economic Recovery Specialist
 I. Position Information Post Title: Level: Project: Supervisor: Duty Station: Duration: Individual Consultant/Contract (IC) Capacity Strengthening of NRA for Resilient Reconstruction Income Generation
I. Position Information Post Title: Level: Project: Supervisor: Duty Station: Duration: Individual Consultant/Contract (IC) Capacity Strengthening of NRA for Resilient Reconstruction Income Generation
WFP (Haiti) SPECIAL OPERATION SO
 WFP (Haiti) SPECIAL OPERATION SO 200108 Country: Type of project: Title: Haiti Special Operation Logistics and Telecommunications Augmentation and Coordination for Relief Operations in Response to the
WFP (Haiti) SPECIAL OPERATION SO 200108 Country: Type of project: Title: Haiti Special Operation Logistics and Telecommunications Augmentation and Coordination for Relief Operations in Response to the
Vaglio di Basilicata, Italy
 Vaglio di Basilicata, Italy Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2013-2014) Mayor: Giancarlo Tamburrino Name of focal point: Giancarlo Tamburrino Organization:
Vaglio di Basilicata, Italy Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2013-2014) Mayor: Giancarlo Tamburrino Name of focal point: Giancarlo Tamburrino Organization:
Technical Note Integrating Gender in WFP Evaluations
 Technical Note Integrating Gender in WFP Evaluations Version September 2017 1. Purpose of this Technical Note 1. This technical note shows how gender equality and empowerment of women (GEEW), hereafter
Technical Note Integrating Gender in WFP Evaluations Version September 2017 1. Purpose of this Technical Note 1. This technical note shows how gender equality and empowerment of women (GEEW), hereafter
7. Police 7. POLICE. Summary
 7. Police Summary The New Zealand Police (Police) are responsible f the maintenance of law and der during an emergency. They may exercise special powers during a state of emergency, and will liaise with
7. Police Summary The New Zealand Police (Police) are responsible f the maintenance of law and der during an emergency. They may exercise special powers during a state of emergency, and will liaise with
MODULE 1 ICS ORIENTATION
 STANDARDIZED EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM APPROVED COURSE OF INSTRUCTION FIELD COURSE MODULE 1 ICS ORIENTATION AUGUST 1995 STUDENT REFERENCE MANUAL CONTENTS CONTENTS... i STUDENT INFORMATION... 1 Course
STANDARDIZED EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM APPROVED COURSE OF INSTRUCTION FIELD COURSE MODULE 1 ICS ORIENTATION AUGUST 1995 STUDENT REFERENCE MANUAL CONTENTS CONTENTS... i STUDENT INFORMATION... 1 Course
IASC Guidelines Common Operational Datasets (CODs) in Disaster Preparedness and Response
 IASC Guidelines Common Operational Datasets (CODs) in Disaster Preparedness and Response As requested by the 77 th IASC Working Group meeting IASC Endorsed November 1 2010 Introduction 1. The IASC Guidelines
IASC Guidelines Common Operational Datasets (CODs) in Disaster Preparedness and Response As requested by the 77 th IASC Working Group meeting IASC Endorsed November 1 2010 Introduction 1. The IASC Guidelines
Factsheet: Social Return on Investment (SROI) as self-assessment method for NRNs
 Factsheet: Social Return on Investment (SROI) as self-assessment method for NRNs NRN Peer-to-peer Training - Module 7 England, May 2014 1. Social Return on Investment (SROI) method 1.1 Overview of the
Factsheet: Social Return on Investment (SROI) as self-assessment method for NRNs NRN Peer-to-peer Training - Module 7 England, May 2014 1. Social Return on Investment (SROI) method 1.1 Overview of the
FAO actions to implement the IASC Transformative Agenda (December 2012)
 Background FAO actions to implement the IASC Transformative Agenda (December 2012) Humanitarian and emergency operations to support livelihoods, food security and food and livestock production have grown
Background FAO actions to implement the IASC Transformative Agenda (December 2012) Humanitarian and emergency operations to support livelihoods, food security and food and livestock production have grown
Draft. Guidelines on addressing Statistical Capacity in the. Country Programming Framework (CPF)
 Draft Guidelines on addressing Statistical Capacity in the Country Programming Framework (CPF) ... To change... The designation employed and the presentation of material in this information product do
Draft Guidelines on addressing Statistical Capacity in the Country Programming Framework (CPF) ... To change... The designation employed and the presentation of material in this information product do
Monitoring and Evaluation Training Modules Table of Contents
 1 ASSESSMENT, MONITORING AND EVALUATION: DEFINITION AND PURPOSE 1.1 MONITORING AND EVALUATION: WHAT, WHY, WHEN 1.1.1 DEMISTIFYING M&E: M&E IN DAILY LIFE FN M&E in daily life CCS - 1.1.2 ASSESSMENT, MONITORING
1 ASSESSMENT, MONITORING AND EVALUATION: DEFINITION AND PURPOSE 1.1 MONITORING AND EVALUATION: WHAT, WHY, WHEN 1.1.1 DEMISTIFYING M&E: M&E IN DAILY LIFE FN M&E in daily life CCS - 1.1.2 ASSESSMENT, MONITORING
Deliverables, added value and limitations of the PDNA
 D1_S1_P1 Rationale and objectives for the PDNA Deliverables, added value and limitations of the PDNA Key actors roles and responsibilities Partnership and results for PDNA What is a PDNA? PDNA is a globally
D1_S1_P1 Rationale and objectives for the PDNA Deliverables, added value and limitations of the PDNA Key actors roles and responsibilities Partnership and results for PDNA What is a PDNA? PDNA is a globally
SEMS Emergency Operations Center (EOC) Course for Schools. Orange County Emergency Management Organization Schools Committee
 SEMS Emergency Operations Center (EOC) Course for Schools Orange County Emergency Management Organization Schools Committee Nine SEMS EOC Course Modules SEMS Overview [C1] Disaster Management Principles
SEMS Emergency Operations Center (EOC) Course for Schools Orange County Emergency Management Organization Schools Committee Nine SEMS EOC Course Modules SEMS Overview [C1] Disaster Management Principles
Terms of Reference for Final Evaluation of Oxfam s Syria Crisis Response programme in Syria
 Terms of Reference for Final Evaluation of Oxfam s Syria Crisis Response programme in Syria Programme title: Oxfam s Syria Crisis Response in Syria Sector of intervention: Water, Sanitation and Hygiene
Terms of Reference for Final Evaluation of Oxfam s Syria Crisis Response programme in Syria Programme title: Oxfam s Syria Crisis Response in Syria Sector of intervention: Water, Sanitation and Hygiene
DISASTER RISK REDUCTION
 DISASTER RISK REDUCTION CONCEPTS AND MEASURES Session 3 Training Module on Climate Change considerations in the coastal zone and Disaster Risk Reduction MFF Regional Training Course Semarang, Indonesia
DISASTER RISK REDUCTION CONCEPTS AND MEASURES Session 3 Training Module on Climate Change considerations in the coastal zone and Disaster Risk Reduction MFF Regional Training Course Semarang, Indonesia
UN YOUTH VOLUNTEER DESCRIPTION OF ASSIGNMENT
 Preamble: UN YOUTH VOLUNTEER DESCRIPTION OF ASSIGNMENT The United Nations Volunteers (UNV) programme is the UN organization that promotes volunteerism to support peace and development worldwide. Volunteerism
Preamble: UN YOUTH VOLUNTEER DESCRIPTION OF ASSIGNMENT The United Nations Volunteers (UNV) programme is the UN organization that promotes volunteerism to support peace and development worldwide. Volunteerism
