QUALITY FRAMEWORK FOR COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION PROGRAMS: A USER S GUIDE
|
|
|
- Kory Wilkerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUALITY FRAMEWORK FOR COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION PROGRAMS: A USER S GUIDE 1
2 KEY CONTRIBUTORS Deborah Bushway, CBE Consultant C-BEN COLLABORATORY CO-AUTHORS AND SPECIAL CONTRIBUTORS: Alison Kadlec, Consultant to Public Agenda Madison Gordon, Public Agenda Charla Long, C-BEN Executive Director Ryan Anderson, University of Wisconsin-Extension Lauren Carris, Western Governors University Jeannie Copley, Northern Arizona University Erin Crisp, Indiana Wesleyan University Donna Diller, Central New Mexico Community College Brooks Doherty, Rasmussen College Emily Dustin, Motivis Learning Franz Feierbach, Salt Lake Community College Shonda Gibson, Texas A&M University-Commerce Josh Herron, Anderson University South Carolina Nina Morel, Lipscomb University Kathy Strang, Walden University Jessica Stumpff, Sinclair College Nan Travers, SUNY Empire State College Anna Van Wie, Learning Objects Heidi Wilkes, Southern New Hampshire University Hadassah Yang, Brandman University Jenny Yu, CBEESC-Sagence Learning WHY QUALITY? WHY NOW? The C-BEN Quality Framework for CBE Programs was developed in response to a growing need for definitions of quality relating to competency-based education. As the number of CBE programs continues to grow, many constituents are looking for guidance to identify high quality CBE programs. Potential students and their families need to know that credentials earned through CBE programs will support them in achieving their goals. Accreditors and regulators want to support innovation and maintain guardrails to protect against fraud and abuse. Institutions need guidance as they create new programs. This Framework is foundational in enabling the ongoing innovation and growth of the CBE field. QUALITY FRAMEWORK FOR COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION PROGRAMS: A User s Guide Released by the Competency-Based Education Network with support from Lumina Foundation. Available online at Copyright 2018 Competency-Based Education Network. 1
3 HOW WAS THIS FRAMEWORK DEVELOPED? It became clear to the leaders of C-BEN that efforts to grow demand, build capacity and remove barriers for CBE were hindered by the lack of a quality definition. In response to this need, the C-BEN Quality Standards Task Force was created. The members of this Task Force drew from the Shared Design Elements and Emerging Practices of Competency- Based Education, and brought together leading program designers and system administrators from C-BEN institutions representing an array of models. This task force worked together over 2016 to create the first edition of Quality Principles & Standards for Competency- Based Education Programs through an iterative and inclusive process, developing principles and standards universal enough to apply to all CBE programs, regardless of model variations. In the future, we envision these universal principles and standards will be augmented by additional stackable principles and standards based on research, as well as modelspecific, programmatic features. The Task Force s goal was to provide elements of quality with related principles and standards that are at once accessible and aspirational. This was achieved by the use of performance indicators embedded in the Development Guides designed to make the principles and standards multidimensional. The performance indicators for each of the principles were released in draft form in May 2017, and feedback was gathered from Spring, 2017 C-BEN convening attendees as well as through an online portal established to solicit feedback from the field. This feedback was incorporated into the final version Development Guides. The process of developing the Framework has been inclusive of both the C-BEN community and the wider field. Not only did C-BEN members from 30 institutions and four state university-systems offer feedback, but also over a hundred other individuals from around the country provided guidance that informed this final version. In addition, a convening of roughly 40 C-BEN members and more than a dozen national experts and regulators was held in late 2016 to finalize the standards and begin ongoing work on development guides. WHO SHOULD USE THE FRAMEWORK? HOW SHOULD WE USE THE FRAMEWORK? C-BEN knows full well that the evolution of the field and the growth of the evidence base will require that these principles and standards be regularly revisited and updated to reflect the state of knowledge. This edition of the Quality Framework for CBE Programs is intended to inform strong program design, ease accreditation, and build the confidence of regulators working to create safe space for responsible innovation. Ongoing refinement and revision from the field at-large will be necessary to ensure its use and relevancy in building and refining quality competency-based education programs. C-BEN s aim with this work is to provide guidance to the field, allowing institutions to draw on these elements, principles and standards to inform the design, implementation or scaling of high-quality programs. The Framework also can provide guideposts and assurances to policymakers and accreditors tasked with regulating this vibrant, and still emerging, field of practice. For institutions, the Framework document by itself can feel overwhelming, and perhaps even confusing. In order to support institutional adoption and use of the Framework, this workbook has been developed. Several institutions have already used the Framework to guide their development of CBE programs, and we think that other institutions can benefit from this process as well. This workbook is intended to serve as a support layer between the Framework and institutions wishing to use the Framework. Our goal is not to offer a pathway or the right answers to developing and/or improving CBE programs, but rather to offer the high-level, highleverage questions to be considered to accelerate and enable your work. 2 3
4 01 Demonstrated Institutional Commitment To and Capacity For CBE Innovation In order to produce a high-quality CBE program, the institution must build a foundational infrastructure in support of competency-based education. This includes the development of a CBE philosophy and commitment as it relates to the institution s mission, the design of the program structure and the definition of appropriate supports for the program and its learners (including people, policy and process supports). The institution must also make appropriate financial investments in the program, understanding that the returns on investment (ROI) for CBE programs are generally longer-term, and recognizing that such investments are often necessary both to achieve regulatory and accreditor compliance and to provide learners with an adequate and appropriate support structure. ILLUSTRATION #1: ILLUSTRATION #2: X College has decided to seriously consider offering a CBE program. As a part of the exploration process, they form a small working group to gather information regarding CBE models, success, challenges and current state programs. They decide to complete both a literature review and to attend a number of conferences in order to learn both the theory and the practice of CBE. They spend a few months gathering information and then come together to synthesize what they learned from college visits, conferences, books and articles. This synthesis results in a recommendation for X College s own variety of a CBE program, as well as which credential ought to be offered first via CBE. X College is ready to design and develop their first CBE program. They start with a kick-off meeting to engage many of the internal and external stakeholders of the College. During this meeting, they share market data they have gathered about the need for this program, alignment of this program to the College s strategic plan, and how the University is defining CBE. They offer a short overview of how CBE is being implemented nationally and explain the vision for X College s approach to CBE. They construct a process to engage attendees deeply collecting their concerns, hopes, challenges and fears about CBE generally and CBE at X College specifically. They build a series of communications and meetings based on the issues identified at this kick-off meeting. How does CBE fit with your institution s mission? What does CBE look like at your institution? What are your regulatory requirements? (institutional and programmatic) What institutional policies need to change to accommodate CBE? Executive sponsor Representatives from governing board/president CBE steering committee Budget/finance representatives Faculty from program s department Financial aid Registrar Instructional designers Curriculum influencers Institutional research IT staff Marketing CBE program sponsor Project management Link to/knowledge of accreditation Information about how other institutions deliver CBE Time and space Change management plan Staff to implement CBE program as designed Intake and screening tools CBE specific orientation What is your business model? What data can you use to measure student success? Clarify your institution s why for this work, and create a roadmap for what you want to accomplish. Have an answer to the question why are we doing this?. Involve all stakeholders early. Develop a guide or roadmap for CBE at your institution. Understand institutional policies and accrediting bodies. Advising 4 5
5 02 Clear, Measurable, Meaningful and Integrated Competencies ILLUSTRATION #1: X College is ready to get to work on identifying the competencies for their first CBE credential. Because it is a healthcare credential, they have invited the local hospital and clinic administrators to attend a daylong workshop. They also have included the faculty with expertise in these programs. At the end of the day, they want to have a rough draft of program-level competencies. After setting a time for the meeting and gathering commitment from external partners to attend (the hardest part of this work), the CBE planning group at X College select a few resources from their earlier work to share with the group. These resources include a case study of another institution s program in a similar area, requirements from employers to hire people with this credential, any relevant licensing requirements and any specialized accreditor requirements. The day begins with an orientation to CBE and an explanation of the vision and definitions for CBE at X College. Small groups review requirements from employers, accreditors and licensing boards, pulling out essential competencies. The groups share their initial competency lists, looking for similarities and gaps. At the end of the day, the group has developed a draft of the overarching competencies for this program, with strong buy-in from across the group. Each competency is explicitly stated and provides unambiguous descriptions of what a learner must master to complete a program of study. Each competency includes the theory and the application of theory required for mastery at the appropriate level for the credential being earned. Each competency connects to content and learning activities designed to support learners in developing the proficiencies required by the program to award a credential. Each competency is measurable and can be reliably and validly assessed. ILLUSTRATION #2: X College is ready to move ahead with the competencies for the credential that they intend to offer. Now, they have to build the base of the program they have to scaffold and organize the competencies so that the assessments can be built to align to the competencies. At X College, this means that they pulled together a smaller working group of faculty experts, instructional designers and an assessment specialist. Since this is the first CBE program at X College, this team had to develop a hierarchy and nomenclature system (and a glossary to capture this) that supports moving from the larger competencies to units and tasks that are transparent and more easily assessed. In this case, X College decided to move to a learning hierarchy that looked like this: Competency Sub- Competency Learning Outcome Criteria. Then, as a team, they tackled each previously defined competency and articulated the flow down to criteria. They were careful to check that they were inclusive of the entire domain covered by each competency, including both cognitive and soft skills where relevant. People who understand and can represent industry standards Employers Faculty Staff Instructional designers C-BEN Competency Development Guide National Institute for Learning Outcomes Assessment (NILOA) resources Relevant professional organization standards and accrediting body resources Time for faculty and SMEs Project manager How have you defined competencies so that they can be distinguished from outcomes or learning objectives? How have levels of achievement for each competency been identified appropriately for the credential being earned? Gather resources and people to develop competencies, onboard/orient stakeholders regarding quality CBE (e.g.: backwards design, assessment), and determine where competencies are mapped and the levels of achievement required. Once the competency development process is established, it can be replicated. Remember that competencies are not complete without clear assessments. 6 7
6 03 Coherent, Competency Driven Program and Curriculum Design Competency-based education programs use an intentional and transparent approach to curricular design that provides a learner with the full range of competencies necessary to meet post-graduation demands. These programs intentionally seek to reduce racial, ethnic, socioeconomic, gender and other potential bias in their design, delivery and implementation. This academic model, which provides clear pathways to completion, builds a unified body of knowledge that leverages frameworks, disciplines, standards, national norms, workforce and societal needs. Learners are at the core of the program s design, and the logic of the program (as well as its associated assessment strategy) supports flexibility in pacing. The curricular design ensures that the level and complexity of the competencies are congruent with the achievements required for the academic level of the credential. ILLUSTRATION: Once X College had built the framework for competencies, one of the next steps (along with assessment creation) was to build out the curriculum. For this work, the faculty and instructional designers broke into smaller working teams, each focused on a specific competency and the pathway to demonstration of mastery for that competency. Each team considered what content was necessary for successful student acquisition and demonstration of their assigned competency. They also considered best delivery format and how to best support any areas that were likely to present larger challenges to students. They began to consider how to best provide and/or acquire this content and support material. They recommended a blend of textbook, open educational resources and some homegrown content in the form of videos and formative quizzes. Do you anticipate internal resistance out of fear of change or concerns about watering down of existing curricular requirements? Faculty Instructional design team Assessment office CIO or IT staff Employers (industry) Students Accrediting body Legal affairs Financial aid staff Project plan Financial resources Market analysis to establish the business case Sample curriculum (lexicon) Communication plan Start with a needs analysis. How does your CBE program solve a gap or problem for employers or your community? Identify key stakeholders, internally and externally. Seek external validation through other frameworks and employer input. Build in methods to gather data for continuous improvement of curriculum. Governance groups 8 9
7 04 Credential-Level Assessment Strategy with Robust Implementation Authentic assessments and their corresponding rubrics are key components of CBE, which is anchored by the belief that progress toward a credential should be determined by what learners know and are able to do. The overarching assessment strategy is comprised of assessments designed both to inform the learning journey (often referred to as assessment for learning, or formative assessment) and to validate mastery (often referred to as assessment of learning, or summative assessment). In CBE models, assessments are intentionally aligned to competencies and cognitive levels, and use a range of assessment types and modalities to measure the transfer of learning and mastery into varied contexts. Authentic assessment design and use follow best practices for assessment professionals. ILLUSTRATION: X College recognized that the faculty at their college used varying forms of assessment, and that many faculty were quite passionate about the approaches they used. They gathered a group of faculty who were affiliated with this new CBE credential to discuss the assessment approach to be used for this credential. They decided to bring in an external CBE assessment expert, as well as their internal assessment team and instructional designers. The group spent two half days together. First, they discussed the goals of assessment in the CBE program and defined terms such as authentic assessment for their institution. They spent time discussing what assessment means in a mastery environment vs. a grades-based environment. They considered what it means to develop assessments that scaffold along with the content to capture demonstration of competency at the credential level rather than at the assignment or course level. At the end of the two days, they emerged with a set of assessment principles for their program and a shared sense of the work to be done next. Faculty (specialty faculty and generalists) Instructional designers SME/field experts Assessment specialists IT staff Accessibility experts Learning analytics experts Expertise in assessment methods Incentives for doing the work Plan for revision and improvement of assessments Technology resources Professional development training on assessment methodologies Built-in flexibility to fit your needs and culture How is your institution equipped to make the mind-set and practice shift? What are the learning analytics you want to collect and analyze? What is needed to support the design of the overall assessment framework and to map it to your roadmap? Gather resources and people to develop competencies, onboard/orient stakeholders regarding quality CBE (e.g.: backwards design, assessment), and determine where competencies are mapped and the levels of achievement required. Consider using external experts to evaluate your institution s assessment strategy and the training associated with it. Align assessment strategies to other institutional efforts and strategic plan
8 05 Intentionally Designed and Engaged Student Experience CBE professionals (faculty and staff) comprehensively understand the strengths and needs of their target learner population, and put those needs at the core of all decisions, processes and systems. CBE programs offer proactive and personalized support for learners, from determining program fit through alumni relations. Faculty and staff are invested in and involved with understanding and improving the entire learner lifecycle by designing, guiding and supporting the learning journey, including processes that facilitate and encourage meaningful interaction with individual learners. A full array of wraparound learner services and social supports, appropriate to the learners being served, is offered by CBE professionals through a wide range of roles and responsibilities. ILLUSTRATION: X College decided to consider three groups of students as they designed the student experience for this credential: underprepared, prepared, and highly-prepared. They first built the learning pathway (including content, placement of both formative and summative assessment, mandatory advising contact, peer interaction, etc.) for the prepared student. From this base, they built a model of support and engagement for the underprepared student, based on the areas in which they were demonstrating their lack of preparation. Then, they considered how to get out of the way of highly prepared students without sacrificing quality or failing to meet any regulatory requirements. What is the life cycle of your current student services? Consider using performance indicators to survey students and faculty. How is your team ready to consider new approaches for the CBE work? Librarians Counseling/career development office Partnership development Student affairs Accessibility experts Student academic support offices (tutoring, writing centers) Alumni office Student representation Faculty Instructional designers Financial aid Professional development time and resources (possible topics: what are wraparound services? CBE deeper dives, training on specific customer-centered processes) Support for doing the research Student experience integration definition (level of users, built into the design, software development cycle, use data gathering, advanced/intermediate technology challenge, stressing testing) Collect data and integrate this into development Research on learner experience (building continuous improvement model) Conversation with development teams Use Quality Framework performance indicators to locate your program s current state and consider how to move to the next level. Develop processes to review data and use continuous improvement process. Consider leveraging existing processes, such as annual program reviews. Think about the data from project inception. Consider how the learning activities integrate with the other section of the 8 elements in the CBE Quality Framework. What does it mean to truly engage the learner consider how to use transformational elements (i.e., Facebook or social learning). Business office 12 13
9 06 Collaborative Engagement with External Partners Institutions strategically identify and secure the commitment of multiple external partners to inform and support the achievement of their CBE programs purpose and their institutional equity goals. External partners are meaningfully engaged in the design, delivery and evaluation of the institutions CBE programs. They work collaboratively to inform and validate CBE program competencies and curriculum, and to ensure the authenticity of assessments. The result is a relevant, transparent credential and authentic learning experience that is endorsed and trusted by external partners as well as learners. ILLUSTRATION: For the credential being developed, X College brainstormed about local and regional firms who would possibly hire graduates with that credential. They contacted the HR heads and CEOs for each of these firms and informed them of X College s goal to create this new program, explaining the innovative role X College was hoping that employers would play in the design and development of the credential. They followed up the conversations with s asking for levels of interest and commitment in participation. They got responses from 5 employers who were willing to meet and help design the competencies. X College pulled together this team for two separate half days during the early phase of the credential development. The first half-day was an explanation of CBE along with an active review of the competencies drafted by the internal team. The goal of this session was to arrive at a shared set of competencies required for graduates from this credential that would allow employers to hire these graduates with confidence. Later sessions were planned to include input into assessment methods and to develop a system of feedback from the employers to X College regarding graduates performance on the job. What existing external partnerships do you have? Or, how will you develop external partners? Do you have the right external partners at the table? Are you asking the right questions to your partners? How does your existing model need to change to adapt to a CBE model? What adequate communication channels do you have for partners? How will your partners provide components of the learning journey? Advisory board members Faculty Core CBE personnel Institutional alumni State representation Economic development leaders in the community Instructional designers Professional associations Accrediting partners Labor data (BLS, ONET, EMSI) Program curriculum Competency review Assessment validation Look at existing practices and programs. Integrate already existing curriculum approaches, such as DACUM (Developing a Curriculum) to identify necessary skills/curriculum. Showcase employer logos on your website and/or materials. Promote or get commitment from employer partners to provide opportunity for apprenticeships or internships. Leverage the Developing a Curriuculum (DACUM) approach, or other resources to support the work
10 07 Transparency of Student Learning USER S GUIDE Registrar Employers Faculty Instructional designers IT staff (related to digital platform) Students Enrollment advisors should be informed One of the central differentiators of CBE programs is their transparency regarding the learning required to earn a credential. This means that the competencies and their alignment, the pathway to mastering those competencies, the assessment methodologies, and the performance requirements for successful demonstration of competency are clearly articulated to learners and all other stakeholders. Transcription practices make demonstrated competencies transparent to learners, faculty, staff, employers, transfer institutions, accreditors and regulators, often in digital form. Transcripts are designed to support portability and transferability to non-cbe environments and include an extended or comprehensive record with details about the learner s complete accomplishments. CBE program alignment documents Program sequence where applicable Technology options (budget) Lumina and other credential/badges resources Examples from other institutions ILLUSTRATION: X College pulled together a working team including the registrar, their transcript provider, faculty, students, employers and IT staff to consider how they hoped to transcribe the CBE program. They developed a vision with an engaging set of visuals as well as a crosswalk between competencies and courses. They then held conversations with their current transcript provider regarding capabilities to achieve their vision. From these conversations, and conversations with the internal IT team, they developed a roadmap to move from current state of transcription to the desired future state. They plan to initially start with a course based transcript that articulates the competencies in each course bucket, but have a plan to flip this as the program develops and as their capabilities are enhanced. How will your institution address this challenge?: Competency programs are often mapped to courses. Many times this mapping is not included on transcripts. How can your institution create transparency in both directions (course to competency and competency to course equivalency) for students and other stakeholders? Look at options (badges, credentials) to visualize the competencies demonstrated in your program. Determine your institutional goal and vision for transparency of learning. Review the work of other institutions using tools such as the extended transcript that includes competencies. Look for and use solution examples from other institutions
11 08 Evidence-Driven Continuous Improvement Processes Data scientists (IR) Learning analysts Assessment leadership Curriculum/journey design Evangelizers Translators (dashboards) IT/ed tech/its External informants Consultants from employers Alumni research Research/impact/ROI study people Accreditation leadership An evidence-driven, continuous improvement methodology is an essential dimension of competency-based education. To ensure program effectiveness, data are collected and analyzed at regular intervals during the program and post-completion. These data are reported and used to inform learners and faculty, identify and prioritize improvements, evaluate and refine assessment strategy and implementation, monitor equitable learner achievement across diverse groups, optimize learner supports to impact program persistence and completion, and enable external validation of learning. Where performance gaps are identified, the institution actively implements and monitors solutions. Varies based on vision, but most aspirational would include: Technology budget Staff expertise Consultants IT foundation, including integration capacity, migration strategy, data security/protection, data dictionary, glossary of measurement, and tech stacks/ architecture/framework QA process and strategy, management strategy/ process/cadence/rationale, to build capacity for change Discipline to practice ILLUSTRATION: X College has been offering its CBE program successfully for about two years. Due to broader institutional considerations, they are migrating to a new learning management system (LMS) platform. This offers the team an opportunity to revise and reconsider the metrics that they have been using for continuous improvement. The new LMS offers new metrics and cannot produce some of the old metrics the institution has been monitoring for quality and continuous improvement purposes. The team pulls together a series of meetings to map out a new set of metrics, enhancing the clarity of the expectations without losing the momentum gathered through use of the past set of metrics. Once a new draft set is developed, this draft set of metrics is reviewed with employers as well as students and a broader group of faculty. Changes are made to the proposed set of metrics based on this input, and these metrics are implemented, with a planned review process. What is your existing continuous improvement strategy? What infrastructure and/or expertise do you have to engage in continuous improvement of the program? How strong is your change leadership? What data do you want to collect? How will you collect it? What will you do with it? Self-assess on the Quality Framework development guide, and ask what do you as an institution or CBE program do/know/need. Start with a cultural commitment to data driven decisions and insights. Build the capacity for evidence-based decision-making. Expand your community of experts, advocates, and accountability partners within and outside of higher education. Policy advocacy and legal affairs Student experience leadership 18 19
12 NOTES Consulting Services & Technical Assistance C-BEN offers consulting services and technical assistance to help institutions, state systems, and other organizations build new and enhance existing CBE programs. If you would like to learn more about how you can best leverage this resource and C-BEN s services, please contact: Charla Long, Executive Director Competency-Based Education Network charla@c-ben.org
13 Grow Demand Build Capacity Remove Barriers Hanson Drive Franklin, TN
Quality Framework for Competency-Based Education Programs: Crosswalk to Other Standards
 Quality Framework for Competency-Based Education Programs: Crosswalk to Other Quality Framework for Competency-Based Education Programs: Crosswalk to Other 1 Introduction The Competency-Based Education
Quality Framework for Competency-Based Education Programs: Crosswalk to Other Quality Framework for Competency-Based Education Programs: Crosswalk to Other 1 Introduction The Competency-Based Education
Quality Framework for Competency- Based Education Programs
 Quality Framework for Competency- Based Education Programs Released September 2017 C-BEN Contributors QUALITY STANDARDS TASK FORCE MEMBERS Deborah Bushway, Ph.D. CBE Consultant Lumina Foundation Jillian
Quality Framework for Competency- Based Education Programs Released September 2017 C-BEN Contributors QUALITY STANDARDS TASK FORCE MEMBERS Deborah Bushway, Ph.D. CBE Consultant Lumina Foundation Jillian
UNDERSTANDING COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION
 STRATEGY LABS State Policy to Increase Higher Education Attainment StrategyLabs.LuminaFoundation.org UNDERSTANDING TOOLKIT The tools in this packet will help states describe and discuss competency-based
STRATEGY LABS State Policy to Increase Higher Education Attainment StrategyLabs.LuminaFoundation.org UNDERSTANDING TOOLKIT The tools in this packet will help states describe and discuss competency-based
Join the most influential, respected, and visible competency-based education organization
 Join the most influential, respected, and visible competency-based education organization Who is C-BEN? A network of colleges, organizations and individuals dedicated to realizing the potential of competency-based
Join the most influential, respected, and visible competency-based education organization Who is C-BEN? A network of colleges, organizations and individuals dedicated to realizing the potential of competency-based
Illinois State Board of Education
 Illinois State Board of Education February 2010 Guidance Document 10-01 Illinois Induction Program Continuum This document is intended to provide non-regulatory guidance on the subject matter listed above.
Illinois State Board of Education February 2010 Guidance Document 10-01 Illinois Induction Program Continuum This document is intended to provide non-regulatory guidance on the subject matter listed above.
Concordia University Portland College of Education Professional Education Plan (PEP) Professional Administrator Certificate
 Concordia University Portland College of Education Professional Education Plan (PEP) Professional Administrator Certificate High-quality, informed district-level leadership for our public school districts
Concordia University Portland College of Education Professional Education Plan (PEP) Professional Administrator Certificate High-quality, informed district-level leadership for our public school districts
Colorado s Great Early Childhood Education Workforce
 Colorado s Great Early Childhood Education Workforce Progress and Deliverables in Strengthening the Early Childhood Professional Development Infrastructure Through the Race to the Top-Early Learning Challenge
Colorado s Great Early Childhood Education Workforce Progress and Deliverables in Strengthening the Early Childhood Professional Development Infrastructure Through the Race to the Top-Early Learning Challenge
the council initiative on public engagement
 public engagement at the city of edmonton share your voice shape our city the council initiative on public engagement new public engagement practice and implementation roadmap final report CITY OF EDMONTON
public engagement at the city of edmonton share your voice shape our city the council initiative on public engagement new public engagement practice and implementation roadmap final report CITY OF EDMONTON
Competency-Based Education: A Higher Return on Investment?
 Competency-Based Education: A Higher Return on Investment? @Education_AIR @EdPolicyAIR #CompetencyEd Thomas Weko Managing Researcher, AIR June 2015 Copyright 2015 American Institutes for Research. All
Competency-Based Education: A Higher Return on Investment? @Education_AIR @EdPolicyAIR #CompetencyEd Thomas Weko Managing Researcher, AIR June 2015 Copyright 2015 American Institutes for Research. All
PHASE IV: IMPLEMENTATION OF THE POWER OF SUNY Draft: October 19, 2010
 PHASE IV: IMPLEMENTATION OF THE POWER OF SUNY Draft: October 19, 2010 Table of Contents I. Introduction II. Implementation Principles III. Organizational Structure and Process IV. Deliverables V. Conclusion
PHASE IV: IMPLEMENTATION OF THE POWER OF SUNY Draft: October 19, 2010 Table of Contents I. Introduction II. Implementation Principles III. Organizational Structure and Process IV. Deliverables V. Conclusion
LEVERAGING COMPETENCY- BASED EDUCATION AND DIRECT ASSESSMENT TO ADVANCE MIDWIFERY EDUCATION
 LEVERAGING COMPETENCY- BASED EDUCATION AND DIRECT ASSESSMENT TO ADVANCE MIDWIFERY EDUCATION Presented by Dr. Charla Long US MERA Direct Assessment Task Force Webinar Learning Objectives Define and describe
LEVERAGING COMPETENCY- BASED EDUCATION AND DIRECT ASSESSMENT TO ADVANCE MIDWIFERY EDUCATION Presented by Dr. Charla Long US MERA Direct Assessment Task Force Webinar Learning Objectives Define and describe
The practice of constantly assessing personal knowledge and skills and following paths for improvement. have been done by
 Selection Process Rubric PERSONAL DOMAIN Personal competencies refer to the qualities, characteristics and attitudes necessary to achieve personal and system goals Continuous Growth The practice of constantly
Selection Process Rubric PERSONAL DOMAIN Personal competencies refer to the qualities, characteristics and attitudes necessary to achieve personal and system goals Continuous Growth The practice of constantly
How it works: Questions from the OCAT 2.0
 Social Sector Practice How it works: Questions from the OCAT 2.0 OCAT 2.0 is an updated and improved version of our original OCAT survey. It asks nonprofit staff to rate their organization s operational
Social Sector Practice How it works: Questions from the OCAT 2.0 OCAT 2.0 is an updated and improved version of our original OCAT survey. It asks nonprofit staff to rate their organization s operational
Standard 5 Appendix 6
 Standard 5 Appendix 6 MPA PROGRAM ASSESSMENT PLAN May 2013 Part I: Overarching Program Components Purpose: To ensure the MPA program has regular and effective assessment of its mission, goals, public service
Standard 5 Appendix 6 MPA PROGRAM ASSESSMENT PLAN May 2013 Part I: Overarching Program Components Purpose: To ensure the MPA program has regular and effective assessment of its mission, goals, public service
Making a Market for Competency-Based Credentials
 Making a Market for Competency-Based Credentials Executive Summary Making a Market for Competency-Based Credentials 2 Acknowledgments This report is part of a multi-year commitment by Corporation for a
Making a Market for Competency-Based Credentials Executive Summary Making a Market for Competency-Based Credentials 2 Acknowledgments This report is part of a multi-year commitment by Corporation for a
Core Element Assessment Tool
 Core Element Assessment Tool The California Accountable Community for Health (CACHI) core element assessment tool was designed to help local collaboratives develop a shared understanding of their strengths,
Core Element Assessment Tool The California Accountable Community for Health (CACHI) core element assessment tool was designed to help local collaboratives develop a shared understanding of their strengths,
THE ROLE OF COMMUNITY COLLEGES IN THE NATION S BROAD AGENDA OF CHANGE: CURRENT AND EMERGING TRENDS
 THE ROLE OF COMMUNITY COLLEGES IN THE NATION S BROAD AGENDA OF CHANGE: CURRENT AND EMERGING TRENDS The Western Alliance of Community College Academic Leaders 2012 Annual Meeting, Change by Design.edu Keith
THE ROLE OF COMMUNITY COLLEGES IN THE NATION S BROAD AGENDA OF CHANGE: CURRENT AND EMERGING TRENDS The Western Alliance of Community College Academic Leaders 2012 Annual Meeting, Change by Design.edu Keith
DIVERSITY. Strategic Plan. Office of Institute Diversity. Achieving Inclusive Excellence
 DIVERSITY Office of Institute Diversity Strategic Plan Achieving Inclusive Excellence From the Vice President Achieving Inclusive Excellence A Strategic Vision and Plan for the Office of Institute Diversity
DIVERSITY Office of Institute Diversity Strategic Plan Achieving Inclusive Excellence From the Vice President Achieving Inclusive Excellence A Strategic Vision and Plan for the Office of Institute Diversity
NEW DIRECTIONS: A Strategic Plan for Piedmont Technical College, CONTENTS. 1. Introduction. 2. Planning Purpose
 NEW DIRECTIONS: A Strategic Plan for Piedmont Technical College, 2009-2014 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Planning Purpose 3. Vision, Mission, Mission Goals, and Values Statement of Vision Statement of Mission
NEW DIRECTIONS: A Strategic Plan for Piedmont Technical College, 2009-2014 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Planning Purpose 3. Vision, Mission, Mission Goals, and Values Statement of Vision Statement of Mission
MAKING THE CASE FOR COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION
 MAKING THE CASE FOR COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION Webinar 3 of 4 Aligning for Learning: Evaluating Connections THE MAKING THE CASE WEBINAR SERIES This is the third of four webinars in a series about Making
MAKING THE CASE FOR COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION Webinar 3 of 4 Aligning for Learning: Evaluating Connections THE MAKING THE CASE WEBINAR SERIES This is the third of four webinars in a series about Making
California Career Pathways Connecting the Work
 California Career Pathways Connecting the Work CLASP studied the core components and criteria incorporated in nine major federal and California-specific career pathways models and legislation. These ingredients
California Career Pathways Connecting the Work CLASP studied the core components and criteria incorporated in nine major federal and California-specific career pathways models and legislation. These ingredients
Lake Erie College Strategic Plan : Supporting. Empowering. Thriving.
 1 Lake Erie College Strategic Plan -2021: Supporting. Empowering. Thriving. Priorities and Strategic Goals for Each Theme Area [NOTE: ACTION STEPS ARE UNDER DEVELOPMENT AND CONSIDERATION AS OF OCTOBER
1 Lake Erie College Strategic Plan -2021: Supporting. Empowering. Thriving. Priorities and Strategic Goals for Each Theme Area [NOTE: ACTION STEPS ARE UNDER DEVELOPMENT AND CONSIDERATION AS OF OCTOBER
California Career Pathways Connecting the Work
 California Career Pathways Connecting the Work CLASP studied the core components and criteria incorporated in nine major federal and California-specific career pathways models and legislation. These ingredients
California Career Pathways Connecting the Work CLASP studied the core components and criteria incorporated in nine major federal and California-specific career pathways models and legislation. These ingredients
Enabling Structure Terms of Reference Draft August 2018
 1 Enabling Structure Terms of Reference Draft August 2018 Our vision - what we aspire to: A community where everyone thrives and no one is left behind. Our mission - why we exist: Working together differently
1 Enabling Structure Terms of Reference Draft August 2018 Our vision - what we aspire to: A community where everyone thrives and no one is left behind. Our mission - why we exist: Working together differently
Report on Organizational Effectiveness Executive Summary General Administration of the University of North Carolina system
 Report on Organizational Effectiveness Executive Summary General Administration of the University of North Carolina system March 28, 2016 Executive Summary With a mission to discover, create, transmit,
Report on Organizational Effectiveness Executive Summary General Administration of the University of North Carolina system March 28, 2016 Executive Summary With a mission to discover, create, transmit,
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
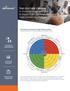 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
Expectations for Student Learning Outcomes Assessment. October 1, 2011
 Expectations for Student Learning Outcomes Assessment for NASPAA COPRA Accreditation October 1, 2011 Authors: David Powell, California State University, Long Beach Michelle Piskulich, Oakland University
Expectations for Student Learning Outcomes Assessment for NASPAA COPRA Accreditation October 1, 2011 Authors: David Powell, California State University, Long Beach Michelle Piskulich, Oakland University
Northeast Transportation Workforce Center (NETWC) Strategic Planning Document (Outcomes Focused) Revised DRAFT: 9/29/15
 Northeast Transportation Workforce Center (NETWC) Strategic Planning Document (Outcomes Focused) Revised DRAFT: 9/29/15 An empowered transportation workforce for the 21 st century The Northeast Transportation
Northeast Transportation Workforce Center (NETWC) Strategic Planning Document (Outcomes Focused) Revised DRAFT: 9/29/15 An empowered transportation workforce for the 21 st century The Northeast Transportation
Target Evaluation Date. Associate Superintendent, Instruction and Institutional Effectiveness
 Institutional Goal 1: Chaffey College will provide quality learning experiences that promote holistic student development and support success and completion in a timely manner. OBJECTIVE 1: Activities
Institutional Goal 1: Chaffey College will provide quality learning experiences that promote holistic student development and support success and completion in a timely manner. OBJECTIVE 1: Activities
Integrated Planning and Institutional Effectiveness: Improvement and Renewal
 T H E U N I V E R S I T Y O F S C R A N T O N Integrated Planning and Institutional Effectiveness: Improvement and Renewal at The University of Scranton S C R A N T O N. Office of Planning & Institutional
T H E U N I V E R S I T Y O F S C R A N T O N Integrated Planning and Institutional Effectiveness: Improvement and Renewal at The University of Scranton S C R A N T O N. Office of Planning & Institutional
Instructional Content and Learning Materials in Competency-Based Education Part I
 Instructional Content and Learning Materials in Competency-Based Education Part I for TAB Lab Dr. Heidi Wilkes, Sr. Director, CAD Kaitlin LeMoine, Assistant Director, CAD February 19, 2016 Session Roadmap
Instructional Content and Learning Materials in Competency-Based Education Part I for TAB Lab Dr. Heidi Wilkes, Sr. Director, CAD Kaitlin LeMoine, Assistant Director, CAD February 19, 2016 Session Roadmap
Guide to Strategic Planning for Schools
 Guide to Strategic Planning for Schools Guide to Strategic Planning for Schools Motivation for Strategic Planning A strategic plan is a document that articulates the school district s mission and vision,
Guide to Strategic Planning for Schools Guide to Strategic Planning for Schools Motivation for Strategic Planning A strategic plan is a document that articulates the school district s mission and vision,
Designing Competency-Based Articulation Agreements: A Framework for State Educational Agencies and Postsecondary Institutions
 Designing Competency-Based Articulation Agreements: A Framework for State Educational Agencies and Postsecondary Institutions Establishing a Stakeholder Team and Defining Goals Handouts November 2016 1000
Designing Competency-Based Articulation Agreements: A Framework for State Educational Agencies and Postsecondary Institutions Establishing a Stakeholder Team and Defining Goals Handouts November 2016 1000
Scope C A S E S T U DY
 Scope CONSULTANCY C A S E S T U DY OVERVIEW Scope, a household charity name in the UK, needed help to audit their existing community, identify sustainable opportunities for rapid growth and gain executive
Scope CONSULTANCY C A S E S T U DY OVERVIEW Scope, a household charity name in the UK, needed help to audit their existing community, identify sustainable opportunities for rapid growth and gain executive
Diversity & Inclusion
 Diversity & Inclusion Framework for an Action Plan to Foster Diversity and Inclusion at Eastern Washington University OVERVIEW Eastern Washington University is committed to building a diverse, inclusive,
Diversity & Inclusion Framework for an Action Plan to Foster Diversity and Inclusion at Eastern Washington University OVERVIEW Eastern Washington University is committed to building a diverse, inclusive,
Democratized Data Driving Discovery RENCI Strategic Plan 2017
 Democratized Data Driving Discovery RENCI Strategic Plan 2017 Stanley C. Ahalt, Ph.D. Director, Renaissance Computing Institute (RENCI) Professor, Department of Computer Science, UNC-Chapel Hill Associate
Democratized Data Driving Discovery RENCI Strategic Plan 2017 Stanley C. Ahalt, Ph.D. Director, Renaissance Computing Institute (RENCI) Professor, Department of Computer Science, UNC-Chapel Hill Associate
Finding the Perfect Fit for Cabrillo s Strategic Plan
 Finding the Perfect Fit for Cabrillo s Strategic Plan The Strategic Planning Update Task Force February 2019 Outline Why do strategic planning? What will happen to the current plan? Vision for Success
Finding the Perfect Fit for Cabrillo s Strategic Plan The Strategic Planning Update Task Force February 2019 Outline Why do strategic planning? What will happen to the current plan? Vision for Success
PRESIDENT & CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER
 POSITION DESCRIPTION FEBRUARY 2019 PRESIDENT & CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER For nearly forty years, (formerly the Corporation for Enterprise Development CFED) has helped make it possible for millions of people
POSITION DESCRIPTION FEBRUARY 2019 PRESIDENT & CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER For nearly forty years, (formerly the Corporation for Enterprise Development CFED) has helped make it possible for millions of people
Korn Ferry Executive to Leader Institute. Accelerating development for senior executives and enterprise leaders.
 Korn Ferry Executive to Leader Institute Accelerating development for senior executives and enterprise leaders. Are your senior leaders ready for enterprise leadership? The transition from executive to
Korn Ferry Executive to Leader Institute Accelerating development for senior executives and enterprise leaders. Are your senior leaders ready for enterprise leadership? The transition from executive to
Systems Appraisal Feedback Report. in response to the Systems Portfolio of. Highland Community College. February 6, for
 Systems Appraisal Feedback Report in response to the Systems Portfolio of February 6, 2015 for The Higher Learning Commission A commission of the North Central Association Contents Elements of the Feedback
Systems Appraisal Feedback Report in response to the Systems Portfolio of February 6, 2015 for The Higher Learning Commission A commission of the North Central Association Contents Elements of the Feedback
Institutional Effectiveness and Assessment Plan
 Institutional Effectiveness and Assessment Plan 1 Table of Contents College of Southern Nevada Institutional Effectiveness and Assessment Plan Vision Statement... 5 Introduction... 5 Institutional Effectiveness
Institutional Effectiveness and Assessment Plan 1 Table of Contents College of Southern Nevada Institutional Effectiveness and Assessment Plan Vision Statement... 5 Introduction... 5 Institutional Effectiveness
Acclaim Badges Promote Skills and Certifications
 Acclaim Badges Promote Skills and Certifications Badges are helping learners tell their professional story Strategic value emerges for human capital management Tips for the webinar Training Industry Our
Acclaim Badges Promote Skills and Certifications Badges are helping learners tell their professional story Strategic value emerges for human capital management Tips for the webinar Training Industry Our
Sustainability Planning Workbook Implementation Guide For Lifespan Respite Grantees and Partners
 Introduction Sustainability Planning Workbook Implementation Guide For Lifespan Respite Grantees and Partners Sustainability is a critical issue for Lifespan Respite Programs. While the Administration
Introduction Sustainability Planning Workbook Implementation Guide For Lifespan Respite Grantees and Partners Sustainability is a critical issue for Lifespan Respite Programs. While the Administration
I. Skills and Knowledge
 Facilitator Core Competencies 1 There are three components to this tool to help you identify strengths and opportunities for growth as a facilitator: (1) skills and knowledge; (2) emotional intelligence;
Facilitator Core Competencies 1 There are three components to this tool to help you identify strengths and opportunities for growth as a facilitator: (1) skills and knowledge; (2) emotional intelligence;
November CFPB Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan
 November 2016 CFPB Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan 2016-2020 Message from Richard Cordray Director of the CFPB At the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), we are dedicated to making sure
November 2016 CFPB Diversity and Inclusion Strategic Plan 2016-2020 Message from Richard Cordray Director of the CFPB At the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), we are dedicated to making sure
Gap Analysis: AQIP Systems Portfolio Review Team Areas to be addressed for the CQR Quality Highlights Report
 Gap Analysis: AQIP Systems Portfolio Review Team Areas to be addressed for the CQR Quality Highlights Report Category One: Helping Students Learn 1. There is a distinct lack of target setting and benchmarking,
Gap Analysis: AQIP Systems Portfolio Review Team Areas to be addressed for the CQR Quality Highlights Report Category One: Helping Students Learn 1. There is a distinct lack of target setting and benchmarking,
Are Your Physicians Aligned?
 WHITE PAPER Are Your Physicians Aligned? An Assessment Tool for Healthcare Leaders Authors: Mark J. Werner, MD and Cynthia Bailey Success in today s uncertain healthcare environment requires engaging physicians
WHITE PAPER Are Your Physicians Aligned? An Assessment Tool for Healthcare Leaders Authors: Mark J. Werner, MD and Cynthia Bailey Success in today s uncertain healthcare environment requires engaging physicians
Leading for change - leadership and management for hospital pharmacy professionals
 CENTRE FOR PHARMACY POSTGRADUATE EDUCATION Leading for change - leadership and management for hospital pharmacy professionals February 2018 Introduction Welcome to the CPPE Leading for change leadership
CENTRE FOR PHARMACY POSTGRADUATE EDUCATION Leading for change - leadership and management for hospital pharmacy professionals February 2018 Introduction Welcome to the CPPE Leading for change leadership
Future-state HR Service Delivery Model Talent Position Descriptions
 Future-state HR Service Delivery Model Talent Position Descriptions Note: Position descriptions are draft and not yet final. Position descriptions are subject to change. 1 P a g e Table of Contents Talent:
Future-state HR Service Delivery Model Talent Position Descriptions Note: Position descriptions are draft and not yet final. Position descriptions are subject to change. 1 P a g e Table of Contents Talent:
Request for Proposals Facilitating Utility Smart Energy Education (FUSED)
 Request for Proposals Facilitating Utility Smart Energy Education (FUSED) Specialized DER Professional Training for Utility Employees Technical point of contact: Business point of contact: Jenny Senff
Request for Proposals Facilitating Utility Smart Energy Education (FUSED) Specialized DER Professional Training for Utility Employees Technical point of contact: Business point of contact: Jenny Senff
Progress Report on Student Success Programs: Using Assessment as a Continual Improvement Strategy
 Progress Report on Student Success Programs: Using Assessment as a Continual Improvement Strategy April 20, 2015 Enrollment Management Student Affairs Assessment Office Office of Curriculum, Learning Design,
Progress Report on Student Success Programs: Using Assessment as a Continual Improvement Strategy April 20, 2015 Enrollment Management Student Affairs Assessment Office Office of Curriculum, Learning Design,
ACAP. Austin Competency Analysis Profile. Advisor. Conducted April 11 th, 2016
 ACAP Austin Competency Analysis Profile Advisor Conducted April 11 th, 2016 Validation Panel Angela Cole-Mota, Advising Supervisor Tung Huynh, Recruiting/Advising Specialist Chris Owens, Advising Supervisor
ACAP Austin Competency Analysis Profile Advisor Conducted April 11 th, 2016 Validation Panel Angela Cole-Mota, Advising Supervisor Tung Huynh, Recruiting/Advising Specialist Chris Owens, Advising Supervisor
APPENDIX E. Sector Specific Objectives
 APPENDIX E Sector Specific Objectives 2018-2019 Each Sector Navigator, in collaboration with Sector Deputy Sector Navigators, has developed Sector Specific Objectives as the first step in fiscal year planning.
APPENDIX E Sector Specific Objectives 2018-2019 Each Sector Navigator, in collaboration with Sector Deputy Sector Navigators, has developed Sector Specific Objectives as the first step in fiscal year planning.
APPENDIX E. Sector Specific Objectives
 APPENDIX E Sector Specific Objectives 2018-2019 Each Sector Navigator, in collaboration with Sector Deputy Sector Navigators, has developed Sector Specific Objectives as the first step in fiscal year planning.
APPENDIX E Sector Specific Objectives 2018-2019 Each Sector Navigator, in collaboration with Sector Deputy Sector Navigators, has developed Sector Specific Objectives as the first step in fiscal year planning.
Career Exploration within Guided Pathways. SUNY Guided Pathways Institutes Julie Thompson Associate Project Director, Connect 4 Completion March 2019
 Career Exploration within Guided Pathways SUNY Guided Pathways Institutes Julie Thompson Associate Project Director, Connect 4 Completion March 2019 I. Career Communities 2018-2019 Career Communities Business
Career Exploration within Guided Pathways SUNY Guided Pathways Institutes Julie Thompson Associate Project Director, Connect 4 Completion March 2019 I. Career Communities 2018-2019 Career Communities Business
Strategic Plan
 2013-2018 Strategic Plan Vision The Florida State University Career Center strives to be the preeminent career center model for designing and delivering comprehensive, innovative, and inclusive career
2013-2018 Strategic Plan Vision The Florida State University Career Center strives to be the preeminent career center model for designing and delivering comprehensive, innovative, and inclusive career
Strategy 5 Table of Contents
 Strategy 5 Table of Contents Introduction and Strategy 5 Learning Objectives 2 Key Terms and Definitions 3 Unit 5.1 Preparing to Engage Providers in Building a Talent Supply Chain Exercise 1 Understanding
Strategy 5 Table of Contents Introduction and Strategy 5 Learning Objectives 2 Key Terms and Definitions 3 Unit 5.1 Preparing to Engage Providers in Building a Talent Supply Chain Exercise 1 Understanding
PORTLAND PUBLIC SCHOOLS HUMAN RESOURCE SERVICES AND DELIVERY
 PORTLAND PUBLIC SCHOOLS HUMAN RESOURCE SERVICES AND DELIVERY January 2013 Overview Portland Public School District (the District or PPS) contracted with AKT to create a new vision and values for their
PORTLAND PUBLIC SCHOOLS HUMAN RESOURCE SERVICES AND DELIVERY January 2013 Overview Portland Public School District (the District or PPS) contracted with AKT to create a new vision and values for their
The State of State Policies for Principal and Superintendent Licensure and Preparation
 The State of State Policies for Principal and Superintendent Licensure and Preparation Participants: Amy L. Reynolds, UCEA, UVA Saroja Warner, CCSSO Michelle D. Young, UCEA, UVA UCEA s State Policy Research
The State of State Policies for Principal and Superintendent Licensure and Preparation Participants: Amy L. Reynolds, UCEA, UVA Saroja Warner, CCSSO Michelle D. Young, UCEA, UVA UCEA s State Policy Research
FOSTERING A CULTURE OF QUALITY
 PROPRIETARY FOSTERING A CULTURE OF QUALITY Ron Lear and Kevin Schaaff Collaboration space, Alexandria, VA LSSSIG MEETING MARCH 29, 2017 AGENDA INTRODUCTION BOOZ ALLEN S APPROACH TO FOSTERING A CULTURE
PROPRIETARY FOSTERING A CULTURE OF QUALITY Ron Lear and Kevin Schaaff Collaboration space, Alexandria, VA LSSSIG MEETING MARCH 29, 2017 AGENDA INTRODUCTION BOOZ ALLEN S APPROACH TO FOSTERING A CULTURE
Tools for Steering Committees
 Tools for Steering Committees What Is a Steering Committee? The Steering Committee is a group comprised of cross-sector community partners representative of the relevant ecosystem that provides strategic
Tools for Steering Committees What Is a Steering Committee? The Steering Committee is a group comprised of cross-sector community partners representative of the relevant ecosystem that provides strategic
P.1 ORGANIZATIONAL DESCRIPTION What are your key organizational characteristics? a. Organizational Environment
 FLATE - Organizational Profile August 2016 This profile is a snapshot of FLATE, the key influences on how it operates and its competitive environment P.1 ORGANIZATIONAL DESCRIPTION What are your key organizational
FLATE - Organizational Profile August 2016 This profile is a snapshot of FLATE, the key influences on how it operates and its competitive environment P.1 ORGANIZATIONAL DESCRIPTION What are your key organizational
Master of Social Welfare (MSW) Program Assessment Plan and Outcomes Assessment Results,
 Assessment Plan and Outcomes Assessment Results, 2013-15 Mission of the Berkeley Social Welfare MSW Program Berkeley Social Welfare s MSW Program develops future leaders of the profession who challenge
Assessment Plan and Outcomes Assessment Results, 2013-15 Mission of the Berkeley Social Welfare MSW Program Berkeley Social Welfare s MSW Program develops future leaders of the profession who challenge
COMPETENCY BASED EDUCATION. A blueprint for planning, executing, measuring, and scaling a student competency assessment infrastructure.
 COMPETENCY BASED EDUCATION A blueprint for planning, executing, measuring, and scaling a student competency assessment infrastructure. CONTENTS BUILDING A CBE HOME 2 GOAL ALIGNMENT 3 CBE BLUEPRINT 4 (The
COMPETENCY BASED EDUCATION A blueprint for planning, executing, measuring, and scaling a student competency assessment infrastructure. CONTENTS BUILDING A CBE HOME 2 GOAL ALIGNMENT 3 CBE BLUEPRINT 4 (The
Specialist Diploma in Search Marketing
 Specialist Diploma in Search Marketing SPECIALIST 30 HOURS STUDY ONLINE digitalmarketinginstitute.com Validated by the Industry Advisory Council. Including members from Content Specialist Diploma in Search
Specialist Diploma in Search Marketing SPECIALIST 30 HOURS STUDY ONLINE digitalmarketinginstitute.com Validated by the Industry Advisory Council. Including members from Content Specialist Diploma in Search
Pillar 4: Workforce Goal: To increase alignment of workforce supply with employer demand Supply & Demand
 2014 Strategic Plan: Workforce Supply & Demand Action Action Item Partner Responsible Due Date Related Activities/ Existing Resources Resources Needed Pillar 4: Workforce Goal: To increase alignment of
2014 Strategic Plan: Workforce Supply & Demand Action Action Item Partner Responsible Due Date Related Activities/ Existing Resources Resources Needed Pillar 4: Workforce Goal: To increase alignment of
Program Review Self-Study Guidance Administrative Units
 Program Review Self-Study Guidance Administrative Units The self-study is the unit s opportunity to present its strategy, accomplishments, and challenges. It should be informative to the external reviewers
Program Review Self-Study Guidance Administrative Units The self-study is the unit s opportunity to present its strategy, accomplishments, and challenges. It should be informative to the external reviewers
Managing Risk In Higher Education. Jeff Mueller, CPA / Ron Bocciardi April 25, 2012
 Managing Risk In Higher Education Jeff Mueller, CPA / Ron Bocciardi April 25, 2012 Agenda What is risk management? Integrating risk management concepts into higher education What do you get? Questions
Managing Risk In Higher Education Jeff Mueller, CPA / Ron Bocciardi April 25, 2012 Agenda What is risk management? Integrating risk management concepts into higher education What do you get? Questions
UNITED WAY PARTNERSHIPS
 United Way s bold goals in education, income and health are designed as a rallying cry to the nation to join together and work collectively on real, lasting solutions that would fundamentally put people
United Way s bold goals in education, income and health are designed as a rallying cry to the nation to join together and work collectively on real, lasting solutions that would fundamentally put people
HLC Criteria and Core Component Crosswalk with AQIP Portfolio Processes
 HLC Criteria and Core Component Crosswalk with AQIP Portfolio Processes General Guidelines for Using this Crosswalk The crosswalk below gives the connections between HLC Criteria/Core Components and AQIP
HLC Criteria and Core Component Crosswalk with AQIP Portfolio Processes General Guidelines for Using this Crosswalk The crosswalk below gives the connections between HLC Criteria/Core Components and AQIP
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ACCOUNTABILITY. SFY STRATEGIC PLAN Oklahoma Department of Human Services
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY SFY 2019-2020 STRATEGIC PLAN Oklahoma Department of Human Services 1 STRATEGY MAP SFY 2019-2020 OUR MISSION We improve the quality of life of vulnerable Oklahomans by increasing people
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY SFY 2019-2020 STRATEGIC PLAN Oklahoma Department of Human Services 1 STRATEGY MAP SFY 2019-2020 OUR MISSION We improve the quality of life of vulnerable Oklahomans by increasing people
Previous efforts from neurodiversity programs have demonstrated that:
 Neurodiversity: From the Classroom to the Workplace A Whitepaper Neurodiversity is an approach to learning and disability that suggests that diverse neurological conditions appear as a result of normal
Neurodiversity: From the Classroom to the Workplace A Whitepaper Neurodiversity is an approach to learning and disability that suggests that diverse neurological conditions appear as a result of normal
Process for University Strategic Planning Examples
 1. Many universities post their strategic plans on the web for public access, but only a few of them disclose the timeline and process of how the strategic plans are developed; the inclusion of institutions
1. Many universities post their strategic plans on the web for public access, but only a few of them disclose the timeline and process of how the strategic plans are developed; the inclusion of institutions
STRATEGIC PLANNING: IMPLEMENTATION ROADMAP
 STRATEGIC PLANNING: IMPLEMENTATION ROADMAP MOVING FROM THE STRATEGIC PLAN TO AN OPERATIONAL PLAN Strategic plans provide broad guidance and direction for a higher education institution s immediate future.
STRATEGIC PLANNING: IMPLEMENTATION ROADMAP MOVING FROM THE STRATEGIC PLAN TO AN OPERATIONAL PLAN Strategic plans provide broad guidance and direction for a higher education institution s immediate future.
TITLE AND TOTAL COMPENSATION STUDY
 HR Design HR Design has enabled the UW-Madison campus to create its own personnel system. One key element is the Title and Total Compensation Study Today s session will update you on the Study progress
HR Design HR Design has enabled the UW-Madison campus to create its own personnel system. One key element is the Title and Total Compensation Study Today s session will update you on the Study progress
Boise State University Alumni Workforce Participation
 Summary of Findings Sample Characteristics: This sample of Boise State University alumni was drawn from members of the graduating classes from 1993 through 2007 who had an active email address on file
Summary of Findings Sample Characteristics: This sample of Boise State University alumni was drawn from members of the graduating classes from 1993 through 2007 who had an active email address on file
(NAME) BACCALAUREATE SOCIAL WORK PROGRAM. ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES ( Academic Year) LAST COMPLETED ON July
 (NAME) BACCALAUREATE SOCIAL WORK PROGRAM ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (2015-16 Academic Year) LAST COMPLETED ON July 20 2016 Form AS4 (B) Duplicate and expand as needed. Provide table(s) to
(NAME) BACCALAUREATE SOCIAL WORK PROGRAM ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (2015-16 Academic Year) LAST COMPLETED ON July 20 2016 Form AS4 (B) Duplicate and expand as needed. Provide table(s) to
Strategic Plan Development. LaToya W. Harrison Assistant Superintendent, Curriculum & Instruction
 Strategic Plan Development LaToya W. Harrison Assistant Superintendent, Curriculum & Instruction 2018-2023 School Board Goals 1. Ensure all students demonstrate academic growth and acquire skills to become
Strategic Plan Development LaToya W. Harrison Assistant Superintendent, Curriculum & Instruction 2018-2023 School Board Goals 1. Ensure all students demonstrate academic growth and acquire skills to become
McGill ITS Strategic Plan
 McGill Strategic Plan Context: Our 5 Year Roadmap Approved in April 205 Focuses on improvements to the following areas Teaching and Learning Research Student systems Campus Administration Must be cyclically
McGill Strategic Plan Context: Our 5 Year Roadmap Approved in April 205 Focuses on improvements to the following areas Teaching and Learning Research Student systems Campus Administration Must be cyclically
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES. KEY PRIORITIES for CSU Information Technology In support of Graduation Initiative 2025
 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES KEY PRIORITIES for CSU Information Technology In support of Graduation Initiative 2025 September 2017 INTRODUCTION The California State University recently embarked on the
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES KEY PRIORITIES for CSU Information Technology In support of Graduation Initiative 2025 September 2017 INTRODUCTION The California State University recently embarked on the
Strategic Planning
 2016-18 Strategic Planning OSM Vision To lead a vibrant media production industry by enabling growth and innovation. OSM Mission To represent, promote and grow the Manitoba media production industry. OSM
2016-18 Strategic Planning OSM Vision To lead a vibrant media production industry by enabling growth and innovation. OSM Mission To represent, promote and grow the Manitoba media production industry. OSM
Workforce Solutions Lower Rio TWIC Response
 Workforce Solutions Lower Rio TWIC Response Lower Rio Grande Valley Workforce Development Board dba Workforce Solutions is an equal opportunity employer/program and auxiliary aids and services are available
Workforce Solutions Lower Rio TWIC Response Lower Rio Grande Valley Workforce Development Board dba Workforce Solutions is an equal opportunity employer/program and auxiliary aids and services are available
EDMONTON AS AN OPEN CITY
 Prepared by City of Edmonton MARCH 2017 OPEN CITY INITIATIVE 2017 Refresh 3 EDMONTON AS AN OPEN CITY As the capital of Alberta, Canada, Edmonton aspires to fulfill its role as a preeminent global city:
Prepared by City of Edmonton MARCH 2017 OPEN CITY INITIATIVE 2017 Refresh 3 EDMONTON AS AN OPEN CITY As the capital of Alberta, Canada, Edmonton aspires to fulfill its role as a preeminent global city:
Strategic Plan
 Strategic Plan 2017-2021 Prepared by Members of the LADD Strategic Planning Committee With assistance from Mel Marsh, Acorn Consulting September, 2016 Contents INTRODUCTION... 2 MISSION, VISION, VALUES...
Strategic Plan 2017-2021 Prepared by Members of the LADD Strategic Planning Committee With assistance from Mel Marsh, Acorn Consulting September, 2016 Contents INTRODUCTION... 2 MISSION, VISION, VALUES...
Portland Public Schools Board of Education 501 N. Dixon Street Portland, Oregon
 Portland Public Schools Board of Education 501 N. Dixon Street Portland, Oregon Performance Appraisal: Superintendent Carole Smith June 2009 to September 2010 In May 2008, the Portland Public Schools Board
Portland Public Schools Board of Education 501 N. Dixon Street Portland, Oregon Performance Appraisal: Superintendent Carole Smith June 2009 to September 2010 In May 2008, the Portland Public Schools Board
SUPPORTING COMPETENCY-BASED LEARNING PROGRAMS
 SUPPORTING COMPETENCY-BASED LEARNING PROGRAMS Topics CBL Defined Fundamentals of CBL Curriculum Development Learning Needs Considerations in the Design of CBL Assessments CBL Technology and Asset Development
SUPPORTING COMPETENCY-BASED LEARNING PROGRAMS Topics CBL Defined Fundamentals of CBL Curriculum Development Learning Needs Considerations in the Design of CBL Assessments CBL Technology and Asset Development
Journey to 2022: Strategic Planning Board of Directors March 19, 2015
 Journey to 2022: Strategic Planning Board of Directors March 19, 2015 Board of Directors Retreat January 2015 Review of Action Planning Board-Identified Priorities Priority #1: Priority #2: Priority #3:
Journey to 2022: Strategic Planning Board of Directors March 19, 2015 Board of Directors Retreat January 2015 Review of Action Planning Board-Identified Priorities Priority #1: Priority #2: Priority #3:
Embracing Quality in Local Public Health
 Embracing Quality in Local Public Health Michigan MLC Quality Improvement Showcase Recognizing our Accomplishments, Sustaining our Gains, and Planning for our Future! Summary Report Prepared by: Michigan
Embracing Quality in Local Public Health Michigan MLC Quality Improvement Showcase Recognizing our Accomplishments, Sustaining our Gains, and Planning for our Future! Summary Report Prepared by: Michigan
The shifting demographics and thriving economy of the San Francisco Bay Area have changed how we must plan for the future and created challenges in:
 2020 STRATEGIC PLAN SYNERGY SCHOOL was founded in 1973 as a teacher cooperative that would provide children of the San Francisco Bay Area a creative and diverse student-centered learning environment.
2020 STRATEGIC PLAN SYNERGY SCHOOL was founded in 1973 as a teacher cooperative that would provide children of the San Francisco Bay Area a creative and diverse student-centered learning environment.
Section 4: Policy, Planning and Monitoring Chapter
 Section 4: Policy, Planning and Monitoring Chapter 17 Policy and Policymaking Boards of trustees govern through the policies they make. A classic definition of the difference between the board and administration
Section 4: Policy, Planning and Monitoring Chapter 17 Policy and Policymaking Boards of trustees govern through the policies they make. A classic definition of the difference between the board and administration
For discussion only. HR_design_plan_presentation_powerpoint Campus Forums Sept 27.pptx
 HR_design_plan_presentation_powerpoint Campus Forums Sept 27.pptx 1 Vision for the HR Design Project The HR Design project is a campus-wide effort to build, through thoughtful design, a more efficient
HR_design_plan_presentation_powerpoint Campus Forums Sept 27.pptx 1 Vision for the HR Design Project The HR Design project is a campus-wide effort to build, through thoughtful design, a more efficient
SECTION 5 SECTOR PARTNERSHIPS
 SECTION 5 SECTOR PARTNERSHIPS Why Sector Partnerships Matter Industry Leadership Sector Partnership Checklist Partnerships Across Industries Photo courtesy of National Renewable Energy Laboratory SECTOR
SECTION 5 SECTOR PARTNERSHIPS Why Sector Partnerships Matter Industry Leadership Sector Partnership Checklist Partnerships Across Industries Photo courtesy of National Renewable Energy Laboratory SECTOR
ADVISORY COUNCIL SUMMIT
 ADVISORY COUNCIL SUMMIT 9/11/18 Agenda 1. Welcome and Introductions 2. Human Resources Vision, Benefits & Philosophy 3. Project Recalibration Details 4. Job Descriptions & Compensation Infrastructure Development
ADVISORY COUNCIL SUMMIT 9/11/18 Agenda 1. Welcome and Introductions 2. Human Resources Vision, Benefits & Philosophy 3. Project Recalibration Details 4. Job Descriptions & Compensation Infrastructure Development
Creating Innovation Zones to Advance the Promise of Competency-Based Pathways
 Creating Innovation Zones to Advance the Promise of Competency-Based Pathways Published in January 2016. CC BY-NC 4.0 Achieve. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial
Creating Innovation Zones to Advance the Promise of Competency-Based Pathways Published in January 2016. CC BY-NC 4.0 Achieve. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial
(NAME) BACCALAUREATE SOCIAL WORK PROGRAM. ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES ( Academic Year) LAST COMPLETED ON July
 (NAME) BACCALAUREATE SOCIAL WORK PROGRAM ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (2015-16 Academic Year) LAST COMPLETED ON July 20 2016 Form AS4 (B) Duplicate and expand as needed. Provide table(s) to
(NAME) BACCALAUREATE SOCIAL WORK PROGRAM ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (2015-16 Academic Year) LAST COMPLETED ON July 20 2016 Form AS4 (B) Duplicate and expand as needed. Provide table(s) to
Guide for Annual and Periodic Program Planning & Self-Study
 Guide for Annual and Periodic Program Planning & Self-Study March 25, 2008 Table of Contents 1. Overview of Academic and Administrative Program Planning and Self Study...3 2. Integrated and Dynamic Planning...3
Guide for Annual and Periodic Program Planning & Self-Study March 25, 2008 Table of Contents 1. Overview of Academic and Administrative Program Planning and Self Study...3 2. Integrated and Dynamic Planning...3
ELK GROVE UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT. CLASS TITLE: Deputy Superintendent of Educational Services and Schools
 ELK GROVE UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT CLASS TITLE: Deputy Superintendent of Educational Services and Schools BASIC FUNCTION: The Deputy Superintendent of Educational Services and Schools will assist the Superintendent
ELK GROVE UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT CLASS TITLE: Deputy Superintendent of Educational Services and Schools BASIC FUNCTION: The Deputy Superintendent of Educational Services and Schools will assist the Superintendent
Arapahoe/Douglas Workforce Development Board
 Arapahoe/Douglas Workforce Development Board Strategic Priorities and Vision, Mission, Values Program Years 2015-2017 The Arapahoe/Douglas Workforce Development Board is dedicated to identifying and promoting
Arapahoe/Douglas Workforce Development Board Strategic Priorities and Vision, Mission, Values Program Years 2015-2017 The Arapahoe/Douglas Workforce Development Board is dedicated to identifying and promoting
STRATEGIC PLAN July 2018
 STRATEGIC PLAN July 2018 www.wrc.umn.edu LETTER FROM THE DIRECTOR I am pleased to present the Water Resources Center (WRC) Strategic Plan. This plan is the result of an extensive process with many contributors.
STRATEGIC PLAN July 2018 www.wrc.umn.edu LETTER FROM THE DIRECTOR I am pleased to present the Water Resources Center (WRC) Strategic Plan. This plan is the result of an extensive process with many contributors.
WALLA WALLA COMMUNITY COLLEGE STRATEGIC PLAN FOR EQUITY AND INCLUSION
 WALLA WALLA COMMUNITY COLLEGE STRATEGIC PLAN FOR EQUITY AND INCLUSION 2014-2020 ESTABLISHED 1967 WALLA WALLA COMMUNITY COLLEGE INTRODUCTION In February 2014, a yearlong, comprehensive planning process
WALLA WALLA COMMUNITY COLLEGE STRATEGIC PLAN FOR EQUITY AND INCLUSION 2014-2020 ESTABLISHED 1967 WALLA WALLA COMMUNITY COLLEGE INTRODUCTION In February 2014, a yearlong, comprehensive planning process
