Standards of Learning Content Review Notes. Grade 6 Mathematics 1 st Nine Weeks,
|
|
|
- Darrell Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Standards of Learning Content Review Notes Grade 6 Mathematics 1 st Nine Weeks, Revised September 2015
2 2
3 Mathematics: Content Review Notes Grade 6 Mathematics: First Nine Weeks This resource is intended to be a guide for parents and students to improve content knowledge and understanding. The information below is detailed information about the Standards of Learning taught during the 1 st grading period and comes from the Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework, Grade 6 issued by the Virginia Department of Education. The Curriculum Framework in its entirety can be found at the following website. s/2001/framewks_math6.pdf SOL 6.1 The student will describe and compare data, using ratios, and will use appropriate notations, such as a/b, a to b, and a:b. A ratio is a comparison of any two quantities and conveys an idea that cannot be expressed as a single number. A ratio is used to represent a variety of relationships within a set and between two sets. A ratio can be written using a fraction ( 2 ), a colon (2:), or the word to (2 to ). A ratio can compare part of a set to the entire set (part-whole comparison). Example: Joseph has 10 coins in his pocket. He has 4 dimes, 2 quarters, 2 nickels, and 2 pennies. What is the ratio of dimes to the total number of coins? ANSWER: Joseph has 4 dimes and 10 total coins. This can be written in three different ways: 4 4:10 4 to Sometimes, simplified answers are required. Simplify by finding the greatest common factor (GCF) and then divide the numerator AND the denominator by the GCF. Example: = 2 5 Using the example above, the answer would be: 2:5 2 to 5 2 5
4 A ratio can compare part of a set to another part of the same set (part-part comparison). 4 Example: Joseph has 10 coins in his pocket. He has 4 dimes, 2 quarters, 2 nickels, and 2 pennies. What is the ratio of quarters to dimes? ANSWER: Joseph has 2 quarters and 4 dimes. This can be written in three different ways: 2 2:4 2 to If simplified, the answer would be: 1:2 1 to 2 2 A ratio can compare part of a set to a corresponding part of another set (part-part comparison). Example: The table shows the number of coins two boys have in their pockets. Dimes Quarters Nickels Joseph Kendrick 1 6 What is the ratio of the number of quarters Joseph has compared to the number of quarters Kendrick has? ANSWER: Joseph has 2 quarters and Kendrick has 1 quarter. This can be written in three different ways: 2:1 2 to 1 A ratio can compare all of a set to all of another set (whole-whole comparison). Example: The table shows the number of coins two boys have in their pockets. Dimes Quarters Nickels Joseph Kendrick 1 6 What is the ratio of the number of coins Joseph has compared to the number of coins Kendrick has? ANSWER: Joseph has 8 coins and Kendrick has 10 coins. This can be written in three different ways: 8 8:10 8 to If simplified, the answer would be: 4:5 4 to 5 5 A ratio is a multiplicative comparison of two numbers, measures, or quantities. All fractions are ratios. 2 1
5 SOL Practice Items provided by the VDOE, Answers are located on the last page of the booklet. SOL 6.1 (Ratios) 1. According to the table, which shows the ratio of the number of red calculators to the number of blue calculators? 4. There are 0 red marbles and 150 blue marbles in a box. What is the ratio of blue marbles to red marbles? 2. The ratio of boys to girls in room B is 15 to 12. What is the ratio of girls to total students in room B? 5. Sam owns a canoe rental company with 120 boats. He has 55 wood boats and the rest are fiberglass. What is the ratio of wood boats to fiberglass boats?. According to the table, what is the ratio of number of A s Camella earned to the number of B s she earned? 5
6 7. Using the picture below. a) Write the ratio of 6 shirts to 5 pants using three different notations. b) Represent the ratio of shirts to pants using numbers other than 6 and 5. 6
7 SOL 6.2 The student will a) investigate and describe fractions, decimals and percents as ratios; b) identify a given fraction, decimal or percent from a representation; c) demonstrate equivalent relationships among fraction, decimals, and percents (No calculator) d) compare and order fractions, decimals and percents. (No calculator) A ratio can compare part of a set to the entire set (part-whole comparison) A fraction can be defined as a number written with the bottom part (the denominator) telling you how many parts the whole is divided into, and the top part (the numerator) telling how many you have. In other words a fraction is a ratio comparing a part to a whole. A decimal is a fraction where the denominator (the bottom number) is a power of ten (such as 10, 100, 1000, etc). A decimal is a ratio comparing a part to a whole = parts to 100 = parts to 1000 Percent means parts per 100. A percent is a ratio comparing the number of parts to 100. Example: 25% means a ratio of shaded parts to total parts 7
8 Fractions, decimals, and percents are three different representations of the same number. Percent means per 100 or how many out of 100 ; percent is another name for hundredths. A number followed by a percent symbol (%) is equivalent to that number with a denominator of 100. Example: 0% = = 10 = 0. Percents can be expressed as fractions with a denominator of 100. Example: 75% = = 4 Percents can be expressed as decimals. Example: 8% = = 0.8 A fraction can be rewritten as an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 100, and, thus, as a decimal or percent. Example: 5 = 60 = 0.60 = 60% 100 Decimals, fractions, and percents can be represented using concrete materials (e.g., base-10 blocks, decimal squares, or grid paper). Percents should be represented by drawing a shaded region on a 10-by-10 grid to represent a given percent. Example: The 10-by-10 grid shows 25%. Percents are used in real life for taxes, sales, data description, and data comparison. 8
9 The decimal point is a symbol that indicates the location of the ones place and all other subsequent place values in the decimal system. The decimal point separates a whole number amount from a number that is less than one. whole numbers numbers less than one decimal point To order fractions, decimals and percents convert to the same form. Examples: Which list is in order from greatest to least? A) 1 5, 0.166, 16% B) 0.166, 1 5, 16% C) 1, 16%, D) 16%, 0.166, 1 5 The answer is A. Which list is in order from least to greatest? A) 7, 4 5, 5 11 B) 4 5, 5 11, 7 C) 5 11, 7, 4 5 D) 7, 5 11, 4 5 The answer is D. 9
10 SOL Practice Items provided by the VDOE, Answers are located on the last page of the booklet. SOL 6.2 (Fraction, Decimals, and Percents) 1. Which of the following figures most closely shows 25% shaded? 1 2. Which number is equivalent to 0%?. Which is true? 10
11 8. Which decimals are ordered from least to greatest? 9. This model represents 1 whole and is divided into equal parts. Shade this model to represent 8 of this whole. 10. Arrange the numbers in order from least to greatest. 11
12 SOL 6.4 The student will demonstrate multiple representations of multiplication and division of fractions. When multiplying a fraction by a fraction such as 2 4 for part of a part., we are asking Below is an example of how this can be represented using models. 2 4 This represents two thirds (the shaded portion). This represents three fourths (the shaded portion). In order to represent the multiplication of fractions visually, we use the 2 shaded grids above, which represent the two fractions we are multiplying. Place the representations on top of each other (as shown below). The shaded area where the 2 grids overlap represents the product of the two fractions. The two grids overlap in 6 out of the 12 blocks. 2 X 4 = 6 = (Always remember to simplify your answer.) 12
13 When multiplying a fraction by a whole number such as 1 2 to find a part of the whole., we are trying Below is an example of how this can be represented using models. This represents one half (the shaded portion). This represents one half (the shaded portion). This represents one half (the shaded portion). The images above show one half of each box shaded and there are three boxes. 1 2 added three times is = What does it mean to divide with fractions? For measurement division, the divisor is the number of groups and the quotient will be the number of groups in the dividend. Division of fractions can be explained as how many of a given divisor is needed to equal the given dividend. In other words, for 1 the question is, 4 2 How many 1 2 make 4? For partition division the divisor is the size of the group, so the quotient answers the question, How much is the whole? or How much for one? divisors will fit into a dividend. Note the models below. dividend divisor = This reads ¾ divided by ½. In other words, how many one halves will fit into ¾? You can visually see that one ½ and half another ½ will fit into ¾. This is 1½. 1
14 You can visually see that one ½ and half another ½ will fit into ¾. This is 1½. You can check with actual math! Same Change Flip ¾ ½ 4 x 2 1 = 6 4 which is 1 ½ Another way to divide with graphics is on a number line. 1 is asking how many one thirds are there in three whole. The answer is 9. 14
15 SOL Practice Items provided by the VDOE, Answers are located on the last page of the booklet. SOL 6.4 (Multiplying and Dividing Fraction Models) 1. Which expression is represented by this model? 2. Each hexagon represents 1 whole. Which product is represented by the shading shown on this model?. Which product is represented by the shading of the model? 4. This figure represents one whole divided into five equal parts. How many 2 are in 7? 5 15
16 SOL 6.6 The student will a) multiply and divide fractions and mixed numbers; (No calculator) b) estimate solutions and then solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions (Calculator) Simplifying fractions to their simplest form assists with uniformity of answers and concepts. *Simplifying fractions: Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and the denominator and then divide the numerator and the denominator by the GCF. 8 Example: Simplify 20 The factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, 8 The factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20 The greatest common factor of 8 and 20 is 4, so divide the numerator and the denominator by = 5 2 so 8 2 = 20 5 Rewriting an improper fraction as a mixed number assists with uniformity of answers and concepts. 17 Example 1: 5 is an improper fraction that needs to be rewritten as a mixed number. Divide the numerator by the denominator = goes into 17 three times. becomes the whole number. There is a remainder of 2. The 2 becomes the new numerator and the 5 stays as the denominator. 16
17 Example 2: 14 is an improper fraction that needs to be rewritten as a mixed number. Divide the numerator by the denominator. 14 = 2 4 goes into 14 four times. 4 becomes the whole number. There is a remainder of 2. The 2 becomes the new numerator and the stays as the denominator. There is implied addition of the whole number part and the fractional part in mixed numbers. Equivalent forms are needed to perform the operations of addition and subtraction with fractions. Adding fractions with unlike denominators: Step 1: Find the least common denominator by identifying the multiples of each denominator. Example: The multiples of are, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, etc. The multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, etc. The least common multiple of and 4 is 12. This is also called the least common denominator (LCD). Step 2: Rename the fractions using the LCD and then add the numerators. *Remember, whatever you do to the numerator, you must also do the same to the denominator! Example: = 12 8 = 12 9 Now add = 17 The denominator stays the same after you add or subtract. Step : Now simplify. The correct answer is Multiplication and division are inverse operations. 17
18 Inverse operations are operations which undo each other. Example 1: 6 4 = 24 therefore 24 6 = 4 (multiplication and division are inverse operations) Example 2: = 15 therefore = 5 (addition and subtraction are inverse operations) It is helpful to simplify before multiplying fractions, using the commutative property of multiplication to change fractions to simplest form before multiplying. Example: Look diagonally to identify a common factor. The greatest common factor of 14 and 4 is 2 so divide by = 7 6 The greatest common factor of and 18 is so divide by. 2 1 = 12 7 This is your answer already in simplest form! *This only works when multiplying fractions. Fractions cannot be simplified before adding, subtracting, or dividing. To divide by a fraction, multiply by its reciprocal. Any two numbers whose product is 1 are called reciprocals. For example, 1 2 and 2 are reciprocals because 1 2 fractions. 4 Example: = 1. You use reciprocals when you divide by = 4 5 x 1 = 12 5 or = Multiply by the reciprocal of 1. Multiply the numerators and denominators and rewrite as a mixed number. 18
19 SOL Practice Items provided by the VDOE, Answers are located on the last page of the booklet. SOL 6.6 (Multiplying and Dividing Fractions) 1. Greg and Sam ordered a pizza for lunch. Greg ate 4 of the pizza, and Sam ate 1 8 of the pizza. How much of the whole pizza was eaten by Greg and Sam? 2. Carl needs 2 2 cups of flour to make a certain cake. He only has cup of flour in 8 the pantry. How many more cups of flour does Carl need for the cake?. Tim mails two boxes of cookies to friends. One box weighs 1 pounds, and the 4 other weighs 2 2 pounds. What is the total weight of the two boxes? 4. Risa drank 5 glass of lemonade. Fola drank 1 glass of lemonade. If the glasses 8 4 held the same amount of lemonade, how much more did Risa drink than Fola? 19
20 5. A farmer has 6 cartons of specialty eggs for sale. Each carton contains 12 eggs. If 2 of the eggs are brown, what is the total number of brown eggs he has for sale? 6. One batch of Derrick s pancake recipe takes 2 cups of milk. If Derrick makes 4 batches of his pancake recipe, how many cups of milk will he need? 7. Jamal walked mile yesterday morning and 1 mile yesterday afternoon. What 4 8 was the total distance walked by Jamal? 8. Maria has a piece of ribbon 5 foot long. She cuts foot off of the piece of ribbon. 6 4 What is the length of the remaining piece of ribbon? 20
21 9. Harry worked 1 hours on Friday and 4 1 hours on Saturday. What was the total 2 amount of time Harry worked on those days? 10. Donna and Darcy collected newspapers for recycling. Donna collected 5 4 pounds of newspaper. Darcy collected 2 1 pounds of newspaper. What was the 4 total amount of newspaper they collected? 11. Which fraction is equivalent to 5 6 1? 12. What is the product of 2 2 and 1 1 6? 1. Nigel has rolls of ribbon. Each roll has 8 feet of ribbon. It takes 4 1 feet of 4 ribbon to make one bow. What is the total number of bows that Nigel can make using these rolls of ribbon? 21
22 SOL 6.16 The student will compare and contrast dependent and independent events and determining probabilities for dependent and independent events. The probability of an event occurring is equal to the ratio of desired outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes (sample space). The probability of an event occurring can be represented as a ratio or the equivalent fraction, decimal, or percent. The probability of an event occurring is a ratio between 0 and 1. A probability of 0 means the event will never occur. A probability of 1 means the event will always occur. A simple event is one event (e.g., pulling one sock out of a drawer and examining the probability of getting one color). Independent events- when one event is not affected by a second event. The probability of an independent event is found by using the following formula: P(A and B) = P(A) P(B) For example, if you roll two number cubes, the number that you roll on the second cube is not affected by the number you rolled on the first cube. The probability of two independent events can be found by multiplying the probability of the first event by the probability of the second event. Example 1: Independent Events A number cube is rolled twice. Find the probability of rolling a five on both of the rolls. P (5) = 1 6 P (5 on 1st roll and 5 on 2nd roll) = or 1 6 So, the probability of rolling a 5 on both rolls is
23 Dependent events- the result of one event affects the result of a second event. The probability of two dependent events is found by using the following formula: P(A and B) = P(A) P(B after A) Example 2: Dependent Events A box contains 4 cupcakes with vanilla frosting, 5 cupcakes with chocolate frosting, and cupcakes with strawberry frosting. Sally reaches in the box and randomly takes two cupcakes, one after the other. Find the probability that she will choose a strawberryfrosted cupcake and then a chocolate-frosted cupcake. P (strawberry) = 12 P (chocolate) = cupcakes, are strawberry 11 cupcakes after 1 strawberry has been removed, 5 are chocolate. P(strawberry, then chocolate) = = 5 44 So, the probability that Sally will choose a strawberry frosted cupcake and then a chocolate frosted cupcake is 5, or about 11%. 44 2
24 SOL Practice Items provided by the VDOE, Answers are located on the last page of the booklet. SOL 6.16 (Probability of dependent and independent events)
25
26 Testing Information 1 st Benchmark Test October 19 th 2 rd SOL s Tested: 6.1, 6.2, 6.4, nd Benchmark Test December 14 th 18 th SOL s Tested: 6.16, 6.7, 6.5, 6.17, 6.19, with a cumulative review of all previous SOLs taught rd Benchmark Test March 14 th 18 th SOL s Tested: 6.18, 6.10, 6., 6.20, 6.11, 6.12, with a cumulative review of all previous SOLs taught Teacher Made Assessments: 6.15, 6.14,
27 Math Smarts! Math + Smart Phone = Math Smarts! Need help with your homework? Wish that your teacher could explain the math concept to you one more time? This resource is for you! Use your smart phone and scan the QR code and instantly watch a to 5 minute video clip to get that extra help. (These videos can also be viewed without the use of a smart phone. Click on the links included in this document.) Directions: Using your Android-based phone/tablet or iphone/ipad, download any QR barcode scanner. How do I do that? 1. Open Google Play (for Android devices) or itunes (for Apple devices). 2. Search for QR Scanner.. Download the app. After downloading, use the app to scan the QR code associated with the topic you need help with. You will be directed to a short video related to that specific topic! It s mobile math help when you need it! So next time you hear, You re always on that phone or Put that phone away! you can say It s homework!!! Access this document electronically on the STAR website through Suffolk Public Schools. ( PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING: This resource is provided as a refresher for lessons learned in class. Each link will connect to a YouTube or TeacherTube video related to the specific skill noted under Concept. Please be aware that advertisements may exist at the beginning of each video. 27
28 SOL Link QR Code 6.19 Identifying properties of real numbers Describing relationships as ratios Representing percents Comparing and ordering fractions, decimals, and percents Representing percents as decimals and fractions 28
29 6.2 Representing fractions as decimals and percents Demonstrating equivalent relationships with fractions, decimals and percents Representing multiplication and division of fractions Representing multiplication and division of fractions Subtracting Mixed Numbers Operations with Fractions (add, subtract, multiply, divide) *Cool Nontraditional Methods* 29
30 ratio Vocabulary Words SOL 6.1 A comparison of two quantities; A ratio is used to represent relationships within and between sets. less than greater than equal to percent equivalent fraction decimal number SOL 6.2 The symbol < is used to describe a numerical term smaller than the one compared to it. The symbol > is used to describe a numerical term larger than the one compared to it. The symbol = is used to show that two numerical terms are equal. Percent means per 100 or how many out of 100 ; percent is another name for hundredths. Expressions that have the same value or that have the same mathematical meaning; For example, ½, 50% and 0.5 are equivalent A number representing some part of a whole or part of a set; one number compared to another in the form a/b Any number written in decimal notation, in which a fractional part is separated from the integer part with a decimal point SOL 6.4/6.6 addition sum The act or process of combining numerical values, so as to find their sum An amount obtained as a result of adding numbers 0
31 subtraction difference reciprocal product division quotient numerator denominator improper fraction mixed number simplest form simplify The arithmetic operation of finding the difference between two quantities or numbers An amount obtained as a result of subtracting numbers Any two numbers whose product is 1. Example: ½ and 2 are reciprocals because ½ x 2 = 1 An amount obtained as a result of multiplying numbers The operation of determining how many times one quantity is contained in another; the inverse of multiplication An amount obtained as a result of dividing numbers The expression written above the line in a fraction The expression written below the line in a fraction that indicates the number of parts into which one whole is divided A fraction in which the numerator is larger than or equal to the denominator; The value of an improper fraction is greater than or equal to one. A numerical value that combines a whole number and a fraction A fraction is in simplest form when the greatest common factor of the numerator and denominator is 1. To reduce the numerator and the denominator in a fraction to the smallest form possible; To divide the numerator and denominator by the GCF is simplifying a fraction. 1
32 LCD estimate The least common multiple of the denominators of two or more fractions; Example: 6 is the least common denominator of 2/ and 1/6 To make an approximate or rough calculation, often based on rounding SOL 6.16 sample space probability outcome ratio event possible outcome dependent events independent events The set of all possible outcomes in a probability experiment The chance of an event occurring expressed using a ratio; The numerator describes how many times the event will occur, while the denominator describes the total number of outcomes for the event. Possible results of a probability event; Example: 4 is an outcome when a number cube is rolled. A comparison of two numbers by division; Example: The ratio 2 to can be expressed as 2 out of, 2:, or 2/. A specific outcome or type of outcome All the possible events in a probability experiment The result of one event affects the result of a second event When one event is not affected by a second event 2
33 Released Test Answers (1 st Nine Weeks) SOL 6.1 (Ratios) 1. A 2. A. D 4. C 5. A 6. A 10. A a.) A 7. 6:5, 6 to 5, B SOL 6.2 (Comparing & Ordering Fractions, Decimals, and Percents) 1. G 2. G. H 4. B 5. D 6. A 7. G 8. B 9. You should have shaded any combination of exactly six boxes. SOL 6.4 (Multiplication and Division of Fractions Models) 1. B 2. B. B ½
34 SOL 6.6 (Multiplication and Division of Fractions) 1. D 2. H. D 4. G 5. A C B B A H G D A C B SOL 6.16 (Sample Space and Probability) 1. F 2. B. C 4. G 5. D 6. B 7. J D A 10.. B or approximately 16 % a.) 49 b.) 1 21 or approximately 6.1% or approximately 4.8% 4
Point out that when you compare two sets by using fractions, the objects in the sets do not need to be the same size or even the same kind.
 Fractions What are some of the ways we use fractions every day? Fractions represent a part of a whole object or unit. (Provide some sets of objects for students to work with to help them understand the
Fractions What are some of the ways we use fractions every day? Fractions represent a part of a whole object or unit. (Provide some sets of objects for students to work with to help them understand the
Grade 4 CCGPS Mathematics Power Standards
 Grade 4 CCGPS Mathematics Power Standards Number and Operations 4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers
Grade 4 CCGPS Mathematics Power Standards Number and Operations 4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers
Fourth Grade Quarter 3 Module 5: Fraction Equivalence, Ordering, and Operations Part 2, Topics D-H Approximately 25 days Begin around January 4 th
 Blackwater Community School Curriculum Map 2015-2016 Fourth Grade Quarter 3 Module 5: Fraction Equivalence, Ordering, and Operations Part 2, Topics D-H Approximately 25 days Begin around January 4 th In
Blackwater Community School Curriculum Map 2015-2016 Fourth Grade Quarter 3 Module 5: Fraction Equivalence, Ordering, and Operations Part 2, Topics D-H Approximately 25 days Begin around January 4 th In
ACTIVITY: Dividing by a Fraction. Work with a partner. Write the division problem and solve it using a model. a. How many two-thirds are in three?
 . Dividing Fractions How can you divide by a fraction? ACTIVITY: Dividing by a Fraction Work with a partner. Write the division problem and solve it using a model. a. How many two-thirds are in three?
. Dividing Fractions How can you divide by a fraction? ACTIVITY: Dividing by a Fraction Work with a partner. Write the division problem and solve it using a model. a. How many two-thirds are in three?
Objectives: Assessment: Possible Resources: Possible Strategies:
 By the end of 3 rd grade, students will: 1. Understand and write simple, including ½ and 1/4, when necessary in real life situations, such as: -dividing pizzas, cookies, oranges, etc. (½ and 1/4) -measurement
By the end of 3 rd grade, students will: 1. Understand and write simple, including ½ and 1/4, when necessary in real life situations, such as: -dividing pizzas, cookies, oranges, etc. (½ and 1/4) -measurement
MATH LEVEL 2 LESSON PLAN 4 FRACTIONS Copyright Vinay Agarwala, Checked: 1/20/18
 Section 1: Unit & Fractions MATH LEVEL 2 LESSON PLAN 4 FRACTIONS 2018 Copyright Vinay Agarwala, Checked: 1/20/18 1. The word fraction means a broken piece. We use fractions to describe a quantity between
Section 1: Unit & Fractions MATH LEVEL 2 LESSON PLAN 4 FRACTIONS 2018 Copyright Vinay Agarwala, Checked: 1/20/18 1. The word fraction means a broken piece. We use fractions to describe a quantity between
2. Fractions. 5. Greatest Common Factor (Sometimes called the Greatest Common Divisor)
 2. Fractions 1. What is a Fraction? 2. Improper Fractions 3. Mixed umbers 4. Comparing Fractions 5. Greatest Common Factor (Sometimes called the Greatest Common Divisor) 6. Least Common Multiple (Sometimes
2. Fractions 1. What is a Fraction? 2. Improper Fractions 3. Mixed umbers 4. Comparing Fractions 5. Greatest Common Factor (Sometimes called the Greatest Common Divisor) 6. Least Common Multiple (Sometimes
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 7th Grade Unit 2
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 7th Grade Unit 2 Unit 2 Fractions Math 702 Fractions Introduction 3 1. Working with Fractions 5 Fractions and Mixed Numbers 5 Equivalent Fractions 12 Divisibility Rules and Prime Factorization
MATH STUDENT BOOK 7th Grade Unit 2 Unit 2 Fractions Math 702 Fractions Introduction 3 1. Working with Fractions 5 Fractions and Mixed Numbers 5 Equivalent Fractions 12 Divisibility Rules and Prime Factorization
*When multiplying regularly, line up your digits left to right it helps to have the number with the more digits on top.
 [6th Grade MIDTERM REVIEW NOTES] Multi-digit Numbers When multiplying multi-digit # s, place values are important and place holders need to be used. When multiplying regularly place holders are added to
[6th Grade MIDTERM REVIEW NOTES] Multi-digit Numbers When multiplying multi-digit # s, place values are important and place holders need to be used. When multiplying regularly place holders are added to
This standard extends the work in third grade by using additional denominators (5, 10, 12, and 100).
 Domain: Number and Operation Fractions Cluster: Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering. Students develop understanding of fraction equivalence and operations with fractions. They recognize
Domain: Number and Operation Fractions Cluster: Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering. Students develop understanding of fraction equivalence and operations with fractions. They recognize
Standard 5.NF.1 5.NF.2 6.EE. 7 5.NBT.7 7.NS.1 7.NS.3
 Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions (Standards 5.NF.1 2). Standard 5.NF.1 Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators (including mixed numbers) by replacing given
Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions (Standards 5.NF.1 2). Standard 5.NF.1 Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators (including mixed numbers) by replacing given
# # Fourth Grade. Understanding Fractions. Slide 1 / 162 Slide 2 / 162. Slide 4 / 162. Slide 3 / 162. Slide 5 / 162. Slide 6 / 162
 Slide / 62 Slide 2 / 62 Fourth Grade Fraction Decimal Concepts 205--23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 62 Slide 4 / 62 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section - Understanding Fractions - Mixed
Slide / 62 Slide 2 / 62 Fourth Grade Fraction Decimal Concepts 205--23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 62 Slide 4 / 62 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section - Understanding Fractions - Mixed
Parent and student guide book for year 7 mathematics in term 4.
 Parent and student guide book for year 7 mathematics in term 4. Dear Parent/Carer, Please use the following booklet so you and your child can work together to help aid their progression in maths over their
Parent and student guide book for year 7 mathematics in term 4. Dear Parent/Carer, Please use the following booklet so you and your child can work together to help aid their progression in maths over their
C if U can. Number. Name
 C if U can Number Name.. How will this booklet help you to move from a D to a C grade? The topic of number is split into six units numbers 1, fractions, decimals and percentages 1, ratio and proportion,
C if U can Number Name.. How will this booklet help you to move from a D to a C grade? The topic of number is split into six units numbers 1, fractions, decimals and percentages 1, ratio and proportion,
And the numerators are the shaded parts We talking fractions. Hook
 Understanding fractions Common Core Standard 3.NF.A.1 Understand a fraction 1/b as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned into b equal parts; understand a fraction a/b as the quantity
Understanding fractions Common Core Standard 3.NF.A.1 Understand a fraction 1/b as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned into b equal parts; understand a fraction a/b as the quantity
Use repeated addition to multiply fractions by whole numbers. is shown. is an improper fraction.
 Student book pages 0 Multiplying a Whole Number by a Fraction You will need counters Use repeated addition to multiply fractions by whole numbers You can use grids and counters to model fractions What
Student book pages 0 Multiplying a Whole Number by a Fraction You will need counters Use repeated addition to multiply fractions by whole numbers You can use grids and counters to model fractions What
Seymour Public Schools Math Grade 4 Unit 6. Grade: 4. Subject: Math Time Frame: 21 days Domains: Number and Operations-Fractions, Measurement and Data
 Grade: 4 Unit 6-Numbers and Operations with Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division using Fractions Standards Enduring Understandings Essential Questions Subject: Math Time Frame: 21 days Domains:
Grade: 4 Unit 6-Numbers and Operations with Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division using Fractions Standards Enduring Understandings Essential Questions Subject: Math Time Frame: 21 days Domains:
Day 5 Decimals and Percentages
 Day 5 Decimals and Percentages What mathematical justification can you give for the rules we teach in dealing with decimals? 1. Which decimal fraction is larger 0.34 or 0.7? 2. Line up the decimal points
Day 5 Decimals and Percentages What mathematical justification can you give for the rules we teach in dealing with decimals? 1. Which decimal fraction is larger 0.34 or 0.7? 2. Line up the decimal points
Term Definition Example
 Clock Model Decomposing or Splitting Denominator The clock model is used to develop the use of landmark fractions for addition and subtraction. With the hour as a common whole (60 minutes) fractions such
Clock Model Decomposing or Splitting Denominator The clock model is used to develop the use of landmark fractions for addition and subtraction. With the hour as a common whole (60 minutes) fractions such
Operations, vocabulary terms and examples
 Operations, vocabulary terms and examples oh my Fraction- a number that names a part of a whole numerator- the part or top number in a fraction denominator-the bottom or the total number in a fraction
Operations, vocabulary terms and examples oh my Fraction- a number that names a part of a whole numerator- the part or top number in a fraction denominator-the bottom or the total number in a fraction
Progressions for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics (draft)
 Progressions for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics (draft) cthe Common Core Standards Writing Team August 0 * 0 This document can be read with Preview on a Mac or with the latest version of
Progressions for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics (draft) cthe Common Core Standards Writing Team August 0 * 0 This document can be read with Preview on a Mac or with the latest version of
SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 4A FRACTION SENSE TOPICS COVERED:
 SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER A FRACTION SENSE TOPICS COVERED: Fraction Sense Equivalent Fractions Simplifying Fractions Least Common Multiple Ordering and Comparing Fractions Mixed Numbers and Improper
SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER A FRACTION SENSE TOPICS COVERED: Fraction Sense Equivalent Fractions Simplifying Fractions Least Common Multiple Ordering and Comparing Fractions Mixed Numbers and Improper
Multiplying Rational Numbers
 LESSON Multiplying Rational Numbers Plug In Multiplying Fractions You can use a model to show multiplication of a fraction and a whole number. You can use models show multiplication of two fractions. Multiply
LESSON Multiplying Rational Numbers Plug In Multiplying Fractions You can use a model to show multiplication of a fraction and a whole number. You can use models show multiplication of two fractions. Multiply
Ratios and Proportional Relationships: Lessons 11-16
 Unit 7-1 Lessons 11-16 Ratios and Proportional Relationships: Lessons 11-16 Name Date Classwork Book Math 7: Mr. Sanford Lesson 11-16: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1-11 Lesson 11: Ratios of Fractions
Unit 7-1 Lessons 11-16 Ratios and Proportional Relationships: Lessons 11-16 Name Date Classwork Book Math 7: Mr. Sanford Lesson 11-16: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1-11 Lesson 11: Ratios of Fractions
Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions.
 Standard 8 Benchmark 1 3 4 5 6 Numbers and Operations - Fractions Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering. Use equivalent fractions as a
Standard 8 Benchmark 1 3 4 5 6 Numbers and Operations - Fractions Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering. Use equivalent fractions as a
MCAS and Common Core Mathematics Student Set
 Grade SAMPLER MCAS and Common Core Mathematics Student Set Click on the book titles below to navigate. MCAS Finish Line MCAS Performance Indicator Finish Line for the Common Core State Standards Contents
Grade SAMPLER MCAS and Common Core Mathematics Student Set Click on the book titles below to navigate. MCAS Finish Line MCAS Performance Indicator Finish Line for the Common Core State Standards Contents
Understanding basic math concepts is an essential. Math Basics COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Math Basics Understanding basic math concepts is an essential part of being a successful professional in the food-service industry. Math is used to control food costs, develop recipes, and control quality.
Math Basics Understanding basic math concepts is an essential part of being a successful professional in the food-service industry. Math is used to control food costs, develop recipes, and control quality.
6-1The Set of Rational Numbers
 6-1The Set of Rational Numbers Equivalent or Equal Fractions Simplifying Fractions Equality of Fractions Ordering Rational Numbers Denseness of Rational Numbers Rational numbers The set of numbers Q such
6-1The Set of Rational Numbers Equivalent or Equal Fractions Simplifying Fractions Equality of Fractions Ordering Rational Numbers Denseness of Rational Numbers Rational numbers The set of numbers Q such
Quarter 2 Curriculum Guide GRADE 5 Mathematical Practices
 Quarter 2 Curriculum Guide GRADE 5 Mathematical Practices 1. Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving them 2. Reasoning Abstractly & Quantitatively 3. Construct Viable Arguments and Critique the
Quarter 2 Curriculum Guide GRADE 5 Mathematical Practices 1. Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving them 2. Reasoning Abstractly & Quantitatively 3. Construct Viable Arguments and Critique the
TIPS FROM JEFF AND SHARON ON TEACHING BUSINESS MATH
 TIPS FROM JEFF AND SHARON ON TEACHING BUSINESS MATH Chapter. Talk to the students about the Wall Street Journal clip Asia Delivers for McDonald s. Talk about how /3 of sales in Egypt are from delivery.
TIPS FROM JEFF AND SHARON ON TEACHING BUSINESS MATH Chapter. Talk to the students about the Wall Street Journal clip Asia Delivers for McDonald s. Talk about how /3 of sales in Egypt are from delivery.
Full file at
 TIPS FROM JEFF AND SHARON ON TEACHING BUSINESS MATH Chapter. Talk to the students about the Wall Street Journal clip Asia Delivers for McDonald s. Talk about how /3 of sales in Egypt are from delivery.
TIPS FROM JEFF AND SHARON ON TEACHING BUSINESS MATH Chapter. Talk to the students about the Wall Street Journal clip Asia Delivers for McDonald s. Talk about how /3 of sales in Egypt are from delivery.
Warm-up. 2) Sixteen friends sold tickets to their fall concert. They each sold 1,472 tickets. How many tickets were sold?
 Monday, September, 207 Warm-up ) Each student in Mr. Kelly's shop class needs a piece of wood /3 foot long to complete a project. Mr. Kelly has one piece of wood that is 6 6 feet long. How many pieces
Monday, September, 207 Warm-up ) Each student in Mr. Kelly's shop class needs a piece of wood /3 foot long to complete a project. Mr. Kelly has one piece of wood that is 6 6 feet long. How many pieces
Give your answer as a mixed number in its simplest form.
 Higher tier unit 4a-1 check in test Non-calculator Q1. Write 18 24 as a fraction in its simplest form. Q2. Which of these fractions is the largest? 5 6 4 7 18 21 11 14 Q3. Work out 11 25 of 2000. Q4. Convert
Higher tier unit 4a-1 check in test Non-calculator Q1. Write 18 24 as a fraction in its simplest form. Q2. Which of these fractions is the largest? 5 6 4 7 18 21 11 14 Q3. Work out 11 25 of 2000. Q4. Convert
3. Each person received 5_ of a block of clay when five samesize blocks were equally divided among six artists. Which
 11-1 1. Which division expression is shown on the number line? 0 A 1 9 B 9 1 C 9 9 D 1 1 1. Which fraction can be written as 15? A 15 B 15 C D 15. Each person received 5_ of a block of clay when five samesize
11-1 1. Which division expression is shown on the number line? 0 A 1 9 B 9 1 C 9 9 D 1 1 1. Which fraction can be written as 15? A 15 B 15 C D 15. Each person received 5_ of a block of clay when five samesize
 Vocabulary partition divide a whole into parts numerator the top number in a fraction; how many equal parts are being considered compose joining numbers to create tens; joining parts to create a whole
Vocabulary partition divide a whole into parts numerator the top number in a fraction; how many equal parts are being considered compose joining numbers to create tens; joining parts to create a whole
ISBN Copyright 2015 The Continental Press, Inc.
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Format of Books Suggestions for Use 7 Annotated Answer Key and Extension Activities 9 Reproducible Tool Set 8 ISBN 978-0-8-7896-7 Copyright 0 The Continental Press, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Format of Books Suggestions for Use 7 Annotated Answer Key and Extension Activities 9 Reproducible Tool Set 8 ISBN 978-0-8-7896-7 Copyright 0 The Continental Press, Inc.
For All Students Taking Consumer Math Summer Review Packet
 For All Students Taking Consumer Math Summer Review Packet Name Period Dear Student and Parent/Guardian, The math department at Central Dauphin School District wants you to be successful in Consumer Math.
For All Students Taking Consumer Math Summer Review Packet Name Period Dear Student and Parent/Guardian, The math department at Central Dauphin School District wants you to be successful in Consumer Math.
1. Use the number line to name a fraction which is equivalent to What number equals h so that the equation is true?
 Standards NF.2 Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n x a)/(n x b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two
Standards NF.2 Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n x a)/(n x b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two
Writing Quotients with Mixed Numbers
 LESSON 8 Writing Quotients with Mixed Numbers Power Up facts mental math Power Up G a. Estimation: Round 8 8 in. to the nearest inch. 9 in. b. Estimation: Round 8 in. to the nearest inch. in. c. Estimation:
LESSON 8 Writing Quotients with Mixed Numbers Power Up facts mental math Power Up G a. Estimation: Round 8 8 in. to the nearest inch. 9 in. b. Estimation: Round 8 in. to the nearest inch. in. c. Estimation:
1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Answers Recall basics of fractions To convert into mixed fraction: improper fraction.
 4 1 Revision Reflect and Recall basics of fractions To convert into mixed fraction: Here is an improper fraction So on dividing 23 by 6 we get Quotient = 3 and Remainder = 5 Thus the mixed fraction form
4 1 Revision Reflect and Recall basics of fractions To convert into mixed fraction: Here is an improper fraction So on dividing 23 by 6 we get Quotient = 3 and Remainder = 5 Thus the mixed fraction form
GRADE LEVEL: FIFTH SUBJECT: MATH DATE: CONTENT STANDARD INDICATORS SKILLS ASSESSMENT VOCABULARY ISTEP
 GRADE LEVEL: FIFTH SUBJECT: MATH DATE: 2015 2016 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 2 MASTER COPY 10 12 15 CONTENT STANDARD INDICATORS SKILLS ASSESSMENT VOCABULARY ISTEP NUMBER SENSE Number line Mixed number Decimal
GRADE LEVEL: FIFTH SUBJECT: MATH DATE: 2015 2016 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 2 MASTER COPY 10 12 15 CONTENT STANDARD INDICATORS SKILLS ASSESSMENT VOCABULARY ISTEP NUMBER SENSE Number line Mixed number Decimal
Math - Grade Five Unit 1 - Number Theory
 1 Time Frame: About 15 days (this includes a review days and testing days) Math - Grade Five Unit 1 - Number Theory Description: - To introduce students to the Student Reference, prime, composite, and
1 Time Frame: About 15 days (this includes a review days and testing days) Math - Grade Five Unit 1 - Number Theory Description: - To introduce students to the Student Reference, prime, composite, and
Rational Numbers in Mathematics. Lecture 2.1: Fractions INTRODUCTION 2.0
 Rational Numbers in Mathematics INTRODUCTION 2.0 In this lesson, we will focus on the exploration of rational numbers in all their forms and operation on rational numbers. We will explore fractions and
Rational Numbers in Mathematics INTRODUCTION 2.0 In this lesson, we will focus on the exploration of rational numbers in all their forms and operation on rational numbers. We will explore fractions and
1: OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING, PART
 3 rd GRADE MATH PACING GUIDE: 1 st Nine Weeks UNIT 1: OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING, PART 1 Week Lesson Standards Learning Target Vocabulary WEEK 1 Aug. 10 Lesson 0 Lessons for the 1 st 5 Days Refer
3 rd GRADE MATH PACING GUIDE: 1 st Nine Weeks UNIT 1: OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING, PART 1 Week Lesson Standards Learning Target Vocabulary WEEK 1 Aug. 10 Lesson 0 Lessons for the 1 st 5 Days Refer
Why Do We Need Fractions Anyway?
 Why Do We Need Fractions Anyway? Conference for the Advancement of Mathematics Teaching San Antonio, TX July 2013 Jennifer North Morris Professional Development Specialist Tucson, AZ Email: jennifer@north-morris.net
Why Do We Need Fractions Anyway? Conference for the Advancement of Mathematics Teaching San Antonio, TX July 2013 Jennifer North Morris Professional Development Specialist Tucson, AZ Email: jennifer@north-morris.net
Decimals and Percents
 Decimals Both decimals and fractions are used to write numbers that are between whole numbers. Decimals use the same base-ten place-value system as whole numbers. You can compute with decimals in the same
Decimals Both decimals and fractions are used to write numbers that are between whole numbers. Decimals use the same base-ten place-value system as whole numbers. You can compute with decimals in the same
Math Entrance Exam is scheduled for Wednesday, January 6:00 p.m.
 Pharmacy Technician Study Guide Practice Math Packet This packet is designed to help prepare you for the Pharmacy Technician Math Entrance Exam. The key has been included to allow the student to check
Pharmacy Technician Study Guide Practice Math Packet This packet is designed to help prepare you for the Pharmacy Technician Math Entrance Exam. The key has been included to allow the student to check
# # Fourth Grade. Understanding Fractions. Slide 1 / 162 Slide 2 / 162. Slide 4 / 162. Slide 3 / 162. Slide 5 / 162. Slide 6 / 162
 Slide / 62 Slide 2 / 62 Fourth Grade Fraction Decimal oncepts 205--23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 62 Slide 4 / 62 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section - Understanding Fractions - Mixed
Slide / 62 Slide 2 / 62 Fourth Grade Fraction Decimal oncepts 205--23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 62 Slide 4 / 62 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section - Understanding Fractions - Mixed
Common Core. Mathematics Instruction
 20 Common Core Mathematics Instruction 7 Table of Contents Unit : The Number System Lesson Understand Addition of Positive and Negative Integers 2 7.NS.A.a, 7.NS.A.b Lesson 2 Understand Subtraction of
20 Common Core Mathematics Instruction 7 Table of Contents Unit : The Number System Lesson Understand Addition of Positive and Negative Integers 2 7.NS.A.a, 7.NS.A.b Lesson 2 Understand Subtraction of
Lesson Notes. Lesson 17. Objective. Materials. For use before Module 9 Ratio, Proportion, and Percent Lesson 7 Understanding Percents
 Lesson 17 For use before Module 9 Ratio, Proportion, and Percent Lesson 7 Understanding Percents Texas Edition: For use before Module 7 Ratio, Proportion, and Percent Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
Lesson 17 For use before Module 9 Ratio, Proportion, and Percent Lesson 7 Understanding Percents Texas Edition: For use before Module 7 Ratio, Proportion, and Percent Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
PROFESSIONAL LEARNING
 . 2. PROFESSIONAL LEARNING www.origoeducation.com ! ORIGO Education ORIGO Education 2 Show 4 in each of these models. For each model, consider the following questions: What attribute is the focus? What
. 2. PROFESSIONAL LEARNING www.origoeducation.com ! ORIGO Education ORIGO Education 2 Show 4 in each of these models. For each model, consider the following questions: What attribute is the focus? What
Decimals, Fractions, Percentages and Significant Figures for Statistics
 Decimals, Fractions, Percentages and Significant Figures for Statistics Baseball is ninety percent mental and the other half is physical. - Yogi Berra In statistics, we frequently use ratios in fraction,
Decimals, Fractions, Percentages and Significant Figures for Statistics Baseball is ninety percent mental and the other half is physical. - Yogi Berra In statistics, we frequently use ratios in fraction,
Brick Math Series TEACHING FRACTIONS USING LEGO BRICKS. Dr. Shirley Disseler
 Brick Math Series TEACHING FRACTIONS USING LEGO BRICKS Dr. Shirley Disseler Teaching Fractions Using LEGO Bricks Copyright 2016 by Shirley Disseler Published by Brigantine Media/Compass Publishing 211
Brick Math Series TEACHING FRACTIONS USING LEGO BRICKS Dr. Shirley Disseler Teaching Fractions Using LEGO Bricks Copyright 2016 by Shirley Disseler Published by Brigantine Media/Compass Publishing 211
Work with a partner. Use base ten blocks to model the division. Then find the quotient. a Begin by modeling
 2.6 Dividing Decimals decimal division? How can you use base ten blocks to model 1 ACTIVITY: Dividing Decimals Work with a partner. Use base ten blocks to model the division. Then find the quotient. a.
2.6 Dividing Decimals decimal division? How can you use base ten blocks to model 1 ACTIVITY: Dividing Decimals Work with a partner. Use base ten blocks to model the division. Then find the quotient. a.
PASIG CATHOLIC COLLEGE Grade School Department School Year MATHEMATICS 5 THIRD QUARTER Activity Sheet No. 1
 Activity Sheet No. 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Concept Development LEARNING OBJECTIVES : Place Value and Value of Decimals : Identify the place value and value of each decimal digit. Read and write decimals. REFERENCE
Activity Sheet No. 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Concept Development LEARNING OBJECTIVES : Place Value and Value of Decimals : Identify the place value and value of each decimal digit. Read and write decimals. REFERENCE
Authors Shannon Mccaw Beth Armstrong matt mccaw sarah schuhl michelle terry scott VAlwAy
 Authors Shannon Mccaw Beth Armstrong matt mccaw sarah schuhl michelle terry scott VAlwAy Oregon Focus On Fractions and Decimals i cover PhOtOgraPh Copyright 2008 by SM c Curriculum LLC. All rights reserved.
Authors Shannon Mccaw Beth Armstrong matt mccaw sarah schuhl michelle terry scott VAlwAy Oregon Focus On Fractions and Decimals i cover PhOtOgraPh Copyright 2008 by SM c Curriculum LLC. All rights reserved.
PROPORTIONS Judo Math Inc.
 PROPORTIONS 2013 Judo Math Inc. 7 th grade Grade Yellow Belt Training: Algebra/Proportions Discipline Order of Mastery: Proportional Thinking 1.Intro to proportions 2. Determining proportionality (tables,
PROPORTIONS 2013 Judo Math Inc. 7 th grade Grade Yellow Belt Training: Algebra/Proportions Discipline Order of Mastery: Proportional Thinking 1.Intro to proportions 2. Determining proportionality (tables,
Rounding a method for estimating a number by increasing or retaining a specific place value digit according to specific rules and changing all
 Unit 1 This unit bundles student expectations that address whole number estimation and computational fluency and proficiency. According to the Texas Education Agency, mathematical process standards including
Unit 1 This unit bundles student expectations that address whole number estimation and computational fluency and proficiency. According to the Texas Education Agency, mathematical process standards including
Decimal Ops. Computing with Decimals and Percents. Name: Hour:
 Decimal Ops Computing with Decimals and Percents Name: Hour: Table of Contents Investigation 1 Investigation 1.2 Page 2 Investigation 1.3 Page 6 Reflection.. Page 10 Investigation 2 Investigation 2.1 Page
Decimal Ops Computing with Decimals and Percents Name: Hour: Table of Contents Investigation 1 Investigation 1.2 Page 2 Investigation 1.3 Page 6 Reflection.. Page 10 Investigation 2 Investigation 2.1 Page
October 12, th Grade. Percents
 6th Grade Percents 2016-10-05 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Percents Percents & Fractions Percents & Decimals Using Percents Glossary & Standards Teacher Notes
6th Grade Percents 2016-10-05 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Percents Percents & Fractions Percents & Decimals Using Percents Glossary & Standards Teacher Notes
Monroe County School District Elementary Pacing Guide
 Grade 5 Unit 1: Place Value/Operations/Algebraic Thinking Timeline: August 3-September 21 CMA: Week of September 24 th I can recite multiplication facts (1-12) Fluency Tests 5.NBT.5 Multi-Digit multiplication
Grade 5 Unit 1: Place Value/Operations/Algebraic Thinking Timeline: August 3-September 21 CMA: Week of September 24 th I can recite multiplication facts (1-12) Fluency Tests 5.NBT.5 Multi-Digit multiplication
Houston County School System Mathematics
 Student Name: Teacher Name: Grade: 6 th Unit #: 4a Unit Title: Rates, Ratios, and Proportional Reasoning Approximate Start Date of Unit: Approximate End Date (and Test Date) of Unit: The following Statements
Student Name: Teacher Name: Grade: 6 th Unit #: 4a Unit Title: Rates, Ratios, and Proportional Reasoning Approximate Start Date of Unit: Approximate End Date (and Test Date) of Unit: The following Statements
Modeling with Expressions
 Locker LESSON.1 Modeling with Expressions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: A-SSE.1a Interpret parts of an expression, such as terms, factors, and coefficients. Also A-SSE.1b, N-Q.
Locker LESSON.1 Modeling with Expressions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: A-SSE.1a Interpret parts of an expression, such as terms, factors, and coefficients. Also A-SSE.1b, N-Q.
Missouri Standards Alignment Grades One through Six
 Missouri Standards Alignment Grades One through Six Trademark of Renaissance Learning, Inc., and its subsidiaries, registered, common law, or pending registration in the United States and other countries.
Missouri Standards Alignment Grades One through Six Trademark of Renaissance Learning, Inc., and its subsidiaries, registered, common law, or pending registration in the United States and other countries.
Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program TCAP. TNReady Grade 4 Math Part I PRACTICE TEST. Student Name. Teacher Name
 Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program TCAP TNReady Grade Math Part I PRACTICE TEST Student Name Teacher Name Tennessee Department of Education Grade Math, Part I Directions This booklet contains sample
Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program TCAP TNReady Grade Math Part I PRACTICE TEST Student Name Teacher Name Tennessee Department of Education Grade Math, Part I Directions This booklet contains sample
Fractions with. Contents. Correlation to Current Math Standards 3 Getting Started: Fractions with Prime Factor Tiles TM 4
 Fractions with by David Bernasconi Contents Correlation to Current Math Standards Getting Started: Fractions with Prime Factor Tiles TM 4 ACTIVITIES. Multiplication with Prime Factor Tiles 6. Prime Factorization
Fractions with by David Bernasconi Contents Correlation to Current Math Standards Getting Started: Fractions with Prime Factor Tiles TM 4 ACTIVITIES. Multiplication with Prime Factor Tiles 6. Prime Factorization
PERCENTS - Teacher Notes Unit 6-7 th grade
 PERCENTS - Teacher Notes Unit 6-7 th grade Percents are special fractions whose denominators are. The number in front of the percent symbol (%) is the numerator. The denominator is not written, but understood
PERCENTS - Teacher Notes Unit 6-7 th grade Percents are special fractions whose denominators are. The number in front of the percent symbol (%) is the numerator. The denominator is not written, but understood
Words for Algebra TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED. Math Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator System
 Math Objectives Students will explore the nature and needs of a word problem and look at the expression and equations implied by the situation. Students will explore the graph of the function that best
Math Objectives Students will explore the nature and needs of a word problem and look at the expression and equations implied by the situation. Students will explore the graph of the function that best
Beaumont Unified School District Grade 5 th Course Guide Mathematics
 Beaumont Unified School District Grade 5 th Course Guide Mathematics 2013-2014 Curriculum and Pacing Guide Grade 5th Mathematics First Trimester Aug. 19 Nov. 8 Chapter Major Concepts: Number and Operation
Beaumont Unified School District Grade 5 th Course Guide Mathematics 2013-2014 Curriculum and Pacing Guide Grade 5th Mathematics First Trimester Aug. 19 Nov. 8 Chapter Major Concepts: Number and Operation
CHAPTER 6: RATIOS, RATES, & PROPORTIONS
 CHAPTER 6: RATIOS, RATES, & PROPORTIONS 6.1 Ratios 6.2 Rates 6.3 Unit Rates 6.4 Proportions 6.5 Applications Chapter 6 Contents 425 CCBC Math 081 Ratios Section 6.1 6 pages 6.1 Ratios One of the pieces
CHAPTER 6: RATIOS, RATES, & PROPORTIONS 6.1 Ratios 6.2 Rates 6.3 Unit Rates 6.4 Proportions 6.5 Applications Chapter 6 Contents 425 CCBC Math 081 Ratios Section 6.1 6 pages 6.1 Ratios One of the pieces
Answers Investigation 1
 Answers Applications 1. a. 560 b. 78, c. 39 to 11 (or 780 to 220) 2. a. 750 2,000 or 3 8 b. 62.5,; Here students need to recognize that the fraction they need is 5 8, and 5, 8 = 0.625. c. 5 to 3 (or 1,250
Answers Applications 1. a. 560 b. 78, c. 39 to 11 (or 780 to 220) 2. a. 750 2,000 or 3 8 b. 62.5,; Here students need to recognize that the fraction they need is 5 8, and 5, 8 = 0.625. c. 5 to 3 (or 1,250
Using Inequalities to Solve Problems
 LESSON 13 Using Inequalities to Solve Problems Plug In Solving One-Step Inequalities An inequality is a sentence that shows one quantity is less than or greater than the other. 13 2 4. 5 1 2 2 3 3, 81
LESSON 13 Using Inequalities to Solve Problems Plug In Solving One-Step Inequalities An inequality is a sentence that shows one quantity is less than or greater than the other. 13 2 4. 5 1 2 2 3 3, 81
N1.1 Understand integers and place value to deal with arbitrarily large positive numbers. If = 6996, work out
 N1.1 Understand integers and place value to deal with arbitrarily large positive numbers. If 53 132 = 6996, work out 6996 530. N1.3 Understand and use number operations and the relationships between them,
N1.1 Understand integers and place value to deal with arbitrarily large positive numbers. If 53 132 = 6996, work out 6996 530. N1.3 Understand and use number operations and the relationships between them,
M8WSB-C02.qxd 3/27/08 11:04 AM Page NEL
 NEL Chapter Fraction Operations GOAL You will be able to multiply and divide fractions by whole numbers, other fractions, and mixed numbers using models, drawings, and symbols estimate products and quotients
NEL Chapter Fraction Operations GOAL You will be able to multiply and divide fractions by whole numbers, other fractions, and mixed numbers using models, drawings, and symbols estimate products and quotients
M8WSB-C02.qxd 3/27/08 11:04 AM Page NEL
 NEL Chapter Fraction Operations GOAL You will be able to multiply and divide fractions by whole numbers, other fractions, and mixed numbers using models, drawings, and symbols estimate products and quotients
NEL Chapter Fraction Operations GOAL You will be able to multiply and divide fractions by whole numbers, other fractions, and mixed numbers using models, drawings, and symbols estimate products and quotients
I m pleased to welcome you to the Tobin s Pizza Family. Congratulations again in receiving this employment.
 Tobin s Pizza Corporation 2901 Morrissey Drive, Rm 2144 Bloomington, IL 61704 August 24, 2016 6th Grade Math Student Evans Junior High Dear 6th Grade Math Scholar: Congratulations on your Tobin s Pizza
Tobin s Pizza Corporation 2901 Morrissey Drive, Rm 2144 Bloomington, IL 61704 August 24, 2016 6th Grade Math Student Evans Junior High Dear 6th Grade Math Scholar: Congratulations on your Tobin s Pizza
Problem Solving: Translating Percent Problems 1. 75% % % % % % 0.85
 Problem Solving: Lesson Planner Skills Maintenance Variables and Proportions Problem Solving: In this lesson, students learn about different situations where percents are used. They learn to use a percent
Problem Solving: Lesson Planner Skills Maintenance Variables and Proportions Problem Solving: In this lesson, students learn about different situations where percents are used. They learn to use a percent
*Remember to teach students to read inequalities from left to right. Which ever end they come to first is how it is read.
 Equations Teacher Equations N.1: Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems. 7.N.1.3 Use properties of the real-number system to explain reasoning
Equations Teacher Equations N.1: Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems. 7.N.1.3 Use properties of the real-number system to explain reasoning
G4_Ratio, Proportion and Percentages_Mid-Term Exam Review #4
 G4_Ratio, Proportion and Percentages_Mid-Term Exam Review #4 Basic Math / FND M020 FA 14 10404-10N30FD04-Nap (Prof. Abdon) Student Name/ID: 1. There are books on a shelf. of these books are new. (a)what
G4_Ratio, Proportion and Percentages_Mid-Term Exam Review #4 Basic Math / FND M020 FA 14 10404-10N30FD04-Nap (Prof. Abdon) Student Name/ID: 1. There are books on a shelf. of these books are new. (a)what
1. A proper fraction is when the numerator is greater than the denominator.
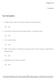 Chapter 02 Fractions True / False Questions 1. A proper fraction is when the numerator is greater than the denominator. True False 2. The writing of a whole number and a proper fraction is an improper
Chapter 02 Fractions True / False Questions 1. A proper fraction is when the numerator is greater than the denominator. True False 2. The writing of a whole number and a proper fraction is an improper
Module 3 Study Guide Proportional Reasoning & Dimensional Analysis
 Module 3 Study Guide Proportional Reasoning & Dimensional Analysis Name: Block: Learning Target #1: Proportional Reasoning 1. I can write a ratio in several ways. Ratio: A comparison of two quantities
Module 3 Study Guide Proportional Reasoning & Dimensional Analysis Name: Block: Learning Target #1: Proportional Reasoning 1. I can write a ratio in several ways. Ratio: A comparison of two quantities
Chapter 3 Fractions, Decimals, and Percent
 Chapter 3 Fractions, Decimals, and Percent 3.1 Fractions to Decimals How can we write a whole number as a decimal or fraction? Example 1. 4 As a Decimal? 1 is 0.10 in decimal form 10 As a Fraction? You
Chapter 3 Fractions, Decimals, and Percent 3.1 Fractions to Decimals How can we write a whole number as a decimal or fraction? Example 1. 4 As a Decimal? 1 is 0.10 in decimal form 10 As a Fraction? You
Example 1: Cost of Operation. Example 2: Education Pays Off. 3.1: Algebraic Translations of English Phrases. 3.2: Strategy for Solving Word Problems
 3.1: Algebraic Translations of English Phrases 3.2: Strategy for Solving Word Problems Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division sum more than increased by plus added to Total of sum of 6 and 7 3 more
3.1: Algebraic Translations of English Phrases 3.2: Strategy for Solving Word Problems Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division sum more than increased by plus added to Total of sum of 6 and 7 3 more
Two-Way Tables ESSENTIAL QUESTION. How can you use two-way frequency tables to solve real-world problems? Real-World Video. my.hrw.
 Two-Way Tables? MODULE ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use two-way frequency tables to solve real-world problems? 15 LESSON 15.1 Two-Way Frequency Tables LESSON 15.2 Two-Way Relative Frequency Tables Image
Two-Way Tables? MODULE ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use two-way frequency tables to solve real-world problems? 15 LESSON 15.1 Two-Way Frequency Tables LESSON 15.2 Two-Way Relative Frequency Tables Image
SAMPLE TASKS I. What number is ten times greater than 128? Explain how you know.
 GRADE 5 Mathematics NUMBER & OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN Understand the place value system. place value Define a number in one place as 1/10 of its value in the place to its left. 5.NBT.1. Recognize that in
GRADE 5 Mathematics NUMBER & OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN Understand the place value system. place value Define a number in one place as 1/10 of its value in the place to its left. 5.NBT.1. Recognize that in
LESSON TITLE: Math in Fashion (by Deborah L. Ives, Ed.D.) GRADE LEVEL: SUBJECT MATTER: Algebra. TIME ALLOTMENT: Two 45-minute class periods
 LESSON TITLE: Math in Fashion (by Deborah L. Ives, Ed.D.) GRADE LEVEL: 7-10 SUBJECT MATTER: Algebra TIME ALLOTMENT: Two 45-minute class periods OVERVIEW Using video segments and web interactives from Get
LESSON TITLE: Math in Fashion (by Deborah L. Ives, Ed.D.) GRADE LEVEL: 7-10 SUBJECT MATTER: Algebra TIME ALLOTMENT: Two 45-minute class periods OVERVIEW Using video segments and web interactives from Get
Summer Math Practice: 7 th Math Entering 8 th Pre-Algebra
 Summer Math Practice: 7 th Math Entering 8 th Pre-Algebra Dear Students and Parents, The summer math requirement is due to Mr. Cyrus the first day back in August. The objective is to make sure you have
Summer Math Practice: 7 th Math Entering 8 th Pre-Algebra Dear Students and Parents, The summer math requirement is due to Mr. Cyrus the first day back in August. The objective is to make sure you have
Grade 4 Mathematics Item Specification C1 TG
 Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Numbers and Operations Fractions
Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Numbers and Operations Fractions
Name Date Class. February Break Interactive Assignment Multiple Choice
 February Break Interactive Assignment Multiple Choice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A triangle has sides with lengths of 2x 7, 5x 3,
February Break Interactive Assignment Multiple Choice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A triangle has sides with lengths of 2x 7, 5x 3,
Unit 2: Accentuate the Negative Investigation 3: Multiplying and Dividing Rational
 Unit 2: Accentuate the Negative Investigation 3: Multiplying and Dividing Rational I can solve operations composed of rational numbers with an understanding of their properties Investigation Practice Problems
Unit 2: Accentuate the Negative Investigation 3: Multiplying and Dividing Rational I can solve operations composed of rational numbers with an understanding of their properties Investigation Practice Problems
1. A proper fraction is when the numerator is greater than the denominator.
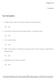 Chapter 02 Fractions True / False Questions 1. A proper fraction is when the numerator is greater than the denominator. True False 2. The writing of a whole number and a proper fraction is an improper
Chapter 02 Fractions True / False Questions 1. A proper fraction is when the numerator is greater than the denominator. True False 2. The writing of a whole number and a proper fraction is an improper
Welcome to IB Math Studies Year 1
 Welcome to IB Math Studies Year 1 Some things to know: 1. Lots of info at www.aleimath.blogspot.com 2. HW yup. You know you love it! Be prepared to present. 3. Content: 4. Grading Ultimately, you need
Welcome to IB Math Studies Year 1 Some things to know: 1. Lots of info at www.aleimath.blogspot.com 2. HW yup. You know you love it! Be prepared to present. 3. Content: 4. Grading Ultimately, you need
The Great Jump-Off Worksheet
 7.45 The Great Jump-Off Worksheet Directions: The best jumping frogs in Caldwell County are competing in The Great Jump-Off. Unfortunately, the jumping measurements have arrived in a variety of forms fractional,
7.45 The Great Jump-Off Worksheet Directions: The best jumping frogs in Caldwell County are competing in The Great Jump-Off. Unfortunately, the jumping measurements have arrived in a variety of forms fractional,
Chapter 2 Fractions and Problem Solving
 . Defining and Reasoning about Fractions - Chapter Fractions and Problem Solving. Defining and Reasoning About Fractions. Answers will vary. Michael needs to learn that the whole or unit amount can be
. Defining and Reasoning about Fractions - Chapter Fractions and Problem Solving. Defining and Reasoning About Fractions. Answers will vary. Michael needs to learn that the whole or unit amount can be
How can the strategy draw a diagram help you solve a decimal multiplication problem?
 ? Name 3.5 Essential Question PROBLEM SOLVING Multiply Money How can the strategy draw a diagram help you solve a decimal multiplication problem? Number and Operations 5.3.D, 5.3.E, Also 5.10.D MATHEMATICAL
? Name 3.5 Essential Question PROBLEM SOLVING Multiply Money How can the strategy draw a diagram help you solve a decimal multiplication problem? Number and Operations 5.3.D, 5.3.E, Also 5.10.D MATHEMATICAL
Grade 5 Mathematics Item Specification C1 TF. Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures
 Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Number and Operations Fractions Target
Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Number and Operations Fractions Target
Alexander, Who Used to Be Rich Last Sunday 3rd grade selection Lesson wants versus needs, money values
 Alexander, Who Used to Be Rich Last Sunday 3rd grade selection Lesson wants versus needs, money values You will need: Copy of Alexander, Who Used to Be Rich Last Sunday - provided Flip chart or chalkboard
Alexander, Who Used to Be Rich Last Sunday 3rd grade selection Lesson wants versus needs, money values You will need: Copy of Alexander, Who Used to Be Rich Last Sunday - provided Flip chart or chalkboard
