Subsea Corrosion Management: Challenges and Limitations
|
|
|
- Preston Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COASTAL & OFFSHORE ENGINEERING IJCOE Vol.1/No. 1/Spring 2017 (27-32) Available online at: Subsea Corrosion Management: Challenges and Limitations Reza Javaherdashti Director, Parscorrosion Consultants, Perth, Australia; ARTICLE INFO Article History: Received: 15 Nov Accepted: 9 Mar Keywords: Subsea structures Integrity Corrosion prediction models CRA Cathodic protection ABSTRACT 1. Introduction Deep sea oil and gas industry is becoming more and more an attractive option for energy-thirsty industry. In addition to its various economical benefits, it also has its dangerous downsides, mainly ecological. With no doubt corrosion is a significant issue in these structures that can lead into ecological disasters. Any failure in the deep sea structures (manifold, line pipe, flow lines ) could be disastrous. Unlike on-shore structures or even shallow water structures, the access for regular monitoring and repair is not an easy option, in terms of both the cost and the accessibility. Therefore corrosion management for the subsea structures mostly rely on the estimation of corrosion rates. These corrosion rates themselves are calculated based on semi-experimental research results and therefore, are always limited in terms of their assumptions and applications. In this paper we will review some important features of deep sea corrosion issues and the main counter-measures to address such issues. 2-Some of the highlights for the corrosion management of deep sea structures: There are mainly three aspects of deep sea structures corrosion management (DSCM) that make them different from on-shore and shallow water structures corrosion management (OF/SW CM) techniques: Materials Corrosion Management Practice Cathodic Protection These three issues are important in the sense that when they are taken together, they can define the job description of a typical subsea corrosion engineer Subsea structures such as manifolds, line pipes and flow lines are important investments. Also because of the sensitivity of environmental issues, corrosion of these structures is of vital importance. Subsea corrosion management is different from on-shore and shallow water off-shore corrosion management in mainly three factors: materials, corrosion management practice and cathodic protection. There are important limitations in many aspects of these three factors that make them different from their counterparts in other industries. In this paper, some of these differences especially with regards to corrosion prediction softwares and associated design strategies are addressed and discussed. and differentiate it from that of a, say, corrosion engineer who works in mining industry. Materials The variety of materials that are used in OF/SW CM applications is not seen with DSCM. This is in fact dictated by the corrosion models and their underlying design philosophy. The materials of frequent use in pipes for subsea applications are [1]: (carbon) steel, stainless, duplex and superduplex stainless steels, clad and titanium pipes. A more general classification of t he materials can be either: -Carbon steel (clad or lined) -Corrosion resistant alloys (CRA) such as but not limited to duplex stainless steels (DSS) Clad steel plate is a composite steel plate made by (metallurgical) bonding the cladding material (such as all types of stainless steels, nickel and nickel-copper alloys and Titanium) to either or both sides of a carbon steel or low alloy steel plate (base metal). While different methods may be used to apply the cladding, both the economy and the available sizes of the final product are important factors, in addition to mechanical properties, that will affect the use of these materials. However, it must be noted that as application of these methods can change the overall microstructure, it can have some unwanted effects as well: a study on stainless-cladded carbon steels by hot-rolling shows that the following changes in the bimetallic microstructure has happened [2]: -formation of a decarburized region near the carbon steel side, 27
2 Reza Javaherdashti / Subsea Corrosion Management: Challenges and Limitations - a hardened region with high carbon content at the stainless steel side where a partial Cr depletion had occurred. These micro structural changes along with the formation of residual stresses which mostly have tensile natures- can be leading into premature failures. An example of CRA is duplex stainless steel. These steels are mainly charcterised by their dual crystal structure, Figure 1: Figure 1. An example of the microstructure of a duplex stainless steel (SAF2205): (bright: austenite, dark: ferrite). The structure shows 52 ± 2 wt% retained austenite. Duplex stainless steels are taken more corrosion resistant than austenitic stainless steels owing to their relatively higher chromium content. A very important issue with duplex stainless steels is the spacing between austenite islands as short austenite spacing is normally preferred due to both shorter hydrogen diffusion paths, more hydrogen tapping and crack stop properties [3].To avoid hydrogen induced stress cracking (HISC), based on deformation mode and induced strains, an austenite spacing from less than or equal to 30μ to 60 μ [4]. Corrosion Management: Corrosion management includes items such as corrosion allowance, corrosion models and inhibitor availability and the like. In contrast to many on-shore corrosion management techniques, subsea corrosion management still applies corrosion allowance. This is in essence the extra thickness of the pipe wall to compensate for corrosion. While it may appear as a simple issue of just adding a few millimeter to the net thickness of the pipe (to get the nominal thickness), this corrosion management technique has huge economical and application impacts, a rather classical example in this regard is for a pipe line of 8-in. diameter and 225 miles (~362 km) long and a wall thickness of inches, by increasing the thickness by only inches, an extra 3700 tons of steel will be needed as well as well as decreasing the internal capacity by 5% [5]. Corrosion modeling and inhibitor availability are the main two features that define the main differences between corrosion prediction models [6]. In these models the type of inhibitor (cathodic, anionic or mixed) is of no importance and the assumption is that whatever the mechanism of action, it is the availability of the inhibitor that matters. Corrosion models can be classified into two groups, conservative BP (Cassandra) and NORSOK (and their various in-house alternatives) and rather liberal Shell model [6]. Figure 2 schematically shows some of the features of these modeling approaches: 28
3 Reza Javaherdashti / IJCOE 2017, 1(1); p Figure 2. Schematic comparison between two most frequently used corrosion prediction models for subsea structures Although so-called BP model is based on papers published by de Waard [7]-[8], and they essentially show similar results, there are slight differences between the model and the work by de Waard, in issues such as use of a correction factor for carbon dioxide fugacity and its lack in the BP model [9]. Figure 3 shows a typical input for a BP 93 (flow insensitive) model: Assumptions: CO2 H2S ph Model - Hold up conservatively assumed to be all water. - DW ph model has been used - We assume a total shear stress of 1 Pa. -The values given for TOL BP93 have been calculated based on the assumption that it is top of line condensing corrosion only and that wetting occurs only 10% of time (F=0.1). Value in mol.% Value in mol.% DW Glycol Value % Internal Value in m Diameter Water SG (specific (Normally accepted as 1.00)_ gravity) Acetates as acid? Water Chemistry (mg/l) False/True Na, K, Ca, Mg, Sr, Ba, Fe, Cl, SO4, HCO3 Figure 3. Typical Input data for a BP 93 Cassandra corrosion prediction model The Norwegian NORSOK model, de Waard model and the BP model predict the same corrosion rates at temperatures below or equal to scaling temperature, after the scaling temperature these models will predict corrosion rates that can be different from each other (Figure 4), and thus will dictate different strategies. Figure 4. Corrosion rates as predicted by three models for temperatures above scaling temperature (NORSOK, by default, calculates ferrous ions unsaturated rates). To illustrate how the same data can result in different corrosion management strategies according to these models, Marsh and Teh consider the example of 100,000ppm sodium chloride brine with 500ppm of bicarbonate ions, 100bara, 5% CO2 (gas phase), 100oC, No significant flow effects considered, 20 year design life. In addition, we can take In this example, Cassandra model by assuming 95% availability upper limit, inhibited corrosion rate 0.1mm/yr will recommend the use of CRA (such as 13% Cr supermartensitic stainless steel or SAF 2205) 29
4 Reza Javaherdashti / Subsea Corrosion Management: Challenges and Limitations whereas for the same set of data, NORSOK M-506 by assuming 99% availability upper limit, inhibited corrosion rate 0.05/0.1 mm/yr (65oC/100oC) recommends carbon steel with 3mm corrosion allowance. Considering that the average costs of 13% Cr supermartensitic stainless steel and SAF 2205 are, respectively, 4 and 10 times of carbon stel, the readers can easily calculate that the economic impact of differences in corrosion rate calculations and design philosophies. In addition to de Waard, Cassandra and NORSOK, there are other corrosion prediction models such as [10] Cormed (Elf), Lipucorr (Total), Predict (InterCorr), CorPos (CorrOcean/FORCE Technology), as it can be Table 1. Methods and techniques for corrosion monitoring expected while all these models have the same basics, the input and results will differ. One important shortcoming of corrosion prediction models is that in models such as BP, dewaard and NORSOK, microbial corrosion is not considered. Cassandra [9] for example, is not valid for liquid velocities less than 1.5 ms -1. It is interesting to know that this is also the velocity limit where microbial corrosion can be expected [11]. Even the standards frequently used in subsea corrosion management (such as DNV) [12] do not address microbial corrosion properly. This matter becomes important when we consider that microbial corrosion has been shown as a cause of failure in subsea structures [13]. 30
5 Reza Javaherdashti / IJCOE 2017, 1(1); p The Concept of Corrosion Monitoring for subsea structures The concept of corrosion monitoring has developed from two distinct areas, plant inspection techniques and laboratory corrosion testing techniques, with the original aim of assessing or predicting corrosion. Use of Corrosion Monitoring Data: To provide operational or management information Corrosion can often be controlled by maintaining a single operational variable (e.g., temperature, ph, humidity) within limits determined by prior monitoring or other investigations. If the significant variable is measured for other reasons, this measurement can be used directly for corrosion control. If the variable is not otherwise measured, or in more complex cases where several variables interact, corrosion monitoring information can be used by plant operators to control plant operation so as to control corrosion. Any process change may have significant effects on corrosion, and corrosion monitoring techniques allow full scale trials to proceed with a minimum of risk to plant. Corrosion Monitoring Techniques A wide range of corrosion monitoring techniques is now available allowing determination of total corrosion, corrosion rate, corrosion state, analytical determination of corrosion product or active species, detection of defects or changes in physical parameters. Associated costs can be small where simple instrumentation and a few measurements are appropriate but in some cases may be extremely costly and require expert skills. Much of the progress which has been made in the past few years has been due to advances in electronics which have allowed multiprobe measurement and recording at a tolerable cost. Instantaneous feedback of corrosion information can be obtained from various parts of the plant, which can be fed to the plant control room and/or plant computer to permit control of the necessary process variable to provide corrosion control. Table 1 indicates corrosion monitoring techniques Selecting a Technique for Corrosion Monitoring Many techniques have been used for corrosion monitoring (see Table 1), it is clearly possible to develop others. Consequently when a possible new application is being considered, a problem arises in choosing the most appropriate technique. Each has its strong points and its limitations, and none is the best for all situations. Any monitoring technique can provide only a limited amount of information, and the techniques should be regarded as complementary rather than competitive. Where more than one technique will give the information required, the information is obtained in different ways; a cross-check can be valuable and differences in detail can add meaning. A corrosion monitoring technique rarely gives wrong information, unless the equipment used is faulty. "Nonsense" results arise because the information is correct, but irrelevant in the corrosion sense. The polarization resistance method, for example, measures the combined rate of any electrochemical reactions at the surface of the test sample. If the main reaction is the corrosion ones, the rate measured is the corrosion rate. If however, other reactions are possible at rates that are comparable or greater, the measured rate includes the other reactions. Useful deductions can still be made provided it is recognized that the corrosion rate has not been measured. The choice of a monitoring technique is a complex problem requiring expert knowledge. The first essential is to establish what type of information is needed. This necessarily involves an input from the management of the plant in question. Cathodic Protection For obvious reasons, impressed current CP cannot be an option for deep sea water applications. According to DNV- OS-F101 [14], duplex and martensitic stainless steel linepipe, and C-Mn steel linepipe with SMYS > 450 MPa require special considerations of the susceptibility of environmentally assisted cracking (including SSC and hydrogen induced cracking related to cathodic protection). NORSOK workshop agreement [4] seems more detailed about the joint use of CP and duplex stainless steels. According to this document duplex stainless steels are well protected for potentials more negative than -600 mv (Ag/AgCl) on the condition that a complete electrical insulation from the structural elements, that are protected at mv, is also applied. Although some modifications in CP system design may be promising in using both CP and supermartinsitic stainless steel together [15]. As it can be seen, two major limitations on applying CP to subsea structures are that only one method of CP can be applied and that we are limited to use of certain alloys whose yield stress is lower than a certain limit. 4- Conclusion Subsea structures like on-shore and other off-shore (shallow water) structures need to be protected from corrosion. However the practice of corrosion management for these structures is different from onshore and off-shore in not only the materials used but also in applications such as cathodic protection. Due to factors such as difficulty in having access to the subsea structures and the costs involved, different corrosion prediction models have been developed. These models-with their in-house variants- are 31
6 Reza Javaherdashti / Subsea Corrosion Management: Challenges and Limitations frequently used in not only estimation of corrosion but also selecting the strategy that will be the most feasible one to apply. Although these models have similar basics, due to their assumptions and conservative approaches, the very same inputs may result in different corrosion,management strategies and therefore different budgeting for the projects. When applying these models, their limitations must be considered and their approaches must be taken with required precautions. 5- References 1. Guide for building and classing subsea pipeline systems-chapter 2, Section1, American Bureau of Shipping (ABS), Houston, TX, USA, May 2006 (updated March 2008). 2. S. Missori, F. Murdolo, A. Sili, Microstructural Characterisation of a stainless steelcladded carbon steel, Metallurgical Science and Technology, Vol.19.No.2, December 2001, p V. Olden FE modeling of hydrogen induced stress cracking in 25% Cr duplex stainless steel, PhD Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, August Design guideline to avoid hydrogen induced stress cracking in subsea duplex stainless steel, NORSOK Workshop Agreement-HISC Guideline for duplex stainless steel-m-wa-01, Rev.1, October H.H. Uhlig, Corrosion and corrosion control. 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, West Sussex, England, J. Marsh and T. The, Conflicting Views: CO2 Corrosion Models, Corrosion Inhibitor Availability Philosophies, and the Effect on Subsea Systems and Pipeline Design, SPE , Offshore Europe 2007, Aberdeen, Scotland, U.K., 4 7 September C. de Waard, U. Lotz, D.E. Milliams, Predictive model for CO 2 corrosion engineering in wet natural gas pipelines, Corrosion, Vol.47, No.12, December 1991, pp C. de Waard, U. Lotz, Prediction of CO 2 corrosion of car bon steel, NACE CORROSION 93, Paper 69, March 1993, New Orleans, 1993, USA. 9. A. Petersen, R. Chapman, B. Hedges Corrosion prediction with Cassnadra, S/UTG/013/03, bp Upstream Technology Group Sunbury, 01/03/ R. Johnsen, Corrosion of carbon steel in hydrocarbon environments, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 20/09/ R. Javaherdashti, Microbiologically influenced corrosion-an engineering insight, Springer, 2008, UK. 12. R. Javaherdashti, MIC myths: Avoiding common pitfalls in the practice of hydrotesting and likelihood of Microbial induced corrosion, Corrosion Management, January-February X. Wang, J. Duan, Y. Li, J. Zhang, S. Ma, B. Hou, Corrosion of steel structures in sea-bed sediments, Bulletin of Materials Science, Vol.28, No.2, pp.81-85, April Offshore Standard DNV- OS-F101, Section 5, B 507, Det Norske Veritas, Norway, January S. Eliassen, New concept for cathodic protection of offshore pipelines to reduce hydrogen induced stress cracking (HISC) in high strength 13% Cr stainless steel, Corrosion Engineering, Science, and Technology, Vol.39, No.1, pp.31-37,
HISC Performance Validation of DSS Welds for Large-Strain, HP/HT Subsea Applications
 HISC Performance Validation of DSS Welds for Large-Strain, HP/HT Subsea Applications Requirements for an Improved Assessment Approach Alexander Amadioha & Andrew Low AOG 2015 Conference, Perth, Australia,
HISC Performance Validation of DSS Welds for Large-Strain, HP/HT Subsea Applications Requirements for an Improved Assessment Approach Alexander Amadioha & Andrew Low AOG 2015 Conference, Perth, Australia,
CP DESIGN OF A SUPER 13% CR FLOWLINE. Are Sjaastad and Harald Osvoll FORCE Technology Norway AS Hornebergveien Trondheim Norway
 CP DESIGN OF A SUPER 13% CR FLOWLINE Are Sjaastad and Harald Osvoll FORCE Technology Norway AS Hornebergveien 7 7038 Trondheim Norway Olav Jan Hauge and Rolf E. Lye Norsk Hydro ASA Norway Guy Bärs Technip
CP DESIGN OF A SUPER 13% CR FLOWLINE Are Sjaastad and Harald Osvoll FORCE Technology Norway AS Hornebergveien 7 7038 Trondheim Norway Olav Jan Hauge and Rolf E. Lye Norsk Hydro ASA Norway Guy Bärs Technip
Materials and Welding. Capability & Experience
 Materials and Welding Capability & Experience Capability Overview Materials and welding is a fundamental engineering discipline that supports key decisions through design phases to ensure successful project
Materials and Welding Capability & Experience Capability Overview Materials and welding is a fundamental engineering discipline that supports key decisions through design phases to ensure successful project
Introduction to CRA Tubulars: Metallurgy and Material Selection for Corrosive Environments September 25th, 2017
 CRA Tubulars and Well Integrity page Introduction to CRA Tubulars: Metallurgy and Material Selection for Corrosive Environments September 25th, 2017 CRA Tubulars and Well Integrity Technical Symposium
CRA Tubulars and Well Integrity page Introduction to CRA Tubulars: Metallurgy and Material Selection for Corrosive Environments September 25th, 2017 CRA Tubulars and Well Integrity Technical Symposium
INTRODUCTION TO ULTRASONIC IN-LINE INSPECTION OF CRA PIPELINES. Herbert Willems, Gerhard Kopp NDT Global, Germany
 INTRODUCTION TO ULTRASONIC IN-LINE INSPECTION OF CRA PIPELINES Herbert Willems, Gerhard Kopp NDT Global, Germany ABSTRACT Pipelines manufactured from corrosion-resistant alloys (CRA) are becoming more
INTRODUCTION TO ULTRASONIC IN-LINE INSPECTION OF CRA PIPELINES Herbert Willems, Gerhard Kopp NDT Global, Germany ABSTRACT Pipelines manufactured from corrosion-resistant alloys (CRA) are becoming more
Area of Use for Z100 (UNS S32760) Superduplex Stainless Steel Wireline.
 Area of Use for Z100 (UNS S32760) Superduplex Stainless Steel Wireline. R Francis and G Warburton Weir Materials & Foundries Abstract Wirelines or slicklines are routinely used in the oil and gas industry
Area of Use for Z100 (UNS S32760) Superduplex Stainless Steel Wireline. R Francis and G Warburton Weir Materials & Foundries Abstract Wirelines or slicklines are routinely used in the oil and gas industry
ZERON 100 FOR DOWNSTREAM PROCESSING IN ACID LEACH MINING. Park Works Manchester M40 2BA UK (*Corresponding author:
 ZERON 100 FOR DOWNSTREAM PROCESSING IN ACID LEACH MINING *Roger Francis 1 and Devin M. Wachowiak 2 1 RA Materials Park Works Manchester M40 2BA UK (*Corresponding author: rfrancis@rolledalloys.com) 2 Rolled
ZERON 100 FOR DOWNSTREAM PROCESSING IN ACID LEACH MINING *Roger Francis 1 and Devin M. Wachowiak 2 1 RA Materials Park Works Manchester M40 2BA UK (*Corresponding author: rfrancis@rolledalloys.com) 2 Rolled
CORRMET LIMITED, 189 St. Georges Terrace, Level 8, Unit 2, Perth, Western Australia 6000,
 Development of a Test Program for Assessing the SCC, Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Behaviour of Selected Corrosion Resistant Alloy Liner Materials for Clad Pipe Offshore Applications Barry GIDEON a and
Development of a Test Program for Assessing the SCC, Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Behaviour of Selected Corrosion Resistant Alloy Liner Materials for Clad Pipe Offshore Applications Barry GIDEON a and
Development of large-diameter line pipe for offshore applications
 Development of large-diameter line pipe for offshore applications Dr. Michael Gräf Europipe Deutschland GmbH, Muelheim, Germany Dr. Hans-Georg Hillenbrand Europipe GmbH, Ratingen, Germany EUROPIPE. The
Development of large-diameter line pipe for offshore applications Dr. Michael Gräf Europipe Deutschland GmbH, Muelheim, Germany Dr. Hans-Georg Hillenbrand Europipe GmbH, Ratingen, Germany EUROPIPE. The
SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sanicro 29 is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel (CRA) for OCTG downhole applications in particularly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized
SANICRO 29 FOR OCTG TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sanicro 29 is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel (CRA) for OCTG downhole applications in particularly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized
Methods of Corrosion Control. Corrosion Control or Corrosion Management?
 Corrosion Control or Corrosion Management? Corrosion control is a process aimed at reducing the corrosion rate to a tolerable level (or predictable limits) Corrosion control focuses mainly on (i) materials
Corrosion Control or Corrosion Management? Corrosion control is a process aimed at reducing the corrosion rate to a tolerable level (or predictable limits) Corrosion control focuses mainly on (i) materials
TEPZZ 9 4 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2015/40
 (19) TEPZZ 9 4_ _A_T (11) EP 2 924 131 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 14162191.2 (22) Date of filing: 28.03.14 (1) Int Cl.: C21D
(19) TEPZZ 9 4_ _A_T (11) EP 2 924 131 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 14162191.2 (22) Date of filing: 28.03.14 (1) Int Cl.: C21D
SULPHIDE STRESS CORROSION CRACKING OF WELDED PLATES
 ANDRITZ AG 1 IWS, TU GRAZ 2 ALICE ORSI 1, YASSAR GHANIMI 1, NORBERT ENZINGER 2 SULPHIDE STRESS CORROSION CRACKING OF 1.4418 WELDED PLATES Abstract Stainless steel 1.4418 is a promising martensitic steel
ANDRITZ AG 1 IWS, TU GRAZ 2 ALICE ORSI 1, YASSAR GHANIMI 1, NORBERT ENZINGER 2 SULPHIDE STRESS CORROSION CRACKING OF 1.4418 WELDED PLATES Abstract Stainless steel 1.4418 is a promising martensitic steel
ATI 2205 ATI Technical Data Sheet. Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES. (UNS S31803 and S32205)
 ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
ATI 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S31803 and S32205) GENERAL PROPERTIES ATI 2205 alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly
Hydrogen Embrittlement of Subsea Structures. David Jones Minton, Treharne & Davies Ltd.
 Hydrogen Embrittlement of Subsea Structures David Jones Minton, Treharne & Davies Ltd. Overview Hydrogen Embrittlement is a failure mechanism typically linked to corrosion and corrosion control processes,
Hydrogen Embrittlement of Subsea Structures David Jones Minton, Treharne & Davies Ltd. Overview Hydrogen Embrittlement is a failure mechanism typically linked to corrosion and corrosion control processes,
Problem Steels 1. Welding Consumables Problem Steels. Section 12 - Welding Consumables. 12 Problem Steels. Welding of Problem Steels 2
 Problem Steels 1 Afrox Product Reference Manual Problem Steels Section - Problem Steels 1 Welding of Problem Steels 2 Problem Steels Electrodes 3 Problem Steels MIG & TIG Wires 7 Problem Steels Flux Cored
Problem Steels 1 Afrox Product Reference Manual Problem Steels Section - Problem Steels 1 Welding of Problem Steels 2 Problem Steels Electrodes 3 Problem Steels MIG & TIG Wires 7 Problem Steels Flux Cored
Influence of stress concentrator on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of a X70 weld simulated coarse grained heat affected zone
 EUROMAT 2015 Warsaw, 2015 September 23 th Influence of stress concentrator on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of a X70 weld simulated coarse grained heat affected zone A. Alvaro *, V. Olden *, B.
EUROMAT 2015 Warsaw, 2015 September 23 th Influence of stress concentrator on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of a X70 weld simulated coarse grained heat affected zone A. Alvaro *, V. Olden *, B.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in CO2 Corrosion Rate Assessment for Upstream Hydrocarbon Industries
 Paper No.24 The 16th Nordic Corrosion Congress, 20-22nd May 2015, Stavanger, Norway Avoiding Common Pitfalls in CO2 Corrosion Rate Assessment for Upstream Hydrocarbon Industries Seyed Mohammad Kazem HOSSEINI
Paper No.24 The 16th Nordic Corrosion Congress, 20-22nd May 2015, Stavanger, Norway Avoiding Common Pitfalls in CO2 Corrosion Rate Assessment for Upstream Hydrocarbon Industries Seyed Mohammad Kazem HOSSEINI
FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR AN UNPIGGABLE SUBSEA PIPELINE A CASE STUDY OF AN OFFSHORE PIPELINE
 FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR AN UNPIGGABLE SUBSEA PIPELINE A CASE STUDY OF AN OFFSHORE PIPELINE James Stewart, Inessa Yablonskikh, Baker Hughes, a GE company (BHGE) ABSTRACT Managing the long-term integrity of
FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR AN UNPIGGABLE SUBSEA PIPELINE A CASE STUDY OF AN OFFSHORE PIPELINE James Stewart, Inessa Yablonskikh, Baker Hughes, a GE company (BHGE) ABSTRACT Managing the long-term integrity of
Prevention Strategies Design and Coatings
 Lecture 14 Prevention Strategies Design and Coatings Keywords: Corrosion Prevention, Designs, Protective Coatings. There are a number of methods to control corrosion. The choice of any one control technique
Lecture 14 Prevention Strategies Design and Coatings Keywords: Corrosion Prevention, Designs, Protective Coatings. There are a number of methods to control corrosion. The choice of any one control technique
WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS
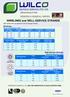 WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS High quality wire and strand for the oil and gas industry. Wirelines Minimum Breaking Loads Diameter in mm HT Carbon EHT Carbon ZERON 100VHX 0.092 2.34 1,950 1,980 1,350
WIRELINES and WELL-SERVICE STRANDS High quality wire and strand for the oil and gas industry. Wirelines Minimum Breaking Loads Diameter in mm HT Carbon EHT Carbon ZERON 100VHX 0.092 2.34 1,950 1,980 1,350
Client Corrosion, NameErosion, and Wetted Parts
 Client Corrosion, NameErosion, and Wetted Parts Location: A Heavy Metal Project Discussion Title Date By Eric Lofland Scope of This Presentation Explain some of the basic features of steels Define the
Client Corrosion, NameErosion, and Wetted Parts Location: A Heavy Metal Project Discussion Title Date By Eric Lofland Scope of This Presentation Explain some of the basic features of steels Define the
THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STAINLESS STEEL
 THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STAINLESS STEEL Stainless steel is primarily utilised on account of its corrosion resistance. However, the scope of excellent mechanical properties the within the family of
THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STAINLESS STEEL Stainless steel is primarily utilised on account of its corrosion resistance. However, the scope of excellent mechanical properties the within the family of
Heat Treatment of Tubes for Condenser, Feedwater Heater, and Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers
 Heat Treatment of Tubes for Condenser, Feedwater Heater, and Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers 1. SCOPE 1.1 The purpose of this document is to provide an overview of the different types of heat treatment processes
Heat Treatment of Tubes for Condenser, Feedwater Heater, and Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers 1. SCOPE 1.1 The purpose of this document is to provide an overview of the different types of heat treatment processes
Erosion-Corrosion Study of Oil-field Materials due to Liquid Impact
 Paper No. 6136 Erosion-Corrosion Study of Oil-field Materials due to Liquid Impact H. Arabnejad, A. Mansouri, S.A. Shirazi, B.S. McLaury, J.R. Shadley Erosion/Corrosion Research Center Department of Mechanical
Paper No. 6136 Erosion-Corrosion Study of Oil-field Materials due to Liquid Impact H. Arabnejad, A. Mansouri, S.A. Shirazi, B.S. McLaury, J.R. Shadley Erosion/Corrosion Research Center Department of Mechanical
Downhole metallurgy and corrosion from the first pipe to current challenges.
 Downhole metallurgy and corrosion from the first pipe to current challenges. ICorr, IOM3; Aberdeen, 27 November 2018 MetalEcosse Ltd, 2018 1 Drake Well (1859) TD: 69.5 ft, 21.18 m...struck oil in the Riceville
Downhole metallurgy and corrosion from the first pipe to current challenges. ICorr, IOM3; Aberdeen, 27 November 2018 MetalEcosse Ltd, 2018 1 Drake Well (1859) TD: 69.5 ft, 21.18 m...struck oil in the Riceville
AL 29-4C AL 29-4C. Technical Data Sheet. Stainless Steel: Superferritic INTRODUCTION (UNS S44735)
 AL 29-4C Stainless Steel: Superferritic (UNS S44735) INTRODUCTION AL 29-4C alloy, is a superferritic stainless steel developed by ATI in the early 1980s specifically for power plant surface condenser tubing.
AL 29-4C Stainless Steel: Superferritic (UNS S44735) INTRODUCTION AL 29-4C alloy, is a superferritic stainless steel developed by ATI in the early 1980s specifically for power plant surface condenser tubing.
Low Nickel austenite a cost efficient alternative to 304/4301. Gabriele Brückner Head of product development EMEA Outokumpu May 27, 2015
 Low Nickel austenite a cost efficient alternative to 304/4301 Gabriele Brückner Head of product development EMEA Outokumpu May 27, 2015 Content 1. Market situation 2. Development of cost-effective CrNi
Low Nickel austenite a cost efficient alternative to 304/4301 Gabriele Brückner Head of product development EMEA Outokumpu May 27, 2015 Content 1. Market situation 2. Development of cost-effective CrNi
Integrity Management of CRA Pipelines. Operator Experiences and Integrity Challenges
 Operator Experiences and Integrity Challenges 2015 Foreword Although CRA materials are selected for their increased resistance to degradation in certain operating environments, Operators have suffered
Operator Experiences and Integrity Challenges 2015 Foreword Although CRA materials are selected for their increased resistance to degradation in certain operating environments, Operators have suffered
CORROSION AND CORROSION CONTROL An Introduction to Corrosion Science and Engineering
 CORROSION AND CORROSION CONTROL An Introduction to Corrosion Science and Engineering FOURTH EDITION R. Winston Revie Senior Research Scientist CANMET Materials Technology Laboratory Natural Resources Canada
CORROSION AND CORROSION CONTROL An Introduction to Corrosion Science and Engineering FOURTH EDITION R. Winston Revie Senior Research Scientist CANMET Materials Technology Laboratory Natural Resources Canada
Stainless Steel & Stainless Steel Fasteners Chemical, Physical and Mechanical Properties
 Stainless Steel & Stainless Steel Fasteners Chemical, Physical and Mechanical Properties Stainless steel describes a family of steels highly resistant to tarnishing and rusting that contain at least two
Stainless Steel & Stainless Steel Fasteners Chemical, Physical and Mechanical Properties Stainless steel describes a family of steels highly resistant to tarnishing and rusting that contain at least two
Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316
 Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316 Manish Kumar Verma Mechanical, Columbia Institute of Engineering & Technology, Raipur (India) ABSTRACT Austenitic Stainless steels
Sensitization & Corrosion Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304 & 316 Manish Kumar Verma Mechanical, Columbia Institute of Engineering & Technology, Raipur (India) ABSTRACT Austenitic Stainless steels
FATIGUE OF DUPLEX STEELS IN CORROSIVE ENVIRONMENT
 5th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING ADDING INNOVATION CAPACITY OF LABOUR FORCE AND ENTREPRENEURS" 20 22 April 2006, Tallinn, Estonia FATIGUE OF DUPLEX STEELS IN CORROSIVE
5th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING ADDING INNOVATION CAPACITY OF LABOUR FORCE AND ENTREPRENEURS" 20 22 April 2006, Tallinn, Estonia FATIGUE OF DUPLEX STEELS IN CORROSIVE
Study on HIC and SSC of the Electric Resistance Welded Linepipe Steel
 CORROSION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, Vol.6, No.3(2007), pp.96~102 Study on HIC and SSC of the Electric Resistance Welded Linepipe Steel Wan Keun Kim 1, Seong Ung Koh 2, Boo Young Yang 2, and Kyoo Young Kim
CORROSION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, Vol.6, No.3(2007), pp.96~102 Study on HIC and SSC of the Electric Resistance Welded Linepipe Steel Wan Keun Kim 1, Seong Ung Koh 2, Boo Young Yang 2, and Kyoo Young Kim
IN-LINE INSPECTION OF PIPES USING CORROSION RESISTANT ALLOYS (CRA) M.Sc. Johannes Keuter PPSA Seminar Aberdeen 19-Nov-2014
 IN-LINE INSPECTION OF PIPES USING CORROSION RESISTANT ALLOYS (CRA) M.Sc. Johannes Keuter PPSA Seminar Aberdeen 19-Nov-2014 CONTENT 1. Challenge 2. Technical Solution 3. Summary Slide 2 CHALLENGE Definition
IN-LINE INSPECTION OF PIPES USING CORROSION RESISTANT ALLOYS (CRA) M.Sc. Johannes Keuter PPSA Seminar Aberdeen 19-Nov-2014 CONTENT 1. Challenge 2. Technical Solution 3. Summary Slide 2 CHALLENGE Definition
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING
 DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS ALLOYS AND PROCESSING ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
Corrosion of Metals. Industrial Metallurgists, LLC Northbrook, IL Copyright 2013 Industrial Metallurgists, LLC
 Corrosion of Metals Industrial Metallurgists, LLC Northbrook, IL 60062 847.528.3467 www.imetllc.com Copyright 2013 Industrial Metallurgists, LLC Course structure Learning modules 1. Introduction to corrosion
Corrosion of Metals Industrial Metallurgists, LLC Northbrook, IL 60062 847.528.3467 www.imetllc.com Copyright 2013 Industrial Metallurgists, LLC Course structure Learning modules 1. Introduction to corrosion
A30-in (0.762-m) subsea crude oil
 Failure Analysis of a 30-in Subsea Oil Pipeline S.K. SRIVASTAVA AND M.V. KATARKI, Institute of Engineering & Ocean Technology, Oil and Natural Gas Corp., Ltd., Panvel, Navi-Mumbai, India VIJU CHERIAN,
Failure Analysis of a 30-in Subsea Oil Pipeline S.K. SRIVASTAVA AND M.V. KATARKI, Institute of Engineering & Ocean Technology, Oil and Natural Gas Corp., Ltd., Panvel, Navi-Mumbai, India VIJU CHERIAN,
CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEM
 CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEM 2018.07 INDEX 1. Business Field 2. Material Supply 3. Application 1. Business Field CONSTRUCTION Design & Engineering Service Maintenance & Repair Works Concrete Rebar (Posts,
CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEM 2018.07 INDEX 1. Business Field 2. Material Supply 3. Application 1. Business Field CONSTRUCTION Design & Engineering Service Maintenance & Repair Works Concrete Rebar (Posts,
Sample Questions for Welding Engineering Examinations
 Sample Questions for Welding Engineering Examinations AWS Welding Engineer Revision 2 August 2003 Part 1 Basic Fundamentals of Science Examination Mathematics 1. Determine the acute angle _ when tan 63
Sample Questions for Welding Engineering Examinations AWS Welding Engineer Revision 2 August 2003 Part 1 Basic Fundamentals of Science Examination Mathematics 1. Determine the acute angle _ when tan 63
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS
 DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS corrosion resistant alloys ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
DATA SHEET ZERON 100 UNS S32760 THE GLOBAL LEADER IN SPECIALTY ALLOYS corrosion resistant alloys ZERON 100 Data Sheet Contents Specifications, Chemical Composition, Applications and Features...2 Performance
ATI ATI 2205 Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel. Technical Data Sheet
 Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogenenhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly improve
Alloy (UNS S31803 and S32205) Duplex Stainless Steel GENERAL PROPERTIES alloy (UNS S31803 and/or S32205) is a nitrogenenhanced duplex stainless steel alloy. The nitrogen serves to significantly improve
Tubing and Pipes.
 Tubing and Pipes FITOK Group FITOK GmbH (Headquarter) Sprendlinger Landstr., 9 Offenbach am Main, Germany Tel.: +49 9 900 449 Fax: +49 9 900 449 FITOK, Inc. 4 North Promenade Blvd., Suite 70, Stafford,
Tubing and Pipes FITOK Group FITOK GmbH (Headquarter) Sprendlinger Landstr., 9 Offenbach am Main, Germany Tel.: +49 9 900 449 Fax: +49 9 900 449 FITOK, Inc. 4 North Promenade Blvd., Suite 70, Stafford,
CATHODIC PROTECTION OF SUBMARINE PIPELINES BY GALVANIC ANODES
 RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNV-RP-F103 CATHODIC PROTECTION OF SUBMARINE PIPELINES BY GALVANIC ANODES OCTOBER 2003 Since issued in print (October 2003), this booklet has been amended, latest in April 2006. See
RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNV-RP-F103 CATHODIC PROTECTION OF SUBMARINE PIPELINES BY GALVANIC ANODES OCTOBER 2003 Since issued in print (October 2003), this booklet has been amended, latest in April 2006. See
Identification. Type Analysis
 Page 1 of 12 Unit Display: English Print Now Custom 455 Stainless E-Mail Datasheet Add to My Materials UNS Number S45500 Identification Type Analysis Carbon 0.05 % Manganese 0.50 % Phosphorus 0.040 % Sulfur
Page 1 of 12 Unit Display: English Print Now Custom 455 Stainless E-Mail Datasheet Add to My Materials UNS Number S45500 Identification Type Analysis Carbon 0.05 % Manganese 0.50 % Phosphorus 0.040 % Sulfur
CATHODIC PROTECTION OF SUBMARINE PIPELINES BY GALVANIC ANODES
 RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNV-RP-F103 CATHODIC PROTECTION OF SUBMARINE PIPELINES BY GALVANIC ANODES OCTOBER 2003 Since issued in print (October 2003), this booklet has been amended, latest in October 2007.
RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNV-RP-F103 CATHODIC PROTECTION OF SUBMARINE PIPELINES BY GALVANIC ANODES OCTOBER 2003 Since issued in print (October 2003), this booklet has been amended, latest in October 2007.
Guidelines for ASTM Specification and Metal Grades
 Guidelines for ASTM Specification and Metal Grades CONTENTS 27/A 27M Standard Specification for Steel Castings, Carbon Suitable For General Applications... 1 A 128/ A 128M Standard Specification for Steel
Guidelines for ASTM Specification and Metal Grades CONTENTS 27/A 27M Standard Specification for Steel Castings, Carbon Suitable For General Applications... 1 A 128/ A 128M Standard Specification for Steel
PIPELINE AND WELL INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT
 FORCE Technology NORWAY AS Foto: BP - Valhall Lifetime assessment of pipelines and wells PIPELINE AND WELL INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT Speaker Håkon Hallem FORCE Technology NORWAY AS Head of Department Integrity
FORCE Technology NORWAY AS Foto: BP - Valhall Lifetime assessment of pipelines and wells PIPELINE AND WELL INTEGRITY MANAGEMENT Speaker Håkon Hallem FORCE Technology NORWAY AS Head of Department Integrity
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Probabilistic Database of Corrosion Rates TECHNOLOGY WEEK OCTOBER 2018
 DNV GL Probabilistic Database of Corrosion Rates TECHNOLOGY WEEK 15-18 OCTOBER 2018 Francois Ayello and Narasi Sridhar 1 DNV GL SAFER, SMARTER, GREENER Corrosion Data Corrosion data comes from various
DNV GL Probabilistic Database of Corrosion Rates TECHNOLOGY WEEK 15-18 OCTOBER 2018 Francois Ayello and Narasi Sridhar 1 DNV GL SAFER, SMARTER, GREENER Corrosion Data Corrosion data comes from various
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 17945 First edition 2015-04-15 Petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries Metallic materials resistant to sulfide stress cracking in corrosive petroleum refining environments
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 17945 First edition 2015-04-15 Petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries Metallic materials resistant to sulfide stress cracking in corrosive petroleum refining environments
SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R65 is a molybdenum-alloyed austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content. STANDARDS ASTM: TP316L, TP316 UNS: S31603, S31600
SANDVIK 3R65 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R65 is a molybdenum-alloyed austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content. STANDARDS ASTM: TP316L, TP316 UNS: S31603, S31600
Stainless Steel Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Laboratory Experiments in Corrosion Engineering II
 Lecture - 40 Laboratory Experiments in Corrosion Engineering II Keywords: Polarization Experiments, Pitting Potentials, Microbial Corrosion. A. Electrochemical tests in a given environment Polarization
Lecture - 40 Laboratory Experiments in Corrosion Engineering II Keywords: Polarization Experiments, Pitting Potentials, Microbial Corrosion. A. Electrochemical tests in a given environment Polarization
Investigation of Diffusible Hydrogen Content and Microstructure Examination of Underwater Welding
 AIJSTPME (2010) 3(3): 45-51 Investigation of Diffusible Hydrogen Content and Microstructure Examination of Underwater Welding Nakpradit T. Department of Production Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
AIJSTPME (2010) 3(3): 45-51 Investigation of Diffusible Hydrogen Content and Microstructure Examination of Underwater Welding Nakpradit T. Department of Production Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels
 High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels Introduction and Overview High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, or microalloyed steels, are designed to provide better mechanical properties and/or greater resistance to
High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels Introduction and Overview High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, or microalloyed steels, are designed to provide better mechanical properties and/or greater resistance to
Alloy Steels. Chapter 7. Copyright 2007 Dr. Ali Ourdjini.
 7 Alloy Steels At the end of this lesson students should be able to: Classify alloy steels Explain: effects of alloying elements to steel properties Discuss: composition, microstructure, mechanical properties
7 Alloy Steels At the end of this lesson students should be able to: Classify alloy steels Explain: effects of alloying elements to steel properties Discuss: composition, microstructure, mechanical properties
Hydrogen compatibility of austenitic stainless steel tubing and orbital welds. Chris San Marchi Sandia National Laboratories, Livermore CA and
 Hydrogen compatibility of austenitic stainless steel tubing and orbital welds Chris San Marchi Sandia National Laboratories, Livermore CA and L.A. Hughes, B.P. Somerday, and D.K. Balch SNL/CA SAND2013-7290C
Hydrogen compatibility of austenitic stainless steel tubing and orbital welds Chris San Marchi Sandia National Laboratories, Livermore CA and L.A. Hughes, B.P. Somerday, and D.K. Balch SNL/CA SAND2013-7290C
SANDVIK SAF 2507 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK SAF 2507 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik SAF 2507 is a super-duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel for service in highly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized by: Excellent
SANDVIK SAF 2507 TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik SAF 2507 is a super-duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel for service in highly corrosive conditions. The grade is characterized by: Excellent
Born from fire, made to endure NICKEL ALLOYS
 Born from fire, made to endure NICKEL ALLOYS Acroni is the largest slovenian steel manufacturer, which in order to produce steel recycles scrap in an electric arc furnace, casts it on continuous caster
Born from fire, made to endure NICKEL ALLOYS Acroni is the largest slovenian steel manufacturer, which in order to produce steel recycles scrap in an electric arc furnace, casts it on continuous caster
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER-1 1.0 INTRODUCTION Contents 1.0 Introduction 1 1.1 Aluminium alloys 2 1.2 Aluminium alloy classification 2 1.2.1 Aluminium alloys (Wrought) 3 1.2.2 Heat treatable alloys (Wrought). 3 1.2.3 Aluminum
1 CHAPTER-1 1.0 INTRODUCTION Contents 1.0 Introduction 1 1.1 Aluminium alloys 2 1.2 Aluminium alloy classification 2 1.2.1 Aluminium alloys (Wrought) 3 1.2.2 Heat treatable alloys (Wrought). 3 1.2.3 Aluminum
STAINLESS STEEL SHEETS
 STAINLESS & NICKEL ALLOY CHATHAM STEEL CORPORATION 59 STAINLESS STEEL SHEETS TYPE 04, 04L, 6, 6L No. 2B Finish Cold Rolled, Annealed *No. 2D Finish No. Finish Polished One Side No. 4 Finish Polished One
STAINLESS & NICKEL ALLOY CHATHAM STEEL CORPORATION 59 STAINLESS STEEL SHEETS TYPE 04, 04L, 6, 6L No. 2B Finish Cold Rolled, Annealed *No. 2D Finish No. Finish Polished One Side No. 4 Finish Polished One
Industeel. Clad plates
 Industeel Clad plates Our Business Industeel Leading special steels producer Industeel is a subsidiary of ArcelorMittal producing special steel hot rolled plates, forged blocks, ingots and formed pieces
Industeel Clad plates Our Business Industeel Leading special steels producer Industeel is a subsidiary of ArcelorMittal producing special steel hot rolled plates, forged blocks, ingots and formed pieces
Stress Corrosion Risk Reduction Guide
 WATER COOLED DEVICES Stress Corrosion Risk Reduction Guide November 2017 White Paper Created by Helen E. Kane, Advanced Energy Industries, Inc. Water Cooled Devices Abstract This report details best practices
WATER COOLED DEVICES Stress Corrosion Risk Reduction Guide November 2017 White Paper Created by Helen E. Kane, Advanced Energy Industries, Inc. Water Cooled Devices Abstract This report details best practices
Paper No. CORROSION MODELING OF CO 2 CORROSION OF MILD STEEL AT HIGH PRESSURES OF CO 2 AND IN THE PRESENCE OF ACETIC ACID
 Paper No. CORROSION 200 0623 MODELING OF CO 2 CORROSION OF MILD STEEL AT HIGH PRESSURES OF CO 2 AND IN THE PRESENCE OF ACETIC ACID Keith George, Shihuai Wang, Srdjan Nesic and Kees de Waard Institute for
Paper No. CORROSION 200 0623 MODELING OF CO 2 CORROSION OF MILD STEEL AT HIGH PRESSURES OF CO 2 AND IN THE PRESENCE OF ACETIC ACID Keith George, Shihuai Wang, Srdjan Nesic and Kees de Waard Institute for
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SEMASPEC Test Method for Metallurgical Analysis for Gas Distribution System Components
 SEMASPEC Test Method for Metallurgical Analysis for Gas Distribution System Components Technology Transfer 91060574B-STD and the logo are registered service marks of, Inc. 1996, Inc. SEMASPEC Test Method
SEMASPEC Test Method for Metallurgical Analysis for Gas Distribution System Components Technology Transfer 91060574B-STD and the logo are registered service marks of, Inc. 1996, Inc. SEMASPEC Test Method
We believe in a world that lasts forever. Contents. Meeting the material challenges of the oil & gas industry...4. Overview of product offering...
 Oil & Gas Contents Meeting the material challenges of the oil & gas industry...4 Overview of product offering...6 Exploration applications...9 Topside applications...10 Onshore applications...12 Cases...13
Oil & Gas Contents Meeting the material challenges of the oil & gas industry...4 Overview of product offering...6 Exploration applications...9 Topside applications...10 Onshore applications...12 Cases...13
Casing Failure Prevention East Texas Gas Producer s Assoc. 9 March 2010
 Casing Failure Prevention East Texas Gas Producer s Assoc. 9 March 2010 The Ideal Casing String For as long as needed, it will: Safely carry all applied loads, Until the next string is set and be free
Casing Failure Prevention East Texas Gas Producer s Assoc. 9 March 2010 The Ideal Casing String For as long as needed, it will: Safely carry all applied loads, Until the next string is set and be free
Stainless Steel (17/4PH&630) Bar
 SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
SPECIFICATIONS Commercial 17/4 PH EN 1.4542 Precipitation hardening stainless steels are chromium and nickel containing steels that provide an optimum combination of the properties of martensitic and austenitic
Product Test Report. PTR-3074 Swagelok Company. Rev. B Solon Road January 2015 Solon, Ohio U.S.A. Page 1 of 5
 Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 1 of 5 TITLE Resistance of SAF 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel to Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking PRODUCT TESTED Test samples were machined from Sandvik SAF 2507 solution-annealed
Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 1 of 5 TITLE Resistance of SAF 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel to Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking PRODUCT TESTED Test samples were machined from Sandvik SAF 2507 solution-annealed
Conditions Under Which Cracks Occur in Modified 13% Chromium Steel in Wet Hydrogen Sulfide Environments
 Conditions Under Which Cracks Occur in Modified 13% Chromium Steel in Wet Hydrogen Sulfide Environments T. Hara and H. Asahi* ABSTRACT Occurrence of cracks in an API 13% Cr steel, modified 13% Cr steel,
Conditions Under Which Cracks Occur in Modified 13% Chromium Steel in Wet Hydrogen Sulfide Environments T. Hara and H. Asahi* ABSTRACT Occurrence of cracks in an API 13% Cr steel, modified 13% Cr steel,
Duplex stainless steels for chemical tankers
 Duplex Stainless Steels 97-5th World Conference D97-018 PAGE 727 Home page by Jacques Charles and Bruno Vincent (CREUSOT-LOIRE INDUSTRIE, France) Abstract Material selection for chemical tanks is of prime
Duplex Stainless Steels 97-5th World Conference D97-018 PAGE 727 Home page by Jacques Charles and Bruno Vincent (CREUSOT-LOIRE INDUSTRIE, France) Abstract Material selection for chemical tanks is of prime
SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES
 SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES A02 (Identical with ASTM Specification A 276-97.) 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers hot-finished or coldfinished bars except bars for reforging (Note
SPECIFICATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL BARS AND SHAPES A02 (Identical with ASTM Specification A 276-97.) 1. Scope 1.1 This specification covers hot-finished or coldfinished bars except bars for reforging (Note
Analysis of High-Collapse Grade P110 Coupling Failures
 Analysis of High-Collapse Grade P110 Coupling Failures Michael G. Burns, P. E., Stress Engineering Services, Inc., Houston, Texas USA W. M. Buehler, Stork Testing and Metallurgical Consulting, Inc., Houston,
Analysis of High-Collapse Grade P110 Coupling Failures Michael G. Burns, P. E., Stress Engineering Services, Inc., Houston, Texas USA W. M. Buehler, Stork Testing and Metallurgical Consulting, Inc., Houston,
CATHODIC PROTECTION DESIGN
 RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNV-RP-B401 CATHODIC PROTECTION DESIGN JANUARY 2005 Since issued in print (January 2005), this booklet has been amended, latest in April 2008. See the reference to Amendments and Corrections
RECOMMENDED PRACTICE DNV-RP-B401 CATHODIC PROTECTION DESIGN JANUARY 2005 Since issued in print (January 2005), this booklet has been amended, latest in April 2008. See the reference to Amendments and Corrections
BiMetal Pipe CRA Pipe Overlay Cladding Pipe Prefabrication
 1 BiMetal Pipe CRA Pipe Overlay Cladding Pipe Prefabrication The Suitability of CRA Lined Pipe for Flowlines SUT Global Pipeline Buckling Symposium, 23-24 February 2011 Duncan Wilmot, Technical Manager
1 BiMetal Pipe CRA Pipe Overlay Cladding Pipe Prefabrication The Suitability of CRA Lined Pipe for Flowlines SUT Global Pipeline Buckling Symposium, 23-24 February 2011 Duncan Wilmot, Technical Manager
SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX SF SPRING WIRE WIRE
 SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX SF SPRING WIRE WIRE DATASHEET Sandvik Springflex SF is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel especially designed for spring applications with extremely high fatigue requirements.
SANDVIK SPRINGFLEX SF SPRING WIRE WIRE DATASHEET Sandvik Springflex SF is a duplex (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel especially designed for spring applications with extremely high fatigue requirements.
The Use of Internal Plastic Coatings to Maximize Sub-Sea System Operations
 The Use of Internal Plastic Coatings to Maximize Sub-Sea System Operations Robert S. Lauer 2835 Holmes Road Houston, Texas 77051 United States of America Abstract For more than 60 years, internal plastic
The Use of Internal Plastic Coatings to Maximize Sub-Sea System Operations Robert S. Lauer 2835 Holmes Road Houston, Texas 77051 United States of America Abstract For more than 60 years, internal plastic
Tubes and Pipes. Tubes and Pipes D-02
 s and Pipes s and Pipes D-0 D-03 s and Pipes Contents s Tubing Selection Tubing Handling Gas Service Tubing Installation Suggested Allowable Working Pressure Tables Stainless Steel Seamless Tubing Carbon
s and Pipes s and Pipes D-0 D-03 s and Pipes Contents s Tubing Selection Tubing Handling Gas Service Tubing Installation Suggested Allowable Working Pressure Tables Stainless Steel Seamless Tubing Carbon
Mechanical Properties
 Mechanical Properties Elastic deformation Plastic deformation Fracture Fatigue Environmental crack growth Crack Instabilty ß σ T The critical crack length for given σ a a c = Q 2 K Ic σ a 2 a r ß a Sources
Mechanical Properties Elastic deformation Plastic deformation Fracture Fatigue Environmental crack growth Crack Instabilty ß σ T The critical crack length for given σ a a c = Q 2 K Ic σ a 2 a r ß a Sources
DX2507 DX2507. Duplex stainless steel offer grade. General characteristics. Chemical composition. Material standards
 Duplex stainless steel offer grade Chemical composition Elements C Cr Ni Mo N PREN* % weight
Duplex stainless steel offer grade Chemical composition Elements C Cr Ni Mo N PREN* % weight
Research on tubing material selection for preventing corrosion in high sour gas well under existence of bacteria corrosion
 ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 8 Issue 9 BTAIJ, 8(9), 2013 [1258-1263] Research on tubing material selection for preventing corrosion in high sour gas well under existence of bacteria corrosion Lingfeng LI 1
ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 8 Issue 9 BTAIJ, 8(9), 2013 [1258-1263] Research on tubing material selection for preventing corrosion in high sour gas well under existence of bacteria corrosion Lingfeng LI 1
Hydrogen Permeation of Pipeline Steel under Sour Condensate Film Condition
 Hydrogen Permeation of Pipeline Steel under Sour Condensate Film Condition Zhaoyang Cui, Lei Zhang, Yanni Sun, Rufei Ma, Mingliang Liu and Minxu Lu Institute of Advanced Materials and Technology, University
Hydrogen Permeation of Pipeline Steel under Sour Condensate Film Condition Zhaoyang Cui, Lei Zhang, Yanni Sun, Rufei Ma, Mingliang Liu and Minxu Lu Institute of Advanced Materials and Technology, University
High strength low alloy (HSLA).
 7 Alloy Steels High strength low alloy (HSLA). a type of steel alloy that provides many benefits over regular steel alloys contain a very small percentage of carbon (less than one-tenth of a percent) and
7 Alloy Steels High strength low alloy (HSLA). a type of steel alloy that provides many benefits over regular steel alloys contain a very small percentage of carbon (less than one-tenth of a percent) and
COCATE. Corrosion and Protection of Pipe Steels in CO 2 Transport. TNO, Bevesierweg, 1780 AM Den Helder, Netherlands b
 COCATE Corrosion and Protection of Pipe Steels in CO 2 Transport X. Zhang a, J.F. Zevenbergen a, M. Borys b, S. Marion c a TNO, Bevesierweg, 1780 AM Den Helder, Netherlands b ACCOAT A/S, Munkegårdsvej
COCATE Corrosion and Protection of Pipe Steels in CO 2 Transport X. Zhang a, J.F. Zevenbergen a, M. Borys b, S. Marion c a TNO, Bevesierweg, 1780 AM Den Helder, Netherlands b ACCOAT A/S, Munkegårdsvej
MATERIAL. III-1 Mechanical Finite Element Analysis and Engineering Critical Assessment Study
 BRINGING THE STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY OF ALLOY 36 (36% NICKEL) PIPES A STEP AHEAD FOR LNG TRANSPORTATION WITH CRYOGENIC PIPE IN PIPE READY FOR EPCI PROJECT PURPOSES Laurent Pomié Jeffrey O Donnell Technip
BRINGING THE STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY OF ALLOY 36 (36% NICKEL) PIPES A STEP AHEAD FOR LNG TRANSPORTATION WITH CRYOGENIC PIPE IN PIPE READY FOR EPCI PROJECT PURPOSES Laurent Pomié Jeffrey O Donnell Technip
MSE-226 Engineering Materials
 MSE-226 Engineering Materials Lecture-7 ALLOY STEELS Tool Steels TYPES of FERROUS ALLOYS FERROUS ALLOYS Plain Carbon Steels Alloy Steels Cast Irons - Low carbon Steel - Medium carbon steel - High carbon
MSE-226 Engineering Materials Lecture-7 ALLOY STEELS Tool Steels TYPES of FERROUS ALLOYS FERROUS ALLOYS Plain Carbon Steels Alloy Steels Cast Irons - Low carbon Steel - Medium carbon steel - High carbon
Results are presented in Table 1. The tube was fabricated from a Type 347 and no unusual conditions were noted.
 1. Introduction Hydroprocessing units such as isomax in oil refineries upgrade hydrocarbon feedstocks by converting heavier feeds into more valuable lighter products. The reactions occur under a hydrogen-rich
1. Introduction Hydroprocessing units such as isomax in oil refineries upgrade hydrocarbon feedstocks by converting heavier feeds into more valuable lighter products. The reactions occur under a hydrogen-rich
Chemical characteristics The chemical composition is shown in Table 1. Outokumpu EN ASTM
 for Bar Applications has a unique combination of characteristics (good corrosion properties, high strength and good machinability), which together with its relative price stability, makes it the material
for Bar Applications has a unique combination of characteristics (good corrosion properties, high strength and good machinability), which together with its relative price stability, makes it the material
Causes of Increased Corrosion in Oil and Gas Pipelines in the Middle East
 Causes of Increased Corrosion in Oil and Gas Pipelines in the Middle East Amir Samimi Young Researchers club, Central Tehran Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, IRAN amirsamimi1161@gmail.com Abstract
Causes of Increased Corrosion in Oil and Gas Pipelines in the Middle East Amir Samimi Young Researchers club, Central Tehran Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, IRAN amirsamimi1161@gmail.com Abstract
SANDVIK 3R12 FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS
 SANDVIK 3R12 FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R12 is an austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content used for medical and dental instruments.
SANDVIK 3R12 FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS TUBE AND PIPE, SEAMLESS DATASHEET Sandvik 3R12 is an austenitic stainless chromium-nickel steel with a low carbon content used for medical and dental instruments.
Bonding strength of Al/Mg/Al alloy tri-metallic laminates fabricated
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 34, No. 4, July 2011, pp. 805 810. Indian Academy of Sciences. Bonding strength of Al/Mg/Al alloy tri-metallic laminates fabricated by hot rolling X P ZHANG, *, M J TAN, T H YANG,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 34, No. 4, July 2011, pp. 805 810. Indian Academy of Sciences. Bonding strength of Al/Mg/Al alloy tri-metallic laminates fabricated by hot rolling X P ZHANG, *, M J TAN, T H YANG,
Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Corrosion Mechanisms
 Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion is defined as corrosion at a metal surface that is associated with microorganisms, or the products of their metabolic activities
Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion is defined as corrosion at a metal surface that is associated with microorganisms, or the products of their metabolic activities
NORSOK STANDARD COMMON REQUIREMENTS CATHODIC PROTECTION M-503. Rev. 2, September 1997
 NORSOK STANDARD COMMON REQUIREMENTS CATHODIC PROTECTION M-503 Rev. 2, September 1997 Please note that whilst every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the NORSOK standards neither OLF nor TBL
NORSOK STANDARD COMMON REQUIREMENTS CATHODIC PROTECTION M-503 Rev. 2, September 1997 Please note that whilst every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the NORSOK standards neither OLF nor TBL
The Influence of Carbon Contents on the Corrosion Resistance of Plain-Carbon Steels in the Water Environments
 - - The Influence of Carbon Contents on the Corrosion Resistance of Plain-Carbon Steels in the Water Environments SobhiIIbrahim YasirAAbdullah Ass Prof Engineer Mech Eng Dept / College of Engineering /
- - The Influence of Carbon Contents on the Corrosion Resistance of Plain-Carbon Steels in the Water Environments SobhiIIbrahim YasirAAbdullah Ass Prof Engineer Mech Eng Dept / College of Engineering /
PROCHEM Stainless Steel Specialists
 PROCHEM Stainless Steel Specialists Product solutions for a world of difference PIPING PRODUCTS PIPING PRODUCTS INSTRUMENTATION VALVES AND ACTUATORS MANUFACTURING INDENT SERVICE HYDRAULIC Duplex Prochem
PROCHEM Stainless Steel Specialists Product solutions for a world of difference PIPING PRODUCTS PIPING PRODUCTS INSTRUMENTATION VALVES AND ACTUATORS MANUFACTURING INDENT SERVICE HYDRAULIC Duplex Prochem
Influence of rapid cooling rates for HIP on mechanical and corrosion properties of UNS S32205
 Influence of rapid cooling rates for HIP on mechanical and corrosion properties of UNS S32205 Arnulf Hörtnagl 1, Paul Gümpel 1, Michael Hamentgen², Beat Hofer³ Institute for Materials System Technology
Influence of rapid cooling rates for HIP on mechanical and corrosion properties of UNS S32205 Arnulf Hörtnagl 1, Paul Gümpel 1, Michael Hamentgen², Beat Hofer³ Institute for Materials System Technology
View from the Penthouse
 View from the Penthouse The DNFM Technical News Letter David N. French Metallurgists Ph: 502-955-9847 Fax: 502-957-5441 Web: www.davidnfrench.com Stress-corrosion-cracking (SCC) is a well-defined failure
View from the Penthouse The DNFM Technical News Letter David N. French Metallurgists Ph: 502-955-9847 Fax: 502-957-5441 Web: www.davidnfrench.com Stress-corrosion-cracking (SCC) is a well-defined failure
Essential factors influencing cathodic protection not covered by standards and recommended practices
 Essential factors influencing cathodic protection not covered by standards and recommended practices Paper no 1022 Harald Osvoll, FORCE Technology Norway AS, Norway 1 Background Cathodic protection calculations
Essential factors influencing cathodic protection not covered by standards and recommended practices Paper no 1022 Harald Osvoll, FORCE Technology Norway AS, Norway 1 Background Cathodic protection calculations
