Assessment of the Completeness of Mineral Exploration by the Application of Fuzzy Arithmetic and Prior Information
|
|
|
- Frank Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Assessment of the Completeness of Mineral Exploration by the Application of Fuzzy Arithmetic and Prior Information György Bárdossy 1 and János Fodor 2 1 Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest, Hungary Tel , h4750bar@helka.iif.hu 2 Department of Biomathematics and Informatics Szent István University, Budapest, Hungary Tel , Fodor.Janos@aotk.szie.hu Abstract: The completeness of an exploration project is of crutial importance for making decision to start or to give up a mining investment, or to continue the exploration to get complementary information. The authors discuss this problem on the example of the Halimba bauxite deposit, Hungary. Resource calculations were carried out in 12 subsequent stages by fuzzy arithmetic with the aim to quantify the uncertainties of ore tonnage and grade. Prior information and prior probabilities were applied to complete the exploration data. Ranges of influence for the main variables were calculated by variograms. Spatial variability and spatial continuity of the ore bodies were mathematically evaluated. The authors found that the main geological, mining and economic factors must be evaluated separately and ranked according to their importance. Keywords: resource assessment, fuzzy arithmetic, prior information, prior probabilities 1. Introduction Exploration of solid mineral deposits is generally an expensive task. Even more expensive and risky is the successive mining investment. It is of paramount importance therefore to optimize the exploration expenses and to minimize the risks of the mining investment. This double task was considered so far as a purely geological and mining- engineering problem, however, in our opinion, the application of some new mathematical methods may considerably improve the results. The aim of this paper is to show the application of these new methods by a case study. The Halimba bauxite deposit in Hungary has been chosen as example.
2 2. Basic concepts The completeness of an exploration campaign is generally expressed by the resource assessment (tonnage and grade) and its overall reliability. The spatial distribution and spatial variability of ore grade and the spatial continuity of ore within the deposit are further important aspects (Henley 2000, Wellmer 1989, Yamamoto 1999). However the traditional methods of resource assessment are not able to quantify the reliability of the estimation results. The fuzzy set theory has been applied by the authors for this purpose on some solid mineral deposits with success ( Bárdossy, Fodor 2004). Fuzzy sets have been applied for the resource assessment of skarn tin deposits by Luo and Dimitrakopoulos (2003). A further improvement can be achieved by applying the concept of Bayesian probabilities. It is well known that the so called frequentist approach requires repeated identical experiments. However, this requirement can be fulfilled only rarely at the geologic investigations. The Bayesian approach, on the other hand, is able to evaluate unrepeatable phenomena as well. Bayesian probability depends only on the state of knowledge about the given problem and it changes with time as new pieces of information are acquired (Bárdossy, Fodor 2004). Mineral exploration has also this changing character as new pieces of information are obtained about the given deposit by drilling new boreholes etc. For this reason,it is reasonable to apply also prior information and Bayesian probabilities for the evaluation of exploration results and other geoscientific problems (Wood and Curtis 2004). 3. Initial data The bauxite deposit of Halimba, selected for this case study has been explored since 1943 and up to the present more than 2600 core boreholes have been performed. Underground mining started in 1950 and is still running. Computerised relational databases have been established (AutoCad) for the main data obtained about the deposit, particularly for the chemical composition of the ore. The sector of the test calculations called Halimba II east - has been intensively explored during the last three years. It covers an area of 15 hectars with 237 borehole sites and it is situated int he southern part of the deposit.(figure 1.). A 10 to 40 m thick bed consisting of bauxite, clayey bauxite and bauxitic clay covers the karstified surface of Upper Triassic dolomite and limestone. The overburden is of Middle Eocene age. The entire deposit is of fluvial origin. The area of the studied sector is of flood-plain facies. The bauxite accumulated during short inundation phases, forming very irregular ore bodies within a continuous clayey bauxitic layer. Underground mining operations started in the western part of the study area in They confermed the above outlined deposit model.
3 Figure 1: The Halimba bauxite deposit, Hungary First the spatial variability of the main variables has been evaluated by us applying the well known methods of geostatistics (Goovaerts 1997). Ranges of influence have been calculated by the Variowin program for the thickness of the bauxitic bed, for the bauxite ore and for the Al 2 O 3, SiO 2,Fe 2 O 3,CaO and MgO contents of the bauxite. Our basic idea was to follow the changes that occurred as the exploration progressed. For this reason resource assessments were carried out by us after every 20 new boreholes finished. Thus a growing number of boreholes served as a base of the successive resource assessments. Alltogether 12 resource assessments have been performed. The three basic components of any resource assessment of solid mineral deposits are the area of the deposit, the thickness of the ore and its bulk density. Fuzzy numbers have been constructed for all the three components. The support of the fuzzy number extends from the minimum to the maximum possible value. In the
4 case of the deposit area the minimum value is determined by straight lines connecting the extreme productive boreholes. The maximum possible area is obtained by connecting the closest improductive boreholes around the productive area. The core of the fuzzy number represents the geologically most possible area, determined by the deposit model and its contour line. This is a relatively simple and unambiguous task in the case of well explored deposits. However, in the early stages of exploration the number of boreholes is often not sufficient for the above outlined constructions. In that cases we extrapolated from the given productive borehole the range of influence of the bauxite thickness in all directions, obtaining this way the minimum possible area. The maximum possible area was obtained by taking in all directions twice the range of influence. In this case an interval has been chosen also for the core of the fuzzy number, expressing the larger uncertainty of the deposit area. The extrapolated resource boundaries are replaced gradually by straight lines connecting the neighbouring boreholes, as new boreholes are drilled. According to our experience, exploration should not be finished before replacing all the extrapolated boundaries by the connecting straight lines. Thus the trapesoidal fuzzy numbers are gradually replaced by triangular ones. As an example the area of the resource assessment at the end of the third stage is shown in Figure 2, and that at the end of the last (12th) stage in Figure 3. Figure 2: The area of the resource assessment at the end of the third stage
5 Figure 3: The area of the resource assessment at the end of the last stage The fuzzy numbers representing the ore thickness correspond to the averages of the borehole results. Before calculating the averages, the main statistics of ore thickness have been calculated by us, applying the 12.0 version of the SPSS program. The histograms and the skewness values indicated a strong rightasymmetrical distribution. To eliminate the corresponding bias, maximum likelihood estimators have been calculated instead of the common averages. Tukey s biweight estimator was found to correspond best to an unbiased average. It has been applied in all cases when the skewness statistic exceeded 1,0. The minimum and the maximum values of the support of the fuzzy numbers correspond to the endpoints of the corresponding confidence interval, at 95 % level of confidence. The core of the fuzzy number is an interval determined by the standard error of the mean. The bulk density of the ore has been measured in the laboratory on borehole cores and in the mine on large samples, several hundred times. The distribution of the results is symmetrical. The mean value is 2,29 tons/ m3. The analytical error is less than 10 relative percents. The variability of the bulk density is very limited over the test area. For this reason the same fuzzy number has been applied for all the twelve resource assessments. In the same way as for the ore thickness, the support corresponds to the confidence interval at 95 % level of confidence and the core to the standard error of the mean, plus the analytical error.
6 The tonnage of the resource is the product of the above discussed three components. Fuzzy multiplication was applied for the three corresponding fuzzy numbers. The uncertainty of the resource assessment is expressed in tons by the length of the support and the core. Additionally relative deviations from the average values expressed as percentages were also calculated. The average grade of the ore has been calculated in a similar way constructing average fuzzy numbers for all the listed chemical components. To avoid biases due to asymmetrical distribution histograms and skewness values were calculated and robust M-estimators were applied whenever the skewness exceeded the value 1,0. As in the case of tonnage, absolute and relative uncertainties have been calculated for all the evaluated chemical components. As mentioned above, all the above listed calculations have been repeated 12 times, adding every time 20 new boreholes. Fuzzy numbers for selected stages are presented in Figure 4. Area Mean thickness Tonnage Stage m m kt Stage m m kt Stage m m kt Figure 4: Fuzzy numbers expressing the area, mean thickness, and tonnage for stages 2, 5, Evaluation of the completeness of the exploration For the starting situation, that is before the drilling of the first bore hole in the sector, the following prior probabilities have been assumed, based on the experiences of the neighbouring explored and mined sectors:
7 the bauxite clayey bauxite bed is continuous over the exploration sector 0.8 probability the bed is not continuous over the exploration sector 0.2 probability Second item of the prior probabilities: - commercial bauxite ore bodies are situated within the above bed 0.6 probability - no commercial bauxite ore bodies occur within the bed 0.4 probability The end situation- after the 12th stage - confirmed both larger prior probabilities. For the first two stages of exploration the number of productive boreholes was not sufficient to calculate reliable variograms. For this reason, the already calculated ranges of influence of the neighbouring sectors were applied, supposing similar values in the study area. At the end of the third stage variograms could be calculated for the ore thickness. By applying different lags and variogram models ranges of influence from 10 to 20 m length were obtained. With growing number of boreholes the variograms became more accurate and after the 12th stage 15 m range of influence was accepted for the entire exploration area. However, locally even smaller ranges of influence exist, as confirmed ba the latest mining operations As outlined later, these changes significantly influenced the results of the successive resource assessments. At the end of each exploration stage circles were constructed around each borehole, expressing the range of influence. The boreholes were placed in a random-stratified grid, with the aim to optimize the contouring of the very irregularly shaped ore bodies. For this reason unknown slices remained between some neighbouring boreholes. Prior probabilities have been calculated for these slices separately and if they exceeded the 0.5 value, they have been included into the resource assessment. This procedure ameliorated considerably the fitting of the resource contours to the real boundaries of the ore bodies. Different variables have been chosen for the quantitative evaluation of the completeness of exploration,first of all the tonnage of the resources. In Figure 5. the successive changes of the minimum and maximum values of the support are represented. The minimum value of the tonnage steeply increases in the first four stages of exploration, followed by much smaller increase in the later stages. The fluctuation of the diagram reflects the randomness of the results at some stages. The possible maximum tonnage also increases steeply in the first stages, but it is followed by an unexpected gradual decrease untill the eighth stage. The last stages show a slight increase. The peculiar form of this diagram can be explained by the higher uncertainty of the maximum tonnage, influenced by the position of the closest improductive boreholes and by the extrapolation of the contour line in the first stages of exploration. The peak between the third and fourth stages is clearly a random effect, that may occur in the first stages of any exploration campaign. As exploration progresses, the difference between the two diagrams diminishes, as the area between the manimum and maximum contours becomes narrower.
8 Figure 5: Quantitative evaluation of tonnage: successive changes of the maximum and minimum of the support and the core, respectively The tonnage expressed by the core of the fuzzy numbers has a much shorter uncertainty interval, presented also in Figure 5. The random overestimation of the tonnage between the third and fourth stages is clearly visible on both diagrams, but it is gradually equalized in the later stages without reaching a constant value. Theoretically, the exploration is still not complete, but the changes of the tonnage are insignificant. Thus the tonnage of the resources alone is in favour of finishing the exploration drilling. A further aspect of the evaluation is the relative uncertainty of the tonnage, expressed as a percentage of the mean (crisp) tonnage. We calculated it separately for the support and for the core of the corresponding fuzzy numbers. The results are presented in Figure 6. It is obvious that the uncertainty of the tonnage expressed by the support is much larger than that of the core. It decreases in the successive stages untill the eighth stage from ±91 % to ±73 %. This is followed in the later stages by a fluctuation and a final value of ±69 %. On the other hand, the relative uncertainty of the tonnages expressed by the core are much smaller. The starting ±46 % relative uncertainty diminishes to ±9 %. This indicates a near complete exploration result.
9 Figure 6: Relative uncertainty of the tonnage for the core and the support, respectively The tonnage values of the fuzzy numbers and their relative uncertainties are presented in Table 1. Let us stress that these data represent a significant complement to the single-valued traditional resource estimation results. But even these data are insufficient in our opinion to make a reliable decision on the completenes of an exploration campaign. The main chemical components have been evaluated by us too, in function of the successive exploration stages.the resulting main statistics, calculated by the SPSS program are presented in Table 2. The Al2O3 content has the smallest relative variance, ±7 %. The distribution of this component is almost normal, thus the mean value is unbiased. It diminished from the second to the latest exploration stage from 52.8 to 51.2 %, considered by us as a very small change. In the same time, the standard error of the mean diminished from ±1.0 to ±0.3 %, indicating a high reliability of the results. It can be concluded that regarding the alumina content the exploration has been complete since the early stages. The Fe 2 O 3 content follows with ±14-16 % relative variance. The distribution is
10 TABLE 1. MAIN RESULTS OF THE RESOURCE CALCULATIONS Stages Number of Deposit area Tonnage Length of the Relative uncertainty Length of the Relative uncertainty boreholes a b c d a b c d core interval of the tonnage (%) support interval of the tonnage (%) Legend: a: lower bound of the support of trapezoidal fuzzy number [a,b,c,d] b: lower bound of the core of trapezoidal fuzzy number [a,b,c,d] b c c: upper bound of the core of trapezoidal fuzzy number [a,b,c,d] d: upper bound of the support of trapezoidal fuzzy number [a,b,c,d] a d
11 symmetrical and the mean decreased from 25.3 to 24.6 % as exploration progressed, close to the range of the analytical error. As with the Al 2 O 3, the standard error of the mean diminished from ±1.0 to ±0.3 %. Thus the exploration is considered complete also in this respect. The SiO 2 content of the ore is more variable, the relative variance ranging from ±39 to 45 %. The distribution is almost symmetrical and the mean remained the same within the range of the analytical error. Only the standard error of the mean diminished from ±0.7 to ±0.2 %, indicating a high reliability of the results. The exploration is complete also in this respect. The CaO is one of the main contaminants in the bauxite. This is the most variable analysed chemical component, the relative variance ranging from ±83 to 114 %. The distribution is strongly skewed, as indicated by the high positive skewness value. For this reason Tukey s M-estimator has been applied intead of the normal mean. It increased gradually from 0.6 to 1,0 % to the last stage of the exploration. It cannot be predicted whether a further increase would occur with the drilling of new boreholes. The reason for this high variability is the presence of CaO in the form of secondary calcite precipitations, irregularly distributed within the ore bodies.thus regarding the evaluated chemical components, the exploration can be considered as completed, except the CaO content. A further aspect influencing the completeness of the exploration is the detection of the spatial distribution of the orebodies and the degree of their variability. The question is, how much increased the precision of these predictions by the exploration and can it be regarded complete after the twelfth stage? To answer these questions prior probabilities have been applied. The borehole sites have been ordered into five categories and a prior probability has been attached to each category, based on the overall exploration experiences of the entire deposit : 1. the site is within the productive arera 0.3 prior probability 2. the site is on the border of the productive area the site is within the possible area the site is on the outer border of the possible area the site is within the improductive area 0.4 alltogether 1.0 prior probability The borehole sites situated beyond the range of influence of bauxite thickness have not been categorized. In the next step all existing borehole sites were categorized based on the resource assessment maps of the 12 exploration stages and the changes of categories were presented in the form of a table. Table 3 shows these changes for 20 selected borehole sites, as the limited extent of this paper does not allow the presentation of all the 237 borehole sites. (The not categorized sites are indicated by question-marks). It is obvious that the number of not categorized sites diminishes in the successive exploration stages. Several boreholes have been drilled at such sites having no prior information. This
12 TABLE 2. MAIN STATISTICS OF SELECTED CHEMICAL COMPONENTS AT THE END OF EXPLORATION STAGES Chemical components Stage 12 Stage 8 Stage 6 Stage 4 Stage 2 SiO2 Mean (%) Standard error of the mean (%) ± 0.20 ± 0.20 ± 0.30 ± 0.30 ± 0.70 Standard deviation (%) ± 2.10 ± 2.30 ± 2.30 ± 2.2 ± 2.40 Coefficient of variation (%) Skewness Min (%) Max (%) Al2O3 Mean (%) Standard error of the mean (%) ± 0.30 ± 0.40 ± 0.40 ± 0.50 ± 1.00 Standard deviation (%) ± 3.60 ± 3.70 ± 3.50 ±3.20 ± 3.70 Coefficient of variation (%) Skewness Min (%) Max (%) Fe2O3 Mean (%) Standard error of the mean (%) ± 0.30 ± 0.40 ± 0.40 ± 0.60 ± 1.00 Standard deviation (%) ± 3.80 ± 3.90 ± 3.50 ± 3.80 ± 3.50 Coefficient of variation (%) Skewness Min (%) Max (%) CaO Mean (%) Standard error of the mean (%) ± 0.08 ± 0.09 ± 0.12 ± 0.19 ± 0.27 Standard deviation (%) ± 0.83 ± 0.81 ± 0.85 ± 0.87 ± 0.55 Coefficient of variation (%) Skewness Min (%) Max (%)
13 haphazard approach leaded to some negative results, as illustrated by the Table 3. The categories of the borehole sites often changed in positive or negative sense indicating the incompleteness of the exploration. Theoretically, exploration should be considered complete if the site-category would not change in the final two or three exploration stages, before the drilling of the given borehole. Unfortunately, this condition was only partly fulfilled even for the last, twelfth stage. Thus, in this respect the exploration cannot be accepted as complete. TABLE 3. PRIOR CATEGORIZATION OF SELECTED BOREHOLE SITES Borehole Exploration stages H-2564? H H-2556?????????? 5 H-2555?????????? 5 H-2554? (1) (1) H-2553? (2) (1) H-2552? (3) H-2551? (1) (1) H H-2549? H-2548?????????? 5 H-2547? H-2546? 5 (1) H-2545? 5 (4) (4) (4) (4) (4) (4) 4 4 n.a. H-2544?? 5???? n.a. H ?????? 5 n.a. H ?????? 4 n.a. H-2541???????? 5 2 n.a. H-2540????????? 2 n.a. H-2539????????? 4 n.a. Legend: 1. Site within the productive area. 2. Site on the border of the productive area 3. Site within the possible area. 4. Site on the outer border of the possible area. 5. Site within improductive area (clayey bauxite and bauxitic clay). ( ) Site categorized by extrapolation.? Not categorized site, outside the ranges of influence. Bold numbers: categories after drilling the corresponding borehole site.
14 Table 4. Summary results of the prior categorization of the first seven exploration stages Categories Productive Possible Improductive Sum of row Productive Possible Improductive Sum of column A more complete evaluation can be obtained if several exploration stages are considered together. Table 4 shows the results of the first seven stages.(obviously, the first stage can not be evaluated). Even more interesting results were obtained, when evaluating all stages together, as presented in Table 5. From the 203 prior probabilities 92 were confirmed by the drilling of the corresponding bore-holes. Even more important is that in 97 cases the prior probabilities were changed positively and only in 14 cases negatively. These result underline the effectiveness of the exploration campaign. Table 5. Summary results of the prior categorization of all the 12 exploration stages Categories Productive Possible Improductive Sum of row Productive Possible Improductive Sum of column A further aspect, important for the planning of a mining investment, is the completeness of the contouring of the orebodies. In our case this means that the orebodies should be surrounded from all sides by improductive boreholes. The evaluation is simple: the exploration is incomplete at all places where the contour of the orebody is determined only by extrapolation. In the study area four places remained incomplete in this respect after ending the 12th stage. An overall relative index can be computed when comparing the length of the completely contoured borders with the length of the extrapolated ones. A further aspect is the rate of lateral changes in the thickness and altitude of the orebodies. This aspect is very important in the case of underground mining, as it can be a limiting factor for the choice of the excavation and production systems. We evaluated this aspect by calculating the specific rates of lateral changes for the bauxite thickness of neighbouring boreholes. An example of this evaluation is presented in Figure 7. In the ore bodies of our test sector these specific rates of lateral changes are often very strong and they may vary quickly in the different directions, making difficulties in the choice of the mining methods. Note that the boreholes beyond the range of influence were excluded from this evaluation. The entire productive sector has been evaluated in this way. The exploration is complete in this respect.
15 Figure 7: Evaluation of the specific rate of changes for ore thickness in an underground mine around a measured central point It is mathematically possible to aggregate all the discussed aspects into one fuzzy completeness index of the exploration, following the methodology of Luo and Dimitrakopoulos (2003) for their fuzzy mineral favourability index. This is a useful estimator for the stakeholder, but for the mining engineer, planning and starting the mining operations, it is more useful to evaluate and to compare all the discussed aspects separately. We recommend therefore the stepwise evaluation of each aspect after every exploration stage and making decisions after ranking them in both respects of completeness (reliability) and the additional costs of the drilling of further boreholes. 5. Verification of the exploration results The underground mining operations quickly followed the above outlined exploration, offering us a possibility to check the validity of our evaluations. In the western part of the deposit boreholes were drilled from the galleries at 5 meter intervals vertically up and down and also laterally. The bauxite has been sampled and analysed at every one meter interval. The bauxite ore of more than 2 meters thickness have been excavated.
16 All these data have been evaluated by us by applying the AutoCAD program and the resulting 2 meters contour has been constructed. This line has been compared with our last (12th) resource assessment map for the selected part of the deposit (Figure 8.). The productive area of our resource assessment is completely confirmed by this contour line. It runs generally within the possible area, and at some places it even extends beyond it. There is no positive or negative bias (overor under estimation) in this respect. Thus our deposit model, applied to our resource assesment has been confirmed by the mining operations. Figure 8: Comparison of estimation and reality Conclusions The completeness of a mineral exploration can be best evaluated by a joint application of the fuzzy set theory and Bayesian (prior) probabilities. The establishment of appropriate computerized databases is indispensable for these tasks. The method consists of the stepwise evaluation of successive exploration stages (contouring the productive and possible areas and calculating the resources). According to our experiences, completeness of exploration is achieved at different stages of exploration regarding the different evaluated variables. The criterion for completeness should be the decrease or complete equalization of the given variable.
17 Even in the case of best planned and evaluated exploration random effects (overor under-estimation of the given variable) cannot be excluded, mainly in the early stages of the exploration campaign. A reliable deposit model is the precondition of any evaluation in this respect. The model can be verified by the evaluation of the successive mining operations. This methodology can be applied to other types of solid mineral deposits as well, taking into account their specific deposit models. References [1] Bárdossy, Gy., R.Szabó,J., Varga, G. 2003: A new method of resource estimation for bauxite and other solid mineral deposits. BHM,148.Jg. pp Leoben [2] Bárdossy,Gy.,Fodor,J. 2004: Evaluation of Uncertainties and Risks in Geology. Springer Verlag. Berlin,Heidelberg, London,New York. 221 pages [3] Henley,S.2000: Resources,reserves and reality. Earth Sciences Computer Applications. Vol.15.No.10.pp1-2. [4] Luo,X., Dimitrakopoulos,R. 2003: Data-driven fuzzy analysis in quantitative mineral resource assessment. Computers and Geosciences. 29.pp [5] Wellmer,F.W. 1989: Economic Evaluations in Exploration. Springer Verlag. Berlin, Heidelberg, London, New York. 150 pages [6] Wood,R. Curtis,A. 2004: Geological prior information, and its applications in solving geo-scientific problems. In: Geological Prior Information Eds: A.Cueris and R.Wood. Geol.Society of London Special Publication (in press) [7] Yamamoto, K. 1999: Quantification of uncertainty in ore reserve estimation. Applications to Chapada Copper Deposit,Brazil. Natural Resources Research. 8. pp
The Bayesian Concept of Probability and its Application to Geologic Problems
 The Bayesian Concept of Probability and its Application to Geologic Problems György Bárdossy 1, János Fodor 2 1 Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest, Hungary E-mail: h4750bar@helka.iif.hu 2 John von
The Bayesian Concept of Probability and its Application to Geologic Problems György Bárdossy 1, János Fodor 2 1 Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest, Hungary E-mail: h4750bar@helka.iif.hu 2 John von
3D Modeling and preliminary ore reserve estimation of Sheikh-Ali Copper deposit
 3D Modeling and preliminary ore reserve estimation of Sheikh-Ali Copper deposit Maryam Sadeghbeigi and Alireza Monazami ABSTRACT In the recent years a number of Copper exploration projects have been conducted
3D Modeling and preliminary ore reserve estimation of Sheikh-Ali Copper deposit Maryam Sadeghbeigi and Alireza Monazami ABSTRACT In the recent years a number of Copper exploration projects have been conducted
Geostatistical Simulation of Optimum Mining Elevations for Nickel Laterite Deposits
 Geostatistical Simulation of Optimum Mining Elevations for Nickel Laterite Deposits J. A. McLennan (jam12@ualberta.ca), J. M. Ortiz (jmo1@ualberta.ca) and C. V. Deutsch (cdeutsch@ualberta.ca) University
Geostatistical Simulation of Optimum Mining Elevations for Nickel Laterite Deposits J. A. McLennan (jam12@ualberta.ca), J. M. Ortiz (jmo1@ualberta.ca) and C. V. Deutsch (cdeutsch@ualberta.ca) University
"Predicting variability in coal quality parameters", Coal Indaba, Johannesburg RSA, November 1998
 "Predicting variability in coal quality parameters", Coal Indaba, Johannesburg RSA, November 1998 Predicting variability in coal quality parameters Dr Isobel Clark, Geostokos Limited Alloa Business Centre,
"Predicting variability in coal quality parameters", Coal Indaba, Johannesburg RSA, November 1998 Predicting variability in coal quality parameters Dr Isobel Clark, Geostokos Limited Alloa Business Centre,
Surrogate Reservoir Models
 Quantifying Uncertainties Associated with Reservoir Simulation Studies Using Surrogate Reservoir Models Shahab D. Mohaghegh West Virginia University & Intelligent Solutions, Inc. 1 Outline Reservoir Simulation
Quantifying Uncertainties Associated with Reservoir Simulation Studies Using Surrogate Reservoir Models Shahab D. Mohaghegh West Virginia University & Intelligent Solutions, Inc. 1 Outline Reservoir Simulation
-Dinesh Dixit, General Manager (Mines) - Prabodh Singh, General Manager (QC) -Emami Cement Limited
 Utilization of limestone above Threshold Value with reference to limestone mine of M/s Emami Cement Limited at villages Kukurdih-Risda, Tehsil Baloda Bazar, district Baloda Bazar- Bhatapara, state Chhattisgarh-
Utilization of limestone above Threshold Value with reference to limestone mine of M/s Emami Cement Limited at villages Kukurdih-Risda, Tehsil Baloda Bazar, district Baloda Bazar- Bhatapara, state Chhattisgarh-
For personal use only
 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT AUSTRALIAN BAUXITE LIMITED ASX: ABZ Binjour Bauxite Resource Increased 46% to 24.5 Million Tonnes Company resources grow to 106 million tonnes 1,2,3,4 24.5 million tonnes of thick, gibbsite-rich
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT AUSTRALIAN BAUXITE LIMITED ASX: ABZ Binjour Bauxite Resource Increased 46% to 24.5 Million Tonnes Company resources grow to 106 million tonnes 1,2,3,4 24.5 million tonnes of thick, gibbsite-rich
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 29 June 2012
 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT AUSTRALIAN BAUXITE LIMITED ASX: ABZ Binjour Bauxite Resource Increased 46% to 24.5 Million Tonnes Company resources grow to 106 million tonnes 1,2,3,4 24.5 million tonnes of thick, gibbsite-rich
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT AUSTRALIAN BAUXITE LIMITED ASX: ABZ Binjour Bauxite Resource Increased 46% to 24.5 Million Tonnes Company resources grow to 106 million tonnes 1,2,3,4 24.5 million tonnes of thick, gibbsite-rich
Estimating and Reporting of
 AUSTRALIAN GUIDELINES FOR Estimating and Reporting of Inventory Coal, Coal Resources and Coal Reserves 2003 EDITION PREPARED BY THE COALFIELDS GEOLOGY COUNCIL OF NEW SOUTH WALES AND THE QUEENSLAND MINING
AUSTRALIAN GUIDELINES FOR Estimating and Reporting of Inventory Coal, Coal Resources and Coal Reserves 2003 EDITION PREPARED BY THE COALFIELDS GEOLOGY COUNCIL OF NEW SOUTH WALES AND THE QUEENSLAND MINING
Optimal Economic Envelope of Joint Open-Pit and Underground Mines*
 Optimal Economic Envelope of Joint Open-Pit and Underground Mines* Cecilia Julio Department of Mining Engineering, University of Chile Jorge Amaya LP Laboratory, Centre for Mathematical Modelling, University
Optimal Economic Envelope of Joint Open-Pit and Underground Mines* Cecilia Julio Department of Mining Engineering, University of Chile Jorge Amaya LP Laboratory, Centre for Mathematical Modelling, University
Strategic mine planning of surface mining projects incorporating sustainability concepts
 6th International Conference on Sustainable Development in the 645 Strategic mine planning of surface mining projects incorporating sustainability concepts C. Roumpos and E. Papacosta Public Power Corporation
6th International Conference on Sustainable Development in the 645 Strategic mine planning of surface mining projects incorporating sustainability concepts C. Roumpos and E. Papacosta Public Power Corporation
Application of Modern Geostatistics for Mine Planning
 Application of Modern Geostatistics for Mine Planning Oy Leuangthong (oy@ualberta.ca) Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta Abstract The application of conditional simulation
Application of Modern Geostatistics for Mine Planning Oy Leuangthong (oy@ualberta.ca) Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta Abstract The application of conditional simulation
Best Practices and Reporting Guidelines for Exploration and Mining Companies
 October 1999 Best Practices and Reporting Guidelines for Exploration and Mining Companies Mineral Exploration Best Practices Guidelines Guidelines for Technical Reports Disclosing Mineral Exploration Information
October 1999 Best Practices and Reporting Guidelines for Exploration and Mining Companies Mineral Exploration Best Practices Guidelines Guidelines for Technical Reports Disclosing Mineral Exploration Information
Simulation of Furnace System with Uncertain Parameter
 Munirah et Malaysian al. / Malaysian Journal Journal of Fundamental of Fundamental and Applied and Applied Sciences Sciences Vol.11, Vol.11, No.1 (2015) No.1 (2015) 5-9 5-9 Simulation of Furnace System
Munirah et Malaysian al. / Malaysian Journal Journal of Fundamental of Fundamental and Applied and Applied Sciences Sciences Vol.11, Vol.11, No.1 (2015) No.1 (2015) 5-9 5-9 Simulation of Furnace System
CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING
 148 CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING 7.1 GENERAL In reality, it is not possible to see into the sub-surface and observe the geological structure and the groundwater flow processes. It is for this reason
148 CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING 7.1 GENERAL In reality, it is not possible to see into the sub-surface and observe the geological structure and the groundwater flow processes. It is for this reason
Aquifer Science Staff, January 2007
 Guidelines for Hydrogeologic Reports and Aquifer Tests Conducted Within the Jurisdictional Boundaries of the Barton Springs / Edwards Aquifer Conservation District I. Introduction Aquifer Science Staff,
Guidelines for Hydrogeologic Reports and Aquifer Tests Conducted Within the Jurisdictional Boundaries of the Barton Springs / Edwards Aquifer Conservation District I. Introduction Aquifer Science Staff,
Optimal Selection of Selective Mining Unit (SMU) Size
 Optimal Selection of Selective Mining Unit (SMU) Size Oy Leuangthong (oy@ualberta.ca), Chad Neufeld (neufeld@ualberta.ca), and Clayton V. Deutsch (cdeutsch@ualberta.ca) Department of Civil and Environmental
Optimal Selection of Selective Mining Unit (SMU) Size Oy Leuangthong (oy@ualberta.ca), Chad Neufeld (neufeld@ualberta.ca), and Clayton V. Deutsch (cdeutsch@ualberta.ca) Department of Civil and Environmental
Distinguish between different types of numerical data and different data collection processes.
 Level: Diploma in Business Learning Outcomes 1.1 1.3 Distinguish between different types of numerical data and different data collection processes. Introduce the course by defining statistics and explaining
Level: Diploma in Business Learning Outcomes 1.1 1.3 Distinguish between different types of numerical data and different data collection processes. Introduce the course by defining statistics and explaining
MAS187/AEF258. University of Newcastle upon Tyne
 MAS187/AEF258 University of Newcastle upon Tyne 2005-6 Contents 1 Collecting and Presenting Data 5 1.1 Introduction...................................... 5 1.1.1 Examples...................................
MAS187/AEF258 University of Newcastle upon Tyne 2005-6 Contents 1 Collecting and Presenting Data 5 1.1 Introduction...................................... 5 1.1.1 Examples...................................
Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site
 Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site Liwen CAO *, Dongmei WU, Yong WANG, Ke HAN, Xue QU and Pan HUO School of Resource and Earth Science, China University of Mining and Technology,
Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site Liwen CAO *, Dongmei WU, Yong WANG, Ke HAN, Xue QU and Pan HUO School of Resource and Earth Science, China University of Mining and Technology,
Business Quantitative Analysis [QU1] Examination Blueprint
![Business Quantitative Analysis [QU1] Examination Blueprint Business Quantitative Analysis [QU1] Examination Blueprint](/thumbs/94/121308410.jpg) Business Quantitative Analysis [QU1] Examination Blueprint 2014-2015 Purpose The Business Quantitative Analysis [QU1] examination has been constructed using an examination blueprint. The blueprint, also
Business Quantitative Analysis [QU1] Examination Blueprint 2014-2015 Purpose The Business Quantitative Analysis [QU1] examination has been constructed using an examination blueprint. The blueprint, also
Welcome To Second Threshold Value of Minerals Workshop. UltraTech Cement Limited
 AT Welcome To Second Threshold Value of Minerals Workshop Threshold Value The threshold value is a component to mineral conservation as it decides the lower limit of sub grade in a mineral deposit and
AT Welcome To Second Threshold Value of Minerals Workshop Threshold Value The threshold value is a component to mineral conservation as it decides the lower limit of sub grade in a mineral deposit and
On-Line Mine Improving mining economy through on-line mineral analysis
 US$/ton On-Line Mine Improving mining economy through on-line mineral analysis Mr. Ilpo O. Auranen, CEO, Mine On-Line Service Oy Background: Mines of today are moving ever increasing tonnages of rock.
US$/ton On-Line Mine Improving mining economy through on-line mineral analysis Mr. Ilpo O. Auranen, CEO, Mine On-Line Service Oy Background: Mines of today are moving ever increasing tonnages of rock.
SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES. Floods. Instructor. Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ
 SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES Floods Instructor Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus SEES 503 Sustainable Water Resources
SEES 503 SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES Floods Instructor Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus SEES 503 Sustainable Water Resources
Conditional Non-Bias of Geostatistical Simulation for Estimation of Recoverable Reserves
 Conditional Non-Bias of Geostatistical Simulation for Estimation of Recoverable Reserves Jason A. Mcennan (am2@ualberta.ca and Clayton V. Deutsch (cdeutsch@ualberta.ca Department of Civil & Environmental
Conditional Non-Bias of Geostatistical Simulation for Estimation of Recoverable Reserves Jason A. Mcennan (am2@ualberta.ca and Clayton V. Deutsch (cdeutsch@ualberta.ca Department of Civil & Environmental
tool applied for forecasting in waste management
 tool applied for forecasting in waste management Dr. Martin PAVLAS Version 1.0, 1.9.2016 Justine represents a sophisticated tool for simultaneous forecasting of waste amounts and waste parameters at different
tool applied for forecasting in waste management Dr. Martin PAVLAS Version 1.0, 1.9.2016 Justine represents a sophisticated tool for simultaneous forecasting of waste amounts and waste parameters at different
Commerce Resources Corp. Reports Significant Increase in Resources and Grade at the Ashram Rare Earth Element Deposit, Northern, Quebec
 Commerce Resources Corp. Reports Significant Increase in Resources and Grade at the Ashram Rare Earth Element Deposit, Northern, Quebec Highlights SGS Geostat has determined a base case Inferred mineral
Commerce Resources Corp. Reports Significant Increase in Resources and Grade at the Ashram Rare Earth Element Deposit, Northern, Quebec Highlights SGS Geostat has determined a base case Inferred mineral
A Decision Support Method for Investment Preference Evaluation *
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 6, No 1 Sofia 2006 A Decision Support Method for Investment Preference Evaluation * Ivan Popchev, Irina Radeva Institute of
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 6, No 1 Sofia 2006 A Decision Support Method for Investment Preference Evaluation * Ivan Popchev, Irina Radeva Institute of
GEOTEHRMAL ENERGY- PROFESSIONAL IMPLEMENTATION
 GEOTEHRMAL ENERGY- PROFESSIONAL IMPLEMENTATION Janos SZANYI 1 Annamaria NADOR 2 Laszlo Zilahy-Sebes 2 and CHPM2030 Team 1 Coordinator of EFG PE on Geothermal Energy 2 Geological and Geophysical Institute
GEOTEHRMAL ENERGY- PROFESSIONAL IMPLEMENTATION Janos SZANYI 1 Annamaria NADOR 2 Laszlo Zilahy-Sebes 2 and CHPM2030 Team 1 Coordinator of EFG PE on Geothermal Energy 2 Geological and Geophysical Institute
Plain bearings Metallic multilayer plain bearings. Part 1: Non-destructive ultrasonic testing of bond of thickness greater than or equal to 0,5 mm
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 4386-1 Third edition 2012-10-15 Plain bearings Metallic multilayer plain bearings Part 1: Non-destructive ultrasonic testing of bond of thickness greater than or equal to 0,5
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 4386-1 Third edition 2012-10-15 Plain bearings Metallic multilayer plain bearings Part 1: Non-destructive ultrasonic testing of bond of thickness greater than or equal to 0,5
Application of the method of data reconciliation for minimizing uncertainty of the weight function in the multicriteria optimization model
 archives of thermodynamics Vol. 36(2015), No. 1, 83 92 DOI: 10.1515/aoter-2015-0006 Application of the method of data reconciliation for minimizing uncertainty of the weight function in the multicriteria
archives of thermodynamics Vol. 36(2015), No. 1, 83 92 DOI: 10.1515/aoter-2015-0006 Application of the method of data reconciliation for minimizing uncertainty of the weight function in the multicriteria
Introduction. Key Words: Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), Fuzzy AHP, Criteria weightings, Decisionmaking
 Application of AHP and Fuzzy AHP to Decision-Making Problems in Construction Sangwook Lee, Ph.D. University of Wisconsin-Platteville Platteville, Wisconsin The approach to selecting key factors has been
Application of AHP and Fuzzy AHP to Decision-Making Problems in Construction Sangwook Lee, Ph.D. University of Wisconsin-Platteville Platteville, Wisconsin The approach to selecting key factors has been
ROADMAP. Introduction to MARSSIM. The Goal of the Roadmap
 ROADMAP Introduction to MARSSIM The Multi-Agency Radiation Survey and Site Investigation Manual (MARSSIM) provides detailed guidance for planning, implementing, and evaluating environmental and facility
ROADMAP Introduction to MARSSIM The Multi-Agency Radiation Survey and Site Investigation Manual (MARSSIM) provides detailed guidance for planning, implementing, and evaluating environmental and facility
ISO 13528:2015 Statistical methods for use in proficiency testing by interlaboratory comparison
 ISO 13528:2015 Statistical methods for use in proficiency testing by interlaboratory comparison ema training workshop August 8-9, 2016 Mexico City Class Schedule Monday, 8 August Types of PT of interest
ISO 13528:2015 Statistical methods for use in proficiency testing by interlaboratory comparison ema training workshop August 8-9, 2016 Mexico City Class Schedule Monday, 8 August Types of PT of interest
For personal use only
 NEWS RELEASE DECEMBER 20, 2013 NEW HIGH-GRADE COPPER PROSPECT SECURED IN CHILE Guayacán copper-gold prospect returns surface channel samples grading up to 4.13% Cu Key Points: Option secured over prospective
NEWS RELEASE DECEMBER 20, 2013 NEW HIGH-GRADE COPPER PROSPECT SECURED IN CHILE Guayacán copper-gold prospect returns surface channel samples grading up to 4.13% Cu Key Points: Option secured over prospective
Energy Efficiency Impact Study
 Energy Efficiency Impact Study for the Preferred Resources Pilot February, 2016 For further information, contact PreferredResources@sce.com 2 1. Executive Summary Southern California Edison (SCE) is interested
Energy Efficiency Impact Study for the Preferred Resources Pilot February, 2016 For further information, contact PreferredResources@sce.com 2 1. Executive Summary Southern California Edison (SCE) is interested
QUANTIFICATION OF AREA FUGITIVE EMISSIONS AT OIL SANDS MINES
 T QUANTIFICATION OF AREA FUGITIVE EMISSIONS AT OIL SANDS MINES Version 2.0 June 2014 Title: Number: ESRD, Program Name: Climate Change Policy Effective Date: June 1, 2014 This document was updated on:
T QUANTIFICATION OF AREA FUGITIVE EMISSIONS AT OIL SANDS MINES Version 2.0 June 2014 Title: Number: ESRD, Program Name: Climate Change Policy Effective Date: June 1, 2014 This document was updated on:
A Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making Model for Benefit-Cost Analysis with Qualitative and Quantitative Attributes
 A Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making Model for Benefit-Cost Analysis with Qualitative and Quantitative Attributes M. Ghazanfari and M. Mellatparast Department of Industrial Engineering Iran University
A Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making Model for Benefit-Cost Analysis with Qualitative and Quantitative Attributes M. Ghazanfari and M. Mellatparast Department of Industrial Engineering Iran University
Evaluation of Risks Related to Ground Water Regime Changes
 The 3 rd International Conference on Water Resources and Arid Environments (2008) and the 1 st Arab Water Forum Evaluation of Risks Related to Ground Water Regime Changes David Duchan, Ales Drab, Ahmed
The 3 rd International Conference on Water Resources and Arid Environments (2008) and the 1 st Arab Water Forum Evaluation of Risks Related to Ground Water Regime Changes David Duchan, Ales Drab, Ahmed
Kristin Gustavson * and Ingrid Borren
 Gustavson and Borren BMC Medical Research Methodology 2014, 14:133 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bias in the study of prediction of change: a Monte Carlo simulation study of the effects of selective attrition
Gustavson and Borren BMC Medical Research Methodology 2014, 14:133 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bias in the study of prediction of change: a Monte Carlo simulation study of the effects of selective attrition
Analysis of the dispersion variance using geostatistical simulation and blending piles
 Analysis of the dispersion variance using geostatistical simulation and blending piles by D.M. Marques* and J.F. Costa* Synopsis The additive property of dispersion variances was found experimentally by
Analysis of the dispersion variance using geostatistical simulation and blending piles by D.M. Marques* and J.F. Costa* Synopsis The additive property of dispersion variances was found experimentally by
Appropriate Modelling in DSSs for River Basin Management
 Appropriate Modelling in DSSs for River Basin Management Yueping Xu and Martijn J. Booij Water Engineering and Management, Faculty of Engineering, University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands (email:
Appropriate Modelling in DSSs for River Basin Management Yueping Xu and Martijn J. Booij Water Engineering and Management, Faculty of Engineering, University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands (email:
Performance criteria
 Performance criteria Q 7-03. What is the usefulness of performance criteria? With any complex and continuing problem such as state debt issuance, it is critical to employ performance criteria - set in
Performance criteria Q 7-03. What is the usefulness of performance criteria? With any complex and continuing problem such as state debt issuance, it is critical to employ performance criteria - set in
Improved depth conversion with FWI a case study
 Improved depth conversion with FWI a case study A.J. O Neill 1* and T.A. Thompson 1 present a case study showing the application of FWI to help solve the problem of heterogeneous shallow carbonates in
Improved depth conversion with FWI a case study A.J. O Neill 1* and T.A. Thompson 1 present a case study showing the application of FWI to help solve the problem of heterogeneous shallow carbonates in
Application of AHP in Education Legislation Project. Ying-ying YAO and Yong-sheng GE *
 2017 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Automation (AMMA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-479-0 Application of AHP in Education Legislation Project Ying-ying YAO and Yong-sheng GE
2017 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Automation (AMMA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-479-0 Application of AHP in Education Legislation Project Ying-ying YAO and Yong-sheng GE
6 June 2017 Georgian Mining Corporation Further Drill Results from Kvemo Bolnisi East s Gold Zone 2 Target
 6 June 2017 Georgian Mining Corporation Further Drill Results from Kvemo Bolnisi East s Gold Zone 2 Target Georgian Mining Corporation ('GEO') is pleased to announce the final set of drill results from
6 June 2017 Georgian Mining Corporation Further Drill Results from Kvemo Bolnisi East s Gold Zone 2 Target Georgian Mining Corporation ('GEO') is pleased to announce the final set of drill results from
FACTORS AFFECTING JOB STRESS AMONG IT PROFESSIONALS IN APPAREL INDUSTRY: A CASE STUDY IN SRI LANKA
 FACTORS AFFECTING JOB STRESS AMONG IT PROFESSIONALS IN APPAREL INDUSTRY: A CASE STUDY IN SRI LANKA W.N. Arsakularathna and S.S.N. Perera Research & Development Centre for Mathematical Modeling, Faculty
FACTORS AFFECTING JOB STRESS AMONG IT PROFESSIONALS IN APPAREL INDUSTRY: A CASE STUDY IN SRI LANKA W.N. Arsakularathna and S.S.N. Perera Research & Development Centre for Mathematical Modeling, Faculty
Text... The giant Johan Sverdrup Field was discovered in 2010, and improvement in seismic imaging played an important role in it's discovery.
 0 Text... The giant Johan Sverdrup Field was discovered in 2010, and improvement in seismic imaging played an important role in it's discovery. Only one year before the discovery, PGS acquired on behalf
0 Text... The giant Johan Sverdrup Field was discovered in 2010, and improvement in seismic imaging played an important role in it's discovery. Only one year before the discovery, PGS acquired on behalf
DEVELOPING A HIGH GRADE ILMENITE DEPOSIT TIO 2 WORLD SUMMIT 3-5 OCTOBER 2017 ALICANTE, SPAIN
 DEVELOPING A HIGH GRADE ILMENITE DEPOSIT TIO 2 WORLD SUMMIT 3-5 OCTOBER 2017 ALICANTE, SPAIN GREENLAND: THE MISUNDERSTOOD ISLAND TOO COLD?????? TOO HARD? TOO ISOLATED???? 1 MAYBE IT S TIME TO TO THINK
DEVELOPING A HIGH GRADE ILMENITE DEPOSIT TIO 2 WORLD SUMMIT 3-5 OCTOBER 2017 ALICANTE, SPAIN GREENLAND: THE MISUNDERSTOOD ISLAND TOO COLD?????? TOO HARD? TOO ISOLATED???? 1 MAYBE IT S TIME TO TO THINK
BEFORE THE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION OF THE STATE OF UTAH ROCKY MOUNTAIN POWER. Exhibit Accompanying Direct Testimony of Robert M.
 Exhibit RMP (RMM-2) BEFORE THE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION OF THE STATE OF UTAH ROCKY MOUNTAIN POWER Exhibit Accompanying Direct Testimony of Robert M. Meredith Load Research Sampling Procedures January
Exhibit RMP (RMM-2) BEFORE THE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION OF THE STATE OF UTAH ROCKY MOUNTAIN POWER Exhibit Accompanying Direct Testimony of Robert M. Meredith Load Research Sampling Procedures January
Life Cycle Assessment A product-oriented method for sustainability analysis. UNEP LCA Training Kit Module f Interpretation 1
 Life Cycle Assessment A product-oriented method for sustainability analysis UNEP LCA Training Kit Module f Interpretation 1 ISO 14040 framework Life cycle assessment framework Goal and scope definition
Life Cycle Assessment A product-oriented method for sustainability analysis UNEP LCA Training Kit Module f Interpretation 1 ISO 14040 framework Life cycle assessment framework Goal and scope definition
Evaluation of Bench Height Selection for Limestone Resource Optimization A Case Study. N K Sharma, R Mazumder, D K Panda, A K Dubey
 Evaluation of Bench Height Selection for Limestone Resource Optimization A Case Study N K Sharma, R Mazumder, D K Panda, A K Dubey Abstract The economic viability of the modern day limestone mine and its
Evaluation of Bench Height Selection for Limestone Resource Optimization A Case Study N K Sharma, R Mazumder, D K Panda, A K Dubey Abstract The economic viability of the modern day limestone mine and its
A. I. Rybkina, A. A. Odintsova, A. D. Gvishiani, O. O. Samokhina, A. A. Astapenkova
 RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF EARTH SCIENCES vol. 16, 6, 2016, doi: 10.2205/2016ES000584 Development of geospatial database on hydrocarbon extraction methods in the 20th century for large and super large oil and
RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF EARTH SCIENCES vol. 16, 6, 2016, doi: 10.2205/2016ES000584 Development of geospatial database on hydrocarbon extraction methods in the 20th century for large and super large oil and
REPORT ON ASSESSMENT OF THE QA/QC PROGRAM FOR DIAMOND DRILLING CAMPAIGNS
 La Josefina Project May 2010 REPORT ON ASSESSMENT OF THE QA/QC PROGRAM FOR 2007 2008-2009 DIAMOND DRILLING CAMPAIGNS Written by: Horacio Puigdomenech. Reviewed by: Gustavo Fernandez. P.Geo. Luis Rodrigo
La Josefina Project May 2010 REPORT ON ASSESSMENT OF THE QA/QC PROGRAM FOR 2007 2008-2009 DIAMOND DRILLING CAMPAIGNS Written by: Horacio Puigdomenech. Reviewed by: Gustavo Fernandez. P.Geo. Luis Rodrigo
CEE3710: Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering
 CEE3710: Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering Lecture 1 September 6, 2017 Why do we need Probability and Statistics?? What is Uncertainty Analysis?? Ex. Consider the average (mean) height of females by
CEE3710: Uncertainty Analysis in Engineering Lecture 1 September 6, 2017 Why do we need Probability and Statistics?? What is Uncertainty Analysis?? Ex. Consider the average (mean) height of females by
Draft agreed by Scientific Advice Working Party 5 September Adopted by CHMP for release for consultation 19 September
 23 January 2014 EMA/CHMP/SAWP/757052/2013 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Qualification Opinion of MCP-Mod as an efficient statistical methodology for model-based design and analysis
23 January 2014 EMA/CHMP/SAWP/757052/2013 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Qualification Opinion of MCP-Mod as an efficient statistical methodology for model-based design and analysis
DESIGN FOR ERGONOMICS: CHAIR DESIGN FOR AGEING EMPLOYEES
 DESIGN FOR ERGONOMICS: CHAIR DESIGN FOR AGEING EMPLOYEES Péter György Horváth Zsolt Kovács University of West-Hungary Faculty of Wood Science Institute of Product Design and Manufacturing Technologies
DESIGN FOR ERGONOMICS: CHAIR DESIGN FOR AGEING EMPLOYEES Péter György Horváth Zsolt Kovács University of West-Hungary Faculty of Wood Science Institute of Product Design and Manufacturing Technologies
Geological carbon sequestration: prediction and verification
 Geological carbon sequestration: prediction and verification GCCC Digital Publication Series #09-13 Ian J. Duncan Jean-Philippe Nicot Changbing Yang Eric Bickel Svetlana Ikonnikova Jong-Won Choi Keywords:
Geological carbon sequestration: prediction and verification GCCC Digital Publication Series #09-13 Ian J. Duncan Jean-Philippe Nicot Changbing Yang Eric Bickel Svetlana Ikonnikova Jong-Won Choi Keywords:
IMPROVING THE PROCESS OF BLENDING CONSISTENT AND PREDICTABLE FEED IN THE NICKEL SMELTING PROCESS USING PGNAA TECHNOLOGY
 IMPROVING THE PROCESS OF BLENDING CONSISTENT AND PREDICTABLE FEED IN THE NICKEL SMELTING PROCESS USING PGNAA TECHNOLOGY April Montera Sales Director SABIA, Inc. amontera@sabiainc.com Michael Loken, P.
IMPROVING THE PROCESS OF BLENDING CONSISTENT AND PREDICTABLE FEED IN THE NICKEL SMELTING PROCESS USING PGNAA TECHNOLOGY April Montera Sales Director SABIA, Inc. amontera@sabiainc.com Michael Loken, P.
SPECIAL CONTROL CHARTS
 INDUSTIAL ENGINEEING APPLICATIONS AND PACTICES: USES ENCYCLOPEDIA SPECIAL CONTOL CHATS A. Sermet Anagun, PhD STATEMENT OF THE POBLEM Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a powerful collection of problem-solving
INDUSTIAL ENGINEEING APPLICATIONS AND PACTICES: USES ENCYCLOPEDIA SPECIAL CONTOL CHATS A. Sermet Anagun, PhD STATEMENT OF THE POBLEM Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a powerful collection of problem-solving
A Statistical Comparison Of Accelerated Concrete Testing Methods
 Journal of Applied Mathematics & Decision Sciences, 1(2), 89-1 (1997) Reprints available directly from the Editor. Printed in New Zealand. A Statistical Comparison Of Accelerated Concrete Testing Methods
Journal of Applied Mathematics & Decision Sciences, 1(2), 89-1 (1997) Reprints available directly from the Editor. Printed in New Zealand. A Statistical Comparison Of Accelerated Concrete Testing Methods
Multiple Choice Questions Sampling Distributions
 Multiple Choice Questions Sampling Distributions 1. The Gallup Poll has decided to increase the size of its random sample of Canadian voters from about 1500 people to about 4000 people. The effect of this
Multiple Choice Questions Sampling Distributions 1. The Gallup Poll has decided to increase the size of its random sample of Canadian voters from about 1500 people to about 4000 people. The effect of this
Appendix 1 Interview Questions for CDM-Related Officials
 Appendix 1 Interview Questions for CDM-Related Officials 1. Would you please let me know the current situation of the development of CDM projects in China? 2. What do you think is the most important factor
Appendix 1 Interview Questions for CDM-Related Officials 1. Would you please let me know the current situation of the development of CDM projects in China? 2. What do you think is the most important factor
Chapter 8 Interpreting Uncertainty for Human Health Risk Assessment
 What s Covered in Chapter 8: Chapter 8 Interpreting Uncertainty for Human Health Risk Assessment 8.1 Uncertainty and Limitations of the Risk Assessment Process 8.2 Types of Uncertainty 8.3 Qualitative
What s Covered in Chapter 8: Chapter 8 Interpreting Uncertainty for Human Health Risk Assessment 8.1 Uncertainty and Limitations of the Risk Assessment Process 8.2 Types of Uncertainty 8.3 Qualitative
THE RELIABILITY AND ACCURACY OF REMNANT LIFE PREDICTIONS IN HIGH PRESSURE STEAM PLANT
 THE RELIABILITY AND ACCURACY OF REMNANT LIFE PREDICTIONS IN HIGH PRESSURE STEAM PLANT Ian Chambers Safety and Reliability Division, Mott MacDonald Studies have been carried out to show how failure probabilities
THE RELIABILITY AND ACCURACY OF REMNANT LIFE PREDICTIONS IN HIGH PRESSURE STEAM PLANT Ian Chambers Safety and Reliability Division, Mott MacDonald Studies have been carried out to show how failure probabilities
Energy savings reporting and uncertainty in Measurement & Verification
 Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference, AUPEC 2014, Curtin University, Perth, Australia, 28 September 1 October 2014 1 Energy savings reporting and uncertainty in Measurement & Verification
Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference, AUPEC 2014, Curtin University, Perth, Australia, 28 September 1 October 2014 1 Energy savings reporting and uncertainty in Measurement & Verification
Combinatorial Optimization Model for Group Decision-Making
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 18, No 2 Sofia 2018 Print ISSN: 1311-9702; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.2478/cait-2018-0028 Combinatorial Optimization Model
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 18, No 2 Sofia 2018 Print ISSN: 1311-9702; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.2478/cait-2018-0028 Combinatorial Optimization Model
VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: METHODOLOGY *)
 VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: METHODOLOGY *) Guideline Title Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology Legislative basis Directive 75/318/EEC as amended Date of first adoption December 1996
VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: METHODOLOGY *) Guideline Title Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology Legislative basis Directive 75/318/EEC as amended Date of first adoption December 1996
For personal use only
 ASX/Media Release 31 January 2018 Orinoco Confirms Outstanding Grades of Gold in Tailings Bulk Sample of 1,000 tonnes of Tailings to Commence Shortly Five one-tonne random samples of tailings recover a
ASX/Media Release 31 January 2018 Orinoco Confirms Outstanding Grades of Gold in Tailings Bulk Sample of 1,000 tonnes of Tailings to Commence Shortly Five one-tonne random samples of tailings recover a
The Use of 3D Modelling for Environmental Site Assessment
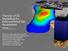 The Use of 3D Modelling for Environmental Site Assessment Reed Copsey C Tech Development Corporation We live in an age of 3D movies and TVs, which means that 99% of the population has an opinion about
The Use of 3D Modelling for Environmental Site Assessment Reed Copsey C Tech Development Corporation We live in an age of 3D movies and TVs, which means that 99% of the population has an opinion about
Exercise Confidence Intervals
 Exercise Confidence Intervals (Fall 2015) Sources (adapted with permission)- T. P. Cronan, Jeff Mullins, Ron Freeze, and David E. Douglas Course and Classroom Notes Enterprise Systems, Sam M. Walton College
Exercise Confidence Intervals (Fall 2015) Sources (adapted with permission)- T. P. Cronan, Jeff Mullins, Ron Freeze, and David E. Douglas Course and Classroom Notes Enterprise Systems, Sam M. Walton College
Application of Statistical Sampling to Audit and Control
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BUSINESS FROM BHARATIYA VIDYA BHAVAN'S M. P. BIRLA INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT, BENGALURU Vol.12, #1 (2018) pp 14-19 ISSN 0974-0082 Application of Statistical Sampling to Audit and
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BUSINESS FROM BHARATIYA VIDYA BHAVAN'S M. P. BIRLA INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT, BENGALURU Vol.12, #1 (2018) pp 14-19 ISSN 0974-0082 Application of Statistical Sampling to Audit and
AP Statistics Scope & Sequence
 AP Statistics Scope & Sequence Grading Period Unit Title Learning Targets Throughout the School Year First Grading Period *Apply mathematics to problems in everyday life *Use a problem-solving model that
AP Statistics Scope & Sequence Grading Period Unit Title Learning Targets Throughout the School Year First Grading Period *Apply mathematics to problems in everyday life *Use a problem-solving model that
Statistical Dependence of Pipe Breaks on Explanatory Variables
 water Article Statistical Dependence of Pipe Breaks on Explanatory Variables Patricia Gómez-Martínez 1, *, Francisco Cubillo 2, Francisco J. Martín-Carrasco 1 and Luis Garrote 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering:
water Article Statistical Dependence of Pipe Breaks on Explanatory Variables Patricia Gómez-Martínez 1, *, Francisco Cubillo 2, Francisco J. Martín-Carrasco 1 and Luis Garrote 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering:
Glossary of Standardized Testing Terms https://www.ets.org/understanding_testing/glossary/
 Glossary of Standardized Testing Terms https://www.ets.org/understanding_testing/glossary/ a parameter In item response theory (IRT), the a parameter is a number that indicates the discrimination of a
Glossary of Standardized Testing Terms https://www.ets.org/understanding_testing/glossary/ a parameter In item response theory (IRT), the a parameter is a number that indicates the discrimination of a
Papua New Guinea Mineral resources and ore reserves
 Harmony Annual Report 2009 139 Papua New Guinea and ore reserves Geology: Papua New Guinea (PNG) lies at the northern end of the Australian Plate and has three major components: a continental cratonic
Harmony Annual Report 2009 139 Papua New Guinea and ore reserves Geology: Papua New Guinea (PNG) lies at the northern end of the Australian Plate and has three major components: a continental cratonic
CERTIFICATION REPORT ACIRS-A1-TR-01
 CERTIFICATION REPORT ACIRS-A1-2016 Fly Ash Reference Material Date of Issue: June, 2016 Valid to: June, 2026 Report Number: ACIRS-A1-TR-01 1. Introduction This report describes the preparation and certification
CERTIFICATION REPORT ACIRS-A1-2016 Fly Ash Reference Material Date of Issue: June, 2016 Valid to: June, 2026 Report Number: ACIRS-A1-TR-01 1. Introduction This report describes the preparation and certification
Task 4.2 Technical Memorandum on Pumping Impacts on Squaw Creek
 Task 4.2 Technical Memorandum on Pumping Impacts on Squaw Creek Aquifer Test 1 Aquifer Test 2 Prepared for: Squaw Valley Public Service District April 2013 Prepared by: This page left intentionally blank
Task 4.2 Technical Memorandum on Pumping Impacts on Squaw Creek Aquifer Test 1 Aquifer Test 2 Prepared for: Squaw Valley Public Service District April 2013 Prepared by: This page left intentionally blank
As with previous editions of the Joint
 Quality control and public reporting in industrial minerals Andrew Scogings*, IM Correspondent, Jacqui Coombes** As with previous editions of the Joint Ore Reserves Committee (JORC) code the 2012 edition
Quality control and public reporting in industrial minerals Andrew Scogings*, IM Correspondent, Jacqui Coombes** As with previous editions of the Joint Ore Reserves Committee (JORC) code the 2012 edition
Short Note: Generating regional permeability maps for large-scale hydrogeological studies
 Short Note: Generating regional permeability maps for large-scale hydrogeological studies Abstract D.K. Khan (dkkhan@ualberta.ca) Department of Earth & Atmospheric Sciences University of Alberta This short
Short Note: Generating regional permeability maps for large-scale hydrogeological studies Abstract D.K. Khan (dkkhan@ualberta.ca) Department of Earth & Atmospheric Sciences University of Alberta This short
Introduction to Research
 Introduction to Research Arun K. Tangirala Arun K. Tangirala, IIT Madras Introduction to Research 1 Objectives To learn the following: I What is data analysis? I Types of analyses I Different types of
Introduction to Research Arun K. Tangirala Arun K. Tangirala, IIT Madras Introduction to Research 1 Objectives To learn the following: I What is data analysis? I Types of analyses I Different types of
Limits for the use of thermal waters on the example of the conceptual model of the Benesov-Usti aquifer system of the Bohemian Cretaceous basin PhD
 Limits for the use of thermal waters on the example of the conceptual model of the Benesov-Usti aquifer system of the Bohemian Cretaceous basin PhD thesis Résumé Josef V. DATEL, MSc. The very work was
Limits for the use of thermal waters on the example of the conceptual model of the Benesov-Usti aquifer system of the Bohemian Cretaceous basin PhD thesis Résumé Josef V. DATEL, MSc. The very work was
For personal use only
 BAUXITE RESOURCES LIMITED ABN 72 119 699 982 ASX/MEDIA RELEASE 2 May 2011 BAUXITE RESOURCE UPDATE FOR NORTH DARLING RANGE HIGHLIGHTS Upgrade in Resource for the Aurora Resource following modelling of recent
BAUXITE RESOURCES LIMITED ABN 72 119 699 982 ASX/MEDIA RELEASE 2 May 2011 BAUXITE RESOURCE UPDATE FOR NORTH DARLING RANGE HIGHLIGHTS Upgrade in Resource for the Aurora Resource following modelling of recent
Richmont Mines Provides a Status Update on an Expansion Case Preliminary Economic Assessment for the Island Gold Mine
 NEWS RELEASE Richmont Mines Provides a Status Update on an Expansion Case Preliminary Economic Assessment for the Island Gold Mine 11/1/2016 Potential for Increased Production to 1,100 Tonnes per Day with
NEWS RELEASE Richmont Mines Provides a Status Update on an Expansion Case Preliminary Economic Assessment for the Island Gold Mine 11/1/2016 Potential for Increased Production to 1,100 Tonnes per Day with
Test lasts for 120 minutes. You must stay for the entire 120 minute period.
 ECO220 Mid-Term Test (June 29, 2005) Page 1 of 15 Last Name: First Name: Student ID #: INSTRUCTIONS: DO NOT OPEN THIS EAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO. Test lasts for 120 minutes. You must stay for the entire 120
ECO220 Mid-Term Test (June 29, 2005) Page 1 of 15 Last Name: First Name: Student ID #: INSTRUCTIONS: DO NOT OPEN THIS EAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO. Test lasts for 120 minutes. You must stay for the entire 120
GRADE CONTROL BLENDING AND SELECTIVITY FOR OPTIMAL PROCESS PERFORMANCE AT THE SKORPION ZINC MINE, NAMIBIA G B GNOINSKI
 GRADE CONTROL BLENDING AND SELECTIVITY FOR OPTIMAL PROCESS PERFORMANCE AT THE SKORPION ZINC MINE, NAMIBIA G B GNOINSKI Namzinc (Pty) Ltd, Private Bag 2003, Rosh Pinah, Namibia Tel: +264 63 271 2408, Fax:
GRADE CONTROL BLENDING AND SELECTIVITY FOR OPTIMAL PROCESS PERFORMANCE AT THE SKORPION ZINC MINE, NAMIBIA G B GNOINSKI Namzinc (Pty) Ltd, Private Bag 2003, Rosh Pinah, Namibia Tel: +264 63 271 2408, Fax:
General Professional Practice Guidelines for Environmental Geoscience
 General Professional Practice Guidelines for Environmental Geoscience Contents 1. Introduction... 1 2. Qualified Person... 2 3. Geoscientific Concept... 2 4. Quality Control and Quality Assurance... 2
General Professional Practice Guidelines for Environmental Geoscience Contents 1. Introduction... 1 2. Qualified Person... 2 3. Geoscientific Concept... 2 4. Quality Control and Quality Assurance... 2
Simulation of 2D Heat Transfer in a Horizontal Plane with Thermal Resistance-Capacitance Model
 Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'16) Budapest, Hungary August 22 23, 2016 Paper No. HTFF 140 DOI: 10.11159/htff16.140 Simulation of 2D Heat
Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'16) Budapest, Hungary August 22 23, 2016 Paper No. HTFF 140 DOI: 10.11159/htff16.140 Simulation of 2D Heat
Measurement and sampling
 Name: Instructions: (1) Answer questions in your blue book. Number each response. (2) Write your name on the cover of your blue book (and only on the cover). (3) You are allowed to use your calculator
Name: Instructions: (1) Answer questions in your blue book. Number each response. (2) Write your name on the cover of your blue book (and only on the cover). (3) You are allowed to use your calculator
Empirical Analysis of Gray Relational Analysis of Employment Structure and Industrial Structure in Guangdong Province
 Journal of Human Resource and Sustainability Studies, 2017, 5, 47-56 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jhrss ISSN Online: 2328-4870 ISSN Print: 2328-4862 Empirical Analysis of Gray Relational Analysis of Employment
Journal of Human Resource and Sustainability Studies, 2017, 5, 47-56 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jhrss ISSN Online: 2328-4870 ISSN Print: 2328-4862 Empirical Analysis of Gray Relational Analysis of Employment
Blast optimisation at limestone quarry operations good fragmentation, less fines
 Abstract Blast optimisation at limestone quarry operations good fragmentation, less fines Benjamin Cebrian Rock blasting at quarries represents multiple challenges not easy to see at first sight. Aggregate
Abstract Blast optimisation at limestone quarry operations good fragmentation, less fines Benjamin Cebrian Rock blasting at quarries represents multiple challenges not easy to see at first sight. Aggregate
4.4 MODEL CODE DESCRIPTION 4.5 WATER SOURCES AND SINKS 4.6 MODEL DOMAIN AND BOUNDARIES. SLR South Africa
 Page 4-18 The developed model should therefore be seen as an initial site model which should be refined and recalibrated once more groundwater monitoring and other data become available. 4.4 MODEL CODE
Page 4-18 The developed model should therefore be seen as an initial site model which should be refined and recalibrated once more groundwater monitoring and other data become available. 4.4 MODEL CODE
X-ray diffraction (XRD) for grade control of iron ores
 XRD APPLICATION NOTE X-ray diffraction (XRD) for grade control of iron ores Beneficiation techniques for iron ore are receiving worldwide attention due to the development of new deposits of lower grade
XRD APPLICATION NOTE X-ray diffraction (XRD) for grade control of iron ores Beneficiation techniques for iron ore are receiving worldwide attention due to the development of new deposits of lower grade
Dynamics of the Surface Water Circulation between a River and Fishponds in a Sub-Mountain Area
 Dynamics of the Surface Water Circulation between a River and Fishponds in a Sub-Mountain Area Maria Anna Szumiec, Danuta Augustyn Polish Academy of Sciences Institute of Ichthyobiology and Aquaculture,
Dynamics of the Surface Water Circulation between a River and Fishponds in a Sub-Mountain Area Maria Anna Szumiec, Danuta Augustyn Polish Academy of Sciences Institute of Ichthyobiology and Aquaculture,
The Use of AHP (Analytical Hierarchy Process) as Multi Criteria Decision Tool for the Selection of Best Water Supply Source for Benin City
 Nigerian Journal of Environmental Sciences and Technology (NIJEST) www.nijest.com Vol 1, No. 1 March 2017, pp 169-176 The Use of AHP (Analytical Hierarchy Process) as Multi Criteria Decision Tool for the
Nigerian Journal of Environmental Sciences and Technology (NIJEST) www.nijest.com Vol 1, No. 1 March 2017, pp 169-176 The Use of AHP (Analytical Hierarchy Process) as Multi Criteria Decision Tool for the
Study of oxygen fugacity influence on redox state of iron in granitoidic melts
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Study of oxygen fugacity influence on redox state of iron in granitoidic melts To cite this article: M V Volovetsky et al 200 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 27 02050 Recent
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Study of oxygen fugacity influence on redox state of iron in granitoidic melts To cite this article: M V Volovetsky et al 200 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 27 02050 Recent
A Fuzzy Optimization Model for Single-Period Inventory Problem
 , July 6-8, 2011, London, U.K. A Fuzzy Optimization Model for Single-Period Inventory Problem H. Behret and C. Kahraman Abstract In this paper, the optimization of single-period inventory problem under
, July 6-8, 2011, London, U.K. A Fuzzy Optimization Model for Single-Period Inventory Problem H. Behret and C. Kahraman Abstract In this paper, the optimization of single-period inventory problem under
FLOTATION CONTROL & OPTIMISATION
 FLOTATION CONTROL & OPTIMISATION A global leader in mineral and metallurgical innovation FLOATSTAR OVERVIEW Flotation is a complex process that is affected by a multitude of factors. These factors may
FLOTATION CONTROL & OPTIMISATION A global leader in mineral and metallurgical innovation FLOATSTAR OVERVIEW Flotation is a complex process that is affected by a multitude of factors. These factors may
A 2-tuple Fuzzy Linguistic RFM Model and Its Implementation
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 55 (2015 ) 1340 1347 Information Technology and Quantitative Management (ITQM 2015) A 2-tuple Fuzzy Linguistic RFM Model
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 55 (2015 ) 1340 1347 Information Technology and Quantitative Management (ITQM 2015) A 2-tuple Fuzzy Linguistic RFM Model
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 15 August 2011
 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT AUSTRALIAN BAUXITE LIMITED ASX: ABZ 6 Million Tonnes Maiden Guyra Resource: High-Grade Bauxite Company resources grow to 68 million tonnes 1,2 Maiden Resource: 6 million tonnes of gibbsite-rich
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT AUSTRALIAN BAUXITE LIMITED ASX: ABZ 6 Million Tonnes Maiden Guyra Resource: High-Grade Bauxite Company resources grow to 68 million tonnes 1,2 Maiden Resource: 6 million tonnes of gibbsite-rich
