MICROMECHANICAL ROCK MODELS
|
|
|
- Cody Waters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MICROMECHANICAL ROCK MODELS HEINZ KONIETZKY PROF. DR.-ING. HABIL. GEOTECHNICAL INSTITUT, TU BERGAKADEMIE FREIBERG, GERMANY 1 INTRODUCTION Micromechanical behavior of rocks is dependent on microstructure. Microstructure in turn is characterized by grain size and grain shape as well as pore size and shape. Also, orientation of grains and pores have influence. In addition we have to consider the physical strength and deformation properties of the grains including binder material and existing microcracks. All these components together define the macroscopic stress-strain relations, the damage evolution and the failure behavior. Numerical simulations at the grain size level can help to understand the complex behavior of rocks and to detect, which components have significant effect on the overall behavior. This article describes research which was performed at the Chair for Rock Mechanics at the Geotechnical Institute of TU Bergakademie Freiberg within the last few years using discontinuum approaches to simulate rocks and rock-like material at the grain size level. The performed research work concentrates on the following topics: Microcrack development (inter- and intra-granular fracturing) Lifetime prediction of rocks under static longterm loading Techniques to duplicate microstructure of rocks (stochastic approaches and digital image processing) Influence of microstructure on poroelasticity Micromechanical backanalysis of laboratory tests Topological analysis of micro structure This article gives an insight into some of the developed procedures and modelling results. 2 GEOMETRICAL MODEL SET-UP Three in principle different approaches were developed to set-up two-dimensional model geometries at the grain size level: Geometrical model set-up for Discrete Element models based on digital image processing of rock surfaces based on thin-section analysis Geometrical model set-up for Discrete Element models based on stochastic evaluation of rock structure at the grain size level Implementation of stochastically distributed microcracks into continuum models (not discussed within this paper) and Discrete Element models Figure 1 illustrates a procedure based on digital image processing. This procedure starts with digital color images of a rock surface, followed by a conversion into a gray-scale image. Different grayscale windows refer to different mineral components (grains) or pores. This digital grayscale image is superimposed by a regular mesh or Voronoi based polyhedra. Depending on the mesh resolution each grain or pore is covered by several or
2 many elements or Voronoi bodies. Exemplary, Figure 2 shows a Voronoi body based numerical model for granite, where each grain is composed of several Voronoi blocks. Each of these blocks can be either stiff or internally meshed. In case of internal meshing, the grains are deformable and will behave according to the specified visco-elasto-plastic constitutive law. Nevertheless, such a model is restricted in such a way, that crack propagation can occur only along the Voronoi block edges. Therefore, sufficient model resolution is necessary. An alternative to a deterministic approach is a stochastic one. In that case grains and/or pores are analyzed in terms of their size, shape and orientation. Based on these data corresponding distribution functions and correlations are obtained. This information is finally used to set-up stochastic equivalent models. Due to the stochastic (random) nature an arbitrary number of equivalent deterministic models can be created. Such a procedure allows to determine robustness and sensitivity of models. Figures 3 shows an example of grain shape and size characterization proposed by Heilbronner & Barett (2013). Based on this proposed scheme, the following procedure was developed. First a huge number of clumps or clusters is created in a fully random fashion based on a pre-defined number of spheres as illustrated in Figure 4. Different overlapping of balls at different angles lead to an unlimited number of clumps or clusters. Then, the parameters according to Heilbronner & Barett (2013) are used to classify all these clumps or clusters. Then, they are compared with grain shapes of the rock and those clumps and clusters, respectively, are selected which fit into the classification. Finally, they are adjusted in size and placed into the model specimen. Afterwards a correction in terms of adequate pore space distribution is necessary. Figure 5 illustrates a specific procedure, which starts with placing spheres inside the specimen according to number and size of grains. In a second step spheres are replaced by clumps to duplicate the grain shape according to the rock analysis. Figure 1. Scheme of model set-up based on digital image (right: gray-scale image, left: numerical model). Finally, this particle arrangement is superimposed to a Voronoi body structure with high resolution which gives the final grain structure. Figure 6 documents a particle based approach with clusters. In that case, the specimen is first filled with spheres. In a second phase, ellipses (2D) or ellipsoids (3D) according to the desired distribution functions of grain size and shape were placed inside the specimen in a random fashion. All spheres within one ellipse/ellipsoid were bonded and form a grain. Figure 2. Exemplary model set-up of a granite by means of Voronoi based clusters.
3 Figure 3. Grain characterization procedure developed by Heilbronner & Barett (2013) with indication of parameters. Figure 7 shows a further approach, which considers in addition to the grain structure also microcracks with different orientation and length at certain points along the edges of the Voronoi bodies. Figure 8 shows two models with focus on porosity. It is remarkable, that under compressive loading such models with high porosity show huge stress concentrations and pronounced force chains. In that case the internal structure is responsible also for strong local tensile stresses even if the outer loading is compressive. Shape, size and orientation of pores has also pronounced effect on poroelastic constants, like Biot s coefficient (Tan & Konietzky 2014). Figure 4. Randomly created clumps based on 5 spheres each. All these different procedures can also be combined to set-up sophisticated models considering complex microstructure. Extensive calibration of model parameters is necessary. This could be performed by inverse optimization on the basis of several laboratory tests in combination with additional measurements or use of already available data for minerals and grains, respectively. Calibration should comprise quiet different loading situations and should involve both, analysis of fracture pattern and macroscopic stress-strain relations. Also, it should be taken into account, that several parameters, like calculation of stress intensity factors, are meshdependent.
4 Figure 5. Specific procedure for set-up of Voronoi based DEM model in four steps as explained inside the text.
5 Figure 6. Sphere based model with clusters representing grains (Groh et al. 2011). Figure 7. Voronoi-based grain structure with randomly placed micro-cracks (white color).
6 Figure 8. Low and high porous specimen with randomly created pores according to pore analysis. 3 2-DIMENSIONAL TIME-DEPENDENT SIMULATIONS The models described above can be used to simulate time-independent and time-dependent behavior. If subcritical crack growth is taken into account, life-time prediction can be performed and time-dependent damage evolution can be investigated. Discontinuum based approaches consider crack propagation along boundaries of discrete elements. In case of subcritical crack growth the strength degradation equation for each element and microcrack i, respectively, based on Charles equation is expressed as: dj i P dt = λ i P [A I ( K Ii K Ic ) n I + AII ( K IIi K IIc ) n II ] (3) where J p is the strength parameter p (e.g. cohesion, tensile strength, friction coefficient etc.); λ P is a degradation constant; AI and AII are related to shares of tensile and shear fracture. The Charles-Hillig approach does not assume the existence of discrete microcracks, but describes a timedependent weakening of contacts: dj i P dt = (λ p i v 0 e u/rt )e Vσ i/rt (4) where V is the molar volume and σi is either the normal or shear stress depending on the considered fracture mode. Figure 15 shows several damage stages as function of time for a granite sample under uniaxial load and Figure 16 shows the fracture pattern in more detail in a zoomed window of the sample for several points in time. Crack propagation and fracture opening is visible.
7 Figure 9. Damage pattern of granite specimen under constant uniaxial loading with ongoing time (Chen & Konietzky 2014). Figure 10. Detailed view on damage development (see figure 9). Figure 11. Observed fracture pattern on slotted discs tested under uniaxial compression, but different orientation. Figure 12. Simulated fracture pattern on slotted discs tested under uniaxial compression, but different orientation (compare with Figure 11).
8 Figure 13. Lifetime versus driving stress ratio: laboratory test results from Lajtai & Bielus (1986) and own simulation results (Chen & Konietzky 2014). Figure 17 shows fracture pattern of slotted Brazilian granite samples (discs). Different orientation of slot against direction of uniaxial compression leads to quite different fracture pattern involving pure tensile fracturing and mixed-mode fracturing including wing-crack propagation. Figure 18 shows the corresponding numerical simulations based on a Discrete Element approach at the grain size level. This procedure was extended by incorporation of time-dependent failure modelling as explained above to predict lifetime as shown in Figure 19. More detailed explanations are given by Chen et al. (2014, 2015, 2016). 4 THREE-DIMENSIONAL MODELLING AND STRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION Increasing computational power including parallel processing allows three-dimensional simulations. The above mentioned techniques to set-up grain based models were extended to third dimension. Exemplary, Figures 14 and 15 show some three-dimensional DEM-models. To set-up Voronoi based models an interesting technique was developed, which starts with packages of spherical objects (weighted point process) followed by the construction of Voronoi bodies around this points (spheres). Figures 16 and 17 illustrate the principal procedure to construct such Voronoi bodies. Based on manipulation of input data inhomogeneous and anisotropic Voronoi structures can be created as shown in Figure 18. Experience has shown, that detailed microstructure has enormous influence on strength and deformability of material. Often more general values like density, porosity or coordination number are not sufficient to characterize the material. In case of sphere-based models more complex functions which considers linear and spherical contact distribution functions, pair correlation functions or Ripley s K-function are useful tools to explain differences in material behavior (Wagner et al. 2010).
9 Figure 14. Three-dimensional models based on spherical elements. Figure 15. Three-dimensional models based on polyhedral.
10 Figure 16. Example: Voronoi diagram with Laguerre decomposition (principle in 2D). Figure 17. Example: Voronoi diagram with Laguerre decomposition (principle in 3D). Figure 18. Example: Voronoi bodies with inhomogeneous (above) and anisotropic (below) structure.
11 Figure 19. Stress-strain, permeability and damage evolution for a salt sample under uniaxial compressive stress using a three-dimensional Voronoi based model (Wagner et al. 2012) Exemplary, Figure 19 illustrates the complex hydro-mechanical behavior of a coarse-grained salt sample under uniaxial compression. The diagram above shows vertical stress vs. vertical strain and volumetric strain, respectively. The volumetric strain curve indicates volumetric compaction at the beginning followed by dilation caused by increasing microcracking at a later stage. The diagram below shows evolution of damage and permeability. On the right hand side the damage pattern in form of developed microcracks are shown for 3 different stages in parallel to the hydraulic pressure distribution inside the sample. 5 CONCLUSIONS Depending on the modelling task, scale and material either continuum (e.g. Konietzky et al. 2009; Li & Konietzky 2014, 2015) and/or discontinuum based approaches are suitable to simulate time-dependent or timeindependent damage development of rocks at the grain size level. The modelling reveals, that grain size distribution, grain shape distribution, grain orientation distribution as well as mineral content and binder between grains in terms of their mechanical properties play important role for lifetime and mechanical behavior in general. The same holds for microcracks and pores, respectively. Especially, Discrete Element based micromechanical models using Voronoi bodies or clusters/clumps based on spheres are very promising to consider micromechanical structure in an explicit manner. Both, inter-granular as well as intra-granular fracturing can be modelled. Use of modelling strategies, which consider grain, pore and microcracks in an explicit manner avoids complicated constitutive relations and reduces the number of model parameters. On the other side it allows to apply fundamental physical relations to describe complex material behavior, like explained for instance by Stahl & Konietzky (2011) for broken rock material (ballast). New mathematical approaches which consider internal network structure of solids are promising tools to explain the material behavior at the microscale.
12 ACKNOWLEDGMENT Several scientific co-workers and PhD students (see also references) working at the Chair for Rock Mechanics at TU Bergakademie Freiberg have been intensively involved into the above mentioned scientific work within the last few years. Their contributions are highly appreciated. REFERENCES Chen, W. & H. Konietzky (2014). Simulation of heterogeneity, creep, damage and lifetime for loaded brittle rocks. Tectonophysics, 633, Chen, W., H. Konietzky, S.M. Abbas (2015). Numerical simulation of time-independent and time-dependent fracturing in sandstone. Engineering Geology, 193(2), Chen, W., H. Konietzky, X. Tan & T. Frühwirt (2016). Pre-failure damage analysis for brittle rocks under triaxial compression. Computers and Geotechnics,74, Groh, U., H. Konietzky, K. Walter & M. Herbst (2011). Damage simulation of brittle heterogeneous materials at the grain size level. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 55, Heilbronner, R. & S. Barett (2013). Image analysis in earth sciences microstructure and textures of earth materials. Springer, Heidelberg, Berlin. Konietzky, H., A. Heftenberger & M. Feige (2009). Life time prediction for rocks under static compressive and tensile loads a new simulation approach. Acta Geotechnica, 4, Lajtai, Z.E. & P.L. Bielus (1986). Stress corrosion cracking of Luc du Bonnet granite in tension and compression. Rock Mechanics Rock Engineering, 19, Li, X. & H. Konietzky (2014). Simulation of time-dependent crack growth in brittle rocks under constant loading conditions. Engi neering Fracture Mechanics, 119, Li, X. & H. Konietzky (2015). Numerical simulation schemes for time-dependent crack growth in hard brittle rock. Acta Geotechnica, 10, Stahl, M. & H. Konietzky (2011). Discrete element simulation of ballast and gravel under special consideration of grainshape, grain size and relative density. Granular Matter, 4, Tan, X. & H. Konietzky (2014). Numerical study of variation in Biot s coefficient with respect to microstructure of rocks. Tectonophysics, 610, Wagner, A., M. Hütter & D. Stoyan (2010). More on the microstructural characterization of dense particle gels. Journal of the Euro pean Ceramic Society, 30, Wagner, A., H. Konietzky, K. Otparlik, C. Müller & C. Lerch, (2012). Microstructure simulation based on discrete element models theory and application in salt mechanics. Publ. Geotechnical Institute of TU Bergakademie Freiberg, H. Konietzky (Ed.), ,
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS OF CONCRETE BEHAVIOUR AT MESO-LEVEL DURING QUASI-STATIC SPLITTING TENSION
 Size effect in concrete under tensile splitting - experiments and DEM analyses for different failure modes V International Conference on Particle-based Methods Fundamentals and Applications PARTICLES 2017
Size effect in concrete under tensile splitting - experiments and DEM analyses for different failure modes V International Conference on Particle-based Methods Fundamentals and Applications PARTICLES 2017
Description of concrete fracture at meso-level using Finite Element Method based on X-ray micro-ct images
 Description of concrete fracture at meso-level using Finite Element Method based on X-ray micro-ct images Ł. Skarżyński 1, J. Tejchman 1 1 Gdansk University of Technology, Narutowicza 11/12, 80-233 Gdańsk,
Description of concrete fracture at meso-level using Finite Element Method based on X-ray micro-ct images Ł. Skarżyński 1, J. Tejchman 1 1 Gdansk University of Technology, Narutowicza 11/12, 80-233 Gdańsk,
LATTICE MODELING OF FRACTURE PROCESSES IN NUMERICAL CONCRETE WITH IRREGULAR SHAPE AGGREGATES
 VIII International Conference on Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures FraMCoS-8 J.G.M. Van Mier, G. Ruiz, C. Andrade, R.C. Yu and X.X. Zhang (Eds) LATTICE MODELING OF FRACTURE PROCESSES
VIII International Conference on Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures FraMCoS-8 J.G.M. Van Mier, G. Ruiz, C. Andrade, R.C. Yu and X.X. Zhang (Eds) LATTICE MODELING OF FRACTURE PROCESSES
Investigations of fracture process in concrete using X-ray micro-ct
 Investigations of fracture process in concrete using X-ray micro-ct Ł. Skarżyński 1, J. Tejchman 1 1 Gdansk University of Technology, Narutowicza 11/12, 80-233 Gdańsk, Poland, Aims The main objective of
Investigations of fracture process in concrete using X-ray micro-ct Ł. Skarżyński 1, J. Tejchman 1 1 Gdansk University of Technology, Narutowicza 11/12, 80-233 Gdańsk, Poland, Aims The main objective of
C. T. Liu Air Force Research Laboratory AFRRL/PRSM 10 E. Saturn Blvd. Edwards AFB CA
 NEAR TIP BEHAVIOR IN A PARTICULATE COMPOSITE MATERIAL UNDER CONSTANT STRAIN RATE INCLUDING TEMPERATURE AND THICKNESS EFFECTS ABSTRACT C. T. Liu Air Force Research Laboratory AFRRL/PRSM 10 E. Saturn Blvd.
NEAR TIP BEHAVIOR IN A PARTICULATE COMPOSITE MATERIAL UNDER CONSTANT STRAIN RATE INCLUDING TEMPERATURE AND THICKNESS EFFECTS ABSTRACT C. T. Liu Air Force Research Laboratory AFRRL/PRSM 10 E. Saturn Blvd.
Modeling of Asphalt Concrete
 CHAPTER 1 Modeling of Asphalt Concrete Y. Richard Kim Introduction Asphalt concrete pavement, one of the largest infrastructure components in the United States, is a complex system that involves multiple
CHAPTER 1 Modeling of Asphalt Concrete Y. Richard Kim Introduction Asphalt concrete pavement, one of the largest infrastructure components in the United States, is a complex system that involves multiple
LONG-TERM CYCLIC TRIAXIAL TESTS WITH DEM SIMULATIONS
 Long-term cyclic triaxial tests with DEM simulations V International Conference on Particle-based Methods Fundamentals and Applications PARTICLES 2017 P. Wriggers, M. Bischoff, E. Oñate, D.R.J. Owen, &
Long-term cyclic triaxial tests with DEM simulations V International Conference on Particle-based Methods Fundamentals and Applications PARTICLES 2017 P. Wriggers, M. Bischoff, E. Oñate, D.R.J. Owen, &
An implicit non-local damage to crack transition framework for ductile materials involving a cohesive band model
 University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering MS49: Abstract 48 EMI 2018 An implicit non-local damage to crack transition framework for ductile materials involving a cohesive band model Julien
University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering MS49: Abstract 48 EMI 2018 An implicit non-local damage to crack transition framework for ductile materials involving a cohesive band model Julien
Some thoughts on the nonlinearity of cracks in structural materials
 The Modelling and Simulation Centre The University of Manchester Some thoughts on the nonlinearity of cracks in structural materials John R Yates Where, and what is, the crack tip? 2.0 mm 7.0 mm 2.0 mm
The Modelling and Simulation Centre The University of Manchester Some thoughts on the nonlinearity of cracks in structural materials John R Yates Where, and what is, the crack tip? 2.0 mm 7.0 mm 2.0 mm
CHAPTER 5 FINITE ELEMENT MODELING
 CHAPTER 5 FINITE ELEMENT MODELING 5.1 INTRODUCTION Masonry is a composite material with the building brick units and the mortar as the joining material, which are bonded together. Guinea [2000] 51 reported
CHAPTER 5 FINITE ELEMENT MODELING 5.1 INTRODUCTION Masonry is a composite material with the building brick units and the mortar as the joining material, which are bonded together. Guinea [2000] 51 reported
Dimensional Stability of Concrete
 Dimensional Stability of Concrete Concrete as a Composite Material Both cement paste and aggregates show linear elastic properties. The non-linear portion of the stress-strain curve for concrete is due
Dimensional Stability of Concrete Concrete as a Composite Material Both cement paste and aggregates show linear elastic properties. The non-linear portion of the stress-strain curve for concrete is due
Mesoscale modeling of failure in partially sintered metals and homogenization to macroscale
 9. LS-DYNA Forum, Bamberg 2010 Mesoscale modeling of failure in partially sintered metals and homogenization to macroscale Nathanaël Durr, Martin Sauer Fraunhofer Institute for High-Speed Dynamics, Freiburg,
9. LS-DYNA Forum, Bamberg 2010 Mesoscale modeling of failure in partially sintered metals and homogenization to macroscale Nathanaël Durr, Martin Sauer Fraunhofer Institute for High-Speed Dynamics, Freiburg,
An Integrated Material Characterization-Multiscale Model for the Prediction of Strain to Failure of Heterogeneous Aluminum Alloys
 An Integrated Material Characterization-Multiscale Model for the Prediction of Strain to Failure of Heterogeneous Aluminum Alloys Daniel Paquet 1 June 2010 1 Introduction An increasing demand for a drastic
An Integrated Material Characterization-Multiscale Model for the Prediction of Strain to Failure of Heterogeneous Aluminum Alloys Daniel Paquet 1 June 2010 1 Introduction An increasing demand for a drastic
Fracture Mechanics. External Course Siemens. Winter
 Fracture Mechanics External Course Siemens Winter 2011-12 Lars Damkilde Division for Structures, Materials and Geotechnics Department of Civil Engineering, Aalborg University 1 Presentation Background
Fracture Mechanics External Course Siemens Winter 2011-12 Lars Damkilde Division for Structures, Materials and Geotechnics Department of Civil Engineering, Aalborg University 1 Presentation Background
Purdue University School of Civil Engineering Geotechnical Engineering CE-597 Non-linear fracture mechanics Term Project
 Purdue University School of Civil Engineering Geotechnical Engineering CE-597 Non-linear fracture mechanics Term Project Numerical Simulation of Crack Propagation in Rocks under Uniaxial Compression Professor:
Purdue University School of Civil Engineering Geotechnical Engineering CE-597 Non-linear fracture mechanics Term Project Numerical Simulation of Crack Propagation in Rocks under Uniaxial Compression Professor:
Energy Dissipation Mechanism Based Materials and Materials Systems Design
 Energy Dissipation Mechanism Based Materials and Materials Systems Design Wing Kam Liu w-liu@northwestern.edu Walter P. Murphy Professor of Mechanical and Civil Engineering President, International Association
Energy Dissipation Mechanism Based Materials and Materials Systems Design Wing Kam Liu w-liu@northwestern.edu Walter P. Murphy Professor of Mechanical and Civil Engineering President, International Association
MODELLING AUTOGENOUS SHRINKAGE OF HYDRATING CEMENT PASTE
 MODELLING AUTOGENOUS SHRINKAGE OF HYDRATING CEMENT PASTE Ines Jaouadi (1), Amor Guidoum (2) and Karen Scrivener (3) (1) Laboratory of Construction Materials, EPFL, Switzerland (2) Laboratory of Construction
MODELLING AUTOGENOUS SHRINKAGE OF HYDRATING CEMENT PASTE Ines Jaouadi (1), Amor Guidoum (2) and Karen Scrivener (3) (1) Laboratory of Construction Materials, EPFL, Switzerland (2) Laboratory of Construction
A nonlocal cohesive zone model for finite thickness interfaces: mathematical formulation, numerical implementation and materials science applications
 A nonlocal cohesive zone model for finite thickness interfaces: mathematical formulation, numerical implementation and materials science applications Dr. Ing. Marco Paggi Politecnico di Torino, Dept. Structural
A nonlocal cohesive zone model for finite thickness interfaces: mathematical formulation, numerical implementation and materials science applications Dr. Ing. Marco Paggi Politecnico di Torino, Dept. Structural
Simulating Intact Rock Behaviour Using Bonded Particle and Bonded Block Models
 Simulating Intact Rock Behaviour Using Bonded Particle and Bonded Block Models Alexandr Turichshev John Hadjigeorgiou Seventh International Conference & Exhibition on Mass Mining MassMin 2016 / Sydney,
Simulating Intact Rock Behaviour Using Bonded Particle and Bonded Block Models Alexandr Turichshev John Hadjigeorgiou Seventh International Conference & Exhibition on Mass Mining MassMin 2016 / Sydney,
63.5 mm Launch Tube Steel Plate. Foam. To Multi-point Interferometer
 GRAIN LEVEL ANALYSIS OF CERAMIC MICROSTRUCTURES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT LOADING ABSTRACT Pablo D. Zavattieri and Horacio D. Espinosa Mechanical Engineering, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 A study
GRAIN LEVEL ANALYSIS OF CERAMIC MICROSTRUCTURES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT LOADING ABSTRACT Pablo D. Zavattieri and Horacio D. Espinosa Mechanical Engineering, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 A study
Structural Requirements of Bituminous Paving Mixtures
 A2D04: Committee on Characteristics of Bituminous Paving Mixtures To Meet Structural Requirements Chairman: Reynaldo Roque Structural Requirements of Bituminous Paving Mixtures AMY EPPS, Texas A&M University
A2D04: Committee on Characteristics of Bituminous Paving Mixtures To Meet Structural Requirements Chairman: Reynaldo Roque Structural Requirements of Bituminous Paving Mixtures AMY EPPS, Texas A&M University
Mechanical Behaviour of Materials Chapter 10 Fracture morpholgy
 Mechanical Behaviour of Materials Chapter 10 Fracture morpholgy Dr.-Ing. 郭瑞昭 Example of fracture Classification of fracture processes: Deformation behavior of materials elastic Linear-elastic fracture
Mechanical Behaviour of Materials Chapter 10 Fracture morpholgy Dr.-Ing. 郭瑞昭 Example of fracture Classification of fracture processes: Deformation behavior of materials elastic Linear-elastic fracture
Chapter 2: Mechanical Behavior of Materials
 Chapter : Mechanical Behavior of Materials Definition Mechanical behavior of a material relationship - its response (deformation) to an applied load or force Examples: strength, hardness, ductility, stiffness
Chapter : Mechanical Behavior of Materials Definition Mechanical behavior of a material relationship - its response (deformation) to an applied load or force Examples: strength, hardness, ductility, stiffness
Inclusion Effect on Heterogeneity of Excess Pore Water Pressure Distribution in Composite Clay
 Inclusion Effect on Heterogeneity of Excess Pore Water Pressure Distribution in Composite Clay J. Jalili Payame Noor University, Iran M. K. Jafari & A. Shafiee International Institute of Earthquake Engineering
Inclusion Effect on Heterogeneity of Excess Pore Water Pressure Distribution in Composite Clay J. Jalili Payame Noor University, Iran M. K. Jafari & A. Shafiee International Institute of Earthquake Engineering
Institute of Mechanics and Fluid Dynamics Research Group Solid Mechanics
 Institute of Mechanics and Fluid Dynamics Research Group Solid Mechanics Prof.Dr.rer.nat.habil. Meinhard Kuna Main research topics Fracture mechanical stress analysis and safety assessment of structural
Institute of Mechanics and Fluid Dynamics Research Group Solid Mechanics Prof.Dr.rer.nat.habil. Meinhard Kuna Main research topics Fracture mechanical stress analysis and safety assessment of structural
Basic concepts for Localization of deformation. Stress vs. displacement/velocity boundary conditions - unstable/stable processes
 Basic concepts for Localization of deformation Weakening vs. strengthening rheologies (P, T, porosity, fluids, grain size) positive vs. negative feedbacks Stress vs. displacement/velocity boundary conditions
Basic concepts for Localization of deformation Weakening vs. strengthening rheologies (P, T, porosity, fluids, grain size) positive vs. negative feedbacks Stress vs. displacement/velocity boundary conditions
3D LATTICE MODELING OF TENSILE TEST ON SIMULATED CEMENT PASTE AT MICROSCALE
 3D LATTICE MODELING OF TENSILE TEST ON SIMULATED CEMENT PASTE AT MICROSCALE Zhiwei Qian (1), Guang Ye (1, 2), E. Schlangen (1) and K. van Breugel (1) (1) Microlab, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences,
3D LATTICE MODELING OF TENSILE TEST ON SIMULATED CEMENT PASTE AT MICROSCALE Zhiwei Qian (1), Guang Ye (1, 2), E. Schlangen (1) and K. van Breugel (1) (1) Microlab, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences,
3-D Microstructural Modeling and Simulation of Microstress for Nickel Superalloys
 3-D Microstructural Modeling and Simulation of Microstress for Nickel Superalloys VEXTEC Corporation, 523 Virginia Way Suite C-2, Brentwood, TN 37027 USA Abstract Statistical elastic micro-stress analysis
3-D Microstructural Modeling and Simulation of Microstress for Nickel Superalloys VEXTEC Corporation, 523 Virginia Way Suite C-2, Brentwood, TN 37027 USA Abstract Statistical elastic micro-stress analysis
1) Fracture, ductile and brittle fracture 2) Fracture mechanics
 Module-08 Failure 1) Fracture, ductile and brittle fracture 2) Fracture mechanics Contents 3) Impact fracture, ductile-to-brittle transition 4) Fatigue, crack initiation and propagation, crack propagation
Module-08 Failure 1) Fracture, ductile and brittle fracture 2) Fracture mechanics Contents 3) Impact fracture, ductile-to-brittle transition 4) Fatigue, crack initiation and propagation, crack propagation
M.C. Christianson Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA
 UDEC Simulation of Triaxial Testing of Lithophysal Tuff UDEC Simulation of Triaxial Testing of Lithophysal Tuff M.C. Christianson Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA 7 M.P. Board
UDEC Simulation of Triaxial Testing of Lithophysal Tuff UDEC Simulation of Triaxial Testing of Lithophysal Tuff M.C. Christianson Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA 7 M.P. Board
STP1220-EB/Aug Subject Index
 STP1220-EB/Aug. 1995 Subject Index A Adhesive bonding, 222, 268 Aircraft, aging, 546, 557 Alumina, 19 Aluminum, 222 alloys, 358, 467, 546 copper alloy, 502 lithium alloy, 502 Antiplane shear effect, 191
STP1220-EB/Aug. 1995 Subject Index A Adhesive bonding, 222, 268 Aircraft, aging, 546, 557 Alumina, 19 Aluminum, 222 alloys, 358, 467, 546 copper alloy, 502 lithium alloy, 502 Antiplane shear effect, 191
A Modeling Platform for Ultrasonic Immersion Testing of Polycrystalline Materials with Flaws
 11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic A Modeling Platform for Ultrasonic Immersion Testing of Polycrystalline Materials with Flaws
11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic A Modeling Platform for Ultrasonic Immersion Testing of Polycrystalline Materials with Flaws
Index. STP523-EB/Jul Magnitudes (see Reliability and Reproducibility under Inplace, Maximum, Minimum, and Relative density) Types, 75, 77, 488
 STP523-EB/Jul. 1973 Index A Allowable fines, 6, 349, 350, 355, 359 Angularity (see Roundness criteria) C Coarse aggregate correction, 221, 224-231, 431 Compressibility Plate load, 277, 395 Sensitivity,
STP523-EB/Jul. 1973 Index A Allowable fines, 6, 349, 350, 355, 359 Angularity (see Roundness criteria) C Coarse aggregate correction, 221, 224-231, 431 Compressibility Plate load, 277, 395 Sensitivity,
Doç. Dr. Halit YAZICI
 Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Đnşaat Mühendisliği Bölümü DIMENSIONAL STABILITY of CONCRETE Doç. Dr. Halit YAZICI http://kisi.deu.edu.tr/halit.yazici/ CIE 5073 DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF CONCRETE Three hours lecture
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Đnşaat Mühendisliği Bölümü DIMENSIONAL STABILITY of CONCRETE Doç. Dr. Halit YAZICI http://kisi.deu.edu.tr/halit.yazici/ CIE 5073 DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF CONCRETE Three hours lecture
INSTRUCTION PROFESSOR K. KOMVOPOULOS. Mechanical Behavior of Engineering Materials (ME 108) (Undergraduate course, junior/senior level)
 INSTRUCTION PROFESSOR K. KOMVOPOULOS. Mechanical Behavior of Engineering Materials (ME 108) (Undergraduate course, junior/senior level) Part I Microstructure and Deformation of Materials Alloying and Hardening
INSTRUCTION PROFESSOR K. KOMVOPOULOS. Mechanical Behavior of Engineering Materials (ME 108) (Undergraduate course, junior/senior level) Part I Microstructure and Deformation of Materials Alloying and Hardening
5th Pan American Conference for NDT 2-6 October 2011, Cancun, Mexico. Scanning Electron Microscopy to Examine Concrete with Carbon Nanofibers
 Scanning Electron Microscopy to Examine Concrete with Carbon Nanofibers Shane M. PALMQUIST 1, Edward KINTZEL 2, Keith ANDREW 2 1 Department of Engineering, Western Kentucky University; Bowling Green, Kentucky,
Scanning Electron Microscopy to Examine Concrete with Carbon Nanofibers Shane M. PALMQUIST 1, Edward KINTZEL 2, Keith ANDREW 2 1 Department of Engineering, Western Kentucky University; Bowling Green, Kentucky,
Chapter 2. Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties
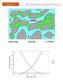 Chapter 2 Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties Table of Contents Pages 1. Introduction... 3 2. Rock and Minerals... 3 3. Porosity... 4 3.1. Porosity Classification... 6 3.2. Range of porosity values for
Chapter 2 Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties Table of Contents Pages 1. Introduction... 3 2. Rock and Minerals... 3 3. Porosity... 4 3.1. Porosity Classification... 6 3.2. Range of porosity values for
Numerical Modeling and Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry Walls
 Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture 11 (2017) 870-878 doi: 10.17265/1934-7359/2017.09.006 D DAVID PUBLISHING Numerical Modeling and Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry Walls Isak Idrizi 1 and Zekirija
Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture 11 (2017) 870-878 doi: 10.17265/1934-7359/2017.09.006 D DAVID PUBLISHING Numerical Modeling and Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry Walls Isak Idrizi 1 and Zekirija
Advances in Engineering Research, volume 103 Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2016)
 Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2016) Modeling and Study of Fracture and Delamination in a Packaging Laminate De-Feng ZHANG 1,2, Md. Shafiqul
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2016) Modeling and Study of Fracture and Delamination in a Packaging Laminate De-Feng ZHANG 1,2, Md. Shafiqul
Modeling of Coupled Nonlinear Shear and Flexural Responses in Medium-Rise RC Walls
 ing of Coupled Nonlinear Shear and Flexural Responses in Medium-Rise RC Walls Burak HOROZ 1, M.Fethi GÜLLÜ 2, and Kutay ORAKÇAL 3 1 Research Assistant Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey 2 Research Assistant
ing of Coupled Nonlinear Shear and Flexural Responses in Medium-Rise RC Walls Burak HOROZ 1, M.Fethi GÜLLÜ 2, and Kutay ORAKÇAL 3 1 Research Assistant Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey 2 Research Assistant
Fracture. Brittle vs. Ductile Fracture Ductile materials more plastic deformation and energy absorption (toughness) before fracture.
 1- Fracture Fracture: Separation of a body into pieces due to stress, at temperatures below the melting point. Steps in fracture: 1-Crack formation 2-Crack propagation There are two modes of fracture depending
1- Fracture Fracture: Separation of a body into pieces due to stress, at temperatures below the melting point. Steps in fracture: 1-Crack formation 2-Crack propagation There are two modes of fracture depending
Importance of tailings properties for closure
 Proceedings of Mine Closure Solutions, 2014 April 26 30, 2014, Ouro Preto, Minas Gerais, Brazil Published by InfoMine, 2014 InfoMine, ISBN: 978-0-9917905-4-8 Importance of tailings properties for closure
Proceedings of Mine Closure Solutions, 2014 April 26 30, 2014, Ouro Preto, Minas Gerais, Brazil Published by InfoMine, 2014 InfoMine, ISBN: 978-0-9917905-4-8 Importance of tailings properties for closure
Chapter 14 Fracture Mechanics
 Chapter 14 Fracture Mechanics Stress Concentrations - discontinuities typically exist in structures (holes, cross-section changes, keyways, etc) - discontinuities locally increase stress (stress raisers)
Chapter 14 Fracture Mechanics Stress Concentrations - discontinuities typically exist in structures (holes, cross-section changes, keyways, etc) - discontinuities locally increase stress (stress raisers)
A variationally consistent coupled isotropic elasto-plastic damage model for the analysis of LCF at finite strains
 A variationally consistent coupled isotropic elasto-plastic damage model for the analysis of LCF at finite strains O. Kintzel, J. Mosler GKSS Forschungszentrum Geesthacht Institute of Materials Research
A variationally consistent coupled isotropic elasto-plastic damage model for the analysis of LCF at finite strains O. Kintzel, J. Mosler GKSS Forschungszentrum Geesthacht Institute of Materials Research
ME -215 ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND PROCESES
 ME -215 ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND PROCESES Instructor: Office: MEC325, Tel.: 973-642-7455 E-mail: samardzi@njit.edu PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS Chapter 3 Materials Properties STRUCTURE PERFORMANCE PROCESSING
ME -215 ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND PROCESES Instructor: Office: MEC325, Tel.: 973-642-7455 E-mail: samardzi@njit.edu PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS Chapter 3 Materials Properties STRUCTURE PERFORMANCE PROCESSING
DISCRETE ELEMENT SIM ULATION OF AN ASSEMBLY OF IRREGULARLY-SHAPED GRAINS: QUANTITATIVE COMPARISON WITH EXPERIMENTS
 DISCRETE ELEMENT SIM ULATION OF AN ASSEMBLY OF IRREGULARLY-SHAPED GRAINS: QUANTITATIVE COMPARISON WITH EXPERIMENTS Takashi Matsushima 1, Hidetaka Saomoto 2, Masaaki Matsumoto 3, Kengo Toda 4 and Yasuo
DISCRETE ELEMENT SIM ULATION OF AN ASSEMBLY OF IRREGULARLY-SHAPED GRAINS: QUANTITATIVE COMPARISON WITH EXPERIMENTS Takashi Matsushima 1, Hidetaka Saomoto 2, Masaaki Matsumoto 3, Kengo Toda 4 and Yasuo
Simulation to the Cyclic Deformation of Polycrystalline Aluminum Alloy Using. Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Method
 APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 213, Singapore Simulation to the Cyclic Deformation of Polycrystalline Aluminum Alloy Using Abstract Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Method Juan Luo, Guozheng Kang*, Mingxing
APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 213, Singapore Simulation to the Cyclic Deformation of Polycrystalline Aluminum Alloy Using Abstract Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Method Juan Luo, Guozheng Kang*, Mingxing
finite element Nimavar ABSTRACT : of masonry specimens are a continuum calibrating Masonry method essays. The second step to build the main structure
 A new approach to numerical modeling of the masonry structures using explicit dynamic finite elements method Nima Taghi Bekloo Nimavar ArtaVage consulting engineers, Vice president/structural engineer,
A new approach to numerical modeling of the masonry structures using explicit dynamic finite elements method Nima Taghi Bekloo Nimavar ArtaVage consulting engineers, Vice president/structural engineer,
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 6, 1994 WIT Press, ISSN
 Finite element modelling of asphalt concrete microstructure K. Sepehr, O.J. Svec, Z.Q. Yue, H.M. El Hussein Centre for Surface Transportation Technology, National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, Ontario,
Finite element modelling of asphalt concrete microstructure K. Sepehr, O.J. Svec, Z.Q. Yue, H.M. El Hussein Centre for Surface Transportation Technology, National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, Ontario,
STIFFNESS, FAILURE & FATIGUE OF FIBER REINFORCED PLASTICS
 STIFFNESS, FAILURE & FATIGUE OF FIBER REINFORCED PLASTICS Jan Seyfarth, Roger Assaker, Maxime Melchior e-xstream engineering (L), Z. I. Bommelscheuer, L-4940 Bascharage, Luxembourg Abstract Following the
STIFFNESS, FAILURE & FATIGUE OF FIBER REINFORCED PLASTICS Jan Seyfarth, Roger Assaker, Maxime Melchior e-xstream engineering (L), Z. I. Bommelscheuer, L-4940 Bascharage, Luxembourg Abstract Following the
Shear Strength of Tire Derived Aggregate (TDA) California State University, Chico
 Shear Strength of Tire Derived Aggregate (TDA) California State University, Chico Background Information At the end of 2005, the U.S. generated approximately 300 million scrap tires Historically, these
Shear Strength of Tire Derived Aggregate (TDA) California State University, Chico Background Information At the end of 2005, the U.S. generated approximately 300 million scrap tires Historically, these
Chapter Outline: Failure
 Chapter Outline: Failure How do Materials Break? Ductile vs. brittle fracture Principles of fracture mechanics Stress concentration Impact fracture testing Fatigue (cyclic stresses) Cyclic stresses, the
Chapter Outline: Failure How do Materials Break? Ductile vs. brittle fracture Principles of fracture mechanics Stress concentration Impact fracture testing Fatigue (cyclic stresses) Cyclic stresses, the
Constitutive models: Elasto-Plastic Models
 Plasticity is the property of the solid body to deform under applied external force and to possess permanent or temporal residual deformation after applied load is removed. Main feature of plasticity:
Plasticity is the property of the solid body to deform under applied external force and to possess permanent or temporal residual deformation after applied load is removed. Main feature of plasticity:
MSE200 Lecture 9 (CH ) Mechanical Properties II Instructor: Yuntian Zhu
 MSE200 Lecture 9 (CH. 7.1-7.2) Mechanical Properties II Instructor: Yuntian Zhu Objectives/outcomes: You will learn the following: Fracture of metals. Ductile and brittle fracture. Toughness and impact
MSE200 Lecture 9 (CH. 7.1-7.2) Mechanical Properties II Instructor: Yuntian Zhu Objectives/outcomes: You will learn the following: Fracture of metals. Ductile and brittle fracture. Toughness and impact
CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading
 CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading Some machine elements are subjected to statics loads and for such elements, statics failure theories are used to predict failure (yielding or fracture).
CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading Some machine elements are subjected to statics loads and for such elements, statics failure theories are used to predict failure (yielding or fracture).
Numerical Modeling of the Crashworthiness of Thin-Walled Cast Magnesium Components
 Numerical Modeling of the Crashworthiness of Thin-Walled Cast Magnesium Components Cato Dørum 1, Odd S. Hopperstad 2, Magnus Langseth 2, Hariaokto Hooputra 3, Stefan Weyer 3 1 SINTEF Materials and Chemistry,
Numerical Modeling of the Crashworthiness of Thin-Walled Cast Magnesium Components Cato Dørum 1, Odd S. Hopperstad 2, Magnus Langseth 2, Hariaokto Hooputra 3, Stefan Weyer 3 1 SINTEF Materials and Chemistry,
Study on the Stability and Reliability of the Whole Life Cycle of Tunnel Structure Youjiang Yang
 2nd International Conference on Machinery, Materials Engineering, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology (MMECEB 2015) Study on the Stability and Reliability of the Whole Life Cycle of Tunnel Structure
2nd International Conference on Machinery, Materials Engineering, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology (MMECEB 2015) Study on the Stability and Reliability of the Whole Life Cycle of Tunnel Structure
Assessment of Masonry Arch Bridges using FEM and Elasto-Plastic Model
 Assessment of Masonry Arch Bridges using FEM and Elasto-Plastic Model LUCIO NOBILE, VERONICA BARTOLOMEO DICAM Department-Campus of Cesena University of Bologna Via Cavalcavia 61-47521 Cesena ITALY lucio.nobile@unibo
Assessment of Masonry Arch Bridges using FEM and Elasto-Plastic Model LUCIO NOBILE, VERONICA BARTOLOMEO DICAM Department-Campus of Cesena University of Bologna Via Cavalcavia 61-47521 Cesena ITALY lucio.nobile@unibo
IJSER 1. INTRODUCTION 2. LITERATURE REVIEW. Indramohan 1, Anand Singh 2,Pankaj Goswami 3
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 12, December-2016 7 Stress-strain behaviour of railway ballast under static loading using Finite element Method Indramohan 1,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 12, December-2016 7 Stress-strain behaviour of railway ballast under static loading using Finite element Method Indramohan 1,
Fatigue Analysis of a Wind Turbine Power Train
 Fatigue Analysis of a Wind Turbine Power Train N. Ghareeb; Inst. of General Mechanics (IAM), Aachen University of Technology, RWTH Aachen Y. Radovcic; SAMTECH Germany GmbH, Hamburg EXTERNAL ARTICLE English
Fatigue Analysis of a Wind Turbine Power Train N. Ghareeb; Inst. of General Mechanics (IAM), Aachen University of Technology, RWTH Aachen Y. Radovcic; SAMTECH Germany GmbH, Hamburg EXTERNAL ARTICLE English
MULTI-SCALE APPROACH TO INVESTIGATE THE TENSILE AND FRACTURE BEHAVIOR OF NANO COMPOSITE MATERIALS
 MULTI-SCALE APPROACH TO INVESTIGATE THE TENSILE AND FRACTURE BEHAVIOR OF NANO COMPOSITE MATERIALS Dr. C. T. Liu AFRL/PRSM, 10 E. Saturn Blvd. Edwards AFB CA 93524-7680 Tel. No. 661-275-5642; Fax No.661-275-5435
MULTI-SCALE APPROACH TO INVESTIGATE THE TENSILE AND FRACTURE BEHAVIOR OF NANO COMPOSITE MATERIALS Dr. C. T. Liu AFRL/PRSM, 10 E. Saturn Blvd. Edwards AFB CA 93524-7680 Tel. No. 661-275-5642; Fax No.661-275-5435
True Stress and True Strain
 True Stress and True Strain For engineering stress ( ) and engineering strain ( ), the original (gauge) dimensions of specimen are employed. However, length and cross-sectional area change in plastic region.
True Stress and True Strain For engineering stress ( ) and engineering strain ( ), the original (gauge) dimensions of specimen are employed. However, length and cross-sectional area change in plastic region.
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF COLLAPSE OF MASONRY ARCHES
 EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF COLLAPSE OF MASONRY ARCHES Łukasz Hojdys*, Tomasz Kamiński + & Piotr Krajewski* * Cracow University of Technology, Institute for Building Materials and Structures
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF COLLAPSE OF MASONRY ARCHES Łukasz Hojdys*, Tomasz Kamiński + & Piotr Krajewski* * Cracow University of Technology, Institute for Building Materials and Structures
This material may be downloaded for personal use only. Any other use requires prior permission of the American Society of Civil Engineers.
 Citation: Jitsangiam P. and Nikraz H. and Siripun K. 2009. Characterization of Hydrated Cement Treated Crushed Rock Base (HCTCRB) as a Road Base Material in Western Australia, in Steyn, W. and Jenkins,
Citation: Jitsangiam P. and Nikraz H. and Siripun K. 2009. Characterization of Hydrated Cement Treated Crushed Rock Base (HCTCRB) as a Road Base Material in Western Australia, in Steyn, W. and Jenkins,
2D and 3D Simulation of Ductile Crack Propagation by Plastic Collapse of Micro-ligaments 1. Geralf Hütter*, Lutz Zybell, Uwe Mühlich and Meinhard Kuna
 2D and 3D Simulation of Ductile Crack Propagation by Plastic Collapse of Micro-ligaments 1 Geralf Hütter*, Lutz Zybell, Uwe Mühlich and Meinhard Kuna TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Institute of Mechanics and
2D and 3D Simulation of Ductile Crack Propagation by Plastic Collapse of Micro-ligaments 1 Geralf Hütter*, Lutz Zybell, Uwe Mühlich and Meinhard Kuna TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Institute of Mechanics and
Electronics materials - Stress and its effect on materials
 Electronics materials - Stress and its effect on materials Introduction You will have already seen in Mechanical properties of metals that stress on materials results in strain first elastic strain and
Electronics materials - Stress and its effect on materials Introduction You will have already seen in Mechanical properties of metals that stress on materials results in strain first elastic strain and
CHAPTER 7 ANALYTICAL PROGRAMME USING ABAQUS
 87 CHAPTER 7 ANALYTICAL PROGRAMME USING ABAQUS 7.1 GENERAL With the advances in modern computing techniques, finite element analysis has become a practical and powerful tool for engineering analysis and
87 CHAPTER 7 ANALYTICAL PROGRAMME USING ABAQUS 7.1 GENERAL With the advances in modern computing techniques, finite element analysis has become a practical and powerful tool for engineering analysis and
Geogrid-Aggregate Interlocking Mechanism Investigated via Discrete Element Modeling
 Geosynthetics 2015 February 15-18, Portland, Oregon Geogrid-Aggregate Interlocking Mechanism Investigated via Discrete Element Modeling Yu Qian, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA, yuqian1@illinois.edu
Geosynthetics 2015 February 15-18, Portland, Oregon Geogrid-Aggregate Interlocking Mechanism Investigated via Discrete Element Modeling Yu Qian, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA, yuqian1@illinois.edu
COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool. Faculty of Civil Engineering UiTM, Malaysia
 COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool Faculty of Civil Engineering, Malaysia Name : COURSE CONTENTS Use of Plaxis Getting Started Exercise 1: Elastic analysis of drained footing
COURSE ON COMPUTATIONAL GEOTECHNICS A Geotechnical Design Tool Faculty of Civil Engineering, Malaysia Name : COURSE CONTENTS Use of Plaxis Getting Started Exercise 1: Elastic analysis of drained footing
SHEAR STRENGTH CHARACTERISTICS AND STATIC RESPONSE OF SAND-TIRE CRUMB MIXTURES FOR SEISMIC ISOLATION
 SHEAR STRENGTH CHARACTERISTICS AND STATIC RESPONSE OF SAND-TIRE CRUMB MIXTURES FOR SEISMIC ISOLATION Anbazhagan Panjamani*, Manohar D.R. Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore,
SHEAR STRENGTH CHARACTERISTICS AND STATIC RESPONSE OF SAND-TIRE CRUMB MIXTURES FOR SEISMIC ISOLATION Anbazhagan Panjamani*, Manohar D.R. Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore,
Compressibility of Soil. Chapter 11
 Compressibility of Soil Chapter 11 TOPICS INTRODUCTION ELASTIC SETTLEMENT Stress distribution in soil masses CONSOLIDATION SETTLEMENT Fundamentals of consolidation Calculation of 1-D Consolidation Settlement
Compressibility of Soil Chapter 11 TOPICS INTRODUCTION ELASTIC SETTLEMENT Stress distribution in soil masses CONSOLIDATION SETTLEMENT Fundamentals of consolidation Calculation of 1-D Consolidation Settlement
Modelling and testing of Thermoplastic composite parts integrating process simulation
 Modelling and testing of Thermoplastic composite parts integrating process simulation Coordinator: Prof. Luigi Garibaldi Tutor: Prof. Massimiliana Carello Nithin Amirth Jayasree (S221262) PhD Research
Modelling and testing of Thermoplastic composite parts integrating process simulation Coordinator: Prof. Luigi Garibaldi Tutor: Prof. Massimiliana Carello Nithin Amirth Jayasree (S221262) PhD Research
MODELLING THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF MONUMENTAL MASONRY STRUCTURES
 MODELLING THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF MONUMENTAL MASONRY STRUCTURES J. AZEVEDO 1, G. SINCRAIAN 2 1 Professor, 2 Research Assistant Civil Engineering and Architecture Department, Instituto Superior Técnico,
MODELLING THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF MONUMENTAL MASONRY STRUCTURES J. AZEVEDO 1, G. SINCRAIAN 2 1 Professor, 2 Research Assistant Civil Engineering and Architecture Department, Instituto Superior Técnico,
FAILURE MECHANISM OF Cu-Al 2 O 3 MICRO AND NANOMATERIALS OBSERVED BY "IN-SITU TENSILE TEST IN SEM"
 Powder Metallurgy Progress, Vol.14 (2014), No 4 228 FAILURE MECHANISM OF Cu-Al 2 O 3 MICRO AND NANOMATERIALS OBSERVED BY "IN-SITU TENSILE TEST IN SEM" M. Besterci, K. Sülleiová, B. Ballóková, O. Velgosová,
Powder Metallurgy Progress, Vol.14 (2014), No 4 228 FAILURE MECHANISM OF Cu-Al 2 O 3 MICRO AND NANOMATERIALS OBSERVED BY "IN-SITU TENSILE TEST IN SEM" M. Besterci, K. Sülleiová, B. Ballóková, O. Velgosová,
Impact Fatigue Failure Investigation of HVOF Coatings
 C. N. David, 1 M. A. Athanasiou, 1 K. G. Anthymidis, 1 and P. K. Gotsis 1 Journal of ASTM International, Vol. 5, No. 6 Paper ID JAI101571 Available online at www.astm.org Impact Fatigue Failure Investigation
C. N. David, 1 M. A. Athanasiou, 1 K. G. Anthymidis, 1 and P. K. Gotsis 1 Journal of ASTM International, Vol. 5, No. 6 Paper ID JAI101571 Available online at www.astm.org Impact Fatigue Failure Investigation
Stress and Strain Distributions During Compressive Deformation of Titanium Alloy Affected by Microstructure
 Stress and Strain Distributions During Compressive Deformation of Titanium Alloy Affected by Microstructure Zhao, Q., Wu, G., & Sha, W. (2013). Stress and Strain Distributions During Compressive Deformation
Stress and Strain Distributions During Compressive Deformation of Titanium Alloy Affected by Microstructure Zhao, Q., Wu, G., & Sha, W. (2013). Stress and Strain Distributions During Compressive Deformation
where n is known as strain hardening exponent.
 5.1 Flow stress: Flow stress is the stress required to sustain a certain plastic strain on the material. Flow stress can be determined form simple uniaxial tensile test, homogeneous compression test, plane
5.1 Flow stress: Flow stress is the stress required to sustain a certain plastic strain on the material. Flow stress can be determined form simple uniaxial tensile test, homogeneous compression test, plane
K. M. Nemati and P. J.M. Monteiro
 EFFECT OF CONFNEMENT ON THE FRACTURE BEHAVOR OF CONCRETE UNDER COMPRESSON K. M. Nemati and P. J.M. Monteiro Department of Civil Engineering Division of Structural Engineering, Mechanics, and Materials
EFFECT OF CONFNEMENT ON THE FRACTURE BEHAVOR OF CONCRETE UNDER COMPRESSON K. M. Nemati and P. J.M. Monteiro Department of Civil Engineering Division of Structural Engineering, Mechanics, and Materials
Numerical Investigations on the Mechanical Properties of Adhesively Bonded Hollow Sphere Structures
 Numerical Investigations on the Mechanical Properties of Adhesively Bonded Hollow Sphere Structures THOMAS FIEDLER*, ANDREAS ÖCHSNER AND JOSÉ GRÁCIO Centre for Mechanical Technology and Automation, Department
Numerical Investigations on the Mechanical Properties of Adhesively Bonded Hollow Sphere Structures THOMAS FIEDLER*, ANDREAS ÖCHSNER AND JOSÉ GRÁCIO Centre for Mechanical Technology and Automation, Department
Multiscale Modeling of Metallic Materials Containing Embedded Particles
 Multiscale Modeling of Metallic Materials Containing Embedded Particles D. R. Phillips * NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA, 23681-2199 E. Iesulauro Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 14853 and E.
Multiscale Modeling of Metallic Materials Containing Embedded Particles D. R. Phillips * NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA, 23681-2199 E. Iesulauro Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 14853 and E.
Bituminous mix design
 Bituminous mix design Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Evolution of road surface 2 2.1 Objectives of mix design..............................
Bituminous mix design Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Evolution of road surface 2 2.1 Objectives of mix design..............................
Fiber Reinforced Concrete (FRC)
 Progress in Fiber Reinforced Concrete (FRC) Concrete is relatively brittle, and its tensile strength is typically only about one tenths of its compressive strength. Regular concrete is therefore normally
Progress in Fiber Reinforced Concrete (FRC) Concrete is relatively brittle, and its tensile strength is typically only about one tenths of its compressive strength. Regular concrete is therefore normally
RECENT ADVANCES IN MODELLING DUCTILE RUPTURE
 RECENT ADVANCES IN MODELLING DUCTILE RUPTURE A.A. Benzerga 1, J. Besson and A. Pineau 1 Department of Aerospace Engineering, Texas A & M University, College Station, TX 77845, USA Ecole des Mines de Paris,
RECENT ADVANCES IN MODELLING DUCTILE RUPTURE A.A. Benzerga 1, J. Besson and A. Pineau 1 Department of Aerospace Engineering, Texas A & M University, College Station, TX 77845, USA Ecole des Mines de Paris,
FME201 Solid & Structural Mechanics I Dr.Hussein Jama Office 414
 FME201 Solid & Structural Mechanics I Dr.Hussein Jama Hussein.jama@uobi.ac.ke Office 414 Lecture: Mon 11am -1pm (CELT) Tutorial Tue 12-1pm (E207) 10/1/2013 1 CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Show relationship of stress
FME201 Solid & Structural Mechanics I Dr.Hussein Jama Hussein.jama@uobi.ac.ke Office 414 Lecture: Mon 11am -1pm (CELT) Tutorial Tue 12-1pm (E207) 10/1/2013 1 CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Show relationship of stress
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF DUCTILE FAILURE IN EXTRUDED ALUMINIUM ALLOYS USING A COUPLED MODEL OF ELASTO-PLASTICITY AND DAMAGE
 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF DUCTILE FAILURE IN EXTRUDED ALUMINIUM ALLOYS USING A COUPLED MODEL OF ELASTO-PLASTICITY AND DAMAGE O.-G. Lademo*, O.S. Hopperstad, T. Berstad and M. Langseth Structural Impact
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF DUCTILE FAILURE IN EXTRUDED ALUMINIUM ALLOYS USING A COUPLED MODEL OF ELASTO-PLASTICITY AND DAMAGE O.-G. Lademo*, O.S. Hopperstad, T. Berstad and M. Langseth Structural Impact
Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Composite Cantilever Beam with External Prestressing
 Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Composite Cantilever Beam with External Prestressing R. I. Liban, N. Tayşi 1 Abstract This paper deals with a nonlinear finite element analysis to examine the behavior
Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Composite Cantilever Beam with External Prestressing R. I. Liban, N. Tayşi 1 Abstract This paper deals with a nonlinear finite element analysis to examine the behavior
Chapter 7. Mechanical properties 7.1. Introduction 7.2. Stress-strain concepts and behaviour 7.3. Mechanical behaviour of metals 7.4.
 Chapter 7. Mechanical properties 7.1. Introduction 7.2. Stress-strain concepts and behaviour 7.3. Mechanical behaviour of metals 7.4. Mechanical behaviour of ceramics 7.5. Mechanical behaviour of polymers
Chapter 7. Mechanical properties 7.1. Introduction 7.2. Stress-strain concepts and behaviour 7.3. Mechanical behaviour of metals 7.4. Mechanical behaviour of ceramics 7.5. Mechanical behaviour of polymers
A Comparative Study of Failure with Incremental Forming
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS A Comparative Study of Failure with Incremental Forming To cite this article: S.H. Wu et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 734 032065 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS A Comparative Study of Failure with Incremental Forming To cite this article: S.H. Wu et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 734 032065 View the article
Reduced Ductility due to Local Variation in Material Properties for 3D-printed Components
 Reduced Ductility due to Local Variation in Material Properties for 3D-printed Components T. Tryland SINTEF Raufoss Manufacturing, Raufoss, Norway 1 Background It is often useful to have a physical model
Reduced Ductility due to Local Variation in Material Properties for 3D-printed Components T. Tryland SINTEF Raufoss Manufacturing, Raufoss, Norway 1 Background It is often useful to have a physical model
Certification of Discontinuous Composite Material Forms for Aircraft Structures: Stiffness and Strength Predictions
 Certification of Discontinuous Composite Material Forms for Aircraft Structures: Stiffness and Strength Predictions Karen Harban and Mark Tuttle Dept Mechanical Engineering University of Washington AMTAS
Certification of Discontinuous Composite Material Forms for Aircraft Structures: Stiffness and Strength Predictions Karen Harban and Mark Tuttle Dept Mechanical Engineering University of Washington AMTAS
Influence of particles-matrix interphase on stress distribution in particulate composite with polymer matrix
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) 143-148 Influence of particles-matrix interphase on stress distribution in particulate composite with polymer matrix Z. Majer a,b, *, P. Hutař a,, L. Náhlík
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) 143-148 Influence of particles-matrix interphase on stress distribution in particulate composite with polymer matrix Z. Majer a,b, *, P. Hutař a,, L. Náhlík
7. The diagram below represents cross sections of equal-size beakers A, B, and C filled with beads.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents four tubes, labeled A, B, C, and D, each containing 150 ml of sediments. Tubes
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents four tubes, labeled A, B, C, and D, each containing 150 ml of sediments. Tubes
A new mixed mode fracture test specimen covering positive and negative values of T-stress
 Engineering Solid Mechanics (014) 67-7 Contents lists available at GrowingScience Engineering Solid Mechanics homepage: www.growingscience.com/esm A new mixed mode fracture test specimen covering positive
Engineering Solid Mechanics (014) 67-7 Contents lists available at GrowingScience Engineering Solid Mechanics homepage: www.growingscience.com/esm A new mixed mode fracture test specimen covering positive
The influence of transition phases on the damage behaviour of an Al/10vol.%SiC composite
 Computational Materials Science 37 (2006) 119 133 www.elsevier.com/locate/commatsci The influence of transition phases on the damage behaviour of an Al/10vol.%SiC composite G. Tursun a, U. Weber a,b, *,
Computational Materials Science 37 (2006) 119 133 www.elsevier.com/locate/commatsci The influence of transition phases on the damage behaviour of an Al/10vol.%SiC composite G. Tursun a, U. Weber a,b, *,
CRACKED BRAZILIAN TESTS OF LAMELLAR TIAL
 CRACKED BRAZILIAN TESTS OF LAMELLAR TIAL Gunes Uzer1,a, Fu-pen Chiang2,a, Andrew H. Rosenberger3,b 1 SUNY Graduate Student, 2 SUNY Distinguished Professor& Chair 3 Materials and Manufacturing Directorate,
CRACKED BRAZILIAN TESTS OF LAMELLAR TIAL Gunes Uzer1,a, Fu-pen Chiang2,a, Andrew H. Rosenberger3,b 1 SUNY Graduate Student, 2 SUNY Distinguished Professor& Chair 3 Materials and Manufacturing Directorate,
Replicating Brittle and Hard Rocks Using 3D Printing with Applications to Rock Dynamics and Crack Propagation
 International Geotechnics Symposium cum International Meeting of CSRME 14 th Biennial National Congress Replicating Brittle and Hard Rocks Using 3D Printing with Applications to Rock Dynamics and Crack
International Geotechnics Symposium cum International Meeting of CSRME 14 th Biennial National Congress Replicating Brittle and Hard Rocks Using 3D Printing with Applications to Rock Dynamics and Crack
CHAPTER 6 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 105 CHAPTER 6 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Several theoretical approaches are considered to analyze the yielding and buckling failure modes of castellated beams. Elastic Finite Element Analysis
105 CHAPTER 6 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Several theoretical approaches are considered to analyze the yielding and buckling failure modes of castellated beams. Elastic Finite Element Analysis
Failure of Heterogenous Composites due to Thermal Stresses in Presence of Pre-Cracks
 Failure of Heterogenous Composites due to Thermal Stresses in Presence of Pre-Cracks EL-SHEIKHY Refat* and NAKA Masaaki** Abstract Heterogeneous composite plates including inclined cracks were exposed
Failure of Heterogenous Composites due to Thermal Stresses in Presence of Pre-Cracks EL-SHEIKHY Refat* and NAKA Masaaki** Abstract Heterogeneous composite plates including inclined cracks were exposed
EFFECT OF LOCAL WALL THINNING ON FRACTURE BEHAVIOR OF STRAIGHT PIPE
 ECF EFFECT OF LOCAL WALL THINNING ON FRACTURE BEHAVIOR OF STRAIGHT PIPE Masato Ono, Ki-Woo Nam*, Koji Takahashi, Kotoji Ando Department of Safety & Energy Engineering, Yokohama National University 79-
ECF EFFECT OF LOCAL WALL THINNING ON FRACTURE BEHAVIOR OF STRAIGHT PIPE Masato Ono, Ki-Woo Nam*, Koji Takahashi, Kotoji Ando Department of Safety & Energy Engineering, Yokohama National University 79-
27th Risø International Symposium on Materials Science, Polymer Composite Materials for Wind Power Turbines, 2006
 27th Risø International Symposium on Materials Science, Polymer Composite Materials for Wind Power Turbines, 2006 SIMULATION OF CRACK INITIATION AND PROPAGATION IN AN ADHESIVE LAYER USING A MESOMECHANICAL
27th Risø International Symposium on Materials Science, Polymer Composite Materials for Wind Power Turbines, 2006 SIMULATION OF CRACK INITIATION AND PROPAGATION IN AN ADHESIVE LAYER USING A MESOMECHANICAL
