Nafion TiO 2 composite DMFC membranes: physico-chemical properties of the filler versus electrochemical performance
|
|
|
- Dayna Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrochimica Acta 50 (2005) Nafion TiO 2 composite DMFC membranes: physico-chemical properties of the filler versus electrochemical performance V. Baglio a,c,, A.S. Aricò a, A. Di Blasi a,c, V. Antonucci a, P.L. Antonucci b, S. Licoccia c, E. Traversa c, F. Serraino Fiory c a CNR-ITAE Institute, via Salita S. Lucia sopra Contesse 5, Messina, Italy b University of Reggio Calabria, Località Feo Di Vito, Reggio Calabria, Italy c University Tor Vergata of Rome, via della Ricerca Scientifica, Roma, Italy Received 25 February 2004; received in revised form 15 July 2004; accepted 24 July 2004 Available online 22 September 2004 Abstract TiO 2 nanometric powders were prepared via a sol gel procedure and calcined at various temperatures to obtain different surface and bulk properties. The calcined powders were used as fillers in composite Nafion membranes for application in high temperature direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs). The powder physico-chemical properties were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and ph measurements. The observed characteristics were correlated to the DMFC electrochemical behaviour. Analysis of the high temperature conductivity and DMFC performance reveals a significant influence of the surface characteristics of the ceramic oxide, such as oxygen functional groups and surface area, on the membrane electrochemical behaviour. A maximum DMFC power density of 350 mw cm 2 was achieved under oxygen feed at 145 C in a pressurized DMFC (2.5 bar, anode and cathode) equipped with TiO 2 nano-particles based composite membranes Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Keywords: TiO 2 ; DMFC; Composite Nafion membranes; Surface properties; Ceramic fillers 1. Introduction Liquid-fuelled solid-polymer-electrolyte fuel cells are very promising as electrochemical power sources for application in portable devices and transportation, due to their simple design and low environmental impact [1 3]. Yet, despite the practical system benefits, the power density and the efficiency of direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs) are low compared to polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) operating with hydrogen because of the slow methanol oxidation kinetics and the fuel cross-over through the membrane [1 9]. In a pioneering work of Watanabe et al., composite membranes containing Pt-modified inorganic fillers have been shown to facilitate the electrolyte self-humidification by the Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: baglio@itae.cnr.it (V. Baglio). recombination of H 2 and O 2 on the filler surface in PEMFC, at moderate temperatures (80 C) [5]. Whereas, great efforts have been addressed to the development of polymeric membranes for high temperature DMFCs [10 14]. Operation temperatures above 120 C are needed to reduce catalyst poisoning by adsorbed CO and enhance methanol oxidation rate. Composite membranes containing finely dispersed hygroscopic inorganic oxides [10,15] or heteropolyacids [16,17] effectively show large water retention properties and, consequently, suitable proton conductivity at high temperatures. Similar evidences have been observed when inorganic proton conductors, such as zirconium phosphate, have been used as fillers in DMFC membranes [11]. In particular DMFC operation at temperatures close to 150 C has been demonstrated with composite Nafion membranes [10,11,15,17]. The adsorption and retention of water on inorganic oxides depends on their surface properties; in particular, the amount of /$ see front matter 2004 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /j.electacta
2 1242 V. Baglio et al. / Electrochimica Acta 50 (2005) co-ordinated water depends on the nature and relative concentration of the surface functional groups [15,18,19]. As a progress of our activity in the development of innovative composite membranes for FCs application, this work deals with an investigation of the influence of morphological and chemical characteristics of TiO 2 as filler for Nafion-based composite membranes. TiO 2 nanometric powders were inhouse prepared via a sol gel procedure. Thermal treatments at different temperatures were performed to tailor the oxide powder properties. The electrochemical behaviour of DM- FCs equipped with the composite membranes based on TiO 2 fillers with different characteristics was investigated. 2. Experimental Nanosized titanium oxide was synthesized by sol gel hydrolysing an alcoholic solution of Ti(OiPr) 4 (Aldrich) according to a previously reported procedure [20]. TG analysis of the obtained titania precursor was carried out in a Netzsch TG/DSC/DTA analyser. The precursor was then thermally treated at different temperatures (500, 650 and 800 C) for 2 h. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed with a Philips X-Pert diffractometer using Cu K source operating at 40 kv and 20 ma. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of the powders was carried out using a Philips CM12 microscope equipped with LaB 6 filament. X- ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements were performed using a Physical Electronics (PHI) spectrometer equipped with a monochromatic Al source operating at 350 W. Element spectra were acquired with pass energy of ev. The ph of slurry was measured at room temperature by an ATC compensated ph probe (Orion). The slurry was composed by 0.5 g of powder suspended in 0.1 L of bidistilled water and stirred for 24 h in the presence of a stream of nitrogen. A steady ph value was typically obtained after a few tens of minutes and no significant ph drift was recorded after 24 h (<0.05 ph units). The ph of slurry was sampled in any case after 24 h. All the composite membranes were prepared by using the recast procedure. The Nafion ionomer was mixed with dimethyl-sulfoxide (DMSO) and TiO 2 powder in an ultrasonic bath. The slurry was cast over a glass substrate. The solution was slowly evaporated at 80 C under vacuum to achieve a dense polymeric film. This latter was detached from the glass substrate by addition of distilled water and hot pressed between two PTFE foils at 160 C for 10 min. Membrane thickness was about 100 ± 5 m. The methanol oxidation catalyst was a 60% Pt Ru (1:1)/Vulcan (E-TEK), whereas a 30% Pt/Vulcan (E-TEK) was used for oxygen reduction. The catalyst layers, including 33 wt.% Nafion ionomer, were supported on a carbon cloth support coated with a diffusion layer. The platinum loading for all the electrodes used in the experiments was 2 ± 0.1 mg cm 2. MEAs were prepared by hot pressing the electrodes onto the membrane at 130 C and 50 bar. Fuel cell tests were performed Fig. 1. TG analysis of the titania precursor obtained from the sol gel procedure. ina5cm 2 single cell (GlobeTech, Inc.) connected to a HP 6060B electronic load. A 2 M aqueous solution of methanol and an oxygen stream were preheated at 85 C and fed to the cell. The methanol solution was fed into the cell at a flow rate of 2.5 ml/min whereas the cathode feed was passed through a humidification bottle with a flow rate of 500 ml/min. The anode and the cathode back pressure was 2.5 bar at 145 C. The cell resistance was determined at the various temperatures by the current interrupter method during cell operation at 400 ma cm Results and discussion The TG scan of the precursor obtained by sol gel shows that only a very slight weight loss (1% wt.) occurs above 450 C(Fig. 1). The powders were then calcined at 500, 650 and 800 C to obtain crystalline TiO 2. Fig. 2 shows the X- ray diffraction patterns of the TiO 2 samples after thermal treatments at the three selected temperatures. The presence Fig. 2. X-ray diffraction patterns of TiO 2 powders calcined at different temperatures; inset: 5 wt.% TiO 2 (calcined at 500 C) based recast Nafion membrane.
3 V. Baglio et al. / Electrochimica Acta 50 (2005) of the crystallographic structure of anatase was observed for the powders calcined at 500 and 650 C while the crystallographic structure of rutile was observed for the sample calcined at 800 C [20]. The crystallite size for the three samples, determined using the Scherrer s equation, was 12, 22 and 39 nm, respectively. The inset of Fig. 2 shows the XRD pattern of the composite Nafion membrane containing 5 wt.% TiO 2 calcined at 500 C. This composite membrane shows the typical diffraction pattern of Nafion and small reflections due to TiO 2 in the anatase phase. Fig. 3 shows the TEM micrographs of the various TiO 2 samples. The particle size is in agreement with the XRD measurements for the powder calcined at the lowest temperature (500 C), although proper determination of the primary particle dimension was not possible because of the presence of agglomerates. Larger particles were observed in the TEM images of the samples fired at 650 and 800 C; as expected, the particle size increases progressively with the thermal treatment temperature. The surface chemistry of the TiO 2 powders was investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (Figs. 4 and 5). The Ti 2p 3/2 and Ti 2p 1/2 photo-electron lines (Fig. 4) occurred at the same binding energies for the three samples Fig. 4. Comparison of the Ti 2p X-ray photoelectron peaks for the TiO 2 powder calcined at different temperatures. Fig. 3. Transmission electron micrographs of the TiO 2 powders calcined at 500 C (a), 650 C (b) and 800 C (c) employed in the preparation of the composite membranes. Fig. 5. Curve fitting of O 1s X-ray photoelectron peaks for the TiO 2 powder calcined at 500 C (a), 650 C (b) and 800 C (c).
4 1244 V. Baglio et al. / Electrochimica Acta 50 (2005) Table 1 B.E. and relative peak areas of O 1s species from curve-fitted XPS spectra for the various TiO 2 powders Species B.E. (ev) Relative peak area (%) TiO 2 calcined at 500 C O 1s TiO 2 calcined at 650 C O 1s TiO 2 calcined at 800 C O 1s (458.4 ± 0.2 ev and ± 0.2 ev, respectively). This B.E. is typical of TiO 2 compounds; accordingly, the photoelectron peaks are mainly associated to the main Ti sites from the titania framework with small influence from surface defects. The O 1s region of the XPS spectra (Fig. 5) showed similar values of B.E. for the main peak (Table 1) of the various TiO 2 samples (529.6 ev). However, the TiO 2 powders treated at 500 and 650 C and characterized by the anatase structure showed a larger content of oxygen species at higher binding energies. These peaks, centered at about ev (Fig. 5), are associated with the presence of surface OH groups. Their intensity is not very high with respect to the main O 1s peak deriving from crystalline TiO 2 framework. However, the occurrence of Ti OH groups on the surface imparts a slight acidic behaviour to the fillers [19]. This finding was confirmed by the measurements of the ph of slurry for the titania powders; the higher the temperature of the powder calcinations, the higher the measured values of the ph of slurry, up to basic value for the powder heated to 800 C(Table 2). The XPS analysis showed that the ratio between the intensities of the acidic Ti OH surface species and the neutral O Ti O species from the framework was slightly larger for the sample treated at the lowest temperature (500 C). The more acidic behaviour of this sample with respect to the powder heated to 650 C can be also ascribed to its smaller particle size, and thus its larger surface area (Fig. 5a and b). The concentration of surface OH groups was lower for the sample calcined at 800 C and having the rutile structure, because of the water elimination reactions induced by the thermal treatment (Fig. 5c). Yet, a small peak was still present in the higher binding energies region of the O 1s spectrum. Table 2 Physico-chemical properties of TiO 2 powders Filler Crystallographic structure Mean particle size a (nm) ph of slurry TiO 2 calcined at 500 C Anatase TiO 2 calcined at 650 C Anatase TiO 2 calcined at 800 C Rutile a From XRD; (1 0 1) reflection for anatase and (1 1 1) reflection for rutile. These surface oxygen species are believed to be responsible of the water co-ordination on the filler surface during membrane operation above 100 C, probably assisting at different extents the proton conduction [18,19]. The XPS O 1s peak component at higher B.E.s (at about 532 ev) could be associated with the presence of surface oxygen containing carbonaceous species adsorbed from the atmosphere. To evaluate the influence of physico-chemical properties of the inorganic filler on the electrochemical behaviour, composite recast Nafion membranes containing 5 wt.% TiO 2 powder calcined at the three different temperatures (500, 650, 800 C) were prepared and tested in fuel cell devices. Fig. 6 shows the polarization curves recorded at 145 C for the various MEAs equipped with the composite Nafion membranes containing 5 wt.% TiO 2 calcined at different temperatures. The inset of Fig. 6 shows the variation of cell resistance as a function of the operating temperature for DMFCs employing these composite membranes. Since the nature of the surface functional groups is essentially the same for the three inorganic fillers, the variation in performance and conductivity can be mainly attributed to the different particle size, and thus to the different specific surface areas (SSA). A powder with a large specific surface area is characterized by a large number of adsorbing sites. Accordingly, a significant number of water molecules will be coordinated by the OH groups present on the surface of TiO 2 particles, promoting the proton transport through the membrane at high temperatures. No specific role appeared to be played by the bulk structure. The membranes treated at 650 and 800 C, containing fillers with the anatase and rutile structure, respectively, showed similar electrochemical properties. In agreement, the XPS analysis showed for these samples essentially similar surface functionalities independently from the crystallographic structure. The main differences among these two powders consisted in the relative concentration of the functional groups capable of water coordination [15,18,19], as determined by XPS. The specific surface area can be roughly evaluated from particle size [21], by assuming an approximately spherical shape for the primary particles; applying Fig. 6. Variation of cell resistance (inset) as a function of the operating temperature and polarization curves at 145 C for the various MEAs equipped with the composite Nafion membranes containing 5 wt.% TiO 2 calcined at different temperatures. 2 M Methanol feed, 2.5 bar; oxygen feed, 2.5 bar.
5 V. Baglio et al. / Electrochimica Acta 50 (2005) Fig. 7. Variation surface area as a function of particle size for the various TiO 2 powders. such model a sudden increase in SSA (m 2 /g) would occur for particle sizes smaller than about 20 nm (Fig. 7); this may explain the improvement in performance and conductivity of the membranes based on TiO 2 powder with an average particle size close to 11 nm (Fig. 6). A maximum power density of 350 mw cm 2 was obtained at 145 C with the cell equipped with the composite membrane containing TiO 2 calcined at 500 C(Fig. 8). The cells equipped with the membranes with larger TiO 2 particles were also operated up to 145 C, but, the performance did not increase significantly going from 130 to 145 C (not shown) because of a significant increase in cell resistance (Fig. 6, inset). A considerable aspect for a successful application of a composite polymer electrolyte in fuel cell devices is the performance stability. Accordingly, the DMFC equipped with Nafion membrane containing TiO 2 calcined at 500 Cwas subjected to 1 month operation with daily-cycles of start up and shut down. The recorded cell current density, at a cell potential of 0.4 V, for a typical day of operation is reported in Fig. 9. A similar behaviour was recorded during all the days of operation. The slight decrease of performance with time was probably due to a poisoning effect by methanolic residues at the anode as well as the formation of oxide species on the cathode surface [22]. After discharging the cell by feeding Fig. 8. Power density curves at 145 C for the various MEAs equipped with the composite Nafion membranes containing 5 wt.% TiO 2 calcined at different temperatures. 2 M Methanol feed, 2.5 bar; oxygen feed, 2.5 bar. Fig. 9. Variation of DMFC current density for the MEA based on composite recast Nafion membrane containing TiO 2 calcined at 500 C as a function of time during a day operation under potentiostatic control. Cell voltage 0.4 V, temperature 145 C, 2 M methanol feed, 2.5 at. rel., oxygen feed, 2.5 at. rel. water at the anode, the day after the cell regained the initial performance. 4. Conclusions The influence of physico-chemical properties of TiO 2 inorganic filler on the electrochemical behaviour of a DMFC based on composite membranes was investigated. It clearly appears that, for materials characterized by similar surface functional groups, the effect of the filler surface area becomes prevailing in determining the water retention properties of the composite membranes at high temperature. This effect appears to be associated to the larger number of wateradsorbing acidic sites on the filler surface. As expected, the surface properties play a role more important than the crystalline structure of the filler, since the water molecules acting as promoters towards the proton migration are effectively coordinated by the surface groups. A further increase of the electrochemical performance may thus be achieved by appropriate tailoring of the surface characteristics of the inorganic filler. References [1] S. Wasmus, A. Kuver, J. Electroanal. Chem. 461 (1999) 14. [2] A.S. Aricò, S. Srinivasan, V. Antonucci, Fuel Cells 2 (2001) 133. [3] M. Neergat, D. Leveratto, U. Stimming, Fuel Cells 2 (2002) 25. [4] X. Ren, M.S. Wilson, S. Gottesfeld, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143 (1996) 12. [5] M. Watanabe, H. Uchida, Y. Seki, M. Emori, P. Stonehart, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143 (1996) [6] O. Savadogo, J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 1 (1998) 47. [7] T.A. Zawodzinski, J. Davey, J. Valerio, S. Gottesfeld, Electrochim. Acta 40 (1995) 297. [8] N. Miyake, J.S. Wainright, R.F. Savinell, J. Electrochem. Soc. 148 (2001) 898. [9] B. Bonnet, D.J. Jones, J. Roziere, L. Tchicaya, G. Alberti, M. Casciola, L. Massinelli, B. Bauer, A. Peraio, E. Ramunni, J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 3 (2000) 87. [10] A.S. Aricò, P. Cretì, P.L. Antonucci, V. Antonucci, Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 1 (1998) 66. [11] C. Yang, S. Srinivasan, A.S. Aricò, P. Cretì, V. Baglio, V. Antonucci, Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 4 (2001) 31.
6 1246 V. Baglio et al. / Electrochimica Acta 50 (2005) [12] K.T. Adjemian, S.L. Lee, S. Srinivasan, J. Benziger, A.B. Bocarsly, J. Electrochem. Soc. 149 (2002) 256. [13] K.D. Kreuer, J. Membr. Sci. 185 (2001) 29. [14] J. Kerres, W. Zhang, L. Jorissen, V. Gogel, J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 5 (2002) 97. [15] A.S. Aricò, V. Baglio, A. Di Blasi, P. Cretì, P.L. Antonucci, V. Antonucci, Solid State Ionics 161 (2003) 251. [16] B. Tazi, O. Savadogo, J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 4 (2001) 187. [17] P. Staiti, A.S. Aricò, V. Baglio, F. Lufrano, E. Passalacqua, V. Antonucci, Solid State Ionics 145 (2001) 101. [18] A.S. Aricò, V. Baglio, A. Di Blasi, V. Antonucci, Electrochem. Commun. 5 (2003) 862. [19] A.S. Aricò, V. Baglio, A. Di Blasi, E. Modica, P.L. Antonucci, V. Antonucci, J. Power Sources 128 (2004) 113. [20] E. Traversa, M.L. Di Vona, S. Licoccia, M. Sacerdoti, M.C. Carotta, L. Crema, G. Martinelli, J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 22 (2001) 167. [21] A.S. Aricò, P.L. Antonucci, E. Modica, V. Baglio, H. Kim, V. Antonucci, Electrochim. Acta 47 (2002) [22] P. Piola, P. Zelenay, Proceedings of the 205th Meeting of The Electrochemical Society, San Antonio, TX, May (abstract 338).
Electrochemical Analysis of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells for Low Temperature Operation
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 1(26)71-79 www.electrochemsci.org Electrochemical Analysis of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells for Low Temperature Operation V. Baglio*, A. Di Blasi, E. Modica, P. Cretì, V. Antonucci,
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 1(26)71-79 www.electrochemsci.org Electrochemical Analysis of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells for Low Temperature Operation V. Baglio*, A. Di Blasi, E. Modica, P. Cretì, V. Antonucci,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Effect of water electrolysis catalysts on carbon corrosion in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells Sang-Eun Jang, Hansung Kim* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Supporting Information Effect of water electrolysis catalysts on carbon corrosion in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells Sang-Eun Jang, Hansung Kim* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Durability study of Pt 3 Ni 1 catalysts as cathode in PEM fuel cells
 Electrochemistry Communications 6 (2004) 795 799 www.elsevier.com/locate/elecom Durability study of Pt 3 Ni 1 catalysts as cathode in PEM fuel cells Hector R. Colon-Mercado, Hansung Kim, Branko N. Popov
Electrochemistry Communications 6 (2004) 795 799 www.elsevier.com/locate/elecom Durability study of Pt 3 Ni 1 catalysts as cathode in PEM fuel cells Hector R. Colon-Mercado, Hansung Kim, Branko N. Popov
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Novel DMSO-based Electrolyte for High Performance Rechargeable Li-O 2 Batteries Dan Xu, a Zhong-li Wang, a Ji-jing Xu, a Lei-lei Zhang, a,b and Xin-bo Zhang a* a State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information Novel DMSO-based Electrolyte for High Performance Rechargeable Li-O 2 Batteries Dan Xu, a Zhong-li Wang, a Ji-jing Xu, a Lei-lei Zhang, a,b and Xin-bo Zhang a* a State Key Laboratory
Novel Fuel Cell MEA Based on Pt-C Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering
 10.1149/08008.0225ecst The Electrochemical Society Novel Fuel Cell MEA Based on Pt-C Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering A. Ostroverkh a, V. Johanek a, M. Dubau a, P. Kus a, K. Veltruska a, M. Vaclavu a,
10.1149/08008.0225ecst The Electrochemical Society Novel Fuel Cell MEA Based on Pt-C Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering A. Ostroverkh a, V. Johanek a, M. Dubau a, P. Kus a, K. Veltruska a, M. Vaclavu a,
Thick-film gas sensors based on vanadium titanium oxide powders prepared by sol-gel synthesis
 Journal of the European Ceramic Society 24 (2004) 1409 1413 www.elsevier.com/locate/jeurceramsoc Thick-film gas sensors based on vanadium titanium oxide powders prepared by sol-gel synthesis Maria Cristina
Journal of the European Ceramic Society 24 (2004) 1409 1413 www.elsevier.com/locate/jeurceramsoc Thick-film gas sensors based on vanadium titanium oxide powders prepared by sol-gel synthesis Maria Cristina
Supporting Information. Christina W. Li and Matthew W. Kanan* *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
 Supporting Information CO 2 Reduction at Low Overpotential on Cu Electrodes Resulting from the Reduction of Thick Cu 2 O Films Christina W. Li and Matthew W. Kanan* *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Supporting Information CO 2 Reduction at Low Overpotential on Cu Electrodes Resulting from the Reduction of Thick Cu 2 O Films Christina W. Li and Matthew W. Kanan* *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 porous nanorods as high-rate and long-life cathode for Li-ion batteries
 Supporting Information LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 porous nanorods as high-rate and long-life cathode for Li-ion batteries Xiaolong Zhang, Fangyi Cheng, Jingang Yang, Jun Chen* Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy
Supporting Information LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 porous nanorods as high-rate and long-life cathode for Li-ion batteries Xiaolong Zhang, Fangyi Cheng, Jingang Yang, Jun Chen* Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy
SHAPE EFFECT OF CERIA ON THE ACTIVITY OF Au/CeO 2 FOR PREFERENTIAL CO OXIDATION
 SHAPE EFFECT OF CERIA ON THE ACTIVITY OF Au/CeO 2 FOR PREFERENTIAL CO OXIDATION Mike Carltonbird a, Apanee Luengnaruemitchai a a) The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University Keywords:
SHAPE EFFECT OF CERIA ON THE ACTIVITY OF Au/CeO 2 FOR PREFERENTIAL CO OXIDATION Mike Carltonbird a, Apanee Luengnaruemitchai a a) The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University Keywords:
Synthesis and Evaluation of Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells
 Synthesis and Evaluation of Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells Jingguang Chen Center for Catalytic Science and Technology (CCST) Department of Chemical Engineering University of Delaware Newark, DE 19711
Synthesis and Evaluation of Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells Jingguang Chen Center for Catalytic Science and Technology (CCST) Department of Chemical Engineering University of Delaware Newark, DE 19711
Catalytic activity of carbon-support oxide for oxygen reduction reaction catalyst in polymer electrolyte fuel
 JAIST Reposi https://dspace.j Title Catalytic activity of carbon-support oxide for oxygen reduction reaction catalyst in polymer electrolyte fuel Author(s)Chang, C. H.; Yuen, T. S.; Nagao, Y. Citation
JAIST Reposi https://dspace.j Title Catalytic activity of carbon-support oxide for oxygen reduction reaction catalyst in polymer electrolyte fuel Author(s)Chang, C. H.; Yuen, T. S.; Nagao, Y. Citation
By *T.Khalil, **J. Bossert,***A.H.Ashor and *F. Abou EL-Nour
 WM 11 EG0100132 Seventh Conference of Nuclear Sciences & Applications 6-10 February 2000. Cairo, Egypt Preparation, Characterization and application of Alumina powder Produced by advanced Preparation Techniques
WM 11 EG0100132 Seventh Conference of Nuclear Sciences & Applications 6-10 February 2000. Cairo, Egypt Preparation, Characterization and application of Alumina powder Produced by advanced Preparation Techniques
Diffusion layer parameters influencing optimal fuel cell performance
 . Journal of Power Sources 86 2000 250 254 www.elsevier.comrlocaterjpowsour Diffusion layer parameters influencing optimal fuel cell performance L.R. Jordan a, A.K. Shukla b, T. Behrsing c, N.R. Avery
. Journal of Power Sources 86 2000 250 254 www.elsevier.comrlocaterjpowsour Diffusion layer parameters influencing optimal fuel cell performance L.R. Jordan a, A.K. Shukla b, T. Behrsing c, N.R. Avery
Performance of a PEM water electrolyser based on metallic. iridium electrocatalyst and an Aquivion membrane
 Performance of a PEM water electrolyser based on metallic iridium electrocatalyst and an Aquivion membrane S. Siracusano 1*, V. Baglio 1, S.A. Grigoriev 2, L. Merlo 3, V.N. Fateev 4, A. S. Arico 1 1 CNR-Institute
Performance of a PEM water electrolyser based on metallic iridium electrocatalyst and an Aquivion membrane S. Siracusano 1*, V. Baglio 1, S.A. Grigoriev 2, L. Merlo 3, V.N. Fateev 4, A. S. Arico 1 1 CNR-Institute
Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells
 Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells Huanying Liu, a, b Xuefeng Zhu, a * Mojie Cheng, c You Cong, a Weishen Yang a * a State Key Laboratory of Catalysis,
Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells Huanying Liu, a, b Xuefeng Zhu, a * Mojie Cheng, c You Cong, a Weishen Yang a * a State Key Laboratory of Catalysis,
Novel concept of rechargeable battery using iron oxide nanorods. anode and nickel hydroxide cathode in aqueous electrolyte
 Supplementary Information for: Novel concept of rechargeable battery using iron oxide nanorods anode and nickel hydroxide cathode in aqueous electrolyte Zhaolin Liu *, Siok Wei Tay and Xu Li Institute
Supplementary Information for: Novel concept of rechargeable battery using iron oxide nanorods anode and nickel hydroxide cathode in aqueous electrolyte Zhaolin Liu *, Siok Wei Tay and Xu Li Institute
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Sustainable Energy & Fuels. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information for Chemical Science, DOI: 10.1039/ ((please add manuscript
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Sustainable Energy & Fuels. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information for Chemical Science, DOI: 10.1039/ ((please add manuscript
A novel rechargeable battery with magnesium anode, titanium dioxide cathode, and magnesim borohydride/tetraglyme electrolyte
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A novel rechargeable battery with magnesium anode, titanium dioxide cathode, and magnesim borohydride/tetraglyme
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A novel rechargeable battery with magnesium anode, titanium dioxide cathode, and magnesim borohydride/tetraglyme
Hybrid organic-inorganic membranes for a medium temperature fuel cell
 Journal of New Materials for Electrochemical Systems, 3, 87-92 (2000) J. New Mat. Electrochem. Systems Hybrid organic-inorganic membranes for a medium temperature fuel cell B. Bonnet a, D. J. Jones a,
Journal of New Materials for Electrochemical Systems, 3, 87-92 (2000) J. New Mat. Electrochem. Systems Hybrid organic-inorganic membranes for a medium temperature fuel cell B. Bonnet a, D. J. Jones a,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of precursor coated on salt template. (a) SEM image of Mo precursor coated on NaCl. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) EDS of Mo precursor coated on
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of precursor coated on salt template. (a) SEM image of Mo precursor coated on NaCl. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) EDS of Mo precursor coated on
Towards High-Safety Potassium-Sulfur Battery Using. Potassium Polysulfide Catholyte and Metal-Free Anode
 Supporting Information Towards High-Safety Potassium-Sulfur Battery Using Potassium Polysulfide Catholyte and Metal-Free Anode Jang-Yeon Hwang, Hee Min Kim, Chong S. Yoon, Yang-Kook Sun* Department of
Supporting Information Towards High-Safety Potassium-Sulfur Battery Using Potassium Polysulfide Catholyte and Metal-Free Anode Jang-Yeon Hwang, Hee Min Kim, Chong S. Yoon, Yang-Kook Sun* Department of
Applied Surface Science
 Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 4192 4196 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Surface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Electrodeposited ruthenium oxide thin films
Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 4192 4196 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Surface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Electrodeposited ruthenium oxide thin films
Tunable Photocatalytic Selectivity of Hollow TiO 2 Microspheres Composed of Anatase Polyhedra with Exposed {001} Facets
 Tunable Photocatalytic Selectivity of Hollow TiO 2 Microspheres Composed of Anatase Polyhedra with Exposed {001} Facets Shengwei Liu, a Jiaguo Yu, a,* and Mietek Jaroniec b,* a State Key Laboratory of
Tunable Photocatalytic Selectivity of Hollow TiO 2 Microspheres Composed of Anatase Polyhedra with Exposed {001} Facets Shengwei Liu, a Jiaguo Yu, a,* and Mietek Jaroniec b,* a State Key Laboratory of
A small mono-polar direct methanol fuel cell stack with passive operation
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Power Sources 178 (2008) 118 124 A small mono-polar direct methanol fuel cell stack with passive operation Y.H. Chan, T.S. Zhao, R. Chen, C. Xu Department
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Power Sources 178 (2008) 118 124 A small mono-polar direct methanol fuel cell stack with passive operation Y.H. Chan, T.S. Zhao, R. Chen, C. Xu Department
Development of Method for Synthesis of Pt Co Cathode Catalysts for PEM Fuel Cells
 1099-0062/2007/10 11 /B201/5/$20.00 The Electrochemical Society Development of Method for Synthesis of Pt Co Cathode Catalysts for PEM Fuel Cells Xuguang Li,* Héctor R. Colón-Mercado, Gang Wu, Jong-Won
1099-0062/2007/10 11 /B201/5/$20.00 The Electrochemical Society Development of Method for Synthesis of Pt Co Cathode Catalysts for PEM Fuel Cells Xuguang Li,* Héctor R. Colón-Mercado, Gang Wu, Jong-Won
Electronic Supporting Information. Synthesis of single crystalline hexagonal nanobricks of
 Electronic Supporting Information Synthesis of single crystalline hexagonal nanobricks of LiNi 1/3 Co 1/3 Mn 1/3 O 2 with high percentage of exposed {010} active facets as high rate performance cathode
Electronic Supporting Information Synthesis of single crystalline hexagonal nanobricks of LiNi 1/3 Co 1/3 Mn 1/3 O 2 with high percentage of exposed {010} active facets as high rate performance cathode
Supporting Information. Hematite photoanode with gradient structure shows an unprecedentedly low onset
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Supporting Information Hematite photoanode with gradient structure shows an unprecedentedly
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Supporting Information Hematite photoanode with gradient structure shows an unprecedentedly
Effect of melt temperature on the oxidation behavior of AZ91D magnesium alloy in 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane/air atmospheres
 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/matchar Effect of melt temperature on the oxidation behavior of AZ91D magnesium alloy in 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane/air atmospheres Hukui Chen
available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/matchar Effect of melt temperature on the oxidation behavior of AZ91D magnesium alloy in 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane/air atmospheres Hukui Chen
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information for Ta and Nb co-doped TiO 2, and Its Carbon-Hybrid
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information for Ta and Nb co-doped TiO 2, and Its Carbon-Hybrid
N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Ruthenium @ N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Ruthenium @ N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 10, No. 2, April - June 2015, p. 715-719 PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD N. EKTHAMMATHAT
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 10, No. 2, April - June 2015, p. 715-719 PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD N. EKTHAMMATHAT
Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs Catalysts Prepared by Pulse Potential Plating Methods
 Solid State Phenomena Vols. 124-126 (2007) pp 1039-1042 Online: 2007-06-15 (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.124-126.1039 Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs
Solid State Phenomena Vols. 124-126 (2007) pp 1039-1042 Online: 2007-06-15 (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.124-126.1039 Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs
Performance characterization of passive direct methanol fuel cells
 Journal of Power Sources 167 (2007) 455 460 Short communication Performance characterization of passive direct methanol fuel cells R. Chen, T.S. Zhao Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Hong Kong
Journal of Power Sources 167 (2007) 455 460 Short communication Performance characterization of passive direct methanol fuel cells R. Chen, T.S. Zhao Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Hong Kong
School of Materials Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology,
 Supporting information Zn/MnO 2 Battery Chemistry With H + and Zn 2+ Co-Insertion Wei Sun, Fei Wang, Singyuk Hou, Chongyin Yang, Xiulin Fan, Zhaohui Ma, Tao Gao, Fudong Han, Renzong Hu, Min Zhu *, Chunsheng
Supporting information Zn/MnO 2 Battery Chemistry With H + and Zn 2+ Co-Insertion Wei Sun, Fei Wang, Singyuk Hou, Chongyin Yang, Xiulin Fan, Zhaohui Ma, Tao Gao, Fudong Han, Renzong Hu, Min Zhu *, Chunsheng
Ru Atom-modified Covalent Triazine Framework as a Robust Electrocatalyst for Selective Alcohol Oxidation in Aqueous Electrolytes
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Ru Atom-modified Covalent Triazine Framework as a Robust Electrocatalyst
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Ru Atom-modified Covalent Triazine Framework as a Robust Electrocatalyst
In situ generation of Li 2 FeSiO 4 coating on MWNT as a high rate cathode material for lithium ion batteries
 Supporting Information: In situ generation of Li 2 FeSiO 4 coating on MWNT as a high rate cathode material for lithium ion batteries Yi Zhao, Jiaxin Li, Ning Wang, Chuxin Wu, Yunhai Ding, Lunhui Guan*
Supporting Information: In situ generation of Li 2 FeSiO 4 coating on MWNT as a high rate cathode material for lithium ion batteries Yi Zhao, Jiaxin Li, Ning Wang, Chuxin Wu, Yunhai Ding, Lunhui Guan*
X-ray Diffraction and Vibrational Spectroscopy of Catalysts for Exhaust Aftertreatment
 Copyright (c)jcpds-international Centre for Diffraction Data 2002, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 45. 139 X-ray Diffraction and Vibrational Spectroscopy of Catalysts for Exhaust Aftertreatment Roger
Copyright (c)jcpds-international Centre for Diffraction Data 2002, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 45. 139 X-ray Diffraction and Vibrational Spectroscopy of Catalysts for Exhaust Aftertreatment Roger
The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell
 , pp.66-71 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.140.14 The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Don-Kyu Lee Electrical Engineering, Dong-Eui University,
, pp.66-71 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.140.14 The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Don-Kyu Lee Electrical Engineering, Dong-Eui University,
Durability of MEA Prepared with PFA-g-PSSA Membrane for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell
 Durability of MEA Prepared with PFA-g-PSSA Membrane for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell D.-H. Peck, S. Kang, B.-R. Lee, D.-H. Jung This document appeared in Detlef Stolten, Thomas Grube (Eds.): 18th World Hydrogen
Durability of MEA Prepared with PFA-g-PSSA Membrane for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell D.-H. Peck, S. Kang, B.-R. Lee, D.-H. Jung This document appeared in Detlef Stolten, Thomas Grube (Eds.): 18th World Hydrogen
PULSE ELECTRODEPOSITION OF Pt Co CATALYST ONTO GLASSY CARBON FOR OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION TO USE IN PEMFC
 PULSE ELECTRODEPOSITION OF Pt Co CATALYST ONTO GLASSY CARBON FOR OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION TO USE IN PEMFC Jittima Sriwannaboot a,b, Nisit Tantavichet a,b,* a) Center of Excellence on Petrochemical and
PULSE ELECTRODEPOSITION OF Pt Co CATALYST ONTO GLASSY CARBON FOR OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION TO USE IN PEMFC Jittima Sriwannaboot a,b, Nisit Tantavichet a,b,* a) Center of Excellence on Petrochemical and
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Improving the Photocatalytic and Photoelectrochemical Activities of Mesoporous Single Crystal Rutile TiO 2 for Water Splitting Wei Jiao, Ying Peng Xie, Run Ze Chen,
Electronic Supplementary Information Improving the Photocatalytic and Photoelectrochemical Activities of Mesoporous Single Crystal Rutile TiO 2 for Water Splitting Wei Jiao, Ying Peng Xie, Run Ze Chen,
Electrospun quaternized polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers with core-shell structure and their composite in alkaline fuel cell application
 1 Electrospun quaternized polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers with core-shell structure and their composite in alkaline fuel cell application S. Jessie Lue, Ph.D. Department Head and Professor Department of Chemical
1 Electrospun quaternized polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers with core-shell structure and their composite in alkaline fuel cell application S. Jessie Lue, Ph.D. Department Head and Professor Department of Chemical
Effect of water transport properties on a PEM fuel cell operating with dry hydrogen
 Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) 6361 6366 Effect of water transport properties on a PEM fuel cell operating with dry hydrogen Yinghua Cai a,b, Jun Hu a, Haipeng Ma a,b, Baolian Yi a,, Huamin Zhang a a Fuel
Electrochimica Acta 51 (2006) 6361 6366 Effect of water transport properties on a PEM fuel cell operating with dry hydrogen Yinghua Cai a,b, Jun Hu a, Haipeng Ma a,b, Baolian Yi a,, Huamin Zhang a a Fuel
Characteristics of Pt-Ru Catalyst Supported on Activated Carbon for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell
 &DUERQ 6FLHQFH Vol. 4, No. 3 September 2003 pp. 121-125 Characteristics of Pt-Ru Catalyst Supported on Activated Carbon for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Doo-Hwan Jung a, N, Jae-Hoon Jung a, Seong-Hwa Hong
&DUERQ 6FLHQFH Vol. 4, No. 3 September 2003 pp. 121-125 Characteristics of Pt-Ru Catalyst Supported on Activated Carbon for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Doo-Hwan Jung a, N, Jae-Hoon Jung a, Seong-Hwa Hong
Applied Energy 106 (2013) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Applied Energy
 Applied Energy 106 (2013) 301 306 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Applied Energy journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apenergy A sandwich structured membrane for direct methanol
Applied Energy 106 (2013) 301 306 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Applied Energy journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apenergy A sandwich structured membrane for direct methanol
PREPARATION OF VISIBLE-LIGHT-DRIVEN TIO 2 PHOTOCATALYST DOPED WITH IRON IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE
 PREPARATION OF VISIBLE-LIGHT-DRIVEN TIO 2 PHOTOCATALYST DOPED WITH IRON IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE Esther Alonso *, Héctor Fernández-Rodríguez and M.J. Cocero Department of Chemical Engineering &
PREPARATION OF VISIBLE-LIGHT-DRIVEN TIO 2 PHOTOCATALYST DOPED WITH IRON IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE Esther Alonso *, Héctor Fernández-Rodríguez and M.J. Cocero Department of Chemical Engineering &
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information High performance potassium-sulfur batteries based
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information High performance potassium-sulfur batteries based
Effect of heat treatment on electrochemical characteristics of spinel lithium titanium oxide
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27(1), 91-95 (2010) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-009-0298-0 RAPID COMMUNICATION Effect of heat treatment on electrochemical characteristics of spinel lithium titanium oxide Sung-Chul Hong*,
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27(1), 91-95 (2010) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-009-0298-0 RAPID COMMUNICATION Effect of heat treatment on electrochemical characteristics of spinel lithium titanium oxide Sung-Chul Hong*,
Preparation and Characterization of Copper Oxide -Water Based Nanofluids by One Step Method for Heat Transfer Applications
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.976 2015, 4(1), 127-132 RESEARCH ARTICLE Preparation and Characterization of Copper Oxide -Water Based Nanofluids by One Step
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.976 2015, 4(1), 127-132 RESEARCH ARTICLE Preparation and Characterization of Copper Oxide -Water Based Nanofluids by One Step
Linlin Xin a and Xuefeng Liu b. School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, , PR China.
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic Supplementary Information Black TiO 2 Inverse Opals for Visible-Light Photocatalysis
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic Supplementary Information Black TiO 2 Inverse Opals for Visible-Light Photocatalysis
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Hydrogenation Driven Conductive Na 2 Nanoarrays as Robust Binder-Free Anodes for Sodium-Ion Batteries Shidong Fu, Jiangfeng Ni, Yong Xu, Qiao Zhang*, and Liang Li*, College of Physics,
Supporting Information Hydrogenation Driven Conductive Na 2 Nanoarrays as Robust Binder-Free Anodes for Sodium-Ion Batteries Shidong Fu, Jiangfeng Ni, Yong Xu, Qiao Zhang*, and Liang Li*, College of Physics,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Sulphonated Polyimide/Acid Functionalized Graphene Oxide Composite Polymer Electrolyte Membranes with Improved Proton Conductivity and Water Retention Properties Ravi P. Pandey,
Supplementary Information Sulphonated Polyimide/Acid Functionalized Graphene Oxide Composite Polymer Electrolyte Membranes with Improved Proton Conductivity and Water Retention Properties Ravi P. Pandey,
Supporting Information. Ultrathin and Large-Sized Vanadium Oxide Nanosheets Mildly. Prepared at Room Temperature for High Performance Fiber-Based
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Ultrathin and Large-Sized Vanadium Oxide Nanosheets
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Ultrathin and Large-Sized Vanadium Oxide Nanosheets
SOFC Powders and Unit Cell Research at NIMTE. Jian Xin Wang, Jing Shao, You Kun Tao, Wei Guo Wang
 595 10.1149/1.3205571 The Electrochemical Society SOFC Powders and Unit Cell Research at NIMTE Jian Xin Wang, Jing Shao, You Kun Tao, Wei Guo Wang Division of Fuel Cell and Energy Technology Ningbo Institute
595 10.1149/1.3205571 The Electrochemical Society SOFC Powders and Unit Cell Research at NIMTE Jian Xin Wang, Jing Shao, You Kun Tao, Wei Guo Wang Division of Fuel Cell and Energy Technology Ningbo Institute
Bi-functional RuO 2 /Co 3 O 4 Core/Shell Nanofibers as a Multi-component One-Dimensional Water Oxidation Catalyst
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 7 8 9 0 7 8 9 0 7 Supporting Information Bi-functional RuO /Co O Core/Shell Nanofibers as a Multi-component One-Dimensional Water Oxidation Catalyst Jong
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 7 8 9 0 7 8 9 0 7 Supporting Information Bi-functional RuO /Co O Core/Shell Nanofibers as a Multi-component One-Dimensional Water Oxidation Catalyst Jong
Crystallized V 2 O 5 as Oxidized Phase for Unexpected Multi- Color Electrochromism in V 2 O 3 thick film
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Crystallized V 2 O 5 as Oxidized Phase for Unexpected Multi- Color Electrochromism in V 2 O 3 thick film Issam Mjejri, Manuel Gaudon, Giljoo Song, Christine Labrugère^ and Aline
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Crystallized V 2 O 5 as Oxidized Phase for Unexpected Multi- Color Electrochromism in V 2 O 3 thick film Issam Mjejri, Manuel Gaudon, Giljoo Song, Christine Labrugère^ and Aline
Bi- and tri-metallic Pt-based anode catalysts for direct ethanol fuel cells
 Journal of Power Sources 131 (24) 217 223 Bi- and tri-metallic Pt-based anode catalysts for direct ethanol fuel cells W.J. Zhou a, W.Z. Li a, S.Q. Song a, Z.H. Zhou a, L.H. Jiang a, G.Q. Sun a, Q. Xin
Journal of Power Sources 131 (24) 217 223 Bi- and tri-metallic Pt-based anode catalysts for direct ethanol fuel cells W.J. Zhou a, W.Z. Li a, S.Q. Song a, Z.H. Zhou a, L.H. Jiang a, G.Q. Sun a, Q. Xin
Influence of preparation method on the performance of Mn Ce O catalysts
 React Kinet Catal Lett (2009) 97:263 268 DOI 10.1007/s11144-009-0024-2 Influence of preparation method on the performance of Mn Ce O catalysts Hua Zhang Æ Weiling Yang Æ Dao Li Æ Xingyi Wang Received:
React Kinet Catal Lett (2009) 97:263 268 DOI 10.1007/s11144-009-0024-2 Influence of preparation method on the performance of Mn Ce O catalysts Hua Zhang Æ Weiling Yang Æ Dao Li Æ Xingyi Wang Received:
Ibn Al-Haitham Jour. for Pure & Appl. Sci Vol. 32 (1) 2019
 Novel Co-Precipitation Method for Synthesis of Nanostructured Nickel Oxide in Accordance to PH: Structural and Optical Properties as an Active Optical Filter Zehraa N. Abdul-Ameer Lecturer Remote Sensing
Novel Co-Precipitation Method for Synthesis of Nanostructured Nickel Oxide in Accordance to PH: Structural and Optical Properties as an Active Optical Filter Zehraa N. Abdul-Ameer Lecturer Remote Sensing
Cs 2.5 H 0.5 PWO 40 /SiO 2 as addition self-humidifying composite membrane for proton exchange membrane fuel cells
 Electrochimica Acta 52 (2007) 5479 5483 Cs 2.5 H 0.5 PWO 40 /SiO 2 as addition self-humidifying composite membrane for proton exchange membrane fuel cells L. Wang a,b, B.L. Yi a,, H.M. Zhang a, D.M. Xing
Electrochimica Acta 52 (2007) 5479 5483 Cs 2.5 H 0.5 PWO 40 /SiO 2 as addition self-humidifying composite membrane for proton exchange membrane fuel cells L. Wang a,b, B.L. Yi a,, H.M. Zhang a, D.M. Xing
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Improved Sodium-Ion Storage Performance of Ultrasmall Iron Selenide Nanoparticles Feipeng Zhao, 1 Sida Shen, 1 Liang Cheng, 1 Lu Ma, 2 Junhua Zhou, 1 Hualin Ye, 1 Na Han, 1 Tianpin
Supporting Information for Improved Sodium-Ion Storage Performance of Ultrasmall Iron Selenide Nanoparticles Feipeng Zhao, 1 Sida Shen, 1 Liang Cheng, 1 Lu Ma, 2 Junhua Zhou, 1 Hualin Ye, 1 Na Han, 1 Tianpin
Supplementary Information. Pt-Au Core/Shell Nanorods: Preparation and Applications as. Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells
 Supplementary Information Pt-Au Core/Shell Nanorods: Preparation and Applications as Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells Chen-Wei Liu, Yu-Chen Wei, Chung-Chiun Liu and Kuan-Wen Wang * Institute of Materials
Supplementary Information Pt-Au Core/Shell Nanorods: Preparation and Applications as Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells Chen-Wei Liu, Yu-Chen Wei, Chung-Chiun Liu and Kuan-Wen Wang * Institute of Materials
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Tuning nanosheet Fe 2 O 3 photoanode with C 3 N 4
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Tuning nanosheet Fe 2 O 3 photoanode with C 3 N 4
Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with high stability and reusability
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information for Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information for Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with
Heng-Pan Yang, Sen Qin, Ying-Na Yue, Li Liu, Huan Wang* and Jia-Xing Lu**
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary information for Entrapment of a pyridine derivative within
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary information for Entrapment of a pyridine derivative within
Simultaneous glucose sensing and bio-hydrogen evolution from direct photoelectrocatalytic glucose oxidation on robust Cu 2 O-TiO 2 electrodes
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Supporting information Simultaneous glucose sensing and bio-hydrogen evolution
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Supporting information Simultaneous glucose sensing and bio-hydrogen evolution
Comparison between the article and script of thesis
 Comparison between the article and script of thesis All nanomaterials and a part of results presented and discussed in this article titled Efficient multi-metallic anode catalysts in a PEM water electrolyzer
Comparison between the article and script of thesis All nanomaterials and a part of results presented and discussed in this article titled Efficient multi-metallic anode catalysts in a PEM water electrolyzer
Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates
 Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 90 (2006) 753 759 www.elsevier.com/locate/solmat Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates K.R. Murali a,, A. Austine
Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 90 (2006) 753 759 www.elsevier.com/locate/solmat Photoelectrochemical cells based on CdSe films brush plated on high-temperature substrates K.R. Murali a,, A. Austine
Supporting Information. Low temperature synthesis of silicon carbide nanomaterials using
 Supporting Information Low temperature synthesis of silicon carbide nanomaterials using solid-state method Mita Dasog, Larissa F. Smith, Tapas K. Purkait and Jonathan G. C. Veinot * Department of Chemistry,
Supporting Information Low temperature synthesis of silicon carbide nanomaterials using solid-state method Mita Dasog, Larissa F. Smith, Tapas K. Purkait and Jonathan G. C. Veinot * Department of Chemistry,
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for 3D Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Aerogel-Supported Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Zhong-Shuai Wu, Shubin Yang, Yi Sun, Khaled
Supporting Information for 3D Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Aerogel-Supported Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Zhong-Shuai Wu, Shubin Yang, Yi Sun, Khaled
Optical, microstructural and electrical studies on sol gel derived TiO 2 thin films
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 55, January 2017, pp. 81-85 Optical, microstructural and electrical studies on sol gel derived TiO 2 thin films M Bilal Tahir*, S Hajra, M Rizwan & M Rafique
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 55, January 2017, pp. 81-85 Optical, microstructural and electrical studies on sol gel derived TiO 2 thin films M Bilal Tahir*, S Hajra, M Rizwan & M Rafique
Single-crystalline LiFePO 4 Nanosheets for High-rate Li-ion Batteries
 /8 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Single-crystalline LiFePO 4 Nanosheets for High-rate Li-ion Batteries Yu Zhao, Lele Peng, Borui Liu, Guihua Yu* Materials Science and Engineering Program and Department of Mechanical
/8 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Single-crystalline LiFePO 4 Nanosheets for High-rate Li-ion Batteries Yu Zhao, Lele Peng, Borui Liu, Guihua Yu* Materials Science and Engineering Program and Department of Mechanical
Morphology of Cadmium Sulfide/Poly(ethylene)Oxide Nanocomposites
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 9 (2014) pp. 469-473 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Morphology of Cadmium Sulfide/Poly(ethylene)Oxide Nanocomposites V.S.Sangawar and R.N.Bhagat* Polymer/Nanomaterials
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 9 (2014) pp. 469-473 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Morphology of Cadmium Sulfide/Poly(ethylene)Oxide Nanocomposites V.S.Sangawar and R.N.Bhagat* Polymer/Nanomaterials
Comparative Studies of a Single Cell and a Stack of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 22(3), 406-411 (2005) Comparative Studies of a Single Cell and a Stack of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells Songki LeeQ, QQ, Daejin KimQ, Jaeyoung LeeQ, Sung Taik ChungQQ and Heung Yong
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 22(3), 406-411 (2005) Comparative Studies of a Single Cell and a Stack of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells Songki LeeQ, QQ, Daejin KimQ, Jaeyoung LeeQ, Sung Taik ChungQQ and Heung Yong
Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes
 Journal of Optoelectronic and Biomedical Materials Volume 1, Issue 1, March 2009, p. 79-84 Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes N. Taşaltin a, S. Öztürk a, H. Yüzer b, Z. Z. Öztürk a,b* a
Journal of Optoelectronic and Biomedical Materials Volume 1, Issue 1, March 2009, p. 79-84 Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes N. Taşaltin a, S. Öztürk a, H. Yüzer b, Z. Z. Öztürk a,b* a
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nanosized Anatase TiO 2 Single Crystals for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity Gang Liu a,b, Chenghua Sun b,c, Hua Gui Yang d, Sean C. Smith c, Lianzhou Wang c, Gao Qing (Max) Lu*
Supporting Information Nanosized Anatase TiO 2 Single Crystals for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity Gang Liu a,b, Chenghua Sun b,c, Hua Gui Yang d, Sean C. Smith c, Lianzhou Wang c, Gao Qing (Max) Lu*
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Earth Abundant Fe/Mn-Based Layered Oxide Interconnected Nanowires for Advanced K-Ion Full Batteries Xuanpeng Wang, Xiaoming Xu, Chaojiang Niu*, Jiashen Meng, Meng Huang, Xiong Liu,
Supporting Information Earth Abundant Fe/Mn-Based Layered Oxide Interconnected Nanowires for Advanced K-Ion Full Batteries Xuanpeng Wang, Xiaoming Xu, Chaojiang Niu*, Jiashen Meng, Meng Huang, Xiong Liu,
Improving cyclic performance of Si anode for lithium-ion batteries by forming an intermetallic skin
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Improving cyclic performance of Si anode for lithium-ion batteries by
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Improving cyclic performance of Si anode for lithium-ion batteries by
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Highly Uniform Platinum Icosahedra Made by the Hot Injection-Assisted GRAILS Method Wei Zhou,, Jianbo Wu, and Hong Yang *, Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, University
Supporting Information Highly Uniform Platinum Icosahedra Made by the Hot Injection-Assisted GRAILS Method Wei Zhou,, Jianbo Wu, and Hong Yang *, Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, University
Three-dimensional NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Film for Highefficiency
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Three-dimensional NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Film for Highefficiency Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Three-dimensional NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Film for Highefficiency Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1200448/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Increasing Solar Absorption for Photocatalysis with Black Hydrogenated Titanium Dioxide Nanocrystals This PDF file
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1200448/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Increasing Solar Absorption for Photocatalysis with Black Hydrogenated Titanium Dioxide Nanocrystals This PDF file
Highly stable and efficient non-precious metal. electrocatalysts of tantalum dioxyfluoride for oxygen
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Material Highly stable and efficient non-precious
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Material Highly stable and efficient non-precious
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Mg 2 B 2 O 5 Nanowires Enabled Multifunctional Solid-State Electrolyte with High Ionic Conductivity, Excellent Mechanical Properties and Flame-retardant Performance Ouwei Sheng,
Supporting Information Mg 2 B 2 O 5 Nanowires Enabled Multifunctional Solid-State Electrolyte with High Ionic Conductivity, Excellent Mechanical Properties and Flame-retardant Performance Ouwei Sheng,
Highly Durable Fuel Cell Electrode Based on Ionomer Dispersed in Glycerol
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Electronic Supplementary Information Highly Durable Fuel Cell Electrode
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Electronic Supplementary Information Highly Durable Fuel Cell Electrode
Sn Wears Super Skin: A New Design For Long Cycling Batteries
 Supporting Information Wears Super Skin: A New Design For Long Cycling Batteries Shuai Kang, Xi Chen, Junjie Niu* Department of Materials Science and Engineering, CEAS, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
Supporting Information Wears Super Skin: A New Design For Long Cycling Batteries Shuai Kang, Xi Chen, Junjie Niu* Department of Materials Science and Engineering, CEAS, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
Electronic Supplementary Information A general method to prepare transition-metal ammonium phosphate nanoflake constructed microspheres
 Electronic Supplementary Information A general method to prepare transition-metal ammonium phosphate nanoflake constructed microspheres Changfeng Zeng, a Wei Wei b and Lixiong Zhang b a College of Mechanic
Electronic Supplementary Information A general method to prepare transition-metal ammonium phosphate nanoflake constructed microspheres Changfeng Zeng, a Wei Wei b and Lixiong Zhang b a College of Mechanic
Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction
 Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction Jing-Fang Huang,* a and Wen-Rhone Chang a Supporting information Experimental Section
Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction Jing-Fang Huang,* a and Wen-Rhone Chang a Supporting information Experimental Section
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental section Materials: Ni(CH 3 COO) 2 4H 2 O, SeO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental section Materials: Ni(CH 3 COO) 2 4H 2 O, SeO
Supporting Information. on Degradation of Dye. Chengsi Pan and Yongfa Zhu* Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, , China
 Supporting Information A New Type of BiPO 4 Oxy-acid Salt Photocatalyst with High Photocatalytic Activity on Degradation of Dye Chengsi Pan and Yongfa Zhu* Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University,
Supporting Information A New Type of BiPO 4 Oxy-acid Salt Photocatalyst with High Photocatalytic Activity on Degradation of Dye Chengsi Pan and Yongfa Zhu* Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University,
Remarkable Reinforcement Effect in Sulfonated. Aromatic Polymers as Fuel Cell Membrane
 Supporting Information Remarkable Reinforcement Effect in Sulfonated Aromatic Polymers as Fuel Cell Membrane Junpei Miyake, Masato Kusakabe, Akihiro Tsutsumida, and Kenji Miyatake*,, Clean Energy Research
Supporting Information Remarkable Reinforcement Effect in Sulfonated Aromatic Polymers as Fuel Cell Membrane Junpei Miyake, Masato Kusakabe, Akihiro Tsutsumida, and Kenji Miyatake*,, Clean Energy Research
Hydrogen sulfide poisoning and recovery of PEMFC Pt-anodes
 Journal of Power Sources 165 (2007) 814 818 Short communication Hydrogen sulfide poisoning and recovery of PEMFC Pt-anodes Weiyu Shi a,b, Baolian Yi a, Ming Hou a,, Fenning Jing a, Pingwen Ming a a Fuel
Journal of Power Sources 165 (2007) 814 818 Short communication Hydrogen sulfide poisoning and recovery of PEMFC Pt-anodes Weiyu Shi a,b, Baolian Yi a, Ming Hou a,, Fenning Jing a, Pingwen Ming a a Fuel
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. A Rechargeable Aluminum-Ion Battery Based on MoS 2. Microsphere Cathode
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION A Rechargeable Aluminum-Ion Battery Based on MoS 2 Microsphere Cathode Zhanyu Li a, Bangbang Niu a, Jian Liu a, Jianling Li a* Feiyu Kang b a School of Metallurgical and Ecological
SUPPORTING INFORMATION A Rechargeable Aluminum-Ion Battery Based on MoS 2 Microsphere Cathode Zhanyu Li a, Bangbang Niu a, Jian Liu a, Jianling Li a* Feiyu Kang b a School of Metallurgical and Ecological
Properties of CdTe films brush plated on high temperature substrates
 Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing 10 (2007) 36 40 Properties of CdTe films brush plated on high temperature substrates K.R. Murali a,, B. Jayasutha b a Electrochemical Materials Science Division,
Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing 10 (2007) 36 40 Properties of CdTe films brush plated on high temperature substrates K.R. Murali a,, B. Jayasutha b a Electrochemical Materials Science Division,
PVP-Functionalized Nanometer Scale Metal Oxide Coatings for. Cathode Materials: Successful Application to LiMn 2 O 4 Spinel.
 PVP-Functionalized Nanometer Scale Metal Oxide Coatings for Cathode Materials: Successful Application to LiMn 2 O 4 Spinel Nanoparticles Hyesun Lim, Jaephil Cho* Department of Applied Chemistry Hanyang
PVP-Functionalized Nanometer Scale Metal Oxide Coatings for Cathode Materials: Successful Application to LiMn 2 O 4 Spinel Nanoparticles Hyesun Lim, Jaephil Cho* Department of Applied Chemistry Hanyang
An XPS and Atomic Force Microscopy Study of the Micro-Wetting Behavior of Water on Pure Chromium* 1
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 3 (2003) pp. 389 to 395 #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals An XPS and Atomic Force Microscopy Study of the Micro-Wetting Behavior of Water on Pure Chromium* 1 Rongguang
Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 3 (2003) pp. 389 to 395 #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals An XPS and Atomic Force Microscopy Study of the Micro-Wetting Behavior of Water on Pure Chromium* 1 Rongguang
High Performance Lithium Battery Anodes Using Silicon Nanowires
 Supporting Online Materials For High Performance Lithium Battery Anodes Using Silicon Nanowires Candace K. Chan, Hailin Peng, Gao Liu, Kevin McIlwrath, Xiao Feng Zhang, Robert A. Huggins and Yi Cui * *To
Supporting Online Materials For High Performance Lithium Battery Anodes Using Silicon Nanowires Candace K. Chan, Hailin Peng, Gao Liu, Kevin McIlwrath, Xiao Feng Zhang, Robert A. Huggins and Yi Cui * *To
CHAPTER 6. SYNTHESIS OF CoFe 2 O 4 POWDER VIA PVA ASSISTED SOL-GEL PROCESS 2
 70 CHAPTER 6 SYNTHESIS OF CoFe 2 O 4 POWDER VIA PVA ASSISTED SOL-GEL PROCESS 2 This chapter discusses the synthesis of CoFe 2 O 4 ferrites with metal nitrates as the precursors and PVA as the surfactant.
70 CHAPTER 6 SYNTHESIS OF CoFe 2 O 4 POWDER VIA PVA ASSISTED SOL-GEL PROCESS 2 This chapter discusses the synthesis of CoFe 2 O 4 ferrites with metal nitrates as the precursors and PVA as the surfactant.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 High Electrochemical Activity of the Oxide Phase in Model Ceria- and Ceria-Ni Composite Anodes William C. Chueh 1,, Yong Hao, WooChul Jung, Sossina M. Haile Materials Science, California Institute of Technology,
High Electrochemical Activity of the Oxide Phase in Model Ceria- and Ceria-Ni Composite Anodes William C. Chueh 1,, Yong Hao, WooChul Jung, Sossina M. Haile Materials Science, California Institute of Technology,
Supplementary Figure 1. Substrate X-ray diffraction patterns Supplementary Figure 2. Substrate XPS.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Substrate X-ray diffraction patterns. Patterns show the main rutile peaks, but only very weak Au peaks from the AuNPs (gold nanoparticles). The top pattern was collected after irradiation
Supplementary Figure 1. Substrate X-ray diffraction patterns. Patterns show the main rutile peaks, but only very weak Au peaks from the AuNPs (gold nanoparticles). The top pattern was collected after irradiation
ALD TiO 2 coated Silicon Nanowires for Lithium Ion Battery Anodes with enhanced Cycling Stability and Coulombic Efficiency
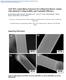 ALD TiO 2 coated Silicon Nanowires for Lithium Ion Battery Anodes with enhanced Cycling Stability and Coulombic Efficiency Elmira Memarzadeh Lotfabad a, Peter Kalisvaart a,*, Kai Cui b, Alireza Kohandehghan
ALD TiO 2 coated Silicon Nanowires for Lithium Ion Battery Anodes with enhanced Cycling Stability and Coulombic Efficiency Elmira Memarzadeh Lotfabad a, Peter Kalisvaart a,*, Kai Cui b, Alireza Kohandehghan
