Is Phaseotus vulgaris for Labeling Neural Grafts?
|
|
|
- Caren Teresa Newton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Is Phaseotus vulgaris for Labeling Neural Grafts? Leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) a Useful Marker J.N. Kott, L.E. Westrum A3 and A.M. Bhatia I Departments ofneurological Surgery1, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA Biological Structure, and Restorative Dentistrya, ABSTRACT The lectin Phaseo/u vu/gada leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) has come into wide use as an anterograde neuroanatomical tracer. The ability of this lectin to fill entire neurons and remain in place over long periods suggested it might be an ideal marker for donor cells to be grafted into hosts for long survival periods. We have used the lectin PHA-L to mark fetal rat olfactory bulb (OB) cells prior to grafting into host rat OBs. Hosts were sacrificed at various times up to 9 weeks after grafting, and tissue was immunohistochemically processed for PHA reactivity. After 2 and 4 weeks survival, sparse patterns of labeled cells were observed within the host OBs. However, after 9 weeks survival, few ff any labeled cells were visible within host tissue. We conclude that PHA-L may be a less than satisfactory marker for fetal rat cells (other than astrocytes) which are to be identified in host tissue after a period of several weeks. Key words: Transplantation; grafting; fetal; donor; host; Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L); olfactory system Reprint address: J.N. Kott, Ph.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, RI-20 University of Washington Seattle, WA In neural grafting paradigms involving replacement of host tissue with homotypic donor cells, results are often ambiguous unless fetal cells are in some way marked prior to grafting. Several different marking methods, including horse-radish peroxidase(hrp), fluorescent dyes, and [ah]thymidine, have been used with varying degrees of success /5,6,8,9,12/. However, HRP and fluorescent dyes may be too short-lived within neurons for many experiments /8,9,11/ is and [ah]thymidine, which only labels nuclei, incorporated only at the time of cell division or DNA repair. Phaseolus vulgaris leueoagglutinin (PHA-L), a leetin commonly used as an anterograde neuro-anatomieal tracer, is longer-lived than HRP within cells/4/. Previous reports suggest that this leetin may (under certain conditions) be a useful marker for donor cells. Specifically, PHA-L has been used to mark cultured astroeytes /5,6[ and cultured human spinal cord tens transplanted into rat motor cortex/7/. In a short-term study (5-21 days survival), PHA-L has been used to mark suspensions of fetal rat brain subsequently grafted into various areas of adult rat brains/10/. However, our experience, as well as that of other researchers with whom we have communicated (Kunkel and Sehwartzloin, unpublished observations; Raisman and Field, personal communication), suggests that PHA-L is a less than satisfactory long-term label for fetal rat neurons. These findings are presented in the hope that our experience may prevent unnecessary duplication of effort. VOLUME 2, NO. 3-4,
2 250 J.N. KOTr, L.E. WESTRUM & A.M. BHATIA Approximately 20 fetal rat olfactory bulbs (OBs) (El8; crown-rump length mm) were removed, trypsinized, and dissociated in glucose enhanced saline solution/2/. Following dissociation, cells were incubated in the same medium with 0.5% PHA-L for 15 minutes. These incubation parameters were similar to those used for cultured human spinal cord cells/7/(1% PHA-L for 10 rain.) and produced strong initial labeling of donor cells (Fig. 1). To remove as much unbound PHAL as possible, labeled cells were washed 4 times by adding at least 20 volumes of medium followed by mild eentrifugation and removal (with a pipette) of excess medium. Host animals were 5-day-old neonates from a single litter of the same strain as the donors. Immediately following preparation of donor cells, grafting was performed under ether anesthesia. The dorsal surface of the right OB was exposed using standard surgical technique. Eight animals each received an injection of approximately 12/1 of cell suspension slowly delivered into the core of the right OB using a drawn glass injector pipette (approx. 400/m O.D.) attached to a 50/xl syringe by a length of PE-100 tubing. Three animals received control injections of a similar volume of medium only. Injections were manually delivered over a period of seconds. In order to help estimate the completeness of labeling, a similar volume of labeled cells was placed in the dorsal cortex of an adult host for in vivo 24-hour incubation. The adult cortex, rather than the OB, was selected for this examination because of ready access and greater mechanical stability during processing. To assess the number of cells per injection, 12/xl portions of the cell suspension were placed on gelatinized slides, fixed, and stained with cresyl violet for immediate microscopic examination. After survival of 2 and 4 weeks, groups composed of 3 animals with grafts and 1 control animal were sacrificed by transeardial perfusion under deep anesthesia with 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer. The remaining 2 animals with grafts and single control were similarly sacrificed after 9 weeks survival. After 1 hour postfixation in the above solution, brains were removed and cryoprotected in phosphate buffered 30% sucrose for at least one day. Subsequently, 33/xm sagittal sections were cut on a freezing microtome and processed for PHA reactivity using Vector ABC reagents for immunoperoxidase/4/. After a 24-hour in vivo incubation period the brain of the single adult host was prepared as above except that 8/xm eryostat sections were processed for PHA reactivity on slides.in all cases, attemate control sections were processed without the primary antibody. Cell counts made from mierographs of the 12 /zl portions of cell suspension applied to slides indicated that each portion contained at least several thousand cells. After 24 hours of in vivo incubation (within the adult cortex) a large number of apparently viable and heavily labeled cells were found "dumped" within the wound channel left by the injection cannula. While most of these cells were well localized within the wound channel and were usually attached to its sides, occasional PHA reactive cells were found within what appeared to be undisturbed adjacent host tissue (Fig.l). After 2 and 4 weeks survival times a few labeled cells were seen in the host OBs (Fig. 2). While the number of animals in each group was too small to allow a meaningful quantitative comparison of the number of labeled cells present after 2 and 4 weeks, the number and pattern of labeled cells were qualitively similar at the two survival times. At both survival times the number of cells exhibiting reactivity appeared quite low compared with the original number of cells injected. By 9 weeks post-grafting, only a small number of reactive cells could be seen in one brain and none at all in the other. The labeling that was present in the first 9 week survival brain was considerably less dense than that in the 2- and 4-week preparations. We have attempted to evaluate the applicability of PHA-L as a marker for a dissociated mixture of cell types grafted into a homotypic host area. When evaluating any marker for donor cells there are several issues to be considered: 1) proportion of cells initially labeled; 2) proportion of labeled cells surviving for a useful time period; 3) survival of marker within labeled cells; 4) dilution of marker through cell division; 5) transfer of marker from donor to host cells (either transynaptieally or from labeled nonviable donor cells); 6) possible JOURNAL OF NEURAL TRANSPLANTATION & PLASTICFI
3 IS PHA-L A USEFUL MARKER? 251 Fig. 1" Uncounterstained cryostat section from deep within adult host cortex into which PHA-L labeled cell suspension was Injected 24 hours earlier. Heavily labeled cells (arrow heads for example) along wound channel () are presumed to be of donor origin, but note labeled cells (arrows) in host cortex. Bar 100 m. Fig. 2: Spame pattern of labeled cells in a 33/m noncounterstained frozen section after a 4-week survival period. Some macrophages (arrow) are still present at this stage. Bar 1 O0/m.
4 252 J.N. KOTT, L.E. WE,STRUM & A.M. BHATIA migration of labeled donor cells away from the graft site. Finally, one must be reasonably assured that unincorporated label can be separated from the donor cells prior to grafting. Obviously, if a marker does not strongly label a significant portion of the donor cells to begin with, the other issues are difficult to address. In some situations/e.g., see ref. 5,6/where the aim is to show the unquantified migration of astroeytes from one part of the CNS to another, PHA-L may be quite appropriate. However, while it would appear that most cells which we originally exposed to this leetin are labeled (Fig. 1), the low yield of labeled cells (even at 2 weeks post-grafting) makes this method highly questionable for many purposes. Such a low proportion of cells containing marker is probably not attributable to dilution of label through cell division, since many had undergone their final division at the stage that the fetal cells were taken /3L Further, in support of a previous report/7/, we found little evidence for extensive migration of labeled cells. Therefore, our low yield of labeled cells may be explained by either of at least two mechanisms acting singly or in combination, i.e., PHA-L may have been degraded within cells or many labeled cells may not survive for as long as 2 weeks. It is possible that the few labeled cells seen in host tissue adjacent to the injeeiton site in our 24 hour in vivo preparation were undergoing migration, and it is possible that migration could explain a small percentage of the labeled cells lost from the graft site. However, it is equally possible that these are host cells labeled by PHA-L either remaining in the injection medium or released from nonviable donor cells. This potentially troublesome finding should be addressed in any future studies attempting to use PHA-L as a marker for grafted cells. The successful use of PHA-L as a marker for neuron-like cells has been reported in at least two cases/7,10/. In the first case, PHA-L labeled human spinal cord material, cultured for an unspecified period (apparently measured in weeks), was grafted into rat motor cortex. It is unclear why spinal cord cells containing PHA-L should survive and retain the label more readily than cells of the OB. It is possible that, prior to labeling, the cultured spinal cord cells may have reached a greater state of maturity and differentiation than our OB cells. Perhaps the loss or retention of PHA reactivity is related to differences in metabolic activity of cells in varying stages of development. In the second ease/10], studies indicated that PHA-L labeled donor cells are readily demonstrated within the host brain after relatively short (5-21 day) survival periods. These studies indicate that lectin toxicity may not be a problem in cell survival but do not address the issue of the final disposition of the leetin in longer term experiments. In confn mation of the findings presented here, PHA-L has proven to be an unsatisfactory marker for fetal donor cells in several other instances: OB fragments grafted into host OB (our laboratory, unpublished); striatal cell suspensions grafted into hippoeampal locations (Kunkel and Sehwartzkroin, unpublished; Raisman and Field, personal communication). This report is presented in the hope that it may prevent duplication of effort that.might be better directed elsewhere. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by NIH Grant NS (LEW) and NS (Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Washington). We acknowledge Paul Schwartz for photographic reproductions and Patrieia Midtskog for secretarial help. REFERENCES 1. Angevine JB Jr, Sidman RL Autoradiographic study of cell migration during histogenesis of cerebral cortex in the mouse. Nature 1961;191: Banker GA, Cowan WM. Rat hippoeampal neuron in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res 1977;126: Bayer SA. 3H-Thymidine-radiographie studies of neurogenesis in the rat olfactory bulb. Exp Brain R 1983;50: Gerfen CR, Sawehenko PE. A method for anterograde axonal tracing of chemically spe,dfied circuits in the central nervous system: combined Phaseolus vulgaris leueoagglutinin (PHA-L) tract tracing and immunohistoehemistry. Brain Res 1985;343: JOURNAL OF NEURAL TRANSPLANTATION & PLASTICFI
5 IS PHA-L A USEFUL MARKER? Goldberg WJ, Bernstein JJ. Transplant-derived astrocytes migrate into host lumbar and cervical spinal cord after implantation of E14 fetal cerebral cortex into adult thoracic spinal cord. J Neurosci Res 1987;17: Goldberg WJ, Bernstein JJ. Migration of cultured fetal spinal cord astrocytes into adult host cervical cord and medulla following transplantation into thoracic spinal cord. J Neurosci Res 1988;19: Kamo H, Kim SU, McGeer PL, Araki M, Tomimoto H, Kimura H. Transplantation of cultured human spinal cord cells into the rat motor cortex: use of Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin as a cell marker. Neurosci Lett 1987;76: McConnell SIC Migration and differentiation of cerebral cortical neurons after transplantation into the brains of ferrets. Science 1985;229: McConnell SIC Fates of visual cortical neurons in the ferret after isochronic and heterochronic transplantation. J Neurosci 1988;8: Stoppinni L, Helm GA, Stringer JL, Lothman EW, Bennett JP Jr. In vitro and in vivo transplantation of fetal rat brain cells following incubation with various anatomic tracing substances. J Neurosci Methods 1989;27: Warr B, DeOlmos JS, Heimer L. Horseradish peroxidase: the basic procedure. In: Heimer L, Robards MJ, Eds, Neuroanatomical Tract-Tracing Methods. New York: Plenum, 1981, pp Wells J, Vietje BP, Wells DG, Boucher M, Bodony RP. Transplantation of labeled brain cell suspensions between species. Soc Neurosci Abstr 1985;11:585. VOLUME 2, NO. 3-4, 1991
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials The potential of Antheraea pernyi silk for spinal cord repair A. Varone 1, D. Knight 2, S. Lesage 2, F. Vollrath 2,3, A.M. Rajnicek 1, W. Huang 1,* 1 Institute of Medical Sciences,
Supplementary Materials The potential of Antheraea pernyi silk for spinal cord repair A. Varone 1, D. Knight 2, S. Lesage 2, F. Vollrath 2,3, A.M. Rajnicek 1, W. Huang 1,* 1 Institute of Medical Sciences,
Transplantation of Axol TM hnpcs into neonatal rat cerebral cortex
 Experts Protocol Series Transplantation of Axol TM hnpcs into neonatal rat cerebral cortex Application Protocol Kindly provided by Melissa R Andrews, University of St Andrews Appli catio n Prot Table of
Experts Protocol Series Transplantation of Axol TM hnpcs into neonatal rat cerebral cortex Application Protocol Kindly provided by Melissa R Andrews, University of St Andrews Appli catio n Prot Table of
Piscataway, NJ February 2007
 Final Progress Report for the New Jersey Commission on Spinal Cord Research Submitted by David P. Crockett, PhD for the late Ira B. Black, MD Department of Neuroscience and Cell Biology UMDNJ-Robert Wood
Final Progress Report for the New Jersey Commission on Spinal Cord Research Submitted by David P. Crockett, PhD for the late Ira B. Black, MD Department of Neuroscience and Cell Biology UMDNJ-Robert Wood
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0941 TITLE: Spinal Cord Repair with Engineered Nervous Tissue PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Douglas H. Smith, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0941 TITLE: Spinal Cord Repair with Engineered Nervous Tissue PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Douglas H. Smith, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia
Translation of Biomaterial-based Therapies for the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury: The Neuro-Spinal Scaffold and Bioengineered Neural Trails
 Translation of Biomaterial-based Therapies for the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury: The Neuro-Spinal Scaffold and Bioengineered Neural Trails Alex A. Aimetti, PhD Sr. Director, Medical Education October
Translation of Biomaterial-based Therapies for the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury: The Neuro-Spinal Scaffold and Bioengineered Neural Trails Alex A. Aimetti, PhD Sr. Director, Medical Education October
Tadanori Ogata 1, Hideki Horiuchi 1, Tadao Morino 1, Sintaro Yamaoka 1, Hiromasa Miura 2.
 Intrathecal injection of autologous macrophages genetically modified to secrete BDNF by ex vivo electroporation improves hind limb motor function after thoracic spinal cord injury in rats. Tadanori Ogata
Intrathecal injection of autologous macrophages genetically modified to secrete BDNF by ex vivo electroporation improves hind limb motor function after thoracic spinal cord injury in rats. Tadanori Ogata
Precocious neurofilament antigen expression
 Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 1987, 79: 91-100 Elsevier JNS 02814 Down's syndrome Precocious neurofilament antigen expression Audrius V. Plioplys Surrey Place Centre and Department of Neurology,
Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 1987, 79: 91-100 Elsevier JNS 02814 Down's syndrome Precocious neurofilament antigen expression Audrius V. Plioplys Surrey Place Centre and Department of Neurology,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fujii et al. 10.1073/pnas.1217563110 A Human Cen chromosome 4q ART3 NUP54 SCARB2 FAM47E CCDC8 Tel B Bac clones RP11-54D17 RP11-628A4 Exon 1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 3 PCR region
Supporting Information Fujii et al. 10.1073/pnas.1217563110 A Human Cen chromosome 4q ART3 NUP54 SCARB2 FAM47E CCDC8 Tel B Bac clones RP11-54D17 RP11-628A4 Exon 1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 3 PCR region
RUTGERS. Executive Director NJ Commission on Spinal Cord Research PO Box 360 Trenton, NJ
 RUTGERS W. M. KECK CENTER FOR COLLABORATIVE NEUROSCIENCE 604 Allison Road, D251, Piscataway, NJ 08854-8082 USA Dept. of Cell Biology and Neuroscience (732) 445-6sn, (732) 445-2061, Fax: (732) 445-2063
RUTGERS W. M. KECK CENTER FOR COLLABORATIVE NEUROSCIENCE 604 Allison Road, D251, Piscataway, NJ 08854-8082 USA Dept. of Cell Biology and Neuroscience (732) 445-6sn, (732) 445-2061, Fax: (732) 445-2063
BrdU IHC Kit. For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells
 K-ASSAY BrdU IHC Kit For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells Cat. No. KT-077 For Research Use Only. Not for Use in
K-ASSAY BrdU IHC Kit For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells Cat. No. KT-077 For Research Use Only. Not for Use in
Supplementary Methods. Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to. graft disease propagation
 1 Supplementary Methods Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to graft disease propagation Neural transplantation and clinical assessment Detailed information
1 Supplementary Methods Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to graft disease propagation Neural transplantation and clinical assessment Detailed information
BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instruction Manual
 BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instruction Manual Features Easy to use system Reagents titered for success Proven protocol Ordering Information Catalog Number X1545K Size 50 Slides Format Immunohistochemistry
BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instruction Manual Features Easy to use system Reagents titered for success Proven protocol Ordering Information Catalog Number X1545K Size 50 Slides Format Immunohistochemistry
ab BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit
 ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray
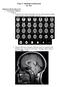 Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray Method in Brain Research 1. Non-Invasive (Human) o Imaging Computerized (Axial) Tomography (X-rays). Static pictures and high spatial resolution. Horizontal plane only.
Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray Method in Brain Research 1. Non-Invasive (Human) o Imaging Computerized (Axial) Tomography (X-rays). Static pictures and high spatial resolution. Horizontal plane only.
NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE.
 NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE. D. R. Aguirre, N. DiMassa, Chrystal Johnson, H. Eran, R. Perez, C.V.R. Sharma, M.V.R. Sharma,
NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE. D. R. Aguirre, N. DiMassa, Chrystal Johnson, H. Eran, R. Perez, C.V.R. Sharma, M.V.R. Sharma,
Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit (rnt-3-elisa)
 Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit (rnt-3-elisa) Cat. No. EK0474 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) is a new member of the nerve growth factor gene family which plays an important
Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit (rnt-3-elisa) Cat. No. EK0474 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) is a new member of the nerve growth factor gene family which plays an important
THE EFFECTS OF POLYETHYLENE PARTICLE PHAGOCYTOSIS ON THE VIABILITY OF MATURE HUMAN MACROPHAGES BY PETER ASPINALL, KYRA BURNETT, JOE MAHER, CAT TJAN
 THE EFFECTS OF POLYETHYLENE PARTICLE PHAGOCYTOSIS ON THE VIABILITY OF MATURE HUMAN MACROPHAGES BY PETER ASPINALL, KYRA BURNETT, JOE MAHER, CAT TJAN THE AUTHORS S. Xing Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical
THE EFFECTS OF POLYETHYLENE PARTICLE PHAGOCYTOSIS ON THE VIABILITY OF MATURE HUMAN MACROPHAGES BY PETER ASPINALL, KYRA BURNETT, JOE MAHER, CAT TJAN THE AUTHORS S. Xing Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical
Therapeutic Cell Replacement. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Therapeutic Cell Replacement Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Neuronal Death Neurons are lost due to four main causes: Trauma Toxin Hypoxia (typically loss of air or blood
Therapeutic Cell Replacement Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Neuronal Death Neurons are lost due to four main causes: Trauma Toxin Hypoxia (typically loss of air or blood
ab CFSE Fluorescent Cell Labeling Kit
 ab113853 CFSE Fluorescent Cell Labeling Kit Instructions for Use For the durable fluorescent labeling of live cells for fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry, population growth studies and within sample
ab113853 CFSE Fluorescent Cell Labeling Kit Instructions for Use For the durable fluorescent labeling of live cells for fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry, population growth studies and within sample
Rat Cortical Stem Cells
 Rat Cortical Stem Cells Catalog Number NSC001 For cortical stem cell expansion and differentiation into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. This package insert must be read in its entirety before
Rat Cortical Stem Cells Catalog Number NSC001 For cortical stem cell expansion and differentiation into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. This package insert must be read in its entirety before
ab CFSE Fluorescent Cell Labeling Kit
 ab113853 CFSE Fluorescent Cell Labeling Kit Instructions for Use For the durable fluorescent labeling of live cells for fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry, population growth studies and within sample
ab113853 CFSE Fluorescent Cell Labeling Kit Instructions for Use For the durable fluorescent labeling of live cells for fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry, population growth studies and within sample
Human BDNF ELISA. For the precise measurement of BDNF in human serum, plasma, body fluids, tissue homogenate or cell culture supernates.
 Product information User s Manual Human BDNF ELISA For the precise measurement of BDNF in human serum, plasma, body fluids, tissue homogenate or cell culture supernates. BE69099 Storage: 96 2-8 C RUO For
Product information User s Manual Human BDNF ELISA For the precise measurement of BDNF in human serum, plasma, body fluids, tissue homogenate or cell culture supernates. BE69099 Storage: 96 2-8 C RUO For
An Outline of the Use of Horseradish Peroxidase in Neuroanatomical Tract-Tracing
 An Outline of the Use of Horseradish Peroxidase in Neuroanatomical Tract-Tracing Lex C. Towns Lex C. Towns is Professor of Anatomy at the Kirksville College of Osteopathic Medicine in Kirksville, Mo, He
An Outline of the Use of Horseradish Peroxidase in Neuroanatomical Tract-Tracing Lex C. Towns Lex C. Towns is Professor of Anatomy at the Kirksville College of Osteopathic Medicine in Kirksville, Mo, He
Input. Pulldown GST. GST-Ahi1
 A kd 250 150 100 75 50 37 25 -GST-Ahi1 +GST-Ahi1 kd 148 98 64 50 37 22 GST GST-Ahi1 C kd 250 148 98 64 50 Control Input Hap1A Hap1 Pulldown GST GST-Ahi1 Hap1A Hap1 Hap1A Hap1 Figure S1. (A) Ahi1 western
A kd 250 150 100 75 50 37 25 -GST-Ahi1 +GST-Ahi1 kd 148 98 64 50 37 22 GST GST-Ahi1 C kd 250 148 98 64 50 Control Input Hap1A Hap1 Pulldown GST GST-Ahi1 Hap1A Hap1 Hap1A Hap1 Figure S1. (A) Ahi1 western
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information hoi et al. 1.173/pnas.1187918 SI Materials and Methods Histology. Mice were killed under deep anesthesia by transcardial perfusion with PS, followed by fixation with 4% formalin
Supporting Information hoi et al. 1.173/pnas.1187918 SI Materials and Methods Histology. Mice were killed under deep anesthesia by transcardial perfusion with PS, followed by fixation with 4% formalin
Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit
 Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit Catalog No. SCR019 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0) 23 8026 2233
Neural Stem Cell Characterization Kit Catalog No. SCR019 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0) 23 8026 2233
Acetyl-p53 (K381) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
 Acetyl-p53 (K381) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit Catalog No. KA8015C Detection and Quantification of Acetyl-p53 (K381) Protein Concentration in Cell. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic
Acetyl-p53 (K381) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit Catalog No. KA8015C Detection and Quantification of Acetyl-p53 (K381) Protein Concentration in Cell. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic
Total PFK-2 liv/tes Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
 Total PFK-2 liv/tes Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit Catalog No. KA3774C Detection and Quantification of PFK-2 liv/tes Protein Concentration in Cell. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic
Total PFK-2 liv/tes Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit Catalog No. KA3774C Detection and Quantification of PFK-2 liv/tes Protein Concentration in Cell. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic
Monoclonal antibodies
 Monoclonal antibodies 1. Boost the best-responded mouse 3-5 days before fusion. 2. Build up frozen stock of myeloma cells (NS-1 or P 3 U 1 etc.) in MEM + 10% FCS containing 0.1
Monoclonal antibodies 1. Boost the best-responded mouse 3-5 days before fusion. 2. Build up frozen stock of myeloma cells (NS-1 or P 3 U 1 etc.) in MEM + 10% FCS containing 0.1
Table of Contents. 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components Additional Required Reagents Required Equipment...
 i Table of Contents 1.0 Overview of the NeuroCult NCFC Assay 2.0 Materials 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components... 4 2.2 Additional Required Reagents... 4 2.3 Required Equipment... 4 3.0 Preparation
i Table of Contents 1.0 Overview of the NeuroCult NCFC Assay 2.0 Materials 2.1 NeuroCult NCFC Assay Kit (Rat) Components... 4 2.2 Additional Required Reagents... 4 2.3 Required Equipment... 4 3.0 Preparation
ab Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis
 ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
ab Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis
 ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
INOS. Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit. Catalog #: OKAG00807
 INOS Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG00807 Please read the provided manual entirely prior to use as suggested experimental protocols may have changed. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended
INOS Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG00807 Please read the provided manual entirely prior to use as suggested experimental protocols may have changed. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended
Final Narrative. Principal Investigator Name, Address, Telephone Number
 Final Narrative Report Principal Investigator Name, Address, Telephone Number Melitta Schachner, Ph.D. W.M. Keck Center for Collaborative Neuroscience 604 Allison Road, 0-251 Piscataway, NJ 08854 Ph: 732-445-1780
Final Narrative Report Principal Investigator Name, Address, Telephone Number Melitta Schachner, Ph.D. W.M. Keck Center for Collaborative Neuroscience 604 Allison Road, 0-251 Piscataway, NJ 08854 Ph: 732-445-1780
**Update Regarding MJFF & UNC-generated AAV Viral Vectors** -- April, 2013
 **Update Regarding MJFF & UNC-generated AAV Viral Vectors** -- April, 2013 Based upon more extensive, long-term analyses using these viral vectors, Drs. Ron Mandel and Deniz Kirik determined that the extent
**Update Regarding MJFF & UNC-generated AAV Viral Vectors** -- April, 2013 Based upon more extensive, long-term analyses using these viral vectors, Drs. Ron Mandel and Deniz Kirik determined that the extent
Banking Human Neural Stem Cells for Clinical Applications. Lisa Fox Director, Cell Process Development & Operations
 Banking Human Neural Stem Cells for Clinical Applications Lisa Fox Director, Cell Process Development & Operations 7 th Annual Somatic Cell Therapy Symposium September 27, 2007 Stem Cells Inc. Approach
Banking Human Neural Stem Cells for Clinical Applications Lisa Fox Director, Cell Process Development & Operations 7 th Annual Somatic Cell Therapy Symposium September 27, 2007 Stem Cells Inc. Approach
Cell Lineage in the Development of the Leech Nervous System
 Cell Lineage in the Development of the Leech Nervous System DAVID A. WEISBLAT Department of Molecular Biology, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 (U.S.A) INTRODUCTION Knowledge of the lines of
Cell Lineage in the Development of the Leech Nervous System DAVID A. WEISBLAT Department of Molecular Biology, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 (U.S.A) INTRODUCTION Knowledge of the lines of
Supplemental Figure S1. PGRN Binding to Sortilin.
 1 Neuron, volume 68 Supplemental Data Sortilin-Mediated Endocytosis Determines Levels of the Frontotemporal Dementia Protein, Progranulin Fenghua Hu, Thihan Padukkavidana, Christian B. Vægter, Owen A.
1 Neuron, volume 68 Supplemental Data Sortilin-Mediated Endocytosis Determines Levels of the Frontotemporal Dementia Protein, Progranulin Fenghua Hu, Thihan Padukkavidana, Christian B. Vægter, Owen A.
Overview of Immunohistochemistry
 Overview of Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemistry (IHC) combines anatomical, immunological and biochemical techniques to identify discrete tissue components by the interaction of target antigens with
Overview of Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemistry (IHC) combines anatomical, immunological and biochemical techniques to identify discrete tissue components by the interaction of target antigens with
ab BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit
 ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
TITLE: Preclinical Studies of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Astrocyte Transplantation in ALS
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-050 TITLE: Preclinical Studies of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Astrocyte Transplantation in ALS PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nicholas J. Maragakis, M.D. Hongjun Song, Ph.D.
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-050 TITLE: Preclinical Studies of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Astrocyte Transplantation in ALS PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nicholas J. Maragakis, M.D. Hongjun Song, Ph.D.
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP019695 TITLE: Fabricating Neural and Cardiomyogenic Stem Cell Structures by a Novel Rapid Prototyping--the Inkjet Printing Method
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP019695 TITLE: Fabricating Neural and Cardiomyogenic Stem Cell Structures by a Novel Rapid Prototyping--the Inkjet Printing Method
Alex A. Aimetti, PhD Sr. Director, Medical Education October 29, InVivo Therapeutics
 Translation of Biomaterial-based Therapies for the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Spinal Cord Injury: The Neuro-Spinal Scaffold and Bioengineered Neural Trails Alex A. Aimetti, PhD Sr. Director, Medical
Translation of Biomaterial-based Therapies for the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Spinal Cord Injury: The Neuro-Spinal Scaffold and Bioengineered Neural Trails Alex A. Aimetti, PhD Sr. Director, Medical
Lab 1 Microdissection 1. Microdissection
 Lab 1 Microdissection 1 Lab 1. Microdissection The goal of this techniques lab is to understand how to dissect and process tissues that have been incubated in bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU). BrdU is a synthetic
Lab 1 Microdissection 1 Lab 1. Microdissection The goal of this techniques lab is to understand how to dissect and process tissues that have been incubated in bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU). BrdU is a synthetic
Cortical Neural Induction Kit. Protocol version 1.0
 Cortical Neural Induction Kit Protocol version 1.0 Protocol version 1.0 Table of Contents Product Information 2 Preparation of Reagents 3 Protocol Overview 4 Seeding ipscs 4 Cortical Neural Induction
Cortical Neural Induction Kit Protocol version 1.0 Protocol version 1.0 Table of Contents Product Information 2 Preparation of Reagents 3 Protocol Overview 4 Seeding ipscs 4 Cortical Neural Induction
Tissue Engineering and the Brain. Susan Perry Bioengineering Program Lehigh University
 Tissue Engineering and the Brain Susan Perry Bioengineering Program Lehigh University ...all the most acute, most powerful, and most deadly diseases, and those which are most difficult to be understood
Tissue Engineering and the Brain Susan Perry Bioengineering Program Lehigh University ...all the most acute, most powerful, and most deadly diseases, and those which are most difficult to be understood
Nerve Regeneration in the Central Nervous System by a Semaphorin Inhibitor
 Nerve Regeneration in the Central Nervous System by a Semaphorin Inhibitor Kazuo KUMAGAI Kaoru KIKUCHI Akiyoshi KISHINO Nobuo HOSOTANI Akira ITO Ikutaro SAJI Toru KIMURA It is well known that injured neurons
Nerve Regeneration in the Central Nervous System by a Semaphorin Inhibitor Kazuo KUMAGAI Kaoru KIKUCHI Akiyoshi KISHINO Nobuo HOSOTANI Akira ITO Ikutaro SAJI Toru KIMURA It is well known that injured neurons
XIAOSONG YU AND RICHARD L. DOTY
 Brain Research Bulletin, Vol. 44, No.2, pp. 199-203, 1997 Copyright @ 1997 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0361-9230/97 $17.00 +.00 ELSEVIER PII 80361-9230(97)00092-0 TECHNICAL
Brain Research Bulletin, Vol. 44, No.2, pp. 199-203, 1997 Copyright @ 1997 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0361-9230/97 $17.00 +.00 ELSEVIER PII 80361-9230(97)00092-0 TECHNICAL
Therapeutic Cell Replacement. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Therapeutic Cell Replacement Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Dec 13) Thursday (Dec 14) Friday (Dec 15) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in
Therapeutic Cell Replacement Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Dec 13) Thursday (Dec 14) Friday (Dec 15) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in
MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE
 Neurodevelopment MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD Brain Development Proliferation Differentiation Migration Axon and dendrite development Synaptogenesis Synapse Pruning Apoptosis
Neurodevelopment MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD Brain Development Proliferation Differentiation Migration Axon and dendrite development Synaptogenesis Synapse Pruning Apoptosis
ISCoS 2016 Annual Scientific Meeting Clinical Trials Update for The INSPIRE Study: Neuro-Spinal Scaffold
 ISCoS 2016 Annual Scientific Meeting Clinical Trials Update for 2016 The INSPIRE Study: Neuro-Spinal Scaffold Kristin M. Neff, MSc VP Clinical Operations & Project Management Agenda 1. Neuro-Spinal Scaffold
ISCoS 2016 Annual Scientific Meeting Clinical Trials Update for 2016 The INSPIRE Study: Neuro-Spinal Scaffold Kristin M. Neff, MSc VP Clinical Operations & Project Management Agenda 1. Neuro-Spinal Scaffold
VDL602.2 RAPID ASSAY FOR DETERMINING ADENOVIRAL VECTOR TITER
 1. Purpose 1.1. The purpose of this protocol is to determine the number of infectious adenoviral particles. 1.2. The starting material is purified adenoviral vectors. 1.3. This protocol is based upon the
1. Purpose 1.1. The purpose of this protocol is to determine the number of infectious adenoviral particles. 1.2. The starting material is purified adenoviral vectors. 1.3. This protocol is based upon the
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS
 PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
Intelligent and automatic in vivo detection and quantification of transplanted cells in MRI (Supporting Material)
 Intelligent and automatic in vivo detection and quantification of transplanted cells in MRI (Supporting Material) Muhammad Jamal Afridi 1, Arun Ross 1, Xiaoming Liu 1, Margaret F. Bennewitz 2, Dorela D.
Intelligent and automatic in vivo detection and quantification of transplanted cells in MRI (Supporting Material) Muhammad Jamal Afridi 1, Arun Ross 1, Xiaoming Liu 1, Margaret F. Bennewitz 2, Dorela D.
CytoGLOW. IKK-α/β. Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit. Catalog #: CB5358
 CytoGLOW IKK-α/β Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: CB5358 Please read the provided manual entirely prior to use as suggested experimental protocols may have changed. Research Purposes Only.
CytoGLOW IKK-α/β Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: CB5358 Please read the provided manual entirely prior to use as suggested experimental protocols may have changed. Research Purposes Only.
Preparation of thin slices for light microscopy
 Preparation of thin slices for light microscopy Optical light microscopy course 23.10.2012 Kirsi Rilla Shortly: Histological sample preparation for microscopy 1. Fixation: To fix the tissue components
Preparation of thin slices for light microscopy Optical light microscopy course 23.10.2012 Kirsi Rilla Shortly: Histological sample preparation for microscopy 1. Fixation: To fix the tissue components
All quality control test results are reported on a lot specific Certificate of Analysis which is available at or upon request.
 PRIME-XV Neural Basal Medium PRIME-XV Neural Basal Medium is a chemically-defined basal medium optimized for the culture and maintenance of neuronal cells when supplemented with PRIME-XV IS21 Supplement
PRIME-XV Neural Basal Medium PRIME-XV Neural Basal Medium is a chemically-defined basal medium optimized for the culture and maintenance of neuronal cells when supplemented with PRIME-XV IS21 Supplement
Human Peptide YY EIA
 KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Human Peptide YY EIA For the quantitative determination of Peptide YY in human serum and plasma. Cat. No. KT-378 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 9822378 PRODUCT INFORMATION Human
KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Human Peptide YY EIA For the quantitative determination of Peptide YY in human serum and plasma. Cat. No. KT-378 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 9822378 PRODUCT INFORMATION Human
Induction of deep layer cortical neurons in vitro
 Development 124, 915-923 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 DEV9511 915 Induction of deep layer cortical neurons in vitro Amy P. Bohner, Rebecca M. Akers and Susan K.
Development 124, 915-923 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 DEV9511 915 Induction of deep layer cortical neurons in vitro Amy P. Bohner, Rebecca M. Akers and Susan K.
Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit
 Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit GenWay ID: GWB-ZZD026 Size 96T(8 12 divisible strips) For quantitative detection of rat Neurotrophin-3 in cell culture supernates and serum. Typical Data Obtained from Rat
Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit GenWay ID: GWB-ZZD026 Size 96T(8 12 divisible strips) For quantitative detection of rat Neurotrophin-3 in cell culture supernates and serum. Typical Data Obtained from Rat
The New News in Stem Cell Research Andrés Bratt-Leal, PhD 12/1/2017
 The New News in Stem Cell Research Andrés Bratt-Leal, PhD 12/1/2017 Cell Therapy and Parkinson s Disease Very specific neural degeneration >50% of DA neurons are gone by diagnosis 1 million in the USA,
The New News in Stem Cell Research Andrés Bratt-Leal, PhD 12/1/2017 Cell Therapy and Parkinson s Disease Very specific neural degeneration >50% of DA neurons are gone by diagnosis 1 million in the USA,
Human Dermal Fibroblast Manual
 Human Dermal Fibroblast Manual INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL ZBM0023.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult or Neonatal Dermal Fibroblast Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders
Human Dermal Fibroblast Manual INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL ZBM0023.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Adult or Neonatal Dermal Fibroblast Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada orders
TNF-α ELISA, Mouse. Cat. No. KT-129 K-ASSAY. For the quantitative determination of TNF-α in mouse serum and culture media. For research use only.
 K-ASSAY TNF-α ELISA, Mouse For the quantitative determination of TNF-α in mouse serum and culture media Cat. No. KT-129 For research use only. 1 Rev. 052708 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION TNF-α ELISA, Mouse
K-ASSAY TNF-α ELISA, Mouse For the quantitative determination of TNF-α in mouse serum and culture media Cat. No. KT-129 For research use only. 1 Rev. 052708 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION TNF-α ELISA, Mouse
Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation
 Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation In vitro neurological research presents many challenges due to the difficulty in establishing high-yield neuronal
Protocols for Neural Progenitor Cell Expansion and Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation In vitro neurological research presents many challenges due to the difficulty in establishing high-yield neuronal
Human Hepatic Organoids
 Human Hepatic Organoids Product Information Catalog. No. Product Name Format ax41163 Human Hepatic Organoids Stock Conc. Storage on Arrival 1 cryopreserved vial N/A Liquid Nitrogen Thawing Instructions
Human Hepatic Organoids Product Information Catalog. No. Product Name Format ax41163 Human Hepatic Organoids Stock Conc. Storage on Arrival 1 cryopreserved vial N/A Liquid Nitrogen Thawing Instructions
Androgen Receptor (Phospho-Tyr363) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit. Catalog #: OKAG02138
 Androgen Receptor (Phospho-Tyr363) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02138 Please read the provided manual entirely prior to use as suggested experimental protocols may have changed. Research
Androgen Receptor (Phospho-Tyr363) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02138 Please read the provided manual entirely prior to use as suggested experimental protocols may have changed. Research
Cell Surface-Anchored Fluorescent Aptamer Sensor Enables. Imaging of Chemical Transmitter Dynamics
 Supporting Information for Cell Surface-Anchored Fluorescent Aptamer Sensor Enables Imaging of Chemical Transmitter Dynamics Takeshi Tokunaga, Shigeyuki Namiki, Katsuhiro Yamada, Takahiro Imaishi, Hiroshi
Supporting Information for Cell Surface-Anchored Fluorescent Aptamer Sensor Enables Imaging of Chemical Transmitter Dynamics Takeshi Tokunaga, Shigeyuki Namiki, Katsuhiro Yamada, Takahiro Imaishi, Hiroshi
Human Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit
 Human Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit CATALOG NO: IRKTAH5200 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE For quantitative detection of human Neurotrophin-3 in cell culture supernates and serum. BACKGROUND Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3)
Human Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit CATALOG NO: IRKTAH5200 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE For quantitative detection of human Neurotrophin-3 in cell culture supernates and serum. BACKGROUND Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3)
Human Skeletal Muscle Myoblast Care Manual: Maintenance and Differentiation from Myoblasts to Myocytes
 Human Skeletal Muscle Myoblast Care Manual: Maintenance and Differentiation from Myoblasts to Myocytes STORAGE CONDITIONS Media: Short Term 4 C 6 months -20 C F or research use only. Not approved for human
Human Skeletal Muscle Myoblast Care Manual: Maintenance and Differentiation from Myoblasts to Myocytes STORAGE CONDITIONS Media: Short Term 4 C 6 months -20 C F or research use only. Not approved for human
Frozen tissue section
 IHC Protocol - Frozen Tissue Author : Dan Souw Immunohistochemistry on Frozen tissues IHC Protocol - Frozen Tissue: An introduction This is the second post in a series on immunohistochemistry (IHC). The
IHC Protocol - Frozen Tissue Author : Dan Souw Immunohistochemistry on Frozen tissues IHC Protocol - Frozen Tissue: An introduction This is the second post in a series on immunohistochemistry (IHC). The
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Zhu J, Zhou L, XingWu F. Tracking neural stem cells in patients
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Zhu J, Zhou L, XingWu F. Tracking neural stem cells in patients
Resolve Panel A A Qualitative Test for the Identification of Unexpected Blood Group Antibodies
 Revised October 2015 Reagent Red Blood Cells Resolve Panel A A Qualitative Test for the Identification of Unexpected Blood Group Antibodies 719510 Rx ONLY SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION When an unexpected antibody
Revised October 2015 Reagent Red Blood Cells Resolve Panel A A Qualitative Test for the Identification of Unexpected Blood Group Antibodies 719510 Rx ONLY SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION When an unexpected antibody
Technical Manual No Version
 TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit Cat. No. L00301 (For Cryopreserved Tissue Sections, FITC-labled POD) Technical Manual No. 0269 Version 01132011 I Description. 1 II Key Features.... 1 III Kit Contents.. 1
TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit Cat. No. L00301 (For Cryopreserved Tissue Sections, FITC-labled POD) Technical Manual No. 0269 Version 01132011 I Description. 1 II Key Features.... 1 III Kit Contents.. 1
EGFR (Phospho-Ser695)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 EGFR (Phospho-Ser695) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02090 Please read the provided manual entirely
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 EGFR (Phospho-Ser695) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02090 Please read the provided manual entirely
Immunohistochemistry guide
 Immunohistochemistry guide overview immunohistochemistry Overview Immunohistochemistry is a laboratory technique utilized for the visual detection of antigens in tissue. When working with cells this technique
Immunohistochemistry guide overview immunohistochemistry Overview Immunohistochemistry is a laboratory technique utilized for the visual detection of antigens in tissue. When working with cells this technique
for SCI: Challenges for Entry and Execution of Phase 1 Clinical Trials Challenges and Opportunities of Cellular Therapeutic Development
 Case Study: Human Embryonic Stem Cell Based Therapy for SCI: Challenges for Entry and Execution of Phase 1 Clinical Trials Jane S Lebkowski Ph.D NHLBI-PACT Workshop Sept 15, 2011 Challenges and Opportunities
Case Study: Human Embryonic Stem Cell Based Therapy for SCI: Challenges for Entry and Execution of Phase 1 Clinical Trials Jane S Lebkowski Ph.D NHLBI-PACT Workshop Sept 15, 2011 Challenges and Opportunities
Methodology for Immunohistochemistry. Learning Objectives:
 Proteomics Methodology for Immunohistochemistry Methodology for Immunohistochemistry A staining process for identifying the proteins location in cells, tissues by using antigen-antibody property. Immuno
Proteomics Methodology for Immunohistochemistry Methodology for Immunohistochemistry A staining process for identifying the proteins location in cells, tissues by using antigen-antibody property. Immuno
HELICA BIOSYSTEMS, INC. MOUSE C-REACTIVE PROTEIN QUANTITATION BY ELISA FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
 HELICA BIOSYSTEMS, INC. MOUSE C-REACTIVE PROTEIN QUANTITATION BY ELISA FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY INTENDED USE The Helica C-reactive protein assay is intended for the detection and quantification of mouse C-reactive
HELICA BIOSYSTEMS, INC. MOUSE C-REACTIVE PROTEIN QUANTITATION BY ELISA FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY INTENDED USE The Helica C-reactive protein assay is intended for the detection and quantification of mouse C-reactive
SeeDB: a simple and morphology-preserving optical clearing agent for neuronal circuit reconstruction
 Nature Neuroscience Supplementary Information SeeDB: a simple and morphology-preserving optical clearing agent for neuronal circuit reconstruction Meng-Tsen Ke, Satoshi Fujimoto, and Takeshi Imai. Correspondence
Nature Neuroscience Supplementary Information SeeDB: a simple and morphology-preserving optical clearing agent for neuronal circuit reconstruction Meng-Tsen Ke, Satoshi Fujimoto, and Takeshi Imai. Correspondence
The kit is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for in vitro quantitative measurement of CCSA-4 in. Reagents Quantity Reagents Quantity
 Catalog No: YLA0017HU 96 Test Human colon cancer-specific antigen-4(ccsa-4)elisa Kit FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH ENTIRE procedure BEFORE BEGINNING!
Catalog No: YLA0017HU 96 Test Human colon cancer-specific antigen-4(ccsa-4)elisa Kit FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH ENTIRE procedure BEFORE BEGINNING!
ebioscience BrdU Kit for IHC/ICC Colorimetric Catalog Number: RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
 Page 1 of 1 ebioscience BrdU Kit for IHC/ICC Colorimetric Catalog Number: 8800-6599 RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Product Information Contents: ebioscience BrdU Kit
Page 1 of 1 ebioscience BrdU Kit for IHC/ICC Colorimetric Catalog Number: 8800-6599 RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Product Information Contents: ebioscience BrdU Kit
BrdU Cell Proliferation ELISA
 K-ASSAY BrdU Cell Proliferation ELISA Non-isotopic immunoassay for the quantitation of BrdU incorporation into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells Cat. No. KT-076 For Research Use Only.
K-ASSAY BrdU Cell Proliferation ELISA Non-isotopic immunoassay for the quantitation of BrdU incorporation into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells Cat. No. KT-076 For Research Use Only.
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Research Article Cell Biology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS ON MESENCHYMAL STROMAL CELLS UNDER XENO-FREE CULTURE CONDITIONS FOR CLINICAL USE JAIANAND
Research Article Cell Biology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS ON MESENCHYMAL STROMAL CELLS UNDER XENO-FREE CULTURE CONDITIONS FOR CLINICAL USE JAIANAND
Mouse/Rat Neural Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit
 Mouse/Rat Neural Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit Catalog Number SC013 Reagents for the identification of mouse/rat Neural Stem Cells (NSCs) by in vitro functional differentiation. This package
Mouse/Rat Neural Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit Catalog Number SC013 Reagents for the identification of mouse/rat Neural Stem Cells (NSCs) by in vitro functional differentiation. This package
CELL THERAPIES FOR SPINAL CORD INJURIES IN DOGS: WILL IT WORK?
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk CELL THERAPIES FOR SPINAL CORD INJURIES IN DOGS: WILL IT WORK? Author : NICOLAS GRANGER, ROBIN FRANKLIN, NICK JEFFERY Categories
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk CELL THERAPIES FOR SPINAL CORD INJURIES IN DOGS: WILL IT WORK? Author : NICOLAS GRANGER, ROBIN FRANKLIN, NICK JEFFERY Categories
MimEX TM GI Human Descending Colon Stem Cells
 MimEX TM GI Human Descending Colon Stem Cells Adult Gastrointestinal Stem Cells for Use With MimEX GI Reagents Catalog Number: MIM006 Size: 1 vial, ~ 100,000 cells PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The MimEX GI Tissue
MimEX TM GI Human Descending Colon Stem Cells Adult Gastrointestinal Stem Cells for Use With MimEX GI Reagents Catalog Number: MIM006 Size: 1 vial, ~ 100,000 cells PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The MimEX GI Tissue
IHC staining protocol. Paraffin, frozen and free-floating sections
 IHC staining protocol Paraffin, frozen and free-floating sections IHC staining protocol Contents Paraffin and frozen sections Immunostaining free-floating sections Signal amplification Paraffin and frozen
IHC staining protocol Paraffin, frozen and free-floating sections IHC staining protocol Contents Paraffin and frozen sections Immunostaining free-floating sections Signal amplification Paraffin and frozen
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes
 Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
Hypoxyprobe -1 Green Kit Kit contents:
 Updated 2015 1 PRODUCT INSERT Hypoxyprobe, Inc 121 Middlesex Turnpike Burlington, MA 01803 USA www.hypoxyprobe.com Hypoxyprobe -1 Green Kit Kit contents: Solid pimonidazole HCl (Hypoxyprobe -1) FITC conjugated
Updated 2015 1 PRODUCT INSERT Hypoxyprobe, Inc 121 Middlesex Turnpike Burlington, MA 01803 USA www.hypoxyprobe.com Hypoxyprobe -1 Green Kit Kit contents: Solid pimonidazole HCl (Hypoxyprobe -1) FITC conjugated
Fluorescence Microscopy. Terms and concepts to know: 10/11/2011. Visible spectrum (of light) and energy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Louisiana Tech University Ruston, Louisiana Microscopy Workshop Dr. Mark DeCoster Associate Professor Biomedical Engineering 1 Terms and concepts to know: Signal to Noise Excitation
Fluorescence Microscopy Louisiana Tech University Ruston, Louisiana Microscopy Workshop Dr. Mark DeCoster Associate Professor Biomedical Engineering 1 Terms and concepts to know: Signal to Noise Excitation
The Ultimate Low Cell Binding Surface
 The Ultimate Low Cell Binding Surface Thermo Scientific Nunc HydroCell Surface SINGLE CELL CULTURES Grow cells that are sensitive to activation and differentiation signals arising from cell adhesion CELL
The Ultimate Low Cell Binding Surface Thermo Scientific Nunc HydroCell Surface SINGLE CELL CULTURES Grow cells that are sensitive to activation and differentiation signals arising from cell adhesion CELL
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
* Presented at the meeting of the American Association of Pathologists and Bacteriologists, Cleveland, Ohio, April 2,
 THE NEUTRALIZATION OR DESTRUCTION OF DIPHTHERIA TOXIN BY TISSUE* BY AUGUSTUS WADSWORTH, M.D., Am) ELLA N. HOPPE (From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Branch
THE NEUTRALIZATION OR DESTRUCTION OF DIPHTHERIA TOXIN BY TISSUE* BY AUGUSTUS WADSWORTH, M.D., Am) ELLA N. HOPPE (From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Branch
NEW STAINS IN TISSUE DIAGNOSIS
 NEW STAINS IN TISSUE DIAGNOSIS CHARLES F. GESCHICKTER, M.D. (Prom the Surgical Pathological Lahoratory of the Johns Hopkins Hospital ami Univel'sily, Baltimore, Maryland) The use of stains has long been
NEW STAINS IN TISSUE DIAGNOSIS CHARLES F. GESCHICKTER, M.D. (Prom the Surgical Pathological Lahoratory of the Johns Hopkins Hospital ami Univel'sily, Baltimore, Maryland) The use of stains has long been
STEMdiff Astrocyte Differentiation Kit and STEMdiff Astrocyte Maturation Kit
 Kit and Kit Catalog #08540 Catalog #08550 1 Kit 1 Kit Product Description Kit (Catalog #08540) is used to rapidly and efficiently generate astrocyte precursors from neural progenitor cells (NPCs) derived
Kit and Kit Catalog #08540 Catalog #08550 1 Kit 1 Kit Product Description Kit (Catalog #08540) is used to rapidly and efficiently generate astrocyte precursors from neural progenitor cells (NPCs) derived
SAMPLE LITERATURE Please refer to included weblink for correct version.
 REVISED & UPDATED Edvo-Kit #269 Introduction to ELISA Reactions Experiment Objective: This experiment introduces concepts and methodologies of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). See page 3 for
REVISED & UPDATED Edvo-Kit #269 Introduction to ELISA Reactions Experiment Objective: This experiment introduces concepts and methodologies of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). See page 3 for
Section of Morphological and Behavioral Neuroscience Protocol for low density primary neuron cultures
 Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology Section of Morphological and Behavioral Neuroscience Protocol for low density primary neuron cultures B. Lardi-Studler, C. Sidler, J.-M. Fritschy Revised March
Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology Section of Morphological and Behavioral Neuroscience Protocol for low density primary neuron cultures B. Lardi-Studler, C. Sidler, J.-M. Fritschy Revised March
Various Methods of Pukinje Cells Transplantation and their Functional Response in Lurcher Mutant Mice
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 1, p. 79 84 79) Various Methods of Pukinje Cells Transplantation and their Functional Response in Lurcher Mutant Mice Schmidtmayerová B., Cendelín J., Korelusová
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 1, p. 79 84 79) Various Methods of Pukinje Cells Transplantation and their Functional Response in Lurcher Mutant Mice Schmidtmayerová B., Cendelín J., Korelusová
Transfection Reagent INTRODUCTION SPECIFICATIONS MATERIALS. For Research Use Only. Materials Supplied. Materials required, but not supplied
 TransIT-Neural Transfection Reagent INTRODUCTION TransIT-Neural Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in various neural cell types.
TransIT-Neural Transfection Reagent INTRODUCTION TransIT-Neural Transfection Reagent is specifically optimized to provide exceptional transfection efficiency of plasmid DNA in various neural cell types.
TUNEL Universal Apoptosis Detection Kit ( Biotin-labeled POD )
 TUNEL Universal Apoptosis Detection Kit ( Biotin-labeled POD ) Cat. No. L00290 Technical Manual No. 0267 Version 03112011 I Description. 1 II Key Features.... 1 III Kit Contents.. 1 IV Storage.. 2 V Procedure...
TUNEL Universal Apoptosis Detection Kit ( Biotin-labeled POD ) Cat. No. L00290 Technical Manual No. 0267 Version 03112011 I Description. 1 II Key Features.... 1 III Kit Contents.. 1 IV Storage.. 2 V Procedure...
