LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT: AN OVERVIEW
|
|
|
- Anne Fletcher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT: AN OVERVIEW 279 Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 31(2)(2015) pp EM International Printed in India. All rights reserved LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT: AN OVERVIEW *PRIYANKA, **HEMANT SHARMA, #MEERA AND #M. K. LAKHOTIYA * MPUAT, Udaipur, ** Agro Economic Research Centre, Vidyanagar, Anand (Gujarat), # CoA, SKRAU, Bikaner (Rajasthan), India (Received 2 March, 2015; accepted 15 May, 2015) Key words : Land, Gujarat, Degradation, Water, Deforestation, Population, Agriculture ABSTRACT Land degradation can be considered in terms of the loss of actual or potential productivity or utility as a result of natural or anthropic factors; it is the decline in land quality or reduction in its productivity. Gujarat is the one of the fastest growing states of India. The state has adopted a novel pattern of progress with the strategic development of the key sectors like energy, industry and agriculture for which it has achieved ambitious double digit growth rate since 10th Five Year Plan period. The state constitutes about 6.2 per cent of total geographical area and 4.99 per cent of total population of India. As per Census 2011, about 3.47 crores people of the state live in rural areas forming about 57.4 per cent of its total population (GOI, 2011). Agriculture in Gujarat is characterized by natural disparities. A large and growing population has placed a great deal of stress on the topsoil resources of this region. Much of the land used for agriculture in the state is of a very marginal nature. This, combined with the intensive nature of the agricultural practices of this region, has placed its soil resources face a constant danger of depletion. Currently, the heavy application of fertilizers is required to maintain basic productive capacity. Rapid urban and industrial development, deforestation, inadequate soil conservation, the cultivation of steep slopes and overgrazing have all had a devastating impact. The resultant effects of the degradation are massive unemployment, migration of labour, regional and intergenerational disparities, loss of natural resource base and ecological imbalance. INTRODUCTION Land degradation may have significant adverse effects, particularly in developing countries (Scherr and Yadav, 1996; Rosegrant and Ringler, 1997). The few in-depth analysis of soil erosion that has been done in temperate areas indicates that the consequences are not large for aggregate agricultural productivity, al- though they are a concern for susceptible soils. Land degradation is the reduction in the capacity of the land to provide ecosystem goods and services and assure its functions over a period of time for the beneficiaries of these. Land degradation affects large areas and many people in dryland regions. Increased population pressures and excessive human expansion into drylands during long wet periods leave an increas- * Corresponding author s priyankasharma.rca@gmail.com (* Ph.D. Scholar, MPUAT, Udaipur, **Asstt. Prof., # M.Sc scholar,)
2 280 PRIYANKA ET AL. ing number of people stranded there during dry periods. In India the cost of land degradation is increasingly felt in terms of declining crop production, productivity, land use intensity, changing cropping pattern from conventional crop, high input use and declining profit (Bownder and Ravi, 1984; Joshi and Agnihotri, 1984; Joshi et al., 1987; Chopra, 1989; Parikh and Ghosh, 1995 and Reedy, 2003).Various micro and macro level of study show that the cost of land degradation is very high in india. In Kheda district of Gujrat due to salinity productivity losses ranges from 70% in the case of local paddy and wheat to 25% in the case of Potato. Productivity losses range from 10% in the low salinity to 85% in the case of high salinity for paddy (Joshi, 1987). In In sultanpur district area paddy and wheat yield went down by more 15% and 56% respectively on salt affected area (Joshi and Jha, 1992). Land degradation seriously undermines the livelihood opportunities, thus leads to poverty, migration and food insecurity. Such loss occurs mainly because of various forms of erosion (by wind and water) and of chemical and physical deterioration. (a) Erosion,The most common form of erosion is the loss of topsoil under the action of water or wind. Water runoff carries the topsoil away; this occurs under most climatic and physical conditions. Displacement of topsoil by wind action is more widespread in arid and semi-arid climates than under more humid conditions. The loss of topsoil reduces fertility because [a] as the soil becomes denser and thinner, it is less penetrable by growing roots and may become too shallow for them; [b] the capacity of the soil to retain water and make it available to plants is reduced; and [c] plant nutrients wash away with soil particles.(b) Chemical deterioration,may consist in: (a) The loss of soil nutrients (mainly nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium) or organic matter. In part, nutrients are lost through erosion: "in the humid tropics, many nutrients are leached during the intense rainstorms, especially on unprotected land"; in addition, they can be "depleted by the crops themselves, particularly if the same crops are grown on the same land year after year". (b) Salinization has "a deleterious effect on soil productivity and crop yields" in extreme cases, " damage from salinization is so great that it is technically unfeasible or totally uneconomic to reverse the process". (c) Acidification, which may occur either because of excessive application of acidifying fertilizer or because of drainage in particular types of soil; and (d) Pollution of various origins (waste accumulation, excessive use of pesticides or manuring, oil spills etc.), can strongly reduce the agricultural potential of lands.(c) Physical deterioration are recognized: (a) Soil compaction, usually resulting from the use of heavy machines on unstable soils or from cattle trampling; sealing and crusting, usually caused by the impact of raindrops. These conditions make tillage more costly and impede seedling emergence. Also, by restricting water infiltration, they cause faster run-off and water erosion. (b) Waterlogging, i.e. the rise of the water table to the root zone of plants, caused by an excessive input of water with respect to drainage capacities. (d) Desertification, is "the reduction or destruction of the land's potential, finally resulting in the appearance of desert conditions. The desertification "is only one extreme aspect of the widespread deterioration of ecosystems under the combined pressure of adverse climate and agricultural exploitation". Gujarat is the one of the fastest growing states of India. The state constitutes about 6.2 per cent of total geographical area and 4.99 per cent (60.43 million) of total population of India (GoI, 2011).The 19th Livestock Census (2012) of India has placed total livestock population at million and total of poultry birds at million (GoI, 2014), out of which, there are lakhs livestock (5.29%) and lakhs poultry (2.06%) in the state of Gujarat. Thus, looking to population pressure of human beings and livestock and their activities in addition to climatic wind and water effects, an attempt was made to measure the extent of land degradation and sustainable agriculture in Gujarat. LAND USE PATTERN At present, to meet the over-growing demand for food, farmers are left only with intensive agriculture as the land available for cultivation is decreasing. The trend not only accelerates the land degradation but also narrows down the chances for increasing the food production. The state of Gujarat occupies the northern extremity of the western sea-board of India. It has the longest coast line of 1290 kms. The state comprises of three geographical regions. The peninsula, traditionally known as Saurashtra, is essentially a hilly tract sprinkled with low mountains. Kutch on the northeast is barren and rocky and contains the famous Rann (desert) of Kutch, the big Rann in the north and the little Rann in the east. The mainland extending from the Rann of Kutch and the Aravalli Hills to the river Damanganga is on the whole a level plain of alluvial
3 LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT: AN OVERVIEW 281 soil.the average rainfall in Gujarat varies from 33 to 152 cms. The southern region of the state has an average rainfall ranging from 76 to 152 cms, Dang district have the highest average of about 190 cms. The northern district have a rainfall ranging from 51 to 102 cms. The rainfall in the southern highlands of Saurashtra and the Gulf of Cambay is approximately 63 cms while the other parts of Saurashtra have a rainfall less than 63 cms. The semi-desert area of Kutch has a very low average rainfall. Certain areas in Ahmedabad, Mehsana, Banaskantha, Panchmahal, Surendranagar, Jamnagar and Kutch districts receives very less or no rains. As the Tropic of Cancer passes through the northern border of Gujarat, the state has an intensely hot or cold climate. But the Arabian sea and the Gulf of Cambay in the west and the forest covered hills in the east soften the rigors of climatic extremes. The present geographical area of the state is 19.6 million hectares. The broad land use patterns vary remarkably across regions and districts. The detail of land use classification from to and overall for this period is shown in Table 1. In order to have proper eco-system balance, one third of the geographical region is required to be under forest cover. The forest cover in the state is 9.36 per cent. Only 5.97 per cent of the geographical area is put under non-geographical purposes such as buildings, roads, rail, canal and other permanent structures. The typographical features often put large share of area under hills, mountains, rocks and so on (classified on barren & uncultivable land) which is per cent in the state. With the proper planning, this land can be put under proper use. About 4.34 per cent area of the state is under permanent pastures and grazing lands which is mainly used for grazing purpose to the livestock. The negligible area is under tree crops and groves. Due to various regions like soil and water quality problems including acute desert cover or permanent water logging condition, per cent area of Gujarat state is under culturable waste land. The scientific reclamation of land use planning strategy is a matter of grave importance in those regions where Table 1. Land Utilization in Gujarat ('000 hectares) S.No. Classification Quinquennial Average 1. Geographical area (for the land utilization purpose) (100) Reporting area for land utilization (96.87) (i) Forest (9.36) (ii) Land put to non Agricultural uses (5.97) (iii) Barren & un culturable land (13.06) (iv) Permanent Pastures & other grazing land (4.34) (v) Land under misc Trees crops & groves (0.02) (vi) Culturable waste (10.02) (vii) Current Fallow (2.32) (viii) Other fallow land (0.09) (ix) Net area sown (51.70) 2. Area sown more than once (8.49) 3. Total cropped area (60.18) Note: Figures in parentheses are percentage of Total Geographical Area (TGA)
4 282 PRIYANKA ET AL. culturable waste land is high. The fragile nature of land and other socio-economic reasons make it necessary to put part of culturable and fallow lands for a whole year. The share of current fallow lands at state level is 2.32 per cent and decreasing over the years. Similarly the other fallow lands which is cultivable lands put fallow for 2 to 5 years to improve the quality of soil is also negligible. The net sown area which is most important class of land use out of nine classes (as mentioned above is about thousand hectare (51.70%). In fact this part of the land plays a vital role in determining the agricultural prosperity in a sustainable manner. The net sown area also increased marginally over the years. Too large share or too small share of net sown area to geographical area is detrimental to sustainable agricultural development of a state/region. Unless we keep out natural resources intact, the sustainable development of the state in general and that of agricultural sector in particular would pose serious challenges in the years to come. The area sown more than once is only 8.49 per cent which shows the poor irrigation or input facility in the state. As a whole, thousand hectare is the total cropped area of the state. A large and growing population has placed a great deal of stress on the topsoil resources of this region. Much of the land used for agriculture in the state is of a very marginal nature. This, combined with the intensive nature of the agricultural practices of this region, has placed its soil resources face a constant danger of depletion. Currently, the heavy application of fertilizers is required to maintain basic productive capacity. Some estimates have placed India's use of arable land resources at 120%, which means that fully one the land currently under cultivation is unable to Table 2. Degraded and Wastelands statistics of Gujarat (Area in ' 000 ha) District Degraded and Wastelands classes Total of Others** Total Classes Ahmedabad Amreli Anand Banaskantha Bharuch Bhavnagar Dahod Dangs Gandhi Nagar Jamnagar Junagarh Kachchh Kheda Mahsana Narmada Navasari Panchmahal Patan Porbandar Rajkot Sabarkantha Surat Surendranagar Vadodara Valsad Total Classes: 1 Exclusively water erosion (>10 tonnes/ha/yr); 2 Water erosion under open forest; 3 Exclusively saline soils; 4 Er oded saline soils; 5 Saline soils under open forest; 6 Exclusively sodic soils; 7 Mining/Industrial waste; 8 Waterlogged area (Permanent). Others**: Normal agricultural lands, water-bodies, rivers, lakes and habitats etc. Source : NBSS &LUP
5 LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT: AN OVERVIEW 283 sustain agriculture in the long term. Several factors contribute to the growing stress that has been placed on this regional agricultural land. Rapid urban and industrial development, deforestation, inadequate soil conservation, the cultivation of steep slopes and overgrazing have all had a devastating impact. The study conducted by NBSS&LUP, shows that Total degraded area in the state is 3,129 thousand ha (about 16% of TGA). The highly affected districts are: Kachchh (595 thousand ha), Surendranagar (404 thousand ha), Patan (317 thousand ha),ahmedabad (255 thousand ha), Jamnagar (196 thousand ha) and Surat (192 thousand ha). Among districts affected by water erosion, Surat ranks first with 156 thousand ha, followed by Bharuch (114 thousand ha), Dangs (84 thousand ha), Valsad (82 thousand ha), Porbandar (67 thousand ha), Navasari (66 thousand ha), Dahod (57 thousand ha) and Banaskantha (55 thousand ha). This includes erosion in open forest area also. Saline soils account for 1495 thousand ha (8% TGA); of which 519 thousand ha is found in Kachchh. Other areas affected by salinity are Surendranagar (222 thousand ha), Jamnagar (185 thousand ha), Ahmedabad (159 thousand ha) and Rajkot (106 thousand ha). Sodicity is also a major problem in Gujarat. Sodicity affected areas account for 545 thousand ha and highly affected districts are Patan (253 thousand ha), Surendranagar (119 thousand ha), Ahmedabad (96 thousand ha) and Kachchh (60 thousand ha),). Wind erosion is observed in Patan district. CONCLUSION A qualitative weighting of the plausible global economic effects of future soil degradation suggests that the greatest problems for food security in the developing countries will be found in the densely populated marginal lands. These areas also have the highest probability of significant degradation without policy action, because combating degradation will require mobilizing long-term investment and new technology development. Degradation of irrigated lands through salinization and waterlogging poses the second greatest threat, because these lands play a central role in commercial food supply. Degradation in marginal lands that are lightly populated is unlikely to impose major global economic costs (as distinct from the likely and significant global environmental costs), though many of the poorest of the poor may farm in these regions. National policy priorities will vary widely and must be determined by each country s resource endowment, the structure of agricultural supply, the geographic distribution of poverty, and the principal agricultural sources of economic growth The problem of soil degradation is therefore, posing and serious threat to the sustained agricultural production and jeopardizing food security not only for the present generation but also for the future generations. Degradation of the ecosystem particularly the land component and the consequential loss of productivity of this scarce resource would severely affect the livelihood of majority of human and livestock population. The resultant effects of the degradation are massive unemployment, migration of labour, regional and intergenerational disparities, loss of natural resource base and ecological imbalance. - Agricultural areas coming under arid and semi arid regions are more prone to erosion and degradation problems therefore more emphasis should be given to these areas. - Economically feasible techniques should be formed to tackle land degradation problems. - More projects related with groundwater development such as water harvesting, watershed management, formation of artificial recharge facilities with wastewater and rainwater should be implemented. REFERENCES Annonymous, Status report. NBSS & LUP, Bownder, B. and Ravi, C Water Logging From Irrigation Projects: An environmental Management Problem, Center for Energy and Technology. Administrative staff college of India Hyderabad. Chopra Kanchan, Land Degradation Dimensions and causalities. Indian Journal of Agricultural Economics. 44 (1) : Govt. of Gujarat, Statistical Abstract Directorate of Economics and Statistics Gujarat, Gandhinagar. GOI, Provisional Population Totals, Office of Registrar General and CensusCommissioner, Govt. of India, New Derlhi. ICAR, Report on Degraded and Wastelands of India Status and Spatial Distribution. ICAR, New Delhi. Joshi, P.K. and Agnihotri, A.K An Assessment of the adverse effects of canal irrigation in India. Indian Journal of Agricultural Economics. 39 (3) : Joshi, P.K. and Jha, D An economic inquiry into the impact of soil alkalinity and water logging. Indian Journal of Agricultural Economics. 47 (3) : Parikhit and Ghosh, Natural Resource Accounting for Soils: Towards an Empirical Estimate of Costs of Soil Degradation for India Dp 48 Indira Gandhi
6 284 PRIYANKA ET AL. Institute of Development and Research, Bombay. Rosegrant, M.W. and Ringler, C Environmental and Resource Policies: Implications for Global Food Markets. Washington, DC: International Food Policy Research Institute, January. Scherr, S.J. and Yadav, S Land Degradation in the Development world: Implications for Food, Agriculture, and the Environment to IFPRI Food Agriculture, and the Environment Discussion Paper No. 14, Washington, DC: International Food Policy Research Institute, May.
CHANGING DYNAMICS OF POPULATION IN GUJARAT: DISTRICT LEVEL ANALYSIS OF POPULATION, SEX RATIO AND URBANIZATION
 CHANGING DYNAMICS OF POPULATION IN GUJARAT: DISTRICT LEVEL ANALYSIS OF POPULATION, SEX RATIO AND URBANIZATION Prof. Tarang Solanki Assistant Professor Economics School of Social Science Gujarat University
CHANGING DYNAMICS OF POPULATION IN GUJARAT: DISTRICT LEVEL ANALYSIS OF POPULATION, SEX RATIO AND URBANIZATION Prof. Tarang Solanki Assistant Professor Economics School of Social Science Gujarat University
Growth Performance of Major Vegetable Crops in Gujarat State
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 30 (No.1) January-June 2017 pp 139-149 DOI: 10.5958/0974-0279.2017.00013.1 Growth Performance of Major Vegetable Crops in Gujarat State Daya Suvagiya, V.C. Shilpa,
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 30 (No.1) January-June 2017 pp 139-149 DOI: 10.5958/0974-0279.2017.00013.1 Growth Performance of Major Vegetable Crops in Gujarat State Daya Suvagiya, V.C. Shilpa,
ISPRS Archives XXXVIII-8/W3 Workshop Proceedings: Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture
 IMPACT ANALYSIS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON DIFFERENT CROPS IN GUJARAT, INDIA Vyas Pandey, H.R. Patel and B.I. Karande Department of Agricultural Meteorology, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110, India
IMPACT ANALYSIS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON DIFFERENT CROPS IN GUJARAT, INDIA Vyas Pandey, H.R. Patel and B.I. Karande Department of Agricultural Meteorology, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110, India
REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT LAND UTILIZATION AND AGRICULTURE
 P a g e 125 CHAPTER FIVE REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT LAND UTILIZATION AND AGRICULTURE After independence, as is well-known, the country recognized the vital link between land and livelihood of the masses in rural
P a g e 125 CHAPTER FIVE REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT LAND UTILIZATION AND AGRICULTURE After independence, as is well-known, the country recognized the vital link between land and livelihood of the masses in rural
Implications of Dynamics of Land Use Shifts in Rajasthan
 Annals of Arid Zone 53(3&4): 177-183, 2014 Implications of Dynamics of Land Use Shifts in Rajasthan Latika Sharma Rajasthan College of Agriculture, MPUAT, Udaipur 313 001, India Abstract: Land use pattern
Annals of Arid Zone 53(3&4): 177-183, 2014 Implications of Dynamics of Land Use Shifts in Rajasthan Latika Sharma Rajasthan College of Agriculture, MPUAT, Udaipur 313 001, India Abstract: Land use pattern
STATE OF LAND RESOURCES
 STATE OF LAND RESOURCES This information deals with three main dimensions pertaining to the status of land resources land use, soils, and agriculture. The first section of this article will deal with the
STATE OF LAND RESOURCES This information deals with three main dimensions pertaining to the status of land resources land use, soils, and agriculture. The first section of this article will deal with the
Table 1: Trend of Water Requirements by Different Sectors Water Requirement(MCM) Domestic
 Micro irrigation for Electricity Saving in Gujarat-A Potentiality Assessment Dr. S.Raman, Advisor, Gujarat Green Revolution Company, Vadodara The Gujarat state is situated on the western part of India.
Micro irrigation for Electricity Saving in Gujarat-A Potentiality Assessment Dr. S.Raman, Advisor, Gujarat Green Revolution Company, Vadodara The Gujarat state is situated on the western part of India.
Estimating Agricultural Sustainability in Gujarat Using Sustainable Livelihood Security Index
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 30 (No.1) January-June 2017 pp 125-131 DOI: 10.5958/0974-0279.2017.00011.8 Estimating Agricultural Sustainability in Gujarat Using Sustainable Livelihood Security
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 30 (No.1) January-June 2017 pp 125-131 DOI: 10.5958/0974-0279.2017.00011.8 Estimating Agricultural Sustainability in Gujarat Using Sustainable Livelihood Security
P.K. Viswanathan Chandra S. Bahinipati
 Determinants of Adopting and Accessing Benefits of Environmentally Benign Technologies: A study of Micro Irrigation Systems in North Gujarat, Western India P.K. Viswanathan Chandra S. Bahinipati GGKP Annual
Determinants of Adopting and Accessing Benefits of Environmentally Benign Technologies: A study of Micro Irrigation Systems in North Gujarat, Western India P.K. Viswanathan Chandra S. Bahinipati GGKP Annual
Development of Irrigation and Its Impact on Agriculture in Punjab: to
 IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 10, Issue 6 Ver. II (June. 2017), PP 57-63 www.iosrjournals.org Development of Irrigation and
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 10, Issue 6 Ver. II (June. 2017), PP 57-63 www.iosrjournals.org Development of Irrigation and
Evaluating Regional Vulnerability to Climate Change: A Case of Saurashtra
 Ind. Jn. of Agri. Econ. Vol.67, No.3, July-Sept. 2012 Evaluating Regional Vulnerability to Climate Change: A Case of Saurashtra Deepa B. Hiremath and R.L. Shiyani* I INTRODUCTION Saurashtra is a region
Ind. Jn. of Agri. Econ. Vol.67, No.3, July-Sept. 2012 Evaluating Regional Vulnerability to Climate Change: A Case of Saurashtra Deepa B. Hiremath and R.L. Shiyani* I INTRODUCTION Saurashtra is a region
Gujarat Ecology Commission Government of Gujarat LAND RESOURCES AND STATUS OF LAND DEGRADATION. (Product of ENVIS - April 2017)
 Gujarat Ecology Commission Government of Gujarat LAND RESOURCES AND STATUS OF LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT (Product of ENVIS - April 2017) LAND RESOURCES AND STATUS OF LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT In India,
Gujarat Ecology Commission Government of Gujarat LAND RESOURCES AND STATUS OF LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT (Product of ENVIS - April 2017) LAND RESOURCES AND STATUS OF LAND DEGRADATION IN GUJARAT In India,
COMBATING CLIMATE CHANGE AND LAND DEGRADATION IN THE WEST AFRICAN SAHEL: A MULTI-COUNTRY STUDY OF MALI, NIGER AND SENEGAL
 COMBATING CLIMATE CHANGE AND LAND DEGRADATION IN THE WEST AFRICAN SAHEL: A MULTI-COUNTRY STUDY OF MALI, NIGER AND SENEGAL BY PROF. S.A. IGBATAYO HEAD, DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT STUDIES AFE BABALOLA
COMBATING CLIMATE CHANGE AND LAND DEGRADATION IN THE WEST AFRICAN SAHEL: A MULTI-COUNTRY STUDY OF MALI, NIGER AND SENEGAL BY PROF. S.A. IGBATAYO HEAD, DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT STUDIES AFE BABALOLA
Dynamics of Land Use Competition in India: Perceptions and Realities. Vijay Paul Sharma
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT AHMEDABAD INDIA Dynamics of Land Use Competition in India: Perceptions and Realities Vijay Paul Sharma W.P. No. 2015-06-02 June 2015 The main objective of the working paper
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT AHMEDABAD INDIA Dynamics of Land Use Competition in India: Perceptions and Realities Vijay Paul Sharma W.P. No. 2015-06-02 June 2015 The main objective of the working paper
Gujcot Trade Association
 Gujcot Trade Association WEEKLY REPORT Market Movement from TH Sep to TH Sep Gujarat Cotton prices of 29 mm remained between, to, Rs./Candy. Outstate arrivals almost ended. All India Daily Arrivals remained
Gujcot Trade Association WEEKLY REPORT Market Movement from TH Sep to TH Sep Gujarat Cotton prices of 29 mm remained between, to, Rs./Candy. Outstate arrivals almost ended. All India Daily Arrivals remained
Family under BPL in Gujarat State District Family Poor Family Ahmedabad Amreli Anand Banaskantha
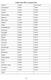 Family under BPL in Gujarat State District Family Poor Family Ahmedabad 85603 72463 Amreli 32649 35260 Anand 78174 75577 Banaskantha 124052 103811 Bharuch 70817 45647 Bhavnagar 27937 52680 Dahod 135365
Family under BPL in Gujarat State District Family Poor Family Ahmedabad 85603 72463 Amreli 32649 35260 Anand 78174 75577 Banaskantha 124052 103811 Bharuch 70817 45647 Bhavnagar 27937 52680 Dahod 135365
Gujcot Trade Association
 Gujcot Trade Association WEEKLY REPORT Market Movement from RD Sep to TH Sep Gujarat Cotton prices of 29 mm remained between, to, Rs./Candy. Outstate arrivals almost ended. All India Daily Arrivals remained
Gujcot Trade Association WEEKLY REPORT Market Movement from RD Sep to TH Sep Gujarat Cotton prices of 29 mm remained between, to, Rs./Candy. Outstate arrivals almost ended. All India Daily Arrivals remained
Chapter 1 Resources and Development
 Chapter 1 Resources and Development Resources Substances available in our environment that can be used for specific purposes and are technologically accessible, economically viable and culturally acceptable
Chapter 1 Resources and Development Resources Substances available in our environment that can be used for specific purposes and are technologically accessible, economically viable and culturally acceptable
Soil Treats, Gaps, and Technical Assessment. Agricultural University of Athens Costas Kosmas
 Soil Treats, Gaps, and Technical Assessment Agricultural University of Athens Costas Kosmas Identified important threats to European soils The European Commission adopted a Soil Thematic Strategy (COM(2006)
Soil Treats, Gaps, and Technical Assessment Agricultural University of Athens Costas Kosmas Identified important threats to European soils The European Commission adopted a Soil Thematic Strategy (COM(2006)
LADA Group Sri Lanka. Natural Resources Management Centre Department of Agriculture Sri Lanka
 LADA Group Sri Lanka Natural Resources Management Centre Department of Agriculture Sri Lanka Lies in the between longitudes 79.5-81.8 E latitudes 5.9-9.8 N Land Area 64,453.6 Km 2 Inland Water 1,156.2
LADA Group Sri Lanka Natural Resources Management Centre Department of Agriculture Sri Lanka Lies in the between longitudes 79.5-81.8 E latitudes 5.9-9.8 N Land Area 64,453.6 Km 2 Inland Water 1,156.2
Soil Degradation. Lesson Plan NRES B2-9
 Soil Degradation Lesson Plan NRES B2-9 Objectives 1. What is soil degradation? 2. How can construction result in soil degradation? 3. What are the sources of contamination, and how do they result in soil
Soil Degradation Lesson Plan NRES B2-9 Objectives 1. What is soil degradation? 2. How can construction result in soil degradation? 3. What are the sources of contamination, and how do they result in soil
ISRMUN Embracing our diversity is the first step to unity. THE UNITED NATIONS FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION
 THE UNITED NATIONS FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION Committee: The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Topic B: Tackling Land Degradation and Desertification Written by: Daniela Martellotto
THE UNITED NATIONS FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION Committee: The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Topic B: Tackling Land Degradation and Desertification Written by: Daniela Martellotto
Economics of Desertification, Land Degradation and Drought in India
 Executive Summary Economics of Desertification, Land Degradation and Drought in India Vol I: Macroeconomic assessment of the costs of degradation in India The Energy and Resources Institute 2016 Project
Executive Summary Economics of Desertification, Land Degradation and Drought in India Vol I: Macroeconomic assessment of the costs of degradation in India The Energy and Resources Institute 2016 Project
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 4.483, ISSN: , Volume 5, Issue 12, January 2018
 AGRICULTURAL LAND USE AND MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF NANGAVALLI SUB-WATERSHED, NANGAVALLI AND TOPPAIODAI(NTSW), MATTURTALUK, SALEM DISTRICT M.BALAMURUGAN* DR.A.ILANTHIRAYAN** * Research Scholar, External
AGRICULTURAL LAND USE AND MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF NANGAVALLI SUB-WATERSHED, NANGAVALLI AND TOPPAIODAI(NTSW), MATTURTALUK, SALEM DISTRICT M.BALAMURUGAN* DR.A.ILANTHIRAYAN** * Research Scholar, External
Foundation for Ecological Security, India Structure of the presentation
 Foundation for Ecological Security, India Structure of the presentation The Indian context Watershed Mgt in India Issues in Watershed Mgt What we do How we work Results Challenges 1 The Indian context
Foundation for Ecological Security, India Structure of the presentation The Indian context Watershed Mgt in India Issues in Watershed Mgt What we do How we work Results Challenges 1 The Indian context
An Economic Analysis of Land Reclamation Technologies for Amelioration of Irrigation-induced Soil Degradation
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 18 January-June 2005 pp 103-116 Research Note An Economic Analysis of Land Reclamation Technologies for Amelioration of Irrigation-induced Soil Degradation B.
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 18 January-June 2005 pp 103-116 Research Note An Economic Analysis of Land Reclamation Technologies for Amelioration of Irrigation-induced Soil Degradation B.
Chapter 13 of Agenda 21
 Chapter 13 of Agenda 21 What is Agenda 21? Agenda 21 is the global plan of action that was adopted at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil,
Chapter 13 of Agenda 21 What is Agenda 21? Agenda 21 is the global plan of action that was adopted at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil,
WASA Quiz Review. Chapter 2
 WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
Land Degradation Control in North Africa
 Land Degradation Control in North Africa By Dr. Ismail Hamdi El-Bagouri Emeritus Professor Soil and Water Conservation Desert Research Center Egypt International Workshop on Climate and Land Degradation
Land Degradation Control in North Africa By Dr. Ismail Hamdi El-Bagouri Emeritus Professor Soil and Water Conservation Desert Research Center Egypt International Workshop on Climate and Land Degradation
3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems
 3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems 3.1 Natural Environment The goals, issues and programmes regarding the natural environment of the Ten Year Perspective Development Plan 2001-2011 are shown
3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems 3.1 Natural Environment The goals, issues and programmes regarding the natural environment of the Ten Year Perspective Development Plan 2001-2011 are shown
ASSESSMENT AND MAPPING OF DESERTIFICATION STATUS IN BELLARY DISTRICT, KARNATAKA STATE, USING IRS DATA
 ASSESSMENT AND MAPPING OF DESERTIFICATION STATUS IN BELLARY DISTRICT, KARNATAKA STATE, USING IRS DATA S.L. Budihal, K. Ganesh Raj 1, R.S. Reddy, A. Natarajan, M.A. Paul 1, S. Bandyopadhyay 1, J.V. Thomas
ASSESSMENT AND MAPPING OF DESERTIFICATION STATUS IN BELLARY DISTRICT, KARNATAKA STATE, USING IRS DATA S.L. Budihal, K. Ganesh Raj 1, R.S. Reddy, A. Natarajan, M.A. Paul 1, S. Bandyopadhyay 1, J.V. Thomas
The State of the World s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific
 The State of the World s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific Resources availability land and water availability in high income countries land
The State of the World s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific Resources availability land and water availability in high income countries land
Temperature extremes, moisture deficiency and their impacts on dryland agriculture in Gujarat, India
 Drought: Research and Science-Policy Interfacing Andreu et al. (Eds) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02779-4 Temperature extremes, moisture deficiency and their impacts on dryland agriculture
Drought: Research and Science-Policy Interfacing Andreu et al. (Eds) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02779-4 Temperature extremes, moisture deficiency and their impacts on dryland agriculture
Davood Nikkami (PhD)
 Country Report of The IR. Iran 28-30 Jan., 2009, Bangkok, Thailand Workshop on Improving Agricultural Productivity, Water Use Efficiency & Strengthening Rural Livelihoods Davood Nikkami (PhD) Soil Conservation
Country Report of The IR. Iran 28-30 Jan., 2009, Bangkok, Thailand Workshop on Improving Agricultural Productivity, Water Use Efficiency & Strengthening Rural Livelihoods Davood Nikkami (PhD) Soil Conservation
Forest Resources. Unit III Population & Natural Resources
 Forest Resources Unit III Population & Natural Resources Topics Forest resources Forest resources-indian Scenario Functions of forests Importance of forests Ecological and Economical Importance Types of
Forest Resources Unit III Population & Natural Resources Topics Forest resources Forest resources-indian Scenario Functions of forests Importance of forests Ecological and Economical Importance Types of
A Comparative Analysis of Production and Marketing of Bt Cotton and Hybrid Cotton in Saurashtra Region of Gujarat State
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 19 July-December 2006 pp 293-300 A Comparative Analysis of Production and Marketing of Bt Cotton and Hybrid Cotton in Saurashtra Region of Gujarat State H.R.
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 19 July-December 2006 pp 293-300 A Comparative Analysis of Production and Marketing of Bt Cotton and Hybrid Cotton in Saurashtra Region of Gujarat State H.R.
Popular Kheti. Volume-2, Issue-3 (July-September), 2014 Available online at popularkheti.info ISSN:
 Watershed Management- Solution to Water Crisis Rahul Chopra*, Ajeet Singh, Pravisha Lahoty and Manisha Rana Rajasthan College of Agriculture, MPUAT, Udaipur-313001 *Email of corresponding author: rahulrockingcool969@gmail.com
Watershed Management- Solution to Water Crisis Rahul Chopra*, Ajeet Singh, Pravisha Lahoty and Manisha Rana Rajasthan College of Agriculture, MPUAT, Udaipur-313001 *Email of corresponding author: rahulrockingcool969@gmail.com
CONCEPT OF SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE
 CONCEPT OF SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE Agriculture is the process of producing food, feed, fibre and other desired products by cultivation of certain plants and raising of domesticated animals. Agriculture
CONCEPT OF SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE Agriculture is the process of producing food, feed, fibre and other desired products by cultivation of certain plants and raising of domesticated animals. Agriculture
MEASUREMENT OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN RAJASTHAN
 Raj. J. Extn. Edu. 20 : 44-49, 2012 MEASUREMENT OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN RAJASTHAN Bhupendra Upadhyay* ABSTRACT The present study was conducted for three points of time i.e. year 1980-81, 1990-91
Raj. J. Extn. Edu. 20 : 44-49, 2012 MEASUREMENT OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN RAJASTHAN Bhupendra Upadhyay* ABSTRACT The present study was conducted for three points of time i.e. year 1980-81, 1990-91
Achieving Land Degradation Neutrality in Landlocked Developing Countries: Challenges and Opportunities. Concept Note
 LLDC High-Level Side Event at: United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), 12 th Conference of the Parties (COP12) Achieving Land Degradation Neutrality in Landlocked Developing Countries:
LLDC High-Level Side Event at: United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), 12 th Conference of the Parties (COP12) Achieving Land Degradation Neutrality in Landlocked Developing Countries:
Sustainable Conservation Practices for Natural Resources
 Sustainable Conservation Practices for Natural Resources Rajdeep Mundiyara 1, Prem Kumar 2 and Mamta Bajya 3 1 Seed Officer, Rajasthan State Seeds Corporation,Mandore, Jodhpure 2 Department of Plant Philology,
Sustainable Conservation Practices for Natural Resources Rajdeep Mundiyara 1, Prem Kumar 2 and Mamta Bajya 3 1 Seed Officer, Rajasthan State Seeds Corporation,Mandore, Jodhpure 2 Department of Plant Philology,
Impact of Land Irrigability Classes on Crop Productivity in Canal Command Area of Gujarat: An Economic Analysis
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 19 January-June 2006 pp 83-94 Impact of Land Irrigability Classes on Crop Productivity in Canal Command Area of Gujarat: An Economic Analysis B.L. Gajja 1, Khem
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 19 January-June 2006 pp 83-94 Impact of Land Irrigability Classes on Crop Productivity in Canal Command Area of Gujarat: An Economic Analysis B.L. Gajja 1, Khem
Management of Water Resources in Gujarat
 Management of Water Resources in Gujarat Compiled by R. G. Patil N. G. Savani S. L. Pawar J. M. Patel R. B. Patel B. M. Solia AICRP on Water Management Soil and Water Management Research Unit Navsari Agricultural
Management of Water Resources in Gujarat Compiled by R. G. Patil N. G. Savani S. L. Pawar J. M. Patel R. B. Patel B. M. Solia AICRP on Water Management Soil and Water Management Research Unit Navsari Agricultural
Preeti Misra, Self Employed Women's Association SEWA, Ahmedabad, India
 Rainwater Harvesting for Drought Proofing Preeti Misra, Self Employed Women's Association SEWA, Ahmedabad, India email: bdmsa@ad1.vsnl.net.in Self Employed Women s Association The Self Employed Women s
Rainwater Harvesting for Drought Proofing Preeti Misra, Self Employed Women's Association SEWA, Ahmedabad, India email: bdmsa@ad1.vsnl.net.in Self Employed Women s Association The Self Employed Women s
WATER RESOURCES SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]
![WATER RESOURCES SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] WATER RESOURCES SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]](/thumbs/81/83970391.jpg) WATER RESOURCES SHT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Which multipurpose project is built on River Satluj How this project has led to the development of the country? The multipurpose project built over
WATER RESOURCES SHT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Which multipurpose project is built on River Satluj How this project has led to the development of the country? The multipurpose project built over
Deforestation in India: Causes and Consequences of Deforestation in India
 Deforestation in India: Causes and Consequences of Deforestation in India Deforestation in India: Causes and Consequences of Deforestation in India! Deforestation is one of the major causes to the environmental
Deforestation in India: Causes and Consequences of Deforestation in India Deforestation in India: Causes and Consequences of Deforestation in India! Deforestation is one of the major causes to the environmental
Land use type and indicators affecting land degradation and desertification. C. Kosmas Agricultural University of Athens
 Land use type and indicators affecting land degradation and desertification C. Kosmas Agricultural University of Athens Desertification The consequence of a series of important degradation processes in
Land use type and indicators affecting land degradation and desertification C. Kosmas Agricultural University of Athens Desertification The consequence of a series of important degradation processes in
SPATE IRRIGATION IN MALAWI: STATUS, POTENTIAL AND CHALLENGES.
 SPATE IRRIGATION IN MALAWI: STATUS, POTENTIAL AND CHALLENGES. Authors; Introduction Henry Njoloma (PhD) The Greenbelt Initiative, Office of President and Cabinet. Chairman, Rainwater Harvesting Association
SPATE IRRIGATION IN MALAWI: STATUS, POTENTIAL AND CHALLENGES. Authors; Introduction Henry Njoloma (PhD) The Greenbelt Initiative, Office of President and Cabinet. Chairman, Rainwater Harvesting Association
CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION
 CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 2 INTRODUCTION 3 DESERTIFICATION FACTORS IN CYPRUS CLIMATE 5 SOIL 5 WATER MANAGEMENT 5 ANTHROPOGENIC FACTORS 6 GENERAL MEASURES TO
CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 2 INTRODUCTION 3 DESERTIFICATION FACTORS IN CYPRUS CLIMATE 5 SOIL 5 WATER MANAGEMENT 5 ANTHROPOGENIC FACTORS 6 GENERAL MEASURES TO
Status, Quality and Management of Groundwater in India
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 717-722 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Status,
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 717-722 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Status,
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS FOR INTEGRATED LAND MANAGEMENT: CASE OF INDIA
 REMOTE SENSING AND GIS FOR INTEGRATED LAND MANAGEMENT: CASE OF INDIA R.B.Singh and Dilip Kumar Department of Geography Delhi School of Economics University of Delhi Delhi-110007, India E-mail:rbsgeo@hotmail.com
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS FOR INTEGRATED LAND MANAGEMENT: CASE OF INDIA R.B.Singh and Dilip Kumar Department of Geography Delhi School of Economics University of Delhi Delhi-110007, India E-mail:rbsgeo@hotmail.com
State of Common Property Land Resources (CPLRs) in Tamil Nadu: Macro-Level Evidence
 State of Common Property Land Resources (CPLRs) in Tamil Nadu: Macro-Level Evidence Dr. Andiyappan Kannan Assistant Professor Department of Economics Madurai Kamaraj University Abstract: Common Property
State of Common Property Land Resources (CPLRs) in Tamil Nadu: Macro-Level Evidence Dr. Andiyappan Kannan Assistant Professor Department of Economics Madurai Kamaraj University Abstract: Common Property
Climate Variability, Urbanization and Water in India
 Climate Variability, Urbanization and Water in India M. Dinesh Kumar Executive Director Institute for Resource Analysis and Policy Hyderabad-82 Email: dinesh@irapindia.org/dineshcgiar@gmail.com Prepared
Climate Variability, Urbanization and Water in India M. Dinesh Kumar Executive Director Institute for Resource Analysis and Policy Hyderabad-82 Email: dinesh@irapindia.org/dineshcgiar@gmail.com Prepared
Economic study of the impact of soil salinization on the productivity of dates and olives in Siwa Oasis
 Middle East Journal of Applied Sciences 4(1): 54-60, 2014 ISSN 2077-4613 54 Economic study of the impact of soil salinization on the productivity of dates and olives in Oasis Dr. Sherine.F. Mansour and
Middle East Journal of Applied Sciences 4(1): 54-60, 2014 ISSN 2077-4613 54 Economic study of the impact of soil salinization on the productivity of dates and olives in Oasis Dr. Sherine.F. Mansour and
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, and RUDAL DEVELOPMENT. 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
 Pehur High Level Canal Extension Project (RRP PAK 47024) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, and RUDAL DEVELOPMENT Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
Pehur High Level Canal Extension Project (RRP PAK 47024) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, and RUDAL DEVELOPMENT Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
Green cane trash blanket Australia - Trash blanket
 Green cane trash blanket Australia - Trash blanket Elimination of burning as a pre-harvest treatment of sugar cane, and managing the resultant trash as a protective blanket to give multiple on and off-site
Green cane trash blanket Australia - Trash blanket Elimination of burning as a pre-harvest treatment of sugar cane, and managing the resultant trash as a protective blanket to give multiple on and off-site
EXAMINATION ON THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS INCLUDING SOIL EROSION IN NEPAL
 EXAMINATION ON THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS INCLUDING SOIL EROSION IN NEPAL RISSHO UNIVERSITY DESHAR BASHU DEV 1. Introduction The key environmental problems of Nepal are related to forests, soil, solid
EXAMINATION ON THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS INCLUDING SOIL EROSION IN NEPAL RISSHO UNIVERSITY DESHAR BASHU DEV 1. Introduction The key environmental problems of Nepal are related to forests, soil, solid
State of Gujarat ( , ) Executive Summary District wise skill gap study for the
 Executive Summary District wise skill gap study for the State of Gujarat (2012-17, 2017-22) 1 1. Executive Summary National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) had mandated KPMG Advisory Services Pvt
Executive Summary District wise skill gap study for the State of Gujarat (2012-17, 2017-22) 1 1. Executive Summary National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) had mandated KPMG Advisory Services Pvt
CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION PROGRAMME IN WATER AND AGRICULTURE IN ANSEBA REGION, ERITREA
 CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION PROGRAMME IN WATER AND AGRICULTURE IN ANSEBA REGION, ERITREA NOVEMBER 2012 Country Eritrea Region Eastern Africa Key Result Area Water resource management Agricultural productivity
CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION PROGRAMME IN WATER AND AGRICULTURE IN ANSEBA REGION, ERITREA NOVEMBER 2012 Country Eritrea Region Eastern Africa Key Result Area Water resource management Agricultural productivity
Chapter 9 Soil and Agriculture Guided Notes
 Chapter 9 Soil and Agriculture Guided Notes This lecture will help you understand: The relationship between and Major agricultural The fundamentals Causes and of soil erosion and Principles of soil No-till
Chapter 9 Soil and Agriculture Guided Notes This lecture will help you understand: The relationship between and Major agricultural The fundamentals Causes and of soil erosion and Principles of soil No-till
Operational Implications: What do we Know and Understand?
 VARIABILITY AND CLIMATE CHANGE Operational Implications: What do we Know and Understand? Jamal Saghir Director Energy, Transport, Water Chair, Water Sector Board Feb 28, 2007 Outline Key Challenges and
VARIABILITY AND CLIMATE CHANGE Operational Implications: What do we Know and Understand? Jamal Saghir Director Energy, Transport, Water Chair, Water Sector Board Feb 28, 2007 Outline Key Challenges and
Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh
 12 29 March 2016 Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh Haweya Ismail Research Analyst Global Food and Water Crises Research Programme Key Points Bangladesh s geographical location, poverty
12 29 March 2016 Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh Haweya Ismail Research Analyst Global Food and Water Crises Research Programme Key Points Bangladesh s geographical location, poverty
IMPO P RT R AN A C N E C E O F G RO R UN U D N W
 Introduction IMPORTANCE OF GROUNDWATER Global Groundwater Situation ACWADAM s database Sources for presentation CGWB, various publications FAO-database Various United Nations publications. UN World Water
Introduction IMPORTANCE OF GROUNDWATER Global Groundwater Situation ACWADAM s database Sources for presentation CGWB, various publications FAO-database Various United Nations publications. UN World Water
Potentialities for CDM in Africa Sudan case Abdalla Gaafar Mohammed Forests National Corporation Sudan
 Potentialities for CDM in Africa Sudan case Abdalla Gaafar Mohammed Forests National Corporation Sudan 1 Forest Cover Background Forest area in the Sudan declined from 43% (estimated by and Harrison and
Potentialities for CDM in Africa Sudan case Abdalla Gaafar Mohammed Forests National Corporation Sudan 1 Forest Cover Background Forest area in the Sudan declined from 43% (estimated by and Harrison and
The region has a wide variety of soil types often affected by serious inherent constraints.
 Inherent Constraints of Southern Africa Soils: Implications for Sustainable Land Use Giuseppe G. Ristori and Luigi P. D Acqui CNR - Institute for Study on Ecosystems Firenze The well being of people, plants
Inherent Constraints of Southern Africa Soils: Implications for Sustainable Land Use Giuseppe G. Ristori and Luigi P. D Acqui CNR - Institute for Study on Ecosystems Firenze The well being of people, plants
Dynamics of Land Use Pattern with Special Reference to Fallow Lands An Empirical Investigation in Tamil Nadu
 Ind. Jn. of Agri. Econ. Vol. 60, No. 4, Oct.-Dec. 2005 Dynamics of Land Use Pattern with Special Reference to Fallow Lands An Empirical Investigation in Tamil Nadu C. Ramasamy, R. Balasubramanian and S.D.
Ind. Jn. of Agri. Econ. Vol. 60, No. 4, Oct.-Dec. 2005 Dynamics of Land Use Pattern with Special Reference to Fallow Lands An Empirical Investigation in Tamil Nadu C. Ramasamy, R. Balasubramanian and S.D.
Soil Organic Matter. Soil degradation has become a major concern in. What is organic matter? Organic matter in virgin and cultivated soils
 Agdex 6- Soil degradation has become a major concern in Canada. Erosion, salinization, acidification and loss of organic matter are the main forms of soil deterioration. This factsheet deals with the role
Agdex 6- Soil degradation has become a major concern in Canada. Erosion, salinization, acidification and loss of organic matter are the main forms of soil deterioration. This factsheet deals with the role
BIODIVERSITY AND MEAT CONSUMPTION
 BIODIVERSITY AND MEAT CONSUMPTION Impacts of meat consumption on biodiversity Carolyn Imede Opio Food and Agriculture Organization - FAO Outline 1. Global livestock sector trends 2. Key features important
BIODIVERSITY AND MEAT CONSUMPTION Impacts of meat consumption on biodiversity Carolyn Imede Opio Food and Agriculture Organization - FAO Outline 1. Global livestock sector trends 2. Key features important
DRINKING WATER FROM SARDAR SAROVAR PROJECT NARMADA CONTROL AUTHORITY
 International Environmental Law Research Centre DRINKING WATER FROM SARDAR SAROVAR PROJECT NARMADA CONTROL AUTHORITY NCA Publication No. 3/91, 1991 This paper can be downloaded in PDF format from IELRC
International Environmental Law Research Centre DRINKING WATER FROM SARDAR SAROVAR PROJECT NARMADA CONTROL AUTHORITY NCA Publication No. 3/91, 1991 This paper can be downloaded in PDF format from IELRC
Environmental impact of (olive) irrigation. Luca Testi IAS-CSIC Córdoba
 Environmental impact of (olive) irrigation Luca Testi IAS-CSIC Córdoba 1 This talk is NOT about the environmental impact of olive growing. Olive growing in general has environmental impacts like any other
Environmental impact of (olive) irrigation Luca Testi IAS-CSIC Córdoba 1 This talk is NOT about the environmental impact of olive growing. Olive growing in general has environmental impacts like any other
S i o l A c A idi d fication o n and n d Fe F rtility y St S atus u of o Ne N pa p l Backgr g ou o n u d
 Soil Acidification and Fertility Status of Nepal Background Nepal - 80 0 4 and 88 0 12 E longitude & 26 0 22 and 30 0 27 N latitude. China in North and India in the East, South India and West Total land
Soil Acidification and Fertility Status of Nepal Background Nepal - 80 0 4 and 88 0 12 E longitude & 26 0 22 and 30 0 27 N latitude. China in North and India in the East, South India and West Total land
Improve Water Resources, Prevent Desertification, Protect Agriculture, Farmers and Rural Livelihoods in Anantapur Dist.
 (Flyer circulated on World Water Day) Improve Water Resources, Prevent Desertification, Protect Agriculture, Farmers and Rural Livelihoods in Anantapur Dist. 1. Introduction: United Nations General Assembly
(Flyer circulated on World Water Day) Improve Water Resources, Prevent Desertification, Protect Agriculture, Farmers and Rural Livelihoods in Anantapur Dist. 1. Introduction: United Nations General Assembly
Very slight to negligible limitations no special land management practices required.
 Land Capability Classes Land and Soil Capability Class 1 Class 1 Definition Very slight to negligible limitations no special land management practices required. On-site impact of land management practices
Land Capability Classes Land and Soil Capability Class 1 Class 1 Definition Very slight to negligible limitations no special land management practices required. On-site impact of land management practices
ISPRS Archives XXXVIII-8/W3 Workshop Proceedings: Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture
 IMPACT ASSESSMENT OF IRRIGATION DEVELOPMENT IN VEDGANGA BASIN A GEOINFORMATIC APPROACH Sachin Panhalkar a and Rucha Joshi b a Lecturer, Department of Geography, Shivaji University Kolhapur, Maharashtra,
IMPACT ASSESSMENT OF IRRIGATION DEVELOPMENT IN VEDGANGA BASIN A GEOINFORMATIC APPROACH Sachin Panhalkar a and Rucha Joshi b a Lecturer, Department of Geography, Shivaji University Kolhapur, Maharashtra,
Of vital importance..
 Soil moisture Of vital importance.. Low and erratic rainfall form a significant cause of low crop production and crop failure in rainfed agriculture in the tropics However, crop and land management do
Soil moisture Of vital importance.. Low and erratic rainfall form a significant cause of low crop production and crop failure in rainfed agriculture in the tropics However, crop and land management do
Performance of Crop Sector in Gujarat during High Growth Period: Some Explorations
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 25(No.2) July-December 2012 pp 195-204 Performance of Crop Sector in Gujarat during High Growth Period: Some Explorations Niti Mehta Sardar Patel Institute of
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 25(No.2) July-December 2012 pp 195-204 Performance of Crop Sector in Gujarat during High Growth Period: Some Explorations Niti Mehta Sardar Patel Institute of
LAND USE PATTERN IN INDIAN AND PAKISTAN PUNJAB
 LAND USE PATTERN IN INDIAN AND PAKISTAN PUNJAB V. K. Sharma Sukhpal Singh and Varinder Pal Singh The states of Punjab in both the countries are main contributor to total agricultural production. The climatic
LAND USE PATTERN IN INDIAN AND PAKISTAN PUNJAB V. K. Sharma Sukhpal Singh and Varinder Pal Singh The states of Punjab in both the countries are main contributor to total agricultural production. The climatic
Dr. Vanaja Ramprasad. GREEN Foundation, Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA.
 Dr. Vanaja Ramprasad GREEN Foundation, Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA. Biogeorgraphic zones TransHimalaya Himalaya Desert Semi-Arid Western Ghats Deccan Peninsula Gangetic Plain Coasts North-East Islands
Dr. Vanaja Ramprasad GREEN Foundation, Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA. Biogeorgraphic zones TransHimalaya Himalaya Desert Semi-Arid Western Ghats Deccan Peninsula Gangetic Plain Coasts North-East Islands
Change in Land Use and Cropping Pattern in Assam: An Economic Analysis
 Economic Affairs, Vol. 63, No. 1, pp. 39-43, March 2018 DOI: 10.30954/0424-2513.2018.00150.5 2018 New Delhi Publishers. All rights reserved Change in and Use and Cropping Pattern in Assam: An Economic
Economic Affairs, Vol. 63, No. 1, pp. 39-43, March 2018 DOI: 10.30954/0424-2513.2018.00150.5 2018 New Delhi Publishers. All rights reserved Change in and Use and Cropping Pattern in Assam: An Economic
Philippine experiences in the implementation of initiatives that address Climate Change and Land Degradation. and Land Degradation
 World Meteorological Organization Philippine experiences in the implementation of initiatives that address Climate Change and Land Degradation International Workshop on Climate Change and Land Degradation
World Meteorological Organization Philippine experiences in the implementation of initiatives that address Climate Change and Land Degradation International Workshop on Climate Change and Land Degradation
Page 1 of 26 (www.unapcaem.org)
 Farm Mechanization in Punjab: Social, Economic and Environmental Implications Gurharminder Singh Sr. Scientific Officer, Punjab State Council for Science & Technology, INDIA Page 1 of 26 () Page 2 of 26
Farm Mechanization in Punjab: Social, Economic and Environmental Implications Gurharminder Singh Sr. Scientific Officer, Punjab State Council for Science & Technology, INDIA Page 1 of 26 () Page 2 of 26
CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS IN GHANA
 CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS IN GHANA OPPONG-BOADI KYEKYEKU PRINCIPAL PROGRAMME OFFICER, ENERGY RESOURCES AND CLIMATE CHANGE UNIT, ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY ACCRA, GHANA. 1 INTRODUCTION Climate change
CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS IN GHANA OPPONG-BOADI KYEKYEKU PRINCIPAL PROGRAMME OFFICER, ENERGY RESOURCES AND CLIMATE CHANGE UNIT, ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY ACCRA, GHANA. 1 INTRODUCTION Climate change
Chapter 9: Soil and Agriculture
 Chapter 9: Soil and Agriculture Terms to know: Agriculture No-till farming Cropland Rangeland Soil Monoculture Polyculture Green Revolution Chemical weathering Biological weathering Physical weathering
Chapter 9: Soil and Agriculture Terms to know: Agriculture No-till farming Cropland Rangeland Soil Monoculture Polyculture Green Revolution Chemical weathering Biological weathering Physical weathering
Improving Reclamation on Oil and Gas Well Pads in the Rocky Mountain West
 Improving Reclamation on Oil and Gas Well Pads in the Rocky Mountain West IPAMS 2008 ROCKY MOUNTAIN ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE September 5, 2008 Ed Redente, Ph.D. MWH Americas, Inc. 3665 JFK Parkway,
Improving Reclamation on Oil and Gas Well Pads in the Rocky Mountain West IPAMS 2008 ROCKY MOUNTAIN ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE September 5, 2008 Ed Redente, Ph.D. MWH Americas, Inc. 3665 JFK Parkway,
A Study on Knowledge Level and Constraints Faced by the Paddy Growers of Jammu District of J&K State
 Agro Economist - An International Journal Citation: AE: 3(1), p. 31-35 June 2016 DOI: 10.5958/2394-8159.2016.00007.4 2016 Renu Publishers. All rights reserved A Study on Knowledge Level and Constraints
Agro Economist - An International Journal Citation: AE: 3(1), p. 31-35 June 2016 DOI: 10.5958/2394-8159.2016.00007.4 2016 Renu Publishers. All rights reserved A Study on Knowledge Level and Constraints
Individual NWRM. Strip cropping along contours
 Individual NWRM Strip cropping along contours This report was prepared by the NWRM project, led by Office International de l Eau (OIEau), in consortium with Actéon Environment (France), AMEC Foster Wheeler
Individual NWRM Strip cropping along contours This report was prepared by the NWRM project, led by Office International de l Eau (OIEau), in consortium with Actéon Environment (France), AMEC Foster Wheeler
Efficient Management of Arid Land
 Efficient Management of Arid Land Prof. Dr. Riaz A. Khattak Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Agricultural University Peshawar Soil is an endangered entity Soil must be treated as living entity Global Soil Erosion According
Efficient Management of Arid Land Prof. Dr. Riaz A. Khattak Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Agricultural University Peshawar Soil is an endangered entity Soil must be treated as living entity Global Soil Erosion According
Environmental Spring Review Part 2
 1 1. The mechanization of many jobs, which resulted in major population shifts from rural areas to urban areas occurred during a. The cold war post WWII b. Ecosystem services c. Industrial Revolution d.
1 1. The mechanization of many jobs, which resulted in major population shifts from rural areas to urban areas occurred during a. The cold war post WWII b. Ecosystem services c. Industrial Revolution d.
CHANGES IN CROPPING INTENSITY IN RAJASTHAN DURING POST LIBERALIZATION STUDY
 CHANGES IN CROPPING INTENSITY IN RAJASTHAN DURING POST LIBERALIZATION STUDY Shamsher Singh Research Scholar, Department of Geography, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra ABSTRACT The intensity of cropping
CHANGES IN CROPPING INTENSITY IN RAJASTHAN DURING POST LIBERALIZATION STUDY Shamsher Singh Research Scholar, Department of Geography, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra ABSTRACT The intensity of cropping
State of Agriculture in the Uplands of Southern Mindanao
 State of Agriculture in the Uplands of Southern Mindanao (focused in UDP covered barangays) Aurea Christie Galvez-Lumaad, Environment Coordinator Resource Management Component Upland Development Programme
State of Agriculture in the Uplands of Southern Mindanao (focused in UDP covered barangays) Aurea Christie Galvez-Lumaad, Environment Coordinator Resource Management Component Upland Development Programme
World Economic and Social Survey (WESS) 2011: The Great Green Technological Transformation
 World Economic and Social Survey (WESS) 2011: The Great Green Technological Transformation Chapter I: Why a green technological transformation is needed Chapter II: The clean energy technological transformation
World Economic and Social Survey (WESS) 2011: The Great Green Technological Transformation Chapter I: Why a green technological transformation is needed Chapter II: The clean energy technological transformation
Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health
 Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health Land degradation and desertification The spread of land degradation and desertification
Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health Land degradation and desertification The spread of land degradation and desertification
Local knowledge for combatting land degradation, desertification and drought
 Local knowledge for combatting land degradation, desertification and drought Prof. Dr. Úrsula Oswald-Spring CRIM-UNAM, Mexico uoswald@gmail.com http://www.afes-press.de/html/download_oswald.html Content
Local knowledge for combatting land degradation, desertification and drought Prof. Dr. Úrsula Oswald-Spring CRIM-UNAM, Mexico uoswald@gmail.com http://www.afes-press.de/html/download_oswald.html Content
Dynamics of Labour Demand and its Determinants in Punjab Agriculture
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 26 (No.2) July-December 2013 pp 267-273 Dynamics of Labour Demand and its Determinants in Punjab Agriculture Y. Latika Devi, Jasdev Singh*, Kamal Vatta and Sanjay
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 26 (No.2) July-December 2013 pp 267-273 Dynamics of Labour Demand and its Determinants in Punjab Agriculture Y. Latika Devi, Jasdev Singh*, Kamal Vatta and Sanjay
Evidence of global warming
 INTRODUCTION Climate Change can be attributed directly or indirectly to human activities (e.g. through burning fossil fuels, deforestation, reforestation, urbanization, desertification) that alters the
INTRODUCTION Climate Change can be attributed directly or indirectly to human activities (e.g. through burning fossil fuels, deforestation, reforestation, urbanization, desertification) that alters the
B.1.5 Sodic and acidic soils
 B.1.5 Sodic and acidic soils Alice Thompson * Sodicity The effects of soil salinity have been well publicised, with dramatic images of bare and badly gullied land glistening with salt crystals, and of
B.1.5 Sodic and acidic soils Alice Thompson * Sodicity The effects of soil salinity have been well publicised, with dramatic images of bare and badly gullied land glistening with salt crystals, and of
Higher Geography Human Environments
 Duncanrig Secondary School Higher Geography Human Environments Rural Geography 1 Rural Land Degradation in the Developing World Case Study: The Sahel The Sahel is a region of semiarid grassland and desert
Duncanrig Secondary School Higher Geography Human Environments Rural Geography 1 Rural Land Degradation in the Developing World Case Study: The Sahel The Sahel is a region of semiarid grassland and desert
NREGA / Watershed Development; Implications for Green Jobs and Climate Change. Prof. Ravindranath Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
 NREGA / Watershed Development; Implications for Green Jobs and Climate Change Prof. Ravindranath Indian Institute of Science Bangalore What is the issue Can Employment Generation, Rural Development, Agricultural
NREGA / Watershed Development; Implications for Green Jobs and Climate Change Prof. Ravindranath Indian Institute of Science Bangalore What is the issue Can Employment Generation, Rural Development, Agricultural
Agriculture and Society: Part II. PA E & E Standards 4.4
 Agriculture and Society: Part II PA E & E Standards 4.4 Let s get Dirty! 1. All agriculture ultimately depends on the soil. What is soil? Soil is the upper layer of the land surface that contains pieces
Agriculture and Society: Part II PA E & E Standards 4.4 Let s get Dirty! 1. All agriculture ultimately depends on the soil. What is soil? Soil is the upper layer of the land surface that contains pieces
Radical Terraces Rwanda - Amaterasi y'indinganire
 Radical Terraces Rwanda - Amaterasi y'indinganire Locally referred to as radical terracing, the method involves earth moving operations that create reverse-slope bench terraces which have properly shaped
Radical Terraces Rwanda - Amaterasi y'indinganire Locally referred to as radical terracing, the method involves earth moving operations that create reverse-slope bench terraces which have properly shaped
