Soil Organic Matter (SOM) Important component in soil fertility The higher the SOM soil more fertile
|
|
|
- Charleen Riley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Soil Organic Matter (SOM) Important component in soil fertility The higher the SOM soil more fertile
2 Advantages of OM Supply nutrients (especially N, P, S) Increase CEC Improve physical properties( soil conditioning ) -- water infiltration -- water holding capacity -- easily tilt Act as surface mulching (control erosion, reduce water loss)
3 Chemical charcteristics of SOM Carbohydrates:- sugar, starch, cellulose and hemicellulose. Almost 75% wt Amino acid and protein Fats, waxes Acid nucleic Lignin and phenol compounds
4 Soil Organic Matter The SOM content of agricultural topsoil is usually in the range of 1 to 6%. This amount is the result of all additions and losses of SOM that have occurred over the years. Citizen Science Kansas State
5 SOM added to soil by addition of plant residues Up to 15% of organic matter is fresh residue Comprised mainly of litter fall Much can be recognized as plant residue
6 Decomposition of SOM Occurs with the help of macro and microorganisms (fungi & bacteria) on plant residue and animals Rate of decomposition depends on SOM composition
7 Rate of decomposition SOM Composition Starch and sugars Protein Hemicelluloses Cellulose Lignin, Fat Rate fast slow Eg Paddy straw decays longer compared to legumes-due to higher lignin content
8 Products of decay : 1. Simple materials: C: CO 2 N : NH 4+ /NH 3, NO 3 -, NO 2 - S: SO 3 -, SO 4 2- P 2. Humus - dark colour/black colloid size 3. Energy for living microbesheterotroph
9 Factors affecting decay of SOM 1) Types of plant: age and species 2) Plant nutrient content - decay process is accelerated by higher N source. 3) Soil nutrient content food for microbes to continue their activity 4) Aeration- Oxygen supply
10 5) Moisture 6) Temperature 7) Type and no. of organism. e.g fungi/bacteria/worm/small animal 8) Type of soil
11 C/N ratio. Soil 10:1 Peanut 20:1 Paddy straw 70:1 Saw dust 200:1 Organic matter high in N content, low C/N ratio, will decay fast SOM with low N has C/N, will decay slowly
12 How is N removed from soil? 1. Erosion: N organic in the litter and humus 2. Harvesting : N organic in the harvest 3. Leaching : NO 3 - and NH Denitrification : NO > N 2 5. Burning of soil residue N- organic - > gas
13 Management of soil N 1) Addition of organic matter: plant and animal residues, fertilizer and green fertilizer 2) Addition of N- fertilizer 3) Planting of legumes to increase N- fixation 4) Use of slow release fertilizer e.g sulfur coated urea
14 1. Influence Function of SOM a) soil aggregates and fertility b) permeability, aeration c) erodibility 2. Increase WHC and CEC 3. Nutrient source : N, S, P and micro nutrients 4. Source of energy for living soil organisms especially heterotroph
15 Management of SOM Addition of plant residues e.g corn stem, legumes, paddy straw, EFB and cow dung or chicken dung However addition of organic residue e.g sewage sludge and POME limits it s use due to increase in heavy metal content, Cd, Ar, and Pb. Control erosion on the top soil with addition of organic matter
16 Mulching with EFB
17 Control erosion on the top soil with addition of organic matter
18 Soil Organic Matter =SOM SOM is labile* -it can decline rapidly if the soil environment changes and renewable -it can be replenished by inputs of organic material to the soil. Adequate levels of SOM can be maintained with proper fertilization, crop rotations, and tillage practices if crop residues are returned to the soil. * Labile = Constantly or readily undergoing chemical, physical, or biological change or breakdown; unstable.
19 How is SOM Measured? SOM is usually measured in the laboratory as organic carbon, Soil organic matter is estimated to contain 58% organic carbon (varies from 40 to 58%) with the rest of the SOM comprising of other elements (eg, 5% N, 0.5% P and 0.5% S). A conversion to SOM from a given organic carbon analysis requires that the organic carbon content be multiplied by a factor of 1.72 (1.00/0.58). Thus, 2% SOM is about 1.2% organic carbon. Testing for Soil Organic Carbon UF/IFAS Extension Soil Testing Laboratory
20 Stable Organic Matter -Humus Thus, soil organic compounds become stabilized and resistant to further changes by microorganisms Stabilized organic matter acts like a sponge and can absorb six times its weight in water
21 HUMUS Newly-formed humus - a) combination of resistant materials from the original plant tissue, b) compounds synthesized as part of the microorganisms' tissue which remain as the organisms die. (Fluvic and Humic Acid) humus is resistant to further microbial attack- N and P are protected from ready solubility. Leaf Humus
22 Function of Humus holds water and nutrients; it sticks together & helps establish and maintain a strong crumb structure & thus reduce soil erosion it provides some nutrients (N & P) as it is slowly decayed by microbial activity, Buffers effects of pesticides humus decomposes at the rate of 2.5% per year Creates good soil Tilth
23 SOM Maintains soil Tilth aiding infiltration of air and water promoting water retention reducing erosion BMI
Fresh Residues. Up to 15% of organic matter is fresh residue Comprised mainly of litter fall Much can be recognized as plant residue
 Organic matter encompasses all organic components of a soil: Fresh residues Decomposing organic matter Stable organic matter Living organisms Soil Organic Matter Fresh Residues Up to 15% of organic matter
Organic matter encompasses all organic components of a soil: Fresh residues Decomposing organic matter Stable organic matter Living organisms Soil Organic Matter Fresh Residues Up to 15% of organic matter
A simplified guide on compost making
 A simplified guide on compost making FANGSOTO FARMER FEDERATION. Mandinaba Village, Kombo East District, West Coast Region, The Gambia. Tel: (220) 7246168 / 6563678 Email: 3158285@gmail.com This guide
A simplified guide on compost making FANGSOTO FARMER FEDERATION. Mandinaba Village, Kombo East District, West Coast Region, The Gambia. Tel: (220) 7246168 / 6563678 Email: 3158285@gmail.com This guide
The Soil Community: Managing it. Kristy Borrelli REACCH Extension Specialist
 The Soil Community: Managing it for Better Crops Kristy Borrelli REACCH Extension Specialist kborrelli@uidaho.edu Outline Soil Community Soil Quality Soil Organic Matter and Carbon Soil Organic Matter
The Soil Community: Managing it for Better Crops Kristy Borrelli REACCH Extension Specialist kborrelli@uidaho.edu Outline Soil Community Soil Quality Soil Organic Matter and Carbon Soil Organic Matter
Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa and Nematodes: Part of the Carbon to Nitrogen Transformation
 1 Nutrient Recycling with Manure and Cover Crops James J. Hoorman and Dr. Rafiq Islam OSU Extension Center at Lima and OSU Piketon Center Ohio State University Extension Introduction Converting from conventional
1 Nutrient Recycling with Manure and Cover Crops James J. Hoorman and Dr. Rafiq Islam OSU Extension Center at Lima and OSU Piketon Center Ohio State University Extension Introduction Converting from conventional
Nutrient Recycling with Manure and Cover Crops
 Nutrient Recycling with Manure and Cover Crops James J. Hoorman and Dr. Rafiq Islam OSU Extension Center at Lima and OSU Piketon Center Ohio State University Extension Introduction Converting from conventional
Nutrient Recycling with Manure and Cover Crops James J. Hoorman and Dr. Rafiq Islam OSU Extension Center at Lima and OSU Piketon Center Ohio State University Extension Introduction Converting from conventional
David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology
 How does carbon influence nitrogen availability and losses? David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology Outline Carbon cycle Global carbon cycle Soil carbon 3
How does carbon influence nitrogen availability and losses? David Rowlings Institute for Sustainable Resources Queensland University of Technology Outline Carbon cycle Global carbon cycle Soil carbon 3
FACT SHEET. Understanding Soil Microbes and Nutrient Recycling. Agriculture and Natural Resources SAG-16-10
 FACT SHEET Agriculture and Natural Resources Understanding Soil Microbes and Nutrient Recycling James J. Hoorman Cover Crops and Water Quality Extension Educator Ohio State University Extension Rafiq Islam
FACT SHEET Agriculture and Natural Resources Understanding Soil Microbes and Nutrient Recycling James J. Hoorman Cover Crops and Water Quality Extension Educator Ohio State University Extension Rafiq Islam
COMPOSTING C:N Ratios of Various Compost Materials
 COMPOSTING Composting is the active process of converting organic material to more stabilized forms of C through the action of microorganisms. Specifically, composting is the biological decomposition of
COMPOSTING Composting is the active process of converting organic material to more stabilized forms of C through the action of microorganisms. Specifically, composting is the biological decomposition of
ECO Farming in the 21 st Century Recycling Soil Nutrients
 ECO Farming in the 21 st Century Recycling Soil Nutrients James J. Hoorman hoorman.1@osu.edu www.mccc@msu.edu Healthy Soil versus Sick Soil Healthy soils have these things in common: 1) Live plants growing
ECO Farming in the 21 st Century Recycling Soil Nutrients James J. Hoorman hoorman.1@osu.edu www.mccc@msu.edu Healthy Soil versus Sick Soil Healthy soils have these things in common: 1) Live plants growing
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 18 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 18 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions
UNDERSTANDING SOIL MICROBES AND NUTRIENT RECYCLING
 O H I O S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y E X T E N S I O N extension.osu.edu agnr.osu.edu UNDERSTANDING SOIL MICROBES AND NUTRIENT RECYCLING SAG 16 Agriculture and Natural Resources Date: 09/07/2010 James
O H I O S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y E X T E N S I O N extension.osu.edu agnr.osu.edu UNDERSTANDING SOIL MICROBES AND NUTRIENT RECYCLING SAG 16 Agriculture and Natural Resources Date: 09/07/2010 James
1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients)
 1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients) Living things are built from water Nutrients: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen 3. Essential nutrients are cycled through environment
1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients) Living things are built from water Nutrients: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen 3. Essential nutrients are cycled through environment
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
SOM management: have your cake and eat it too. Organic Fertility
 SOM management: have your cake and eat it too Michelle M. Wander mwander@uiuc.edu Natural Resouces and Environmetnal Sciences UIUC Organic Fertility Soil and soil management is the foundation of organic
SOM management: have your cake and eat it too Michelle M. Wander mwander@uiuc.edu Natural Resouces and Environmetnal Sciences UIUC Organic Fertility Soil and soil management is the foundation of organic
COMPOSTING 101 to 450 Paul Walker Illinois State University - Normal
 COMPOSTING 101 to 450 Paul Walker Illinois State University - Normal COMPOST DEVELOPMENT COMPOST QUALITY ON-SIGHT QUALITY DETERMINATION POLLUTANT REMOVAL EROSION / SEDIMENT CONTROL COMPOST PROCESS FLOW
COMPOSTING 101 to 450 Paul Walker Illinois State University - Normal COMPOST DEVELOPMENT COMPOST QUALITY ON-SIGHT QUALITY DETERMINATION POLLUTANT REMOVAL EROSION / SEDIMENT CONTROL COMPOST PROCESS FLOW
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 24 September 2013 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 24 September 2013 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification
Soil organic matter consists of a variety of components. These include, in varying proportions and many Intermediate stages:
 This article is adapted in part from a publication of the Alberta Department of Agriculture and Rural Development by J. Lickacz and D. Penny in the Plant Industry Division. What is Organic Matter? Soil
This article is adapted in part from a publication of the Alberta Department of Agriculture and Rural Development by J. Lickacz and D. Penny in the Plant Industry Division. What is Organic Matter? Soil
Digestate - Maximizing its Value and Use
 Digestate - Maximizing its Value and Use Compost Matters Workshop February 4, 2016 Christine Brown - OMAFRA Digestate use for Agriculture Land Sources Farm - manure-based with other feedstocks Municipal
Digestate - Maximizing its Value and Use Compost Matters Workshop February 4, 2016 Christine Brown - OMAFRA Digestate use for Agriculture Land Sources Farm - manure-based with other feedstocks Municipal
Participant Identification. Compost for the Small and Midsize Farm. Motivations: Why use Compost?
 Participant Identification Compost for the Small and Midsize Farm John Biernbaum Michigan State University Compost producers or suppliers? Vegetable and fruit farmers? Field crop, forage, and grain farmers?
Participant Identification Compost for the Small and Midsize Farm John Biernbaum Michigan State University Compost producers or suppliers? Vegetable and fruit farmers? Field crop, forage, and grain farmers?
Sustainable Soil Conditions and Pruning Removal from Vineyards
 Project Workshop in Santorini (Greece) Congress Hall of the "Wine Tourism Center" Take-off for sustainable supply of woody biomass from agrarian pruning and plantation removal Sustainable Soil Conditions
Project Workshop in Santorini (Greece) Congress Hall of the "Wine Tourism Center" Take-off for sustainable supply of woody biomass from agrarian pruning and plantation removal Sustainable Soil Conditions
Lab today Finish Inventory work at Rest Area Site
 Lubrecht Forest, Montana NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Day 23 Nov 10, 2009 Nutrient Cycling (Chapters 16-18) Lab today Finish Inventory work at Rest Area Site Quiz on Thursday Also record trees & shrubs
Lubrecht Forest, Montana NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Day 23 Nov 10, 2009 Nutrient Cycling (Chapters 16-18) Lab today Finish Inventory work at Rest Area Site Quiz on Thursday Also record trees & shrubs
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger,, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger,, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from
Enhancing Soil Fertility with Cover Crops. Mike Daniels Professor, Extension Water Quality and Nutrient Management
 Enhancing Soil Fertility with Cover Crops Mike Daniels Professor, Extension Water Quality and Nutrient Management Outline Definitions and Basics How Cover Crops enhance Soil Fertility Cover Crops and Water
Enhancing Soil Fertility with Cover Crops Mike Daniels Professor, Extension Water Quality and Nutrient Management Outline Definitions and Basics How Cover Crops enhance Soil Fertility Cover Crops and Water
Soil Ecology, Nutrient Recycling, Improving Soil Structure James J. Hoorman
 Soil Ecology, Nutrient Recycling, Improving Soil Structure James J. Hoorman hoorman.1@osu.edu www.mccc.msu.edu EMPOWERMENT THROUGH EDUCATION Ideal Soil Composition 25% Water 45% Inorganic (mineral materials)
Soil Ecology, Nutrient Recycling, Improving Soil Structure James J. Hoorman hoorman.1@osu.edu www.mccc.msu.edu EMPOWERMENT THROUGH EDUCATION Ideal Soil Composition 25% Water 45% Inorganic (mineral materials)
The Enigma of Soil Nitrogen George Rehm, University of Minnesota
 The Enigma of Soil Nitrogen George Rehm, University of Minnesota 1. Introduction Throughout the northern and western Corn Belt, nitrogen (N) is the most dominant nutrient in the world of plant nutrition.
The Enigma of Soil Nitrogen George Rehm, University of Minnesota 1. Introduction Throughout the northern and western Corn Belt, nitrogen (N) is the most dominant nutrient in the world of plant nutrition.
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
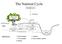 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 23 September 2014 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2014 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 23 September 2014 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2014 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
2/11/16. Materials in ecosystems are constantly reused Three cycles: The Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle
 Materials in ecosystems are constantly reused Three cycles: The Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle The Cycle Carbon is essential in proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, which make up all organisms Carbon cycle
Materials in ecosystems are constantly reused Three cycles: The Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle The Cycle Carbon is essential in proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, which make up all organisms Carbon cycle
LF-C 1, 2 HF-C 1, 2 Humic acid-c 1
 Table. Carbon of particulate organic matter, i.e. litter (size >2 mm and -2 mm), light and heavy fractions and humic acid in sandy soils (0-5 cm depth) under different land-use systems Litter C LF-C, 2
Table. Carbon of particulate organic matter, i.e. litter (size >2 mm and -2 mm), light and heavy fractions and humic acid in sandy soils (0-5 cm depth) under different land-use systems Litter C LF-C, 2
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Digestate - Maximizing its Value and Use
 Digestate - Maximizing its Value and Use National Compost Conference September 16-18, 2015 Christine Brown - OMAFRA On-Farm Anaerobic Digestion Research Project Anna Crolla Alfred College June 2015 On-Farm
Digestate - Maximizing its Value and Use National Compost Conference September 16-18, 2015 Christine Brown - OMAFRA On-Farm Anaerobic Digestion Research Project Anna Crolla Alfred College June 2015 On-Farm
Inherent Factors Affecting Soil Respiration
 Soil respiration is a measure of the carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) released from soil. It is released as a result of decomposition of soil organic matter (SOM) and plant litter by soil microbes and through plant
Soil respiration is a measure of the carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) released from soil. It is released as a result of decomposition of soil organic matter (SOM) and plant litter by soil microbes and through plant
DECOMPOSITION OF ORGANIC MATTER IN SOIL
 DECOMPOSITION OF ORGANIC MATTER IN SOIL The rapidity with which a given organic amendment is decomposed depends on temperature, the supply of oxygen, moisture, and available minerals, the C/N ratio of
DECOMPOSITION OF ORGANIC MATTER IN SOIL The rapidity with which a given organic amendment is decomposed depends on temperature, the supply of oxygen, moisture, and available minerals, the C/N ratio of
Where do you start? Managing Soil Health. Three parts to soil health 3/3/2014. First, have a yard stick to measure by
 Where do you start? Managing Soil Health By Donald A. Horneck, Ph.D. CCA, CPAg, CPSS Oregon State University - HAREC First, have a yard stick to measure by Three parts to soil health Rick Haney-soil test,
Where do you start? Managing Soil Health By Donald A. Horneck, Ph.D. CCA, CPAg, CPSS Oregon State University - HAREC First, have a yard stick to measure by Three parts to soil health Rick Haney-soil test,
Agricultural and Biological Engineering. Biological Manipulation of Manure: Getting What You Want from Animal Manure
 College of Agricultural Sciences Cooperative Extension Agricultural and Biological Engineering Biological Manipulation of Manure: Getting What You Want from Animal Manure G 87 Jeannie A. Leggett, Extension
College of Agricultural Sciences Cooperative Extension Agricultural and Biological Engineering Biological Manipulation of Manure: Getting What You Want from Animal Manure G 87 Jeannie A. Leggett, Extension
Balancing the Nitrogen Budget
 University of California Tulare County Cooperative Extension Balancing the Nitrogen Budget Bill Peacock Pub. NG2-96 Sources of nitrogen in the soil/water system other than fertilizer should be considered
University of California Tulare County Cooperative Extension Balancing the Nitrogen Budget Bill Peacock Pub. NG2-96 Sources of nitrogen in the soil/water system other than fertilizer should be considered
Managing Nitrogen for Yield and Protein in Winter Wheat
 Wheat Academy 2015 Managing Nitrogen for Yield and Protein in Winter Wheat Haiying Tao Aaron Esser Department of Crop and Soil Sciences Haiying.tao@wsu.edu 509-335-4389 Outline N Cycle in the soil-plant-atmosphere
Wheat Academy 2015 Managing Nitrogen for Yield and Protein in Winter Wheat Haiying Tao Aaron Esser Department of Crop and Soil Sciences Haiying.tao@wsu.edu 509-335-4389 Outline N Cycle in the soil-plant-atmosphere
Basics of Composting Penn State Mushroom Conference David M. Beyer Professor-Extension Specialist
 Basics of Composting 2009 Penn State Mushroom Conference David M. Beyer Professor-Extension Specialist Mushroom substrate has developed from a hodge-podge of ingredients mixed with water, fed through a
Basics of Composting 2009 Penn State Mushroom Conference David M. Beyer Professor-Extension Specialist Mushroom substrate has developed from a hodge-podge of ingredients mixed with water, fed through a
 JOHN S CORNER Soil Amendments -Animal Manures- By John Ferguson Last week we talked about human manure (sewage sludge or bio-solids). So this week we will cover the other manures. For centuries farmers
JOHN S CORNER Soil Amendments -Animal Manures- By John Ferguson Last week we talked about human manure (sewage sludge or bio-solids). So this week we will cover the other manures. For centuries farmers
Tillage Management and Soil Organic Matter
 Resources Conservation Practices Tillage Management and Soil Organic Matter Conservation Quiz 1. What are the two classes of soil organic matter? 2. How does soil disturbance by tillage decrease soil organic
Resources Conservation Practices Tillage Management and Soil Organic Matter Conservation Quiz 1. What are the two classes of soil organic matter? 2. How does soil disturbance by tillage decrease soil organic
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 19 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2017 Frank Sansone Outline 1. Nitrogen cycle
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 19 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2017 Frank Sansone Outline 1. Nitrogen cycle
Soils and their Sustainable Management (2016) Trish Steinhilber extension.umd.edu/anmp
 Soils and their Sustainable Management (2016) Trish Steinhilber psteinhi@umd.edu extension.umd.edu/anmp What is Soil? the living skin of the Earth (Ian Pepper, soil microbiologist) crucible of terrestrial
Soils and their Sustainable Management (2016) Trish Steinhilber psteinhi@umd.edu extension.umd.edu/anmp What is Soil? the living skin of the Earth (Ian Pepper, soil microbiologist) crucible of terrestrial
Lesson 2.4 Biogeochemical Cycles
 Lesson 2.4 Biogeochemical Cycles A carbon atom in your body today may have been part of a blade of grass last year, or a dinosaur bone millions of years ago. Fossilized bones in a Colorado dig. Lesson
Lesson 2.4 Biogeochemical Cycles A carbon atom in your body today may have been part of a blade of grass last year, or a dinosaur bone millions of years ago. Fossilized bones in a Colorado dig. Lesson
TECHNIQUE The processes in bio - transformation occur in lesser time when the components are placed in heaps.
 COMPOSTING PREAMBLE Composting comprises all the complex biological reactions which make up the decomposition of the organic material in aerobic conditions (viz., living microorganisms coming into contact
COMPOSTING PREAMBLE Composting comprises all the complex biological reactions which make up the decomposition of the organic material in aerobic conditions (viz., living microorganisms coming into contact
Building Soil Health: for Crop Production and the Environment
 Building Soil Health: for Crop Production and the Environment Richard Smith, Farm Advisor University of California Cooperative Extension Monterey, Santa Cruz and San Benito Counties How do We Achieve Healthy
Building Soil Health: for Crop Production and the Environment Richard Smith, Farm Advisor University of California Cooperative Extension Monterey, Santa Cruz and San Benito Counties How do We Achieve Healthy
Preparing for Organic Production. Ron Godin, Ph.D. Research Scientist Colorado State University Rogers Mesa Research Center, Hotchkiss, Colorado
 Preparing for Organic Production Ron Godin, Ph.D. Research Scientist Colorado State University Rogers Mesa Research Center, Hotchkiss, Colorado Preparing for Organic Production Part 1: Planning for the
Preparing for Organic Production Ron Godin, Ph.D. Research Scientist Colorado State University Rogers Mesa Research Center, Hotchkiss, Colorado Preparing for Organic Production Part 1: Planning for the
Problems and profit with waste. Standard Grade Biology Biotechnology
 Problems and profit with waste Standard Grade Biology Biotechnology Learning Outcomes Describe some examples of the damage caused to the environment by disposal of untreated sewage. Give examples of diseases
Problems and profit with waste Standard Grade Biology Biotechnology Learning Outcomes Describe some examples of the damage caused to the environment by disposal of untreated sewage. Give examples of diseases
Intensification and nutrient management in dryland cropping systems. Jay B. Norton
 Intensification and nutrient management in dryland cropping systems Jay B. Norton Nutrient supply = yield potential f(available water). To increase yields must enhance: Nutrient supply to the crop Available
Intensification and nutrient management in dryland cropping systems Jay B. Norton Nutrient supply = yield potential f(available water). To increase yields must enhance: Nutrient supply to the crop Available
APPENDIX NO. 12 MAINTENANCE OF SOIL ORGANIC MATTER
 Environmental Impact Statement March 2017 APPENDIX NO. 12 MAINTENANCE OF SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Eoin O' Brien - Piggery- Annistown, Killeagh, Co. Cork. Maintenance of soil organic matter Introduction - The
Environmental Impact Statement March 2017 APPENDIX NO. 12 MAINTENANCE OF SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Eoin O' Brien - Piggery- Annistown, Killeagh, Co. Cork. Maintenance of soil organic matter Introduction - The
Developing Effective Plant Nutrition Programs for North Coast Vineyards
 Developing Effective Plant Nutrition Programs for North Coast Vineyards Glenn McGourty, Winegrowing and Plant Science Advisor UCCE Mendocino and Lake Counties OFAC & North Coast CAPCA Sustainable /Organic
Developing Effective Plant Nutrition Programs for North Coast Vineyards Glenn McGourty, Winegrowing and Plant Science Advisor UCCE Mendocino and Lake Counties OFAC & North Coast CAPCA Sustainable /Organic
Monitoring carbon budgets
 Monitoring carbon budgets Suess effect on 14 C/ 12 C in CO 2, from Stuiver and Quay, 1981, EPSL 53:349-362 1 Figure from IPCC 4 th assessment report 2 Biogeochemical cycling (on land) Living tissue C H
Monitoring carbon budgets Suess effect on 14 C/ 12 C in CO 2, from Stuiver and Quay, 1981, EPSL 53:349-362 1 Figure from IPCC 4 th assessment report 2 Biogeochemical cycling (on land) Living tissue C H
10/18/2010 THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE RECYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE RECYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE
 THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE 3.4 Mrs. Michaelsen A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them
THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE 3.4 Mrs. Michaelsen A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them
Soil health and fertility
 Soil health and fertility Two statements: tillage reduces soil productivity conservation agriculture benefits the soil Conventional tillage Advantages Disadvantages Machinery is present Incorporates fertilizers
Soil health and fertility Two statements: tillage reduces soil productivity conservation agriculture benefits the soil Conventional tillage Advantages Disadvantages Machinery is present Incorporates fertilizers
Chapter 3 Reading/Homework Quiz
 Name Chapter 3 Reading/Homework Quiz Date APES 1. Scientists estimate that tropical rain forests contain up to half of the earth s land plants and animal species. What percentage of the world s land surface
Name Chapter 3 Reading/Homework Quiz Date APES 1. Scientists estimate that tropical rain forests contain up to half of the earth s land plants and animal species. What percentage of the world s land surface
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils
 Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Nutrient Sources, are not all Equal. John Lauzon
 Nutrient Sources, are not all Equal John Lauzon Managing Organic Sources of Nutrients Organic forms of nitrogen aregenerally not plant available Need an understanding of if, and how much plant available
Nutrient Sources, are not all Equal John Lauzon Managing Organic Sources of Nutrients Organic forms of nitrogen aregenerally not plant available Need an understanding of if, and how much plant available
ACTIVE HUMIC TECHNOLOGY
 www.organocat.com ACTIVE HUMIC TECHNOLOGY ACTIVE HUMIC TECHNOLOGY What are Humic Substances? Humic Substances are very stable, organic compounds found in brown and oxidized black coal, peat, manure, compost,
www.organocat.com ACTIVE HUMIC TECHNOLOGY ACTIVE HUMIC TECHNOLOGY What are Humic Substances? Humic Substances are very stable, organic compounds found in brown and oxidized black coal, peat, manure, compost,
Liquid Organic Bio Fertilizer and Pesticides
 Liquid Organic Bio Fertilizer and Pesticides What is Bio Fertilizer Bio Fertilizer is a Natural organic fertilizer known that helps to provide all the nutrients required by the plants and helps to increase
Liquid Organic Bio Fertilizer and Pesticides What is Bio Fertilizer Bio Fertilizer is a Natural organic fertilizer known that helps to provide all the nutrients required by the plants and helps to increase
Using SMRC Compost on Your Farm
 For all enquiries: Farmer Demonstration Project: Organic Farming Systems PO Box 419 Cottesloe WA 6911 Tel 08 9384 3789 Fax 08 9384 3379 www.organicfarming.com.au Using SMRC Compost on Your Farm Compost
For all enquiries: Farmer Demonstration Project: Organic Farming Systems PO Box 419 Cottesloe WA 6911 Tel 08 9384 3789 Fax 08 9384 3379 www.organicfarming.com.au Using SMRC Compost on Your Farm Compost
Lesson Overview. Cycles of Matter. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Soil Organic Matter. What is it How to build it. Clive Kirkby
 Soil Organic Matter What is it How to build it Clive Kirkby CSIRO Plant Industry Charles Sturt University EH Graham Centre for Agricultural Innovation John Kirkegaard Alan Richardson Graeme Batten Chris
Soil Organic Matter What is it How to build it Clive Kirkby CSIRO Plant Industry Charles Sturt University EH Graham Centre for Agricultural Innovation John Kirkegaard Alan Richardson Graeme Batten Chris
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Mulching - Chapter Mulching
 Mulching - Chapter 12 12. Mulching M ulching is Fundamental #6. It will conserve topsoil and moisture, as well as provide fertilizer. When straw or crop residue covers the topsoil, it holds it in place
Mulching - Chapter 12 12. Mulching M ulching is Fundamental #6. It will conserve topsoil and moisture, as well as provide fertilizer. When straw or crop residue covers the topsoil, it holds it in place
MWELO Providing Insight on Soil and Compost Requirements. Will Bakx
 MWELO Providing Insight on Soil and Compost Requirements Will Bakx www.sonomacompost.com willbakx@sonomacompost.com Soils: 2 Sections 492.5 Soil Management report 492.6(3) Soil Preparation, Mulch and Amendments
MWELO Providing Insight on Soil and Compost Requirements Will Bakx www.sonomacompost.com willbakx@sonomacompost.com Soils: 2 Sections 492.5 Soil Management report 492.6(3) Soil Preparation, Mulch and Amendments
Microbes and Soil Health
 Microbes and Soil Health It All Begins (and Ends) with Soil Fertility In one of our earlier articles, Humic Acid and Healthy Soil, we noted that there are three basic types of soil: Clay, Silt (Loam) and
Microbes and Soil Health It All Begins (and Ends) with Soil Fertility In one of our earlier articles, Humic Acid and Healthy Soil, we noted that there are three basic types of soil: Clay, Silt (Loam) and
Nutrient Cycling in Soils
 Nutrient Cycling in Soils Kristin A. Fisher, Ph.D. Nutrient Management Specialist Agricultural Nutrient Management Program University of Maryland, College Park Nutrient Cycling in Soils N, P & K cycles
Nutrient Cycling in Soils Kristin A. Fisher, Ph.D. Nutrient Management Specialist Agricultural Nutrient Management Program University of Maryland, College Park Nutrient Cycling in Soils N, P & K cycles
NK.L. Wells, ITROGENAGR-43. in Kentucky Soils. Plants growing with a low available N supply are
 C O O P E R A T I V E E X T E N S I O N S E R V I C E U N I V E R S I T Y O F K E N T U C K Y C O L L E G E O F A G R I C U L T U R E NK.L. Wells, J.L. Sims and M.S. Smith ITROGENAGR-43 in Kentucky Soils
C O O P E R A T I V E E X T E N S I O N S E R V I C E U N I V E R S I T Y O F K E N T U C K Y C O L L E G E O F A G R I C U L T U R E NK.L. Wells, J.L. Sims and M.S. Smith ITROGENAGR-43 in Kentucky Soils
Green Manuring. Reviving Our Time Tested Practices
 Green Manuring Reviving Our Time Tested Practices What Is Green Manuring This is a technique where we grow the manure in the field itself and plough it back in. Traditionally, we grow a green manure crop
Green Manuring Reviving Our Time Tested Practices What Is Green Manuring This is a technique where we grow the manure in the field itself and plough it back in. Traditionally, we grow a green manure crop
Soil Quality: Soil Indicators. Dr. Paul Hargreaves SRUC Dairy Research and Innovation Centre
 Soil Quality: Soil Indicators Dr. Paul Hargreaves SRUC Dairy Research and Innovation Centre 1 Soil air, water, minerals Soil functions Support hooves and wheels Reduce gas losses, N 2 O, N 2, NH 3 and
Soil Quality: Soil Indicators Dr. Paul Hargreaves SRUC Dairy Research and Innovation Centre 1 Soil air, water, minerals Soil functions Support hooves and wheels Reduce gas losses, N 2 O, N 2, NH 3 and
How Ecosystems Work Section 2
 Objectives List the three stages of the carbon cycle. Describe where fossil fuels are located. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the tree stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Objectives List the three stages of the carbon cycle. Describe where fossil fuels are located. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the tree stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Organic materials as fertilizers and soil amendments. Andy Bary WSU Puyallup
 Organic materials as fertilizers and soil amendments Andy Bary WSU Puyallup Nitrogen Cycle Organic N Ammonium NH 4 + Nitrate NO 3 - Soil organic matter, Plant residues, Manure Plants, Microbes N fixation
Organic materials as fertilizers and soil amendments Andy Bary WSU Puyallup Nitrogen Cycle Organic N Ammonium NH 4 + Nitrate NO 3 - Soil organic matter, Plant residues, Manure Plants, Microbes N fixation
Session 2: Fundamentals of the Composting Process. Gary Felton University of Maryland
 Session 2: Fundamentals of the Composting Process Gary Felton University of Maryland Learning Objectives Part 1: Understand BIOLOGY of compost pile Part 2: Learn factors used to control composting process:
Session 2: Fundamentals of the Composting Process Gary Felton University of Maryland Learning Objectives Part 1: Understand BIOLOGY of compost pile Part 2: Learn factors used to control composting process:
Nutrient Cycling in Soils: The Big 3 and Carbon
 Fundamentals of Nutrient Management Nutrient Cycling in Soils: The Big 3 and Carbon Gurpal Toor Department of Environmental Science & Technology University of Maryland College Park @ToorUMD N deficiency
Fundamentals of Nutrient Management Nutrient Cycling in Soils: The Big 3 and Carbon Gurpal Toor Department of Environmental Science & Technology University of Maryland College Park @ToorUMD N deficiency
Managing Carbon in Wisconsin Soils. Dick Wolkowski Extension Soil Scientist UW-Madison
 Managing Carbon in Wisconsin Soils Dick Wolkowski Extension Soil Scientist UW-Madison Carbon: The key element for life Outline: The ultimate essential plant nutrient needed for life as we know it Soil
Managing Carbon in Wisconsin Soils Dick Wolkowski Extension Soil Scientist UW-Madison Carbon: The key element for life Outline: The ultimate essential plant nutrient needed for life as we know it Soil
Soil Quality: What is it & how do you improve it? Bill Crooks
 Soil Quality: What is it & how do you improve it? Bill Crooks Soil Quality: What is it? More productive? Nutrient status ph Drainage Structure More biodiversity? Organic content Amount and type Plant (crop)
Soil Quality: What is it & how do you improve it? Bill Crooks Soil Quality: What is it? More productive? Nutrient status ph Drainage Structure More biodiversity? Organic content Amount and type Plant (crop)
WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein!
 Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Section 2: The Cycling of Matter
 Section 2: The Cycling of Matter Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Section 2: The Cycling of Matter Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Developing a Recipe for Composting Livestock Manure
 112 Developing a Recipe for Composting Livestock Manure Petra Loro, Livestock Environment Specialist, Animal Industry Branch, Manitoba Agriculture, Food and Rural Initiatives, Winnipeg, MB, R3T 5S6. E-mail:
112 Developing a Recipe for Composting Livestock Manure Petra Loro, Livestock Environment Specialist, Animal Industry Branch, Manitoba Agriculture, Food and Rural Initiatives, Winnipeg, MB, R3T 5S6. E-mail:
Soil Organic Matter. Soil degradation has become a major concern in. What is organic matter? Organic matter in virgin and cultivated soils
 Agdex 6- Soil degradation has become a major concern in Canada. Erosion, salinization, acidification and loss of organic matter are the main forms of soil deterioration. This factsheet deals with the role
Agdex 6- Soil degradation has become a major concern in Canada. Erosion, salinization, acidification and loss of organic matter are the main forms of soil deterioration. This factsheet deals with the role
Managing Soils for Improved Pasture
 Managing Soils for Improved Pasture Jonathan Deenik, PhD Department of Tropical Plant and Soil Sciences University of Hawaii Rota Grazing and Livestock Management Workshop June 10-12, 12, 2010 1 Water
Managing Soils for Improved Pasture Jonathan Deenik, PhD Department of Tropical Plant and Soil Sciences University of Hawaii Rota Grazing and Livestock Management Workshop June 10-12, 12, 2010 1 Water
Cover Crops for Soil Health and Water Quality
 Cover Crops for Soil Health and Water Quality 2014 SURFACE WATER FORUM - NOVEMBER 12, 2014 JILL L. SACKETT EXTENSION EDUCATOR 1 BACKGROUND University of Minnesota Extension Local Extension Educator, Ag
Cover Crops for Soil Health and Water Quality 2014 SURFACE WATER FORUM - NOVEMBER 12, 2014 JILL L. SACKETT EXTENSION EDUCATOR 1 BACKGROUND University of Minnesota Extension Local Extension Educator, Ag
Section 2: The Cycling of Materials
 Section 2: The Cycling of Materials Preview Bellringer Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Section 2: The Cycling of Materials Preview Bellringer Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Optimizing Fertilizer Applications on Big Horn Basin Crops
 Optimizing Fertilizer Applications on Big Horn Basin Crops Westi Ag Days, Worland, Wyoming February 4, 2009 Jay Norton, Soil Fertility Specialist Renewable Resources Department University of Wyoming 307-766
Optimizing Fertilizer Applications on Big Horn Basin Crops Westi Ag Days, Worland, Wyoming February 4, 2009 Jay Norton, Soil Fertility Specialist Renewable Resources Department University of Wyoming 307-766
SOIL INCORPORATION OF COVERCROP BIOMASS: EFFECTS ON SOIL MICROORGANISMS AND NITROGEN LEVELS
 Hawaii Agriculture Research Center Diversified Crops Report No. 23 November 23 SOIL INCORPORATION OF COVERCROP BIOMASS: EFFECTS ON SOIL MICROORGANISMS AND NITROGEN LEVELS S. Schenck Summary Biomass production,
Hawaii Agriculture Research Center Diversified Crops Report No. 23 November 23 SOIL INCORPORATION OF COVERCROP BIOMASS: EFFECTS ON SOIL MICROORGANISMS AND NITROGEN LEVELS S. Schenck Summary Biomass production,
Best Management Practices ADDING ORGANIC AMENDMENTS
 Best Management Practices ADDING ORGANIC AMENDMENTS The amount of organic matter strongly influences the health, productivity, and resilience of cropland soils. Building and maintaining the level of organic
Best Management Practices ADDING ORGANIC AMENDMENTS The amount of organic matter strongly influences the health, productivity, and resilience of cropland soils. Building and maintaining the level of organic
Living organisms are composed of mainly four elements: Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen In smaller amounts: Sulfur & Phosphorus Organisms cannot
 Living organisms are composed of mainly four elements: Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen In smaller amounts: Sulfur & Phosphorus Organisms cannot make any of these elements and do not use them up Question:
Living organisms are composed of mainly four elements: Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen In smaller amounts: Sulfur & Phosphorus Organisms cannot make any of these elements and do not use them up Question:
Ecosystems and Nutrient Cycles Chapters 3
 Ecosystems and Nutrient Cycles Chapters 3 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells Figure 3-2 Prokaryotic cells: Have organelles. Bacteria and Archaea are composed of prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells: cells,
Ecosystems and Nutrient Cycles Chapters 3 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells Figure 3-2 Prokaryotic cells: Have organelles. Bacteria and Archaea are composed of prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells: cells,
Principles of Soil Health Management
 Principles of Soil Health Management John Idowu Extension Agronomist, New Mexico State University April 24 th, 2014 Extension Plant Sciences Online Contact: John Idowu Email: jidowu@nmsu.edu Phone: 575-646-2571
Principles of Soil Health Management John Idowu Extension Agronomist, New Mexico State University April 24 th, 2014 Extension Plant Sciences Online Contact: John Idowu Email: jidowu@nmsu.edu Phone: 575-646-2571
Building Soil Organic Matter: What, Why, How?
 FarmSmart Conference, Guelph Ontario 20 January 2018 Building Soil Organic Matter: What, Why, How? Ray Weil Biosphere-2. A parable about soil organic matter and the carbon cycle. Biospherians in Biosphere2
FarmSmart Conference, Guelph Ontario 20 January 2018 Building Soil Organic Matter: What, Why, How? Ray Weil Biosphere-2. A parable about soil organic matter and the carbon cycle. Biospherians in Biosphere2
Agriculture and Society: Part II. PA E & E Standards 4.4
 Agriculture and Society: Part II PA E & E Standards 4.4 Let s get Dirty! 1. All agriculture ultimately depends on the soil. What is soil? Soil is the upper layer of the land surface that contains pieces
Agriculture and Society: Part II PA E & E Standards 4.4 Let s get Dirty! 1. All agriculture ultimately depends on the soil. What is soil? Soil is the upper layer of the land surface that contains pieces
How Ecosystems Work Section 2. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1 The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back Carbon is the
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1 The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back Carbon is the
The Management of Soil Nutrients: Chemical Fertilisers or Not?
 30 May 2017 The Management of Soil Nutrients: Chemical Fertilisers or Not? Christopher Johns Research Manager Northern Australia and Landcare Research Programme Key Points There are 17 chemical elements
30 May 2017 The Management of Soil Nutrients: Chemical Fertilisers or Not? Christopher Johns Research Manager Northern Australia and Landcare Research Programme Key Points There are 17 chemical elements
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
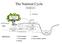 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
Soils Are Alive! When Biology and Agronomy Meet. FarmSmart Presented by Lori A. Phillips and Jake Munroe Guelph, January 20, 2017
 Soils Are Alive! When Biology and Agronomy Meet FarmSmart 2017 Presented by Lori A. Phillips and Jake Munroe Guelph, January 20, 2017 Soils contain 25% of our planet s biodiversity One teaspoon of soil
Soils Are Alive! When Biology and Agronomy Meet FarmSmart 2017 Presented by Lori A. Phillips and Jake Munroe Guelph, January 20, 2017 Soils contain 25% of our planet s biodiversity One teaspoon of soil
CHAPTER # 4. Fate of Pollutants in the Environment
 CHAPTER # 4 Fate of Pollutants in the Environment Once a pesticide is introduced into the environment, whether through an application, a disposal or a spill, it is influenced by many processes. These processes
CHAPTER # 4 Fate of Pollutants in the Environment Once a pesticide is introduced into the environment, whether through an application, a disposal or a spill, it is influenced by many processes. These processes
Available nitrogen and phosphorus in soil
 Environmental Chemistry Laboratory exercise Available nitrogen and phosphorus in soil GENERAL CONSIDERATION The compounds of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) are of great interest to environmental engineers
Environmental Chemistry Laboratory exercise Available nitrogen and phosphorus in soil GENERAL CONSIDERATION The compounds of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) are of great interest to environmental engineers
Moderator: Vicki Morrone, Outreach Specialist for Organic Fruit and Vegetable Growers, MSU
 Great Lakes Fruit, Vegetable & Farm Market EXPO Michigan Greenhouse Growers EXPO December 6-8, 2011 DeVos Place Convention Center, Grand Rapids, MI Organic Soil Management Where: Gallery Overlook (upper
Great Lakes Fruit, Vegetable & Farm Market EXPO Michigan Greenhouse Growers EXPO December 6-8, 2011 DeVos Place Convention Center, Grand Rapids, MI Organic Soil Management Where: Gallery Overlook (upper
Earth s Life-Support Atmosphere- gases surrounding earth s surface. Troposphere= air we breathe; weather 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.
 1 2 3 4 Ecosystems APES CH 3 But First: Cells Complex organic compounds called macromolecules make up the basic molecular units found in cells. Complex carbohydrates Cellulose and starch Proteins- made
1 2 3 4 Ecosystems APES CH 3 But First: Cells Complex organic compounds called macromolecules make up the basic molecular units found in cells. Complex carbohydrates Cellulose and starch Proteins- made
UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS
 UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS Chapter 2 Biogeochemical Cycles Science 10 Change & Recovery in Ecosystems (you do not need to copy) What happens to the materials that make up a truck when it begins to rust?
UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS Chapter 2 Biogeochemical Cycles Science 10 Change & Recovery in Ecosystems (you do not need to copy) What happens to the materials that make up a truck when it begins to rust?
