Historical Background and Scientific Foundations
|
|
|
- Evangeline Rogers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Cloning Biotechnology: In Context, 2012 Introduction A clone is an exact genetic copy. Bacteria and plants can be cloned naturally, but animal cloning is much more difficult. When Dolly the sheep was cloned in 1997, however, it showed that animal cells could be reprogrammed under certain experimental conditions, and achieving this in one mammalian species suggested cloning would be possible in others, including humans. Human cloning can refer to either therapeutic cloning or reproductive cloning. Both can, in theory at least, be achieved using the same technology, nuclear transfer, used to create other clones in other species. In therapeutic cloning, a human embryo is created from a somatic cell, such as a skin cell, and the cells in this embryo are then used to make cells and tissues of various types, such as blood cells or neural cells, that can be used to repair the body. In human reproductive cloning, a process in which nuclear transfer would also be the first step, the goal would be to create an embryo that could develop to term rather than being harvested for its cells. As of 2011, there have been no scientifically verifiable cases of human reproductive cloning. Words to Know Human embryonic stem cells Human embryonic stem cells are just one source of stem cells. They are found, as the name suggests, in the human embryo and have the capacity to develop into all the cells and tissues of the human body. Parthenogenesis The development of a whole organism from an unfertilized egg, which is the main type of reproduction in some organisms, including several insect species, such as some aphids, and certain reptiles and fish. Somatic cell nuclear transfer The process by which animal cloning is achieved, involving transfer of a somatic, or body, cell to an egg from which the nucleus has been removed. The transferred somatic cell begins to divide and develop into an embryo. Stem cell A stem cell is a cell that is characterized by its potential to develop into many other cell types and its ability to keep renewing itself through cell division. Totipotent Stem cells that have the ability to develop into any cell type and create a whole organism are said to be totipotent. Plant cells and animal embryonic stem cells are totipotent. Historical Background and Scientific Foundations Since the nineteenth century, scientists have been intrigued by the question of whether cells are capable of growing into a whole organism. Plant cells are totipotent, with an entire plant being generated easily
2 from a leaf or stem cutting. Moreover, the unfertilized eggs of some small invertebrates, and certain fish and lizard species, are capable of parthenogenesis. In 1962 British developmental biologist John Gurdon (1933 ) achieved cloning in tadpoles when he inserted cells from the intestine of an adult frog into frog eggs lacking a nucleus. The cloned tadpoles did not, however, survive to adulthood, but these early attempts at nuclear transfer laid the groundwork for further work in animal cloning. In 1995, after many attempts, researchers at the Roslin Institute near Edinburgh, Scotland, announced the birth of two cloned sheep, Megan and Morag, from embryonic cells transferred into empty sheep eggs. This was a landmark, showing that the differentiation of an embryo could be reversed. A natural next step was to see if the clock could be similarly reversed in adult cells. Nuclear transfer was used again to clone Dolly the sheep, born in 1996, from an udder cell. Three sheep were involved in the creation of Dolly. The egg came from a Scottish Blackface with the original nucleus removed. A Finn Dorset ewe donated a sample of udder cells, which were placed in a glass dish and given enough nutrients to keep them alive, but not enough to let them grow and divide in the usual way. This approach stopped the cells from developing and made them revert to a primitive stem cell state. One of these cells was then inserted into the egg and a pulse of electric current was applied to it to start off the development making the egg behave as if it had been fertilized. The egg was then placed into the womb of a third sheep who was Dolly s mother in the sense of carrying, nurturing, and giving birth to the developing fetus. However, Dolly did not have a mother, or a father, in the usual sense of the word. Analysis of her DNA showed that her genetic blueprint was that of the udder cell of the Finn Dorset sheep. Had she been conceived in the usual way, her genetic blueprint would have come half from her mother (the egg) and half from her father (the sperm). Since Dolly, many other animals have been cloned mice, goats, rabbits, cows, pigs, dogs, cats, monkeys, and a gaur (a type of wild ox that is an endangered species). There is no scientific reason why the nuclear transfer approach could not be used to clone a human. In 2004 Hwang Woo-Suk (1953 ), of Seoul National University, South Korea, announced the cloning of a number of human embryos but later admitted that the claim had been fabricated. Thus far, human cloning has not been achieved, although many scientists believe it is sure to happen at some point in the future unless prohibited by law or industry ethics agreements. Note that the clone is not an exact copy of the somatic cell donor, because the empty egg has lost its nucleus, but it will still contain the original mitochondria, which carry a small number of genes. These will also be present in the clone, as well as the genes from the donor somatic cell. In Context: Disputed Claims of Human Cloning In 2001, a company called Advanced Cell Technology successfully cloned human embryonic cells that were allowed to undergo several rounds of division. While not yet recognizable as an embryo, the experiment demonstrated that the process was possible. With the realization that cloning was achievable, public concern about the possibility that a human could be cloned grew. The debate was further fueled by one group's highly disputed, and scientifically dubious, claim to have produced a human clone. In May 1997, an international religious cult called the Raelians announced it was creating a company called Clonaid to sponsor research in human cloning. By 2001 the company
3 claimed to have cloned a human embryo, a baby called Eve, allegedly born in Clonaid refused, however, to allow genetic tests to prove its case. The company's CEO promised to deliver proof of the successful clone in 2003, but produced only a photograph. Without any scientific proof, the vast majority of reproductive scientists also dismissed the cult's claims to have produced other living clones. Impacts and Issues Human therapeutic cloning could play an important role in regenerative medicine by providing embryonic stem cells for treatment that are derived from the patient s own cells. For instance, patients requiring a bone marrow transplant would no longer have to wait for a compatible donor. They could be treated with their own bone marrow stem cells, derived from a nuclear transfer experiment. Other potential applications of regenerative medicine include brain repair in stroke, Parkinson s disease, and Alzheimer s disease, repair of the heart after a heart attack, and supply of insulin-producing cells to the pancreas to treat Type 1 Diabetes. Many of these treatments are still at the research stage, but some are already being used in clinical trials to treat patients using stem cells from various sources. Regenerative medicine opens up the possibility of renewing and repairing the human body as it ages and promises to be a viable alternative to drug therapies. However, there are ethical objections to human therapeutic cloning because it involves creating an embryo solely for someone else s use. It will never be implanted into a woman s womb, so it can never have a life of its own. Some people argue that an embryo is not a person until it has been implanted in the womb.
4 Others believe that life begins at conception, so an embryo of any age is a person. For these people, therapeutic cloning is unacceptable, whatever benefit it brings, because it is against human dignity. Additionally, animal cloning has also proved to be very inefficient, with 277 attempts needed to create Dolly. There is no reason to think that human cloning would be any more successful, so a large supply of donated human eggs would be required. When women donate eggs, it is usually as part of an in vitro fertilization (IVF) program intended to create a baby. Egg donation is not a trivial process, because it involves administration of powerful drugs and a surgical egg retrieval procedure, so there are some risks to the woman. It may not, therefore, be practical or ethical to use human eggs for nuclear transfer until the success rate of the process improves. This has led some scientists to propose the use of cow eggs instead, and a few laboratories around the world have permission to research interspecies nuclear transfer. The new procedure is controversial because it creates a chimeric or hybrid embryo with a mixture of cow and human cells. The second possible fate of a cloned human embryo, if one could be created, is to grow and develop into a baby. Reproductive cloning has a number of potential applications. Bereaved parents could replace a dead child or an infertile woman could use a cell from anywhere in her body to create a baby. Cloning plants and animals has now been widely used to reproduce high value crops and valuable farm animals or racehorses. Perhaps, if they had access to the technology, powerful businesspeople or politicians would try to clone armies of obedient workers or disciplined soldiers. It is also possible that tissue preserved from deceased celebrities could be used to clone new copies of them. Also concerning is the prospect of people creating a clone that could be killed for its organs if they were in need of a transplant, which could be considered a more extreme version of therapeutic cloning. The numerous possibilities offered by human cloning mean it is important to have discussions about where the boundaries lie. Currently, human reproductive cloning is outlawed in countries that have legislated cloning science, whereas research on therapeutic cloning is allowed in some countries. Besides the general ethical arguments over whether reproductive cloning is right or wrong, there are also practical and safety issues to be considered. For instance, the embryo would need to be implanted in the womb of a so-called surrogate mother. A woman would have to consent to have her womb used in this way. Then there is the health of the clone itself to consider. Dolly the sheep suffered from arthritis and excessive weight, although she did give birth to some normal lambs. Studies on other animal clones have shown they are often much bigger than normal and have abnormally large organs, which leads to breathing, circulation, and other medical problems. Often it is said that cloning is wrong because it is unnatural. However, organ transplants and IVF were thought unnatural when they were first introduced, and many of the same arguments, now being used against cloning, were advanced. In 2011, a number of public surveys in the United States and United Kingdom indicated that most (but not all) people accepted transplantation and assisted reproduction. Further Readings Books Brown, Terry. Gene Cloning and DNA Analysis: An Introduction, 5th ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Science, 2006.
5 Caplan, Arthur and Glenn McGee, eds. The Human Cloning Debate. Berkeley: Berkeley Hills Books, Harris, John. On Cloning. New York: Routledge, Wilmut, Ian, and Roger Highfield. After Dolly: The Promise and Perils of Cloning. New York: W.W. Norton, Web Sites U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Genomes Programs. Cloning Fact Sheet. genomics.energy.gov. (accessed September 9, 2011). Full Text: COPYRIGHT 2012 Gale, Cengage Learning. Source Citation Aldridge, Susan. "Human Cloning." Biotechnology: In Context. Ed. Brenda Wilmoth Lerner and K. Lee Lerner. Detroit: Gale, In Context Series. Student Resources in Context. Web. 12 Nov Document URL OverType=&query=&prodId=SUIC&windowstate=normal&contentModules=& amp;mode=view&displaygroupname=reference&limiter=&currpage=&disa blehighlighting=false&displaygroups=&sortby=&search_within_results=& amp;p=suic&action=e&catid=&activitytype=&scanid=&documentid= GALE%7CTTGGVK &source=Bookmark&u=ever24551&jsid=bb4d51765 e91 f806e6f68b46b4aa436c Gale Document Number: GALE TTGGVK
Biotechnology. Chapter 20. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Cloning genes into animals. Transgenic animal carries foreign gene inserted into its genome.
 Cloning genes into animals Transgenic animal carries foreign gene inserted into its genome. Transgenic goats Ch. 10 pg. 281 Produce human protein (drug) in milk Pharming Transgenic animals to produce human
Cloning genes into animals Transgenic animal carries foreign gene inserted into its genome. Transgenic goats Ch. 10 pg. 281 Produce human protein (drug) in milk Pharming Transgenic animals to produce human
Produced by Chloe Williams
 Biological systems: stems: Biotechnology - Cloning ng Links to curriculum learning outcomes: Biotechnology Fourth (SCN 4-13c): o I can debate the moral and ethical issues associated with some controversial
Biological systems: stems: Biotechnology - Cloning ng Links to curriculum learning outcomes: Biotechnology Fourth (SCN 4-13c): o I can debate the moral and ethical issues associated with some controversial
Social and Ethical Issues in Systems Biology. HW: pg 120 #1-5, 9-11, 14
 Social and Ethical Issues in Systems Biology HW: pg 120 #1-5, 9-11, 14 Transplanting Organs Organ transplantation involves the removal of an organ from donor body and placement in a recipient body, wherein
Social and Ethical Issues in Systems Biology HW: pg 120 #1-5, 9-11, 14 Transplanting Organs Organ transplantation involves the removal of an organ from donor body and placement in a recipient body, wherein
John Gurdon was testing the hypothesis of genomic equivalence or that when cells divide they retain a full genomic compliment.
 1. (15 pts) John Gurdon won the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for work he did in the 1960 s. What was the major developmental hypothesis he set out to test? What techniques did he development
1. (15 pts) John Gurdon won the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for work he did in the 1960 s. What was the major developmental hypothesis he set out to test? What techniques did he development
What are clones? Genetically identical copies
 Cloning What are clones? Genetically identical copies The possibility of human cloning was raised when Scottish scientists at Roslin Institute created the much-celebrated sheep "Dolly" Cloning Cloning
Cloning What are clones? Genetically identical copies The possibility of human cloning was raised when Scottish scientists at Roslin Institute created the much-celebrated sheep "Dolly" Cloning Cloning
Stem Cell Research 101
 Stem Cell Research : A promising type of bioscience research The Stem Cell debate and the impact of the induced pluripotent stem cell procedure Why Is Vocabulary Important? Key terms frame the debate Mature
Stem Cell Research : A promising type of bioscience research The Stem Cell debate and the impact of the induced pluripotent stem cell procedure Why Is Vocabulary Important? Key terms frame the debate Mature
Future of Stem Cell Engineering. Jaeseung Jeong, Ph.D Department of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
 Future of Stem Cell Engineering i Jaeseung Jeong, Ph.D Department of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST Keywords of Stem Cell Engineering g Embryo and Fetus (Foetus) Adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells
Future of Stem Cell Engineering i Jaeseung Jeong, Ph.D Department of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST Keywords of Stem Cell Engineering g Embryo and Fetus (Foetus) Adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells
Which of the following comes closest to your view? no genetic engineering whatsoever should be performed on humans.
 Which of the following comes closest to your view? GREEN: BLUE: RED: YELLOW: no genetic engineering whatsoever should be performed on humans. gene therapy is OK, but nothing else. I m OK with gene therapy
Which of the following comes closest to your view? GREEN: BLUE: RED: YELLOW: no genetic engineering whatsoever should be performed on humans. gene therapy is OK, but nothing else. I m OK with gene therapy
Ad Hoc Committee Zenith Model United Nations 2014 BACKGROUND GUIDE. Agenda: Banning of Reproductive Cloning of Human Beings
 Ad Hoc Committee Zenith Model United Nations 2014 BACKGROUND GUIDE Agenda: Banning of Reproductive Cloning of Human Beings Introduction Human cloning is defined as the creation of human embryos having
Ad Hoc Committee Zenith Model United Nations 2014 BACKGROUND GUIDE Agenda: Banning of Reproductive Cloning of Human Beings Introduction Human cloning is defined as the creation of human embryos having
Cloning from plant cells
 Cloning plants, animals, and cells Take a cutting from a plant, put it in a pot of soil, and you have cloned an organism. The plant that grows from the cutting will be genetically identical to the one
Cloning plants, animals, and cells Take a cutting from a plant, put it in a pot of soil, and you have cloned an organism. The plant that grows from the cutting will be genetically identical to the one
Stem Cells. Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? STO Stem cells are unspecialized. What does this mean?
 STO-120 Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell
STO-120 Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell
Genetic Engineering- GMO S and Clones
 Genetic Engineering- GMO S and Clones I) Medical Applications A) Genetic Engineering is unraveling the mysteries of gene function during development and may eventually provide therapies for disease. B)
Genetic Engineering- GMO S and Clones I) Medical Applications A) Genetic Engineering is unraveling the mysteries of gene function during development and may eventually provide therapies for disease. B)
What is Biotechnology? 15.1 What is Biotechnology? Transgenic Biotechnology Transgenic Biotechnology. Biotechnology. Transgenic organism
 What is Biotechnology? 15.1 What is Biotechnology? Biotechnology the use of technology to control biological processes as a means of meeting societal needs Gene therapy Genetic engineering Bioremediation
What is Biotechnology? 15.1 What is Biotechnology? Biotechnology the use of technology to control biological processes as a means of meeting societal needs Gene therapy Genetic engineering Bioremediation
ANAT 2341 Embryology Lecture 18 Stem Cells
 ANAT 2341 Embryology Lecture 18 Stem Cells 29 September 2010 Dr Antonio Lee Neuromuscular & Regenera
ANAT 2341 Embryology Lecture 18 Stem Cells 29 September 2010 Dr Antonio Lee Neuromuscular & Regenera
Biotechnology: Genomics: field that compares the entire DNA content of different organisms
 Biotechnology: New Terms Today: Genome Genetic engineering, transgenic organisms, GM food, Reproductive and therapeutic cloning Stem cells, plouripotent, totipotent Gene therapy Genomics: field that compares
Biotechnology: New Terms Today: Genome Genetic engineering, transgenic organisms, GM food, Reproductive and therapeutic cloning Stem cells, plouripotent, totipotent Gene therapy Genomics: field that compares
Differentiation = Making specialized cells. Self-renewal = copying. What is a stem cell?
 Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? What the photo shows A lump of metal and lots of different kinds of screws that can be made from it. Things to think about What is a specialized
Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? What the photo shows A lump of metal and lots of different kinds of screws that can be made from it. Things to think about What is a specialized
KEY Reproductive cloning Therapeutic cloning
 1. (20 pts) Define Reproductive and Therapeutic cloning. Make sure your descriptions clearly distinguish the critical differences between them. Describe an example of each. Reproductive cloning refers
1. (20 pts) Define Reproductive and Therapeutic cloning. Make sure your descriptions clearly distinguish the critical differences between them. Describe an example of each. Reproductive cloning refers
BIOTECHNOLOGY. Unit 8
 BIOTECHNOLOGY Unit 8 PART 1 BASIC/FUNDAMENTAL SCIENCE VS. APPLIED SCIENCE! Basic/Fundamental Science the development and establishment of information to aid our understanding of the world.! Applied Science
BIOTECHNOLOGY Unit 8 PART 1 BASIC/FUNDAMENTAL SCIENCE VS. APPLIED SCIENCE! Basic/Fundamental Science the development and establishment of information to aid our understanding of the world.! Applied Science
Chapter 11: Applications of Biotechnology
 Chapter 11: Applications of Biotechnology Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 11-1 Why Biotechnology Works 11-2 Biotechnology
Chapter 11: Applications of Biotechnology Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 11-1 Why Biotechnology Works 11-2 Biotechnology
Asexu. Figure 6 A small glass tube, called a micropipette, is used to remove the nucleus from a cell and later introduce a new nucleus.
 While plant cloning experiments were being conducted, Robert Briggs and Thomas King were busy investigating nuclear transplants in frogs. Working with the common grass frog, the scientists extracted the
While plant cloning experiments were being conducted, Robert Briggs and Thomas King were busy investigating nuclear transplants in frogs. Working with the common grass frog, the scientists extracted the
The Cloning of Dolly
 The Cloning of Dolly Dr Jamie Love 27 November 1997-2009 I've decided to make cloning one of the first topics in this first issue of Science Explained because the folks who created Dolly are acquaintances
The Cloning of Dolly Dr Jamie Love 27 November 1997-2009 I've decided to make cloning one of the first topics in this first issue of Science Explained because the folks who created Dolly are acquaintances
Biotechnology. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc., unless otherwise noted
 Biotechnology Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc., unless otherwise noted Biotechnology Any technical procedure used to isolate, analyze or manipulate genes
Biotechnology Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc., unless otherwise noted Biotechnology Any technical procedure used to isolate, analyze or manipulate genes
Chapter 11. How Genes Are Controlled. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Introduction This is an exam style question on stem cells that might be useful towards the end of the topic.
 Teacher Notes Introduction This is an exam style question on stem cells that might be useful towards the end of the topic. Suggested mark scheme (a) (i) a non-specialised cell any 1 for 1 a cell that can
Teacher Notes Introduction This is an exam style question on stem cells that might be useful towards the end of the topic. Suggested mark scheme (a) (i) a non-specialised cell any 1 for 1 a cell that can
Human Genome Project
 Human Genome Project How they did it DNA from 5 humans 2 males, 3 females 2 caucasians, one each of asian, african, hispanic Cut up DNA with restriction enzymes Ligated into BACs & YACs, then grew them
Human Genome Project How they did it DNA from 5 humans 2 males, 3 females 2 caucasians, one each of asian, african, hispanic Cut up DNA with restriction enzymes Ligated into BACs & YACs, then grew them
What information does the nucleus of a cell contain? Why is it so important? What is a donor animal? Why don t clones grow in the same way?
 CLONING- EXERCISES 1 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN YOUR OWN WORDS AS FAR AS POSSIBLE! What information does the nucleus of a cell contain? Why is it so important? What is a donor animal? Why don t
CLONING- EXERCISES 1 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN YOUR OWN WORDS AS FAR AS POSSIBLE! What information does the nucleus of a cell contain? Why is it so important? What is a donor animal? Why don t
BIOTECHNOLOGY. Understanding the Application
 BIOTECHNOLOGY Understanding the Application GENETIC ENGINEERING Genetic engineering refers to any process in which man alters an organism s DNA Examples: cloning, genetically modified organisms (GMO),
BIOTECHNOLOGY Understanding the Application GENETIC ENGINEERING Genetic engineering refers to any process in which man alters an organism s DNA Examples: cloning, genetically modified organisms (GMO),
Lecture 24 Differentiation and stem cells
 Lecture 24 Differentiation and stem cells *Stem cells and differentiation in plants Totipotency Stem cells in animals Therapeutic use Cloning Therapeutic Reproductive Therapeutic cloning in humans Stem
Lecture 24 Differentiation and stem cells *Stem cells and differentiation in plants Totipotency Stem cells in animals Therapeutic use Cloning Therapeutic Reproductive Therapeutic cloning in humans Stem
Lesson 7A Specialized Cells, Stem Cells & Cellular Differentiation
 Lesson 7A Specialized Cells, Stem Cells & Cellular Differentiation Learning Goals I can explain the concept of cell differentiation and cell specialization. I can explain how the cell structure relates
Lesson 7A Specialized Cells, Stem Cells & Cellular Differentiation Learning Goals I can explain the concept of cell differentiation and cell specialization. I can explain how the cell structure relates
BIOTECHNOLOGY. Understanding the Application
 BELLRINGER-5/4/15 1. What method would you guess forensic scientists use to identify criminals at crime scenes? 2. What do you think we mean by the term biotechnology? BIOTECHNOLOGY Understanding the Application
BELLRINGER-5/4/15 1. What method would you guess forensic scientists use to identify criminals at crime scenes? 2. What do you think we mean by the term biotechnology? BIOTECHNOLOGY Understanding the Application
From Stem Cell to Any Cell
 sciencenewsforkids.org http://www.sciencenewsforkids.org/2005/10/from-stem-cell-to-any-cell-2/ From Stem Cell to Any Cell By Emily Sohn / October 11, 2005 For maybe a day, about 9 months before you were
sciencenewsforkids.org http://www.sciencenewsforkids.org/2005/10/from-stem-cell-to-any-cell-2/ From Stem Cell to Any Cell By Emily Sohn / October 11, 2005 For maybe a day, about 9 months before you were
Stem Cells & Neurological Disorders. Said Ismail Faculty of Medicine University of Jordan
 Stem Cells & Neurological Disorders Said Ismail Faculty of Medicine University of Jordan Outline: - Introduction - Types & Potency of Stem Cells - Embryonic Stem Cells - Adult Stem Cells - ipscs -Tissue
Stem Cells & Neurological Disorders Said Ismail Faculty of Medicine University of Jordan Outline: - Introduction - Types & Potency of Stem Cells - Embryonic Stem Cells - Adult Stem Cells - ipscs -Tissue
3/9/04 Cloning/Stem Cells
 3/9/04 Cloning/Stem Cells 1 Meet (left to right): Rainbow, Allie and cc (carbon copy) who is a genetic clone of Rainbow. Allie is cc s surrogate mom 2 To see entire article: http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/2.14.02nytcat.pdf
3/9/04 Cloning/Stem Cells 1 Meet (left to right): Rainbow, Allie and cc (carbon copy) who is a genetic clone of Rainbow. Allie is cc s surrogate mom 2 To see entire article: http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/2.14.02nytcat.pdf
WHAT IS EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS
 31 March, 2018 WHAT IS EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS Document Filetype: PDF 436.17 KB 0 WHAT IS EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS Explore Current Stem Cell Treatments. Embryonic stem cells - Embryonic stem cells include those
31 March, 2018 WHAT IS EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS Document Filetype: PDF 436.17 KB 0 WHAT IS EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS Explore Current Stem Cell Treatments. Embryonic stem cells - Embryonic stem cells include those
Genetics Lecture 19 Stem Cells. Stem Cells 4/10/2012
 Genetics Lecture 19 Stem Cells Stem Cells Much of the excitement about stem cells in the scientific and medical communities comes from their largely untapped and unproven potential for treating human conditions)
Genetics Lecture 19 Stem Cells Stem Cells Much of the excitement about stem cells in the scientific and medical communities comes from their largely untapped and unproven potential for treating human conditions)
MAGNIFICATION? Human Embryonic Stem Cell
 Stem Cells: The Silver Lining Behind the Dark Clouds by Fr. Robert Gahl Associate Professor of Ethics Pontifical University of the Holy Cross Human Embryonic Stem Cell MAGNIFICATION? Stem Cells: The Silver
Stem Cells: The Silver Lining Behind the Dark Clouds by Fr. Robert Gahl Associate Professor of Ethics Pontifical University of the Holy Cross Human Embryonic Stem Cell MAGNIFICATION? Stem Cells: The Silver
Cloning. 1. What is cloning: Natural and artificial 2. Cloning of what? 3. Embryonic development of multi-cellular organisms:
 Cloning 1. What is cloning: Natural and artificial 2. Cloning of what? 3. Embryonic development of multi-cellular organisms: cell division, morphogenesis, differentiation 2. Plant cloning 3. Animal cloning
Cloning 1. What is cloning: Natural and artificial 2. Cloning of what? 3. Embryonic development of multi-cellular organisms: cell division, morphogenesis, differentiation 2. Plant cloning 3. Animal cloning
- What is Animal Biotechnology?
 Animal Biotechnology - What is Animal Biotechnology? - Animal biotechnology is the application of scientific and engineering principles to the processing or production of materials by animals or aquatic
Animal Biotechnology - What is Animal Biotechnology? - Animal biotechnology is the application of scientific and engineering principles to the processing or production of materials by animals or aquatic
REPRODUCTIVE CLONING OF HUMAN BEINGS: CURRENT SITUATION. Report of the Regional Director
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION REGIONAL OFFICE FOR AFRICA ORGANISATION MONDIALE DE LA SANTE BUREAU REGIONAL DE L AFRIQUE ORGANIZAÇÃO MUNDIAL DE SAÚDE ESCRITÓRIO REGIONAL AFRICANO PROGRAMME SUBCOMMITTEE Fifty-fifth
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION REGIONAL OFFICE FOR AFRICA ORGANISATION MONDIALE DE LA SANTE BUREAU REGIONAL DE L AFRIQUE ORGANIZAÇÃO MUNDIAL DE SAÚDE ESCRITÓRIO REGIONAL AFRICANO PROGRAMME SUBCOMMITTEE Fifty-fifth
LifeNOTES. Cloning: No Longer Science Fiction. How Cloning Works. Misguided Therapy
 LifeNOTES Cloning: No Longer Science Fiction As we stand at a time when technology is quickly advancing, researchers have begun to bombard our nation and the rest of the world with questions of how far
LifeNOTES Cloning: No Longer Science Fiction As we stand at a time when technology is quickly advancing, researchers have begun to bombard our nation and the rest of the world with questions of how far
Making Sense of Stem Cell Research and Cloning. Alan Shlemon Stand to Reason
 Making Sense of Stem Cell Research and Cloning Alan Shlemon Stand to Reason www.str.org The body has over 200 different types of specialized cells. Stem Cells A stem cell is an unspecialized cell Unspecialized
Making Sense of Stem Cell Research and Cloning Alan Shlemon Stand to Reason www.str.org The body has over 200 different types of specialized cells. Stem Cells A stem cell is an unspecialized cell Unspecialized
4. Agricultural Implications
 Name: Date: 4. Agricultural Implications I can describe agricultural applications of asexual reproduction. Examples: cloning, cuttings, grafting (vegetative propogation), bulbs Vegetative Propagation:
Name: Date: 4. Agricultural Implications I can describe agricultural applications of asexual reproduction. Examples: cloning, cuttings, grafting (vegetative propogation), bulbs Vegetative Propagation:
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web
 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21096 December 19, 2001 Summary Human Cloning Judith A. Johnson Specialist in Life Sciences Domestic Social Policy Division On November
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21096 December 19, 2001 Summary Human Cloning Judith A. Johnson Specialist in Life Sciences Domestic Social Policy Division On November
Presenter: Teresa Holm
 Slides are from Level 3 Biology Course Content Day, 7 th November 2012 Presenter: Teresa Holm Teachers are free to use these for teaching purposes with appropriate acknowledgement Human Stem cells Dr Teresa
Slides are from Level 3 Biology Course Content Day, 7 th November 2012 Presenter: Teresa Holm Teachers are free to use these for teaching purposes with appropriate acknowledgement Human Stem cells Dr Teresa
Stem Cell review/cloning Section. If false, correct only one of the underlined words to make the statement true.
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Stem Cell review/cloning Section A. True/False: Circle
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Stem Cell review/cloning Section A. True/False: Circle
Advances in Genetics #101
 Questions: Five study Questions EQ1: What are 3 ways of producing organisms with desired traits? EQ2: What are 2 applications of DNA technology in human genetics? Like your fingerprints, your DNA is different
Questions: Five study Questions EQ1: What are 3 ways of producing organisms with desired traits? EQ2: What are 2 applications of DNA technology in human genetics? Like your fingerprints, your DNA is different
STEM CELL RESEARCH PRIMER
 STEM CELL RESEARCH PRIMER WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT STEM CELLS AND STEM CELL RESEARCH What Stem Cells Are And Why They Are Important Stem cells are the body s very own internal repair system. They are
STEM CELL RESEARCH PRIMER WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT STEM CELLS AND STEM CELL RESEARCH What Stem Cells Are And Why They Are Important Stem cells are the body s very own internal repair system. They are
Stem Cel s Key Words:
 Stem Cells Key Words: Embryonic stem cells, Adult stem cells, ips cells, self-renewal, differentiation, pluripotent, multipotent, Inner cell mass, Nuclear transfer (Therapeutic cloning), Feeder cells,
Stem Cells Key Words: Embryonic stem cells, Adult stem cells, ips cells, self-renewal, differentiation, pluripotent, multipotent, Inner cell mass, Nuclear transfer (Therapeutic cloning), Feeder cells,
Genetic Engineering. Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO s)
 Genetic Engineering The manipulation of genetic material for practical purposes Involves the changing of DNA in an organism Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO s) An organism whose genetic make up has
Genetic Engineering The manipulation of genetic material for practical purposes Involves the changing of DNA in an organism Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO s) An organism whose genetic make up has
Therapeutic cloning: A scientific breakthrough or a step too far? Ben Good George Collins. Word Count: Approx Grade Awarded June 2006: PASS
 Therapeutic cloning: A scientific breakthrough or a step too far? BY Ben Good George Collins Word Count: Approx 1400 Grade Awarded June 2006: PASS 1 Abstract The purpose of our paper is to investigate
Therapeutic cloning: A scientific breakthrough or a step too far? BY Ben Good George Collins Word Count: Approx 1400 Grade Awarded June 2006: PASS 1 Abstract The purpose of our paper is to investigate
Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Here s one thing genetic engineers do: Techniques for gene cloning enable scientists to prepare multiple identical copies of gene-sized pieces of DNA. Cloning means to make copies, in this case, copies
Here s one thing genetic engineers do: Techniques for gene cloning enable scientists to prepare multiple identical copies of gene-sized pieces of DNA. Cloning means to make copies, in this case, copies
9.4. Genetic Engineering. Entire organisms can be cloned. Web
 9.4 Genetic Engineering VOCABULARY clone genetic engineering recombinant DNA plasmid transgenic gene knockout 3D, 3D evaluate the impact of scientific research on society and the environment and 6H describe
9.4 Genetic Engineering VOCABULARY clone genetic engineering recombinant DNA plasmid transgenic gene knockout 3D, 3D evaluate the impact of scientific research on society and the environment and 6H describe
Cloning For Embryonic Stem Cells
 Cloning For Embryonic Stem Cells Defining the Terms Types of cloning - There are three types of cloning: (1) reproductive cloning, (2) therapeutic cloning and (3) recombinant DNA technology or gene cloning.
Cloning For Embryonic Stem Cells Defining the Terms Types of cloning - There are three types of cloning: (1) reproductive cloning, (2) therapeutic cloning and (3) recombinant DNA technology or gene cloning.
ANAT 3231 Cell Biology Lecture 21 Stem Cells
 ANAT 3231 Cell Biology Lecture 21 Stem Cells Outline What are Stem Cells? Totipotency - Pluripotency - Multipotency What are different sources of Stem Cells? Embryonic vs Adult Pros and Cons for each type
ANAT 3231 Cell Biology Lecture 21 Stem Cells Outline What are Stem Cells? Totipotency - Pluripotency - Multipotency What are different sources of Stem Cells? Embryonic vs Adult Pros and Cons for each type
Goodbye Dolly. In re Roslin Institute (Edinburgh) ( ; May 8, 2014; Federal Circuit)
 Goodbye Dolly In re Roslin Institute (Edinburgh) (2013-1407; May 8, 2014; Federal Circuit) The History of Dolly Early, 1995 - Scientists at the Roslin Institute clone two sheep, Megan and Morag, from differentiated
Goodbye Dolly In re Roslin Institute (Edinburgh) (2013-1407; May 8, 2014; Federal Circuit) The History of Dolly Early, 1995 - Scientists at the Roslin Institute clone two sheep, Megan and Morag, from differentiated
Name: Date: IF YOU GOT BELOW A 70% RETAKING THE TEST IS MANDATORY.
 IF YOU GOT BELOW A 70% RETAKING THE TEST IS MANDATORY. 1. What is a mutation? Any change in a DNA sequence 2. Name and describe the two categories types of gene mutations. Point: substitution, one nucleotide
IF YOU GOT BELOW A 70% RETAKING THE TEST IS MANDATORY. 1. What is a mutation? Any change in a DNA sequence 2. Name and describe the two categories types of gene mutations. Point: substitution, one nucleotide
3. In vitro- Cell culture (IVM, IVF, IVG) GC Class Discussion
 No Subject : Cellular Lecturer Note 1. Introduction-Recent dev of. Anim Biotech:Mol-Cell 2 Basic Mol-Cell Laboratory Practice, In vitro. 3 Chromosome Bio-Cell Analysis GC GC Class Discussion Class Discussion
No Subject : Cellular Lecturer Note 1. Introduction-Recent dev of. Anim Biotech:Mol-Cell 2 Basic Mol-Cell Laboratory Practice, In vitro. 3 Chromosome Bio-Cell Analysis GC GC Class Discussion Class Discussion
Stem cells and motor neurone disease
 Stem cells and motor neurone disease F Stem cell research has fuelled hope of a treatment for a variety of conditions. This information sheet explains what these cells are and includes details of the current
Stem cells and motor neurone disease F Stem cell research has fuelled hope of a treatment for a variety of conditions. This information sheet explains what these cells are and includes details of the current
Should Embryonic Stem Cell Research be Permitted to Continue? Over the past few years a debate has been going on over the moral implications of
 Courtesy of Christopher Waits. Used with permission. Waits 1 Should Embryonic Stem Cell Research be Permitted to Continue? Over the past few years a debate has been going on over the moral implications
Courtesy of Christopher Waits. Used with permission. Waits 1 Should Embryonic Stem Cell Research be Permitted to Continue? Over the past few years a debate has been going on over the moral implications
2 Gene Technologies in Our Lives
 CHAPTER 15 2 Gene Technologies in Our Lives SECTION Gene Technologies and Human Applications KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: For what purposes are genes and proteins manipulated?
CHAPTER 15 2 Gene Technologies in Our Lives SECTION Gene Technologies and Human Applications KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: For what purposes are genes and proteins manipulated?
Will Stem Cells Finally Deliver Without Controversy?
 Will Stem Cells Finally Deliver Without Controversy? Keith Gary, Ph.D. Director of Program Development Kansas City Area Life Sciences Institute Olathe North Life Sciences 1 February 2012 What s the Buzz?
Will Stem Cells Finally Deliver Without Controversy? Keith Gary, Ph.D. Director of Program Development Kansas City Area Life Sciences Institute Olathe North Life Sciences 1 February 2012 What s the Buzz?
Pick up 3 handout from back. Draw this on the back side of the handout called Concepts of biotechnology. After you have read and highlighted
 Pick up 3 handout from back. Draw this on the back side of the handout called Concepts of biotechnology. After you have read and highlighted important information from the reading, see if you cann identify
Pick up 3 handout from back. Draw this on the back side of the handout called Concepts of biotechnology. After you have read and highlighted important information from the reading, see if you cann identify
Stem Cells: Introduction and Prospects in Regenerative Medicine.
 Stem Cells: Introduction and Prospects in Regenerative Medicine www.gothamgazette.com/.../stemcell/stem_cell.jpg Ode to a Stem Cell, Part II by VCW There once was stem cell stuck in the hood Dividing endlessly,
Stem Cells: Introduction and Prospects in Regenerative Medicine www.gothamgazette.com/.../stemcell/stem_cell.jpg Ode to a Stem Cell, Part II by VCW There once was stem cell stuck in the hood Dividing endlessly,
What are the origins of medical practice? Humans have been involved with medical biotechnology
 Name: Score: / Quiz 8 on Medical Biotechnology Part 1 What are the origins of medical practice? Humans have been involved with medical biotechnology A. since the cloning of the insulin gene in the 1980s
Name: Score: / Quiz 8 on Medical Biotechnology Part 1 What are the origins of medical practice? Humans have been involved with medical biotechnology A. since the cloning of the insulin gene in the 1980s
UNIT III: Genetics Chapter 9 Frontiers of Biotechnology
 UNIT III: Genetics Chapter 9 Frontiers of Biotechnology I. Manipulating DNA (9.1) A. Scientists use several techniques to manipulate DNA 1. DNA is a very large molecule 2. Still to small to see or work
UNIT III: Genetics Chapter 9 Frontiers of Biotechnology I. Manipulating DNA (9.1) A. Scientists use several techniques to manipulate DNA 1. DNA is a very large molecule 2. Still to small to see or work
Page 3. 18) The diagram below illustrates some key steps of a procedure in one area of biotechnology.
 Name: 1117 1 Page 1 1) A small amount of DNA was taken from a fossil of a mammoth found frozen in glacial ice. Genetic technology can be used to produce a large quantity of identical DNA from this mammoth's
Name: 1117 1 Page 1 1) A small amount of DNA was taken from a fossil of a mammoth found frozen in glacial ice. Genetic technology can be used to produce a large quantity of identical DNA from this mammoth's
Editors, Reporters, and other interested persons
 To: From: Re: Editors, Reporters, and other interested persons Douglas Johnson, Legislative Director, National Right to Life Committee (202) 626-8820, Legfederal@aol.com, www.nrlc.org Senator Tim Johnson
To: From: Re: Editors, Reporters, and other interested persons Douglas Johnson, Legislative Director, National Right to Life Committee (202) 626-8820, Legfederal@aol.com, www.nrlc.org Senator Tim Johnson
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 24. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 24 2 of 24 Transgenic Organisms Transgenic Organisms An organism described as transgenic, contains genes from other species. 3 of 24 Transgenic Organisms How are transgenic organisms
Biology Biology 1 of 24 2 of 24 Transgenic Organisms Transgenic Organisms An organism described as transgenic, contains genes from other species. 3 of 24 Transgenic Organisms How are transgenic organisms
Chapter 8 Healthcare Biotechnology
 Chapter 8 Healthcare Biotechnology Outline: 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Biopharming 8.3 Models of Human Disease 8.4 Detecting and Diagnosing Human Disease 8.5 Monoclonal Antibodies 8.6 Gene Therapy 8.7 Tissue
Chapter 8 Healthcare Biotechnology Outline: 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Biopharming 8.3 Models of Human Disease 8.4 Detecting and Diagnosing Human Disease 8.5 Monoclonal Antibodies 8.6 Gene Therapy 8.7 Tissue
IRB USE ONLY Approval Date: September 10, 2013 Expiration Date: September 10, 2014
 Approval : September 10, 2013 Expiration : September 10, 2014 DESCRIPTION: You are invited to donate your excess sperm and/or testicular biopsy material, as well as your somatic cells (ordinary body cells
Approval : September 10, 2013 Expiration : September 10, 2014 DESCRIPTION: You are invited to donate your excess sperm and/or testicular biopsy material, as well as your somatic cells (ordinary body cells
IRB USE ONLY Approval Date: September 10, 2013 Expiration Date: September 10, 2014
 Approval : September 10, 2013 Expiration : September 10, 2014 DESCRIPTION: You are invited to donate your leftover frozen eggs and/or ovarian tissues generated during your fertility preservation treatment
Approval : September 10, 2013 Expiration : September 10, 2014 DESCRIPTION: You are invited to donate your leftover frozen eggs and/or ovarian tissues generated during your fertility preservation treatment
Human stem cells The perspective of a Catholic physician-scientist
 Human stem cells The perspective of a Catholic physician-scientist Jose C. Florez MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Outline Intro on human development What are stem cells?
Human stem cells The perspective of a Catholic physician-scientist Jose C. Florez MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Outline Intro on human development What are stem cells?
Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10
 Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following has the disadvantage of possibly bringing
Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following has the disadvantage of possibly bringing
If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?!
 If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?! Genetic engineering Genetic and environmental differences B1.6 Variation Inheritance Types of reproduction
If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?! Genetic engineering Genetic and environmental differences B1.6 Variation Inheritance Types of reproduction
DB3230 Midterm 1 11/15/2013 Name:
 1. (15 pts) Nuclear cloning by John Gurdon was rarely successful in producing fertile adults. Why not? Explain why serial transplantation improves the success rate. What else could you do to improve the
1. (15 pts) Nuclear cloning by John Gurdon was rarely successful in producing fertile adults. Why not? Explain why serial transplantation improves the success rate. What else could you do to improve the
1500 Words on Human and Therapeutic Cloning. Germany in Armin Meiwes, a computer technician and all-around nice guy, posted an ad
 De La Espriella 1 Luis De La Espriella Daniel Richards ENC 1102.003 28 July 2011 1500 Words on Human and Therapeutic Cloning The law not being clear on a subject can turn out to be quite interesting as
De La Espriella 1 Luis De La Espriella Daniel Richards ENC 1102.003 28 July 2011 1500 Words on Human and Therapeutic Cloning The law not being clear on a subject can turn out to be quite interesting as
CHAPTER 13. Genetic Engineering
 CHAPTER 13 Genetic Engineering 13-1 Changing the Living World Choosing the best traits for breeding Most domestic animals are products of SB Even Cows, Sheep, & Pigs All Products of Selective Breeding
CHAPTER 13 Genetic Engineering 13-1 Changing the Living World Choosing the best traits for breeding Most domestic animals are products of SB Even Cows, Sheep, & Pigs All Products of Selective Breeding
Stem cell: a cell capable of 1) tissue plasticity - make different cell types 2) infinite self renewal through asymmetric division
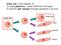 Stem cell: a cell capable of 1) tissue plasticity - make different cell types 2) infinite self renewal through asymmetric division stem cell stem cell skin muscle nerve Properties of STEM cells Plasticity
Stem cell: a cell capable of 1) tissue plasticity - make different cell types 2) infinite self renewal through asymmetric division stem cell stem cell skin muscle nerve Properties of STEM cells Plasticity
body chromosomes clones cytoplasm genes nucleus sex Information is passed from parents to their young in... cells.
 Genetic variation and its control 1. The diagram shows a human cell and some of its contents. (a) Choose words from this list to label the diagrams. chromosome cytoplasm gene nucleus Choose words from
Genetic variation and its control 1. The diagram shows a human cell and some of its contents. (a) Choose words from this list to label the diagrams. chromosome cytoplasm gene nucleus Choose words from
Unit 1: DNA and the Genome. Sub-Topic (1.4) Cellular Differentiation
 Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.4) Cellular Differentiation Duncanrig 2016 Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.4) Cellular Differentiation On completion of this subtopic I will be able to Cellular
Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.4) Cellular Differentiation Duncanrig 2016 Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.4) Cellular Differentiation On completion of this subtopic I will be able to Cellular
Recombinant DNA. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Recombinant DNA
 Lesson Overview 15.2 Finding Genes In 1987, Douglas Prasher, a biologist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute in Massachusetts, wanted to find a specific gene in a jellyfish that codes for a molecule
Lesson Overview 15.2 Finding Genes In 1987, Douglas Prasher, a biologist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute in Massachusetts, wanted to find a specific gene in a jellyfish that codes for a molecule
STEM CELL RESEARCH MEDICAL REVOLUTION OR ETHICAL DILEMMA? BY LAURA HOBBS NATALIE KSEIB. Word count: Approx 2100
 STEM CELL RESEARCH MEDICAL REVOLUTION OR ETHICAL DILEMMA? BY LAURA HOBBS NATALIE KSEIB Word count: Approx 2100 Grade awarded June 2006: PASS WITH MERIT RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK
STEM CELL RESEARCH MEDICAL REVOLUTION OR ETHICAL DILEMMA? BY LAURA HOBBS NATALIE KSEIB Word count: Approx 2100 Grade awarded June 2006: PASS WITH MERIT RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK
Intelectual Property Rights: Cloning; The Pros And Cons R.H.Shivaramun* Introduction:
 Intelectual Property Rights: Cloning; The Pros And Cons R.H.Shivaramun* Introduction: The intellectual property in India is important at all levels of statutory, administrative and judiciary. India ratified
Intelectual Property Rights: Cloning; The Pros And Cons R.H.Shivaramun* Introduction: The intellectual property in India is important at all levels of statutory, administrative and judiciary. India ratified
DNA Technology Outline
 I) Tools of DNA technology A. PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): method of copying DNA sequences 1. DNA is copied in a similar way to natural replication in our cells, but much faster. 2.PCR consists of
I) Tools of DNA technology A. PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): method of copying DNA sequences 1. DNA is copied in a similar way to natural replication in our cells, but much faster. 2.PCR consists of
Duncanrig Secondary School
 National 4 Biology Unit 1Topic 3: Therapeutic Uses of Cells, Duncanrig Secondary School Duncanrig Secondary School National 4 Biology Unit 1 Topic 3: Therapeutic Uses of Cells Pupils Activity Booklet National
National 4 Biology Unit 1Topic 3: Therapeutic Uses of Cells, Duncanrig Secondary School Duncanrig Secondary School National 4 Biology Unit 1 Topic 3: Therapeutic Uses of Cells Pupils Activity Booklet National
SNC2D BIOLOGY 3/31/2013. TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Stem Cells & Meristematic Cells (P.40-41) Specialized Cells. Stem Cells
 SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L & Meristematic Cells (P.40-41) Specialized Cells The cell theory states that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Every cell that makes up an animal s body
SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L & Meristematic Cells (P.40-41) Specialized Cells The cell theory states that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Every cell that makes up an animal s body
Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function.
 (4) Q.Living organisms are made of cells. (a) Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function. Draw one line from each cell part to the correct function of that part. (b)
(4) Q.Living organisms are made of cells. (a) Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function. Draw one line from each cell part to the correct function of that part. (b)
The 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka
 PRESS RELEASE 2012-10-08 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided to award The 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly to John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka for the discovery
PRESS RELEASE 2012-10-08 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided to award The 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly to John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka for the discovery
The 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka
 PRESS RELEASE 2012-10-08 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided to award The 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly to John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka for the discovery
PRESS RELEASE 2012-10-08 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided to award The 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly to John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka for the discovery
Stem Cells: Ethics and Oversight May 24, Sidney H. Golub, Ph.D. Interim Director Sue & Bill Gross Stem Cell Research Center
 Stem Cells: Ethics and Oversight May 24, 2017 Sidney H. Golub, Ph.D. Interim Director Sue & Bill Gross Stem Cell Research Center Nobel Laureates 2012 John Gurdon Shinya Yamanaka Pluripotent Stem Cell PLURIPOTENT
Stem Cells: Ethics and Oversight May 24, 2017 Sidney H. Golub, Ph.D. Interim Director Sue & Bill Gross Stem Cell Research Center Nobel Laureates 2012 John Gurdon Shinya Yamanaka Pluripotent Stem Cell PLURIPOTENT
Thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 2.1 Cloning in plants and animals Notes & Questions
 Thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 2.1 Cloning in plants and animals Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Outline the differences between reproductive and non-reproductive
Thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 2.1 Cloning in plants and animals Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Outline the differences between reproductive and non-reproductive
A RESPONSE to THE NUFFIELD COUNCIL ON BIOETHICS CONSULTATION PAPER on EMERGING BIOTECHNOLOGIES
 This response was submitted to the consultation held by the Nuffield Council on Bioethics on Emerging biotechnologies between April 2011 and June 2011. The views expressed are solely those of the respondent(s)
This response was submitted to the consultation held by the Nuffield Council on Bioethics on Emerging biotechnologies between April 2011 and June 2011. The views expressed are solely those of the respondent(s)
STEM CELL RESEARCH EBENEZER ANOM ENGLISH 1311 CLASS UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT EL PASO
 STEM CELL RESEARCH BY EBENEZER ANOM ENGLISH 1311 CLASS UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT EL PASO ABSTRACT In our communities today, relatives, neighbors, friends and even those we don t know have been incapacitated
STEM CELL RESEARCH BY EBENEZER ANOM ENGLISH 1311 CLASS UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT EL PASO ABSTRACT In our communities today, relatives, neighbors, friends and even those we don t know have been incapacitated
7.012 Stem Cell review/cloning Section. If false, correct only one of the underlined words to make the statement true.
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.012 Stem Cell review/cloning Section A. True/False:
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.012 Stem Cell review/cloning Section A. True/False:
Remarks to the Nation on Stem Cell Research. delivered 9 August 2001
 George W. Bush Remarks to the Nation on Stem Cell Research delivered 9 August 2001 Good evening. I appreciate you giving me a few minutes of your time tonight so I can discuss with you a complex and difficult
George W. Bush Remarks to the Nation on Stem Cell Research delivered 9 August 2001 Good evening. I appreciate you giving me a few minutes of your time tonight so I can discuss with you a complex and difficult
INTRODUCTION KEY WORDS CFMUNESCO 2018
 CFMUNESCO 2018 COMMITTEE: World Health Organisation TOPIC: The Question of defining a Regulation for the use of Stem Cells CHAIRS: Cristina Lauretig, Lucrezia Rosina INTRODUCTION There is at present a
CFMUNESCO 2018 COMMITTEE: World Health Organisation TOPIC: The Question of defining a Regulation for the use of Stem Cells CHAIRS: Cristina Lauretig, Lucrezia Rosina INTRODUCTION There is at present a
Andrew Burnett, PhD DeGroot Center, Sanford Health Ethics & Humanities Section, SSOM USD
 Stem Cells in Context Andrew Burnett, PhD DeGroot Center, Sanford Health Ethics & Humanities Section, SSOM USD Overview Basic science of stem cells Some possible biomedical applications The federal funding
Stem Cells in Context Andrew Burnett, PhD DeGroot Center, Sanford Health Ethics & Humanities Section, SSOM USD Overview Basic science of stem cells Some possible biomedical applications The federal funding
Genetic Basis of Development & Biotechnologies
 Genetic Basis of Development & Biotechnologies 1. Steps of embryonic development: cell division, morphogenesis, differentiation Totipotency and pluripotency 2. Plant cloning 3. Animal cloning Reproductive
Genetic Basis of Development & Biotechnologies 1. Steps of embryonic development: cell division, morphogenesis, differentiation Totipotency and pluripotency 2. Plant cloning 3. Animal cloning Reproductive
Cells, Tissues and Organs
 Cells, Tissues and Organs You have already learned the basic function of cells, but how do these cells work together to make you the truly amazing organism that you are? Some of the key words you will
Cells, Tissues and Organs You have already learned the basic function of cells, but how do these cells work together to make you the truly amazing organism that you are? Some of the key words you will
